

Top 10 Argumentative Essay Introduction Examples
When writing an argumentative essay , the introduction might be the most important part of your paper. The introduction to your argumentative essay must grab your readers’ attention and draw them to the topic. There are many points that you need to include in your introduction when writing an argumentative essay.
An attention-getter can set up what will follow throughout the rest of the paper, make the reader see what you are trying to prove, and provide an example to show why your topic is important.
Creating a sense of importance or urgency brings the reader into the essay because they feel they should know more about it. This will allow readers to become engaged in your topic and stay interested throughout the rest of your argumentative essay.
Here are a few examples of good argumentative essay introductions.
Argumentative essay introduction example 1
Gambling, or gambling addiction, is a complex subject to understand. Some people often win, which may lead others to believe that they are lucky rather than skilled. Many people gamble to escape reality for a bit and have fun. Others gamble for the thrill of it because their lives are boring. It is difficult to determine when a person’s behavior turns from a hobby into a problem. It is even more challenging to decide if that something is indeed an addiction. Although gambling may be harmful in specific ways, I believe that the negatives do not outweigh the positives.
Argumentative essay introduction example 2
In today’s society, there are many different opinions about what is right and wrong. From drinking alcohol to smoking, each person has a different set of standards. Where people differ, the most is about morality. Morality is the standard of conduct in society, being considered right or wrong by most people. There are different schools of thought on morality, including classical, evolutionary ethics, and social contract theory. This paper will discuss how these three theories define moral law.
Argumentative essay introduction example 3
The purpose of this paper is to examine the role that the media has played in stoking debates about ethnic diversity, multiculturalism, and national identity. I will discuss ways in which print journalism promoted political agendas by using certain news stories as examples. For example, The Globe & Mail’s coverage of ‘ethnic voters’ during the 1993 federal election attempted to explain why the Canadian electorate was leaning toward a change in government. The paper also illustrated the consequences of public opinion on legislation throughout Canada’s history, such as passing anti-Chinese legislation in B.C., and more recently, Quebec’s Bill 101.
Argumentative essay introduction example 4
People often consider athletes to be role models for society. They say that athletes are good, clean-cut people who live out the American dream. People think of them as successful individuals who have earned their money through hard work and determination. They usually leave out that many famous athletes today are just in it for the money and don’t care who they hurt in the process. They will do whatever it takes to make more money and become even more famous, even if it means ruining their reputation and hurting people. Many athletes have had problems with steroids, drinking alcohol underage, drugs, etc., yet fans continue to look up to them because of their athletic abilities.
Argumentative essay introduction example 5
Does the United States need a military draft? Many people think so, and there are many examples of why it would be effective. A military draft has several benefits but is not without its disadvantages. People believe that an all-volunteer army is better than conscription for various reasons, but the cons outweigh the pros. The benefits of compulsory military service are that it would increase the number of troops drastically overnight, solve unemployment problems, and ensure loyalty to America rather than other countries. The disadvantages include low-quality individuals in the armed forces, unfairness towards people who cannot enlist because they have certain health problems or are married with children, and the adverse effects of war on those drafted into service.
Argumentative essay introduction example 6
The first several decades of the twentieth century were marked by peace and tranquillity in North America and Europe. This era was known as the ‘American Dream.’ The world’s economy had never been stronger, and all shared this newfound wealth. The economy improved with the automobile industry, the oil business, the steel industry, and radio broadcasting. What led to this era of prosperity that people were experiencing? Were there policies or circumstances that created economic stability worldwide? There were many reasons for this era of peace, but the leading cause was that most economies were based on gold. People bought and sold goods with real money, rather than government-issued paper or funny money.
Argumentative essay introduction example 7
The use of animals in scientific research is a highly controversial issue. Opponents say it is cruel and immoral to use animals for experiments, whereas proponents argue that developing life-saving drugs and treatments is necessary. It is necessary to use animals in scientific experiments for medical research because humans and animals are similar in complex ways. The brain, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and immune systems of different species are so alike that studying the effects of drugs on non-human subjects is highly beneficial to advancing knowledge about how various substances will affect people.
Argumentative essay introduction example 8
Driving while talking on a cell phone can be very dangerous. If you drive while using your cell phone, you become four times more likely to get into an accident. For this reason, many countries and provinces in Canada have banned the use of hand-held cell phones while driving. Using a headset or speakerphone is an alternative to holding the phone, but it does not eliminate the risk. One of the concerns is that talking on a cell phone slows reaction time and causes people to miss visual cues they would otherwise notice.
Argumentative essay introduction example 9
Does the average person really need to drink eight glasses of water a day? This idea has been passed down, but is it based on scientific facts, or is it a myth? Some people say that drinking eight glasses of water a day is an old wives’ tale, whereas others insist that one should drink at least this amount of water every day. The main point is that the body requires a certain amount of daily fluid intake, and it is important to maintain proper hydration levels for overall health. It is not necessary to drink eight glasses of water each day, but one should drink enough to urinate at least four times per day.
Argumentative essay introduction example 10
Is the U.S. directly responsible for spreading democracy across the world? The United States has been involved in various activities which have led to regime changes in other countries, where democratically elected governments replaced leaders. Countries that have received military training from the U.S., such as El Salvador and Colombia, are flourishing democracies. This has led many people to believe that the U.S.’s interest in spreading democracy across the world is genuine. Still, others are skeptical because it benefits America when other countries join NATO or accept free trade deals.
How to Create a Sense of Importance or Urgency in Your Introduction

Here are some tips for creating a sense of importance or urgency in your introduction:
- Watch your tone. If you want to be urgent, use words like “need,” and if you want it to feel important, use words like “should.”
- Use a relevant quote.
- Make an example out of someone in the past or present that agrees with your opinion.
- Take a stand and let readers know right away your opinion with a command like “don’t believe the hype” or “it’s time we do something about it.”
- Emphasize the benefits of having your opinion with words like, “Imagine if everyone was responsible enough to recycle.”
- Link it back to history. Let readers know that what you’re saying is nothing new with phrases like that, it’s “a tale as old as time.”
- Explain how this is happening in the present with phrases like “the effects of” and “we see a rise in.”
- Use persuasive words. Persuasive essay writing uses words that make your readers feel guilty, like “deserve,” and inspire them to change and take action with words like “must.
What Influences an Excellent Argumentative Essay Introduction?

Several factors come into play when it comes to writing a good introduction. The most important points to consider are:
- Choice of the argumentative essay topic
Picking interesting argumentative essay topics makes it easier to write an interesting introduction. Another set of topics that guarantee good introductions are the controversial argumentative essay topics.
Writing argumentative essays need proper research done. It does not matter if you are writing a basic argumentative essay or an argumentative research paper. You need to do proper research for your introduction to be effective.
You have to choose the audience targeted in your introduction. For instance, use formal language when addressing professors and informal language when speaking with friends. You can also adjust the thought process of your audience by using certain words. Choice of words targeted for middle school students will be different from a postgraduate audience.
Tips for Writing an Effective Argumentative Essay Introduction

Here are some tips you can use when you write an argumentative essay introduction. They include:
Introduce the conflicting ideas with a comparison or analogy.
Give a brief background on the conflicting ideas to show your readers how they came to be. Make a clear and concise statement that sums up both sides of the argument, like “some say X while others say Y.” Make sure it’s something that can be backed up with evidence later on.
End your introduction with a thesis statement that states which side of the argument you’re taking and what type of claim it is, like “I believe we should eliminate homework because doing so will improve students’ test scores.”
Ask readers questions that get them thinking about your idea.
Questions have proven to be an effective way to get readers thinking about what you’re trying to say. You can ask questions that help them relate it back to their lives, like “What would happen if there was no drinking water?” or “What if everyone decided they didn’t want to eat meat anymore?”
Introduce the opposing side.
If you’re going to be arguing against a popular opinion , you’ll need to state what that opinion is briefly. Let readers know how you plan to argue against it with a word like “despite” or “although” that shows you’re aware of the other side.
Describe your audience.
People are more likely to read something if they feel it’s written specifically for them, so mention your audience right away by saying something like “for all students.” You can also mention a specific group of people, like “for all teens.”
Present readers with a thought-provoking quote.
Quotes can be a great way to grab readers’ attention and get them thinking about what you plan to say. You don’t want your quote to sound like something that was copied and pasted from a textbook, so try using one that has creative language or has been taken out of its original context.
Mistakes to Avoid While Writing Introductions for Argumentative Essays

There are many mistakes that writers commonly make while writing introductory paragraphs. These include:
Being too basic.
People are reading your essay to learn more about your argument, so give them what they need with concrete examples. You don’t need to tell readers something they already know if you are not adding any new information or angle.
- Being too wordy.
Writing too much can cause your introduction to be confusing and messy. Readers will stop reading if they feel like their eyes are glazing over, so try not to use five words when one would do the job just as well. If you’re having trouble cutting down on the length of your statements, ask yourself what your main point is and what you’re hoping to accomplish with your introduction.
- Not narrowing down your argument.
Narrowing down your argument is important because it allows readers to focus on the main point of your essay. If you’re having trouble narrowing down your ideas, try listing reasons why one option would be better than the other or what impact it will have if certain things are changed.
- Not strengthening your argument by using evidence.
Your thesis statement should be supported by evidence , so make sure your introductory paragraph flows easily into the body. If you’re struggling with what types of evidence to include, think about what can be seen as common sense, backed up by research or stated by an expert.
- Not using transitional words.
Transitional words help the flow of your writing because they signal an upcoming change in idea or direction. Words like “however,” “for example,” and “despite this” can be used to show readers when the tone of your argument is changing.
- Not using a hook.
A hook draws a reader in by making them curious about what you’re going to say next or how it relates to them, so choosing one that best suits your argument can help improve the effectiveness of your introduction.
Writing a good introduction for an argumentative essay is key to catching your readers’ attention and making them want to learn more. A strong introduction should consist of ideas relevant to your argument, clarify how you plan to form an argument and provide readers with a compelling reason to continue reading. Remember not to include too much information or make mistakes common among new writers, like being wordy or not including evidence.

I ‘m a freelance content and SEO writer with a passion for finding the perfect combination of words to capture attention and express a message . I create catchy, SEO-friendly content for websites, blogs, articles, and social media. My experience spans many industries, including health and wellness, technology, education, business, and lifestyle. My clients appreciate my ability to craft compelling stories that engage their target audience, but also help to improve their website’s search engine rankings. I’m also an avid learner and stay up to date on the latest SEO trends. I enjoy exploring new places and reading up on the latest marketing and SEO strategies in my free time.
Similar Posts

Revising an Essay- the do’s, the don’ts, and a Sample
We all know that we should revise our essays before submitting them to ensure the best possible grade, but we will discuss how and why in this article. We will cover what you can do to improve your essay during revision and what not to do so that you don’t accidentally make it worse. Finally, I’ll show you an example of a revised essay using these techniques and provide feedback on its strengths and weaknesses…

Example of Analysis in Essays
Analytical essays provide substantive analysis of a given topic. Analytical essays can be about literary works, music, art, current events, scientific research, historical events, among many other issues…

The 5 Types of Writing Formats Explained
While there are many reasons why you would write, these are categories of writing styles: expository, descriptive, persuasive, narrative, and creative writing…

Top 4 SAT Essay Examples to Make you Succeed
Sat essay examples are the most popular SAT essay topics. These prompts to test your ability to read and analyze various types of texts, focusing on how an author’s use of language affects their meaning…

How to Write an Autobiography Essay
Introduction People write autobiographies to tell the story of their life. As with any self-expression, it can be difficult to think about how you will put your life into words. Unlike most forms of writing, where the goal is to communicate information or an idea concisely, autobiographies are incredibly personal and expansive in scope. On…
Supporting Arguments-Definition, Use, and Examples
The term “argument” refers to a discussion or line of reasoning that seeks to convince someone of an idea, point, or attitude. Arguments can be structured as “positive” (the positive argument is based on facts and data) or as “negative” (the negative argument completely disregards fact and data). In general, the purpose of an argument…

- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Guide to Writing Strong Introductions for Argumentative Essays
Table of contents
Have you ever stared at a blank document, the cursor blinking back at you, as your mind races to conjure the perfect starting line for your argumentative essay? If so, you're in good company.
Opening an essay is often the most daunting part for many students. They oscillate between typing out a line and hastily hitting the backspace, feeling the pressure of that first sentence. After all, first impressions matter, right? So, your introduction should be nothing short of spectacular.
But here's the good news - crafting a powerful introduction for your argumentative essay is not as elusive as it seems. In fact, we've got a few tricks up our sleeve to help you out, and trust us, they work!
This blog post is dedicated to anyone who has ever struggled with introducing their argumentative essay - so essentially, every student ever! We're going to break it down, step by step, showing you the do's and don'ts, the tips and tricks, and even providing you with some solid examples.
Hire Us To Write Your Argumentative Essay
And if you're worried about whether you can do it on your own, don't fret! Our expert argumentative essay writers at Writers Per Hour are always ready to help you.
So, let's dive into the art of crafting a compelling introduction for an argumentative essay, shall we?
Understanding the Purpose of an Introduction
Before we get into the nuts and bolts of writing a killer introduction, it's important to understand why it matters so much.
Your introduction, essentially, sets the stage for your argumentative essay. It is your reader's first glimpse into the argument you're about to unfold. An effective introduction grabs your reader's attention, piques their interest, and provides a clear road map for what's to come in the essay.
In simpler words, the purpose of an introduction in an argumentative essay is threefold:
Engage the reader : A well-crafted introduction acts as a hook, capturing the reader's attention and encouraging them to read further.
Provide background information : It sets the context of the argument by offering necessary background details about the topic.
Present the thesis statement : Arguably the most critical part of your introduction - the thesis statement clearly outlines your position on the argument.
REMEMBER : a great introduction is your ticket to a good grade. It is the first impression you make on your reader. So, if it isn't engaging, concise, and clear, you might lose your reader before they even get to the main argument.
The Anatomy of a Good Argumentative Essay Introduction
Now that you understand the purpose of an introduction, let's break down the structure.
An effective introduction to an argumentative essay will generally have three main sections: a hook, background information, and a thesis statement.
The Hook : This is the first sentence of your introduction, and it needs to grab your reader’s attention. An effective hook could be a surprising fact, a rhetorical question, or an intriguing statement that challenges common perceptions. This needs to be relevant to your topic and should provoke curiosity, pushing the reader to continue.
Background Information : Following the hook, provide some context to your argument. Explain the relevance of your topic or problem, its history or evolution, or the common debates surrounding it. This provides a basic understanding for your reader and sets the stage for your argument.
Thesis Statement : This is where you state your position clearly and concisely. The thesis statement is arguably the most important part of your introduction—it is the crux of your argument and should be compelling and thought-provoking. It needs to clearly indicate what your argument is and give a hint of how you plan to approach it.
IMPORTANT : your introduction is not a place to present all your evidence or explain every aspect of your argument—that's what the body of your essay is for. Instead, your introduction should hint at these things, creating a roadmap for the reader.
Dos and Don’ts of Writing an Introduction for an Argumentative Essay
Crafting a strong introduction for your argumentative essay is about adhering to some key dos and don’ts. Let's take a look at some of these:
1. Engage your reader : Your introduction's first job is to engage the reader. You can achieve this with a compelling hook that draws them into your essay. Remember, first impressions matter!
2. Provide relevant background information : Your reader may not be as knowledgeable about your topic as you are, so be sure to provide some context and background information to help them understand your argument.
3. State your thesis clearly : Your thesis statement should be clear, concise, and debatable. The reader should have no doubts about your stance on the issue.
4. Preview your argument : Give your reader a sense of what's to come by previewing your main points or arguments. This prepares them for the rest of your essay.
1. Don't make your introduction too long : Remember, the introduction is just a sneak peek into your essay, not the main event. Keep it concise and to the point.
2. Don't use clichés : Starting your essay with clichéd phrases or overused quotes can make your introduction feel unoriginal. Instead, aim for a fresh and unique opening line that will pique your reader's interest.
3. Don't be vague : Be clear and precise in your introduction. Vague statements can confuse your reader and make your argument seem weak.
4. Don't forget your audience : Always keep your audience in mind while writing. Your language, tone, and the context you provide should be appropriate for your audience.
REMEMBER : your introduction sets the tone for the rest of your essay, so take your time with it.
Step-by-Step Guide on Writing the Introduction
Crafting an engaging introduction for your argumentative essay is like setting the stage for a compelling drama. It should hook your audience, provide context, and present your stance on the issue. But how can you bring all these elements together effectively? Let's break it down step-by-step. Here's your comprehensive guide to writing a riveting introduction for your argumentative essay.
Step 1: Understanding Your Topic
Before you begin writing, ensure that you thoroughly understand the topic and the argument you wish to present. This means going beyond surface-level research and really digging deep into the subject matter.
Step 2: Define Your Stance
Clearly outline your stance on the argument. This will be the foundation of your thesis statement and guide the tone and direction of your essay.
Step 3: Craft a Compelling Hook
Begin your introduction with a hook - an interesting fact, a question, a quote, or a compelling statement that grabs the reader's attention.
Step 4: Provide Background Information
Next, provide some context to your reader about the topic at hand. Remember not to delve too deep into the specifics - just enough information to guide the reader to understand the relevance of your argument.
Step 5: State Your Thesis
Lastly, present your thesis statement - a concise summary of your main argument. This should be clear, precise, and strongly worded. The thesis statement will guide the entirety of your essay, so make sure it's impactful.
Step 6: Preview Your Main Points
Briefly preview the main points that you will elaborate on in the body of your essay. This helps your reader to understand what to expect from the rest of your argumentative essay.
Step 7: Revise and Edit
Always revise and edit your introduction after writing. Look for any grammar mistakes, unclear sentences or ideas, and ensure that your introduction smoothly transitions into the body of your essay.
REMEMBER : the introduction is the first impression your reader gets of your argumentative essay. Make it impactful, clear, and concise, and you'll have set a strong foundation for the rest of your essay. If you're ever in doubt, reach out to our legal essay writing service , and we'll help guide you on your journey to mastering argumentative essays.
Case Study: Good vs. Bad Introduction
Bad Introduction : "The topic I am writing about is the use of social media. It is very popular. People are always on their phones checking their social media accounts. I am going to talk about if it is good or bad."
Analysis : This introduction falls flat for several reasons. It doesn't grab the reader's attention, and the thesis statement is unclear and broad. It doesn't offer any specific viewpoint or direction for the argument to follow.
Good Introduction : "Every minute, approximately 500 hours of video are uploaded to YouTube, 347,222 stories are posted on Instagram, and 2.4 million snaps are created on Snapchat. The rise of social media platforms is more than a trend - it's a global phenomenon. But as these virtual communities continue to grow, a vital question arises: Is the widespread use of social media enhancing human connection or creating deeper isolation? This essay will delve into the multifaceted impacts of social media, arguing that despite its potential for fostering a global network, it often serves as a platform that promotes isolation and disconnection."
Analysis : This introduction starts with an attention-grabbing statistic, clearly showing the extent of social media usage. The background information provided is concise and relevant, offering enough context without overshadowing the argument. The thesis statement is clear, arguable, and offers a specific direction for the essay to take.
By comparing these two examples, you can see how a well-crafted introduction sets the tone for the entire essay, providing a clear, compelling roadmap for the argument to follow.
Final Thoughts
There you have it! Crafting an engaging introduction for an argumentative essay doesn't have to be an intimidating process. By understanding the crucial elements involved, practicing, and continuously refining your writing, you're well on your way to creating introductions that captivate your audience and set a strong precedent for your arguments.
- Start with a powerful hook.
- Provide necessary background information.
- State your thesis clearly and concisely.
- Set the stage for your main argument.
- And most importantly, revise and refine your introduction.
And there's one more thing to bear in mind: you're not alone in this journey. Writing can be challenging, but help is always within reach.
Additional Resources
To further solidify your introduction writing skills and broaden your understanding of argumentative essays, here are some additional resources that are worth diving into:
Posts from Writers Per Hour Blog
- How to Write Conclusion for an Argumentative Essay
- How Significant Are Opposing Points of View in an Argument
- Argumentative Essay Topics Ideas
- Rebuttal in Argumentative Essay
External Resources
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Introduction to Argumentative Essays
- University of North Carolina Writing Center: Introductions
- Harvard College Writing Center: How to Write an Essay
Remember, becoming proficient in writing argumentative essays is a journey, not a destination. It takes time, practice, and patience. But don't forget - if you ever find yourself in need of help, our argumentative essay writing service is here for you. Our American essay writing service is adept at crafting essays and can support you in reaching your academic goals.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without AI-assistance
Imagine you’re a scientist who just made a ground-breaking discovery! You want to share your…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS style
In today’s digital age, the internet serves as an invaluable resource for researchers across all…
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Start an Argumentative Essay: Tips For The Introduction
by Antony W
August 10, 2023

The opening paragraph can make or break your argumentative essay .
If you write it well, you'll not only pique the interest of your reader but also get them to read the following subsequent paragraphs.
If you write it randomly, you’ll lose the reader even before the get to the thesis statement.
If you think about it, professors often read an argument's title and its opening statement before they can look at your actual arguments.
Depending on how you frame the introduction, they may read all the way to the bottom of the page or not bother to read the essay at all.
So what’s the best way to start an argumentative essay to make it engaging for the reader? And what should you avoid?
Introduction to an Argumentative Essay
The introduction isn’t a space to provide an analysis of your arguments.
Instead, its purpose is to lay a foundation that introduces the topic and provides a clear roadmap for the rest of the assignment.
A good introduction must be clear, concise, and direct to the point.
In other words, if a word or phrase doesn’t add any value to the introductory paragraph, do away with it. A good introduction should serve its purpose without the filler information.
How to Start an Argumentative Essay
The introduction of an argumentative essay is almost synonymous to the opening statement in a trial.
Just like an attorney, you have to present your claim, provide background information, and present your primary argument.
While you’re at it, you have to do so in both intellectual and logical manner.
1. Start Your Argumentative Essay with Good a Hook
The introductions to many argumentative essays are seriously boring to read. Either they’re too general or they don’t go straight to the point, as a good intro should.
To be clear, general and randomly written introductions won’t make your essay click with your reader. So you should avoid this.
Remember that even if you’re not the most creative student when it comes to working on an argumentative essay in your class, you have to start the assignment with an impactful introduction for it to attract eyeballs.
And if your opening sentence can grab the attention of your reader on the spot, they’ll definitely read the second, the third, and eventually all the way to the last sentence.
The question is:
How do you write a good hook for your argumentative essay?
- 1 Ask a rhetorical question that relates to the title of the argument
- 2 Write one or two sentences that make assertive claims about the arguments you’re about to make in the essay
- 3 Start with facts or statistics, provided they revolve around the central theme of the essay and come from credible sources
- 4 Start with a story that’s relevant to the topic in question, but make sure to keep it short and direct to the point.
- 5 You can start the essay with a quote but only if it’s absolutely necessary
If you can start the opening paragraph like this, you should be able to grab the attention of the reader and, even more importantly, arouse their interest to keep reading the essay.
2. State the Background Information
It’s important to include the background information in the introduction of your argumentative essay for two reasons.
First, it makes it easy for your reader to understand the issue that you’re about to present.
Second, it provides you with a solid context that you can use to explain and argue your points.
3. State the Thesis Statement
An essay introduction that doesn’t feature a thesis statement to an argument is straight out flat and 100% irrelevant.
Without it, it’s hard for a reader to understand the primary point that you’re trying to make.
When it comes to writing the thesis for the essay, it’s best to take a position on a particular issue, one in which a reader can easily argue against.
In other words, the thesis of an argumentative essay cannot be a fact. And you’ll use the rest of the essay to provide arguments and evidence that support the thesis statement.
What Not to Write In the Introduction
Don’t present any argument.
The last mistake you want to make is to present your argument(s) in the introduction.
Doing so makes the paper hard to read, not to mention give your readers a reason to not continue reading the essay.
Keep in mind that the goal of the introduction is to provide a clear roadmap for the essay.
By laying a good foundation, it should be easy for your reader to know what to expect from the essay beforehand.
Avoid Lengthy Introductions
There’s nothing worse about an introductions than length. It’s easy to get bogged down to adding tons of words to fill up this section.
However, chances are you’re more likely to sound boring and less interesting.
When it comes to length, short and precise is better. In fact, short introductions are easy to read.
Add to this the one or two sentences for the thesis statement, and what you have is a killer introduction that will get your audience reading.
Don’t Start the Introduction with a Quote
There’s nothing wrong with starting an essay with a quote.
However, we don’t recommend writing a quotation in the introduction of an argumentative essay unless it’s absolutely necessary.
Quotes don’t reflect your own thoughts about a topic and can limit your writing and arguing prowess as far as the topic in question is concerned.
Stick to a strong hook instead, making sure you present a killer opening statement that will make your reader(s) wanting to read more.
Now that you know how to start an argumentative essay the right way, it shouldn’t be hard for you to start and complete the assignment on your own.
If you need help to write an argumentative essay , don’t hesitate to get in touch with us.
Our professional writer have years of experience in essay writing, which means we can help you to write essays that leave your readers agreeing with you more than they’d like to oppose your point of view in a written argument.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Argumentative Essay Examples to Inspire You (+ Free Formula)
.webp)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Have you ever been asked to explain your opinion on a controversial issue?
- Maybe your family got into a discussion about chemical pesticides
- Someone at work argues against investing resources into your project
- Your partner thinks intermittent fasting is the best way to lose weight and you disagree
Proving your point in an argumentative essay can be challenging, unless you are using a proven formula.
Argumentative essay formula & example
In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments. Then, again, development of the rebuttal. This is followed by an example, and ends with a summary. This is a very basic structure, but it gives you a bird-eye-view of how a proper argumentative essay can be built.

