
Statistics Made Easy

How to Write a Null Hypothesis (5 Examples)
A hypothesis test uses sample data to determine whether or not some claim about a population parameter is true.
Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms:
H 0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter =, ≤, ≥ some value
H A (Alternative Hypothesis): Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value
Note that the null hypothesis always contains the equal sign .
We interpret the hypotheses as follows:
Null hypothesis: The sample data provides no evidence to support some claim being made by an individual.
Alternative hypothesis: The sample data does provide sufficient evidence to support the claim being made by an individual.
For example, suppose it’s assumed that the average height of a certain species of plant is 20 inches tall. However, one botanist claims the true average height is greater than 20 inches.
To test this claim, she may go out and collect a random sample of plants. She can then use this sample data to perform a hypothesis test using the following two hypotheses:
H 0 : μ ≤ 20 (the true mean height of plants is equal to or even less than 20 inches)
H A : μ > 20 (the true mean height of plants is greater than 20 inches)
If the sample data gathered by the botanist shows that the mean height of this species of plants is significantly greater than 20 inches, she can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the mean height is greater than 20 inches.
Read through the following examples to gain a better understanding of how to write a null hypothesis in different situations.
Example 1: Weight of Turtles
A biologist wants to test whether or not the true mean weight of a certain species of turtles is 300 pounds. To test this, he goes out and measures the weight of a random sample of 40 turtles.
Here is how to write the null and alternative hypotheses for this scenario:
H 0 : μ = 300 (the true mean weight is equal to 300 pounds)
H A : μ ≠ 300 (the true mean weight is not equal to 300 pounds)
Example 2: Height of Males
It’s assumed that the mean height of males in a certain city is 68 inches. However, an independent researcher believes the true mean height is greater than 68 inches. To test this, he goes out and collects the height of 50 males in the city.
H 0 : μ ≤ 68 (the true mean height is equal to or even less than 68 inches)
H A : μ > 68 (the true mean height is greater than 68 inches)
Example 3: Graduation Rates
A university states that 80% of all students graduate on time. However, an independent researcher believes that less than 80% of all students graduate on time. To test this, she collects data on the proportion of students who graduated on time last year at the university.
H 0 : p ≥ 0.80 (the true proportion of students who graduate on time is 80% or higher)
H A : μ < 0.80 (the true proportion of students who graduate on time is less than 80%)
Example 4: Burger Weights
A food researcher wants to test whether or not the true mean weight of a burger at a certain restaurant is 7 ounces. To test this, he goes out and measures the weight of a random sample of 20 burgers from this restaurant.
H 0 : μ = 7 (the true mean weight is equal to 7 ounces)
H A : μ ≠ 7 (the true mean weight is not equal to 7 ounces)
Example 5: Citizen Support
A politician claims that less than 30% of citizens in a certain town support a certain law. To test this, he goes out and surveys 200 citizens on whether or not they support the law.
H 0 : p ≥ .30 (the true proportion of citizens who support the law is greater than or equal to 30%)
H A : μ < 0.30 (the true proportion of citizens who support the law is less than 30%)
Additional Resources
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing Introduction to Confidence Intervals An Explanation of P-Values and Statistical Significance
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.1: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 10211

- Kyle Siegrist
- University of Alabama in Huntsville via Random Services
Basic Theory
Preliminaries.
As usual, our starting point is a random experiment with an underlying sample space and a probability measure \(\P\). In the basic statistical model, we have an observable random variable \(\bs{X}\) taking values in a set \(S\). In general, \(\bs{X}\) can have quite a complicated structure. For example, if the experiment is to sample \(n\) objects from a population and record various measurements of interest, then \[ \bs{X} = (X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n) \] where \(X_i\) is the vector of measurements for the \(i\)th object. The most important special case occurs when \((X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n)\) are independent and identically distributed. In this case, we have a random sample of size \(n\) from the common distribution.
The purpose of this section is to define and discuss the basic concepts of statistical hypothesis testing . Collectively, these concepts are sometimes referred to as the Neyman-Pearson framework, in honor of Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson, who first formalized them.
A statistical hypothesis is a statement about the distribution of \(\bs{X}\). Equivalently, a statistical hypothesis specifies a set of possible distributions of \(\bs{X}\): the set of distributions for which the statement is true. A hypothesis that specifies a single distribution for \(\bs{X}\) is called simple ; a hypothesis that specifies more than one distribution for \(\bs{X}\) is called composite .
In hypothesis testing , the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis . The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\).
An hypothesis test is a statistical decision ; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or to fail to reject the null hypothesis. The decision that we make must, of course, be based on the observed value \(\bs{x}\) of the data vector \(\bs{X}\). Thus, we will find an appropriate subset \(R\) of the sample space \(S\) and reject \(H_0\) if and only if \(\bs{x} \in R\). The set \(R\) is known as the rejection region or the critical region . Note the asymmetry between the null and alternative hypotheses. This asymmetry is due to the fact that we assume the null hypothesis, in a sense, and then see if there is sufficient evidence in \(\bs{x}\) to overturn this assumption in favor of the alternative.
An hypothesis test is a statistical analogy to proof by contradiction, in a sense. Suppose for a moment that \(H_1\) is a statement in a mathematical theory and that \(H_0\) is its negation. One way that we can prove \(H_1\) is to assume \(H_0\) and work our way logically to a contradiction. In an hypothesis test, we don't prove anything of course, but there are similarities. We assume \(H_0\) and then see if the data \(\bs{x}\) are sufficiently at odds with that assumption that we feel justified in rejecting \(H_0\) in favor of \(H_1\).
Often, the critical region is defined in terms of a statistic \(w(\bs{X})\), known as a test statistic , where \(w\) is a function from \(S\) into another set \(T\). We find an appropriate rejection region \(R_T \subseteq T\) and reject \(H_0\) when the observed value \(w(\bs{x}) \in R_T\). Thus, the rejection region in \(S\) is then \(R = w^{-1}(R_T) = \left\{\bs{x} \in S: w(\bs{x}) \in R_T\right\}\). As usual, the use of a statistic often allows significant data reduction when the dimension of the test statistic is much smaller than the dimension of the data vector.
The ultimate decision may be correct or may be in error. There are two types of errors, depending on which of the hypotheses is actually true.
Types of errors:
- A type 1 error is rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when \(H_0\) is true.
- A type 2 error is failing to reject the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when the alternative hypothesis \(H_1\) is true.
Similarly, there are two ways to make a correct decision: we could reject \(H_0\) when \(H_1\) is true or we could fail to reject \(H_0\) when \(H_0\) is true. The possibilities are summarized in the following table:
Of course, when we observe \(\bs{X} = \bs{x}\) and make our decision, either we will have made the correct decision or we will have committed an error, and usually we will never know which of these events has occurred. Prior to gathering the data, however, we can consider the probabilities of the various errors.
If \(H_0\) is true (that is, the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_0\)), then \(\P(\bs{X} \in R)\) is the probability of a type 1 error for this distribution. If \(H_0\) is composite, then \(H_0\) specifies a variety of different distributions for \(\bs{X}\) and thus there is a set of type 1 error probabilities.
The maximum probability of a type 1 error, over the set of distributions specified by \( H_0 \), is the significance level of the test or the size of the critical region.
The significance level is often denoted by \(\alpha\). Usually, the rejection region is constructed so that the significance level is a prescribed, small value (typically 0.1, 0.05, 0.01).
If \(H_1\) is true (that is, the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_1\)), then \(\P(\bs{X} \notin R)\) is the probability of a type 2 error for this distribution. Again, if \(H_1\) is composite then \(H_1\) specifies a variety of different distributions for \(\bs{X}\), and thus there will be a set of type 2 error probabilities. Generally, there is a tradeoff between the type 1 and type 2 error probabilities. If we reduce the probability of a type 1 error, by making the rejection region \(R\) smaller, we necessarily increase the probability of a type 2 error because the complementary region \(S \setminus R\) is larger.
The extreme cases can give us some insight. First consider the decision rule in which we never reject \(H_0\), regardless of the evidence \(\bs{x}\). This corresponds to the rejection region \(R = \emptyset\). A type 1 error is impossible, so the significance level is 0. On the other hand, the probability of a type 2 error is 1 for any distribution defined by \(H_1\). At the other extreme, consider the decision rule in which we always rejects \(H_0\) regardless of the evidence \(\bs{x}\). This corresponds to the rejection region \(R = S\). A type 2 error is impossible, but now the probability of a type 1 error is 1 for any distribution defined by \(H_0\). In between these two worthless tests are meaningful tests that take the evidence \(\bs{x}\) into account.
If \(H_1\) is true, so that the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_1\), then \(\P(\bs{X} \in R)\), the probability of rejecting \(H_0\) is the power of the test for that distribution.
Thus the power of the test for a distribution specified by \( H_1 \) is the probability of making the correct decision.
Suppose that we have two tests, corresponding to rejection regions \(R_1\) and \(R_2\), respectively, each having significance level \(\alpha\). The test with region \(R_1\) is uniformly more powerful than the test with region \(R_2\) if \[ \P(\bs{X} \in R_1) \ge \P(\bs{X} \in R_2) \text{ for every distribution of } \bs{X} \text{ specified by } H_1 \]
Naturally, in this case, we would prefer the first test. Often, however, two tests will not be uniformly ordered; one test will be more powerful for some distributions specified by \(H_1\) while the other test will be more powerful for other distributions specified by \(H_1\).
If a test has significance level \(\alpha\) and is uniformly more powerful than any other test with significance level \(\alpha\), then the test is said to be a uniformly most powerful test at level \(\alpha\).
Clearly a uniformly most powerful test is the best we can do.
\(P\)-value
In most cases, we have a general procedure that allows us to construct a test (that is, a rejection region \(R_\alpha\)) for any given significance level \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\). Typically, \(R_\alpha\) decreases (in the subset sense) as \(\alpha\) decreases.
The \(P\)-value of the observed value \(\bs{x}\) of \(\bs{X}\), denoted \(P(\bs{x})\), is defined to be the smallest \(\alpha\) for which \(\bs{x} \in R_\alpha\); that is, the smallest significance level for which \(H_0\) is rejected, given \(\bs{X} = \bs{x}\).
Knowing \(P(\bs{x})\) allows us to test \(H_0\) at any significance level for the given data \(\bs{x}\): If \(P(\bs{x}) \le \alpha\) then we would reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\); if \(P(\bs{x}) \gt \alpha\) then we fail to reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\). Note that \(P(\bs{X})\) is a statistic . Informally, \(P(\bs{x})\) can often be thought of as the probability of an outcome as or more extreme than the observed value \(\bs{x}\), where extreme is interpreted relative to the null hypothesis \(H_0\).
Analogy with Justice Systems
There is a helpful analogy between statistical hypothesis testing and the criminal justice system in the US and various other countries. Consider a person charged with a crime. The presumed null hypothesis is that the person is innocent of the crime; the conjectured alternative hypothesis is that the person is guilty of the crime. The test of the hypotheses is a trial with evidence presented by both sides playing the role of the data. After considering the evidence, the jury delivers the decision as either not guilty or guilty . Note that innocent is not a possible verdict of the jury, because it is not the point of the trial to prove the person innocent. Rather, the point of the trial is to see whether there is sufficient evidence to overturn the null hypothesis that the person is innocent in favor of the alternative hypothesis of that the person is guilty. A type 1 error is convicting a person who is innocent; a type 2 error is acquitting a person who is guilty. Generally, a type 1 error is considered the more serious of the two possible errors, so in an attempt to hold the chance of a type 1 error to a very low level, the standard for conviction in serious criminal cases is beyond a reasonable doubt .
Tests of an Unknown Parameter
Hypothesis testing is a very general concept, but an important special class occurs when the distribution of the data variable \(\bs{X}\) depends on a parameter \(\theta\) taking values in a parameter space \(\Theta\). The parameter may be vector-valued, so that \(\bs{\theta} = (\theta_1, \theta_2, \ldots, \theta_n)\) and \(\Theta \subseteq \R^k\) for some \(k \in \N_+\). The hypotheses generally take the form \[ H_0: \theta \in \Theta_0 \text{ versus } H_1: \theta \notin \Theta_0 \] where \(\Theta_0\) is a prescribed subset of the parameter space \(\Theta\). In this setting, the probabilities of making an error or a correct decision depend on the true value of \(\theta\). If \(R\) is the rejection region, then the power function \( Q \) is given by \[ Q(\theta) = \P_\theta(\bs{X} \in R), \quad \theta \in \Theta \] The power function gives a lot of information about the test.
The power function satisfies the following properties:
- \(Q(\theta)\) is the probability of a type 1 error when \(\theta \in \Theta_0\).
- \(\max\left\{Q(\theta): \theta \in \Theta_0\right\}\) is the significance level of the test.
- \(1 - Q(\theta)\) is the probability of a type 2 error when \(\theta \notin \Theta_0\).
- \(Q(\theta)\) is the power of the test when \(\theta \notin \Theta_0\).
If we have two tests, we can compare them by means of their power functions.
Suppose that we have two tests, corresponding to rejection regions \(R_1\) and \(R_2\), respectively, each having significance level \(\alpha\). The test with rejection region \(R_1\) is uniformly more powerful than the test with rejection region \(R_2\) if \( Q_1(\theta) \ge Q_2(\theta)\) for all \( \theta \notin \Theta_0 \).
Most hypothesis tests of an unknown real parameter \(\theta\) fall into three special cases:
Suppose that \( \theta \) is a real parameter and \( \theta_0 \in \Theta \) a specified value. The tests below are respectively the two-sided test , the left-tailed test , and the right-tailed test .
- \(H_0: \theta = \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0\)
- \(H_0: \theta \ge \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \lt \theta_0\)
- \(H_0: \theta \le \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \gt \theta_0\)
Thus the tests are named after the conjectured alternative. Of course, there may be other unknown parameters besides \(\theta\) (known as nuisance parameters ).
Equivalence Between Hypothesis Test and Confidence Sets
There is an equivalence between hypothesis tests and confidence sets for a parameter \(\theta\).
Suppose that \(C(\bs{x})\) is a \(1 - \alpha\) level confidence set for \(\theta\). The following test has significance level \(\alpha\) for the hypothesis \( H_0: \theta = \theta_0 \) versus \( H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0 \): Reject \(H_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \notin C(\bs{x})\)
By definition, \(\P[\theta \in C(\bs{X})] = 1 - \alpha\). Hence if \(H_0\) is true so that \(\theta = \theta_0\), then the probability of a type 1 error is \(P[\theta \notin C(\bs{X})] = \alpha\).
Equivalently, we fail to reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\) if and only if \(\theta_0\) is in the corresponding \(1 - \alpha\) level confidence set. In particular, this equivalence applies to interval estimates of a real parameter \(\theta\) and the common tests for \(\theta\) given above .
In each case below, the confidence interval has confidence level \(1 - \alpha\) and the test has significance level \(\alpha\).
- Suppose that \(\left[L(\bs{X}, U(\bs{X})\right]\) is a two-sided confidence interval for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta = \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \lt L(\bs{X})\) or \(\theta_0 \gt U(\bs{X})\).
- Suppose that \(L(\bs{X})\) is a confidence lower bound for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta \le \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \gt \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \lt L(\bs{X})\).
- Suppose that \(U(\bs{X})\) is a confidence upper bound for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta \ge \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \lt \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \gt U(\bs{X})\).
Pivot Variables and Test Statistics
Recall that confidence sets of an unknown parameter \(\theta\) are often constructed through a pivot variable , that is, a random variable \(W(\bs{X}, \theta)\) that depends on the data vector \(\bs{X}\) and the parameter \(\theta\), but whose distribution does not depend on \(\theta\) and is known. In this case, a natural test statistic for the basic tests given above is \(W(\bs{X}, \theta_0)\).
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Jan 23, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 13: Inferential Statistics
Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
Learning Objectives
- Explain the purpose of null hypothesis testing, including the role of sampling error.
- Describe the basic logic of null hypothesis testing.
- Describe the role of relationship strength and sample size in determining statistical significance and make reasonable judgments about statistical significance based on these two factors.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters . Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 clinically depressed adults and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for clinically depressed adults).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. The mean number of depressive symptoms might be 8.73 in one sample of clinically depressed adults, 6.45 in a second sample, and 9.44 in a third—even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. Similarly, the correlation (Pearson’s r ) between two variables might be +.24 in one sample, −.04 in a second sample, and +.15 in a third—again, even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error . (Note that the term error here refers to random variability and does not imply that anyone has made a mistake. No one “commits a sampling error.”)
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H 0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H 1 ). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis .
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value . A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant . If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to conclude that it is true. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994) [1] . Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect . The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Table 13.1 shows roughly how relationship strength and sample size combine to determine whether a sample result is statistically significant. The columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: weak, medium, and strong. The rows represent four sample sizes that can be considered small, medium, large, and extra large in the context of psychological research. Thus each cell in the table represents a combination of relationship strength and sample size. If a cell contains the word Yes , then this combination would be statistically significant for both Cohen’s d and Pearson’s r . If it contains the word No , then it would not be statistically significant for either. There is one cell where the decision for d and r would be different and another where it might be different depending on some additional considerations, which are discussed in Section 13.2 “Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests”
Although Table 13.1 provides only a rough guideline, it shows very clearly that weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this lesson in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
Table 13.1 illustrates another extremely important point. A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007) [2] . The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.
Key Takeaways
- Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
- The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
- The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
- Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
- Discussion: Imagine a study showing that people who eat more broccoli tend to be happier. Explain for someone who knows nothing about statistics why the researchers would conduct a null hypothesis test.
- The correlation between two variables is r = −.78 based on a sample size of 137.
- The mean score on a psychological characteristic for women is 25 ( SD = 5) and the mean score for men is 24 ( SD = 5). There were 12 women and 10 men in this study.
- In a memory experiment, the mean number of items recalled by the 40 participants in Condition A was 0.50 standard deviations greater than the mean number recalled by the 40 participants in Condition B.
- In another memory experiment, the mean scores for participants in Condition A and Condition B came out exactly the same!
- A student finds a correlation of r = .04 between the number of units the students in his research methods class are taking and the students’ level of stress.
Long Descriptions
“Null Hypothesis” long description: A comic depicting a man and a woman talking in the foreground. In the background is a child working at a desk. The man says to the woman, “I can’t believe schools are still teaching kids about the null hypothesis. I remember reading a big study that conclusively disproved it years ago.” [Return to “Null Hypothesis”]
“Conditional Risk” long description: A comic depicting two hikers beside a tree during a thunderstorm. A bolt of lightning goes “crack” in the dark sky as thunder booms. One of the hikers says, “Whoa! We should get inside!” The other hiker says, “It’s okay! Lightning only kills about 45 Americans a year, so the chances of dying are only one in 7,000,000. Let’s go on!” The comic’s caption says, “The annual death rate among people who know that statistic is one in six.” [Return to “Conditional Risk”]
Media Attributions
- Null Hypothesis by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Conditional Risk by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p < .05. American Psychologist, 49 , 997–1003. ↵
- Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16 , 259–263. ↵
Values in a population that correspond to variables measured in a study.
The random variability in a statistic from sample to sample.
A formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample.
The idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
When the relationship found in the sample would be extremely unlikely, the idea that the relationship occurred “by chance” is rejected.
When the relationship found in the sample is likely to have occurred by chance, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
The probability that, if the null hypothesis were true, the result found in the sample would occur.
How low the p value must be before the sample result is considered unlikely in null hypothesis testing.
When there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result occurring and the null hypothesis is rejected.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Step 1. Ask a question
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is your plagiarism score.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
Writing Null Hypotheses in Research and Statistics
Last Updated: January 17, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Joseph Quinones and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Joseph Quinones is a High School Physics Teacher working at South Bronx Community Charter High School. Joseph specializes in astronomy and astrophysics and is interested in science education and science outreach, currently practicing ways to make physics accessible to more students with the goal of bringing more students of color into the STEM fields. He has experience working on Astrophysics research projects at the Museum of Natural History (AMNH). Joseph recieved his Bachelor's degree in Physics from Lehman College and his Masters in Physics Education from City College of New York (CCNY). He is also a member of a network called New York City Men Teach. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 22,257 times.
Are you working on a research project and struggling with how to write a null hypothesis? Well, you've come to the right place! Start by recognizing that the basic definition of "null" is "none" or "zero"—that's your biggest clue as to what a null hypothesis should say. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about the null hypothesis, including how it relates to your research question and your alternative hypothesis as well as how to use it in different types of studies.
Things You Should Know
- Write a research null hypothesis as a statement that the studied variables have no relationship to each other, or that there's no difference between 2 groups.

