All Formats

20+ Sample College Application Letters – PDF, DOC
College application letters are used in various academic applications when college students request an entrance or transfer. It may be a requirement of the academic institution where they currently attend or it can also be used for special functions that the college or university student would like to undertake. Whether it’s nursing, engineering, architecture, accounting, or medical students, application letters are prominent in college enrollment processes.

Free University Application Letter

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
University Application Letter Sample

Application Letter For College Admission

Application Format For University Students
College Application Letter
Example Of Application Letter For College Admission
Eligibility Letter For University
Sample Application Letter For College Admission

Application Letter For Studying

Application For Enrollment In University

Best College Application Letter

College Application Letter Sample PDF

College Application Letters Used in Academic Transactions
- A college application letter is used by a student who would like to enroll in a learning institution. Most of the time, it is one of the requirements for enrollment which is why it is essential to be done.
- A college leave application letter is written by a student who will have a temporary absence in the course that he or she is currently studying due to valid reasons.
- A college admission application letter is used by a student who would like to apply for an academic slot for a specific course offered by a school. You may also see Academic Letters
- College scholarship application letters are written by students who would like to get a scholarship grant—be it from the high school template, a government institution, or any other entity offering education assistance.
- College workshop application letters are created by students who want to be a part of a specific academic workshop that will be conducted within the premises of the institution.
- College application reference letters are written by the references of a student applicant so that there will be a supporting document that may be used either for admissions, enrollment, or other special academic functions.
- College withdrawal application letters are used to formally announce the decision of the student to not push through with his or her college studies in the academic institution where s/he is currently attending.
Parts Of application Letter For College Admission

Sample Application Letter For A Course

College Application Recommendation Reference Letter Template

College Withdrawal Request Application Letter Format Template

College Instructor Application Letter Writing Template

Business College F ull Block Style Application Letter Template

Architecture College Application Letter Template

Accounting College Application Letter Template

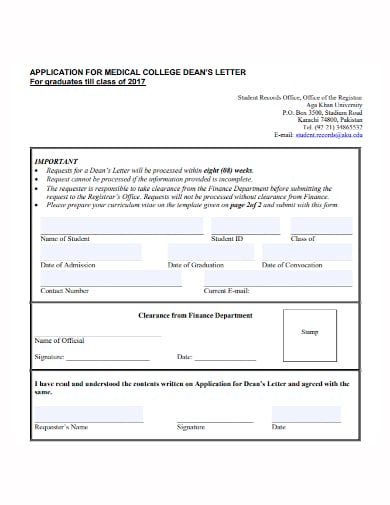
Medical College Application Letter Template
College Application Letters Used for Work Purposes
- The internship experiences of the applicant
- The seminars and training that the applicant has attended
- The academic achievements of the student
- The skills, talents, and other competencies of the graduate may be helpful in the operations of the business.
- The experiences of the applicant in terms of teaching
- The field of study that the applicant can teach
- The kind of teaching commitment that the applicant can provide to the academic institution
- It can be used to apply for a part-time job. You may also see Admission Letters .
- It can be given to the management of the school so they can provide a student assistant job function to the student.
More in Letters
Welcome letter to new college students, job application letter for accountant assistant, college essay template about yourself, college admission essay template, college application essay template, scholarship application letter sample for college, college transfer application rejection letter template, college application rejection letter template, letter of intent for college application, college application letter of recommendation.
- FREE 26+ Covid-19 Letter Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs
- Thank You Letter for Appreciation – 19+ Free Word, Excel, PDF Format Download!
- 69+ Resignation Letter Templates – Word, PDF, IPages
- 12+ Letter of Introduction Templates – PDF, DOC
- 14+ Nurse Resignation Letter Templates – Word, PDF
- 16+ Sample Adoption Reference Letter Templates
- 10+ Sample Work Reference Letters
- 28+ Invitation Letter Templates
- 19+ Rental Termination Letter Templates – Free Sample, Example Format Download!
- 23+ Retirement Letter Templates – Word, PDF
- 12+ Thank You Letters for Your Service – PDF, DOC
- 12+ Job Appointment Letter Templates – Google DOC, PDF, Apple Pages
- 21+ Professional Resignation Letter Templates – PDF, DOC
- 14+ Training Acknowledgement Letter Templates
- 49+ Job Application Form Templates

University Admission Application Letter (with Samples & PDFs)
I have listed sample templates to help you craft an effective and professional university admission application letter.
Also, I would like to point out that you can also download a PDF containing all the samples at the end of this post.
Successful Application Letter for University Admission
First, find the sample template for university admission application letter below.
To, The Admissions Committee, [Name of the University], [Address of the University], [City], [State], [Postal Code]
Subject: Application for Admission to [Name of the Course]
Respected Sir/Madam,
I, [Your Full Name], resident of [Your Address], am writing this letter to show my keen interest in applying for the [Name of the Course] at your esteemed university for the academic year [Year].
I have recently completed my [last educational qualification] from [Name of School/College] with an aggregate of [Your Percentage/CGPA], and I am eager to further my studies in the field of [Field of Study]. I believe that studying at [Name of the University] will provide me the right knowledge, skills, and exposure to excel in this field.
I am particularly drawn to the [Name of the Course] at [Name of the University] because of its reputation for providing high-quality education and its focus on practical learning. I am confident that this course will help me achieve my academic and career goals.
Enclosed with this letter are my mark sheets, certificates, and other required documents. I kindly request you to consider my application and provide me with an opportunity to prove my potential and contribute to the university.
I am looking forward to being a part of your esteemed institution and assure you that I will put in my best efforts in all my endeavours.
Thank you for considering my application. I am eager to hear from you soon.
Yours sincerely,
[Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information] [Your Email Address]
Below I have listed 5 different sample applications for “university admission application letter” that you will certainly find useful for specific scenarios:
Crafting a Persuasive University Application Letter to Showcase Leadership Skills

