Education (Online), EdD
School of education.
To address the dramatically changing landscape of education in the 21st century, which includes new research on the science of learning, advances in technology, and the emergence of a for-profit education sector, the Johns Hopkins School of Education offers an innovative online Doctor of Education degree program. This EdD program is designed to prepare an exceptional corps of educational practitioner-scholars, both nationally and internationally, who can set a high standard for transformational leadership in education, apply evidence-based practices to improve educational outcomes, and meet the vast challenges associated with improving learning outcomes in both public and private educational environments.
For more information about the EdD program, please visit https://education.jhu.edu/academics/edd/ . If you have any questions about the EdD program, please contact [email protected] .

Admission Requirements
At minimum, applicants to the EdD program should hold a master’s degree from an accredited college or university. Previous degrees must document high academic achievement (a minimum GPA of 3.0) in an area of study closely associated with the objectives of the program. If the earned degree or credit is from an educational institution abroad, the candidate’s academic record must be evaluated by a credential evaluation agency before consideration for admission. Applicants must submit the online admission application form, application fee, official transcripts from all post-secondary institutions attended, a curriculum vitae (résumé), online interview, and two letters of recommendation signed by each recommender. These letters should include the following:
- A professor with whom the applicant worked in their master's program who can speak to the applicant's competency to conduct rigorous scholarly work, and
- A colleague/supervisor from the applicant’s professional context/industry who can attest to the applicant's qualifications to pursue a doctorate, the applicant's impact on the recommender’s professional practice, and knowledge of and support for the applicant's proposed area of research/Problem of Practice.
Additionally, applicants will submit a personal statement including responses to the following:
- Describe a significant Problem of Practice relevant to your current context/industry of professional practice.
- Indicate the importance of this problem within the applicant’s industry and/or their specific context of professional practice.
- Discuss the potential underlying causes for or contributing factors related to this Problem of Practice.
- Discuss the ways in which this problem aligns with at least one or two areas of interest.
All applicants who meet the entrance requirements will be asked to submit video and written responses to question prompts.
International students must fulfill the general requirements for admission and complete additional requirements—see https://education.jhu.edu/admission-financial-aid/admissions/international-applicants/ .
Note: This program is not eligible for student visa sponsorship .
Students who enter the program will be required to successfully complete a series of pre-orientation modules prior to enrollment in the program. All students are expected to show competence in the content areas of these modules.
Please note that for the online EdD program, an offer of admission is for the specific cohort to which an application is submitted. Students may accept or decline the admission offer only; deferring to a future cohort is not an option.
Program Requirements
Program structure and requirements.
Program requirements include a minimum of 90 graduate credits. Students must enter the program with a master’s degree with a minimum of 36 graduate-level credits, which will be transferred into the EdD program. If a student does not have the required 36 master’s credits, the student will be admitted on a conditional basis and must complete the additional graduate-level credits at an accredited college or university. Students with post-master’s graduate credit in related education content completed prior to admission to the EdD program may petition to transfer in an additional six credits of equivalent coursework with appropriate documentation and with the approval of the EdD program director. Thus, students must complete between 48 and 54 credits at the doctoral level at JHU. The program includes the following required coursework components (subject to change):
- Foundations of Education (15 credit hours)
- Applied Research & Evaluation (12 credit hours)
- Areas of Interest / Electives (15 elective credit hours)
- Doctoral Dossier Research (12 credit hours)*
In addition to successfully completing all the coursework requirements, candidates must also satisfy written assessments and an oral comprehensive examination that document attainment of competencies. They must also complete either an Applied Dissertation or a Dossier Style Dissertation research project, depending upon the year the candidate was admitted to the program as per the following table:
Students who extend their program of study may be required to enroll in additional independent study credits.
With permission, students admitted between Fall 2013 and Fall 2020 may opt into the Dossier Style Dissertation if they choose not to do an intervention.
Problems of Practice and Doctoral Dossier
Students examine a Problem of Practice (POP)—an area of concern they have observed within their professional context—that becomes the focus of the student's Doctoral Dossier, which consists of three main projects described below.
As part of our commitment to social justice, the EdD program does not privilege one form of communication over another. Thus, all components of the Doctoral Dossier can be communicated in a modality of the student’s choosing: video, oral, scholarly writing, or public-facing writing. The Doctoral Dossier is embedded within the EdD program coursework, providing students the unique opportunity to examine an issue important to their field.
To begin their Doctoral Dossier process, students will spend their first year working on a Scholarship of Integration project (Project 1) that focuses on exploration and identification of underlying causes of and factors associated with their chosen POP. Using systems thinking, which includes perspective-taking, and the research literature, students will document their exploration in an introductory narrative that provides the rationale and supporting evidence for their decision to further pursue their research topic throughout their doctoral journey.
During the second year, following completion of the Scholarship of Integration project, students will choose one of the following two options for Project 2:
1. Scholarship of Application: Demonstrate the application of the research to practice. The purpose of this project is to a) consider how the research perpetuates and/or disrupts oppression, b) critique relevant systems, structures, and institutions, and c) determine avenues to effectively disseminate evidence to a wider audience and stakeholder group.
Example projects include: historical analysis of a topic, curriculum creation, community organization, autoethnography, instructional pedagogy, and others.
2. Scholarship of Teaching: Development and improvement of pedagogical practices. Students examine teaching processes and assessments improve practice.
Example projects include : autoethnography of one’s teaching, innovative teaching materials, curricula, development of new courses, or development of a new pedagogical framework.
During the third year, following completion of Project 2, students will choose one of the following:
- The scholarship option NOT chosen for Project 2, or
- Scholarship of Discovery: Search for new knowledge. Students conduct evidence-based research that leads to knowledge creation.
Example projects include: written, oral, or other modalities of research, scholarly publications, empirical study, working paper, or book chapters.
During the fourth year, students will complete Project 3, write an Executive Summary that ties their three projects together, and write a final reflection of their doctoral journey. The Doctoral Dossier will be presented and assessed during the fourth year.
Students are expected to complete four years of coursework and independent research concurrently. This program is cohort-based, thus if students require a leave of absence for any reason, they will return in the appropriate course sequence with the next cohort the following year.
Problems of Practice and Dossier Style Dissertation (for students admitted Fall 2021 and Fall 2022*)
Students examine a Problem of Practice (POP), which is an area of concern that they have observed within their professional context. This POP becomes the focus of the student's Dossier Style Dissertation. The Dossier Style Dissertation is embedded within the EdD program coursework, which provides students with a unique opportunity to examine an issue important to the organization in which they are employed.
During the first year in the program, students synthesize research literature to understand factors relevant to the POP from a broader systems perspective. During the second year of the program, students conduct an empirical project to investigate their POP within their professional context. Students are expected to collect and analyze data to further understand and refine their identified problem. Based on the evidence in the literature review and empirical project, students will engage in a final project that may further explore an aspect of their POP or articulate a potential solution.
Students will demonstrate mastery of first- and second-year competencies through written and oral comprehensive assessments, which will serve as indicators of readiness for conducting their applied research. Students will then evaluate the effectiveness of this solution as their Applied Project (Year 3). Characteristics of the Dossier Style Dissertation that make it unique to this program include:
- Written assignments within courses that focus on the student's POP.
- Coursework that leads students to consider applications that hold the potential for significant change or impact within their organization and/or have implications for policy.
- Dossier Style Dissertation components that are embedded within coursework and distributed across the three years of the program.
Although somewhat different from a traditional dissertation in its completion and focus, students are nevertheless expected to demonstrate mastery of the relevant literature, to obtain extant and/or collect additional data, and to interpret the results in light of previous studies. The Dossier Style Dissertation will be presented at a final oral defense before a Dossier Style Dissertation Panel.
Typically, we expect that students would complete three years of coursework and independent research concurrently. It is possible that some students may need more than three years to complete their research, in which case they will be required to enroll in at least one credit hour per semester after completion of the required 90 credit hours.
*Students admitted Fall 2021 can choose to complete either the Dossier Style Dissertation or the Applied Dissertation described below. Fall 2022 students may only complete the Dossier Style Dissertation.
Problems of Practice and Applied Dissertation (for students admitted Fall 2013-2021*)
Students examine a Problem of Practice (POP), which is an area of concern that they have observed within their professional context. This POP becomes the focus of the student's Applied Dissertation research. The Applied Dissertation is embedded within the EdD program coursework, which provides students with a unique opportunity to examine an issue important to the organization in which they are employed.
During the first year in the program, students examine their articulated POP to identify underlying causes and associated factors. During the second year of the program, students develop a potential solution, such as an intervention or policy change, and a plan to study the implementation of this intervention as well as proximal outcomes. Students will demonstrate mastery of first- and second-year competencies through written and oral comprehensive assessments, which will serve as indicators of readiness for conducting their applied research. Students will then evaluate the effectiveness of this solution as their Applied Dissertation (Year 3). Characteristics of the Applied Dissertation that make it unique to this program include:
- Coursework that leads students to consider solutions that hold the potential for significant change or impact within their organization and/or have implications for policy.
- Dissertation components that are embedded within coursework and distributed across the three years of the program.
Although somewhat different from a traditional dissertation in its completion and focus, students are nevertheless expected to demonstrate mastery of the relevant literature, to obtain extant and/or collect additional data, and to interpret the results in light of previous studies. The dissertation will be presented at a final oral defense before the student’s Dissertation Advisory Committee.
Typically, students will complete three years of coursework and independent research concurrently. It is possible that some students may need more than three years to complete their research, in which case they will be required to enroll in at least one credit hour per semester after completion of the required 90 credit hours.
*Students admitted Fall 2013-2020 must complete the Applied Dissertation. Students admitted Fall 2021 can choose to complete either the Dossier Style Dissertation or the Applied Dissertation. Fall 2022 students may only complete the Dossier Style Dissertation.
Learning Outcomes
Program goals.
Upon successful completion of the EdD, we expect that graduates will:
- Participate as a self-reflexive, social justice-oriented learner within diverse educational or learning communities.
- Analyze and critique educational practice and research from a social justice and systems perspective.
- Apply relevant methodologies to address critical challenges in education.
- Demonstrate a curiosity for, and a systematic approach to, at least one major topic of study within education resulting in an emerging expertise.
- Integrate research and practice-based knowledge to develop research-informed decisions and opinions about educational experiences, processes, policies, and institutions.
- Communicate effectively to diverse audiences about educational research, experiences, processes, policies, and institutions.

College of Professional Studies
Northeastern University’s online Doctor of Education program provides experienced adult learners, working professionals, and scholar-practitioners from diverse backgrounds and perspectives with the practical knowledge and experience they need to transform the learning landscape. Students gain innovative approaches to create authentic change in their communities. The program was selected as the Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate's Program of the Year for 2022-2023.
The Doctor of Education program is designed to be completed in three to four years of study—following a fast-paced quarter system in lieu of a traditional semester format. Students choose from five concentrations to create a curriculum that matches personal and professional interests. The program's dissertation in practice process will begin at the onset of your coursework as you identify your problem of practice and develop an action plan—incorporating cycles of data collection and analysis, collaboration, change work, and reflection—culminating in the dissemination of your action research findings. Our students come from diverse disciplines and professions, seeking more than just a degree. You'll gain a practical education that translates to your everyday working environment.
While all EdD courses can be completed online (except for hybrid courses in Seattle and Charlotte), annual in-person two-day residencies are held on campus. Residencies focus on networking and tools for career success and allow you to connect with faculty and fellow scholars to share knowledge and experience. You'll attend residencies* in your first and second years of the program at one of our campuses in Boston, Charlotte, or Seattle.
The Northeastern Doctor of Education degree is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education (NECHE) and was selected as Program of the Year by the Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate Program for 2022-2023.
*Please note: International students enrolling in the online EdD program will be provided with an option to complete the residency through online participation in interactive sessions with fellow scholars offered during the residency period.
More Details
Unique features.
- You will choose one of five concentrations—higher education administration, innovative teaching and learning, transformative school leadership, workplace learning, and integrative studies—to focus your studies and further customize your curriculum.
- You'll begin dissertation in practice work at the onset of your program. You'll select a compelling educational/organizational challenge and will be assigned a faculty advisor to support your research throughout the program.
- All coursework is online—providing flexibility for working professionals. Your residencies will be fulfilled in person*, at one of our campuses in Boston, Charlotte, or Seattle.
- You'll learn alongside faculty practitioners—engaging with respected leaders who contribute to the field as authors, journal editors, school board members, bloggers, and podcasters.
*In-person participation in the residency is also available for international students.
Concentrations
- Higher Education Administration: The higher education administration concentration provides an opportunity for experienced higher education professionals to expand their previous understanding of practices within all sectors of postsecondary education—and also advance their professional practice by developing and deepening their understanding of the roles of colleges and universities in our society. Sectors examined include community colleges, four-year colleges, for-profit institutions, and research universities.
- Innovative Teaching and Learning: The innovative teaching and learning concentration focuses on transforming education through innovation, justice, and policy, by providing engaging opportunities for current and aspiring teaching and learning specialists working in various education spaces. The concentration focuses on teaching and learning both inside and outside the bounds of P-20 schools and focuses on developing and leading innovative curricula as well as professional development.
- Transformative School Leadership: The transformative school leadership concentration provides innovative opportunities for experienced education professionals who are current and aspiring leaders of early childhood centers, public or private schools, or school districts. The concentration prepares students to lead and transform educational spaces and be equipped to shape the needs of education in K-12, higher education, organizational contexts, and beyond.
- Workplace Learning: The workplace learning concentration helps professionals gain a deeper understanding of, recognize, and influence real-life social inequalities faced by marginalized populations in the workplace. Courses allow students to advance their professional practice by developing and deepening their knowledge of workplace learning, organizational dynamics, learning strategy, and ethics.
- Integrative Studies: The integrative studies concentration provides an opportunity for students to design a program of study that fits their own professional goals and includes the required foundation and research courses, concentration courses from any EdD concentration, and electives from the Doctor of Education or Doctor of Law and Policy programs.
Program Objectives
Northeastern's Doctor of Education program is designed for experienced professionals interested in deepening their understanding of education, organizational development, and leadership. Throughout the program, students examine various approaches to critical, practice-based issues, learn research methods, and conduct a doctoral research study that investigates a compelling educational or organizational challenge.
2022-2023 Doctor of Education Program of the Year
The Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate selected Northeastern's EdD program as the 2022-2023 Program of the Year, noting the “redesigned Dissertation in Practice Curriculum and the adoption of action research as its guiding methodology …” The committee praised “the program’s efforts to move beyond the typical five-chapter dissertation and engage scholarly practitioners in the acquisition of skills to realize meaningful change in their local contexts, emphasizing social justice.”
Testimonials
– sara ewell, phd, assistant dean, graduate school of education, – frawn morgan, current student, doctor of education, – aaron b., program graduate, looking for something different.
A graduate degree or certificate from Northeastern—a top-ranked university—can accelerate your career through rigorous academic coursework and hands-on professional experience in the area of your interest. Apply now—and take your career to the next level.
Program Costs
Finance Your Education We offer a variety of resources, including scholarships and assistantships.
How to Apply Learn more about the application process and requirements.
Requirements
- Online application
- Academic transcripts: Official undergraduate and graduate degree documentation
- Describe the problem of practice
- Explain why you want to investigate it
- Provide a strong rationale for the significance of the problem
- Minimum work experience: Three years in a related field
- Professional resumé: Must summarize work and education history, include an outline of your educational/academic skills with examples such as research and teaching experience, affiliations, publications, certifications, presentations, and other professional skills.
- Faculty recommendation: Must be from a faculty member in your previous graduate program who can attest to your readiness for doctoral work. If you are no longer acquainted with a faculty member, please choose a professional who can speak of your academic capabilities to engage in doctoral-level research and writing. Recommendations should be presented as a letter attached to the general recommendation form.
- Two professional recommendations: Must be from individuals who have either academic or professional knowledge of your capabilities, a supervisor, mentor, or colleague. It is preferred that one letter of recommendation come from your current employer and/or supervisor. Recommendations should be presented as a letter attached to the general recommendation form.
- Proof of English language proficiency: ONLY for students for whom English is not their primary language.
Are You an International Student? Find out what additional documents are required to apply.
Admissions Details Learn more about the College of Professional Studies admissions process, policies, and required materials.
Admissions Dates
Our admissions process operates on a rolling basis; however, we do recommend the application guidelines below to ensure you can begin during your desired start term:
Domestic Application Guidelines
International Application Guidelines *
*International deadlines are only applicable if the program is F1 compliant.
Industry-aligned courses for in-demand careers.
For 100+ years, we’ve designed our programs with one thing in mind—your success. Explore the current program requirements and course descriptions, all designed to meet today’s industry needs and must-have skills.
View curriculum
The core of the mission of the program is to allow educators to remain in the places they work, focus on a problem of practice, and through experiential learning and site-specific research opportunities in the program, make an immediate impact in their professional environments. The program explicitly integrates research and practice for professionals so they develop the requisite skills for conceiving, designing, conducting, and producing original site-based research in order to effect ethical change related to real-life problems of practice.
Our Faculty
Northeastern University faculty represents a broad cross-section of professional practices and fields, including finance, education, biomedical science, management, and the U.S. military. They serve as mentors and advisors and collaborate alongside you to solve the most pressing global challenges facing established and emerging markets.