- Adjust the format of your null hypothesis to match the statistical method you used to test it, such as using "mean" if you're comparing the mean between 2 groups.
What is a null hypothesis?

- Research hypothesis: States in plain language that there's no relationship between the 2 variables or there's no difference between the 2 groups being studied.
- Statistical hypothesis: States the predicted outcome of statistical analysis through a mathematical equation related to the statistical method you're using.
Examples of Null Hypotheses

Null Hypothesis vs. Alternative Hypothesis

- For example, your alternative hypothesis could state a positive correlation between 2 variables while your null hypothesis states there's no relationship. If there's a negative correlation, then both hypotheses are false.

- You need additional data or evidence to show that your alternative hypothesis is correct—proving the null hypothesis false is just the first step.
- In smaller studies, sometimes it's enough to show that there's some relationship and your hypothesis could be correct—you can leave the additional proof as an open question for other researchers to tackle.
How do I test a null hypothesis?

- Group means: Compare the mean of the variable in your sample with the mean of the variable in the general population. [6] X Research source
- Group proportions: Compare the proportion of the variable in your sample with the proportion of the variable in the general population. [7] X Research source
- Correlation: Correlation analysis looks at the relationship between 2 variables—specifically, whether they tend to happen together. [8] X Research source
- Regression: Regression analysis reveals the correlation between 2 variables while also controlling for the effect of other, interrelated variables. [9] X Research source
Templates for Null Hypotheses

- Research null hypothesis: There is no difference in the mean [dependent variable] between [group 1] and [group 2].

- Research null hypothesis: The proportion of [dependent variable] in [group 1] and [group 2] is the same.

- Research null hypothesis: There is no correlation between [independent variable] and [dependent variable] in the population.

- Research null hypothesis: There is no relationship between [independent variable] and [dependent variable] in the population.

