Graphic Design
- USER EXPERIENCE (UX) DESIGN
- User Interface (UI) Design
- Interior Design
- Motion Graphics
- Graphic design
- USER EXPERIENCE Design
- Motion graphics
- Interior design


Your Ultimate Graphic Design Glossary: 50+ Graphic Design Terms Explained
Graphic design is a multifaceted field with its own unique language. Learn all the most important terminology with our ultimate graphic design glossary.
Perhaps you’re thinking about becoming a graphic designer—or collaborating with one on your next creative project. Maybe you’re just curious about the field. Either way, you might find yourself stumped by some of the industry terminology.
From gradients, grids, and gutters to padding, pixels, and prototypes; the language of graphic design can be confusing!
But fear not. We’ve put together a beginner-friendly glossary of all the most important graphic design terms, together with examples. Here they are, ordered from A to Z.
1. Alignment
Alignment is one of the fundamental principles of graphic design . It refers to the arrangement or positioning of elements relative to each other within a design. Alignment helps to create a sense of order and organisation, ensuring a visually cohesive layout. The different types of alignment include left, right, centre, and justified.
Example: In a magazine layout, the headlines, text, and images are aligned along a common vertical or horizontal axis, creating a neat and structured appearance.
2. Analogous (colours)
Analogous colours are groups of colours that are adjacent to each other on the colour wheel and therefore share similar hues. Analogous colour palettes are ideal for achieving a harmonious aesthetic but are not so high on contrast.
Example: Red, orange, and yellow are analogous colours because of where they are located on the colour wheel. See number 12 in our glossary to learn more about the colour wheel.
3. Asymmetry
Asymmetry in design refers to a lack of symmetry or balance between elements. It involves arranging elements in such a way that they do not mirror each other on either side of a central axis. Asymmetry is used to create visual interest and dynamism.
Example: A poster design might have a large graphic element (say, an image) on one side of the page and smaller text on the other, creating asymmetry that draws the viewer’s eye across the composition.
Another fundamental graphic design principle, balance refers to the distribution of visual weight in a layout. It’s achieved by arranging elements so that they create a sense of equilibrium. Balance can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial (where elements radiate outwards from a central point).
Example: In a design with symmetrical balance, elements are distributed evenly around a central axis to create a sense of stability and order. If you’re designing an event poster, for example, you might achieve balance by dividing the poster into two equal halves (vertically) and placing the event title and date in the very centre. You might then place an image directly above this central information, with more text details below.
Example: In a design with symmetrical balance, elements are distributed evenly around a central axis. This creates a sense of stability and order.

Bleed is a term used in print design (one of the many different types of graphic design ). It refers to the area beyond the trim edge of a printed page or graphic where the ink extends. It ensures that there are no white borders when the page is trimmed after printing, allowing colours and images to extend all the way to the edge of the paper.
Example: Imagine you’re designing a flyer for a concert. You want the vibrant background colour to extend right to the edges of the page, without any visible white borders after the flyer is printed and trimmed. So, you add a ‘bleed area’—an additional margin that extends about 3mm beyond the trim edge of the flyer. You then make sure to extend your background colour into this bleed area. After printing, the flyer is trimmed to its final size—with no unsightly white edges to be seen.
6. Body copy
Body copy, or body text, refers to the main text content in a particular design. It is usually the longest piece of text so it’s typically styled in a legible typeface and size for easy reading. See number 50 in our glossary to learn more about typefaces.
Example: In a blog article, the main article text is the body copy, accompanied by a heading and subheadings.
7. Branding
Branding is all about how a product, service, or organisation is perceived by its consumers. It’s a strategic process that focuses on creating a distinctive identity that sets the brand apart from competitors and resonates with the target audience. Branding encompasses visual elements such as logos , colours, and typography, as well as intangible elements such as brand values, personality, tone of voice, and the overall customer experience.
Example: Nike’s branding is instantly recognisable through its iconic swoosh logo, distinctive typography, and “Just Do It” slogan, which collectively evokes a sense of athleticism, empowerment, and quality.
8. Calligraphy
Calligraphy is the art of decorative handwriting or lettering created with a pen or brush. It often emphasises the aesthetic qualities of handwriting such as fluidity, rhythm, and varying line thicknesses. Calligraphy can range from traditional script styles to more contemporary and experimental forms. To see calligraphy in action, check out these 25 calligraphy fonts .
Example: Wedding invitations may feature elegant calligraphy to evoke a sense of sophistication and personalisation.
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (black), which make up the subtractive colour model used in printing. In this model, colours are created by subtracting varying amounts of these four ink colours. CMYK is commonly used in colour printing processes such as offset printing and digital printing.
Example: A designer preparing a brochure for print would convert their digital artwork from RGB (Red, Green, Blue—see number 40 in our glossary) to CMYK mode to ensure that the colours appear accurately when printed using cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks.
10. Colour palette
A colour palette is a predetermined selection of colours chosen for use in a specific design project, or to form part of a brand’s visual identity. There are six different types of colour palettes: analogous, monochromatic, complementary, split-complementary, triadic, and tetradic. The type of colour palette you choose will shape the overall visual aesthetic, ranging from harmonious and soothing to high-contrast and dynamic. You can learn all about colour palettes in this guide .
Example: A website might use a harmonious colour palette comprising shades of blue and green to create a calming and natural feel, with accents of yellow throughout for contrast and emphasis.
11. Colour theory
Colour theory is the study of how colours interact with each other and how they affect human perception and emotions. It explores principles such as hue, saturation, brightness, contrast, and colour harmony, providing guidelines for effective colour usage in art, design, and communication.
Example: Understanding colour theory helps designers create visually appealing compositions by balancing warm and cool colours, creating focal points, and evoking specific moods or emotions through colour choices.
Learn more: A Complete Guide to Colour Theory in Design .
12. Colour wheel

The colour wheel is an important graphic design tool. It’s a circular diagram that depicts the relationship between colours, as well as their respective tints, tones, hues, and shades. The traditional colour wheel consists of the three primary colours (red, blue, and yellow), the three secondary colours (orange, green, and purple) and the six tertiary colours (chartreuse, teal, violet, magenta, vermillion, and amber).
The best way to get acquainted with the colour wheel is to create your own. We show you how to design a colour wheel in this step-by-step guide .
13. Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement and organisation of visual elements within a design. It involves the deliberate placement of elements such as text, images, and shapes to create a balanced and visually appealing whole. Composition considers factors such as balance, alignment, hierarchy, and focal points to guide the viewer/s as they perceive the design.
Example: If you were designing a poster for a music festival, you’d think carefully about where to place all the different elements such as the name of the festival, performer names, images, and event details. These strategic design choices all come together to create the overall composition of the poster.
14. Contrast
Contrast describes the degree of visual difference between elements in a design. It can refer to differences in colour, texture, size, shape, or weight. Contrast helps to create visual interest, to emphasise important elements, and to establish visual hierarchy (see number 19 in our glossary). In the case of written content, contrast is crucial for ensuring that all text is legible and accessible.
Example: Placing black text on a white background creates high contrast, ensuring that the text is easy to read. Pink text on an orange background, on the other hand, creates low contrast and would be considerably more difficult to read.
In typography, font refers to how you apply and style a particular typeface. While the terms typeface and font are often used interchangeably, there is technically a difference between the two. A typeface refers to a particular style of lettering—for example, Times New Roman—while font describes how that typeface is implemented—for example, bold, size 12.
Learn more: Font Types 101—The Ultimate Guide to Font Styles and Their Families .
Example: If you open up a Google Doc and select, for example, EB Garamond from the dropdown list of available typefaces, you then have the option to apply various font styles such as normal, medium, semi-bold, or extra bold.

16. Gradient
A gradient is a gradual transition between two or more colours or shades. It can be linear, radial, or angular, and is often used to add depth, dimension, and visual interest to designs.
Example: A website background featuring a gradient that fades from blue to white creates a sense of depth and adds visual appeal, making the website more engaging for its users.
A grid is a framework of intersecting horizontal and vertical lines used to align and organise content within a design. Grids provide structure, consistency, and visual hierarchy, making it easier for designers to arrange elements and create balanced compositions. Grids are also used in UX and UI design to support responsive design—a design that adapts to different screen sizes.
Example: In graphic design, you might create a magazine layout based on a grid system to ensure that text, images, and other elements are aligned and spaced consistently across multiple pages, resulting in a cohesive and professional-looking design.
In graphic design, a gutter refers to the space between columns or other elements in a layout. It helps to visually separate content and improve readability by providing breathing room between different sections.
Example: In a brochure layout, a gutter is the space between two columns of text or images. This prevents them from visually merging and ensures that each element stands out on its own.
19. Hierarchy
Hierarchy refers to the organisation of elements based on their importance or significance within a specific design. It involves establishing a visual order that guides the viewer’s attention and emphasises key information. You can achieve hierarchy by varying the size and colour of different elements, and through contrast, typography, white space, and where you position elements on the page.
Example: If you’re designing a website homepage, you’d want the main heading to stand out in the visual hierarchy. To achieve this, you’d make it larger than other elements on the page, and position it above the fold so that the viewer notices it first.
Hue is one of several terms used to describe the properties of colour. A hue is the purest form of a particular colour—the original, base colour without any shade (black), tint (white), or tone (grey). When you add black, white, or grey to a base hue (for example, red), you can achieve variations of that hue—such as light red, deep red, or vibrant red.
21. Ideation
Ideation is the creative process of coming up with different ideas. It involves brainstorming, sketching, and prototyping—essentially any technique that encourages you to explore different concepts and design directions. Ideation is all about experimentation, collaboration, and remaining open-minded. The goal is to innovate and come up with unique, novel ideas.
Example: Before designing a logo, you might hold an ideation session to come up with multiple concepts and explore different angles and directions the logo might take.
22. Iteration
Iteration is the process of repeating a sequence of steps or actions with the aim of refining and improving a design or concept. It involves creating multiple versions, prototypes, or drafts, where each new version is an improvement on the last based on feedback and insights you’ve gained from testing or design reviews.
Example: When creating a logo, designers will often iterate by creating several versions of the logo concept based on feedback from the client. The logo will go through multiple iterations until everybody is happy with it.
23. Kerning
A typography-related term, kerning is the adjustment of spacing between individual characters in a piece of text. Kerning helps to achieve balance, create visual harmony, and enhance readability.
Example: A designer might run through a piece of text and adjust the kerning between certain letters manually if there are any awkward gaps or overlaps between characters.
24. Leading
Another typographic term, leading (pronounced “ledding”) refers to the vertical space between lines of text. The term originates from the strips of lead that were used to separate lines of metal type in traditional printing presses. Leading impacts the readability and visual appearance of text. Tighter leading results in denser, more compact text, while looser leading creates more breathing room.
Example: In a book layout, the leading determines the spacing between lines of text. Optimal leading ensures that the text is comfortably readable without lines appearing too crowded or spread out.
25. Lettermark
A lettermark, also known as a monogram logo, is a type of logo design that consists of letters, usually initials, formed into a unique symbol. Lettermarks are often used by companies with long names to create a concise and recognisable visual identity. You can learn all about the different types of logo design in this guide .
Example: IBM's logo, consisting of the letters "IBM" arranged in a distinctive, geometric form, is a classic example of a lettermark logo.
A logo is a graphic symbol, emblem, or mark that represents a company, brand, product, or organisation. It serves as a visual identifier and plays a crucial role in establishing brand recognition and differentiation in the marketplace.
Example: The Apple logo, a simple bitten apple silhouette, is instantly recognisable and synonymous with the technology giant's brand identity.
Learn more: Everything You Need to Know About Logo Design .
27. Microcopy
Microcopy refers to the small snippets of text used throughout a website, app, or digital interface to provide guidance, instructions, feedback, and reassurance to the end user. Microcopy enhances the user experience by clarifying actions, reducing confusion, and adding personality to the overall interaction.
Example: Error messages, button labels, form fields, and pop-up messages are all examples of microcopy that help the user navigate digital products with ease.
A mockup is a realistic representation or model of a design concept, typically created to showcase how a final product will look and function. Mockups can be static or interactive and are often used for presentations, client approvals, or testing before the final implementation.
Example: A graphic designer might create a mockup of a website design using design software or prototyping tools to simulate user interactions and demonstrate the layout, typography, colours, and functionality of the website before development begins.
29. Monochrome
A monochrome design is one that uses a monochromatic colour palette—a colour scheme comprising just a single base colour in varying shades, tints, and tones. Monochrome designs inspire a cohesive, harmonious, and minimalist aesthetic.
Example: You might choose a monochrome blue colour scheme for your design project. This would comprise a base hue of blue and then lighter and darker variations of that hue.
30. Moodboard
A moodboard is a visual collage or collection of images, colours, textures, patterns, and other design elements assembled to convey a particular style, theme, or mood. It serves as a tool for designers to explore ideas, gather inspiration, and communicate concepts to clients or team members.
Example: Before starting a branding project for a nature-inspired skincare brand, a designer might create a moodboard featuring images of nature, vibrant colours, and organic textures to evoke a sense of freshness, vitality, and eco-friendliness.
31. Opacity
Opacity refers to the degree of transparency or translucency of an object or layer in a design. It determines how much light can pass through an element, affecting its visibility and appearance. An object with low opacity is more transparent, allowing underlying elements to show through, while an object with high opacity is more opaque, obscuring underlying elements.
Example: In graphic design software , designers can adjust the opacity of layers or objects to create effects such as overlays, fades, and blends, enhancing the depth and visual interest of the design.
32. Padding
Padding refers to the space between the content of an element and its border or edge. It provides breathing room and visual separation between elements, improving readability and enhancing the overall appearance of the design. Padding can be applied to text, images, buttons, and other elements in a layout.
Example: In a website layout, padding around text blocks or images ensures that content is not cramped against neighbouring elements, creating a more balanced and visually pleasing design.
The term pixels comes from “picture elements”, and it refers to the smallest individual units of colour that make up a digital image or display. Pixels are square-shaped and arranged in a grid pattern, with each pixel representing a single point of light. Pixels are fundamental to digital imagery, used to create and display everything from photographs and illustrations to text and graphics on screens.
Example: The resolution of a digital photograph is measured in pixels, with higher resolutions containing more pixels per inch (PPI) or pixels per centimetre (PPC), resulting in sharper and more detailed images.
34. Proportion
Proportion refers to the relative size, scale, and relationship of elements within a design. It involves balancing the visual weight of different components to create a harmonious and aesthetically pleasing composition. Proportion helps to establish hierarchy, emphasise key elements, and maintain visual balance.
Example: In typography, headings and subheadings are often set in larger font sizes than body text to establish a clear hierarchy of information and guide the reader's attention.
35. Prototype
A prototype is a preliminary version or mockup of a product, design, or concept, created to test and validate ideas, functionalities, and user interactions before proceeding to full-scale production or development. Prototypes can be low-fidelity sketches, wireframes, or high-fidelity interactive simulations, depending on the stage of the design process and the goals of testing.
Example: A UX designer creates a clickable prototype of a mobile app interface to demonstrate user flows, navigation paths, and interactions to stakeholders and gather feedback before finalising the design.
36. Proximity
Proximity is a fundamental graphic design principle. It refers to the visual closeness or grouping of different elements within a layout. Elements positioned in close proximity to each other appear related or connected, helping the viewer to understand that there is a relationship between them.
Example: If you were designing the packaging for a sandwich, you’d use the proximity principle to group essential and related information such as ingredients and nutritional values. This makes it easier for the consumer to find the information they need.
37. Raster / raster images
Raster refers to a type of graphic composed of a grid of pixels, where each pixel contains colour information. Raster images are resolution-dependent, meaning they have a fixed number of pixels and can lose quality when resized or scaled up. Common raster file formats include JPEG, PNG, and GIF.
Example: Photographs captured with digital cameras (e.g. your smartphone camera) are raster images as they are composed of pixels arranged in a grid to form the image.
38. Readability (legibility)
Readability, or legibility, describes the ease with which text can be read and understood. It is influenced by factors such as font choice, font size, line spacing, contrast, and background colour. Designers must strive to enhance readability in order to ensure that text is accessible and comprehensible for readers.
Example: You can improve readability by using a legible typeface (such as a sans-serif typeface—see number 41 in our glossary) and ensuring sufficient contrast between the text and the background colour (for example, black text on a white background).
39. Resolution
Resolution refers to the clarity and level of detail in an image or display, typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Higher-resolution images contain more pixels per unit of measurement, resulting in sharper and more detailed visuals. Resolution also applies to displays (e.g. a smartphone display or TV screen), indicating the number of pixels available for rendering content.
Example: A high-resolution image printed at 300 DPI (dots per inch) contains more dots per inch than a low-resolution image printed at 72 DPI, resulting in a crisper and more detailed print.
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, which are the primary colours of light used in digital displays and colour reproduction systems. In the RGB colour model, colours are created by combining different intensities of red, green, and blue light. RGB is an additive colour model, meaning that combining the maximum intensities of all three primary colours produces white light. See also CMYK , a subtractive colour model used in print (number 9 in our glossary).
Example: Computer monitors and television screens use RGB to display colours, with each pixel containing red, green, and blue subpixels that emit light to create a wide range of colours.
41. Sans-serif
Sans-serif refers to a typeface—that is, a particular style of lettering—that does not have small decorative strokes (serifs) at the ends of its characters. Sans-serif typefaces are characterised by a clean and modern appearance and optimal readability. As such, they are a popular choice for digital design projects such as websites and apps.
Examples: Arial and Helvetica are well-known examples of sans-serif typefaces commonly used for text on websites and other digital products.
Serif typefaces are those that feature small decorative strokes, known as serifs, at the ends of their characters. Serif typefaces are often associated with tradition, formality, and readability in print media. See also: sans-serif (number 41 in our graphic design glossary), typeface (number 50), and font (number 15).
Example: Times New Roman and Georgia are classic serif typefaces commonly used in newspapers, magazines, and books for body text.
A colour-related term, shade refers to a variation of a colour that has been darkened by adding black to the base hue. Shades are created by reducing the lightness or brightness of a colour, resulting in a deeper or darker version of the original hue.
Example: Adding black to the base hue of blue creates shades of navy or midnight blue, which are darker variations of the original blue colour.
44. SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics, an XML-based vector image format used for displaying graphics on the web. SVG graphics are composed of mathematical shapes and lines rather than pixels, allowing them to be scaled infinitely without loss of quality. SVGs are ideal for logos, icons, illustrations, and other graphics that need to be displayed in different sizes and resolutions. See also: pixels (number 33 in our glossary).
Example: A website logo created as an SVG can be resized to fit various screen sizes and resolutions without losing quality, ensuring crisp and clear rendering on all devices.
45. Texture
Texture refers to the tactile quality or surface appearance of an object or material, both in the physical world and in visual representations. In graphic design, texture is simulated or implied through the use of visual elements such as patterns, gradients, and brush strokes to add depth, dimension, and visual interest.
Example: A website background featuring a subtle grunge texture adds depth and character, giving the design a tactile feel and enhancing its visual appeal.