To, The Admissions Committee, [University Name], [University Address].
Subject: Application for Admission to [Desired Course Name]
I, [Your Full Name], a student of Class XII from [Your School Name], am writing to express my keen interest in applying for the [Desired Course Name] at your esteemed university. I believe that my strong leadership skills, coupled with my academic accomplishments, make me an ideal candidate for this course.
I have consistently excelled in my studies, but more importantly, I have taken the initiative to lead and guide my peers through various activities. As the Head Boy/Girl of my school, I’ve learned to inspire and motivate my fellow students, organize events, and address issues efficiently. These experiences have honed my leadership abilities and have taught me how to balance my academic commitments with extracurricular responsibilities.
I played a pivotal role in initiating a ‘Clean Campus Drive’ in my school, where I led a team of students to maintain cleanliness and fostered a sense of responsibility among them. This initiative not only improved the school environment but also instilled a sense of community and teamwork among the students.
Moreover, I represented my school at the [Local/State/National] Leadership Summit, where I had the opportunity to interact with other young leaders and share innovative ideas to improve our communities. This experience broadened my perspective and reinforced my desire to lead and make a difference.
If given the opportunity to join [University Name], I assure you that I will bring these leadership qualities to contribute positively to the university community. I am eager to leverage my experiences to participate actively in student-led initiatives and further develop my leadership skills.
I am confident that [University Name] is the perfect platform for me to grow not just acadically but also as a leader. I humbly request you to consider my application favorably. I look forward to the opportunity to be a part of your esteemed institution.
Thank you for considering my application.
Yours Sincerely, [Your Full Name], [Your Contact Information].
Writing a Compelling University Application Letter Highlighting Athletic Achievements

To, The Admissions Committee, [Name of the University], [Address of the University]
Subject: Application for Admission and Highlighting Athletic Achievements
I hope this letter finds you in the best of health and spirits. I am [Your Name], a student from [Your School Name], [Your City], intending to apply for the [Course Name] at your esteemed university.
Academically, I have consistently performed well, securing a GPA of [Your GPA] in the previous year. However, I am not just a diligent student in the classroom, but also a passionate sportsperson. I believe my athletic achievements will contribute to the vibrant sports culture at your university.
Over the last few years, I have been an active participant in athletics and have had the honour of representing my school at various district, state, and national level competitions. In the recent [Name of Sports Event], I clinched the gold medal in [Name of the Sport], making my school and family immensely proud. Additionally, I was also the recipient of the prestigious [Name of the Award] given for outstanding performance in sports.
My commitment to sports has not only honed my physical abilities but has also helped me develop leadership skills, team spirit, and resilience. I believe that these qualities will not only aid me in my academic pursuit but also contribute to the overall diversity and vitality of your university’s student community.
I am enthusiastic about bringing the same dedication and spirit to your esteemed university and contributing to its athletic teams. I am certain that the comprehensive education and diverse opportunities provided by your university will help me grow, both acadically and athletically.
I am hopeful that you will consider my application favourably. Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the possibility of becoming a part of your prestigious university.
Yours sincerely, [Your Name] [Your Contact Information]
Articulating Academic Excellence in a University Admission Application Letter

The Dean of Admissions, [University Name], [University Address], [City], [State], [Pin Code]
Subject: Application for Admission
Dear Sir/Madam,
I, [Your Name], am writing this letter seeking admission to the [Course Name] course at your prestigious institution for the academic year [Year]. I have recently completed my [last academic degree/course] from [Your School/College Name] in [City, State].
I have always been passionate about [subject(s) related to the course], and I am confident that my academic achievements reflect this. I have consistently maintained a high academic standing in my schooling years, ranking in the top [percentage/rank] of my class. My teachers have commended me for my dedication and commitment to learning, which is evident from my grades and participation in various academic competitions.
Moreover, I have been an active participant in various extracurricular activities that have helped me develop a holistic understanding of the world. I have led [mention some leadership roles], worked on [mention any projects or initiatives], and engaged in [mention any community service or volunteer work]. These experiences have taught me the importance of teamwork, leadership, and responsibility, and have fuelled my desire to further my learning.
Your institution, with its exemplary faculty and state-of-the-art facilities, stands as the ideal platform for me to deepen my knowledge and broaden my horizon. I am particularly drawn to the [mention specific aspects of the course or university that attract you], and I am confident that these will provide the right environment to nurture my academic and personal growth.
I am committed to maintaining my academic excellence and contributing positively to the university community. I am hopeful that I will be given the opportunity to bring my passion, dedication, and academic prowess to your esteemed institution.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of contributing to and learning from the [University Name] community.
Yours Sincerely, [Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Pin Code] [Email Address] [Phone Number]
Tailoring a University Application Letter to Highlight Community Service Experiences

