Introduction to a Variety of Qualitative Research Methods
- First Online: 02 January 2023

Cite this chapter

- Janet Mola Okoko 4 ,
- Scott Tunison 4 &
- Keith D. Walker 4
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
4070 Accesses
2 Citations
This book is compilation of qualitative research concepts authored by academics and research practitioners from all over the world. The editors have observed that as the world gets smaller and increasingly interconnected, the field of qualitative research has become more diverse and inclusive of varied ways of knowing and inquiring.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education at the University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko, Scott Tunison & Keith D. Walker
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Janet Mola Okoko .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko
Scott Tunison
Department of Educational Administration, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Keith D. Walker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (2023). Introduction to a Variety of Qualitative Research Methods. In: Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (eds) Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_1
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04396-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04394-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Library 160: Introduction to College-Level Research
(8 reviews)
Iowa State University Library Instruction Services, Iowa State University
Copyright Year: 2021
Publisher: Iowa State University
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Morgan Montgomery, Assistant Library Director, Claflin University on 12/5/23
The book's table of contents made it easy to focus on the chapters that interested me the most. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The book's table of contents made it easy to focus on the chapters that interested me the most.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The book provided wonderful examples of scenarios in teaching and instruction of research.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The contents of this textbook are timely and relevant. I will definitely be implementing it in to my information literacy lesson plans and instruction.
Clarity rating: 5
The book was easy to follow, the chapters flowed and it was brimming with examples.
Consistency rating: 4
The book is consistent with terminology and examples.
Modularity rating: 5
I like the fact that the topics ranging from locating primary sources to newspapers are broken down into sections. I would recommend a particular section to our English 101 professors.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book's structure and flow is easy to follow. It starts from the beginning explaining what is research to building up selecting searches and web (internet research).
Interface rating: 5
The book's interface and design made it easy to jump from chapter to chapter and focus on headings highlighted in the book.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The book contained no errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
This book is a natural fit for learning, improving, and implementing research building blocks into your information literacy classes. I well definitely be utilizing this book this semester.
Reviewed by Maletta Payne, Systems Administrator/Reference Librarian, Southern University on 11/14/23
The text appropriately covers all information literacy areas and provides a practical glossary. read more
The text appropriately covers all information literacy areas and provides a practical glossary.
The content is accurate, moderately error-free, and unbiased.
The text is up-to-date and reflects the current information landscape.
The clarity of language and accessibility of the prose, coupled with sufficient context for jargon and technical terminology, are commendable attributes of the information literacy text.
Consistency rating: 5
The book's consistency and framework make it an invaluable resource for undergraduate students seeking a structured and cohesive approach to understanding the research process.
The book's modularity is apparent, allowing readers to navigate the content in a flexible and personalized manner.
The text's topic is presented logically and clearly, with each section building on the appropriate research practices.
The interface is easy to navigate. Additionally, this textbook contains a video to guide users on the book layout and "Check your understanding" interactive elements for users to practice concepts outlined in the chapters.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
There are very minimal grammatical errors in this textbook.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The textbook does not contain culturally insensitive or offensive materials; however, the book can benefit from images of various ethnicities.
Library 160: Introduction to College-Level Research consistency across chapters, in writing style and terminology, makes it a reliable guide for readers navigating the intricate landscape of information literacy.
Reviewed by Rachel Milani, Assistant Librarian, Minnesota North College on 12/6/22
This textbook comprehensively covers the research process in a concise, comprehensible format that should be easily understood by students at the community college level. This book additionally provides information on ethical use of information,... read more
This textbook comprehensively covers the research process in a concise, comprehensible format that should be easily understood by students at the community college level. This book additionally provides information on ethical use of information, resources for students who wish to learn how to develop a citation, and a brief overview of how research fits into the overall writing process. I also like that this book introduces the SIFT method and explains why the CRAAP method may no longer be the most effective evaluation tool. One critique would be that this book fails to mention that students should cite their sources as they find them so that they can more easily find those sources again if necessary and more effectively prevent plagiarism. Understanding when a source requires citation is one thing, but students often leave citing those sources until the very end of the writing process, which can lead to confusion and errors in citations.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
Content within this text is accurate and unbiased.
While this book was written for a specific institution and program, this text makes an effort to generalize certain topics (like database availability and selection) to be broadly applicable to other institutions that might utilize different platforms and tools or have other options available. This is something that can be easily customized by anyone with access to Pressbooks. This does detract slightly from the comprehensiveness of the book, but not by much. This book seems to be most relevant to an undergraduate "Introduction to College" course or to segments of a Freshman Composition course. That said, this book could also easily be incorporated into other courses that assign research papers.
Again, this textbook comprehensively covers the research process in a concise, comprehensible format that should be easily understood by students at the community college level. This book covers some complex concepts (like copyright and fair use) and makes them accessible to students.
The language, tone of voice, and terminology used within this text are consistent. The use of Glossary Terms easily enables students to learn the terminology and ensures continuity of terminology throughout the book, as well as clear definitions of each term.
At no point does this text refer the reader to another internal section. Each topic is further subdivided into smaller segments that could be utilized in a stand-alone manner as needed.
This text is organized in a linear, logical manner, proceeding from one step to the next logical area of consideration.
All aspects of the Pressbooks interface for this text seem to be free of navigation issues or distortions. The only potential issue could be that the "next page" button is a little easy to overlook, but that's nitpicking.
From what I could see, there were no blatant grammatical errors in this textbook.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. It serves as a "how-to" manual regarding the steps of the research and citation process.
Reviewed by Annie Cifelli, Reference Librarian, Cape Cod Community College on 11/7/22
As an introductory text book, Library160 does a good job covering the basics. The 5 chapters address "Getting Started," "Locating Information," Search Techniques," "Evaluating Information," and "Using Information Ethically." Each chapter begins... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
As an introductory text book, Library160 does a good job covering the basics. The 5 chapters address "Getting Started," "Locating Information," Search Techniques," "Evaluating Information," and "Using Information Ethically." Each chapter begins with clearly stated learning objectives. The sub-sections within the chapters proceed in a logical and well-organized manner. There is a thorough glossary at the end.
The content in Library 160 is accurate; however, examples rely rather too-heavily on the authors' (Iowa State University Library Instruction Services) unique library features. Adapting this text book would require substantial editing. For example, some screen grabs are from ISU's specific search interface, record examples and unique “pay for” tools like Map It and Get It. But explanation of Library of Congress call numbers is quite good.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Content is up-to-date. Again, using ISU's specific website to illustrate content may prove problematic in the future. Likewise, the database search pages change not infrequently and may not reflect what students see when they login to their own school's library page.
One of the strengths of Library 160 is the way in which it is written. The language used is accessible and friendly. I made note of several "real world" examples (like avoiding "BS") that help make the content real to students.
Library 160 does an excellent job using terminology consistently. One issue with information literacy classes is the lack of standard terms. For instance, faculty often use phrases like "scholarly articles,” "academic journals,” and "peer reviewed sources," interchangeably, which can be confusing for students new to the research process. Also, between disciplines what constitutes a primary source can vary. This textbook explains all of the "jargon" and offers clear visuals as to how the terms interrelate.
As mentioned above, the 5 chapters are each divided into smaller sub-sections. The Table of Contents is always on the left side of the screen, making it easy to move around between sections or return to previously covered content. Moving between pages is also straightforward--the arrows at the bottom of the screen show what's "previous" and what's "next."
Overall, the organization of Library 160 makes sense. However, the early mentions of "how to cite" work represent something of an issue. Ethical information use is covered in the last chapter book, but opportunities for additional coverage abound. The style guides (MLA, APA, Chicago) are only just mentioned. Likewise, fair use, copyright, plagiarism are all addressed but only in most generic terms.
The interface is fantastic! There are a lot of great visuals (bullet points, charts, graphs) and several embedded YouTube videos break up large sections of text. Plus, there are quizzes to check understanding. Yay quizzes!
I did not find any grammatical errors. At first, the use of the second person "You" seemed too informal for a textbook, but by the end of the book, it felt collaborative as "you" can be singular or plural--"you" the individual student as well as "you" all the students in this class.
There is one curse word in this book (BS), but in context and with a solid reason. I was surprised to see it, but not offended.
At the very end of Library 160, there is a small section on "Promoting Yourself as a Student Researcher." The idea of sharing student work through scholarly channels and encouraging students to think about themselves as “student researchers” is a powerful one. More energy should devoted to that concept in information literacy instruction. Too often students feel like they're just “pretending” to be scholars. Perhaps Library 160 can help change that!
Reviewed by Maribel Pagan, Librarian, Klamath Community College on 10/25/22
The book is extremely down-to-earth with easy to access chapters, sections, and information. read more
The book is extremely down-to-earth with easy to access chapters, sections, and information.
The book is very accurate to today's libraries, but I wish it covered a bit more about the CRAAP test which is still relevant in some libraries today.
