share this!
August 16, 2021

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Using CO₂ and biomass, researchers find path to more environmentally friendly recyclable plastics
9 hours ago

Precision agriculture research identifies gene that controls production of flowers and fruits in pea plants

Long-term forest study shows tornado's effects linger 25 years later
10 hours ago
A new coating method in mRNA engineering points the way to advanced therapies

ATLAS provides first measurement of the W-boson width at the LHC
11 hours ago
Smart vest turns fish into underwater spies, providing a glimpse into aquatic life like never before

Ants in Colorado are on the move due to climate change

Caterpillar 'noses' are surprisingly sophisticated, researchers find

Building footprints could help identify neighborhood sociodemographic traits
12 hours ago
Fossilized dinosaur eggshells can preserve amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, over millions of years
13 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Motivating high school physics students with popcorn physics.
Apr 3, 2024
How is Physics taught without Calculus?
Mar 29, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
The New California Math Framework: Another Step Backwards?
Mar 14, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024

Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published, study finds
Mar 23, 2024

Using Twitter/X to promote research findings found to have little impact on number of citations
Mar 22, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- NICU Sims Set Stage for Lifesaving Care
- How a Social Media Post Led a Teen to Find a ‘Kidney Buddy’ for Life
- Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder in Young Children
- New Liver Gives a Toddler a Renewed Chance at Life
- Family Turns Newborn’s Rare Diagnosis Into Something Beautiful

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford Medicine
- Stanford University
- Stanford Health Care

Homework Struggles May Not Be a Behavior Problem
Exploring some options to understand and help..
Posted August 2, 2022 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework.
- Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation of a behavior problem—is key.
- Sleep and mental health needs can take priority over homework completion.
Chelsea was in 10th grade the first time I told her directly to stop doing her homework and get some sleep. I had been working with her since she was in middle school, treating her anxiety disorder. She deeply feared disappointing anyone—especially her teachers—and spent hours trying to finish homework perfectly. The more tired and anxious she got, the harder it got for her to finish the assignments.

One night Chelsea called me in despair, feeling hopeless. She was exhausted and couldn’t think straight. She felt like a failure and that she was a burden to everyone because she couldn’t finish her homework.
She was shocked when I told her that my prescription for her was to go to sleep now—not to figure out how to finish her work. I told her to leave her homework incomplete and go to sleep. We briefly discussed how we would figure it out the next day, with her mom and her teachers. At that moment, it clicked for her that it was futile to keep working—because nothing was getting done.
This was an inflection point for her awareness of when she was emotionally over-cooked and when she needed to stop and take a break or get some sleep. We repeated versions of this phone call several times over the course of her high school and college years, but she got much better at being able to do this for herself most of the time.
When Mental Health Symptoms Interfere with Homework
Kids with mental health or neurodevelopmental challenges often struggle mightily with homework. Challenges can come up in every step of the homework process, including, but not limited to:
- Remembering and tracking assignments and materials
- Getting the mental energy/organization to start homework
- Filtering distractions enough to persist with assignments
- Understanding unspoken or implied parts of the homework
- Remembering to bring finished homework to class
- Being in class long enough to know the material
- Tolerating the fear of not knowing or failing
- Not giving up the assignment because of a panic attack
- Tolerating frustration—such as not understanding—without emotional dysregulation
- Being able to ask for help—from a peer or a teacher and not being afraid to reach out
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD , autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety , generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression , dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and mental health challenges cause numerous learning differences and symptoms that can specifically and frequently interfere with getting homework done.

The Usual Diagnosis for Homework Problems is "Not Trying Hard Enough"
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their homework. That is the default “diagnosis” in classrooms and living rooms. And once this framework is drawn, the student is often seen as not trying hard enough, disrespectful, manipulative, or just plain lazy.
The fundamental disconnect here is that the diagnosis of homework struggles as a behavioral choice is, in fact, only one explanation, while there are so many other diagnoses and differences that impair children's ability to consistently do their homework. If we are trying to create solutions based on only one understanding of the problem, the solutions will not work. More devastatingly, the wrong solutions can worsen the child’s mental health and their long-term engagement with school and learning.
To be clear, we aren’t talking about children who sometimes struggle with or skip homework—kids who can change and adapt their behaviors and patterns in response to the outcomes of that struggle. For this discussion, we are talking about children with mental health and/or neurodevelopmental symptoms and challenges that create chronic difficulties with meeting homework demands.
How Can You Help a Child Who Struggles with Homework?
How can you help your child who is struggling to meet homework demands because of their ADHD, depression, anxiety, OCD , school avoidance, or any other neurodevelopmental or mental health differences? Let’s break this down into two broad areas—things you can do at home, and things you can do in communication with the school.

Helping at Home
The following suggestions for managing school demands at home can feel counterintuitive to parents—because we usually focus on helping our kids to complete their tasks. But mental health needs jump the line ahead of task completion. And starting at home will be key to developing an idea of what needs to change at school.
- Set an end time in the evening after which no more homework will be attempted. Kids need time to decompress and they need sleep—and pushing homework too close to or past bedtime doesn’t serve their educational needs. Even if your child hasn’t been able to approach the homework at all, even if they have avoided and argued the whole evening, it is still important for everyone to have a predictable time to shut down the whole process.
- If there are arguments almost every night about homework, if your child isn’t starting homework or finishing it, reframe it from failure into information. It’s data to put into problem-solving. We need to consider other possible explanations besides “behavioral choice” when trying to understand the problem and create effective solutions. What problems are getting in the way of our child’s meeting homework demands that their peers are meeting most of the time?
- Try not to argue about homework. If you can check your own anxiety and frustration, it can be more productive to ally with your child and be curious with them. Kids usually can’t tell you a clear “why” but maybe they can tell you how they are feeling and what they are thinking. And if your child can’t talk about it or just keeps saying “I don't know,” try not to push. Come back another time. Rushing, forcing, yelling, and threatening will predictably not help kids do homework.

Helping at School
The second area to explore when your neurodiverse child struggles frequently with homework is building communication and connections with school and teachers. Some places to focus on include the following.
- Label your child’s diagnoses and break down specific symptoms for the teachers and school team. Nonjudgmental, but specific language is essential for teachers to understand your child’s struggles. Breaking their challenges down into the problems specific to homework can help with building solutions. As your child gets older, help them identify their difficulties and communicate them to teachers.
- Let teachers and the school team know that your child’s mental health needs—including sleep—take priority over finishing homework. If your child is always struggling to complete homework and get enough sleep, or if completing homework is leading to emotional meltdowns every night, adjusting their homework demands will be more successful than continuing to push them into sleep deprivation or meltdowns.
- Request a child study team evaluation to determine if your child qualifies for services under special education law such as an IEP, or accommodations through section 504—and be sure that homework adjustments are included in any plan. Or if such a plan is already in place, be clear that modification of homework expectations needs to be part of it.
The Long-Term Story
I still work with Chelsea and she recently mentioned how those conversations so many years ago are still part of how she approaches work tasks or other demands that are spiking her anxiety when she finds herself in a vortex of distress. She stops what she is doing and prioritizes reducing her anxiety—whether it’s a break during her day or an ending to the task for the evening. She sees that this is crucial to managing her anxiety in her life and still succeeding at what she is doing.
Task completion at all costs is not a solution for kids with emotional needs. Her story (and the story of many of my patients) make this crystal clear.