Joseph McNabb, PhD

Cherese Childers-McKee, PhD
By enrolling in Northeastern, you’ll gain access to students at 13 campus locations, 300,000+ alumni, and 3,000 employer partners worldwide. Our global university system provides students unique opportunities to think locally and act globally while serving as a platform for scaling ideas, talent, and solutions.
Below is a look at where our Education & Learning alumni work, the positions they hold, and the skills they bring to their organization.
Where They Work
- Boston Public Schools
- Chicago Public Schools
- NYC Department of Education
- Lockheed Martin
- Veterans Affairs
- Johns Hopkins
- Columbia University
What They Do
- Media Consultant
- College President
- Chief Information Officer
- Instructional Designer
- Diversity Officer
- Founder-CEO
- VP of Student Services
- Community Services Director
What They're Skilled At
- Experiential Learning
- Team Building
- International Education
- Change Agency
- Entrepreneurship
- Urban Education
- Strategic Management
- Student Engagement
Learn more about Northeastern Alumni on Linkedin .
Related Articles

Top Higher Education Conferences to Attend in 2023

How Much Do Instructional Designers Make?

5 Instructional Design Models You Should Know
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

Admissions & Aid
- Admissions Home
- Application Requirements
- Financing Options
- Diversity Profile

You are here
Application requirements for all doctoral programs (phd).
All of our doctoral programs are designed to develop outstanding educational researchers who have a deep understanding of the scientific, practical and policy issues they study. All require full-time study, and we promise five years of full-time financial support for every student we admit. Our doctoral programs are small, typically ranging from about 25 to 35 new students a year. The small size of our doctoral cohorts creates big educational advantages for students: the classes are almost always small, students receive individualized attention from their advisors, and they have many opportunities to develop close collegial relationships with fellow students.
It is extremely important to demonstrate in your statement of purpose that your interests converge closely with the current research of faculty who work in the program to which you are applying. Other doctoral applicants will certainly do this, and if you don't, you will forfeit an important competitive advantage to them.
If you wish to contact faculty, please read our Which Degree Which Program article, by Professor Eamonn Callan, which outlines the appropriate process for contacting faculty with whom you share research interests.
- Program website: Degrees and Programs/PhD
- Length of Program: 5 years (average length)
- Tuition: fellowship/assistantship salary and tuition guaranteed for first five years of the program (autumn, winter and spring quarters) for all students, including international students. Funding includes two summers.
Application Requirements:
Application form.
Complete and submit Stanford's graduate online application .
Application Fee
The application fee is $125 , is non-refundable, and must be received by the application deadline.
Application Fee Waivers
Stanford offers three types of application fee waivers for which GSE applicants may apply and be considered:
- GRE Fee Reduction Certificate-Based Waiver
- Diversity Program Participation-Based Waiver
- School-Based Waiver
Please visit the Stanford Graduate Diversity website for instructions, deadlines, and the fee waiver application form.
Statement of Purpose
A Statement of Purpose is required. Your statement should be typed, single-spaced and should be between one to two pages . Describe succinctly your reasons for applying to the proposed program, your preparation for this field of study, and why our program is a good fit for you, your future career plans, and other aspects of your background as well as interests which may aid the admissions committee in evaluating your aptitude and motivation for graduate study. You may indicate potential faculty mentors as part of your study and research interests. Be sure to keep a copy for your records. What's a Good Statement of Purpose?
A resume or CV is required of all applicants, depending on which document is most appropriate for your background. There is no page limit for resumes or CVs, though we typically see resumes of one page in length. Please upload your resume or CV in the online application.
Three (3) Letters of Recommendation
Applicants are required to submit three letters of recommendation . In the online application, you will be asked to identify your recommenders and their email addresses. Please notify your recommenders that they will receive an email prompt to submit their recommendation online. You can submit your request for letters of recommendation through the system without submitting the entire online application. Stanford GSE only accepts online recommendations through the application system ; Stanford GSE cannot accept mailed, emailed or faxed recommendations.
Recommendations should be written by people who have supervised you in an academic, employment, or community service setting. We very strongly recommend that at least one of these letters be from a university professor familiar with your academic work. Your recommendations should directly address your suitability for admission to a graduate program at Stanford GSE.
It is the applicant's responsibility to ensure that all three letters of recommendation are submitted through the system by the application deadline , so please work closely with your recommenders to remind them of the deadline.
College and University Transcripts
Transcripts are required from every college and university you have attended for at least one academic year as a full-time student. When submitting your online application, transcripts should be uploaded to the application as a scanned copy or PDF ; this is sufficient for the application review process. Please refrain from sending a secured PDF/transcript with a digital signature as our system cannot upload these properly. The best way to ensure we receive an upload-able document is for you to print out the secured transcript, scan it, and upload the scanned copy (not to exceed 10MB) as a PDF.
If you earned a degree at the institution from which you are submitting a transcript, please ensure that the degree conferral date and the degree conferred is clearly visible on the document. If you are currently enrolled in a degree program and will not have earned the respective degree by the time of submitting your GSE application, you should submit your most recent in-progress transcript from your institution.
Only if admitted will we contact you with instructions on sending two copies of your official transcripts to our office. We cannot accept mailed, emailed or faxed copies of your transcripts during the application process. Please note: the instructions for sending transcripts on the online application and on the general Stanford Graduate Admissions Office website differ from this Stanford GSE requirement.
Concerning course work completed in a study abroad program
If the coursework and grades are reflected on the transcript of your home institution, you do not need to submit original transcripts from the study abroad institution.
Concerning foreign institutions
If your institution provides a transcript in a language other than English, we require that you submit a translation of the transcript that is either provided by the institution or a certified translator. Translations must be literal and complete versions of the original records.
If your transcript does not include your degree conferral date and the degree conferred , please submit a scanned copy of your diploma, a conferral statement, or a conferral document in addition to your transcript . If you are currently enrolled in a degree program and will not have earned the respective degree by the time of submitting your GSE application, you should submit your most recent in-progress transcript from your institution.
Stanford University requires the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) from all applicants whose native language is not English. The GSE requires a minimum TOEFL score of 250 for the computer-based test, 600 for the paper-based test or 100 for the internet-based test in order to be considered for admission. The Test of Written English (TWE) portion of the TOEFL is not required. Applicants who have completed a four-year bachelor's degree or a two-year master's program (or its equivalent) in the U.S. or at an institution where English is the main language of instruction are not required to take the TOEFL. For more information on TOEFL requirements, please refer to the Required Exams page on the main Stanford Graduate Admissions website. You may register for the TOEFL test directly at the ETS website .
TOEFL Dates and Deadlines
PhD applicants who are required to take the TOEFL should plan to take the internet-based TOEFL test and have official TOEFL scores sent electronically to Stanford at institution code 4704 (department code does not matter) no later than November 1 . This will give your official TOEFL scores time to be sent from ETS and be received by our system in time for the December 1 deadline. PhD applicants to Knight-Hennessy Scholars should plan to take the internet-based TOEFL test no later than October 16 so your scores can be received by our system in time for the November 16 KHS GSE deadline. Please note that the TOEFL may be taken no earlier than 18 months prior to the application deadline.
Does Stanford accept tests other than TOEFL?
No. We accept only TOEFL scores; we do not accept IELTS or other test scores.
Contact Information
Admissions: [email protected]
- Financial Aid
- Current Student Info
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Become a Celtic
- By Location
- All Locations
- Satellite Locations
- By Degree Type
- All Degree Types
- Undergraduate
- Certificates
- All Subjects
- Art & Design
- Business & Management
- Data Analytics
- English & Communications
- Law & Criminal Justice
- Psychology & Counseling
- Science & Math
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- Academic Information
- Professional Development
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Support
- General Education Curriculum
- Course Catalogs
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Study Abroad
- Faculty & Student Research
- Institutional Review Board
- College in High School
- Apply to Carlow
- International
- Military & Veterans
- For Counselors & Consultants
- Meet our Admissions Team
- Visit Campus
- Schedule Your Visit
- Enrollment Events
- Virtual Tours
- Questions You Should Ask
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Tuition & Fees
- Financial Aid
- Financial Aid Forms
- Payment Options
- Net Price Calculator
- Scholarships & Awards
- New Student Information
- New Student Checklist
- Helpful Links
- Deals & Discounts
- Carlow Identity
- Mission & Vision
- Core Values
- Diversity Statement
- Philosophy Statement
- Catholic Intellectual Tradition
- Heritage & Mission
- The Sisters Of Mercy
- 90th Anniversary
- Mercy & Justice
- Worship Opportunities
- Campus Ministry
- Mercy Service
- Social Justice Institutes
- Atkins Center for Ethics
- Campus Life
- Equity & Inclusion
- U-Pass Program
- Parking & Public Transportation
- Pittsburgh & Our Neighborhood
- Clubs & Activities
- Campus Safety
- Contact Campus Police
- Download Campus Safety App
- Police & Security Services
- Safety & Security Policies
- Student Services
- Technology Support
- Tutoring & Academic Coaching
- Pittsburgh Promise at Carlow
- TRiO Student Support Services
- Disability Services
- Career Development
- The Mercy Center for Care
- Domestic & Sexual Violence Support
- Health & Wellness
- Health Services
- Counseling Services
- Emergency Care
- Alumni Newsletter: Celtic Connection
- Carlow Connect
- Alumni Events
- Class Ambassadors
- Support Carlow
- Give to Carlow
- Mentorship Program
- Volunteer Opportunities
- Request Transcripts
- President’s Report
- Alumni Benefits
- Career Services
- Continue your education
- About University Advancement & Alumni Engagement
- Meet the Staff
- Alumni Council
- About Carlow
- The Carlow Commitment: Our Five-Year Strategic Plan
Quick Facts
- Campus & Locations
- Maps, Directions & Parking
- About Pittsburgh
- Center for 21st Century Innovation & Workforce Development
- Administration
- President’s Office
- Board of Trustees
- Departments & Offices
- Faculty & Staff Directory
- Event Rental Space
- Women of Spirit
- Carlow in the News
- Commencement
- University Events
- Carlow Impact Series
- Request Info
- Employee Login
- Student Login
- Request Transcript
- Celtic Leadership Institute
Doctorate in Education Program
Carlow university’s new edd program: devoted to the future of education.
Carlow University’s new Doctorate in Education (EdD) program is geared toward teachers and administrators who recognize the need for a new brand of leadership to re-imagine the future of education now. This three-year practice-based inquiry program is for people who are devoted to extending their voices beyond their particular disciplines to help change the world for their future students. It offers four learning tracks:
Leadership | Curriculum and Learning | Literacy | Early Childhood Policy and Leadership

Credits Required:
Cost per credit:, time to completion:.
As few as 36 months
100% online – Dissertation defense is in person.
EdD courses at Carlow are different from other programs because they feature a distinctly integrated doctoral study design, with each course building upon previous ideas while preparing students to engage with new concepts that can inform their practice. Throughout the program, students are invited to study systems design, to engage in discursive deliberation, and to explore new transformational approaches to education.
- Our EdD is rooted in our rich history and traditions of social justice and mercy values.
- We invite and respect diversity of thinking and expression as we learn together to challenge social injustices and inequities in schools.
- This program positions students as innovative thinkers as they present their ideas and practice-based research.
- Students can learn and work with other innovative system thinkers.
Alternate Degree Completion Options
Online Degree Gain the knowledge you need at your convenience with our online degree option. When applying, indicate your interest in the online option.
Accelerated Fast track your way to a master’s by taking graduate courses as an undergraduate student. Course credits count towards both degrees. Apply for this option after your sophomore year.

Career Opportunities for EdD
The EdD degree is the highest degree that can be awarded in the field of education. It signifies unparalleled expertise and concentrated study in the field. This degree is valued by individuals seeking a career as principals, school district superintendents, assistant superintendents, college faculty, executive directors, or heads of foundations.
Full-Time Faculty

Keely Baronak, EdD Chair, Professor, Education

Sean Freeland Assistant Professor
Tammi McMillan Director, Early Childhood Apprenticeship Hub

MiIsha Reid Assistant Professor, Special Education

Patricia McMahon, PhD Professor, Education

Valerie Piccini, MEd Instructor, Reading Specialist, Education
Marissa mcclure-sweeny faculty and program director, early childhood , admission requirements and application process.
- 3.0 GPA Minimum for Admission
- Apply anytime, start date in the Fall Semester.
- It is possible to transfer up to 18 post-Masters credits
- This program accepts international students
- Current CV, graduate transcript, and an essay are required to apply
- Three (3) professional recommendations are required
Start Terms:
Fall, Spring, and Summer
Contact Admissions
If you are interested in this doctorate program, our Admissions team is available to assist you with the next steps, including scheduling an on-campus visit .
Doctor of Education Leadership

