Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples

How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
Published on November 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
A problem statement is a concise and concrete summary of the research problem you seek to address. It should:
- Contextualize the problem. What do we already know?
- Describe the exact issue your research will address. What do we still need to know?
- Show the relevance of the problem. Why do we need to know more about this?
- Set the objectives of the research. What will you do to find out more?
Table of contents
When should you write a problem statement, step 1: contextualize the problem, step 2: show why it matters, step 3: set your aims and objectives.
Problem statement example
Other interesting articles
Frequently asked questions about problem statements.
There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement.
In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualize and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal . Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction .
A problem statement looks different depending on whether you’re dealing with a practical, real-world problem or a theoretical issue. Regardless, all problem statements follow a similar process.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The problem statement should frame your research problem, giving some background on what is already known.
Practical research problems
For practical research, focus on the concrete details of the situation:
- Where and when does the problem arise?
- Who does the problem affect?
- What attempts have been made to solve the problem?
Theoretical research problems
For theoretical research, think about the scientific, social, geographical and/or historical background:
- What is already known about the problem?
- Is the problem limited to a certain time period or geographical area?
- How has the problem been defined and debated in the scholarly literature?
The problem statement should also address the relevance of the research. Why is it important that the problem is addressed?
Don’t worry, this doesn’t mean you have to do something groundbreaking or world-changing. It’s more important that the problem is researchable, feasible, and clearly addresses a relevant issue in your field.
Practical research is directly relevant to a specific problem that affects an organization, institution, social group, or society more broadly. To make it clear why your research problem matters, you can ask yourself:
- What will happen if the problem is not solved?
- Who will feel the consequences?
- Does the problem have wider relevance? Are similar issues found in other contexts?
Sometimes theoretical issues have clear practical consequences, but sometimes their relevance is less immediately obvious. To identify why the problem matters, ask:
- How will resolving the problem advance understanding of the topic?
- What benefits will it have for future research?
- Does the problem have direct or indirect consequences for society?
Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it.
The research aim is the overall purpose of your research. It is generally written in the infinitive form:
- The aim of this study is to determine …
- This project aims to explore …
- This research aims to investigate …
The research objectives are the concrete steps you will take to achieve the aim:
- Qualitative methods will be used to identify …
- This work will use surveys to collect …
- Using statistical analysis, the research will measure …
The aims and objectives should lead directly to your research questions.
Learn how to formulate research questions
You can use these steps to write your own problem statement, like the example below.
Step 1: Contextualize the problem A family-owned shoe manufacturer has been in business in New England for several generations, employing thousands of local workers in a variety of roles, from assembly to supply-chain to customer service and retail. Employee tenure in the past always had an upward trend, with the average employee staying at the company for 10+ years. However, in the past decade, the trend has reversed, with some employees lasting only a few months, and others leaving abruptly after many years.
Step 2: Show why it matters As the perceived loyalty of their employees has long been a source of pride for the company, they employed an outside consultant firm to see why there was so much turnover. The firm focused on the new hires, concluding that a rival shoe company located in the next town offered higher hourly wages and better “perks”, such as pizza parties. They claimed this was what was leading employees to switch. However, to gain a fuller understanding of why the turnover persists even after the consultant study, in-depth qualitative research focused on long-term employees is also needed. Focusing on why established workers leave can help develop a more telling reason why turnover is so high, rather than just due to salaries. It can also potentially identify points of change or conflict in the company’s culture that may cause workers to leave.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives This project aims to better understand why established workers choose to leave the company. Qualitative methods such as surveys and interviews will be conducted comparing the views of those who have worked 10+ years at the company and chose to stay, compared with those who chose to leave.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/problem-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Ultimate Guide to the AP Research Course and Assessment

Is your profile on track for college admissions?
Our free guidance platform determines your real college chances using your current profile and provides personalized recommendations for how to improve it.
The Advanced Placement (AP) curriculum is administered by the College Board and serves as a standardized set of year-long high school classes that are roughly equivalent to one semester of college-level coursework. Although most students enroll in an actual course to prepare for their AP exams, many others will self-study for the exams without enrolling in the actual AP class.
AP classes are generally stand-alone subjects that easily translate to traditional college courses. Typically, they culminate in a standardized exam on which students are graded using a 5-point scale, which colleges and universities will use to determine credit or advanced standing. Starting in fall of 2014, though, this traditional AP course and exam format has begun to adapt in efforts by the College Board to reflect less stringent rote curriculum and a heavier emphasis on critical thinking skills.
The AP Capstone program is at the center of these changes, and its culmination course is AP Research. If you are interested in learning more about the AP Research Course and Assessment, and how they can prepare you for college-level work, read on for CollegeVine’s Ultimate Guide to the AP Research Course and Assessment.
About the Course and Assessment
The AP Research course is the second of two classes required for the AP Capstone™ Diploma . In order to enroll in this course you need to have completed the AP Seminar course during a previous year. Through that course, you will have learned to collect and analyze information with accuracy and precision, developed arguments based on facts, and effectively communicated your conclusions. During the AP Research course, you apply these skills on a larger platform. In the AP Research course, you can expect to learn and apply research methods and practices to address a real-world topic of your choosing, with the end result being the production and defense of a scholarly academic paper. Students who receive a score of 3 or higher on both the AP Seminar and AP Research courses earn an AP Seminar and Research Certificate™. Students who receive a score of 3 or higher on both courses and on four additional AP exams of their choosing receive the AP Capstone Diploma™.
The AP Research course will guide you through the design, planning, and implementation of a year-long, research-based investigation to address a research question of interest to you. While working with an expert advisor, chosen by you with the help of your teacher, you will explore an academic topic, problem, or issue of your choosing and cultivate the skills and discipline necessary to conduct independent research and produce and defend a scholarly academic paper. Through explicit instruction in research methodology, ethical research practices, and documentation processes, you will develop a portfolio of scholarly work to frame your research paper and subsequent presentation of it.
Although the core content and skills remain standardized for every AP Research course, the implementation of this instruction may vary. Some AP Research courses may have a specific disciplinary focus wherein the course content is rooted in a specific subject, such as AP Research STEM Inquiries or AP Research Performing and Visual Arts. Similarly, other AP Research courses are offered in conjunction with a separate and specific AP class, such as AP Research and AP Biology wherein students are concurrently enrolled in both AP courses and content is presented in a cross-curricular approach. Alternatively, AP Research may be presented in the form of an internship wherein students who are already working with a discipline-specific expert adviser conduct independent studies and research of the student’s choosing while taking the AP Research class. Finally, some AP Research courses are delivered independently as a research methods class. In this style of class, students develop inquiry methods for the purpose of determining which method best fits their chosen topic of inquiry/research question, and each student then uses a selected method to complete his or her investigation.
Only schools that currently offer the AP Capstone Diploma may offer the AP Research course. Because it is a part of a larger comprehensive, skills-based program, students may not self-study for the AP Research course or final paper. At this time, home-schooled students, home-school organizations, and online providers are not eligible to participate in AP Capstone.
Your performance in the AP Research course is assessed through two performance tasks. The first is the Academic Paper, which accounts for 75% of your total AP score. In this paper, you will present the findings of your yearlong research in 4,000-5,000 words. Although the official submission deadline for this task is April 30, the College Board strongly recommends that this portion of your assessment be completed by April 15 in order to allow enough time for the second of your performance tasks.
The second performance task is your Presentation and Oral Defense, which accounts for the remaining 25% of your total AP score. Using your research topic, your will prepare a 15-20 minute presentation in an appropriate format with appropriate accompanying media. Your defense will include fielding three to four questions from a panel consisting of your AP Research teacher and two additional panel members chosen at the discretion of your teacher.
In 2016, fewer than 3,000 students submitted an AP Research project, but enrollment is projected to grow rapidly, since 12,000 students took the AP Seminar assessment in 2016 and most will presumably go on to submit an AP Research project in 2017. Scores from the 2016 AP Research projects reveal a high pass rate (score of three or higher) but a difficult rate of mastery. While 67.1% of students taking the assessments scored a three or higher, only 11.6% received the highest score of a five, while nearly 40% received a three. Only 2% of students submitting research projects received the lowest score of one.
A full course description that can help to guide your planning and understanding of the knowledge required for the AP Research course and assessments can be found in the College Board course description .
Read on for tips for successfully completing the AP Research course.
How Should I Prepare for the AP Research Course?
As you undertake the AP Research course and performance tasks, you will be expected to conduct research, write a scholarly paper, and defend your work in a formal presentation. Having already completed the AP Seminar course, these skills should be familiar to you. You should use your scores on the AP Seminar performance task to help guide your preparations for the AP Research performance tasks.
Carefully review your scores from AP Seminar. Make sure you understand where points were lost and why. It may be helpful to schedule a meeting with your AP Seminar teacher to review your work. Alternatively, your AP Research teacher may be willing to go over your AP Seminar projects with you. You might also ask a classmate to review your projects together to get a better idea of where points were earned and where points were lost. Use this review as a jumping point for your AP Research studies. You should go into the course with a good idea of where your strengths lie, and where you need to focus on improving.
A sample timeline for the AP Research course is available on page 36 of the course description . One detail worth noting is that the recommended timeline actually begins not in September with the start of the new school year, but instead begins in May with the completion of the AP Seminar course during the previous school year. It is then that you should begin to consider research topics, problems, or ideas. By September of the following school year, it is recommended that you have already finalized a research question and proposal, completed an annotated bibliography, and prepared to begin a preliminary inquiry proposal for peer review.
What Content Will I Be Held Accountable For During the AP Research Course?
To be successful in the AP Research class, you will begin with learning to investigate relevant topics, compose insightful problem statements, and develop compelling research questions, with consideration of scope, to extend your thinking. Your teacher will expect you to demonstrate perseverance through setting goals, managing time, and working independently on a long-term project. Specifically, you will prepare for your research project by:
- Identifying, applying, and implementing appropriate methods for research and data collection
- Accessing information using effective strategies
- Evaluating the relevance and credibility of information from sources and data
- Reading a bibliography for the purpose of understanding that it is a source for other research and for determining context, credibility, and scope
- Attributing knowledge and ideas accurately and ethically, using an appropriate citation style
- Evaluating strengths and weaknesses of others’ inquiries and studies
As in the AP Research course, you will continue to investigate real-world issues from multiple perspectives, gathering and analyzing information from various sources in order to develop credible and valid evidence- based arguments. You will accomplish this through instruction in the AP Research Big Ideas, also called the QUEST Framework. These include:
- Question and Explore: Questioning begins with an initial exploration of complex topics or issues. Perspectives and questions emerge that spark one’s curiosity, leading to an investigation that challenges and expands the boundaries of one’s current knowledge.
- Understand and Analyze Arguments: Understanding various perspectives requires contextualizing arguments and evaluating the authors’ claims and lines of reasoning.
- Evaluate Multiple Perspectives: Evaluating an issue involves considering and evaluating multiple perspectives, both individually and in comparison to one another.
- Synthesize Ideas: Synthesizing others’ ideas with one’s own may lead to new understandings and is the foundation of a well-reasoned argument that conveys one’s perspective.
- Team, Transform, and Transmit: Teaming allows one to combine personal strengths and talents with those of others to reach a common goal. Transformation and growth occur upon thoughtful reflection. Transmitting requires the adaptation of one’s message based on audience and context.
In addition, you will use four distinct reasoning processes as you approach your research. The reasoning processes are situating, choosing, defending , and connecting . When you situate ideas, you are aware of their context in your own perspective and the perspective of others, ensuring that biases do not lead to false assumptions. When you make choices about ideas and themes, you recognize that these choices will have both intended and unintentional consequences. As you defend your choices, you explain and justify them using a logical line of reasoning. Finally, when you connect ideas you see intersections within and/or across concepts, disciplines, and cultures.
For a glossary of research terms that you should become familiar with, see page 62 of the course description .
How Will I Know If I’m Doing Well in the AP Research Course?
Because your entire score for the AP Research course is determined by your research paper and presentation, which come at the very end of the course, it can be difficult to gauge your success until that point. Do yourself a favor and do not wait until your final scores come back to determine how successful you have been in the course.
As you undertake the AP Research course, there will be many opportunities for formative assessments throughout the semester. These assessments are used to give both you and your teacher an idea of the direction of instruction needed for you to master the skills required in the AP Research course. You should use these assessments to your advantage and capitalize on the feedback you receive through each. A list of possible activities used for these assessments can be found on page 41 of the course description .
Another way that you and your teacher will track your progress is through your Process and Reflection Portfolio (PREP). The PREP serves to document your development as you investigate your research questions, thereby providing evidence that you have demonstrated a sustained effort during the entire inquiry process. You will review your PREP periodically with your teacher, who will use it as a formative assessment to evaluate your progress.
Throughout the course, you will be assigned prompts and questions to respond to in your PREP. You will use this portfolio to document your research or artistic processes, communication with your expert adviser, and reflections on your thought processes. You should also write freely, journaling about your strengths and weaknesses with regard to implementing such processes and developing your arguments or aesthetic rationales.
Your final PREP should include:
- Table of contents
- Completed and approved proposal form
- Specific pieces of work selected by the student to represent what he or she considers to be the best showcase for his or her work. (Examples might include: in-class (teacher-directed) free-writing about the inquiry process, resource list, annotated bibliography of any source important to the student’s work, photographs, charts, spreadsheets, and/or links to videos or other relevant visual research/project artifacts, draft versions of selected sections of the academic paper, or notes in preparation for presentation and oral defense.)
- Documentation of permission(s) received from primary sources, if required — for example, permission(s) from an IRB or other agreements with individuals, institutions, or organizations that provide primary and private data such as interviews, surveys, or investigations
- Documentation or log of the student’s interaction with expert adviser(s) and the role the expert adviser(s) played in the student’s learning and inquiry process (e.g., What areas of expertise did the expert adviser have that the student needed to draw from? Did the student get the help he or she needed — and if not, what did he or she do to ensure that the research process was successful? Which avenues of exploration did the expert adviser help the student to discover?)
- Questions asked to and feedback received from peer and adult reviewers both in the initial stages and at key points along the way
- Reflection on whether or not the feedback was accepted or rejected and why
- Attestation signed by the student which states, “I hereby affirm that the work contained in this Process and Reflection Portfolio is my own and that I have read and understand the AP Capstone TM Policy on Plagiarism and Falsification or Fabrication of Information”
It cannot be stressed enough how important it is to maintain strong communications with your teacher as you progress through the AP Research course. Not only is your teacher your best resource for learning new skills and knowledge, but also it is your teacher who will be responsible for grading your final performance tasks and as such, you should always have a strong understanding of how your work is being assessed and the ways in which you can improve it. Remember, your teacher wants you to succeed just as much as you do; work together as a team to optimize your chances.
How Should I Choose a Research Topic?
You will begin to consider research topics before the school year even starts. If your AP Research class is offered in conjunction with another course, such as those rooted in a specific subject or linked to another concurrent AP course, you will have some idea of the direction in which your research should head. Regardless of whether you know the precise subject matter of your topic, you should begin by asking yourself what you want to know, learn, or understand. The AP Research class provides a unique opportunity for you to guide your own learning in a direction that is genuinely interesting to you. You will find your work more engaging, exciting, and worthwhile if you choose a topic that you want to learn more about.
As you begin to consider research topics, you should:
- Develop a list of topics and high-level questions that spark your interest to engage in an individual research project
- Identify potential expert advisers to guide you in the planning and development of your research project (For tips on how to find a mentor, read CollegeVine’s “ How to Choose a Winning Science Fair Project Idea ”)
- Identify potential opportunities (if you are interested) to perform primary research with an expert adviser during the summer, via internships or summer research projects for high school students offered in the community and local higher education institutions
- Discuss research project planning skills and ideas with students who are currently taking or have already taken the AP Research course
You might also find inspiration from reading about past AP Research topics. One list of potential research questions can be found here and another can be found here . Keep in mind that these lists make great starting points and do a good job of getting you thinking about important subjects, but your research topic should ultimately be something that you develop independently as the result of careful introspection, discussions with your teacher and peers, and your own preliminary research.
Finally, keep in mind that if you pursue a research project that involves human subjects, your proposal will need to be reviewed and approved by an institutional review board (IRB) before experimentation begins. Talk with your teacher to decide if this is the right path for you before you get too involved in a project that may not be feasible.
Once you have decided on a research topic, complete an Inquiry Proposal Form. This will be distributed by your teacher and can also be found on page 55 of the course description .
How Do I Conduct My Research?
By the time you begin your AP Research course, you will have already learned many of the basics about research methods during your AP Seminar course. You should be comfortable collecting and analyzing information with accuracy and precision, developing arguments based on facts, and effectively communicating your point of view. These will be essential skills as you move forward in your AP Research project.
As you undertake your work, remember the skills you’ve already learned about research:
- Use strategies to aid your comprehension as you tackle difficult texts.
- Identify the author’s main idea and the methods that he or she uses to support it.
- Think about biases and whether other perspectives are acknowledged.
- Assess the strength of research, products, and arguments.
- Look for patterns and trends as you strive to make connections between multiple arguments.
- Think about what other issues, questions, or topics could be explored further.
You should be certain to keep track of all sources used in your research and cite them appropriately. The College Board has a strict policy against plagiarism. You can read more about its specifics on page 60 of the course description .
How Do I Write My Paper?
Before you begin writing your final paper, make sure to thoroughly read the Task Overview handout which will be distributed by your teacher. If you would like to see it beforehand, it can be found on page 56 of the course description . You should also review the outline of required paper sections on page 49 of the course description .
Your paper must contain the following sections:
› Introduction
› Method, Process, or Approach
› Results, Product, or Findings
› Discussion, Analysis, and/or Evaluation
› Conclusion and Future Directions
› Bibliography
Before you begin writing, organize your ideas and findings into an outline using the sections listed above. Be sure to consider how you can connect and analyze the evidence in order to develop an argument and support a conclusion. Also think about if there are any alternate conclusions that could be supported by your evidence and how you can acknowledge and account for your own biases and assumptions.
Begin your paper by introducing and contextualizing your research question or problem. Make sure to include your initial assumptions and/or hypothesis. Next, include a literature review of previous work in the field and various perspectives on your topic. Use the literature review to highlight the gap in the current field of knowledge to be addressed by your research project. Then, explain and justify your methodology, present your findings, evidence, or data, and interpret the significance of these findings. Discuss implications for further research or limitations of your existing project. Finally, reflect on the project, how it could impact its field, and any possible next steps. Your paper should conclude with a comprehensive bibliography including all of the sources used in your process.
Make sure to proofread and edit your paper yourself, have it proofread and edited by a friend, and then proofread and edit it again before you complete your final draft.
How Do I Prepare For My Oral Defense?
Once your paper is finished, you may be tempted to sit back and rest on your laurels. Although you’ve no doubt expended a tremendous about of energy in producing a final product you can be proud of, don’t forget that the work is not over yet. Your oral defense accounts for 25% of your total score so it should be taken seriously.
Your oral defense is a 15-20 minute presentation that uses appropriate media to present your findings to an oral defense panel. You may choose any appropriate format for your presentation, as long as the presentation reflects the depth of your research. If your academic paper was accompanied by an additional piece of scholarly work (e.g., performance, exhibit, product), you should arrange with your teacher for him or her, along with the panelists, to view the scholarly work prior to your presentation.
As you plan your presentation, consider how you can best appeal to your audience. Consider different mediums for your presentation, and how those mediums might affect your credibility as a presenter. You want to be engaging to your audience while still being taken seriously.
Following your presentation, you will field three or four questions from your panelists. These will include one question pertaining to your research or inquiry process, one question focused on your depth of understanding, and one question about your reflection throughout the inquiry process as evidenced in your PREP. The fourth question and any follow-up questions are at the discretion of the panel. A list of sample oral defense questions begins on page 52 of the course description . For a complete outline of the oral defense, see page 49 of the course description .
How Will My Work Be Assessed?
Because this assessment is only available to students enrolled in the AP Capstone program, your teacher will register you for the assessment when you enroll in the course. You should confirm with your teacher that you are registered for the assessment no later than March 1.
You will submit your final paper and complete your oral presentation no later than April 30, at which point your teacher will submit your work and scores through an AP Digital Portfolio. Your presentation will be scored by your teacher alone. Your paper will be scored by your teacher and validated by the College Board.
You may find the scoring rubric from the 2016 performance tasks available here . You may find a collection authentic student research papers and scoring explanations available here .
Preparing for any AP assessment can be a stressful process. Having a specific plan of attack and a firm grasp of how your work is assessed will help you to feel prepared and score well. Use CollegeVine’s Ultimate Guide to the AP Research Course and Assessment to help shape your understanding of the course and how to complete your performance tasks effectively. When submission day arrives, you should feel better prepared and informed about the work you have produced.
For more about information about APs, check out these CollegeVine posts:
• Can AP Tests Actually Save You Thousands of Dollars?
• Should I Take AP/IB/Honors Classes?
• How to Choose Which AP Courses and Exams to Take
• What If My School Doesn’t Offer AP or IB Courses?
• Are All APs Created Equal in Admissions?
Want access to expert college guidance — for free? When you create your free CollegeVine account, you will find out your real admissions chances, build a best-fit school list, learn how to improve your profile, and get your questions answered by experts and peers—all for free. Sign up for your CollegeVine account today to get a boost on your college journey.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