Source: 254 Online
A tint is a variation of a colour that has been lightened by adding white to the base hue. Tints are created by increasing the lightness or brightness of a colour, resulting in a softer or pastel version of the original colour. See also: hue (number 20 in our glossary), shade (number 43) and tone (number 47).
Example: Adding white to the base hue of red creates tints of pink or rose, which are lighter variations of the original red colour.
Tone refers to the addition of both black and white (i.e. grey) to alter the saturation or brightness of a base colour or hue. When you edit a photo on your phone, you can dial the saturation up and down. The same goes for colour—you can add different amounts of black and white to a base colour to create more muted tones.
Example: In a grayscale image, different shades of grey represent variations in tone, ranging from light grey (highlights) to dark grey (shadows).
48. Tracking
A typography-related term, tracking—also known as letter-spacing—refers to the uniform adjustment of spacing between all characters in a block of text. It’s used to improve readability and visual consistency, adjust text density, and create visual balance in typography.
Example: Increasing the tracking of a headline or title can help to improve legibility and create a more airy and spacious appearance, while decreasing the tracking can make text appear denser and more compact. See also: kerning (number 23 in our glossary) and leading (number 24).
Trim refers to the final size of a printed document or graphic after it has been cut to its intended dimensions. It represents the finished size of the product as specified in the printing specifications or design layout.
Example: In print production, designers include trim marks on the layout to indicate where the printed piece should be trimmed to its final size after printing.
50. Typeface
In typography, a typeface is a set of characters, letters, and symbols that share a consistent design style. Choosing an appropriate typeface is essential for creating a meaningful brand identity and ensuring that the text is legible. Within a typeface, you have various font styles, weights, and variations such as regular, bold, italic, and condensed. This enables you to create contrast and emphasis while maintaining a cohesive visual appearance.
Example: Helvetica is a popular typeface known for its clean and versatile design, available in various styles and weights for use in print and digital media. See also: sans-serif (number 41 in our glossary) and serif typefaces (number 42).
51. Typography
Typography is the art and technique of arranging typefaces, fonts, and text within a design to enhance readability, legibility, and visual appeal. It involves selecting appropriate typefaces, font sizes, line spacing, and alignment to convey information effectively and create a cohesive visual hierarchy.
Example: A magazine layout utilises typography to establish a consistent visual identity, with headlines, subheadings, body text, and captions styled and arranged to guide the reader's attention and create an engaging reading experience.
For an in-depth exploration of this fascinating discipline, read our full guide: What Is Typography? Everything You Need To Know .
52. Vector image
A vector image is a graphic composed of geometric shapes, lines, and curves defined by mathematical equations rather than pixels. Vector images are resolution-independent, meaning they can be scaled infinitely without loss of quality, making them ideal for designs requiring scalability and flexibility.
Example: Logos, icons, and illustrations created as vector images can be resized for various applications, from small icons on a website to large banners on billboards, without losing clarity or sharpness.
53. White space
White space, also known as negative space, refers to the empty or unmarked areas in a design layout that surround or separate visual elements. White space plays a crucial role in design composition by providing breathing room, improving readability, emphasising content, and creating visual balance.
Example: In a minimalist website design, ample white space around navigation menus and content blocks creates a clean and uncluttered layout, allowing users to focus on the essential information and navigate the site with ease.
Learn more about graphic design
You’re now fluent in the most important graphic design terms. Great stuff! We hope this will enable you to approach your work, studies, or creative endeavours with confidence. And remember: you can always bookmark this post and return to refresh your memory.
If you’d like to learn more about the wonderful world of graphic design, continue with these guides:
- The 15 Best Graphic Design Quotes of All Time
- 21 Graphic Design Books to Add to Your Reading List in 2024
How To Learn Graphic Design: A Step-by-Step Guide (Including Resources)
In case you need further assistance, here are some of our resources you can consider:
- Watch this session by design veteran and AND’s Academic Head, Prachi Mittal, and our Course Lead, Soumya Tiwari.
- Talk to a course advisor to discuss how you can transform your career with one of our courses.
- Pursue our Graphic Design courses - all courses are taught through live, interactive classes by industry experts, and some even offer a Job Guarantee.
- Take advantage of the scholarship and funding options that come with our courses to overcome any financial hurdle on the path of your career transformation.
Note: All information and/or data from external sources is believed to be accurate as of the date of publication.

Why You Should Pursue a Logo Design Course
With the growing importance of branding in establishing consumer relations, logo design has emerged as a popular profession. Read on to learn how pursuing...…

Why Graphic Design Is Much More Than Software Proficiency
Is software training sufficient to become a graphic designer? What other skills are needed to excel in the field? Read on for a comprehensive understanding of the scope of graphic design...…

20 Business Logo Design Examples To Inspire You
Wish to see some of the best business logos ever created? Our diverse list includes classics from over 200 years ago and recent creations. Read on to learn more about these iconic logos defining...…

Top 8 Graphic Design Schools in New York for 2024
Thinking of becoming a graphic designer? Learn at some of the best graphic design schools in New York that offer graphic design courses for you to take in 2024 to help you take your passion and turn...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in London to Consider in 2024
Master graphic design in 2024 by pursuing any one of the 9 courses in London listed in this article. This guide will offer key details regarding the curriculum, duration, and tuition for each course...…

Top 10 Graphic Design Courses in LA to Consider in 2024
Eager to launch your design career with a qualification that aligns with industry standards? Our compilation of the best graphic design courses in LA, complete with a detailed review of prominent...…

Top 13 Graphic Design Courses in Chicago to Consider in 2024
Looking to pursue a graphic design program in Chicago? This comprehensive list of courses is exactly what you need. Read on for a detailed review of online and on-campus programs with insights...…

25 Calligraphy Fonts to Consider Downloading in 2024
Are you looking for the best calligraphy fonts to download? Discover 25 beautiful options to consider for your next project, right here. …

Font Types 101: The Ultimate Guide to Font Styles and Their Families
What are the different font types and styles? What are some examples of font families? Consider this your ultimate beginner’s guide to fonts. …

21 Cool Fonts to Spruce Up Your Design Project
Looking for some cool fonts for your next design project? Discover our top picks—including the best fonts for logos, cursive and handwriting fonts...…

The 7 Best Free Graphic Design Courses to Consider in 2024
Are you looking to kick-start your graphic design education? Free courses are an excellent place to start. Keep reading to discover the best free graphic design courses available in 2024. …

A Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Website Colour Palette
Looking for the perfect website colour palette? Read this guide to understand our practical 6-step framework to find the most effective colour combinations for your brand. …

A Designer’s Guide to Colour Combinations
Are you seeking colour inspiration for your next project? Discover some of the most beautiful colour combinations in this guide.…

A Complete Guide to Colour Palettes and How To Use Them
Colour palettes have the power to make or break your designs—so choose wisely! Learn about the six different colour palettes and how to use them in this guide. …

How To Design a Colour Wheel: Your Step-by-Step Guide (With Images)
Are you curious about the color wheel and how to craft one yourself? Delve into the world of color theory as you embark on a journey to construct...…

A Complete Guide to Colour Theory in Design
Colour theory considers how different colours work together and how they’re perceived by the end-user or viewer. Are you ready to master... …

20 Stellar Logo Design Examples from Fashion, Music, Sports, and Pop Culture
Looking for some logo design inspiration to make your day? Read on for a walkthrough of logo design examples (and images) from the world of fashion....…

The 16 Best Logo Design Tools and Software To Use in 2024 (Free & Paid)
Compare the best logo design tools and software (free and paid) for 2023—including Canva, LogoMakr, and Adobe Illustrator.…

How To Design a Logo: Your Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to design an outstanding logo from scratch with this practical step-by-step guide—including common mistakes to avoid.…

13 Impressive Logo Design Ideas & Trends (With Examples)
Want to design a logo that stands out from the crowd? Take inspiration from these remarkable logo design trends.…

Everything You Need To Know About Logo Design
Logos form the foundation of a strong brand identity—but what exactly is logo design and why does it matter? Consider this guide your ultimate introduction....…

A Guide to the 7 Different Types of Logo Design (With Examples)
Not sure what kind of logo to design? Learn about the 7 different types of logo design in this guide, complete with real-world examples...…

15 Best Graphic Design Quotes of All Time
Got a graphic design project to finish but are feeling uninspired? Here are some all-time great Graphic Design quotes to pick you up and motivate you..... …

5 Common Typography Applications and Use Cases (and How To Design for Them)
What role does typography play in different contexts? How do you design typography for different use cases, such as logos, posters, or websites? Find out here. …

30 Outstanding Typography Examples To Inspire You
Are you looking for typography inspiration? Prepare to be impressed by these 30 great examples of typography for logos, books, websites, t-shirts, and more. …

Typography Design 101: Key Elements, Rules, and Principles of Good Typography
Are you looking for a practical guide to typography? Then you’re in the right place. Keep reading to learn all the key elements, rules, and principles of good typography—and how to apply them.…

What Is Typography? Everything You Need To Know
Typography is a crucial part of any design project, determining how text is styled and arranged. Learn everything you need to know about typography in this guide.…

Top 10 Graphic Design Colleges in India to Consider in 2024
If you’re looking to pursue a degree course in the field of graphic design but are unable to zero in on a good college, you’ve come to the right place. This holistic blog is here to walk you through... …

The Top 10 Graphic Design Companies in India: A Jobseeker’s Guide
What are the best graphic design companies to work for in India? Discover our top 10 graphic design employers in this guide. …

The 21 Graphic Design Books You Should Have on Your Reading List in 2024
Graphic design books are an endless source of insight and inspiration. Discover the top 21 graphic design books for 2023 right here.…

A Complete Guide to Motion Graphic Design
Read to know in-depth about every facet of Motion Graphic Design. Uncover career insights, salary details, nature of work, key skills, and essential advice to help you pursue a successful career...…

What Are the Different Types of Graphic Design? Everything You Need To Know (With Examples)
There are many different types of graphic design, each requiring a unique set of skills, tools, and know-how. Read on to discover the eight fundamental types of graphic design. …

Do you want to learn graphic design from scratch? Then you’ve come to the right place. Here you’ll find an actionable step-by-step guide, complete with helpful resources to get ...…

Fundamental Graphic Design Principles and How to Apply Them
Graphic design principles are the golden rules of design. Learn what they are and how to apply them in this guide.…

The Complete Guide to Graphic Design Salaries in 2024
Graphic design is a popular career path—but how much do graphic design professionals actually earn? Find all the latest salary data in this guide. …

Why You Should Pursue Graphic Design Internships? (And How To Get One)
A graphic design internship is a great way to learn on-the-job skills and break into the industry. Learn how to secure a graphic design internship, and why it’s...…

17 Graphic Design Interview Questions (and How To Prepare for Them)
Are you preparing for a graphic design job interview? In this guide, we set out the most common questions you’re likely to be asked—and show you how to answer them. …

9 Graphic Design Examples To Inspire Your Next Project
Are you seeking inspiration for your next graphic design project? Want to see how other experts in the field create impactful designs? Here are 9 outstanding...…

How To Become a Graphic Designer in 2024: The Ultimate Guide
Are you considering a career in graphic design but not sure where to start? Discover how to become a graphic designer in this step-by-step guide.…

How To Create a Graphic Design Portfolio That Will Get You Hired (With Examples)
A graphic design portfolio is a digital showcase of your best work. It could take the form of your own personal website, or it may be hosted on another... …

An In-Depth Guide to the Top Graphic Design Jobs in 2024 (and Their Salaries)
esides creativity, a career in graphic design offers great flexibility and variety. Once you’ve learnt the fundamentals of graphic design, you can specialise...…

What Skills Does a Graphic Designer Need in 2024? A Complete Guide
If you're interested in knowing the most crucial skills a graphic designer should have in 2023, then you've come to the right place! This guide will provide... …

What Is Graphic Design? Everything You Need To Know
Graphic design is a creative, artistic discipline that originates from the printing industry. Graphic design is a form of visual communication, using...…

The Best Graphic Design Software and Tools in 2024
Every graphic designer needs a good set of tools. Whether you’re creating simple, template-based designs or whipping up complex graphics from...…

The 9 Best Graphic Design Courses and Certifications in 2024
Graphic design is a popular career choice among those looking for variety and creativity in their day-to-day work. Designers are also in high demand, providing yet...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Surat for 2024
Exploring the best graphic design courses in Surat? Discover the top courses for aspiring designers with our list that uncovers insights into curriculum, pricing...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Nagpur for 2024
Peruse this article for a comprehensive list of Graphic Design courses in Nagpur. Discover key details such as curriculum, format, medium, and pricing to empower your decision-making process. …

Best Graphic Design Courses in Jaipur for 2024
Undertaking a comprehensive graphic design course with an industry-relevant curriculum could be the ticket to a prosperous career.....…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Ahmedabad for 2024
Are you searching for the ideal graphic design course to advance your career? Look no further. In this guide, we've meticulously selected the premier Graphic Design....…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Indore for 2024
Interested in pursuing a career in graphic design? Enrolling in an industry-relevant course could be an excellent way to get started in the field...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Kerala for 2024
Planning to enrol for a graphic design course in Kerala? Let this guide be your compass. Explore a detailed list of industry-relevant courses with insights...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Kolkata in 2024
Seeking to enhance your graphic design skills or embark on a promising career in Kolkata's flourishing creative landscape? Look no further.....…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Chennai for 2024
Want to gain proficiency in graphic design skills and scale professionally? An industry-relevant course with a comprehensive curriculum is one of the best ways to get started......…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Guwahati in 2024
Let us be your guide for the city tour in Guwahati in your search for the best graphic design courses. Find out almost every important piece of information...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Bangalore for 2024
In search of a Graphic Design course in Bangalore that helps you develop a solid understanding of the fundamentals and create an impressive portfolio?…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Delhi for 2024
Wish to learn Graphic Design in Delhi NCR? You'll need a course that equips you with industry-relevant knowledge and skills. Here is a comprehensive list of the top...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Hyderabad for 2024
When it comes to Graphic Design, you could go the self-study route but it might not be the best way forward. If you are considering pursuing a career...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Pune for 2024
Looking for the best graphic design courses in Pune to enhance your skills or start a career in the field? Read on for our top picks! This list offers options...…

Best Graphic Design Courses in Mumbai for 2024
Searching for the perfect Graphic Design course in Mumbai? Explore our list of the top courses in 2023, along with the pros, cons, duration and cost of each. …
Consult Course Advisors
Hire Our Graduate / Upskill Your Team
Become An Instructor
Course(s) you can teach
Graphic Design Terminology: 120 Graphic Design Terms to Help Cut Through the Jargon
Graphic design isn’t just a profession, it’s also a language. And, if you’re not up to scratch with the design lingo, then a conversation with a designer can be bewildering. A ‘creep’ definitely isn’t what you think it is, isn’t a baseline something to do with basketball? And, what on earth is kerning?
Don’t fret, we’ve put together this list of 120 design terms—from alignment to x-height—to help you make sense of the jargon and be talking the (designer) talk in no time. This dictionary of sorts is written for designers and non-designers alike, this list will help you make sense of any of the graphic design terminology you might not be able to put your finger on.

