Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema. Learn more →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Business news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Business Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes

Business Planning - Introduction
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
The business plan sets out how the owners/managers of a business intend to realise its objectives. Without such a plan a business is likely to drift.
The business plan serves several purposes:it
(1) enables management to think through the business in a logical and structured way and to set out the stages in the achievement of the business objectives.
(2) enables management to plot progress against the plan (through the management accounts)
(3) ensures that both the resources needed to carry out the strategy and the time when they are required are identified.
(4) is a means for making all employees aware of the business's direction (assuming the key features of the business plan are communicated to employees)
(5) is an important document for for discussion with prospective investors and lenders of finance (e.g. banks and venture capitalists).
(6) links into the detailed, short-term, one-year budget.
The Link Between the Business Plan and the Budget
A budget can be defined as "a financial or quantitative statement", prepared for a specific accounting period (typically a year), containing the plans and policies to be pursued during that period.
The main purposes of a budget are:
(1) to monitor business unit and managerial performance (the latter possibly linking into bonus arrangements)
(2 )to forecast the out-turn of the period's trading (through the use of flexed budgets and based on variance analyses)
(3 )to assist with cost control.
Generally, a functional budget is prepared for each functional area within a business (e.g. call-centre, marketing, production, research and development, finance and administration). In addition, it is also normal to produce a "capital budget" detailing the capital investment required for the period, a "cash flow budget", a "stock budget" and a "master budget", which includes the budgeted profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Preparing a Business Plan
A business plan has to be particular to the organisation in question, its situation and time. However, a business plan is not just a document, to be produced and filed. Business planning is a continuous process. The business plan has to be a living document, constantly in use to monitor, control and guide the progress of a business. That means it should be under regular review and will need to be amended in line with changing circumstances.
Before preparing the plan management should: - review previous business plans (if any) and their outcome. This review will help highlight which areas of the business have proved difficult to forecast historically. For example, are sales difficult to estimate? If so why? - be very clear as to their objectives - a business plan must have a purpose - set out the key business assumptions on which their plans will be based (e.g. inflation, exchange rates, market growth, competitive pressures, etc.) - take a critical look at their business. The classical way is by means of the strengths-weaknesses-opportunities-threats (SWOT) analysis, which identifies the business's situation from four key angles. The strategies adopted by a business will be largely based on the outcome of this analysis.
Preparing the Budget
A typical business plan looks up to three years forward and it is normal for the first year of the plan to be set out in considerable detail. This one-year plan, or budget, will be prepared in such a way that progress can be regularly monitored (usually monthly) by checking the variance between the actual performance and the budget, which will be phased to take account of seasonal variations.
The budget will show financial figures (cash, profit/loss working capital, etc) and also non-financial items such as personnel numbers, output, order book, etc. Budgets can be produced for units, departments and products as well as for the total organisation. Budgets for the forthcoming period are usually produced before the end of the current period. While it is not usual for budgets to be changed during the period to which they relate (apart from the most extraordinary circumstances) it is common practice for revised forecasts to be produced during the year as circumstances change.
A further refinement is to flex the budgets, i.e. to show performance at different levels of business. This makes comparisons with actual outcomes more meaningful in cases where activity levels differ from those included in the budget.
What Providers of Finance Want from a Business Plan
Almost invariably bank managers and other providers of finance will want to see a business plan before agreeing to provide finance. Not to have a business plan will be regarded as a bad sign. They will be looking not only at the plan, but at the persons behind it. They will want details of the owner/managers of the business, their background and experience, other activities, etc. They will be looking for management commitment, with enthusiasm tempered by realism. The plan must be thought through and not be a skimpy piece of work. A few figures on a spreadsheet are not enough.
The plan must be used to run the business and there must be a means for checking progress against the plan. An information system must be in place to provide regular details of progress against plan. Bank managers are particularly wary of businesses that are slow in producing internal performance figures. Lenders will want to guard against risk. In particular they will be looking for two assurances:
(1) that the business has the means of making regular payment of interest on the amount loaned, and
(2) that if everything goes wrong the bank can still get its money back (i.e. by having a debenture over the business's assets). Forward-looking financial statements, particularly the cash flow forecast, are therefore of critical importance. The bank wants openness and no surprises. If something is going wrong it does not want this covered up, it wants to be informed - quickly.
- Strategic planning
- Marketing planning
- Corporate planning
- Business plan
You might also like
Marketing planning (revision presentation).
Teaching PowerPoints
Marketing Planning (Overview)
Business planning for a new business (revision presentation), analysing marketing data (revision presentation), corporate objectives, marketing objectives (revision presentation), internal and external influences on marketing objectives, planning a new business (gcse), our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