The Admission Committee, [University Name], [University Address], [City, State, Zip Code]
I hope this letter finds you in good health. I am [Your Name], a student of [Your School Name], seeking admission to your esteemed university for the upcoming academic year.
I am writing this letter to express my keen interest in the [Course Name] program at your prestigious institution. I have always been intrigued by [Subject Name], and I am eager to explore this field under the guidance of the accomplished faculty at [University Name].
During my time at high school, I have actively participated in various community service programs that have not only enriched my life but have also enhanced my understanding of society and its needs. I was a part of the ‘Clean-Up Drive’ in my local community, where we focused on maintaining cleanliness and educating people about the importance of hygiene.
In addition, I volunteered in the ‘Joy of Giving’ initiative, aimed at providing essential supplies to underprivileged children. This experience truly humbled me and made me realize the value of giving back to society. I believe these experiences have shaped me as an individual and have taught me the importance of empathy, teamwork, and leadership.
I am certain that these experiences will enable me to contribute to the diverse community at [University Name]. I am eager to bring my commitment to service and dedication to learning to your campus, and I look forward to the possibility of contributing my skills and experiences to your distinguished institution.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of discussing my application with you further.
Yours faithfully,
[Your Name] [Your Contact Information]
Penning a University Application Letter Expressing a Deep Passion for a Specific Field of Study

To, The Admissions Office, [University Name], [University Address],
Subject: Application for Admission in [Specific Field of Study]
I, [Your Full Name], a resident of [Your City Name], am writing this letter to express my deep interest in applying for the [Specific Field of Study] program at your esteemed university for the academic year [Year of Admission].
My passion for [Specific Field of Study] was kindled during my school years, when I found myself fascinated by [Mention something specific about the field that fascinated you]. Since then, my curiosity and interest in this field have only grown. I have spent countless hours learning and honing my skills, and now I aspire to take this passion forward and delve deeper into this field at a university level.
Your esteemed university, with its excellent faculty, state-of-the-art facilities, and a rich history of producing exceptional talent in the field of [Specific Field of Study], is my dream institution. I am especially drawn to the [mention a specific aspect/feature of the university’s program that appeals to you], which I believe would greatly enhance my learning experience and provide me with a holistic understanding of the subject.
I have consistently excelled in this field during my school years [mention any achievements, awards, or recognition received]. I am confident that my dedication, coupled with the guidance of the exceptional faculty at [University Name], will equip me with the necessary skills and knowledge to contribute positively to this field.
I assure you of my utmost commitment and dedication towards my studies, and I am eager to make the most of the opportunities offered at your prestigious institution. I am hopeful that you will consider my application favorably.
Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the opportunity of being a part of [University Name].
Yours Sincerely,
[Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information]
How to Write University Admission Application Letter
Some writing tips to help you craft a better application:
- Start with your personal information including your full name, address, the date, and the recipient’s address.
- Open the letter with a formal salutation, addressing the admissions committee or specific admission officer, if known.
- Introduce yourself, your current educational status and the program you’re applying to.
- Describe your academic interests, why you chose this university, and how it aligns with your career goals.
- Highlight your academic achievements, extracurricular activities, and any relevant work or volunteer experience.
- Explain any gaps or anomalies in your academic record, if applicable.
- State how you could contribute to the university and its community.
- End with a strong closing statement expressing your enthusiasm and gratitude for being considered.
- Include a formal sign-off, your full name and signature.
- Proofread your letter multiple times for any grammatical errors, spelling mistakes or typos.
Related Topics:
- University Admission Application Fee Payment Slip
- Application for Address Change
- SBI Bank Address Change Application
View all topics →
I am sure you will get some insights from here on how to write “university admission application letter”. And to help further, you can also download all the above application samples as PDFs by clicking here .
And if you have any related queries, kindly feel free to let me know in the comments below.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