The list is alphabetised but if you’re looking for any specific graphic design terms then use CMD+F to find what you’re after!
1. Alignment
Alignment is the way that the different elements in a design are arranged, usually in relation to a page or document. In typography, alignment, which can also be called range, is the setting of text relative to a column, tab or page. It’s very easy to notice when elements in a design aren’t aligned.
2. Analogous (Colours)
Think of these as the neighbours of the colour world—analogous colours are colours that sit next to each other on the colour wheel. Think, in simple terms, red, orange and yellow—there’s a dominant colour, a primary or secondary colour and a tertiary colour. Analogous colours match really well and create a proper colour harmony—resulting in a composed design. A famous use of analogous colours in the iconic Pentagram-designed Mastercard logo .
3. Aperture
The white space at the end of an open counter in typography.
In typography, the top point where two strokes are joined together.
When a horizontal stroke is not attached to a stem on one end.
6. Ascenders
Ascenders refer to the parts of lower case letters that extend above the x-height of a typeface. If you look back at that first sentence, you’ll see loads of them—and that one too. In a majority of typefaces, the lowercase letters b, d, f, h, k and l are ascenders. Careful though, the letter t is not an ascender. In certain fonts, such as Garamond, the ascenders rise above the cap height.
7. Aspect ratio
Aspect ratio is most easily explained as the ratio of the width to the height of a rectangle—which usually, in design terms, is a picture or a screen. Aspect ratios are usually expressed as a mathematical ratio but, no fear, there’s no maths involved—it’s just two numbers separated by a colon. It’s usually width:height so, for instance, the aspect ratio for an iMac is 16:9—16 inches wide by 9 inches high.
8. Backslanted
Italics leaning backward.
9. Ball Terminal
Ball-shape extension of a letter.
10. Baseline
In typography, the baseline is the invisible line that text sits on—think of it as the floor, but for text. It’s also the place that x-height and other important parts of a font are measured from. There is also parts of fonts that don’t sit on the baseline, but we’ll get to them later.
That little bit extra—the bleed is a printing term that refers to the edge of the sheet that will be trimmed off. In design terms, the bleed is the artwork or background colour that extends in to this area, in case the cut made to the design or sheet isn’t exact. It’s a way of ensuring that none of the design gets accidentally cut off or there’s no unexpected borders.
12. Body Copy
The main text that people will read on a design. The body copy refers to the paragraphs, sentences or other text that are the main content in any publication, whether print or digital. Put in real life terms, the body copy of a magazine is the articles themselves rather than the titles, subtitles, authors, etc.
A heavy weight of any given typeface, often used for emphasis.
The generally round or elliptical forms which are the basic body shape of letters such as C, G, O in the uppercase, and b, c, e, o, p in the lowercase.
15. Bracket
A curved connection between the stem and serif of some fonts. Not all serifs are bracketed serifs.
16. Brand Identity
The visual version of a brand. The brand identity is made up of everything that relates to the brand—logos, typefaces, colour palettes, slogans, tone of voice, website, packaging and other marketing material. When designers talk about ‘branding’, it usually involves developing all aspects of the brand identity.
17. Calligraphy
The art of writing letters with a very specific tool (e.g., broad nib pen, brush pen, etc.).
18. Cap Height
Back to our friend the baseline—the cap height is the height of the top of a capital letter in any given font above the baseline. The cap height refers specifically to letters with a flat top, such as H and I. Round letters like ‘O’ and pointed ones like ‘A” may rise above the cap height in their capital forms.
19. Centre Aligned
When text is aligned to the centre of a text frame, with the rag on the left and right sides of the text frame.
20. Character
A letter, number, punctuation mark or symbol.
21. Character Set
Entire collection of characters for any given typeface weight.
RGB’s printing brother, CMYK, is the colour mode which should be used when designing for print. The four colours the name stands for, Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Key (Black), are the four colours most widely used in printing. Similarly to RGB, these four colours can be combined in lots of different ways to produce a majority of colours in print—though, unlike RGB, these colours are subtractive so get darker as they are combined. Key/black is added on top of the other three as mixing them will never produce a pure black.
23. Complementary (Colours)
Think of these as the best friends of the colour world—complementary colours are the colours that sit directly opposite each other on the colour wheel. Examples of complementary colours are red and green, blue and orange and purple and yellow. Using complementary colours will make a design more aesthetically pleasing—and can also be used in things like logos and retail displays to make a design stand out more.
24. Contrast
Contrast is the arrangement of opposite elements on a page—in other words, when two things on a page are different. This can be light vs. dark colours, smooth vs. rough textures, text colour vs. background colour. Contrast can be used to create areas of visual interest or even drama within a design.
25. Counter
The white space enclosed by a letterform, whether wholly enclosed, as in ‘d’ or ‘o’, or partially, as in ‘c’ or a double-story ‘a’.
Definitely not what you are thinking—creep, alternatively known as shingling, is the inside margin of a book, magazine or other publication. With some bindings, the creep often has to be made larger so that no content is covered when it is being read. Printing companies will sometimes have charts to calculate the size of the creep for their different paper stocks.
27. Crop Marks
Also known as trim marks, crop marks are specific marks (they kind of look like two lines crossing with a target) that indicate to a printer where the paper should be trimmed. They’re essential when designing for print and make it much easier to communicate with the printers.
28. Crossbar
A stroke across a stem (as in the horizontal line of the letter ‘T’, ‘H’, ‘E’, etc.).
29. Descenders
Descenders are the opposite of ascenders, they’re the tail of letters—the part of the letter that descends below the baseline. Generally, only the lowercase letters g, j, q, p and y are descenders. Though, in some fonts, the lowercase f, capital Q and J and certain numbers are also descenders. Both ascenders and descenders increase the recognisability of words to the extent that British road signs stopped using all capital letters and instead opted for their specialised font .
30. Display
Display type is fonts that are designed to make an impact and catch the eye—they’re used for things that need to stand out: headlines, posters, billboards, logo. Famous examples of display type will often be seen across different mediums—Stencil, for instance, was used for the TV shows The A-Team, M A S*H and Recess but also in The Home Depot logo and on the 2001/02 Real Madrid kits.
The stroke attached to the bowl of the lowercase g. Some typographers use the same term for the lowercase r.
32. Ellipsis
Character composed of three dots…
33. Embossing & Debossing
Embossing and its counterpart debossing are finishing processes that involve creating dimensional relief images in to a piece of paper or card. The practice uses a printing press to, in the case of embossing, lift the design into the material or, in the case of debossing, sunk the design into the material.
34. Extended
Character with an exaggerated width a character such as an accent mark.
35. Foiling
A process also known as foil stamping, foiling is a type of printing where metallic or pigmented foil is applied to a surface through the application of heat and a die. A relatively uncomplicated process, foiling can add extra dimensions to a design especially packaging—they’re excellent for catching a potential customers’ eye on shop shelves.
36. Font Colour
Used in web design to specify a colour.
37. Font Size
The height of a typeface. It is usually measured in points (8, 10, 12, etc.), from baseline to baseline.
38. Font Weight
Font weight refers quite literally to the thickness of a font, in terms of both an individual font and different styles of a font—black, bold, light etc. Font weight ranges from 100 to 900 with “normal” font being 400 so 100 being extra light or equivalent and 900 being extra black or equivalent. Though, you’ll rarely need to use the numbers as Adobe Creative Cloud and similar programs give the font weight as their names.
39. Golden Ratio
First studied by the Ancient Greeks in the 5th Century B, the Golden Ratio is when you take two objects, divide the larger by smaller and get the result of 1.6180 (or near it). We could get way more mathematical than that but we’ll just confuse ourselves. The most famous example of the golden ratio is the golden rectangle—this can be split into a perfect square and a rectangle of the same aspect ratio. The golden ratio can be used to make designs well formatted and attractive.
40. Gradient
Sometimes specifically called a colour gradient, gradients are a gradual change of colour or shade—for instance a red slowly fading into an orange—or a colour gradually fading into transparency. There are two types of gradients, axial/linear or radial, and both show the range of different shades and hues.
41. Greyscale
Greyscale is a colour palette that only uses black, white and different shades of grey. The most obvious examples of greyscale are black and white films or photographs (which seeing as they contain greys, strictly aren’t black and white). Greyscale can also be used in design for many different reasons—from evoking nostalgia to helping you to learn how to design better with colour.
We can’t stress enough how important grids are to designers! Grids are an underlying system of horizontal and vertical columns and guides used to provide structure, consistency, accuracy in any design. They also make a designer’s life a whole lot easier.
43. Hand-lettering
Creating custom letters from scratch for a specific purpose/client.
44. Hard Return / Soft Return
Both of these terms refer to hitting the ‘return’ key and moving to a new line of text. They differ in that a hard return creates a whole new paragraph, whilst a soft return drops the text down remaining in the same paragraph.
Though designers will usually find their colours using the aforementioned RGB or CMYK, hex is still an important term to know. Hex is a six digit code used to represent a colour. For example, The Simpsons’ yellow has the hex code FCD901. Hex codes are found alongside RGB and CMYK in a lot of design applications, but are most often used in HTML and CSS.
46. Hierarchy
One of the five basic principles of typography design, hierarchy creates organisation and direction in a design—it helps to give order to the text elements. Though it may not be immediately obvious to someone not in the know, you’ll definitely have seen hierarchy in action in pretty much anything you have read. It makes text more understandable and easier to read.
Curved arch (such as on the letter ‘f’).
Icons are something we all see practically every day—they’re images used to represent objects or actions. One of the most common examples of an icon is a magnifying glass used to signify a search, which is used on Google and countless other websites. Though, icons are used across a wide spectrum of industries—from supermarkets to the Olympics. Just make sure they’re clear and not going to cause any confusion!
49. Italics
Forward-slanting characters, developed in early 1500s.
A stroke that connects with a stem.
51. Justified
Instances when text is aligned to the left and right margin within a text frame, with no rag on either side.
52. Kerning
Kern is the space between two specific letters or characters, and the process of adjusting the space between letters or characters. Kerning can increase the legibility of a word or a entire block of text. It helps to create proportional and balanced typography and, in turn, better looking typography.
53. Leading
Pronounced ‘ledding’, leading is graphic design jargon for ‘line-spacing’. It refers to the space between two baselines of text. The larger the leading, the more space between the text giving it more room to breathe and, generally, making it look nicer. Bonus fact: the term originates from the strips of lead in typewriters which were used to spread the lines out evenly.
54. Left-aligned
Text that is aligned with the left margin.
Short stroke in a downward direction.
56. Letterpress
Letterpress is a distinctive printing process that dates back back over 500 years, but the origins of which date back at least 1000 years. It a kind of relief printing in which a press is used to apply the direct impression of a raised surface, in this case letters, which has been covered in ink against paper. It has seen a resurgence in popularity as a craft recently after a decline following the introduction of computers in the 1970s.
57. Ligature
A ligature occurs where two or more letters are joined together as one character.
The stroke connecting the bowl and the loop of the lowercase g.
59. Logomark
A logo of a company that does not contain the brand name itself—usually a shape or character used to visually represent the company. Logomarks are more easily shown than described, so think of Twitter’s bird (which in case you didn’t know is called Larry after basketball legend Larry Bird) or Apple’s iconic apple with a bite.
60. Logotype
Also known as a wordmark, a logotype is a brand name styled as a logo—designed in a visually unique way for a company. They’re usually very obvious and quickly associate a business with its visual identity. Some famous and recognisable examples include Disney, Coca Cola and Google.
61. Lowercase
Lowercase characters are the non-capital letters of the alphabet. They make up the bulk of written text, with uppercase or capital letters used primarily only to start sentences or proper names. The term lowercase is derived from the days of metal type where the more frequently used letters were kept near at hand in the lower case while the less frequently used capital letters were kept in the harder to reach upper case.
The margin is the blank space between the edge of a page and the content within it. The margin ensures that everything, but especially text and body copy, sits properly and comfortably in the document. The width of a margin can really affect the overall feel and look of a design.
63. Masthead
Though it sounds like it should be something to do with a ship, the masthead is simply the title design for the name of a publication, usually found on the front cover of a magazine. Masthead can also refer to graphic image or text title at the top of a webpage.
64. Mock-up
A mock-up is a realistic, normally 3D representation of a design, used to demonstrate how a design will look in the real world. There’s mock-ups for everything from tote bags to iPads so they can be used to show how an entire campaign or brand roll-out would look. Check out our list of 50 free mock-ups to help bring your designs to life.
65. Monochrome
Monochrome is a colour palette made up of various different shades and tones of a single colour. It’s important to note that while grayscale is monochrome, monochrome is not necessarily greyscale—monochrome images can be made up of any colour, for example an image made up of different shades and tones of purple.
66. Monospaced
A monospaced typeface is a typeface where each character is the same width, all occupying the same amount of horizontal space. They can also be called fixed-pitch, fixed-width or non-proportional typefaces.
67. Moodboard
The starting point for a lot of designers, a moodboard is a way for designers to collect together lots of visual references for a new design project—these can be photos, images or typography. Moodboards are used to develop the project’s aesthetic, for inspiration or to help communicate a specific idea or concept.
A widow’s (see below) partner in crime, orphans is a single word (or very short line of two or three words) that sits on its own on a new line or new page/column. Like widows, they can be very frustrating but any designer worth their salt knows to always look out for these tricksy bits of text.
69. Palette
A palette is the colour scheme that is chosen for a specific design or brand—making up part of a brand’s style guide. A palette should be carefully chosen so that the colours in it work harmoniously together and help make a design as successful as possible. The term comes from an artists’ palette, which is a board or slab where artists would lay and mix different paint colours.
70. Pantone (PMS)
The Pantone Matching System is a standardised colour scheme used for printing, in addition to graphic design, it is used in a number of other industries including product and fashion design and manufacturing. Each colour has it’s own individual number and name—this year’s Pantone Colour of the Year is Living Coral , which has the Pantone number 16-1546. The numbers make reproducing and referencing colours super easy.
71. Pilcrow
A pilcrow is the name of the symbol, this one ¶, used to mark the beginning of a new paragraph or section of text. Pilcrows also appear on some software as a toolbar icon—it’s used on Adobe Photoshop as the icon for the paragraph tab, which allows the user to make changes to their paragraph structure. It’s also a great tidbit to know for any future pub quizzes.
It’s all good explaining the difference between pixels and dots, but what exactly is a pixel? A contraction of the words ‘picture’ and ‘element’, a pixel are the smallest basic unit of programmable colour on a computer and all digital images are made up of a large number of individual pixels. Basically, they’re very, very small but very, very important.
73. Placeholder Text
You’ve probably seen the words ‘Lorem Ipsum’ before and thought “umm what?”—well, that’s a placeholder text, which can also be called a filler text or dummy text. The placeholder text is used for testing purposes—they fill the gap where the words will be in order to show where and how the final copy will sit. The words ‘Lorem Ipsum’ themselves have been the industry standard since the 1500s—and were invented randomly by an unknown printer.
74. Point Size
The distance from the top of the highest ascender to the bottom of the lowest descender is the point size of any given typeface. Originally, this was the height of the face of the metal block on which each individual letter was cast.
75. PPI / DPI
The two measurements used to measure the resolution (see below). PPI stands for pixels per inch whilst DPI stands for dots per inch—they refer to the amount of pixels or dots, respectively, that can be placed in a line across one linear inch. PPI is used to describe the resolution of a digital image and DPI is used to describe the amount of ink dots per inch in a printed image. PPI can also affect the print size and quality of a design, but DPI has no affect on a digital design.
76. Printer’s Proof
Never underestimate the importance of a printer’s proof—these are mock-ups or a print sample of design that you can have in front of you, read, check and double check to ensure everything is correct and sign it off before sending it to the printer for the final print run.
77. Quick Keys / Shortcuts
Whatever you call them, quick keys or shortcuts are one of the most important things for a designer to know! They refer to the certain keys on your keyboard that allow you to carry out specific functions in a single click, rather than a longer, more complicated process. A majority of shortcuts combine pressing the cmd ⌘ key on Mac or the ctrl key on Windows and a combination of one or two letters, numbers or symbols. Here’s one to try—put your cursor on the word ‘shortcuts’ and press ⌘+ctrl+D.
78. Ragged Edge/Rag
Nothing to do with early 2000s R&B group Jagged Edge, ragged edges refers to when the body copy in a piece of design has uneven line lengths and the shape that this creates. They’re relatively easy to clean up through kerning and tracking—whose definitions can also be found in this article!
Another kind of graphic image, a raster (which can also be called a bitmap image) is an image made up of a certain number of pixels. Each pixel has its own colour, hue, saturation and transparency which helps to make up the image as a whole. Unlike vectors, due to them being made up of pixels, raster images will lose quality and become blurry as they’re resized.
80. Readability
Degree to which text can easily be read.
81. Repetition
Repetition simply means using the same element in a design more than once. Repetition simply means using the same element in a design more than once. Repetition simply means using the same element in a design more than once. It can create a sense of unity, cohesion and consistency.
82. Resolution
The term resolution refers to the number of units, measured in either DPI or PPI, that occupy a linear inch an image, both on screen and in print. Resolution is used to denote the quality of an image—it can generally be assumed that the higher the resolution, the better the quality of the image. You can tell if the resolution is too low as the image will appear blurry or pixelated.
Not to be confused with RBG (US Supreme Court Justice Ruth Bader Ginsberg), RGB stands, somewhat simply, for Red Green Blue, and is the colour mode which should be used when designing for digital applications. The three colours, Red, Green and Blue, can be combined in many different proportions to create any colour in the visible spectrum and as each colour refers to light, they grow brighter the more they are combined—it’s not magic, it’s design.
84. Right-aligned
When text is aligned to the right margin with the rag on the left side of the text frame.
85. Rule of Thirds
The rule of thirds is a helpful way of aligning the subject of an image and making it aesthetically pleasing as possible. Imagine a 3×3 grid (or even add one in Photoshop or InDesign) over your picture and align the picture’s subject with the guidelines or intersection points (where the lines meet) or allow the picture’s different elements to flow through the grid.
86. Sans Serif
Sans is French for ‘without’ so you can probably guess that San Serif Fonts are fonts without serifs on the end of their letters. Usually, sans serif fonts are easier to read on the web and digital screens—for instance, Apple use the sans serif font Helvetica Neue, across all their operating systems. Alongside Helvetica Neue, some of the most well known examples of sans serif fonts are Futura and Brandon Grotesque.
87. Saturation
Saturation is a term used in chemistry and photography, but design-wise it’s about colour. Put simply, saturation is the intensity and brilliance of a colour. Saturation is usually expressed as a number which represents the degree to which it differs from white—this means that, if the saturation is very low a colour will appear white or close to it and if the saturation is very high a colour will appear brighter and more intense.
Scale is the relative size of an object or the different objects within a single design. Scale is something that can be used very cleverly in a design and even be used to deliver a message. Two objects of the same scale are usually seen as being equal, whilst if one object is considerably larger then it could be seen as being more important. It can be used to create hierarchy or drama.
89. Script Type
Script type is a font that is based on modern or traditional handwriting styles. There’s two forms of script fonts—formal and casual. Formal script fonts, the more traditional of the two, are based on seventeenth and eighteenth century letterforms. They are used, on documents like invitations and diplomas, to give a sense of elegance. Casual script fonts became popular in the 1970s and often appear to be created by a wet brush—showing a more active hand.
A serif is the small line that appears on the end of a letter in some typefaces—these typefaces are known as Serif Fonts. Serif fonts are easier to read in printed designs as the serifs make letters more distinctive and their shape makes even letter easier to recognise. Famous examples of serif fonts include Baskerville, Times New Roman and Garamond.
91. Shoulder
A curved stroke connected to a stem.
92. Skeuomorphism
A word that is fun to both say and write, skeuomorphism is when something, most usually a digital element, is designed to look like a physical replica of that thing, while not behaving in the same way or necessarily having the same function. Apple Macs have several examples of skeuomorphs on their operating system—have a look at the phonebook icon for the Contacts app for one such example.
93. Slab Serif Type
We’re not done yet with serifs, Slab Serif fonts are an offshoot of serif fonts that are characterised by thick serifs—the serifs can either be block or rounded. One popular example of a rounded slab serif font is Courier, which was widely used in typewriters. Slab serifs became popular in the nineteenth century as printed advertising became widespread.
A vertical stroke in a letterform. Can be found in both lowercase and uppercase letters.
95. Stock Photo
Stock photos are licensed images that designers are able to use so they don’t have to organise an entire photoshoot to get the images they need for a project. The stock photo industry has been around since the 1920s and there’s stock photographs for pretty much everything—from wildlife to sport to architecture and everything in between—even the infamous Boyfriend Looking Back meme came from a stock photo.
A diagonal or vertical change in stroke width across a letter.
Any linear feature on a letter.
98. Style Guide
A style guide is an important part of branding. They determine the correct set of standards for the branding of a business or publication—anything from a business card to a multi-page website. A style guide is used to ensure that all a brands’ assets have complete uniformity and are kept looking spick and span. Now you know what a style guide is, you’ll definitely keep noticing when brands have one!
Addition of a decorative stroke in typography.
100. Symmetry
In everyday terms, symmetry refers to a sense of harmonious balance and proportion. It’s something most people are introduced to at an early age. In design terms, one of the fundamental principles of design, it does much the same—symmetry is used to add balance and create a sense of harmony in a design.
101. System Font
Main font used by a computer operating system.
102. Terminal
Any stroke which does not terminate in a serif is a terminal. It can be either straight or curved.
103. Texture
In design, texture refers to the visual appearance of a design. In others, adding rich, layered graphics to a design can help to create a visual texture. Designs can also imitate textures such as metal or fabric to likewise create a visual texture or add a fabricated tactile feel. Finally, texture can also be added to a print design through printing on different paper stocks or materials.
104. Thumbnail
A thumbnail is a small, rough sketches of how a designer wants their design to look—they can be used to help decide upon a layout or how a design will come together. They’re usually done by hand in the very early stages of a design so all the different options can be explored before any work is done on a computer.
105. Tittle
A tittle (also known as, the much less interesting, superscript dot) is a small distinguishing mark—most commonly used to refer to the dot on a lowercase i or j. Tittles also appear above other letters in various other languages. It’s also a great fact to know for your next pub quiz.
Probably the most delicious word in this list, tofu is slang that refers to the little squares that are displayed when a typeface is not loaded on to a computer or when a font doesn’t have a specific glyph. Noto is a font family that aims to remove tofu from the web entirely—it’s short for ‘No tofu’.
107. Tracking
Though they are similar, be careful not to confuse tracking with kerning. Tracking is the spacing of an entire word or paragraph (not just between two letters)—the act of tracking changes the space between every letter in a word/paragraph at the same time. It can be used to change the density and structure of a word or paragraph.
108. Triadic (Colours)
Triadic colours, or a triadic colour scheme, are three colours that are equally dispersed around a colour wheel. The most common of these are the primary colours; red, yellow and blue. Triadic colours tend to be more vibrant than complementary or analogous colours so it’s important to consider how the colours balance together—there should be one dominant colour and the others used as secondary colours or accents.
109. Type Classification
Type of characters based on style.
110. Type Properties
Specific qualities that allow characters to fit on a grid.
111. Typeface Design
The process of creating a complete set of characters in a specific style. This could include uppercase and lowercase characters, mathematical symbols, punctuation, numerals, etc.
112. Typesetting
The process of laying out large amounts of text (e.g., a book, a magazine, etc.) and making sure it’s legible and readable.
113. Type Size
The distance from the top of the highest ascender to the bottom of the lowest descender. It is usually measured in points.
114. Typography
The term typography refers to two things. Firstly, the style and appearance of printed words. Secondly and more importantly, it refers to the art and procedure of arranging type to make it readable, legible, attractive and engaging in print or digital designs. Typography is something that all graphic designers will deal with in their careers—whether they are working at a type foundry, creating their own typefaces, or working in UX design.
Want to learn more about typography? Check out Shillington New York teacher Nikita Prokhorov’s deep dive into typography , its history, rules and terms (some of which are included in this article).
115. Uppercase
Uppercase characters are the capital letters of the alphabet. Uppercase letters are normally used at the beginning of sentences and as the first letter of proper names. The term uppercase is derived from the days of metal type where the lesser used capital letters were kept in the harder to reach upper case while the more frequently used letters were kept nearer at hand, in the lower case.
116. Vector
A vector is a graphic image that is made with mathematical equations—they’re defined in terms of 2D points connected by lines and curves to form shapes. Basically this means that vectors can be resized or scaled to any size without losing quality or getting blurry. They’re very, very useful!
117. Vertex
The bottom point where two strokes are joined together.
118. White Space
White space, despite its seemingly misleading name, does not need to be white. It is the space, which can be any colour, pattern or texture, between different elements in a design that are essential in creating a successful design. Think of white space as giving a design visual breathing room, like some sort of design meditation. It can also be called negative space—which is slightly less misleading.
119. Widows
In typesetting, widows are the lines of text that are separated from the main body of paragraph—usually the end of a paragraph that goes over on to a new page or column or the opposite of that, the start of a paragraph that is at the very bottom of a page. They’re the bane of a designer’s life.
120. X-Height
X-Height refers very literally to the height of a lowercase x in a specific font. You may question why such a specific height is so important, but the x-height affects the proportion of any font and, in turn, its legibility. It can generally be assumed that as the x-height increases, legibility improves.
There we go—you should now know all the graphic design vocabulary to be able to decipher your new creative director’s feedback or ask your designer for exactly what you need. Reckon we’ve missed any? Let us know and we’ll add them to the list!
Has this list made you want to learn more? Consider taking the online graphic design course at Shillington and launch your creative career!
Oliver Stevenson January 7, 2020
Posts you might like