Writing an argumentative essay (for a class, a news outlet, or just for fun) can help you improve your understanding of an issue and sharpen your thinking on the matter. Using researched facts and data, you can explain why you or others think the way you do, even while other reasonable people disagree.
Free AI argumentative essay generator > Free AI argumentative essay generator >
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an explanatory essay that takes a side.
Instead of appealing to emotion and personal experience to change the reader’s mind, an argumentative essay uses logic and well-researched factual information to explain why the thesis in question is the most reasonable opinion on the matter.
Over several paragraphs or pages, the author systematically walks through:
- The opposition (and supporting evidence)
- The chosen thesis (and its supporting evidence)
At the end, the author leaves the decision up to the reader, trusting that the case they’ve made will do the work of changing the reader’s mind. Even if the reader’s opinion doesn’t change, they come away from the essay with a greater understanding of the perspective presented — and perhaps a better understanding of their original opinion.
All of that might make it seem like writing an argumentative essay is way harder than an emotionally-driven persuasive essay — but if you’re like me and much more comfortable spouting facts and figures than making impassioned pleas, you may find that an argumentative essay is easier to write.
Plus, the process of researching an argumentative essay means you can check your assumptions and develop an opinion that’s more based in reality than what you originally thought. I know for sure that my opinions need to be fact checked — don’t yours?
So how exactly do we write the argumentative essay?
How do you start an argumentative essay
First, gain a clear understanding of what exactly an argumentative essay is. To formulate a proper topic sentence, you have to be clear on your topic, and to explore it through research.
Students have difficulty starting an essay because the whole task seems intimidating, and they are afraid of spending too much time on the topic sentence. Experienced writers, however, know that there is no set time to spend on figuring out your topic. It's a real exploration that is based to a large extent on intuition.
6 Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay (Persuasion Formula)
Use this checklist to tackle your essay one step at a time:

1. Research an issue with an arguable question
To start, you need to identify an issue that well-informed people have varying opinions on. Here, it’s helpful to think of one core topic and how it intersects with another (or several other) issues. That intersection is where hot takes and reasonable (or unreasonable) opinions abound.
I find it helpful to stage the issue as a question.
For example:
Is it better to legislate the minimum size of chicken enclosures or to outlaw the sale of eggs from chickens who don’t have enough space?
Should snow removal policies focus more on effectively keeping roads clear for traffic or the environmental impacts of snow removal methods?
Once you have your arguable question ready, start researching the basic facts and specific opinions and arguments on the issue. Do your best to stay focused on gathering information that is directly relevant to your topic. Depending on what your essay is for, you may reference academic studies, government reports, or newspaper articles.
Research your opposition and the facts that support their viewpoint as much as you research your own position . You’ll need to address your opposition in your essay, so you’ll want to know their argument from the inside out.
2. Choose a side based on your research
You likely started with an inclination toward one side or the other, but your research should ultimately shape your perspective. So once you’ve completed the research, nail down your opinion and start articulating the what and why of your take.
What: I think it’s better to outlaw selling eggs from chickens whose enclosures are too small.
Why: Because if you regulate the enclosure size directly, egg producers outside of the government’s jurisdiction could ship eggs into your territory and put nearby egg producers out of business by offering better prices because they don’t have the added cost of larger enclosures.
This is an early form of your thesis and the basic logic of your argument. You’ll want to iterate on this a few times and develop a one-sentence statement that sums up the thesis of your essay.
Thesis: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with cramped living spaces is better for business than regulating the size of chicken enclosures.
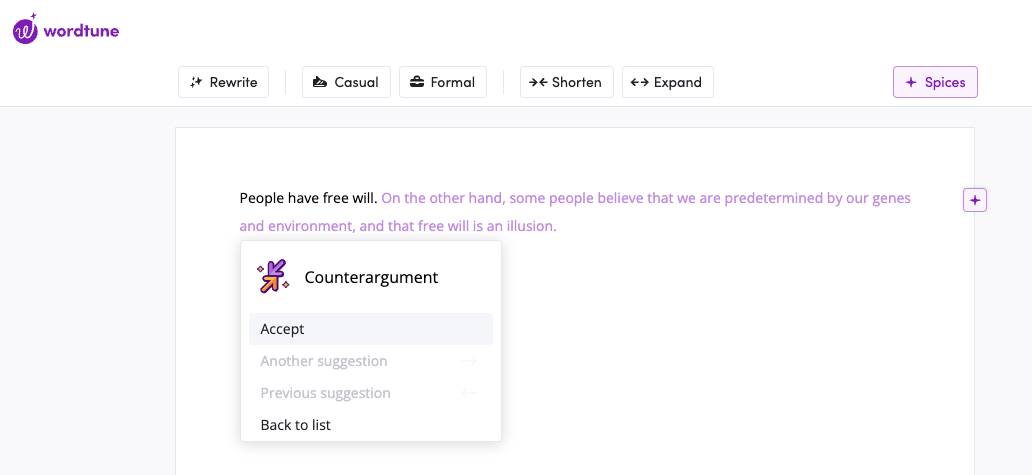
Now that you’ve articulated your thesis , spell out the counterargument(s) as well. Putting your opposition’s take into words will help you throughout the rest of the essay-writing process. (You can start by choosing the counter argument option with Wordtune Spices .)

Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers, making the low-cost protein source harder to afford — especially for low-income consumers.
There may be one main counterargument to articulate, or several. Write them all out and start thinking about how you’ll use evidence to address each of them or show why your argument is still the best option.
3. Organize the evidence — for your side and the opposition
You did all of that research for a reason. Now’s the time to use it.
Hopefully, you kept detailed notes in a document, complete with links and titles of all your source material. Go through your research document and copy the evidence for your argument and your opposition’s into another document.
List the main points of your argument. Then, below each point, paste the evidence that backs them up.
If you’re writing about chicken enclosures, maybe you found evidence that shows the spread of disease among birds kept in close quarters is worse than among birds who have more space. Or maybe you found information that says eggs from free-range chickens are more flavorful or nutritious. Put that information next to the appropriate part of your argument.
Repeat the process with your opposition’s argument: What information did you find that supports your opposition? Paste it beside your opposition’s argument.
You could also put information here that refutes your opposition, but organize it in a way that clearly tells you — at a glance — that the information disproves their point.
Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers.
BUT: Sicknesses like avian flu spread more easily through small enclosures and could cause a shortage that would drive up egg prices naturally, so ensuring larger enclosures is still a better policy for consumers over the long term.
As you organize your research and see the evidence all together, start thinking through the best way to order your points.
Will it be better to present your argument all at once or to break it up with opposition claims you can quickly refute? Would some points set up other points well? Does a more complicated point require that the reader understands a simpler point first?
Play around and rearrange your notes to see how your essay might flow one way or another.
4. Freewrite or outline to think through your argument
Is your brain buzzing yet? At this point in the process, it can be helpful to take out a notebook or open a fresh document and dump whatever you’re thinking on the page.
Where should your essay start? What ground-level information do you need to provide your readers before you can dive into the issue?
Use your organized evidence document from step 3 to think through your argument from beginning to end, and determine the structure of your essay.
There are three typical structures for argumentative essays:
- Make your argument and tackle opposition claims one by one, as they come up in relation to the points of your argument - In this approach, the whole essay — from beginning to end — focuses on your argument, but as you make each point, you address the relevant opposition claims individually. This approach works well if your opposition’s views can be quickly explained and refuted and if they directly relate to specific points in your argument.
- Make the bulk of your argument, and then address the opposition all at once in a paragraph (or a few) - This approach puts the opposition in its own section, separate from your main argument. After you’ve made your case, with ample evidence to convince your readers, you write about the opposition, explaining their viewpoint and supporting evidence — and showing readers why the opposition’s argument is unconvincing. Once you’ve addressed the opposition, you write a conclusion that sums up why your argument is the better one.
- Open your essay by talking about the opposition and where it falls short. Build your entire argument to show how it is superior to that opposition - With this structure, you’re showing your readers “a better way” to address the issue. After opening your piece by showing how your opposition’s approaches fail, you launch into your argument, providing readers with ample evidence that backs you up.
As you think through your argument and examine your evidence document, consider which structure will serve your argument best. Sketch out an outline to give yourself a map to follow in the writing process. You could also rearrange your evidence document again to match your outline, so it will be easy to find what you need when you start writing.
5. Write your first draft
You have an outline and an organized document with all your points and evidence lined up and ready. Now you just have to write your essay.
In your first draft, focus on getting your ideas on the page. Your wording may not be perfect (whose is?), but you know what you’re trying to say — so even if you’re overly wordy and taking too much space to say what you need to say, put those words on the page.
Follow your outline, and draw from that evidence document to flesh out each point of your argument. Explain what the evidence means for your argument and your opposition. Connect the dots for your readers so they can follow you, point by point, and understand what you’re trying to say.
As you write, be sure to include:
1. Any background information your reader needs in order to understand the issue in question.
2. Evidence for both your argument and the counterargument(s). This shows that you’ve done your homework and builds trust with your reader, while also setting you up to make a more convincing argument. (If you find gaps in your research while you’re writing, Wordtune Spices can source statistics or historical facts on the fly!)

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. A conclusion that sums up your overall argument and evidence — and leaves the reader with an understanding of the issue and its significance. This sort of conclusion brings your essay to a strong ending that doesn’t waste readers’ time, but actually adds value to your case.
6. Revise (with Wordtune)
The hard work is done: you have a first draft. Now, let’s fine tune your writing.
I like to step away from what I’ve written for a day (or at least a night of sleep) before attempting to revise. It helps me approach clunky phrases and rough transitions with fresh eyes. If you don’t have that luxury, just get away from your computer for a few minutes — use the bathroom, do some jumping jacks, eat an apple — and then come back and read through your piece.
As you revise, make sure you …
- Get the facts right. An argument with false evidence falls apart pretty quickly, so check your facts to make yours rock solid.
- Don’t misrepresent the opposition or their evidence. If someone who holds the opposing view reads your essay, they should affirm how you explain their side — even if they disagree with your rebuttal.
- Present a case that builds over the course of your essay, makes sense, and ends on a strong note. One point should naturally lead to the next. Your readers shouldn’t feel like you’re constantly changing subjects. You’re making a variety of points, but your argument should feel like a cohesive whole.
- Paraphrase sources and cite them appropriately. Did you skip citations when writing your first draft? No worries — you can add them now. And check that you don’t overly rely on quotations. (Need help paraphrasing? Wordtune can help. Simply highlight the sentence or phrase you want to adjust and sort through Wordtune’s suggestions.)
- Tighten up overly wordy explanations and sharpen any convoluted ideas. Wordtune makes a great sidekick for this too 😉

Words to start an argumentative essay
The best way to introduce a convincing argument is to provide a strong thesis statement . These are the words I usually use to start an argumentative essay:
- It is indisputable that the world today is facing a multitude of issues
- With the rise of ____, the potential to make a positive difference has never been more accessible
- It is essential that we take action now and tackle these issues head-on
- it is critical to understand the underlying causes of the problems standing before us
- Opponents of this idea claim
- Those who are against these ideas may say
- Some people may disagree with this idea
- Some people may say that ____, however
When refuting an opposing concept, use:
- These researchers have a point in thinking
- To a certain extent they are right
- After seeing this evidence, there is no way one can agree with this idea
- This argument is irrelevant to the topic
Are you convinced by your own argument yet? Ready to brave the next get-together where everyone’s talking like they know something about intermittent fasting , chicken enclosures , or snow removal policies?
Now if someone asks you to explain your evidence-based but controversial opinion, you can hand them your essay and ask them to report back after they’ve read it.
Share This Article:

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How to Write an Argumentative Essay Introduction: Expert Tips

Argumentative Essay Introduction
Many a time we get into arguments to which we try and convince someone or an audience about a subject or an issue. Through this, we tend to take positions on various subject matters we support.
This can be termed as an argument and so do such essays exist. In fact, argumentative essays account for 7% of the essays that our college essay writers complete on a daily basis. Feel free to hire one of them if you need such help.
Argumentative essays are based on logical analysis, facts, and situations. It means that the debate is for or against something. As a writer, you must try to convince the reader to accept your position of thoughts through facts and evidence.

This guide teaches how to write a good introduction to an argumentative essay for all levels of writing. I will also explain the features of a good introduction for such essays, along with the dos and don’ts.
We will particularly explore the following;
- An argumentative essay introduction.
- Elements of a good argumentative essay.
- Thesis for an introduction in an argumentative essay.
- The number of paragraphs in an introduction of an argumentative essay
- Length of an introduction in an argumentative essay.
First and foremost, have a title that is clear, understandable, and appealing title. Moreover, you have to be comfortable to debate the topic so have enough evidence
The topic should be interesting as long as it has strong points of argument. In case you choose an interesting one without much evidence, your arguments might turn out to be weak.
Let us Write your Essays! No Plagiarism
Get an expert writer to score an A in your next essay assignment. Place your order today, and you will enjoy it.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay Introduction

An introduction welcomes the reader to the essay’s subject matter. A good argumentative essay should:
- Use a language style that is clear and precise with convincing facts.
- Focus on what is essential to explain the point.
- Have evidence that is strong and can be verified.
- Use clearly worded and understandable arguments.
- Have a thesis statement that gives a brief account of the essay.
1. Prepare an Outline of the Importance of the Topic
Here you tell the readers the importance, the reason for reading your argumentative essay, and the purpose of the essay.
It is important that you explore the underlying problem in the essay plus the objectives of the essay. This will go a long way in convincing the reader about the importance of the topic.
2. Write a Good Introduction to begin the Essay
- Ensure you have a background information on the topic.
If the essay is about “The government efforts to combat COVID 19 disease,” begin with the current efforts it is undertaking and ask yourself:
- What has it done?
- Has it been successful?
- What are other governments in the world doing?
These will give the reader the urge to want to know much about the topic.
- In addition, have a clearly defined thesis statement and the position you would like it to take. It should outline all the topic details without creating assumptions draft the thesis well and let it appear in the introduction.
- Do not elaborate or take a stance on your topic in the introduction.