This book uses information that tends to stay the same. For example, even with databases, boolean operators do not tend to change even when the databases do. This makes it easier to follow along and makes it accessible to all regardless of which databases they use.
The book is extremely accessible with its use of down-to-earth language that's extremely easy to understand. It feels wordy at times as a result, but I feel it also makes it more personable to both staff and students.
Very consistent in its explanations, its down-to-earth language, and all the steps needed to effectively conduct research.
Very easy to take out sections of it and utilize in a class section. The book often separated each section of a chapter into subsections, which makes it easy to adapt and utilize the text.
This book follows a clear organization and goes step by step, following all the outcomes that are first outlined in each chapter.
The interface is pretty interactive, allowing the user of this text to simply read or to also engage with the material through interactive activities.
Did not notice any grammatical errors in the text.
Did not notice any culturally insensitive aspects of the book and felt the piece was pretty inclusive.
The book is very down-to-earth, easy to read, and easy to utilize parts of. I love how the user of this text can simply read or also engage with the material through interactive activities, which I'll be sure to incorporate some of these interactive activities in my own information literacy classes. I wish they also adapted more visual learners by providing some linked videos or something akin to that. I also wish that the book had a print version that I could have at hand and offer students if they expressed any interest in learning more. Some students have come to me before asking for print copies of their books, and it would be nice to have a print copy at hand for students to pick up and look through.
The sections on teaching students strengths and weaknesses of each information source helps tremendously as well. It shows how one can evaluate different resources and understand the different types of sources that may come up. I feel there could be some additional coverage of how to utilize research for research powerpoints, presentations, etc.
Overall, a wonderfully written book that provides accessibility to all.
Reviewed by Stefania Hiltgen, Public Services Librarian at Newberry College, Newberry College on 3/9/22
This book goes into great detail and includes modern research concepts such as using Wikipedia for background information and how to search Google. read more
This book goes into great detail and includes modern research concepts such as using Wikipedia for background information and how to search Google.
I found no issues with accuracy.
The length was just right-not exhaustive, but inclusive of all topics needed to understand how to conduct modern-day research.
It also includes a helpful Glossary.
It is consistent in the terminology it uses.
It is organized in good-sized chunks.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The fluid nature of research makes organizing it a little difficult. This is no fault of the authors; it is just a difficult subject to unravel linearly.
The e-book version flowed very well. Indid not take a look at the PDF version.
I found no grammatical errors.
I found no examples that were offensive or insensitive.
I found it very helpful and look forward to using it in the near future, myself.
Reviewed by Meridith Wolnick, Director of Teaching and Learning, University of Virginia on 12/16/21
Library 160: Introduction to College-Level Research is written for students attending a particular course at Iowa State University. It has a full table of contents and is easy to navigate. Sections are short and include clearly labeled... read more
Library 160: Introduction to College-Level Research is written for students attending a particular course at Iowa State University. It has a full table of contents and is easy to navigate. Sections are short and include clearly labeled subsections. While there is no index, the linked table of contents handily provides user-friendly navigation.
Generally, the text is accurate and unbiased. However, Web Search Engines are incorrectly identified as not having filters for advanced search or narrowing a search (Table 2.1, pg. 28). In the case of Google, there is a capacity for advanced search, searches can be narrowed by time, and images can be narrowed by type of image, usage rights, etc. This is something the authors acknowledge further in the text (Section 4.6, pg. 129).
The content is up-to-date and relevant to today’s readers. The text does link to tutorials and other resources from other universities. Given that those links are out of the hands of the authors and ISU, broken links may go unnoticed. Additionally, there are several figures that look like they are from the ISU Library catalog. While those helpfully illustrate the text, they may become dated as web pages change. That said, given their placement in the text, updates should be easy to make.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear and terms are defined for those new to the concepts. Each chapter includes learning outcomes that are achieved by the end of the chapter. Terms (like 'popular information' and 'peer review') are well-defined with examples. However, the use of bolding for terminology is not consistent throughout the book. Some terms (like 'thesis' and 'finding tools') are bolded and explained but others (like 'item records' and 'DOI') are just explained, not bolded. It also would be helpful to have bolded terms and concepts in a central list in the book for easy reference. In Section 1.4 (pg. 8), it’s not clear by Books whether the authors are referring to scholarly books or all books. Section 3.3 covering nesting and Boolean operators was complex compared to the rest of the text. It was helpful when the text differentiated between the ISU Quick Search function and a search engine. For instance, when discussing Boolean operators, the text identifies how to do a search similar to Quick Search in Google using a – instead of NOT.
The text is consistently written and cohesive.
The text is logically divided, and individual sections can be assigned independently. Sections are generally small and concise, easy to take in and understand. Page numbers did not consistently appear in the downloaded PDF.
The flow of the text is logical. The sequence of the sections, particularly illustrating the steps in beginning the research process, are clear and aligned with the student experience. The sections on Keywords are particularly organized and well-defined.
Interface rating: 4
Navigation throughout the text is easy and logical. A few things I noted that could be improved: Figure 1.1 on page 10 in the section defining journal articles/issues/volumes is mid-quality and not ultimately necessary for the text since it is well explained in the preceding section. It may become dated since the journal clearly shows publication dates.
I didn’t observe any grammatical errors.
While the examples used throughout the text assume some knowledge about the United States, they are inclusive and cover a wide range of topics. Since the book is clearly written specifically for ISU students, reliance on U.S. concepts is less of an issue. The sub-section on outdated and offensive subject headings (pg. 80) was a helpful addition to the text.
This text is written for students early in their college careers. It would be useful for any student undertaking academic research for the first time. The text adds helpful sections that go beyond basic research skills, such as the Did You Know section (pg. 30) about free accounts. There are interactive checks for understanding that are relevant to the subject matter being reviewed. They include the opportunity to retry if answered incorrectly and give immediate feedback to the student. In the PDF, the checks are labeled “An Interactive H5P element” which may cause a student who is unfamiliar with H5P to avoid clicking.
Reviewed by Elena Rodriguez, Research and Instruction Librarian, College of Charleston on 9/28/21
The Introduction to College-Level Research provides a straightforward and thorough review of the research process. The five chapters cover the primary elements students should be considering as they become proficient in locating, evaluating, and... read more
The Introduction to College-Level Research provides a straightforward and thorough review of the research process. The five chapters cover the primary elements students should be considering as they become proficient in locating, evaluating, and using information. Being a student centered textbook, I can understand why there isn't any mention of the ACRL Framework for Information Literacy or a specific section that discusses why this book was created, but these are elements that would be helpful for instructors using this textbook outside of the institution. Additionally, as this appears to be for a specific course, including a glossary of terms would be helpful as a reference. While definitions are provided throughout each chapter, they can get lost in the text.
The content appears to be accurate, error-free and unbiased. Any included references were relevant and functioned properly. I appreciated that, in the section concerning Wikipedia, the authors did address the issue that the majority of editors are male and there are inherent biases and exclusions in those articles.
Given that these chapters cover topics with a general approach, it is unlikely that this content will be obsolete in the near future. However, some of the images from the institution's interface may become outdated.
The authors clearly define concepts and terms, and provide excellent examples throughout. Some of these examples, however, may edge into the overwhelming for novice researchers. A particular example is the graphic provided in the Boolean Operators section, 3.2. The very detailed search example (that includes AND, OR, and NOT with nesting) is simultaneously effective and a lot to take in. I very much appreciated their approach of including "strengths" and "weaknesses" at the end of certain section; this summarized information very concisely and helps demonstrate that there isn't one source or tool that is perfect.
Despite being written and compiled by the Library Instruction Services unit, this book manages to have a consistent voice and approach to how each chapter and subsequent section is presented.
Keeping to 5 chapters with quick subsections makes this book easy to use and read, either as a professor assigning work or a student using it as a resource. The sections are, for the most part, very reasonable in length, and the ones that verge on being too long are appropriately divided. I did not find the text to be disruptive.
The book is thoughtfully organized with a clear and simple structure. The order of the chapters is logical and follows a typical research process.
No issues noted with the interface. The occasional “check your understanding” quizzes were very effective and added to the overall experience of using the textbook online.
I did not note any grammatical errors during my review of the text.
The text did not appear to be culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. Generally, all their examples and screenshots were very generic and represented authors from different backgrounds and fields of study. However, there is certainly opportunity to provide more inclusive examples or to discuss critical information literacy and social justice.
Overall, a good resource for an introductory college research course. It is simple in its approach, which makes the material approachable for novice researchers. For instructors not at the home institution wanting to use this book, certain sections may be confusing for students given the very specific screenshots, but this is expected given it’s attachment to the 160 course offered at Iowa State University. It would be useful to have more details about the course itself and the institution, as well as the makeup of the Instruction Services team that authored this source.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Getting started with research
Chapter 2: Locating information
Chapter 3: Search techniques
Chapter 4: Evaluating information
Chapter 5: Using information ethically
Ancillary Material
About the book.
You will learn how scholarly information is produced, organized, and accessed; how to construct and use effective search strategies in a variety of web tools and scholarly databases; how to choose finding tools appropriate to the type of information you need; critical thinking skills in the evaluation of resources; and best practices in the ethical use of information.
About the Contributors
Iowa State University Library Instruction Services , Iowa State University
Contribute to this Page
- I'M AN INSTRUCTOR
- I'M A STUDENT

