
Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing (Differences, Examples, How To)

It can be confusing to know when to paraphrase and when to summarize. Many people use the terms interchangeably even though the two have different meanings and uses.
Today, let’s understand the basic differences between paraphrasing vs. summarizing and when to use which . We’ll also look at types and examples of paraphrasing and summarizing, as well as how to do both effectively.
Let’s look at paraphrasing first.
What is paraphrasing?
It refers to rewriting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
It’s important to rewrite the whole idea in your words rather than just replacing a few words with their synonyms. That way, you present an idea in a way that your audience will understand easily and also avoid plagiarism.
It’s also important to cite your sources when paraphrasing so that the original author of the work gets due credit.
When should you paraphrase?
The main purpose of paraphrasing is often to clarify an existing passage. You should use paraphrasing when you want to show that you understand the concept, like while writing an essay about a specific topic.
You may also use it when you’re quoting someone but can’t remember their exact words.
Finally, paraphrasing is a very effective way to rewrite outdated content in a way that’s relevant to your current audience.
How to paraphrase effectively
Follow these steps to paraphrase any piece of text effectively:
- Read the full text and ensure that you understand it completely. It helps to look up words you don’t fully understand in an online or offline dictionary.
- Once you understand the text, rewrite it in your own words. Remember to rewrite it instead of just substituting words with their synonyms.
- Edit the text to ensure it’s easy to understand for your audience.
- Mix in your own insights while rewriting the text to make it more relevant.
- Run the text through a plagiarism checker to ensure that it does not have any of the original content.
Example of paraphrasing
Here’s an example of paraphrasing:
- Original: The national park is full of trees, water bodies, and various species of flora and fauna.
- Paraphrased: Many animal species thrive in the verdant national park that is served by lakes and rivers flowing through it.
What is summarizing?
Summarizing is also based on someone else’s text but rather than presenting their ideas in your words, you only sum up their main ideas in a smaller piece of text.
It’s important to not use their exact words or phrases when summarizing to avoid plagiarism. It’s best to make your own notes while reading through the text and writing a summary based on your notes.
You must only summarize the most important ideas from a piece of text as summaries are essentially very short compared to the original work. And just like paraphrasing, you should cite the original text as a reference.
When should you summarize?
The main purpose of summarizing is to reduce a passage or other text to fewer words while ensuring that everything important is covered.
Summaries are useful when you want to cut to the chase and lay down the most important points from a piece of text or convey the entire message in fewer words. You should summarize when you have to write a short essay about a larger piece of text, such as writing a book review.
You can also summarize when you want to provide background information about something without taking up too much space.
How to summarize effectively
Follow these steps to summarize any prose effectively:
- Read the text to fully understand it. It helps to read it a few times instead of just going through it once.
- Pay attention to the larger theme of the text rather than trying to rewrite it sentence for sentence.
- Understand how all the main ideas are linked and piece them together to form an overview.
- Remove all the information that’s not crucial to the main ideas or theme. Remember, summaries must only include the most essential points and information.
- Edit your overview to ensure that the information is organized logically and follows the correct chronology where applicable.
- Review and edit the summary again to make it clearer, ensure that it’s accurate, and make it even more concise where you can.
- Ensure that you cite the original text.
Example of summarization
You can summarize any text into a shorter version. For example, this entire article can be summarized in just a few sentences as follows:
- Summary: The article discusses paraphrasing vs. summarizing by explaining the two concepts. It specifies when you should use paraphrasing and when you should summarize a piece of text and describes the process of each. It ends with examples of both paraphrasing and summarizing to provide a better understanding to the reader.

Paraphrasing vs. summarizing has been a long-standing point of confusion for writers of all levels, whether you’re writing a college essay or reviewing a research paper or book. The above tips and examples can help you identify when to use paraphrasing or summarizing and how to go about them effectively.
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

Comparing Summary vs Paraphrase – What are the Key Differences?
Key Takeaways: Summarizing vs Paraphrasing
How They Are Similar: Paraphrasing and summarizing are both writing techniques that allow us to use other people’s ideas without direct copying.
How They Are Different: Paraphrasing involves rewording text to create new written content with the same meaning as the original. On the other hand, summarizing condenses the text to an overview of the main points. Both require proper citation to avoid plagiarism!
Have you ever done a bunch of research, then sat down to work on a report or written document, and then realized: I don’t whether I should summarize this work or paraphrase it?
In the context of summary vs paraphrase, both techniques allow us to incorporate the ideas of others into our own work without copying them directly.
Yet, these methods are often misunderstood or misused. This article will explain these two techniques, and give examples of both. Plus, learn how you can use AI to do some of the summarizing and paraphrasing for you!
This post may contain affiliate links, which means I’ll receive a commission if you purchase through my links, at no extra cost to you. Please read full disclosure for more information.

Understanding Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is a powerful technique that allows us to take someone else’s words and ideas and express them in our own unique way. At its core, paraphrasing is rewriting a text to produce original content while preserving the original meaning.
It is a valuable skill that can help us better understand complex material, communicate ideas more effectively, and avoid plagiarism.
Definition of Paraphrasing
This process involves reworking the text line by line, simplifying grammar and vocabulary, rearranging words and sentences, and transforming passive expressions into active ones.
The result is a “new” text that maintains the essence of the original but is expressed in our unique way.
Uses of Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing can serve various purposes, such as clarifying a message, making it more relevant to the audience, or emphasizing specific key points.
It can also support our arguments or viewpoints, maintain a consistent writing style, and avoid lengthy citations from the original text or discourse.
Paraphrasing helps us engage more deeply with the source material and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the materials used in our research.
Understanding Summarizing

To summarize means the process of concisely expressing the most pertinent facts or ideas about something, often in our own words. It is a method of condensing a large selection of complex text while retaining its essential information.
Summarizing can help us quickly grasp the key points of a text, making it easier to communicate those main points to others as a brief overview.
Definition of Summarizing
Its objective is to condense information into a concise and clear summary that will be understandable for readers.
By extracting the essential ideas from a text and condensing them into a shorter version, we can more easily digest and understand the underlying message of the original work.
Summaries can be used to quickly grasp the main points of a text. They can also be used to review and recall information.
Uses of Summarizing
Summarizing is a versatile technique with many applications. It can be employed to better understand the primary concept of a written work or to condense a longer original text into a more concise version.
Summarizing is also valuable for academic writing , as it allows us to introduce background information, summarize knowledge from multiple sources on a topic, or identify the main points of a single source. Summarizing lets us focus on the most critical information and present it clearly and concisely.
Summarizing a document is a great way to save both time and energy in your life!
Key Differences

