myCBSEguide
- Social Science
- Class 10 Social Science...

Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for CBSE Class 10 Social Science case study questions, myCBSEguide provides all the resources you need. We have a wide range of Class 10 Social Science case studies covering various topics, and our team of experts is on hand to provide guidance and support to Class 10 students. Whether you’re struggling with a particular topic or just need some extra help, myCBSEguide is the perfect place to turn.
Purpose of Class 10 Social Science
Up to the secondary level of schooling, social science is a core course. It is an essential component of a general education because it assists Class 10 Social Science students in comprehending the environment as a whole and acquiring a broader perspective as well as an empirical, reasonable, and humanitarian outlook. This is critical because it helps Class 10 Social Science students into well-informed and responsible citizens with the required qualities and skills to effectively engage and contribute to the process of development and nation-building.
Case Study Questions in Class 10 Social Science
Class 10 social science curriculum includes a wide range of topics. One way to help students learn and retain information from these topics is to incorporate case studies into the classroom. Case studies can provide real-world examples of the concepts being taught, and help students to understand how the theory can be applied in practice.
Incorporating case studies into the Class 10 social science curriculum can also help to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By working through a case study, Class 10 social science students can learn how to identify key issues, consider different options and make decisions. These skills will be valuable in their future studies and careers.
Whichever way case studies are used, they can be a valuable addition to the Class 10 social science curriculum.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions Samples
Students must solve a range of Class 10 Social Science case study questions in order to achieve good grades in Social Science. Students in Class 10 Social Science must be looking for some samples of case study questions in order to improve their grades. myCBSEguide has collected a variety of case study questions for Class 10 Social Science that will undoubtedly assist all students studying the subject. We’ve put created a collection of Class 10 Social Science case study questions for you.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 1
Class 10 HISTORY: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: Frederic Sorrieu prepared a series of four prints visualizing his dream of a world made up of ‘democratic and social Republics’, as he called them. The first print of the series shows the peoples of Europe and America – men and women of all ages and social classes – marching in a long train, and offering homage to the Statue of Liberty as they pass by it. Artists of the time of the French Revolution personified Liberty as a female figure. She bears the torch of Enlightenment in one hand and the Charter of the Rights of Man in the other. On the earth in the foreground of the image lie the shattered remains of the symbols of absolutist institutions. In Sorrieu’s utopian vision, the peoples of the world are grouped as distinct nations, identified through their flags and national costume. Leading the procession, way past the Statue of Liberty, are the United States and Switzerland, which by this time were already nation-states. France, identifiable by the revolutionary tricolour, has just reached the statue. She is followed by the peoples of Germany, bearing the black, red and gold flag. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Who was Frederic Sorrieu?
- French artist
- German Artist
- Italian Artist
- British Artist
In which year did Frederic Sorrier prepare a series of four prints?
Which of the following statements correctly describes “absolutist”?
- Monarchical Government
- Democratic Government
- Uncentralised Government
- Bureaucratic Government
Which of the following is correct with respect to “utopian vision”?
- Homogenous society
- Monarchical society
- Ideal society
- All are correct
Answer Key:
- (a) French artist
- (a) Monarchical Government
- (c) Ideal society
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 2
Class 10 GEOGRAPHY: Lifelines of National Economy
Read the extract and answer the question that follows:
We use different materials and services in our daily life. Some of these are available in our immediate surroundings, while other requirements are met by bringing things from other places. Goods and services do not move from supply locales to demand locales on their own. The movement of these goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport. Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to be traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation. Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space. Therefore, efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development.
The movement of these goods and services can be over three important domains of our earth i.e. land, water and air. Based on these, transport can also be classified into the land, water and air transport. For a long time, trade and transport were restricted to limited space. With the development in science and technology, the area of influence of trade and transport expanded far and wide.
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast-moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of an equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
- Explain the necessity of means of transport in modern times. (1)
- Enumerate the domains and means of transport. (2)
- Why are efficient means of transport pre-requisites for the fast development of the country? (2)
- The movement of goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport.
- The movement of these goods and services can be over three important domains of our earth i.e. land, water and air.
- Based on these, transport can also be classified into the land, water and air transport.
- (Any two relevant points)
- Efficient and good transport for speedy movement of goods and services to different parts of India and to fulfill the needs of the people is needed.
- Goods and services do not move from supply locations to demand locations on their own. This necessitates the need for transport.
- Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. They go to traders who make the products and take them to the consumers by transportation.
- Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movements over space.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 3
Class 10 POLITICAL SCIENCE: Power-sharing
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: The Belgian leaders recognised the existence of regional differences and cultural diversities. Between 1970 and 1993, they amended their constitution four times so as to work out an arrangement that would enable everyone to live together within the same country. The arrangement they worked out is different from any other country and is very innovative. Here are some of the elements of the Belgian model:
- Constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government. Some special laws require the support of the majority of members from each linguistic group.
- Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.
- Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation. The French-speaking people accepted equal representation in Brussels because the Dutch-speaking community has accepted equal representation in the Central Government.
- Apart from the Central and the State Government, there is a third kind of government. This ‘community government’ is elected by people belonging to one language community – Dutch, French and German-speaking – no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- India, Srilanka
- Belgium, Sri Lanka
- Wallonia, Brussels
- Flemish, Wallonia
- Which of the following is not the element of “Belgian model”?
- Equal number of ministers for both the groups
- Setting up of Community Government
- More power to the central government
- Equal representation at the state and central level
- “Apart from the Central and the State Government, there is a third kind of government”. Which of the following is incorrect with respect to this?
- The unique government is Community Government
- A single social group is given powers to handle community-related affairs
- Elected by people belonging to Dutch, French and German-speaking
- Power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues
- Which of the following title best describes the given passage?
- The ethnic composition of Belgium
- Accommodation in Sri Lanka
- Accommodation in Belgium
- The ethnic composition of Sri Lanka
- (b) Belgium, Sri Lanka
- (c) More power to central government. [Explanation: Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.]
- (b) Single social group is given powers to handle the community-related affairs. [Explanation: A community government is one in which different social groups are given powers to handle community-related affairs.]
- (c) Accommodation in Belgium
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 4
Class 10 ECONOMICS: Development
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: Besides seeking more income, oneway or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All of these are important goals. In fact, in some cases, these may be more important than more income or more consumption because material goods are not all that you need to live. Money, or material things that one can buy with it, is one factor on which our life depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things. Consider an example: If you get a job in a far-off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom. Similarly, for development, people look at a mix of goals. It is true that if women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases. However, it is also the case that if there is respect for women there would be more sharing of housework and a greater acceptance of women working outside. A safe and secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business. Hence, the developmental goals that people have are not only about better income but also about other important things in life. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- Opportunity to learn
- Working atmosphere
- Job security
- All of the above
- The approach of living a life in bungalows, with costly cars, bikes and international tours is ________ life.
- Materialistic
- Both a and c
- “Women, who are engaged in paid jobs are an example of persons who fulfil a mix of goals.” Which of the following statement is incorrect with the given statement?
- A secure environment may allow more women to take up a variety of jobs or run a business.
- If there is respect for women, there would be greater acceptance of women working outside.
- If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society decreases.
- “Besides seeking more income, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security and respect of others”. What does the given statement signify?
- Mixed goals are important for people for development.
- Common goals are important for people for development.
- Conflicting goals are important for people for development.
- Similar goals are important for people for development.
- (d) All of the above
- (a) Materialistic
- (c) If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society decreases. [Explanation: If women are engaged in paid work, their dignity in the household and society increases.]
- (a) Mixed goals are important for people for development.
Class 10 Social Science curriculum at a glance
The material of the Class 10 Social Science curriculum is mostly drawn from history, geography, politics, and economics. There are also elements of Sociology and Commerce. They provide a holistic vision of society in space and time, as well as in relation to one another. The numerous methods of inquiry used in each topic assist Class 10 Social Science students in understanding society from various perspectives and forming a comprehensive vision. Class 10 Social Science curriculum is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of various disciplines like History, Geography, Economics and Political Science.
The table below provides the complete syllabus structure for Class 10 Social Science curriculum.
Class 10 SOCIAL SCIENCE COURSE CONTENT
Reasons to choose myCBSEguide for class 10
There are many reasons to choose myCBSEguide for CBSE social science Class 10.
- First and foremost, myCBSEguide provides comprehensive and up-to-date study material for the entire syllabus including class 10 social science case study questions. In addition, myCBSEguide also provides practice questions, sample papers and previous year question papers to help students prepare for the exams.
- Another reason to choose myCBSEguide is the online tests. Online tests are a great way to test your knowledge and prepare for the exams.
- Finally, myCBSEguide also provides a “Home Work help” forum where students can ask questions and get answers.
In conclusion, myCBSEguide is the ideal resource for CBSE social science Class 10 students, offering everything they need to excel in their studies.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
4 thoughts on “Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions”
I want all case study questions of sst
I want case study question for maths (standard)
It helped me a lot
GK MCQ Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Exam Tomorrow: Practice Important Case Study Questions for High Score
Cbse class 10 social science case study questions: find here important case study questions to practise for the cbse class 10 social science exam which is scheduled for march 7, 2024. all questions are provided with answers for quick revision..

CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions: CBSE Class 10 Social Science Paper which is scheduled for tomorrow, March 7, 2024, will have a section comprising, entirely, of questions based on case studies. Section E of the paper will have 3 case based questions (question no. 34 to 36) with each carrying 4 marks. In such questions, students will be given a passage discussing a specific global issue or an incident. Each passage or paragraph will be followed by a set of questions. These questions will have to be answered on a student’s understanding of the passage. In this article, we have provided some important case study based questions for Class 10 Social Science which are going to be very helpful in your last minute preparations for the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Board Exam 2023. Practise with all questions and answers given below to get prepared for the exam and secure maximum marks in CBSE Class 10 SSt Exam 2024.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Based Questions 2024
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity. Such losses have increasingly marginalized and impoverished many indigenous and other forest-dependent communities, who directly depend on various components of the forest and wildlife for food, drink, medicine, culture, spirituality, etc. Within the poor, women are affected more than men. In many societies, women bear the major responsibility of collection of fuel, fodder, water and other basic subsistence needs. As these resources are depleted, the drudgery of women increases and sometimes they have to walk for more than 10 km to collect these resources. This causes serious health problems for women and negligence of home and children because of the increased hours of work, which often has serious social implications. The indirect impact of degradation such as severe drought or deforestation-induced floods, etc. also hits the poor the hardest.
(i)Mention the importance of forests in our life. (ii) How does biological loss of forest and wildlife correlate with the loss of cultural diversity?
(i)Importance of forests in our life: Forests provide us with wood, food, medicines, honey, etc. Forests are a habitat for a number of animals. Forests help to maintain ecological balance and food chain, rain, oxygen, etc. (ii)Loss of cultural diversity: Many indigenous communities depend on forests for various components of forest and wildlife will be increasingly marginalized and impoverished Women have to walk long distance to collect basic necessities, increased hours of work,this causes health problems. Natural calamities like severe drought and deforestation induced floods will increase. If forests are destroyed poor people will be deprived of the basic necessities.
Related: C BSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions for Board Exam 2024
2.Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: Irrigation has also changed the cropping pattern of many regions with farmers shifting to water intensive and commercial crops. This has great ecological consequences like Stalinization of soil. At the same time, it has transformed the social landscape for e.g.; increasing the social gap between the richer land owners and landless poor. As a result, we can see, the dams did create conflicts between people wanting different uses and benefits from the same water resources. In Gujarat, the Sabarmati basin farmers were agitated and almost caused a riot over the higher priority given to water supply in Urban areas, particularly during droughts. Inter-state water disputes were also becoming common with regard to sharing the costs and benefits of multi-purpose projects. (i) How did cropping pattern change by irrigation? (ii) Analyse the statement “Dams created conflict between people.” (iii) What are the consequences of irrigation on Soil and social landscape
(i) Many farmers because of increased availability of water have switched over to the cultivation of water intensive commercial crops such as Jute/Cotton and Tea, rather than food grains such as Bajra, Wheat and Ragi. (ii) Dams cause mostly internal disputes for the sharing and non-sharing of water benefits to each other. Displacement of local people of the area. (iii) Water logging and salinisation of soil is common problem associated with irrigation.
3.Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Industrial locations are complex in nature. These are influenced by availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market, etc. It is rarely possible to find all these factors available at one place. Consequently, manufacturing activity tends to locate at the most appropriate place where all the factors of industrial location are either available or can be arranged at lower cost. After an industrial activity starts, urbanisation follows. Sometimes, industries are located in or near the cities. Thus, industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to the industry. Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. Gradually, a large industrial agglomeration takes place. (i) On what factors are the location of the industry dependent on? (ii) What do you understand by agglomeration economies? (iii) How do industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand?
(i) It is dependent on availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market, etc. (ii) Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. (iii) Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to the industry.
4.Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a central government ministry. This Ministry, with the help of various government departments of all the Indian states and union territories, collects information relating to total volume of goods and services and their prices and then estimates the GDP. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. The secondary sector in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under the tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process. (i) Which sector has emerged as the largest producing sector in India? (ii) Life insurance is an activity of which sector? (iii) What is GDP?
(i)Tertiary Sector (ii) Tertiary Sector (iii) The money value of all the final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year.
5.Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: In 1956, an Act was passed to recognise Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil. The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs. A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism. All these government measures, coming one after the other, gradually increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils. They felt that none of the major political parties led by the Buddhist Sinhala leaders was sensitive to their language and culture. They felt that the constitution and government policies denied them equal political rights, discriminated against them in getting jobs and other opportunities and ignored their interests. As a result, the relations between the Sinhala and Tamil communities strained over time. The Sri Lankan Tamils launched parties and struggles for the recognition of Tamil as an official language, for regional autonomy and equality of opportunity in securing education and jobs. But their demand for more autonomy to provinces populated by the Tamils was repeatedly denied. By 1980s several political organisations were formed demanding an independent Tamil Eelam in northern and eastern parts of Sri Lanka. 1. What is the moral reason behind power sharing? A. It gives absolute power to the government B. It gives absolute power to the people. C. It is the very spirit of democracy D. It ensures development. 2. Which is the official language of Sri-Lanka? A. Hindi B. Tamil C. Sinhala D. None of these 3. Sri-Lanka emerged as an independent country in---- A.1956 B.1948 C .1947 D.1951 4. Sri-Lanka is an island nation, just a few kilometres off the southern coast of A. Tamil Nadu B. Kerala C. Goa D. Karnataka 5. Population of Sri-Lankan Tamils is concentrated in- regions of Sri-Lanka. A. North and East B. North and south C. North and West D. South and west
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus for Board Exam 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper and Marking Scheme 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Map Work 2024
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- How can I get full marks in CBSE Class 10 Social Science Exam 2023? + Check expert tips for full marks: Be thorough with the revised syllabus. Solve sample paper, practice paper and previous year question papers. Read NCERT Books only. Revise map work to secure maximum marks in exam.
- Where can I get important questions for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Exam 2023? + Get important questions based on latest exam pattern for CBSE Class 10 Social Science only at Jgran Josh. All questions are curated by subject experts. Answers are provided for all questions.
- IAF Agniveer Result 2024
- AP Intermediate Result 2024
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- resultsbie.ap.gov.in Results 2024
- AP Inter Result 2024 Link
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024
- Manabadi AP Inter Result 2024
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024 AP
- AP Inter Results 2024 with Jagran Josh
- AP Inter Toppers List 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
UP Board Result 2024 Date: UPMSP Class 10, 12 Result Kab Aayega?, Check Latest Updates
(Updated) KKR vs LSG Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
Today’s IPL Match (14 April) - KKR vs LSG: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
Weekly Current Affairs Questions and Answers: 08 april to 14 april 2024
Weekly Current Affairs Quiz Hindi: 08 अप्रैल से 14 अप्रैल 2024
Happy Vishu 2024: 45+ Wishes, Images, Quotes, Greetings to Celebrate Malayalam New Year
Happy Puthandu 2024: 45+ Wishes, Images, Messages to Share on Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram Status and Stories
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: PBKS vs RR, Match 27, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
Top 10 Weekly Current Affairs in Hindi: 08 अप्रैल से 14 अप्रैल 2024
IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, राजस्थान टॉप पर
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Only 2% With Eagle Vision Can Spot A Snowman In 12 Seconds!
You have sniper vision if you can find the bright yellow car in the traffic scene in 7 seconds!
When Is Puthandu In 2024? Check Date And All About Tamil New Year
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre: 105 years of Tragedy|Causes & its Impact
NIACL Assistant Mains Expected Cut Off 2024, Check Minimum Qualifying Marks
Accept The Challenge To Find The THIEF Who Stole Money In The Spa Centre. 15 Seconds Left!
Happy Baisakhi 2024: 55+ Wishes, Images, Quotes, Greeting Message to Share and Wish Harvest Festival of Punjab and North India
Who is Sandhya Devanathan, the Newly Appointed Head of META India?
Summary on Jainism: Teaching of Mahavira | Spread of Jainism
UPSC NDA Exam Date 2024: Check Written Exam Shift Timing
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions Download Free PDF
If you are looking for the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Social Science Subject is available here. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study.