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about physics, check out our in-depth interview with Joseph Quinones .
- ↑ https://online.stat.psu.edu/stat100/lesson/10/10.1
- ↑ https://online.stat.psu.edu/stat501/lesson/2/2.12
- ↑ https://support.minitab.com/en-us/minitab/21/help-and-how-to/statistics/basic-statistics/supporting-topics/basics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5635437/
- ↑ https://online.stat.psu.edu/statprogram/reviews/statistical-concepts/hypothesis-testing
- ↑ https://education.arcus.chop.edu/null-hypothesis-testing/
- ↑ https://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/mph-modules/bs/bs704_hypothesistest-means-proportions/bs704_hypothesistest-means-proportions_print.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 3, 2022
Did this article help you?
Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
PM Images / Getty Images
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
In a scientific experiment, the null hypothesis is the proposition that there is no effect or no relationship between phenomena or populations. If the null hypothesis is true, any observed difference in phenomena or populations would be due to sampling error (random chance) or experimental error. The null hypothesis is useful because it can be tested and found to be false, which then implies that there is a relationship between the observed data. It may be easier to think of it as a nullifiable hypothesis or one that the researcher seeks to nullify. The null hypothesis is also known as the H 0, or no-difference hypothesis.
The alternate hypothesis, H A or H 1 , proposes that observations are influenced by a non-random factor. In an experiment, the alternate hypothesis suggests that the experimental or independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable .
How to State a Null Hypothesis
There are two ways to state a null hypothesis. One is to state it as a declarative sentence, and the other is to present it as a mathematical statement.
For example, say a researcher suspects that exercise is correlated to weight loss, assuming diet remains unchanged. The average length of time to achieve a certain amount of weight loss is six weeks when a person works out five times a week. The researcher wants to test whether weight loss takes longer to occur if the number of workouts is reduced to three times a week.
The first step to writing the null hypothesis is to find the (alternate) hypothesis. In a word problem like this, you're looking for what you expect to be the outcome of the experiment. In this case, the hypothesis is "I expect weight loss to take longer than six weeks."
This can be written mathematically as: H 1 : μ > 6
In this example, μ is the average.
Now, the null hypothesis is what you expect if this hypothesis does not happen. In this case, if weight loss isn't achieved in greater than six weeks, then it must occur at a time equal to or less than six weeks. This can be written mathematically as:
H 0 : μ ≤ 6
The other way to state the null hypothesis is to make no assumption about the outcome of the experiment. In this case, the null hypothesis is simply that the treatment or change will have no effect on the outcome of the experiment. For this example, it would be that reducing the number of workouts would not affect the time needed to achieve weight loss:
H 0 : μ = 6
- Null Hypothesis Examples
"Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar " is an example of a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is tested and found to be false, using statistics, then a connection between hyperactivity and sugar ingestion may be indicated. A significance test is the most common statistical test used to establish confidence in a null hypothesis.
Another example of a null hypothesis is "Plant growth rate is unaffected by the presence of cadmium in the soil ." A researcher could test the hypothesis by measuring the growth rate of plants grown in a medium lacking cadmium, compared with the growth rate of plants grown in mediums containing different amounts of cadmium. Disproving the null hypothesis would set the groundwork for further research into the effects of different concentrations of the element in soil.
Why Test a Null Hypothesis?
You may be wondering why you would want to test a hypothesis just to find it false. Why not just test an alternate hypothesis and find it true? The short answer is that it is part of the scientific method. In science, propositions are not explicitly "proven." Rather, science uses math to determine the probability that a statement is true or false. It turns out it's much easier to disprove a hypothesis than to positively prove one. Also, while the null hypothesis may be simply stated, there's a good chance the alternate hypothesis is incorrect.
For example, if your null hypothesis is that plant growth is unaffected by duration of sunlight, you could state the alternate hypothesis in several different ways. Some of these statements might be incorrect. You could say plants are harmed by more than 12 hours of sunlight or that plants need at least three hours of sunlight, etc. There are clear exceptions to those alternate hypotheses, so if you test the wrong plants, you could reach the wrong conclusion. The null hypothesis is a general statement that can be used to develop an alternate hypothesis, which may or may not be correct.
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
- What Is a Control Group?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- How to Conduct a Hypothesis Test
- Type I and Type II Errors in Statistics
- An Example of a Hypothesis Test
- Hypothesis Test for the Difference of Two Population Proportions
What is The Null Hypothesis & When Do You Reject The Null Hypothesis
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, Ph.D., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years experience of working in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A null hypothesis is a statistical concept suggesting no significant difference or relationship between measured variables. It’s the default assumption unless empirical evidence proves otherwise.
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (i.e., one variable does not affect the other).
The null hypothesis is the statement that a researcher or an investigator wants to disprove.
Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effects of manipulating the dependent variable or due to random chance.
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Null hypotheses (H0) start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as statements indicating no effect or relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
It is a default position that your research aims to challenge or confirm.
For example, if studying the impact of exercise on weight loss, your null hypothesis might be:
There is no significant difference in weight loss between individuals who exercise daily and those who do not.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
When do we reject the null hypothesis .
We reject the null hypothesis when the data provide strong enough evidence to conclude that it is likely incorrect. This often occurs when the p-value (probability of observing the data given the null hypothesis is true) is below a predetermined significance level.
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected.
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant ( p > 0.05).
If the data collected from the random sample is not statistically significance , then the null hypothesis will be accepted, and the researchers can conclude that there is no relationship between the variables.
You need to perform a statistical test on your data in order to evaluate how consistent it is with the null hypothesis. A p-value is one statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
Calculating the p-value is a critical part of null-hypothesis significance testing because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradicts the null hypothesis.
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p -value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
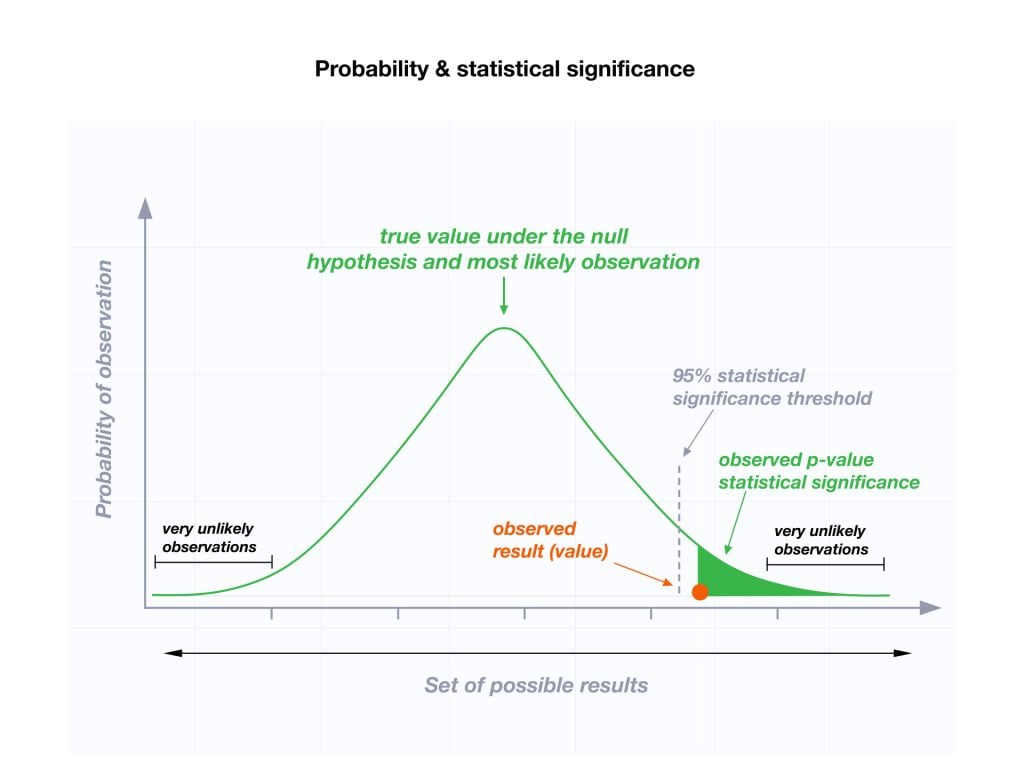
Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01) as general guidelines to decide if you should reject or keep the null.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, smaller p-values are taken as stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In this case, the sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population.
Because you can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population, your inferences about a population will sometimes be incorrect.
When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error. When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s called a type II error.
Why Do We Never Accept The Null Hypothesis?
The reason we do not say “accept the null” is because we are always assuming the null hypothesis is true and then conducting a study to see if there is evidence against it. And, even if we don’t find evidence against it, a null hypothesis is not accepted.
A lack of evidence only means that you haven’t proven that something exists. It does not prove that something doesn’t exist.
It is risky to conclude that the null hypothesis is true merely because we did not find evidence to reject it. It is always possible that researchers elsewhere have disproved the null hypothesis, so we cannot accept it as true, but instead, we state that we failed to reject the null.
One can either reject the null hypothesis, or fail to reject it, but can never accept it.
Why Do We Use The Null Hypothesis?
We can never prove with 100% certainty that a hypothesis is true; We can only collect evidence that supports a theory. However, testing a hypothesis can set the stage for rejecting or accepting this hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
The null hypothesis is useful because it can tell us whether the results of our study are due to random chance or the manipulation of a variable (with a certain level of confidence).
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis.
Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Hypothesis testing is a critical part of the scientific method as it helps decide whether the results of a research study support a particular theory about a given population. Hypothesis testing is a systematic way of backing up researchers’ predictions with statistical analysis.
It helps provide sufficient statistical evidence that either favors or rejects a certain hypothesis about the population parameter.
Purpose of a Null Hypothesis
- The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption.
- Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases.
- A null hypothesis can be used to ascertain how consistent the outcomes of multiple studies are.
Do you always need both a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis?
The null (H0) and alternative (Ha or H1) hypotheses are two competing claims that describe the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. They are mutually exclusive, which means that only one of the two hypotheses can be true.
While the null hypothesis states that there is no effect in the population, an alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. Both hypotheses are required to cover every possible outcome of the study.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population.
It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are always mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
What are some problems with the null hypothesis?
One major problem with the null hypothesis is that researchers typically will assume that accepting the null is a failure of the experiment. However, accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is a positive result. Even if the null is not refuted, the researchers will still learn something new.
Why can a null hypothesis not be accepted?
We can either reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis, but never accept it. If your test fails to detect an effect, this is not proof that the effect doesn’t exist. It just means that your sample did not have enough evidence to conclude that it exists.
We can’t accept a null hypothesis because a lack of evidence does not prove something that does not exist. Instead, we fail to reject it.
Failing to reject the null indicates that the sample did not provide sufficient enough evidence to conclude that an effect exists.
If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Is a null hypothesis directional or non-directional?
A hypothesis test can either contain an alternative directional hypothesis or a non-directional alternative hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one that contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign.
A nondirectional hypothesis contains the not equal sign (“≠”). However, a null hypothesis is neither directional nor non-directional.
A null hypothesis is a prediction that there will be no change, relationship, or difference between two variables.
The directional hypothesis or nondirectional hypothesis would then be considered alternative hypotheses to the null hypothesis.
Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political research quarterly , 52 (3), 647-674.
Krueger, J. (2001). Null hypothesis significance testing: On the survival of a flawed method. American Psychologist , 56 (1), 16.
Masson, M. E. (2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods , 43 , 679-690.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological bulletin , 57 (5), 416.
How to State the Conclusion about a Hypothesis Test
After you have completed the statistical analysis and decided to reject or fail to reject the Null hypothesis, you need to state your conclusion about the claim. To get the correct wording, you need to recall which hypothesis was the claim.
If the claim was the null, then your conclusion is about whether there was sufficient evidence to reject the claim. Remember, we can never prove the null to be true, but failing to reject it is the next best thing. So, it is not correct to say, “Accept the Null.”
If the claim is the alternative hypothesis, your conclusion can be whether there was sufficient evidence to support (prove) the alternative is true.
Use the following table to help you make a good conclusion.

The best way to state the conclusion is to include the significance level of the test and a bit about the claim itself.
For example, if the claim was the alternative that the mean score on a test was greater than 85, and your decision was to Reject then Null , then you could conclude: “ At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean score on the test was greater than 85. ”
The reason you should include the significance level is that the decision, and thus the conclusion, could be different if the significance level was not 5%.
If you are curious why we say “Fail to Reject the Null” instead of “Accept the Null,” this short video might be of interest: Here

2 thoughts on “How to State the Conclusion about a Hypothesis Test”
It is concluded that the null hypothesis Ho is not rejected proportion p is greater than 0.5, at the 0.05 significance
People living in rural Idaho community live longer than 77 years
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
How to Write Hypothesis Test Conclusions (With Examples)
A hypothesis test is used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.
To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ): The sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
If the p-value of the hypothesis test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then we reject the null hypothesis .
Otherwise, if the p-value is not less than some significance level then we fail to reject the null hypothesis .
When writing the conclusion of a hypothesis test, we typically include:
- Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- The significance level.
- A short explanation in the context of the hypothesis test.
For example, we would write:
We reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that…
Or, we would write:
We fail to reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that…
The following examples show how to write a hypothesis test conclusion in both scenarios.
Example 1: Reject the Null Hypothesis Conclusion
Suppose a biologist believes that a certain fertilizer will cause plants to grow more during a one-month period than they normally do, which is currently 20 inches. To test this, she applies the fertilizer to each of the plants in her laboratory for one month.
She then performs a hypothesis test at a 5% significance level using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = 20 inches (the fertilizer will have no effect on the mean plant growth)
- H A : μ > 20 inches (the fertilizer will cause mean plant growth to increase)
Suppose the p-value of the test turns out to be 0.002.
Here is how she would report the results of the hypothesis test:
We reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that this particular fertilizer causes plants to grow more during a one-month period than they normally do.
Example 2: Fail to Reject the Null Hypothesis Conclusion
Suppose the manager of a manufacturing plant wants to test whether or not some new method changes the number of defective widgets produced per month, which is currently 250. To test this, he measures the mean number of defective widgets produced before and after using the new method for one month.
He performs a hypothesis test at a 10% significance level using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean number of defective widgets is the same before and after using the new method)
- H A : μ after ≠ μ before (the mean number of defective widgets produced is different before and after using the new method)
Suppose the p-value of the test turns out to be 0.27.
Here is how he would report the results of the hypothesis test:
We fail to reject the null hypothesis at the 10% significance level. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the new method leads to a change in the number of defective widgets produced per month.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials provide additional information about hypothesis testing:
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing 4 Examples of Hypothesis Testing in Real Life How to Write a Null Hypothesis
10 Examples of Using Probability in Real Life
Mongodb: how to find document by id, related posts, how to normalize data between -1 and 1, how to interpret f-values in a two-way anova, how to create a vector of ones in..., vba: how to check if string contains another..., how to determine if a probability distribution is..., what is a symmetric histogram (definition & examples), how to find the mode of a histogram..., how to find quartiles in even and odd..., how to calculate sxy in statistics (with example), how to calculate sxx in statistics (with example).