College Application Letters: Cover Letters & Letters of Continued Interest
College Application Letters
College application cover letters support your college applications, college resume, and college application essay prompts. In combination with the other elements of your college applications, particularly your college entrance essay, college application letters help establish your “why.” In short, a college application letter is a cover letter for your college applications that describes your background, skills, and interest in the school. When looking at college application cover letter examples, pay attention to the values that they express. College application letters and college entrance essays are similar in that they are exercises in personal branding. When reading college application cover letter examples, pay attention to the messages they convey.
If you’re wondering how to write a college application letter, CollegeAdvisor.com has advisors who can walk you through every part of the process. If your goal is to get into top colleges, CollegeAdvisor.com can help. We’ll analyze examples of college application letters and discuss the letter of continued interest to help you craft successful applications.
In this guide, we’ll break down the different kinds of college application letters you may encounter when completing your college applications. We’ll discuss the college application letter and the letter of continued interest, as well as teacher recommendation letters.
If you want to read college application cover letter samples, you’ve come to the right place!
What is a college application letter?
To learn how to write a college application letter, you must first understand its purpose. Do this by checking out college application cover letter examples. College application letters and college resumes serve as introductions for your college applications. Unlike college application essay prompts, there are no specific questions to answer in your cover letter. Instead, include the essential elements of university application letters: your background, what makes you unique, and your reasons for wanting to attend that particular college. In short, what makes you, you .
As you’ll see when reading example college application letters, college application cover letters are not all that different from what you would write in a cover letter when applying for a job or graduate school. The purpose of college application cover letters, college entrance essays, and college resumes is to persuade colleges that you are the strongest candidate for admissions.
College application cover letters are not the time to be shy, but they’re not the time to be pretentious either. When reading college application cover letter examples, you’ll see that there’s a fine line. Your tone matters. In your university application letters, show your experiences and accomplishments while portraying character traits that colleges value. To get into top colleges, find a balance between being proud of your accomplishments and being humble.
College application letters – Who requires them?
Unlike college entrance essays, college application letters are required by very few colleges. However, the skills you’ll develop by writing university application letters will serve you well as you approach your college application essay prompts. When researching college application examples, you’ll notice that there are optional materials to submit. If you’re serious about your college applications, submit university application letters to show your interest.
College application cover letters are particularly effective if the college does not have college application essay prompts that ask you to explain why you want to attend the school and/or why you want to study your major. They are even more strongly recommended when applying to colleges that don’t have any supplemental essays. You’ll see many college application cover letter examples that focus primarily on academics, but you can include so much more.
Though university application letters are rarely required, they provide an ideal way to introduce yourself. After all, you’ll notice when reading college application cover letter samples that the goal is to help the admissions committee get to know you as a person. You are more than just your grades and scores.
If you want to get into top colleges that don’t allow you to submit a college resume or don’t provide interviews, you need to take extra steps to earn acceptance. Often, you can repurpose content from college application essay prompts that ask why you want to study your major! The college application essay format differs from that of a college application letter, but they serve a very similar purpose.
What is a letter of continued interest?
A letter of continued interest (LOCI) is a letter you send to a college when you are deferred or placed on the waitlist. So, not everyone will need to write a college application letter of continued interest.
Your letter of continued interest has three primary goals:
- Reaffirm your interest in the school.
- Provide additional context for your application.
- Discuss accomplishments on your college resume that have occurred since you submitted your application.
In this guide on how to write a college application letter, we discuss all forms of college application letters in detail. We’ll expand on the above goals to explain the strategies for writing effective letters.
Explaining teacher recommendation letters
In addition to submitting a college application cover letter and, potentially, a letter of continued interest, your application will also include recommendation letters . These letters enhance your college application entrance essay and build on answers to supplemental college application essay prompts.
Due to the shift away from standardized testing, other parts of your college applications are inevitably getting more attention in the evaluation process. When assessing your college applications, admissions committees will often rely on letters from your teachers and counselor in place of interviews.
When reading sample college application letters of recommendation, you’ll observe that some are better than others. But, it can be a bit harder to find example teacher recommendations than it is to find college application cover letter examples. To ensure high-quality letters, create a plan well in advance of your senior year. You’ll want to ask teachers to write your recommendations who know you best beyond your grades. The strongest sample college application letters of recommendation speak to both your personal and academic strengths.
College application sample recommendation letters with the biggest impact typically come from teachers from your core junior year courses – math, science, English, and social studies. If there’s a teacher from your junior year who taught you during your sophomore or senior year too, even better! Teachers who know you through multiple environments – clubs, classes, sports, or other areas – can often do the best job speaking to your growth and achievement over time.
Choose teachers who know you best
Ultimately, the most effective sample college application letters of recommendation are written by the teachers who know you best. Pay attention to the college application requirements for each school on your list. Note when reading example college application letters of recommendation who the intended audience is. Some schools require math or science teachers for STEM and business majors , while others require English or social studies teachers for humanities majors .
For example, when looking at college application sample requirements, MIT writes “One recommendation should be from a math or science teacher, and one should be from a humanities, social science, or language teacher.” Caltech also requires one math or science teacher evaluation and one humanities or social sciences teacher evaluation.
Some applicants are tempted to send more letters than the college applications require. However, aim for quality over quantity. If you want to ask another teacher to write a recommendation letter for you, ask yourself what perspective they will bring to your college applications that isn’t already covered in your college entrance essay or other recommendation letters.
Don’t hesitate to provide materials to help your teachers and guidance counselor write their letters of recommendation for you. In fact, you should! When reading college application sample letters of recommendation, you’ll note that they are specific and provide examples where possible. Some teachers will even have you fill out a standard form to gather information from you. So, by having additional information already prepared, you are helping them tremendously.
Here are some materials you can provide to help your recommendations augment your college applications:
- College entrance essay
- College resume or a list of your extracurricular activities and awards
- Responses to college application essay prompts.
- A sample college application letter that you’re sending to one of your colleges.
- A few paragraphs about why you want to study your major or pursue your intended career.
- Key elements of the course you took with them, such as a favorite project or unit.
When preparing materials to give to teachers, read the instructions given to recommenders by MIT. Even if you aren’t applying to MIT, the information can still be helpful to know. By understanding the process of writing recommendation letters on the teacher’s side, you can see what information will help them write a strong letter for you.
Don’t wait until you’re submitting your college applications to ask your teachers for recommendations. Some teachers limit the number that they will write, and you want them to have plenty of time to write a quality recommendation. To make sure you have the best recommendations , ask teachers late in your junior year or early in your senior year.
The College Application Letter
As we’ve mentioned, a college application letter is a cover letter for your college applications. It describes your background, skills, and interest in the school. It’s different from both the college application essay format and the letter of continued interest. When reviewing college application samples, you’ll see that your cover letter works together with your college resume and college entrance essay to help admissions officers get to know you.
Below, we’ll discuss how to write a college application letter and walk through a sample college application letter. But remember, you want your letter to be original! Don’t feel limited by what’s in any examples of college application letters.
Do all schools require a college application letter?
No — few schools actually require college application letters. However, learning to write a strong college application letter can help you in other aspects of the college admissions process. Reading college application cover letter examples can also help you learn how to write for the admissions committee audience.
One of the ways to learn how to write a college application letter is to read sample college application letters. For instance, the same skills that help you write a strong and concise college application letter will help you in the college essay format, too.
The college application letter – What should I include?
So, you know the purpose of college application letters, but what should you include in them? Reading college application cover letter samples can help you determine this. While the college application essay format lends itself to focusing on one topic or story, college application cover letter examples highlight the importance of covering several different topics.