The Social Science Subject case study for class 10th covers a wide range of chapters from the Social Science. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve such kinds of questions.
CBSE 10th Social Science Exam 2022-23 : Case Study Questions With Answers
In class 10th board exams 2023, students will observe new types of case study questions. For the first time, the board introduced the case study questions in the board exam. we have provided the chapter-wise case study question with answers.
The above Case studies for Class 10 Social Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Study’s have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Maths Case Study Questions
- Class 10th Science Case Study Questions
For CBSE Class 10, the board has decided to introduce a minimum of 30 percent competency-based questions in form of case study questions, MCQs, source-based integrated questions, etc. in the new exam pattern 2022-2023. Therefore, students should make themselves familiar with the case study questions to learn the right process for approaching these new types of questions with accuracy.
Case Study Type Questions in Social Science Class 10
Case Study Type Questions in Social Science Class 10 include the information or data. Students willing to solve them are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them. While solving the paragraph the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data.
Because later it will ease them to write the final answers. Science Case study type questions consist of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in an MCQ manner.
While reading the paragraph students will get the clue in between about the possible answer of the question. They should definitely highlight those questions. This is the best way to solve such kind of Case study Type Questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Meghnaunni.com
Paintings, Drawings, Articles, Speeches, Bharathanatyam
Social Issues Report for CBSE Std 10 | Gender Inequality
Social Issues Report for CBSE Std 10. I took the topic of Gender Inequality for this project to be done for my Social Science subject enrichment activity for class 10.

Reasons for gender inequality in India, Government policies, programmes and schemes etc. are discussed in the report. I have taken the case study of Gender Inequality in tribal women in India – A Case study of Lepcha Society.
Since many people asked for more clear pictures the graphs used, sharing what is available with me now.

- ← Speech on the Topic “Advertisements are misleading !”
- Class 10 Biology Diagram | Binary Fission in Amoeba & Leishmania →
45 thoughts on “ Social Issues Report for CBSE Std 10 | Gender Inequality ”
this is very good i like it and it also help me thank you
It was very much helpfull…… Thank you so much 😊😊😊
Is this full topic is social issues ?
Yes Super uhhhh Thanks ☺️☺️☺️☺️
case study likhna compalsary hai ???
It was very helpful
It is a very good topic and help me a lot on making my project
Thank you 🙂
Thanks for this project.
Can I get this fill
Thanks for this project. It really helped me.
Osm sis thanks a lot. It helped me to prepare my project for boards.
thank you 🙂
Thanks you so much it helps me to prepare Sst project
From where you got this graph … actually I also want it for my activity but it’s not clear .. btw thanks for this activity it’s very helpfull.
I have attached two of the pictures of graphs separately now. Hope this is helpful. That is all I have now. Don’t remember the source now. Sorry.
Pictures not clear pls re-upload . this file is very good for ss project.
Sorry. I do not have the original file with me now.
Pls can u share it without watermark to me pls sis I just want for school tomorrow is last day for submission I will be really grateful.
The project is very good 👍. But there is little bit difficulty to see some words because the image is not clear. But overall it was good 👍🏻 & THANKS FOR the wonderful project.
Thank You. I do not have the hard copy of that with me now. So unable to put a more clear picture.
What a project is this!!!!!Tq for it and it helped me alot for my sst project and tq to u for it….. this project gave me full marks!!!!! Once again Tq
Thanks alot for this, it helped a lot!!
what a project it has really helped me. I got 50/50. All thanks to u
Thank You. Happy that it helped you..
thanks a lot for this project …….it’s rlly nice it helped me too. thankyou again
Writing is very bad . Kuch samaj he nahi aa rha 😔😔
If you did not like it don’t take it. I got full marks for this and many others too found it useful.
Thank you so much! This really helped me, hope you have/had a great day, Stay safe!
It’s very nice and also helpful project
Where would I find all the pictures that are used in this project
Thanks so much 👍👍😍😍😍
How can I join with u any(Instagram id)
QUALITY OF PICTURE IS VERY BAD 🤮
This project has helped many. It is put here just as a reference, not for printing as such.
really a very amazing project it helped me a lot thanks
THANKYOU SO MUCH , IT GAVE ME AN IDEA HOW TO COMPLETE MY PROJECT , ITS REALLY VERY HELPFUL
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Notice: It seems you have Javascript disabled in your Browser. In order to submit a comment to this post, please write this code along with your comment: 52a6f0d3893da5de4ff7bef9eec214a4

Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions for PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Are you a Class 10 student studying Social Science? Do you find Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions challenging and need some extra practice? Look no further! In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive collection of case study questions specifically designed for Class 10 Social Science . These questions will help you enhance your understanding of the subject and improve your performance in exams. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of case study questions!
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

Case study questions are an integral part of the Social Science curriculum in Class 10. They require students to analyze a real-life situation or scenario and apply their knowledge of various concepts and principles to understand and solve the problem at hand. Case study questions are designed to assess students’ critical thinking, analytical skills, and ability to connect theoretical concepts with practical situations.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !.
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions CBSE 10th Social Science
Case study questions play a vital role in Social Science as they enable students to develop a deep understanding of the subject. By analyzing real-life case studies, students can grasp the complexities of social, political, economic, and geographical issues. Case studie s provide a practical context for learning and allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. They also help students develop problem-solving and decision-making skills, which are essential for their future endeavors.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Social Science
In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The above Case studies for Class 10 Social Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 10th Maths Case Study Questions
- Class 10th Science Case Study Questions
For CBSE Class 10, the board has decided to introduce a minimum of 30 percent competency-based questions in form of case study questions, MCQs, source-based integrated questions, etc. in the new exam pattern. Therefore, students should make themselves familiar with the case study questions to learn the right process for approaching these new types of questions with accuracy.
How to Approach Case Study Questions
To effectively tackle case study questions, it is crucial to follow a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you approach and answer case study questions:
Step 1: Read the Case Study Carefully Start by reading the case study thoroughly and understanding the context, characters, and key issues involved. Highlight or underline important information that will be useful in answering the questions.
Step 2: Identify the Problem or Objective Determine the central problem or objective presented in the case study. This will help you focus your analysis and provide relevant answers.
Step 3: Analyze the Case Study Break down the case study into different components and analyze each aspect individually. Identify relevant concepts, theories, and principles that are applicable to the situation.
Step 4: Apply Your Knowledge Use your understanding of the subject and the concepts learned in class to analyze the case study. Connect the theoretical concepts to the practical situation and provide logical explanations or solutions.
Step 5: Support Your Answers with Evidence Back up your answers with evidence from the case study or additional research. This will add credibility to your responses and showcase a deeper understanding of the topic.
Step 6: Present Your Answers Clearly Organize your answers in a structured manner, ensuring clarity and coherence. Use proper headings, paragraphs, and bullet points to make your answers more readable and understandable.
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions
When answering case study questions, keep the following tips in mind:
- Read the question carefully and understand its requirements.
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your answers effectively.
- Support your answers with relevant facts, examples, and evidence.
- Use clear and concise language to convey your thoughts.
- Revise and proofread your answers for clarity, grammar, and spelling.
MCQ Questions on Class 10 Social Science
Mcq questions for class 10 social science history.
- The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Class 10 MCQ Questions
- The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Nationalism in India Class 10 MCQ Questions
- The Making of Global World Class 10 MCQ Questions
- The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Work, Life and Leisure Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Print Culture and the Modern World Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Novels, Society and History Class 10 MCQ Questions
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Geography
- Resources and Development Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Water Resources Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Agriculture Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Manufacturing Industries Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 MCQ Questions
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Civics
- Power Sharing Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Federalism Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Democracy and Diversity Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Gender Religion and Caste Class 10 MCQ questions
- Popular Struggles and Movements Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Political Parties Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Outcomes of Democracy Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Challenges to Democracy Class 10 MCQ Questions
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Economics
- Development Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Sectors of Indian Economy Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Money and Credit Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 MCQ Questions
- Consumer Rights Class 10 MCQ Questions
Case study questions are a valuable tool for learning and assessing your understanding of Social Science. By practicing these questions, you can strengthen your analytical skills, critical thinking abilities, and subject knowledge. Remember to approach case study questions systematically, apply your knowledge effectively, and present your answers in a clear and organized manner. With regular practice and a solid understanding of the subject, you will excel in answering case study questions and achieve success in your Class 10 Social Science exams.
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science Case Study Questions
Q: where can i download the pdf with the case study questions.
A: You can download the PDF with the case study questions by clicking the following link
Q: Are these case study questions based on the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science?
A: Yes, these case study questions are designed based on the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science.
Q: Is it necessary to practice case study questions for Social Science?
A: Practicing case study questions is highly recommended as it enhances your critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills. It also helps you develop a deeper understanding of the subject by applying theoretical concepts to real-life situations.
You Might Also Like
Mcq class 10 social science geography lifelines of national economy quiz with answers.

Best Reference Books for Class 10 2024 CBSE Preparation
Mcq class 10 english a letter to god questions with answers english chapter 1, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 10 Social Science 2023 : Important Case Study Questions for Last-Minute Revision