Candida Fink, M.D. , is board certified in child/adolescent and general psychiatry. She practices in New York and has co-authored two books— The Ups and Downs of Raising a Bipolar Child and Bipolar Disorder for Dummies.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/72583075/GettyImages_1467004682.0.jpg)
Filed under:
- Even Better
How to make school life a little less difficult for kids
Actually useful ways to help children with homework, bullying, and mental health.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: How to make school life a little less difficult for kids
In early 2020, around the onset of Covid-19 lockdowns, Jessica Mungekar noticed her seventh grade honor student, Layla, retreat. “I knew that she felt really uncomfortable and she wanted to fall into the background,” Mungekar says. “She didn’t want to be noticed and I didn’t quite understand it.”
Meanwhile, Layla was keeping the source of her pain secret from her mother: She was being bullied and was struggling with her identity as a biracial teen in a predominantly white town. Layla feared if she told her mom about the extent of the bullying, Jessica would have called the school, making the problem even worse.
Do you have a question or idea for Even Better?
Submit it by filling out this form .
Things came to a head the summer before Layla’s first year of high school when she shared with her mom details of a traumatic event. Layla urged her mother not to make decisions on her behalf in the aftermath. Instead, Jessica went into what she calls “mama bear mode” and made demands of her daughter: Cut off contact with these friends, join these extracurricular activities, you are only allowed out of the house during these hours. Layla felt like her autonomy was being taken away.
Over the course of a few months, mother and daughter worked to repair their relationship and communication. Now, Jessica says she is sure to listen to Layla instead of immediately offering advice, validates her daughter’s feelings, and gives her freedom to express herself. For her part, Layla confides in her mother all the time, even about her dating life. Her friends often seek out Jessica for counsel, too. “She’s become a safe place where people go to get advice,” Layla, now 16, says. “She’s joyous and doesn’t pass judgment.”
Students are faced with a daily barrage of potential stressors: a demanding course load, tricky social dynamics, managing both their time and emotions. In a four-year study designed to estimate the prevalence of mental disorders in kindergarteners through 12th graders, findings showed one in six students exhibited enough symptoms to meet the criteria for one or more childhood mental disorders, such as anxiety disorders and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. According to a 2019 Pew Research Center report, 61 percent of teens said they felt a lot of pressure to get good grades. About 22 percent of 12- to 18-year-old students reported being bullied during the school year in 2019, per a National Center for Education Statistics survey . None of these statistics takes into account the toll of the pandemic, which set students back academically and had negative effects on their mental health .
Once kids leave the house, parents and other adults in their lives have little influence on their students’ school days. Unable to witness or guide children through the difficulties in and out of the classroom, parents often get piecemeal or incomplete views of how their kids spent the last hours, especially if the child is young and can’t adequately verbalize their struggles or frustrations. Signs that a student may be experiencing hardship at school include increased irritability, difficulty sleeping or lack of sleep, and changes in appetite, says Jessica Kendorski , the chair of the school psychology department and professor at the Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine. They may also say they feel sick in order to stay home, when in reality they may be stressed or anxious about school, Kendorski says.
Another indicator of a struggling child includes extreme people-pleasing, says Meredith Draughn , the school counselor at B. Everett Jordan Elementary School in Graham, NC, and the 2023 American School Counselor Association Counselor of the Year. High school students may also exhibit a “freeze” response, Draughn says. “It’s like well, that kid just doesn’t care, right? That kid’s super apathetic,” she says. “What we find when we dig into it more is they’re so overwhelmed by everything that’s happening that they just choose to do nothing because they don’t know how to address it.”
What, then, is the right way to support the students in your life? The tactics will vary based on the age of your child and the issues they’re facing. Regardless of your approach, experts say to always keep your kids in the loop of any decisions you’re making about their emotional and academic success.
Encourage growth mindset tactics for academic achievement
From homework to challenging classes, students experience a number of academic hurdles. Sometimes, they may fail a test or drop the ball on a project. While some students may criticize themselves (“I’m not smart enough”) or claim the material was too difficult, parents should promote a growth mindset : the ability to learn from setbacks, implement new processes, and improve. “You want to praise the effort and the strategies that they used,” Kendorski says. “If they fail something, you want to talk through ‘Why did you fail this? Let’s talk about what you can do to be successful next time.’”
A fixed mindset is one where people believe their skills are set in stone and they have no possibility of improving. When students in his classroom share fixed mindset sentiments like “I can’t do this,” elementary school teacher Josh Monroe is quick to amend the statement: “You can’t do this yet .” The power of yet helps students “understand that you don’t have to know it all right now — and it’s important that you don’t, that’s how you grow,” he says.
While it’s crucial to encourage a growth mindset with students who use negative self-talk, like “I’ll never learn this” or “I’m not good enough,” a fixed mindset can also backfire if you constantly tell a student “You’re so smart,” Kendorski says. “When things start to get really difficult, you might find kids that don’t want to take chances,” she says, “because they think that if I fail, I’m going to lose that ‘I’m so smart’ title.” Instead, she says, focus on accomplishments based on effort and strategies: “I’m really proud of you for organizing a study group with your friends.”
To help ensure your kids get their homework done and prepare for tests, Kendorski encourages a routine: dedicating a time and a place for schoolwork. If your student retains information more effectively if they study for a little bit each day instead of cramming, offer that as an option.
When the kid in your life asks for help with homework and you’re a little rusty on, say, algebra, don’t feel ashamed to admit you don’t know how to solve the problem, Draughn says. Monroe recommends the online educational tool Khan Academy , which features videos that guide both parents and students through all levels of educational concepts and lessons. For additional academic resources, reach out to your student’s teacher who will know about after-school tutoring sessions or extra guidance, Draughn says. “Going to teachers early and often, when help is needed, is the most crucial part of it,” she says, “because there are those programs, but they do fill up pretty quickly.”
Empower students to navigate difficult social situations with confidence
School can be a social minefield, with kids learning how to independently interact with peers and regulate their emotions. If your child shares that they’re being picked on or ostracized in school, Draughn suggests that you first validate their experience and never downplay their emotions. Ask them what level of support they want: Do they think it would be helpful to talk to a school counselor or a teacher? Or do they prefer you to reach out to the teacher directly? In Layla Mungekar’s experience, she would have opted for her mother to not interfere with her social life. “Letting them lead the way on that is important,” Draughn says. “They may say, I feel like I have the tools to handle this — and that’s great. Then you check in. But doing nothing and just not mentioning it again is not going to help anything.”
You might also start counseling your kid on self-advocacy and assertiveness at home, too, Draughn says, helping them identify moments where they should speak out against bad behavior and pointing out trustworthy adults to whom they can report issues, regardless of whether they are on the receiving end or have witnessed another student being bullied. “If someone is making you feel socially or physically unsafe, that’s the time to speak up,” says Tracee Perryman , the author of Elevating Futures: A Model For Empowering Black Elementary Student Success . Again, only reach out to the school yourself after talking it over with your kid.
However, your child may simply be shy and reserved, not the victim of bullying. Perryman says to help build confidence with the kids in your life by reminding them that what they have to say is important and they have valuable interests and insights worth sharing with others.
When it comes to social media, Jessica Mungekar discovered teens will “do what they’re going to do, whether you want them to or not,” she says. It’s better to listen if your child is involved with social media-related conflict, remind them they are not in trouble, and support them as you work to create a plan together. “I think it’s important in this day and age for kids to have social media because otherwise they get [alienated] by their peers,” Layla Mungekar says. “But it’s a lot safer when parents have those conversations, like yeah, this is going to happen and when it does happen, you should feel safe to come to me and not be blamed for that.”
Experts emphasize the transitory nature of school. While it’s crucial for students to apply themselves academically and make strides socially, remind them that one speed bump, fight with a friend, blunder, or bad grade will not drastically alter the trajectory of their lives. “It’s better that I make those mistakes now,” Layla says, “while I have someone there to help me.”
Promote balance to minimize stress
Just like adults, kids can get stressed due to the demands of school and extracurriculars, as well as conflicts with friends and family. If kids are sleeping very late on weekends or too tired to do activities they typically enjoy, like spending time with friends, they might need more balance in their schedules, Perryman says.
Ask your kid directly: “Are you playing T-ball three nights a week because you like it or you feel like you have to?” or “You had three extracurriculars last semester and it was really overwhelming for you. Do you want to pick two for this coming semester?” Draughn suggests. Remind your kid that just because they step away from a hobby now doesn’t mean they can’t come back to it in the future. Make sure students have one weeknight and one weekend day solely devoted to downtime, too, Draughn says. However, don’t discount the fact that sports and other activities can be rejuvenating for kids, even if they’re not resting.
Parents and supportive adults are quick to problem-solve for the kids in their lives, but Kendorski stresses the importance of asking, “Do you want me to listen? Or do you want me to help?” Your child might just want to vent about a tough baseball practice. When Layla wants validation and a hug from her mom, she asks her “to be a waterfall.” When she’s feeling less emotionally charged, then Layla and her mom can problem-solve.
For high-achieving students who may be stressed about grades and college applications, Kendorski suggests asking your kids what story they’re telling themselves about success. For example, they might worry that a bad test grade means they’ll never get into their dream college. Help them map more realistic outcomes by thinking about the absolute worst-case scenario and alternative paths. For example, the worst that could happen if they fail a single test is maybe they get a C for the quarter. But reinforce how if they study and complete all their homework, the likelihood of failing is minimized.
Remember not to make your stress their stress. Children are intuitive and can pick up on how the adults in their lives are feeling, Kendorski says. Instead of turning away from uncomfortable emotions, encourage open communication. If you’re disappointed in a mediocre grade, try saying, “I’m feeling a little bummed about the C on that test, but that’s my issue. I know you work hard and with some more practice, I know you’ll do better next time.”
Parents should always validate their child’s struggles and encourage caring for their mental health. Whether they’re seeking support from a trusted teacher or you think they’d benefit from speaking with a therapist — ask them how they’d feel about chatting with a professional before scheduling an appointment — remind them that “mental health is health,” Draughn says. That matters more than any test score.
Will you support Vox today?
We believe that everyone deserves to understand the world that they live in. That kind of knowledge helps create better citizens, neighbors, friends, parents, and stewards of this planet. Producing deeply researched, explanatory journalism takes resources. You can support this mission by making a financial gift to Vox today. Will you join us?
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
The Vatican’s new statement on trans rights undercuts its attempts at inclusion
The lies that sell fast fashion, streaming got expensive. now what, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Homework as a Mental Health Concern It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health practitioners, especially those who work in schools. Over the years, we have tried to emphasize the idea that schools need to ensure that homework is designed as "motivated practice," and parents need to avoid turning homework into a battleground. These views are embedded in many of the Center documents. At this time, we hope you will join in a discussion of what problems you see arising related to homework and what you recommend as ways to deal with such problems, what positive homework practices you know about, and so forth. Read the material that follows, and then, let us hear from you on this topic. Contact: [email protected] ######################### As one stimulus, here's a piece by Sharon Cromwell from Education World prepared for teachers " The Homework Dilemma: How Much Should Parents Get Involved? " http://www.education-world.com/a_curr/curr053.shtml . What can teachers do to help parents help their children with homework? Just what kind of parental involvement -- and how much involvement -- truly helps children with their homework? The most useful stance parents can take, many experts agree, is to be somewhat but not overly involved in homework. The emphasis needs to be on parents' helping children do their homework themselves -- not on doing it for them. In an Instructor magazine article, How to Make Parents Your Homework Partner s, study-skills consultant Judy Dodge maintains that involving students in homework is largely the teacher's job, yet parents can help by "creating a home environment that's conducive to kids getting their homework done." Children who spend more time on homework, on average, do better academically than children who don't, and the academic benefits of homework increase in the upper grades, according to Helping Your Child With Homework , a handbook by the Office of Education Research and Improvement in the U.S. Department of Education. The handbook offers ideas for helping children finish homework assignments successfully and answers questions that parents and people who care for elementary and junior high school students often ask about homework. One of the Goals 2000 goals involves the parent/school relationship. The goal reads, "Every school will promote partnerships that will increase parental involvement and participation in promoting the social, emotional, and academic growth of children." Teachers can pursue the goal, in part, by communicating to parents their reasons for assigning homework. For example, the handbook states, homework can help children to review and practice what they have learned; prepare for the next day's class; use resources, such as libraries and reference materials; investigate topics more fully than time allows in the classroom. Parents can help children excel at homework by setting a regular time; choosing a place; removing distractions; having supplies and resources on hand; monitoring assignments; and providing guidance. The handbook cautions against actually doing the homework for a child, but talking about the assignment so the child can figure out what needs to be done is OK. And reviewing a completed assignment with a child can also be helpful. The kind of help that works best depends, of course, partly on the child's age. Elementary school students who are doing homework for the first time may need more direct involvement than older students. HOMEWORK "TIPS" Specific methods have been developed for encouraging the optimal parental involvement in homework. TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) Interactive Homework process was designed by researchers at Johns Hopkins University and teachers in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia to meet parents' and teachers' needs, says the Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin . The September 1997 bulletin reported the effects of TIPS-Language Arts on middle-grade students' writing skills, language arts report card grades, and attitudes toward TIPS as well as parents' reactions to interactive homework. TIPS interactive homework assignments involve students in demonstrating or discussing homework with a family member. Parents are asked to monitor, interact, and support their children. They are not required to read or direct the students' assignments because that is the students' responsibility. All TIPS homework has a section for home-to-school communication where parents indicate their interaction with the student about the homework. The goals of the TIPS process are for parents to gain knowledge about their children's school work, students to gain mastery in academic subjects by enhancing school lessons at home, and teachers to have an understanding of the parental contribution to student learning. "TIPS" RESULTS Nearly all parents involved in the TIPS program said TIPS provided them with information about what their children were studying in school. About 90 percent of the parents wanted the school to continue TIPS the following year. More than 80 percent of the families liked the TIPS process (44 percent a lot; 36% a little). TIPS activities were better than regular homework, according to 60 percent of the students who participated. About 70 percent wanted the school to use TIPS the next year. According to Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin , more family involvement helped students' writing skills increase, even when prior writing skills were taken into account. And completing more TIPS assignments improved students' language arts grades on report cards, even after prior report card grades and attendance were taken into account. Of the eight teachers involved, six liked the TIPS process and intended to go on using it without help or supplies from the researchers. Furthermore, seven of the eight teachers said TIPS "helps families see what their children are learning in class." OTHER TIPS In "How to Make Parents Your Homework Partners," Judy Dodge suggests that teachers begin giving parent workshops to provide practical tips for "winning the homework battle." At the workshop, teachers should focus on three key study skills: Organizational skills -- Help put students in control of work and to feel sure that they can master what they need to learn and do. Parents can, for example, help students find a "steady study spot" with the materials they need at hand. Time-management skills -- Enable students to complete work without feeling too much pressure and to have free time. By working with students to set a definite study time, for example, parents can help with time management. Active study strategies -- Help students to achieve better outcomes from studying. Parents suggest, for instance, that students write questions they think will be on a test and then recite their answers out loud. Related Resources Homework Without Tears by Lee Canter and Lee Hauser (Perennial Library, 1987). A down-to-earth book by well-known experts suggests how to deal with specific homework problems. Megaskills: How Families Can Help Children Succeed in School and Beyond by Dorothy Rich (Houghton Mifflin Company, 1992). Families can help children develop skills that nurture success in and out of school. "Helping Your Student Get the Most Out of Homework" by the National PTA and the National Education Association (1995). This booklet for teachers to use with students is sold in packages of 25 through the National PTA. The Catalog item is #B307. Call 312-549-3253 or write National PTA Orders, 135 South LaSalle Street, Dept. 1860, Chicago, IL 60674-1860. Related Sites A cornucopia of homework help is available for children who use a computer or whose parents are willing to help them get started online. The following LINKS include Internet sites that can be used for reference, research, and overall resources for both homework and schoolwork. Dr. Internet. The Dr. Internet Web site, part of the Internet Public Library, helps students with science and math homework or projects. It includes a science project resource guide Help With Homework. His extensive listing of Internet links is divided into Language Art Links, Science Links, Social Studies Links, Homework Help, Kids Education, and Universities. If students know what they are looking for, the site could be invaluable. Kidz-Net... Links to places where you can get help with homework. An array of homework help links is offered here, from Ask Dr. Math (which provides answers to math questions) to Roget's Thesaurus and the White House. Surfing the Net With Kids: Got Questions? Links to people -- such as teachers, librarians, experts, authors, and other students -- who will help students with questions about homework. Barbara J. Feldman put together the links. Kidsurfer: For Kids and Teens The site, from the National Children's Coalition, includes a Homework/Reference section for many subjects, including science, geography, music, history, and language arts. Homework: Parents' Work, Kid's Work, or School Work? A quick search of this title in the Education Week Archives and you'll find an article presenting a parent's viewpoint on helping children with homework. @#@#@#@@# As another stimulus for the discussion, here is an excerpt from our online continuing education module Enhancing Classroom Approaches for Addressing Barriers to Learning ( https://smhp.psych.ucla.edu ) Turning Homework into Motivated Practice Most of us have had the experience of wanting to be good at something such as playing a musical instrument or participating in a sport. What we found out was that becoming good at it meant a great deal of practice, and the practicing often was not very much fun. In the face of this fact, many of us turned to other pursuits. In some cases, individuals were compelled by their parents to labor on, and many of these sufferers grew to dislike the activity. (A few, of course, commend their parents for pushing them, but be assured these are a small minority. Ask your friends who were compelled to practice the piano.) Becoming good at reading, mathematics, writing, and other academic pursuits requires practice outside the classroom. This, of course, is called homework. Properly designed, homework can benefit students. Inappropriately designed homework, however, can lead to avoidance, parent-child conflicts, teacher reproval, and student dislike of various arenas of learning. Well-designed homework involves assignments that emphasize motivated practice. As with all learning processes that engage students, motivated practice requires designing activities that the student perceives as worthwhile and doable with an appropriate amount of effort. In effect, the intent is to personalize in-class practice and homework. This does not mean every student has a different practice activity. Teachers quickly learn what their students find engaging and can provide three or four practice options that will be effective for most students in a class. The idea of motivated practice is not without its critics. I don't doubt that students would prefer an approach to homework that emphasized motivated practice. But �� that's not preparing them properly for the real world. People need to work even when it isn't fun, and most of the time work isn't fun. Also, if a person wants to be good at something, they need to practice it day in and day out, and that's not fun! In the end, won't all this emphasis on motivation spoil people so that they won't want to work unless it's personally relevant and interesting? We believe that a great deal of learning and practice activities can be enjoyable. But even if they are not, they can be motivating if they are viewed as worthwhile and experienced as satisfying. At the same time, we do recognize that there are many things people have to do in their lives that will not be viewed and experienced in a positive way. How we all learn to put up with such circumstances is an interesting question, but one for which psychologists have yet to find a satisfactory answer. It is doubtful, however, that people have to experience the learning and practice of basic knowledge and skills as drudgery in order to learn to tolerate boring situations. Also in response to critics of motivated practice, there is the reality that many students do not master what they have been learning because they do not pursue the necessary practice activities. Thus, at least for such individuals, it seems essential to facilitate motivated practice. Minimally, facilitating motivated practice requires establishing a variety of task options that are potentially challenging -- neither too easy nor too hard. However, as we have stressed, the processes by which tasks are chosen must lead to perceptions on the part of the learner that practice activities, task outcomes, or both are worthwhile -- especially as potential sources of personal satisfaction. The examples in the following exhibit illustrate ways in which activities can be varied to provide for motivated learning and practice. Because most people have experienced a variety of reading and writing activities, the focus here is on other types of activity. Students can be encouraged to pursue such activity with classsmates and/or family members. Friends with common interests can provide positive models and support that can enhance productivity and even creativity. Research on motivation indicates that one of the most powerful factors keeping a person on a task is the expectation of feeling some sense of satisfaction when the task is completed. For example, task persistence results from the expectation that one will feel smart or competent while performing the task or at least will feel that way after the skill is mastered. Within some limits, the stronger the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more likely practice will be pursued even when the practice activities are rather dull. The weaker the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more the practice activities themselves need to be positively motivating. Exhibit � Homework and Motivated Practice Learning and practicing by (1) doing using movement and manipulation of objects to explore a topic (e.g., using coins to learn to add and subtract) dramatization of events (e.g., historical, current) role playing and simulations (e.g., learning about democratic vs. autocratic government by trying different models in class; learning about contemporary life and finances by living on a budget) actual interactions (e.g., learning about human psychology through analysis of daily behavior) applied activities (e.g., school newspapers, film and video productions, band, sports) actual work experience (e.g., on-the-job learning) (2) listening reading to students (e.g., to enhance their valuing of literature) audio media (e.g., tapes, records, and radio presentations of music, stories, events) listening games and activities (e.g., Simon Says; imitating rhymes, rhythms, and animal sounds) analyzing actual oral material (e.g., learning to detect details and ideas in advertisements or propaganda presented on radio or television, learning to identify feelings and motives underlying statements of others) (3) looking directly observing experts, role models, and demonstrations visual media visual games and activities (e.g., puzzles, reproducing designs, map activities) analyzing actual visual material (e.g., learning to find and identify ideas observed in daily events) (4) asking information gathering (e.g., investigative reporting, interviewing, and opinion sampling at school and in the community) brainstorming answers to current problems and puzzling questions inquiry learning (e.g., learning social studies and science by identifying puzzling questions, formulating hypotheses, gathering and interpreting information, generalizing answers, and raising new questions) question-and-answer games and activities (e.g., twenty questions, provocative and confrontational questions) questioning everyday events (e.g., learning about a topic by asking people about how it effects their lives) O.K. That's should be enough to get you going. What's your take on all this? What do you think we all should be telling teachers and parents about homework? Let us hear from you ( [email protected] ). Back to Hot Topic Home Page Hot Topic Home Page --> Table of Contents Home Page Search Send Us Email School Mental Health Project-UCLA Center for Mental Health in Schools WebMaster: Perry Nelson ([email protected])
August 22, 2022
Children’s Risk of Suicide Increases on School Days
Unlike in adults, suicide risk among children is lowest during the summer and higher during the school year. Understanding these patterns can help prevent and treat suicidality
By Tyler Black
Amanda Montañez
Reading about death and suicidality can be distressing. Please read this in a moment where you feel safest and ready to do so.
Pediatricians, child psychologists and psychiatrists, social workers and pediatric emergency teams know something that many people who care for children don’t: we are much busier during the school year. I’m a full-time emergency psychiatrist who works at a major children’s hospital, and often when children come in for a mental health crisis, one of the main stressors they discuss is school.
I’m sure most people assume I commonly prescribe medications as a physician, but one of my most common “prescriptions” is advocating for reducing school burden and load. In a 2013 American Psychological Association survey, 83 percent of adolescents stated that school was a cause or significant source of stress . In a 2017 survey of school leaders in the U.K., 82 percent reported increased mental health issues among primary school children during the time of national examinations. In studies in 2013 and 2015, scientists studying homework in the U.S. found that primary school children were averaging 30 minutes of such work per night, while high-performing secondary students were averaging more than three hours per night, at the cost of their physical health and schoolwork-life balance.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Whether we are talking about referrals to mental health programs for crisis, presentations to emergency departments for mental health issues, admissions to intensive care units for urgent treatment of suicide attempts or deaths by suicide, an association with school is clear. We are able to visualize this in a number of ways.
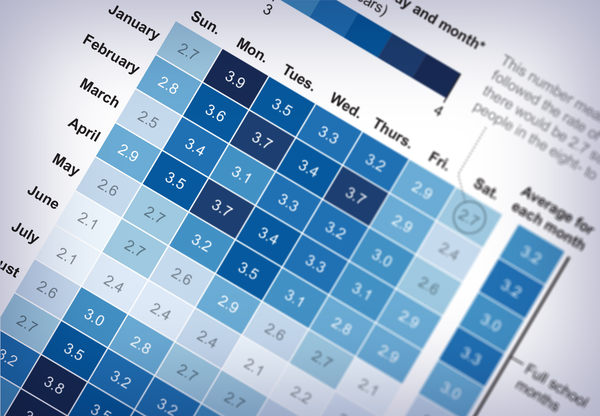
By using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wonder database to find information on pediatric (17 years of age or younger) deaths by suicide, I have created a “heat map” of youth suicide, and a school-day association is plain to see. On weekdays and during school months, there is a significant elevation of suicide deaths in children.
Credit: Amanda Montañez; Source: CDC Wonder , Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Data analysis by Tyler Black
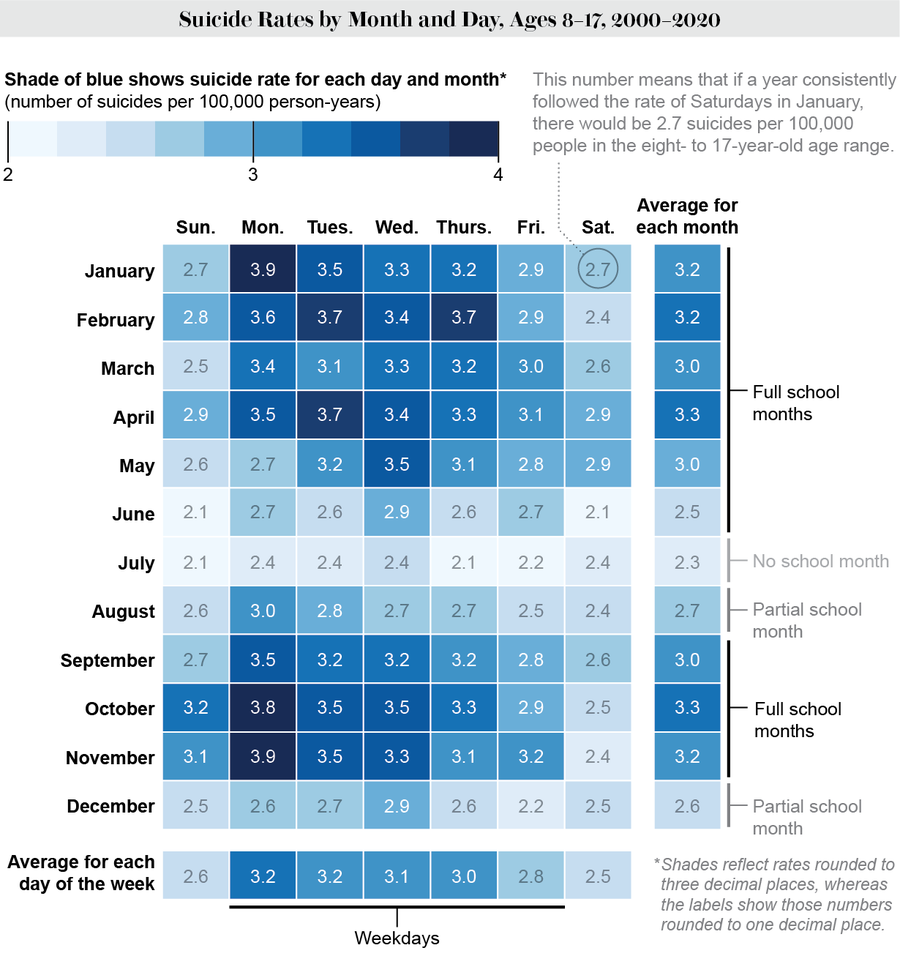
Looking at the monthly data, we can see that this elevation is not trivial: during school months, the increase in pediatric suicides ranges between 30 and 43 percent. This is in sharp contrast with adults, where we see suicide rates typically peak in summer months.
This situation has not improved over time: Compared with summer weekends, school-month weekdays from 2016 to 2019 show a pediatric suicide rate increase of 62 percent. The increase was 42% from 1999 to 2015.
If we look at far more common events, such as emergency room visits for mental health conditions, we see a strikingly similar pattern. These data come from participating hospitals in a collection done by the CDC.
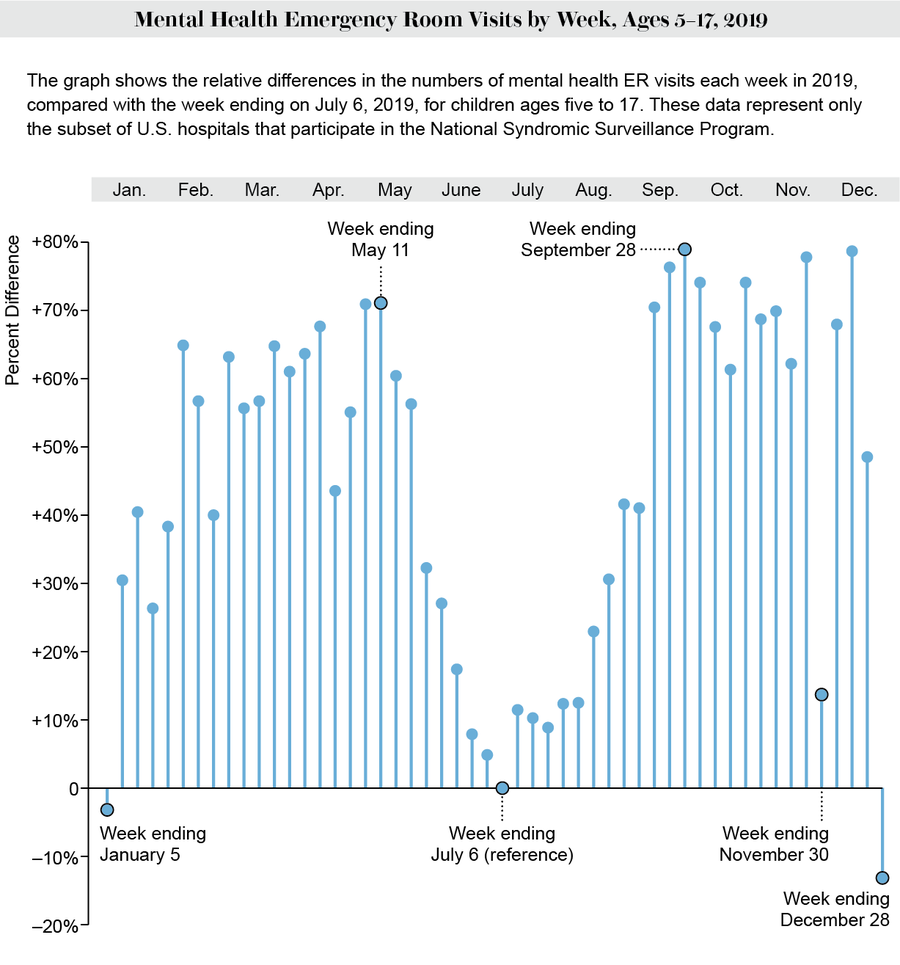
Credit: Amanda Montañez; National Syndromic Surveillance Program via Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
School comes with many things, good and bad. School can be wonderful, with learning experiences, social successes and a sense of connection to others. But it can also be incredibly stressful because of academic burden, bullying, health- and disability-related barriers, discrimination, lack of sleep and sometimes abuse. I often liken going to school to a child’s full-time job. The child has co-workers (classmates arranged by hierarchy), supervisors (teachers), bosses (administrators and principals) and overtime (homework). And they have very early work hours (most schools have hours that are very incompatible with children’s sleep patterns). Of course, work can be rewarding, but it’s also stressful.
Any time I present these data to teachers, parents, principals or school administrators, they are shocked. This should be common knowledge. Pediatric suicides and mental health crisis rates increase sharply when school is in and ease when school is out. This pattern is also found in other jurisdictions, such as Japan , Germany and Finland .
There are a number of ways to potentially mitigate this distress that I wish those responsible for our children’s education would explore. Some suggestions I’d put forth:
Reduce homework (preferably get rid of it). Some of the best educational science available shows that excessive homework is of limited benefit and in fact harms children’s health and well-being.
Add a mental health curriculum. We have developed incredible educational goals for math, reading, science and the arts. There should be a dedicated pathway for a much more universal and necessary learning: how to take care of yourself; how to look out for and help others; and how to improve both the detection and prevention of mental health crises.
Take bullying seriously and don’t just focus on the bullies. The bullied and bullies often come from similar backgrounds (histories of abuse, trauma, chaos, deprivation, parental detachment, though this certainly isn’t universally the case). But whereas the bullied tend to be internalizers, the bullies are more often externalizers. Bullies who were once victims of bullying have the highest risk of having psychiatric problems in the future.
Restore funding for playtime, music and art in school and de-emphasize academic overload. Children need relaxation, comfort, beauty, fun and play. Children who have opportunities to play and rest will learn more in their academics, and they will be able to sustain their development as they grow.
End “perfect attendance” awards and goals. While problematic truancy should be addressed, there is no less realistic notion for the rest of one’s life than the idea of “perfect attendance.” We should all, from time to time, recognize when we are at our limit and need a break. Children should be encouraged to report when they can do so and be supported.
Start school later. How many more decades of research do we need to show that children need more sleep and that adolescents do better in school when the day starts later? It’s time to make serious structural changes to the early-morning wake-up times.
Be nonjudgmental and respect children’s identity and identity formation. This is not a “woke” concept. This is a caring, compassionate concept that works for all children all the time.
Recognize and address child abuse within schools. There exist (and many readers may likely recall) teachers who are abusive, punitive and cruel. In one 2015 study, 44 percent of undergraduates recalled a time in K–12 school that they labeled as emotional abuse by a teacher . And in another study published in 2019, 3.4 percent of seventh- and eighth-grade students reported teachers bullied them .
Every year my colleagues in the emergency department brace for the coming mid-September wave, as every year our mental health crisis presentation volumes double and our days become much busier. Likely not coincidentally, in my jurisdiction, school starts in the second week of September.
In the new school year, if you are someone who works with school-age children, ask yourself what you could be doing to reduce pressure or improve quality of life for the children in your care. This would truly be suicide prevention.
IF YOU NEED HELP If you or someone you know is struggling or having thoughts of suicide, help is available. Call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or use the online Lifeline Chat . LGBTQ+ Americans can reach out to the Trevor Project by texting START to 678-678 or calling 1-866-488-7386.
This is an opinion and analysis article, and the views expressed by the author or authors are not necessarily those of Scientific American .