- Research Process
What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
- 5 minute read
- 859.6K views
Table of Contents
The statement of the problem is one of the first things that a colleague or potential client will read. With the vastness of the information available at one’s fingertips in the online9 world, your work may have just a few seconds to draw in a reader to take a deeper look at your proposal before moving on to the next option. It explains quickly to the reader, the problem at hand, the need for research, and how you intend to do it.
A strong, clear description of the problem that drew you to your research has to be straightforward, easy to read and, most important, relevant. Why do you care about this problem? How can solving this problem impact the world? The problem statement is your opportunity to explain why you care and what you propose to do in the way of researching the problem.
A problem statement is an explanation in research that describes the issue that is in need of study . What problem is the research attempting to address? Having a Problem Statement allows the reader to quickly understand the purpose and intent of the research. The importance of writing your research proposal cannot be stressed enough. Check for more information on Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal .
It is expected to be brief and concise , and should not include the findings of the research or detailed data . The average length of a research statement is generally about one page . It is going to define the problem, which can be thought of as a gap in the information base. There may be several solutions to this gap or lack of information, but that is not the concern of the problem statement. Its purpose is to summarize the current information and where a lack of knowledge may be presenting a problem that needs to be investigated .
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way . It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
What is Included in a Problem Statement?
Besides identifying the gap of understanding or the weakness of necessary data, it is important to explain the significance of this lack.
-How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge base in your field of study?
-How is it significant?
-Why does it matter?
Not all problems have only one solution so demonstrating the need for additional research can also be included in your problem statement. Once you identify the problem and the need for a solution, or for further study, then you can show how you intend to collect the needed data and present it.
How to Write a Statement of Problem in Research Proposal
It is helpful to begin with your goal. What do you see as the achievable goal if the problem you outline is solved? How will the proposed research theoretically change anything? What are the potential outcomes?
Then you can discuss how the problem prevents the ability to reach your realistic and achievable solution. It is what stands in the way of changing an issue for the better. Talk about the present state of affairs and how the problem impacts a person’s life, for example.
It’s helpful at this point to generally layout the present knowledge and understanding of the subject at hand, before then describing the gaps of knowledge that are currently in need of study. Your problem statement is a proposed solution to address one of these gaps.
A good problem statement will also layout the repercussions of leaving the problem as it currently stands. What is the significance of not addressing this problem? What are the possible future outcomes?
Example of Problem Statement in Research Proposal
If, for example , you intended to research the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the immune system , you would begin with a review of the current knowledge of vitamin D’s known function in relation to the immune system and how a deficiency of it impacts a person’s defenses.
You would describe the ideal environment in the body when there is a sufficient level of vitamin D. Then, begin to identify the problems associated with vitamin D deficiency and the difficulty of raising the level through supplementation, along with the consequences of that deficiency. Here you are beginning to identify the problem of a common deficiency and the current difficulty of increasing the level of vitamin D in the blood.
At this stage, you may begin to identify the problem and narrow it down in a way that is practical to a research project. Perhaps you are proposing a novel way of introducing Vitamin D in a way that allows for better absorption by the gut, or in a combination with another product that increases its level in the blood.
Describe the way your research in this area will contribute to the knowledge base on how to increase levels of vitamin D in a specific group of subjects, perhaps menopausal women with breast cancer. The research proposal is then described in practical terms.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Problem statements differ depending on the type and topic of research and vary between a few sentences to a few paragraphs.
However, the problem statement should not drag on needlessly. Despite the absence of a fixed format, a good research problem statement usually consists of three main parts:
Context: This section explains the background for your research. It identifies the problem and describes an ideal scenario that could exist in the absence of the problem. It also includes any past attempts and shortcomings at solving the problem.
Significance: This section defines how the problem prevents the ideal scenario from being achieved, including its negative impacts on the society or field of research. It should include who will be the most affected by a solution to the problem, the relevance of the study that you are proposing, and how it can contribute to the existing body of research.
Solution: This section describes the aim and objectives of your research, and your solution to overcome the problem. Finally, it need not focus on the perfect solution, but rather on addressing a realistic goal to move closer to the ideal scenario.
Here is a cheat sheet to help you with formulating a good problem statement.
1. Begin with a clear indication that the problem statement is going to be discussed next. You can start with a generic sentence like, “The problem that this study addresses…” This will inform your readers of what to expect next.
2. Next, mention the consequences of not solving the problem . You can touch upon who is or will be affected if the problem continues, and how.
3. Conclude with indicating the type of research /information that is needed to solve the problem. Be sure to reference authors who may have suggested the necessity of such research.
This will then directly lead to your proposed research objective and workplan and how that is expected to solve the problem i.e., close the research gap.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier Language Editing Plus service will provide you with a thorough language review of your thesis, article or presentation. It offers review of logic and flow, reference checks, document formatting, a customized cover letter and more.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?

How to Use Tables and Figures effectively in Research Papers
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
The Research Problem & Statement
What they are & how to write them (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and Types
Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and Types
Table of Contents