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
America needs transformative leaders in preK–12 education whose passion for education quality and equity is matched by a knowledge of learning and development, the organizational management skills to translate visionary ideas into practical success, and a firm grasp of the role of context and politics in shaping leadership. Graduates of the three-year, multidisciplinary Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.) Program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education will be prepared to become those leaders.
The Ed.L.D Program — taught by faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School — will train you for system-level leadership positions in school systems, state and federal departments of education, and national nonprofit organizations. Ed.L.D. is a full-time, three-year program built on a cohort learning model. Cohorts consist of up to 25 students from diverse professional backgrounds (including district/charter management leaders, nonprofit directors, principals, teachers, and policy researchers) who progress through the program together.
All Ed.L.D. students receive a full tuition funding package plus stipends, work opportunities, and a paid third-year residency at a partner organization.
The Ed.L.D. Program prepares graduates to do work for the public good in the American public education sector, whether that be at the system or state level. Specifically, the program is designed to accelerate the progress graduates make toward achieving meaningful impact in influential roles and/or crossing boundaries in the following spaces in the public education sector:
- PreK–12 district or CMO leadership roles : superintendent of schools, chief academic officer, and/or deputy superintendent
- Foundation/philanthropy roles: director, president and CEO, senior fellow
- Education nonprofit roles : president or executive director of backbone or collective impact organizations which support preK–12 schools. Ed.L.D. graduates will lead education nonprofits that explicitly focus on improving outcomes and opportunities for children, families, and communities.
- State or federal education leadership roles : commissioner or deputy commissioner roles. Could also include public education advocacy or education policy advisers to senior government officials.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Innovation roles: Founder, CEO, president
Curriculum Information
The Ed.L.D. curriculum is a balance of multidisciplinary coursework and practice-based learning. Core courses and electives are taught by recognized leaders from across Harvard’s graduate programs in fields like data-based education reform, organizational change and innovation, and effective leadership strategies for urban schools. You will develop and test your leadership skills through team projects and an immersive third-year residency.
All students in the cohort take the same classes in four foundational content areas: learning and teaching, leadership and organizational change, politics and policy, adult development, and leadership inside and out (including one-on-one executive coaching). Courses taken during the first-year focus on practice-based learning and serve as the framework of your first-year experience.
Sample HGSE Courses
- Leading Change
- How People Learn
- Ed.L.D. Proseminar
- Leadership, Entrepreneurship, and Learning
- Race, Equity, and Leadership
- Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Sector Change
- The Workplace Lab for System-Level Leaders
View all courses in the Academic Catalog.
Each cohort member works with program advisers to choose an individualized sequence of electives from any of the Harvard graduate schools. You will work closely with the program faculty and staff during your second year to determine the best match with a partner organization for your third-year residency. Matches are driven by mutual interest between the resident and the partner organization, and each student's career and learning goals and geographic preferences.
- Second Year Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Driving Change
- Education Sector Nonprofits
- Negotiation Workshop
- Coaching with Equity in Mind
- Ethnic Studies and Education
- Deeper Learning for All: Designing a 21st Century School System
- Institutional Change in School Organizations, Systems, and Sectors
You will take part in a 10-month paid residency at one of our partner organizations. There, you will work on a strategic project which synthesizes your experience and learning into a written Capstone project. You will stay connected to your Ed.L.D. cohort and HGSE through technology and by returning to Harvard periodically for intensive workshops.
Paid Residency
Our partner organizations include school systems and departments of education, as well as some of the nation's most influential and dynamic nonprofit, mission-based for-profit, and philanthropic organizations.
You will be intentionally pushed out of your comfort zones and asked to work systemically and make a significant contribution to the partner organization. In addition, the residency will provide you with the professional mentoring, practical experiences, and network of connections they need to position themselves as future leaders in the education sector.
Strategic Project
You will define (with supervisors from your partner organization) a strategic project on which to focus. You will have the opportunity to lead one or two major efforts on behalf of the organization, such as the creation or implementation of current initiatives. The project allows you to practice and improve leadership skills, add important value to the mission and strategy of the partner organization, work systemically, and hold high-level accountability.
During the residency period, you will produce a written Capstone. The Capstone is a descriptive, analytic, and reflective account of your third-year leadership contributions to a strategic project within an Ed.L.D. partner organization. It is a demonstration of your ability to engage others, develop strategy to successfully address and diagnose challenges, work toward a vision and goals, and learn from the results.
Sample Topics
- Accountability, Coherence, and Improvement: Leadership Reflection and Growth in the Los Angeles Unified School District
- Leadership Development for Entrepreneurial Education Leaders Working to Build Public & Private Sector Support
- Disrupting Teacher Preparation: Lessons in Collaboration and Innovation Across the Learning to Teach Community of Practice
- Pursuing Educational Equality for English Language Learners
Sample Summaries
- Breaking Down Silos in a School District: Findings from an Ed.L.D. Project in Montgomery County
- Expanding Students' Access to Meaningful STEM Learning Opportunities Through Strategic Community Partnerships
- Developing a New Teacher Leadership and Compensation System in Iowa: A Consensus-Based Process
- Finding Great Teachers for Blended-Learning Schools
GSE Theses and Dissertations from Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH)
Program Faculty
Ed.L.D. students learn with renowned faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, Harvard Business School, and Harvard Kennedy School. Faculty from the three schools share their individual expertise in the Ed.L.D. Program and work collaboratively to provide a challenging and coherent experience for students. Faculty who teach in the Ed.L.D. core curriculum and advise Ed.L.D. students include:
Faculty Director

Frank D. Barnes
Frank Barnes is faculty director of the Doctor of Education Leadership Program. He has over 30 years experience as an educator, researcher, and organizer. As a chief accountability officer, he led turnaround efforts for large public school districts, including Boston Public Schools and Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools.
Kathryn Parker Boudett

Ebony N. Bridwell-Mitchell

Jennifer Perry Cheatham

Elizabeth City

Candice Crawford-Zakian

Marshall Ganz

Adria D. Goodson
Deborah helsing.

Monica C. Higgins

Deborah Jewell-Sherman

Lisa Laskow Lahey

Mary Grassa O'Neill

Irvin Leon Scott

Catherine Snow

Michael L. Tushman
Martin west.

How is the third third-year residency determined? Will I get to choose where I go and for whom I work?
You will work closely with Ed.L.D. Program faculty during your second year to determine the best partner organization match for your third-year residency. In ascertaining a match, faculty take a number of factors into account, including a students' career goals and geographic preferences. The program expects that the current list of partners will continue to grow based on organizational and student interest.
The Ed.L.D. Program has partnered with organizations that are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in American preK–12 education. The partners are school systems, nonprofit organizations, mission-based for-profit organizations, and government agencies, all pursuing a common goal of ensuring that every child has the opportunity to achieve their full potential. You will work directly with partner organizations in the third-year residency and have some exposure to partner representatives in the first two years of the program. Your work with our partner organizations will be encapsulated in a Capstone, which is descriptive, analytic, and reflective account of the your leadership and contributions to a strategic project. Summaries of Capstones by several members of the first cohort of Ed.L.D. graduates are available in the curriculum section.
Partner Organizations
Below is a sample list of current and/or previous Ed.L.D. partner organizations:
- Bellingham Public Schools
- Big Picture Learning
- Boston Public Schools
- Denver Public Schools
- Education First
- Harlem Children's Zone
- Jobs for the Future
- John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation
- Madison Metropolitan School District
- New Haven Mayor’s Office
- New Schools for Baton Rouge
- New Schools Venture Fund
- New York City Department of Education
- The Leadership Academy
- Phi Delta Kappa/Educators Rising
- Providence Public Schools
- Rhode Island Department of Education
- South Carolina Public Charter School District
- Virginia Department of Education
Student Directory
An opt-in listing of current Ed.L.D. students with information about their interests, research, personal web pages, and contact information:
Doctor of Education Leadership Student Directory
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Education Leadership experience and the impact its community is making on the field:

Combatting Chronic Absenteeism with Family Engagement
As post-COVID absenteeism rates continue unabated, a look at how strong family-school engagement can help
Math, the Great (Potential) Equalizer
How current practices in math education around tracking and teaching can be dismantled to achieve the promise of equity in math classrooms

- May 24, 2022
- Academic Advice
Doctorate in Education: Requirements, Career & Salary
UOTP Marketing

What makes education a unique profession is its massive impact on the world since academic professionals help, teach, and guide students toward their future careers. A more self-seeking reason behind advancing in the education field can be the income increase.
If you recently earned a Master’s degree in education and want to make an influence in the area while also increasing your salary, you can do so by getting a doctorate in education. But, what about Doctorate in Education salary, requirements, and possible career paths? Keep reading and find out.
What is a Doctorate in Education?
A Doctorate in Education, known as EdD, is the most advanced degree which prepares students for administrative, academic positions, and field leadership. If you are wondering what you will learn during this crucial stage of your academic development, we are listing below some of the courses the University of the Potomac offers you:
- Organizational Development
- Applied Research
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Defense
FREE RESOURCE

Download Our Free Guide to Effective Leadership in the 21st Century
Learn what you need to know about the challenges, trends, and skills shaping today’s leaders.
Doctorate in Education entry requirements

If you are interested in pursuing EdD but are wondering if you are eligible, here is a list of standard doctor of education requirements that U.S. universities usually have:
- Academic interviews
- A Bachelor’s and Master’s degree
- A GPA of 3.0-3.5
- Resume, including qualifications, motivation letter, and letters of recommendation)
- Student visa (only applies to international students)
How long does it take to get a Doctorate in Education?
When it comes to seeking higher education, time is essential. An EdD’s duration varies depending on the University and may last up to 4 years, which can be a lot for some people as they may not have enough time between work and school. We are aware of that; so, to be flexible while still having time to relax or continue working, the UOTP offers online learning where you will experience the same high quality as students on campus.
Doctorate in Education qualifications and skills
Now that you know the degree’s requirements and duration, let us tell you about the qualification and skills you will obtain. In the Doctor of Education Program , you will learn how to interpret research literature, identify solutions, and develop contextual applications. Some of the main skills you will obtain throughout the degree are:
- Communication skills
- Organizational skills
- Feedback and evaluation skills
- Mentoring Skills
- Critical thinking Skills
- Collaboration skills
Doctorate in Education Career Possibilities

A question that we hear a lot is regarding the career possibilities that you can get from this degree. Some may be confused that the education field is only for people who want to teach. In contrast, the education field offers a variety of career opportunities that may be in academic or non-academic areas. So, let’s dive right into some doctor of education jobs you may have in the future.
Academic career paths
After finishing your degree, you may want to start looking at academic career paths that fit into the goal objectives that you have set for yourself. Below, we provide you with some academic positions you can get with a doctorate in education.
University professor

In this career path, your primary responsibility will be to guide students in the right direction while adding value to the University. Professors do that by:
- Building course curriculums
- Preparing course syllabuses
- Presenting lectures
- Mentoring and supervising
- Grading and providing feedback
- Attending training sessions to gain new experience

Academic Dean
As an academic dean, you will be responsible for a specific university department where you will supervise all academic and administrative operations. Academic deans do that by:
- Providing academic support to students
- Monitoring the budget and allocating it to different activities
- Developing strategic plans
- Recruiting potential students
- Conducting instructor evaluations
- Recruiting university staff
- Dealing with disciplinary actions
School principal
This position holds a huge responsibility as school principals deal with almost every school aspect, starting from teacher expectations up to student successes. So, if you are wondering what they do daily, here are a few day-to-day tasks of school principals:
- Setting academic goals
- Supervising school staff and students
- Managing the school budget
- Ensuring school security
- Counseling and disciplining students
- Assuring school funding by meeting with potential donors
Non-academic career paths
Now that you know about academic paths you can pursue, let’s start with non-academic career ones.
As individuals, we all have unique views on the future. While some students may seek academic employment options after graduation, others may be more interested in non-academic career options. We will go over these non-academic employment choices in greater detail below.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
Training and development specialist

This position helps businesses create, develop, and implement training programs for employees. They do that by:
- Assessing surveys, interviews, and communication
- Holding training for employees to improve their job performance
- Maintaining attendance, test results, and retraining requirements
- Managing the training budget
- Developing course materials and guides for assignments
Healthcare administrator
A healthcare administrator’s primary responsibility is to monitor the operation of healthcare organizations and improve patients’ experiences. Healthcare administrators do that by:
- Managing patients bills
- Training staff members
- Monitoring budget
- Communicating with the staff
- Developing work schedules for the healthcare staff
Human resources manager

This position helps organizations succeed by building a staff that achieves success along with the company. They do that by:
- Interviewing, selecting, hiring, and training potential candidates
- Supervising the HR staff
- Administering payroll and benefits for employees
- Dealing with and resolving workplace issues
- Conducting surveys for workplace improvement.
Doctorate in Education Salary and Job Outlook
The salary and job outlook are essential for choosing a career. The average Doctorate in Education annual salary in the U.S. is 80,000$ , and depending on the position and experience, it may go up to 236,000$. As for the job outlook, BLS expects a 10% increase in education sector employment from 2020 to 2030, with 920,500 new jobs predicted. So, by now, you may know the value of this degree.
All in all, enrolling in a Doctorate in Education can be beneficial for you in terms of advancing your career and boosting your income. It is the highest degree of education which takes time, patience, persistence, and hard work, so make sure to find the right time before starting. Consequently, all hard work will be rewarded by being a part of a growing industry now and in the future. Now that you have all of the details for a Doctorate in Education, all there is left for you is to seize the opportunity !
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do With a Hospitality Management Degree? Best Hospitality Careers

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information
- Best Online Doctoral Programs
Best Online Doctoral Programs Of 2024

Published: Apr 23, 2024, 1:42pm
The best online doctoral programs offer flexibility and convenience that can make it easier for you to pursue an advanced degree, often while working full time.
Earning a doctorate can help you advance to the highest roles in your field and increase your salary potential. It’s also a chance for you to gain an advanced understanding of impactful issues and develop the skills to generate new ideas, solve problems and create meaningful change.
Below, learn about the best online doctoral programs in a variety of fields, including social work, psychology, education and nursing.
Why You Can Trust Forbes Advisor Education
Forbes Advisor’s education editors are committed to producing unbiased rankings and informative articles covering online colleges, tech bootcamps and career paths. Our ranking methodologies use data from the National Center for Education Statistics , education providers, and reputable educational and professional organizations. An advisory board of educators and other subject matter experts reviews and verifies our content to bring you trustworthy, up-to-date information. Advertisers do not influence our rankings or editorial content.
- 6,290 accredited, nonprofit colleges and universities analyzed nationwide
- 52 reputable tech bootcamp providers evaluated for our rankings
- All content is fact-checked and updated on an annual basis
- Rankings undergo five rounds of fact-checking
- Only 7.12% of all colleges, universities and bootcamp providers we consider are awarded
Our Methodology
We ranked accredited, nonprofit colleges offering online doctoral degree programs in the U.S. using metrics in the categories of student experience, credibility, student outcomes and affordability. We pulled data for these categories from reliable resources such as the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System ; private, third-party data sources; and individual school and program websites.
We scored schools based on the following data points:
Student Experience:
- Student-to-faculty ratio
- Socioeconomic diversity
- Availability of online coursework
- Total number of graduate assistants
- Portion of graduate students enrolled in at least some distance education
Credibility:
- Fully accredited
- Programmatic accreditation status
- Nonprofit status
Student Outcomes:
- Overall graduation rate
- Median earnings 10 years after graduation
Affordability:
- In-state graduate student tuition and fees
- Alternative tuition plans offered
- Median federal student loan debt
- Student loan default rate
We chose the best schools to display in 10 categories of doctoral degrees.
Find our full list of methodologies here .
- Best Online Colleges With A 100% Acceptance Rate
- Best HBCUs With Online Degrees
- Best Online Colleges
- Best Online Master's Programs
- What Are The Best Online Public Universities
Degree Finder
Best online doctoral program options.
- Featured partners
Should You Enroll in an Online Ph.D. Program or Doctorate?
Accreditation for online doctoral degrees, how to find the right online doctorate for you, frequently asked questions (faqs) about online ph.d. programs and doctorates.
- Best online Psy.D.: Rivier University
- Best online Doctor of Nursing Practice: University of Central Florida
- Best online Doctor of Business Administration: Walsh College
- Best online doctorate in physical therapy: Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
- Best online doctorate in education: Johns Hopkins University
- Best online Ph.D. in organizational leadership: Indiana Wesleyan University
- Best online Ph.D. in counseling: Concordia University-Irvine
- Best online Doctor of Social Work: University of Southern California
- Best online Ph.D. in public administration: West Chester University of Pennsylvania
- Best online doctorate in educational leadership: Fairfield University
Featured Online Schools
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial credit and much more by clicking 'Visit Site'
Best Online Psy.D.
Rivier university.

Program Tuition Rate
$1,275/credit
Percentage of Grad Students Enrolled in Distance Education
Overall Graduation Rate
Located in Nashua, New Hampshire, Rivier University offers a hybrid Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.) with a limited number of online classes. The American Psychology Association-accredited program focuses on school psychology and counseling and prepares you to work as a psychologist in various environments. You’ll learn clinical diagnosis, assessment, prevention and intervention skills.
Students must attend full time and can work no more than 20 hours per week. It takes a minimum of five years to graduate.
- Our Flexibility Rating: Learn on a set schedule
- School Type: Private
- Application Fee: $100
- Degree Credit Requirements: 60-130 credits
- Program Enrollment Options: Full-time
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Fundamentals of research, group counseling
- Concentrations Available: N/A
- In-Person Requirements: Yes, includes a 2,000-hour internship and at least six practicum experiences
Best Doctor of Nursing Practice
University of central florida.