While paraphrasing and summarizing allow us to incorporate other authors’ ideas into our work, their key differences lie in their purpose, length, detail, style, and citation requirements.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effectively mastering and using these techniques in our writing endeavors.
The following sections will explore the differences between paraphrasing vs summarizing, exploring their unique characteristics and applications. Here’s a quick summary of the two:
The purpose of paraphrasing is to reword a text to generate original content with the same meaning while summarizing is to condense a longer text into a significantly shorter version that conveys the key ideas.
In essence, paraphrasing focuses on rewriting the text to create a new, unique version, while summarizing aims to provide a brief overview of the original material.
Another key difference between paraphrasing and summarizing is the length of the rewritten or condensed text. A paraphrased text is generally similar in length to the original text, maintaining the same level of detail.
In contrast, a summary is significantly shorter than the original text, as it only includes the most pertinent points and necessary information.
Paraphrasing involves rewording a text to generate original content while preserving the same level of detail. In other words, a paraphrase should include all relevant details from the original text, expressed differently.
On the other hand, summarizing focuses on extracting the main ideas from the original text and condensing them into a succinct overview, often omitting superfluous details.
In terms of style, paraphrasing involves altering the phrasing of a text while maintaining the original meaning, often employing synonyms and restructured sentences.
Summarizing, conversely, involves condensing the text by focusing only on the main ideas and key points. Both techniques require using our own words and writing style, but summarizing often necessitates a more concise and focused approach.
Proper citation is essential when performing both paraphrasing and summarizing, as the idea originates from another writing.
To avoid plagiarism, it is crucial to include an in-text citation and a reference in the bibliography or works cited list, depending on the formatting style required for the assignment.
This ensures that we give proper credit to the original author and avoid any potential consequences of plagiarism.
Tips and Tricks
Now that we have a deeper understanding of the differences between paraphrasing vs summarizing, it’s important to learn how to apply these techniques effectively.
Some effective paraphrasing and summarizing tips include using unique words, representative phrases, accurate synonyms, and only including key points and essential information.
In the following sections, we will explore specific techniques for both paraphrasing and summarizing, providing practical advice for mastering these valuable skills.
Paraphrasing Techniques
Effective paraphrasing involves several techniques, such as utilizing synonyms, altering the form of words, changing the grammatical structure, modifying the sentence structure, and transforming the word class or form.
It is essential to comprehend and articulate the source material in our own words while preserving the original meaning.
By employing these techniques, we can create a well-crafted paraphrase that accurately conveys the original author’s ideas.
Summarizing Techniques
To create an effective summary, we can employ various techniques, such as selecting a short passage that supports an idea, underlining the main point, breaking down the text into sections to pinpoint essential points, and summarizing without disregarding pertinent details.
Additionally, it is crucial to compare the summary to the original text, ensuring that we have accurately captured the main ideas and essential information.
When to Use Each

Paraphrasing and summarizing are appropriate for different situations, depending on our writing goals and the specific needs of our audience. Paraphrasing is suitable when we need to better understand, communicate effectively, gain new perspectives, improve our writing, and avoid plagiarism.
Summarizing is useful when we need to condense a longer text into something that is shorter than the original, grasp the gist without context loss, identify key concepts, find information quickly, visualize the structure, and locate gaps.
By understanding when to use each technique, we can enhance our writing and effectively convey the ideas of others.
When to Paraphrase
Paraphrasing is suitable in various situations, such as avoiding plagiarism, simplifying complex concepts, or incorporating evidence and source material into our assignments.
For instance, we might use paraphrasing to explain the information contained in tables, charts, and diagrams, making them more accessible to our audience.
By employing paraphrasing effectively, we can enhance our writing and ensure that we accurately convey the ideas of others.
When to Summarize
Summarizing is appropriate when brevity is a priority or our reader requires a concise overview of the material.
For example, we might use summarizing to provide a quick synopsis of a topic, construct a backdrop, depict knowledge from multiple sources concerning a topic, or ascertain the principal notions of a single source.
By effectively summarizing, we can give our readers the essential information they need to understand the main points without overwhelming them with unnecessary details.
Avoiding Plagiarism
In academic writing, it is essential to provide proper citations when paraphrasing and summarizing to avoid plagiarism – or presenting someone else’s words or ideas as your own.
Plagiarism is a grave infraction that can lead to severe consequences, such as failing the assignment or even facing legal action.
By adhering to proper citation guidelines, we can ensure that we give proper credit to the original author and maintain our integrity as writers.
Citing Paraphrased Texts
When citing paraphrased texts, it is essential to include the original source in the first mention.
The citation should include the author’s last name and publication date. We may use the APA or MLA format depending on the assignment’s requirements.
Citing Summarized Texts
Citing summarized texts is just as important as citing paraphrased texts. According to APA 7, an in-text citation should be included when referring to, summarizing, paraphrasing, or quoting from another source.
This citation should include the author’s last name and the year of publication.
Real-Life Examples
Real-life examples of paraphrasing vs summarizing can be found in various contexts, such as rewording a news article, condensing a dialogue, or restating a research paper or essay.
These demonstrate how these techniques can be used to effectively incorporate the ideas of others without copying them directly, ensuring that our writing is both original and informative.
Using AI for Paraphrasing vs Summarizing
These days, there are so many great AI writing tools that can help you with your writing. Let’s take a look at two of my favorite AI content creation options.

Using Jasper to summarize or paraphrase content is easy and efficient. Follow these steps to generate a concise summary or a differently-worded paraphrase of any text:
- Open Jasper : Access the Jasper platform by visiting jasper.ai and logging into your account.
- Create a new document : Click on the “Create New Content” button, and then the “New Document” section to open a blank document where you can input the original text you want to summarize or paraphrase.

- Paste the content : Copy the text you want to summarize and paste it into the document. Make sure the content is well-structured and within Jasper’s word limit.
- Use the summarization command : In a new line, type a command such as “Please summarize the above content in 100 words” or “Provide a brief summary of the text above.” You can specify the desired length or ask for a brief summary, depending on your needs.
To demonstrate the Jasper summary command, I’ve taken a section from one of my articles on “How to Write Relatable Characters.” I’ve pasted it into Jasper, and I’m showing the prompt in the prompt box below.

- Run the command : Press Ctrl+Enter (or Cmd+Enter on Mac) or click “Run Command” to run the command. Based on your command, Jasper will then generate a summarized or paraphrased version of the provided text. Here’s Jasper’s summarized version of my text:

To paraphrase, you’ll use this prompt instead:
- Use the paraphrasing command : Follow the steps above to access Jasper and paste your content into a document. In a new line, type a command such as “Please paraphrase the above text” or “Rewrite the text above in a witty tone of voice.”

Here’s what Jasper gave me. Don’t forget that you can ask the program to rewrite the text in any tone you like (professional, conversational, friendly, etc.)!

WriteSonic is another AI-powered writing tool that can help you summarize content. To use WriteSonic for summarizing, follow these steps:
- Open WriteSonic : Visit the WriteSonic website at writesonic.com and log in to your account.
- Access the writing tools : On your dashboard, you will find various writing tools offered by WriteSonic. Look for the “Content Shorten” tool.

- Paste the content : Copy the text you want to summarize and paste it into the input box. Make sure the content is well-structured and within WriteSonic’s word limit.
- Choose summary length : If the tool provides an option to choose the length of the summary, select the desired length according to your needs.
- Generate the summary : Click the “Generate” button to initiate the summarization process. WriteSonic will then create a summarized version of your text based on the provided information. You can even ask Writesonic to give you multiple different versions of the output.
Here’s what I got from WriteSonic for my summary. I love how it gave me two different lengths!

Using WriteSonic to paraphrase content is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to generate a rephrased version of any text:
- Access the writing tools : On your dashboard, you will find various writing tools offered by WriteSonic. Look for the “Content Rephrase” tool.

- Paste the content : Copy the text you want to paraphrase and paste it into the input box provided in the paraphrasing tool. Make sure the content is well-structured and within WriteSonic’s word limit. You can even add a tone of voice, such as “witty,” “professional,” or “creative.” For this example, I used a witty tone of voice.
- Generate the paraphrased text : Click the “Generate” button to initiate the paraphrasing process. WriteSonic will then create a paraphrased version of your text based on the provided information. I asked WriteSonic to give me two different versions of the paraphrased text.

Final Thoughts
In conclusion, paraphrasing and summarizing are important techniques for any writer, allowing us to incorporate the ideas of others into our work without copying them directly.
Mastering the techniques involved in these methods, understanding their differences, and knowing when to use each can help you convey others’ ideas effectively.
Remember to use proper citations to avoid plagiarism and maintain your integrity as a writer. So, embrace these techniques and harness their power to create engaging, informative, and original content!