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Connect with NIMH
- Digital Shareables
- Science Education
- Upcoming Observances and Related Events
Digital Shareables on Child and Adolescent Mental Health
Use these resources to raise awareness about the importance of child and adolescent mental health.

Mental health is an important part of overall health for children and adolescents. Many adults with mental disorders had symptoms that were not recognized or addressed in childhood or adolescence.
Help raise awareness about the importance of children’s mental health and early diagnosis and treatment by sharing information and materials based on the latest research.
Share these graphics and social media messages
Download and share these messages to help spread the word about child and adolescent mental health. You can copy and paste the text and graphic into a tweet, email, or post. We encourage you to use the hashtag #shareNIMH in your social media posts to connect with people and organizations with similar goals. For more ideas on how to use these resources, visit our help page .

Child and Adolescent Mental Health
Help raise awareness about the importance of child and adolescent mental health by sharing informational materials based on the latest research. Share science. Share hope. https://go.nih.gov/diK806G #shareNIMH
Copy post to clipboard

Children and Mental Health
Disponible en español
It can be tough to tell if troubling behavior in a child or teen is just part of growing up or a problem that should be discussed with a health care provider. Learn more about warning signs: https://go.nih.gov/VDeJ75X #shareNIMH

Teen Depression
Being a teenager can be tough, but it shouldn’t feel hopeless. Check your symptoms, and find out what you can do if you think you might have depression. https://go.nih.gov/dGGEwYi #shareNIMH

I’m So Stressed Out!
Life can be stressful. If you are struggling to cope, or the symptoms of your stress or anxiety won’t go away, it could affect your health. Learn more at https://go.nih.gov/HcjwFWe . #shareNIMH

The Teen Brain is Resilient
Did you know that big and important changes are happening in the brain during adolescence? Here are 7 things you should know about the teen brain: https://go.nih.gov/cX8gB6u #shareNIMH

Know the Signs of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is not the same as the typical ups and downs every kid goes through, but with help, children and teens can manage their symptoms and lead successful lives. Learn more at https://go.nih.gov/UzIGOVj #shareNIMH
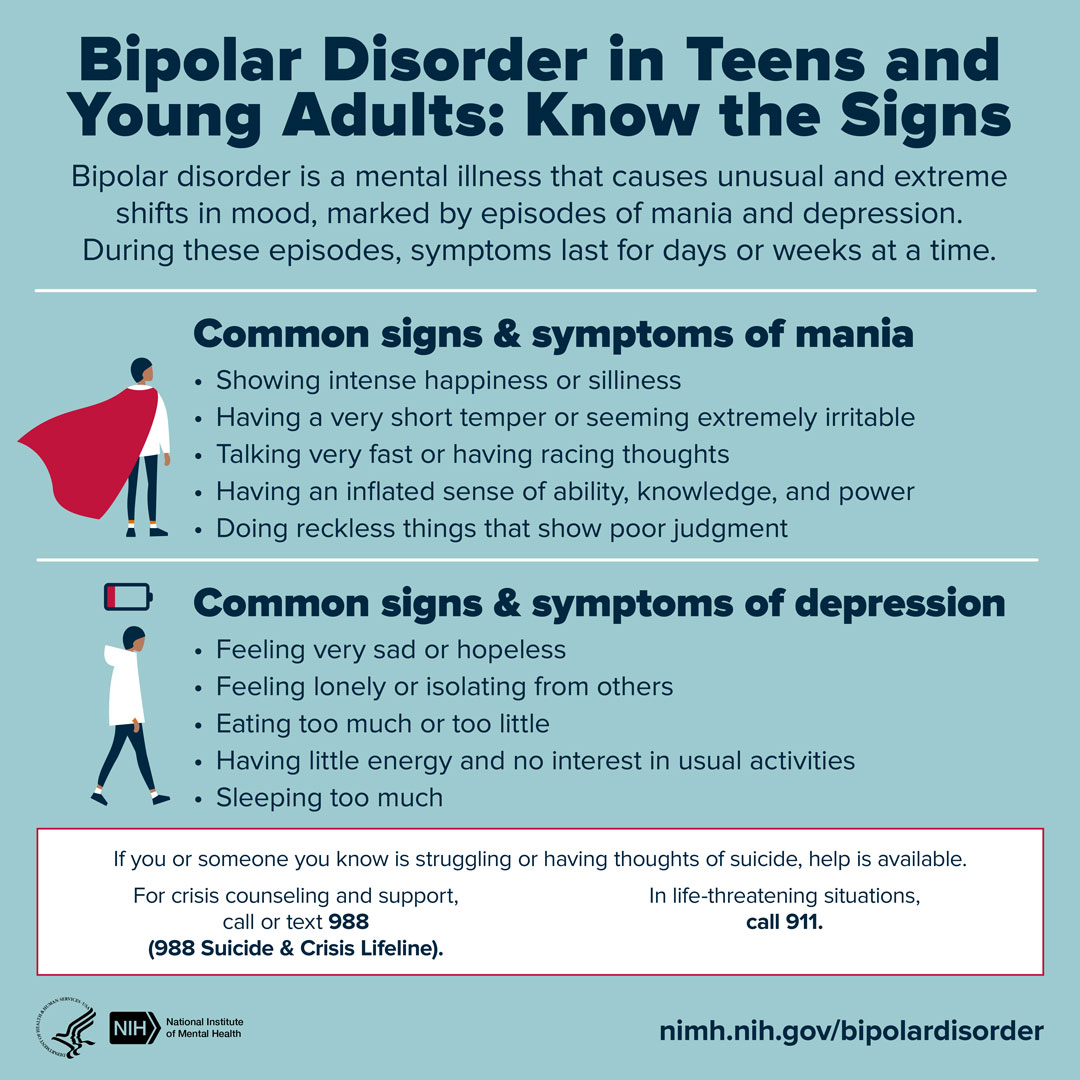
Bipolar Disorder in Teens and Young Adults
Bipolar disorder is a serious mental disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood, marked by episodes of mania and depression. Know the signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder in teens and young adults: https://go.nih.gov/uU4NAlG #shareNIMH