$372/credit (in-state)
At University of Central Florida (UCF), practicing nurses can earn a Doctor of Nursing Practice. The advanced track program is accredited by the Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education and prepares nurses for clinical leadership roles in the field.
Coursework explores clinical management, communication skills and epidemiology principles. You’ll develop research and practice skills, learn to improve healthcare systems, develop health policy and analyze data to improve individual and population health.
- Our Flexibility Rating: Learn around your 9-to-5
- School Type: Public
- Application Fee: $30
- Degree Credit Requirements: 42 credits
- Program Enrollment Options: Part-time, full-time
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Healthcare systems and policy, nursing environment management
- In-Person Requirements: Yes, includes clinical hours (but all coursework is available online)
Best Doctor of Business Administration
Walsh college.
$1,038/credit
You can earn an online Doctor of Business Administration from Walsh College in Troy, Michigan. The part-time, online program includes asynchronous coursework and real-time Zoom classes, as well as optional opportunities to interact on campus. You can develop advanced business knowledge and skills to become a business leader or consultant.
In addition to coursework, you must pass a preliminary exam and complete a 15-credit dissertation process. The program requires students to graduate within seven years.
- Application Fee: $50
- Degree Credit Requirements: 60 credits
- Program Enrollment Options: Part-time
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Foundations for business success, qualitative and exploratory research methods
- In-Person Requirements: No
Best Doctorate in Physical Therapy
Texas tech university health sciences center.

$265/credit (in-state)
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center designed its hybrid Doctor of Science in physical therapy to help practicing physical therapists advance their careers. The post-professional 36-credit program takes four to five years to complete part time.
The flexible format makes it possible for students to keep working while attending school. Learners attend weekend lectures and labs at the Lubbock, Texas, campus. During the week, they supplement their in-person instruction with online assignments.
- Application Fee: $75
- Degree Credit Requirements: 36 credits
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Medical screening for rehabilitation sciences, motor control in orthopedics
- Concentrations Available: Research track, teaching track
- In-Person Requirements: Yes
Best Online Doctorate in Education
Johns hopkins university.

$2,100/credit
Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland offers an online Ed.D. The part-time degree takes four years to complete and explores topics like the social determinants of education, entrepreneurship and technology.
You can customize the degree by choosing electives that align with your professional interests and by selecting one or more “areas of interest,” such as urban leadership or digital age learning and educational technology. Applicants need a master’s degree with at least 36 graduate credits to qualify for the program.
- Application Fee: $80
- Degree Credit Requirements: 54 credits
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Approaches to urban education, partnerships and community organizing
- Concentrations Available: Creativity, advanced learning, and twice exceptionality; digital age learning and educational technology; entrepreneurial leadership in education; mind, brain, and teaching; urban leadership
Best Online Ph.D. in Organizational Leadership
Indiana wesleyan university.

$890/credit
Located in Marion, Indiana Wesleyan University offers an online Ph.D. in organizational leadership that can prepare you to become an effective leader in as few as four years. The program focuses on inclusion, multiculturalism and international perspectives and develops research, presentation and executive skills.
You must attend an in-person residency during the July session, but the rest of the program takes place online and offers flexibility for working professionals. The school’s tuition guarantee locks in your tuition rate when you start the program.
- Application Fee: Free
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Advanced leadership theory, statistical research design
- In-Person Requirements: Yes, includes an in-person residency
Best Online Ph.D. in Counseling
Concordia university – irvine.

$795/credit
Concordia University – Irvine in Irvine, California, is a Christian institution that offers a “biblically informed” online Ph.D. in counselor education and supervision from its Townsend Institute. Designed for licensed mental health professionals, the degree develops advanced skills and prepares you for leadership roles in counseling, teaching and advocacy.
The accelerated program takes three to four years to complete. It requires two in-person residencies and a total of 700 hours of internship and practicum field experiences. In addition to coursework, you must complete a culminating 12-credit dissertation that includes original counseling research and a successful oral defense.
- Program Enrollment Options: Accelerated
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Advanced counseling and career theories, advanced multicultural issues in counselor education and supervision
- In-Person Requirements: Yes, requires two in-person residencies, a practicum and an internship
Best Online Doctor of Social Work
University of southern california.
$2,137/credit
University of Southern California ‘s online Doctor of Social Work from the Suzanne Dworak-Peck School of Social Work emphasizes the importance of scholarship and practice in the field. Created for experienced social work professionals, the program can help you become a leader working toward social change and innovation.
The program offers a seven-semester accelerated track and a standard nine-semester option. In a capstone experience, learners research and create a prototype that addresses a current problem in social work.
- Application Fee: $90
- Program Enrollment Options: Accelerated, full-time
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Leading public discourse, financial management for social change
Best Online Ph.D. in Public Administration
West chester university of pennsylvania.

$645/credit (in-state)
West Chester University of Pennsylvania ’s online Doctor of Public Administration can prepare you for high-level roles in public affairs and administration. The program is offered by the College of Business and Public Management, accredited by Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business, and the Department of Public Policy and Administration, accredited by the Network of Schools of Public Policy, Affairs, and Administration.
The curriculum explores strategic management, policy advocacy and decision-making in the public sector. The dissertation allows you to complete an applied research project. You can take electives and choose a concentration from multiple departments, including psychology, graduate social work and criminal justice.
- Degree Credit Requirements: 45 credits
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Strategic public sector management and governance, research design for program and policy evaluation
- Concentrations Available: Options from multiple departments
Best Online Doctorate in Educational Leadership
Fairfield university.

$1,120/credit
At Fairfield University in Fairfield, Connecticut, you can earn an online, low-residency Doctor of Education in educational leadership. The program offers two tracks: teacher leader for certified working educators or higher education administration for higher education professionals.
Students enroll in the cohort-style program in the fall and graduate in three years by taking six credits per semester. Learners can build community during two one-week summer residencies. Applicants need a master’s degree in a relevant field and a minimum 3.0 GPA.
- Our Flexibility Rating: Learn on your schedule
- Application Fee: $65
- Degree Credit Requirements: 57
- Example Major-Specific Courses: Action research for educational change, framing and critical analysis of problems of practice
- Concentrations Available: Teacher leader, higher education administration
- In-Person Requirements: Yes, requires two one-week residencies
An online Ph.D. program or doctorate can offer many compelling features for students, but it might not be the right choice for everyone. Consider the questions below when deciding whether to pursue your doctorate online or in person.
- What type of schedule do you need? Online programs typically offer more flexibility that appeals to students who work full time or have personal responsibilities to fit around their school schedule. Online degrees allow learners to pursue higher education without putting their career on hold. This is especially true for programs that offer asynchronous coursework that students complete on their own time.
- What learning style works best for you? Do you work well independently and with a lot of freedom? If so, an online doctorate might be a good fit for you. If you think you’d prefer the camaraderie of an in-person cohort graduate program and structured opportunities to interact with instructors, an on-campus or hybrid program might suit you better.
- How does the program format affect your budget? Online programs can help you save on tuition, housing and transportation costs. For example, many public schools allow you to pay the same tuition, regardless of where you live. However, you might miss funding opportunities typically reserved for on-campus students, such as graduate teaching assistantships, research assistantships and fellowships.
The U.S. Department of Education and the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA) approve accrediting agencies that give schools institutional accreditation in the U.S.
Institutional accreditation means that a university has met minimum quality requirements related to its academics, financial management, faculty and staff, and student resources and services. To qualify for federal financial aid, you must attend an accredited college.
Programmatic accreditation is a separate process that gives special recognition to individual degrees, programs or departments within a university. Depending on your field, you might need a programmatically accredited degree to get a job or qualify for professional licenses or certifications.
You can search for a prospective school’s accreditation status on CHEA’s website .
Consider Your Future Goals
An online doctorate has the potential to help you achieve your career aspirations. However, not every program in your field will necessarily align with your goals. Before you choose an online doctorate program, think about your post-graduation plans.
For example, some online doctorate programs require professional experience through an internship or a practicum. This type of hands-on learning can help you develop your expertise and professional network. But these experiences usually take place in person and can be hard to fit into your schedule if you’re working full time.
You should also consider if you need a specific license or certification to get the job you want. If so, research the credential’s requirements to learn if your degree needs to meet certain criteria. For example, you may need to complete an accredited program or complete supervised clinical hours.
Understand Your Expenses and Financing Options
Tuition rates for online doctoral programs in our guide vary significantly, from $265 to $2,137 per credit. Most programs required 42 to 60 credits, with some exceptions. In total, the degrees ranked on our list cost between $9,540 and $113,400.
According to the National Center for Education Statistics , grad students at private, nonprofit schools paid an average tuition of $20,408 in 2022–23, while public school tuition cost $11,554 per year. Doctorate programs typically take at least three years to complete, putting total costs between $34,662 and $61,224.
Find funding for your online Ph.D. by filling out the FAFSA®, which can connect you with scholarships, grants and student loans. Many schools also provide funding to graduate students through scholarships, grants and fellowships.
Can you do a Ph.D. fully online?
Yes, many schools offer fully online Ph.D. programs. However, depending on the program and the field of study, you may need to complete on-campus residencies or field experiences like internships or practicums that take place in person.
What is the fastest Ph.D. to get online?
Program length for online Ph.D. programs varies depending on your field of study. You might be able to find some accelerated online Ph.D. programs that you can finish in less than two years. However, the best online doctoral programs on our list take at least three years to complete.
Are online doctoral degrees respected?
An online doctoral degree from an accredited university can provide the same rigorous education and training as a comparable on-campus program. If you’re concerned about whether or not your degree will be respected, consider doing some research about the way that your field or profession tends to view online doctoral degrees.
What is the best online school for a Ph.D.?
The best online school for a Ph.D. depends on your field of study, personal interests and career goals. Make sure that any prospective online school is institutionally accredited. Depending on the degree you want to pursue, it might also be important to find a program with separate programmatic accreditation.

Liz Simmons has been writing for various online publications about career development, higher education and college affordability for nearly a decade. Her articles demystify the college application process and help prospective students figure out how to choose a major or career path.
Jack N. Averitt College of Graduate Studies
Educational Leadership, Ed.D. (Online)
About the program.
Format : Online Credit Hours : 36 – 69 Entry Term : Fall
The Doctor of Education Degree program in Educational Leadership is designed to enhance the experienced school administrator’s leadership skills through: (1) advanced preparation that strengthens decision-making, problem-solving, and leadership skills essential to the management of increasingly complex educational organizations, and (2) engagement in guided field research that develops the inquiry skills necessary for effective leadership and management practice.
The program uses an inquiry approach that employs problem-solving and research skills applicable to multiple problems and issues. The purpose is to generate an inquiry orientation so that participants will learn to solve problems from broad perspectives. Participants identify, diagnose, and define problems, analyze their component parts contextually and systematically, and develop solutions that are immediately applicable and that deal with underlying issues. Experiences over the course of the doctoral program in Educational Leadership become candidate-led, field-based investigations of educational problems and potential solutions.
The Ed.D. in Educational Leadership provides two concentration options: P-12 Educational Leadership Higher Education Leadership
Ready to Apply?
Request information, visit campus, or, you can :, admission requirements.
- Select a concentration : Higher Education Leadership or P-12 Educational Leadership
- For admission to Stage I, candidates must possess a master’s degree. For admission to Stage II, candidates must possess a terminal degree in a related field.
- There is no admission into Stage I. For admission to Stage II, candidates must possess an Ed.S. degree in Educational Leadership or another related field and certification in Educational Leadership – Tier II.
- Present a minimum grade point average of 3.25 (4.0 scale) in previous graduate work.
- Submit a current resume or CV that highlights the personal and professional achievements of the applicant.
- Submit a personal statement of purpose, not to exceed 1000 words, that identifies the applicant’s reasons for pursuing graduate study and how admission into the program relates to the applicant’s professional aspirations.
- Submit a completed “Disclosure and Affirmation Form” that addresses misconduct disclosure, the Code of Ethics for Educators, and tort liability insurance.
- Complete a writing sample if requested.
- Complete an interview if requested.
*International transcripts must be evaluated by a NACES accredited evaluation service and must be a course by course evaluation and include a GPA. ( naces.or g )
NOTE: Meeting admission or qualification criteria does not guarantee admissions.
Final: April 1
Does not admit
*The application and all required documents listed on the “admissions requirements” tab for the program must be received by the deadline. If all required documents are not received by the deadline your application will not be considered for admission.
Program Contact Information
Graduate Academic Services Center [email protected] 912-478-1447
Last updated: 6/29/2023
- Preferred Graduate Admissions
- All Graduate Programs
- Certificate Programs
- Endorsement Programs
- Online Programs
- Tuition Classification
- Graduate Assistantships
- Financial Aid
- Request More Information
- Schedule A Visit
Contact Information
Office of Graduate Admissions Physical Address: 261 Forest Drive PO Box 8113 Statesboro, GA 30460 Georgia Southern University Phone: 912-478-5384 Fax: 912-478-0740 gradadmissions @georgiasouthern.edu
Follow us on Facebook!
Georgia Southern University College of Graduate Studies
Office of Graduate Admissions • P.O. Box 8113 Statesboro, GA 30460 • 912-478-5384 • [email protected]
Privacy Overview