College application letters should contain the following elements:
1. school name and address.
You college application letter should follow formal letter formatting guidelines, which include writing the full name of the college or university you are applying to in the upper left hand corner of the letter. Try to be as specific as possible with the address you choose to use.
2. Salutation
A standard salutation is suitable for your college application letter. However, it is a great idea to do your research and use the full name of the admissions officer assigned to your region.
3. Introduction
The best examples of college application letters open strong. Thank the admissions committee for reviewing your application, and introduce yourself. Do you have a unique connection to the school? Can you hook the reader in some way to make them want to keep reading?
4. Explanation of academic interests
Your primary purpose in college is to earn a degree, so notice that in example college application letters most of the space is often devoted to discussing academic plans. Include your intended major and career path, as well as interdisciplinary interests.
5. Discussion of extracurricular interests
The college application essay format may be a place for you to discuss extracurricular involvement, so use this space to elaborate or discuss additional interests. These could be connected to your academic plans, but they don’t have to be.
6. Conclusion
Express your interest in the school! Impactful example college application letters have a clear and brief conclusion that reaffirms your desire to attend and enthusiasm for the opportunity to join the next class of undergraduates. Point to specific classes, professors, programs, organizations, and aspects of the college that pique your interest. No one is going to hold you to your plan, but colleges want to see that you have one.
8. Complimentary Close
Lastly, every good college application letter should include an expression of gratitude alongside your close and your signature.

In the example of a college application letter above, there are a few key details to highlight. The letter is essentially a five-paragraph essay, with one paragraph for each of the five elements. This differs significantly from the college application essay format. In this college application example, the college application letter has clear and distinct sections, and this is very common in college application cover letter samples.
Depending on your interests and plans, you could take a more integrated approach. You’ll read some examples of college application letters that center around a theme or broad plan rather than separated into individual paragraphs.
This sample college application letter is a narrative. The applicant’s goal is to tell her story to the admissions committee. The best sample college application letters paint a picture for the reader and draw the reader into the storyline. Though it can feel like being vivid and descriptive is a waste of your space, “showing instead of telling makes for stronger college applications.
How to format your college application letter?
When reading sample college application letters, you’ll observe that they are formatted very similarly to professional cover letters. Your university application letters should be one page single-spaced. The heading should also be consistent across college application letters.
- Your full address
- The date you will send the letter
- The admission officer’s name
- The college name
- The college address
Then, open your letter with a salutation. Many examples of college application letters open with “Dear” and are addressed to the admission officer. If you cannot find your regional admissions officer, it is fine to address the letter to the admissions office as was done in the sample college application letter above. Once you write the body of your letter, don’t forget your closing salutation – “Sincerely,” and then your name.
Once you read several sample college application letters, you’ll understand the best practices. After writing a university application letter for one school, you don’t need to start from scratch for additional schools. Adapt what you have to fit the next college’s context and your specific interests on their campus.
Being concise is key. Your university application letter should not be redundant. If it exceeds one page, see where information you mention is repeated elsewhere in your application. In your cover letter, focus on the content that makes you as original and unique as possible. Most importantly, don’t forget to proofread your university application letters!
Can a college application letter help me with other parts of my application?
Think of the college application cover letter as the glue that holds your college applications together. When writing it, think about it as your opportunity to show your best self. After brainstorming the content, you’ll be better equipped to craft your candidate profile into a cohesive narrative and articulate why you want to attend the college.
Though many parts of your college applications will be out of your control by the time you reach your senior fall, the college application cover letter is one that you can control. Use it to elevate your college applications, show interest in your top schools , and make yourself stand out among other applicants!

The Letter of Continued Interest
Another form of college application letter is a letter of continued interest . In sample college application letters of continued interest, you’ll see that the primary purpose is to reaffirm your candidacy for a spot in the next incoming class of undergraduates.
Though it can feel like a waiting game, the waitlist should not be passive. As soon as you are waitlisted or deferred, begin crafting a letter of continued interest. The best college application sample LOCIs are submitted promptly. Put in the effort to show you’re serious about attending.
College application example LOCIs should focus on recent updates. Likely, a lot has happened since you submitted your application, particularly if you applied by the early deadlines. Strong college application sample LOCIs convey accomplishments and experiences that either add to previously mentioned ones or provide another dimension to your application.
Letter of continued interest – When and where to submit?
Learn as much as you can by reading college application example LOCIs, but know that each school’s process for when and how to submit them is different. Additionally, the process may vary based on whether you were deferred to the regular decision round of admissions or waitlisted after the regular decision round. It’s important to follow each university’s directions.
Many schools will request that you upload your letter of continued interest to a portal. Some will request that you email it to an address – typically the admissions office. Others won’t allow you to submit any additional materials. If you’re in doubt, call or email the admissions office and ask.
What to include in your letter of continued interest?
You’ll notice common trends when reading college application sample LOCIs. Effective college application example LOCIs convey a tone of sincerity, gratitude, and enthusiasm for an opportunity to attend. A strong sample college application letter of continued interest includes four elements.
First, reaffirm your interest in attending the school if offered the chance to matriculate. Then, discuss relevant developments to your application, such as additional extracurricular accolades and continued academic successes. Sometimes, you’ll see a sample college application letter of continued interest that mentions how a student improved a lower mid-year grade or discusses a new leadership role.
When reading a sample college application letter of continued interest, remember that colleges are looking for reasons to admit you, so don’t be shy! Offer to answer any questions they have and provide additional info in the conclusion of your letter.
It’s important to back up your claims with supporting evidence. Strong college application sample LOCIs provide examples and specific details, just as you would in a cover letter or essay. Be vivid and descriptive as you share your story!
However, college application example LOCIs that include overly emotional appeals or merely complement the university are unlikely to be effective. Your letter of continued interest should be all about you. Though it can be difficult to realize this when reading college application example LOCIs, recognize that the content of your letter should fit within the context of the rest of your application.
The many types of college application letters – Final Thoughts
In this guide, we covered several types of letters associated with your college process – college application cover letters, teacher recommendation letters, and letters of continued interest. Reading sample college application letters, whether they are college application cover letter samples or LOCIs, can help you do your best work. But, remember that every applicant’s college application process is unique.
Our final tips for writing college application letters:
- Proofread. College application letters with typos or grammatical errors reflect poorly on your effort and candidacy. Use a polished and professional tone in everything you write for your college applications.
- Be yourself. Though this goal can get lost in the requirements, scores, and grades, you should focus on helping the colleges on your list get to know who you are .
- Follow the requirements. Each college has their own requirements for how they want you to submit materials. Pay close attention to the details for each college as you go through the admissions process.
CollegeAdvisor.com can help guide you through every step of the college application process. Check out our blog , webinars , or register with CollegeAdvisor.com today. Good luck!