Helping Children and Adolescents Cope with Traumatic Events
Learn what caregivers and family members can do to help children and adolescents cope with traumatic events. https://go.nih.gov/FhVDaFG #shareNIMH

My Mental Health: Do I Need Help?
Do you need help with your mental health? If you don't know where to start, this infographic may help guide you. https://go.nih.gov/1VtK7eA #shareNIMH

Help for Mental Illnesses
If you or someone you know has a mental illness, is struggling emotionally, or has concerns about their mental health, use these resources to find help for yourself, a friend, or a family member: https://go.nih.gov/Fx6cHCZ . #shareNIMH
Use videos to educate others
Click the “Copy Link” link to post these videos on social media, or embed them on your website.
Childhood Irritability : Learn about symptoms of irritability, why it's important to study irritability, NIMH-supported research in this area, and new treatments for severe irritability in youth.
Get to Know Your Brain: Your brain is an incredible and complex organ! It helps you think, learn, create, and feel emotions, and it controls every blink, breath, and heartbeat. Learn more about the parts of the brain and what each area helps control.
Mental Health Minute: Stress and Anxiety in Adolescents: Got 60 seconds? Take a mental health minute to learn about stress and anxiety in adolescents.
NIMH Expert Discusses Bipolar Disorder in Adolescents and Young Adults: Learn the signs, symptoms, and treatments of bipolar disorder as well as tips for managing bipolar disorder during the pandemic.
NIMH Deputy Director Dr. Shelli Avenevoli Discusses the Youth Mental Health Crisis: Learn about youth suicide, the effects of technology and the pandemic on the developing brain, and tips for supporting the mental health of youth.
Getting to Know Your Brain: Dealing with Stress: Test your knowledge about stress and the brain. Also learn how to create and use a “ stress catcher ” to practice strategies to deal with stress.
Guided Visualization: Dealing with Stress: Learn how the brain handles stress and practice a guided visualization activity.
Diagnosis and Treatment in Children and Adolescents: Learn about research related to stress on children and adolescent brains, and diagnosis and treatments for severe irritability disorder.
Use these materials to educate kids about mental health
Print or order these educational tools to help teach kids about mental health and the brain. Resources are available in English and Spanish.

Get Excited About Mental Health Research!
This free coloring and activity book introduces kids to the exciting world of mental health research.

Stand Up to Stress!
This free coloring and activity book teaches children about stress and anxiety and offers tips for coping in a healthy way.

Get Excited About the Brain!
This free coloring and activity book for children ages 8-12 features exciting facts about the human brain and mental health.

Stress Catcher
Life can get challenging sometimes, and it’s important for kids (and adults!) to develop strategies for coping with stress or anxiety. This printable stress catcher “fortune teller” offers some strategies children can practice and use to help manage stress and other difficult emotions.
Learn more about children and adolescent mental health
more information about children and adolescent mental health, brochures and fact sheets.
Last Reviewed: April 2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health

School educational models and child mental health among K-12 students: a scoping review
1 The International Peace Maternity & Child Health Hospital, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Embryo Original Diseases, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, No. 910 Hengshan Road, Shanghai, 200030 China
Yining Jiang
Xiangrong guo.
2 MOE-Shanghai Key Laboratory of Children’s Environmental Health, Department of Child and Adolescent Healthcare, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200092 China
Associated Data
The data analysed in this review are available from the corresponding author upon request.
The promotion of mental health among children and adolescents is a public health imperative worldwide, and schools have been proposed as the primary and targeted settings for mental health promotion for students in grades K-12. This review sought to provide a comprehensive understanding of key factors involved in models of school education contributing to student mental health development, interrelationships among these factors and the cross-cultural differences across nations and societies.
This scoping review followed the framework of Arksey and O’Malley and holistically reviewed the current evidence on the potential impacts of school-related factors or school-based interventions on student mental health in recent 5 years based on the PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and PsycExtra databases.
Results/findings
After screening 558 full-texts, this review contained a total of 197 original articles on school education and student mental health. Based on the five key factors (including curriculum, homework and tests, physical activities, interpersonal relationships and after-school activities) identified in student mental development according to thematic analyses, a multi-component school educational model integrating academic, social and physical factors was proposed so as to conceptualize the five school-based dimensions for K-12 students to promote student mental health development.
Conclusions
The lessons learned from previous studies indicate that developing multi-component school strategies to promote student mental health remains a major challenge. This review may help establish appropriate school educational models and call for a greater emphasis on advancement of student mental health in the K-12 school context among different nations or societies.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13034-022-00469-8.

Introduction
In recent years, mental health conditions among children and adolescents have received considerable attention as a public health concern. Globally about 10–20% of children and adolescents experience mental health problems [ 1 , 2 ], and mental health problems in early life may have the potential for long-term adverse consequences [ 3 , 4 ]. In 2019, the World Health Organization has pointed out that childhood and adolescence are critical periods for the acquisition of socio-emotional capabilities and for prevention of mental health problems [ 5 ]. A comprehensive multi-level solution to child mental health problems needs to be put forward for the sake of a healthier lifestyle and environment for future generations.
The school is a unique resource to help children improve their mental health. A few generations ago, schools’ priority was to teach the traditional subjects, such as reading, writing, and arithmetic. However, children are now spending a large amount of time at school where they learn, play and socialize. For some students, schools have a positive influence on their mental health. While for others, schools can present as a considerable source of stress, worry, and unhappiness, and hinder academic achievement [ 2 ]. According to Greenberg et al., today’s schools need to teach beyond basic skills (such as reading, writing, and counting skills) and enhance students’ social-emotional competence, characters, health, and civic engagement [ 6 ]. Therefore, universal mental health promotion in school settings is recognized to be particularly effective in improving students’ emotional well-being [ 2 , 7 ].
Research evidence over the last two decades has shown that schools can make a difference to students’ mental health [ 8 ]. Previous related systematic reviews or meta-analyses focused on the effects of a particular school-based intervention on child mental health [ 9 , 10 ] and answered a specific question with available research, however, reviews covering different school-related factors or school-based interventions are still lacking. An appropriate model of school education requires the combination of different school-related factors (such as curriculum, homework, and physical activities) and therefore needs to focus on multiple primary outcomes. Thus, we consider that a scoping review may be more appropriate to help us synthesize the recent evidence than a systematic review or meta-analysis, as the wide coverage and the heterogeneous nature of related literature focusing on multiple primary outcomes are not amenable to a more precise systematic review or meta-analysis [ 11 ]. To the best of our knowledge, this review is among the first to provide a comprehensive overview of available evidence on the potential impacts of multiple school-related factors or school-based interventions on student mental health, and identify school-related risk/protective factors involved in the development of mental health problems among K-12 students, and therefore, to help develop a holistic model of K-12 education.
A scoping review was systematically conducted following the methodological framework of Arksey and O'Malley [ 12 ]: defining the research question; identifying relevant studies; study selection; data extraction; and summarizing and reporting results. The protocol for this review was specified in advance and submitted for registration in the PROSPERO database (Reference number, CRD42019123126).
Defining the research question (stage 1)
For this review, we sought to answer the following questions:
- What is known from the existing literature on the potential impacts of school-related factors or school-based interventions on student mental health?
- What are the interrelationships among these factors involved in the school educational process?
- What are the cross-cultural differences in K-12 education process across nations and societies?
Identifying relevant studies (stage 2)
The search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science and Embase electronic databases, and the dates of the published articles included in the search were limited to the last 5 years until 23 March 2021. The PsycExtra database was also searched to identify relevant evidence in the grey literature [ 13 ]. In recent 5 years, mental disorders among children and adolescents have increased at an alarming rate [ 14 , 15 ] and relevant policies calling for a greater role of schools in promoting student mental health have been issued in different countries [ 16 – 18 ], making educational settings at the forefront of the prevention initiative globally. Therefore, limiting research source published in the past 5 years was pre-defined since these publications reflected the newest discoveries, theories, processes, or practices. Search terms were selected based on the eligibility criteria and outcomes of interest were described as follows (Additional file 1 : Table S1). The search strategy was peer-reviewed by the librarian of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Study selection (stage 3)
T.Y. and Y.J. independently identified relevant articles by screening the titles, reviewing the abstracts and full-text articles. If any disagreement arises, the disagreement shall be resolved by discussion between the two reviewers and a third reviewer (J. X.).
Inclusion criteria were (1) according to the study designs: only randomized controlled trials (RCT)/quasi-RCT, longitudinal and cross-sectional studies; (2) according to the languages: articles only published in English or Chinese; (3) according to the ages of the subjects: preschoolers (3.5–5 years of age), children (6–11 years of age) and adolescents (12–18 years of age); and (4) according to the study topics: only articles examining the associations between factors involved in the school education and student mental health outcomes (psychological distress, such as depression, anxiety, stress, self-injury, suicide; and/or psychological well-being, such as self-esteem, self-concept, self-efficacy, optimism and happiness) in educational settings. Exclusion criteria: (1) Conference abstracts, case report/series, and descriptive articles were excluded due to overall quality and reliability. (2) Studies investigating problems potentially on a causal pathway to mental health disorders but without close associations with school education models (such as problems probably caused by family backgrounds) were excluded. (3) Studies using schools as the recruitment places but without school-related topics were also excluded.
Data extraction (stage 4)
T.Y. and Y.J., and X.G., Y. Z., H.H. extracted data from the included studies using a pre-defined extraction sheet. Researchers extracted the following information from each eligible study: study background (name of the first author, publication year, and study location), sample characteristics (number of participants, ages of participants, and sex proportion), design [intervention (RCT or quasi-RCT), or observational (cross-sectional or longitudinal) study], and instruments used to assess exposures in school settings and mental health outcomes. For intervention studies (RCTs and quasi-RCTs), we also extracted weeks of intervention, descriptions of the program, duration and frequency. T.Y. reviewed all the data extraction sheets under the supervision of J. X.
Summarizing and reporting the results (stage 5)
Results were summarized and reported using a narrative synthesis approach. Studies were sorted according to (a) factors/exposures associated with child and adolescent mental health in educational settings, and (b) components of school-based interventions to facilitate student mental health development. Key findings from the studies were then compared, contrasted and synthesized to illuminate themes which appeared across multiple investigations.
Search results and characteristics of the included articles
The search yielded 25,338 citations, from which 558 were screened in full-text. Finally, a total of 197 original articles were included in this scoping review: 72 RCTs (including individually randomized and cluster-randomized trials), 27 quasi-RCTs, 29 longitudinal studies and 69 cross-sectional studies (Fig. 1 for details). Based on thematic analyses, the included studies were analyzed and thematically grouped into five overarching categories based on the common themes in the types of intervention programs or exposures in the school context: curriculum, homework and tests, interpersonal relationships, physical activity and after-school activities. Table Table1 1 provided a numerical summary of the characteristics of the included articles. The 197 articles included data from 46 countries in total, covering 24 European countries, 13 Asian countries, 4 American countries, 3 African countries, and 2 Oceanian countries. Most intervention studies were conducted in the United States of America (n = 16), followed by Australia (n = 11) and the United Kingdom (n = 11). Most observational studies were conducted in the United States of America (n = 19), followed by China (n = 15) and Canada (n = 8). Figure 2 illustrated the geographical distribution of the included studies. Further detailed descriptions of the intervention studies or observational studies were provided in Additional file 1 : Tables S2 and S3, respectively.

Study selection process
Summary of the included articles

Geographical distribution of included studies: A intervention studies; B observational studies
The association between school curriculum and student mental health was investigated in four cross-sectional studies. Mathematics performance was found to be adversely associated with levels of anxiety or negative emotional responses among primary school students [ 19 ]. However, in middle schools, difficulties and stressors students may encounter in learning academic lessons (such as difficulties/stressors in taking notes and understanding teachers’ instructions) could contribute to lowered self-esteem [ 20 ] and increased suicidal ideation or attempts [ 21 ]. Innovative integration of different courses instead of the traditional approach of teaching biology, chemistry, and physics separately, could improve students’ self-concept [ 22 ].
To promote student mental health, 64 intervention studies were involved in innovative curricula integrating different types of competencies, including social emotional learning (SEL), mindfulness-intervention, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)-based curriculum, life skills training, stress management curriculum, and so on (Fig. 3 ). Curricula focusing on SEL put an emphasis on the development of child social-emotional skills such as managing emotions, coping skills and empathy [ 23 ], and showed positive effects on depression, anxiety, stress, negative affect and emotional problems [ 23 – 37 ], especially in children with psychological symptoms [ 24 ] and girls [ 23 , 27 ], as well as increased prosocial behaviors [ 38 ], self-esteem [ 39 – 42 ] and positive affect [ 43 ]. However, four programs reported non-significant effects of SEL on student mental health outcomes [ 44 – 47 ], while two programs demonstrated increased levels of anxiety [ 48 ] and a reduction of subjective well-being [ 49 ] at post-intervention. Mindfulness-based curriculum showed its potential to endorse positive outcomes for youth including reduced emotional problems and negative affect [ 50 – 56 ] as well as increased well-being and positive emotions [ 51 , 52 , 57 – 60 ], especially among high-risk children with emotional problems or perceived stress before interventions [ 50 , 53 ]. However, non-significant effects were also reported in an Australian study in secondary schools [ 61 ]. Curricula based on CBT targeted children at risk or with early symptoms of mental illness [ 62 – 67 ], or all students regardless of symptom levels as a universal program [ 68 – 70 ], and could impose a positive effect on self-esteem, well-being, distress, stress and suicidality. However, a universal CBT trial in Swedish primary schools found no evidence of long-term effects of such program on anxiety prevention [ 71 ]. Five intervention studies based on life-skill-training were found to be effective in promoting self-efficacy [ 72 , 73 ], self-esteem [ 73 , 74 ], and reducing depression/anxiety-like symptoms [ 72 , 75 , 76 ]. Courses covering stress management skills have also been reported to improve life satisfaction, increase happiness and decrease anxiety levels among students in developing countries [ 77 – 79 ]. In practice, innovative teaching forms such as the game play [ 67 , 80 , 81 ] and outdoor learning [ 82 , 83 ] embedded in the traditional classes could help address the mental health and social participation concerns for children and youth. Limited evidence supported the mental health benefits of resilience-based curricula [ 84 – 86 ], which deserve further studies.