Problem Statement
Definition:
Problem statement is a clear, concise, and well-defined statement that outlines the issue or challenge that needs to be addressed. It is a crucial element in any project or research as it provides a clear understanding of the problem, its context, and its potential impact.
Types of Problem Statements
There are various types of problem statements, and the type of problem statement used depends on the context and purpose of the project or research. Some common types of problem statements are:
Business Problem Statement
Business Problem Statement identifies a problem or challenge within an organization that needs to be solved. It typically includes the impact of the problem on the organization and its stakeholders, such as customers, employees, or shareholders.
Research Problem Statement
Research Problem Statement outlines the research question or problem that the study aims to address. It describes the research objectives, the significance of the research, and the potential impact of the research findings.
Design Problem Statement
Design Problem Statement defines the problem or challenge that a design project aims to solve. It includes the user’s needs, the design constraints, and the desired outcomes of the design project.
Social Problem Statement
Social Problem Statement describes a problem or challenge in society that needs to be addressed. It typically includes the social, economic, or political impact of the problem and its effect on individuals or communities.
Technical Problem Statement
Technical Problem Statement defines a problem or challenge related to technology or engineering. It includes the technical requirements, constraints, and potential solutions to the problem.
Components of Problem Statement
The components of a problem statement may vary depending on the context and purpose of the project or research, but some common components include:
- Problem description : This component provides a clear and concise description of the problem, its context, and its impact. It should explain what the problem is, who is affected by it, and why it needs to be addressed.
- Background information : This component provides context for the problem by describing the current state of knowledge or practice related to the problem. It may include a review of relevant literature, data, or other sources of information.
- Objectives : This component outlines the specific objectives that the project or research aims to achieve. It should explain what the project or research team hopes to accomplish by addressing the problem.
- Scope : This component defines the boundaries of the problem by specifying what is included and excluded from the problem statement. It should clarify the limits of the project or research and ensure that the team remains focused on the core problem.
- Methodology : This component outlines the approach or methodology that the project or research team will use to address the problem. It may include details about data collection, analysis, or other methods used to achieve the objectives.
- Expected outcomes : This component describes the potential impact or outcomes that the project or research aims to achieve. It should explain how the solution or findings will address the problem and benefit the stakeholders.
How to write Problem Statement
Here are some general steps to follow when writing a problem statement:
- Identify the problem : Clearly identify the problem that needs to be addressed. Consider the context, stakeholders, and potential consequences of the problem.
- Research the problem: Conduct research to gather data and information about the problem. This may involve reviewing literature, analyzing data, or consulting with experts.
- Define the problem: Define the problem clearly and concisely, using specific language and avoiding vague or ambiguous terms. Be sure to include the impact of the problem and the context in which it occurs.
- State the objectives : Clearly state the objectives that the project or research aims to achieve. This should be specific and measurable, with clear outcomes that can be evaluated.
- Identify the scope: Identify the boundaries of the problem, including what is included and excluded from the problem statement. This helps to ensure that the team remains focused on the core problem.
- Outline the methodology : Outline the approach or methodology that the project or research team will use to address the problem. This should be based on research and best practices, and should be feasible and realistic.
- Describe the expected outcomes : Describe the potential impact or outcomes that the project or research aims to achieve. Be specific about how the solution or findings will address the problem and benefit the stakeholders.
- Revise and refine : Review the problem statement and revise it as needed to ensure clarity, accuracy, and completeness.
Applications of Problem Statement
Here are some of the applications of problem statements:
- Research : In academic research, problem statements are used to clearly define the research problem, identify the research question, and justify the need for the study. A well-crafted problem statement is essential for the success of any research project.
- Project management: In project management, problem statements are used to identify the issues or challenges that a project team needs to address. Problem statements help project managers to define project scope, set project goals, and develop project plans.
- Business strategy: In business strategy, problem statements are used to identify business challenges and opportunities. Problem statements help businesses to define their strategic objectives, develop action plans, and allocate resources.
- Product development : In product development, problem statements are used to identify customer needs and develop new products that address those needs. Problem statements help product developers to define product requirements, develop product features, and test product prototypes.
- Policy-making: In public policy-making, problem statements are used to identify social, economic, and environmental issues that require government intervention. Problem statements help policymakers to define policy objectives, develop policy options, and evaluate policy outcomes.
Examples of Problem Statements
Examples of Problem Statements are as follows:
- High student-to-teacher ratios are leading to decreased individualized attention and lower academic achievement.
- Limited funding for extracurricular activities is limiting opportunities for student development and engagement.
- The lack of diversity and inclusion in curriculum is limiting cultural understanding and perpetuating inequalities.
- The need for continuous professional development for teachers is crucial to improving teaching quality and student outcomes.
- Unequal access to education due to socio-economic status, geographical location, or other factors is contributing to disparities in academic achievement.
- The shortage of healthcare professionals is leading to increased patient wait times and decreased quality of care.
- Limited access to mental health services is contributing to the high prevalence of mental health issues and suicides.
- The over-prescription of opioids is contributing to the current opioid epidemic and increasing rates of addiction and overdose.
- Limited access to affordable and nutritious food is leading to poor nutrition and increased rates of chronic diseases.
- The lack of standardized electronic health record systems is limiting coordination of care and leading to medical errors.
Environmental Science
- Pollution from industrial and agricultural practices is contributing to climate change and increased health risks.
- The overexploitation of natural resources is leading to decreased biodiversity and ecological imbalance.
- Limited access to clean water is leading to health issues and affecting agriculture and economic development.
- The destruction of natural habitats is leading to the extinction of many species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Climate change is leading to more frequent and severe natural disasters, causing significant damage to infrastructure and displacement of populations.
Engineering
- The inadequate design and maintenance of bridges and roads is leading to increased accidents and fatalities.
- The lack of reliable and sustainable energy sources is contributing to environmental degradation and limiting economic growth.
- The lack of cybersecurity measures in critical infrastructure is making it vulnerable to cyber attacks and compromising public safety.
- The lack of efficient waste management systems is contributing to pollution and environmental degradation.
- The need for developing technologies that are environmentally friendly and sustainable is crucial to addressing climate change.
Social Work
- The lack of resources for mental health and social services is contributing to homelessness and the need for emergency assistance.
- The high prevalence of child abuse and neglect is leading to long-term physical and emotional harm to children.
- The lack of affordable and accessible childcare is limiting the opportunities for working parents, especially mothers.
- The stigmatization of mental health issues is limiting access to mental health services and perpetuating discrimination.
- The limited access to education, employment, and housing opportunities is contributing to poverty and social inequality.
- The increasing use of ad-blocking software is limiting the effectiveness of traditional digital advertising.
- The lack of transparency in digital advertising is leading to ad fraud and decreased trust in online marketing.
- The need to adapt marketing strategies to changing consumer behaviors and preferences is crucial to reaching target audiences effectively.
- The high competition in the marketplace is making it challenging for small businesses to compete with larger corporations.
- The need to balance marketing goals with ethical considerations is crucial to maintaining consumer trust and avoiding negative publicity.
- The high prevalence of anxiety and depression is leading to decreased productivity and increased healthcare costs.
- The limited access to mental health services in certain geographic areas is limiting access to care and contributing to disparities in mental health outcomes.
- The need for effective prevention and intervention programs for substance abuse and addiction is crucial to reducing rates of addiction and overdose.
- The lack of awareness and understanding of mental health issues is perpetuating stigma and limiting access to care.
- The need for culturally sensitive mental health services that are tailored to the needs of diverse populations is crucial to improving mental health outcomes.
Purpose of Problem Statement
The purpose of a problem statement is to clearly and concisely describe a specific problem or issue that needs to be addressed. It serves as a clear and succinct explanation of the problem, its context, and its importance, providing the necessary information to understand why the problem is worth solving. A well-crafted problem statement also helps to define the scope of the problem, which in turn helps to guide the research or problem-solving process. In essence, a problem statement sets the stage for identifying potential solutions and determining the best approach to solve the problem.
Characteristics of Problem Statement
The characteristics of a good problem statement include:
- Clear and concise : A problem statement should be written in clear and concise language, free of technical jargon, and easily understandable to the intended audience.
- Specific : The statement should clearly define the problem and its scope. It should identify the who, what, where, when, and why of the problem.
- Measurable : A problem statement should be measurable in some way, whether through quantitative or qualitative methods. This allows for objective assessment of progress towards solving the problem.
- Relevant : The problem statement should be relevant to the context in which it is presented. It should relate to the needs and concerns of stakeholders and the broader community.
- Feasible : The problem statement should be realistic and achievable, given the available resources and constraints.
- Innovative: A good problem statement should inspire creative and innovative solutions.
- Actionable : The problem statement should lead to actionable steps that can be taken to address the problem. It should provide a roadmap for moving forward.
Advantages of Problem Statement
Advantages of Problem Statement are as follows:
- Focus : A problem statement helps to clearly define the problem at hand and provides focus to the problem-solving process. It helps to avoid wasting time and resources on issues that are not relevant.
- Alignment : A well-written problem statement ensures that everyone involved in the problem-solving process is on the same page and understands the issue at hand. This alignment helps to ensure that efforts are focused in the right direction and that everyone is working towards the same goal.
- Clarity : A problem statement provides clarity about the nature of the problem and its impact. This clarity helps to facilitate communication and decision-making, making it easier to develop effective solutions.
- Innovation : A well-crafted problem statement can inspire creativity and encourage innovative thinking. By clearly defining the problem, it can help to identify new approaches and solutions that may not have been considered before.
- Measurability : A problem statement that is clear and specific can be used to measure progress and success. It helps to ensure that efforts are focused on addressing the root cause of the problem and that progress towards a solution can be tracked and evaluated.
Limitations of Problem Statement
While problem statements have many advantages, they also have some limitations, such as:
- Limited Scope: A problem statement is usually focused on a specific issue or challenge. As a result, it may not capture the full complexity of a larger problem, which can limit the effectiveness of the solutions developed.
- Lack of Detail : In some cases, problem statements may be too broad or lack sufficient detail, which can make it difficult to develop effective solutions. It’s important to ensure that the problem statement is specific enough to guide the problem-solving process.
- Bias : The way in which a problem statement is written can sometimes reflect the biases or assumptions of the person or group writing it. This can lead to a narrow or incomplete understanding of the problem and limit the effectiveness of the solutions developed.
- Inflexibility : A problem statement may be too rigid or inflexible, which can limit the exploration of alternative solutions. It’s important to keep an open mind and be willing to adapt the problem statement as new information or perspectives emerge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Problem Statement?
A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and specific statement that describes the issue or problem that the research project addresses. It should be written in a way that is easily understandable to both experts and non-experts in the field.
To write a research problem statement, you should:
- Identify the general area of interest: Start by identifying the general area of research that interests you.
- Define the specific problem: Narrow down the general area of interest to a specific problem or issue.
- Explain the significance of the problem: Provide context for the problem by explaining why it is important to study and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
- Provide a clear and concise statement: State the problem in a clear and concise manner, making sure to use language that is easily understood by your intended audience.
- Use a scientific and objective tone: The problem statement should be written in a neutral and objective tone, avoiding any subjective language and personal bias .
An Example of a Research Problem Statement
“The increasing prevalence of obesity in children is a growing public health concern. Despite the availability of information on healthy eating and physical activity, many children are still not engaging in healthy lifestyle behaviors. The problem this study addresses is the lack of understanding of the barriers and facilitators to healthy lifestyle behaviors in children.”
When to Write a Problem Statement in Research?
A research problem statement should be written at the beginning of the research process, before any data collection or analysis takes place. This is because the statement sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the problem that the research is trying to address.
Writing a problem statement early in the research process helps to guide the research design and methodology , and ensures that the research is focused on addressing the specific problem at hand. It also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and addresses a gap in current knowledge or understanding.
In addition, a well-written problem statement effectively communicates the purpose and significance of the research to potential funders, collaborators, and other stakeholders. It also generates interest and support for the research project.
It’s also important to note that, during the research process, the statement can be refined or updated as new information is discovered or as the research progresses. This is normal and it’s a good idea to revise the statement as needed to ensure that it remains clear and concise and that it accurately reflects the current focus of the research project.
What Does a Research Problem Statement Include?
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements:
1. The research topic:
The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses.
2. The specific problem or issue:
A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address.
3. The significance of the problem:
A discussion of why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
4. The research questions:
A set of questions that the research project aims to answer, in order to address the problem or issue.
5. The research objectives:
A set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
6. The scope of the research:
A description of the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
7. The theoretical framework:
A discussion of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
8. The research design:
A description of the research methodologies that will be used to collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
It’s important to note that the problem statement is usually brief and concise, typically a few sentences or a short paragraph. But it should provide enough information to convey the main idea of the research project.
Important Features of Research Problem Statement
The problem statement should be clear and easy to understand. Write it in a way that is accessible to both experts and non-experts in the field.
2. Specificity
The statement should be specific and clearly define the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It should be narrow enough to be manageable, but broad enough to be of interest to others in the field.
3. Significance
The statement should explain why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills. It should provide context for the research project and help to justify its importance.
4. Relevance
The statement should be relevant to the field of study and address an issue that is currently of concern to researchers.
5. Research questions
The statement should include a set of research questions that the research project aims to answer in order to address the problem or issue.
6. Research objectives
The statement should include a set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
The statement should define the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
8. Theoretical framework
The statement should provide an overview of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
9. Research design
The statement should provide an overview of the research methodologies. This will be useful collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
Difference Between a Thesis Statement and a Problem Statement
A thesis statement and a problem statement are related but distinct elements of a research project.
A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the central argument or claim of a research paper or essay. It presents the main idea of the paper and sets the direction for the rest of the content. It’s usually located at the end of the introduction, and it’s often one sentence.
A problem statement, on the other hand, is a statement that describes a specific problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the research problem. It is usually located at the beginning of a research paper or proposal, and is of one or a few paragraphs.
In summary, a thesis statement is a summary of the main point or key argument of the research paper. A problem statement describes the specific issue that the research project aims to address. A thesis statement is more focused on the final outcome of the research. While a problem statement is focused on the current state of knowledge and the gap in understanding that the research project aims to fill.
In Conclusion
A problem statement is a critical component of the research project, as it provides a clear and concise roadmap for the research, and helps to ensure that the research is well-designed and addresses a significant and relevant issue.
We hope this blog has clarified your doubts and confusion associated with research problem statement and helps you write an effective statement for your research project!
comprehensive contents. thanks!
Very good writing and easy to understand
WOW..its easy to understand…
This has opened up my mind, Systematically outlined steps.
Wow I’ve gained Alot from this!
WOW…This was much helpful.
Good and straightforward explanations with ease of understanding for all the students and teachers alike.
Beautiful work
I enjoy and understand every bit of the explanations on each topic. Kudos to the team.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Industry News
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research
Language as a Bridge, Not a Barrier: ESL researchers’ path to successful…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

When should AI tools be used in university labs?

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
Effective problem statements have these 5 components

Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test

We’ve all encountered problems on the job. After all, that’s what a lot of work is about. Solving meaningful problems to help improve something.
Developing a problem statement that provides a brief description of an issue you want to solve is an important early step in problem-solving .
It sounds deceptively simple. But creating an effective problem statement isn’t that easy, even for a genius like Albert Einstein. Given one hour to work on a problem, he’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and five minutes finding solutions. (Or so the story goes.)
Einstein was probably exaggerating to make a point. But considering his success in solving complex problems, we think he was on to something.
As humans, we’re wired to jump past the problem and go directly to the solution stage. In emergencies, this behavior can be lifesaving, as in leaping out of the way of a speeding car. But when dealing with longer-range issues in the workplace, this can lead to bad decisions or half-baked solutions.
That’s where problem statements come in handy. They help to meaningfully outline objectives to reach effective solutions. Knowing how to develop a great problem statement is also a valuable tool for honing your management skills .
But what exactly is a problem statement, when should you use one, and how do you go about writing one? In this article, we'll answer those questions and give you some tips for writing effective problem statements. Then you'll be ready to take on more challenges large and small.
What is a problem statement?
First, let’s start by defining a problem statement.
A problem statement is a short, clear explanation of an issue or challenge that sums up what you want to change. It helps you, team members, and other stakeholders to focus on the problem, why it’s important, and who it impacts.
A good problem statement should create awareness and stimulate creative thinking . It should not identify a solution or create a bias toward a specific strategy.
Taking time to work on a problem statement is a great way to short-circuit the tendency to rush to solutions. It helps to make sure you’re focusing on the right problem and have a well-informed understanding of the root causes. The process can also help you take a more proactive than reactive approach to problem-solving . This can help position you and your team to avoid getting stuck in constant fire-fighting mode. That way, you can take advantage of more growth opportunities.

When to use a problem statement
The best time to create a problem statement is before you start thinking of solutions. If you catch yourself or your team rushing to the solution stage when you’re first discussing a problem, hit the brakes. Go back and work on the statement of the problem to make sure everyone understands and agrees on what the real problem is.
Here are some common situations where writing problem statements might come in handy:
- Writing an executive summary for a project proposal or research project
- Collaborating on a cross-functional project with several team members
- Defining the customer issue that a proposed product or service aims to solve
- Using design thinking to improve user experience
- Tackling a problem that previous actions failed to solve