4. The Actual Writing of the Introduction
We all agree to some extent that the toughest part of writing an essay is starting it and as they say first impressions last. If you begin an argumentative essay well, the rest of it will be very easy to write.
The introduction, therefore, gives an indication of what the essay will look like. The following dos and don’ts will help you understand how to write a proper introduction for this essay.
The dos:
- Keep the reader hooked
- Introduce the topic
- Outline the importance of the topic
- Provide the background information
- Present the thesis
- Improper planning
- Presenting arguments
- Long introductions
- Weak thesis statement
- An uninteresting or boring introduction
In the real sense, an introduction provides the topic and draws the attention of the reader prompting them to want more information.
The introduction should therefore have an impact on the reader. This means that after reading the introduction to the argumentative essay, people will want to read the remaining part.
Your introduction should achieve the following:
4. Keep the Reader Hooked
The initial first and second sentences are known as the essay hook.
These sentences create the readers’ interests in the essay eventually gabbing their attention therefore it should therefore be catchy so as to improve your chances of scoring well.
The hook can begin as:
- Personal story
- A statistic
- A rhetoric question
- Introduce a joke
- A shocking fact
- An anecdote
These forms will make your hook attractive thereby roping in the reader.
Write the Topic introduction

This is simply what you are going to write about in the argumentative essay and relates more to your topic. You can learn how to write a good argumentative question and practice some of the examples given in that post.
For instance, if you are writing an argumentative essay on whether corporal punishment should be banned in schools, it is here that you will provide the introduction to your argument, which will set a foundation for your next course of discussion.
5. Provide Background Information
You and your readers must be on the same page. To the readers, it makes it easier for them to understand your arguments.
Since the topic has already been introduced and its importance stated, you can provide the background information and context. The context can be social, political, economic, personal, cultural, geographical, or scientific.
The reader appreciates the role and the position of the writer. Therefore, the background information in an argumentative essay allows for a better understanding of whatever is being presented. It is crucial in arguing and explaining your point.
6. Craft a Good Thesis
This is the most important part of the introduction in an argumentative essay as it presents your stand and justification to the essay by providing it with structure and direction.
The thesis of an argumentative essay should be:
- Clear and precise in explanation of the main argument of the essay
- It should not be a general statement rather, it should be debatable so that it can be agreed or disagreed on
- A thesis should focus solely on the chosen topic therefore it should not be broad or vague.
- It should not go beyond two sentences.
- Debatable, logical, specific and crisp.

Best Professional Essay Writers for Hire: Cheap but Vetted
What to Avoid when writing the Introduction to an Argumentative Essay
Improper planning.
This includes not creating an outline, a plan that creates a structure of the introduction that improves your job. You should therefore create your pointers as you take note of how the introduction will flow.
Presenting Arguments in the Introduction
The introduction is a place to state your main point of argument in the thesis statement. Do not present your arguments here because the readers will not see the need to read your essay further. Therefore do not explain what you will be arguing about.
Weak Thesis Statement
A weak thesis statement is not broad but unreasonable and undebatable. It, therefore, makes the reader not understand the writer’s stand.
It is worth noting that the essay is not about your opinion but the position you are taking through your arguments.
Do not waste time but begin with a sample thesis and then improve it later after writing the entire essay.
Long Introduction
Do not waste words on not-so-important information which might be key in the body of the essay.
Boring and Uninteresting
The essay should not be boring to read at first glance rather the introductory part should be strong and engaging. Do not repeat the instructions or write definitions since they are not required.
Be short, precise, and straight to the point. Since the introduction presents the real issues, provides background, and argues in a logical and intellectual manner.
How to Write a Good Thesis Statement for an Argumentative Essay
This is a sentence or two that provides the main idea and asserts the issue you are writing about in your essay.
It should not reveal what the essay is all about or what you are going to discuss.
Whatever you assert in the thesis is very crucial to your essay so it should be clear and direct so that the reader or the audience does not doubt your point.
The assertiveness is dependent on the type of argumentative essay that is if the argument is classical, present your side of the issue and if it is Rogerian, bring both sides of the issue.
An argumentative thesis takes a stand on an issue and thought you might have your own opinion about the issue or topic in discussion, you should not remind the reader that it is ‘your opinion.’ Readers, therefore, need to disagree with your thesis.
In addition, argumentative thesis statements have words like: ought to, need to be, must, or should.
For instance:
The government should ban further use of plastic bags.
A good thesis for an argumentative essay should:
- Be one or two sentences.
- Vividly present the main idea.
- Announce what the essay is all about.
- Make the audience understand your point since it is the most important sentence.
Characteristics of Thesis Statements in Argumentative Essays
Thesis statements in these essays should be:
1. Debatable
You should come up with a claim which is disagreeable among reasonable people. If a few people disagree with it, then it does not qualify to be an argumentative thesis rather it appears as a fact or a general argument.
2. Assertive
This is all about taking a stand or position by the writer. Quotes, arguments or questions do not qualify as argumentative thesis since they do not give a strong stance on the writer’s point of view.
3. Reasonable
The argumentative thesis should be as logical as possible in its claim. The claims should be possible and reasonable at the same time.
4. Evidence based
The argumentative thesis must be accompanied by evidence. Values, norms, religion, and morals cannot be proven by evidence so they do not qualify as argumentative.
Evidence is important in presenting your point, findings, or argument. In our guide on how to write an introduction to writing issue papers, we found the need to use evidence when need be, and this applies when writing argumentative essay .
5. Narrow and Focused
The thesis statement in this essay should be narrow and focused to the point to make it clearer. The reason for this is that it is easier to provide evidence and be more persuasive than having a general claim. This creates a proper understanding of the essay by the reader.
The three steps in writing a thesis statement in an argumentative essay are:
- Make the topic specific.
- Have a debatable phrase.
- Give the importance to the audience.
In conclusion, as you write the thesis statement:
- Avoid phrases like ‘it seems.’
- Do not turn the thesis into a question.
- Present the thesis in your own words.
- Let the thesis appear at the end of the introduction.
Get a Brilliant Essay today!
Let our essay writing experts help you get that A in your next essay. Place your order today, and you will enjoy the benefits.
Best Length of an Introduction in an Argumentative Essay
The introduction for a five-paragraph argumentative essay should be half a page or a page at most.
If it is for a thousand-word essay, you might have four to five paragraphs on the introduction.
The introduction should have at least 130 words for a normal essay.
It should form about six percent of the entire essay.
- Make the topic specific
- Have a debatable phrase
- Give the importance to the audience
Number of Paragraphs for an Argumentative Essay Introduction
An argumentative essay introduction should have at least three paragraphs which will comprise of:
- The hook which develops the readers’ interest.
- The topic introduction which informs the reader of what the essay is all about together with the background information
- The thesis presentation which provides the main idea about the argumentative essay.
If you follow the above steps and explanations, you will surely have an outstanding introduction to your argumentative essay. You can learn more about the best argumentative essay writers and why you should hire one to do your homework.

With over 10 years in academia and academic assistance, Alicia Smart is the epitome of excellence in the writing industry. She is our managing editor and is in charge of the writing operations at Grade Bees.
Related posts

Pay Someone to Write Essays
How Much to Pay Someone to Write Essays: Tips before Paying

Write Argumentative Questions and Topic
How to Select and Write Argumentative Questions and Topic

Paying for Essay Writing Services Works
Does Paying for Essay Writing Services work? Truths & Myths

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics
How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay Introduction
- College & Higher Education
Related Articles
What does it mean to have an objective tone in an essay, how to write an explanation essay, the importance of writing an effective thesis statement.
- What Are the Four Tips for Writing a Good Thesis Statement for an Expository Essay?
- How to Write a Five-Sentence Paragraph in Middle School
A good introduction in an argumentative essay acts like a good opening statement in a trial. Just like a lawyer, a writer must present the issue at hand, give background, and put forth the main argument -- all in a logical, intellectual and persuasive way.
Start With a Hook
Start your introduction with a sentence that gets the reader interested in the topic. To pique the reader's interest, you can begin with a quote, a personal story, a surprising statistic or an interesting question. For example, if you are arguing that smoking should be banned from all public places, you can start your introduction by referencing a statistic from a verified source: "Tobacco use kills more than five million people every year -- more than HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria combined, according to the World Health Organization." This strategy grabs the reader's attention while introducing the topic of the essay.
Include Background
Providing readers with background on the topic allows them to better understand the issue being presented. This information provides context and history that can be crucial to explaining and arguing your point. For example, if you are arguing that there should never be a military draft in the United States, your introduction can include information about the history of the U.S. draft and the events that led to it being abolished.
State Your Thesis
The thesis is the essence of an argumentative essay. In a single, clear sentence, it sums up what point you are trying to make. The thesis statement should assert a position on a particular issue -- one that a reader can potentially argue against. Therefore, the thesis cannot be a fact. For example, if a professor assigns the general topic of war, you can formulate the following thesis statement: "The United Nations must be redesigned because it is currently incapable of preventing wars." The rest of your essay serves to explain and provide evidence in support of your thesis statement.
What to Leave Out
A good introduction should not be describing arguments or providing analysis that belong in the body paragraphs. Your introduction should introduce and set up your point, rather than lay out evidence to support it. Also, while your intro is a road map for the rest of the essay, you shouldn't explicitly announce what and how you will be arguing: "I am going to prove to you that ..." This type of set up does not add any pertinent information and only serves as filler.
- Utah State University Writing Guide: Introduction and Conclusion
- Purdue University: Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper
Soheila Battaglia is a published and award-winning author and filmmaker. She holds an MA in literary cultures from New York University and a BA in ethnic studies from UC Berkeley. She is a college professor of literature and composition.
How to Write a College Expository Essay
How to write a persuasive essay, teacher tips: how to write thesis statements for high school papers, how to develop and write a paragraph, how to write a higher level essay introduction, how to write an essay for the ged test, how to write a pros & cons essay, important elements in writing argument essays, rhetorical essay format, most popular.
- 1 How to Write a College Expository Essay
- 2 How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 3 Teacher Tips: How to Write Thesis Statements for High School Papers
- 4 How to Develop and Write a Paragraph
- SAT BootCamp
- SAT MasterClass
- SAT Private Tutoring
- SAT Proctored Practice Test
- ACT Private Tutoring
- Academic Subjects
- College Essay Workshop
- Academic Writing Workshop
- AP English FRQ BootCamp
- 1:1 College Essay Help
- Online Instruction
- Free Resources
99 Great Handpicked Ideas for Argumentative Essays
99 argumentative essay ideas.
Bonus Material: 5-step thesis machine and essay checklist
If you want to write a great argumentative essay, then these are the foolproof steps to do it.
Grab this guide to help you craft a strong thesis statement and check that you haven’t forgotten a crucial part of your essay.
Or skip to the bottom for a list of fantastic argumentative essay ideas that have been vetted by a Princeton grad and professional editor who has taught writing at Notre Dame.
Keep reading to learn more about what an argumentative essay is, and how is it different from other types of academic writing? What are the most important features of an effective argumentative essay? How do you write this kind of essay—where should you start, how do you make sure that you have an argument, and what are the most common pitfalls?
In this post we’ll cover:
- What is an academic argumentative essay?
- What are the elements of a good argumentative essay? What are the most common mistakes?
- How do you create an effective thesis for an argumentative essay?
- How do you present your evidence for an academic argumentative essay?
- What are good topics for an argumentative essay?
- Bonus: essential essay checklist + 5-step thesis machine

Bonus: download our 5-step guide to creating a great thesis statement and essential essay checklist .
What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is a common assignment in many high school and college classes. But many students don’t know how to write a great argumentative essay!
In order to avoid some of the most common pitfalls, it’s important to know what this kind of essay is not .
We can divide academic writing into three broad categories:
- Analytical: analyze the tools an author uses to make their point
- Research: delve deeply into a research topic and share your findings
- Persuasive: argue a specific and nuanced position backed by evidence
An argumentative essay falls into the third category. It’s crucial that your essay presents an argument , not just a series of facts or observations!
In elementary or middle school, you may have been assigned a version of this assignment—something like “write a persuasive essay arguing for a bigger allowance from your parents.”
Maybe you wrote a five-paragraph essay explaining why you deserved an allowance for completing your weekly chores, the ways in which your current allowance limited your ability to join your friends in social activities, and examples of some of the educational things you’d spend your increased allowance on.
This is the more mature version of that assignment. The goal is to present a nuanced argument with deep thinking . Often the essay explores an ethical question.