User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
6a.2 - steps for hypothesis tests, the logic of hypothesis testing section .
A hypothesis, in statistics, is a statement about a population parameter, where this statement typically is represented by some specific numerical value. In testing a hypothesis, we use a method where we gather data in an effort to gather evidence about the hypothesis.
How do we decide whether to reject the null hypothesis?
- If the sample data are consistent with the null hypothesis, then we do not reject it.
- If the sample data are inconsistent with the null hypothesis, but consistent with the alternative, then we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the alternative hypothesis is true.
Six Steps for Hypothesis Tests Section
In hypothesis testing, there are certain steps one must follow. Below these are summarized into six such steps to conducting a test of a hypothesis.
- Set up the hypotheses and check conditions : Each hypothesis test includes two hypotheses about the population. One is the null hypothesis, notated as \(H_0 \), which is a statement of a particular parameter value. This hypothesis is assumed to be true until there is evidence to suggest otherwise. The second hypothesis is called the alternative, or research hypothesis, notated as \(H_a \). The alternative hypothesis is a statement of a range of alternative values in which the parameter may fall. One must also check that any conditions (assumptions) needed to run the test have been satisfied e.g. normality of data, independence, and number of success and failure outcomes.
- Decide on the significance level, \(\alpha \): This value is used as a probability cutoff for making decisions about the null hypothesis. This alpha value represents the probability we are willing to place on our test for making an incorrect decision in regards to rejecting the null hypothesis. The most common \(\alpha \) value is 0.05 or 5%. Other popular choices are 0.01 (1%) and 0.1 (10%).
- Calculate the test statistic: Gather sample data and calculate a test statistic where the sample statistic is compared to the parameter value. The test statistic is calculated under the assumption the null hypothesis is true and incorporates a measure of standard error and assumptions (conditions) related to the sampling distribution.
- Calculate probability value (p-value), or find the rejection region: A p-value is found by using the test statistic to calculate the probability of the sample data producing such a test statistic or one more extreme. The rejection region is found by using alpha to find a critical value; the rejection region is the area that is more extreme than the critical value. We discuss the p-value and rejection region in more detail in the next section.
- Make a decision about the null hypothesis: In this step, we decide to either reject the null hypothesis or decide to fail to reject the null hypothesis. Notice we do not make a decision where we will accept the null hypothesis.
- State an overall conclusion : Once we have found the p-value or rejection region, and made a statistical decision about the null hypothesis (i.e. we will reject the null or fail to reject the null), we then want to summarize our results into an overall conclusion for our test.
We will follow these six steps for the remainder of this Lesson. In the future Lessons, the steps will be followed but may not be explained explicitly.
Step 1 is a very important step to set up correctly. If your hypotheses are incorrect, your conclusion will be incorrect. In this next section, we practice with Step 1 for the one sample situations.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Statistics
Course: ap®︎/college statistics > unit 10.
- Idea behind hypothesis testing
Examples of null and alternative hypotheses
- Writing null and alternative hypotheses
- P-values and significance tests
- Comparing P-values to different significance levels
- Estimating a P-value from a simulation
- Estimating P-values from simulations
- Using P-values to make conclusions
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
Chapter 3: Hypothesis Testing
The previous two chapters introduced methods for organizing and summarizing sample data, and using sample statistics to estimate population parameters. This chapter introduces the next major topic of inferential statistics: hypothesis testing.
A hypothesis is a statement or claim about a property of a population.
The Fundamentals of Hypothesis Testing
When conducting scientific research, typically there is some known information, perhaps from some past work or from a long accepted idea. We want to test whether this claim is believable. This is the basic idea behind a hypothesis test:
- State what we think is true.
- Quantify how confident we are about our claim.
- Use sample statistics to make inferences about population parameters.
For example, past research tells us that the average life span for a hummingbird is about four years. You have been studying the hummingbirds in the southeastern United States and find a sample mean lifespan of 4.8 years. Should you reject the known or accepted information in favor of your results? How confident are you in your estimate? At what point would you say that there is enough evidence to reject the known information and support your alternative claim? How far from the known mean of four years can the sample mean be before we reject the idea that the average lifespan of a hummingbird is four years?
Hypothesis testing is a procedure, based on sample evidence and probability, used to test claims regarding a characteristic of a population.
A hypothesis is a claim or statement about a characteristic of a population of interest to us. A hypothesis test is a way for us to use our sample statistics to test a specific claim.
The population mean weight is known to be 157 lb. We want to test the claim that the mean weight has increased.
Two years ago, the proportion of infected plants was 37%. We believe that a treatment has helped, and we want to test the claim that there has been a reduction in the proportion of infected plants.
Components of a Formal Hypothesis Test
The null hypothesis is a statement about the value of a population parameter, such as the population mean (µ) or the population proportion ( p ). It contains the condition of equality and is denoted as H 0 (H-naught).
H 0 : µ = 157 or H 0 : p = 0.37
The alternative hypothesis is the claim to be tested, the opposite of the null hypothesis. It contains the value of the parameter that we consider plausible and is denoted as H 1 .
H 1 : µ > 157 or H 1 : p ≠ 0.37
The test statistic is a value computed from the sample data that is used in making a decision about the rejection of the null hypothesis. The test statistic converts the sample mean ( x̄ ) or sample proportion ( p̂ ) to a Z- or t-score under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true . It is used to decide whether the difference between the sample statistic and the hypothesized claim is significant.
The p-value is the area under the curve to the left or right of the test statistic. It is compared to the level of significance ( α ).
The critical value is the value that defines the rejection zone (the test statistic values that would lead to rejection of the null hypothesis). It is defined by the level of significance.
The level of significance ( α ) is the probability that the test statistic will fall into the critical region when the null hypothesis is true. This level is set by the researcher.
The conclusion is the final decision of the hypothesis test. The conclusion must always be clearly stated, communicating the decision based on the components of the test. It is important to realize that we never prove or accept the null hypothesis. We are merely saying that the sample evidence is not strong enough to warrant the rejection of the null hypothesis. The conclusion is made up of two parts:
1) Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and 2) there is or is not enough evidence to support the alternative claim.
Option 1) Reject the null hypothesis (H 0 ). This means that you have enough statistical evidence to support the alternative claim (H 1 ).
Option 2) Fail to reject the null hypothesis (H 0 ). This means that you do NOT have enough evidence to support the alternative claim (H 1 ).
Another way to think about hypothesis testing is to compare it to the US justice system. A defendant is innocent until proven guilty (Null hypothesis—innocent). The prosecuting attorney tries to prove that the defendant is guilty (Alternative hypothesis—guilty). There are two possible conclusions that the jury can reach. First, the defendant is guilty (Reject the null hypothesis). Second, the defendant is not guilty (Fail to reject the null hypothesis). This is NOT the same thing as saying the defendant is innocent! In the first case, the prosecutor had enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis (innocent) and support the alternative claim (guilty). In the second case, the prosecutor did NOT have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis (innocent) and support the alternative claim of guilty.
The Null and Alternative Hypotheses
There are three different pairs of null and alternative hypotheses:
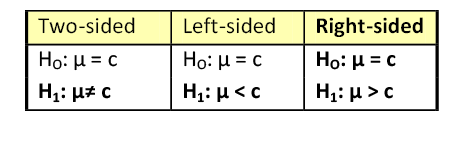
where c is some known value.
A Two-sided Test
This tests whether the population parameter is equal to, versus not equal to, some specific value.
H o : μ = 12 vs. H 1 : μ ≠ 12
The critical region is divided equally into the two tails and the critical values are ± values that define the rejection zones.
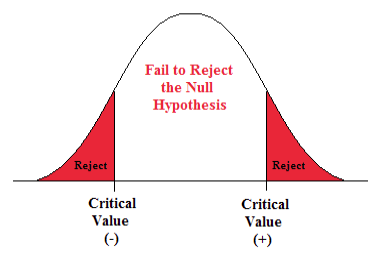
Figure 1. The rejection zone for a two-sided hypothesis test.
A forester studying diameter growth of red pine believes that the mean diameter growth will be different if a fertilization treatment is applied to the stand.
- H o : μ = 1.2 in./ year
- H 1 : μ ≠ 1.2 in./ year
This is a two-sided question, as the forester doesn’t state whether population mean diameter growth will increase or decrease.
A Right-sided Test
This tests whether the population parameter is equal to, versus greater than, some specific value.
H o : μ = 12 vs. H 1 : μ > 12
The critical region is in the right tail and the critical value is a positive value that defines the rejection zone.
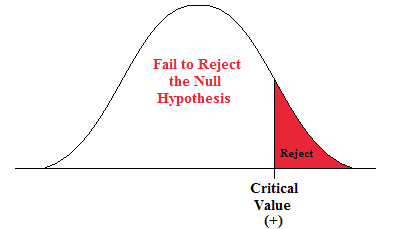
Figure 2. The rejection zone for a right-sided hypothesis test.
A biologist believes that there has been an increase in the mean number of lakes infected with milfoil, an invasive species, since the last study five years ago.
- H o : μ = 15 lakes
- H 1 : μ >15 lakes
This is a right-sided question, as the biologist believes that there has been an increase in population mean number of infected lakes.
A Left-sided Test
This tests whether the population parameter is equal to, versus less than, some specific value.
H o : μ = 12 vs. H 1 : μ < 12
The critical region is in the left tail and the critical value is a negative value that defines the rejection zone.
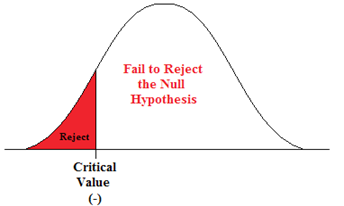
Figure 3. The rejection zone for a left-sided hypothesis test.
A scientist’s research indicates that there has been a change in the proportion of people who support certain environmental policies. He wants to test the claim that there has been a reduction in the proportion of people who support these policies.
- H o : p = 0.57
- H 1 : p < 0.57
This is a left-sided question, as the scientist believes that there has been a reduction in the true population proportion.
Statistically Significant
When the observed results (the sample statistics) are unlikely (a low probability) under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true, we say that the result is statistically significant, and we reject the null hypothesis. This result depends on the level of significance, the sample statistic, sample size, and whether it is a one- or two-sided alternative hypothesis.
Types of Errors
When testing, we arrive at a conclusion of rejecting the null hypothesis or failing to reject the null hypothesis. Such conclusions are sometimes correct and sometimes incorrect (even when we have followed all the correct procedures). We use incomplete sample data to reach a conclusion and there is always the possibility of reaching the wrong conclusion. There are four possible conclusions to reach from hypothesis testing. Of the four possible outcomes, two are correct and two are NOT correct.