How to identify a problem statement
Like the unseen body of an iceberg, the root cause of a specific problem isn’t always obvious. So when developing a problem statement, how do you go about identifying the true, underlying problem?
These two steps will help you uncover the root cause of a problem :
- Collect information from the research and previous experience with the problem
- Talk to multiple stakeholders who are impacted by the problem
People often perceive problems differently. Interviewing stakeholders will help you understand the problem from diverse points of view. It can also help you develop some case studies to illustrate the problem.
Combining these insights with research data will help you identify root causes more accurately. In turn, this methodology will help you craft a problem statement that will lead to more viable solutions.
What are problem statements used for?
You can use problem statements for a variety of purposes. For an organization, it might be solving customer and employee issues. For the government, it could be improving public health. For individuals, it can mean enhancing their own personal well-being . Generally, problem statements can be used to:
- Identify opportunities for improvement
- Focus on the right problems or issues to launch more successful initiatives – a common challenge in leadership
- Help you communicate a problem to others who need to be involved in finding a solution
- Serve as the basis for developing an action plan or goals that need to be accomplished to help solve the problem
- Stimulate thinking outside the box and other types of creative brainstorming techniques
3 examples of problem statements
When you want to be sure you understand a concept or tool, it helps to see an example. There can also be some differences in opinion about what a problem statement should look like. For instance, some frameworks include a proposed solution as part of the problem statement. But if the goal is to stimulate fresh ideas, it’s better not to suggest a solution within the problem statement.
In our experience, an effective problem statement is brief, preferably one sentence. It’s also specific and descriptive without being prescriptive.
Here are three problem statement examples. While these examples represent three types of problems or goals, keep in mind that there can be many other types of problem statements.
Example Problem Statement 1: The Status Quo Problem Statement
Example:
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons.
This can be used to describe a current pain point within an organization that may need to be addressed. Note that the statement specifies that the issue occurs during the company’s slow time as well as the busy season. This is helpful in performing the root cause analysis and determining how this problem can be solved.
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons. The company is currently understaffed and customer service representatives are overwhelmed.
Background:
Example company is facing a significant challenge in managing their customer service on-hold times. In the past, the company had been known for its efficient and timely customer service, but due to a combination of factors, including understaffing and increased customer demand, the on-hold times have exceeded five minutes consistently. This has resulted in frustration and dissatisfaction among customers, negatively impacting the company's reputation and customer loyalty.
Reducing the on-hold times for customer service callers is crucial for Example company. Prolonged waiting times have a detrimental effect on customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to potential customer churn and loss of revenue. Additionally, the company's declining reputation in terms of customer service can have a lasting impact on its competitive position in the market. Addressing this problem is of utmost importance to improve customer experience and maintain a positive brand image.
Objectives:
The primary objective of this project is to reduce the on-hold times for customer service callers at Example company. The specific objectives include:
- Analyzing the current customer service workflow and identifying bottlenecks contributing to increased on-hold times.
- Assessing the staffing levels and resource allocation to determine the extent of understaffing and its impact on customer service.
- Developing strategies and implementing measures to optimize the customer service workflow and reduce on-hold times.
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented measures through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average on-hold time, customer satisfaction ratings, and customer feedback.
- Establishing a sustainable approach to maintain reduced on-hold times, taking into account both busy and slow seasons, through proper resource planning, training, and process improvements.
Example Problem Statement 2: The Destination Problem Statement
Leaders at Example company want to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year.
This approach can be used to describe where an organization wants to be in the future. This type of problem statement is useful for launching initiatives to help an organization achieve its desired state.
Like creating SMART goals , you want to be as specific as possible. Note that the statement specifies “net revenue” instead of “gross revenue." This will help keep options open for potential actions. It also makes it clear that merely increasing sales is not an acceptable solution if higher marketing costs offset the net gains.
Leaders at Example company aim to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year. However, the company currently lacks the necessary teams to tackle this objective effectively. To achieve this growth target, the company needs to expand its marketing and PR teams, as well as its product development teams, to prepare for scaling.
Example company faces the challenge of generating a 5% increase in net revenue for its premium product line of widgets in the upcoming fiscal year. Currently, the company lacks the required workforce to drive this growth. Without adequate staff in the marketing, PR, and product development departments, the company's ability to effectively promote, position, and innovate its premium product line will be hindered. To achieve this kind of growth, it is essential that Example company expands teams, enhances capabilities, and strategically taps into the existing pool of loyal customers.
Increasing net revenue for the premium product line is crucial for Example company's overall business success. Failure to achieve the targeted growth rate can lead to missed revenue opportunities and stagnation in the market. By expanding the marketing and PR teams, Example company can strengthen its brand presence, effectively communicate the value proposition of its premium product line, and attract new customers.
Additionally, expanding the product development teams will enable the company to introduce new features and innovations, further enticing existing and potential customers. Therefore, addressing the workforce shortage and investing in the necessary resources are vital for achieving the revenue growth objective.
The primary objective of this project is to increase net revenue for Example company's premium product line of widgets by 5% in the next fiscal year. The specific objectives include:
- Assessing the current workforce and identifying the gaps in the marketing, PR, and product development teams.
- Expanding the marketing and PR teams by hiring skilled professionals who can effectively promote the premium product line and engage with the target audience.
- Strengthening the product development teams by recruiting qualified individuals who can drive innovation, enhance product features, and meet customer demands.
- Developing a comprehensive marketing and PR strategy to effectively communicate the value proposition of the premium product line and attract new customers.
- Leveraging the existing base of loyal customers to increase repeat purchases, referrals, and brand advocacy.
- Allocating sufficient resources, both time and manpower, to support the expansion and scaling efforts required to achieve the ambitious revenue growth target.
- Monitoring and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as net revenue, customer acquisition, customer retention, and customer satisfaction to measure the success of the growth initiatives.
- Establishing a sustainable plan to maintain the increased revenue growth beyond the next fiscal year by implementing strategies for continuous improvement and adaptation to market dynamics.
Example Problem Statement 3 The Stakeholder Problem Statement
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys , less than 30% of employees at Eample company stated that they feel valued by the company. This represents a 20% decline compared to the same period in the year prior.
This strategy can be used to describe how a specific stakeholder group views the organization. It can be useful for exploring issues and potential solutions that impact specific groups of people.
Note the statement makes it clear that the issue has been present in multiple surveys and it's significantly worse than the previous year. When researching root causes, the HR team will want to zero in on factors that changed since the previous year.
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys, less than 30% of employees at the Example company stated that they feel valued by the company. This indicates a significant decline of 20% compared to the same period in the previous year.
The company aspires to reduce this percentage further to under 10%. However, achieving this goal would require filling specialized roles and implementing substantial cultural changes within the organization.
Example company is facing a pressing issue regarding employee engagement and perceived value within the company. Over the past year, there has been a notable decline in the percentage of employees who feel valued. This decline is evident in the results of the quarterly employee engagement surveys, which consistently show less than 30% of employees reporting a sense of value by the company.
This decline of 20% compared to the previous year's data signifies a concerning trend. To address this problem effectively, Example company needs to undertake significant measures that go beyond superficial changes and necessitate filling specialized roles and transforming the company culture.
Employee engagement and a sense of value are crucial for organizational success. When employees feel valued, they tend to be more productive, committed, and motivated. Conversely, a lack of perceived value can lead to decreased morale, increased turnover rates, and diminished overall performance.
By addressing the decline in employees feeling valued, Example company can improve employee satisfaction, retention, and ultimately, overall productivity. Achieving the desired reduction to under 10% is essential to restore a positive work environment and build a culture of appreciation and respect.
The primary objective of this project is to increase the percentage of employees who feel valued by Example company, aiming to reduce it to under 10%. The specific objectives include:
- Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to the decline in employees feeling valued, including organizational policies, communication practices, leadership styles, and cultural norms.
- Identifying and filling specialized roles, such as employee engagement specialists or culture change agents, who can provide expertise and guidance in fostering a culture of value and appreciation.
- Developing a holistic employee engagement strategy that encompasses various initiatives, including training programs, recognition programs, feedback mechanisms, and communication channels, to enhance employee value perception.
- Implementing cultural changes within the organization that align with the values of appreciation, respect, and recognition, while fostering an environment where employees feel valued.
- Communicating the importance of employee value and engagement throughout all levels of the organization, including leadership teams, managers, and supervisors, to ensure consistent messaging and support.
- Monitoring progress through regular employee surveys, feedback sessions, and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to employee satisfaction, turnover rates, and overall engagement levels.
- Providing ongoing support, resources, and training to managers and supervisors to enable them to effectively recognize and appreciate their teams and foster a culture of value within their respective departments.
- Establishing a sustainable framework for maintaining high employee value perception in the long term, including regular evaluation and adaptation of employee engagement initiatives to address evolving needs and expectations.

What are the 5 components of a problem statement?
In developing a problem statement, it helps to think like a journalist by focusing on the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why or how. Keep in mind that every statement may not explicitly include each component. But asking these questions is a good way to make sure you’re covering the key elements:
- Who: Who are the stakeholders that are affected by the problem?
- What: What is the current state, desired state, or unmet need?
- When: When is the issue occurring or what is the timeframe involved?
- Where: Where is the problem occurring? For example, is it in a specific department, location, or region?
- Why: Why is this important or worth solving? How is the problem impacting your customers, employees, other stakeholders, or the organization? What is the magnitude of the problem? How large is the gap between the current and desired state?
How do you write a problem statement?
There are many frameworks designed to help people write a problem statement. One example is outlined in the book, The Conclusion Trap: Four Steps to Better Decisions, ” by Daniel Markovitz. A faculty member at the Lean Enterprise Institute, the author uses many case studies from his work as a business consultant.
To simplify the process, we’ve broken it down into three steps:
1. Gather data and observe
Use data from research and reports, as well as facts from direct observation to answer the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why.
Whenever possible, get out in the field and talk directly with stakeholders impacted by the problem. Get a firsthand look at the work environment and equipment. This may mean spending time on the production floor asking employees questions about their work and challenges. Or taking customer service calls to learn more about customer pain points and problems your employees may be grappling with.
2. Frame the problem properly
A well-framed problem will help you avoid cognitive bias and open avenues for discussion. It will also encourage the exploration of more options.
A good way to test a problem statement for bias is to ask questions like these:
3. Keep asking why (and check in on the progress)
When it comes to problem-solving, stay curious. Lean on your growth mindset to keep asking why — and check in on the progress.
Asking why until you’re satisfied that you’ve uncovered the root cause of the problem will help you avoid ineffective band-aid solutions.
Refining your problem statements
When solving any sort of problem, there’s likely a slew of questions that might arise for you. In order to holistically understand the root cause of the problem at hand, your workforce needs to stay curious.
An effective problem statement creates the space you and your team need to explore, gain insight, and get buy-in before taking action.
If you have embarked on a proposed solution, it’s also important to understand that solutions are malleable. There may be no single best solution. Solutions can change and adapt as external factors change, too. It’s more important than ever that organizations stay agile . This means that interactive check-ins are critical to solving tough problems. By keeping a good pulse on your course of action, you’ll be better equipped to pivot when the time comes to change.
BetterUp can help. With access to virtual coaching , your people can get personalized support to help solve tough problems of the future.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.
The future of AI: where does your job stand?
18 excellent educational podcasts to fuel your love of learning, 6 ai prompt generator tools to boost your creativity, 20 ai tools to help boost productivity in 2023, applications of ai: 10 common examples, how to use 100% of your brain: is it possible, 6 chatgpt prompts to save time and boost productivity, experimentation brings innovation: create an experimental workplace, the 10 best work productivity tools to maximize your time, similar articles, 10 problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head, writing a value statement: your guide to keeping your team aligned, 10 personal brand statements to put all eyes on you, how core competencies can set your business — and you — apart, discover 4 types of innovation and how to encourage them, what is organizational structure and why is it important, create smart kpis to strategically grow your business, what is a career statement, and should you write one, how to craft an impactful company mission statement, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- How it works
How to Write a Statement of a Problem in Research with Steps
Published by Grace Graffin at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Research is a systematic investigation to find new techniques, products or processes to solve problems. Apart from being systematic, research is empirical in nature: it’s based on observations and measurement of those observations.
It’s what comes before the development. Impacts and policies that are born in society are borne out of the research.
The most important step to perform any research is to identify a problem that needs to be solved. Therefore, it is necessary to define a research problem before starting the actual research process. Once a research problem has been identified, the next step is to write a problem statement.
Philosopher Kaoru Ishikawa said: “You will have a problem half-solved by defining it correctly on the first day.”
This quote perfectly reflects the importance of a problem statement in research. Before writing a problem statement, it is essential to pinpoint a specific problem, the difficulties you can expect to face as you try to solve it and the research gaps you aim to fill with your research.
The last part—how your research aims to fill a gap in the existing literature—will act as a springboard to the solution(s) that policy makers, for instance, might eventually take to solve that problem.
Filling a gap, therefore, is very important towards solving an existing problem.
What is a Problem Statement?
A problem statement is a clear and concise description of an issue or challenge that needs to be addressed. It typically outlines the existing gap between the current state (what currently is) and the desired state (what should be). Crafting a well-defined problem statement is critical for problem-solving, research, or project planning, as it serves as a guidepost and sets the direction for the subsequent steps.
Research Problem and Research Method – A Cyclical Process
The type of research strategy used in research determines whether you will be analysing theoretical problems to add value to existing knowledge, discussing practical issues to become an agent of change for an organisation or industry or looking at both aspects in relation to any given problem.
However, the kind of problem you aim to tackle with your research, to begin with, will also help you narrow down which research design , method or strategy to opt for.
This is therefore a cyclical process. Your research aim guides your research design can help you focus on a specific kind of research gap/problem.
However, generally, your research will focus on one or the other.
Here is all you need to know about how to write a statement of the problem in research, also called problem statement by some research writers .
Why do you Need a Statement of the Problem, to Begin with?
You need a statement of the problem to transform a generalised problem into a well-defined, brief, targeted statement to perform research in the decision-making process. The problem statement helps the researcher to identify the purpose of the ongoing research.
The problem statement in the dissertation is the pillar of the introduction chapter through which the reader can understand the research questions and scope of the project. If you do not define the problem statement properly, the results might become unmanageable.