Keep reading to learn our foolproof way of confirming that you have something that’s arguable . Our hand-picked list of 99 essay topics below gives a great starting place!
For example, you might start with the question “is animal testing ethical?”
The idea is not to give a simple yes or no answer, but dig into the complexities of the question. Are there circumstances where it would be okay, but not other circumstances?
Maybe you draw a distinction between animal testing that is part of efforts to find cures for serious human illnesses versus animal testing to develop cosmetics. So instead of just answering yes or no, you give a more nuanced answer.
In this example, you might even further qualify your position. Maybe you think that animal testing for medical research should be subject to careful regulations.
Or maybe you think that only certain animals should be involved in testing. Are tests using fruitflies okay? How about horseshoe crabs? Mice? Dogs? Primates?
How about genetically modifying the animals as part of the testing?
Is animal testing for certain kinds of medical research more ethical than others?
See how there are a lot of different directions you can take this in beyond just “yes” or “no”? This is what will make your writing more mature and interesting!
For an academic argumentative essay, you will then need to support all of your points with evidence from reputable sources (we’ll explore this more below ). Remember, your opinion is a component of the essay, but it’s also supported by evidence.

The skills that you build when you’re writing an academic argumentative essay will be incredibly useful throughout your life. They’re applicable in nearly any job that you can imagine!
According to the National Association of Colleges and Employers , 73.4% of employers want a candidate with strong written communication skills. Writing skills are in high demand for employers in every industry and can be crucial to your future success, even if you’re in a STEM-based career.
Download our 5-step guide to creating a great thesis statement and essential essay checklist .
Download now
Elements of a good argumentative essay
What makes a good academic argumentative essay?
A good argumentative essay should open with an engaging introduction.
A well-crafted introduction makes a smooth funnel that starts more broadly and smoothly zeroes in on the specific argument:
- It begins with some kind of “hook”: this can be an anecdote, quote, statistic, provocative statement, question, etc.
- It gives some background information that is relevant to understand the ethical dilemma or debate
- It has a lead-up to the thesis
- At the end of the introduction, the thesis is clearly stated

Check out examples of great introductions here.
Crucially, a good argumentative essay has a strong, clear thesis.
The thesis should be:
- Arguable: it’s not just the facts—someone could disagree with this position
- Narrow & specific: don’t pick a position that’s so broad you could never back it up
- Complex: show that you are thinking deeply—one way to do this is to consider objections/qualifiers in your thesis
We’ll talk more about how to craft a good thesis below , and you can download our 5-step worksheet to make a great thesis statement.
The body of the essay should have at least three paragraphs.
These be clearly organized, and each paragraph should have a distinct idea. Together, the paragraphs cover all the points raised in the thesis. They should be in a logical order that best supports the argument.
Each paragraph contains:
- Transition from the previous sentence: this can be just a word or phrase, or it can be 1–2 whole sentences
- Topic sentence: the main idea of the paragraph, taken from one “chunk” of your thesis
- Context: introduce your piece of evidence and any relevant background info
- Explanation: explain what the quote/paraphrase means in your own words
- Analysis: analyze how this piece of evidence proves your thesis
- Relate it back to the thesis: don’t forget to relate this point back to your overarching thesis!
- Summarizing sentence: restate topic sentence
Keep reading for more tips on how to use evidence effectively in your essay.
Your essay should also have a conclusion.
The conclusion should summarize your entire argument without being redundant. It should also point to the larger significance of the issue.
So to recap, your essay needs:
- An engaging introduction
- A great thesis statement
- Organized paragraphs with evidence from reputable sources
- A conclusion
Make sure your essay has all of these parts! Download our detailed checklist to make sure your essay avoids the most common mistakes.
To see how all these parts work together, check out our examples of great argumentative essays.

5 steps to develop a great thesis for an argumentative essay
Having a great thesis statement is a make-or-break component of an argumentative essay.
In order to write a great thesis statement for an argumentative essay, use these five steps :
- State the topic ( check out our list of great topics below !)
- Turn it into a debatable issue
- Provide a rationale for your position
- Add qualifier(s) to refine your position
- Reverse your statement to confirm it’s arguable and to anticipate possible counterarguments
(Adapted from Sheridan Baker, The Practical Stylist .)

Using this method with our example of animal testing, we might write:
- The idea: Animal testing
- Your position: Animal testing should only be used in certain circumstances.
- Give a reason for your position: Animal testing causes suffering or injury to animals, which we should avoid as much as possible—but this is outweighed by the enormous potential for scientific discoveries.
- Add nuance and detail to your position: The ethical problems with animal testing are outweighed by the potential to advance cures for both animal and human diseases, but animal testing should be carefully limited to only applications that reduce suffering and disease, not for cosmetic or recreational applications.
- Check that it’s arguable and someone could argue the opposite side: Animal testing causes suffering to animals, which is unethical, and can often be misused for profit.
Download our 5-step worksheet to help guide you through these steps to write a great thesis statement!
How to use evidence in an argumentative essay
Using evidence to support your points is key to making an academic argument.
When you were in elementary or middle school, perhaps you did a version of this assignment with just your own observations and opinions.
When you’re writing a more advanced essay, however, you want to support your ideas with evidence from reputable sources.

One of the big differences between a research paper and an argumentative essay is that you don’t need to do your own original research with primary sources. Original research would be things like running experiments, administering surveys, deciphering ancient inscriptions, interviewing people, or reading archival material.
Instead, you can rely on secondary sources . These are publications of other people’s research or analysis .
For an academic essay, you want to make sure that your secondary sources are reputable .
How do you know a source is reputable? One good indication is that it’s published in a book by a major publisher (like Penguin), especially an academic publisher (like Princeton University Press, Harvard University Press, Oxford University Press, Cambridge University Press. . . basically anything with “university press” in the name!).
Another good kind of source is articles published in major academic journals . Some famous journals are Nature (all science), The Lancet (medicine), and The American Historical Review (history).
More accessible sources might be in other national magazines or newspapers , like The Atlantic, The Economist, or The New York Times.

How do you gather evidence for your essay? When you’re reading sources and taking notes, think:
- What is the author’s main argument? Supporting arguments?
- What specific evidence does the author use to support that argument?
- How does this argument relate to the argument in other sources? Does it agree/disagree or complicate the argument in other sources?
When you’re selecting your evidence, make sure that it directly supports the argument of that paragraph and the essay in general.
Once you have your evidence gathered, you need to analyze it! You can’t just dump evidence on your readers without explaining its significance to your sub-point and your overall argument.
If you’re representing an author’s perspective, or if the quote is especially strong, quote it directly with quote marks: “ ”. As much as you can, try and quote only part of a sentence, and interweave it with your own writing.
The rest of the time, paraphrase the evidence in your own words.
Make sure to cite your sources ! There are lots of different citation styles. Which style is most appropriate will depend on which field you’re working in. Usually your teacher/professor will tell you which one to use. If it’s not clear, it’s always a good question to ask your instructor.
(You still cite when you paraphrase, unless it’s common knowledge that you find in virtually all the sources you read.)

How to write analysis
A balanced essay will have at least two sentences of analysis for every one sentence of direct quotation. For our essay about animal testing, this might look like:
“Whenever possible, animal testing should be avoided. Fortunately, advances in technology have made many alternatives to animal testing possible. For example, the polio vaccine, which has saved millions of human lives, used to be made in the kidney cells of monkeys, which meant that tens of thousands of monkeys died each year to produce the vaccine. However, by the 1970s the live monkeys had been replaced by cells in culture, which meant that many monkey lives were saved (Bookchin and Schumacher, 2005). An added benefit of this newer technique is that it also eliminated the risk of contamination with animal viruses (Taylor, 2019). Similarly, the vaccine against yellow fever used to be checked on live animals, but in the 1970s this was replaced with a cell culture test (World Health Organization, 2007). Scientists have also been able to avoid using animals for testing because our understanding of the diseases themselves has improved. For example, scientists used to perform a “particularly unpleasant” test using mice to check batches of insulin which involved sending mice into convulsions (Taylor, 2019). Since every batch of insulin needed to be tested on 600 mice, tens of thousands of mice were involved in the testing every year in the UK alone. Now, however, scientists know how to measure the components of insulin directly, and the mice are no longer needed (Taylor, 2019). Through these advances in scientific understanding and techniques, researchers have been able to reduce the amount of animal testing without compromising important work for human health.”
You should introduce your evidence by providing some context. Next, present your evidence. Then explain what it means and how it supports your argument.
For a really great paper, you can also show how different sources relate to one another! Use transition words or phrases throughout your paragraphs to guide the reader along your thought process.
Your analysis should be:
- Nuanced and specific
- Takes into account multiple perspectives and ideas; draws distinctions and connections among them
- Backed by evidence all relating back to the argument
For more mature writing, avoid clunky phrases like “On page 12, McKitterick states that. . . ” or “This evidence reveals that. . . ” Instead, try to weave the evidence into your writing seamlessly.
Wondering what this looks like when you put it all together? Check out our examples of great student essays.

Download our 5-step thesis guide
99 great topic ideas for argumentative essays
All of these essay ideas have been vetted by a Princeton grad to confirm that they’re actually arguable . That means that they all would make great starting points for argumentative essays!
Use our foolproof 5-step guide to turn one of these ideas into a great thesis statement!
Student issues
- Should sodas or other unhealthy food be banned at schools?
- Should students hold jobs?
- Should gym class be required?
- Are parents responsible for childhood obesity?
- Should schools require uniforms?
- Should schools have tracking (honors classes, AP classes) or should classes be the same for all students in the same grade?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- Should children be allowed to play sports that have been proven to have a high risk of permanent brain damage from concussions? Is it ethical for adult athletes to be paid to play these sports?
- How much should parents get involved in their child’s physical education? Is it ethical for young athletes to compete at the highest levels? (e.g. Olympic athletes who are under 18 years of age.)
- If social media has been demonstrated to have harmful effects on mental health, should minors have unregulated access to it?
- Should media for children and teens be regulated?
- Should college be free of cost? Should future income be tied to the cost of a college degree?
- Should public preschool be a right for all children?
- Should all students receive free breakfast and lunch at school?
- Should the school day start after 9am?
- Should school libraries ban certain books?
- Is marketing designed for children ethical?
- Should the legal drinking age in the US be lowered to 18?
Animal rights
- Should animal testing be banned?
- Should animals be kept in zoos?
- Is having pets ethical?
- Should wild animals be allowed to be kept as pets?
- Should you adopt a pet from a shelter or buy a specific breed from a breeder?
- Can eating meat be justified?
- Is animal hunting ethical?
Politics and human relations
- Should smoking be illegal? Smoking in public? Smoking around children?
- Should drug possession be decriminalized?
- Should some items be taxed more than others? Is there anything that should be exempt from sales tax?
- Are knock-off fashion “dupes” unethical?
- Should museum items be returned (repatriated) to the country where they were created?
- Should charities and humanitarian aid organizations use images of graphic suffering in their advertising campaigns?
- Is it acceptable to risk harming others in order to benefit one who is clearly in need? For example, is it okay to drive over the speed limit because you need to help someone get to the hospital who is in urgent crisis? What if you cause a crash on the way to the hospital because of dangerous driving?
- Should there be any limits to lawyer-client confidentiality?
- Is the death penalty ever warranted? Should the death penalty exist?
- Is torture ever justified?
- Is it ever right to steal, even if you have a great need?
- Is it unethical to be extremely rich?
- Should unpaid internships be legal?
- Should companies be required to meet diversity quotes for their hiring practices?
- Should parental leave be equal for all parents, regardless of who gives birth?
- Should the minimum wage be raised?
- Can war be ethical?
- Should nuclear weapons be banned globally?
- Should all new cars be electric?
- Should we impose population controls? Should people have children, if that greatly increases one’s carbon footprint?
- Should countries that produce disproportionate carbon emissions and other environmental damage have to help other countries with the effects of climate change?
- Should individuals be able to sue the government when the government has failed to provide a basic standard of living?
- Should we invest in military weapons development?
- Should we land machines, or humans, on planets, comets or other extraterrestrial bodies in order to study them?
- Should we explore space colonization?
- If people engage in risky behaviors, should they be charged a fine if they need to be rescued? (For example, swimming in the ocean at night while drunk.)
- Should we distribute universal income?
- How much control should the state have on the press?
- Should law enforcement be able to work undercover? Is working undercover deception?
- Should law enforcement be able to use tracking data from phones?
- Should people serving prison sentences be allowed to vote?
- Should gender quotas be used in government elections?
- Can modern societies still be held accountable for what their nation did in the past?
- Should public transit be free?
- Should social media companies be regulated?
- Should everyone have access to the internet for free?
- Should elections be decided by popular vote? Should citizens over age 18 be legally required to vote?
- Should certain kinds of speech on social media be banned?
Tech, AI, and data
- Should tech devices come with an addiction warning label?
- Will AI help the world or hurt it?
- Should there be financial penalties for buying soda or other unhealthy foods?
- Do people have a right to privacy online?
- Should our data be used to determine insurance policies or legal consequences? For example, should we create a diabetic insulin implant that could notify your doctor or insurance company when you make poor diet choices, and should that decision make you ineligible for certain types of medical treatment? Should cars be equipped to monitor speed and other measures of good driving, and should this data be subpoenaed by authorities following a crash?
- Should law enforcement be able to access someone’s online data or phone with a warrant?
- Can hacking ever be morally justified?
Medical ethics
- Is healthcare a fundamental human right? Should universal healthcare be free?
- In cases of terminal illness, do you think that a patient should be able to request medically assisted suicide?
- Should terminally ill patients who have exhausted all approved drug therapies be able to access drugs that have not been approved for sale by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (commonly called “ Right to Try ”)?
- Under what conditions should people be kept artificially alive?
- How should we decide who receives organ transplants? Is it ethical to de-prioritize a transplant candidate who smokes cigarettes, for example?
- Should there be any limits to doctor-patient confidentiality?
- Is it ethical for medical study participants to be financially compensated?
- Is it ethical for blood, plasma, or bone marrow donors to be financially compensated?
- Should uninsured patients be offered free clinical trials ?
- Is it ethical for individuals who donate genetic material for fertility purposes (e.g. egg or sperm donors) to be financially compensated?
- Should vaccines and medications be patented? Should individuals or corporations be able to profit from vaccines and medications?
- Should individuals or corporations be able to profit from healthcare?
- Is plastic surgery ethical?
- Should vaccinations be mandatory for everyone?
- Should medical personnel collect healthy tissues of a deceased person without their consent?
- What are the ethics of extremely expensive medical treatments? What if the treatment is not curative, but only extends life for a few more months?
- As medical data becomes increasingly less “non-identifiable”—i.e. with AI, bigger data, and increasing knowledge of genetics it is less possible to guarantee that research study participants will remain anonymous—what are the ethical implications?
- Now that whole genome sequencing allows prospective parents to check the risks of conceiving children, what are the ethical obligations for the best interests of future possible children on the part of the prospective parents? If you know that your children will inherit a serious disease, should you have biological children? Should social policies govern such decisions? Should those policies protect parental procreative liberty or enhance social responsibility for the best interests of those future possible children?
- Is it ethical to collect extra samples from a patient (for example, an extra vial of blood) before obtaining consent to be enrolled in a study? (Assume that in this scenario the sample would be discarded if the patient declines to enroll in the study.)
- If, in the course of an unrelated medical or scientific study, a genetic predisposition to a certain illness or condition is discovered, should the study participant be notified? Does it matter if the findings are medically actionable or not? For example, “In a specific study, researchers were performing NGS on tissue banked samples of healthy controls and colon cancer patients to validate an assay. The use of healthy controls in a study like this is not uncommon; however, what happens if one of the healthy controls tests positive for a mutation that predisposes to colon cancer using an unvalidated research assay? The samples were obtained from a tissue bank and the researchers were unclear about what the informed consent stated about returning incidental findings, raising the question whether to contact the subject and if contact is attempted, how to do it.”
- Should parents decide medical treatment for their children? Should parents be allowed to opt out of medically-advised treatment because of personal beliefs?
- Should parents who are researchers be able to enroll their own children in their research study ?
- Should DNA be used for genealogical research?
- Should we create synthetic forms of life ? Should we let them loose in the world?
- Should we use geo-engineering to attempt to combat global warming?
- Should we create genetically-modified organisms (like food crops)?
- Should we resurrect extinct species?
- If we had the ability to eliminate aberrant thought patterns and enforce social conformity through technological or pharmacological means, would it be the right thing to do? Or do people have an inalienable right to be themselves, provided they pose no immediate risk to themselves or others?
- Are human enhancements ethical? Pharmaceutical, surgical, mechanical and neurological enhancements are already available for therapeutic purposes. But these same enhancements can be used to magnify human biological function beyond the societal norm. Where do we draw the line between therapy and enhancement? How do we justify enhancing human bodies when so many individuals still lack access to basic therapeutic medicine? Should neuro-enhancing drugs be legal? Is it ethical to improve memory functions with brain stimulation?
Bonus: download the essential essay checklist + 5-step thesis machine
Working on writing your own essay?
Grab our handy checklist to make sure that your essay has everything it needs! It also comes with our foolproof 5-step worksheet for creating great thesis statements every time.