Common Questions (FAQs)
Can a paraphrase be a summary.
Yes, a paraphrase can be a summary. Paraphrasing is restating someone else’s ideas in your own language. Summarizing involves reducing the essential points of someone else’s work into a shorter form. Both techniques can be used to simplify complex information or ideas.
Is paraphrasing better than summarizing?
Summarizing is generally considered to be a better option than paraphrasing. Summarizing requires you to re-write the material in your own words, but more importantly, it also encourages you to retain only the most critical elements of the original passage. This allows you to process and interpret the material more deeply.
How is summarizing different from paraphrasing?
Summarizing involves condensing an original text into its main idea and expressing it in your own words. In contrast, paraphrasing is recreating an author’s ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. For example, summarizing the story of Romeo and Juliet would include mentioning the essential plot points, while paraphrasing the same story might include restating the dialogue and narration.
What is an example of a paraphrase?
Paraphrasing sentences reframe an original idea into your own words. For example, take the original statement: “Any trip to Italy should include visiting Tuscany to sample their exquisite wines.” The paraphrased material could be: “A journey to Italy wouldn’t be complete without experiencing the exquisite wines of Tuscany.”
Filmmaker, Author, Actor and Story Consultant
Neil Chase is an award-winning, produced screenwriter, independent filmmaker, professional actor, and author of the horror-western novel Iron Dogs. His latest feature film is an apocalyptic thriller called Spin The Wheel.
Neil has been featured on Celtx, No Film School, Script Revolution, Raindance, The Write Practice, Lifewire, and MSN.com, and his work has won awards from Script Summit, ScreamFest, FilmQuest and Cinequest (among others).
Neil believes that all writers have the potential to create great work. His passion is helping writers find their voice and develop their skills so that they can create stories that are entertaining and meaningful. If you’re ready to take your writing to the next level, he's here to help!
Similar Posts
![compare paraphrasing and summarizing using a venn diagram How to Find Inspiration for Creativity [7 Brilliant Methods!]](https://neilchasefilm.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/inspiration-for-creativity-768x402.webp)
How to Find Inspiration for Creativity [7 Brilliant Methods!]
![compare paraphrasing and summarizing using a venn diagram 50+ Horror Story Ideas [Scary Movie Prompts to Creep You Out!]](https://neilchasefilm.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/horror-story-ideas-768x402.webp)
50+ Horror Story Ideas [Scary Movie Prompts to Creep You Out!]
![compare paraphrasing and summarizing using a venn diagram What Are Minor Characters? [A Guide to Better Storytelling]](https://neilchasefilm.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/minor-characters-768x402.webp)
What Are Minor Characters? [A Guide to Better Storytelling]
![compare paraphrasing and summarizing using a venn diagram What is the Setting of a Story? [Definition, Examples & How To Write!]](https://neilchasefilm.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/setting-of-a-story-768x402.webp)
What is the Setting of a Story? [Definition, Examples & How To Write!]

Story Structure: 9 Powerful Narrative Structures for Writers
![compare paraphrasing and summarizing using a venn diagram The Sage Archetype [In-Depth Guide With 7+ Examples!]](https://neilchasefilm.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/sage-archetype-768x402.webp)
The Sage Archetype [In-Depth Guide With 7+ Examples!]
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

What’s the Difference? Summarizing, Paraphrasing, & Quoting
- Posted on November 29, 2023 November 29, 2023
What’s the Difference? Summarizing , Paraphrasing , & Quoting
Quoting, paraphrasing , and summarizing are three methods for including the ideas or research of other writers in your own work. In academic writing , such as essay writing or research papers , it is often necessary to utilize other people’s writing.
Outside sources are helpful in providing evidence or support written claims when arguing a point or persuading an audience. Being able to link the content of a piece to similar points made by other authors illustrates that one’s writing is not based entirely off personal thoughts or opinions and has support found from other credible individuals. In scientific work such as reports or experiment related writing, being able to point to another published or peer-reviewed writer can strengthen your personal research and even aid in explaining surprising or unusual findings. In all situations, referencing outside sources also elevates the integrity and quality of your work.
When pulling information from an outside source it is critical to properly use quotations, paraphrasing , or summarizing to avoid plagiarizing from the original passage . Plagiarism is portraying another’s work, ideas, and research as one’s own, and is an extremely serious disciplinary offense. Without using proper quotations, paraphrasing and summarizing , it can be easy to unintentionally plagiarize from the original source . Including citations that reference the author also helps ensure proper credit is given, and no accidental plagiarism occurs. Regardless of if APA , MLA or Chicago style are used, a citation must accompany the work of another author.
This article will compare these three concepts, to help users become more comfortable with each of them and the differing scenarios to utilize each. The article will also provide examples and give pointers to further increase familiarity with these essential techniques and prevent the happening of plagiarism .
What is Quoting?
Quoting is the restatement of a phrase, sentence, thought, or fact that was previously written by another author. A proper direct quotation includes the identical text without any words or punctuation adjusted.
One might use a quotation when they want to use the exact words from the original author , or when the author has introduced a new concept or idea that was of their conception. Oftentimes, the author already used concise, well-thought-out wording for an idea and it may be difficult to restate without using a direct quote .
However when repeating content from someone else’s work, one must use quotation marks with a corresponding citation or it will be considered plagiarism . The proper citation may also vary based on the citation style being used.
Examples of Quoting
In order to further the understanding of how to utilize quotes, some examples of incorrect and correct quotation are provided below.
Original Text: As natural selection acts solely by accumulating slight, successive, favorable variations, it can produce no great or sudden modification; it can act only by very short and slow steps
Incorrect Quotation Example: “Because natural selection acts only by accumulating slight, successive favorable variations. It can produce no greater or sudden modification and can only act by very short and slow steps
Correct Quotation Example: “As natural selection acts solely by accumulating slight, successive, favorable variations, it can produce no great or sudden modification; it can act only by very short and slow steps,” (Darwin 510).
The bad example provided does not include the identical text or identical grammar and punctuation to that of the original source . The quote is also lacking one quotation mark and a citation to attribute the initial author. Meanwhile, the good example i s completely identical to the original text and features a correct citation, making it a great example of a quote in use.
What is Paraphrasing ?
Paraphrasing is taking the written work, thoughts, or research of another author and putting it in one’s own words . Correct paraphrasing is done through the restatement of key ideas from another person’s work, but utilizing different words to avoid copying them. Oftentimes, finding synonyms to the words used by the original author helps to paraphrase .
One would use paraphrasing when they hope to capture the key points of a written work in their own writing . Paraphrasing should also be employed when the content of the original source is more important than the wording used. This writing technique is a good strategy to maintain one’s personal writing style throughout a written work.
Similar to quoting, even paraphrased material should be accompanied by the proper citation to avoid plagiarizing the initial author.
Examples of Paraphrasing
Original Content: The Statue of Liberty, one of the most recognizable symbols of freedom and democracy across the world, was a gift of friendship to America from France. Inaugurated in 1886, the statue is 305 feet tall and represents Libertas, the Roman liberty goddess, bearing a torch in her right hand and a tablet in her left hand with the date of the US Declaration of Independence. Broken shackles lay underneath the statue’s drapery, to symbolize the end of all types of servitude and oppression.
Incorrect Paraphrasing Example: The Statue of Liberty is an evident display of freedom and democracy for the whole world, and was created by France for America to represent their friendship. The 305 foot statue of the Roman liberty goddess Libertas was installed in 1886. The Statue of Liberty has a tablet with the US Declaration of Independence date in one hand and a torch in her other. She also has broken shackles on the ground to represent an end to enslavement and oppression.
Correct Paraphrasing Example: France presented the United States with the Statue of Liberty in 1886 to commemorate the two countries friendship. The Roman goddess of liberty, Libertas, stands 305 feet tall as a well-known tribute to freedom and democracy. The statue commemorates the US Declaration of Independence though the tablet in her left hand that accompanies a torch in her right. The Statue of Liberty also celebrates an end to oppression and servitude, indicated by broken chains by her feet ( Diaz, 2019 ).
The incorrect example provided featured a sentence structure that followed too closely to that of the original text. Additionally, the writer only swapped out a few words for very common synonyms so the paraphrased content is ultimately too similar to the original text. An academic work that used this paraphrase would be cited for plagiarism .
On the other hand, the correct example featured paraphrased content that is properly cited, with variety to the sentence structure and text that includes words beyond just synonyms to words in the original content. This example also contains the main ideas, but is ultimately slightly condensed from the original text.
What Is Summarizing ?
Summarizing is providing a brief description of the key ideas from a written work. This description should be in one’s own writing , and is typically significantly shorter than the source material because it only touches on the main points .
Summaries are commonly used when a writer hopes to capture the central idea of a work, without relying on the specific wording that the original author used to explain the idea. They also can provide a background or overview of content needed to understand a topic being discussed. This strategy still captures the meaning of the original text without straying from one’s personal tone and writing style.
Unlike paraphrasing and quoting, a summary does not require an in- text citation and only occasionally needs accreditation to the original writer’s work .
Examples of Summarizing
In order to further the understanding of how to summarize content in your writing, some examples of incorrect and correct summaries for the short children’s story Goldilocks and The Three Bears are provided below.
Incorrect Summary Example: Once upon a time, Goldilocks went for a walk on the beach when she saw a house and went in it. In the house she found three bowls of soup and decided to try them all, but one was too hot, one was too cold and one was just right. Next, Goldilocks tried to sit in three different chairs but only found one that fit her perfectly. Lastly, she went to the back of the house and found three beds. Just like the soup and chairs she tested all of them before picking one that she liked the best and taking a nice long nap. The End.
Correct Summary Example: In Goldilocks and the Three Bears by Robert Southy, a young girl wanders into the house of three bears where she tastes three different porridges; sits in three different chairs; and naps in three different beds before finding one of each that fits her. Goldilocks is eventually found by the bears who are upset about her intrusion and usage of their personal belongings.
The incorrect example provided would not be considered a good summary for a few reasons. Primarily, this summary does not summarize well, as provides too much unnecessary detail and an individual would still be able to comprehend the main point of the story without it. The summary also ends without touching on the most important point , which is the lesson of the story. This summary also provides inaccurate information, and lacks a citation.
Meanwhile, the correct example is a good summary because it does not spend too much time on any certain aspect of the story. The reader is still able to understand exactly what happens to Goldilocks without consuming any non-essential details. This summary also provides completely accurate information and touches on the main point or lesson from the story.
Differences and Similarities
There are a few major differences and similarities between the three writing techniques discussed.
Quoting, paraphrasing , and summarizing are similar in that they are all writing techniques that can be used to include the work of other authors in one’s own writing . It is common for writers to use these strategies collectively in one piece to provide variety in their references and across their work. These three strategies also share the similarity of helping to prevent plagiarizing the content from the original source . All three of these methods require some form of citation and attribution to the original author to completely avoid plagiarizing.
Oppositely, the main difference between quoting, paraphrasing , and summarizing is that quoting is done word for word from the original work . Both paraphrasing and summarizing only touch on the key points and are written with some variation from the initial author’s work , usually in the style and tone of the new author. When comparing just the latter two, paraphrased material tends to be closer in length to the actual material, because it only slightly condenses the original passage . On the other hand, a summary is most likely significantly shorter than the original author’s work since this method only pulls from the most important points .
Final Thoughts
It is extremely common to utilize the previous writing of others, especially in academic writing . These original works enhance the quality and honesty of one’s work while also providing backing and emphasis to the points made.
Quoting, paraphrasing , and summarizing are all strategies for incorporating the thoughts, ideas, research, and writing from another author in one’s own work. The three methods explained are also safe strategies to employ to avoid accidental plagiarism of the original passage .
Another strategy to ensure one’s writing is properly quoted, paraphrased, and summarized is by using a plagiarism checker. Quetext provides an easy-to-use plagiarism checker that verifies the originality of work and can create citations for any sources cited throughout the paper.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Empowering Educators: How AI Detection Enhances Teachers’ Workload
- Posted on March 14, 2024