Writing Problem Statement for a Business or Organisation
In the business world, problem statements provide the basis for the enhancement and refinement of projects. Without identifying and understanding the problem, it will be hard to find and effectively implement solutions.
A stand-alone document that solely provides an in-depth and detailed problem statement is usually the answer for organisations and businesses when it becomes imperative to find the solution to a problem.
Writing Problem Statement for Academic Research
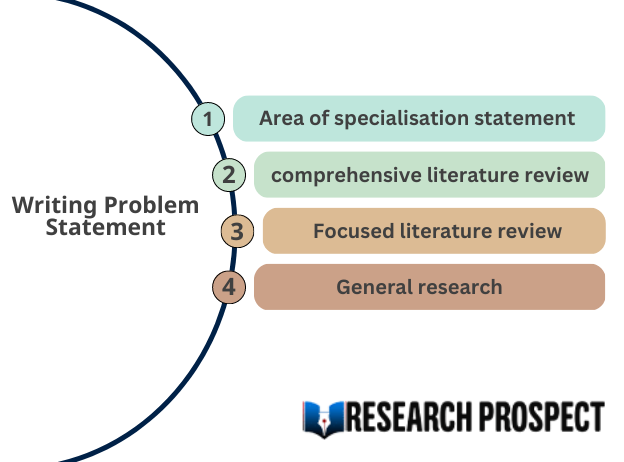
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Problem Statement – How to Write it
Ask yourself the following questions before writing the problem statement:
- What is wrong in the research area/subarea XYZ?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- To what extent (how much)?
- I know that because…(evidence)
‘What’ always defines the defect of the problem at hand and explains why it matters? ‘Where’ defines the geological location of the problem. ‘When’ defines the history and the pattern of the problem, the goal of the stated problem and the scope of research.
‘How much’ defines the trend of the problem as to how many objects are facing the same defect and to what extent. The last part, ‘I know this because…’, will help the researcher identify the standard(s) that he must meet.
Step 1: Understanding the Problem
The problem statement should provide a clear and concise background to the research problem you are investigating. Before starting your research , review the literature about the specific problem and find a gap to fill with your own research.
Practical Research Problem Statement
If you are doing experimental research , you can identify problems by talking to people working in a relevant field, studying research reports, and reviewing previous research. Here are some examples of practical research problems:
- A problem that hinders the efficiency of a company
- An institutional process that needs interventions
- An area of concern in your field/sub-field of interest
- Members of a society facing a specific difficulty
The problem statement should focus on the details related to the problem, such as:
- When and where was the problem observed?
- Who is/are affected by it?
- What research has been conducted and what practical steps have been taken to resolve the problem?
Example of Practical Research Problem Statement
The production of a company is low for the months of July and August every year. Initial research has been conducted by the company, which revealed poor production in July and August is due to the unavailability of local raw material.
The company has made some effective attempts at engaging the local suppliers to ensure an uninterrupted supply of the raw material, but these efforts are yet to have any significant impact on the production levels.
Theoretical Research Problem Statement
According to USC Libraries, “A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study…theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts…relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.”
The theoretical research indirectly contributes to the change by identifying the problem, expanding knowledge and improving understanding. The researcher can find a specific problem by brainstorming the topic and reviewing already published theories and research.
When writing a problem statement based on a theoretical research problem , it is important to recognise the historical, geographical, social and scientific background. Here are the elements of the theoretical problem statement framework that you should consider:
- What are the facts about the problem?
- Does the problem relate to a certain geographical area or time period?
- How is the problem discussed and explained in the existing literature?
Example of Theoretical Research Problem Statement
The production of a company is low for July and August every year. Initial research has been conducted by the company, which revealed poor production in July and August is due to the unavailability of local raw material. The company has made some effective attempts to engage the local suppliers to ensure an uninterrupted raw material supply. Still, these efforts are yet to have any significant impact on the production levels.
Looking for Dissertation Help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step 2 – Show why it’s Important and Relevant
By discussing the importance of the problem under investigation, you are demonstrating the relevance of your research. However, this does not mean that you will end up discovering something unimaginable or extraordinary.
The objective here is to clearly state how and why your research problem is relevant in your chosen area of study and why it requires further research.
As indicated previously, practical research deals with a problem affecting society, social group, firm or organisation on a broader scale. To elaborate on why it is important to solve this problem and why your research is significant, you could consider the following questions:
- What will be the consequences if the problem remains unsolved?
- Who do these consequences have the most implications for?
- What is the wider relevance of the problem being investigated?
Low production in July and August negatively affects the company’s marketing capital, thereby becoming an area of deep concern for the directors and stakeholders. The marketing budget cut in July and August is hindering its ability to promote its products uninterruptedly.
Addressing this problem will have practical benefits for the company and help establish the reasons for disruption in raw material supply.
The relevance of all theoretical issues may not be too obvious, even though most theoretical problems do have practical implications. Here are some questions for you to ponder to establish the importance of your research problem:
- Will your research help to advance understanding of the topic under investigation?
- Are there any benefits of you resolving the problem for other researchers who wish to explore this topic further in the future?
- What are the direct or indirect implications (s) of the problem you are trying to solving?
The new forms of employment such as freelance, contract-based work and zero-hour work arrangements are recognised as either a manipulative last option or a flexible active choice. It is necessary to conduct comprehensive qualitative research to uncover why fresh graduates take up these types of employment in the gig economy. There is a need to advance more vigorous concepts relating to instability and flexibility in modern forms of employment from employees’ perspectives, which will also help shape future policies.
Also see: How to Write the Abstract for Dissertation
Step 3 – Declaring the Problem
Before you jump on to state your research’s problem statements, it’s important to devote a sentence or two to let your readers know the precise, narrowed-down research problem you will be discussing about.
For language clarity purposes, here are some strong opening statements to achieve this step:
- Recently, there has been growing interest in …
- The possibility of…has generated wide interest in …
- The development of…is a classic problem in…
- The development of…has led to the hope that …
- The…has become a favourite topic for analysis …
- Knowledge of…has great importance for …
- The study of…has become an important aspect of …
- A central issue in…is…
- The…has been extensively studied in recent years.
- Many investigators have recently turned to …
- The relationship between…has been investigated by many researchers.
- Many recent studies have found out…
Step 4 – Establishing Aim and Objectives
The last step in writing a problem statement is to provide a framework for solving the problem. This will help you, the researcher, stay focused on your research aims and not stray; it will also help you readers keep in mind the reason as to why you conducted this study, to begin with.
A good problem statement does not provide the exact solution to any problem. Rather, it focuses more on how to effectively understand or tackle a problem by establishing the possible causes.
The aim of a research study is its end goal or overall purpose. Following are some examples of how you can craft your research aim statements:
- This research study aims to investigate…
- This paper is aimed at exploring…
- This research aims to identify…
On the other hand, objectives are the smaller steps that a researcher must take to address the aim of the research. Once you have laid out the research problem your research will deal with, it’s important to next mention the how behind that. Objectives are mostly imperative statements, often beginning with transitive verbs like ‘to analyse,’ ‘to investigate,’ etc.
Some more examples are:
- Statistical analysis will be conducted to determine…
- Both quantitative and qualitative research methods will be employed to probe…
- Face-to-face interviews will be carried out with the participants to establish…
Practical Research Aim and Objectives
This project aims to identify the causes of disturbed supply of raw material in the region, which resulted in low production for the company in July and August. This will be achieved by conducting interviews and surveys with the suppliers to understand why the supply is unpredictable in those two months and what can be done to ensure orderliness. Practical experiments will also be conducted to observe the effectiveness of proposed solutions.
Theoretical Research Aim and Objectives
This study aims to understand and unearth the experiences of fresh graduates in the modern economy. The sample population will participate in this study through qualitative research methods, which are expected to provide a deeper insight into the perceptions and motives of these fresh graduates working as freelancers and contract-based employees. The data collected from this exercise and the existing literature on the topic will be analysed in statistical analysis software.
TIP: Search the common themes of the problem statement in your field of research before writing a problem statement.
Also see: Argumentative Essay Writing Service
Problem Statement versus Significance of the Study
Even though both may sound similar, the statement of the problem and the significance of your study are going to be different. The latter does develop upon and from the former, though.
The problem statement tells your readers what’s wrong, whereas the significance of the study will tell them how your research contributed to that problem. You can’t have a significance of a study without mentioning the problem statement first.
Furthermore, signifying your study implies mentioning 4 key points related to it:
- How your study will further develop the theory behind the existing problem
- Practical solutions that might be implemented to solve the problem (especially in field research work)
- Whether your study or research will pave way for innovative methods to solve the existing problem.
- How your study can help in policy making and implementation, impact studies, etc.
Problem statement in research is the description of an existing issue that needs to be addressed. The problem statement is a focal point of any research and a bridge between the literature review and the research methodology .
Problem statement often has three elements; the problem itself, the method of solving the problem, and the purpose. There are five aspects of every problem: What, Where, When, to what extent, and what defects you know about the topic. Here is an example of a problem statement in a research proposal for your better understanding.
If you wish to know more about how to start your research process, then you might want to take a look at the “ Starting the Research Process ” section on our website, which has several articles relating to a research problem , problem statement, research aim and objectives, and research proposal .
ResearchProspect is a UK-registered business that offers academic support and assistance to students across the globe. Our writers can help you with individual chapters of your dissertation or the full dissertation writing service , no matter how urgent or complex your requirements might be.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it necessary to write a problem statement.
Yes, the most important step to perform any research is to identify a problem that needs to be solved. Therefore, it is necessary to define a research problem before starting the actual research process .
How is a problem statement different from a problem statement written for an organisation?
In the business world, problem statements provide the basis for the enhancement and refinement of projects. Whereas, in academic research, A problem statement helps researchers understand and realise organised the significance of a research problem .
What is a practical research problem?
Doing experimental research can identify problems by talking to people working in a relevant field, studying research reports, and reviewing previous research.
What is a theoretical research problem?
A theoretical research problem is when the researcher finds a specific problem by brainstorming and reviewing already published theories and research.
You May Also Like
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
SURF Workshop Resources: Problem Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These resources discuss the importance of problem crafting strong problem statements when presenting and writing up your research.
Problem Statements: A Brief Introduction
A problem statement is a move that a document makes to help the reader realize why the document is important. Problem statements can be either formal--like a thesis statement--or they can be informal--usually a sentence that explains how what you are saying will impact the reader. A carefully crafted problem statement will help you to connect with your audience and will help your audience to see why your document is important.
In order to write a strong problem statement, you should consider the following questions:
- What does my reader already know about my topic?
- What will I need to explicitly explain to my reader for them to understand the significance of my topic?
In order to answer these questions, you will need to consider: the kind of terminology that your audience will be comfortable with; what beliefs, or mindsets, are shared between you and your intended audience; and, what canonical works your audience will be familiar with.
In regards to terminology, you should carefully choose what discipline specific terms to use and how to define them. This decision should be based on who your audience is. For example, if you are writing to a lay audience about first and second language users, you would not want to use the terms "L1" and "L2" without first defining them.
When considering the beliefs and mindsets of your audience, you should keep in mind that the audiences' beliefs/mindset may change the way that they interpret or understand the statements that you make in your document.
Finally, canonical research refers to texts and/or theories that the majority of experts in a given field find foundational to their work. When you're writing your problem statement, you want to be careful not to assume that everyone knows of all of the major works that you're referencing.
This serves as a very brief introduction to writing effective problem statements. Protracted examples of each of these can be found in the SURF Workshop: Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation .
Resources Available
The materials for the workshop include a PowerPoint slide presentation that details how audience considerations affect the construction of problem statements, as well as handouts that provide students with opportunities to share, summarize, and recontextualize their research for different audiences.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a problem statement

What is a problem statement?
Why write a problem statement, when are problem statements commonly written, how do i write a problem statement, the format of a problem statement, the trademarks of a good problem statement, an example of a problem statement, frequently asked questions about problem statements, related articles.
A problem statement is a clear and concise description of the problem or issue a team aims to address in a project.
A problem statement identifies a problem’s current state, desired future state, and the gaps that lie between the two. It doesn't define the solution to the problem or provide a road map for solving the problem; it only gives an outline of what the problem is.
However, the researcher or team can later use the problem statement to validate that their work delivered an outcome that resulted in the solution.
A problem statement is a useful communication tool, as it keeps the whole team on track and tells them why the project is important. A problem statement helps someone to define and understand the problem, identify the goals of the project, and outline the scope of work.
A problem statement is especially relevant for projects that aim to improve processes, as it allows for the easier development of solutions. Referencing it helps guide the activities carried out and aids the research team in staying focused. The information in a problem statement also helps a team make important decisions.
When the desired solution is implemented later on, a problem statement can help make sure that steps are put into place to prevent the original problem from recurring in the future.
Problem statements are used in both academic and business contexts. In a business environment, project managers can use them to help execute process improvement projects.
But in an academic setting, they can help researchers to contextualize and understand the significance of the problem in a research project. This guide focuses on academic problem statements.
Before planning or writing out your academic problem statement, ask yourself some important questions, and make notes with your answers:
- What is the problem?
- How often does the problem occur?
- Where does the problem occur?
- When does the problem occur?
- Who does the problem impact?
- What causes the problem?
- How would things ideally work if the problem wasn't present?
- Why is this a problem, and why does it matter?
- What impact does the problem cause?
- Which possible solution/s to the problem are you going to propose?
- What are the predicted benefits or outcomes of your solutions?
When you write your problem statement, split it into four sections:
- Problem: Here, simply define what your problem is, clearly and concisely. Make it no longer than one or two sentences.
- Background: This is the section where you can describe what causes the problem, how often it occurs, where and when it occurs, and who the problem impacts.
- Relevance: You'll want to show how the problem is relevant, as well as why it matters and requires a solution. This is a great space to specify why it's a problem and what impacts it causes. If it fits comfortably, you can also articulate how things would ideally work if the problem wasn't present.
- Objectives: This section doesn't require great detail or length, as the problem statement isn't the area of your research project in which to specifically problem-solve. However, you should lay out a brief plan of what you're going to do to investigate and how that should help you formulate solutions. You can also hypothesize on possible solutions you're going to propose, and the benefits you predict from these.
A quality problem statement should be:
- Concise: You should be able to summarize your problem, as well as the different elements of how and why it's a problem, in succinct sentences. If you can't, revisit your initial notes and clarify what you want to achieve with your project.
- Specific: Only write about one issue in a problem statement, even if there's more than one impact of that issue. Your research and actions then only have to focus on solving the one problem, and there's no confusion.
- Measurable: Be clear about how you're able to measure and convey both the problem and your proposed objectives. This is usually by communicating the problem in terms of degree and frequency.
Below is an academic problem statement example. You don't need to include any headers in your real problem statement, but we'll do so here to show you how the sections of the document function in practice.
There is worryingly low uptake of free cervical cancer screening in the UK amongst women aged 25 to 35.
According to an assessment conducted by X Health Trust, only 60% of 25- to 35-year-old female patients attended cervical cancer screening appointments within the last two years.
This could be due to several contributing factors:
- Female patients in this age group may be more likely to believe they are not susceptible to cervical cancer due to their younger age.
- There has been an absence of regular and informative public health announcements on this subject within the last seven years.
- Cervical cancer screening has a reputation for being an unpleasant experience, which could be off-putting for patients due to attend one.
Cervical cancer is the 14th most common cancer in females in the UK, representing a notable health risk. As of 2017, there were around 3,200 new cervical cancer cases, with 850 consequent deaths, in the UK every year.
Although mortality rates in the UK for cervical cancer are highest in females aged 85 to 89, incidence rates for the disease are still highest in females aged 30 to 34.
When cervical cancer is diagnosed at its earliest stage, 96% of people diagnosed will survive their disease for one year or more. This is compared with only 50% of people when the disease is diagnosed at the latest stage.
Screening is a vital health service as many cervical cancer patients will be symptomless until they are in a later stage of the disease.
We are going to conduct a survey of 10,000 females in the UK between the ages of 25 and 35. We will first ask them the question of whether they have attended a cervical screening appointment in the last five years. For those who answer “no,” we will then present them with multiple-choice options that answer the question, “why not?”
From the results we gather, we should be able to accurately assess the most common reasons why there is a low uptake in cervical cancer screening in this age group. We will then propose interventions to the medical community based on our findings.
Our ultimate goal is to increase the uptake of cervical cancer screening by females between 25 and 35 in the UK over the next five years.
🔲 Background
🔲 Relevance
🔲 Objectives
A problem statement helps you define and understand a problem, identify the goals of your project, and outline the scope of your work. A problem statement is especially important for projects that aim to improve processes, as it allows for the easier development of solutions.
A good problem statement is concise, specific and measurable. It summarizes the different elements of how and why it's a problem. It focusses on solving this one problem, and there is no confusion as to what the problem is and how it is solved. It is clear how the problem can be solved and how this can be measured.
To start a problem statement, first ask yourself some important questions to define the problem, like:
- Which possible solutions to the problem are you going to propose?
When you write your problem statement, split it into these sections:
A smart problem statement is concise, specific and measurable. It should briefly describe the problem, where it is occurring, the timeframe over which it has been occurring, and the size and magnitude of the problem.

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Statement of the Problem in Research