Table 1. Possible outcomes from a hypothesis test.
A Type I error is when we reject the null hypothesis when it is true. The symbol α (alpha) is used to represent Type I errors. This is the same alpha we use as the level of significance. By setting alpha as low as reasonably possible, we try to control the Type I error through the level of significance.
A Type II error is when we fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is false. The symbol β (beta) is used to represent Type II errors.
In general, Type I errors are considered more serious. One step in the hypothesis test procedure involves selecting the significance level ( α ), which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is correct. So the researcher can select the level of significance that minimizes Type I errors. However, there is a mathematical relationship between α, β , and n (sample size).
- As α increases, β decreases
- As α decreases, β increases
- As sample size increases (n), both α and β decrease
The natural inclination is to select the smallest possible value for α, thinking to minimize the possibility of causing a Type I error. Unfortunately, this forces an increase in Type II errors. By making the rejection zone too small, you may fail to reject the null hypothesis, when, in fact, it is false. Typically, we select the best sample size and level of significance, automatically setting β .
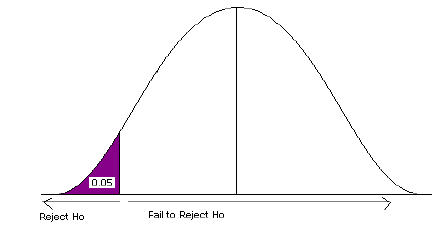
Figure 4. Type 1 error.
Power of the Test
A Type II error ( β ) is the probability of failing to reject a false null hypothesis. It follows that 1- β is the probability of rejecting a false null hypothesis. This probability is identified as the power of the test, and is often used to gauge the test’s effectiveness in recognizing that a null hypothesis is false.
The probability that at a fixed level α significance test will reject H 0 , when a particular alternative value of the parameter is true is called the power of the test.
Power is also directly linked to sample size. For example, suppose the null hypothesis is that the mean fish weight is 8.7 lb. Given sample data, a level of significance of 5%, and an alternative weight of 9.2 lb., we can compute the power of the test to reject μ = 8.7 lb. If we have a small sample size, the power will be low. However, increasing the sample size will increase the power of the test. Increasing the level of significance will also increase power. A 5% test of significance will have a greater chance of rejecting the null hypothesis than a 1% test because the strength of evidence required for the rejection is less. Decreasing the standard deviation has the same effect as increasing the sample size: there is more information about μ .
Hypothesis Test about the Population Mean ( μ ) when the Population Standard Deviation ( σ ) is Known
We are going to examine two equivalent ways to perform a hypothesis test: the classical approach and the p-value approach. The classical approach is based on standard deviations. This method compares the test statistic (Z-score) to a critical value (Z-score) from the standard normal table. If the test statistic falls in the rejection zone, you reject the null hypothesis. The p-value approach is based on area under the normal curve. This method compares the area associated with the test statistic to alpha ( α ), the level of significance (which is also area under the normal curve). If the p-value is less than alpha, you would reject the null hypothesis.
As a past student poetically said: If the p-value is a wee value, Reject Ho
Both methods must have:
- Data from a random sample.
- Verification of the assumption of normality.
- A null and alternative hypothesis.
- A criterion that determines if we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- A conclusion that answers the question.
There are four steps required for a hypothesis test:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- State the level of significance and the critical value.
- Compute the test statistic.
- State a conclusion.
The Classical Method for Testing a Claim about the Population Mean ( μ ) when the Population Standard Deviation ( σ ) is Known
A forester studying diameter growth of red pine believes that the mean diameter growth will be different from the known mean growth of 1.35 inches/year if a fertilization treatment is applied to the stand. He conducts his experiment, collects data from a sample of 32 plots, and gets a sample mean diameter growth of 1.6 in./year. The population standard deviation for this stand is known to be 0.46 in./year. Does he have enough evidence to support his claim?
Step 1) State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H o : μ = 1.35 in./year
- H 1 : μ ≠ 1.35 in./year
Step 2) State the level of significance and the critical value.
- We will choose a level of significance of 5% ( α = 0.05).
- For a two-sided question, we need a two-sided critical value – Z α /2 and + Z α /2 .
- The level of significance is divided by 2 (since we are only testing “not equal”). We must have two rejection zones that can deal with either a greater than or less than outcome (to the right (+) or to the left (-)).
- We need to find the Z-score associated with the area of 0.025. The red areas are equal to α /2 = 0.05/2 = 0.025 or 2.5% of the area under the normal curve.
- Go into the body of values and find the negative Z-score associated with the area 0.025.
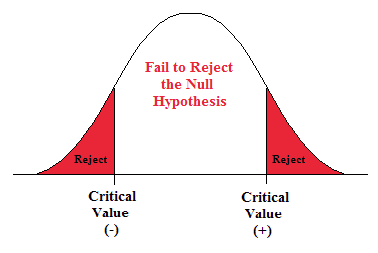
Figure 5. The rejection zone for a two-sided test.
- The negative critical value is -1.96. Since the curve is symmetric, we know that the positive critical value is 1.96.
- ±1.96 are the critical values. These values set up the rejection zone. If the test statistic falls within these red rejection zones, we reject the null hypothesis.
Step 3) Compute the test statistic.
- The test statistic is the number of standard deviations the sample mean is from the known mean. It is also a Z-score, just like the critical value.
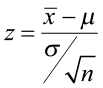
- For this problem, the test statistic is
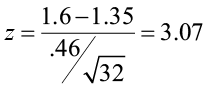
Step 4) State a conclusion.
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value. If the test statistic falls into the rejection zones, reject the null hypothesis. In other words, if the test statistic is greater than +1.96 or less than -1.96, reject the null hypothesis.
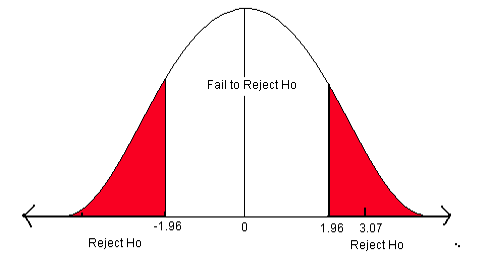
Figure 6. The critical values for a two-sided test when α = 0.05.
In this problem, the test statistic falls in the red rejection zone. The test statistic of 3.07 is greater than the critical value of 1.96.We will reject the null hypothesis. We have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean diameter growth is different from (not equal to) 1.35 in./year.
A researcher believes that there has been an increase in the average farm size in his state since the last study five years ago. The previous study reported a mean size of 450 acres with a population standard deviation ( σ ) of 167 acres. He samples 45 farms and gets a sample mean of 485.8 acres. Is there enough information to support his claim?
- H o : μ = 450 acres
- H 1 : μ >450 acres
- For a one-sided question, we need a one-sided positive critical value Z α .
- The level of significance is all in the right side (the rejection zone is just on the right side).
- We need to find the Z-score associated with the 5% area in the right tail.
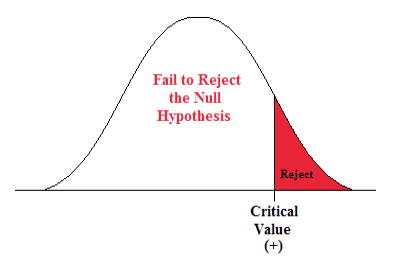
Figure 7. Rejection zone for a right-sided hypothesis test.
- Go into the body of values in the standard normal table and find the Z-score that separates the lower 95% from the upper 5%.
- The critical value is 1.645. This value sets up the rejection zone.
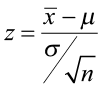
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value.
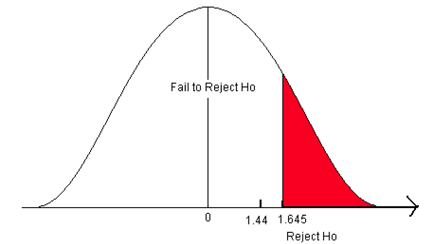
Figure 8. The critical value for a right-sided test when α = 0.05.
- The test statistic does not fall in the rejection zone. It is less than the critical value.
We fail to reject the null hypothesis. We do not have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean farm size has increased from 450 acres.
A researcher believes that there has been a reduction in the mean number of hours that college students spend preparing for final exams. A national study stated that students at a 4-year college spend an average of 23 hours preparing for 5 final exams each semester with a population standard deviation of 7.3 hours. The researcher sampled 227 students and found a sample mean study time of 19.6 hours. Does this indicate that the average study time for final exams has decreased? Use a 1% level of significance to test this claim.
- H o : μ = 23 hours
- H 1 : μ < 23 hours
- This is a left-sided test so alpha (0.01) is all in the left tail.
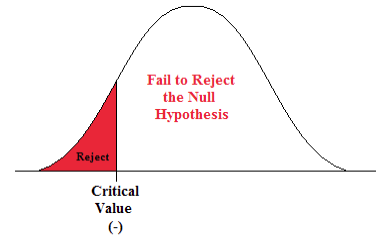
Figure 9. The rejection zone for a left-sided hypothesis test.
- Go into the body of values in the standard normal table and find the Z-score that defines the lower 1% of the area.
- The critical value is -2.33. This value sets up the rejection zone.
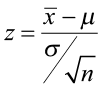
Figure 10. The critical value for a left-sided test when α = 0.01.
- The test statistic falls in the rejection zone. The test statistic of -7.02 is less than the critical value of -2.33.
We reject the null hypothesis. We have sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean final exam study time has decreased below 23 hours.
Testing a Hypothesis using P-values
The p-value is the probability of observing our sample mean given that the null hypothesis is true. It is the area under the curve to the left or right of the test statistic. If the probability of observing such a sample mean is very small (less than the level of significance), we would reject the null hypothesis. Computations for the p-value depend on whether it is a one- or two-sided test.
Steps for a hypothesis test using p-values:
- State the level of significance.
- Compute the test statistic and find the area associated with it (this is the p-value).
- Compare the p-value to alpha ( α ) and state a conclusion.
Instead of comparing Z-score test statistic to Z-score critical value, as in the classical method, we compare area of the test statistic to area of the level of significance.
The Decision Rule: If the p-value is less than alpha, we reject the null hypothesis
Computing P-values
If it is a two-sided test (the alternative claim is ≠), the p-value is equal to two times the probability of the absolute value of the test statistic. If the test is a left-sided test (the alternative claim is “<”), then the p-value is equal to the area to the left of the test statistic. If the test is a right-sided test (the alternative claim is “>”), then the p-value is equal to the area to the right of the test statistic.
Let’s look at Example 6 again.
A forester studying diameter growth of red pine believes that the mean diameter growth will be different from the known mean growth of 1.35 in./year if a fertilization treatment is applied to the stand. He conducts his experiment, collects data from a sample of 32 plots, and gets a sample mean diameter growth of 1.6 in./year. The population standard deviation for this stand is known to be 0.46 in./year. Does he have enough evidence to support his claim?
Step 2) State the level of significance.
- For this problem, the test statistic is:
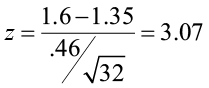
The p-value is two times the area of the absolute value of the test statistic (because the alternative claim is “not equal”).
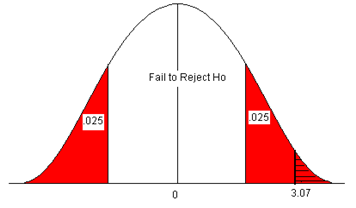
Figure 11. The p-value compared to the level of significance.
- Look up the area for the Z-score 3.07 in the standard normal table. The area (probability) is equal to 1 – 0.9989 = 0.0011.
- Multiply this by 2 to get the p-value = 2 * 0.0011 = 0.0022.
Step 4) Compare the p-value to alpha and state a conclusion.
- Use the Decision Rule (if the p-value is less than α , reject H 0 ).
- In this problem, the p-value (0.0022) is less than alpha (0.05).
- We reject the H 0 . We have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean diameter growth is different from 1.35 inches/year.
Let’s look at Example 7 again.
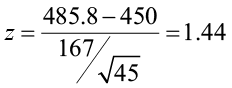
The p-value is the area to the right of the Z-score 1.44 (the hatched area).
- This is equal to 1 – 0.9251 = 0.0749.
- The p-value is 0.0749.
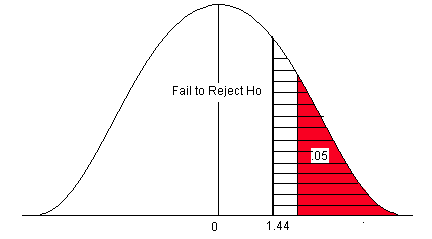
Figure 12. The p-value compared to the level of significance for a right-sided test.
- Use the Decision Rule.
- In this problem, the p-value (0.0749) is greater than alpha (0.05), so we Fail to Reject the H 0 .
- The area of the test statistic is greater than the area of alpha ( α ).
We fail to reject the null hypothesis. We do not have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean farm size has increased.
Let’s look at Example 8 again.
- H 0 : μ = 23 hours
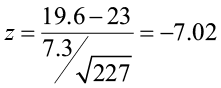
The p-value is the area to the left of the test statistic (the little black area to the left of -7.02). The Z-score of -7.02 is not on the standard normal table. The smallest probability on the table is 0.0002. We know that the area for the Z-score -7.02 is smaller than this area (probability). Therefore, the p-value is <0.0002.
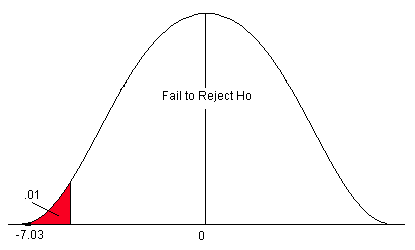
Figure 13. The p-value compared to the level of significance for a left-sided test.
- In this problem, the p-value (p<0.0002) is less than alpha (0.01), so we Reject the H 0 .
- The area of the test statistic is much less than the area of alpha ( α ).