This guide to college application letters and letters of continued interest was written by Caroline Marapese, Notre Dame ‘22. At CollegeAdvisor, we have built our reputation by providing comprehensive information that offers real assistance to students. If you want to get help with your college applications from CollegeAdvisor.com Admissions Experts , click here to schedule a free meeting with one of our Admissions Specialists. During your meeting, our team will discuss your profile and help you find targeted ways to increase your admissions odds at top schools. We’ll also answer any questions and discuss how CollegeAdvisor.com can support you in the college application process.
Personalized and effective college advising for high school students.
- Advisor Application
- Popular Colleges
- Privacy Policy and Cookie Notice
- Student Login
- California Privacy Notice
- Terms and Conditions
- Your Privacy Choices
By using the College Advisor site and/or working with College Advisor, you agree to our updated Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy , including an arbitration clause that covers any disputes relating to our policies and your use of our products and services.
Published In: Letters
Writing a College Application Letter (Samples & Examples)
Writing a great college application letter can be one of the most challenging prose pages that one has to put together in their high school career. On the one hand, it is just but a simple single-page document, but on the other, how do you talk about the things you need to talk about without boring the reader? A well-written college application letter will give you an edge among the thousands of applicants sending in their applications for the same college. A well-drafted college application letter should highlight your academic achievements, extracurricular, athletic, and community service achievements that will help you stand out during the highly competitive selection process.
What is a College Application Letter?
A college application letter is a letter used in several academic applications that college students need to undergo. It is usually a requirement of the academic institution where the student is currently attending. The letter can also be used for other special functions that the applicant would like to undertake.
How to Write a Great College Application Letter
Read the instructions carefully.
It is said that starting an application letter is usually the most challenging part. You may think that it is redundant that we mention that you need to go through the instructions carefully, but with all the stress and excitement that characterizes this period, you need to be keen on this.
If you fail to follow the application guidelines, you may come off as someone who won’t follow simple instructions of the university’s program. The page and word count limits are usually included in the instructions for a reason, and you should be able to organize your submission by following the set guidelines.
Go through the instructions several times and gather your notes before creating an outline to organize your application letter and decide what message you would like to send.
Do some research
Before writing your application letter, it is important that you do some research about the institution and their preferred candidates. By doing so, you will be able to tailor your application to fit their preferences, thereby increasing your chances of being selected.
Include your contact information
When writing, make sure to include your contact details. Use your professional email and provide a phone number that is always active to not miss out on any important communications.
Confirm the recipient’s contact information
When doing your research, also make sure to find out the correct address to send your application. You don’t want to go through the trouble of drafting your application to send it to the wrong address. The contact information is usually included in the instructions, but if not included, you can check the college’s website or contact the institution directly to find out to whom you should address the letter.
Create a great subject line
To make sure that the recipient clearly understands your letter’s purpose immediately, they start reading it and explain it in a few words. For example, you can write something like “Application for an intern position at ABC college.”
If you are sending the letter via mail, make sure to include such wording in the subject line.
Introduce yourself
Start your application letter with a compelling introduction. Although great writing may be hard to achieve, it is always possible to do so if you are smart about it. Introduce yourself properly as this will determine if the reader continues to read your document or if they will throw it in the trash. The recipient will only spend a few minutes reviewing your essay, so you have to start your introduction with a great introduction about yourself that will keep them engaged.
Tell the recipient about your education
Since you are a recent graduate or student, your educational background is your key asset. Make sure to properly highlight this at the very beginning of your application letter. Tell the recipient what you studied along with where and when you will be graduating if applicable.
Explain why you are the best candidate
Colleges are always looking for authenticity and quality thinking, so you should not try to shape your application around ideas or phrases that people have used several times before, but base it on your genuine beliefs.
In one or two paragraphs, explain to the recipient why your education and skills make you the best candidate. If you have already gained any relevant experience through summer jobs or interviews, you can also mention it in your application.
Include a call to action
End your application letter with a call to action- ask the recipient for an interview and direct them to review read your portfolio or resume. You can also be proactive and inform the recipient that you will be following up with an email or with a call to schedule an interview.
Show gratitude
Conclude your application by expressing your gratitude to the recipient for their time and consideration. After finishing your letter, make sure to sign it professionally.
Check your grammar and spelling
Even though you can write conventionally, spelling and grammar still need to be correct. Go through your letter and make sure that it is free of any grammatical errors before submitting it.
What Should Be Included in Your Application Letter
Regardless of the recommended length, your college application letter should show evidence that you performed due diligence concerning the selected college. You don’t want to include any irrelevant information or that you “think” should be included. Conduct your research and lay down the facts. You can visit the college website and look at local news to find out what is happening on campus.
Sound structure
An application letter should be both formal and professional. Structure your application letter in business letter format, and include your contact information, your name, title, date, and address of the recipient. Also, make sure to use a proper salutation, e.g., “Dear Application Committee,” alternatively, if you already have their name and title, you can use “Dear (their last name)”
Even college application letters, although formal, can showcase a person’s personality, passion, and sense of humor. Just as college application essays are meant to add color to the applicant’s back and white representation, so too can the college application letter tell a little more about the applicant. Choosing a single area from your application on which t expound tells the recipient what you consider important.
College Connection
When writing your application, you should highlight how you see yourself fitting in on the college campus. Legacy students may speak to their family’s pride in their family’s rich history at the college. Others with political affiliations might refer to their intentions of becoming active student leaders. And athletes might talk about their previous high school success and how they expect to contribute to their college teams.
College Application Letter Samples
Every student wants to stand out and be chosen for a position at the college of their choice. With thousands of students sending in their application letters each day, you have to make sure that your letter is perfectly crafted to give you a competitive edge. This is where we come in! Our college application letter templates are simple, unique, and impressive, and they are beautifully crafted to help you stand out. Choose and download our free and premium templates to help you in your writing.