Table of Contents
The problem statement is a foundation of academic research writing , providing a precise representation of an existing gap or issue in a particular field of study.
Crafting a sharp and focused problem statement lays the groundwork for your research project.
- It highlights the research's significance .
- Emphasizes its potential to influence the broader academic community.
- Represents the initial step for you to make a meaningful contribution to your discipline.
Therefore, in this article, we will discuss what is a statement of the problem in research and how to craft a compelling research problem statement.
What is a research problem statement?
A research problem statement is a concise, clear, and specific articulation of a gap in current knowledge that your research aims to bridge. It not only sets forth the scope and direction of your research but also establishes its relevance and significance.
Your problem statement in your research paper aims to:
- Define the gap : Clearly identify and articulate a specific gap or issue in the existing knowledge.
- Provide direction : Serve as a roadmap, guiding the course of your research and ensuring you remain focused.
- Establish relevance : Highlight the importance and significance of the problem in the context of your field or the broader world.
- Guide inquiry : Formulate the research questions or hypotheses you'll explore.
- Communicate intent : Succinctly convey the core purpose of your research to stakeholders, peers, and any audience.
- Set boundaries : Clearly define the scope of your research to ensure it's focused and achievable.
When should you write a problem statement in research?
Initiate your research by crafting a clear problem statement. This should be done before any data collection or analysis, serving as a foundational anchor that clearly identifies the specific issue you aim to address.
By establishing this early on, you shape the direction of your research, ensuring it targets a genuine knowledge gap.
Furthermore, an effective and a concise statement of the problem in research attracts collaborators, funders, and supporters, resonating with its clarity and purpose. Remember, as your research unfolds, the statement might evolve, reflecting new insights and staying pertinent.
But how do you distinguish between a well-crafted problem statement and one that falls short?
Effective vs. ineffective research problem statements
Imagine a scenario where medical researchers aim to tackle a new strain of virus. Their effective problem statement wouldn't merely state the existence of the virus. Instead, it would delve into the specifics — the regions most affected, the demographics most vulnerable, and the current limitations in medical interventions.
Whereas an ineffective research problem statement is vague, overly broad, or ambiguous, failing to provide a clear direction for the research. It may not be rooted in existing literature, might lack clarity on its significance, or could be framed in a way that makes the research objectives unachievable or irrelevant.
To understand it better, let's consider the topic of “Remote work and employee productivity.”
Effective problem statement
“Over the past decade, there has been a 70% increase in organizations adopting remote work policies. While some studies suggest remote work enhances employee productivity, others indicate potential declines due to distractions at home.
However, there’s a lack of comprehensive research examining the specific factors in a remote environment that influence productivity. This study aims to identify and analyze these factors, providing organizations with actionable insights to optimize remote work policies.”
Why is this statement of a problem in research effective?
- Specificity : The statement provides a clear percentage to highlight the rise in remote work.
- Context : It acknowledges existing research and the conflicting findings.
- Clear gap identification : It points out the lack of comprehensive research on specific factors affecting productivity in remote work.
- Purpose : The statement concludes with a clear aim for the research.
Ineffective problem statement
"People are working from home a lot now, especially since there are so many internet tools. Some say it's good; others say it's not that great. This research will just look into the whole work-from-home thing and see what's up."
Why is this statement of a problem in research ineffective?
- Informal language : Phrases like "what's up" and "the whole work-from-home thing" are not suitable for academic writing.
- Vagueness : The statement doesn't provide any specific data or context about the rise of remote work.
- Lack of clear focus : It's unclear what aspect of remote work the research will address.
- Ambiguous purpose : The statement doesn't specify the research's objectives or expected outcomes.
After gaining an understanding of what an effective research problem statement looks like, let's dive deeper into how to write one.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Drafting your research problem statement at the onset of your research journey ensures that your research remains anchored. That means by defining and articulating the main issue or challenge you intend to address at the very beginning of your research process; you provide a clear focus and direction for the entire study.
Here's a detailed guide to how you can write an effective statement of the problem in research.
Identify the research area : Before addressing a specific problem, you need to know the broader domain or field of your study. This helps in contextualizing your research and ensuring it aligns with existing academic disciplines.
Example: If you're curious about the effects of digital technology on human behavior, your broader research area might be Digital Sociology or Media Studies.
Conduct preliminary literature review : Familiarize yourself with existing research related to your topic. This will help you understand what's already known and, more importantly, identify gaps or unresolved questions in the existing knowledge. This step also ensures you're advancing upon existing work rather than replicating it.
Example: Upon reviewing literature on digital technology and behavior, you find many studies on social media's impact on youth but fewer on its effects on the elderly.
Read how to conduct an effective literature review .
Define the specific problem : After thoroughly reviewing the literature, pinpoint a particular issue that your research will address. Ensure that this chosen issue is not only of substantial importance in its field but also realistically approachable given your resources and expertise. To define it precisely, you might consider:
- Highlighting discrepancies or contradictions in existing literature.
- Emphasizing the real-world implications of this gap.
- Assessing the feasibility of exploring this issue within your means and timeframe.
Example: You decide to investigate how digital technology, especially social media, affects the mental well-being of the elderly, given the limited research in this area.
Articulate clearly and concisely : Your problem statement should be straightforward and devoid of jargon. It needs to convey the essence of your research issue in a manner that's understandable to both experts and non-experts.
Example: " The impact of social media on the mental well-being of elderly individuals remains underexplored, despite the growing adoption of digital technology in this age group. "
Highlight the significance : Explain why your chosen research problem matters. This could be due to its real-world implications, its potential to fill a knowledge gap or its relevance to current events or trends.
Example: As the elderly population grows and becomes more digitally connected, understanding the psychological effects of social media on this demographic could inform digital literacy programs and mental health interventions.
Ensure feasibility : Your research problem should be something you can realistically study, given your resources, timeframe, and expertise. It's essential to ensure that you can gather data, conduct experiments, or access necessary materials or participants.
Example: You plan to survey elderly individuals in local community centers about their social media usage and perceived mental well-being, ensuring you have the means to reach this demographic.
Seek feedback : Discuss your preliminary problem statement with peers, mentors, or experts in the field. They can provide insights, point out potential pitfalls, or suggest refinements.
Example: After discussing with a gerontologist, you decide to also consider the role of digital training in moderating the effects of social media on the elderly.
Refine and Revise : Based on feedback and further reflection, revise and improve your problem statement. This iterative process ensures clarity, relevance, and precision.
Example: Your refined statement reads: Despite the increasing digital connectivity of the elderly, the effects of social media on their mental well-being, especially in the context of digital training, remain underexplored.
By following these detailed steps, you can craft a research problem statement that is both compelling and academically rigorous.
Having explored the details of crafting a research problem statement, it's crucial to distinguish it from another fundamental element in academic research: the thesis statement.
Difference between a thesis statement and a problem statement
While both terms are central to research, a thesis statement presents your primary claim or argument, whereas a problem statement describes the specific issue your research aims to address.
Think of the thesis statement as the conclusion you're driving towards, while the problem statement identifies a specific gap in current knowledge.
For instance, a problem statement might highlight the rising mental health issues among teenagers, while the thesis statement could propose that increased screen time is a significant contributor.
Refer to the comparison table between what is a thesis and a problem statement in the research below:
Common mistakes to avoid in writing statement of the problem in research
Mistakes in the research problem statement can lead to a domino effect, causing misalignment in research objectives, wasted resources, and even inconclusive or irrelevant results.
Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls not only strengthens the foundation of your research but also ensures that your efforts concede impactful insights.
Here's a detailed exploration of frequent subjective, qualitative, quantitative and measurable mistakes and how you can sidestep them.
Being too broad or too narrow
A problem statement that's too broad can lack focus, making it challenging to derive specific research questions or objectives. Conversely, a statement that's too narrow might limit the scope of your research or make it too trivial.
Example of mistake: "Studying the effects of diet on health" is too broad, while "Studying the effects of eating green apples at 3 pm on heart health" is overly narrow.
You can refine the scope based on preliminary research. The correct way to write this problem statement will be "Studying the effects of a high-fiber diet on heart health in adults over 50." This statement is neither too broad nor too narrow, and it provides a clear direction for the research.
Using unnecessary jargon or technical language
While academic writing often involves academic terms, overloading your problem statement with jargon can alienate readers and obscure the actual problem.
Example of Mistake: "Examining the diurnal variations in macronutrient ingestion vis-à-vis metabolic homeostasis."
To ensure it’s not complicated, you can simplify and clarify. "Examining how daily changes in nutrient intake affect metabolic balance" conveys the same idea more accessible.
Not emphasizing the "Why" of the problem
It's not enough to state a problem; you must also convey its significance. Why does this problem matter? What are the implications of not addressing it?
Example of Mistake: "Many students are not engaging with online learning platforms."
You can proceed with the approach of highlighting the significance here. "Many students are not engaging with online learning platforms, leading to decreased academic performance and widening educational disparities."
Circular reasoning and lack of relevance
Your problem statement should be grounded in existing research or observed phenomena. Avoid statements that assume what they set out to prove or lack a clear basis in current knowledge.
Example of Mistake: "We need to study X because not enough research has been done on X."
Instead, try grounding your statement based on already-known facts. "While several studies have explored Y, the specific impact of X remains unclear, necessitating further research."
Being overly ambitious
While it's commendable to aim high, your problem statement should reflect a challenge that's achievable within your means, timeframe, and resources.
Example of Mistake: "This research will solve world hunger."
Here, you need to be realistic and focused. "This research aims to develop sustainable agricultural techniques to increase crop yields in arid regions."
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can craft a problem statement that is clear, relevant and sets a solid foundation for your research.
Over-reliance on outdated data
Using data that is no longer relevant can mislead the direction of your research. It's essential to ensure that the statistics or findings you reference are current and pertinent to the present scenario.
Example of Mistake: "According to a 1995 study, only 5% of the population uses the internet for daily tasks."
You always cross-check the dates and relevance of the data you're using. For a contemporary study on internet usage, you'd want to reference more recent statistics.
Not specifying the sample size or demographic
A problem statement should be clear about the population or sample size being studied, especially when making generalizations or claims.
Example of Mistake: "People prefer online shopping to in-store shopping."
Here, you would benefit from specifying the demographic or sample size when presenting data to avoid overgeneralization. " In a survey of 1,000 urban residents aged 18-35, 70% expressed a preference for online shopping over in-store shopping. "
Ignoring conflicting data
Cherry-picking data that supports your hypothesis while ignoring conflicting data can lead to a biased problem statement.
Example of Mistake: "Research shows that all students benefit from online learning."
You’ve to ensure a balanced view by considering all relevant data, even if it contradicts your hypothesis. " While many studies highlight the advantages of online learning for students, some research points to challenges such as decreased motivation and lack of face-to-face interaction. "
Making unsubstantiated predictions
Projecting future trends without solid data can weaken the credibility of your problem statement.
Example of Mistake: "The demand for electric cars will increase by 500% in the next year."
Base your predictions on current trends and reliable data sources, avoiding hyperbolic or unsupported claims. " With the current growth rate and recent advancements in battery technology, there's potential for a significant rise in the demand for electric cars. "
Wrapping Up
A well-crafted problem statement ensures that your research is focused, relevant, and contributes meaningfully to the broader academic community.
However, the consequences of an incorrect or poorly constructed problem statement can be severe. It can lead to misdirected research efforts, wasted resources, compromised credibility, and even ethical concerns. Such pitfalls underscore the importance of dedicating time and effort to craft a precise and impactful problem statement.
So, as you start your research journey , remember that a well-defined problem statement is not just a starting point; it guides your entire research journey, ensuring clarity, relevance, and meaningful contributions to your field.
Frequently Asked Questions
A problem statement is a clear, concise and specific articulation of a gap in current knowledge that your research aims to bridge.
The Problem Statement should highlight existing gaps in current knowledge and also the significance of the research. It should also include the research question and purpose of the research.
Clear articulation of the problem and establishing relevance; Working thesis (methods to solve the problem); Purpose and scope of study — are the 3 parts of the problem statement.
While the statement of the problem articulates and delineates a particular research problem, Objectives designates the aims, purpose and strategies to address the particular problem.
Here’s an example — “The study aims to identify and analyze the specific factors that impact employee productivity, providing organizations with actionable insights to optimize remote work policies.”
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
How to Write a Statement of the Problem for Your Research Proposal
Defining your research problem is essential when conducting an experiment. In this article, you will learn how to write a statement of the problem for your research proposal. Learn about the characteristics of a good statement of the problem and examples of research questions.
Updated on May 17, 2022

You are a great researcher. You are full of ideas and questions as to where to go next with your work. You would not be in this position if you were not good at coming up with interesting questions within your area.
One problem, though, is knowing where to spend your time, energy, and money. Which ideas, questions, and problems are worthwhile?
You need to be able to define a good research problem. A research problem addresses an existing gap in knowledge in your field and leads to further investigations by you and other researchers. Inspiring others with your research problem will lead to citations, enhancing your and your institution's impact.
In order to write a clear and useful problem statement, you need to describe a question and its consequences.
One key way to assess the ‘usefulness' of your research ideas is to learn how to express them as clear problems.
In this article, we will talk about how to write a statement of the problem for your next research proposal. This is important not just for assessing the ‘usefulness' of research ideas, but also for formulating a grant application or proposal. We'll talk about how to explain your research ideas to others in the form of a problem statement in your proposal.
What is a statement of the problem in research?
All research projects should start with a clear problem statement. A problem statement is a formulation of an issue which is usually a ‘gap' within your area. A research gap is an unanswered question, an issue, controversy, or untested hypothesis that has not yet been addressed.
The trick with research problems is working out whether they are actually worth investing the time, energy, and money to figure out. This comes with experience, or you could just read on!
Since a clear problem statement is going to form the basis of your next research project, the question is: How can I write one?
How is this done? The first step is to become familiar with the basic elements of a problem statement in effective research.
Characteristics of a problem statement
A research problem statement has two key attributes:
- The problem must be challenging and original, but also potentially achievable by your team.
- The problem must not be incremental. In other words, don't try to address a small change or advance on an existing study that leads to no new scientific insight. This could be damaging to your and your team's reputation, and will likely not lead to a meaningful publication.
Developing a ‘good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable.
You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense. They must be usable. In other words, you must be able to acquire statistically sufficient and relevant data that is reproducible.
Finally, the problem you define means you'll need to train team members in this particular research area and methods.
Writing a statement of the problem
Stating a research problem is done by defining it within the general area of your research. This depends on your previous work and experience. It may be an area you want to move into or a topic related to what you have already worked on as a researcher. Examples could include a question in astrophysics within physics, robotics within engineering, nutrition within medicine, or marine biology within ocean and Earth science.
Once you've determined your overall area (and you'll know this already of course), it's time to drill down, decide, and define a research problem within that field.
First , your statement should identify a problem that needs to be addressed within your selected sub-area.
This will almost certainly require literature work, but the idea may arise from:
- Discussions you've had with colleagues;
- Discussions at a conference;
- A paper you've read.
Second , your problem statement should be a “good research problem.” This will require further investigation and reading as you consider “what has been done?” and “what needs to be done?”
Third , search for more information, perhaps by:
- Locating relevant books, papers and other materials;
- Evaluating the quality and authority of the information collected;
- Maintaining a regular literature review throughout the project;
- Making regular notes on background material;
- Deciding how this literature search will be carried out within the research group;
- Deciding how information gained will be disseminated to the group (e.g., via each researcher carrying out a regular literature review in their sub-area and information disseminated at group meetings or via email at regular intervals).
This process may well change or modify how your research problem is stated or formulated.
Once your research problem has been identified, research questions within the problem need to be specified.
How long should your statement of the problem be?
Not too long. One page is more than enough for a clear and effective problem statement.
Research questions within your problem
The first stage of writing your research problem statement involves formulating your questions in a meaningful way. In the context of important questions, we are looking for things that many readers across different disciplines find to be interesting. But at the same time, set your question within your field.
Thus, once a research problem has been established, several questions can be written down. These questions should specify exactly what needs to be determined to address the problem.
These questions should also be specific enough that they can be answered using appropriate available research methods - or methods that could be made available to the research group (e.g. by buying or borrowing equipment).
These questions should require complex in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. They should not be simple enough that they can be answered easily with well-established facts or yes/no answers.
All research questions should be focused, specific, appropriately complex, and relevant to the overall aims of the project.
Examples of questions and next steps
- How do government regulations prevent companies from polluting water systems?
- What factors have influenced population growth in the fastest growing countries?
- How can a bespoke thermal desorption unit be designed and built for use in detection of trace particulate matter in a polluted environment (e.g., a busy city street)?
- What methods and procedures can be used to understand, and hence control, fundamental chemical processes that occur in flames?
- How can measurement protocols used in mass spectrometry in a university research laboratory be developed and standardized to enable direct comparison with related measurements in a government laboratory?
Once the problem and questions have been identified, the resources required to carry out the research will need to be assessed. This will involve:
- Identifying the equipment needed. Find out what is available and what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing which consumables (e.g., chemicals) are needed for the project, and determining if they can be obtained on a regular basis (i.e., in the right quantities at the appropriate times).
- Identifying the software, data-analyses and other computer support needed. Assess what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing what laboratory and office space is needed. And if more is required, discuss this with the relevant laboratory manager.
- Identifying what support for travel is needed for the group, as well as what resources are required for the group to attend relevant conferences and training of group personnel.
Final thoughts
Defining and writing a clear statement of a problem as the basis of a project is the first - and most important - step in any research. The tips and ideas in this article will help you clearly identify the purpose of the research you are developing.
A clear research problem statement will likely form the skeleton of the Introduction of your final article. If you are able to clearly direct your reader (the most important person in the publishing process) to an important and interesting question, they will likely stay engaged, and use and cite your article in the future.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Problem Statement