Find what you need to succeed.
- Our Mission
- Our Leadership
- Learning Science
- Macmillan Learning AI
- Sustainability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Accessibility
- Astronomy Biochemistry Biology Chemistry College Success Communication Economics Electrical Engineering English Environmental Science Geography Geology History Mathematics Music & Theater Nutrition and Health Philosophy & Religion Physics Psychology Sociology Statistics Value
- Digital Offerings
- Inclusive Access
- Lab Solutions
- LMS Integration
- Curriculum Solutions
- Training and Demos
- First Day of Class
- Administrators
- Affordable Solutions
- Badging & Certification
- iClicker and Your Content
- Student Store
- News & Media
- Contact Us & FAQs
- Find Your Rep
- Booksellers
- Macmillan International Support
- International Translation Rights
- Request Permissions
- Report Piracy
Research Methods
Psychology in Everyday Life
Concepts and connections third edition | ©2021 michael passer.
ISBN:9781319363536
Take notes, add highlights, and download our mobile-friendly e-books.
ISBN:9781319363529
Save money with our hole-punched, loose-leaf textbook.
ISBN:9781319184513
Read and study old-school with our bound texts.
PACKAGE WITH LAUNCHPAD SOLO FOR RESEARCH METHODS The book professors can depend on—for introducing research methods to any kind of student
With over two decades of classroom experience, Michael Passer knows how to guide students through the ins and outs of research methods. In this remarkable text, Passer’s experience leads to chapters filled with clear explanations, resonant examples, and contemporary research from across the breadth of modern psychology, all while anticipating common questions and misunderstandings. The new edition has been fully updated to reflect the latest APA style guidelines, as well as the updated APA Code of Conduct and ethical principles. It features full-page infographics summarizing key concepts and fully updated research. It can be packaged FREE with Worth Publishers’ LaunchPad Solo for Research Methods —the ideal online component for the text, featuring videos and activities that put students in the role of either experimenter or research subject.
New to This Edition
“I do appreciate [the author’s] realistic expectation of research methods. I believe his focus on diverse subfields while understanding the planned trajectory of students, gives this book a lot of street credibility.” -Ryan Hjelle, University of Minnesota “The book is well designed. I particularly like the mix of academic knowledge, aligned with pop-culture grounded by research and attractive graphics and illustrations.” -Karen Thomas-Brown, University of Michigan - Dearborn “It is straightforward, concise, and carries fundamental information for research methods.” -Guangying Wu, George Washington University “The tone is conversational, and easy for students to understand. The concepts are presented accurately” -Guangying Wu, George Washington University “It was very detailed and advanced, but presented in an accessible way. Students will gain a very sophisticated understanding of scale development and measurement.” -Lauren Coursey, University of North Texas – Dallas “The text is amazing and one of the best research methods texts on the market.” -Chrysalis Wright, University of Central Florida “The book is well designed with appropriate, meaningful figures and expected (and useful) practice opportunities” -Pam Marek, Kennesaw State University “I am a fan of this text. I have used it for a few years and both me and my students really like it. I find that it covers the main concepts in a way that is easy for students to grasp and it provides a very good foundation for me to further explain issues during lectures.” -Karen Lawson, University of Saskatchewan “Passer has done an excellent job of covering survey research, considerably better than many research methods textbooks I have reviewed.” -Carie Buchanan, St. Thomas More College “I have found over the last few years that the text covers the material to a degree that is appropriate for the level of student in my course. The text is well- written” -George Alder, Simon Fraser University – Burnaby
Third Edition | ©2021
Michael Passer
Digital Options
Read online (or offline) with all the highlighting and notetaking tools you need to be successful in this course.
Learn About E-book
Third Edition | 2021
Table of Contents

Michael W. Passer is Senior Lecturer in Psychology at the University of Washington. Born and raised in Brooklyn, New York, he entered the University of Rochester fully expecting to be a physics or chemistry major, but he became hooked on psychological science after taking introductory psychology and a seminar course on the nature of the mind. He got his start as an undergraduate researcher under the mentorship of Dr. Harold Sigall, was a volunteer undergraduate introductory psychology Teaching Assistant, and received a Danforth Foundation Fellowship that partly funded his graduate studies and exposed him to highly enriching national conferences on college teaching. Dr. Passer received his Ph.D. from UCLA, where he conducted laboratory research on attribution theory under the primary mentorship of Dr. Harold Kelley and gained several years of field research experience studying competitive stress, self-esteem, and attributional processes among boys and girls playing youth sports, mainly working with Dr. Tara Scanlan in the Department of Kinesiology. At the University of Washington he has conducted hypothesistesting field research on competitive stress with youth sport participants, collaborated on several applied research projects in the fi eld of industrial-organizational psychology, and for the past 20 years has been a Senior Lecturer and faculty coordinator of U.W.’s introductory psychology courses. In this role, he annually teaches courses in introductory psychology and research methods, developed a graduate course on the teaching of psychology, and is a U.W. Distinguished Teaching Award nominee. With his colleague Ronald Smith, he has coauthored five editions of the introductory textbook Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior (McGraw-Hill), and has published more than 20 scientific articles and chapters, mostly on attribution theory and competitive stress.  
Third Edition | 2021
Instructor Resources
Need instructor resources for your course, access test bank.
You need to sign in as a verified instructor to access the Test Bank.
Test Bank for Research Methods
Download resources.
You need to sign in to unlock your resources.
Clicker Questions
Image slides, instructor's resource manual, instructor's resource manual for research methods (online only), lecture slides, lecture slides for research methods (online only).
You've selected:
Click the E-mail Download Link button and we'll send you an e-mail at with links to download your instructor resources. Please note there may be a delay in delivering your e-mail depending on the size of the files.
Your download request has been received and your download link will be sent to .
Please note you could wait up to 30 to 60 minutes to receive your download e-mail depending on the number and size of the files. We appreciate your patience while we process your request.
Check your inbox, trash, and spam folders for an e-mail from [email protected] .
If you do not receive your e-mail, please visit macmillanlearning.com/support .
Related Titles
Select a demo to view:
These materials are owned by Macmillan Learning or its licensors and are protected by United States copyright law. They are being provided solely for evaluation purposes only by instructors who are considering adopting Macmillan Learning's textbooks or online products for use by students in their courses. These materials may not be copied, distributed, sold, shared, posted online, or used, in print or electronic format, except in the limited circumstances set forth in the Macmillan Learning Terms of Use and any other reproduction or distribution is illegal. These materials may not be made publicly available under any circumstances. All other rights reserved. © 2020 Macmillan Learning. BY CLICKING ON THE SAMPLE CHAPTER LINK BELOW, YOU ARE AGREEING TO USE THESE MATERIALS ONLY IN ACCORDANCE WITH MACMILLAN LEARNING'S TERMS OF USE.
Select a file to view:
Chapter 8: Single-Factor Experimental Designs
We are happy to offer free Achieve access in addition to the physical sample you have selected. Sample this version now as opposed to waiting for the physical edition.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Research Methods
1.4 Understanding Key Research Concepts and Terms
In this textbook you will be exposed to many terms and concepts associated with research methods, particularly as they relate to the research planning decisions you must make along the way. Figure 1.1 will help you contextualize many of these terms and understand the research process. This general chart begins with two key concepts: ontology and epistemology, advances through other concepts, and concludes with three research methodological approaches: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods.
Research does not end with making decisions about the type of methods you will use; we could argue that the work is just beginning at this point. Figure 1.3 does not represent an all-encompassing list of concepts and terms related to research methods. Keep in mind that each strategy has its own data collection and analysis approaches associated with the various methodological approaches you choose. Figure 1.1 is intentioned to provide a general overview of the research concept. You may want to keep this figure handy as you read through the various chapters.