- Education Graduate Programs
Doctorate in Educational Leadership (EdD)
A william woods university signature course.
The field of education is facing increasingly complex challenges. It has never been more critical that these challenges be met by new research and new ideas, developed by a new generation of leaders. The William Woods University Doctorate in Educational Leadership is designed to provide you with the tools you need to become one of these people.
The Doctorate in Educational Leadership will provide you with advanced professional training and develop your abilities in the scholarly study of the issues that challenge education. You will study curricular and instructional issues and develop leadership and organizational skills that you can apply within your own educational setting. The doctorate program will also reinforce the research skills you need to reach a leadership position in the field.
One of things that makes this program a William Woods signature course is that training is only part of the program. It is also designed to challenge and motivate you to go out and find the solutions that education needs.
At William Woods, you’ll be participating in an Education graduate program known for its excellence and for providing a significant number of the leaders in Missouri’s state school system. As one of our students, you will have the opportunity to learn from active practitioners in the field and make the connections you need for leadership and career growth.
This Education doctorate degree is designed to fit the schedules of working pk-12 and collegiate teachers, staff and administrators, and can be completed in two years or less through evening courses taught in convenient locations around the state. You can expect rigorous coursework with real-world relevance, designed and taught by professionals who have proven their expertise. We structure the schedule so as to keep students together, allowing you to develop lasting relationships with peers focused on similar career goals. And, to make this an investment you can count on, your tuition will not go up as long as you stay continuously enrolled.
Your Doctorate in Educational Leadership degree at work
This program is intended for you to further develop your skills as an educational leader. Graduates will possess advanced skills to generate and apply research to practical solutions that address real-world problems.
You will be able to take these skills to your present K12 position which may include teacher educator, curriculum director, teacher, principal, or superintendent. Through the connections that you will form in the program, you will join our many graduates as scholar practitioners ready to bring higher level leadership skills in school districts and at the collegiate level.
William Woods is the largest certifier of school leaders in Missouri
Requirements/curriculum.
You will earn the degree by completing 9 courses leading to research and a doctoral dissertation.
Courses you may take
As the world constantly changes, the expectations of leaders continue to increase. The effectiveness of a leader requires a high level of ability to work with others and respond to change. With the number of issues leaders continually face, the ability to create a vision of leadership and organize others into collective efforts to respond to the changing needs of society is a must. This course assumes that each individual has leadership potential and that leadership qualities can be developed through a series of experiences and reflections. Class activities will create opportunities to evaluate and assess leadership roles and practices along with documenting leadership experiences. Success in this course requires demonstrated mastery of theoretical concepts, capacity for collaborative work and the thoughtful integration of theory and practice.
This course is designed to assist educational leaders in assessing needs and planning and communicating the importance and content of the effective school improvement plan. Building curriculum, designing instructional activities, maintaining positive school climate and assessing organizational performance through improvement planning are primary responsibilities of school/district leadership. This course will utilize an inquiry format into school effectiveness with students taking major responsibility for guiding the class discussion. The work will take a critical slant, interrogating traditional ideas about the means and ends of public education and proposing alternative solutions. This course is designed to encourage and assist students in deconstructing traditional ways of thinking about effectiveness and to critically examine traditional measures of effectiveness (i.e., assessment scores, dropout rates, etc.). The intent of the deconstruction and critical examination is not to diminish the importance of measuring school effectiveness, but rather to appreciate the inherent complexity of the issue and to understand and acknowledge relevant limitations in ways that can inform the work of scholarly practitioners.
This course focuses on systems thinking, personal and organizational behaviors, and leadership approaches to the change process. Students will demonstrate ethical thinking and action in organizational settings by re-conceptualizing leadership roles and organizational structures. Students will learn concepts and theories and be able to apply them to their educational organizations. The design is to use case studies, experiential exercises, dialogue and group activities to interact with the pedagogy and concepts learned during the course.
This course will examine concepts, methods and approaches in the field of evaluation research. Students will be exposed to the theoretical and methodological diversity inherent in current evaluation practices. This course will also incorporate strategic planning models, forecasting methods, trend analysis, and future planning. Students will learn how to manage growth, change, and organizational improvement through the evaluation of educational programming.
Students exchange drafts of the first three chapters of their dissertation with their committee chair. A proposal hearing occurs during EDU781 or the following course (EDU799) when the chair and other committee members believe that the introduction to the topic, the literature review and the proposed methodology form the framework of quality dissertation research. Students complete the University’s online research inventory by the end of EDU781. Institutional Review Board approval is pursued after the dissertation committee accepts the proposal. Prerequisite: RSH 720, RSH 740, RSH 780, and passing the EdD comprehensive exam
This course consists solely of the weekend workshop. The weekend workshop provides an overview of chapters one, two, and three of the dissertation. Students are expected to progress in their dissertation over the weekend by writing several sections in the first three chapters. This 0.5 cr course is the first of two on-site workshops for doctoral students. The workshop is a credit or no credit course. The workshop is available three times a year and is located in Columbia, MO. The workshop begins Friday afternoon and finishes on Sunday afternoon. Students are required to concurrently take their first semester of Research Seminar (first 16-week research seminar course). Students should bring a hard copy of their dissertation draft, and it is highly recommended for students to bring a laptop computer while working with their dissertation chair for editing purposes. Prerequisite: EDU781 Corequisite: Students are required to be concurrently enrolled in first semester EDU 790.
This course consists solely of the weekend workshop. The weekend workshop provides an overview of chapters four and five of the dissertation. Students are expected to progress in their dissertation over the weekend by writing several sections in chapters four and five. This 0.5 cr course is the second of two on-site workshops for doctoral students. The workshop is a credit or no credit course. The workshop is available three times a year and is located in Columbia, MO. The workshop begins Friday afternoon and finishes on Sunday afternoon. Students are required to participate in the workshop while concurrently taking their third semester of Research Seminar (third 16-week research seminar course). Students should bring a hard copy of their dissertation draft, and it is highly recommended for students to bring a laptop computer while working with their dissertation chair for editing purposes. Prerequisite: EDU792 Corequisite: Students are required to be concurrently enrolled in third semester of EDU 790.
This course is designed to allow students time to continue in writing their dissertation. Students will enroll in the course every term until completion and defense of their dissertation. The communication between chairs and students is vital during EDU 799. Just as important it is for chairs to reach out to students; students must consistently communicate with chairs. Prerequisites: EDU781
This course will provide the educational practitioner with the support and further training to the quantitative skills needed for scientific research and data analysis. The course will include a review of basic statistical concepts as well as an introduction to the following statistical methodologies: Correlation, Regression, t-Test, ANOVA, Repeated Measures, Non-parametric test, Factor Analysis, and Categorical Data (Chi-Square). Series of practice problems, discussion, and weekly assessments from the textbook will take the students one step further on various experimental design and statistical test and data analysis. This course is designed with the dissertation in mind to provide foundation of knowledge and skill if a student chooses to do a quantitative analysis for his/her final dissertation. Prerequisite: Graduate Level Introductory Research and Introductory Statistics Course
This course will introduce leaders to concepts and strategies of qualitative research in preparation for conducting independent research. The course is designed for students to critically understand and develop a qualitative research design as it applies to a variety of research questions. Course topics will include the framing of research questions, identifying data and data sources, and using theory in the design and analysis process. Prerequisite: Graduate Level Introductory Research and Introductory Statistics Course or This course will introduce educational leaders to concepts and strategies in qualitative research in preparation for conducting independent research. Students will discuss future trends, issues, and problems in academic educational systems. Students will critically understand and develop a qualitative research design as it applies to an educational issue. Course topics will include the framing of research questions, identifying data and data sources, and using theory in the design process. Prerequisite: Graduate Level Introductory Research and Introductory Statistics Course
This course is an introduction to dissertation proposal requirements. Course assignments are designed to familiarize students with the information they will need to compile the first three chapters of their dissertation. Techniques for integrating peer-reviewed research into a cohesive literature review are presented. Requirements of the Introduction and Research Methods chapters are also examined. University policies and procedures covering the proposal defense and the dissertation defense are explained. Prerequisite: EDU720 and EDU740 or This course is an introduction to dissertation proposal requirements. Course assignments are designed to familiarize students with the information they will need to compile the first three chapters of their dissertation. Techniques for integrating peer-reviewed research into a cohesive literature review are presented. Requirements of the Introduction and Research Methods chapters are also examined. University policies and procedures covering the proposal defense and the dissertation defense are explained. Prerequisite: RSH720 and RSH740
View a complete list of courses and electives »
Requirements
25-hour completion
Program Qualifications
- Education Specialist degree from a regionally accredited college or university
- Graduate GPA of 3.6 on a 4.0 scale
- Two years of experience working as an educator
Prerequisite Coursework
- Research Methods/Design
- Research Statistics
The following must be submitted before consideration for admission:
- Completed application
- Official transcripts showing masters and specialist degrees. Only transcripts received in a sealed envelope directly from the sending school will be considered official. Students graduating from William Woods University masters and/or specialist programs do not need to submit new copies of transcripts already on file.
- Two academic letters of reference from professionals who can address the candidate’s academic ability, potential for success in strenuous scholarly work, and past performance as an educator in the field. One letter must be from a supervisor.
- Professional vita.
- Philosophy of leadership statement highlighting the applicant’s personal leadership characteristics and past professional leadership experiences, as well as the applicant’s purpose in pursuing the doctoral degree and expectation of the benefit of obtaining the doctorate. This statement must be at least 750 words.
Cohorts available across Missouri
Cohorts available across Missouri William Woods advanced education programs bring evening classrooms to educators in districts where there is interest. Historically, cohorts were available in districts in Fulton, Columbia, Jefferson City, St. Louis, Kansas City, Springfield, Cape Girardeau and many more locations.
Our graduate education programs are available online and are ranked among the best online programs in Missouri by US News and World Report.
William Woods in the real world
Many of our graduates hold leadership positions in Missouri’s schools. All of them are great teachers.
Perspectives
What separates William Woods University is the quality of our instructors. They're successful school leaders from around the state, actually out there doing what we're teaching others to do.
— James C. Head, Director of Administrative Field Experience
One more thing
A high percentage of our students have impressive day jobs. They’re building level administrators, central office administrators, superintendents, special education directors, curriculum directors, instructional coaches, and professional development coordinators. As a student in our program, you’ll have the opportunity to learn from practitioners like these and form connections that later may lead to job opportunities.
Admissions Information
Learn more about graduate admissions requirements, deadlines, tuition and financial aid available to you.
Admissions and Financial Aid »

The degrees you need for the fastest-growing health care jobs in America
Posted: December 23, 2023 | Last updated: December 23, 2023

The education requirements for the fastest-growing health care jobs
Health care professionals are already some of the most sought-after workers in the job market, and their prospects are only increasing. Bureau of Labor Statistics data indicates health care job opportunities will grow faster in the next decade than in other career fields. Every year, the number of projected openings in health care sits at just below 2 million.
Incredible Health identified the most common educational requirements among fast-growing health care jobs. Before sighing in disappointment, imagining long years of study and the debt accumulated from medical school, keep in mind that only one of the 20 fastest-growing professions in the health care industry requires a medical degree or a doctorate. According to the BLS , most vacancies only require a high school diploma or equivalent.
Across the nation, the Health Resources and Services Administration estimates that at least 17,477 practitioners are needed to serve 101 million people lacking adequate primary medical care. Also, 76 million people require dental services, and 166 million do not have access to professional mental health care.
The demand for health care services will only grow as the U.S. population ages. All baby boomers—the second-largest adult generation—will be 65 or older by 2030, according to the Census Bureau .
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth grew exponentially for first-time consultations and follow-ups. And long after lockdown and social restrictions ended, telehealth has remained an alternative for outpatient consultations and pre-office evaluations, increasing the demand for digital health or health tech workers.
The following analysis ranks education levels based on the BLS' projections of how many jobs will be added requiring that level of education . The fastest-growing occupations within each education category are also listed.

#6. Doctoral or professional degree
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +87,500 jobs (+5.2%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Physical therapists (Projected job growth: +15.1%) --- Audiologists (+10.6%) --- Chiropractors (+8.8%)
Obtaining a doctorate can mean getting a Doctor of Medicine, a Doctor of Philosophy, or several other doctoral degrees, such as a Doctor of Physical Therapy, Audiology, or Chiropractic. These degrees all take several years of research and study. Candidates must have at least a bachelor's degree. Ph.D. candidates typically have one or more master's degrees.
Some degrees are field-specific, but others can be more generalized. Ph.D. graduates in the health care industry , for instance, may be highly specialized professionals in medical practices or hold the topmost executive positions in hospitals and pharmaceutical companies. Or they might participate in research in sensitive, complex areas such as neuroscience, oncology, epidemiology, or genetic engineering. They might even design software or other technical or technological tools for medical care.

#5. Associate's degree
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +107,100 jobs (+10.7%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Physical therapist assistants (Projected job growth: +26.1%) --- Occupational therapy assistants (+24.0%) --- Health information technologists and medical registrars (+16.5%)
Health care professionals with associate's degrees working in medical offices may be the intake clerk or the person processing insurance claims. Thousands of people in the health care industry have earned two- or three-year degrees, often at a community or technical college.
The annual income for associate degree holders in the medical field ranges significantly. For example, the median yearly pay for a medical assistant in 2022 was $38,000, while it was around $70,000 for a respiratory therapist.

#4. Master's degree
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +221,100 jobs (+24.8%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Nurse practitioners (Projected job growth: +44.5%) --- Physician assistants (+26.5%) --- Speech-language pathologists (+19.3%)
A master's degree in the health care industry can make one's annual income grow to a six-digit number, a salary significantly higher than the $77,000 median wage paid to health care practitioners and technical workers.
Most medical specialists, such as advanced practice registered nurses or orthotists, need at least a master's degree before applying for a license to work with patients. In most cases, mid- and high-level medical professionals must keep their knowledge up-to-date through certifications and courses to periodically renew their licenses.

#3. Postsecondary nondegree award
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +326,800 jobs (+7.3%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Massage therapists (Projected job growth: +18.3%) --- Medical assistants (+13.9%) --- Ophthalmic medical technicians (+12.7%)
An educational institution confers a postsecondary nondegree award, while a certification is issued by a professional organization or certifying body. Some postsecondary programs can take a few weeks of schooling, others up to a year or two.
Health care occupations requiring this type of credentials include phlebotomists, specialists who draw blood for testing, emergency medical technicians, and paramedics. The median annual wage for workers in this category has been above $37,000 since 2018.

#2. Bachelor's degree
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +351,700 jobs (+8.4%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Medical and health services managers (Projected job growth: 28.4%) --- Therapists, all other (+12.2%) --- Exercise physiologists (+10.2%)
Countless opportunities in high-paying posts are available for professionals with bachelor's degrees who do not wish to attend medical school.
Although some occupations at this level are linked to medical practices, others are managerial or commercial positions , such as product managers in health care, who can earn a median $87,000 a year, or pharmaceutical sales representatives, whose median pay is $118,000 a year.