9 Min. Read
Airbnb rental business plan

5 Min. Read
Life coaching business plan

3 Min. Read
Outline your marketing strategy

Break-even analysis
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

2.1.4 Planning - Theme 2 Edexcel A Level Business
Subject: Business and finance
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
29 February 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This set of resources (1x PPT and 8x word docs) can be delivered over 3-4 lessons and introduces learners to the importance of business planning with an emphasis on cash flow forecasting. We start by looking at what’s included in a business plan and the purpose of creating one, a group matching cards activity to consolidate the contents of the business plan.
We then go on to looking at the importance of a positive cash flow, and how to construct a cash flow forecast from scratch step by step (although this isn’t required it helps understand the topic well). Students then go on to consolidate this by creating a cash flow forecast for Ian Beale’s fish and chip shop, some further calculation practice followed.
This is followed by 2 x 12 mark questions, one on business planning and one on cash flow forecasting based on Ian Beale’s forecast. Both comes with structure guidance and concise model answers for students to peer assess with. Two links to kahoot quizzes on the topic and a box plenary to finish with.
Colourful, concise and engaging slides!
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 42%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Edexcel A Level Business YEAR 1 (Theme 1 & 2)
**This bundle for Edexcel's A Level Year 1 Bundle is the ultimate pack for teachers delivering this course to year 12s. Updated for 2021 with more engaging and colourful slides to cater for remote learning needs. The highest quality, unrivalled lesson experiences from start to finish.** Filled with real life examples, concise case studies to save time and focus on key skills of knowledge, application, analysis and evaluation. Questions with structured guidance and modelled answers for self/peer assessments - to save your time and to build their skills at the same time rather than just going through theory slide after slide. Please have a look at individual files to see previews. All you need - open the powerpoint, run through it, and deliver quality lessons whilst saving precious time. Colourful, concise and engaging slides! - all files in zip folder. Thank you
Edexcel A Level Business Theme 2- 2.1 Raising finance
This 7-9 lesson bundle covers: 2.1.1 Internal finance 2.1.2 External finance - 2-3 lessons 2.1.3 Liability 2.1.4 Planning 3-4 lessons Filled with real life examples, case studies, questions, concise model answers to improve exam practice and kahoot quizzes to consolidate learning in an engaging way. All you need - open the powerpoint, run through it, and deliver quality lessons whilst saving precious time. Colourful, concise and engaging slides! - all files in zip folder. Thank you
Edexcel A Level Business Theme 2 (COMPLETE COURSE)
This bundle for Edexcel's A Level Theme 2 is the ultimate pack for teachers delivering this course. Updated for 2021 with more engaging and colourful slides to cater for remote learning needs. The highest quality, unrivalled lesson experiences from start to finish. Filled with real life examples, concise case studies to save time and focus on key skills of knowledge, application, analysis and evaluation. Questions with structured guidance and modelled answers for self/peer assessments - to save your time and to build their skills at the same time rather than just going through theory slide after slide. Please have a look at individual files to see previews. All you need - open the powerpoint, run through it, and deliver quality lessons whilst saving precious time. Colourful, concise and engaging slides! - all files in zip folder. Thank you
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Module 8: Entrepreneurship
Introduction to business plans, what you’ll learn to do: list and describe the key components of a business plan.

Alan Lakein, an author who writes about personal time, sets the stage for this section. He says, “Planning is bringing the future into the present so that you can do something about it now.”
Business planning forces an entrepreneur to develop a detailed understanding of the market—including their unique value proposition, competitive strategy, and what it will take to succeed. This understanding includes specific operating and financial statement terms, which often take a significant amount of research and time to discover.
In this section, we will focus in on the business plan, which pulls together the research, analysis, and self-assessment of prior sections.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Introduction to Business Plans. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Photo of signpost. Authored by : Greyerbaby. Located at : http://pixabay.com/en/sign-places-travel-information-429419/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