The Ethical Dimension | Navigating the Challenges of AI Detection in Education
- Posted on March 8, 2024

How to Write a Thesis Statement & Essay Outline
- Posted on February 29, 2024 February 29, 2024

The Crucial Role of Grammar and Spell Check in Student Assignments
- Posted on February 23, 2024 February 23, 2024

Revolutionizing Education: The Role of AI Detection in Academic Integrity
- Posted on February 15, 2024

How Reliable are AI Content Detectors? Which is Most Reliable?
- Posted on February 8, 2024 February 8, 2024

What Is an Article Spinner?
- Posted on February 2, 2024 February 2, 2024

Recognizing & Avoiding Plagiarism in Your Research Paper
- Posted on January 26, 2024 January 26, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing: Knowing the Difference
Writers who write informative or academic papers will need to understand the difference between paraphrasing vs. summarizing. Learn more in this article.
Paraphrasing and summarizing are similar writing techniques where an author takes an original passage and puts it into their own words without using the author’s exact words. Yet the goal of these two techniques is different. With one, you rephrase the content in your own words, but you pull out the main ideas and shorten the work with the other.
With both paraphrasing and summarizing, you can use someone else’s ideas in your writing to give it meaning and back up the claims you make. However, you do need to know how to use the tools to properly portray the ideas you wish to convey without falling guilty of plagiarism.
As you work on creating research papers and projects, you’re going to want to know the difference between paraphrasing vs. summarizing. This guide will help you understand how these are different, so you can use the right tool when you need it.
Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing: The Key Is in the Goal
The dangers of plagiarism, when to paraphrase, when to summarize, similarities between paraphrasing and summarizing, paraphrasing and summarizing often go hand in hand, creating a works cited or bibliography page, paraphrasing vs. summarizing: both make your writing stronger, paraphrasing vs. summarizing: key points.
What is the primary difference between summarizing and paraphrasing in your writing? The key is in the goal of your writing.
Both paraphrasing and summarizing are ways to avoid plagiarism in your writing by ensuring you are not using the original author’s exact words, but they are done for different reasons. With paraphrasing, you are rewording the original author’s work, but by summarizing, you boil down the main points into a more concise version of the original post.
In academic writing, plagiarism is a serious offense . To avoid this offense, you must include a proper citation whenever you have a quote, paraphrase, and summary statement. If the original work is not your idea or something considered common knowledge, it requires a citation.
If you are found guilty of plagiarism, you will have serious repercussions. This often means failing the assignment or even the class in academic settings. You may face expulsion, too.
If you are preparing something for publication, you risk having your work completely discredited. Your reputation as a writer is ruined. While few people go to jail for plagiarism, you could face lawsuits or fines for breaking the law.
You might also be wondering do you need quotation marks when paraphrasing?
The Definition of Paraphrasing
When you paraphrase something, you take the original material and rewrite it, changing the sentence structure or verb tense to say the same thing differently. The new sentence or paragraph will have enough differences that you cannot point out that it came from the source material.
This process is different from a direct quote. With a direct quote, you use the same wording, word for word, and put it in quotation marks. With a paraphrase, you have no wording that is the same, but instead, you use synonyms and new sentence structure to make it your own. However, the meaning of the original text stays consistent.
Paraphrased works in academic writing still require a citation using the APA or MLA format , depending on the assignment. The original idea still comes from the original author, and you can’t take that and claim it as your own without proper citation.
The best time to paraphrase is when you want to show that you can read someone else’s ideas but then put them in your own words. It shows that you understand the concepts and ideas you are writing about. You still want to credit the original author, but you don’t want to make a paper or article from quotes.
Paraphrasing shows that you understand the concepts of your sources. If you can paraphrase well, you have a clear grasp of the topic.
These paraphrasing exercises might be helpful.
The Definition of Summarizing