How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
10 min read
Published on: Mar 6, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 5, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
Share this article
A well-written problem statement is a compass that guides your research journey. In this guide, we'll show you how to create a strong problem statement with clear examples.
Whether you're an established researcher or new to academic research, this guide will help you enhance the impact of your work. Let's explore together how to define the scope of your research and capture your audience's attention from the start.
Let's get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Problem Statement?
In a research paper , a problem statement is a concise and clear articulation of a specific issue or challenge that a research study aims to address. It defines the scope, context, and significance of the problem, guiding the research towards meaningful exploration and resolution.
According to Creswell (2014) , a problem statement acts as a "key component" in the early stages of the research process, helping to focus the study.
Where Does the Problem Statement Go in Your Paper?
The problem statement is usually placed in the early sections of a research paper, following the introduction and preceding headings related to research objectives, purpose, and questions.
This strategic positioning helps establish the specific problem under investigation and sets the stage for the entire paper.
When to Write a Problem Statement?
The creation of a problem statement is a pivotal early step in the research process. It should be written:
- At the Project Inception: Develop the problem statement as you initiate your research project.
- Before Data Collection: Craft the problem statement before gathering data to provide a clear research direction.
- During Proposal Writing: Include the problem statement in research proposals to outline the study's purpose.
- Prior to Literature Review : Define the problem before delving into existing literature to guide your review effectively.
- In Initial Drafts: Begin drafting the problem statement early, refining it as your understanding of the research evolves.
Writing the problem statement at these stages ensures a strong foundation, guiding your research with a focused and well-defined purpose.
What to Include in a Problem Statement?
Writing an effective problem statement involves incorporating essential elements to clearly define the research challenge. To create a robust problem statement, consider including:
- Clear Description: Define the problem concisely.
- Contextual Background: Provide context to help readers understand the issue's relevance.
- Scope Limitations: Specify the boundaries of the problem to focus the study.
- Significance: Explain why the problem is worth investigating.
- Research Purpose: State the overall objective or aim of the study.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: Pose your hypothesis or specific inquiries to guide the investigation.
Now letâs move on to the most awaited part of the guide, which is how to write a problem statement for a research paper:
Step 1: Define the Research Context
To effectively define the research context in your statement of the problem, consider the following detailed approach:
Practical Research Problem
For practical research, delve into the tangible aspects of the issue. Specify where and when the problem occurs, pinpointing the affected demographic and detailing any prior attempts to address the problem.
Theoretical Research Problem
For theoretical research, explore the scientific, social, geographical, or historical background of the problem. Outline what is already known, the time or geographical constraints, and how scholars have defined and debated the issue.
Step 2: Highlight the Significance
To effectively highlight the significance of your research problem in the statement, consider the following detailed approach:
Practical Research Problems
For practical research, elucidate the potential outcomes if the problem remains unresolved. Consider who will be affected and the wider implications. Evaluate if similar issues exist in other contexts.
Theoretical Research Problems
For theoretical research, explore how resolving the problem contributes to a deeper comprehension of the subject. Assess the benefits for future research and whether the problem has direct or indirect consequences for society.
Step 3: Formulate Clear Objectives
To formulate clear objectives in your statement of the problem, follow these guidelines:
Define the Research Aim
Clearly articulate the overall purpose of your research using infinitive phrases like "The aim of this study is to..."
Specify Research Objectives
Concrete steps to achieve the aim should be outlined and written in a clear and measurable manner.
Step 4: Identify Limitations and Scope
When addressing limitations and scope in your statement of the problem, it's crucial to provide a transparent and realistic framework for your research. Follow these guidelines:
Acknowledge Inherent Limitations
Be upfront about the constraints and challenges your research might face. This could include time, budget, access to data, or methodological limitations.
Define the Scope of Your Study
Clearly outline the boundaries of your research. Specify the aspects you will focus on and those you will exclude. This helps readers understand the context and depth of your investigation.
Consider Implications of Limitations
Briefly discuss how these limitations might impact the interpretation of results or the generalizability of findings.
Step 5: Consider the Research Questions
In formulating research questions in your statement of the problem, follow these guidelines to ensure clarity and precision:
Align Questions with Objectives
Ensure that each research question directly corresponds to the objectives you outlined earlier. This alignment helps maintain focus and relevance.
Make Questions Specific and Clear
Formulate questions that are specific, unambiguous, and directly related to the problem. Avoid vague or overly broad inquiries.
Ensure Researchability
Confirm that your research questions are feasible and can be effectively addressed with the chosen research methods and available resources.
Step 6: Write and Refine the Final Problem Statement
After carefully navigating through the preceding steps, the final step involves crafting the ultimate problem statement for your research paper.
Here is an example of what a polished problem statement looks like:
Problem Statement Examples
Here is a list of problem statement examples you can look at and get inspiration.
Example of Problem Statement in Research Paper
Statement of the Problem Example Quantitative Research
Statement of the Problem Example Qualitative Research
Problem Statement In Research Proposal
Problem Statement Template
To sum it up,
Writing a strong problem statement is a vital step in shaping the direction of your research. By following the six steps outlined, you can articulate a clear and focused problem that sets the stage for a successful study.
Remember, precision is key when it comes to writing the problem statement for your research paper. Therefore, if you find yourself struggling, don't hesitate to seek professional help.
At CollegeEssay.org , our online writing service is ready to assist you with your research paper assignments.
Connect with our research paper writing service today for expert guidance and ensure your problem statement aligns with your research objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a research problem statement be.
A research problem statement should be concise, typically ranging from one to three paragraphs. It should convey the essence of the problem clearly without unnecessary details, ensuring a focused and impactful presentation.
Should the problem statement be written before or after the literature review?
Ideally, the problem statement is crafted before the literature review. Defining the research problem provides a foundational framework, guiding the subsequent literature review to explore existing knowledge and identify gaps in understanding.
Is it necessary to propose solutions in the problem statement?
No, the problem statement is primarily focused on articulating the research problem rather than proposing solutions. Solutions to solve the problem are typically addressed in the later stages of the research paper, allowing the problem statement to set the stage for the investigation without prematurely suggesting answers.
Betty P. (Literature, Natural Sciences)
Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A problem statement is a concise and concrete summary of the research problem you seek to address. It should:
- Contextualise the problem. What do we already know?
- Describe the exact issue your research will address. What do we still need to know?
- Show the relevance of the problem. Why do we need to know more about this?
- Set the objectives of the research. What will you do to find out more?
Table of contents
When should you write a problem statement, step 1: contextualise the problem, step 2: show why it matters, step 3: set your aims and objectives.
Problem statement example
Frequently asked questions about problem statements
There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement.
In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualise and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal . Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction .
A problem statement looks different depending on whether you’re dealing with a practical, real-world problem or a theoretical issue. Regardless, all problem statements follow a similar process.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The problem statement should frame your research problem, giving some background on what is already known.
Practical research problems
For practical research, focus on the concrete details of the situation:
- Where and when does the problem arise?
- Who does the problem affect?
- What attempts have been made to solve the problem?
Theoretical research problems
For theoretical research, think about the scientific, social, geographical and/or historical background:
- What is already known about the problem?
- Is the problem limited to a certain time period or geographical area?
- How has the problem been defined and debated in the scholarly literature?
The problem statement should also address the relevance of the research. Why is it important that the problem is addressed?
Don’t worry, this doesn’t mean you have to do something groundbreaking or world-changing. It’s more important that the problem is researchable, feasible, and clearly addresses a relevant issue in your field.
Practical research is directly relevant to a specific problem that affects an organisation, institution, social group, or society more broadly. To make it clear why your research problem matters, you can ask yourself:
- What will happen if the problem is not solved?
- Who will feel the consequences?
- Does the problem have wider relevance? Are similar issues found in other contexts?
Sometimes theoretical issues have clear practical consequences, but sometimes their relevance is less immediately obvious. To identify why the problem matters, ask:
- How will resolving the problem advance understanding of the topic?
- What benefits will it have for future research?
- Does the problem have direct or indirect consequences for society?
Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it.
The research aim is the overall purpose of your research. It is generally written in the infinitive form:
- The aim of this study is to determine …
- This project aims to explore …
- This research aims to investigate …
The research objectives are the concrete steps you will take to achieve the aim:
- Qualitative methods will be used to identify …
- This work will use surveys to collect …
- Using statistical analysis, the research will measure …
The aims and objectives should lead directly to your research questions.
Learn how to formulate research questions
You can use these steps to write your own problem statement, like the example below.
Step 1: Contextualise the problem A family-owned shoe manufacturer has been in business in New England for several generations, employing thousands of local workers in a variety of roles, from assembly to supply-chain to customer service and retail. Employee tenure in the past always had an upward trend, with the average employee staying at the company for 10+ years. However, in the past decade, the trend has reversed, with some employees lasting only a few months, and others leaving abruptly after many years.
Step 2: Show why it matters As the perceived loyalty of their employees has long been a source of pride for the company, they employed an outside consultant firm to see why there was so much turnover. The firm focused on the new hires, concluding that a rival shoe company located in the next town offered higher hourly wages and better “perks”, such as pizza parties. They claimed this was what was leading employees to switch. However, to gain a fuller understanding of why the turnover persists even after the consultant study, in-depth qualitative research focused on long-term employees is also needed. Focusing on why established workers leave can help develop a more telling reason why turnover is so high, rather than just due to salaries. It can also potentially identify points of change or conflict in the company’s culture that may cause workers to leave.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives This project aims to better understand why established workers choose to leave the company. Qualitative methods such as surveys and interviews will be conducted comparing the views of those who have worked 10+ years at the company and chose to stay, compared with those who chose to leave.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 8 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/write-a-problem-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.
EXPLAINER: What to Know About the Change Healthcare Cyberattack
The attack by a ransomware group has sparked concern about health care revenues and providers’ ability to offer care.
EXPLAINER: Change Healthcare Cyberattack

Patrick Sison | AP
Pages from the United Healthcare website are displayed on a computer screen in New York on Feb. 29, 2024.
The ramifications of a cyberattack on a critical health care technology company are still being felt in the U.S.
The hack of Change Healthcare reportedly affected billing and care authorization portals . It’s led to prescription backlogs and missed revenue for providers, posing potential threats to worker paychecks and even patient care.
The attack also prompted high-level calls for action from the likes of Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer of New York and leading medical organizations. The American Medical Association called on the Department of Health and Human Services to “use all its available authorities to ensure that physician practices can continue to function, and patients can continue to receive the care that they need.”
“This massive breach and its wide-ranging repercussions have hit physician practices across the country, risking patients’ access to their doctors and straining viability of medical practices themselves,” the AMA’s president, Dr. Jesse Ehrenfeld, said in a March 4 statement . “This is an immense crisis demanding immediate attention.”
Similarly, the American Hospital Association told HHS in late February that hospitals and health systems may require “immediate federal support” amid the fallout, noting the vast reach of Change Healthcare’s systems and warning that a prolonged disruption “will negatively impact many hospitals’ ability to offer the full set of health care services to their communities.”
AHA President and CEO Rick Pollack called the cyberattack “the most serious incident of its kind leveled against a U.S. health care organization.”
What Is Change Healthcare?
Change Healthcare, which is owned by UnitedHealth Group, manages health care technology pipelines connected to tasks such as processing insurance claims and billing, reportedly handling 15 billion transactions annually.
As noted by The Washington Post , the Justice Department in a 2022 lawsuit cited United as stating that 50% of U.S. medical claims go through Change’s “electronic data interchange clearinghouse.”
What Happened?
“On Feb. 21, 2024, we discovered a threat actor gained access to one of our Change Healthcare environments,” UnitedHealth Group said . “Once we became aware of the outside threat, in the interest of protecting our partners and patients, we took immediate action to disconnect Change Healthcare’s systems to prevent further impact.”
A specific timeline for restoration of services was not provided in the initial wake of the attack. But in a March 7 statement , UnitedHealth Group said electronic prescribing for pharmacy services was “fully functional with claim submission and payment transmission” available as of that date.
The company said its electronic payment platform would be reestablished beginning March 15, and that it expected to start testing and establishing claims network connectivity on March 18, with service restored through the week.
“As workarounds continue to be deployed, our latest data shows 90% of claims are flowing uninterrupted,” the company said , though it acknowledged “there are still a number of providers who are not able to submit claims or receive payment.”
Meanwhile, a temporary funding assistance program for providers has been set up through Optum, which is also owned by UnitedHealth Group. UnitedHealth Group said in its March 7 update that “further funding solutions” involving advance payments would be offered to provider partners of UnitedHealthcare, its health benefits business, and that the Optum program would be expanded “to include providers who have exhausted all available connection options, and who work with a payer who has opted not to advance funds to providers during the period when Change Healthcare systems remain down.”
“This expansion is a funding mechanism of last resort, especially for small and regional providers, and will be evaluated on a case-by-case basis,” the statement said.
What’s the Impact of the Health Care Hack?
Many physician practices have not been able to submit claims, according to the AMA , and “a considerable proportion of revenue cycle processes have ground to a halt.” The group in a March 1 letter to HHS identified top concerns among practices since the incident, including the interruption of administrative and billing processes, practices having to take on “enormous” administrative burdens and significant data privacy fears.
The outage cost some health care providers over $100 million a day, according to an estimate from First Health Advisory , a digital health risk assurance firm. Schumer, in a March 1 letter to the federal Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, said Change Healthcare had suspended more than 100 services and that hospitals and other providers were facing adverse impacts on their financial solvency.
“Hospitals are struggling to process claims, bill patients, and receive electronic payments, leaving them financially vulnerable,” Schumer said. “Many hospitals are approaching a financial cliff where they will no longer be able to rely on their cash on hand.”
Schumer asked CMS to make accelerated and advanced payments available for affected providers, akin to what was offered during the COVID-19 pandemic . On March 5, federal officials said hospitals could submit requests for accelerated payments to Medicare administrators "for individual consideration," and urged Medicare Advantage organizations, as well as Medicaid managed care plans, to relax prior authorization requirements for care and to consider offering advance funding to providers.
Who Is Responsible for the Hack?
Change Healthcare said the group identified itself as ALPHV/BlackCat.
According to a report from Wired, the group of hackers recently received a $22 million transaction that looks like it could be a large ransom payment related to the attack. A spokesperson affiliated with Change Healthcare declined to answer whether a ransom has been paid, according to Wired.
In December, the Justice Department announced it had targeted ALPHV in a disruption campaign.
“In disrupting the BlackCat ransomware group, the Justice Department has once again hacked the hackers,” Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco said in a statement. “With a decryption tool provided by the FBI to hundreds of ransomware victims worldwide, businesses and schools were able to reopen, and health care and emergency services were able to come back online.”
Join the Conversation
Tags: health care , cybersecurity , UnitedHealth Group , health insurance

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Senate Beats Shutdown Deadline
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder March 8, 2024