How to make a business plan
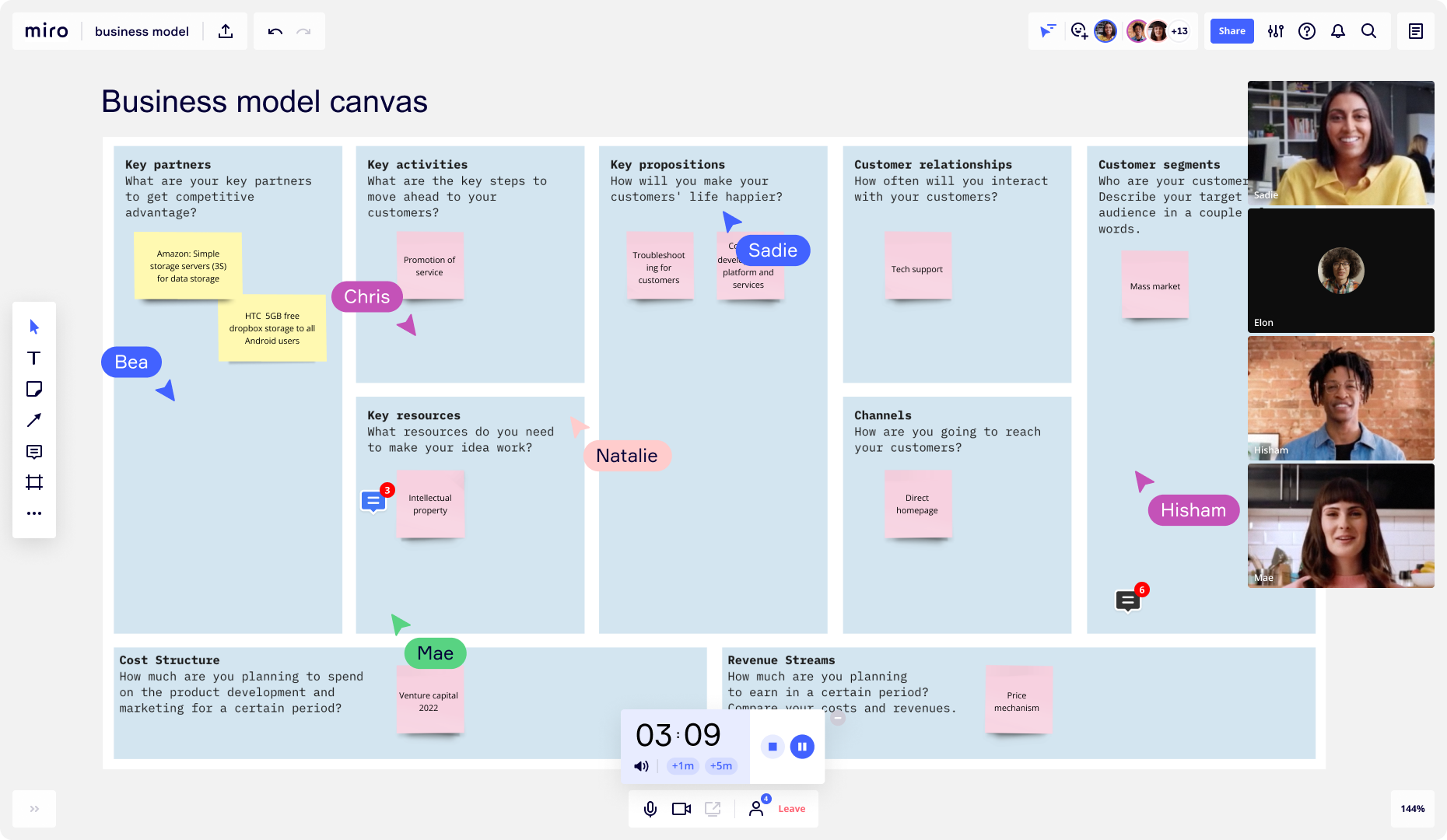
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.

Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Programmes & Qualifications
Cambridge international as & a level business (9609).
- Syllabus overview
The syllabus enables students to understand and appreciate the nature and scope of business, and the role it plays in society. It encourages students to examine the process of decision-making in a dynamic and changing business environment and to develop critical understanding of business organisations. They learn about business and its environment, human resource management, marketing, operations management and finance and accounting. At Cambridge International A Level, students also learn how to develop a business strategy.
The syllabus year refers to the year in which the examination will be taken.
- -->2023-2025 Syllabus (PDF, 403KB)
- -->2026 - 2028 Syllabus (PDF, 763KB)
Syllabus updates
We revise our qualifications regularly to make sure that they continue to meet the needs of learners, schools and higher education institutions around the world and reflect current thinking. We have consulted and worked with subject experts to review the syllabus, so that the breadth and depth is clearer. Please see the 2023–2025 syllabus document for full details on the changes.
What are the main changes to the syllabus?
- clarified the assessment objectives and made small changes to their weightings
- five topics now at Cambridge International A Level
- embedded business strategy within the five main topics at Cambridge International A Level. Students are now encouraged to learn this within context
- included formulae for ratios to support the analysis of published accounts
- included a list of command words and their meanings.
What are the main changes to the assessment?
- There are now two papers at Cambridge International A Level, Paper 3 and Paper 4. We have reduced the duration for Paper 3.
- We have retitled all papers to better describe the focus of each one.
- We have revised the levels-based marking criteria for all papers to maintain validity and reliability of assessment.
When do these changes take place?
The updated syllabus is for examination from June 2023 onwards. Examinations are available in March 2023 for India only. Please see the 2023-2025 syllabus above for full details.
We are developing a comprehensive range of materials to help you teach the updated syllabus. These resources will be available from June 2021 onwards (before first teaching) through our School Support Hub and include:
- Scheme of work
- Learner guide
- Example Candidate Responses (after first examination).
Face-to-face and online training will be available. For up-to-date information, visit our Events and training calendar .
Endorsed resources
View the latest resources that are being developed by our Endorsement Partners for the Cambridge International AS & A Level Business syllabus (9609).