One of the best things about graphic design is that it never stands still for a moment. But that does mean that keeping up with...

The best graphic design books can take you on an exciting journey of the imagination, transport you to new creative worlds or...
We’ve all been feeling the squeeze over the past few years, but at Shillington we don’t want this to stop anyone getting the...

Are you considering becoming a graphic designer but want to be working online? With the increasing demand for digital design...

To ensure Shillington's commitment to the LGBTQ+ community extends beyond Pride Month, we’ve collated a list of incredible...

Are you looking to teach yourself graphic design? If so, you may be wondering if it is possible. The answer is yes—it can...

We're excited to announce Shillington's Diversity in Design Full Scholarship and Industry Mentorships and Global Half...
Are you interested in becoming a graphic designer but don't know where to start? You may be wondering if it's possible to...
Want to win some amazing prizes and stay in the loop with all things Shillington? Sign up to our newsletter to automatically go in the draw.
- How did you hear about us? * Please select Art & Design Resource Guide ArtsHub Collective Magazine Computer Arts (Magazine) Email Facebook Fashion Journal Finders Keepers Frankie Google Search I'm a Shillington Graduate Instagram LinkedIn London Tube Monster Children Other Outdoor Advertising Pedestrian Peppermint Magazine Pinterest Public Transport Shillington Design Blog The Design Kids (TDK) The Loop Twitter Word Of Mouth
- Yes, I want to hear Shillington news, get free resources and be invited to special events.
Kickstart your creative career at Shillington.
Our Contributors
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design
15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
By Krystle Wong , Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation & why is it important?
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

4. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
5. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
6. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
8. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

9. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo . But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s tools enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Ultimately, creating a memorable visual presentation isn’t just about throwing together pretty slides. It’s about mastering the art of making your message stick, captivating your audience and leaving a mark.
Lucky for you, Venngage simplifies the process of creating great presentations, empowering you to concentrate on delivering a compelling message. Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.
- AI Content Writer – New!
- Creative Studio
- Analytics (soon)
- Success Stories
- Help center

- AI Content Writer - New!
45 Graphic Design Terms You Need to Know

What you will learn
- What is graphic design
- Graphic design terms
What Is Graphic Design?
Before learning new vocabulary, it’s important to briefly go over what graphic design actually is. The American Institute of Graphic Arts (AIGA) defines graphic design as “ the art and practice of planning and projecting ideas and experiences with visual and textual content.” Graphic design expresses ideas or messages in a visual way. These visuals can be logos, websites, page layouts, images, etc.
If you are creating graphic designs, check out some basics to help you work better! Firstly, using the right tools to design the idea you want to communicate is essential. With the help of Canva or Creasquare , you will be able to develop your work in a fantastic way.
After selecting the graphic design tool of your liking, there are some specific terms that may help you understand graphic designs better and create some great designs of your own. If you want to communicate something, you must know how to do it correctly. Below, we’ve put together 45 graphic design terms that you need to know to become a great graphic designer.
45 Graphic Design Terms You Need To Know
1. alignment.
Alignment refers to how elements are arranged in a design, usually left, center or right. It is straightforward to notice when elements in a design are not aligned.

The Creative Studio allows you to easily and rapidly align elements in your designs.
2. Analogous Colors
These are colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. Analogous colors match really well and create the right color harmony.
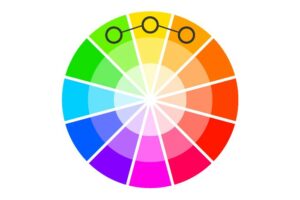
3. Body Copy
The body copy refers to the main text people will read on a design, and it is the paragraphs, sentences, or any type of text that appears in a publication.
This is basically round or elliptical forms which are the body shape letters such as C, G, and O in the uppercase, and b, c, e, o, p in the lowercase.
5. Brand Identity
A brand is the essence of a company. To be able to show it to the public, you can create a visual version of your brand (brand identity), which can include a logo, slogan, website, packaging, and other marketing tools. For example, Mcdonald’s is well known due to its yellow logo and slogan, “I’m lovin’ it.”

6. Brandmark
A brandmark is a particular type of logo that uses a symbol instead of a company name.
7. Cap Height
The cap height is the height of the top of a capital letter, and it refers mainly to letters with a flat top, like H and I.
CMYK is a color model that is designed for printing purposes. The colors used are cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black). CMYK creates color by adding color together: it makes images darker.

9. Cool Colors
These are blues, greens, and violets. They add a cooler look to the design by highlighting the blue tones. (Opposite of “Warm Colors”).
10. Complementary Colors
These are colors that are opposite to each other on the color wheel. For example: red and green or orange and blue.
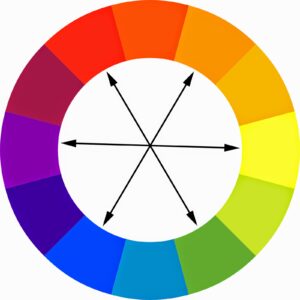
11. Crop Marks/Trim Marks
Crop marks or trim marks are marks that specify to a printer where the paper should be trimmed. It is a handy tool that helps you communicate with printers much easier.
12. Display Type
Refers to large and prominent fonts designed to stand out and catch the viewer’s eye – for example, movie titles on posters or newspaper headlines.
This is the opposite of skeuomorphism. This flat design tends to be more minimal focusing on the space and two-dimensional images.
Foil is a process where a metallic or pigmented foil is applied to a surface (logos or business cards) through heat. The most common are gold foil and silver foil.
15. Golden Ratio
The Golden Ratio is a mathematical ratio: you take two objects and divide the larger by the smaller and get the result of 1.6180 (or near). It is used to make well-designed and attractive works.
16. Gradient
A gradient is a slight color change that starts in one tone and morphs into another. Another type of gradient is when you use a gradient that fades from one color into transparent, which is an effect often used on images and designs, as it overlays on them.
Graphic designers use a grid on their screens as a guide to ensure the elements are straight, balanced, and aligned correctly.
A hex is a six-digit number used in applications to represent colors.
You can precisely define your colors with the Hex feature in the Creative Studio on Creasquare .
An icon is an image used to represent a particular object or action. As a graphic designer, you must think clearly about what your icon wants to mean so there is no confusion about it and your audience can easily understand it.
20. Kerning
Kerning is the spacing between two specific letters or characters. It can help with the legibility of a word or a sentence.
21. Leading
In contrast to kerning, leading is the spacing between two text baselines.
22. Logomark
The logo of a company does not always have the name of the brand. For example, the logomark of Twitter is the iconic bird.