We reject the null hypothesis. We have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean final exam study time has decreased below 23 hours.
Both the classical method and p-value method for testing a hypothesis will arrive at the same conclusion. In the classical method, the critical Z-score is the number on the z-axis that defines the level of significance ( α ). The test statistic converts the sample mean to units of standard deviation (a Z-score). If the test statistic falls in the rejection zone defined by the critical value, we will reject the null hypothesis. In this approach, two Z-scores, which are numbers on the z-axis, are compared. In the p-value approach, the p-value is the area associated with the test statistic. In this method, we compare α (which is also area under the curve) to the p-value. If the p-value is less than α , we reject the null hypothesis. The p-value is the probability of observing such a sample mean when the null hypothesis is true. If the probability is too small (less than the level of significance), then we believe we have enough statistical evidence to reject the null hypothesis and support the alternative claim.
Software Solutions
(referring to Ex. 8)
One-Sample Z
Excel does not offer 1-sample hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis Test about the Population Mean ( μ ) when the Population Standard Deviation ( σ ) is Unknown
Frequently, the population standard deviation (σ) is not known. We can estimate the population standard deviation (σ) with the sample standard deviation (s). However, the test statistic will no longer follow the standard normal distribution. We must rely on the student’s t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom. Because we use the sample standard deviation (s), the test statistic will change from a Z-score to a t-score.
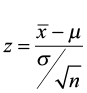
Steps for a hypothesis test are the same that we covered in Section 2.
Just as with the hypothesis test from the previous section, the data for this test must be from a random sample and requires either that the population from which the sample was drawn be normal or that the sample size is sufficiently large (n≥30). A t-test is robust, so small departures from normality will not adversely affect the results of the test. That being said, if the sample size is smaller than 30, it is always good to verify the assumption of normality through a normal probability plot.
We will still have the same three pairs of null and alternative hypotheses and we can still use either the classical approach or the p-value approach.
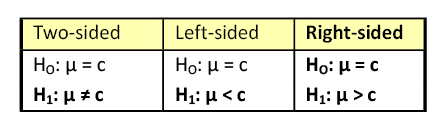
Selecting the correct critical value from the student’s t-distribution table depends on three factors: the type of test (one-sided or two-sided alternative hypothesis), the sample size, and the level of significance.
For a two-sided test (“not equal” alternative hypothesis), the critical value (t α /2 ), is determined by alpha ( α ), the level of significance, divided by two, to deal with the possibility that the result could be less than OR greater than the known value.
- If your level of significance was 0.05, you would use the 0.025 column to find the correct critical value (0.05/2 = 0.025).
- If your level of significance was 0.01, you would use the 0.005 column to find the correct critical value (0.01/2 = 0.005).
For a one-sided test (“a less than” or “greater than” alternative hypothesis), the critical value (t α ) , is determined by alpha ( α ), the level of significance, being all in the one side.
- If your level of significance was 0.05, you would use the 0.05 column to find the correct critical value for either a left or right-side question. If you are asking a “less than” (left-sided question, your critical value will be negative. If you are asking a “greater than” (right-sided question), your critical value will be positive.
Find the critical value you would use to test the claim that μ ≠ 112 with a sample size of 18 and a 5% level of significance.
In this case, the critical value (t α /2 ) would be 2.110. This is a two-sided question (≠) so you would divide alpha by 2 (0.05/2 = 0.025) and go down the 0.025 column to 17 degrees of freedom.
What would the critical value be if you wanted to test that μ < 112 for the same data?
In this case, the critical value would be 1.740. This is a one-sided question (<) so alpha would be divided by 1 (0.05/1 = 0.05). You would go down the 0.05 column with 17 degrees of freedom to get the correct critical value.
In 2005, the mean pH level of rain in a county in northern New York was 5.41. A biologist believes that the rain acidity has changed. He takes a random sample of 11 rain dates in 2010 and obtains the following data. Use a 1% level of significance to test his claim.
4.70, 5.63, 5.02, 5.78, 4.99, 5.91, 5.76, 5.54, 5.25, 5.18, 5.01
The sample size is small and we don’t know anything about the distribution of the population, so we examine a normal probability plot. The distribution looks normal so we will continue with our test.
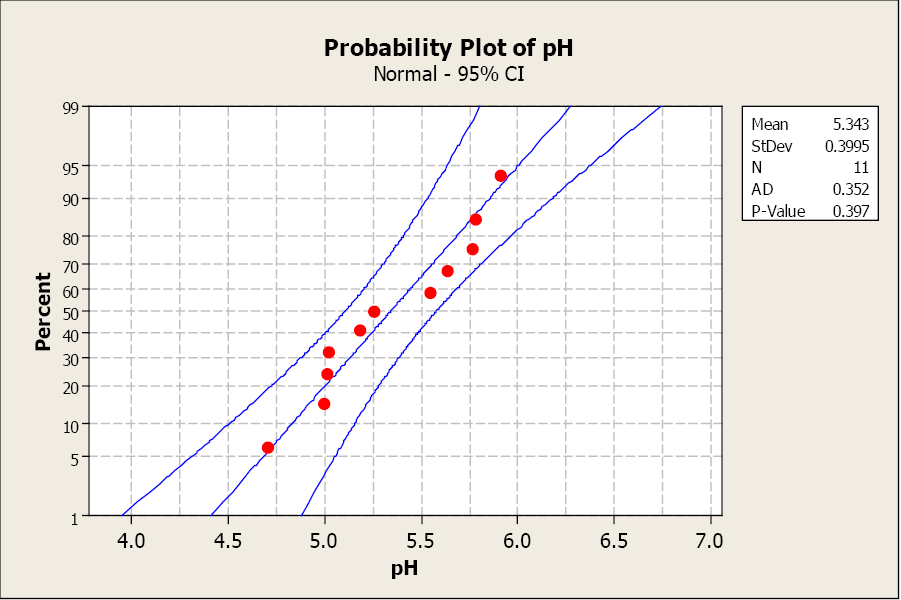
Figure 14. A normal probability plot for Example 9.
The sample mean is 5.343 with a sample standard deviation of 0.397.
- H o : μ = 5.41
- H 1 : μ ≠ 5.41
- This is a two-sided question so alpha is divided by two.
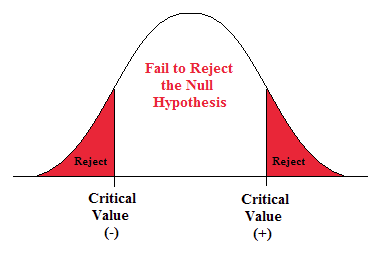
Figure 15. The rejection zones for a two-sided test.
- t α /2 is found by going down the 0.005 column with 14 degrees of freedom.
- t α /2 = ±3.169.
- The test statistic is a t-score.
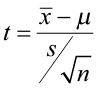
Figure 16. The critical values for a two-sided test when α = 0.01.
- The test statistic does not fall in the rejection zone.
We will fail to reject the null hypothesis. We do not have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean rain pH has changed.
A One-sided Test
Cadmium, a heavy metal, is toxic to animals. Mushrooms, however, are able to absorb and accumulate cadmium at high concentrations. The government has set safety limits for cadmium in dry vegetables at 0.5 ppm. Biologists believe that the mean level of cadmium in mushrooms growing near strip mines is greater than the recommended limit of 0.5 ppm, negatively impacting the animals that live in this ecosystem. A random sample of 51 mushrooms gave a sample mean of 0.59 ppm with a sample standard deviation of 0.29 ppm. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the mean cadmium level is greater than the acceptable limit of 0.5 ppm.
The sample size is greater than 30 so we are assured of a normal distribution of the means.
- H o : μ = 0.5 ppm
- H 1 : μ > 0.5 ppm
- This is a right-sided question so alpha is all in the right tail.
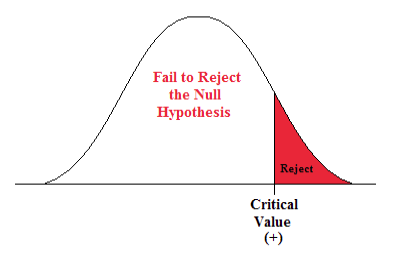
Figure 17. Rejection zone for a right-sided test.
- t α is found by going down the 0.05 column with 50 degrees of freedom.
- t α = 1.676
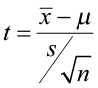
Step 4) State a Conclusion.
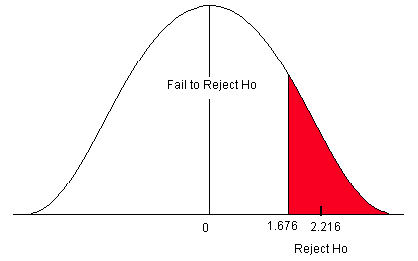
Figure 18. Critical value for a right-sided test when α = 0.05.
The test statistic falls in the rejection zone. We will reject the null hypothesis. We have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean cadmium level is greater than the acceptable safe limit.
BUT, what happens if the significance level changes to 1%?
The critical value is now found by going down the 0.01 column with 50 degrees of freedom. The critical value is 2.403. The test statistic is now LESS THAN the critical value. The test statistic does not fall in the rejection zone. The conclusion will change. We do NOT have enough evidence to support the claim that the mean cadmium level is greater than the acceptable safe limit of 0.5 ppm.
The level of significance is the probability that you, as the researcher, set to decide if there is enough statistical evidence to support the alternative claim. It should be set before the experiment begins.
P-value Approach
We can also use the p-value approach for a hypothesis test about the mean when the population standard deviation ( σ ) is unknown. However, when using a student’s t-table, we can only estimate the range of the p-value, not a specific value as when using the standard normal table. The student’s t-table has area (probability) across the top row in the table, with t-scores in the body of the table.
- To find the p-value (the area associated with the test statistic), you would go to the row with the number of degrees of freedom.
- Go across that row until you find the two values that your test statistic is between, then go up those columns to find the estimated range for the p-value.
Estimating P-value from a Student’s T-table
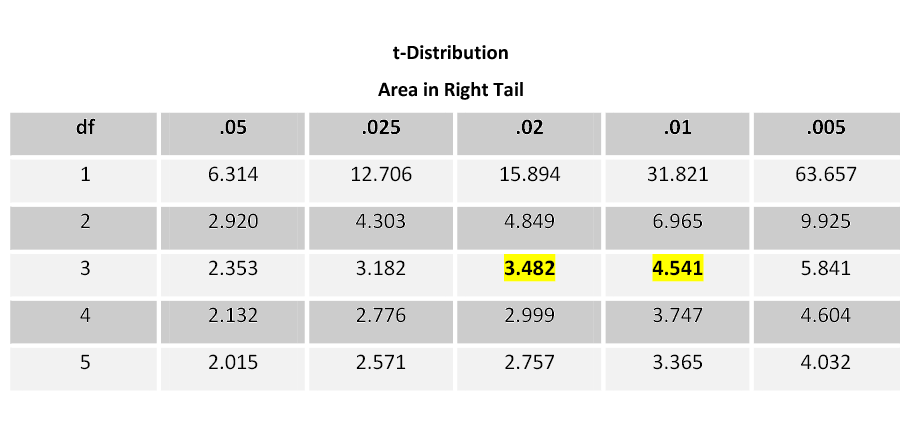
If your test statistic is 3.789 with 3 degrees of freedom, you would go across the 3 df row. The value 3.789 falls between the values 3.482 and 4.541 in that row. Therefore, the p-value is between 0.02 and 0.01. The p-value will be greater than 0.01 but less than 0.02 (0.01<p<0.02).
If your level of significance is 5%, you would reject the null hypothesis as the p-value (0.01-0.02) is less than alpha ( α ) of 0.05.
If your level of significance is 1%, you would fail to reject the null hypothesis as the p-value (0.01-0.02) is greater than alpha ( α ) of 0.01.
Software packages typically output p-values. It is easy to use the Decision Rule to answer your research question by the p-value method.
(referring to Ex. 12)
One-Sample T
Test of mu = 0.5 vs. > 0.5
Additional example: www.youtube.com/watch?v=WwdSjO4VUsg .
Hypothesis Test for a Population Proportion ( p )
Frequently, the parameter we are testing is the population proportion.
- We are studying the proportion of trees with cavities for wildlife habitat.
- We need to know if the proportion of people who support green building materials has changed.
- Has the proportion of wolves that died last year in Yellowstone increased from the year before?
Recall that the best point estimate of p , the population proportion, is given by
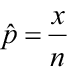
when np (1 – p )≥10. We can use both the classical approach and the p-value approach for testing.
The steps for a hypothesis test are the same that we covered in Section 2.
The test statistic follows the standard normal distribution. Notice that the standard error (the denominator) uses p instead of p̂ , which was used when constructing a confidence interval about the population proportion. In a hypothesis test, the null hypothesis is assumed to be true, so the known proportion is used.
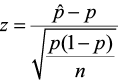
- The critical value comes from the standard normal table, just as in Section 2. We will still use the same three pairs of null and alternative hypotheses as we used in the previous sections, but the parameter is now p instead of μ :
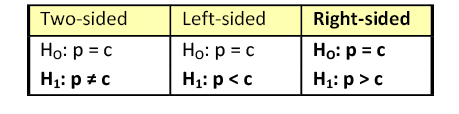
- For a two-sided test, alpha will be divided by 2 giving a ± Z α /2 critical value.
- For a left-sided test, alpha will be all in the left tail giving a – Z α critical value.
- For a right-sided test, alpha will be all in the right tail giving a Z α critical value.
A botanist has produced a new variety of hybrid soy plant that is better able to withstand drought than other varieties. The botanist knows the seed germination for the parent plants is 75%, but does not know the seed germination for the new hybrid. He tests the claim that it is different from the parent plants. To test this claim, 450 seeds from the hybrid plant are tested and 321 have germinated. Use a 5% level of significance to test this claim that the germination rate is different from 75%.
- H o : p = 0.75
- H 1 : p ≠ 0.75
This is a two-sided question so alpha is divided by 2.
- Alpha is 0.05 so the critical values are ± Z α /2 = ± Z .025 .
- Look on the negative side of the standard normal table, in the body of values for 0.025.
- The critical values are ± 1.96.
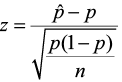
Figure 19. Critical values for a two-sided test when α = 0.05.
The test statistic does not fall in the rejection zone. We fail to reject the null hypothesis. We do not have enough evidence to support the claim that the germination rate of the hybrid plant is different from the parent plants.
Let’s answer this question using the p-value approach. Remember, for a two-sided alternative hypothesis (“not equal”), the p-value is two times the area of the test statistic. The test statistic is -1.81 and we want to find the area to the left of -1.81 from the standard normal table.
- On the negative page, find the Z-score -1.81. Find the area associated with this Z-score.
- The area = 0.0351.
- This is a two-sided test so multiply the area times 2 to get the p-value = 0.0351 x 2 = 0.0702.
Now compare the p-value to alpha. The Decision Rule states that if the p-value is less than alpha, reject the H 0 . In this case, the p-value (0.0702) is greater than alpha (0.05) so we will fail to reject H 0 . We do not have enough evidence to support the claim that the germination rate of the hybrid plant is different from the parent plants.
You are a biologist studying the wildlife habitat in the Monongahela National Forest. Cavities in older trees provide excellent habitat for a variety of birds and small mammals. A study five years ago stated that 32% of the trees in this forest had suitable cavities for this type of wildlife. You believe that the proportion of cavity trees has increased. You sample 196 trees and find that 79 trees have cavities. Does this evidence support your claim that there has been an increase in the proportion of cavity trees?
Use a 10% level of significance to test this claim.
- H o : p = 0.32
- H 1 : p > 0.32
This is a one-sided question so alpha is divided by 1.
- Alpha is 0.10 so the critical value is Z α = Z .10