Business for Cambridge International AS & A Level (Fourth edition) (Cambridge University Press)
From studying real-life business scenarios, to ESL support with language worksheets, the new edition of this series gives students the support they need to study this course effectively, and helps prepare them for assessment.
Read more on the Cambridge University Press website

Cambridge International AS & A Level Business (Second edition) (Hodder Education)
Build strong subject knowledge and skills and an international outlook with expert author guidance and in-depth coverage of the revised Cambridge International AS & A Level Business syllabus (9609).
Read more on the Hodder Education website
Important notices
For some subjects, we publish grade descriptions to help understand the level of performance candidates’ grades represent.
We paused the publication of grade descriptions in response to the Covid-19 pandemic and the temporary changes to the awarding standard in 2020, 2021 and 2022.
As the awarding standard has now returned to the pre-pandemic standard, we are working to produce up-to-date grade descriptions for most of our general qualifications. These will be based on the awarding standards in place from June 2023 onwards.
School Support Hub
Teachers at registered Cambridge schools can unlock over 30 000 teaching and learning resources to help plan and deliver Cambridge programmes and qualifications, including Schemes of work, Example candidate responses, Past papers, Specimen paper answers, as well as digital and multimedia resources.
Schemes of work
Example responses, past papers, specimen paper answers.
Register your interest in becoming a Cambridge School
Stay up to date
Sign up for updates about changes to the syllabuses you teach
- Past papers, examiner reports and specimen papers
- Published resources
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
Understanding the Nature and Purpose of Business
Reasons for choosing different forms of business and for changing business form.
The way the business is formed means how it is owned. Each form of ownership has advantages and disadvantages.
Some business will change their form over time, others will stay the same for many years.
When you consider which form is best for each business, you need to understand the objectives of the business and how much risk the owners want to take.
Businesses which are owned by shareholders have responsibilities to meet their shareholders’ needs. These needs can impact on the business objectives and decision-making processes.
Types of Business
A business is either corporate or non-corporate.
A corporate business __ __is a separate legal entity. That means it can make contracts, sue and be sued. The owners of that business are not liable for any costs incurred should the business go bankrupt.
A non-corporate business is a person (or persons). They are personally liable for any costs incurred by the business and they can be sued personally.
Sole traders and some partnerships are non-corporate. Private limited companies, public limited companies, mutual and charities are corporate.
Limited Liability
A corporate business has limited liability. Shareholders (owners) are only liable for the money they have put into the business. Limited liability protects these owners should the business go bankrupt. Any outstanding debts that the business cannot pay will not be paid by the shareholders.
Sole Traders
As a non-corporate business a sole trader, and some partnerships that are not incorporated, bear all responsibility for the liabilities generated by the business. A sole trader is not necessarily a one person business as it may have employees.
Advantages : Cheap to set up, all the profits go to the owner, the owner makes the decisions and doesn’t have to publish results for shareholders or file accounts with Companies House.
Disadvantages : Unlimited liability, may have difficulty raising finance.
Private Limited Companies
One or more shareholders (owners), who share the profits. The owners may or may not be the business managers. The business enjoys limited liability but has more administrative costs as a result. A private limited company can raise money by issuing and selling more shares.
Advantages : Limited liability, easier to borrow money than sole traders, doesn’t have to disclose as much detail as public limited companies.
Disadvantages : More difficult to sell shares – majority of shareholders need an agreement with other shareholders first, cannot raise the same sort of finance as PLCs, and it has some administration fees, although not as much as PLCs.
Public Limited Companies (PLCs)
Many owners, who share the profits. Shares are bought and sold in the open market. It’s unlikely that major shareholders will be directors, though directors may well have shares.
Advantages : Limited liability, greater access to finance, easier to gain credit from suppliers.
Disadvantages : Needs to meet needs of shareholders, disclose more information, and subject to regulatory regime of stock exchanges and markets. Expensive to administer.
Private and public sector businesses
Private sector companies are owned by the members of the public, or other businesses. Public sector companies are owned by the government. Therefore, there are no shareholders in a public sector company. They don’t make profits, they make surpluses.
NPOs, Mutuals and Charities
Non-profit organisations plough any surpluses back into their operations. They will be keen to generate surpluses, because these surpluses can be used to invest in the organisation and allow it to grow.
Mutuals are businesses which are “owned” by their members, for example, building societies. They aim to generate returns for the members.
Charities don’t have owners but are run by a board of directors who are trustees required to follow the objects set out in the trust deed. They are subject to regulation by the Charities Commission.
The Role of Shareholders and Why They Invest
Unlimited liability is dangerous for any business which must buy goods or services on credit before turning them into products to sell. This doesn’t matter so much for the type of one-person business, such as a window cleaner or supply teacher who sell their own time.
Therefore, if there’s a risk of losing the money a shareholder has invested, a major advantage of being incorporated is limited liability.
Also, because the investor knows the limit of their risk, it’s easier to raise money.
Money raised in this way is called share capital. It comes from selling shares in the business, which means selling a ticket to claim a proportion of future profits. These tickets are known as ordinary share capital. A shareholder or a group of shareholders need 50.1% of the share capital to control the business.
Shareholders provide capital at the foundation of a business when they buy the first issue of shares. After that, any time that a share is sold, the money goes to the owner of the share, not the business.
The incentive to own shares is twofold:
- Every year, a shareholder may receive a dividend. This is a small proportion of the profit.
- The value of shares may grow. If the business is successful, its dividends will increase and thus the shares become more valuable.
Dividends are a proportion of the profit paid out to shareholders as a reward for their investment and for bearing the risk. The total dividend is distributed in accordance with the relative proportion of each shareholder’s share ownership.
A business would almost never pay a dividend if it makes a loss, although it is not obliged to pay a dividend if it makes a profit. It may say it wants to use the profits to reinvest in the firm.
Market capitalisation __ __is total value of all the shares. It is calculated by the total number of shares multiplied by the value of each share. It is a good measure of the general size of the business and whether it’s becoming more valuable in relation to other businesses.