Your college application letter will serve as a shortcut through the pile of thousands of papers sent in by applicants each day. The letter is not a synopsis of your transcripts, nor is it a prompt of your resume. Rather, it is a cover letter that introduces you as an applicant and offers the recipient a glimpse into your potential fit at the college. Make sure that you are meticulous with your writing and that everything is as it should. You don’t want to send a letter that is half baked and expects to stand out. Take your time and draft a great letter. We wish you nothing but luck in your application.
Related Documents
College Admission Letter Example: Free & Effective
In this article, I will share a step-by-step process with personal insights and a customizable template to begin your journey.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the Purpose : Recognize that your letter is more than just an application; it’s a narrative of your academic journey, achievements, and the unique qualities you bring to the university.
- Be Authentic : Authenticity resonates. Share real-life examples that highlight your strengths, resilience, and character.
- Structure is Key : A well-structured letter includes an introduction, body paragraphs detailing achievements and experiences, and a conclusion that reaffirms your interest in the program.
- Customize Your Letter : Tailor your letter to each college by mentioning specific programs, professors, or opportunities that excite you about attending.
- Proofread and Revise : Ensuring your letter is free from errors is crucial. Seek feedback and make revisions to polish your narrative.
- Free Template : Start with a template but personalize it to reflect your genuine interest and enthusiasm for the college and program.
Step 1: Start with a Strong Introduction
Your opening sentence sets the tone for your entire letter. Begin by introducing yourself and expressing your enthusiastic interest in the college and the specific program you are applying to.
Mention what draws you to the institution and how you believe it aligns with your academic goals and career aspirations.
Example Introduction : “I am thrilled to submit my application for the [Program Name] at [College Name]. The innovative curriculum and the college’s commitment to [specific aspect, like ‘community service’ or ‘research excellence’] resonate deeply with my academic interests and personal values.”
Step 2: Highlight Your Academic and Personal Achievements
In this section, delve into your academic journey, significant achievements, and the challenges you’ve overcome. Emphasize any unique experiences that have shaped your perspective and prepared you for college. This could include leadership roles, community service, internships, or special projects.

- List of Achievements : Include awards, recognitions, or notable projects.
- Personal Growth : Share experiences that demonstrate resilience, leadership, and personal growth.
- Relevance : Connect your experiences to how they’ve prepared you for the program you’re applying to.
Step 3: Explain Why You’ve Chosen This College
This is where your research about the college pays off. Discuss specific aspects of the college or program that excite you. Mention any professors whose work you admire, the unique opportunities the college offers, and how these align with your academic and career goals.
- Program Specifics : Courses, professors, or research opportunities that attract you.
- College Culture : Aspects of the college’s culture or values that resonate with you.
- Career Goals : How the program aligns with your career aspirations.
Step 4: Conclude with Confidence
Your concluding paragraph should reiterate your excitement and readiness for the college experience. Affirm your belief that the college is the ideal place for you to achieve your academic and professional goals. Express your eagerness to contribute to the college community.

Example Conclusion : “I am eager to bring my passion for [your field of interest], along with my dedication to [specific contribution, like ‘community service’ or ‘academic research’], to [College Name].
I am confident that [College Name] is the perfect environment for me to thrive academically and personally, and I look forward to the opportunity to contribute to your vibrant community.”
Tips from Personal Experience
- Be Yourself : Authenticity cannot be overstated. Admission officers are adept at distinguishing genuine narratives from embellished ones.
- Customization Is Key : A generic letter won’t stand out. Customize your letter for each application to reflect your genuine interest in the program and college.
- Seek Feedback : Before submitting, have someone review your letter. Fresh eyes can catch errors and offer valuable perspective.
- Follow Instructions : Adhere to any specific guidelines provided by the college. This demonstrates attention to detail and respect for the application process.
College Application Letter Sample
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, Zip] [Email Address] [Phone Number] [Date]
[Admissions Office] [College Name] [College Address] [City, State, Zip]
Dear Admissions Committee,
[Introduction: Introduce yourself and express your interest in the specific program and college.]
[Body Paragraph 1: Highlight your academic achievements and any relevant experiences.]
[Body Paragraph 2: Discuss specific aspects of the college or program that appeal to you and how they align with your goals.]
[Conclusion: Reiterate your excitement about the opportunity to attend and your belief in the fit between your aspirations and the college’s offerings.]
[Your Name]
I invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Whether you’re embarking on writing your own admission letter or refining an existing draft, I’m here to offer guidance and support. What challenges are you facing in your writing process? Let’s start a conversation to navigate this journey together.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