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
This article provides a list of important case study questions for students preparing for the CBSE Class 10 Social Science exam in 2023. It is designed to help students revise key concepts and improve their exam performance in the final days leading up to the exam.
Case-Based Questions
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity. Such losses have increasingly marginalized and impoverished many indigenous and other forest-dependent communities, who directly depend on various components of the forest and wildlife for food, drink, medicine, culture, spirituality, etc. Within the poor, women are affected more than men. In many societies, women bear the major responsibility of collection of fuel, fodder, water and other basic subsistence needs. As these resources are depleted, the drudgery of women increases and sometimes they have to walk for more than 10 km to collect these resources. This causes serious health problems for women and negligence of home and children because of the increased hours of work, which often has serious social implications.
The indirect impact of degradation such as severe drought or deforestation-induced floods, etc. also hits the poor the hardest.
(i)Mention the importance of forests in our life. (1)
(ii) How does biological loss of forest and wildlife correlate with the loss of cultural diversity? (2)
(i) Importance of forests in our life: Forests provide us with wood, food, medicines, honey, etc. Forests are a habitat for a number of animals. Forests help to maintain ecological balance and food chain, rain, oxygen, etc.
(ii) Loss of cultural diversity: Many indigenous communities depend on forests for various components of forest and wildlife will be increasingly marginalized and impoverished Women have to walk long distance to collect basic necessities, increased hours of work,this causes health problems. Natural calamities like severe drought and deforestation induced floods will increase. If forests are destroyed poor people will be deprived of the basic necessities.
2. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Irrigation has also changed the cropping pattern of many regions with farmers shifting to water intensive and commercial crops. This has great ecological consequences like Stalinization of soil. At the same time, it has transformed the social landscape for e.g.; increasing the social gap between the richer land owners and landless poor. As a result, we can see, the dams did create conflicts between people wanting different uses and benefits from the same water resources. In Gujarat, the Sabarmati basin farmers were agitated and almost caused a riot over the higher priority given to water supply in Urban areas, particularly during droughts. Inter-state water disputes were also becoming common with regard to sharing the costs and benefits of multi-purpose projects.
(i) How did cropping pattern change by irrigation? (ii) Analyse the statement “Dams created conflict between people.” (iii) What are the consequences of irrigation on Soil and social landscape
(i) Many farmers because of increased availability of water have switched over to the cultivation of water intensive commercial crops such as Jute/Cotton and Tea, rather than food grains such as Bajra, Wheat and Ragi.
(ii) Dams cause mostly internal disputes for the sharing and non-sharing of water benefits to each other. Displacement of local people of the area.
(iii) Water logging and salinisation of soil is common problem associated with irrigation.
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Industrial locations are complex in nature. These are influenced by availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market, etc. It is rarely possible to find all these factors available at one place. Consequently, manufacturing activity tends to locate at the most appropriate place where all the factors of industrial location are either available or can be arranged at lower cost. After an industrial activity starts, urbanisation follows. Sometimes, industries are located in or near the cities. Thus, industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to the industry. Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. Gradually, a large industrial agglomeration takes place.
(i) On what factors are the location of the industry dependent on? (ii) What do you understand by agglomeration economies? (iii) How do industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand?
(i) It is dependent on availability of raw material, labour, capital, power and market, etc. (ii) Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. (iii) Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to the industry.
4.Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is. In India, the mammoth task of measuring GDP is undertaken by a central government ministry. This Ministry, with the help of various government departments of all the Indian states and union territories, collects information relating to total volume of goods and services and their prices and then estimates the GDP. When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. The secondary sector in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we associate with industrial activity. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under the tertiary sector and is different from the above two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or a support for the production process.
(i) Which sector has emerged as the largest producing sector in India? (ii) Life insurance is an activity of which sector? (iii) What is GDP?
(i)Tertiary Sector (ii) Tertiary Sector (iii) The money value of all the final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year.
5.Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
In 1956, an Act was passed to recognise Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil. The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs. A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism. All these government measures, coming one after the other, gradually increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils. They felt that none of the major political parties led by the Buddhist Sinhala leaders was sensitive to their language and culture. They felt that the constitution and government policies denied them equal political rights, discriminated against them in getting jobs and other opportunities and ignored their interests. As a result, the relations between the Sinhala and Tamil communities strained over time. The Sri Lankan Tamils launched parties and struggles for the recognition of Tamil as an official language, for regional autonomy and equality of opportunity in securing education and jobs. But their demand for more autonomy to provinces populated by the Tamils was repeatedly denied. By 1980s several political organisations were formed demanding an independent Tamil Eelam in northern and eastern parts of Sri Lanka.
1. What is the moral reason behind power sharing? A. It gives absolute power to the government B. It gives absolute power to the people. C. It is the very spirit of democracy D. It ensures development.
2. Which is the official language of Sri-Lanka? A. Hindi B. Tamil C. Sinhala D. None of these
3. Sri-Lanka emerged as an independent country in---- A.1956 B.1948 C .1947 D.1951
4. Sri-Lanka is an island nation, just a few kilometres off the southern coast of A. Tamil Nadu B. Kerala C. Goa D. Karnataka
5. Population of Sri-Lankan Tamils is concentrated in-regions of Sri-Lanka. A. North and East B. North and south C. North and West D. South and west
1. C.It is the very spirit of democracy 2. C Sinhala 3. B.1948 4. A. Tamil Nadu 5. A. North and East
CBSE Class 10 Study Material

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 10 Exams Finish, When Can You Expect Results? Details Here 14 March, 2024, 11:45 am
- CBSE Board Class 10 Information Technology Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs 13 March, 2024, 12:46 pm
- CBSE Board Class 10 Computer Applications Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs 13 March, 2024, 12:41 pm
- CBSE Class 10 Information Technology Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision 12 March, 2024, 1:24 pm
- CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision 12 March, 2024, 12:08 pm
- CBSE Board Class 10 Maths Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs 11 March, 2024, 1:34 pm
- CBSE Class 10th Maths Exam 2024 : Most Important Assertion Reason & Case Study Question For Last Minute Revision 9 March, 2024, 4:04 pm
- CBSE Class 10th Maths Exam 2024 : Most Expected Question For Last Minute Revision 8 March, 2024, 6:19 pm
- CBSE 10th Maths Exam 2024 : Practice Paper Important Last Days Revision Notes; Download PDF 8 March, 2024, 6:11 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science History Chapter 5 Print Culture and the Modern World

CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Social Science History Print Culture and the Modern World. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Print Culture and the Modern World.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
Case Study 1
Print culture and modern world
1) One of the most stringent regulations on the freedom of the press in India was the Vernacular Press Act of 1878. This act, introduced by then Viceroy, Lord Lytton, granted the government extensive powers to censor reports and editorials in the vernacular press. Its purpose was to prevent criticism of British policies by the vernacular press. The Vernacular Press Act was implemented as a response to the ineffectiveness of the ‘Gagging Act’, which the press had been unaffected by. Between 1908 and 1912, four additional measures were enacted: the Newspapers (Incitement to Offences) Act and the Criminal Law Amendment Act of 1908, the Press Act of 1910, and the Prevention of Seditious Meetings Act of 1911. The Press Act of 1910 had a particularly significant impact on Indian newspapers. It granted the local government the authority to demand a security fee for any content deemed ‘offensive’ towards the government. Nearly 1,000 papers were prosecuted under this Act. During Mahatma Gandhi’s Salt Satyagraha, the press played a crucial role in mobilizing the masses against the British. This further strained the relationship between the press and the government. Following Gandhi’s arrest in 1930, the government enacted The Press (Emergency Powers) Act of 1931, which granted provincial governments the power of censorship.
Q1) What was the role on press and media in India freedom movement? Mark 2
Answer The press played a pivotal role in India’s freedom movement by disseminating information, fostering nationalistic sentiment, and challenging British colonial rule through newspapers, magazines, and pamphlets. Prominent figures like Gandhi and Nehru used the press as a powerful tool for mobilizing public opinion and rallying support for the struggle for independence.
Q2) Name the newspaper published by Bal Gangadhar Tilak and role it played in India freedom struggle? Mark 2
Answer Bal Gangadhar Tilak published the newspaper “Kesari” in Marathi and “The Maratha” in English. These newspapers were instrumental in galvanizing the masses and promoting nationalist ideals. Tilak’s fiery editorials and writings inspired a sense of pride and unity, contributing significantly to the Indian freedom struggle against British colonial rule.
Case Study 2
2) The 19th century in India, particularly the final quarter, witnessed the emergence of significant religious movements that would have a lasting impact on India and beyond. These movements were characterized by the concept of social “reform” and the associated idea of religious revival. They encompassed a wide range of discussions regarding existing religious traditions among Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs, the necessity to adapt them to social and political transformations, notions of modernity, and the establishment of educational and social institutions. Furthermore, the concept of community identity underwent a transformation, exemplified by the recognition of “Hinduism” as a global religion. These debates took place within three main contexts: the formalization of colonial rule, the development of socio-religious institutions, and the influence of anti-colonial nationalism. The nature of colonial power in India evolved from trade expansion and conquest to direct control by the crown throughout the 19th century, profoundly impacting religious movements, reform ideologies, and social change. India’s major religious traditions faced various challenges, both direct through the presence of missionaries and indirect through the introduction of new social and political ideas.
Q1) What was the role of press in social religious reform movement in India ? Mark 2
Answer The press played a vital role in the social and religious reform movements in India by spreading progressive ideas, advocating for caste and gender equality, and challenging regressive practices. Prominent reformers like Raja Ram Mohan Roy and Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar used newspapers and journals to educate and mobilize public opinion, fostering a climate of intellectual awakening and change during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Q2) Name some prominent personalities who used press to bring social and religious reforms in India? Mark 2
Answer Prominent personalities who used the press for social and religious reforms in India include Raja Ram Mohan Roy, who founded “Sambad Kaumudi” and “Mirat-ul-Akbar.” Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar published “Tattwabodhini Patrika.” Swami Vivekananda wrote for “Udbodhan.” Keshab Chandra Sen’s “Theistic Quarterly Review” and Annie Besant’s “New India” also played crucial roles in advocating reform and change.
Case Study 3
3) The influence of print media, namely newspapers and magazines, is significantly limited in developing countries due to the prevalence of illiteracy. Despite this, print media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and determining what is deemed newsworthy. Margaret Gallagher’s research in the early 1980s revealed that women and women’s issues were given minimal coverage in newspapers, with gender stereotypes being reinforced in general. However, with the rise of feminist criticism of print media and the involvement of feminist professionals in the industry, there has been some progress. In the past, women and their issues were rarely featured on the front page of newspapers and were often portrayed as victims of violence. Today, women are more visible in mainstream print media, although they still coexist with outdated sexist images and back page pin-ups..
Q1) What do you mean by the term penny magazine? Also add name of prominent women writer in history of print media. Mark 2
Answer . Penny magazines were especially meant for women, as were manuals teaching proper behaviour and housekeeping. Some of the bestknown novelists were women: Jane Austen, the Bronte sisters, George Eliot.
Q2) Write about Rashsundari Debi ? Mark 1
Answer Rashsundari Debi, a young married girl in a very orthodox household, learnt to read in the secrecy of her kitchen. Later, she wrote her autobiography Amar Jiban which was published in 1876. It was the first full-length autobiography published in the Bengali language.
Q3) What was the role of press in liberating the rights of women in India? Mark 1
Answer The press played a significant role in advocating for women’s rights in India. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, various newspapers and journals, including “Stri Dharma” by Pandita Ramabai and “Bharati” by Kandukuri Veeresalingam, highlighted issues such as women’s education, widow remarriage, and their overall empowerment. These publications helped raise awareness and contributed to the evolving discourse on women’s rights in India. The press continued to be an essential platform for addressing and advancing women’s rights throughout the 20th century and beyond.
Case Study 4
4) During the era when Gutenberg’s printing press gained popularity, there had been persistent calls for reforms within the Catholic Church for several centuries. However, it was approximately 50 years after the invention of the printing press that it played a crucial role in accelerating the Protestant Reformation. This unexpected alliance commenced in 1517, when Martin Luther, a Catholic priest, publicly presented his renowned Ninety-Five Theses, which demanded significant changes within the Church. Ironically, Luther’s propositions also included the abolition of indulgences, a practice that Gutenberg’s printing press had been instrumental in disseminating. Historically, these calls for reform had either been gradually accepted or disregarded, spanning numerous centuries. Nevertheless, rather than fading away, the advent of the printing press facilitated the rapid and forceful dissemination of Luther’s passionate writings, swiftly spreading throughout Europe like wildfire.
Q1) What do you mean by the term Protestant reformation? Mark 1
Answer A sixteenth-century movement to reform the Catholic Church dominated by Rome. Martin Luther was one of the main Protestant reformers. Several traditions of anti-Catholic Christianity developed out of the movement.
Q2) What was the fear of roman catholic institution against the press? Mark 2
Answer The Roman Catholic Church historically feared the press due to concerns about the dissemination of dissenting or heretical ideas that could challenge its authority. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century played a role in the Protestant Reformation, leading to religious schisms. The Church sought to control and censor printed materials to prevent the spread of ideas deemed contrary to Catholic doctrine.
Q3) What do you understand by the term The macabre dance? Mark 1
Answer Sixteenth-century print shows how the fear of printing was dramatised in visual representations of the time. In this highly interesting woodcut the coming of print is associated with the end of the world. The interior of the printer’s workshop here is the site of a dance of death. Skeletal figures control the printer and his workers, define and dictate what is to be done and what is to be produced.
Case Study 5
5) The introduction of the printing press with movable metal type to Europe in the 1450s CE had significant and enduring consequences. Johannes Gutenberg, a renowned German printer, is widely recognized for this innovation, particularly for his notable printing of the Bible in 1456 CE. Initially, religious texts and educational materials were printed, but soon presses were producing a wide range of literature, from Reformation pamphlets to romantic novels. This led to a substantial increase in the number of books available, while their cost decreased, resulting in a greater number of people engaging in reading. The dissemination of ideas across Europe was facilitated as scholars published their own works, commentaries on ancient texts, and critiques of one another. However, certain authorities, such as the Catholic Church, objected to certain books and resorted to censorship or even burning them. Nevertheless, the public’s perception of books and reading had already been permanently transformed by this time.
The invention of the movable metal type printer in Europe is commonly attributed to Johannes Gutenberg, a German printer. However, there are alternative claims, including those of Laurens Janszoon Coster, a Dutch printer (c. 1370-1440 CE), as well as two other early German printers, Johann Fust (c. 1400-1465 CE) and his son-in-law Peter Schöffer (c. 1425-1502 CE). Additionally, evidence suggests that movable metal type printers had already been developed in Korea in 1234 CE during the Goryeo Kingdom (918-1392 CE).
Q1) What was the impact of press in Europe? Mark 2
Answer Impact of press in Europe included
An increase in literacy rates, The rapid spread of ideas concerning religion, history, science, poetry, art, and daily life, An increase in the accuracy of ancient canonical texts.
Q2) What do you understand by the term platen? Mark 2
Answer In letterpress printing, platen is a board which is pressed onto the back of the paper to get the impression from the type. At one time it used to be a wooden board; later it was made of steel.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts

RS Aggarwal Class 8 Math First Chapter Rational Numbers Exercise 1A Solution
Factors promoting growth of nationalism foundation of the indian national congress class 10 icse chapter 2 complete notes pdf, the first war of independence 1857 class 10 icse complete notes pdf, justify the statement “industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand” in details.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India - Free PDF Download
Social Science is a subject which holds a deep study of how our society works. The book has 7 chapters in total. The chapters touch upon topics like how do we procure our resources, what are the different kinds of resources and how to conserve these resources? In the first few chapters, most discussion in the chapters is about resources and the different kinds like water, forest and wildlife resources etc. These chapters also discuss where in India these resources can be found and what is their distribution over the country.
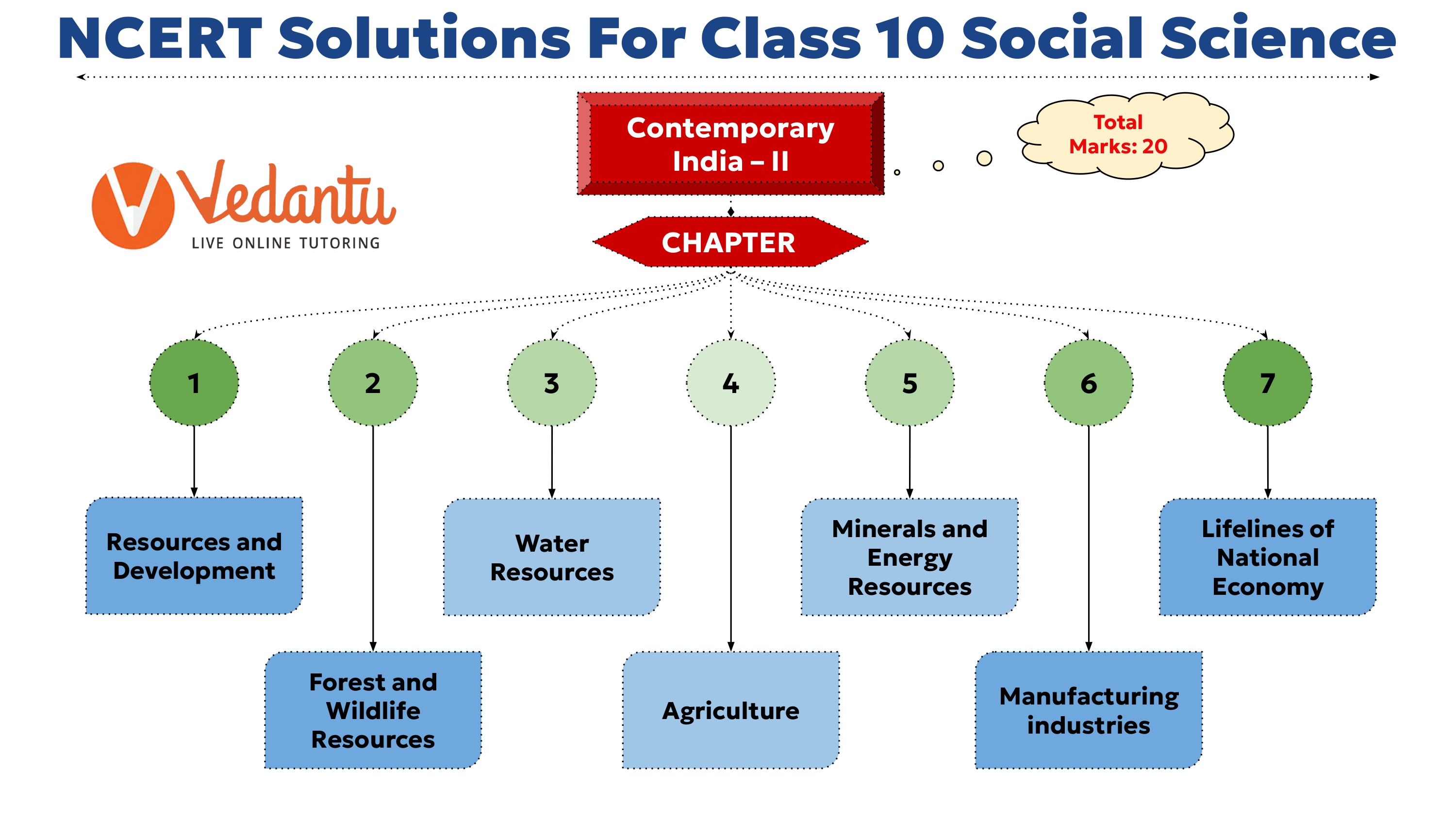
Where Chapter 1 to 3 talks about resources, Chapter 4 of Geography class 10 NCERT solutions specifically talks about agriculture and its importance in our country. Agriculture is said to be the backbone of the Indian economy. It also introduced the students to the agricultural practices prevalent in India. NCERT solutions for Class 10 Geography can help you grasp the concepts better.
Chapter 5 talks about the different minerals and resources that are used in industries or otherwise, their distribution and how we can judiciously use them. Chapter 6 focuses on the industrial sector of the country. It highlights the importance of the sector in terms of employment and how it helps the economy. It also talks about the uneven distribution of these industries over the country due to availability of resources and what can be done to rectify this by the government.
The last chapter talks about how communication and technology can be improved to connect us better. It also talks about the transportation system and how it is important to keep us intact.
Class 10 is a competitive class for students. It is the first time the students have to appear for the board exams. Class 10 is also important as your performance in this class and the subjects can help you decide what subject you may choose in Class 11 and 12. Getting good marks to get admission in the school of your choice and the subject of your choice for 11th and 12th is important.
If you decide to choose humanities as a subject in Class 11 and 12 it is important that your Social Sciences concepts from Class 9 and 10 are clear. These classes and the topics taught in these classes help to form a strong base for what you will be taught in higher classes and sometimes in colleges as well. It is important that you are regular with the subject and revise everyday what you are being taught in school. Social Sciences largely covers topics dealing with history, politics and geography. The students depending on their strengths and weaknesses should divide equal time for each sub-division. All of the chapters in Social Sciences in each division can be found on the Vedantu website. You will find chapter-wise solutions for each part, like Social Science teachers who believe that problems arise because students’ concepts don’t get clear and they avoid reading books with heavy texts. Also, students lack proper use of vocabulary, which makes it difficult for them to answer certain questions. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has a particular record of answering strategy which has to be observed. Every learner ought to observe those regulations while answering the questions to score high.
To solve those problems, Vedantu has prepared NCERT Solutions for class 10 Geography which is designed as per the CBSE curriculum in an organized manner that helps the students to understand the chapter well. Students can ensure better learning by following NCERT Class 10 Social Science Solutions which is easily available online for download from Vedantu Portal which is one of the leading educational portals in India right now. Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 NCERT Solution PDF is available Online. Students can even get the CBSE Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 7 Solutions from the Vedantu app. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Science Students who are looking for Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions will also find the Solutions curated by our Master Teachers really Helpful.
All the solutions PDFs have been prepared keeping in mind the answer-key guidelines from the CBSE and are up to date with any other guidelines that may be added by the CBSE for the academic year. Going through the answers and solutions in the pdf that are according to the guidelines will give you an idea on how to formulate and write your answers in the exam. If you practice enough questions from the pdf and go through all the solutions given from the NCERT social science class 10 you will be able to easily answer during the exam. You will not fumble about what to write and you will also be able to complete everything in time and manage your time well. A well written answer can easily fetch you full marks for a particular question. Social Sciences is a subject in which if you answer well and in a concise manner you will be able to score full marks for that answer. It can be a highly scoring subject for the students and can bring your overall aggregate up as well.
The NCERT textbook like NCERT Geography book class 10 solutions has short answer type questions after each chapter in the textbook for the students to attempt. The answers to all these questions can be found in the Solutions pdf and many similar questions for the students to practice.
Detailed Overview of Class 10 Social Science - Contemporary India NCERT Solutions
Significance of ncert solutions class 10 social science contemporary india .
For Class 10 students, Geography is an important subject dealing with the earth and the various processes and functions that it performs. Students of class 10 have to complete their Geography chapters in order to get a strong grasp of the concepts. To help make things easier, the subject matter experts at Vedantu have created NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India . Students will be able to learn a lot of important things from the chapters such as Natural Resources, Forest and Wildlife, Terms of Employment, Economy, Distribution of Industries, Communication, etc.
The Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapters will guide the students through the entirety of the world. They will be able to learn about the development of the world through these chapters. After completing their syllabus, students can practise from the NCERT solutions. These solutions have been crafted by the subject matter experts at Vedantu for the Class 10 students. Following the solutions will help them understand the chapters in detail. Download Social Science Contemporary India Guide For Class 10 from Vedantu and start practising to see the results.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science - Chapter-wise List
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science . The experts provide these solutions at Vedantu in a detailed manner. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India
Overview of Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapters for CBSE 2024-25
Resources and Development: This chapter teaches students about natural resources, their value, the importance of utilising natural resources judiciously and their conservation. The important topics covered in this chapter are listed below.
Types of Resources
Development of Resources
Resource Planning in India
Land Resources and Utilisation
Pattern of Land-use in India
Land Degradation and Measures of Land Conservation
Soil as a natural resource
Classification of Soils
Soil Erosion
Soil Conservation
Water Resources: This chapter primarily deals with the importance of water as a natural resource. It helps to develop awareness among the readers about the judicious use of water and its conservation. The various dams in our country are discussed in this chapter. The main topics covered in this chapter are as follows.
Water Scarcity
Need for Water Conservation and its Management
Multipurpose River Projects
Integrated Water Resources Management
Rainwater Harvesting
Agriculture: This chapter deals with the importance of agriculture in the economy of our country. The various types of farming methods, the spatial distribution of major crops and the relationship between rainfall and cropping patterns are discussed in this chapter. Also, some of the government policies that have been employed since independence for the institutional and technological reforms are covered in this chapter. The main topics covered in this chapter are as follows.
Types of Farming
Major Crops
Cropping Patterns
Impact of Globalisation on Agriculture
Technological and Institutional Reforms
Minerals and Energy Resources: Students will learn about the different types of minerals and energy resources, sites where these resources are available, the need for using these resources judiciously and conserving them. The important topics covered in the chapter are as follows.
What is a mineral?
Mode of occurrence of minerals
Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
Non-metallic minerals
Rock minerals
Conservation of Minerals
Conventional and non-conventional resources
Conservation of energy resources
Manufacturing Industries: From this chapter, students will learn about the importance of industries in our economy, the regional disparities that resulted due to the concentration of resources in some regions, why a planned industrial development is needed and the role of government toward sustainable development. Topics covered in the chapter include:
Importance of manufacturing
Industry’s contribution to the national economy
Locations of Industries
Classification of Industries
Spatial distribution of Industries
Industrial Pollution & Environmental Degradation
Control of Environmental Degradation
Life Lines of National Economy: This chapter explains the importance of transportation and communication and the role of trade and tourism in the economic development of any country. The main topics covered in this chapter are as follows.
Transport: Roadways, Railways, Pipelines, Airways, Waterways
International Trade
Communication
Tourism as a Trade
Why Do We Need to Refer to NCERT Solution for History Class 10th?
History Class 10 Syllabus is vast and requires extensive knowledge to appear for your board exams. Apart from your textbooks and other Notes resources you need to refer to Class 10 History Solution for enhancing your writing skills and a better understanding of various concepts. Class 10 History Chapter 1 NCERT Solution gives you a brief idea. CBSE Class 10 Social Science India and Contemporary World is divided into subtopics like Rising in Nationalism, the Nationalist of Indo-China Movements, Nationalism in India, Making of the World, Work-life and Leisure, Print Culture, and Modern History.
Class 10 Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy also explains the concept of Satyagraha which is described very precisely. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 SST History guides you to write subjective answers and helps you to give logical thinking over objective questions.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Weightage 2024-25
Internal assessment class 10 cbse social science, ncert solutions for class 10 social science for cbse.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science PDFs (Geography, Political Science/Civics and Economics) are available on Vedantu. The links to all other NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science are given below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science India and the Contemporary World-II
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Democratic Politics II
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics

Benefits of Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Solutions
One of the main advantages of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography is that students can develop their concepts about the chapters in a better way. The solutions have been explained in detail using different explanations, examples, and descriptions for the students of Class 10.
Another main benefit is that all the solutions have been arranged in a systematic format. Students can search for the Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India All Chapter Name and get access to all the links to the solutions and that too chapter-wise. This makes it easier for them to get the solutions to any specific chapter.
All the topics and chapters have been explained in detail by the experts at Vedantu. Students can rely on the accuracy and authenticity of the solutions. Following the guide will help the students in improving their own answering skills.
Vedantu’s Class 10 Contemporary India solutions are extremely helpful for students because they can clarify any doubts about the chapter from these. The solutions are extremely beneficial as these can help students get the right guidance to form their own answers.
During the time of exams, students don’t really have the time to go through the textbook to read the chapters one by one. This is where NCERT Solutions for Contemporary India will help students. They can go through these solutions and gain insights about the chapters easily. This will make the process of revision much quicker.
All Subjects Class 10 NCERT Solutions for CBSE 2024-25
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths, Science, English, Social Science and Hindi are available on Vedantu. Click on the below-given links to download these NCERT Solution PDFs for free and prepare for the CBSE Class 10 exams 2024-25.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
Competitive Answering Pattern
NCERT Solution of Class 10th History gives students an idea about all past events with its implications in today’s World. Human Nature has always taken inspiration from past events to bring radical changes in the present World. NCERT Solution of History Class 10 th is arranged in a proper structure so that every student can easily get good scores while referring to it. Class 10 History Chapter 1 NCERT Solution gives a competitive flat form to the students to perform well in final exams by providing them with accurate answers as per the format laid by CBSE.
Important Related Links for NCERT Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
NCERT Books for Class 10
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
CBSE Class 10 Maths Formulas
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Contemporary India
The NCERT Solutions will help students understand what is Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India as it provides a helpful guide to all the chapters. These solutions have been prepared by some of the best experts at Vedantu and are extremely helpful to the students. They can rely on the solutions to each chapter and complete their syllabus on time. Download Class 10 Contemporary India solutions from Vedantu and gain a better understanding of the chapters easily.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India
1. How Many Chapters are Included in CBSE Class 10 Social Science India and The Contemporary World?
NCERT Solution of History Class 10 covers almost all the topics and subtopics however majorly there are almost five chapters which are explained in details:
The Rise of Nationalism.
Nationalism in India.
The making of the Global World.
The Age of Industrialization.
Print Culture and the Modern World.
2. How will you be Benefitted by Using Vedantu NCERT Solutions for Class 10 SST History?
The content in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 SST History downloaded from Vedantu is always accurate and understandable for the students from all categories. This NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Sst History covers all detail concepts and is framed in a very planned way to avoid wastage of time. They help students to not only memorise the whole subject matter but provide important key points to score well.
3. Why do we Need Vedantu for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions PDF?
Vedantu is one of the best Educational websites which helps students to find accurate solutions as per the CBSE Subjects. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography are in PDF format which can be easily downloaded and caters to different learning ability learners because they are modulated by best educators. NCERT solutions for class 10 SST is constantly updated as per the need of the CBSE curriculum and makes it easier for the learners to understand all the chapters in a very short time.
4. List out the chapters present in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India.
The chapters present in Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India are:
Chapter 1 - Resources and Development
Chapter 2 - Forest and Wildlife Resources
Chapter 3 - Water Resources
Chapter 4 - Agriculture
Chapter 5 - Minerals and Energy Resources
Chapter 6 - Manufacturing Industries
Chapter 7 - Lifelines of National Economy
You can also refer to these solutions free of cost for added explanations of the chapter.
5. Are chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India available for download?
Yes, Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India are provided separately for each chapter. Here is how to download them:
Visit the page-NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India.
Scroll down on the next page and click on the chapter of your choice.
On the subsequent page, scroll down and click on the option to "Download Pdf."
You will be taken to a new page containing the link for automatic download of the required PDF.
Alternatively, download these solutions from the Vedantu mobile app.
6. Are all the textbook questions covered in Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India?
Yes, Vedantu provides answers to every question mentioned in the NCERT textbook. We aim to provide our students with a wholesome study experience. For this reason, we take immense care that no question of the textbook is left unanswered. Furthermore, we ensure that only highly experienced teachers are recruited for this job. We understand that Class 10 is a crucial point in a student's life and thus we leave no stone unturned in bringing you the best possible study experience.
7. Are Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India reliable?
The NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India are completely reliable. You can blindly trust these solutions for the following reasons:
These are the most authentic solutions available online.
The solutions are prepared by teachers who have taught Social Science in CBSE Schools for years.
The solutions are prepared to focus on the CBSE Board Examination requirements.
Solutions are regularly updated to keep up with the latest CBSE Guidelines.
8. Suggest a study plan to study Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India.
You can easily score perfect marks in Social Science Board exams if you follow these simple tips:
Make sure you know the NCERT textbook content inside out.
Familiarize yourself with the weightage of chapters and plan your study schedule accordingly.
Make a weekly study plan and stick to it from the beginning.
Thoroughly prepare the answers using Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India.
Go through as many sample papers and previous years’ question papers as you can.