The share price could rise or fall for the following reasons:
- If the dividend changes or is predicted to change. A higher dividend makes the share more valuable. A profitable business or potentially profitable business will see its share price increase.
- If the business might be sold to another company.
- If the business launches a new product.
- If the business fails to meet objectives, especially financial targets, its share price could fall
- If the external environment changes, which might affect the market in which the business operates.
Shareholders want the share price to increase. If it doesn’t, they will put pressure on the board of directors to make changes. If the directors fail, then the shareholders can sack the directors and replace them with people who they think will do the job more effectively.
The Effects of Ownership on Mission Objectives Decisions and Performance
Sole traders make all their own decisions without pressure from shareholders.
By contrast, shareholders are interested in the growth in value of their shareholdings and returns on their investment. That might make the business look to generate short-term profits at the expense of long-term profits.
In private limited companies, the shareholders may have a longer term view because they are likely to be more closely related to the business and its management.
In PLCs, there’s normally a greater separation as between the owners and the directors.
Definitions:

A Level Business Studies: What is a business plan?

- It serves as a roadmap for the business, providing a clear and concise vision of where the company is headed and how it intends to get there.
- A business plan is a formal document that outlines a company’s goals and strategies for achieving them.
- A business plan typically includes sections on the company’s mission, market analysis, product or service offerings, marketing and sales strategies, management and organizational structure, financial projections, and risk analysis.
- A business plan is a vital tool for any company, helping to clarify goals and objectives, attract investors and funding, guide business operations, identify and mitigate risks, and evaluate progress and success.
- A well-crafted business plan can set a company on a path to long-term success, providing a clear and concise roadmap for achieving its goals.
Purpose of a Business Plan:
- Clarify Business Goals and Objectives:
- A business plan helps to define and clarify the company’s goals and objectives, as well as the strategies for achieving them.
- This ensures that everyone in the organization is working towards the same vision, and that resources are allocated effectively to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Attract Investors and Funding:
- A well-crafted business plan can attract investors and funding by demonstrating the potential for profitability and growth.
- This may include detailed financial projections, market analysis, and competitive advantages that make the business an attractive investment opportunity.
- Guide Business Operations:
- A business plan provides a roadmap for the day-to-day operations of the business, outlining the steps needed to achieve the company’s goals.
- This may include sales and marketing strategies, product development, operational processes, and staffing requirements.
- Identify and Mitigate Risks:
- A business plan includes a risk analysis, identifying potential threats to the company’s success and strategies for mitigating them.
- This may include contingency plans for unexpected events, such as changes in market conditions or disruptions to the supply chain.
- Evaluate Progress and Success:
- A business plan serves as a benchmark for evaluating the company’s progress and success.
- This may include regular reviews of financial performance, market share, customer satisfaction, and employee engagement, among other metrics.