Figure 1.3: Shows the research paradigms and research process © JIBC 2019
Ontology & Epistemology
Thinking about what you know and how you know what you know involves questions of ontology and epistemology. Perhaps you have heard these concepts before in a philosophy class? These concepts are relevant to the work of sociologists as well. As sociologists (those who undertake socially-focused research), we want to understand some aspect of our social world. Usually, we are not starting with zero knowledge. In fact, we usually start with some understanding of three concepts: 1) what is; 2) what can be known about what is; and, 3) what the best mechanism happens to be for learning about what is (Saylor Academy, 2012). In the following sections, we will define these concepts and provide an example of the terms, ontology and epistemology.
Ontology is a Greek word that means the study, theory, or science of being. Ontology is concerned with the what is or the nature of reality (Saunders, Lewis, & Thornhill, 2009). It can involve some very large and difficult to answer questions, such as:
- What is the purpose of life?
- What, if anything, exists beyond our universe?
- What categories does it belong to?
- Is there such a thing as objective reality?
- What does the verb “to be” mean?
Ontology is comprised of two aspects: objectivism and subjectivism. Objectivism means that social entities exist externally to the social actors who are concerned with their existence. Subjectivism means that social phenomena are created from the perceptions and actions of the social actors who are concerned with their existence (Saunders, et al., 2009). Figure 1.2 provides an example of a similar research project to be undertaken by two different students. While the projects being proposed by the students are similar, they each have different research questions. Read the scenario and then answer the questions that follow.
Subjectivist and objectivist approaches (adapted from Saunders et al., 2009)
Ana is an Emergency & Security Management Studies (ESMS) student at a local college. She is just beginning her capstone research project and she plans to do research at the City of Vancouver. Her research question is: What is the role of City of Vancouver managers in the Emergency Management Department (EMD) in enabling positive community relationships? She will be collecting data related to the roles and duties of managers in enabling positive community relationships.
Robert is also an ESMS student at the same college. He, too, will be undertaking his research at the City of Vancouver. His research question is: What is the effect of the City of Vancouver’s corporate culture in enabling EMD managers to develop a positive relationship with the local community? He will be collecting data related to perceptions of corporate culture and its effect on enabling positive community-emergency management department relationships.
Before the students begin collecting data, they learn that six months ago, the long-time emergency department manager and assistance manager both retired. They have been replaced by two senior staff managers who have Bachelor’s degrees in Emergency Services Management. These new managers are considered more up-to-date and knowledgeable on emergency services management, given their specialized academic training and practical on-the-job work experience in this department. The new managers have essentially the same job duties and operate under the same procedures as the managers they replaced. When Ana and Robert approach the managers to ask them to participate in their separate studies, the new managers state that they are just new on the job and probably cannot answer the research questions; they decline to participate. Ana and Robert are worried that they will need to start all over again with a new research project. They return to their supervisors to get their opinions on what they should do.
Before reading about their supervisors’ responses, answer the following questions:
- Is Ana’s research question indicative of an objectivist or a subjectivist approach?
- Is Robert’s research question indicative of an objectivist or a subjectivist approach?
- Given your answer in question 1, which managers could Ana interview (new, old, or both) for her research study? Why?
- Given your answer in question 2, which managers could Robert interview (new, old, or both) for his research study? Why?
Ana’s supervisor tells her that her research question is set up for an objectivist approach. Her supervisor tells her that in her study the social entity (the City) exists in reality external to the social actors (the managers), i.e., there is a formal management structure at the City that has largely remained unchanged since the old managers left and the new ones started. The procedures remain the same regardless of whoever occupies those positions. As such, Ana, using an objectivist approach, could state that the new managers have job descriptions which describe their duties and that they are a part of a formal structure with a hierarchy of people reporting to them and to whom they report. She could further state that this hierarchy, which is unique to this organization, also resembles hierarchies found in other similar organizations. As such, she can argue that the new managers will be able to speak about the role they play in enabling positive community relationships. Their answers would likely be no different than those of the old managers, because the management structure and the procedures remain the same. Therefore, she could go back to the new managers and ask them to participate in her research study.
Robert’s supervisor tells him that his research is set up for a subjectivist approach. In his study, the social phenomena (the effect of corporate culture on the relationship with the community) is created from the perceptions and consequent actions of the social actors (the managers); i.e., the corporate culture at the City continually influences the process of social interaction, and these interactions influence perceptions of the relationship with the community. The relationship is in a constant state of revision. As such, Robert, using a subjectivist approach, could state that the new managers may have had few interactions with the community members to date and therefore may not be fully cognizant of how the corporate culture affects the department’s relationship with the community. While it would be important to get the new managers’ perceptions, he would also need to speak with the previous managers to get their perceptions from the time they were employed in their positions. This is because the community-department relationship is in a state of constant revision, which is influenced by the various managers’ perceptions of the corporate culture and its effect on their ability to form positive community relationships. Therefore, he could go back to the current managers and ask them to participate in his study, and also ask that the department please contact the previous managers to see if they would be willing to participate in his study.
As you can see the research question of each study guides the decision as to whether the researcher should take a subjective or an objective ontological approach. This decision, in turn, guides their approach to the research study, including whom they should interview.
Epistemology
Epistemology has to do with knowledge. Rather than dealing with questions about what is, epistemology deals with questions of how we know what is. In sociology, there are many ways to uncover knowledge. We might interview people to understand public opinion about a topic, or perhaps observe them in their natural environment. We could avoid face-to-face interaction altogether by mailing people surveys to complete on their own or by reading people’s opinions in newspaper editorials. Each method of data collection comes with its own set of epistemological assumptions about how to find things out (Saylor Academy, 2012). There are two main subsections of epistemology: positivist and interpretivist philosophies. We will examine these philosophies or paradigms in the following sections.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Brill | Nijhoff
Brill | Wageningen Academic
Brill Germany / Austria
Böhlau
Brill | Fink
Brill | mentis
Brill | Schöningh
Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht
V&R unipress
Open Access
Open Access for Authors
Open Access and Research Funding
Open Access for Librarians
Open Access for Academic Societies
Discover Brill’s Open Access Content
Organization
Stay updated
Corporate Social Responsiblity
Investor Relations
Policies, rights & permissions
Review a Brill Book
Author Portal
How to publish with Brill: Files & Guides
Fonts, Scripts and Unicode
Publication Ethics & COPE Compliance
Data Sharing Policy
Brill MyBook
Ordering from Brill
Author Newsletter
Piracy Reporting Form
Sales Managers and Sales Contacts
Ordering From Brill
Titles No Longer Published by Brill
Catalogs, Flyers and Price Lists
E-Book Collections Title Lists and MARC Records
How to Manage your Online Holdings
LibLynx Access Management
Discovery Services
KBART Files
MARC Records
Online User and Order Help
Rights and Permissions
Latest Key Figures
Latest Financial Press Releases and Reports
Annual General Meeting of Shareholders
Share Information
Specialty Products
Press and Reviews
Research Concepts for the Practitioner of Educational Leadership
Prices from (excl. shipping):
- Paperback: €38.00
- Hardback: €108.00
- E-Book (PDF): €108.00
- View PDF Flyer
- Copyright page
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Overview of Research
- Chapter 3 Beginning the Research Project
- Chapter 4 Finding and Reviewing Literature for Credible Research
- Chapter 5 Populations and Samples
- Chapter 6 Measurement of Variables
- Chapter 7 Internal and External Validity and Threats to Validity
- Chapter 8 Research Designs and Their Limitations
- Chapter 9 Qualitative Research
- Chapter 10 Analysis of Data
- Chapter 11 Research Results
Biographical Note
Share link with colleague or librarian, product details.
- Research Methodology
Collection Information
- Educational Research E-Books Online, Collection 2018
Related Content
Reference Works
Primary source collections
COVID-19 Collection
How to publish with Brill
Open Access Content
Contact & Info
Sales contacts
Publishing contacts
Stay Updated
Newsletters
Social Media Overview
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Statement
Cookie Settings
Accessibility
Legal Notice
Terms and Conditions | Privacy Statement | Cookie Settings | Accessibility | Legal Notice | Copyright © 2016-2024
Copyright © 2016-2024
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.174]
- 81.177.182.174
Character limit 500 /500

The Best 20 Concept Books That Will Make Learning Fun for Your Child

Inside: Concept books don’t have to be dry and boring. The best concept books make learning fun for kids. Here are the children’s concept books you’ll actually enjoy sharing with your child.
You’ve probably already heard that reading aloud to your child helps their brain grow .
And what’s amazing is that to get all the benefits of reading aloud, you don’t even have to read something overtly “educational.” No matter whether you read Where the Wild Things Are for the 72 billionth time or the back of the Cheerios box to your child, their brain will soak up new words and knowledge like a sponge.
Or if you want to be more proactive, books are an excellent tool for teaching your child basic concepts, like the alphabet, counting, shapes, colors, and so on. In fact, a whole category of children’s books is devoted to this endeavor, called “concept books” because their goal is to teach kids basic concepts.
But unfortunately, a significant portion of those concept books are missing one essential ingredient for the learning process: fun.
The Problem With Some Concept Books for Kids
Some concept books approach their subject a bit like a drill sergeant might, standing at a blackboard and running through the concepts without warmth, a sense of wonder, or any trace of humor.
And yet, brain research suggests that fun isn’t just a “nice to have” for the learning process but that it may be required for authentic learning and for storage in long-term memory. According to Research-Based Strategies to Ignite Student Learning :
“When a lesson starts with humor, there is more alerting, and the subsequent information is attached to the positive emotional event as an event or flashbulb memory… Optimal brain activation occurs when subjects are in positive emotional states or when the material holds personal meaning, connects to their interests, is presented with elements of novelty, or evokes wonder. This is why attentiveness is so closely linked to positive emotional cueing and personal meaning. When there is connection to prior knowledge or positive emotional experience, new information passage through the limbic system will be enhanced. The thalamus will then ‘decide’ to pay attention to the information.”
In other words, the best concept books make learning fun for kids. If a concept book fails to surprise your child, tickle their funny bone, or inspire a sense of awe, it probably won’t teach them anything anyway.
Related: The Ultimate List of the Best Books for Toddlers