#1. High school diploma or equivalent
- Health care job growth at this education level, 2022-32: +847,800 jobs (+18.4%) - Fastest-growing health care jobs at this education level: --- Home health and personal care aides (Projected job growth: +21.7%) --- Hearing aid specialists (+14.5%) --- Health care support workers, all other (+5.7%)
More than 4 in 10 health care jobs that will be added in the next decade only require a high school diploma, and, according to a U.S. News study, more than 10 of the 25 best jobs for high school graduates are in the health care industry.
Skilled practitioners provide home health care to patients in their own homes under the direction of a physician. The vast majority of patients who require home health care are older people or those with chronic conditions that impair their ability to live independently. Even though this occupation doesn't require a postsecondary degree, workers assisting people with physical or cognitive challenges must possess specific qualities, such as empathy, compassion, reliability, and communication skills.
Training requirements for health and personal care aides differ from state to state.
Story editing by Jeff Inglis. Copy editing by Kristen Wegrzyn.
This story originally appeared on Incredible Health and was produced and distributed in partnership with Stacker Studio.
More for You
Beware, Swifties. A major British bank just issued a warning after fans lost an estimated $1 million in Taylor Swift concert ticket scams
Pro-Palestinian Group Issues Warning About Joe Biden Commencement Speech
The 19 most hated movie and TV characters ever, ranked
I moved my family from California to Austin, Texas, and regretted it. Here are 10 things to consider before making an expensive mistake.
Map reveals best places to live in the US if nuclear war breaks out
Melatonin Overdose Warning
Watch these dance moves from a happy toddler when her mom's best friend comes over
Lost Planet Theia Is Hidden Inside the Earth, New Study Says
Aldi’s Latest $4 Williams-Sonoma Copycat Is an Absolute Must for Summer
The Bond Market Is Sounding Its Most Severe Alarm in Decades, and It Could Mean Trouble for the Stock Market
20 facts you might not know about 'The Little Mermaid'
Patti Smith Comments on Taylor Swift Name Dropping Her in the Tortured Poets Department
This type of supplement may increase heart disease risk, new study finds
Why You Need To Be Careful Peeling Off The Stickers On Your Fruit
Columbia faculty members walk out after pro-Palestinian protesters arrested
One of Earth's nine 'eternal flames' discovered inside a waterfall
UAE Floods Shown in Incredible Before-and-After Satellite Photos
Seattle hospital won't turn over gender-affirming care records in lawsuit settlement with Texas
Fallout Proves That Halo Never Learned its Most Important Lesson
The 50 best conservative places to live in America today, according to data
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
Causes and outcomes of at-risk underperforming pharmacy students: implications for policy and practice
- Alice Campbell 1 ,
- Tina Hinton 1 , 2 ,
- Narelle C. da Costa 1 ,
- Sian E. O’Brian 1 ,
- Danielle R. Liang 1 &
- Nial J. Wheate 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 421 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
104 Accesses
Metrics details
This study aimed to understand the key determinants for poor academic performance of students completing a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm), Bachelor of Pharmacy and Management (BPharmMgmt), or Master of Pharmacy (MPharm) degree.
Data were collected on pharmacy students who had not met academic progression requirements between 2008 and 2018 at The University of Sydney, Australia. This included: age at the start of pharmacy degree; gender; whether they transferred from another university; whether they were a domestic or international student; Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank upon entry, previous studies in biology, chemistry, or mathematics; show cause triggers (units of study failed); number of show causes; students’ written show cause responses; weighted average mark at last show cause or graduation; whether they graduated and were a registered pharmacist; and, the number of years they spent studying the degree. Descriptive studies were used to analyse student characteristics using SPSS software, and student self-reported reasons for poor performance were analysed reflexively using thematic analysis procedures using NVivo.
This study included 164 pharmacy students enrolled in a BPharm (79.3%, n = 130), BPharmMgmt (1.2%, n = 2), or MPharm (19.5%, n = 32). Of the students, 54% ( n = 88) were men, 81% ( n = 133) were domestic students, 15% ( n = 24) transferred from another degree program, and 38% ( n = 62) graduated from the course. Show cause students were less likely to graduate if they transferred from another degree program ( P = 0.0002) or failed more than three units of study (UoS; P < 0.0001). The most commonly failed UoS were related to organic or pharmaceutical chemistry, and the top student self-reported reasons for poor performance was stress/anxiety, physical health, and depression.
Pharmacy schools should aim to address student foundational knowledge in chemistry, identify at-risk students early using pre-subject testing, and provide better services to address student mental health.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
A student’s academic performance in higher education is typically defined by their achievement of learning outcomes and demonstration of their ability to apply the concepts taught. Measurement of these attributes can include assessments, quizzes, role plays, field work, practical placements, workshops, tutorials, laboratories, and examinations. In most higher education programs, a minimum standard of academic achievement is required in order to progress through the course, to ensure the student has gained adequate knowledge and skills, and that they have achieved the specified learning outcomes. In this regard, poor academic performance can be defined by instances where a student fails to meet the expected minimum academic standard. Usually this comprises a minimum overall score in a subject and/or passing a specific barrier assessment, which is ultimately linked to their retention or attrition.
Understanding the key determinants of student success, failure, retention, and attrition has become increasingly important for higher education institutions, and has been the subject of extensive research over the past few decades. Early studies on student attrition focused primarily on student characteristics [ 1 ], before attention shifted to interactions between the student and their institutions. Prominent researchers, including Spady [ 2 , 3 ], Tinto [ 4 , 5 ], and Bean [ 6 ] proposed models to explain the interplay between academic and social integration leading to underperformance, and eventually, attrition. More recently, interest has increased in examining student engagement [ 7 , 8 , 9 ], where the student and institutions have a joint responsibility for academic success. To be successful, a student needs to participate, and higher education institutions need to provide an appropriate learning environment, opportunities, and support [ 10 ].
Studies on the key determinants of student underperformance reveal an array of contributing factors. Recent systematic reviews on underperformance and dropout rates show that key determinants fall into categories relating to the institution, personal life, demographics, and social integration [ 11 , 12 ]. Within higher education institutions, studies have found that an academic’s professional knowledge and pedagogical skills, along with the institution’s learning resources, course structure, and environment, are key factors that influence academic performance and non-completion [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Teaching methods that higher institutions adopt have also been evaluated, with student-centered approaches that encourage active learning resulting in better performance when compared with a traditional teacher-centered approach [ 15 , 16 ].
In terms of individual factors, studies have found a lack of effort, distraction, poor time management, and no longer being interested in the course as having a negative impact on academic performance [ 14 , 15 , 18 , 19 ]. Active learning (e.g. self-quizzes, completing problem sets, and explaining concepts) has been found to yield better academic outcomes when compared with passive learning (e.g. reading lecture slides or class notes, watching lecture videos, and reading textbooks) [ 20 , 21 ]. In the same study, how early a student studied in relation to their exam did not affect their outcome, whereas students who were more distracted during the time they allocated for study, performed worst [ 20 , 22 ]. Education-related stress, poor mental health, exam anxiety, and sleep quality are also factors found to cause poor performance [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. Other studies have shown that part-time students and those who have previously failed subjects are at risk of further poor performance and attrition [ 17 , 28 , 29 ]. Social factors including cyberbullying [ 30 ], homesickness for international students [ 31 ], and excessive socialising [ 16 ] also have a negative effect on academic performance.
Working status was found to negatively impact academic performance [ 27 ], where poor academic outcomes were correlated with a longer time spent at work [ 16 , 28 , 32 ]. Many studies have associated the lower socioeconomic status of students and their family, or financial strain with poor academic performance [ 27 , 28 , 29 ]; whereas, other studies have shown that students in families where one parent has attended higher education tend to achieve higher grades [ 31 ]. Some studies have found men and minority students are more at risk of poor performance [ 31 , 33 ]. Part-time students are much more likely cite work and family responsibilities as reasons for stopping their studies [ 17 ]. Research on students whose first language is not that of the higher education institution is mixed, with some confirming it to be a key attributor to underperformance [ 34 , 35 , 36 ], along with students with a migrant background or who are first-generation university attendees (commonly referred to as first-in-family) [ 31 , 37 , 38 ]. In contrast, other studies have found that academic performance of international students was similar, or better, than domestic students [ 39 , 40 ].
A government panel in Australia reported that the leading drivers for non-completion in higher education are both institution-related (learning environment, an academic’s ability to teach, student to staff ratios, student engagement, and support services) and student-related (health, finance, and personal responsibilities) [ 41 ]. A survey conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) identified the top three reasons for attrition for students studying a bachelors degree to be: loss of interest, employment/financial reasons, and personal reasons (health, family, or other personal reasons). For postgraduate courses, reasons for attrition were highest in the order of personal reasons, employment/financial, followed by loss of interest [ 42 ].
Where a student has underperformed, they may be offered remediation assessments; to re-enroll and attempt the entire subject again, which may result in a delay in degree completion; or in some cases, be excluded from reenrolling into the same course for a period of time [ 43 , 44 ].
Consequences of poor performance vary across higher education institutions and may depend on the reasoning provided, extent of underperformance, and number of failed subjects. Key stake holders impacted by poor performance and attrition from higher education can include the students and their families, the higher education institution they are enrolled in, their community workforce, and government. Non-completion directly impacts the funding and reputation of an institution [ 17 , 45 , 46 ]. In Australia, where the cost of higher education for domestic students is subsidised by the federal government, non-completion incurs a direct cost to both the student and the tax-payer. The cost to the student includes lost time, psychological health, student debt, and forgone income [ 9 ]. From the perspective of workforce planning, a delay or non-completion of study reduces the number of employees entering into the workforce, and can lead to workforce shortages and place a burden on those currently in the field.
There are many studies that have examined the key determinants for student success or underperformance and attrition in health; however, most have focused on nursing or medical education [ 13 , 15 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ]. Consequently there are limited studies that have examined the rate and reasons for attrition within pharmacy degrees. Being a degree known to be difficult in technical content, and which requires students to achieve a high level of competence, it is important to investigate reasons for attrition and potential opportunities for improvement in student teaching and engagement.
In this study we analysed 10 years of demographic data and responses to why academic progression requirements had not been met in a cohort of students enrolled in a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm), Bachelor of Pharmacy and Management (BPharmMgmt), or Master of Pharmacy (MPharm) degree at The University of Sydney. Our aim was to understand the key determinants for poor performance within this group of students and identify opportunities for policy and practice to reduce underperformance in the future.
Approval for this study was granted by the Human Research Ethics Committee of The University of Sydney (2022/815).
Data collection
The inclusion criteria for this study were students enrolled in a BPharm, BPharmMgmt, or MPharm degree between the period of 2008 and 2018 (inclusive), who were required to provide a minimum of one show cause at any stage of their study. Data collected on each student included: age at the start of pharmacy degree; gender; whether they transferred from another university; whether they were a domestic or international student; Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank (ATAR) upon entry, which is a percentile score that ranks Australian students finishing secondary school in relation to their academic achievement [ 51 ]; previous studies in biology, chemistry, or mathematics; show cause triggers (units of study failed); number of show causes; students’ written show cause responses; weighted average mark (WAM) at last show cause or graduation (WAM is an average grade score indicating a student’s overall academic performance over the course of their degree and is similar to a grade point average) [ 52 ]; whether they graduated; and, the number of years they spent studying the degree. Whether those students who had graduated were currently registered as a pharmacist in Australia was retrieved using the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency online registry list [accessed in 2023].
Data analysis
Researchers Da Costa, O’Brien, and Liang collected, screened, and de-identified the data, and researchers Campbell, Hinton, and Wheate analysed the data. Descriptive statistics, including mean ± SD, median, and frequencies (count and percentage) were calculated using Microsoft Excel. Mann-Whitney U tests were undertaken in GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA) to ascertain any differences between ATAR scores. Chi Square analyses were undertaken in GraphPad Prism 9.0 to compare categorical data including differences between men and women, domestic and international students, transferring and non-transferring students, and graduating and non-graduating students.
Written show cause responses were transcribed by Campbell and uploaded into NVivo (1.5.1) software (QSR International, Massachussets USA). The show cause responses were analysed reflexively using inductive thematic analysis procedures [ 53 ].This involved manually reviewing each show cause response to identify emerging themes relating to the reasons stated by the student for their poor performance. From the themes identified, a total of 43 codes were generated based on the ideas, trends, and content. Coding was conducted in a theory-driven manner, seeking to code information referencing the specific themes arising from the show cause response [ 53 ]. Themes were guided by the frequency of mention, and reported in the results if there was more than a single mention. The frequency of the subthemes was analysed to demonstrate the prevalence of stated factors that the student believed led to their poor performance.
Show cause process
Pharmacy students who do not meet the progression requirements of their degree enter one of three stages of academic intervention (Fig. 1 ). Triggers for a student not meeting the requirements for progression include: awarded a fail grade in over 50% of total units of study (subjects; UoS) taken in a semester or teaching period; an average grade (WAM) less than 50 across all UoS in a semester or teaching period; failing one, or more, barrier or compulsory UoS which includes CHEM1611, CHEM1612, PHAR2822, and any 3000 or 4000 level UoS for BPharm/BPharmMgmt; and any single UoS for MPharm; any practical component (e.g. field work or clinical work), failing the same UoS twice, having unsatisfactory attendance, or exceeding the maximum time limit allowed for the degree to be completed.
Students who fail to meet progression requirements for the first time are placed on Stage 1 of the at-risk register at which point they receive a letter from the Faculty of Medicine and Health, and are advised to complete a ‘Stay on Track’ survey and information session. At the discretion of the Associate Dean of Education, some students at Stage 1 may be required to consult an academic adviser. If a student is enrolled in a degree with a duration of less than two years full-time (e.g. MPharm), they are advised that should they fail to meet progression requirements in the following semester, they would be asked to ‘show good cause’ in order to be allowed to re-enrol in the same program; that is, they would be excluded from the degree for two years unless they could give reasons for why they should be allowed to remain studying. They are also recommended to speak to an academic advisor.
Stage 2 is triggered for a student in a 4 or 5 year undergraduate degree program (e.g. BPharm and BPharmMgmt) if they fail to meet progression requirements after being placed on Stage 1 in the previous semester, at which point the faculty sends a letter, advising the student to complete the ‘Staying on Track’ survey if they had not yet done so, and to consult an academic adviser. Stage 3 is triggered if a student fails to meet progression requirements a third time, or fails the same compulsory or barrier UoS, or any practical component twice. Students on Stage 3 are required to ‘show good cause’ and provide reasonable evidence to be allowed to re-enrol into the degree program.
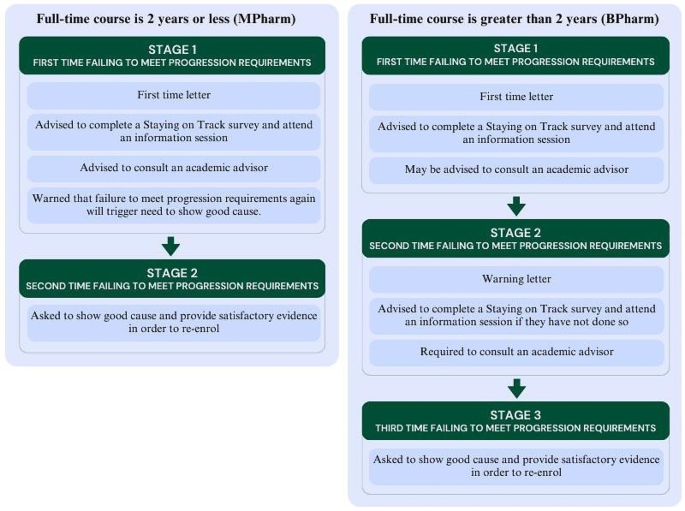
The three at-risk stages of academic intervention for students who fail to meet course progression requirements. Show cause is required at Stage 2 (MPharm) or Stage 3 (BPharm/BPharmMgmt) in order to re-enrol
Demographics
In total, 164 pharmacy students received at least one show cause notification between the period of 2008 to 2018 (inclusive) and were enrolled in a BPharm (79.3%, n = 130), BPharmMgmt (1.2%, n = 2), or MPharm (19.5%, n = 32) degree (Table 1 ). Of the students, 54% ( n = 88) were men, and 81% ( n = 133) were domestic students.
Students who transferred from another degree program made up 15% ( n = 24) of the sample, and were a median two years older than those who did not transfer (median age 21, range 19–43 years). All students who transferred from another degree, were enrolled in the BPharm. Ninety-two percent of transfer students ( n = 22) were domestic and 71% ( n = 17) were women.