Business Studies
Discover more comprehensive and exam-focused ZIMSEC Advanced Level Business Studies Notes.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: garikaib.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Company News
Masimo Stock Surges After Proposed Spinoff of Consumer Business
Company Aims to Improve Profitability of Healthcare Business
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/tim_1978_linkedin__tim_smith-5bfc261946e0fb00265aea0e.jpg)
Key Takeaways
- Masimo shares jumped 13% in extemded trading Friday after the company announced that it plans to spin off its consumer unit to improve profitability in its healthcare business.
- The company said it expects to separate its consumer audio and consumer health products, but will retain its professional healthcare and telehealth products.
- The proposed separation comes several years after the company acquired audio products maker Sound United LLC to bolster its consumer-facing healthcare products.
- Masimo shares sit poised to break out from a symmetrical triangle, but may find resistance around $197 near the April 2023 swing high.
Share in Masimo ( MASI ) surged 13% in extended trading on Friday after the company announced that it is planning a spinoff of its consumer unit to improve the profitability of its primary healthcare business.
The Irvine, California-based medical devices company said it expects the separation to include its consumer audio and consumer health products, including the Stork baby monitor and the Freedom smartwatch, but said it will retain its professional healthcare and telehealth products. It anticipates CEO Joe Kiani to remain as chief executive of Masimo and become chairman of the newly created company.
Masimo acquired audio products maker Sound United LLC for $1 billion in 2022 to add the company’s premium audio and home entertainment brands to its portfolio of hospital and home medical technology solutions, aimed at bolstering its consumer-facing healthcare products. However, the company’s stock plunged 37% after announcing the deal, with investors skeptical that the non-healthcare acquisition was a suitable fit. Several months after the transaction closed, activist investor Politan Capital Management took a 9% stake in the company, vowing at the time to speak with management and the board about possible changes.
The company, which also reaffirmed its guidance for the first quarter and fiscal year 2024, said Friday it seeks to complete the spinoff as soon as feasible after it undergoes due diligence and gains regulatory approval.
“I proposed a separation of the consumer business in January and the Board has agreed to move forward. This approach is expected to maximize shareholder value as well as give both Masimo healthcare and the new consumer business the best path for success,” said Kiani in a statement released late Friday afternoon.
Since the 50-day moving average crossed above the 200-day moving average to form a golden cross signal in mid-February, the Masimo share price has consolidated within a symmetrical triangle —a chart pattern that indicates a continuation of the current uptrend. In addition, the triangle sits just above the neckline of an inverse head and shoulders formation, indicating a potential market bottom. If the stock continues to move higher, keep an eye on the $197 level, which may find overhead resistance from the April 2023 swing high.
Masimo shares gained 13.4% to $153.00 in afterhours trading Friday.
The comments, opinions, and analyses expressed on Investopedia are for informational purposes only. Read our warranty and liability disclaimer for more info.
As of the date this article was written, the author does not own any of the above securities.
Masimo. " Masimo Corporation Board of Directors Authorizes Management to Evaluate the Separation of Consumer Business ."
Masimo. " Masimo Closes Acquisition of Sound United ."
Reuters, " Masimo Plans to Spinoff Consumer Business ."
Reuters. " Koffey's Politan Takes 9% Stake in Masimo, to Push for Change ."
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
More From Forbes
2023 tax guide to the entertainment and meal tax deduction.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Sorry tickets to see Taylor Swift perform are not tax deductible. SAO PAULO, BRAZIL - NOVEMBER 24: ... [+] (EDITORIAL USE ONLY. NO BOOK COVERS.) Taylor Swift performs onstage during "Taylor Swift | The Eras Tour" at Allianz Parque on November 24, 2023 in Sao Paulo, Brazil. (Photo by Buda Mendes/TAS23/Getty Images for TAS Rights Management )
Tax planning is a great way to optimize your take-home pay if you run your own business. Essentially, the fewer taxes you pay, the higher your net income. The entertainment and meals tax deduction has been a great way for successful business owners or self-employed people to maximize their tax deductions yearly. Unfortunately, the Trump tax plan cut the value of the meals and entertainment tax deduction by 50% in 2023.