Emily graduated summa cum laude from Princeton University and holds an MA from the University of Notre Dame. She was a National Merit Scholar and has won numerous academic prizes and fellowships. A veteran of the publishing industry, she has helped professors at Harvard, Yale, and Princeton revise their books and articles. Over the last decade, Emily has successfully mentored hundreds of students in all aspects of the college admissions process, including the SAT, ACT, and college application essay.
CHECK OUT THESE RELATED POSTS

7 Qualities of a Successful College Essay
May 1, 2021
What makes a college application essay successful? We've analyzed many essays of applicants admitted to Ivy League institutions and here are the results!

5 Ways to Structure Your College Essay
May 18, 2020
A successful college essay begins with a compelling structure. Here are 5 sample college essay structures with actual examples from essays that worked.

6 Tips for Choosing That Winning College Essay Topic
You've done the brainstorming. Now how do you choose the college essay topic that will result in a successful piece? Our 6 tips will help.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
52 Argumentative Essay Ideas that are Actually Interesting
What’s covered:, how to pick a good argumentative essay topic, elements of a strong argumentative essay, argumentative essay idea example topics.
Are you having writer’s block? Coming up with an essay topic can be the hardest part of the process. You have very likely encountered argumentative essay writing in high school and have been asked to write your own. If you’re having trouble finding a topic, we’ve created a list of 52 essay ideas to help jumpstart your brainstorming process! In addition, this post will cover strategies for picking a topic and how to make your argument a strong one. Ultimately, the goal is to convince your reader.
An argumentative essay tasks the writer with presenting an assertion and bolstering that assertion with proper research. You’ll present the claim’s authenticity. This means that whatever argument you’re making must be empirically true! Writing an argumentative essay without any evidence will leave you stranded without any facts to back up your claim. When choosing your essay topic, begin by thinking about themes that have been researched before. Readers will be more engaged with an argument that is supported by data.
This isn’t to say that your argumentative essay topic has to be as well-known, like “Gravity: Does it Exist?” but it shouldn’t be so obscure that there isn’t ample evidence. Finding a topic with multiple sources confirming its validity will help you support your thesis throughout your essay. If upon review of these articles you begin to doubt their worth due to small sample sizes, biased funding sources, or scientific disintegrity, don’t be afraid to move on to a different topic. Your ultimate goal should be proving to your audience that your argument is true because the data supports it.
The hardest essays to write are the ones that you don’t care about. If you don’t care about your topic, why should someone else? Topics that are more personal to the reader are immediately more thoughtful and meaningful because the author’s passion shines through. If you are free to choose an argumentative essay topic, find a topic where the papers you read and cite are fun to read. It’s much easier to write when the passion is already inside of you!
However, you won’t always have the choice to pick your topic. You may receive an assignment to write an argumentative essay that you feel is boring. There is still value in writing an argumentative essay on a topic that may not be of interest to you. It will push you to study a new topic, and broaden your ability to write on a variety of topics. Getting good at proving a point thoroughly and effectively will help you to both understand different fields more completely and increase your comfort with scientific writing.
Convincing Thesis Statement
It’s important to remember the general essay structure: an introduction paragraph with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. A strong thesis statement will set your essay up for success. What is it? A succinct, concise, and pithy sentence found in your first paragraph that summarizes your main point. Pour over this statement to ensure that you can set up your reader to understand your essay. You should also restate your thesis throughout your essay to keep your reader focused on your point.
Ample Research
A typical argumentative essay prompt may look like this: “What has been the most important invention of the 21st century? Support your claim with evidence.” This question is open-ended and gives you flexibility. But that also means it requires research to prove your point convincingly. The strongest essays weave scientific quotes and results into your writing. You can use recent articles, primary sources, or news sources. Maybe you even cite your own research. Remember, this process takes time, so be sure you set aside enough time to dive deep into your topic.
Clear Structure
If the reader can’t follow your argument, all your research could be for nothing! Structure is key to persuading your audience. Below are two common argumentative essay structures that you can use to organize your essays.
The Toulmin argument and the Rogerian argument each contain the four sections mentioned above but executes them in different ways. Be sure to familiarize yourself with both essay structures so that your essay is the most effective it can be.
The Toulmin argument has a straightforward presentation. You begin with your assertion, your thesis statement. You then list the evidence that supports your point and why these are valid sources. The bulk of your essay should be explaining how your sources support your claim. You then end your essay by acknowledging and discussing the problems or flaws that readers may find in your presentation. Then, you should list the solutions to these and alternative perspectives and prove your argument is stronger.
The Rogerian argument has a more complex structure. You begin with a discussion of what opposing sides do right and the validity of their arguments. This is effective because it allows you to piece apart your opponent’s argument. The next section contains your position on the questions. In this section, it is important to list problems with your opponent’s argument that your argument fixes. This way, your position feels much stronger. Your essay ends with suggesting a possible compromise between the two sides. A combination of the two sides could be the most effective solution.
- Is the death penalty effective?
- Is our election process fair?
- Is the electoral college outdated?
- Should we have lower taxes?
- How many Supreme Court Justices should there be?
- Should there be different term limits for elected officials?
- Should the drinking age be lowered?
- Does religion cause war?
- Should the country legalize marijuana?
- Should the country have tighter gun control laws?
- Should men get paternity leave?
- Should maternity leave be longer?
- Should smoking be banned?
- Should the government have a say in our diet?
- Should birth control be free?
- Should we increase access to condoms for teens?
- Should abortion be legal?
- Do school uniforms help educational attainment?
- Are kids better or worse students than they were ten years ago?
- Should students be allowed to cheat?
- Is school too long?
- Does school start too early?
- Are there benefits to attending a single-sex school?
- Is summer break still relevant?
- Is college too expensive?
Art / Culture
- How can you reform copyright law?
- What was the best decade for music?
- Do video games cause students to be more violent?
- Should content online be more harshly regulated?
- Should graffiti be considered art or vandalism?
- Should schools ban books?
- How important is art education?
- Should music be taught in school?
- Are music-sharing services helpful to artists?
- What is the best way to teach science in a religious school?
- Should fracking be legal?
- Should parents be allowed to modify their unborn children?
- Should vaccinations be required for attending school?
- Are GMOs helpful or harmful?
- Are we too dependent on our phones?
- Should everyone have internet access?
- Should internet access be free?
- Should the police force be required to wear body cams?
- Should social media companies be allowed to collect data from their users?
- How has the internet impacted human society?
- Should self-driving cars be allowed on the streets?
- Should athletes be held to high moral standards?
- Are professional athletes paid too much?
- Should the U.S. have more professional sports teams?
- Should sports be separated by gender?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- What are the best ways to increase safety in sports?
Where to Get More Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original argumentative essay ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write an Introduction for a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: October 2, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Gale McCreary and by wikiHow staff writer, Kyle Hall . Gale McCreary is the Founder and Chief Coordinator of SpeechStory, a nonprofit organization focused on improving communication skills in youth. She was previously a Silicon Valley CEO and President of a Toastmasters International chapter. She has been recognized as Santa Barbara Entrepreneurial Woman of the Year and received Congressional recognition for providing a Family-Friendly work environment. She has a BS in Biology from Stanford University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 150,640 times.
A persuasive speech is meant to convince an audience to agree with your point of view or argument relating to a specific topic. While the body of your persuasive speech is where the bulk of your argument will go, it’s important that you don’t overlook the introduction. A good introduction will capture your audience’s attention, which is crucial if you want to persuade them. Fortunately, there are some simple rules you can follow that will make the introduction to your persuasive essay more engaging and memorable.
Organizing Your Introduction

- For example, if your speech is about sleep deprivation in the workplace, you could start with something like “Workplace accidents and mistakes related to sleep deprivation cost companies $31 billion every single year.”
- Or, if your speech is about animal rights, you could open with a quote like “The English philosopher Jeremy Bentham once said, ‘The question is not, Can they reason? Nor, Can they talk? But, Can they suffer?’”
- For a speech about unpaid internships, you could start with a relevant anecdote like “In 2018, Tiffany Green got her dream internship, unpaid, working for a rental company. Unfortunately, a few months later Tiffany returned home from work to find an eviction notice on the door of her apartment, owned by that same rental company, because she was unable to pay her rent.

- For example, your thesis statement could look something like “Today, I’m going to talk to you about why medical marijuana should be legalized in all 50 states, and I’ll explain why that would improve the lives of average Americans and boost the economy.”

- For example, if you’re a marine biologist who’s writing a persuasive speech about ocean acidification, you could write something like “I’ve studied the effects of ocean acidification on local marine ecosystems for over a decade now, and what I’ve found is staggering.”
- Or, if you’re not an expert on your topic, you could include something like “Earlier this year, renowned marine biologist Ayana Elizabeth Johnson published a decade-long study on the acidification of our oceans, and what she found is deeply concerning.”

- For example, you could sum up your conclusion by writing something like, “To show you that a shorter work week would benefit not only employees but also their employers, first I will touch on the history of the modern average work week. Then, I’ll discuss the mental and physical toll that a long work week can take on a person. Finally, I’ll wrap up by going over fairer, better systems that we as a society could implement.”

- For example, if you time yourself giving your speech (introduction included) and it takes you 5 minutes, your introduction should only take up about 45 seconds of your speech.
- However, if you were giving a speech that’s 20 minutes long, your introduction should be around 3 minutes.
- On average, you’ll want about 150 words for every 1 minute you need to speak for. For example, if your introduction should be 2 minutes, you’d want to write around 300 words.
Tip: If you know how long your speech is going to be before you write it, make the first draft of your introduction the right length so you don’t have to add or delete a lot later.
Polishing Your Writing

- To make your writing more conversational, try to use brief sentences, and avoid including jargon unless you need it to make your point.
- Using contractions, like “I’ll” instead of “I will,” “wouldn’t” instead of “would not,” and “they’re” instead of “they are,” can help make your writing sound more conversational.