The age of students at the start of their degree was positively skewed, with a median age of 19 years for BPharm and BPharmMgmt (range 17–43 years). For MPharm, the median age at commencement was 24 (range 20–24) years. The median age of domestic students at the start of their BPharm or BPharmMgmt degree was 19 (range 17–43) years compared with international students at 22 (range 18–33) years. For MPharm, the median age for domestic students at commencement was 24 (range 20–54) years while for international students it was 24.5 (range 22–38) years.
Performance on entry and exit of the degree
The ATAR scores of the students in either the BPharm or BPharmMgmt were not normally distributed ( n = 78, mean ATAR 88.8 ± 4.8) (Supplementary Figure S1 ). The average ATAR required for entry into BPharm and BPharm/Mgmt at the University of Sydney is around 90. Of the 24 students who transferred from another degree program, the ATAR score was available for four students, with an average of 78.8 ± 9.8, including two outliers who had ATAR scores of 67.80 and 74.15. The average ATAR on entry to the degree of the students who graduated was 89.4 ± 3.4, which was similar to those who did not graduate, 88.5 ± 5.4. A Mann-Whitney U test showed this difference was not statistically significant (W = 702.5, p = 0.937).
The proportion of students who graduated after receiving at least one show cause was 37.8% ( n = 62), of which 77.4% ( n = 48) were registered as pharmacists at the time of data collection (Fig. 2 ). One student did not graduate their BPharm; however, they did return and complete the MPharm degree and was registered as a pharmacist at the time of data collection. The median time taken to graduation was 7 (range 1–9) years for students enrolled in the BPharm and 3 (range 2.5-8) years for those enrolled in the MPharm. During the study period, 188 students were enrolled in the BPharmMgmt degree but only two (1.1%) were required to show cause due to poor performance. Neither of those two students graduated.
A WAM score was available for all but three of the 164 students. The overall average WAM either at last show cause, if the student had not graduated, or at degree completion was 52.1 ± 12.0. For students who graduated (38.5%, n = 62), the average WAM was 62.2 ± 5.1, while for those who did not graduate (61.5%, n = 99), the average WAM was 45.7 ± 10.5.
When the proportion of students who graduated was compared across the ATAR bands (Table S1 ), it was evident that show cause students who entered their degree with an ATAR between 85 and 89.99 were more likely to graduate (44%) when compared with those who entered their degree with lower (27%) and higher (25–35%) ATAR scores.
Units failed
Across the cohort, show cause students received between 1 and 8 show cause notifications (Fig. 1 ). When the proportion of students who graduated was compared across the number of show causes received for those who received 1–5 show causes, the rate of graduation ranged from 36 to 50%, while none of the students who received six or more show causes graduated.
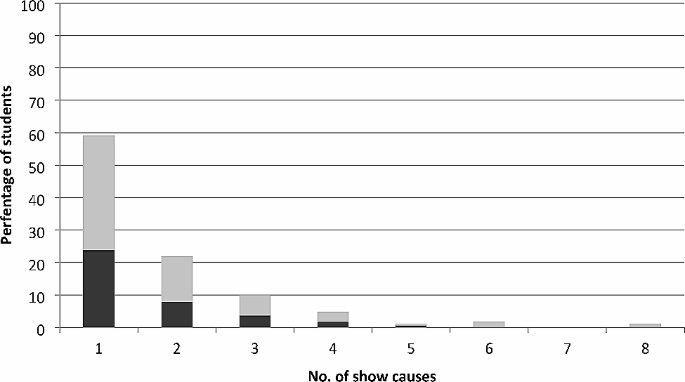
Percentage of students who graduated (black) and did not graduate (grey) by number of show causes received
Number of failed UoS
The median number of UoS failed across the three degree programs was 8 (BPharm, range 2–33), 9 (BPharmMgmt, range 5–13), and 5 (MPharm, range 2–12), respectively. In total, 8.5% ( n = 14) students were required to show cause because they failed 2 or 3 UoS, 19.5% ( n = 32) students failed 4 or 5 UoS and 72% ( n = 118) students failed more than 6 UoS. Of the 14 students who failed 2 or 3 UoS, 86% were studying the MPharm degree and the remaining were BPharm students. Students who failed 4 or 5 UoS, were studying a BPharm (66%), BPharmMgmt (3%), or MPharm (31%) degree. The majority of students who failed more than 6 units were studying BPharm (91%), followed by MPharm (8%), and BPharmMgmt (1%). Students who failed 2 or 3 UoS were significantly more likely to graduate when compared with those who failed 4 or 5 UoS, or more than 6 UoS \( (X_2^2=21.86, \text{P}<0.0001)\) (Supplementary Figure S2 ).
Type of failed UoS
The most failed UoS that triggered a show cause across students in the BPharm and BPharmMgmt degrees were a mix of pharmaceutical sciences, chemistry and biology, across the first and second years of the degree programs (Table 2 ). The top five UoS failed were Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences (8.8%, 116/1314 fails; unit code: PHAR1812), Chemistry 1B (Pharmacy) (6.9%, 91/1314 fails; unit code: CHEM1612), Drug Discovery and Design 1 (6.7%, 88/1465 fails; unit code: PHAR2811), Molecular Biology and Genetics (6.5%, 86/1314 fails; unit Code: MBLG1001), and Chemistry 1A (6.2%, 81/1314 fails; unit code: CHEM1611).
For students studying the MPharm, the majority of UoS failed were for pharmaceutical sciences in first year and one specific pharmacy practice unit (PHAR5717) in the second year. The top three UoS failed for MPharm were Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1A (12.6% 19/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5513), Pharmaceutical Science (7.9%, 12/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5515), and Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1B (7.9%, 12/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5516) (Table 3 ).
Gender, transfer and international students
There was no significant difference between the number of men and women who graduated after receiving at least one show cause \( (X_1^2=0.056, \text{P}=0.813)\) . There was also no significant difference in the number of UoS failed \( (X_2^2=2.249, \text{P}\hspace{0.17em}=\hspace{0.17em}0.325)\) or number of show causes received \( (X_6^2=2.829, \text{P}=0.830)\) between men and women.
Students who transferred from another degree program were significantly less likely to graduate \( (X_1^2=13.53, \text{P}\hspace{0.17em}=\hspace{0.17em}0.0002)\) . The likelihood of graduating was not statistically significant different between domestic and international students who received a show cause \( (X_1^2=0.88, \text{P}<0.348)\) (Supplementary Figure S3 ).
Student responses to show causes
There were 293 show causes in total, of which only 141 show cause response letters were available. Reasons given by students for their poor performance could be classified under four major themes: personal life matters, institutional aspects, social integration, and interest in the course (Fig. 3 ). Personal life matters could be further sub-divided into health, study familiarity, responsibilities, and other personal life matters.
The majority of show cause responses attributed poor performance to personal life reasons (87%, 396 responses), followed by institution-related (8.8%, 40 responses), lack of interest in the degree (2.2%, 10 responses), and social integration (2%, 9 responses). The five most mentioned personal life reasons that led to poor performance were stress and anxiety ( n = 63, 45%), physical health ( n = 51, 36%), and depression ( n = 39 28%). This was followed by family health, mentioned 37 times (26%), and reasons relating to employment or financial health, mentioned 33 times (23%). Reasons that related to the institution totalled 40, interest of the course totalled 10, and social reasons totalled 9. Personal life health-related reasons accounted for 41% of show cause responses. These included a combination of physical, mental, and unspecified health issues.
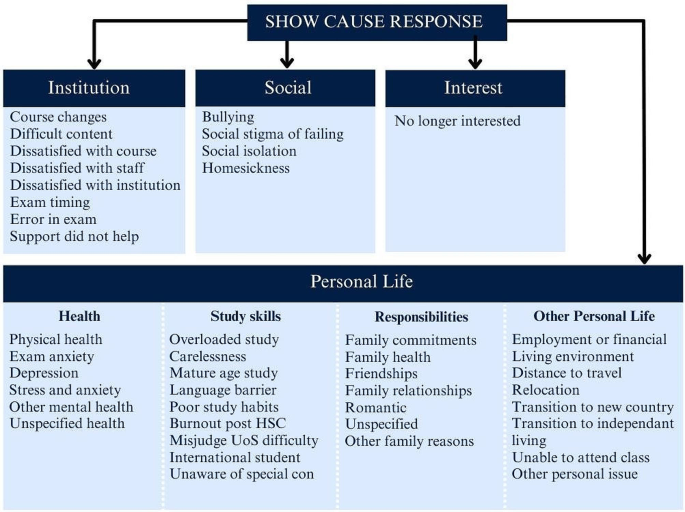
All show cause responses provided by students could be categorised into four major themes. Personal life was subcategorised into health, study skills, responsibilities, and other personal life
Some students identified a lack of study-related skills and study familiarity as a source of underperformance. Reasons included: carelessness in exams, poor study habits, language barrier, being an international student or mature age student, misjudging the course difficulty, overloading, burning out after high school, and being unaware of opportunities to apply for special consideration. Another set of reasons provided for underperformance included: needing to meet responsibilities and commitments for family, friendships, and romantic relationships. A variety of other personal life reasons were provided, which included: employment, finance, transition to independent living or a new country, living environment, distance to travel to the university, needing to relocate, and being physically unable to attend classes.
Student show cause responses that attributed poor performance to inefficiencies within the institution included UoS changes, error or poor timing of exams, dissatisfaction with the course and staff, and unhelpful support. Some students found the UoS content too difficult. Social reasons that lead to poor performance included: bullying, stigma from peers once failing, and homesickness (for those studying abroad). Another reason provided was no longer being interested or committed to the course.
This study investigated the key determinants of underperformance by pharmacy students at an Australian higher education institution. Our findings indicate that across the students enrolled in BPharm, BPharmMgmt, and MPharm degrees, those who had failed more UoS overall, were less likely to graduate. The types of UoS failed were weighted towards chemistry-based subjects, and the most frequent student-reported reasons for poor performance were related to personal health.
Our study also found that students who transferred from another higher education institution were less likely to graduate compared with students who had not transferred. Some studies in the US have found that students who transfer to bachelors programs from similar institutions or community colleges, which are US institutions that only offer two year undergraduate associate degrees that lead to a specific skilled job or can be used to transfer into a bachelor course [ 54 ], experience ‘transfer shock’ where grade point average (GPA) declines at the post transfer institution, which can eventually result in attrition [ 55 , 56 ]. In contrast, other studies have found no significant effects from transfers, and an overall lack of consensus on this as a universal experience [ 57 , 58 ]. A study that examined transferring engineering students found that students who transferred from similar degrees were more likely to graduate when compared with students who transferred from less comprehensive degrees [ 56 ]. A literature review that examined transferring student performance found factors that negatively influenced persistence and course completion included: a lack of social integration, limited transferrable credits, lower GPAs, lack of funding, distance from institution, academic rigour, and personal work/life balance [ 57 ].
Our analysis also found that students failing more than three UoS were more likely to not graduate when compared with those who failed fewer UoS. This finding parallels many studies that show students with poor academic outcomes are more likely to not complete their degree [ 59 , 60 ]. A recent study on student attrition, found that students who failed one subject were more likely to fail more subjects, and also had a four-fold higher likelihood of not graduating [ 27 ]. The Grattan Institute presents similar statistics, where students who consistently fail to meet academic progression requirements eventually decide to leave or are excluded from re-enrolling by the university [ 61 ].
The high occurrence of underperformance in relation to chemistry is consistent with other studies [ 62 , 63 ]. Pancyk et al. found that chemistry marks were correlated with attrition while biology marks predicted likelihood of delayed graduation for Master of Science (in Pharmacy) students. Another study found that the prior attainment of a Bachelor of Science degree to be a predictor of performance in a Doctor of Pharmacy program [ 64 ]. In countries, such as the US, where a specialised pre-admissions pharmacy test (Pharmacy College Admissions Test; PCAT) is used for entrance into a pharmacy program, the PCAT score correlated with student academic performance in the pharmacy course [ 65 ]. There are five areas examined by the PCAT, including: writing, biological processes, chemical processes, critical reading, and quantitative reasoning [ 66 ]. There is also evidence that better outcomes attained in pre-pharmacy biology and mathematics GPA [ 67 , 68 ], or having completed a four-year bachelor course, contributes to student performance in American pharmacy colleges [ 64 , 69 , 70 ]. Another study found prior academic achievement in secondary school, or pre-university study, can predict performance in an UK MPharm course; however, not the likelihood of graduation [ 71 ]. Other studies have found that pre-tests, for certain UoS, like biochemistry and pharmaceutical calculations conducted before starting a subject are correlated with overall subject performance, which makes these tests a good predictor for at-risk students [ 67 , 68 ].
The most common reasons reported by students for their underperformance in the present study were stress and anxiety, personal health, and depression. This is consistent with current literature [ 17 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ], and the 2022 Australian Student Experience Survey [ 72 ], which reported that health or stress, followed by work/life balance were the leading causes for students attrition. A specific study in pharmacy students found that exam anxiety had a negative impact on student performance in pharmacy practical exams [ 26 ]. Psychological distress among students completing a higher education degree in Norway showed negative impacts on their self-perceived academic ability, and course progression [ 73 ]. Another study investigating students’ self-reported explanations for their poor academic performance found mental health as a contributing factor, and vice versa, where poor performance intensified mental distress [ 27 ]. Although the Australian Bureau of Statistics also reported personal health reasons as a major contributor for non-completion in bachelor programs between 2018 and 2019, the leading reason was that students were no longer interested in their chosen degree. In the same report, non-completion of masters degrees was driven by family, health, or other personal reasons [ 42 ]. Student mental health is a significant driver of attrition and is common across both private and public higher institutions in Australia [ 41 ]. The mental health burden on students is recognised at The University of Sydney and so significant mental health support is offered. All students are able to access free counselling and psychological support sessions, there is a 24/7 mental health support telephone line, and additional self-help resources (like mindfulness and relaxation) are provided through the university’s website. Mental health first health training is also included in the curricula for all pharmacy degree programs at the university.
Successful completion of a pharmacy degree requires not only academic ability, but a certain level of pre-knowledge, in particular, biology and chemistry, to decrease failure rates in these subjects, avoid delays in degree completion, and possible attrition. Institutions should aim to address these barriers by introducing pre-requisite subjects or mandate compulsory bridging courses if a prior level of knowledge attainment in these subject areas is not provided. Alternatively, pre-tests for certain UoS can be conducted prior to the course commencement to identify at-risk students, and additional academic support services can be offered.
With student poor mental health found as the most common self-reported reason for poor performance in this study, often exacerbated by academic performance pressures, institutions should implement policies for early detection and support for students going through challenging times. Such policies could include more frequent reminders for students to self-assess their mental health, and information on where to seek support services. This could take form in programs being introduced prior to lectures, access to support portals made more prominent on online learning platforms, or self-check surveys to be taken at a frequency deemed appropriate.
Limitations
The present study had a number of limitation. Not all student’s ATAR scores (or equivalent) were available. The method of collecting whether a student was registered as a pharmacist was based on them not having changed their last name which may be the case for some students who changed their name after graduation (e.g. upon marriage). Students who may be registered as a pharmacist in countries other than Australia could not be determined. Not all student show cause reasons were available because of the change from physical to electronic filing over the period studied. The limited number of students who received five or more show causes also meant the study was not powered to establish a cut-off whereby after receiving a certain number of show causes, the chance of graduating is highly unlikely.
Conclusions
This study investigated the key determinants for poor academic performance in a cohort of pharmacy students enrolled in a BPharm, BPharmMgmt, and MPharm degree. The key factors that influenced whether a show cause student completed their studies included whether they transferred from another institution, and failed more than three UoS. The UoS with the highest fail rates were chemistry based, and the most frequent student self-reported reason for poor performance was personal stress and anxiety. The results indicate that pharmacy schools should aim to address student foundation knowledge in chemistry, identify at-risk students early using pre-subject testing, and provide better access and knowledge of available services to address student mental burden. Future studies should investigate whether students who have completed chemistry and biology pre-requisites perform better in their pharmacy degree.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, N.J.W.
Aljohani O. A comprehensive review of the major studies and theoretical models of student retention in higher education. High Educ Stud. 2016;6:1–18.
Article Google Scholar
Spady WG. Dropouts from higher education: an interdisciplinary review and synthesis. Interchange 1984. 1970;1(1):64–85.
Spady WG. Dropouts from higher education: toward an empirical model. Interchange. 1971;2(3):38–62.
Tinto V. Dropout from higher education: a theoretical synthesis of recent research. Rev Educ Res. 1975;45(1):89–125.
Tinto V. Leaving college: rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. 2nd ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1993.
Google Scholar
Bean JP. Dropouts and turnover: the synthesis and test of a causal model of student attrition. Res High Educ. 1980;12(2):155–87.
Tight M. Student retention and engagement in higher education. J Furth High Educ. 2020;44(5):689–704.
Carini RM, Kuh GD, Klein SP. Student engagement and student learning: testing the linkages. Res High Educ. 2006;47(1):1–32.
Thomas L, Kift S, Shah M. Student retention and success in higher education. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. pp. 1–16.
Book Google Scholar
Coates H. The value of student engagement for higher education quality assurance. Qual High Educ. 2005;11(1):25–36.
Al-Tameemi RAN, Johnson C, Gitay R, Abdel-Salam A-SG, Hazaa KA, BenSaid A, et al. Determinants of poor academic performance among undergraduate students—A systematic literature review. Int J Educ Res. 2023;4:100232.
Lorenzo-Quiles O, Galdón-López S, Lendínez-Turón A. Factors contributing to university dropout: a review. Front Educ Res. 2023;8.
Wilkinson TJ, McKenzie JM, Ali AN, Rudland J, Carter FA, Bell CJ. Identifying medical students at risk of underperformance from significant stressors. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:43.
Le HTTN, La HTT, Le TP, Nguyen TTT, Nguyen NT, Tran TP. Factors affecting academic performance of first-year university students: a case of a Vietnamese university. Int J Educ Prac. 2020;8(2):221–32.
Sharma P, Singh P, Kalhan S, Garg S. Analysis of factors affecting academic performance of MBBS students in pathology. Ann Int Med Dent Res. 2017;2.
Mascolo M, Castillo J. The origins of underperformance in higher education in America: proximal systems of influence. Pedgog Hum Sci. 2015;5(1):1–40.