6 Major Social Issues in India: Causes and Measures
India suffers from a host of social issues ranging from poverty to gendered violence. This article covers the concept of social issues and highlights the different experiences of rural and urban sectors. Further, it studies six important social issues namely poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, the caste system, gendered violence and communalism by analyzing their causes and the specific measures adopted to combat them.
What Are Social Issues?

An individual problem is one that affects only a particular individual or group. On the other hand, public issues are those faced by society as a whole. A social issue is when a situation is deemed less than the social ideal. It must result in unfavourable circumstances that can only be handled collectively. India has undergone many changes in the last decades. Social change brings with it a new set of circumstances wherein an otherwise overlooked issue might be given importance. For example, the population explosion in India was not viewed as a serious issue until the 1950s. It is also important to note that any problem only becomes a social issue when enough number of people find it undesirable. Sati was not deemed a social issue until Raja Ram Mohan Roy criticized the practice and a considerable number of people started supporting him (Ahuja 2014).
Rural versus Urban Social Issues
Many scholars have identified fundamental differences between the causes and consequences of issues experienced the rural and urban sectors.
The rural sector has five identifying characteristics. Firstly, people are either directly or indirectly dependent upon agriculture. Next, the upper caste citizens are the largest landholders. Thirdly, the roles and values of rural people are traditional. Also, the farmers receive inadequate compensation for their hard work. Finally, people are scattered in rural areas as compared to urban cities. This isolation means that their access to services like banks, hospitals and schools is also minimal.
Read: Farmers’ suicides in India
On the other hand, the urban sector is characterized by the concentration of large populations in small areas. This results in many issues such as slums, high crime rates, pollution, drug abuse and unemployment. Also, cities are highly interdependent on every small part. For example, a strike by bus workers could result in many problems for the functioning of a city.
Poverty can be defined as the inability to secure the minimum standard of living appropriate to society. According to the Planning Commission, 22% of India’s population lived below the poverty line in 2012.
Causes of Poverty
The sociologist David Elesh determined three causes of poverty namely individual, culture of poverty and social structure. The first ideology is propagated by those who believe that if an individual ends up in poverty, it is their own fault and due to a lack of hard work and initiative. This thought is rooted in the functionalist approach of sociology. It maintains that poverty is a good thing for society since it propagates the survival of the fittest. The culture of poverty concept was introduced in 1959 by Oscar Lewis. He believed that the lifestyle of the lower socio-economic classes fostered behaviours and attitudes associated with poverty. Hence, no amount of economic rehabilitation could help alleviate the poor. Finally, the social structure approach was propagated by sociologist Herbert Gans . He associated poverty with unjust social conditions and pointed out that the middle and higher classes had a vested interest in the poor. For example, the existence of the poor helped alleviate their social status. Thus, they had no interest in changing the social structure (Ahuja 2014).
Within the Indian context, many unique causes of poverty have been identified. The first is the rapidly rising population. This year, the population reached 138.72 crores which was a 1.26% increase from last year. Such a high population raised the demand for consumption of a limited number of resources. The second is low agricultural productivity due to lack of capital, technology and fragmented land holding. The next cause is unemployment which is present in the form of both underemployment and disguised unemployment in the agricultural sector. Social factors have also contributed to poverty through the caste system , gendered laws of inheritance and a lack of infrastructure. Finally, political factors such as the British exploitation of natural resources also led to a weakened Indian economy.
Poverty Alleviation Programs
The Indian government has launched many poverty alleviation programs for the rural and urban poor. A few major schemes have been described below. The Indira Awaas Yojna (IAY) was launched to aid the construction of houses for those belonging to scheduled tribes, scheduled castes, freed bonded laborers and the rural poor living below the poverty line. The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGA) was introduced in 2005 all over India. Under this scheme, every rural household was guaranteed 100 days of wage employment in the form of unskilled manual labor each fiscal year. Finally, the food security scheme introduced in 2003 distributed allocated amounts of food grains to priority and antyodya households for free. This scheme covered almost 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population (Ahuja 2014).
Unemployment
Unemployment has often been described as the most significant social issue in society. This is because an individual is dependent on their work for both their livelihood and their status. Sociologically, unemployment is defined as the inability to find remunerative work in the face of both potential and desire to earn. The three elements of unemployment are that the individual must be capable, willing and making an effort to be gainfully employed.
Types of Unemployment
There are three major classifications of unemployment, namely, seasonal, cyclical and technological.
Seasonal unemployment is a characteristic of the agricultural sector. Any cultivator in India is unemployed for almost four to six months every year. Workers at some manufacturing units like ice or sugar factories are also seasonally unemployed due to the nature of the work.
Cyclical unemployment is a result of the ups and downs in business. For example, an entrepreneur earning high profits might invest them in a startup thus creating employment. But when they start suffering losses, they might reduce the number of workers present in their industries.
Technological unemployment is caused because of the introduction of new technologies that displace manual labor. The adoption of automation in almost every industry has resulted in a loss of economic security for the average man (Ahuja 2014).
Causes of Unemployment
Sociologists have suggested that unemployment is a result of both economic and social factors.
Degrading social status means that many people consider themselves overqualified for certain jobs and thus prefer to remain unemployed. For example, many youths consider teaching in universities to be a prestigious job whereas teaching in a school is looked down upon.
Geographical immobility refers to surplus labor in one location and inadequate labor in another. People may be unable to move to areas with higher job opportunities due to a lack of information, language barriers or family responsibilities. For example, women in rural areas often lose out on paid work because they do not get the opportunity to migrate to cities like their husbands.
Population explosion has led to increased unemployment due to the limited number of job opportunities in the economy. Many people lose out on work due to personal reasons such as lack of education or experience or even illness and disability. The high rates of unemployment increase the dependency on parents to provide for their children and for the government to assume responsibility for them.
The defective education system fails to give importance to primary education and vocational training. The benefits of education are mostly availed only by middle- and high-income youth with access to private schools and universities. The conditions in most government schools are unsuitable for studying and are often a result for many girls to drop out (Ahuja 2014).
Remedial Measures
The Indian government has recognized the issue of unemployment within the country. They have taken many steps in the form of employment generation schemes. The MGNREGA scheme mentioned previously is one major measure. Unemployment cannot be solved by making India more labour-intensive which has been suggested in the past. Instead, the focus should be on educating the youth and making them employable within the upcoming service sector.
Unemployment: Definition, Types, Causes, Solutions and The Way Ahead
As mentioned in the previous section, illiteracy is a major barrier to development since it results in unskilled labor. According to the Census Commission of India, literacy refers to any person who can read and write with understanding in a recognized Indian language. The 2011 census revealed that the literacy rate of India was around 74% with many regional variations and gender disparities. All over India, Kerala has the highest literacy rate and Bihar the lowest.
Measures to Eradicate Illiteracy
Many programs have been introduced by the government in accordance with the education policies of India. A few of these have been mentioned below.
The National Adult Education (NAE) program was introduced in 1978 to promoted education within the age group of 15-35 years. The Rural Functional Literacy (RFL) program is a sub-program of the NAE and was launched in 1986. It aimed at creating awareness among adults about the numerous government schemes they could benefit from. Moreover, it involved student volunteers from universities in teaching adults. Finally, the National Literacy Mission was launched in 1988 by Rajiv Gandhi and aimed at involving volunteer agencies in the mission to educate illiterate persons all over the country (Ahuja 2014).
Caste System
The Indian caste system is based on the cultural features of hierarchy, pollution and purity. It subscribes to the doctrines of Karma and Dharma. The Indian government introduced the category of Scheduled Castes (SCs) to the constitution in 1935. Currently, SCs constitute around 16% of the Indian population. The main issues faced by Dalits are those of untouchability, exploitation, exclusion from religious and educational institutions and social discrimination.
Dalit Empowerment Measures
The government’s approach towards the upliftment of SCs was based on two ideas. The first was to overcome deprivations in terms of education, housing and employment that the SCs have inherited due to their historical exclusion from society. The second was to encourage their participation in the economic, social and political processes of the country.
Protective measures included acts such as the protection of the Civil Rights Act passed in 1976 and the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Prevention of Atrocities Act passed in 1989. Together, these acts protected Dalits from untouchability, discrimination and violence in public places. Reservation policies within educational institutions, government services and political bodies are also a part of protective measures. These ensure adequate participation of SCs in public spheres though they are restricted to only the government sectors.
Development measures were introduced within the educational, economic and social spheres. To increase educational development the government has attempted to include reservations within educational institutions, provide financial support and coaching facilities and emphasized on girls education. Economic empowerment includes distribution of land to landless laborers and implementation of wage labor programs. Finally, social welfare schemes to increase access to sanitation, housing, drinking water and electricity have been introduced by the government (Thorat 2009).
Read: Dalit and Backward Classes Movements
Gendered Violence
Women have always been victims of exploitation and violence within the Indian subcontinent. Violence against women consists of criminal, domestic and social violence. Criminal violence consists of rape, murder, female foeticide and abduction. Domestic violence includes wife battering, dowry deaths and sexual violence. Social violence comprises eve-teasing, inheritance laws favouring men etc.
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released that 33,356 cases of rape were reported all over India in 2018. Most of these are instances where the rapist is known to the victim. Moreover, these statistics fail to reveal the high number of rapes that are not even reported by the victim. Instances of rape cut across geographical locations, class and caste. Female employees are raped by employers, women inmates are raped by superintendents, female patients are raped by hospital staff and domestic helpers by their employers. Within the context of marriage, violence against women becomes harder to navigate. The Indian constitution does not recognize marital rape as a criminal offence (Ahuja 2014).
Measures to Prevent Women’s Harassment
The government in collaboration with volunteer organizations has taken a few steps for the safety of women. Shelters for women suffering from abusive husbands or in-laws have been established. But such accommodations suffer from issues of overcrowding and a lack of financial support. Helplines for women have been publicized by the police in various cities such as New Delhi. Legal institutions that provide free legal assistance to women have also been promoted by the government. But despite all these measures, the most important change that is required to combat women’s harassment is a change in attitude. The patriarchal society of India has oppressed women for too long. This pattern needs to change by taking small steps such as ending victim-blaming for sexual and violent assaults.
Communalism
Communalism refers to attempts to overemphasize the importance of religious identity and stimulate communal violence between different religious groups. Within India, tensions between Hindus, Muslims and Sikhs have been present since the India-Pakistan partition. Muslims, Sikhs and other religious minorities are protected by the Indian constitution under provisions for justice, tolerance, equality and freedom. Despite these provisions, communal violence has been a part of India since independence. The recent case of the Babri Masjid and associated riots is a popular example of religious discord. Violence can take many forms of mass mobilizations, insurgency and riots. Usually, communal violence is more politically motivated than fueled by religion. Hindu- Muslim riots in Andhra Pradesh in 1990 led to more than a hundred deaths (Ahuja 2014).
Prescriptive Measures
India has suffered at the hands of communalism for too long. The government and the citizens must work together towards harmony. Symbolic gestures are not enough for Muslims as they must be empowered through literacy and employment. Secularism must be promoted through education. Moreover, communal minded politicians should be boycotted during elections and the police and military must be sensitized and encouraged to adopt a secular outlook.
This article has covered many social issues faced by Indian citizens on a daily basis. It is essential that such problems be recognized by individuals and governments alike so that they may work together towards a better future.
Ahuja, R. (2014). Social problems in India . Jaipur: Rawat Publications.
Thorat, S. (2009). Dalits in India: Search for a common destiny . New Delhi: SAGE Publications India Pvt. http://dx.doi.org/10.4135/9788132101086.n1
Arushi is a sociology and environmental studies. She is passionate about writing and researching about these two fields. She has a keen interest in social work and has collaborated with many volunteering programs in the past. Her hobbies include horse riding, trekking and painting.