No Labels to Run Presidential Candidate
Lauren Camera March 8, 2024

Labor Market Keeps Rolling
Tim Smart March 8, 2024

Trump’s Grim Math Problem
Lauren Camera and Susan Milligan March 8, 2024

Fiery Biden Takes on Trump
Susan Milligan March 8, 2024

READ: Biden's State of the Union Address
U.S. News Staff March 7, 2024


Why so many South Korean women are refusing to date, marry or have kids
Postdoctoral Fellow, Indiana University
Disclosure statement
Min Joo Lee does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Indiana University provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
- Bahasa Indonesia
South Korea finds itself embroiled in an all-out gender war – and it keeps getting worse.
The animosity between Korean men and women has reached a point where some women are outright refusing to date, marry and have kids with men – a phenomenon known as the 4B movement .
As a Korean feminist scholar living in the U.S., I’ve followed this gender war from afar as I conducted research on contemporary Korean gender politics.
However, I also became embroiled in it myself after my research on Korean masculinity was published by CNN .
The article described foreign women who traveled to Korea after becoming enamored of the idea of dating Korean men from watching Korean television dramas. I pointed out that since the tourists’ fantasies were based on fictional characters, some of them ended up disappointed with the Korean men they dated in real life.
The article was about racial politics and the masculine ideals. But some Korean readers thought that I was simply criticizing Korean men for not being romantic and handsome enough. One enraged Korean man commented that I was an “ugly feminist.”
But this was tame in comparison to what women living in South Korea have endured in recent years.
Extreme misogyny and a feminist backlash
Over the past couple of decades, there have been flash points in this gender war.
In 2010, Ilbe, a right-wing website that traffics in misogyny, started attracting users who peppered the forums with vulgar posts about women.
Then in 2015, an online extremist feminist group named Megalia arose. Its goal was to fight back by demeaning Korean men in ways that mirrored the rhetoric on sites like Ilbe.
A year later, a man who had professed his hatred of women murdered a random woman in a public bathroom near a Seoul subway station. He was eventually sentenced to decades in prison, but the lines were quickly drawn. On one side were feminists, who saw misogyny as the underlying motive. On the other side were men who claimed that it was merely the isolated actions of a mentally ill man. The two groups violently clashed during competing protests at the site of the murder.
A backdrop of digital sex crimes
However, none of these events have elicited as much public controversy as the steep rise in digital sex crimes. These are newer forms of sexual violence facilitated by technology: revenge porn ; upskirting , which refers to surreptitiously snapping photos under women’s skirts in public; and the use of hidden cameras to film women having sex or undressing.
In 2018, there were 2,289 reported cases of digital sex crimes; in 2021, the number snowballed to 10,353 .
In 2019, there were two major incidents that involved digital sex crimes.
In one, a number of male K-pop stars were indicted for filming and circulating videos of women in group chatrooms without their consent .
A few months later, Koreans were shocked to learn about what became known as the “ Nth Room Incident ,” during which hundreds of perpetrators – mostly men – committed digital sex crimes on dozens of women and minors.
They tended to target poorer women – sex workers, or women who wanted to make a few bucks by sharing anonymous nude photos of themselves. The perpetrators either hacked into their social media accounts or approached these women and offered them money, but asked for their personal information so they could transmit the funds. Once they obtained this information, they blackmailed the women by threatening to reveal their sex work and their nudes to their friends and family.
Since sex work and posting nude images of yourself online are illegal in Korea, the women, fearing arrest or being ostracized by friends and family, complied with the perpetrators’ demands to send even more compromising images of themselves. The men would then swap these images in chatrooms.

And yet a 2019 survey conducted by the Korean government found that large swaths of the population blamed women for these sex crimes: 52% said that they believed sexual violence occurs because women wear revealing clothes, while 37% thought if women experienced sexual assault while drunk, they are partly to blame for their victimization.
In other words, a significant percentage of the Korean population believes that female sexuality is the problem – not the sexual violence.
Government policy lays the groundwork
Digital sex crimes are too widespread to lay the blame at the feet of a handful of bad actors.
To me, part of the problem stems from the long history of “gendered citizenship.”
Korean feminist scholar Seungsook Moon has written about the ways in which the government created one track for men and another for women as the country sought to modernize in the second half of the 20th century:
“Men were mobilized for mandatory military service and then, as conscripts, utilized as workers and researchers in the industrializing economy. Women were consigned to lesser factory jobs, and their roles as members of the modern nation were defined largely in terms of biological reproduction and household management.”
Although these policies are no longer officially carried out, the underlying attitudes about gender roles remain embedded in Korean life and culture. Women who veer from being mothers and housewives expose themselves to public and private backlash.
The government has created gender quotas in certain industries to try to unravel this system of gendered citizenship.
For instance, some government jobs have minimum gender quotas for new hires, and the government encourages the private sector to implement similar policies . In historically male-dominant industries, such as construction, there are quotas for female hires, while in historically female-dominant industries, such as education, there are male quotas .
In some ways, this has only made things worse. Each gender feels as if the other is receiving special treatment due to these affirmative action policies. Resentment festers.
‘The generation that has given up’
Today, the sense of competition between young men and women is exacerbated by the soaring cost of living and rampant unemployment.
Called the “ N-Po Generation ,” which roughly translates as “the generation that has given up,” many young South Koreans don’t think they can achieve certain milestones that previous generations took for granted: marriage, having kids, finding a job, owning a home and even friendships.

Although all genders find themselves discouraged, the act of “giving up” has caused more problems for women. Men see women who forgo marriage and having kids as selfish. And when they then try to compete against men for jobs, some men become incensed.
Many of the men who have become radicalized commit digital sex crimes to take revenge on women who, in their view, have abandoned their duties.
Ultimately, the competitive dynamic created by the Korean government’s embrace of gendered citizenship has stoked the virulent gender war between Korean men and women, with digital sex crimes used as ammunition.
The 4B movement, whereby Korean women forego heterosexual dating, marriage, and childbirth, represents a radical escalation of the gender war by seeking to create an online and offline world devoid of men. Rather than engaging in altercations, these women are refusing to interact with men, period.
Digital sex crimes are a global problem
To be sure, digital sex crimes are not unique to Korea.
When I teach my college class on digital sex crimes in the U.S., I’m surprised by how many of my students admit that they’ve been victims of digital sex crimes, or knew of it happening at their high schools. And at the National Women’s Studies Association’s annual conference in 2022 , I watched feminist activists and scholars from all over the world present their findings about digital sex crimes back home.
Since each country has its own cultural context for the rise in digital sex crimes, there isn’t a single solution to solve the problems. But in South Korea, continuing to unravel the system of gendered citizenship could be part of the solution.
- Relationships
- South Korea
- Gender politics
- Cyberbullying
- Culture wars
- Revenge porn
- Sexist oppression

School of Social Sciences – Academic appointment opportunities

Union Organiser (part-time 0.8)

Director, Indigenous Education Research Centre

Communications Specialist

AUSTRALIAN PESTICIDES AND VETERINARY MEDICINES AUTHORITY (APVMA) BOARD CHAIR
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
BREAKING NEWS
THE LIST: 2024 Academy Awards Winners
A rip current statement in effect for coastal broward and coastal miami dade regions, ap decision notes: what to expect in hawaii's republican caucuses.
Robert Yoon
Associated Press
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.
Republican presidential candidate former President Donald Trump speaks at a Super Tuesday election night party, Tuesday, March 5, 2024, at Mar-a-Lago in Palm Beach, Fla. (AP Photo/Rebecca Blackwell)
WASHINGTON – Hawaii Republicans will hold caucuses Tuesday to cast votes in a presidential nomination contest in which former incumbent Donald Trump is the only remaining major candidate competing. Former United Nations Ambassador Nikki Haley ended her campaign this week.
Trump won 14 of 15 contests held on Super Tuesday, putting him near the number of delegates needed to clinch the Republican nomination. But he’ll need to win the bulk of delegates at stake Tuesday in Hawaii, Georgia, Mississippi and Washington to close the deal.
Recommended Videos
In 2016, Trump won the caucuses against a much more competitive field. He received 43% of the vote, ahead of U.S. Sen. Ted Cruz of Texas, who had 32% of the vote. U.S. Sen. Marco Rubio and former Ohio Gov. John Kasich were a distant third and fourth.
Hawaii Democrats held their caucuses, which President Joe Biden won with 66% of the vote, this week. “Uncommitted” won 29% of the vote and picked up 7 of the state's 22 Democratic delegates. He could also clinch on March 12.
The Associated Press allocated delegates from Delaware and Florida to Biden on Friday, as both states have canceled their Democratic presidential primaries, with all their delegates going to the sitting president. With that allocation, Biden’s first possible date to clinch moves up to March 12, when he needs to win just 40% of the available delegates to do so.
Here’s a look at what to expect on election night:
PRIMARY DAY
The Hawaii Republican presidential caucuses will be held Tuesday. Caucus hours are from 6-8 p.m. local time, which is 12-2 a.m. ET.
WHAT’S ON THE BALLOT
The Associated Press will provide coverage for the Republican presidential caucuses. The candidates are Trump, Haley, Florida businessman David Stuckenberg and former candidates Ryan Binkley, Doug Burgum, Chris Christie, Ron DeSantis and Vivek Ramaswamy. Write-in votes are allowed for any candidate who has filed with the Federal Election Commission.
WHO CAN VOTE
Caucusgoers must be registered voters in Hawaii and members of the Hawaiian Republican Party. Hawaii doesn’t register voters by party, but all participants must sign paperwork with the state party confirming their membership before they vote. Same-day voter registration will be permitted on caucus day.
DELEGATE ALLOCATION RULES
Hawaii has 19 Republican delegates at stake in the caucuses. These delegates fall into four subgroups that are each awarded to candidates separately but using the same method. The 10 at-large delegates are awarded to candidates in proportion to the statewide vote. Three additional delegates, the state party chair and the Republican National Committeeman and Committeewoman, are also awarded to candidates in proportion to the statewide vote. Finally, three delegates in each congressional district are awarded to candidates in proportion to the vote results in that district. Candidates are not required to meet a minimum vote percentage to qualify for delegates.
DECISION NOTES
Tuesday’s caucuses in Hawaii are unlikely to be competitive, as Trump faces no major opposition in his campaign for renomination. The first indication that Trump is winning statewide on a level consistent with the overwhelming margins seen in most other contests held so far this year may be sufficient to determine the statewide winner.
The AP does not make projections and will declare a winner only when it’s determined there is no scenario that would allow the trailing candidates to close the gap. If a race has not been called, the AP will continue to cover any newsworthy developments, such as candidate concessions or declarations of victory. In doing so, the AP will make clear that it has not yet declared a winner and explain why.
WHAT DO TURNOUT AND ADVANCE VOTE LOOK LIKE
The total number of votes cast in the last competitive GOP caucuses in 2016 was 15,672, which was about 2% of registered voters at the time. In the 2012 caucuses, 10,228 votes were cast, which was about 1% of registered voters. The caucuses do not allow early voting or absentee voting.
HOW LONG DOES VOTE-COUNTING USUALLY TAKE?
A breakdown of the vote-reporting timeline is not available for the 2012 or 2016 caucuses. But the party expects to begin to release votes at about 8:30 p.m. local time, which is 2:30 a.m. ET.
ARE WE THERE YET?
As of Tuesday, there will be 125 days until the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee and 238 until the November general election.
Follow the AP's coverage of the 2024 election at https://apnews.com/hub/election-2024 .
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
Sample: E Score: 3. This paper earned a score of 3. A method of content analysis is presented on page 4, followed by a description of the method on pages 4-5. The methods, however, are inconsistent, with two different descriptions given for how movies were chosen on pages 4 and 5.
The Advanced Placement (AP) curriculum is administered by the College Board and serves as a standardized set of year-long high school classes that are roughly equivalent to one semester of college-level coursework. Although most students enroll in an actual course to prepare for their AP exams, many others will self-study for the exams without ...
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way. It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
AP Research is an interdisciplinary course that encourages students to demonstrate critical thinking and academic research skills on a topic of the student's choosing. To accommodate the wide range of student topics, typical college course equivalents include introductory research or general elective courses. ... Identifying a problem or ...
A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem, the consequence and the solution or response. A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem, typically contained within one paragraph.
AP Research, the second course in the AP Capstone experience, allows students to deeply explore an academic topic, problem, issue, or idea of individual interest. Students design, plan, and implement a yearlong investigation to address a research question. Through this inquiry, they further the skills they acquired in the AP Seminar course by ...
Describes a nonreplicable research method . OR . provides an oversimplified description of a method, with questionable alignment to the purpose of the inquiry. Describes a reasonably replicable research method, with questionable alignment to the purpose of the inquiry. Logically defends the alignment of a detailed, replicable research method
AP® RESEARCH 2017 SCORING GUIDELINES Performance Task Rubric: Academic Paper. The paper identifies a broad topic of inquiry The paper identifies a focused topic of inquiry and The paper explains the topic, purpose, and focus of the and/or a purpose. describes the purpose. inquiry and why further investigation of the topic is needed by ...
Here are some general steps to follow when writing a problem statement: Identify the problem: Clearly identify the problem that needs to be addressed. Consider the context, stakeholders, and potential consequences of the problem. Research the problem: Conduct research to gather data and information about the problem.
A research problem statement is the descriptive statement which conveys the issue a researcher is trying to address through the study with the aim of informing the reader the context and significance of performing the study at hand. The research problem statement is crucial for researchers to focus on a particular component of a vast field of ...
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements: 1. The research topic: The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses. 2. The specific problem or issue: A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. 3.
Gather data and observe. Use data from research and reports, as well as facts from direct observation to answer the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why. Whenever possible, get out in the field and talk directly with stakeholders impacted by the problem. Get a firsthand look at the work environment and equipment.
Problem statement in research is the description of an existing issue that needs to be addressed. The problem statement is a focal point of any research and a bridge between the literature review and the research methodology. Problem statement often has three elements; the problem itself, the method of solving the problem, and the purpose.
A problem statement is a move that a document makes to help the reader realize why the document is important. Problem statements can be either formal--like a thesis statement--or they can be informal--usually a sentence that explains how what you are saying will impact the reader. A carefully crafted problem statement will help you to connect ...
The format of a problem statement. When you write your problem statement, split it into four sections: Problem: Here, simply define what your problem is, clearly and concisely. Make it no longer than one or two sentences. Background: This is the section where you can describe what causes the problem, how often it occurs, where and when it ...
The problem statement is a foundation of academic research writing, providing a precise representation of an existing gap or issue in a particular field of study.. Crafting a sharp and focused problem statement lays the groundwork for your research project. It highlights the research's significance.; Emphasizes its potential to influence the broader academic community.
Developing a 'good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable. You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense.
The answer is yes, for at least three reasons. 1) branding is important - a good title will help the reviewer establish a connection with your proposal 2) a negative first impression will likely linger with the reviewer while reading the rest of the problem statement, and 3) if the title is confusing, chances are the rest of the problem ...
AP Research: Writing a Research Problem Statement. Research Questions and Problem Statements: Overview. A research problem is a definite statement about an area of concern, a real-world problem requiring a solution, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful ...
AP ® Research Academic Paper Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary ... There is a significant problem with the way false information is dealt with in social media. Despite the laws forbidding the spreading or creation of false information, ... falsehood is "A lie or statement that is not correct". Many of the falsehoods that can be
Before Data Collection: Craft the problem statement before gathering data to provide a clear research direction. During Proposal Writing: Include the problem statement in research proposals to outline the study's purpose. Prior to Literature Review: Define the problem before delving into existing literature to guide your review effectively.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
The ramifications of a cyberattack on a critical health care technology company are still being felt across the U.S. nearly two weeks later. Change Healthcare has acknowledged the hack, which ...
Research shows that women face many challenges in the tech industry. The gender pay gap is severe. Women do not get the same opportunities as men ; for example, only 18% of the chief information ...
Disclosure statement. Min Joo Lee does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant ...
Few Americans say the United States should take a more active role in solving global problems, but partisans are split on whether they think the U.S. should take a less active role on the world ...
Hawaii Democrats held their caucuses, which President Joe Biden won with 66% of the vote, this week. "Uncommitted" won 29% of the vote and picked up 7 of the state's 22 Democratic delegates ...