You can add Logos to your designs for free with the Creative Studio on Creasquare .
23. Logotype
A logotype is a logo that uses only the brand’s name. Coca-Cola and Google are one of the most famous examples of logotypes.
24. Mock-up
This is a realistic representation of how your design will look.
25. Monochrome
Monochrome is a graphic design term for a color palette of many different shades and tones of one particular color.
26. Moodboard
Designers use a moodboard to organize their brainstorming and references (including images, videos, or typography) for a new project.
27. Palette
A color palette is a selection of colors for a design. These colors usually complement each other and create a beautiful design.

You can define your color palette within the Creative Studio on Creasquare .
28. Pantone (PMS)
The Pantone Matching System is a standardized color-matching system. This system includes colors that cannot be mixed in CMYK.


29. Resolution
This term describes the sharpness and clarity of an image.
30. Rule of thirds
Use the rule of thirds to create balanced designs. It is usually used in photography: divide your image into three vertical columns and three horizontal columns to align the important elements of the picture.

31. Sand-Serif Typeface
This term refers to fonts that do not use serifs at the end of their letters. By using this, you make your fonts more modern and simple.
The scale refers to the relationship between an object’s size and another object’s size. You can use it to catch your viewer’s attention.
33. Script Typeface
This is a font based on modern or traditional handwriting styles. There are two forms of script fonts: formal and casual. The formal script is mainly based on seventeenth and eighteenth-century styles. But casual script fonts show a more creative hand.
You have access to thousands of free fonts within the Creative Studio on Creasquare . Including many Script typefaces!
34. Serif Typeface
Unlike Sand-Serif typefaces, Serif typefaces have small decorative strokes (found at the end of each line in the letters). These types of fonts look fancy and professional.
35. Shortcuts
A shortcut is s particular key on your keyboard that allows you to do a specific function but in a short and easier process.
36. Skeuomorphism
Skeuomorphism is when a digital design resembles a physical object. An example of a brand that uses this is Apple .
37. Style Guide
This is a guideline often used for branding as well as for color schemes, typefaces, and how logos are used.
38. Thumbnail Sketch
In the process of creating a design, designers tend to make small and rough drawings to brainstorm their ideas. This is called a thumbnail sketch.
39. Tracking
Tracking is similar, yet different, from kerning. It involves adjusting the spacing throughout an entire word. First, you use kerning to determine the right spacing between each letter, and then, you use tracking to change the spacing equally between every letter.
40. Triadic Colours
Triadic colors are three colors that are equally distributed around a color wheel. Usually, there is one dominant color and two secondary colors.
41. Typography
Typography refers to the style and appearance of printed words. Also, it refers to the art and process of printed or digital designs.
You have access to thousands of free fonts within the Creative Studio on Creasquare .
42. Warm Colors
Unlike cool colors, warm colors tend to be reds, oranges, and yellows.
43. White Space (or Negative Space)
Spaces in a design that aren’t filled with text or images are called white spaces (or negative spaces).
This is not what you think it is! In graphic design, widows are words or short sentences that are at the end of a paragraph but fall into the next page or column, separating from the rest of the text.
45. X-Height
X-Height refers to the height of lowercase letters. It is measured by comparing other letters with the height of the “x” in the font that is being used.
Not everyone has all the tools and materials to be a qualified graphic designer. But knowing some of the vocabulary is a good starting point. While it might be a bit tiring and confusing at first, you will soon realize that using these words will help you make more professional graphic designs as you analyze your work. Of course, you could find more new terms related to graphic design, and it would be fantastic to use them in your work, but in this list, you will find at least, the most popular terms designers tend to use. Commit them to memory and you will realize how frequently you use them.
We hope you find this list helpful, keep studying and feel free to share any questions or thoughts!
I encourage you to try out Creasquare to plan your posts and automate your process, it really makes a difference!
You should be all set for a great start. Check out our other articles here to discover more tips to grow your content creation business!
Related Articles

11 Social Media KPIs You Need To Track for Business Growth

How are Creators Making Money in 2022?

10 Steps to Become a Content Creator

- Contents What you will learn What Is Graphic Design? 45 Graphic Design Terms You Need To Know 1. Alignment 2. Analogous Colors 3. Body Copy 4. Bowl 5. Brand Identity 6. Brandmark 7. Cap Height 8. CMYK 9. Cool Colors 10. Complementary Colors 11. Crop Marks/Trim Marks 12. Display Type 13. Flat 14. Foil 15. Golden Ratio 16. Gradient 17. Grid 18. Hex 19. Icon 20. Kerning 21. Leading 22. Logomark 23. Logotype 24. Mock-up 25. Monochrome 26. Moodboard 27. Palette 28. Pantone (PMS) 29. Resolution 30. Rule of thirds 31. Sand-Serif Typeface 32. Scale 33. Script Typeface 34. Serif Typeface 35. Shortcuts 36. Skeuomorphism 37. Style Guide 38. Thumbnail Sketch 39. Tracking 40. Triadic Colours 41. Typography 42. Warm Colors 43. White Space (or Negative Space) 44. Widow 45. X-Height Conclusion
Privacy Overview
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
100+ Free PowerPoint Graphics For Better Presentations [Free PPT]
PowerPoint graphics to move your presentation up a level, and plenty of top quality free options.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Lyudmil Enchev
in Freebies , Insights
4 years ago
Viewed 111,200 times
Spread the word about this article:
![other term for presentation graphics 100+ PowerPoint Graphics For Better Presentations [Free PPT]](https://i.graphicmama.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/10085624/Free-PowerPoint-Graphics-Free-PPT.png)
PowerPoint graphics are a great addition to all PowerPoint presentations no matter what the audience. A Powerpoint simply containing text and bullet points is not going to hold the attention, even with your hot topic content. You run the risk of being dry and dull, and simply put graphics are more visual and therefore more interesting. You know it too if you are happy with your material you feel better and more confident as a speaker. Double plus.
Of course, the quality of your PowerPoint Graphics is important, this isn’t just a case of adding visuals for visual’s sake. High quality, highly appropriate, thoughtful graphics will enhance any presentation and will be a vital tool in getting your message across, succinctly and memorably. Equally poor quality clip art type graphics, blurry, pointless, and inappropriate images may get you to remember as well, but probably not how you would wish.
So let’s look at some great keys ways you can impress with a presentation, it’s not hard but it is effective.
In this article: 1. How to insert graphics into PowerPoint 2. 100+ Free PowerPoint Graphics by GraphicMama 2.1. Free PowerPoint Templates 2.2. Free Arrows, Pointers, Bullets for PowerPoint 2.3. Free Icons for PowerPoint 2.4. Free Stats, Charts, Graphs for PowerPoint 2.5. Free Numbers and Steps Graphics for PowerPoint 2.6. Free Text Section Graphics for PowerPoint 2.7. Free Presentation Graphics for PowerPoint 2.8. Free Speech Bubble Graphics for PowerPoint 2.9. Free Sale Graphics for PowerPoint 2.10. Free Infographic Kit 2.11. Free Infographic Templates 3. More places to find PowerPoint Graphics
In the meanwhile, do you know, that you can use premade infographic templates? Check out our 50 Free Timeline Infographic Templates .
1. How to insert graphics into PowerPoint
Once you’ve created your presentation it’s time to add those all-important PowerPoint Graphics. And it’s easy, easy, easy.
Step 1: Go to the slide and create a space for your graphic Step 2: Go to insert on the toolbar at the top of PowerPoint, click on it Step 3: This will open up insert options depending on your version of PowerPoint ( 2019 reveals online pictures, photo albums, pictures, or screenshots, older versions are similar but replace online pictures with clip art.) Step 4: Choose an image from your files or online through categories or the search bar – filter general images through creative commons only licensed pictures (free to use), select, click on insert. Step 5: Resize and reposition
Alternatively:
Step 1: Select an image, right-click, and copy. (Ctrl+C) Step 2: Right-click and paste on the desired slide. (Ctrl+V)
It really is that easy.
2. 100+ Free PowerPoint Graphics by GraphicMama
One of the best ways to make your presentation look professional is by using professionally designed PowerPoint graphics and one of the best design agencies, Graphic Mama has plenty of options to choose from. As well as paid-for bundles of design icons you can take advantage of a great range of free graphics from sales icons, holiday icons, speech bubbles, people avatars, and many more. These are graphics designed in a vector file format, so the quality will stay as good even when resized. there are free backgrounds, templates, and infographic bundles too. It’s a no-risk option that will certainly add a high-quality, professionally designed look to your slideshow. Just click on the links below and you are almost there.
2.1. Free PowerPoint Templates
A tremendously good way to create a stunning professional look is by using templates for your PowerPoint Design and the good news is there are lots of free options out there just waiting for you to fill with content.

Free Hand-Drawn PowerPoint Presentation
This freebie from Graphic Mamas’s collection of free templates shows off the power of a sketched hand-drawn style in adding a customized look that is both attractive and clear.

Free Corporate Presentation Template
Ideally suited to a business proposal, this free template can be edited and customized for anything that would benefit from fresh, clear colors and fantastically designed and organized slides.

Free Business PowerPoint Presentation Template
Another free business template that benefits from strong structural elements and a great mix of text boxes and images in this modern-looking option. Superb editable infographics to get that all-important message to stand out.

Free Minimalist Presentation Template
This minimalist template broken up into large blocks of strong color is perfect for making a statement. Instant impact and full of confidence.
Take a look at Graphic Mama’s Modern Templates for the New Era of PowerPoint Presentations
2.2. Free Arrows, Pointers, Bullets for PowerPoint
Basic icons such as arrows, bullets, and pointers are so ubiquitous that they are often forgotten about. Big mistake. These free PowerPoint graphics show just how much impact well-designed elements can make and they’re a quick and easy way of raising your presentation to another level, and all for free.
2.3. Free Icons for PowerPoint
The cool, simplicity of these PowerPoint graphic icons can add swagger and style to your show. This completely free bundle gives a great selection all in the same consistent style and multiple usages will hold a presentation together in a subtle way.
2.4. Free Stats, Charts, Graphs for PowerPoint
Powerful infographics give you a great chance to get inventive and creative. Fully customizable, fully editable, and a fantastically varied and imaginative selection of all kinds of charts, graphs, and pictograms. It’s difficult to believe they are free but they really are.

2.5. Free Numbers and Steps Graphics for PowerPoint
You will need numbers, so why not take advantage of this free collection and make the mundane come alive. The key is to keep a consistent design and it will create a magical flow throughout the whole show from beginning to end.

2.6. Free Text Section Graphics for PowerPoint
PowerPoint graphics for text sections do a vital job. It is well known that text-heavy presentations are not popular and therefore less effective but you do need text. A great way of drawing the eye, focusing on text content, and still keeping people awake are these text section graphics. Customizable colors (ideal for branding), all forms and functions, a fully flexible and fully free bundle of creativity.

2.7. Free Presentation Graphics for PowerPoint
PowerPoint Graphics come in all shapes and sizes and illustrate all kinds of ideas. Download this free pack and check out a wide range of options to create visual impact, a professionally customized look, and vitality.

2.8. Free Speech Bubble Graphics
Speech bubble PowerPoint graphics can make your presentation pop, and with this stylish selection, you can’t go wrong. Flat, shaded, angular, rounded, clouds, and all sorts of variations on the theme. Impactful and fun they help create the conversation you want to have.

2.9. Free Sale Graphics
PowerPoint graphics for sales will do the crucial job of getting you and your product noticed. Fit your show with these free high-quality vector graphics and watch the crowds flock in. Once you’ve downloaded the graphics, you are not limited to PowerPoint, use the same images on posters, advertising, social media, etc., and get selling. The vectors’ technique means that there will be no loss of quality whatever the size and function.

2.10. Free Infographic Kit
A fully comprehensive infographic PowerPoint graphic pack that is crammed full of everything you could want to bring your statistics to the audience. Carefully crafted, tremendously varied, customizable, editable, flexible, and all this with the added professional pizzaz of expert design. It’s free and it’s ready to rock.

2.11. 20 Free Infographic Templates
If you want to speed things up, you can try using premade PowerPoint templates for your presentation. In this huge bundle of 539 infographics, you will find 20 free infographic templates. They are made with a lot of graphics, and you can easily grab some of the elements and adapt it to your presentation.
3. More places to find PowerPoint Graphics
Although it’s difficult to believe you haven’t found exactly what you are looking for already in our classic collection, let’s not worry. The one thing we do have now is plenty and plenty of choice. Here are some paid-for possibilities that you may want to jazz up that make or break a presentation.
PresentationPro
For $49.00 you could check out this royalty-free Graphics pack from PresentationPro. This pack contains thousands of graphics, clipart, and illustration in all sorts of categories from geography to calendars, from Scrabble to sport, and in differing styles. The graphics can be used in other formats too so you are not limited to PowerPoint.
GraphicMama
As well as the free offers, already covered Graphic Mama has a top-class selection of paid-for bundles ranging from characters to graphics assets, backgrounds , and templates from a little as $31 per set. This is ideal if you’d like to theme your presentation around a character as there are multiple gestures and poses for each. All are easily customizable, editable, and adaptable to any project and design. A gallery of cartoon characters , including businessmen, animals, robots, superheroes, doctors, ninjas, and more. Graphic Mama also offers custom designs, so you can turn yourself into a caricature and animated puppets to really make waves.
GetMyGraphics
At GetMyGrpahics you can take up a subscription giving you access to over 9,000 professional PowerPoint graphics starting at $49 per month or a Pro package at $99 per month. Obviously, at this price, it is not for a one-off or occasional piece but for professionals it does provide plenty of options. They include infographics and illustrations in a wide range of categories and differing styles.
Final Words
The old PowerPoint presentation. It’s been around for years and it truly isn’t enough to just churn out the old stuff. Vital though they may be, people always expect more, always expect better, and why not? With a little extra effort, you can turn your slideshow presentation into something that isn’t just a time filler but that really makes a difference, communication, and shows you off in the best light. PowerPoint graphics can make all the difference by breathing life and energy into your presentation and consequently your performance. If you feel confident in your material it will help your delivery. Best of all you can step it up for free, so why wouldn’t you?
You may also be interested in some of these related articles:
- The Best Free PowerPoint Templates to Download in 2022
- Need PowerPoint Backgrounds? The Best Places to Check Out [+ Freebies]
- 10 PowerPoint Tutorials to Help You Master PowerPoint

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
16 cool apps for instagram to change your ‘gram game for the better, what is a storyboard [theory, examples and mega inspiration], 35+ free infographic powerpoint templates to power your presentations, 20 great free google slides and powerpoint templates for teachers, 30+ free presentation clipart graphics and resources for great powerpoint visuals, 500+ free and paid powerpoint infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (0)

Lyudmil Enchev
Lyudmil is an avid movie fan which influences his passion for video editing. You will often see him making animations and video tutorials for GraphicMama. Lyudmil is also passionate for photography, video making, and writing scripts.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

Free Facebook Cover Templates: 6 Sources to Check Out
by Iveta Pavlova

Can You Become a Graphic Designer Without a Design Degree in 2022?

Infographics for Marketing: How to Grab and Hold the Attention
by Lyudmil Enchev
Looking for Design Bundles or Cartoon Characters?
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.