Summarizing is done when the original writer’s work is lengthy, and you need the main points, but not a direct quotation or full sentences that copy the meaning. For example, if you are using an entire chapter of a book as a resource for one point in a paragraph, you aren’t going to be able to include all of the ideas from the book. Instead, you will simplify those ideas into something shorter, keeping the main points intact and concisely expressing them.
Summaries, like paraphrases, do not require quotation marks. You won’t use quotation marks even if the main headings or points are repeated in your work. However, you will cite the original author and the original article or book using proper formatting.
A summary works well when you have a large chunk of text you want to pull the main ideas from in your piece. It allows you to get to the main idea of the author’s piece, only pulling out what is necessary for you to make your point. It provides background information to the reader, as well.
Summaries also work well if you need just the main points of the writer’s work instead of all of the added material. This strategy works particularly well when you need to argue a point and want to use an entire work to do so but do not have enough space to quote the source material. You might also be interested in our analogy vs. metaphor guide.
Though they are different, paraphrases and summaries have some similarities. Both allow writers to use other writers’ ideas in their pieces. They both make concepts easier to understand or help them flow in the writer’s own words and writing style. Both keep the passage’s main ideas in place even while changing the wording or shortening the piece.
In academic writing, you will often paraphrase and summarize source materials in the same work. Sometimes, the author’s ideas are already concise, so all you need to do is restate them in your writing. This is paraphrasing.
Sometimes, the author’s ideas are too lengthy for you to include in your work as they are. In these cases, simplification is necessary to flow with your work. Thus, you will summarize.
Paraphrases and summaries are also preferred over direct quotes. They allow you to show your writing skills and ability to pull ideas from someone else’s works without relying entirely on the other writer’s work.
After you finish your writing, you will need to include a list of all of the works you used to create it. This bibliography or works cited page will have formatting based on the publication manual used in the assignment. It will include all of the books, articles, and journals you used to write the essay or paper, whether you quoted, summarized, or paraphrased.
Most writing will borrow from another person’s ideas and even words, as long as the author properly cites and credits the original author. Paraphrasing and summaries are tools writers use to use the ideas of others without copying them directly effectively.
Anyone can copy and paste work from other writers to put together an informative paper or paragraph. Quotes have their place, as they can give the writing a sense of authority and provide strong evidence that the claims you make are valid. However, it takes a skilled writer to summarize or paraphrase the works of other writers.
Both summaries and paraphrases make writing stronger and show that you clearly understand the materials you used in your research. Most academic papers are a mixture of paraphrases, summaries, and quotes. All three require citations, but you will find that paraphrasing and summarizing allow you to put your flair into the writing.
Paraphrasing and summarizing both offer a way to use someone else’s idea as your own in your writing. Paraphrasing transforms the writing into your own words but keeps the same basic length and idea in writing. Summarizing condenses the writing into its main points.
Both paraphrasing and summarizing require proper citation because the idea comes from another writing. You can use your research skills to write engaging essays and papers with these tools.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our paraphrasing vs. plagiarism guide!

Nicole Harms has been writing professionally since 2006. She specializes in education content and real estate writing but enjoys a wide gamut of topics. Her goal is to connect with the reader in an engaging, but informative way. Her work has been featured on USA Today, and she ghostwrites for many high-profile companies. As a former teacher, she is passionate about both research and grammar, giving her clients the quality they demand in today's online marketing world.
View all posts
Direct Quotes vs. Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing: Know the Difference
- Written By Lorraine Roberte
- Updated: February 22, 2024
Knowing the differences between direct quotes, paraphrasing, and summarizing is crucial no matter your occupation, from business owner to content marketer.
Why? Because it can prevent you from accidentally plagiarizing in the work you do for yourself and from breeching best practices.
Incorporating a mixture of these elements in your content can also help you tell a better story, so your audience keeps reading.
Direct quotes vs. paraphrasing vs. summarizing — understanding the difference
We’re breaking down the differences between direct quotes vs. paraphrasing and summarizing and how you can use them in your writing.
From press releases for your business to engaging blog posts for your target audience, you can make your writing more interesting by including trustworthy sources.

Direct quotes
Direct quotes include the exact words that someone said, with quotation marks and name attribution. They’re especially common when writing about people .
Example: “Elon Musk said in a tweet that Starlink’s satellite broadband service coverage will be available on ‘most of Earth by end of year,’ although he noted that ‘cellular will always have the advantage in dense urban areas.'”
When to use direct quotes
According to the APA style guide , you’ll need to use direct quotes when:
- Copying an exact definition
- The author’s words are memorable and succinct
- Responding or reacting to someone’s exact words
How to use direct quotes
In general, direct quotes are written verbatim. But you can make these small changes without alerting your readers:
- Changing the first letter of the quote to an upper or lowercase so that the quotation matches the context sentence’s syntax. Can also modify the punctuation at the end of the quote.
- Swapping single quotation marks to double quotation marks and vice versa
- Omitting footnote or endnote number references
Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is when you restate someone else’s words, but not word for word.
Example (original quote): “It’s risky trusting employees as much as we do. Giving them as much freedom as we do. But it’s essential in creative companies where you have much greater risk from lack of innovation.” — Reed Hastings, Netflix CEO and co-founder .
Example (paraphrase): “Netflix’s CEO and co-founder, Reed Hastings, feels that micromanaging workers can stifle innovation in creative businesses.”
When to paraphrase
It can be helpful to paraphrase if you want to keep your writing more conversational. It’s also useful when breaking up direct quotes or explaining the original source in simpler terms. That way, the information better fits the tone and style of your writing.
How to paraphrase
Paraphrasing involves putting a section of the source information entirely into your own words while staying true to its original meaning. You can link to the source in the place that makes the most sense, such as “report” for an industry report.
You can keep from plagiarizing when paraphrasing by using synonyms for words mentioned in the source. It’s important to restate phrases differently (even if they’re just a few words) to avoid the same sentence structure. If you don’t, you could still be plagiarizing, despite crediting the source.
If you use exact words from the original material while paraphrasing, you must put the word or words in quotes. The exception is generic terms that are difficult to find synonyms for.

Summarizing
When you summarize, you use your own words to describe the critical points of what someone else said or that you heard or read in a source.
Example (original quote): “In a diverse population of older patients who were hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure, an early, transitional, tailored, progressive rehabilitation intervention that included multiple physical-function domains resulted in greater improvement in physical function than usual care.” — Study in the New England Journal of Medicine
Example (summary): “A recent study shows physical rehabilitation programs to be helpful for older populations with hospitalizations from heart failure.”
When to summarize
Summaries are excellent at giving readers the key insights they need from a longer text when proving your point. They also add context while keeping at a manageable length whatever type of article you’re writing.
How to summarize
You don’t need to include any quotes or attribution when summarizing, just a brief overview that often links back to the original material for more details. It may also introduce essential points from the original text, allowing readers to understand the source without clicking through it.
Now that you know the difference between direct quotes, paraphrasing, and summarizing, you can confidently write content for your business.
Need help creating engaging blog posts for your business? Talk to a content specialist at ClearVoice today about your needs.