The Best Concept Books That Will Get Kids Excited to Learn
A while ago, my kids and I spent months putting together a list of the best books for 2-year-olds , and parents message me every week to express gratitude for that list. But since then, I’ve been getting lots of follow-up questions from parents on one section from that list in particular: What other learning books for toddlers and preschoolers do you recommend?
Then not too long ago, I was excited to hear from the awesome folks at Candlewick Press because not only did they want to share a copy of This Is a Book of Shapes for the purposes of an honest review, but they also offered to sponsor a whole post about the best concept books for children. And so my family set out on a months-long research project to find fun concept books that both kids and parents will enjoy. (Because if kids are going to ask us to read it again and again, it may as well be something we’ll get a kick out of, too!)
To be clear, all opinions expressed in this post are my own, and I was not required or influenced to give anything but an honest appraisal. I have high standards for children’s books, and I recommend only books I’ve enjoyed with my own family.
What Makes This List of Children’s Concept Books Different
Over the years, we’d already read tons of concept books, but we wanted to do a thorough review to uncover all the best concept books. So every week, I put 30+ books on hold at the library, plus at every visit I browsed the shelves for even more concept books. All told, my kids and I read hundreds of children’s concept books to prepare this list.
The list below is the cream of the crop from those hundreds of concept books: the books I loved reading, and the books my kids couldn’t get enough of. Read these concept books with your child, and you’ll infuse the learning experience with a major dose of fun.
Note: indicates my family’s absolute top favorites on the list. These are the books my kids absolutely can’t get enough of!

Counting Books for Kids
One large category of concept books involves counting and numbers because number sense is a precursor to later math skills. But in order for the knowledge to sink in with your child, it’s important to have a book you both enjoy. Here are the counting books that stand out from the pack:

1. 123 Dream

Tip: Haven’t heard of Bookshop yet? It’s an online bookstore with a mission to support local, independent bookstores. As of March 2023, they’ve raised more than 25 million dollars for local bookstores! If you want to order books online while also supporting local bookstores, feel free to use the Bookshop buttons under each book recommendation in this post.

2. Ten, Nine, Eight

3. Have You Seen My Dragon?
Shape books for kids.
These books about shapes are the perfect complement to hands-on learning about shapes.

4. This Is a Book of Shapes

5. Triangle

6. Shapes by Anne Woodhull and Shelley Rotner
Alphabet books for kids.
Alphabet books pose a conundrum because toddlers and preschoolers don’t yet understand the concept of first letter. In other words, when young kids see a picture of an apple next to the letter “A”, their brains don’t yet make the connection that apple starts the short “a” vowel sound, which is represented by the letter “A.” (For more on this, see “Concept Books and Young Children” in Ways of Knowing: Literature and the Intellectual Life of Children .)
Experts say most kids start making sound-letter associations around age 4 or even age 5 . So when sharing alphabet books with young kids, don’t stress if your child doesn’t seem to be picking up on first letter sounds quite yet. For young kids, it’s more valuable to talk about the objects they’re seeing to grow their understanding of the world and with it, their vocabulary.

7. ABC Dream

8. Eating the Alphabet: Fruits and Vegetables from A to Z

9. Creature ABC
Books about colors.
When it comes to concept books, books about colors abound. But here are the books about colors you and your child will actually want to come back to again and again:

10. Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See?
11. My Favorite Color

12. Mouse Paint
Books about opposites.
These books about opposites create fun opportunities for building your child’s vocabulary while also helping them to understand how objects and ideas relate to each other.

13. Hippopposites

14. Hello Hello

15. Yummy Yucky
Concept books that cover multiple concepts.
If you’re looking for a book that will cover a few areas of knowledge at the same time, you can’t go wrong with these children’s concept books.

16. Technicolor Treasure Hunt

17. Perfect Square

18. Numbers Colors Shapes
Bonus more concept books for kids.
These concept books don’t fall into the traditional categories like alphabet or counting, but they still introduce kids to important ideas and concepts. Plus, they’re fun to share with your child!

19. Actual Size

20. Somewhere In the World Right Now
Before you go, get my free cheat sheet: 75 positive phrases every child needs to hear.
What are your favorite concept books for children? Share in a comment below!
I'm a mom of four, a Certified Parent Educator, and the author of Happy You, Happy Family . I believe if you want a loving parent-child relationship that will last into the teenage years and beyond, the time for nurturing that kind of relationship is now . The good news? All you need is 10 minutes a day. Start here »
Note: All information on this site is for educational purposes only. Happy You, Happy Family does not provide medical advice. If you suspect medical problems or need professional advice, please consult a physician.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This post is brilliant and so helpful! Thank you!! I have a few preschoolers that I am working with each week and we are learning about weather. Oh Say Can You Say what’s the Weather Today is great, but is a bit over their heads. They liked Miss Maisy’s Wonderful Weather but were more interested in the Pop Ups than the info. :) I am still looking.
For weather, how about Boom Boom by Sarvinder Naberhaus and Margaret Chodos-Irvine?
What a nice round-up! Some old favorites and many new books to check out! Thank you!