Keep reading as we share what you need to know about the meals and entertainment deduction for 2023 and 2024. This tax deduction guide can help you take advantage of these valuable money-saving tax deductions. I know quite a few entrepreneurs who conduct most of their business meetings out and about over meals at restaurants. These folks can rack up some substantial tax savings.
You may be able to deduction your meals with clients is it serves a business purpose.
How To Deduct Meals And Entertainment Expenses As A Business Owner
The value of meal and entertainment tax deductions has changed over the past few years. With the ratification of the 2018 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) , aka the Trump Tax Plan, entertainment expenses can no longer be deducted. Similarly, ticket costs are no longer deductible if you take clients to a sporting event or Broadway show.
There are other ways to deduct some expenses that qualify for a Meals and Entertainment Tax deduction.
2023 / 2024 Meals and Entertainment Allowable Tax Deductions
Best tax software of 2022, best tax software for the self-employed of 2022, income tax calculator: estimate your taxes.
The meals and entertainment tax deduction rules are the same for tax years 2023 and 2024.
It will be helpful to know what still qualifies for the meals and entertainment tax deduction in 2023 and 2024. Here are some potential dining expenses that may be half to fully deductible when incurred by your business.
· Food for company holiday parties (100%)
· Food and beverages given to the public (100%)
· Dinner for employees working late at the office (100%)
· Business meals with clients (50%)
· Food items for the office (50%)
· Meals while traveling for work (50%)
· Meals at a conference (50%)
Your Guide To Meal Tax Deduction For 2023 And 2024
For 2023 and 2024, most business meals are only 50% deductible, according to the current IRS rules. Let's say you take your favorite client to a beautiful lunch (to discuss business); you can deduct half the cost of the meal. On the other hand, if you go out for a meal with a client with no business purpose, the meal is not deductible.
The change to the meal deduction could cause some confusion since meals were 100% deductible in 2021 and 2022. This was a temporary change to help boost spending at restaurants during the Covid-19 pandemic.
How To Document Your Tax-Deductible Meal Expenses
If you want to deduct a business meal that costs more than $75, you must keep receipts or documentation of the meal expense. For meals below $75, the IRS does not require you to keep receipts to document the expense. Either way, you will still want to keep a record of your deductible meal, including the following information: date of the meal, total including tax and tip, name of the restaurant, details of the business meal (who attended and how it related to your business).
Your Guide To The Entertainment Tax Deduction 2023 And 2024
Unfortunately, most entertainment expenses are no longer deductible.
Here are some of the most common exceptions that may still be tax deductible in 2023 or 2024—expenses for events like the company holiday party, rewards trip, or costs tied to business meetings (think chamber meetings, professional associations, or even a conference). Also, if you sell entertainment to your customers, there are exceptions to the entertainment deductions.
For example, a bar owner paying a band to perform for customers would likely be a deductible business expense. Buying tickets to see Taylor Swift perform (with or without clients) would not be deductible. If you took clients to dinner first, and discussed business, the meal would likely be deductible.
How To Make Up For Reduced Meal Deductions In 2023 And 2024
Make sure you have the best retirement plan for your small business. Look to increase your contributions to your 401(k) plan . You can contribute up to $69,000 to your Solo 401(k) in 2024, more if you are 50 or older. Consider setting up a Cash Balance Pension Plan if you need even more valuable tax deductions. The pension plan could allow you to sock away several hundred thousand dollars annually (depending on your age and income).
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
House Republicans want to raise the Social Security age. It could hurt those who 'work their whole lives and die sooner,' the agency's head says.
- House Republicans proposed raising the age for receiving Social Security benefits.
- Social Security benefits are already facing funding issues over the next decade.
- The proposed change has sparked criticism from both Democrats and some Republicans.