The Ultimate Spring Cleaning Checklist for Your Freelance Business


The Art of Freelance Pricing: How to Value Your Work and Elevate Your Income

Building Your Freelance Brand: Strategies for Effective Self-Promotion
- Content Production
- Build Your SEO
- Amplify Your Content
- For Agencies
Why ClearVoice
- Talent Network
- How It Works
- Freelance For Us
- Statement on AI
- Talk to a Specialist
Get Insights In Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Intellectual Property Claims
- Data Collection Preferences
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
- Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Get a free Grammar Adventure! Choose a single Adventure and add coupon code ADVENTURE during checkout. (All-Adventure licenses aren’t included.)
Sign up or login to use the bookmarking feature.
- 20 Summaries, Paraphrases, and Abstracts

Start-Up Activity
Display Einstein's famous letter to FDR . Seek a student volunteer to read the letter aloud to your class. Afterward, ask a simple question: "What is the letter about?" Let multiple students respond, and then distinguish their responses. Did they use their own words? Did they cite exact words from the letter? Did they respond to one portion of the text or the whole thing?
Tell students that the question "what is this about" is the focus of every summary. Writing a summary requires students to use their own words and, in special occasions, a few exact words from the source to reveal the heart of the matter. This chapter introduces strategies for summarizing as well as paraphrasing and quoting. Students will use all three strategies to write an effective abstract.
Think About It
“Vigorous writing is concise. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.”
—William Strunk, Jr.
State Standards Covered in This Chapter
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.11-12.2
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.11-12.8
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.11-12.5
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.11-12.9
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.11-12.1
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.11-12.3
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.11-12.9
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.11-12.7
LAFS Covered in This Chapter
Lafs.1112.ri.1.2, lafs.1112.w.3.8, lafs.1112.w.2.5, lafs.1112.ri.3.9, lafs.1112.ri.1.1, lafs.1112.ri.1.3, lafs.1112.w.3.9, lafs.1112.ri.3.7, teks covered in this chapter, 110.38.c.4.g, 110.38.c.5.d, 110.38.c.7.d.i, 110.39.c.4.g, 110.39.c.5.d, 110.39.c.7.d.i, 110.38.c.11.e, 110.38.c.11.f, 110.38.c.11.g, 110.39.c.11.e, 110.39.c.11.f, 110.39.c.11.g, 110.38.c.9.a, 110.38.c.9.c, 110.38.c.9.d, 110.39.c.9.a, 110.39.c.9.c, 110.39.c.9.d, 110.38.c.4.f, 110.38.c.5.c, 110.39.c.4.f, 110.39.c.5.c, 110.38.c.7.d.ii, 110.39.c.7.d.ii, 110.38.c.11, 110.38.c.4.h, 110.39.c.11, 110.39.c.4.h, page 278 from write for college, writing a summary.
A summary extracts main ideas from a piece of writing and then shapes that material clearly and coherently. Summarizing helps students (1) sharpen reading and thinking skills, (2) support ideas in essays, (3) write abstracts for research projects, and (4) prepare for workplace summaries of documents and meetings.
Students need to see a summary as more than simply skimming an article and copying some sentences. Highlight these points for creating effective summaries:
- Annotate the reading (if they own the material).
- Skim material for its purpose, audience, main idea, and structure.
- Locate key ideas by looking at topic sentences, concluding sentences, and transition words.
- Leave out secondary material such as background information, examples, and unnecessary descriptive details.
Note: Consider connecting a summary assignment with another writing project. For example, have students summarize an article on rising ocean levels for a research paper in that subject area.
Related Resource Tags
Click to view a list of tags that tie into other resources on our site
Page 279 from Write for College
Summary writing in action.
Provide students time to read the original and revised summaries. Ask volunteers to point out the differences between the two summaries. For further enrichment, either (1) ask students to evaluate and improve a previous draft of a summary they have written, or (2) share examples of summaries in newspaper and magazine articles, textbooks, or research abstracts. Have students discuss the purpose and usefulness of the summaries and propose revisions to improve them.
Page 280 from Write for College
Additional summaries.
Display a blank T-chart or Venn diagram. Have your students read through the objective textbook summary and personal summary. As a class, compare and contrast the two summaries for content and writing style. Fill in the T-chart or Venn diagram with your students' observations.
As an alternative, display a current news story or other brief article about an interesting topic. Have students read the article. Immediately afterward, ask them to "stop 'n' write" to reflect on what they have read. They should use a relaxed writing style like that of the personal summary.
Comparing with a Venn Diagram
Analyze similarities and differences.

Page 281 from Write for College
Writing a paraphrase.
Paraphrasing is a key skill for research, but also for learning in general. A student who can put a concept into his or her own words understands the concept.
Educate students about the differences between summarizing and paraphrasing. Both skills involve rewording source material, often in more-accessible language. However, while a summary always attempts to capture only the main idea and key supporting details of another source, a paraphrase may focus on the entire source or just a single detail that directly relates to a research topic. In that way, paraphrasing is a more flexible move than summarizing. Remind students that any summarized or paraphrased material in a research project must include a citation to the original work.
Next, lead your students through the guidelines for paraphrasing. For practice, have students work individually to paraphrase a key idea from a common source or the source as a whole. One possible source could be a public speech or document. (Possible authors include Susan B. Anthony, Frederick Douglass, Malcolm X, Patrick Henry, Abraham Lincoln, or Tecumseh.) Afterward, ask for volunteers to share their paraphrases. Note how different responses to the same source exemplify original thinking.
Page 282 from Write for College
Examples of paraphrases.
Ask students to cover up the two sample paraphrases at the bottom of the page as they read and paraphrase the selection at the top of the page. When they finish, suggest that they compare their own paraphrase to the samples: How are they similar? How are they different? Did their versions miss anything important? What about the samples?
Point out that both sample paraphrases conclude with a citation to the original source, in this case, following MLA style. Note that the second sample paraphrase includes a word-for-word quotation from the reading, a technique your students will examine on the next page.
Page 283 from Write for College
Using quoted material.
Your students may be wondering when it is appropriate to quote a source word for word instead of paraphrasing or summarizing it. In general, students should quote material when . . .
- the specificity of the source's words is necessary to understanding the idea;
- a specific word, phrase, or passage is particularly striking or has a heightened sense of importance in relation to the research topic; or
- the author of the quoted material is a noted authority whose name will lend credence to the paper's argument or investigation.
After sharing this information, lead students through the formatting and punctuation guidelines for quoted material. To see quoted material in action, have students seek short quotations in the sample MLA research paper on pages 327–334. For a long quotation, see the bottom of page 338.
Using Quotation Marks
Use quotation marks with titles and quotations.