- Look on the positive side of the standard normal table, in the body of values for 0.90.
- The critical value is 1.28.
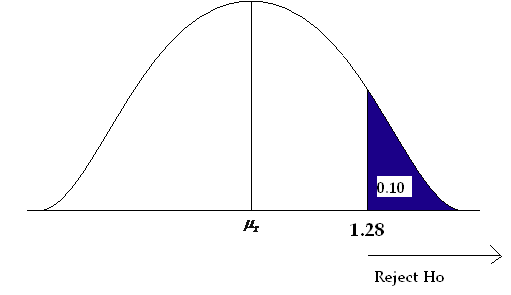
Figure 20. Critical value for a right-sided test where α = 0.10.
- The test statistic is the number of standard deviations the sample proportion is from the known proportion. It is also a Z-score, just like the critical value.
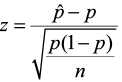
Figure 21. Comparison of the test statistic and the critical value.
The test statistic is larger than the critical value (it falls in the rejection zone). We will reject the null hypothesis. We have enough evidence to support the claim that there has been an increase in the proportion of cavity trees.
Now use the p-value approach to answer the question. This is a right-sided question (“greater than”), so the p-value is equal to the area to the right of the test statistic. Go to the positive side of the standard normal table and find the area associated with the Z-score of 2.49. The area is 0.9936. Remember that this table is cumulative from the left. To find the area to the right of 2.49, we subtract from one.
p-value = (1 – 0.9936) = 0.0064
The p-value is less than the level of significance (0.10), so we reject the null hypothesis. We have enough evidence to support the claim that the proportion of cavity trees has increased.
(referring to Ex. 15)
Test and CI for One Proportion
Test of p = 0.32 vs. p > 0.32
Hypothesis Test about a Variance
When people think of statistical inference, they usually think of inferences involving population means or proportions. However, the particular population parameter needed to answer an experimenter’s practical questions varies from one situation to another, and sometimes a population’s variability is more important than its mean. Thus, product quality is often defined in terms of low variability.
Sample variance S 2 can be used for inferences concerning a population variance σ 2 . For a random sample of n measurements drawn from a normal population with mean μ and variance σ 2 , the value S 2 provides a point estimate for σ 2 . In addition, the quantity ( n – 1) S 2 / σ 2 follows a Chi-square ( χ 2 ) distribution, with df = n – 1.
The properties of Chi-square ( χ 2 ) distribution are:
- Unlike Z and t distributions, the values in a chi-square distribution are all positive.
- The chi-square distribution is asymmetric, unlike the Z and t distributions.
- There are many chi-square distributions. We obtain a particular one by specifying the degrees of freedom (df = n – 1) associated with the sample variances S 2 .
Figure 22. The chi-square distribution.
One-sample χ 2 test for testing the hypotheses:
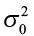
Alternative hypothesis:
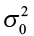
where the χ 2 critical value in the rejection region is based on degrees of freedom df = n – 1 and a specified significance level of α .
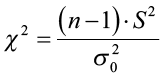
As with previous sections, if the test statistic falls in the rejection zone set by the critical value, you will reject the null hypothesis.
A forester wants to control a dense understory of striped maple that is interfering with desirable hardwood regeneration using a mist blower to apply an herbicide treatment. She wants to make sure that treatment has a consistent application rate, in other words, low variability not exceeding 0.25 gal./acre (0.06 gal. 2 ). She collects sample data (n = 11) on this type of mist blower and gets a sample variance of 0.064 gal. 2 Using a 5% level of significance, test the claim that the variance is significantly greater than 0.06 gal. 2
H 0 : σ 2 = 0.06
H 1 : σ 2 >0.06
The critical value is 18.307. Any test statistic greater than this value will cause you to reject the null hypothesis.
The test statistic is
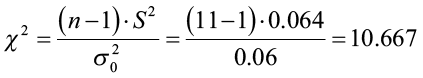
We fail to reject the null hypothesis. The forester does NOT have enough evidence to support the claim that the variance is greater than 0.06 gal. 2 You can also estimate the p-value using the same method as for the student t-table. Go across the row for degrees of freedom until you find the two values that your test statistic falls between. In this case going across the row 10, the two table values are 4.865 and 15.987. Now go up those two columns to the top row to estimate the p-value (0.1-0.9). The p-value is greater than 0.1 and less than 0.9. Both are greater than the level of significance (0.05) causing us to fail to reject the null hypothesis.
(referring to Ex. 16)
Test and CI for One Variance
The chi-square method is only for the normal distribution.
Excel does not offer 1-sample χ 2 testing.
Putting it all Together Using the Classical Method
To test a claim about μ when σ is known.
- Write the null and alternative hypotheses.
- State the level of significance and get the critical value from the standard normal table.
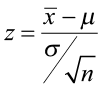
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value (Z-score) and write the conclusion.
To Test a Claim about μ When σ is Unknown
- State the level of significance and get the critical value from the student’s t-table with n-1 degrees of freedom.
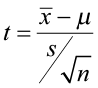
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value (t-score) and write the conclusion.
To Test a Claim about p
- State the level of significance and get the critical value from the standard normal distribution.
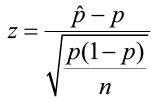
Table 4. A summary table for critical Z-scores.
To Test a Claim about Variance
- State the level of significance and get the critical value from the chi-square table using n-1 degrees of freedom.
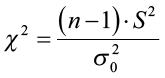
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value and write the conclusion.
- Natural Resources Biometrics. Authored by : Diane Kiernan. Located at : https://textbooks.opensuny.org/natural-resources-biometrics/ . Project : Open SUNY Textbooks. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- Area and Perimeter of Shapes | Formula and Examples
- Perfect Cubes - Definition, List, Chart and Examples
- Measurement
- Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Additive Inverse and Multiplicative Inverse
- Number Symbols
- Denominator in Maths
- Predecessor and Successor
- Probability and Statistics
- Greater Than and Less Than Symbols | Meaning of Signs and Examples
- Expanded Form
- Divisibility Rule of 11
- Square Root of 4
- Binary Multiplication
- Numerator in Mathematics
- Perfect Numbers
- Linear Algebra Symbols
- Digits in Maths
- Factors of 60
Null Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis , often denoted as H 0, is a foundational concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It represents an assumption that no significant difference, effect, or relationship exists between variables within a population. It serves as a baseline assumption, positing no observed change or effect occurring. The null is t he truth or falsity of an idea in analysis.
In this article, we will discuss the null hypothesis in detail, along with some solved examples and questions on the null hypothesis.
Table of Content
- What Is a Null Hypothesis?
Symbol of Null Hypothesis
Formula of null hypothesis, types of null hypothesis, principle of null hypothesis, how do you find null hypothesis, what is a null hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis in statistical analysis suggests the absence of statistical significance within a specific set of observed data. Hypothesis testing, using sample data, evaluates the validity of this hypothesis. Commonly denoted as H 0 or simply “null,” it plays an important role in quantitative analysis, examining theories related to markets, investment strategies, or economies to determine their validity.
Definition of Null Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis represent a default position, often suggesting no effect or difference, against which researchers compare their experimental results. The Null Hypothesis, often denoted as H 0 , asserts a default assumption in statistical analysis. It posits no significant difference or effect, serving as a baseline for comparison in hypothesis testing.
Null Hypothesis is represented as H 0 , the Null Hypothesis symbolizes the absence of a measurable effect or difference in the variables under examination.
Certainly, a simple example would be asserting that the mean score of a group is equal to a specified value like stating that the average IQ of a population is 100.
The Null Hypothesis is typically formulated as a statement of equality or absence of a specific parameter in the population being studied. It provides a clear and testable prediction for comparison with the alternative hypothesis. The formulation of the Null Hypothesis typically follows a concise structure, stating the equality or absence of a specific parameter in the population.
Mean Comparison (Two-sample t-test)
H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2
This asserts that there is no significant difference between the means of two populations or groups.
Proportion Comparison
H 0 : p 1 − p 2 = 0
This suggests no significant difference in proportions between two populations or conditions.
Equality in Variance (F-test in ANOVA)
H 0 : σ 1 = σ 2
This states that there’s no significant difference in variances between groups or populations.
Independence (Chi-square Test of Independence):
H 0 : Variables are independent
This asserts that there’s no association or relationship between categorical variables.
Null Hypotheses vary including simple and composite forms, each tailored to the complexity of the research question. Understanding these types is pivotal for effective hypothesis testing.
Equality Null Hypothesis (Simple Null Hypothesis)
The Equality Null Hypothesis, also known as the Simple Null Hypothesis, is a fundamental concept in statistical hypothesis testing that assumes no difference, effect or relationship between groups, conditions or populations being compared.
Non-Inferiority Null Hypothesis
In some studies, the focus might be on demonstrating that a new treatment or method is not significantly worse than the standard or existing one.
Superiority Null Hypothesis
The concept of a superiority null hypothesis comes into play when a study aims to demonstrate that a new treatment, method, or intervention is significantly better than an existing or standard one.
Independence Null Hypothesis
In certain statistical tests, such as chi-square tests for independence, the null hypothesis assumes no association or independence between categorical variables.
Homogeneity Null Hypothesis
In tests like ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), the null hypothesis suggests that there’s no difference in population means across different groups.
Examples of Null Hypothesis
- Medicine: Null Hypothesis: “No significant difference exists in blood pressure levels between patients given the experimental drug versus those given a placebo.”
- Education: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no significant variation in test scores between students using a new teaching method and those using traditional teaching.”
- Economics: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no significant change in consumer spending pre- and post-implementation of a new taxation policy.”
- Environmental Science: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no substantial difference in pollution levels before and after a water treatment plant’s establishment.”
The principle of the null hypothesis is a fundamental concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It involves making an assumption about the population parameter or the absence of an effect or relationship between variables.
In essence, the null hypothesis (H 0 ) proposes that there is no significant difference, effect, or relationship between variables. It serves as a starting point or a default assumption that there is no real change, no effect or no difference between groups or conditions.
Null Hypothesis Rejection
Rejecting the Null Hypothesis occurs when statistical evidence suggests a significant departure from the assumed baseline. It implies that there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis, indicating a meaningful effect or difference. Null Hypothesis rejection occurs when statistical evidence suggests a deviation from the assumed baseline, prompting a reconsideration of the initial hypothesis.
Identifying the Null Hypothesis involves defining the status quotient, asserting no effect and formulating a statement suitable for statistical analysis.
When is Null Hypothesis Rejected?
The Null Hypothesis is rejected when statistical tests indicate a significant departure from the expected outcome, leading to the consideration of alternative hypotheses. It occurs when statistical evidence suggests a deviation from the assumed baseline, prompting a reconsideration of the initial hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
In the realm of hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis (H 0 ) and alternative hypothesis (H₁ or Ha) play critical roles. The null hypothesis generally assumes no difference, effect, or relationship between variables, suggesting that any observed change or effect is due to random chance. Its counterpart, the alternative hypothesis, asserts the presence of a significant difference, effect, or relationship between variables, challenging the null hypothesis. These hypotheses are formulated based on the research question and guide statistical analyses.