The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Look up definitions & meanings of terms
Impromptu Speech
A speech that is given without any preparation, notes, or cards, is called an impromptu speech. It is often delivered at private events (e.g., weddings or birthdays) or for training presentation skills.
Manuscript Speech
For a manuscript speech, the speaker has an entire manuscript to read from. The benefit is that, as every single word is scripted, no important parts will be missed. However, speeches that are fully written down often seem unnatural and may bore the audience.
Declamation Speech
A declamation speech describes the re-giving of an important speech that has been given in the past. It is usually given with a lot of emotion and passion.
Extemporaneous Speech
An extemporaneous speech is a speech that involves little preparation, as the speaker may use notes or cards to give his talk. It is important that speakers will still use their own words and talk naturally. .
Eulogy Speech
A eulogy speech is given at a funeral. It is given by familiy members or friends of the deceased. The aim is to say goodbye and pay tribute to the person who has passed away.
Valedictory Speech
A valedictory speech is given in order to say goodbye, usually at graduation. It should inspire listeners and functions as a send-off into "real life".
.ppt file extension
A .ppt file is a presentation which was made with PowerPoint, that includes different slides with texts, images and transition effects.
.potx file extension
A .potx file is a file which contains, styles, texts, layouts and formatting of a PowerPoint (.ppt) file. It's like a template and useful if you want to have more than one presentation with the same formatting.
.pot file extension
They are used to create more PowerPoint files with the same formatting and later got replaced by .potx files.
.odp file extension
.odp files are similar to .ppt files. It's a presentation which was created with Impress and contains slides with images, texts, effects and media.
.ppsx file extension
A ppsx file is a presentation file. When you open the file the slide show opens and not the editing mode like in ppt files.
.pps file extension
A .pps file is a slide show. They are similiar to .ppt files but they open as a slide show if you double-klick them. They later got replaced by .ppsx files.
.pptm file extension
A .pptm file is a macro-enabled presentation created by MS PowerPoint which contains slides with layout, images, texts and embedded macros.
.potm file extension
A .potm file is a template for macro-enabled presentations. They are used for creating more .pptm files with the same macro settings and the same formatting.
.ppsm file extension
A .ppsm file includes one or more macro-enabled slides. They are used to show presentations with embedded macros, but not for editing them.
Learning on Demand
Learning on Demand means that the content is available extactly when it's needed by the learner
Microlearning
Microlearning means learning in small quantities. It is especially used in E-Learning.
Learning Chunk
Learning Chunk means, like Microlearning, learning in small quantities. The learning content is really small and can be absorbed quickly.
Massive Open Online Course (MOOC)
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) are digital courses (online) with many participants (massive) that are available for free.
Web-Based-Training (WBT)
Web-Based-Training (WBT) is an older term for learnmethods that can be accessed over the internet.
A webinar is a seminar that takes place in a specific digital location at a specific time. It's a seminar that combines live and online formats.
Hybrid Learning
Hybrid learning means that one group of students are in class at school. Another group of students takes part in class from home at the same time. They both get taught at the same time.
Flipped Classroom
Flipped Classroom means that students work out the subject matter themselves at home through tasks such as reading, videos, etc. Interactive learning activities and exercises then take place in class.
Live Online Training (LOT)
In live online training, participants and teachers are not in the same physical room but in the same virtual room. This is usually possible through an online platform or a software system.
Break-out-Room
In live online training, it is sometimes useful to divide the students into small groups for certain exercises, as it would be impossible to have conversations at the same time. Break-out-rooms are used so that people can talk to each other without disturbing the others. When the exercise is over, they are sent back to the main room.
mLearning means mobile learning, which comes from "Mobile Telephone". You can access the learning material over your mobile phone anywhere, which makes learning mobile.
Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous Learning means that the learning is time-shifted. The communication between student and teacher are time-delayed.
Tutorials are videos with instructions that show how for example a product or a software works.
A podcast is an audio or video contribution that can be listened to or viewed via the Internet. Podcasts can be used for information on specific topics but also for entertainment.
Computer Based Training (CBT)
Computer Based Traing (CBT) means digital learning programs, which work without internet. Exercises can be downloaded over the internet or can be distributed via storage media like a USB stick or a CD.
Virtual Reality
With Virtual Reality people can practice situations and important processes in a virtual room by putting on special digital glasses. They can influence what happens themselves.
Blended Learning
Blended Learning is a teaching / learning method that includes both in-person and online instruction. The technique has gained a lot of popularity, as it combines the benefits of teaching live and online, which makes it very successful, according to several studies.
Game-based Learning
Game-based learning is a popular approach where the instrument for a learning process is a game. Game-based learning scenarios are often found online - they are often favored because they engage learners in a way that few other learning methods do.
WWTBAM is an acronym for "Who wants to be a Millionaire", which is a famous quiz show that airs in several countries.
An e-lecture is a lecture that is held online. Many schools and universities offer e-lectures as technical opportunities improve.
Open Educational Resources (OER)
Open Educational Resources are free learning and teaching materials provided on the web. They have an open license (e.g., Creative Commons), which allows anyone to use and benefit from these resources.
Learning Management System (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are online platforms that provide learning resources and support the organisation of learning processes.
Student Response System (SRS)
With Student Response Systems (SRS) it is possible to get live student feedback in the classroom. Questions and answers can usually be asked and given anonymously, which increases participation and engagement. An SRS may be used for any grade, including university.
Classroom Communication System (CCS)
A Classroom Communication System allows students and teachers to communicate efficently online. It improves students' engagement as they are animated to ask questions, give feedback and take notes. There are various companies that offer CCS solutions.
Personal Response System (PRS)
A Personal Response System (PRS) provides lecturers, presenters or teachers with the opportunity to ask a group of students or their audience questions. The questions are usually in a multiple choice format. PRS increase student engagement and provide an opportunity to receive instant feeback.
Informative Presentations
An information presentation is created when no solution is currently available. Facts, data and figures or study results are presented and current processes are described.
Instructive Presentations
Instructive Presentations are similar to informative presentations, but it's more than just giving informations. People attend instructive presentations to learn something new and to understand the topic of the presentation better.
Persuasive Presentations
A persuasive presentation is made, for example, to introduce an amendment. There are usually several options to choose from. It is particularly important to provide good arguments and reasons.
Solution Presentation
A solution has already been found during a solution presentation. The only thing that remains is to find a solution on how to realize the decision.
Concept Presentation
In a concept presentation, you have to give general information as well as try to convince the audience with good arguments and deliver a solution concept.
Motivational Presentation
A motivational presentation is meant to inspire people. In a company, for example, you could tell the company's story in a motivational presentation.
Screen presentation
A screen presentation is a graphic support and accompaniment to a spoken presentation. A popular programme for creating screen presentations is PowerPoint.
TOK Presentation
The Theory of knowledge (TOK) presentation is an essential part of the International Baccalaureate Diploma Program (IB). The TOK presentation assesses a student's ability to apply theoretical thinking to real-life situations.
A pitch is a short presentation that is given with the intention of persuading someone (a person or company) to buy or invest. There are various forms of pitches, depending on the goal and intended outcome.
Audience Demographics
Audience Demographics are the characteristics of listeners like age, gender, cultural backgrounds, group affiliations and educational level. The speaker has to consider all these characteristics when adapting to an audience.
Audience Dynamics
Audience Dynamics means the motivations, attitudes, beliefs and values, which influence the listener's behaviour.
Internal Summary
Internal summary means to remind listeners about the major points which were already presented in a speech before coming to new ideas.
Internal Preview
An Internal Preview is a statement, which is made in the body of the speech, so that the audience knows what the speaker is going to discuss next.
Multimedia Presentation
A multmedia presentation is a speech in which several types of visual and audio aids are combined in the same speech with the help of computer software. .
Hybrid Audience
A mix between in-person and virtual participants for an event or a lecture is called a hybrid audience. Working with a hybrid audience may be challenging, as it requires the presenter to find ways to engage both the live and the virtual audience.
Distributed Audience
A Distributed Audience means that the audience you are trying to reach is spread over long distances.
Virtual Audience
A virtual audience consist of people who join an event / a meeting / a presentation via an electronic device (computer or smartphone) over the Internet. Each member may be located in a different place while an event takes place. Virtual audiences are becoming increasingly important as the amount of events held online is rising.
Co-located Audience
Co-located Audience means that the speaker talks to the audience in person. It is used verbal and non-verbal methods to communicate a message. The speaker makes gestures with their hands, changes their face expression and shows images.
Audience Response System (ARS)
Audience Response Systems (ARS) are technical solutions that are used in presentations in order to increase the interaction between the presenter and the audience. There are various forms of ARS that offer different features.
Glossophobia
Glossophobia means the strong fear of public speaking.
Slide Master
To create your own Template in PowerPoint it is best to use the Slide Master. After updating the Slide Master with your design, all slides (fonts, colours, images, …) adapt to those of the Slide Master.
PowerPoint Online
PowerPoint Online is the web version of PowerPoint. You can present and edit your PowerPoint presentation with it, without having PowerPoint installed on your computer. It's only necessary to have a Microsoft - or a Microsoft 365 account.
Normal view (slide view)
The normal view or slide view is the main working window in your PowerPoint presentation. You can see the slides at their full size on screen.
Outline view
The outline view in PowerPoint shows a list with the whole text of all slides on the left of the screen. There are no images and graphics displayed in this view. It's useful for editing the presentation and can also be saved as a Word document.
Slide Sorter view
The Slide Sorter view in PowerPoint shows thumbnails of all your slides in horizontal rows.The view is useful for applying global changes to several slides at once. Also it's useful for deleting and rearranging slides.
Notes Page view
The Notes Page view in PowerPoint shows a smaller version of the slide with a small area for notes underneath. In the presentation every slide has it's own space for notes. During the presentation the notes do not appear on screen. They are just visible in the presentation mode.
Master view
In the master view in PowerPoint you can edit the Slide Master.
Slide Layouts
PowerPoint has different types of Slide Layouts. Depending on which type of presentation you make, you will use more or less different slide layouts. Some Slide Types are: title slides, section heading slides, picture with caption slides, blank slides.
Slide transitions
Slide transitions are visual effects which appear in PowerPoint when one slide moves to the next. There are many different transitions, like for example fade and dissolve.
Animations in PowerPoint
Animations in PowerPoint are visual effects that are applied to different items like graphics, title or bullet points, instead of the slides. There are many different animations like: Appear, Fade, Fly in.
Effect Options
In the effect options in PowerPoint, further details can be specified for the selected effect.
Display duration
Under display duration in PowerPoint, the start of the animation, the duration, repetition and delay can be controlled.
Keynote is a programme which, like PowerPoint, is used to create digital screen presentations. It is mainly used by Apple users.
SmartArts are diagrams that convey processes, connections or hierarchies. They can also be edited individually and easily be added to your presentations.
Animated GIF
An animated GIF enables images to be played in a specific order. It is created when several individual images are saved in a GIF file.
Title Slide
The title slide is the first slide of a presentation. It usually contains a title and a subtitle.
Verbal Communication
Communication is verbal if it includes talking with other people. This can be face-to-face but also over the telephone or via Skype
Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication means that the communication is based on someone's voice and body instead on the use of words.
Panel Discussion
A panel discussion is a structured conversation in front of an audience on a given topic between several people.
Vocalized pause
A vocalized pause means the pause when the silence between words is filled by the speaker with vocalizations like "um", "uh" and "er".
Vocal distractions
In vocal distractions filler words like um, er, and you know are used during a pause.
Body language
Body language is communication through movements, hand gestures and body posture.
To interview somebody means to ask a person different questions. An interview is often done by journalists.
Face-to-face
If you are talking to someone face-to-face you are directly facing each other.
Interpersonal communication
Interpersonal communication is face-to-face communication. It means that people exchange information and feelings through verbal and non-verbal messages.
Written Communication
The goal of written communication is to spread messages clear and explicit. Written Communication can be: emails, a contract, a memo, a text message or a Facebook Post.
Visual Communication
If there are used images or videos for communication, it is visual communication. Visual Communication is almost used everywhere like on television, posts on social media (Instagram, Facebook), advertisement.
Listening is a very important part of communication. To be good in communication you need to be a good listener. That doesn't mean just hearing what the other person is saying. But you need to listen active, engage your mind and intently focus on what your talking partner is saying.
Formal Communication
formal communication should be used for speeches or at work
Informal Communication
informal communication can be used when talking to your friends or your family
Online Communication
Online communication is communication over the internet. Online communication is often anonymous and over social media platforms you can communicate with people around the world.
Vertical Communication
Vertical communication means that information is passed from one person to the next according to a linear system based on their titles. This type of communication is used when a company follows a hierarchical structure or for important, sensitive information.
Horizontal Communication
Horizontal communication is the exchange of information between people, departments or units within the same level of an organisational hierarchy of a company.
Diagonal Communication
Diagonal communication means that the employees of a company communicate with each other regardless of their function and their level in the organisational hierarchy and regardless of their department within the company.
Internal Communication
Internal communication is particularly important for corporate communication. It communicates important information from leadership to staff so that they can do their jobs in the best possible way and work processes run well.
External Communication
External communication is the exchange of information between two organisations. For example, it can be an exchange with customers, clients or traders. Feedback from a customer also counts as external communication.
Closed Questions
Closed questions are followed by a short, clear answer. There are several answer options from which you can choose one or more.
Open Questions
In contrast to closed questions, the answer to open questions can be more detailed and creative. You can convey more information.
Leading Questions
Leading questions subconsciously make the respondent think in a certain direction.
Recall Questions
With recall questions, you have to remember something or something has to be recalled. Example: A teacher asks his students a question so that they remember the material from the last lesson.
Process Questions
Process questions are similar to recall questions but they need some deeper thoughts and maybe also analysis.
Hybrid Event
When an event consist of both virtual and in-person parts, this is called a hybrid event. This type of event is popular as it combines the benefits of both online and live events.
Virtual Event
Virtual events take place entirely online. They are very convenient as anyone may join from wherever they are via a smartphone or computer.
Corporate Events
A corporate event is an event organised by a company and intended for employees, stakeholders, customers, a charity event or public. The audience depends on the goal of the event.
Social Events
Social events in companys can be to celebrate an anniversary or to bond better as a team. They should address the personal interests of employees and revolve around things like entertainment and food.
Fundraising Events
The aim of fundraising events is to raise funds for a specific organisation. They are often organised by charities and non-profit organisations.
Community Events
Community events are about bringing people together, creating positive change and making new friends.
Pop-up Events
Pop-up events only last for a short period of time, such as only for one night or one month. An example: Another location of a shop is opened for only one month to extend the reach.
B2B means Business to Business. B2B events are between at least two companys. They help to build interpersonal relationships, which are important for a successful company.
B2C means Business to Customer. A B2C event is hosted by a company for its customers. It's important for gaining new customers and for satisfieing regular clients.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
30 Graphic Design Terms & What They Mean
Graphic design is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, driven by innovation and creativity. It’s a realm where visuals, ideas, and messages converge to create impactful and compelling narratives. However, for those new to the world of graphic design, the array of terminologies and jargon used by designers can seem overwhelming. This guide serves as an introduction to some of the most important terms in the world of graphic design, providing a helpful reference for beginners and a useful refresher for more seasoned designers.
From basic principles of design to the more technical aspects, understanding graphic design terms not only helps in learning the craft but also improves communication within a team or with clients. With a solid understanding of these terms, you’ll find it easier to discuss and critique designs, give and receive feedback, and articulate your creative ideas more effectively.
So, whether you’re an aspiring designer looking to navigate this exciting field, a business owner working with designers, or simply someone interested in understanding more about graphic design, this guide to 30 essential graphic design terms will offer invaluable insights.
Each term is explained in detail, offering a comprehensive overview of its relevance and application in the day-to-day world of graphic design.
2 Million+ Digital Assets, With Unlimited Downloads
Get unlimited downloads of 2 million+ design resources, themes, templates, photos, graphics and more. Envato Elements starts at $16 per month, and is the best creative subscription we've ever seen.
CMS Templates
Shopify, tumblr & more.
Web Templates
Landing pages & email.
Icons, Vectors & More

Sans Serif, Script & More
Presentation Templates
Powerpoint & keynote.