Page 284 from Write for College
Writing an abstract.
Let students know that an abstract is essentially a summary of one's own research paper or report. Lead students through the writing guidelines, and refer back to this page whenever you assign an abstract.
Note: MLA papers do not require an abstract, but APA papers do. You may also wish to have students write an abstract prior to beginning their research papers. Writing an abstract so early in the process forces students to conceptualize a general focus for their papers. It also gives you an opportunity to provide early feedback, steering them in a new direction, if necessary. Of course, students should revise their initial abstract to reflect the information in their completed paper.
- 01 One Writer's Process
- 02 Traits of Writing
- 03 Prewriting
- 05 Revising
- 07 Publishing
- 08 Improving Sentences
- 09 Building Paragraphs
- 10 Mastering Essays
- 11 Writing with Style
- 12 Writing Terms and Techniques
- 13 Personal Writing
- 14 Narrative Writing
- 15 Explanatory Writing
- 16 Argument Writing
- 17 Literary Response Writing
- 18 Creative Writing
- 19 Conducting Research
- 21 Report Writing
- 22 Writing the Research Paper
- 23 MLA Research Paper
- 24 APA Research Paper
- 25 Writing in Science
- 26 Writing in Social Studies
- 27 Writing in Math
- 28 Writing in the Workplace
- 29 Reading Nonfiction
- 30 Reading Literature
- 31 Reading Graphics
- 32 Listening and Note Taking
- 33 Speaking Effectively
- 34 Building Vocabulary
- 35 Writing on Demand
- 36 Answering Document-Based Questions
- 37 Taking Exit and Entrance Exams
- 38 Taking Advanced Placement* Exams
- 39 Marking Punctuation
- 40 Checking Mechanics
- 41 Understanding Idioms
- 42 Using the Right Word
- 43 Parts of Speech
- 44 Using the Language
- 45 Student Almanac
- Toggle navigation
University of New Haven
- About This Site
- Thesis Components
- Information Literacy
- Organization
Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Quoting
By: Selena Soto
When we integrate information from our sources into our writing, we usually utilize paraphrasing, summarizing, or quoting, and in some cases a combination of all three. Utilizing these three tools in our writing is also important in regards to how we analyze and synthesize our information. Before I go into describing the difference between the three, when to use them, and how to effectively incorporate them into your writing, it is important to explore why we use them in the first place.
We use paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting for a variety of reasons that include (John E. Mayfield Library, 2014):
- Providing support for claims
- Integrating sources into your paper
- Giving examples of several points of view on a subject
- Highlighting and discussing a position that you agree or disagree with
- Including certain points, phrases, sentences, passages, and etc. from one source or multiple sources
- Adding depth to your writing
- Referring to past research that has been done on your topic (Especially important for your lit review section of your paper)
There is a clear difference between paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting but they do share some rules in common if you are going to utilize them. The first rule that they share in common is that when using these three tools you need to reference the original source that you are taking information from. The second rule that they share in common is that when you are referencing the original source that you are drawing information from, you need to include in-text citations in your writing in the appropriate styling format you are being asked to use (Ex. APA, MLA, etc.) If you need to refresh your memory or need some guidance on how to successfully include in-text citations in your writing, I have included a link below to Purdue Owl Writing Lab (OWL), a highly recommended source.
Source: Purdue OWL // Purdue Writing Lab
Below I have included a table that discusses the major difference between paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting that I found on a website and thought was super helpful:
(Table from Custom Essay Meister, 2019)
Paraphrasing
You should paraphrase in your writing: (George Mason University The Writing Center, 2021):
- As another option to quoting or to avoid the over use of quotes
- To rewrite someone else’s ideas without changing the meaning
- To support claims in your writing and when you want to report numerical data or statistics (common in APA style writing)
How to paraphrase (The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center, 2021):
- Read the text carefully and make sure you understand the main ideas and points of the text
- After you have read the text, put it aside, and write out the essential information in your own words
- Explain why the paraphrase is important
Example (University of Connecticut Library Guides, 2020):
- People who are naturally morning people have been shown to also display traits that are considered proactive, and late risers display fewer of these traits because they don’t get enough sleep on days when they have to go to work or school. (Randler, 2009, p. 2793).
(Replacing a few words and not writing it in your own words is considered plagiarism)
For more information on the Do’s and Don’ts of Paraphrasing check out the link below:
Source: How to Paraphrase: Dos, Don’ts, and Strategies for Success | Scribendi
Summarizing
You should summarize when (George Mason University The Writing Center, 2021):
- A passage from a source is too long to quote or paraphrase
- To establish background information or an overview of a topic
- When you want to describe knowledge (from several sources) about a topic
How to summarize (The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center, 2021):
- Read the text and highlight the main points
- Reread the text and make notes of the main points, leaving out examples, evidence, etc.
- Without the text, rewrite your notes in your own words. Include the main idea at the beginning of the summary and include all the main points, conclusions, and final findings of the work.
Original Source:
- These results suggest that morning people, or early chronotypes—as measured on the morningness–eveningness continuum are more proactive than are evening types. Additionally, the misalignment of social and biological time, as assessed by the difference between rise times on weekdays and on free days, correlated with proactivity, suggesting that people with a high misalignment of social and biological time may be less able to act in a proactive manner, probably because of sleep delay. Their biological schedules seem not to fit neatly into social demands (e.g., school, university, work schedules) as do those of less misaligned people.
(Randler, C. (2009). Proactive people are morning people. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 39(12), 2787-2797.)
Summarized Version:
- Recent research shows that people who are not naturally early risers often have persistent issues adjusting themselves to the morning-oriented schedule of most schools and workplaces, and because of this may be less proactive in their behaviors (Randler, 2009).
You should use quoting in your writing when:
- You are introducing the position of author of a source that you want to discuss
- When you want to include a particular point or statement that was made that you don’t want to express or can’t express in your own words.
Use the ICE method (Introduce, Cite, and Explain) method when you are quoting (The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center, 2021):
- Introduce your quotation by identifying who said it or where it came from and add a signal verb (Ex: Stated, Argued, etc.)
- Cite the phrase or words you are using with quotation marks and proper in-text citation in the expected formatting style (Ex: APA, MLA., etc.)
- Explain the importance of the quote you are using. Consider what this information is adding to the points you are trying to convey.
Example (APA format):
- As stated (Signal Verb) by Cormac McCarthy in his 2006 novel The Road : “You forget what you want to remember, and you remember what you want to forget” (p. 12).
I hope that this this was helpful and here is a friendly reminder that YOU GOT THIS!!!
Reference (In APA Format):
Inc, S. (n.d.). How to PARAPHRASE: Dos, DON’TS, and strategies for success. Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/how_to_paraphrase.en.html
Custom Essay Meister. (2019). Quote vs paraphrase vs summary. Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://www.customessaymeister.com/blog/quote-vs-paraphrase-vs-summary
George Mason University.(n.d.). When to summarize, paraphrase, and quote. Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/when-to-summarize-paraphrase-and-quote
John E. Mayfield Library. (2014). Online library workshops: Quoting, paraphrasing and summarizing. Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://nscc.libguides.com/Onlineworkshops/quoting
The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center (n.d.). Quoting, paraphrasing, & summarizing.Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/quoting-paraphrasing-summarizing
University of Connecticut. (n.d.). Understand citations: Quoting, paraphrasing, summarizing. Retrieved March 07, 2021, from https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/understandcitations/integrating
Uncategorized
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Search this site
© 2024 A Guide to Writing an Honors Thesis
Theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑
Welcome to OpenLab at the University of New Haven!
Read our mission statement at our About page to learn more about how we hope you'll take advantage of this platform.
Send an email to [email protected]
Powered by:
Research Guides
Psyd22: socialization processes.
- APA PsycInfo (ProQuest) Tutorials
- Other Article Databases
- Reading Articles
- Canadian Statistics This link opens in a new window
Paraphrasing, Summarizing, Quoting
- Writing Support
- Workshop FAQs

Mark, J. (n.d.). [JPEG image of a Venn diagram comparing quoting, summarizing, and paraphrasing]. Retrieved October 6, 2021, from http://writingscape.com/summary-vs-paraphrase-vs-quote/
- Citations, quoting and paraphrasing (U of T - Academic Integrity)
- << Previous: APA Style (7th ed.)
- Next: Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: Jan 16, 2024 10:07 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.utoronto.ca/psyd22
Library links
- UTSC Library home
- U of T Libraries home
- Catalogue Search
- Renew items and pay fines
- All U of T Libraries' hours
- Engineering
- UT Mississauga Library
- UT Scarborough Library
- Information Commons
- All libraries
University of Toronto Scarborough Library 1265 Military Trail, Toronto, ON M1C 1A4 Canada Email help 416-287-7500 Map About web accessibility . Tell us about a web accessibility problem . About online privacy and data collection .
© University of Toronto . All rights reserved.
Connect with us
- more social media
- louisville.edu
- PeopleSoft HR
- PeopleSoft Campus Solutions
- PeopleSoft Financials
- Business Ops
- Cardinal Careers