You can nurture a warm + loving relationship with your child—in just 10 minutes a day.
I’m Kelly—a mom of four, a Certified Parent Educator, and an author.
If you want to nurture a loving parent-child relationship that will last into the teenage years and beyond, the time for nurturing that kind of relationship is now .
I believe with a few small tweaks, you can build a home your kids will want to come home to—without having to sacrifice your own personal needs.
Before you go, get my FREE cheat sheet: 75 Positive Phrases Every Child Needs to Hear
Enter your email + click the button below. You’ll join my weekly-ish newsletter, plus get the free printable as a bonus!
This form collects information I will use to send you free printables and other resources. I promise to keep your personal information safe. You can unsubscribe at any time. See my privacy policy .
Enter your email + click the button.
You'll join my newsletter, plus get the free printable as a bonus!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
In this textbook you will be exposed to many terms and concepts associated with research methods, particularly as they relate to the research planning decisions you must make along the way. Figure 1.1 will help you contextualize many of these terms and understand the research process. This general chart begins with two key concepts: ontology and epistemology, advances through other concepts, and concludes with three research methodological approaches: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods.
Research does not end with making decisions about the type of methods you will use; we could argue that the work is just beginning at this point. Figure 1.3 does not represent an all-encompassing list of concepts and terms related to research methods. Keep in mind that each strategy has its own data collection and analysis approaches associated with the various methodological approaches you choose. Figure 1.1 is intentioned to provide a general overview of the research concept. You may want to keep this figure handy as you read through the various chapters.
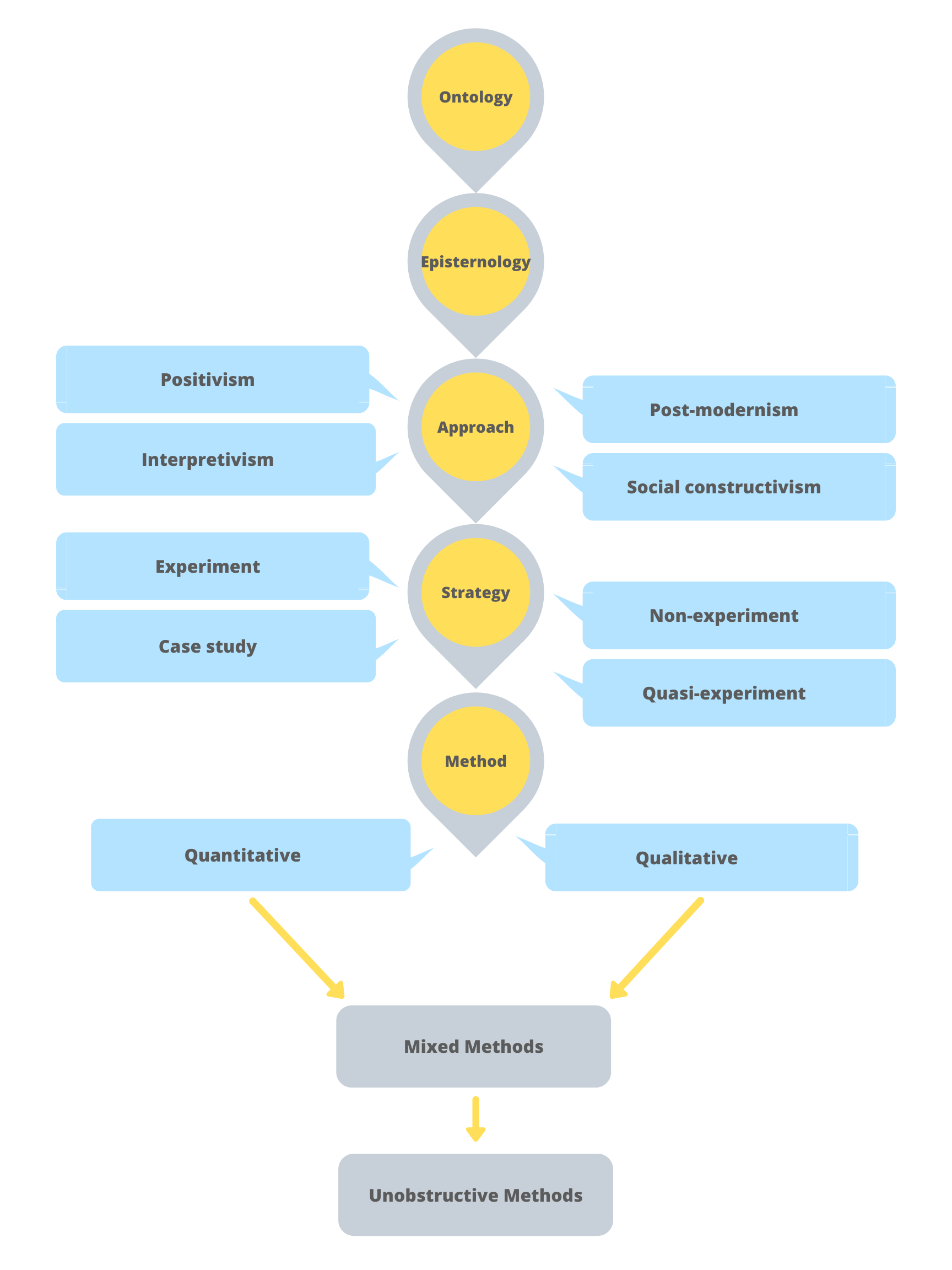
Figure 1.3: Shows the research paradigms and research process © JIBC 2019
Ontology & Epistemology
Thinking about what you know and how you know what you know involves questions of ontology and epistemology. Perhaps you have heard these concepts before in a philosophy class? These concepts are relevant to the work of sociologists as well. As sociologists (those who undertake socially-focused research), we want to understand some aspect of our social world. Usually, we are not starting with zero knowledge. In fact, we usually start with some understanding of three concepts: 1) what is; 2) what can be known about what is; and, 3) what the best mechanism happens to be for learning about what is (Saylor Academy, 2012). In the following sections, we will define these concepts and provide an example of the terms, ontology and epistemology.
Ontology is a Greek word that means the study, theory, or science of being. Ontology is concerned with the what is or the nature of reality (Saunders, Lewis, & Thornhill, 2009). It can involve some very large and difficult to answer questions, such as:
- What is the purpose of life?
- What, if anything, exists beyond our universe?
- What categories does it belong to?
- Is there such a thing as objective reality?
- What does the verb “to be” mean?
Ontology is comprised of two aspects: objectivism and subjectivism. Objectivism means that social entities exist externally to the social actors who are concerned with their existence. Subjectivism means that social phenomena are created from the perceptions and actions of the social actors who are concerned with their existence (Saunders, et al., 2009). Figure 1.2 provides an example of a similar research project to be undertaken by two different students. While the projects being proposed by the students are similar, they each have different research questions. Read the scenario and then answer the questions that follow.
Subjectivist and objectivist approaches (adapted from Saunders et al., 2009)
Ana is an Emergency & Security Management Studies (ESMS) student at a local college. She is just beginning her capstone research project and she plans to do research at the City of Vancouver. Her research question is: What is the role of City of Vancouver managers in the Emergency Management Department (EMD) in enabling positive community relationships? She will be collecting data related to the roles and duties of managers in enabling positive community relationships.
Robert is also an ESMS student at the same college. He, too, will be undertaking his research at the City of Vancouver. His research question is: What is the effect of the City of Vancouver’s corporate culture in enabling EMD managers to develop a positive relationship with the local community? He will be collecting data related to perceptions of corporate culture and its effect on enabling positive community-emergency management department relationships.
Before the students begin collecting data, they learn that six months ago, the long-time emergency department manager and assistance manager both retired. They have been replaced by two senior staff managers who have Bachelor’s degrees in Emergency Services Management. These new managers are considered more up-to-date and knowledgeable on emergency services management, given their specialized academic training and practical on-the-job work experience in this department. The new managers have essentially the same job duties and operate under the same procedures as the managers they replaced. When Ana and Robert approach the managers to ask them to participate in their separate studies, the new managers state that they are just new on the job and probably cannot answer the research questions; they decline to participate. Ana and Robert are worried that they will need to start all over again with a new research project. They return to their supervisors to get their opinions on what they should do.
Before reading about their supervisors’ responses, answer the following questions:
- Is Ana’s research question indicative of an objectivist or a subjectivist approach?
- Is Robert’s research question indicative of an objectivist or a subjectivist approach?
- Given your answer in question 1, which managers could Ana interview (new, old, or both) for her research study? Why?
- Given your answer in question 2, which managers could Robert interview (new, old, or both) for his research study? Why?
Ana’s supervisor tells her that her research question is set up for an objectivist approach. Her supervisor tells her that in her study the social entity (the City) exists in reality external to the social actors (the managers), i.e., there is a formal management structure at the City that has largely remained unchanged since the old managers left and the new ones started. The procedures remain the same regardless of whoever occupies those positions. As such, Ana, using an objectivist approach, could state that the new managers have job descriptions which describe their duties and that they are a part of a formal structure with a hierarchy of people reporting to them and to whom they report. She could further state that this hierarchy, which is unique to this organization, also resembles hierarchies found in other similar organizations. As such, she can argue that the new managers will be able to speak about the role they play in enabling positive community relationships. Their answers would likely be no different than those of the old managers, because the management structure and the procedures remain the same. Therefore, she could go back to the new managers and ask them to participate in her research study.
Robert’s supervisor tells him that his research is set up for a subjectivist approach. In his study, the social phenomena (the effect of corporate culture on the relationship with the community) is created from the perceptions and consequent actions of the social actors (the managers); i.e., the corporate culture at the City continually influences the process of social interaction, and these interactions influence perceptions of the relationship with the community. The relationship is in a constant state of revision. As such, Robert, using a subjectivist approach, could state that the new managers may have had few interactions with the community members to date and therefore may not be fully cognizant of how the corporate culture affects the department’s relationship with the community. While it would be important to get the new managers’ perceptions, he would also need to speak with the previous managers to get their perceptions from the time they were employed in their positions. This is because the community-department relationship is in a state of constant revision, which is influenced by the various managers’ perceptions of the corporate culture and its effect on their ability to form positive community relationships. Therefore, he could go back to the current managers and ask them to participate in his study, and also ask that the department please contact the previous managers to see if they would be willing to participate in his study.
As you can see the research question of each study guides the decision as to whether the researcher should take a subjective or an objective ontological approach. This decision, in turn, guides their approach to the research study, including whom they should interview.
Epistemology
Epistemology has to do with knowledge. Rather than dealing with questions about what is, epistemology deals with questions of how we know what is. In sociology, there are many ways to uncover knowledge. We might interview people to understand public opinion about a topic, or perhaps observe them in their natural environment. We could avoid face-to-face interaction altogether by mailing people surveys to complete on their own or by reading people’s opinions in newspaper editorials. Each method of data collection comes with its own set of epistemological assumptions about how to find things out (Saylor Academy, 2012). There are two main subsections of epistemology: positivist and interpretivist philosophies. We will examine these philosophies or paradigms in the following sections.
Research Methods, Data Collection and Ethics Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

High School Students Thrive as Researchers
Authentic exploratory research hones students’ investigation and analysis skills..
Posted April 1, 2024 | Reviewed by Monica Vilhauer
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist

This post is Part I in a series.
I got to speak with students at Laguna Beach High School (LBHS) recently when giving a career talk there. They kept asking me advanced questions about conducting studies, writing, and science, and they spoke with passion about their own research projects. I was taken aback by how much these high school teens sounded like my adult college students and peers. They kept mentioning “AER”, and I had to learn more.
LBHS’s Authentic Exploratory Research (AER) Program is an independent research course inspired by Palo Alto Unified School District’s Advanced Authentic Research Program. In AER, students are paired with adult mentors (such as LBUSD staff, industry experts, and academics) who assist the teens in researching their own big questions in fields of their choice. Students spend about 60 hours per semester on coursework that includes both instruction and working on each project itself.
No such courses were offered at LBHS when I graduated there back in 1990, and I wonder how much sooner I could have enjoyed my career as a researcher if I had gotten to participate in AER as a youth. Though the program was introduced in 2019 by Laguna Beach Unified School District (LBUSD) Superintendent Jason Viloria, Ed.D., Jun Shen is the passionate teacher and edtech coordinator who runs it. I had the pleasure of partnering with Shen for an interview series where we’ll first explore how AER works before hearing from students about their experiences with AER honing skills for future success. Students’ feedback (in interviews to follow) and Shen’s answers (which follow each question below) can help others implement such a program.
Jenny Grant Rankin: What were the biggest challenges to implementing a successful AER program, and how did you tackle them?
Jun Shen: The biggest ongoing challenge is to find the balance between respecting the students’ individual freedom in their projects on one hand, and on the other, closely managing the students so they’d make adequate progress. Tackling this is an iterative process. Through the last four years, I have tried many different methods like online journaling, different grading rubrics and requirements, different communication protocols, and it seems to be steadily getting better.
JGR: When pairing students with adult mentors, how do you find and secure mentors who are appropriate for students' different interests?
JS: We have a dedicated Mentor Coordinator for AER, at first the ASB Director Jennifer Lundblad, then our District’s Career Education Coordinator Kellee Shearer. After students register for AER in March, we interview them in April and May to get a good feel for their field of interest, and Kellee spends the summer finding them mentors.
JGR: When speaking to your students about AER, I was impressed by the sophistication with which they discussed their studies. What was the most powerful strategy you used to help high schoolers understand research concepts that are hard for even college students to grasp?
JS: Most AER students are definitely wise beyond their years but I can’t claim credit for this one. It’s definitely a team effort, with a splash of selection bias thrown in. Most (though not all) students who take on the challenge of AER are already high-performing and highly-motivated students; thus, they’ve already learned a lot of the research and analysis skills in some of their other upper-level classes. In addition to that, we have a full-time Library Media Specialist, first Stephanie Gamache then Glen Warren, who works with the students to help them find what they need. Their mentor is another obviously valuable asset. As for me, I do very little whole-group, one-size-fits-all instruction about research and data analysis. Most of the students’ research methodologies are created individually with my advice.
JGR: What can you tell educators who are nervous about giving students so much independence and freedom in a course?
JS: First, be curious. If you love learning new things, then you’ll have a great time with your students as you explore some obscure topics together. The more you communicate that you’re personally invested in their study, the harder they will work with you. Second, it won’t be perfect your first year and that’s OK. Looking back, my first year running AER was rather lackluster, with a sizable portion of students dropping out or barely finishing their projects. Every year we learn our lessons and improve the course for the following year. Third, don’t reinvent the wheel. We based our program on Palo Alto USD’s program and, year after year, have modified it to suit our culture and needs. Start with their or our curriculum and see where it leads you.
JGR: What else should readers know about AER?
JS: It’s one of the highlights of my career. I’ve always been that kid who watched as many Discovery Channel Documentaries as I could because I loved learning about everything. I never thought that I’d get to geek out with kids about Aerospace Engineering and Fashion Design in a high school teaching job!
I’ve always been that kid, too. It’s heartwarming to learn how AER can be as rewarding for staff as it is for students, who we’ll hear from next. To continue reading, look for Part II.

Jenny Grant Rankin, Ph.D., is a Fulbright Specialist for the U.S. Department of State.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Strategic Concepts That Set High-Performing Companies Apart
- Kaihan Krippendorff

Lessons from Microsoft, NVIDIA, Netflix, Tesla, and others.
Strategic concepts come in and out of fashion as the needs and dynamics of the marketplace change. Research and analysis of today’s landscape identifies six key strategic concepts that set outperforming companies apart: Borrow someone’s road, partner with a third party, reveal your strategy, be good, let the competition go, and adopt small scale attacks.
At the close of 2023, the California-based chip company Nvidia announced yet another quarter of record sales — an achievement that came hot on the heels of its entry to the elite club of U.S. enterprises with a $1 trillion market valuation earlier in the year. The company, whose success has been fueled by the AI boom, now holds approximately 80% of the global market share for GPU semiconductor chips .
- Kaihan Krippendorff is the co-author, with Robert C. Wolcott, of Proximity: How Coming Breakthroughs in Just-in-Time Transform Business, Society, and Daily Life and founder of Outthinker Networks .
Partner Center
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A New Chapter for Irish Historians’ ‘Saddest Book’
A globe-spanning research project has turned the catalog of a public archive destroyed in Ireland’s civil war into a model for reconstruction.