Norton AC, I. and, Mackey W. Dropping out: the benefits and costs of trying university. The Grattan Institute, 2018. p. 1–65.
van Rooij E, Jansen EPWA, Van de Grift W. First-year university students’ academic success: the importance of academic adjustment. Eu J Psychol Educ. 2017;33:1–19.
Arshad M, Zaidi SM, Mahmood D. Self-esteem and academic performance among university students. J Educ Pract. 2015;6:2015.
Walck-Shannon EM, Rowell SF, Frey RF. To what extent do study habits relate to performance? CBE - Life Sci Educ. 2021;20(1):ar6.
Roick J, Ringeisen T. Students’ math performance in higher education: examining the role of self-regulated learning and self-efficacy. Learn Individ Differ. 2018;65:148–58.
Nonis SA, Hudson GI. Performance of college students: impact of study time and study habits. J Educ Bus. 2010;85(4):229–38.
Jevons C, Lindsay S. The middle years slump: addressing student-reported barriers to academic progress. High Educ Res Dev. 2018;37(6):1156–70.
Pascoe MC, Hetrick SE, Parker AG. The impact of stress on students in secondary school and higher education. Int J Adolesc Youth. 2020;25(1):104–12.
May RW, Bauer KN, Seibert GS, Jaurequi ME, Fincham FD. School burnout is related to sleep quality and perseverative cognition regulation at bedtime in young adults. Learn Individ Differ. 2020;78:101821.
Hadi MA, Ali M, Haseeb A, Mohamed MMA, Elrggal ME, Cheema E. Impact of test anxiety on pharmacy students’ performance in Objective Structured Clinical examination: a cross-sectional survey. Int J Pharm Pract. 2018;26(2):191–4.
Ajjawi R, Dracup M, Zacharias N, Bennett S, Boud D. Persisting students’ explanations of and emotional responses to academic failure. High Educ Res Dev. 2020;39(2):185–99.
Rodríguez-Hernández CF, Cascallar E, Kyndt E. Socio-economic status and academic performance in higher education: a systematic review. Educ Res Rev. 2019;29:100305.
Tomul E, Polat G. The effects of socioeconomic characteristics of ctudents on their academic achievement in higher education. Am J Educ Res. 2013;1:449–55.
Peled Y. Cyberbullying and its influence on academic, social, and emotional development of undergraduate students. Heliyon. 2019;5(3):e01393.
Sun J, Hagedorn L, Zhang Y. Homesickness at college: its impact on academic performance and retention. J Coll Stud Dev. 2016;57:943–57.
Triventi M. Does working during higher education affect students’ academic progression? Econ Educ Rev. 2014;41:1–13.
Voyer D, Voyer SD. Gender differences in scholastic achievement: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. 2014;140(4):1174–204.
Dafouz E, Camacho-Miñano MM. Exploring the impact of English-medium instruction on university student academic achievement: the case of accounting. Engl Specif Purp. 2016;44:57–67.
Civan A, Coskun A. The effect of the medium of instruction language on the academic success of university students. Educ Sci: Theory Prac. 2016;16:1981–2004.
Sawir E. Language difficulties of international students in Australia: the effects of prior learning experience. Int Educ J. 2005;6:567–80.
Mishra S. Social networks, social capital, social support and academic success in higher education: a systematic review with a special focus on ‘underrepresented’ students. Educ Res Rev. 2020;29:100307.
López MJ, Santelices MV, Carmen Maura T. Academic performance and adjustment of first-generation students to higher education: a systematic review. Cogent Educ. 2023;10(1).
Zheng RX, Everett B, Glew P, Salamonson Y. Unravelling the differences in attrition and academic performance of international and domestic nursing students with English as an additional language. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(12):1455–9.
Rienties B, Beausaert S, Grohnert T, Niemantsverdriet S, Kommers P. Understanding academic performance of international students: the role of ethnicity, academic and social integration. High Educ. 2012;63(6):685–700.
Final Report -. Improving retention, completion and success in higher education. Higher Education Standards Panel; Australian Government Department of Education; 2017.
Qualifications. and Work, 2018-19. Australian Bureau of Statistics; 2020.
Academic Progression. The University of Sydney [updated 31 March 2023; cited 2023 September ]. Available from: https://www.sydney.edu.au/students/academic-progression.html .
Failed. withheld and invalid units: Monash University; [updated 2023; cited 2023 September]. Available from: https://www.monash.edu/students/admin/enrolments/change/failed-withheld-invalid-units .
OCED. Education at a Glance 2023. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Publishing 2023 [Available from: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/content/publication/e13bef63-en .
Yorke M, Longden B. Retention and student success in higher education. McGraw-Hill Education (UK); 2004.
Faisal R, Shinwari L, Hussain S. Academic performance of male in comparison with female undergraduate medical students in pharmacology examinations. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67:204–8.
van Moppes NM, Willems S, Nasori M, Bont J, Akkermans R, van Dijk N et al. Ethnic minority GP trainees at risk for underperformance assessments: a quantitative cohort study. Br J Gen Pract Open. 2023;7(1).
Liu XL, Wang T, Bressington D, Nic Giolla Easpaig B, Wikander L, Tan JB. Factors influencing retention among regional, rural and remote undergraduate nursing students in Australia: a systematic review of current research evidence. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(5).
Caponnetto V, Dante A, Masotta V, La Cerra C, Petrucci C, Alfes CM, et al. Examining nursing student academic outcomes: a forty-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;100:104823.
Australian Tertiary Admission Rank. Universities Admission Centre; [cited 2023 November ]. Available from: https://www.uac.edu.au/future-applicants/atar .
Weighted Average Mark (WAM). The University of Sydney; 2023 [cited 2023 November]. Available from: https://www.sydney.edu.au/students/weighted-average-mark.html .
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Community College. Education USA; [cited 2023 November ]. Available from: https://educationusa.state.gov/ .
Ivins T, Copenhaver K, Koclanes A. Adult transitional theory and transfer shock in higher education: practices from the literature. Ref Serv Rev. 2017;45(2):244–57.
Smith NL, Grohs JR, Van Aken EM. Comparison of transfer shock and graduation rates across engineering transfer student populations. J Eng Educ. 2022;111(1):65–81.
Aulck L, West J. Attrition and performance of community college transfers. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0174683.
Diaz PE. Effects of transfer on academic performance of community college students at the four-year institution community. Coll J Res Prac. 1992;16(3):279–91.
Li I, Carroll D. Factors influencing university student satisfaction, dropout and academic performance: an Australian higher education equity perspective. Perth: National Centre for Student Equity in Higher Education, Curtin University;; 2017. p. 56.
Sosu EM, Pheunpha P. Trajectory of university dropout: investigating the cumulative effect of academic vulnerability and proximity to family support. Front Educ. 2019;4.
Cherastidtham I, Norton A, Mackey W. University attrition: what helps and what hinders university completion? Grattan Institute; 2018.
Panczyk M, Rebandel H, Belowska J, Zarzeka A, Gotlib J. Risk of attrition from master of science in pharmacy degree program: 15-year predictive evaluation. Ind J Pharm Educ Res. 2016;50(1):70–9.
Houglum JE, Aparasu RR, Delfinis TM. Predictors of academic success and failure in a pharmacy professional program. Am J Pharm Educ. 2005;69(1–5):283–9.
McCall KL, Allen DD, Fike DS. Predictors of academic success in a doctor of pharmacy program. Am J Pharm Educ. 2006;70(5):106.
Meagher DG, Pan T, Perez CD. Predicting performance in the first-year of pharmacy school. Am J Pharm Educ. 2011;75(5):81.
Pharmacy College Admission Test American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. [updated 2023; cited 2023 October]. Available from: https://www.aacp.org/resource/pharmacy-college-admission-test .
Vinall R, Khansari P, McDowell J, Ried LD, Kreys E. Impact of completion of a pre-pharmacy biochemistry course and competency levels in pre-pharmacy courses on pharmacy student performance. Pharm 2019;7(3).
Aronson BD, Eddy E, Long B, Welch OK, Grundey J, Hinson JL. Identifying low pharmaceutical calculation performers using an algebra-based pretest. Am J Pharm Educ. 2022;86(1):8473.
Chisholm MA, Cobb HH, DiPiro JT, Lauthenschlager GJ. Development and validation of a model that predicts the academic ranking of first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ. 1999;63(4):388–93.
Chisholm MA, Cobb HH, Kotzan JA. Significant factors for predicting academic success of first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ. 1995;59(4):364–70.
Bush J. Entry characteristics and academic performance of students in a master of pharmacy degree program in the United Kingdom. Am J Pharm Educ. 2012;76(7).
2022 Student Experience Survery. National Report. 2023.
Grøtan K, Sund ER, Bjerkeset O. Mental health, academic self-efficacy and study progress among college students - the SHoT Study, Norway. Front Psychol. 2019;10:45.
Download references
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sydney Pharmacy School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, 2006, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Alice Campbell, Tina Hinton, Narelle C. da Costa, Sian E. O’Brian, Danielle R. Liang & Nial J. Wheate
Charles Perkin Centre, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney NSW, 2006, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Tina Hinton
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ND, SO, and DL collated and de-identified the data. AC, TH, and NW analysed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nial J. Wheate .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The University of Sydney Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) reviewed and approved this study (Approval number 2022/815). All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. As this study utilised de-identified data collected retrospectively, The University of Sydney Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) gave ethics approval for an informed consent waiver so consent did not need to be obtained from the students whose data was used in the analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Campbell, A., Hinton, T., da Costa, N.C. et al. Causes and outcomes of at-risk underperforming pharmacy students: implications for policy and practice. BMC Med Educ 24 , 421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05327-z
Download citation
Received : 16 January 2024
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05327-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Higher education
- Underperformance
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A doctorate in education typically requires between 48 and 72 credits of coursework. Students can usually earn their degree within three or four years, including time to complete a dissertation ...
Requirements for an Ed.D. Application. Check Circle. Master's Degree: Ed.D. programs require a master's degree for admission. Candidates with an Ed.S. also meet the requirement. Most programs require a minimum 3.0 GPA. Check Circle. Professional Experience: Ed.D. programs often expect professional experience.
For other students, a doctorate degree may be a personal goal. 7 Steps to Get a Doctorate Degree in Education. The requirements for admission into a doctorate program can vary from school to school, but below are the general steps one must accomplish to get a doctorate degree in education. Earn a Bachelor's Degree
Admission Requirements. At minimum, applicants to the EdD program should hold a master's degree from an accredited college or university. Previous degrees must document high academic achievement (a minimum GPA of 3.0) in an area of study closely associated with the objectives of the program.
The doctoral degree in Education at the GSE includes doctoral program requirements as well as a specialization, as listed below, overseen by a faculty committee from one of the GSE's three academic areas. Doctoral programs by academic area Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education (CTE)
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice. Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides ...
Admission Requirements. Most doctorate in education programs require a master's degree. Beyond that, Ph.D. in education requirements can vary. Some programs may prefer several years of related work experience. Others look for candidates who have leadership skills in an educational setting or teacher certifications.
HGSE students come from a wide range of backgrounds and experiences, but hold in common a fundamental commitment to social justice and changing the world through education. With the help of our exceptional faculty, highly personalized degree plans, and extensive network of alumni making a difference at all levels and across all roles, you will ...
The Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D) is a three-year, practice-based program designed to produce system-level leaders in American pre-K-12 education. The Ed.L.D. curriculum mines the vast intellectual and professional resources of HGSE, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School, and includes a 10-month residency in the ...
The focus of a Doctor of Education degree is building the knowledge and skills you need to become a leader or strategist in schools. Students in EdD programs study a variety of educational and leadership styles, education policy, and organizational change. ... The admission requirements for a doctorate of education program include an ...
The Northeastern Doctor of Education degree is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education (NECHE) and was selected as Program of the Year by the Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate Program for 2022-2023. ... Explore the current program requirements and course descriptions, all designed to meet today's industry needs ...
Degree Requirements: Both an Ed.D. and Ph.D. usually require a dissertation. The Ed.D. dissertation generally focuses on applied research topics. Ed.S. vs. Ed.D. The Ed.S. differs from the Ed.D. because it does not require a dissertation and is possible to finish in 1-2 years. For this reason, it is not considered a doctoral degree.
Johns Hopkins' newly redesigned, global online Doctor of Education is at the forefront of education doctoral programs with the most innovative, challenging, and student-centered program of its kind. Celebrating its 10th anniversary, the program continues to lead with the "EdD 2.0" offering, which is ideal for the busy education ...
The minimum unit requirement for the PhD at Stanford and the GSE is 135 units*. This is known as residency credit at Stanford, which focuses on unit-counting. Specific degree requirements are determined by the department or school. Up to 45 units of applicable graduate level coursework transferred from another institution or completed in ...
Completion Time 4+ years. Credits 72. The Johns Hopkins School of Education's full-time PhD program offers an individually tailored learning experience based on a student's interest in finding solutions to pressing education problems. Select applicants receive full tuition and a stipend. The program provides rigorous interdisciplinary ...
The average cost of a doctorate degree in education varies widely, ranging from $30,000 to $100,000 or more, depending on the institution, program length, and other factors. At the Johns Hopkins School of Education, resources for financial aid, loans, scholarships, and other sources of funding are available to help you navigate your finances.
All of our doctoral programs are designed to develop outstanding educational researchers who have a deep understanding of the scientific, practical and policy issues they study. All require full-time study, and we promise five years of full-time financial support for every student we admit. Our doctoral programs are small, typically ranging from about 25 to 35 new students a year.
A doctorate in educational leadership focuses on leadership theory and practice, research, ethics and implementing change in education. With a doctorate in educational leadership, you can work in ...
The EdD degree is the highest degree that can be awarded in the field of education. It signifies unparalleled expertise and concentrated study in the field. This degree is valued by individuals seeking a career as principals, school district superintendents, assistant superintendents, college faculty, executive directors, or heads of foundations.
The Ed.L.D Program — taught by faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School — will train you for system-level leadership positions in school systems, state and federal departments of education, and national nonprofit organizations. Ed.L.D. is a full-time, three-year ...
The average Doctorate in Education annual salary in the U.S. is 80,000$, and depending on the position and experience, it may go up to 236,000$. As for the job outlook, BLS expects a 10% increase in education sector employment from 2020 to 2030, with 920,500 new jobs predicted. So, by now, you may know the value of this degree.
Best online Doctor of Nursing Practice: University of Central Florida. Best online Doctor of Business Administration: Walsh College. Best online doctorate in physical therapy: Texas Tech ...
About the Program. Format: Online Credit Hours: 36 - 69 Entry Term: Fall. The Doctor of Education Degree program in Educational Leadership is designed to enhance the experienced school administrator's leadership skills through: (1) advanced preparation that strengthens decision-making, problem-solving, and leadership skills essential to the management of increasingly complex educational ...
This Education doctorate degree is designed to fit the schedules of working pk-12 and collegiate teachers, staff and administrators, and can be completed in two years or less through evening courses taught in convenient locations around the state. ... Requirements of the Introduction and Research Methods chapters are also examined. University ...
Prepared by: Dr. Marcia A. B. Delcourt, Coordinator, EdD in Instructional Leadership, Revised 4/19/2024 3 1. Is this an accredited program? This online Doctor of Education in Instructional Leadership degree program at WCSU is approved by the Connecticut State Department of Education (CSDE) and the New England
Mostly, people ask how long a PhD take before they enroll in any PhD program. The doctoral degree (PhD) can last up to seven years. However, it usually lasts five to seven. The goal of a PhD is to produce original, freshly brewed research. However, it can occasionally become laborious and take longer than anticipated to finish.
Of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Education School of Behavioral Sciences Liberty University 2024 . 2 ... A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Education School of Behavioral Sciences Liberty University, Lynchburg, VA 2024 TO BE APPROVED BY: Courtney Evans-Thompson. Ph.D., M.S ...
Online Nursing Doctorate [Ph.D.] Program Guide. A doctorate in nursing is the terminal degree in the field and comes in two forms: a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) and a doctor of philosophy in nursing (Ph.D.). Compared to the more clinical DNP, a nursing Ph.D. focuses more on research, education, and policy.
The education requirements for the fastest-growing health care jobs. ... a Doctor of Philosophy, or several other doctoral degrees, such as a Doctor of Physical Therapy, Audiology, or Chiropractic
Objective This study aimed to understand the key determinants for poor academic performance of students completing a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm), Bachelor of Pharmacy and Management (BPharmMgmt), or Master of Pharmacy (MPharm) degree. Methods Data were collected on pharmacy students who had not met academic progression requirements between 2008 and 2018 at The University of Sydney, Australia ...