Null Hypothesis vs Alternative Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) serves as the baseline assumption in statistical testing, suggesting no significant effect, relationship, or difference within the data. It often proposes that any observed change or correlation is merely due to chance or random variation. Conversely, the alternative hypothesis (H 1 or Ha) contradicts the null hypothesis, positing the existence of a genuine effect, relationship or difference in the data. It represents the researcher’s intended focus, seeking to provide evidence against the null hypothesis and support for a specific outcome or theory. These hypotheses form the crux of hypothesis testing, guiding the assessment of data to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Example of Alternative and Null Hypothesis
Let’s envision a scenario where a researcher aims to examine the impact of a new medication on reducing blood pressure among patients. In this context:
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): “The new medication does not produce a significant effect in reducing blood pressure levels among patients.”
Alternative Hypothesis (H 1 or Ha): “The new medication yields a significant effect in reducing blood pressure levels among patients.”
The null hypothesis implies that any observed alterations in blood pressure subsequent to the medication’s administration are a result of random fluctuations rather than a consequence of the medication itself. Conversely, the alternative hypothesis contends that the medication does indeed generate a meaningful alteration in blood pressure levels, distinct from what might naturally occur or by random chance.
Also, Check
Solved Examples on Null Hypothesis
Example 1: A researcher claims that the average time students spend on homework is 2 hours per night.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average time students spend on homework is equal to 2 hours per night. Data: A random sample of 30 students has an average homework time of 1.8 hours with a standard deviation of 0.5 hours. Test Statistic and Decision: Using a t-test, if the calculated t-statistic falls within the acceptance region, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. If it falls in the rejection region, we reject the null hypothesis. Conclusion: Based on the statistical analysis, we fail to reject the null hypothesis, suggesting that there is not enough evidence to dispute the claim of the average homework time being 2 hours per night.
Example 2: A company asserts that the error rate in its production process is less than 1%.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The error rate in the production process is 1% or higher. Data: A sample of 500 products shows an error rate of 0.8%. Test Statistic and Decision: Using a z-test, if the calculated z-statistic falls within the acceptance region, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. If it falls in the rejection region, we reject the null hypothesis. Conclusion: The statistical analysis supports rejecting the null hypothesis, indicating that there is enough evidence to dispute the company’s claim of an error rate of 1% or higher.
Null Hypothesis – Practice Problems
Q1. A researcher claims that the average time spent by students on homework is less than 2 hours per day. Formulate the null hypothesis for this claim?
Q2. A manufacturing company states that their new machine produces widgets with a defect rate of less than 5%. Write the null hypothesis to test this claim?
Q3. An educational institute believes that their online course completion rate is at least 60%. Develop the null hypothesis to validate this assertion?
Q4. A restaurant claims that the waiting time for customers during peak hours is not more than 15 minutes. Formulate the null hypothesis for this claim?
Q5. A study suggests that the mean weight loss after following a specific diet plan for a month is more than 8 pounds. Construct the null hypothesis to evaluate this statement?
Null Hypothesis – Frequently Asked Questions
How to form a null hypothesis.
A null hypothesis is formed based on the assumption that there is no significant difference or effect between the groups being compared or no association between variables being tested. It often involves stating that there is no relationship, no change, or no effect in the population being studied.
When Do we reject the Null Hypothesis?
In statistical hypothesis testing, if the p-value (the probability of obtaining the observed results) is lower than the chosen significance level (commonly 0.05), we reject the null hypothesis. This suggests that the data provides enough evidence to refute the assumption made in the null hypothesis.
What is a Null Hypothesis in Research?
In research, the null hypothesis represents the default assumption or position that there is no significant difference or effect. Researchers often try to test this hypothesis by collecting data and performing statistical analyses to see if the observed results contradict the assumption.
What Are Alternative and Null Hypotheses?
The null hypothesis (H0) is the default assumption that there is no significant difference or effect. The alternative hypothesis (H1 or Ha) is the opposite, suggesting there is a significant difference, effect or relationship.
What Does it Mean to Reject the Null Hypothesis?
Rejecting the null hypothesis implies that there is enough evidence in the data to support the alternative hypothesis. In simpler terms, it suggests that there might be a significant difference, effect or relationship between the groups or variables being studied.
How to Find Null Hypothesis?
Formulating a null hypothesis often involves considering the research question and assuming that no difference or effect exists. It should be a statement that can be tested through data collection and statistical analysis, typically stating no relationship or no change between variables or groups.
How is Null Hypothesis denoted?
The null hypothesis is commonly symbolized as H 0 in statistical notation.
What is the Purpose of the Null hypothesis in Statistical Analysis?
The null hypothesis serves as a starting point for hypothesis testing, enabling researchers to assess if there’s enough evidence to reject it in favor of an alternative hypothesis.
What happens if we Reject the Null hypothesis?
Rejecting the null hypothesis implies that there is sufficient evidence to support an alternative hypothesis, suggesting a significant effect or relationship between variables.
Is it Possible to Prove the Null Hypothesis?
No, statistical testing aims to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on evidence from sample data. It does not prove the null hypothesis to be true.
What are Test for Null Hypothesis?
Various statistical tests, such as t-tests or chi-square tests, are employed to evaluate the validity of the Null Hypothesis in different scenarios.
Please Login to comment...
- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Math-Concepts
- Geeks Premier League
- School Learning
- School Mathematics
- Google Maps testing a new feature that shows entrance to buildings
- ChatGPT Gets a Voice: Introducing the New Read Aloud Feature
- Meta Quest+ is Now Like Game Pass For Your VR Headset
- MLB World Series Champions - Major League Baseball Winners List
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A hypothesis test is used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.. To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:. Null Hypothesis (H 0): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
The null hypothesis varies by the type of statistic and hypothesis test. Remember that inferential statistics use samples to draw conclusions about populations. Consequently, when you write a null hypothesis, it must make a claim about the relevant population parameter. Further, that claim usually indicates that the effect does not exist in the ...
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question. When the research question asks "Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?": The null hypothesis ( H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis ( Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the ...
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
Basic definitions. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise.. The statement being tested in a test of statistical significance is called the null hypothesis. . The test of significance is designed ...
Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms: H0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter =, ≤, ≥ some value. HA (Alternative Hypothesis): Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value. Note that the null hypothesis always contains the equal sign.
Table of contents. Step 1: State your null and alternate hypothesis. Step 2: Collect data. Step 3: Perform a statistical test. Step 4: Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Step 5: Present your findings. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
In hypothesis testing, the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis.The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\). An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor ...
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
The alternative hypothesis is typically denoted as H a or H 1. This is the statement that one wants to conclude. It is also called the research hypothesis. The goal of hypothesis testing is to see if there is enough evidence against the null hypothesis. In other words, to see if there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing. As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher's goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the ...
6. Write a null hypothesis. If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing, you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a.
Write a research null hypothesis as a statement that the studied variables have no relationship to each other, or that there's no difference between 2 groups. Write a statistical null hypothesis as a mathematical equation, such as. μ 1 = μ 2 {\displaystyle \mu _ {1}=\mu _ {2}} if you're comparing group means.
Null Hypothesis Examples. "Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar " is an example of a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is tested and found to be false, using statistics, then a connection between hyperactivity and sugar ingestion may be indicated. A significance test is the most common statistical test used to establish confidence in a ...
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis. Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Onward! We use p -values to make conclusions in significance testing. More specifically, we compare the p -value to a significance level α to make conclusions about our hypotheses. If the p -value is lower than the significance level we chose, then we reject the null hypothesis H 0 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H a .
The best way to state the conclusion is to include the significance level of the test and a bit about the claim itself. For example, if the claim was the alternative that the mean score on a test was greater than 85, and your decision was to Reject then Null, then you could conclude: " At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient ...
A hypothesis test is used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.. To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:. Null Hypothesis (H 0): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
Below these are summarized into six such steps to conducting a test of a hypothesis. Set up the hypotheses and check conditions: Each hypothesis test includes two hypotheses about the population. One is the null hypothesis, notated as H 0, which is a statement of a particular parameter value. This hypothesis is assumed to be true until there is ...
It is the opposite of your research hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis--that is, the research hypothesis--is the idea, phenomenon, observation that you want to prove. If you suspect that girls take longer to get ready for school than boys, then: Alternative: girls time > boys time. Null: girls time <= boys time.
Components of a Formal Hypothesis Test. The null hypothesis is a statement about the value of a population parameter, such as the population mean (µ) or the population proportion (p).It contains the condition of equality and is denoted as H 0 (H-naught).. H 0: µ = 157 or H 0: p = 0.37. The alternative hypothesis is the claim to be tested, the opposite of the null hypothesis.
Typically, the null states there is no effect/no relationship. That's true for 99% of hypothesis tests. However, there are some equivalence tests where you are trying to prove that the groups are equal. In that case, the null hypothesis states that groups are not equal. The null hypothesis is typically what you *don't* want to find.
Null hypothesis, often denoted as H0, is a foundational concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It represents an assumption that no significant difference, effect, or relationship exists between variables within a population. ... we reject the null hypothesis. Conclusion: The statistical analysis supports rejecting the null hypothesis ...
What is your conclusion about evolution at this gene in this population? (Keep in mind the proper language about null hypothesis and if possible incorporate mention of the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions. You might make mention of what outside information you have about Sickle-Cell.)