Harvest plots for overview of curriculum-based intervention studies, grouped by different types of curriculum-based interventions. The height of the bars corresponded to the sample sizes on a logarithmic scale of each study. Red bars represented positive effects of interventions on student mental health outcomes, grey bars represented non-significant effects on student mental health outcomes, and black bars represented negative effects on student mental health outcomes
Large cluster-randomized trials utilizing multi-component whole-school interventions which involves various aspects of school life (curriculum, interpersonal relationships, activities), such as the Strengthening Evidence base on scHool-based intErventions for pRomoting adolescent health (SEHER) program in India and the Together at School program in Finland, have been proved to be beneficial for prevention from depression [ 87 – 89 ] and psychological problems [ 90 ].
Homework and tests
The association between homework and psychological ill-being outcomes was investigated in four cross-sectional studies and one longitudinal study. Incomplete homework and longer homework durations were associated with a higher risk of anxiety symptoms [ 91 , 92 ], negative emotions [ 93 – 95 ] and even psychological distress in adulthood [ 96 ].
Innumerable exams during the educational process starting from primary schools may lead to increased anxiety and depression levels [ 97 , 98 ], particularly among senior students preparing for college entrance examinations [ 99 ]. Students with higher test scores had a lower probability to have emotional and behavioral problems [ 100 ], in comparison with students who failed examinations [ 93 , 101 ]. Depression and test anxiety were found to be highly correlated [ 102 ]. In terms of psychological well-being outcomes, findings were consistent in the negative associations between student test anxiety and self-esteem/life-satisfaction levels [ 103 , 104 ]. Regarding intervention studies, adolescent students at a high risk of test anxiety benefited from CBT or attention training by strengthening sense of control and meta-cognitive beliefs [ 105 , 106 ]. However, more knowledge about the criteria for an upcoming test was not related to anxiety levels during lessons [ 107 ].
Interpersonal relationships
School-based interpersonal (student–student or student–teacher) relationships are also important to student mental health. Low support from schoolmates/teachers and negative interpersonal events were reported to be associated with psychosomatic health complaints [ 108 – 113 ]. In contrast, positive interpersonal relationships in schools could promote emotional well-being [ 114 – 117 ] and reduce depressive symptoms in students [ 118 – 120 ].
Student–teacher relationships
Negative teaching behaviors were associated with negative affect [ 121 , 122 ] and low self-efficacy [ 123 ] among primary and high school students. Student–teacher conflicts at the beginning of the school year were associated with higher anxiety levels in students at the end of the year, and high-achieving girls were most susceptible to such negative associations [ 124 ]. Higher levels of perceived teachers’ support were correlated with decreased risks of depression [ 125 ], mental health problems [ 126 ] as well as increased positive affect [ 127 , 128 ] and improved mental well-being [ 129 , 130 ]. Better student–teacher relationships were positively associated with self-esteem/efficacy [ 131 ], while negatively associated with the risks of adolescents’ externalizing behaviors [ 132 ] among secondary school students. Longitudinal studies demonstrated that high intimacy levels between students and teachers were correlated with reduced emotional symptoms [ 133 ] and increased life-satisfaction among students [ 134 ]. In addition, more respect to teachers in 10th grade students was associated with higher self-efficacy and lower stress levels 1 year later [ 135 ].
A growing body of research focused on the issue of how to increase positive interactions between teachers and students in teaching practices. Actually, interventions on improving teaching skills to promote a positive classroom atmosphere could potentially benefit children, especially those experiencing a moderate to high level of risks of mental health problems [ 136 , 137 ].
Student–student relationships
Findings were consistent in considering the positive peer relationship as a protective factor against internalizing and externalizing behaviors [ 138 – 142 ], depression [ 143 – 145 ], anxiety [ 146 ], self-harm [ 147 ] and suicide [ 148 ], and as a favorable factor for positive affect [ 149 , 150 ], increased happiness [ 151 ], self-efficacy [ 152 ], optimism [ 153 , 154 ] and mental well-being [ 155 ]. In contrast, peer-hassles, friendlessness, negative peer-beliefs, peer-conflicts/isolation and peer-rejection, have been identified in the development of psychological distress among students [ 141 , 143 , 149 , 156 – 165 ].
As schools and classrooms are common settings to build peer relationships, student social skills to enhance the student–student relationship can be incorporated into school education. Training of interpersonal skills among secondary school students with depressive symptoms appeared to be effective in decreasing adolescent internalizing and externalizing symptoms [ 166 ]. In addition, recent studies also identified the effectiveness of small-group learning activities in the cognitive development and mental health promotion among students [ 87 – 90 , 167 ].
Physical activity in school
Moderate-to-high-intensity physical activity during school days has been confirmed to benefit children and adolescents in relation to various psychosocial outcomes, such as reduced symptoms of depression [ 168 ], emotional problems [ 169 ] and mental distress [ 170 ] as well as improved self-efficacy [ 171 ] and mental well-being [ 172 , 173 ]. In addition, participation in physical education (PE) at least twice a week was significantly associated with a lower likelihood of suicidal ideation and stress [ 174 ].
A variety of school‐based physical activity interventions or lessons have been proposed in previous studies to promote physical activity levels and psychosocial fitness in students, including integrating physical activities into classroom settings [ 175 – 178 ], assigning physical activity homework [ 178 ], physically-active academic lessons [ 179 , 180 ] as well as an obligation of ensuring the participation of various kinds of sports (such as aerobic exercises, resistance exercises, yoga) in PE lessons [ 181 – 192 ]. Although the effectiveness of these proposed physical activity interventions was not consistent, physical education is suggested to implement sustainably as other academic courses with special attention.
After-school activities
Several cross-sectional studies have synthesized evidence on the positive effects of leisure-time physical activity against student depression, anxiety, stress, and psychological distress [ 193 – 199 ]. Extracurricular sport participation (such as sports, dance, and martial arts) could foster perceived self-efficacy, self-esteem, improve mental health status [ 200 – 203 ], and reduce emotional problems [ 204 ] and depressive symptoms [ 205 ]. Participation in team sports was more strongly related to beneficial mental health outcomes than individual sports, especially in high school girls [ 199 ]. Other forms of organized activities, such as youth organizations and arts, have also been demonstrated to benefit self-esteem [ 201 ], self-worth [ 206 ], satisfaction with life and optimism [ 207 , 208 ].
However, different types of after-school activities may result in different impacts on student mental health. Previous studies demonstrated that students participating in after-school programs of yoga or sports had better well-being and self-efficacy [ 209 ], and decreased levels of anxiety [ 210 ] and negative mood [ 211 ], while another study showed that the after-school yoga program induced no significant changes in levels of depression, anxiety and stress among students [ 212 ]. Inconsistent findings on the effects of participation in art activities on student mental health were also reported [ 213 , 214 ]. Another study also highlighted the benefits of after-school clubs, demonstrating an improvement in socio-emotional competencies and emotional status, and sustained effects at 12-month follow-up [ 215 ].
Based on the potential importance of the five school-based factors identified in student mental development, a multi-component school educational model is therefore proposed to conceptualize the five school-based dimensions (including curriculum, homework and tests, interpersonal relationships, physical activity, and after-school activities) for K-12 students to promote their mental health (Fig. 4 ). The interrelationships among the five dimensions and cross-cultural comparisons are further discussed as follows in a holistic way.

The multi-component school educational model is proposed to conceptualize the five school-based dimensions (including curriculum set, homework and tests, physical activity, interpersonal relationships and after-school activities) for K-12 students to promote student mental health
Comprehensive understanding of K-12 school educational models: the reciprocal relationships among factors
Students’ experiences in the school educational context are dynamic processes which englobe a variety of educational elements (such as curriculum, homework, tests) and social elements (such as interpersonal relationships and social activities in schools). Based on the educational model proposed in this review, these educational/social elements are closely related and interact with each other, which play an important role in students’ psychosocial development.
Being aware of this, initiatives aimed to improve student social and emotional competencies may certainly impact student psychological well-being, at least in part, in a way of developing supportive relationships between teachers-students or between peers [ 35 , 89 ]. On the other hand, the enhancement of interpersonal relationships at school could serve as a potent source of motivation for student academic progress so as to further promote psychological well-being [ 131 , 132 ]. In addition, school education reforms intended to provide pupils with more varied teaching and learning practices to promote supportive interpersonal relationships between students and teachers or between peers, such as education programs outside the classroom [ 82 ], cooperative learning [ 167 ] and adaptive classroom management [ 136 , 137 ], have also been advocated among nations recently.
Our findings also suggested that participation in non-academic activities was an important component of positive youth development. Actually, these school-based activities in different contexts also require teacher–student interactions or peer interactions. Social aspects of physical activities have been proposed to strengthen relationship-building and other interpersonal skills that may additionally protect students against the development of mental health problems [ 130 , 203 ]. Among various types of sports, team sports seemed to be associated with more beneficial outcomes compared with individual sports due to the social aspect of being part of a team [ 194 , 199 ]. Participation in music, student council, and other clubs/organizations may also provide students with frequent connections with peers, and opportunities to build relationships with others that share similar interests [ 201 ]. Further, frequent and supportive interactions with teachers and peers in sports and clubs may promote student positive views of the self and encourage their health-promoting behaviors (such as physical activities).
However, due to increasing academic pressure, children have to spend a large amount of time on academic studies, and inevitably displace time on sleep, leisure, exercises/sports, and extracurricular activities [ 92 ]. Although the right amount of homework may improve school achievements [ 216 ] and higher test scores may help prevent students from mental distress [ 100 – 102 ], over-emphasis on academic achivements may lead to elevated stress levels and poor health outcomes ultimately. The anxiety specifically related to academic achievement and test-taking at school was frequently reported among students who felt pressured and overwhelmed by the continuous evaluation of their academic performance [ 98 , 103 , 104 ]. In such high-pressure academic environments, strategies to alleviate the levels of stress among students should be incorporated into intervention efforts, such as stress management skill training [ 77 – 79 ], CBT-based curriculum [ 62 , 64 , 66 , 105 ], and attention training [ 106 ]. Therefore, school supportive policies that allow students continued access to various non-academic activities as well as improve their social aspect of participation may be one fruitful avenue to promote student well-being.
Cross-cultural differences in K-12 educational models among different nations and societies
As we reviewed above, heavy academic burden exists as an important school-related stressor for students [ 91 , 92 , 94 – 96 ], probably due to excessive examinations [ 97 – 99 ] and unsatisfactory academic performance [ 100 – 102 ]. Actually, extrinsic cultural factors significantly impact upon student academic burden. In most countries, college admission policies affect the entire ecological system of K-12 education, because success in life or careers is determined by examination performance to a large extent [ 217 ]. The impacts of heavy academic burden may be greatest in Asian cultures where more after-school time of students is spent on homework, exam preparations, and extracurricular classes for academic improvement (such as in Korea, Japan, China and Singapore) [ 92 , 95 , 218 ]. As a consequence, the high proportion of adolescents fall in the “academic burnout group” in Asian countries [ 219 ], which highlights the need to take further measures to combat the issue. As an issue of concern, the “double reduction” policy has been implemented nationwide in China since 2021, being aimed to relieve students of excessive study burden, and the effects of the policy are anticipated but remain unknown up to now.
Other factors such as school curriculum and extra-curricular commitments, vary among societies and nations and may explain the cross-cultural differences in educational models [ 220 ]. For example, in Finland, the primary science subject is as important as mathematics or reading, while Chinese schools often lack time to arrange a sufficient number of science courses [ 221 ], which could be explained by different educational traditions of the two countries. In addition, approximately 75% of high schools in Korea failed to implement national curriculum guidelines for physical education (150 min/week), instead replacing that time with self-guided study to prepare for university admission exams [ 174 ]. In terms of the arrangement of the after-school time, Asian students spend most of their after-school time on private tutoring or doing homework [ 222 ], 2–3 times longer than the time spent by adolescents in most western countries/cities [ 92 ]. However, according to our analyses and summaries, most intervention studies targeting the improvement of mental health of students by school education were conducted in western countries (Fig. 2 ), suggesting that special attention needs to be paid to the students’ mental health issue on campus, especially in countries where students have heavy study-loads. Merits of the different educational traditions also need to be considered in the designs of educational models among different countries.
Strengths and limitations
This study focuses on an interdisciplinary topic covering the fields of developmental behavioral pediatrics and education, and the establishment of appropriate school educational models is teamwork involving multiple disciplines including pediatrics, prevention, education, services and policy. Although there are lots of studies focusing on a particular factor in school educational processes to promote student mental health, comprehensive analysis/understanding on multi-component educational model is lacking, which is important and urgently needed for the development of multi-dimensional educational models/strategies. Therefore, we included a wide range of related studies, summarized a comprehensive understanding of the evidence base, and discussed the interrelationships among the components/factors of school educational models and the cross-cultural gaps in K-12 education across different societies, which may have significant implications for future policy-making.
Some limitations also exist and are worth noting. First, this review used the method of the scoping review which adopted a descriptive approach, rather than the meta-analysis or systematic review which provided a rigorous method of synthesizing the literature. Under the subject (appropriate school education model among K-12 students) of this scoping review, multiple related topics (including curriculum, homework and tests, physical activities, interpersonal relationships and after-school activities) were included rather than one specific topic. Therefore, we consider that the method of the scoping-review is appropriate, given that the aim of this review is to chart or map the available literature on a given subject rather than answering a specific question by providing effect sizes across multiple studies. Second, we limited the study search within recent 5 years. Although we consider that the fields involved in this scoping review change quickly with the acquisition of new knowledge/information in recent 5 years, limiting the literature search within recent 5 years may make us miss some related but relatively old literature. Third, we only included studies disseminated in English or Chinese, which may limit the generalizability of our results to other non-English/Chinese speaking countries.
This scoping review has revealed that the K-12 schools are unique settings where almost all the children and adolescents can be reached, and through which existing educational components (such as curriculum, homework and tests, physical activities, interpersonal relationships and after-school activities) can be leveraged and integrated to form a holistic model of school education, and therefore to promote student mental health. In future, the school may be considered as an ideal setting to implement school-based mental health interventions. Our review suggests the need of comprehensive multi-component educational model, which involves academic, social and physical factors, to be established to improve student academic achievement and simultaneously maintain their mental health.
However, questions still remain as to what is optimal integration of various educational components to form the best model of school education, and how to promote the wide application of the appropriate school educational model. Individual differences among students/schools and cross-cultural differences may need to be considered in the model design process.
Acknowledgements
We thank the librarian of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine for their help.
Abbreviations
Author contributions.
JX conceived the scoping review, supervised the review process and reviewed the manuscript. TY conducted study selection and data extraction, charted, synthesized the data, and drafted the manuscript. YJ conducted study selection and data extraction. XG, YZ and HH conducted data extraction. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 81974486, 81673189) (to Jian Xu), Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (20172016) (to Jian Xu), Shanghai Sailing Program (21YF1451500) (to Hui Hua).
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