Tip: An easy way to make your writing more concise is to start your sentences with the subject. Also, try to limit the number of adverbs and adjectives you use.

- For example, if your audience will be made up of the other students in your college class, including a pop culture reference in your introduction might be an effective way to grab their attention and help them relate to your topic. However, if you’re giving your speech in a more formal setting, a pop culture reference might fall flat.

- For example, you could write something like, “I know a lot of you may strongly disagree with me on this. However, I think if you give me a chance and hear me out, we might end up finding some common ground.”
- Or, you could include a question like “How many of you here tonight have ever come across plastic that's washed up on the beach?” Then, you can have audience members raise their hands.

- You can even record yourself reading your introduction to get a sense of how you'll look delivering the opening of your speech.
Example Introduction for a Persuasive Speech

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/chapter/11-2-persuasive-speaking/
- ↑ https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/public-speaking-practice-and-ethics/s12-introductions-matter-how-to-be.html
- ↑ https://www.middlesex.mass.edu/ace/downloads/tipsheets/persvsargu.pdf
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/14-1-four-methods-of-delivery/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/speechlab/connecting-with-the-audience-26.htm
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/speechlab/practicing-presentations-33.htm
About This Article

To write an introduction for a persuasive speech, start with a hook that will grab your audience's attention, like a surprising statistic or meaningful quote. Then, introduce your thesis statement, which should explain what you are arguing for and why. From here, you'll need to demonstrate the credibility of your argument if you want your audience to believe what you're saying. Depending on if you are an expert or not, you should either share your personal credentials or reference papers and studies by experts in the field that legitimize your argument. Finally, conclude with a brief preview of the main points you'll cover in your speech, so your audience knows what to expect and can follow along more easily. For more tips from our co-author, including how to polish your introduction, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Jun 6, 2021
Noela Ebaneck
Dec 30, 2019
Imani Wilson
May 12, 2019
Mila Del Giudice
Nov 24, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
73 Essay Hook Examples

An essay hook is the first one or two sentences of your essay that are used to grab the reader’s attention and draw them into your discussion.
It is called a hook because it “grabs” the reader and doesn’t let them go! It should have something in there that makes the reader feel curious and intrigued, compelling them to continue reading.
Techniques for Good Essay Hooks
Here are a few techniques that you can use to write a good essay hook:
- Use a Quotation : Sometimes, a relevant quotation from a well-known author or expert can help establish the context or theme of your essay. Next time you’re conducting research for an essay, keep an eye out for a really compelling quote that you could use as your hook for that essay.
- Start with a Statement that is Surprising or Unusual: A surprising or unusually statement will draw a reader in, making them want to know more about that topic. It’s good if the statement contradicts common knowledge or reveals an insight about your topic that isn’t immediately obvious. These can be particularly good for argumentative essays where you’re putting forward a controversial or compelling argument as your thesis statement .
- Tell a Brief Anecdote : A short, interesting story related to your topic can personaize the story, making it more than just a dry essay, and turning it into a compelling narrative that’s worth reading.
- Use Statistics or Facts: Interesting, surprising, or shocking facts or statistics work similarly to surprising statements: they make us want to know more about a topic. Statistics and facts in your introductions are particularly useful for analytical, expository , and argumentative essays.
- Start with a Question: Questions that make the reader think deeply about an issue, or pose a question that the reader themselves has considered, can be really effecitve. But remember, questions tend to be better for informal and personal essays, and are generally not allowed in formal argumentative essays. If you’re not sure if you’re allowed to use questions in your essays, check with your teacher first.
Below, I’ll present some examples of hooks that you could use as inspiration when writing your own essay hook.
Essay Hook Examples
These examples might help stimulate your thinking. However, keep in mind that your essay hook needs to be unique to your essay, so use these as inspiration but write your own essay hook that’s perfect for your own essay.
1. For an Essay About Yourself
An essay about yourself can be personal, use “I” statements, and include memories or thoughts that are deeply personal to you.
- Question: “Have you ever met someone who could turn even the most mundane events into a thrilling adventure? Let me introduce myself.”
- Anecdote: “The smell of freshly baked cookies always takes me back to the day when I accidentally started a baking business at the age of nine.”
- Intriguing Statement: “I’ve always believed that you haven’t truly lived until you’ve read a book upside down, danced in the rain, or taught a parrot to say ‘I love pizza.'”
- Quotation: “As Mark Twain once said, ‘The secret of getting ahead is getting started.’ That’s a philosophy I’ve embraced in every aspect of my life.”
- Humorous Statement: “I’m a self-proclaimed ‘professional chocolate tester’ – a title that’s not only delicious but also requires extreme dedication.”
- Start with your Mission Statement : “My life motto is simple but powerful: be the person who decided to go for it.
- Fact or Statistic: “According to a study, people who speak more than one language tend to be better at multitasking . As a polyglot, I certainly live up to that statistic.”
- Comparison or Metaphor: “If my life were a book, it would be a blend of an adventurous novel, a suspense thriller, and a pinch of romantic comedy.”
- Personal Revelation: “Ever since I was a child, I’ve had an uncanny ability to communicate with animals. It’s an unusual skill, but one that has shaped my life in many ways.”
- Narrative: “The day everything changed for me was an ordinary Tuesday. Little did I know, a single conversation would lead me to discover my true passion.”
2. For a Reflective Essay
A reflective essay often explores personal experiences, feelings, and thoughts. So, your hooks for reflective essays can usually be more personal, intriguing, and engaging than other types of essays. Here are some examples for inspiration:
- Question: “Have you ever felt as though a single moment could change your entire life? This essay is going to explore that moment for me.”
- Anecdote: “I was standing on the edge of the Grand Canyon, looking at the vast emptiness, and for the first time, I truly understood the word ‘perspective’.”
- Bold Statement: “There is a part of me that is still trapped in that room, on that rainy afternoon, holding the letter that would change everything.”
- Personal Revelation: “The first time I truly felt a sense of belonging wasn’t in a crowded room full of friends, but in the quiet solitude of a forest.”
- Intriguing Statement: “In my life, silence has been a teacher more profound than any words could ever be.”
- Quotation: “Einstein once said, ‘The only source of knowledge is experience.’ Now, looking back, I realize how profound that statement truly is.”
- Comparison or Metaphor: “If my life is a tapestry, then that summer was the vibrant thread that changed the entire pattern.”
- Narrative: “As the train pulled out of the station, I realized I wasn’t just leaving my hometown, I was leaving my old self behind.”
- Philosophical Statement: “In the theater of life, we are both the actor and the audience, playing our part and watching ourselves simultaneously.”
- Emotive Statement: “There is a sort of sweet sorrow in remembering, a joy tinged with a hint of sadness, like the last notes of a beautiful song.”
For an Argumentative Essay
Essay hooks for argumentative essays are often the hardest. This type of essay tends to require the most formal type of academic writing, meaning your hook shouldn’t use first person, and should be more based on fact and objectivity, often at the expense of creativity. Here are some examples.
- Quotation: “Thomas Jefferson once said, ‘Whenever the people are well-informed, they can be trusted with their own government.’ If Jefferson were alive today, he would likely feel that this meed for a well-informed citizenry is falling well short of where he would aspire.”
- Provocative Statement: “Despite what romantic films may portray, love at first sight is merely a myth perpetuated by society. This essay will prosecute the argument that love at first sight is a myth.”
- Statistical Fact: “According to the World Health Organization, depression is the leading psychological disability worldwide. Yet, mental health is still stigmatized and often overlooked. This essay will argue that depression should be seen as a health issue, and stigmatization of depression causes serious harm to society.”
- Comparison: “Much like an unchecked infection, climate change, if left ignored, can spread far beyond what it is today, causing long-term economic and social problems that may even threaten the longevity of humanity itself.”
- Contradiction : “While we live in an era of unprecedented technological advancements, millions around the world are still denied basic internet access.”
- Bold Declaration: “Animal testing is not only ethically unacceptable, but it also undermines the progress of medical research.”
- Challenging Belief: “Despite popular belief, the automation of jobs is not a threat but an opportunity for society to evolve.”
- Quotation: “George Orwell wrote in ‘1984’, ‘Big Brother is Watching You.’ In our modern society, with the advancement of technology, this is becoming more of a reality than fiction.”
- Intriguing Statement: “Despite countless diet fads and fitness trends, obesity rates continue to rise. This argumentative essay will argue that this is because medical practitioners’ approaches to health and weight loss are fundamentally flawed.”
- Statistical Fact: “Research reveals that over 90% of the world’s plastic waste is not recycled. This alarming figure calls for a drastic change in social attitudes towards consumption and waste management.”
- Challenging Assumption: “Society often assumes that progress and growth are intrinsically good, but this is not always the case in the realm of economic development.”
- Contradiction: “Western society upholds the value of freedom, yet every day, members of society cede personal liberties in the name of convenience and security.”
- Analogy: “Like an overplayed song, when a news story is repeated too often, it loses its impact. In the era of digital media, society is becoming desensitized to critical issues.”
- Relevant Anecdote: “In a village in India, the arrival of a single computer transformed the lives of the residents. This small anecdote underscores the importance of digital inclusion in today’s world.”
- Call to Rethink: “In a world where success is often equated with financial wealth, it is time for society to reconsidered what truly constitutes a successful life.”
For a Compare and Contrast Essay
A compare and contrast essay examines two issues, looking at both the similarities and differences between them. A good hook for a compare and contrast essay will immediately signal to the reader the subjects that are being compared and why they’re being compared. Here are sine ideas for hooks for a compare and contrast essay:
- Quotation: “As Charles Dickens wrote in his novel ‘A Tale of Two Cities’, ‘It was the best of times, it was the worst of times’. This could equally apply to the contrasting dynamics of urban and rural living.”
- Provocative Statement: “Despite popular belief, cats and dogs have more in common than society tends to think.”
- Comparison: “Comparing being an only child to growing up with siblings is like contrasting a solo performance with an orchestral symphony.”
- Contradiction: “While many view classic literature and contemporary fiction as worlds apart, they are more akin to two sides of the same coin.”
- Bold Declaration: “Android and iPhone may compete in the same market, but their philosophies could not be more different.”
- Statistical Fact: “Statistics show that children who grow up reading books tend to perform better academically than those who do not. But, the jury is out on how reading traditional books compares to reading e-books on screens.”
- Quotation: “As Robert Louis Stevenson once wrote, ‘Sooner or later, we all sit down to a banquet of consequences.’ This statement can be used to frame a comparison between short-term and long-term thinking.”
- Provocative Statement: “Democracy and dictatorship are often seen as polar opposites, but are they are not as different as they seem.”
- Comparison: “Climate change and plastic pollution are two major environmental issues, yet they demand different approaches and solutions.”
- Contradiction: “While traditional classrooms and online learning are seen as separate modes of education, they can often blend into a cohesive learning experience.”
- Bold Declaration: “Though both based on merit, the structures of capitalism and socialism lead to vastly different societal outcomes.”
- Imagery: “The painting styles of Van Gogh and Monet can be contrasted as a stormy sea versus a tranquil pond.”
- Historical Reference: “The philosophies of the Cold War-era – capitalism and communism – provide a lens to contrast economic systems.”
- Literary Comparison: “The dystopian societies portrayed in George Orwell’s ‘1984’ and Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World’ serve as contrasting visions of the future.”
- Philosophical Question: “Individualism and collectivism shape societies in distinct ways, but neither one can truly exist without the other.”
See Here for my Guide on Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay
For a Psychology Essay
Writing an engaging hook for a psychology essay involves sparking the reader’s interest in the human mind, behavior, or the specific psychology topic you’re discussing. Here are some stimulating hooks for a psychology essay:
- Rhetorical Question: “How much control do we truly have over our own actions?”
- Quotation: “Sigmund Freud once said, ‘Unexpressed emotions will never die. They are buried alive and will come forth later in uglier ways.’ This essay will explore whether this is universally true.”
- Provocative Statement: “Contrary to popular belief, ‘venting out’ anger might actually be fueling the fire of fury.”
- Comparison: “Just as an iceberg reveals only a fraction of its bulk above water, conscious minds may only be a small piece of who humans truly are.”
- Contradiction: “While it may seem counterintuitive, studies show that individuals who are more intelligent are also more likely to suffer from mental health issues.”
- Bold Declaration: “Despite advances in technology, understanding the human brain remains one of the final frontiers in science.”
- Statistical Fact: “According to a study by the American Psychological Association, nearly one in five adults in the U.S. lives with a mental illness. Yet, mental health continues to be a topic shrouded in stigma.”
For a Sociology Essay
Writing an engaging hook for a sociology essay involves sparking the reader’s interest in social behaviors, cultural phenomena, or the specific sociology topic you’re discussing. Here are ideas for hooks for a sociology essay:
- Quotation: “As Karl Marx once noted, ‘Social progress can be measured exactly by the social position of the fair sex.’ Sadly, society has not made much progress in gender equality.”
- Provocative Statement: “Social media, initially created to connect people, is ironically leading society into an era of unprecedented isolation.”
- Comparison: “Comparing society to a theater, where each individual plays a role, it is possible to start to see patterns and scripts embedded in daily interactions.”
- Contradiction: “While people often believe that technology is bringing society closer together, evidence suggests that it’s actually driving a wedge between people, creating ‘digital divides’.”
- Bold Declaration: “Human societies are constructed on deeply ingrained systems of inequality, often invisible to those benefiting from them.”
- Statistical Fact: “A recent study found that women still earn only 81 cents for every dollar earned by men. This stark wage gap raises questions about equality in the workforce.”
For a College Application Essay
A college essay is a personal statement where you can showcase who you are beyond your grades and resume. It’s your chance to tell your unique story. Here are ten potential hooks for a college essay:
- Anecdote: “At the age of seven, with a wooden spoon as my baton, I confidently conducted an orchestra of pots and pans in my grandmother’s kitchen.”
- Provocative Statement: “I believe that life is like a game of chess. The king might be the most important piece, but it’s the pawns that can change the entire course of the game.”
- Personal Revelation: “It wasn’t until I was lost in a foreign city, armed with nothing but a map in a language I didn’t understand, that I truly discovered my love for adventure.”
- Intriguing Question: “Have you ever wondered how it feels to be part of two completely different cultures, yet wholly belong to neither?”
- Bold Declaration: “Breaking a bone can be a painful experience. Breaking stereotypes, however, is an entirely different kind of challenge.”
- Unusual Fact: “I can recite the periodic table backwards while juggling three tennis balls. It’s a strange talent, but it’s a perfect metaphor for how I tackle challenges.”
- Quotation: “As Albert Einstein once said, ‘Imagination is more important than knowledge.’ This quote has defined my approach to learning.”
- Narrative: “It was a cold winter’s day when I first discovered the magic of turning a blank page into a world full of characters, stories, and ideas.”
- Metaphor: “Like a caterpillar transforming into a butterfly, my high school years have been a period of profound metamorphosis.”
- Humorous Statement: “Being the youngest of five siblings, I quickly learned that the best way to be heard was to become the family’s unofficial lawyer.”
Conclusion: The Qualities of a Good Essay Hook
As I wrap up this article, I want to share a few last tips on qualities that a good essay hook should have. Keep these tips in mind when writing your essay hook and using the above essay hook examples:
First, relevance . A good hook should be directly relevant to the topic or theme of your essay. The hook should provide a preview of what’s to come without giving too much away.
Second, Intrigue. A great hook should make the reader want to continue reading. It should create a question in the reader’s mind or present a fascinating idea that they want to know more about.
Third, uniqueness. An effective hook should be original and unique. It should stand out from the many other essays that the reader might be going through.
Fourth, clarity. Even though a hook should be captivating and original, it should also be clear and easy to understand. Avoid complex sentences and jargon that might confuse the reader.
Fifth, genre conventions. Too often, my students try to be so creative in their essay hooks that they forget genre conventions . The more formal an essay, the harder it is to write the hook. My general approach is to focus on statistics and facts, and avoid rhetorical questions , with more formal essay hooks.
Keep in mind that you should run your essay hook by your teacher by showing them your first draft before you submit your essay for grading. This will help you to make sure it follows genre conventions and is well-written.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Supreme Court Got It Wrong: Abortion Is Not Settled Law