By Ed O’Loughlin
Reporting from Dublin
In the first pitched battle of the civil war that shaped a newly independent Ireland, seven centuries of history burned.
On June 30, 1922, forces for and against an accommodation with Britain, Ireland’s former colonial ruler, had been fighting for three days around Dublin’s main court complex. The national Public Record Office was part of the complex, and that day it was caught in a colossal explosion . The blast and the resulting fire destroyed state secrets, church records, property deeds, tax receipts, legal documents, financial data, census returns and much more, dating back to the Middle Ages.
“It was a catastrophe,” said Peter Crooks, a medieval historian at Trinity College Dublin. “This happened just after the First World War, when all over Europe new states like Ireland were emerging from old empires. They were all trying to recover and celebrate their own histories and cultures, and now Ireland had just lost the heart of its own.”
But perhaps it was not lost forever. Over the past seven years, a team of historians, librarians and computer experts based at Trinity has located duplicates for a quarter of a million pages of these lost records in forgotten volumes housed at far-flung libraries and archives, including several in the United States. The team then creates digital copies of any documents that it finds for inclusion in the Virtual Record Treasury of Ireland , an online reconstruction of the archive. Still a work in progress, the project says its website has had more than two million visits in less than two years.
Funded by the Irish government as part of its commemorations of a century of independence, the Virtual Treasury relies in part on modern technologies — virtual imaging, online networks, artificial intelligence language models and the growing digital indexes of archives around the world — but also on dusty printed catalogs and old-school human contacts. Key to the enterprise has been a book, “A Guide to the Records Deposited in the Public Record Office of Ireland,” published three years before the fire by the office’s head archivist, Herbert Wood.
“For a long time, Wood’s catalog was known to Irish historians as the saddest book in the world, because it only showed what was lost in the fire,” Dr. Crooks said. “But now it has become the basis for our model to recreate the national archive. There were 4,500 series of records listed in Wood’s book, and we went out to look for as many of them as we could find.”
A major partner in this hunt was the National Archives in Britain, to which centuries of Irish government records — notably tax receipts — had been sent in duplicate. The Public Record Office of Northern Ireland, which remains part of the United Kingdom, has also been a major partner, contributing records from the centuries before Ireland was partitioned in 1921.
A considerable haul of documents has also been uncovered in the United States. The Library of Congress, for example, dug up dozens of volumes of lost debates from Ireland’s 18th-century Parliament. According to David Brown, who leads the Virtual Treasury’s trawl through domestic and overseas archives, before this trove of political history came into Congress’s possession, one previous owner had tried to sell it as fuel. Serendipity has often played a role in such U.S. discoveries, he said.
“You would have old family records stored away in some gentleman’s library, and he’d move to the colonies, and take the books with him,” Dr. Brown said. “Or else heirs would eventually sell the old library off to collectors, and eventually an American university or library might buy the collection, maybe because they wanted something important in it, and they took everything else that came with it. Archivists may not always know what they have, but they never throw anything out.”
The Huntington Library in California, and libraries of the universities of Kansas, Chicago, Notre Dame, Yale and Harvard are among around a dozen U.S. organizations to respond positively to the hopeful request from the Irish: “Do you have anything there that might be of interest to us?” And in the process of hunting down material that is already on its radar, the Virtual Treasury team is also uncovering, and incorporating, unexpected treasures.
One is a previously unnoticed 1595 letter shown to Dr. Brown late last year while he was visiting Yale’s Lewis Walpole Library to view some other material. In it, Sir Ralph Lane — a founder and survivor of the infamous lost colony of Roanoke, off North Carolina, which had vanished in the decade before this letter was written — petitions Queen Elizabeth I to order the conquest of Ulster, then a Gaelic stronghold in the north of English-ruled Ireland.
Dr. Brown, a specialist in early modern Atlantic history, said the letter — long overlooked because it was bound in a volume with much later documents — showed the close connection between England’s colonial conquests in North America and Ireland, both in the personalities involved and their motivation. The letter suggests conquering Ulster primarily so that the English could seize the inhabitants’ land, and it proposes paying for the war by looting the Ulster chiefs’ cattle. The area was ultimately conquered and colonized in 1609, six years after Lane’s death.
“For the Elizabethan adventurers, colonialism was a branch of piracy. All they wanted was land,” Dr. Brown said. “Roanoke hadn’t worked out for Lane, and Elizabeth had just granted Sir Walter Raleigh 10,000 acres of land in Munster,” in the south of Ireland. “So Lane thought, if Raleigh got 10,000 acres in Munster, why can’t I have 10,000 acres in Ulster?”
Another contribution to the project could be seen in contemporary Northern Ireland, at the Public Record Office in Belfast. The head of conservation, Sarah Graham, was restoring and preserving a collection of records and letters kept by Archbishop John Swayne, who led the church in Ireland in the 15th century. Watching her at work was Lynn Kilgallon, research fellow in medieval history for the Virtual Treasury. Once preserved, its pages will be digitized and added to Dublin’s online archive.
“If you don’t understand the words in a book, it becomes just an object,” Ms. Graham said. “You need someone to read it — medievalists like Lynn here, to bring it to life.”
You do not necessarily need to be a specialist to read the documents in the Virtual Treasury, however. New artificial intelligence models developed for the project allow archivists to turn ancient handwriting into searchable digital text, with modern translations.
The site went online in June 2022, the 100th anniversary of the records office fire, and is aiming for 100 million searchable words by 2025, a target it says it is three-quarters of the way to reaching. Eventually, it hopes to recover 50 to 90 percent of records from some priority areas, such as censuses from before and after Ireland’s Great Famine in the mid-19th century, which are of particular value to historians, and to people of Irish descent tracing their roots. More than half of the details of the first nationwide census of Ireland, a religious head count in 1766, have been retrieved and published.
“Cultural loss is sadly a very prominent theme in the world right now, and I don’t think there is an example like this, where there’s been so much international cooperation in the reconstruction of a lost archive,” Dr. Crooks said. “It shows that the collective culture of many countries can be brought together to achieve a goal. Borders are fluid.”
Chemical Science
Robust vibrational coherence protected by core-shell structure in silver nanoclusters.
Vibrational coherence has attracted considerable research interests because of its potential functions in light harvesting systems. Although the positive sign of vibrational coherence in metal nanoclusters has been observed, the underlying mechanism remains to be verified. Here, we demonstrate that robust vibrational coherence with a lifetime of 1 ps can be clearly identified in Ag44(SR)30 core-shell nanoclusters, in which an icosahedral Ag12 core is well protected by a dodecahedral Ag20 cage. Ultrafast spectroscopy reveals that two vibrational modes around 2.4 THz and 1.6 THz, corresponding the breathing mode and the quadrupolar-like mode of the icosahedral Ag12 core, respectively, are responsible to the generation of vibrational coherence. Besides, the vibrational coherence of Ag44 has an additional high frequency mode (2.4 THz) compared with that of Ag29, in which there is only one low frequency vibration mode (1.6 THz). And the relatively faster dephasing in two-layer Ag29 relative to that in Ag44 further supports the robust vibrational coherence in Ag44 is ascribed to its unique matryoshka-like core-shell structure.. Our findings not only present unambiguous experimental evidence for multi-layer core-shell structure protected vibrational coherence under ambient conditions bus also offer a practical strategy for the design of highly efficient quantum optoelectronic devices.
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (2015K)
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
J. Kong, Z. Kuang, W. Zhang, Y. Song, G. Yao, C. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. Luo and M. Zhou, Chem. Sci. , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D4SC00009A
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication , please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This book is designed to introduce doctoral and postgraduate students to the process of conducting scientific research in the social sciences, business, education, public health, and related disciplines. It is a one-stop, comprehensive, and compact source for foundational concepts in behavioural research, and can serve as a standalone text or as a supplement to research readings in any ...
Abstract. A perennial bestseller since 1997, this updated tenth edition of Understanding Research Methods provides a detailed overview of all the important concepts traditionally covered in a ...
ences between them is found in the basic philosophical assumptions research - ers bring to the study, the types of research strategies used in the research (e.g., quantitative experiments or qualitative case studies), and the specific methods employed in conducting these strategies (e.g., collecting data quantitatively
Basic understanding of research methods is needed to understand and interpret statistical . results. This chapter is a brief, nontechnical introduction to selected research methods terms mentioned in the GAISE (GAISE College Report ASA Revision Committee, 2016) numeracy guidelines in Chapter 1. The . design
This textbook provides students with an understanding of the concepts and techniques of qualitative and quantitative research, grants for research, report writing, data collection etc. It uses ...
INTRODUCTION; Chapter 1: Critical Research Literacy PHILOSOPHICAL AND THEORETICAL ASPECTS OF RESEARCH; Chapter 2: Research Methodologies Chapter 3: Conceptual Frameworks, Theories, and Models ORIENTING AND SUPPORTIVE ELEMENTS OF RESEARCH; Chapter 4: Orienting and Supportive Elements of a Journal Article Chapter 5: Peer-Reviewed Journals RESEARCH JUSTIFICATIONS, AUGMENTATION, AND RATIONALES
Social constructivism. World view. With thematic further reading stretching across the social sciences, Research Methods: The Key Concepts will help readers develop a firm understanding of the rationale and principles behind key research methods, and is a must-have for new researchers at all levels, from undergraduate to postgraduate and beyond.
Research Methods: Concepts and Connections. $201.99. (6) This title has not yet been released. With over two decades of classroom experience, Michael Passer knows how to guide students through the ins and outs of research methods in ways they can actually understand and put into practice. In this remarkable text, Passer's experience leads to ...
This book provides an overview of ninety key concepts which often trouble those who are new to researching within the social sciences. It covers theories of knowledge, methodologies and methods. Each entry offers a definition of a concept, shows how researchers have used that concept in their research and discusses difficulties that the concept presents.
His highly anticipated new book, Research Concepts and Connections, offers students clear and compelling explanations and examples drawn from cutting-edge research from across the subfields of psychology. Readers come away with an unparalleled understanding of behavioral research practice in today's world and how those skills apply to ...
Variety of Qualitative Research Methods is concise, just enough, and just in time. This book uncovers concepts and methods used internationally, and also demonstrates different ways of knowing and world views with integrity, rigor, and relevance. The topics are not explored in a significant depth but work as signposts with provision of relevant ...
It also would be helpful to have bolded terms and concepts in a central list in the book for easy reference. In Section 1.4 (pg. 8), it's not clear by Books whether the authors are referring to scholarly books or all books. Section 3.3 covering nesting and Boolean operators was complex compared to the rest of the text.
Chapter 1: Setting the scene in educational research. Chapter 2: Designing and managing your research in education in the early stages. Chapter 3: Designing your research in education. Chapter 4: Constructing knowledge through social research: Debates in epistemology and ontology. Chapter 5: Ethical issues and considerations.
1. FOREWORD. Fundamental of Research Methodology and Data Collection is an excellent book tha t has a. collection of basic concepts and terminologies in research method. It is filled with good ...
Research Methods. Concepts and ConnectionsThird Edition|©2021Michael Passer. With over two decades of classroom experience, Michael Passer knows how to guide students through the ins and outs of research methods. In this remarkable text, Passer's experience leads to chapters filled with clear explanations, resonant examples, and contemporary ...
The book addresses the specific needs of the students, research scholars & managers by successfully blending concepts of research with its literal applications. The key strengths of this book ...
Figure 1.1 is a general chart that will help you contextualize many of these terms and also understand the research process. As you can see, Figure 1.1 begins with two key concepts: ontology and epistemology, advances through other concepts and concludes with three research methodological approaches: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods ...
Figure 1.3 does not represent an all-encompassing list of concepts and terms related to research methods. Keep in mind that each strategy has its own data collection and analysis approaches associated with the various methodological approaches you choose. Figure 1.1 is intentioned to provide a general overview of the research concept.
This book helps to bridge the gap between the complex world of data analysis with the ever-changing dynamics of education leadership. In Research Concepts for the Practitioner of Educational Leadership, the author acquaints the reader with principles of educational research that are most applicable to today's educational leaders.
If purchased from FlatWorld, the publisher, this version includes Online Access, Homework and a Print copy via a redeemable code shipped with the print book. Research Core Concepts and Skills for Psychology focuses on the concepts and skills that are most widely shared within the discipline, while emphasizing both their centrality to the field ...
These books about opposites create fun opportunities for building your child's vocabulary while also helping them to understand how objects and ideas relate to each other. 13. Hippopposites. This book takes a playful approach to teaching opposites, which is the best way for your child to learn.
This general chart begins with two key concepts: ontology and epistemology, advances through other concepts, and concludes with three research methodological approaches: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods. Research does not end with making decisions about the type of methods you will use; we could argue that the work is just beginning ...
understanding the basic concepts before they read any book on research methodology. This book is useful those students who offer the Research Methodology at Post Graduation and M.Phil. Level. ... products, new facts, new concepts and new ways of doing things are being found due to ever-increasing significant research in the physical, the ...
LBHS's Authentic Exploratory Research (AER) Program is an independent research course inspired by Palo Alto Unified School District's Advanced Authentic Research Program. In AER, students are ...
Abstract. Academic research is a relatively simple process when a PhD student knows the methodologies, methods and tools that underpin it. Although it is assumed that students holding a master's ...
Research and analysis of today's landscape identifies six key strategic concepts that set outperforming companies apart: Borrow someone's road, partner with a third party, reveal your strategy ...
In January, SRI began to disclose its plans for PARC, describing a combined nonprofit research organization, called the Future Concepts division, intent on reclaiming some of the original wizardry ...
A globe-spanning research project has turned the catalog of a public archive destroyed in Ireland's civil war into a model for reconstruction. By Ed O'Loughlin Reporting from Dublin In the ...
For the first time, scientists have built a fusion experiment known as a stellarator using permanent magnets, a technique that could show a simple way to build future devices for less cost and allow researchers to test new concepts for future fusion power plants. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Labor...
Vibrational coherence has attracted considerable research interests because of its potential functions in light harvesting systems. Although the positive sign of vibrational coherence in metal nanoclusters has been observed, the underlying mechanism remains to be verified. Here, we demonstrate that robust vi