Is My Kid’s Therapy Helping? Plus 7 Steps to Take if It’s Not
When it comes to therapy for children, parents and caregivers often have an active role to play in the helping process. Here’s a guide.
If as a parent you’re concerned about your child’s mental and emotional health, you’re not alone.
Several recent reports — including a December 2021 advisory from the U.S. Surgeon General and a joint statement issued in October 2021 by several major medical groups, including the American Academy of Pediatrics — have deemed the state of youth mental health in the United States either a crisis or emergency . Those reports cited high rates among young people of hospital visits due to mental health issues and suicide attempts.
One in 10 American children ages 5 to 17 received counseling or therapy for mental health in 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . And that data, the most recent available on the prevalence of youth utilizing mental health therapy, comes from before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has undoubtedly contributed to a rise in mental health struggles for people of all ages, experts say.
“The mental health crisis was there before the pandemic, but the pandemic really brought it to light,” says Jill Emanuele, PhD , a New York City–based clinical psychologist and vice president of clinical training at the Child Mind Institute, a national nonprofit dedicated to transforming the lives of children and families struggling with mental health and learning disorders.
“Things are really problematic and troubling right now,” she says.
Behind each of those children is a concerned parent or caregiver wanting to know if their child is getting the care and support they need, and what to do if they’re not.
Here’s a guide to helping your child get the most out of therapy.
First, Determine if Your Kid’s Therapist Is a Good Fit
Part of helping your child get the care they need is determining whether they are seeing the right person to help them with their current challenges.
“I always want people to remember that this is a relationship. Choosing a therapist is very much the same as choosing any other professional that you work with,” Dr. Emanuele says. You want the therapist to be someone you and your child are comfortable with.
You can ask the therapist upfront about their training and approach to therapy, Emanuele says. It’s a positive sign if the therapist has experience helping children whose symptoms are similar to your child’s right now. Likewise, how the therapist answers your questions and addresses your concerns right off the bat can give you a sense of whether you’re in good hands, Emanuele adds.
If your child struggles with multiple aspects of their mental health (which isn’t uncommon), their therapy plan should account for that, according to the Child Mind Institute .
And if your child’s needs change over the course of starting therapy with one provider, it can be a good idea to reevaluate if your child’s therapist is still a good fit.
“ Key to ensuring good therapeutic outcomes in therapy are open and direct communication between parent or guardian, the therapist, and, most importantly, the child or adolescent,” says Patrice Harris, MD, MA, FAPA , psychiatrist who specializes in child and adolescent psychiatry and Everyday Health’s chief health and medical editor. “This should occur prior to seeking therapy and throughout the process.”
And don’t forget to ask your child about their preferences, including when it comes to race and gender, Dr. Harris says. You might not find a provider who meets all of the preferences of your child who is in your area or network, but engaging your child in the conversation will help.
Getting Involved: Help Your Kid Show Up and Do the Work
Effective therapy requires consistency, and, as a parent, you have a significant role to play.
You can help your child arrive at their virtual or in-person appointments on time, every time.
Parents can physically help their children get through the office doors or logged on to telehealth says Alysha Thompson, PhD , a clinical psychologist and clinical director at the Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Unit at Seattle Children's and assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Washington.
If your child doesn’t want to go, taking time to hear and thoughtfully address their concerns can go a long way, according to the Child Mind Institute .
And for therapy to be most effective, your child will likely need to work on their mental health outside of sessions, too. Many therapists also assign work between sessions. Ask your child about their therapy homework and look for ways to get it done.
“A therapist doesn't wave a magic wand and make everything better. It is a collaborative process between the therapist, the parent, and the child,” says Emanuele. That’s different from a pediatrician’s appointment, where the provider does most of the work, she points out.
The appropriate level of parental involvement depends on the situation. For younger children, the level tends to be quite high; the therapist might spend more time talking with you than with your child in sessions, Dr. Thompson says.
An approach called parent management training (in which parents learn skills to help manage their children’s behavior) has a lot of evidence to back it up; it requires parents to practice those strategies at home between sessions.
And it may take time, Harris adds. “Some therapeutic goals may take time to achieve, and it often takes time for youth to develop a therapeutic alliance with their mental health professional.”
How to Tell if Your Kid Is Getting the Help They Need
Once therapy is underway, it’s normal to wonder whether it’s working. Use these strategies to check in and determine whether your child’s therapy is doing what it should:
- Look for changes in your child’s behavior. If therapy is helping, you may notice your child begin to act differently. This could look like wanting to hang out with friends after a period of withdrawing or appearing to enjoy a favorite hobby after previously seeming disinterested. “Some people make slow and steady progress,” says Emanuele. “Most of the time, though, it’s a bumpy road where there are days when it's better and days when it's worse. But you’re overall looking for the upward trajectory.”
- Ask your child. Go straight to the source. Even if your child doesn’t respond right away, regularly asking them open-ended questions can help get them ready to share with you when they do feel ready to talk. Emanuele suggests asking questions like: How do you think therapy is going? What do you think is working? What do you think isn’t working? If your child has negative things to say, it’s not necessarily a sign to stop treatment. “Parents know their kids, so they’ll know if you can count on that statement right away or if it’s better to wait,” says Emanuele.
- Talk to your child’s therapist. “One of the things I see over and over and over again is parents are having doubts, and they're not really sure what to do. And the only person they don't talk to about it is the therapist — and that’s the person you need to talk to,” says Emanuele. Ask your child’s therapist questions like: How do you think my child is progressing? Do we need to try something different? “Therapists are trained to have those open, frank conversations about what’s going well, what’s not,” Thompson adds.
Remember, no hard and fast rule dictates the frequency of these conversations. You’ll likely have more check-ins earlier in the process and fewer as time passes, but it’s appropriate to check in anytime.
If your child doesn’t think therapy is going well and you’re seeing them act in ways that concern you, including showing warning signs for suicide , that may be a sign your child’s needs aren’t being met in therapy, Thompson says.
7 Steps to Take if Your Child’s Therapy Doesn’t Seem to Be Helping
If your kid is seeing a therapist but still struggling, don’t give up hope. You can help your child in other ways, many of which are also useful if you’re stuck on a waitlist.
1. Educate Yourself About Mental Health
If you know your child’s mental health diagnosis or have an idea of what it might be, you can look for nonprofit organizations particular to that disorder. For example, if your child struggles with anxiety or depression, check out the Anxiety and Depression Association of America .
You don’t have to have a diagnosis in mind to start learning about mental health. The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) offers a free, six-session online course called NAMI Basics OnDemand for parents and caregivers who want to support youth with mental health symptoms.
2. Cultivate Healthy Lifestyle Habits at Home
Healthy habits aren’t a substitute for mental health treatment, according to the Child Mind Institute, but they are a critical complement to mental healthcare.
In particular, proper sleep should be a priority because many mental health disorders are linked with poor sleep, including depression, research shows.
3. Draw on Social and School Support
Emanuele and Thompson both encourage caregivers to lean on the power of their community. Your friends and family can offer general support and may have particular advice about therapists or organizations that have helped other children in your circle. It’s also key to loop in your child’s school, which can connect you to local resources.
4. Give It Time
When your child is suffering, it’s natural to want it to stop — yesterday. But mental health therapy doesn’t work like that.
“Therapy is more a long game than a short game,” says Emanuele. A course of evidence-based therapy generally takes between 8 and 16 weeks, says Thompson. More complex and severe cases can take more time. If you feel like your child’s therapy isn’t working, it may be that it isn’t working yet .
5. Request a Second Opinion and Consider Switching Therapists
If you’re not sold on your child’s therapy, you can get a second opinion. Your current therapist may be able to provide a referral or loop in a colleague for a consultation. If you decide to stop working with a therapist, you shouldn’t just stop coming, adds Emanuele. Ending formally can provide closure and model healthy relationships for your child.
6. Consider More Intensive Therapy Options
If weekly or biweekly sessions aren’t helping with your child’s mental health issues , there are more intensive options. Families in this situation may want to consider a range of more intensive mental health services, including partial hospitalization programs (PHP), intensive outpatient programs (IOP), day treatment programs, and residential treatment programs, according to the PACER Center’s Inspiring Opportunities Project, a nonprofit funded by the U.S. Department of Education's Office of Special Education Programs.
What these programs look like varies by your location, your child’s age, and your child’s specific needs. Features of many of these programs include meeting multiple days per week for a combination of individual therapy, group therapy, skill building, and medication management.
Research indicates higher levels of care, like PHPs, can provide lasting positive impact on children’s mental health without requiring more restrictive types of care (like full hospitalization).
Ask your therapist about programs in your area or ask parents in your community what programs have worked for their children. You can also use the treatment locator from the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), which includes some intensive mental health treatment options for children.
7. Get Help in a Crisis
Take it seriously if your child is in therapy but shows warning signs for suicide, like those the Society for the Prevention of Teen Suicide (PDF) describes.
You can call the national 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline in a crisis. Or if you suspect your child needs urgent help, visit the ER. “If a parent is really concerned that their child is going to imminently harm themselves or has already harmed themselves, they should bring them to the ER,” urges Thompson. Hospital staff are there to keep your child safe and assist with the next steps.
28 Mental Health Games, Activities & Worksheets (& PDF)

Despite this, increasing mental health awareness is crucial as it can have many positive outcomes.
For example, one study examining a British anti-stigma campaign found that people who were more familiar with the campaign were more likely to feel comfortable disclosing mental health issues to family, friends, or an employer, and were also more likely to seek professional help (Henderson et al., 2017).
Fortunately, there are all sorts of ways to learn about mental health issues, whether one is an introvert, an extrovert, or somewhere in between.
This article will cover tools that can supplement mental health interventions, worksheets and activities that help people learn about mental health, books dealing with mental health for adults and children, Facebook groups for mental health issues, and finally World Mental Health Day activities and events.
Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values and self-compassion and will give you the tools to enhance the mental health of your clients, students or employees.
This Article Contains:
5 tools for mental health interventions.
- 5 Mental Health Worksheets & Awareness Activities (PDF)
5 Most Popular Books About Mental Health
- 5 Most Popular Children’s Books About Mental Health
Facebook Groups for Mental Health
World mental health day ideas for schools and workplaces, a take-home message.
Here are some tools that will help a psychotherapy treatment plan go more smoothly for both the client and the clinician:
1. Thought Record Worksheet
This PDF is a way to record one’s thoughts and reflect on them. It asks the user to log their emotions and thoughts as well as what was going on to make them feel that way, then has the user reflect on whether or not there is evidence to back up their automatic thoughts. This could be a valuable supplement to a psychotherapist-led CBT treatment, but could also help people teach themselves about CBT .
In fact, one study has shown that thought records are an effective way to modify beliefs, even when used by themselves and not in conjunction with a CBT treatment plan (McManus et al., 2012). Find the Thought Record Worksheet here.
2. The Feeling Wheel
The Feeling Wheel is a simple printout with 72 feelings sorted into 6 groups: angry, sad, scared, joyful, peaceful, and powerful. Represented as a colorful pie, it can be an excellent tool for psychotherapy clients who have difficulty articulating or expressing their feelings.
While this can make it easier for clients to describe their relationships and experiences outside of therapy, it can also help them give immediate feedback on how they feel during a session.
This technique is commonly used to help clients identify emotions, expand their emotional vocabulary, and develop their emotional regulation (Kircanski et al., 2012).
3. Daily Mood Tracker
This Daily Mood Tracker was developed for people dealing with anger management issues but can be helpful for anyone who wants to track their mood.
It splits the day up into several two-hour blocks and asks the user to track their emotions, as well as allowing for notes to explain these moods.
This can also be helpful for clients who have trouble expressing themselves but can provide valuable self-reflection opportunities for anybody. Interestingly, some research has even shown that depressed clients can improve their mood by tracking it (Harmon et al., 1980).
4. Self-Care Checkup
This worksheet is a self-report Self-Care Checkup that therapists can give their clients after each appointment, to fill in between the sessions. The client is meant to consider the activities they are engaging in to keep up good mental health and wellbeing.
While many could be considered routine, such as exercising or getting sufficient sleep, they can often be neglected when they matter most – during times of stress.
This way, the Self-Care Checkup invites clients to become more aware of the frequency with which they practice self-care, categorizing these activities into five groups:
- Professional; and
- Spiritual self-care.
By filling it out regularly, clients can compare their self-care practices from week to week, spotting areas for development and brainstorming more activities that might help them maintain their mental health.
5. Preventing Mental Health Relapse
This is a worksheet that can help clients learn more about possible mental health relapse. It can be used near the end of a therapy treatment plan to help the client recognize a relapse when it is coming, but can also teach strategies to avoid relapse.
This would likely be most helpful for mental health issues that flare up at specific times (as opposed to more chronic mental health issues), and can also be helpful during treatment changes.
For example, patients with anxiety disorders receiving both psychotherapy and antidepressants are at risk of relapse when they discontinue their antidepressant treatment (Batelaan et al., 2017).
Download and use this Preventing Mental Health Relapse activity here.
5 Mental Health Games & Awareness Activities (PDF)

One way to get around this is to have them complete worksheets or participate in activities related to mental health awareness, so they can learn in a more hands-on way.
These worksheets and activities are excellent for cultivating mental health awareness:
1. Mindfulness Exercises For Children
This article includes a huge collection of easy mindfulness exercises that children can do to learn more about mindfulness. It includes activities for teachers, parents, caregivers, and teenagers, along with a host of meditation scripts, books, quotes, and more.
Check out the following, too, for some great ways to get children thinking about mindfulness, while subtly introducing them to mental health issues more broadly: 18 Mindfulness Games, Worksheets and Activities for Kids .
2. Mental Illness: Myths and Reality
Mental Illness – Myths and Reality is a helpful lesson plan for teachers who want to educate students about mental illness stigma.
This activity requires less than 30 minutes and very little preparation – it’s also great for any class size and can be a useful talking point to start insightful discussions around mental health.
It includes 8 myths and 8 facts about mental illness for students to sort out in pairs, to distinguish between common misconceptions and objective facts about diagnosis and life with a mental health condition.
3. Exercise and Mental Health
Exercise and Mental Health introduces younger children to the importance of exercise and physical activity, illustrating how they go hand-in-hand before giving suggestions for students who want to get more active on a daily basis.
This informational resource is a great handout as part of a lesson about mental health.
4. Understanding Mental Health Stigma
Introducing youths to the concept of stigma can be quite tough, but it’s important.
This Understanding Mental Health Stigma sheet can be used as an aid to help raise awareness of the stigma that surrounds mental illness , as well as what it looks like.
5. Mental Health Management Bingo
Mental Health Management Bingo is a fun classroom game that can be played with slightly older students.
While it aims to raise awareness about the importance of positive coping strategies, it can also be a great way for students to bond with one another and discover new, healthy ways to look after their mental health..
To play, students require a copy of each sheet and a pencil, and each Bingo square worksheet contains 22 positive coping mechanisms that are related to maintaining good mental health. It’s easy for students to play, and just as easy for teachers or parents to join in!