Graphic Templates
Logos, print & mockups.
Explore Design Resources
Table of Contents
- Raster Images
- Vector Images
- White Space
- Aspect Ratio
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, the primary colors of light. In digital design, colors are often represented as a combination of these three hues. RGB is the color model used for on-screen or digital designs as screens emit light. When all RGB colors are mixed together, they create pure white.
Different combinations can produce a vast range of other colors. Understanding the RGB color model is essential for anyone working in any digital design medium, including graphic design, digital art, web design, and more.
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). Unlike RGB, which is used for digital screens, CMYK is the color model used in print design. It’s called a subtractive model because the printed ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected.
The colors are mixed during the printing process, which can lead to a wider range of colors than if the colors were pre-mixed. A deep understanding of the CMYK process can help graphic designers ensure the colors they use in their designs will appear as expected when printed.
PMS, or the Pantone Matching System, is a standardized color reproduction system. By standardizing the colors, different manufacturers can refer to the Pantone system to ensure colors match without direct contact with one another.
This is especially useful for brand consistency across different print materials. Each Pantone shade is given a specific number, making it easy for designers and manufacturers to communicate exactly which colors are to be used on a project.
Pixels are the smallest unit of a digital image or display. Each pixel is a tiny square that emits a certain amount of light and color. In the context of graphic design, pixels are important when creating digital images or elements, as the number of pixels can directly impact the quality of an image.
High-resolution images contain more pixels, which result in a sharper and clearer image, particularly when viewed at a close distance. However, higher resolution images also take up more storage space. Understanding pixels allows designers to balance between image quality and file size.
In contrast to pixel-based raster images, vector graphics are based on mathematical equations and are made up of points, lines, and curves. This means that they can be scaled indefinitely without any loss of quality or resolution, making them ideal for logos, icons, and other designs that need to be displayed at various sizes.
Because of their scalability, vector graphics are essential for any kind of design work that may need to be resized. They’re typically created using software like Adobe Illustrator, which provides tools for creating and manipulating these mathematical paths.
Raster graphics, also known as bitmap graphics, are made up of a grid of individual pixels. Each pixel holds color information for the image. Raster graphics are great for complex images that have a lot of detail and color variation, like photographs.
However, the main disadvantage of raster graphics is that they don’t scale well. If a raster image is enlarged too much, the individual pixels become visible, resulting in a pixelated and blurry image. Therefore, when working with raster images, graphic designers need to consider the final size of the image right from the start.
DPI stands for Dots Per Inch and is a measure of spatial printing or video dot density. It’s a crucial term in both digital and print design as it directly impacts the quality of the output. The higher the DPI, the better the resolution and detail in the final printed output.
However, higher DPI also means larger file sizes, so designers need to strike a balance between quality and efficiency. When creating graphics for print, a DPI of 300 is usually recommended. For web graphics, where high resolution is less important and smaller file sizes are preferred, a DPI of 72 is standard.
Hex refers to a hexadecimal color code, which is a six-digit combination of numbers and letters defined by its mix of red, green, and blue (RGB). The first two digits represent the red component, the middle two green, and the last two blue. The values range from 00 to FF (in hexadecimal base).
Hexadecimal color codes are predominantly used in web design, as they’re understood by all browsers. For example, white is represented as #FFFFFF, black as #000000, and the full range of colors can be represented in this system. This standardization helps ensure colors are consistent across digital platforms.
Opacity refers to the degree to which light is allowed to travel through an object. In graphic design, the opacity level of an element can be adjusted to create different effects. A lower opacity means that the object is more transparent and that objects beneath it are more visible.
Manipulating opacity is common in layer-based design software like Photoshop. It can be used to overlay text on an image, create watermarks, or even to build up complex effects using multiple layers. Understanding and controlling opacity is a crucial skill in creating visually appealing designs.
10. Kerning
Kerning refers to the adjustment of space between two individual letters or characters. The goal of kerning is to achieve a balanced and proportional spacing for better readability and aesthetics. It’s especially important in typography and logo design, where small adjustments can make a big difference in the overall appearance and readability.
Automated kerning options in design software often do a good job, but there are times when manual adjustment is needed. Particularly with larger sizes or unique font combinations, individual kerning adjustments can make a noticeable difference to the overall presentation of a design.
11. Leading
Leading is a typography term that refers to the space between lines of text. It originates from the days of metal type, when thin strips of lead were used to create vertical spacing. Leading is important for readability – too little can make text dense and difficult to read, while too much can disconnect the lines of text.
Good leading makes your text legible and guides the reader’s eye through the lines. It’s often calculated based on type size and line length to achieve optimal reading comfort. For instance, if your type size is 12 points, a good starting point for your leading would be 14 points.
12. Tracking
Tracking, sometimes called letter-spacing, is the adjustment of the space for groups of letters and entire blocks of text. Unlike kerning, which adjusts space between individual letter pairs, tracking applies to a broader range of text. It impacts the overall character density of the copy.
Proper tracking ensures optimal readability and aesthetic balance. Too tight tracking may cause letters to overlap, making the text hard to read, while too loose tracking can disrupt the reader’s flow and make the text appear disjointed. Many typography experts consider tracking an essential tool for effective type setting.
A mockup is a full-scale model used for design evaluation, demonstration, or promotion. It’s used to visualize how the final design will look in a real-life context, such as how a website will look on a computer screen or how a product package will look on a retail shelf.
Mockups can help clients, design teams, and stakeholders understand a design better, as they provide context and showcase functionality. They are usually created using digital tools, and there are numerous online resources available for generating mockups for various purposes and mediums.
14. Gradient
A gradient is a gradual blend between two or more colors or between shades of the same color. Gradients can be linear (blending from one color to another along a line), radial (blending in a circular or elliptical pattern), or in a freeform path.
Gradients are often used to add depth, volume, and visual interest to flat designs. They can be used subtly to give a design a more natural, organic feel or dramatically for a bold, modern look. Digital design tools offer a range of options for creating and customizing gradients.
Bleed is a term used in print design to refer to any design or elements that extend beyond the print boundaries. In other words, the bleed is the part of the design that will be trimmed off after printing. The purpose of the bleed is to ensure that no unprinted edges occur in the final trimmed document.
In general, a bleed of 1/8 inch or 3mm is used to accommodate for small shifts during printing and trimming. When preparing a design for print, it’s important to extend the design into the bleed area to prevent any white edges in the final print.
16. Contrast
Contrast is a key principle in graphic design and refers to the difference between elements in a design. These elements can include color, size, shape, and type. By creating contrast, a designer can emphasize or highlight key elements in a design.
Contrast creates visual interest and directs the viewer’s attention. It can be used to create a focal point, organize information, or add visual intrigue. For instance, a headline in a large, bold font creates contrast with the body text, helping to draw the viewer’s attention.
17. Negative Space
Negative space, also known as white space, is the unmarked or empty areas between or within the elements of a design. Despite its name, negative space isn’t necessarily white; it refers to any area not occupied by a design element.
Negative space is an important component of a balanced composition. It gives the design elements room to breathe, creating balance and helping guide the viewer’s eye through the design. It can also be used creatively to form shapes and convey additional meaning, as seen in many well-known logos.
18. Color Wheel
The color wheel is a circular diagram of colors arranged by their chromatic relationship. It is a useful tool for understanding color theory and creating harmonious color combinations. The color wheel consists of primary colors (red, yellow, and blue), secondary colors (created by mixing primary colors), and tertiary colors (created by mixing primary and secondary colors).
Using the color wheel, designers can create a variety of color schemes, such as complementary (colors opposite each other), analogous (colors next to each other), or triadic (three colors evenly spaced). Understanding the color wheel and its principles can significantly improve a designer’s work.
19. Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within a design. It’s about how the elements of a design interact with each other and the space around them. A well-composed design leads the viewer’s eye through the piece in a way that makes sense and reinforces the message or mood.
In graphic design, there are many rules and guidelines for creating effective compositions, such as the Rule of Thirds or the Golden Ratio. However, these rules are often broken or adapted to suit the designer’s purpose. An understanding of composition is essential for creating effective, compelling designs.
A pixel, short for “picture element,” is the smallest basic unit of programmable color on a digital display. Pixels are tiny squares that make up an image or display. When viewed from a distance, these squares merge into a clear image.
Understanding pixels is crucial for digital designers because the pixel count, or pixel density, can significantly impact the quality of a design. Low pixel density leads to pixelation, where individual pixels are visible to the naked eye, causing the image to appear blocky or blurry. High pixel density creates crisper, more detailed images.
21. Resolution
Resolution refers to the amount of detail an image holds and is typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI) in the case of print output. A higher resolution means more image detail. In the digital world, resolution can also refer to the number of pixels displayed on a screen, commonly referred to as screen resolution.
Designers must consider resolution in their work, especially when designing for different mediums. An image that looks crisp on a website may look blurry when printed, or vice versa. For this reason, understanding and properly applying resolution is crucial for producing high-quality design work.
22. Hierarchy
Hierarchy in graphic design refers to the arrangement of elements in a way that implies importance. It’s a visual technique that organizes information or elements to guide the viewer’s eye to the most important parts of the design first.
Designers create hierarchy using scale, color, contrast, and spatial arrangements, among other techniques. A clear hierarchy helps viewers navigate the design more intuitively and digest information more easily. Whether it’s a website, a poster, or a brochure, effective use of hierarchy is essential for any successful design.
A grid is a framework of intersecting vertical and horizontal lines used to structure content in a design. Grids create consistency, help to align elements, and provide a basic structure for a design layout.
Grids can be simple, with just a few columns for basic alignment, or complex, with multiple columns and rows for intricate designs. They can be visible (as in a spreadsheet) or invisible (used for layout purposes only). The use of grids is a fundamental part of many design disciplines, including graphic design, web design, and industrial design.
24. Typography
Typography refers to the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. It involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line-spacing, and letter-spacing, and adjusting the space between pairs of letters.
Good typography enhances the reading experience and reflects on the overall quality of the design. It’s a critical aspect of graphic design, and understanding and skillfully applying typography principles can greatly improve a piece of design work.
A vector is a type of digital image created using mathematical formulas. This allows the image to be scaled up or down without losing quality. Vectors are typically used for logos, icons, and other designs that need to be resized frequently.
Unlike raster images, which are made up of pixels, vectors consist of paths, each with a mathematical formula (vector) that determines the path’s direction and length. This makes vector images resolution-independent. Most graphic design software allows designers to create and manipulate vector images.
Raster images, also known as bitmap images, are made up of a grid of pixels where each pixel represents a different color within the image. Raster images are resolution-dependent – they can’t be scaled up without losing quality. When these images are enlarged, the pixels are stretched, making the image appear blurry or pixelated.
Raster graphics are best used for complex, multi-colored designs, such as photographs. Common raster file formats include JPEG, PNG, GIF, and TIFF. Unlike vectors, editing raster files requires a raster-based software such as Adobe Photoshop.
27. Color Spectrum
The color spectrum refers to the full range of colors that can be seen by the human eye, represented as a continuous image in graphic design. It’s typically visualized as a circular wheel or linear gradient going from red to violet, including all the colors in between.
Designers use the color spectrum as a guide for combining colors and creating palettes. The concept of the color spectrum is also closely tied to the RGB (red, green, blue) color model used in digital design, where colors are created by combining red, green, and blue light at various intensities.
28. Print vs. Digital Design
Print and digital design are two distinct areas within the field of graphic design. Print design is a form of graphic design that involves creating artwork and layouts that will be printed on physical surfaces, such as paper, cardboard, etc. Examples include brochures, posters, packaging, and business cards.
Digital design, on the other hand, involves creating graphics and layouts to be displayed on digital platforms, such as websites, mobile apps, digital advertising, etc. Although there’s overlap in the principles and skills required, each area has its own specific considerations and best practices, such as resolution and color modes.
29. Visual Identity
Visual identity refers to the visual elements that represent a company, product, or brand. It’s a subset of brand identity and includes logos, typography, colors, packaging, and imagery. The visual identity is used across all mediums and touchpoints to represent the brand consistently.
Creating a visual identity is a key part of branding. It involves defining the visual elements that will represent the brand, and how they’ll be applied across different mediums. A strong visual identity can help a brand stand out, inspire trust, and create a memorable impression on its audience.
30. Mood Board
A mood board is a type of visual presentation or collage consisting of images, text, and samples of objects in a composition. It’s used as a tool in design processes to convey a general idea or feel of a design concept. Mood boards help to visualize ideas, set the mood, and provide inspiration for a project.
Mood boards can be created physically with printed elements, or digitally using graphic design software. They’re often used at the beginning of a project to establish the visual direction of the work. This can be especially helpful when communicating a design idea to a client or team.
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Hard-Copy Devices in Computer Graphics
- What is Computer Art?
- What is Color CRT Display?
- Beam Penetration Technique in Computer Graphics
- Geometric Computing in Computer Graphics
- What is Graphics Software?
- Graphics Monitors and Workstations
- Pointing and Positioning Techniques in Computer Graphics
- Concept of Mask
- HSV Color Model in Computer Graphics
- Constant-Intensity Shading in Computer Graphics
- Clipping in Homogeneous Coordinates
- Line Attributes in Computer Graphics
- Computer Graphics Homogeneous Coordinates
- Computer Graphics Curve in Computer Graphics
- Polygon-Rendering Methods in Computer Graphics
- Projections in Computer Graphics
- Gouraud Shading in Computer Graphics
- C++ Implementation of Scaling in Computer Graphics
What are Presentation Graphics?
Pre-requisites: Introduction to Computer Graphics
Graphics are defined as any sketch or a drawing or a special network that pictorially represents some meaningful information. Computer Graphics is used where a set of images needs to be manipulated or the creation of the image in the form of pixels and is drawn on the computer. Computer Graphics can be used in digital photography, film, entertainment, electronic gadgets, and all other core technologies which are required. It is a vast subject and area in the field of computer science. Computer Graphics can be used in UI design, rendering, geometric objects, animation, and many more.
Presentation graphics provides predefined backgrounds and simple page layouts to help in the creation of slides. These slides can be moved automatically within seconds.
Slides:
Slides mean we have text, graphics, audio clips, video clips, animations, and other effects Presentation graphics is also known as Presentation Software. The best example of presentation graphics is Microsoft PowerPoint.
In recent days we have a new presentation tool that is: our Web browser and that is for creating Web pages, like Microsoft’s FrontPage and Adobe’s PageMill.
Rules to Design Presentation:
- Keep it simple: Make it simple to understand. It only contains information regarding your topic.
- Correct Spelling: We have to be careful with the spelling that we have written.
- Consistency: There is need to be continuous flow from one slide to another.
- Don’t put too much on a Slide: Don’t write too much. just give a brief description and important points.
- Use Fonts Properly: Only you can use two font styles in the presentation.
- Find Your Equipment: First, you have to be confident with your topic and details about it.
Uses:
Presentation graphics programs are mainly concerned with the display of graphs and charts but now allow users to attach anything from text to animations. When Compared to other programs like Excel, PowerPoint follows a slideshow format.
Applications:
In the following areas we can use presentation software:
- Google Slides
- Microsoft Office
- WPS Office
- Photo Slideshow with Music
Advantages:
- Less Cost: The cost is low to use presentation software
- Logical Ideas: Tables and graphs are used to represent information then a logical order is created to give a clear idea for viewers.
- Acceptability: By using this busy person can easily get an idea about the topic.
Disadvantages:
- Time-taking process. It needs more time to prepare.
- Data can sometimes be lost.
- Errors and Mistakes can occur during design.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Computer Graphics Basics
- Computer Graphics

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center
Synonyms of graphic
- as in illustration
- as in vivid
- as in visual
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Thesaurus Definition of graphic
(Entry 1 of 2)
Synonyms & Similar Words
- illustration
- representation
- illumination
- explanation
- clarification
- elucidation
- explication
- pictorialization
Thesaurus Definition of graphic (Entry 2 of 2)
- descriptive
- picturesque
- photographic
Antonyms & Near Antonyms
- indeterminate
- indistinguishable
- inscrutable
- enigmatical
- illustrative
- illustrational
- represented
- iconographical
- iconographic
- pictographic
- hieroglyphical
- hieroglyphic
- ideographic
- ideogrammic
- ideogrammatic
Synonym Chooser
How does the adjective graphic differ from other similar words?
The words picturesque and vivid are common synonyms of graphic . While all three words mean "giving a clear visual impression in words," graphic stresses the evoking of a clear lifelike picture.
When can picturesque be used instead of graphic ?
Although the words picturesque and graphic have much in common, picturesque suggests the presentation of a striking or effective picture composed of features notable for their distinctness and charm.
When would vivid be a good substitute for graphic ?
In some situations, the words vivid and graphic are roughly equivalent. However, vivid suggests an impressing on the mind of the vigorous aliveness of something.
Thesaurus Entries Near graphic
graphic novel
Cite this Entry
“Graphic.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/graphic. Accessed 23 Apr. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on graphic
Nglish: Translation of graphic for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of graphic for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, on 'biweekly' and 'bimonthly', popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 19, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), a great big list of bread words, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, games & quizzes.

bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
Our approach
- Responsibility
- Infrastructure
- Try Meta AI
RECOMMENDED READS
- 5 Steps to Getting Started with Llama 2
- The Llama Ecosystem: Past, Present, and Future
- Introducing Code Llama, a state-of-the-art large language model for coding
- Meta and Microsoft Introduce the Next Generation of Llama
- Today, we’re introducing Meta Llama 3, the next generation of our state-of-the-art open source large language model.
- Llama 3 models will soon be available on AWS, Databricks, Google Cloud, Hugging Face, Kaggle, IBM WatsonX, Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA NIM, and Snowflake, and with support from hardware platforms offered by AMD, AWS, Dell, Intel, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm.
- We’re dedicated to developing Llama 3 in a responsible way, and we’re offering various resources to help others use it responsibly as well. This includes introducing new trust and safety tools with Llama Guard 2, Code Shield, and CyberSec Eval 2.
- In the coming months, we expect to introduce new capabilities, longer context windows, additional model sizes, and enhanced performance, and we’ll share the Llama 3 research paper.
- Meta AI, built with Llama 3 technology, is now one of the world’s leading AI assistants that can boost your intelligence and lighten your load—helping you learn, get things done, create content, and connect to make the most out of every moment. You can try Meta AI here .
Today, we’re excited to share the first two models of the next generation of Llama, Meta Llama 3, available for broad use. This release features pretrained and instruction-fine-tuned language models with 8B and 70B parameters that can support a broad range of use cases. This next generation of Llama demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of industry benchmarks and offers new capabilities, including improved reasoning. We believe these are the best open source models of their class, period. In support of our longstanding open approach, we’re putting Llama 3 in the hands of the community. We want to kickstart the next wave of innovation in AI across the stack—from applications to developer tools to evals to inference optimizations and more. We can’t wait to see what you build and look forward to your feedback.
Our goals for Llama 3
With Llama 3, we set out to build the best open models that are on par with the best proprietary models available today. We wanted to address developer feedback to increase the overall helpfulness of Llama 3 and are doing so while continuing to play a leading role on responsible use and deployment of LLMs. We are embracing the open source ethos of releasing early and often to enable the community to get access to these models while they are still in development. The text-based models we are releasing today are the first in the Llama 3 collection of models. Our goal in the near future is to make Llama 3 multilingual and multimodal, have longer context, and continue to improve overall performance across core LLM capabilities such as reasoning and coding.
State-of-the-art performance
Our new 8B and 70B parameter Llama 3 models are a major leap over Llama 2 and establish a new state-of-the-art for LLM models at those scales. Thanks to improvements in pretraining and post-training, our pretrained and instruction-fine-tuned models are the best models existing today at the 8B and 70B parameter scale. Improvements in our post-training procedures substantially reduced false refusal rates, improved alignment, and increased diversity in model responses. We also saw greatly improved capabilities like reasoning, code generation, and instruction following making Llama 3 more steerable.