Social Issues In India Project For Class – 12
Table of Contents
1- INTRODUCTION
Social concerns are issues that significantly affect people’s lives and society. These problems might include everything from poverty, injustice, and prejudice in the matters of healthcare, education, and the environment. In this project, we’ll look at one of today’s most important societal challenges and how it affects both people and communities.
We will investigate the root causes of [ social issue ] and how it manifests in our society throughout this research. We will also examine how this problem affects various groups, including [insert examples of groups that are impacted, such as women, children, or minorities]. Additionally, we will look at recent attempts and fixes intended to solve [social issue].
We want to use this initiative to motivate people and communities to take action toward a more just and equitable society by increasing knowledge of the complexity of [social issue].
Millions of people worldwide are impacted by poverty, which is a complicated and multidimensional socioeconomic issue. Poverty, which is defined as the absence of the means of subsistence, can have a significant negative effect on people, families, and communities. We will examine the causes, effects, and potential solutions to this enduring social issue of poverty in this study.
Wide-ranging effects of poverty on people’s life include health inequalities, restricted access to opportunities and education, and greater vulnerability to crime and violence. Give examples of how poverty impacts people and communities in your region or nation.
Although attempts have been made to reduce poverty, this societal issue nevertheless poses a serious challenge to governments, charities, and communities all over the world. The policies and programmes now in place to combat poverty, such as social welfare measures, initiatives for job training and education, and microfinance programs, will be examined in this study.
Through this project, we seek to increase awareness of poverty as a social problem and spur action to build more just and equitable society.

3- CAUSES OF POVERTY IN INDIA
India is the second-most populated nation in the world with a population of over 1.3 billion. India continues to struggle with poverty despite recent economic growth and progress that have been swift. More than 270 million Indians, who make less than $1.90 a day, live below the poverty line, according to the World Bank. The causes of poverty in India and how it impacts people and communities across will be examined in this research.
For effective policies and actions to be developed and implemented to solve this societal challenge, it is essential to understand the causes of poverty. We will examine current measures, such as social welfare programs, job and education programs, and microfinance programs, in our project to reduce poverty in India.
We believe that this project will increase public knowledge of the underlying causes of poverty in India and motivate action to build a more just and equitable society.
4- EFFECT OF POVERTY
Millions of people around the world are impacted by poverty, which has terrible effects on people, families, and communities. Every element of life, including health, education, work, and access to needs, can be significantly impacted by poverty. In this research, we will investigate the effects of poverty on people and communities as well as the ways in which it supports injustice and inequality.
Poverty not only has an immediate negative impact on people, but it also feeds social injustice and institutional inequity. Other forms of marginalization, such as bias against certain races, genders, or castes, are frequently linked to poverty. In addition to contributing to social and political marginalization, poverty can also create cycles of poverty that last for several generations.
With the help of this research, we seek to better understand how poverty affects both individuals and society as a whole and to spur action for the development of more just and equitable societies.
5- CASE STUDIES ON POVERTY
Millions of individuals around the world are impacted by the complicated and varied social problem of poverty. While statistics might make poverty challenging to comprehend, case studies can give a more intimate and human perspective on how poverty affects people. In order to better understand how poverty contributes to structural inequality and social injustice, we will look at case studies of poor people and communities.
We want to offer a more nuanced picture of the effects of poverty on people and communities through these case studies. Additionally, we want to emphasise the fortitude and tenacity of those who are poor and the need of using community-based approaches to solve poverty and its problems.
Through this initiative, we want to encourage people to take action in the direction of more just and equitable communities, where everyone has access to the tools and chances they need to prosper.
In various civilizations all throughout the world, notably in South Asia, where it is still widely practiced in many groups, dowry has a long history. When a couple gets married, the bride’s family is required to give the groom’s family some property or money. This is referred to as the “dowry.” While the dowry’s original purpose was to give the bride financial stability in the event of her husband’s passing, it has since evolved into a means of abuse and exploitation for many women. In this research, we will investigate the practice of dowry, its cultural and historical origins, and the manner in which it contributes to violence against women and gender inequality.

In many parts of the world, including South Asia where it is frequently considered as a necessary expense for families trying to arrange a marriage for their daughter, dower has become a ubiquitous social issue. The need to pay a sizable dowry can put a financial strain on the family of the bride and, in extreme circumstances, end in violence and abuse directed against the bride. As it implies that women are viewed as financial liabilities rather than valuable members of society, the practise of dowry furthers gender inequality.
Through this study, we will investigate how dowries affect women’s lives and how they contribute to violence against women and gender inequality. We will also look at the current dowry-related activities, such as community-based programmes and legal reforms, as well as the difficulties still facing this practise.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the negative effects of dowries and motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where women are valued and respected as full participants in society.
7- ORIGIN OF DOWRY
For ages, various societies all throughout the world have used the dowry system. While dowry practises differ from culture to culture, the fundamental idea of a bride’s family giving money or property to the groom’s family at the time of marriage is universal. A multitude of cultural, historical, and economic variables have influenced the development of dowry, making it a complicated and varied concept. In this study, we will investigate the dowry’s historical development in various cultural and historical situations.
From ancient Rome through mediaeval Europe to contemporary South Asia, dowry has been used in varied forms around the world. The practise of dowry has several justifications, some of which are economic, such as ways to give the bride financial security or to make up for the loss of a potential worker for the groom’s family. Dowry may also be related to societal considerations like the need to uphold family honour or maintain social standing.
Through this study, we will investigate the intricate history and cultural influences that have shaped the development of dowry. We will also look at how dowries have changed and evolved across cultures and circumstances, as well as how these changes have affected gender dynamics and social dynamics.
Through this study, we seek to learn more about the history of dowry and how it has influenced and been influenced by cultural and historical circumstances. We also seek to raise awareness of the ways that dowries support social injustice and gender inequality, and to motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where women are recognised and valued as full participants in society.
8- DOWRY IS AN ILLEGAL ACT
In many parts of the world, especially in South Asia, where it is still common in many cultures, the practise of dowry has long been a source of debate and cause for concern. Many nations have passed legislation outlawing the practise of dowry and giving women legal protection in an effort to address this problem. In order to end the practise of dowry and the violence and abuse it causes against women, the Dowry Prohibition Act was passed in India in 1961. In this study, we’ll look at the Dowry Prohibition Act’s history, development, and effects on the dowry industry in India.
The Dowry Prohibition Act was a significant piece of Indian legislation that sought to outlaw the practise of dowry and protect women from it. The act makes it illegal to give or receive dowry and makes it a crime that is punishable by jail time and/or a fine. The act also establishes dowry prohibition officers to look into dowry-related complaints and provides rules for the avoidance of dowry harassment.
We will investigate the history, breadth, and effects of the Dowry Prohibition Act in-depth through this research. We will also look at the difficulties that still exist in executing the law, including the pervasive societal and cultural attitudes that support the practise of dowry and the demand for more information and education on the subject.
Through this project, we seek to raise awareness of the role that legal frameworks have in addressing societal issues like dowry and to motivate action in the direction of building more just and equitable communities where women are cherished and respected as equal members of society.
9- DOWRY CASE STUDY
Millions of women and their families continue to be affected by the dowry tradition, which has been a chronic problem in many cultures around the world. Even though the practise of dowry is outlawed in many nations, it nevertheless exists in a number of forms and frequently results in violence, abuse, and discrimination against women. In this research, we’ll look at a dowry case study and investigate how the practise has influenced the lives of women, families, and communities.
Dowry can put enormous pressure on families to live up to the expectations of the groom’s family because it is frequently viewed as a symbol of social prestige and a source of financial security. This pressure can result in a range of abuses, such as domestic violence, harassment, and in the worst cases, even murder. The practise of dowry remains a problem throughout most of the world, especially in South Asia, despite the efforts of governments and activists to end it.
In this project, we will look at a dowry case study, concentrating on the experiences of the women and families impacted by this custom. We will examine the different dowry-related kinds of discrimination and abuse, as well as how these abuses may affect women’s and families’ lives. We will also look at the obstacles activists and organisations confront in their fight against the practise of dowry.
Through this initiative, we seek to raise awareness of the effects of dowries on women and families and to motivate action in the direction of the development of more just and equitable communities, where women are appreciated and respected as full participants in society.
10- CHILD LABOR
Millions of children worldwide are impacted by the global problem of child labor, which is frequently associated with poverty and a lack of educational opportunities. Working kids frequently miss out on childhood, education, and the chance to reach their full potential. In this project, we will investigate the problem of child labour and look at its sources, effects, and attempts at prevention.
There are many different types of child labor, including domestic work, agricultural work, and employment in factories and mines. Children who labour are frequently put in risky and exploitative situations and run the risk of suffering from physical, emotional, and psychological problems. The problem of child employment persists in many parts of the world, especially in developing nations, despite the efforts of governments and organisations to address it.
Through this study, we will explore the economic, social, and cultural aspects that contribute to the persistence of child labor, as well as its causes and effects. We will also look at the initiatives taken by governments, groups, and people to address the problem of child labor, including laws and initiatives designed to protect children’s rights and deal with its underlying causes.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the problem of child labour and motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where kids are safe and given the tools they need to reach their full potential.

11- TYPES OF CHILD LABOUR
Child labour is a complicated problem that affects kids of various ages and socioeconomic situations worldwide. Although the phrase “child labour” frequently conjures up pictures of kids toiling away in factories or mines, it actually refers to a wide range of activities that can harm kids’ development, education, and health. In this study, we will investigate the many forms of child work, looking at its traits, frequency, and effects on kids.
Hazardous and non-hazardous kinds of child labour exist, and it can take place in a range of locales such as homes, streets, and workplaces. Domestic work, agricultural work, and employment in factories and mines are a few of the most prevalent types of child labour. Children who participate in these activities are frequently subjected to risky situations, long hours, and low remuneration, and they run the risk of suffering bodily, emotional, and psychological harm.
Through this research, we will investigate the various forms of child labor, looking at each one’s distinctive traits and the difficulties they provide for kids’ development, education, and well-being. We will also look at the causes of various forms of child labor, such as poverty, a lack of educational opportunities, and cultural and societal standards.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the various forms of child labour and encourage action to build more just and equitable communities where kids are protected and given the tools they need to reach their full potential.
12- CAUSES AND EFFECT
Child labour is a complicated subject that is influenced by numerous economic, social, and cultural elements. It has a significant negative impact on children’s health, development, and education. It is essential to comprehend child labour’s causes and effects in order to establish methods that will effectively address the problem and advance the welfare of children everywhere. In this project, we’ll look at the root causes of child labour and consider how it affects kids, families, and communities.
The root reasons of child labour are complex and include elements like poverty, limited educational opportunities, and societal and cultural norms that place little importance on children’s education and general well-being. These elements frequently interact with one another to produce a complicated web of conditions that forces kids into the labour force. Child labour has a variety of detrimental repercussions on children’s development, education, and overall health as well as on their families and communities.
Through this study, we will explore the economic, social, and cultural aspects of child labour’s persistence as well as its underlying causes. We will also look at how child labour affects children, their families, communities, and how it contributes to social injustice and continued poverty.
In order to create more equitable and just societies where children are safeguarded and given the opportunity to attain their full potential, we want to increase public understanding of child labour’s fundamental causes and far-reaching effects.
13- CASE STUDIES ON CHILD LABOR
Millions of children worldwide are impacted by the widespread problem of child labor, which robs them of their childhoods and prevents them from pursuing their educations and realising their full potential. Although there are many distinct types of child labor, each one involves a violation of children’s rights and a failing on the part of society to safeguard its most defenceless citizens. We will look at a specific case study of child labour in this project, examining the conditions that lead to the kid’s exploitation, the effects on the child and their family, and the initiatives taken to address the problem.
In the case study we’ll be looking at, a young child was made to labour in risky circumstances in a factory where they were exposed to harmful chemicals, long hours, and low pay. The youngster’s family was struggling to make ends meet because they were so poor, so the money the child brought in was crucial. The rigours of the job interfered with the child’s education, and the dangerous conditions had an adverse effect on their health.
Through this research, we will thoroughly examine the case study, examining the underlying reasons why the child was exploited and the effects it had on the child’s health, development, and education. We will also look at the measures taken to address the problem, such as the assistance programmes for the child and their family and broader legislative and lobbying initiatives to end child labour.
Through this project, we want to increase public awareness of child labour’s harmful effects on children and their families. We can better appreciate the complicated problems that lead to child labour and the efforts being taken to address them by looking at specific case studies.
In conclusion, socioeconomic problems including poverty, dowry, and child labour are intricate, diverse concerns with significant repercussions for people, families, and societies. These problems are caused by several economic, social, and cultural causes, therefore resolving them will take all-encompassing and coordinated action. We have learned more about the underlying causes and effects of poverty, the history and repercussions of dowries, and the forms, causes, and effects of child labour as a result of our investigation into these issues.
Despite the difficulties these societal concerns provide, several efforts are being undertaken to address them. There are numerous strategies that can be used to address these problems and advance social justice and equity, from grassroots community activities to global policy and advocacy campaigns. We can contribute to the creation of a more just and equitable world where everyone has the chance to realise their full potential by increasing awareness of these concerns and working to support these initiatives.
In the end, dealing with social difficulties necessitates a commitment to understanding, empathy, and group action. We can make the world more just and equitable for everyone by acknowledging the humanity of those impacted by poverty, dowry, and child labour and collaborating to improve their well-being.
Certificate of Completion
I, [Your Name], a student of Class 12 at [Your School/College Name], am proud to receive this certificate for successfully completing the project on “Social Issues in India. ” This project delved into the complex and significant societal challenges that affect people and communities in our country.
Throughout this project, I thoroughly investigated and analyzed various social issues, including poverty, dowry, and child labor. I examined their root causes, effects, and the measures taken to address these problems. This research has provided me with valuable insights into the complexities of social issues and the need for collective action to build a more just and equitable society.
I express my heartfelt gratitude to [Teacher’s Name], my project guide, for their unwavering support, guidance, and encouragement throughout this project. Their expertise and mentorship have been instrumental in deepening my understanding of the social issues in India and helping me shape my research effectively.
I would also like to extend my thanks to [School/College Name] for providing me with the opportunity to explore and analyze the critical social issues prevalent in our country. This project has not only enriched my knowledge but also heightened my awareness of the importance of addressing these issues to create a better society.
With great pride, I accept this certificate, symbolizing my dedication and hard work in completing the project on “Social Issues in India. “
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Social Issues In India Project For Class – 12 PDF
Related articles.