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
We suggest picking at least one of these popular to broaden your understanding of mental health.
1. Mental Health Emergencies: A Guide to Recognizing and Handling Mental Health Crises – Nick Benas and Michele Hart

Written by a mental health associate and a social worker, this book aims to help people recognize mental health crises in the people around them.
This book also aims to teach the reader how to support people in the midst of a mental health crisis.
The authors targeted this book to teachers, human resources workers and other professionals who are concerned with the mental wellbeing of other people, but it can be helpful for anyone who wishes to know more about mental health.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. Ten Days in a Mad-House – Nellie Bly

This book details investigative reporter Nellie Bly’s exposé of a New York City insane asylum in the late 1800s.
In the book, the author details how she checked into a boarding house, feigned insanity and was promptly declared insane and sent to an insane asylum.
Bly spent 10 days in the asylum, during which she uncovered the horrific conditions that patients were subjected to, causing the city and the country to reevaluate how they treated the mentally ill.
This book illustrates how horribly mental health patients were treated in the late 1800s, but can also cause the reader to think about how society treats mental health issues today.
3. Stigma: The Many Faces Of Mental Illness – Joy Bruce M.D.

This book, from a doctor with a mood disorder, aims to educate people about mental health issues and ultimately destigmatize mental health issues.
The book describes various mental health disorders and the nuances of them, making it a great educational book.
The author also discusses a wide variety of people with mental health issues, breaking down stereotypes about mental health along the way. This is a great book for someone who wants to understand more about mental health issues in themselves or others.
4. Look Me in the Eye: My Life with Asperger’s – John Elder Robison

This memoir discusses the author’s experience of living with Asperger’s syndrome.
The author was not diagnosed with Asperger’s syndrome until he was 40 years old, so before then he just lived as someone who felt that he could not connect very well with others for some reason but displayed an affinity for machines and electronics.
This book is an excellent way to gain some insight into the world of Asperger’s syndrome and may help the reader better understand someone in their life who deals with Asperger’s syndrome.
5. Man Who Mistook His Wife For A Hat – Oliver Sacks and Jonathan Davis

This book from Oliver Sacks is a pop psychology classic. In it, Sacks discusses a few different cases of mental health disorders, focusing on the person rather than the disorder the whole way through.
This is an excellent book for learning about mental health disorders in a way that doesn’t necessarily otherize people with mental health issues. The book’s scope also makes it a great introduction to mental health disorders.
5 Most Popular Children’s Books About Mental Health
Nurturing an understanding of mental health from a young age can be done with these great reads.
1. Can I Catch It Like a Cold?: Coping With a Parent’s Depression – Centre for Addiction and Mental Health and Joe Weissmann

This book from the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) in Canada is aimed at children whose parents struggle with depression.
The book describes what depression is and is not, and gives the reader strategies to cope with the situation. It is aimed at children as young as five years old and can be a child’s first official introduction to mental health disorders.
2. Dear Allison : Explaining Mental Illness to Young Readers – Emma Northup Flinn

This book discusses mental health in an adventurous, conversational way that can help children start to understand the subject.
Written from the perspective of the reader’s cousin (who has teamed up with an ant to explore mental health issues across parts of the United States), this is another excellent book for introducing children to mental health.
The book is partially a collection of letters from the narrator to her nine-year-old cousin, “Allison”, so this book is definitely appropriate for children as young as 9 to start learning about mental health.
3. Marvin’s Monster Diary: ADHD Attacks! (But I Rock It, Big Time) – Raun Melmed, Annette Sexton, and Jeff Harvey

This book is an excellent way to teach children as young as 7 years old about attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), particularly if they have it.
Aside from helping children understand ADHD, it offers a mindfulness-based solution the author calls ST4 – “Stop, Take Time To Think”.
This book is an excellent resource for children with ADHD to learn more about themselves and strategies they can use every day to focus.
4. How Full Is Your Bucket? For Kids – Tom Rath, Mary Reckmeyer, and Maurie J. Manning

This book was written by Tom Rath, an important author in positive psychology and particularly strengths finding (as he wrote StrengthsFinder 2.0).
It is a children’s adaptation of another one of his popular books, How Full Is Your Bucket?, which claims that people can either “fill your bucket” with positivity or “dip from your bucket” with negativity.
This is an excellent book to show kids how social interactions can affect their self-esteem and wellbeing, and how the way they treat people can affect the self-esteem and wellbeing of others.
5. Please Explain Anxiety to Me! Simple Biology and Solutions for Children and Parents – Laurie E. Zelinger, Jordan Zelinger, and Elisa Sabella

This book, co-authored by a play therapist and a child psychologist, aims to explain anxiety to children in a simplified but still accurate way.
This means describing the physiology of anxiety in a way that children as young as 5 can start to understand.
It also includes some actionable exercises that children can use when they are feeling anxious. This book can help children deal with their own anxiety and learn some concrete psychology along the way.

Sometimes, the best thing for someone struggling with mental health issues is the ability to reach out to someone who will understand them.
Facebook is great for this, as people can start community-based groups focused around mental health issues.
That said, as is always the case with the internet, anybody can contribute to these groups, which has the potential to be harmful to members of that group.
For that reason, we have only highlighted closed groups (as opposed to open groups), which require admin approval to join. This way, it is more likely that someone will find a group full of people who only want to help.
Someone looking for a Facebook group to discuss mental health should try joining one of these:
Adult ADHD/ADD Support Group… By Reach2Change
This is a support group for adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or attention deficit disorder (ADD).
Anxiety/Depression Mental Health Support Group
This is a support group for people (18+) who struggle with depression or anxiety .
Bipolar Disorder
This is a support group for people with bipolar disorder, people who know someone with bipolar disorder, or people who want to learn more about bipolar disorder.
Mental Health Inspiration (Support & Awareness)
This is a support group for people with all sorts of mental health issues, as well as people who wish to be an ally or learn more about mental health.
PTSD Buddies
This is a support group for people (19+) with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
30 Minute relaxing yoga for mental health – Jessica Richburg
October 10th is World Mental Health Day.
The objective of this important day is to spread awareness about mental health issues, express thanks to mental health care providers, and do more to make mental health care a reality for those who need it. Overall, the day represents a valuable opportunity to start a dialog about mental health with others in your life.
If you’re a teacher, manager, or principal looking for ways to start this conversation in your school or workplace, here are four ideas to get started.
Yoga and pilates have both been shown to reduce a range of mental health symptoms, such as fatigue and feelings of anxiety, while simultaneously increasing feelings of energy (Fleming & Herring, 2018; Hagen & Nayar, 2014).
To leverage these benefits, consider bringing in a yoga or pilates expert (or linking up with a nearby studio) to do a guided class with your staff or students.
Host a charity event
There are many charitable organizations around the world that are working hard to provide mental health support to those who may otherwise not have access to it.
To help, you can work with your students or staff to identify a cause they feel passionate about and run an event to raise money for a worthy cause. For example, consider hosting a raffle, games evening, cake stall, or fete open to the public.
Wellness gift exchange
A simple gift can do a lot to start a conversation, so consider hosting a wellness gift exchange.
To start, randomly assign your students or staff a ‘gift buddy.’ If you like, you can make the identity of gift-givers and receivers anonymous, much like a Secret Santa, by having your staff or students draw names from a hat.
Next, allocate a spending limit and have each person purchase a gift for someone else. The focus of the gift should encourage the recipient to relax and take some time out for him or herself. Examples of good gifts include movie tickets, a pampering face mask, or a soap and candle gift basket.
Information sessions
Teaching children how to start a conversation with someone about mental health is a skill that can serve them for a lifetime. At the same time, the stigma associated with mental illness may act as a barrier for adults to start a conversation with someone they’re concerned about or seek help.
To help, consider bringing in a mental health speaker or expert and host an information session. The aim of the session should be to connect your students or staff to resources and give them the skills to check in with the mental health of those they care about.
Further, you can take this opportunity to remind your students or staff about internal support services in your school or office, such as forms of personal leave or internal counselors.
In addition to the ideas above, it is likely that public spaces around you, such as libraries and community centers, will have planned events around World Mental Health Day. So consider linking up with groups in your local community to support this important cause.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
At the end of the day, nobody can know everything there is to know about mental health issues. The key is constantly being willing to learn, so that you know how to help when someone you love deals with mental health issues, and have the strategies to deal with your own mental health issues if and when they arise.
Some people prefer reading books, others prefer more hands-on learning such as worksheets, and still, others just prefer going out and talking to people. No matter what type of learning you prefer, the important thing is that you make an effort to make this world a better place for everyone, no matter what mental health issues they are or aren’t facing.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Batelaan, N.M., Bosman, R.C., Muntingh, A., Scholten, W.D., Huijbregts, K.M., van Balkom, A.J.L.M. (2017). Risk of relapse after antidepressant discontinuation in anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of relapse prevention trials. BMJ, 358(1) , j3927.
- Fleming, K. M., & Herring, M. P. (2018). The effects of pilates on mental health outcomes: A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Complementary Therapies in Medicine , 37, 80-95.
- Hagen, I., & Nayar, U. S. (2014). Yoga for children and young people’s mental health and well-being: research review and reflections on the mental health potentials of yoga. Frontiers in Psychiatry , 5.
- Harmon, T.M., Nelson, R.O., Hayes, S.C. (1980). Self-monitoring of mood versus activity by depressed clients. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48(1) , 30-38.
- Henderson, C., Robinson, E., Evans-Lacko, S., Thornicroft, G. (2017). Relationships between anti-stigma programme awareness, disclosure comfort and intended help-seeking regarding a mental health problem. British Journal of Psychiatry, 211(5) , 316-322.
- Kaduson, H.G., Schaefer, C.E. (Eds.). (2003). 101 favorite play therapy techniques. Volume III. Lanham, MA: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
- Kircanski, K., Lieberman, M. D., & Craske, M. G. (2012). Feelings into words: contributions of language to exposure therapy. Psychological Science, 23 (10), 1086.
- Lambert, M.J. (2015). Progress Feedback and the OQ-System: The Past and the Future. Psychotherapy, 52(4) , 381-390.
- McManus, F., Van Doorn, K., Yiend, J. (2012). Examining the effects of thought records and behavioral experiments in instigating belief change. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 43(1) , 540-547.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Hi , I am a mental health advocate in south Sudan. Do you have project documents to address PTSD for Military personnel returning from frontline?
Sounds like you’re doing important work. Could you please provide a little more information about what specifically you’re looking for? For instance, are you looking for a scale to assess the presence of PTSD symptoms or resources to aid in the treatment of PTSD among returning military personnel? Let me know, and I’ll see if I can’t point you in the right direction.
– Nicole | Community Manager
this was fantastic, it was great reading what people thought and getting new ideas
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Positive Pain Management: How to Better Manage Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a condition that causes widespread, constant pain and distress and fills both sufferers and the healthcare professionals who treat them with dread. [...]

Mental Health in Teens: 10 Risk & Protective Factors
31.9% of adolescents have anxiety-related disorders (ADAA, n.d.). According to Solmi et al. (2022), the age at which mental health disorders most commonly begin to [...]

18 Effective Thought-Stopping Techniques (& 10 PDFs)
From time to time, we all experience intrusive, unwanted thoughts in our stream of consciousness (Shackelford & Zeigler-Hill, 2020). While many are frivolous, such as [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (48)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (17)
- Positive Parenting (3)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (36)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (31)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
3 Positive Psychology Tools (PDF)
Data and Statistics on Children’s Mental Health
Mental health is an important part of children’s overall health and well-being. Mental health includes children’s mental, emotional, and behavioral well-being. It affects how children think, feel, and act. It also plays a role in how children handle stress, relate to others, and make healthy choices.
Mental disorders among children are described as serious changes in the way children typically learn, behave, or handle their emotions, causing distress and problems getting through the day. 1 Among the more common mental disorders that can be diagnosed in childhood are attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, and behavior disorders.
There are different ways to assess mental health and mental disorders in children. CDC uses surveys, like the National Survey of Children’s Health, to describe the presence of positive indicators of children’s mental health and to understand the number of children with diagnosed mental disorders and whether they received treatment. In this type of survey, parents report on indicators of positive mental health for their child and report any diagnoses their child has received from a healthcare provider. The information on this page provides data about indicators of positive mental health in children and mental health disorders that are most common in children.
Facts about mental health in U.S. children
National data on positive mental health indicators that describe mental, emotional, and behavioral well-being for children are limited. Based on the data we do have:
- Affection (97.0%), resilience (87.9%), positivity (98.7%) and curiosity (93.9%) among children ages 3-5 years 2
- Curiosity (93.0%), persistence (84.2%), and self-control (73.8%) among children ages 6-11 years 2
- Curiosity (86.5 %), persistence (84.7%), and self-control (79.8%) among children ages 12-17 years 2
Facts about mental disorders in U.S. children
- ADHD 9.8% (approximately 6.0 million) 2
- Anxiety 9.4% (approximately 5.8 million) 2
- Behavior problems 8.9% (approximately 5.5 million) 2
- Depression 4.4% (approximately 2.7 million) 2
- Having another mental disorder was most common in children with depression: about 3 in 4 children with depression also had anxiety (73.8%) and almost 1 in 2 had behavior problems (47.2%). 3
- For children with anxiety, more than 1 in 3 also had behavior problems (37.9%) and about 1 in 3 also had depression (32.3%). 3
- For children with behavior problems, more than 1 in 3 also had anxiety (36.6%) and about 1 in 5 also had depression (20.3%). 3
- “Ever having been diagnosed with either anxiety or depression” among children aged 6–17 years increased from 5.4% in 2003 to 8% in 2007 and to 8.4% in 2011–2012. 4
- “Ever having been diagnosed with anxiety” increased from 5.5% in 2007 to 6.4% in 2011–2012. 4
- “Ever having been diagnosed with depression” did not change between 2007 (4.7%) and 2011-2012 (4.9%). 4
- For adolescents, depression, substance use and suicide are important concerns. Among adolescents aged 12-17 years in 2018-2019 reporting on the past year:
- 15.1% had a major depressive episode. 2
- 36.7% had persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness. 2
- 4.1% had a substance use disorder. 2
- 1.6% had an alcohol use disorder. 2
- 3.2% had an illicit drug use disorder. 2
- 18.8% seriously considered attempting suicide. 2
- 15.7% made a suicide plan. 2
- 8.9% attempted suicide. 2
- 2.5% made a suicide attempt requiring medical treatment. 2
Learn more about high-risk substance use among youth . Learn more about suicide .