Q: What is a College Application Letter?
Answer : A College Application Letter is a document that a student submits to a college or university as part of their application for admission. The letter typically provides information about the student’s academic background, extracurricular activities, personal qualities, and other factors that make them a good candidate for admission.
Q: What should be included in a College Application Letter?
Answer : A College Application Letter should include the student’s name, contact information, and the name of the college or university they are applying to.
It should also provide information about the student’s academic background, including their GPA, test scores, and any relevant coursework or academic achievements.
Additionally, the letter should highlight the student’s extracurricular activities, personal qualities, and other factors that make them a good candidate for admission.
Q: How long should a College Application Letter be?
Answer : The length of a College Application Letter can vary, but it is generally recommended that the letter be no longer than one page. The letter should be concise, well-organized, and easy to read.
Q: What is the purpose of a College Application Letter?
Answer : The purpose of a College Application Letter is to provide the college or university with information about the student that is not included in other parts of the application, such as transcripts and test scores.
The letter is an opportunity for the student to showcase their personality, interests, and achievements, and to demonstrate why they would be a good fit for the college or university.
Q: How important is a College Application Letter in the admissions process?
Answer : A College Application Letter can be an important factor in the admissions process, as it provides the college or university with additional information about the student that is not included in other parts of the application.
The letter can help the student stand out from other applicants and demonstrate why they would be a good fit for the college or university. However, the weight placed on the letter can vary depending on the specific college or university and their admissions process
Related Articles
Sample letter of withdrawal of enrollment: free & effective, school transfer letter sample: free & effective, 7 great summer jobs for college students, how to get on college mailing lists, college admissions cover letter [free sample], letter of withdrawal from college due to personal problems: free & effective, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A college admission application letter is a professional letter a student writes to send to a college with their college application. Writing a college admission application letter is a great way to make your college admission application stand out in the highly competitive application process. Write your letter in a professional format and tone and double-check for errors.
The college application letter will be:. Dear Admissions Committee,. I am writing to express my strong interest in applying to [University Name] for the upcoming academic year. As a dedicated and ambitious student, I am confident that this institution will provide me with the resources and opportunities I need to achieve my academic and career goals. ...
9+ Trainee Appointment Letters. Download Samples in DOC, PDF, or Other Formats to Compose a College Application Letters for a School Admission. Quickly Prepare a Document for Entrance into Any College or University. Enjoy Free Downloads Now and Write a College Application in Google Docs, MS Word, and More.
Successful Application Letter for University Admission. First, find the sample template for university admission application letter below. I, [Your Full Name], resident of [Your Address], am writing this letter to show my keen interest in applying for the [Name of the Course] at your esteemed university for the academic year [Year].
Answer: A college application letter is used by a student who would like to enrol in a learning institution. ... A college admission application letter is used by a student who would like to apply for an academic slot for a specific course offered by a school. You may also see Academic Application Letters.
1. School Name and Address. You college application letter should follow formal letter formatting guidelines, which include writing the full name of the college or university you are applying to in the upper left hand corner of the letter. Try to be as specific as possible with the address you choose to use. 2.
For example: Name of admission officer, Name of college Street address City, state, zip code. Include a salutation. The admission application letter is a formal correspondence, which means you must address the reader formally and try to avoid adding some sort of language as To whom it may concern, Hi, Hello or good morning.
Use a proper salutation. Begin your college application letter with a formal salutation. The standard, in this case, is "Dear". Be sure to avoid informal salutations such as "Hey", "Hi", and "Hello". 💡 Tip: Do your best to personalize your university application letter in every way that you can.
Our college application letter templates are simple, unique, and impressive, and they are beautifully crafted to help you stand out. Choose and download our free and premium templates to help you in your writing. College Application Letter Sample 01. Download. College Application Letter Sample 02.
Example Introduction: "I am thrilled to submit my application for the [Program Name] at [College Name]. The innovative curriculum and the college's commitment to [specific aspect, like 'community service' or 'research excellence'] resonate deeply with my academic interests and personal values.".
Follow these steps to write an impressive college application cover letter: 1. Write your name and street address. At the top of your cover letter, write your first and last name. On a separate line include your street address, followed by your city, state and zip code on another line. 2.
I appreciate your time and consideration and look forward to hearing from you soon. Sincerely, . Signature of Applicant. Printed Name of Applicant. Enclosure: Application Form, high school marks list, Advanced Placement scores, SAT scores and all other required information. Sample 2 - College Application Letter. Name of Applicant.
Answer: Dear Admissions Committee, I am writing this letter to express my strong interest in applying to [Name of College/University]. I have always been interested in pursuing higher education in [Major or Field of Study], and after extensive research and conversations with alumni and current students, I have come to the conclusion that [Name ...
Explanation: This application letter sample shows the correct format you should use when sending out your application letter in print form. If you plan on submitting your application letter via email, refer to the second application letter sample below. Advertisement.