Automated Roti and Puri Maker Press project

The Oil Skimmer RC Boat

Secure Digi Locker Application Project

Software Piracy Protection Project
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
Nationalism in India
Class 10 - ncert history india & contemporary world 2 solutions, intext activity.
What did Mahatma Gandhi mean when he said satyagraha is active resistance?
According to Mahatma Gandhi satyagraha is active resistance and not a weapon of the weak, but the power which can be used only by the strong. This power calls for intense activity. Satyagraha is pure soul-force. Truth is the very substance of the soul. Therefore, it cannot be termed as a passive resistance.
If you were a peasant in Uttar Pradesh in 1920, how would you have responded to Gandhiji's call for Swaraj? Give reasons for your response.
If I were a peasant in Uttar Pradesh in 1920, I would have responded to Gandhiji's call for Swaraj by supporting him. I would have convinced my village people to do the same. My reasons for supporting him would have been the following:
- Economic exploitation — I have faced economic challenges due to exorbitantly high rents and a variety of other cesses. I have to do begar and work at landlords' farms without any payment. By supporting Swaraj, I could demand for reduction of revenue, abolition of begar, and social boycott of oppressive landlords.
- Non-Violent Resistance — Gandhi's philosophy of non-violence appealed to me a lot. The idea of achieving freedom through non-violent means would have provided a moral high ground and a peaceful way to express dissent against oppressive colonial policies.
- Desire for Political Representation — Supporting Swaraj would mean establishing a more inclusive and representative political system that would address the concerns of all sections of society, including peasants.
Find out about other participants in the National Movement who were captured and put to death by the British. Can you think of a similar example from the national movement in Indo-China (Chapter 2)?
Participants in the National Movement who were captured and put to death or otherwise killed by the British are Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, Sukhdev, Lala Lajpat Rai, Khudiram Bose and Madan Lal Dhingra. Chandrashekhar Azad was though not captured but killed himself before being captured by British.
A similar example from the nationalist movement of Vietnam was Hyunh Phu So, the founder of the Hoa Hao movement against the French. They declared him mad and put him in a mental asylum. The French authorities exiled him to Laos and sent many of his followers to concentration camps.
Look at Figs. 12 and 14. Do you think these images will appeal to all castes and communities? Explain your views briefly.
No, I don't think these images will appeal to all castes and communities because in both the images Bharat Mata is depicted as Hindu Goddess. These images will only appeal to Hindus and other communities will not be able to relate with it.
Intext Discuss
Why did various classes and groups of Indians participate in the Civil Disobedience Movement?
Various classes and groups of Indians participated in the Civil Disobedience Movement for their own reasons.
- Rich peasant communities like the Patidars of Gujarat and the Jats of Uttar Pradesh were very hard hit by the trade depression and falling prices. The refusal of the government to reduce the revenue led to widespread resentment. This made rich peasants enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- Poorer peasants participated in the movement as they found it difficult to pay their rent to landlords. They wanted the unpaid rent to the landlord to be remitted.
- The business classes reacted against colonial policies that restricted business activities. They wanted protection against imports of foreign goods, and a rupee-sterling foreign exchange ratio that would discourage imports. The industrialists attacked colonial control over the Indian economy, and therefore, supported the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- Industrial workers supported the movement as a part of their own movements against low wages and poor working conditions.
- Women participated in the movement as they were moved by Gandhiji's call and they began to see service to the nation as a sacred duty of women.
Read the Source D carefully. Do you agree with Iqbal’s idea of communalism? Can you define communalism in a different way?
In 1930, Sir Muhammad Iqbal, as president of the Muslim League, reiterated the importance of separate electorates for the Muslims as an important safeguard for their minority political interests. His statement is supposed to have provided the intellectual justification for the Pakistan demand that came up in subsequent years. This is what he said:
I have no hesitation in declaring that if the principle that the Indian Muslim is entitled to full and free development on the lines of his own culture and tradition in his own Indian home lands is recognized as the basis of a permanent communal settlement, he will be ready to stake his all for the freedom of India. The principle that each group is entitled for free development on its own lines is not inspired by any feeling of narrow communalism. A community which is inspired by feelings of ill-will towards other communities is low and ignoble. I entertain the highest respect for the customs, laws, religions and social institutions of other communities. Nay, it is my duty according to the teachings of the Quran, even to defend their places of worship, if need be. Even though I love the communal group which is the source of life and behavior and which has formed me what I am by giving me its religion, its literature, it’s thought, its culture and thereby its whole past as a living operative factor in my present consciousness. Communalism in its higher aspect, is indispensable to the formation of a harmonious whole in a country like India. The units of Indian society are not territorial as in European countries. The principle of European democracy can-not be applied to India without recognising the fact of communal groups.
The Muslim demand for the separate electorates are contrary to the spirit of true nationalism, because he understands the word ‘nation’ a kind of universal amalgamation in which no communal entity ought to retain its private individuality. Such a state of things, however, does not exist. India is a land of racial and religious variety. Add to this the general economic inferiority of the Muslims, their enormous debt, especially in the Punjab, and their insufficient majorities in some of the provinces, as at present constituted and you will begin to see clearly the meaning of our anxiety to retain separate electorates.
I don't agree with Iqbal's idea of communalism. His thoughts of separate electorate was to safeguard interest of Muslims but it was against nationalism. Nation and its integrity is more important than any community.
According to me communalism and nationalism are two different things. However, communalism can be seen as respecting each others culture and growing together as in diverse country like India.
Write in brief
(a) Why growth of nationalism in the colonies is linked to an anti-colonial movement.
(b) How the First World War helped in the growth of the National Movement in India.
(c) Why Indians were outraged by the Rowlatt Act.
(d) Why Gandhiji decided to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement.
(a) People in the colonies suffered oppression at the hands of colonial power. This created resentment and unrest among the people and led to growth of nationalism. The people fought against the colonial powers for their rights. Therefore, growth of nationalism in the colonies is linked to an anti-colonial movement.
(b) The First World war created a new economic and political situation. It led to a huge increase in defence expenditure which was financed by war loans and increasing taxes: customs duties were raised and income tax introduced. Through the war years prices increased – doubling between 1913 and 1918 – leading to extreme hardship for the common people. Villages were called upon to supply soldiers, and the forced recruitment in rural areas caused widespread anger. All this led to resentment and as a result there was growth of the National Movement in India.
(c) Indians were outraged by the Rowlatt Act because it gave the government enormous powers to repress political activities, and allowed detention of political prisoners without trial for two years.
(d) At Chauri Chaura in Gorakhpur, a peaceful demonstration in a bazaar turned into a violent clash with the police. Hearing of the incident, Mahatma Gandhi called a halt to the Non-Cooperation Movement. He decided to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement because he felt that the movement was turning violent in many places and satyagrahis needed to be properly trained before they would be ready for mass struggles.
What is meant by the idea of satyagraha?
The idea of satyagraha emphasised the power of truth and the need to search for truth. It suggested that if the cause was true, if the struggle was against injustice, then physical force was not necessary to fight the oppressor. Without seeking vengeance or being aggressive, a satyagrahi could win the battle through non-violence. This could be done by appealing to the conscience of the oppressor. People – including the oppressors – had to be persuaded to see the truth, instead of being forced to accept truth through the use of violence.
Write a newspaper report on:
(a) The Jallianwala Bagh massacre
(b) The Simon Commission
(a) 13th April 1919, Amritsar, a tragic and heinous incident shook the country today. General Dyer ordered to open fire on a crowd killing hundreds. Thousands of people gathered at Jalliawalah bagh, some to peacefully protest against the British government’s repressive measures while others to attend the annual Baishakhi Fair. These people were mostly villagers and were unaware of the imposition of Martial Law in the city. General Dyer, the Commander, blocked the exit points of the campus and opened fire upon the innocent citizens killing women, kids and men. It is being told that General wanted to create a ripple of fear among Indians. He has declared that it was to ‘produce a moral effect’, to create in the minds of satyagrahis a feeling of terror and awe. The country, however, is shocked and in anger over the brutal act.
(b) November,1927, Tory government in Britain has constituted a Statutory Commission under Sir John Simon. It has been set up in response to the nationalist movement. The commission is to look into the functioning of the constitutional system in India and suggest changes. The commission do not have a single Indian member. They are all British. How can a committee with no Indian member take decisions about constitution of India? This commission will not be welcomed in India. We deserve the right to make our own constitution.
Compare the images of Bharat Mata in this chapter with the image of Germania in Chapter 1.
List all the different social groups which joined the Non-Cooperation Movement of 1921. Then choose any three and write about their hopes and struggles to show why they joined the movement.
The different social groups which joined the Non-Cooperation Movement of 1921 were:
- Merchants and traders
- Plantation workers
Plantation workers — For plantation workers in Assam, freedom meant the right to move freely in and out of the confined space in which they were enclosed, and it meant retaining a link with the village from which they had come. Under the Inland Emigration Act of 1859, plantation workers were not permitted to leave the tea gardens without permission, and in fact they were rarely given such permission. When they heard of the Non-Cooperation Movement, thousands of workers defied the authorities, left the plantations and headed home.
Peasants — The movement of peasants was against talukdars and landlords who demanded from peasants exorbitantly high rents and a variety of other cesses. Peasants had to do begar and work at landlords’ farms without any payment. As tenants they had no security of tenure, being regularly evicted so that they could acquire no right over the leased land. The peasant movement demanded reduction of revenue, abolition of begar, and social boycott of oppressive landlords. In many places nai – dhobi bandhs were organised by panchayats to deprive landlords of the services of even barbers and washermen.
Tribals — In the Gudem Hills of Andhra Pradesh, the colonial government had closed large forest areas, preventing people from entering the forests to graze their cattle, or to collect fuelwood and fruits. This enraged the hill people. Not only were their livelihoods affected but they felt that their traditional rights were being denied. When the government began forcing them to contribute begar for road building, the hill people revolted. Alluri Sitaram Raju, who was inspired by non-cooperation, became their leader.
Discuss the Salt March to make clear why it was an effective symbol of resistance against colonialism.
Salt was something consumed by the rich and the poor alike, and it was one of the most essential items of food. The tax on salt and the government monopoly over its production was seen as the most oppressive face of British rule. Mahatma Gandhi started his salt march accompanied by 78 of his trusted volunteers. The march was over 240 miles, from Gandhiji's ashram in Sabarmati to the Gujarati coastal town of Dandi. The volunteers walked for 24 days, about 10 miles a day. Thousands came to hear Mahatma Gandhi wherever he stopped, and he told them what he meant by swaraj and urged them to peacefully defy the British. On 6 April 1930, he reached Dandi, and ceremonially violated the law, manufacturing salt by boiling sea water. Therefore, salt march was a clear indication that Indians were united against British rule. It also showed defiance of colonial power by Indians.
Imagine you are a woman participating in the Civil Disobedience Movement. Explain what the experience meant to your life.
Participating in the Civil Disobedience Movement as a woman was a transformative and empowering experience, shaping various aspects of my life. For the first time, I was doing something different from my household chores. I was outside my home in the company of great people and for a great reason. I was there for my motherland. My participation in Civil Disobedience movement gave a meaning to my life and a direction to my thoughts. I had heard Gandhiji speaking and asking us to participate in this movement. I feel service to the nation is our sacred duty. Inspired by him, I also offered Satyagraha, picketed liquor shops and shops selling foreign cloth and also courted arrest. I felt empowered by these activities and felt that women also can help the men in the ultimate goal of achieving independence from the British. But sometimes I felt that women should make more efforts and make their place among the big political names.
Why did political leaders differ sharply over the question of separate electorates?
The political leaders during that time were of different mentality. While some gave importance to nation others were worried about the fate of community they belonged to. Muslims leaders like Jinnah and Mohammad Iqbal feared that without Separate electorates the interest and desires of Muslims in India would be undermined. Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru were against the system of separate electorates and they believed that this will only add communalism in new India. They believed that Muslims are no different from Hindus in India and in the same way untouchables are no different from Hindus and separate electorates would further slow down the process of their integration into society. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar proposed a separate electorate for Dalits. An atmosphere of suspicion and distrust between communities prevailed which further led to division of India and reservations for minorities. Therefore, we can say that political leaders differ sharply over the question of separate electorates.
- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
- Social Issues In India
Social Issues in India - Major Classifications
Social issues in India are in plenty and they need to be addressed systematically to achieve social justice and economic justice to all the citizens of India. The founding fathers of India were keen on addressing the social issues of India by framing the constitution accordingly. Information on the major social issues will help the aspirants of the IAS Exam .
Classification of Social Issues
The below table gives a broad classification of major social issues in India.
Gender Issues
The details of 3 major gender issues are given below.
- As per the report of the Economic Survey 2017-18, there are 63 million missing women in India.
- Missing women are women who are not alive due to foeticide or infanticide.
- As per the World Economic Forum, India is ranked very low at 87th position in the “Global Gender Parity Report.”
- Indian Government launched the ‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ scheme to address the problem of the gender gap.
- The government has been carrying out information campaigns to address the problems by bringing in behavioural change in society.
Read about Gender Inequality in India in the linked article.
Triple Talaq
- Many Muslim-majority countries have banned triple talaq.
- To bring equality and justice to women, the Government of India has passed the Triple Talaq Bill, henceforth all declarations of talaq including written and electronic forms will be null and void.
Use the information given in the Triple Talaq Essay to substantiate your answers in the Mains exam.
Sexual Harassment at Workplace
- The government passed the Sexual Harassment at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act in 2013.
- It aims to protect the rights of women in any workplace in any capacity.
Learn in detail about Sexual Harassment at the Workplace in the linked article.
Poverty Report
- As per the World Bank Brookings Institute report, as of May 2018, there are only 73 million people in the poorest of the poor index.
- As per the report, 44 people in India are taken out of poverty every minute.
- If the growth continues at the same pace, then 50 million people will move out of poverty by 2022.
- India is no longer the country with the highest poverty.
Read about Poverty-related topics from the links given below:
Caste Related Issues
The details of caste-related issues are given below .
Lynchings because of caste-related issues occur in the country. There was no specific section to handle mob lynchings under the IPC but under the new Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, there is a provision for life imprisonment or death for such a crime. The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita “adds murder or grievous hurt by five or more people on specified grounds, as an offence. These grounds include race, caste, sex, language, or personal belief. The punishment for such murder is life imprisonment or death”.
Information and Broadcasting Advisory
- Information and Broadcasting Ministry has issued an advisory that the word ‘Dalit’ can no longer be used, this is as per the directive of the Bombay High Court and Madhya Pradesh High Courts. This is because the word found no mention in the Constitution of India or any statute.
- There was another directive from the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry to use only the term ‘Scheduled Castes’.
Implications of Caste Census
- The next caste census will take place in 2021, the problems associated with it is that it will encourage caste-based politics rather than concentrating on developmental activities. Also, there will be strong sentiments for or against reservations.
This is also one of the major social issues in India. The details are given below.
Changing Pattern of Migration
- As per recent reports, the number of women migrating in India is increasing at a faster pace than men. Marriage continues to play an important role in the migration of women; however, now other economic factors like employment, business, and education are also playing an important role in migration.
Know about Migration from India’s context in the linked article.
Plight of Migrants
- There has been an increase in violence against migrants coming to a state from different parts of the country.
- Lack of job opportunities for the locals has led to growing resentment against the migrants who are dubbed ‘outsiders’
Learn the challenges of migration that are mentioned in the linked article.
A country’s sustainable progress is dependent on the availability of healthy human resources. With a deteriorating environment and unhealthy lifestyle, health is turning out to be one of the major social issues in India.
Impact of Air Pollution
- As per the India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative report, India faces 26% of the world’s premature deaths and disease burden due to air pollution.
- 1 in 8 deaths in India was attributed to air pollution, which makes it a leading risk factor for death.
- Poor air quality is responsible for heart ailments as well.
Campaign against Drugs
- The drug menace is extremely severe in Punjab.
- Punjab’s prisons are overcrowded with drug users and peddlers.
- Punjab set up a Special Task Force to tackle the menace.
Substance Abuse in India
- As per a recent report released by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, India has 6 crore alcohol addicts
- More than 3 crore Indians are using cannabis products.
- 8.5 lakh people in India inject drugs.
Know the relevant facts about Drug Abuse in India from the linked article.
Other Issues
Increasing Youth Suicides
- As per reports from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) between 2014 and 2016; 26,476 students committed suicide in India. Of these around 7,500 committed suicide due to failure in various examinations.
- The main blame lies with India’s education system.
- The education system has not been able to generate enough jobs.
Social Issues in India- UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
The above details would help candidates prepare for UPSC 2024 .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science History Chapter 2 Nationalism in India
- Last modified on: 12 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for Class 10 Social Science History Chapter 2 Nationalism in India.
Case Study Question 1:
Emboldened with this success, Gandhiji in 1919 decided to launch a nationwide satyagraha against the proposed Rowlatt Act (1919). This Act had been hurriedly passed through the Imperial Legislative Council despite the united opposition of the Indian members. It gave the government enormous powers to repress political activities, and allowed detention of political prisoners without trial for two years. Mahatma Gandhi wanted non-violent civil disobedience against such unjust laws, which would start with a hartal on 6 April.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) Name the act which is being described in the passage. (a) Satyagraha Act (b) Rowlatt Act (c) Government of India Act (d) East India Company Act
(ii) Who opposed this Act? (a) Gandhiji (b) Lord lrwin (c) Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru (d) Subhas Chandra Bose
(iii) ______ was not a provision of this act. (a) Organisation of Rallies (b) Detention of Political prisoners (c) Curb political activities (d) All of these
(iv) This act was initiated through the efforts of (a) Imperial Legislative council (b) Indian members (c) East India company (d) Gandhiji
Related Posts
Tips to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science.
Preparing for case study and passage-based questions in class 10 social science can be challenging, but it is important to remember that with the right approach, you can effectively tackle these types of questions. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science:
- Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like history, geography, economics, or civics.
- Read and analyze the case study or passage carefully: The first step in answering case study questions is to read the scenario or passage carefully. Try to identify the main idea or theme of the passage and note down any important details that you think are relevant. Pay attention to any maps, graphs, or charts that are included as they can be helpful in answering the questions.
- Identify the type of questions being asked: After reading the case study or passage, you should analyze the questions being asked. Try to identify the type of question, whether it is a factual question or an analytical question. Factual questions require you to provide specific details from the passage, while analytical questions require you to use your critical thinking skills to analyze the information presented in the passage.
- Use your textbook and notes: To prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the topics covered in your textbook. Go through your notes and textbook to revise the relevant topics and concepts. This will help you to answer the questions more accurately.
- Practice sample questions: One of the best ways to prepare for case study questions is to practice answering sample questions. Try to find sample questions online or in your textbook and practice answering them. This will help you to get comfortable with the format of the questions and improve your speed and accuracy.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- India Today
- Business Today
- Reader’s Digest
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Cosmopolitan
- Aaj Tak Campus
- India Today Hindi
CBSE Class 10 Social Science paper analysis shows balanced paper with moderate difficulty
The cbse class 10 social science board exam, held on march 7, 2024, was considered reasonably easy. the paper was of easy to moderate level in difficulty with ncert questions..
Listen to Story