*Please see evaluation details for setting and parameters with which these evaluations are calculated.
In the development of Llama 3, we looked at model performance on standard benchmarks and also sought to optimize for performance for real-world scenarios. To this end, we developed a new high-quality human evaluation set. This evaluation set contains 1,800 prompts that cover 12 key use cases: asking for advice, brainstorming, classification, closed question answering, coding, creative writing, extraction, inhabiting a character/persona, open question answering, reasoning, rewriting, and summarization. To prevent accidental overfitting of our models on this evaluation set, even our own modeling teams do not have access to it. The chart below shows aggregated results of our human evaluations across of these categories and prompts against Claude Sonnet, Mistral Medium, and GPT-3.5.

Preference rankings by human annotators based on this evaluation set highlight the strong performance of our 70B instruction-following model compared to competing models of comparable size in real-world scenarios.
Our pretrained model also establishes a new state-of-the-art for LLM models at those scales.

To develop a great language model, we believe it’s important to innovate, scale, and optimize for simplicity. We adopted this design philosophy throughout the Llama 3 project with a focus on four key ingredients: the model architecture, the pretraining data, scaling up pretraining, and instruction fine-tuning.
Model architecture
In line with our design philosophy, we opted for a relatively standard decoder-only transformer architecture in Llama 3. Compared to Llama 2, we made several key improvements. Llama 3 uses a tokenizer with a vocabulary of 128K tokens that encodes language much more efficiently, which leads to substantially improved model performance. To improve the inference efficiency of Llama 3 models, we’ve adopted grouped query attention (GQA) across both the 8B and 70B sizes. We trained the models on sequences of 8,192 tokens, using a mask to ensure self-attention does not cross document boundaries.
Training data
To train the best language model, the curation of a large, high-quality training dataset is paramount. In line with our design principles, we invested heavily in pretraining data. Llama 3 is pretrained on over 15T tokens that were all collected from publicly available sources. Our training dataset is seven times larger than that used for Llama 2, and it includes four times more code. To prepare for upcoming multilingual use cases, over 5% of the Llama 3 pretraining dataset consists of high-quality non-English data that covers over 30 languages. However, we do not expect the same level of performance in these languages as in English.
To ensure Llama 3 is trained on data of the highest quality, we developed a series of data-filtering pipelines. These pipelines include using heuristic filters, NSFW filters, semantic deduplication approaches, and text classifiers to predict data quality. We found that previous generations of Llama are surprisingly good at identifying high-quality data, hence we used Llama 2 to generate the training data for the text-quality classifiers that are powering Llama 3.
We also performed extensive experiments to evaluate the best ways of mixing data from different sources in our final pretraining dataset. These experiments enabled us to select a data mix that ensures that Llama 3 performs well across use cases including trivia questions, STEM, coding, historical knowledge, etc.
Scaling up pretraining
To effectively leverage our pretraining data in Llama 3 models, we put substantial effort into scaling up pretraining. Specifically, we have developed a series of detailed scaling laws for downstream benchmark evaluations. These scaling laws enable us to select an optimal data mix and to make informed decisions on how to best use our training compute. Importantly, scaling laws allow us to predict the performance of our largest models on key tasks (for example, code generation as evaluated on the HumanEval benchmark—see above) before we actually train the models. This helps us ensure strong performance of our final models across a variety of use cases and capabilities.
We made several new observations on scaling behavior during the development of Llama 3. For example, while the Chinchilla-optimal amount of training compute for an 8B parameter model corresponds to ~200B tokens, we found that model performance continues to improve even after the model is trained on two orders of magnitude more data. Both our 8B and 70B parameter models continued to improve log-linearly after we trained them on up to 15T tokens. Larger models can match the performance of these smaller models with less training compute, but smaller models are generally preferred because they are much more efficient during inference.
To train our largest Llama 3 models, we combined three types of parallelization: data parallelization, model parallelization, and pipeline parallelization. Our most efficient implementation achieves a compute utilization of over 400 TFLOPS per GPU when trained on 16K GPUs simultaneously. We performed training runs on two custom-built 24K GPU clusters . To maximize GPU uptime, we developed an advanced new training stack that automates error detection, handling, and maintenance. We also greatly improved our hardware reliability and detection mechanisms for silent data corruption, and we developed new scalable storage systems that reduce overheads of checkpointing and rollback. Those improvements resulted in an overall effective training time of more than 95%. Combined, these improvements increased the efficiency of Llama 3 training by ~three times compared to Llama 2.
Instruction fine-tuning
To fully unlock the potential of our pretrained models in chat use cases, we innovated on our approach to instruction-tuning as well. Our approach to post-training is a combination of supervised fine-tuning (SFT), rejection sampling, proximal policy optimization (PPO), and direct preference optimization (DPO). The quality of the prompts that are used in SFT and the preference rankings that are used in PPO and DPO has an outsized influence on the performance of aligned models. Some of our biggest improvements in model quality came from carefully curating this data and performing multiple rounds of quality assurance on annotations provided by human annotators.
Learning from preference rankings via PPO and DPO also greatly improved the performance of Llama 3 on reasoning and coding tasks. We found that if you ask a model a reasoning question that it struggles to answer, the model will sometimes produce the right reasoning trace: The model knows how to produce the right answer, but it does not know how to select it. Training on preference rankings enables the model to learn how to select it.
Building with Llama 3
Our vision is to enable developers to customize Llama 3 to support relevant use cases and to make it easier to adopt best practices and improve the open ecosystem. With this release, we’re providing new trust and safety tools including updated components with both Llama Guard 2 and Cybersec Eval 2, and the introduction of Code Shield—an inference time guardrail for filtering insecure code produced by LLMs.
We’ve also co-developed Llama 3 with torchtune , the new PyTorch-native library for easily authoring, fine-tuning, and experimenting with LLMs. torchtune provides memory efficient and hackable training recipes written entirely in PyTorch. The library is integrated with popular platforms such as Hugging Face, Weights & Biases, and EleutherAI and even supports Executorch for enabling efficient inference to be run on a wide variety of mobile and edge devices. For everything from prompt engineering to using Llama 3 with LangChain we have a comprehensive getting started guide and takes you from downloading Llama 3 all the way to deployment at scale within your generative AI application.
A system-level approach to responsibility
We have designed Llama 3 models to be maximally helpful while ensuring an industry leading approach to responsibly deploying them. To achieve this, we have adopted a new, system-level approach to the responsible development and deployment of Llama. We envision Llama models as part of a broader system that puts the developer in the driver’s seat. Llama models will serve as a foundational piece of a system that developers design with their unique end goals in mind.

Instruction fine-tuning also plays a major role in ensuring the safety of our models. Our instruction-fine-tuned models have been red-teamed (tested) for safety through internal and external efforts. Our red teaming approach leverages human experts and automation methods to generate adversarial prompts that try to elicit problematic responses. For instance, we apply comprehensive testing to assess risks of misuse related to Chemical, Biological, Cyber Security, and other risk areas. All of these efforts are iterative and used to inform safety fine-tuning of the models being released. You can read more about our efforts in the model card .
Llama Guard models are meant to be a foundation for prompt and response safety and can easily be fine-tuned to create a new taxonomy depending on application needs. As a starting point, the new Llama Guard 2 uses the recently announced MLCommons taxonomy, in an effort to support the emergence of industry standards in this important area. Additionally, CyberSecEval 2 expands on its predecessor by adding measures of an LLM’s propensity to allow for abuse of its code interpreter, offensive cybersecurity capabilities, and susceptibility to prompt injection attacks (learn more in our technical paper ). Finally, we’re introducing Code Shield which adds support for inference-time filtering of insecure code produced by LLMs. This offers mitigation of risks around insecure code suggestions, code interpreter abuse prevention, and secure command execution.
With the speed at which the generative AI space is moving, we believe an open approach is an important way to bring the ecosystem together and mitigate these potential harms. As part of that, we’re updating our Responsible Use Guide (RUG) that provides a comprehensive guide to responsible development with LLMs. As we outlined in the RUG, we recommend that all inputs and outputs be checked and filtered in accordance with content guidelines appropriate to the application. Additionally, many cloud service providers offer content moderation APIs and other tools for responsible deployment, and we encourage developers to also consider using these options.
Deploying Llama 3 at scale
Llama 3 will soon be available on all major platforms including cloud providers, model API providers, and much more. Llama 3 will be everywhere .
Our benchmarks show the tokenizer offers improved token efficiency, yielding up to 15% fewer tokens compared to Llama 2. Also, Group Query Attention (GQA) now has been added to Llama 3 8B as well. As a result, we observed that despite the model having 1B more parameters compared to Llama 2 7B, the improved tokenizer efficiency and GQA contribute to maintaining the inference efficiency on par with Llama 2 7B.
For examples of how to leverage all of these capabilities, check out Llama Recipes which contains all of our open source code that can be leveraged for everything from fine-tuning to deployment to model evaluation.
What’s next for Llama 3?
The Llama 3 8B and 70B models mark the beginning of what we plan to release for Llama 3. And there’s a lot more to come.
Our largest models are over 400B parameters and, while these models are still training, our team is excited about how they’re trending. Over the coming months, we’ll release multiple models with new capabilities including multimodality, the ability to converse in multiple languages, a much longer context window, and stronger overall capabilities. We will also publish a detailed research paper once we are done training Llama 3.
To give you a sneak preview for where these models are today as they continue training, we thought we could share some snapshots of how our largest LLM model is trending. Please note that this data is based on an early checkpoint of Llama 3 that is still training and these capabilities are not supported as part of the models released today.

We’re committed to the continued growth and development of an open AI ecosystem for releasing our models responsibly. We have long believed that openness leads to better, safer products, faster innovation, and a healthier overall market. This is good for Meta, and it is good for society. We’re taking a community-first approach with Llama 3, and starting today, these models are available on the leading cloud, hosting, and hardware platforms with many more to come.
Try Meta Llama 3 today
We’ve integrated our latest models into Meta AI, which we believe is the world’s leading AI assistant. It’s now built with Llama 3 technology and it’s available in more countries across our apps.
You can use Meta AI on Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Messenger, and the web to get things done, learn, create, and connect with the things that matter to you. You can read more about the Meta AI experience here .
Visit the Llama 3 website to download the models and reference the Getting Started Guide for the latest list of all available platforms.
You’ll also soon be able to test multimodal Meta AI on our Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses.
As always, we look forward to seeing all the amazing products and experiences you will build with Meta Llama 3.
Our latest updates delivered to your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with Meta AI news, events, research breakthroughs, and more.
Join us in the pursuit of what’s possible with AI.

Product experiences
Foundational models
Latest news
Meta © 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
10 other terms for presentation graphics - words and phrases with similar meaning. Lists. synonyms. antonyms. definitions. sentences. thesaurus. suggest new. Another way to say Presentation Graphics?
6. Multimedia. Multimedia refers to the combination of different types of media — such as text, images, audio, video, and animation — within a single presentation. Incorporating multimedia elements can make a presentation more engaging, cater to different learning styles, and aid in explaining complex ideas.
Example: Nike's branding is instantly recognisable through its iconic swoosh logo, distinctive typography, and "Just Do It" slogan, which collectively evokes a sense of athleticism, empowerment, and quality. 8. Calligraphy. Calligraphy is the art of decorative handwriting or lettering created with a pen or brush.
11. Bleed. That little bit extra—the bleed is a printing term that refers to the edge of the sheet that will be trimmed off. In design terms, the bleed is the artwork or background colour that extends in to this area, in case the cut made to the design or sheet isn't exact.
The best PPT graphics templates have a range of infographics, shapes, and more. This PowerPoint presentation graphics-focused template's got all the above. Plus, it's easy to edit these cool presentation graphics thanks to smartly constructed slides. These three templates are just the start of graphics for presentations included on Elements.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls. To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It's like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable. 8.
17. Grid. Graphic designers use a grid on their screens as a guide to ensure the elements are straight, balanced, and aligned correctly. 18. Hex. A hex is a six-digit number used in applications to represent colors. You can precisely define your colors with the Hex feature in the Creative Studio on Creasquare. 19.
The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says "any slide with more than 10 words is a document.". If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
1. How to insert graphics into PowerPoint. Once you've created your presentation it's time to add those all-important PowerPoint Graphics. And it's easy, easy, easy. Step 1: Go to the slide and create a space for your graphic. Step 2: Go to insert on the toolbar at the top of PowerPoint, click on it.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) is a color model used on screens. It works by combining red, green, and blue light to create other colors. RGB is the standard for web design since all monitors display in this format. Any design that will be viewed on a screen should be created in the RGB color mode, as opposed to CMYK.
The SlideLizard presentation glossary is a large collection of explanations and definitions of terms in the area of presentations, communication, speaking, events, PowerPoint and education. ... A screen presentation is a graphic support and accompaniment to a spoken presentation. ... Another location of a shop is opened for only one month to ...
Presentation graphics software provides predefined backgrounds and sample page layouts to assist in the creation of computer-driven slide shows, which, in combination with a data projector, made ...
30 Graphic Design Terms & What They Mean. Graphic design is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, driven by innovation and creativity. It's a realm where visuals, ideas, and messages converge to create impactful and compelling narratives. However, for those new to the world of graphic design, the array of terminologies and jargon used by ...
presentation software (presentation graphics): Presentation software (sometimes called "presentation graphics") is a category of application program used to create sequences of words and pictures that tell a story or help support a speech or public presentation of information. Presentation software can be divided into business presentation ...
Presentation graphics provides predefined backgrounds and simple page layouts to help in the creation of slides. These slides can be moved automatically within seconds. Slides: Slides mean we have text, graphics, audio clips, video clips, animations, and other effects Presentation graphics is also known as Presentation Software.
Summary. A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you're pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing ...
Synonyms for GRAPHIC: illustration, diagram, visual, image, drawing, picture, plate, caption; Antonyms of GRAPHIC: vague, sketchy, obscure, unclear, indeterminate ...
Find 253 synonyms for "graphic representation" and other similar words that you can use instead based on 2 separate contexts from our thesaurus.. What's another word for ... presentation. setout. dimensions. geography. look. lay. make-up. set-up. cutaway. physical arrangement. game. description. line drawing.
Additionally, many cloud service providers offer content moderation APIs and other tools for responsible deployment, and we encourage developers to also consider using these options. Deploying Llama 3 at scale. Llama 3 will soon be available on all major platforms including cloud providers, model API providers, and much more. ...