By Melissa Murray and Kate Shaw
Ms. Murray is a law professor at New York University. Ms. Shaw is a contributing Opinion writer.
In his majority opinion in the case overturning Roe v. Wade, Justice Samuel Alito insisted that the high court was finally settling the vexed abortion debate by returning the “authority to regulate abortion” to the “people and their elected representatives.”
Despite these assurances, less than two years after Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, abortion is back at the Supreme Court. In the next month, the justices will hear arguments in two high-stakes cases that may shape the future of access to medication abortion and to lifesaving care for pregnancy emergencies. These cases make clear that Dobbs did not settle the question of abortion in America — instead, it generated a new slate of questions. One of those questions involves the interaction of existing legal rules with the concept of fetal personhood — the view, held by many in the anti-abortion movement, that a fetus is a person entitled to the same rights and protections as any other person.
The first case , scheduled for argument on Tuesday, F.D.A. v. Alliance for Hippocratic Medicine, is a challenge to the Food and Drug Administration’s protocols for approving and regulating mifepristone, one of the two drugs used for medication abortions. An anti-abortion physicians’ group argues that the F.D.A. acted unlawfully when it relaxed existing restrictions on the use and distribution of mifepristone in 2016 and 2021. In 2016, the agency implemented changes that allowed the use of mifepristone up to 10 weeks of pregnancy, rather than seven; reduced the number of required in-person visits for dispensing the drug from three to one; and allowed the drug to be prescribed by individuals like nurse practitioners. In 2021, it eliminated the in-person visit requirement, clearing the way for the drug to be dispensed by mail. The physicians’ group has urged the court to throw out those regulations and reinstate the previous, more restrictive regulations surrounding the drug — a ruling that could affect access to the drug in every state, regardless of the state’s abortion politics.
The second case, scheduled for argument on April 24, involves the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (known by doctors and health policymakers as EMTALA ), which requires federally funded hospitals to provide patients, including pregnant patients, with stabilizing care or transfer to a hospital that can provide such care. At issue is the law’s interaction with state laws that severely restrict abortion, like an Idaho law that bans abortion except in cases of rape or incest and circumstances where abortion is “necessary to prevent the death of the pregnant woman.”
Although the Idaho law limits the provision of abortion care to circumstances where death is imminent, the federal government argues that under EMTALA and basic principles of federal supremacy, pregnant patients experiencing emergencies at federally funded hospitals in Idaho are entitled to abortion care, even if they are not in danger of imminent death.
These cases may be framed in the technical jargon of administrative law and federal pre-emption doctrine, but both cases involve incredibly high-stakes issues for the lives and health of pregnant persons — and offer the court an opportunity to shape the landscape of abortion access in the post-Roe era.
These two cases may also give the court a chance to seed new ground for fetal personhood. Woven throughout both cases are arguments that gesture toward the view that a fetus is a person.
If that is the case, the legal rules that would typically hold sway in these cases might not apply. If these questions must account for the rights and entitlements of the fetus, the entire calculus is upended.
In this new scenario, the issue is not simply whether EMTALA’s protections for pregnant patients pre-empt Idaho’s abortion ban, but rather which set of interests — the patient’s or the fetus’s — should be prioritized in the contest between state and federal law. Likewise, the analysis of F.D.A. regulatory protocols is entirely different if one of the arguments is that the drug to be regulated may be used to end a life.
Neither case presents the justices with a clear opportunity to endorse the notion of fetal personhood — but such claims are lurking beneath the surface. The Idaho abortion ban is called the Defense of Life Act, and in its first bill introduced in 2024, the Idaho Legislature proposed replacing the term “fetus” with “preborn child” in existing Idaho law. In its briefs before the court, Idaho continues to beat the drum of fetal personhood, insisting that EMTALA protects the unborn — rather than pregnant women who need abortions during health emergencies.
According to the state, nothing in EMTALA imposes an obligation to provide stabilizing abortion care for pregnant women. Rather, the law “actually requires stabilizing treatment for the unborn children of pregnant women.” In the mifepristone case, advocates referred to fetuses as “unborn children,” while the district judge in Texas who invalidated F.D.A. approval of the drug described it as one that “starves the unborn human until death.”
Fetal personhood language is in ascent throughout the country. In a recent decision , the Alabama Supreme Court allowed a wrongful-death suit for the destruction of frozen embryos intended for in vitro fertilization, or I.V.F. — embryos that the court characterized as “extrauterine children.”
Less discussed but as worrisome is a recent oral argument at the Florida Supreme Court concerning a proposed ballot initiative intended to enshrine a right to reproductive freedom in the state’s Constitution. In considering the proposed initiative, the chief justice of the state Supreme Court repeatedly peppered Nathan Forrester, the senior deputy solicitor general who was representing the state, with questions about whether the state recognized the fetus as a person under the Florida Constitution. The point was plain: If the fetus was a person, then the proposed ballot initiative, and its protections for reproductive rights, would change the fetus’s rights under the law, raising constitutional questions.
As these cases make clear, the drive toward fetal personhood goes beyond simply recasting abortion as homicide. If the fetus is a person, any act that involves reproduction may implicate fetal rights. Fetal personhood thus has strong potential to raise questions about access to abortion, contraception and various forms of assisted reproductive technology, including I.V.F.
In response to the shifting landscape of reproductive rights, President Biden has pledged to “restore Roe v. Wade as the law of the land.” Roe and its successor, Planned Parenthood v. Casey, were far from perfect; they afforded states significant leeway to impose onerous restrictions on abortion, making meaningful access an empty promise for many women and families of limited means. But the two decisions reflected a constitutional vision that, at least in theory, protected the liberty to make certain intimate choices — including choices surrounding if, when and how to become a parent.
Under the logic of Roe and Casey, the enforceability of EMTALA, the F.D.A.’s power to regulate mifepristone and access to I.V.F. weren’t in question. But in the post-Dobbs landscape, all bets are off. We no longer live in a world in which a shared conception of constitutional liberty makes a ban on I.V.F. or certain forms of contraception beyond the pale.
Melissa Murray, a law professor at New York University and a host of the Supreme Court podcast “ Strict Scrutiny ,” is a co-author of “ The Trump Indictments : The Historic Charging Documents With Commentary.”
Kate Shaw is a contributing Opinion writer, a professor of law at the University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School and a host of the Supreme Court podcast “Strict Scrutiny.” She served as a law clerk to Justice John Paul Stevens and Judge Richard Posner.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are a few examples of good argumentative essay introductions. Argumentative essay introduction example 1. Gambling, or gambling addiction, is a complex subject to understand. Some people often win, which may lead others to believe that they are lucky rather than skilled. Many people gamble to escape reality for a bit and have fun.
Keep it concise and to the point. 2. Don't use clichés: Starting your essay with clichéd phrases or overused quotes can make your introduction feel unoriginal. Instead, aim for a fresh and unique opening line that will pique your reader's interest. 3. Don't be vague: Be clear and precise in your introduction.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay: 1. Introduction. Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader's attention. Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
Ask a rhetorical question that relates to the title of the argument. 2. Write one or two sentences that make assertive claims about the arguments you're about to make in the essay. 3. Start with facts or statistics, provided they revolve around the central theme of the essay and come from credible sources. 4.
Introduction paragraph with a thesis statement (which we just talked about); New paragraph that starts with a topic sentence presenting Argumentative Point #1 . Support Point #1 with evidence; Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary (AKA, the fun part!); New paragraph that starts with a topic sentence presenting Argumentative Point #2
1. Introductory paragraph. The first paragraph of your essay should outline the topic, provide background information necessary to understand your argument, outline the evidence you will present and states your thesis. 2. The thesis statement. This is part of your first paragraph.
*The examples given were taken from past AP Lang Exams. https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/courses/ap-english-language-and-composition/exam/past-exam-questio...
Argumentative essay formula & example. In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments.
Looking for good argumentative essay examples? Check out our full analysis of 3 argumentative essay samples to help you write your own. Call Direct: 1 (866) 811-5546 ... the author would be making a stronger argument. The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
6. Craft a Good Thesis. This is the most important part of the introduction in an argumentative essay as it presents your stand and justification to the essay by providing it with structure and direction. The thesis of an argumentative essay should be: Clear and precise in explanation of the main argument of the essay.
Developing an argument requires a significant understanding of the subject matter from all angles. Let's take a look at the steps to writing an argumentative essay: 1. Choose appropriate argumentative essay topics. Although topics for an argumentative essay are highly diverse, they are based on a controversial stance.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
College & Higher Education. By Soheila Battaglia. A good introduction in an argumentative essay acts like a good opening statement in a trial. Just like a lawyer, a writer must present the issue at hand, give background, and put forth the main argument -- all in a logical, intellectual and persuasive way.
A good argumentative essay should open with an engaging introduction. A well-crafted introduction makes a smooth funnel that starts more broadly and smoothly zeroes in on the specific argument: It begins with some kind of "hook": this can be an anecdote, quote, statistic, provocative statement, question, etc.
How to Pick a Good Argumentative Essay Topic ... It's important to remember the general essay structure: an introduction paragraph with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. A strong thesis statement will set your essay up for success. What is it? A succinct, concise, and pithy sentence found in your first paragraph that ...
If you enjoy these questions, know that you can find all of our argumentative writing prompts, as they publish, here. Students 13 and up from anywhere in the world are invited to comment.
Tip: An easy way to make your writing more concise is to start your sentences with the subject. Also, try to limit the number of adverbs and adjectives you use. 3. Tailor your writing to your audience. Being aware of your audience while you're writing will help you craft a more persuasive message.
Techniques for Good Essay Hooks. Here are a few techniques that you can use to write a good essay hook: Use a Quotation: Sometimes, a relevant quotation from a well-known author or expert can help establish the context or theme of your essay.Next time you're conducting research for an essay, keep an eye out for a really compelling quote that you could use as your hook for that essay.
Proper Structure of a Good Persuasive Essay. A persuasive essay has a standard essay structure. Often, writers prefer a 5-paragraph essay format the most. In general, an essay requires a strong and attention-grabbing introduction, informative main body parts, and a short and snappy conclusion. Introduction; The opening part of an essay must be ...
Ms. Murray is a law professor at New York University. Ms. Shaw is a contributing Opinion writer. In his majority opinion in the case overturning Roe v. Wade, Justice Samuel Alito insisted that the ...