- CBSE Class 10 Social Science exam took place on March 7, 2024
- Students found the paper easy to moderate, with a manageable level of difficulty
- Feedback indicates the mapping section was easy, while some students found case study questions challenging
The CBSE board exam 2024 began for both Classes 10 and 12 on February 15 and the Class 10 Social Science paper was held on March 7. Students said that the Social Science paper was of easy to moderate level in difficulty.
The paper was easier compared to last year's and the sample papers. Most students found the mapping section easy. However, some felt the case study questions were a bit tough.
The exam wasn't too long, and most questions were from the NCERT.
"The exam was easy and everything was from the syllabus. Questions were repeated from last year's paper and sample paper. Maps section was extremely easy. It was from the sample paper," says Aditya from Cambridge School, Noida.
Aman Sharma from the same school found the paper a little tough. He clarified that it was cause of his preparation level as the paper was easier than that of last year and the sample paper.
"The 5-mark questions and case studies were difficult," Yadhvi from Bal Bharti Public School says, adding that the paper was tougher than the sample paper and last year's paper.
WHAT TEACHERS HAVE TO SAY
"The question paper was as per the syllabus and the difficulty level of the question paper was easy and comforting. A few multiple-choice questions (MCQs) were challenging, but the rest were simple and accommodating," says Manisha Pundir, Subject Coordinator at VidyaGyan Sitapur.
"Some questions based on the G20 summit were expected as per the learning objectives of Chapter ‘Globalisation and Indian Economy’, but somehow, they were totally excluded from the paper. Case-based questions had answers in the provided paragraphs. Internal choices were provided," she says.
"Though some questions necessitated in-depth concept grasps, most of the subjective questions were also straightforward, well-placed and maintained the equilibrium," she adds.
"It was not lengthy, and students got enough time to revise before submissions of answer scripts. To sum up, the question paper was balanced and reassuring," the teacher adds.
“The CBSE Class 10 Social Science paper offered a balanced mix of questions, testing knowledge, analysis, and application skills with a moderate difficulty level,” says Jasmeet Kaur, HOD Social Science at Bhai Parmanand Vidya Mandir.
“Sections B, C, and D contained subjective questions, while Section D was particularly challenging. Section E featured case-based questions, and Section F focused on map skills,” the teacher said.
Overall, the paper aimed to assess comprehension, critical thinking, and articulation skills, aligning with the NCERT curriculum, Kaur added.
“It aimed to evaluate students' comprehension of prescribed texts, their ability to engage in critical analysis, and their proficiency in articulating knowledge effectively,” the teacher said.
Abhilasha Pandey, TGT Social Science, Seth Anandram Jaipuria School, Lucknow, also said that the CBSE Class 10 Social Science paper was very balanced.
“The question paper maintained a moderate difficulty level, effectively testing students' reasoning, analytical, and critical thinking skills,” she said.
“Those who had familiarised themselves with CBSE sample papers were well-prepared to navigate the paper with confidence, leading to promising outcomes,” the teacher added.
"The difficulty level of the paper was moderate to easy," says Shruti Sharma, PGT History at Silverline Prestige School, Ghaziabad. "The map question was easy. Feedback from the students was that the paper was easy," she adds.
"The social science paper was a balanced mix of analysis and application-based questions; the level of difficulty was moderate," Priyanka Swami, TGT Social science, KIIT World School, Gurugram.
"The paper was a bit lengthy, and therefore, time management could have been a challenge for the class 10 students in today’s social science exam. Overall, students found that the CBSE social science paper was easy and straight from the prescribed syllabus and NCERT books," she adds.
"The Social Science paper for the Class 10 board examination was moderate, with most of the questions found to be from the syllabus. While the paper predominantly focused on conceptual understanding, it also included a few questions that tested theoretical knowledge and application skills," says Anshul Kumar, Manager- BYJU’S.
The History section focused majorly on chapters like Rise of Nationalism in Europe and Nationalism in India. Geography drew questions mainly from Minerals and Energy Resources. Civics and Economics questions were centered around Political Parties and Power Sharing, Sectors of the Indian Economy and Globalisation, he notes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By working through a case study, Class 10 social science students can learn how to identify key issues, consider different options and make decisions. ... Efficient and good transport for speedy movement of goods and services to different parts of India and to fulfill the needs of the people is needed.
Check CBSE Class 10 Social Science case study questions for Term 2 Exam 2022. Practice important questions (by experts) to score good marks in exam. Check Karnataka Board 2nd PUC Result 2024 Online
Step 1 Identification and mapping of resource across the country. Step 2 Planning structure of skills , institution etc. Step 3 Matching resource development plans with national economic plans. Q3) "There is enough for everybody need but not for anybody greed". Explain Mark 2.
Related: C BSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions for Board Exam 2024. 2.Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: Irrigation has also changed the cropping pattern ...
Case Study 1. Nationalism in India. 1) According to the historical account presented in Shahid Amin's work, "Event, Metaphor, Memory: Chauri Chaura, 1922-1992," on February 4, 1922, a significant group of peasants set fire to the police station in Chauri Chaura, resulting in the tragic death of 22 policemen.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. Case Study 1: India, the world's largest democracy, is a remarkable exemplar of democratic principles in action.
These CBSE Class 10 Social Science Case Study's have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for benefit of Class 10 students. For CBSE Class 10, the board has decided to introduce a minimum of 30 percent competency-based questions in form of case study questions, MCQs, source-based integrated questions, etc. in the new exam ...
Social Issues Report for CBSE Std 10. I took the topic of Gender Inequality for this project to be done for my Social Science subject enrichment activity for class 10. Reasons for gender inequality in India, Government policies, programmes and schemes etc. are discussed in the report. I have taken the case study of Gender Inequality in tribal ...
To effectively tackle case study questions, it is crucial to follow a systematic approach. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you approach and answer case study questions: Step 1: Read the Case Study Carefully Start by reading the case study thoroughly and understanding the context, characters, and key issues involved.
Economics Chapters for Case Study Questions. Development. Sectors of the Indian Economy. Money and Credit. Globalisation and the Indian Economy. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Social Studies students. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert ...
Here on this website, we offer India And the Contemporary World - II Case Study for Class 10 Social Science with solutions in PDF for free of cost. The PDF file can be accessed for free of cost and it is available 24×7 to learn and practise the questions from.
Tips to Prepare for Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science. Preparing for case study and passage-based questions in class 10 social science can be challenging, but it is important to remember that with the right approach, you can effectively tackle these types of questions. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study ...
Case-Based Questions. 1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity. Such losses have increasingly marginalized and impoverished many indigenous and other forest-dependent communities, who directly depend on various components of the forest and ...
Economic costs: Social problems with economic repercussions include poverty, unemployment, and inequality. Lost productivity, slower economic development, and higher costs for social services are all possible outcomes of the problems we've identified. Health problems: Social difficulties may have negative consequences on health as well.
Case Study 1. Print culture and modern world. 1) One of the most stringent regulations on the freedom of the press in India was the Vernacular Press Act of 1878. This act, introduced by then Viceroy, Lord Lytton, granted the government extensive powers to censor reports and editorials in the vernacular press.
Class 10 History Chapter 1 NCERT Solution gives you a brief idea. CBSE Class 10 Social Science India and Contemporary World is divided into subtopics like Rising in Nationalism, the Nationalist of Indo-China Movements, Nationalism in India, Making of the World, Work-life and Leisure, Print Culture, and Modern History.
This article covers the concept of social issues and highlights the different experiences of rural and urban sectors. Further, it studies six important social issues namely poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, the caste system, gendered violence and communalism by analyzing their causes and the specific measures adopted to combat them.
India has traditionally been a patriarchal country. In all its institutions and structures, patriarchy is reflected in power and resource allocation. Marriage is one such social institution. Except during the pre-Vedic era, in which women were supposed to be emancipated, India has had restrictive traditions, laws and customs for
1- INTRODUCTION. Social concerns are issues that significantly affect people's lives and society. These problems might include everything from poverty, injustice, and prejudice in the matters of healthcare, education, and the environment. In this project, we'll look at one of today's most important societal challenges and how it affects ...
Solutions of Chapter 2 Nationalism in India NCERT History India and the Contemporary World 2 Class 10. Meticulously crafted NCERT solutions to boost your CBSE board exam preparation. Easily score more marks in History CBSE exam.
As per the report of the Economic Survey 2017-18, there are 63 million missing women in India. Missing women are women who are not alive due to foeticide or infanticide. As per the World Economic Forum, India is ranked very low at 87th position in the "Global Gender Parity Report.". Indian Government launched the 'Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao ...
Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science: Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like ...
In Short. CBSE Class 10 Social Science exam took place on March 7, 2024. Students found the paper easy to moderate, with a manageable level of difficulty. Feedback indicates the mapping section was easy, while some students found case study questions challenging. The CBSE board exam 2024 began for both Classes 10 and 12 on February 15 and the ...