- Nearly 8 in 10 children (78.1%) with depression received treatment. 3
- 6 in 10 children (59.3%) with anxiety received treatment. 3
- More than 5 in 10 children (53.5%) with behavior disorders received treatment. 3
- 1 in 6 U.S. children aged 2–8 years (17.4%) had a diagnosed mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder. 5
- Diagnoses of ADHD, anxiety, and depression become are more common with increased age. 3
- Behavior problems are more common among children aged 6–11 years than younger or older children. 3
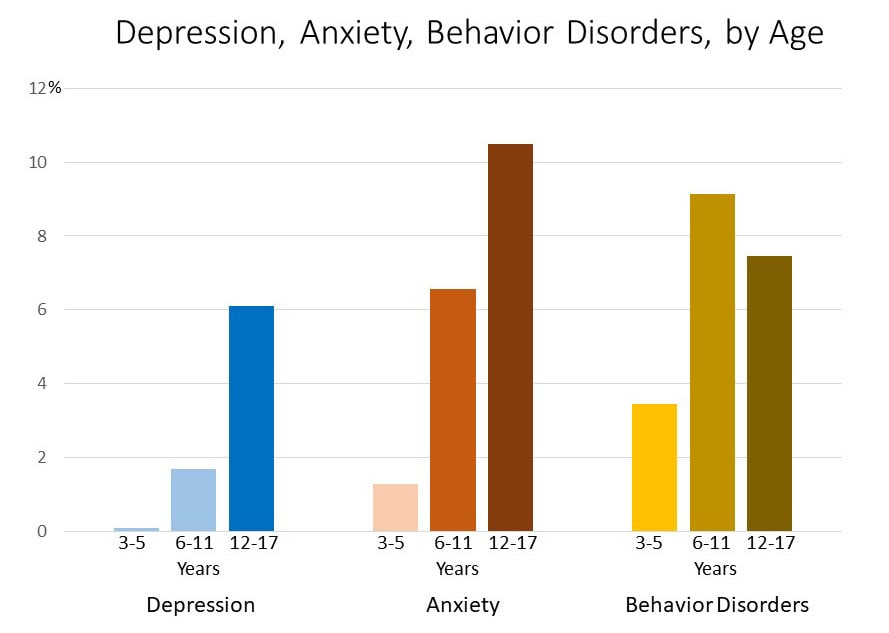
- Among children aged 2-8 years, boys were more likely than girls to have a mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder. 5
- Among children living below 100% of the federal poverty level, more than 1 in 5 (22%) had a mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder. 5
- Age and poverty level affected the likelihood of children receiving treatment for anxiety, depression, or behavior problems. 3
- Children who were discriminated against based on race or ethnicity had higher percentages of one or more physical health conditions (37.8% versus 27.1%), and one or more mental health conditions (28.9% versus 17.8%). 6
- Racial/ethnic discrimination was almost seven times as common among children with three other ACEs compared to those with no other ACEs. 6
Note : The estimates reported on this page are based on parent report, using nationally representative surveys. This method has several limitations. It is not known to what extent children receive these diagnoses accurately. Estimates based on parent-reported diagnoses may match those based on medical records, 7 but some children may also have mental disorders that have not been diagnosed, or receive diagnoses that may not be the best fit for their symptoms. Limited information on measuring children’s mental health nationally is available 2 .
Read more about children’s mental health from a community study .
Access to mental health treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate services for children and their families can make a difference in the lives of children with mental disorders. 7 Access to providers who can offer services, including screening, referrals, and treatment, varies by location. CDC is working to learn more about access to behavioral health services and supports for children and their families.
View information by state describing the rates of different types of providers who can offer behavioral health services providers by county.
Read a recent report describing shortages of services, barriers to treatment, and how integration of behavioral health care with pediatric primary care could address the issues.
Read a policy brief on potential ways to increase access to mental health services for children in rural areas
What is It and Why is It Important?
Data sources for mental health and related conditions
There are many different datasets which include information on children’s mental health and related conditions for children living in the United States.
Healthy People 2030 Healthy People 2030 sets data-driven national objectives to improve health and well-being over the next decade, including children’s mental health and well-being.
National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) NSFG gathers information on family life, marriage and divorce, pregnancy, infertility, use of contraception, and general and reproductive health.
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) NHANES assesses health and nutritional status through interviews and physical examinations, and includes conditions, symptoms, and concerns associated with mental health and substance abuse, as well as the use and need for mental health services.
National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) NHIS collects data on children’s mental health, mental disorders, such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, depression and anxiety problems, and use and need for mental health services.
National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH) NSCH examines the health of children, with emphasis on well-being, including medical homes, family interactions, the health of parents, school and after-school experiences, and safe neighborhoods. This survey was redesigned in 2016.
For previous versions of this survey, see also: National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH 2003, 2007, 2011-12) National Survey of Children with Special Healthcare Needs (NS-CSHCN 2001, 2005-6, 2009-10)
National Survey of the Diagnosis and Treatment of ADHD and Tourette Syndrome (NS-DATA) NS-DATA collects information about children, 2-15 years old in 2011-2012, who had ever been diagnosed with ADHD and/or Tourette syndrome (TS), with the goal of better understanding diagnostic practices, level of impairment, and treatments for this group of children.
National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) NSDUH, administered by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), provides national- and state-level data on the use of tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs (including non-medical use of prescription drugs), as well as data on mental health in the United States.
National Vital Statistics System (NVSS) NVSS contains vital statistics from the official records of live births, deaths, causes of death, marriages, divorces, and annulment recorded by states and independent registration areas
National Youth Tobacco Survey (NYTS) NYTS is a nationally representative school-based survey on tobacco use by public school students enrolled in grades 6-12.
School Associated Violent Death Study (SAVD) SAVD plays an important role in monitoring trends related to school-associated violent deaths (including suicide), identifying the factors that increase the risk, and assessing the effects of prevention efforts.
School Health Policies and Programs Study (SHPPS) SHPPS is a national survey assessing school health policies and practices at the state, district, school, and classroom levels. Collected data includes mental health and social service policies.
Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS) WISQARS is an interactive database system that provides customized reports of injury-related data.
Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System (YRBSS) The YRBSS monitors health-risk behaviors, including tobacco use, substance abuse, unintentional injuries and violence, sexual behaviors that contribute to unintended pregnancy, and sexually transmitted diseases.
- Perou R, Bitsko RH, Blumberg SJ, Pastor P, Ghandour RM, Gfroerer JC, Hedden SL, Crosby AE, Visser SN, Schieve LA, Parks SE, Hall JE, Brody D, Simile CM, Thompson WW, Baio J, Avenevoli S, Kogan MD, Huang LN. Mental health surveillance among children – United States, 2005—2011. MMWR 2013;62(Suppl; May 16, 2013):1-35. [ Read summary ]
- Bitsko RH, Claussen AH, Lichtstein J, Black LJ, Everett Jones S, Danielson MD, Hoenig JM, Davis Jack SP, Brody DJ, Gyawali S, Maenner MM, Warner M, Holland KM, Perou R, Crosby AE, Blumberg SJ, Avenevoli S, Kaminski JW, Ghandour RM. Surveillance of Children’s Mental Health – United States, 2013 – 2019 MMWR, , 2022 / 71(Suppl-2);1–42. [Read article]
- Ghandour RM, Sherman LJ, Vladutiu CJ, Ali MM, Lynch SE, Bitsko RH, Blumberg SJ. Prevalence and treatment of depression, anxiety, and conduct problems in U.S. children. The Journal of Pediatrics , 2018. Published online before print October 12, 2018 [ Read summary ]
- Bitsko RH, Holbrook JR, Ghandour RM, Blumberg SJ, Visser SN, Perou R, Walkup J. Epidemiology and impact of healthcare provider diagnosed anxiety and depression among US children. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics . Published online before print April 24, 2018 [ Read summary ]
- Cree RA, Bitsko RH, Robinson LR, Holbrook JR, Danielson ML, Smith DS, Kaminski JW, Kenney MK, Peacock G. Health care, family, and community factors associated with mental, behavioral, and developmental disorders and poverty among children aged 2–8 years — United States, 2016. MMWR , 2018;67(5):1377-1383. [ Read article ]
- Hutchins HJ, Barry CM, Valentine V, Bacon S, Njai R, Claussen AH, Ghandour RM, Lebrun-Harris LA, Perkins K, Robinson LR (submitted). Perceived racial/ethnic discrimination, physical and mental health conditions in childhood, and the relative role of other adverse experiences. Adversity and Resilience Science published online May 23, 2022. [ Read summary ]
- US Department of Health and Human Services Health Resources and Services Administration & Maternal and Child Health Bureau. Mental health: A report of the Surgeon General . Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Mental Health Services, and National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Mental Health; 1999. [ Read report ]
To receive email updates about this topic, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

More mental health support in schools makes sense – but some children may fall through gaps
Senior Fellow, Health Services Management Centre, School of Social Policy, University of Birmingham
Disclosure statement
Jo Ellins receives funding from the National Institute for Health and Care Research.
University of Birmingham provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
Schools and colleges have a crucial role to play in supporting children’s mental health. They are places where young people’s mental health difficulties are identified and help is provided, and they can promote all pupils’ emotional wellbeing.
Most children spend more time in school than anywhere else other than home, and parents who are concerned about their child’s mental health turn to teachers and school staff for advice more than any other professionals. Investing more in schools-based mental health services makes good sense.
This is something the government has been doing in England through the creation of mental health support teams. These are teams of mental health practitioners who work with clusters of schools and colleges. Most are based within the NHS, although some are provided by voluntary sector organisations or local councils.
The first 58 mental health support teams went live in 2020, working in and with more than 1,000 schools and colleges. By 2025, more than 600 teams will have been created, serving around half the schools in England.
I led an early national evaluation of the first 58 teams . This study looked at how they were set up, what support they were providing and how they were progressing. Together with colleagues, I found that increasing mental health support in schools was well received, but that some young people still faced difficulties getting appropriate help.
Mental health support teams are intended to provide support to young people with “mild to moderate” mental health difficulties, such as anxiety and low mood. Their role also includes working with school staff to develop a positive culture focused on wellbeing, and giving schools and parents advice to help them access other types of support. This includes specialist mental health services for young people with more serious or complex problems.
Much of the day-to-day work with young people and schools is delivered by education mental health practitioners . This is a new role in the mental health workforce, created specifically for mental health support teams.
Education mental health practitioners receive one year’s training with a focus on developing the skills to deliver cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) to young people, either one-to-one or in small groups.
We heard from staff in the teams, schools and colleges, and those working in other local services supporting children’s mental health. We also spoke to young people at schools with mental health support teams.
Our study confirmed the importance of investing in schools-based mental health. School staff told us how valuable it was having ready access to advice when they were concerned about a pupil’s emotional wellbeing, and that they felt more knowledgeable and confident talking to young people about their mental health.
Having access to a team made it easier for some young people to get support at the right time. Timely access is crucial for many reasons, not least because more than half of young people experience a deterioration in their mental health while they are waiting for support.
Through the gaps
However, we also found that not all young people were benefiting from this investment. We heard that some young people were at risk of falling between gaps in provision. They had mental health problems that were neither “mild to moderate”, nor were they judged serious or urgent enough to meet the threshold for specialist NHS help.
There is evidence that thresholds for specialist NHS help are rising in response to growing demand, and so increasing numbers of young people may be falling into this gap between services.
Our early study was not designed to assess the effectiveness of the support that the teams were providing, but people we spoke to were keen to share their views about this. There were concerns from schools and colleges that the teams usually offered only one type of support, and that this was not suitable or beneficial for all young people.
The teams’ early experiences suggested that the CBT approaches that education mental health practitioners were trained to deliver didn’t work well for several groups. These included young people who had special education needs, or were neurodiverse, or whose mental health problems were related to traumatic circumstances or life events, such as poverty or domestic violence.
Wider research shows that CBT can be effective for these groups, but only when it is carefully tailored to their particular needs and circumstances, or is delivered in trauma-informed ways .
These findings offer valuable information about how well mental health support teams are working, but our study only looked at the first wave of teams. We don’t know if these experiences are the same for the teams that were set up later.
I am now co-leading a second, much larger, study of almost 400 mental health support teams, assessing their impact and cost-effectiveness. One of the main aims of our current study is to assess the impact of this support on young people’s mental health outcomes. As the study progresses, we will know more about how well this support works and who it works for.
- Young people
- Youth mental health
- Child wellbeing
- Keep me on trend

Research Fellow – Beyond The Resource Curse

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

IMAGES
COMMENTS
"School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared." ... Citation: Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in (2021, August 16 ...
Health Hazards of Homework. Pediatrics. A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework "experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.".
My Safe Spaces. worksheet. A safe space is a person, place, or activity that helps you feel calm, comfortable, and supported, and lets you be yourself. Your safe space is there for you no matter how you feel—happy or sad, talkative or quiet, brave or scared. A safe space is free of judgment and is full of acceptance.
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. The researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress, such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep ...
Key points. Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework. Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Actually useful ways to help children with homework, bullying, and mental health. By Allie Volpe @allieevolpe Aug 27, 2023, 8:00am EDT Share this story
Homework as a Mental Health Concern. It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health ...
MENTAL HEALTH. All children are sad, anxious, irritable, or aggressive at times, and many find it occasionally challenging. to sit still, pay attention, or interact with others. In most cases, these are just typical developmental phases. However, such behaviors may also indicate a more serious problem in some children.
Some of the best educational science available shows that excessive homework is of limited benefit and in fact harms children's health and well-being. Add a mental health curriculum.
The mental health crisis among children and teens: How parents can help. March 8, 2022. By Claire McCarthy, MD, Senior Faculty Editor, Harvard Health Publishing. We are in the midst of a pediatric mental health crisis — and parents need to take action. Over the past couple of years, the pandemic has not only killed hundreds of thousands; it ...
All children are sad, anxious, irritable, or aggressive at times, or they occasionally find it challenging to sit still, pay attention, or interact with others. In most cases, these are just typical developmental phases. However, such behaviors may indicate a more serious problem in some children. Mental disorders can begin in childhood.
It helps to pick a spot where your child always does homework - the kitchen table for example. By using the same location each day, it will be easier for the child to stay on task. Agree on a Time To Do Homework. You know your child's behavior patterns. Some kids need time to transition back home after a long day at school.
Last Reviewed: August 23, 2023. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Mental health in childhood means reaching developmental and emotional milestones, and learning healthy social skills and how to cope when there are problems.
Introduction. Homework, or between-session practice of skills learned during therapy, is one of the most integral, yet underutilized components of high-quality, evidence-based mental health care (Kazantzis & Deane, 1999).Homework activities (e.g., self-monitoring, relaxation, exposure, parent behavior management) are assigned by providers in-session and completed by patients between sessions ...
Mental health is an important part of overall health for children and adolescents. Many adults with mental disorders had symptoms that were not recognized or addressed in childhood or adolescence. Help raise awareness about the importance of children's mental health and early diagnosis and treatment by sharing information and materials based ...
The promotion of mental health among children and adolescents is a public health imperative worldwide, and schools have been proposed as the primary and targeted settings for mental health promotion for students in grades K-12. This review sought to provide a comprehensive understanding of key factors involved in models of school education ...
1. Educate Yourself About Mental Health. If you know your child's mental health diagnosis or have an idea of what it might be, you can look for nonprofit organizations particular to that ...
A 504 plan is created for a child identified with a disability that ensures they receive accommodations to be successful at school. Students with either physical or mental health conditions - including anxiety or depression - are eligible to develop a formalized 504 plan with their school system. A 504 plan outlines specific at‑school ...
This Understanding Mental Health Stigma sheet can be used as an aid to help raise awareness of the stigma that surrounds mental illness, as well as what it looks like. 5. Mental Health Management Bingo. Mental Health Management Bingo is a fun classroom game that can be played with slightly older students.
A recent study focused on children from affluent areas. Kids were doing an average of three hours of homework each night. Another report says kids' homework load hasn't changed since 1984
Many family, community, and healthcare factors are related to children's mental health. Among children aged 2-8 years, boys were more likely than girls to have a mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder. 5 Among children living below 100% of the federal poverty level, more than 1 in 5 (22%) had a mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder. 5 ...
Write down important information so it can be accessed easily. This infographic. Set up a consistent time for your child to do homework. It's important to establish routines and expectations. Use a timer to manage attention and help your child stay on task. Schedule short breaks (5-10 minutes).
Published: April 8, 2024 10:21am EDT. Schools and colleges have a crucial role to play in supporting children's mental health. They are places where young people's mental health difficulties ...