House Republicans have a plan to raise the age at which Americans receive Social Security benefits — and the agency's leader isn't on board.
Earlier this week, the Republican Study Committee unveiled their fiscal year 2025 budget proposal — called Fiscal Sanity to Save America — which consisted of nearly 200 pages of funding priorities for key issues, including taxes , higher education , and healthcare.
The budget also addressed an issue that has long been contentious across both parties: Social Security. According to the proposal, the committee wants to "make modest adjustments to the retirement age for future retirees to account for increases in life expectancy." The proposal did not specify the exact age they're eyeing for Americans to receive their benefits, but it would likely be above the current threshold of 67 years old.
The committee's chairman Kevin Hern emphasized in the budget that "we cannot be clearer: we WILL NOT adjust or delay retirement benefits for any senior in or near retirement."
Still, the proposal has some administration officials concerned for future retirees. During a House Ways and Means Committee hearing on Thursday, Social Security Commissioner Martin O'Malley said that "we have to be mindful of people who really do hard work, hard labor, their whole lives, and who die sooner than those of us who are privileged enough to do work that is not as taxing on our bodies and our physical well-being."
Related stories
Full Social Security benefits are already in jeopardy over the next decade. In March 2023, the Social Security and Medicare Board of Trustees estimated that the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance (OASI) Trust Fund might only be able to pay out full benefits over the next decade, which is earlier than anticipated.
"My dad had an expression, 'Don't tell me what you value. Show me your budget, and I'll tell you what you value.' The Republican Study Committee budget shows what Republicans value," President Biden said in a statement on the RSC budget. "This extreme budget will cut Medicare, Social Security, and the Affordable Care Act. It endorses a national abortion ban. The Republican budget will raise housing costs and prescription drugs costs for families. And it will shower giveaways on the wealthy and biggest corporations. Let me be clear: I will stop them."
Even some Republican lawmakers have been critical of the House's budget proposal. GOP Sen. Josh Hawley called the plan "the stupidest thing I ever heard," according to The Hill, and GOP Sen. Mitt Romney warned his House colleagues of the consequences of putting forth this plan during an election year.
"Talk about a gift to the Democrats," Romney said . "Seems like people have lost their political ear if they think any adjustments to the benefits of Social Security makes sense to talk about at any time, let alone during an election year."
Retirement is already looking bleak for some seniors, who are facing lower incomes and high healthcare and housing costs . A little over half of Americans over the age of 65 are earning under $30,000 a year, according to Census Bureau's Current Population Survey . And for many Americans, Social Security is a financial lifeline in their later years. Among typical retirees , just under 80% say Social Security is a source of income — a far greater share than retirement savings or wages.
Biden said that his "budget represents a different future," one where "we protect Social Security so the working people who built this country can retire with dignity."
"I see a future for all Americans and I will never stop fighting for that future," he said.
Watch: Surprising misconceptions about Trump and Biden ahead of the 2024 election
- Main content
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is a written document that outlines a company's objectives and how it plans to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap for strategic planning and implementation. Business planning plays a pivotal role in setting the direction and establishing targets for a business. It helps minimise risk and provides a sense of direction.
In this A level Business revision tutorial, we take a look at the topic of Business Plans, examining the main sections of a business plan as well as the stre...
The business plan sets out how the owners/managers of a business intend to realise its objectives. Without such a plan a business is likely to drift. The business plan serves several purposes:it. (1) enables management to think through the business in a logical and structured way and to set out the stages in the achievement of the business ...
GCSE; Edexcel; Business plans - Edexcel The role and importance of a business plan. A business plan is an essential part of starting any business. Entrepreneurs create business plans to help them ...
Business Plans Explained - GCSE and A Level Business Revision 📝 This video explains what a business plan is, includes the contents of a business plan as we...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
The main aim of producing a business plan is to reduce the risk associated with starting a new business. A business plan is a document produced by the owner at start-up, which provides forecasts of items such as sales, costs and cash flow. It shows potential lenders or investors that the business has done their research.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Edexcel A Level Business Theme 2- 2.1 Raising finance. This 7-9 lesson bundle covers: 2.1.1 Internal finance 2.1.2 External finance - 2-3 lessons 2.1.3 Liability 2.1.4 Planning 3-4 lessons Filled with real life examples, case studies, questions, concise model answers to improve exam practice and kahoot quizzes to consolidate learning in an ...
Business planning forces an entrepreneur to develop a detailed understanding of the market—including their unique value proposition, competitive strategy, and what it will take to succeed. This understanding includes specific operating and financial statement terms, which often take a significant amount of research and time to discover. In ...
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following: ... The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The ...
7. Goals. The goals portion of your business plan gives readers a better idea of where your business is headed. Try to include a mix of quarterly goals, annual goals, and goals that span five or 10 years. For each goal you share, include a few bullet points explaining: Your timeline for reaching the goal.
The Business syllabus enables learners to understand and appreciate the nature and scope of business, and the role it plays in society. The syllabus covers economic, environmental, ethical, governmental, legal, social and technological issues, and encourages a critical understanding of organisations, the markets they serve and the process of adding value.
Describe your services or products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including: Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials.
Now that we have looked at what a business plan is and why it is important it is time to look at how you can create a business plan. Preparing a business plan requires thorough research, strategic planning, financial forecasting, and risk analysis. A well-crafted business plan can serve as a roadmap for achieving your business goals, attracting ...
Types of Business. A business is either corporate or non-corporate. A corporate business__ __is a separate legal entity. That means it can make contracts, sue and be sued. The owners of that business are not liable for any costs incurred should the business go bankrupt. A non-corporate business is a person (or persons). They are personally ...
A well-crafted business plan can set a company on a path to long-term success, providing a clear and concise roadmap for achieving its goals. Purpose of a Business Plan: Clarify Business Goals and Objectives: A business plan helps to define and clarify the company's goals and objectives, as well as the strategies for achieving them.
Derived from the firm's overall aim and mission statement. Corporate objectives may focus on achieving specified levels of market share , profit, sales growth or new product/market development. Mind UK. 'Provide 3 million employees in low-paid sectors with workplace wellbeing support'. Functional Objective.
Bottom line. Key takeaway: Former GE executive Dan Henson and his son, Dan Henson Jr., with experience in insurance have gone into business together, opening a new restaurant in the Rosemary District of Sarasota. Core challenge: Overcoming industry regulations, the state and local permit process and more. What's next: More development, in new condo projects and commercial spaces, is ...
Share in Masimo surged 13% in extended trading on Friday after the company announced that it is planning a spinoff of its consumer unit to improve the profitability of its primary healthcare business.
Make sure you have the best retirement plan for your small business. Look to increase your contributions to your 401(k) plan. You can contribute up to $69,000 to your Solo 401(k) in 2024, more if ...
Boeing Co. directors plan to meet with top executives from some of their largest airline customers, who are growing increasingly frustrated about the planemaker's crisis tearing into their business.
Budgets can encourage managers to focus on the short-term rather than the long-term success of the business as budgets are usually set year on year. Unrealistic budgets (over or under) can lead to a lack of motivation amongst those tasked to achieve the financial plan. The conflict between budget holders may arise, reducing the effectiveness of ...
House Republicans have a plan to raise the age at which Americans receive Social Security benefits — and the agency's leader isn't on board.. Earlier this week, the Republican Study Committee ...
The US proposed to its Group of Seven allies that they create a special purpose vehicle to issue at least $50 billion of bonds backed by the profits generated by frozen Russian sovereign assets ...