- Undergraduate
- International
- Online Learning
University of Louisville Writing Center
- University Writing Center FAQs
- Virtual Writing Center FAQs
- HSC Writing Center FAQs
- Writing FAQs
- Handouts and Videos
- Graduate Student Writing
- Spring Dissertation Writing Retreat
- Graduate Student Writing Workshops
- Faculty and Graduate Student Writing Group
- Creative Writing Group
- Accessibility and Accommodations
- LGBTQ+ Writing Group
- The University Writing Center and Your Students
- Request a Presentation about the University Writing Center
- Resources for Teaching Writing
- The Writing Center and Your Writing
- University Writing Center Mission Statement
- Meet Our Staff
- Statement on Diversity, Inclusion, and Equity
- Research at the University Writing Center
- How I Write Blog Posts
- Our Community Writing Values and Approaches
- Community Writing Internships and Volunteering
- Family Scholar House
- Western Branch Library
- How can I make myself a stronger writer?
- What makes college writing different than the writing I’ve done up to this point?
- How are the papers I'm asked to write in my major different from those in English 101, 102, and 105 courses?
- What can I do if I don’t completely understand the writing assignment?
- I want to get started writing early, but how do I begin?
- How do I get started writing a personal statement?
- I have a lot to say, but how can I organize my thoughts?
- How can I learn how to write in a new genre (for example, personal statement, resume, or literature review)?
- How do I expand a rough draft to make it meet the assignment’s length requirement?
- How can I find good sources for my research paper?
- What are some strategies for working sources into my research paper?
- What is the difference between quotation, paraphrase, and summary?
- How can I revise my draft if it doesn’t seem to “flow”?
- What does my teacher mean by “substantial revision?”
- How do I write an essay that makes an “argument”?
- How can I avoid plagiarizing?
- What are some strategies for improving my grammar and punctuation?
- How can I format my document properly in Word, PowerPoint or Excel?
- How should I approach writing a literature review at the graduate level?
- / Resources for Students
- / Writing FAQs
- / What is the difference between quotation, paraphrase, and summary?
Writing in college often means using ideas from other sources. There are times when it may be best to quote the sources directly, while other times may be better served by paraphrasing or summary. In order to decide which technique to use, it is helpful to think about how you are using the information in your paper.
Definitions
- Quotation reproduces a statement word-for-word as it appears in its original source
- Paraphrase explains a statement by using your own words and sentence structure
- Summary explains a statement using your words, but typically condenses a larger statement into a shorter explanation
How to decide which approach to use
Direct quotations can be useful when the exact wording of a statement is important. The exact wording of a quotation may be significant to your claim. In example 1 below, the contrast between adjectives are important to the claim. Also, direct quotation may be important when you want to make sure you are being precise in representing the author’s position. Finally, you might choose to use a direct quotation when the original statement is particularly well written or structurally persuasive. If a statement uses elements such as parallelism or alliteration, you might not be able to recreate that same effect. An important element of the quotation in example 1 is the parallel structure between "lowest and vilest alleys" and "smiling and beautiful countryside."
When Sherlock tells Watson "the lowest and vilest alleys in London do not present a more dreadful record of sin than does the smiling and beautiful countryside,” he intensifies suspense by equating innocence with evil ("The Adventure of the Copper Beeches" 502).
Paraphrasing is usually expected in research and argumentative essays. These type of papers benefit from paraphrasing because it shows that you understand the source and are therefore a reliable voice on that source. Paraphrasing can make the evidence more straightforward. Another reason to paraphrase is to adjust your tone for your audience. If the assignment asks you to write a presentation for your classmates, you do not want to quote scientific jargon. Your source is only persuasive and supportive if your readers understand it. The paraphrase of the quotation below is shorter, and more direct.
Original quotation: “In the case of Facebook, it has changed its format multiple times, and merged other literacy practices – email, instant messaging, games – into its structure in an attempt to keep users on the site” (Keller 2014, 74).
Paraphrase: Facebook has tried to hold on to its users by incorporating new functions like games and email (Keller 2014).
Summaries can also be used in reviews, research papers, and argumentative essays. They have a similar purpose as paraphrasing, but they condense a large work (i.e. an entire chapter, article, or book) into a shorter text such as a paragraph or a short essay. Summaries allow you to focus your description on the parts that are relevant to your discussion. Example 3 briefly summarizes Anne of Green Gables, focusing on Anne as a strong female character and could lead into a discussion of how the series teaches girls self-respect while also cherishing romance.
Anne of Green Gables is a book series that follows the life of an unruly red-headed orphan as she grows from an romantic adolescent into an independent young woman.
What can the Writing Center do to help?
Writing Center consultants can help you if you aren't sure what style of source integration works best for an assignment. Some essays require a mix of methods. Consultants can help you determine if your writing needs a better balance of integration methods. If you are less familiar with one of the three uses of sources, the Writing Center can give you additional pointers.
See our section on how to incorporate sources for more on punctuating and introducing quotations. Also see our section on avoiding plagiarism to learn how to paraphrase and summarize.
Getting Comfortable with Directive Practices in the Writing Center Mar 08, 2024
International Mother Language Day 2024 Mar 04, 2024
University and High School Writing Centers Feb 26, 2024
How Time Affects a Writing Center Session Feb 16, 2024
ESL Instruction in the University of Louisville Writing Center Feb 09, 2024
Mapping Emotional Labor in Our Writing Center Feb 02, 2024
UofL Writing Center Blog - More…
University Writing Center
Ekstrom Library 132
Kornhauser Library 221
University of Louisville
Louisville, Kentucky 40292
Spring 2024
Ekstrom Library
M -Th 9 am - 5 pm
F 9 am - 4 pm
Kornhauser Library
T & Th 9 am - 12 pm
Closed on student breaks and holidays
(502) 852-2173
Social Media
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics / Quoting vs. Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing
Quoting vs. Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing
If you’ve ever written a research essay, you know the struggle is real. Should you use a direct quote? Should you put it in your own words? And how is summarizing different from paraphrasing—aren’t they kind of the same thing?
Knowing how you should include your source takes some finesse, and knowing when to quote directly, paraphrase, or summarize can make or break your argument. Let’s take a look at the nuances among these three ways of using an outside source in an essay.
What is quoting?
The concept of quoting is pretty straightforward. If you use quotation marks, you must use precisely the same words as the original , even if the language is vulgar or the grammar is incorrect. In fact, when scholars quote writers with bad grammar, they may correct it by using typographical notes [like this] to show readers they have made a change.
“I never like[d] peas as a child.”
Conversely, if a passage with odd or incorrect language is quoted as is, the note [sic] may be used to show that no changes were made to the original language despite any errors.
“I never like [sic] peas as a child.”
The professional world looks very seriously on quotations. You cannot change a single comma or letter without documentation when you quote a source. Not only that, but the quote must be accompanied by an attribution, commonly called a citation. A misquote or failure to cite can be considered plagiarism.
When writing an academic paper, scholars must use in-text citations in parentheses followed by a complete entry on a references page. When you quote someone using MLA format , for example, it might look like this:
“The orphan is above all a character out of place, forced to make his or her own home in the world. The novel itself grew up as a genre representing the efforts of an ordinary individual to navigate his or her way through the trials of life. The orphan is therefore an essentially novelistic character, set loose from established conventions to face a world of endless possibilities (and dangers)” (Mullan).
This quote is from www.bl.uk/romantics-and-victorians/articles/orphans-in-fiction , which discusses the portrayal of orphans in Victorian English literature. The citation as it would look on the references page (called Works Cited in MLA) is available at the end of this guide.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing means taking a quote and putting it in your own words.
You translate what another writer has said into terms both you and your reader can more easily understand. Unlike summarizing, which focuses on the big picture, paraphrasing is involved with single lines or passages. Paraphrasing means you should focus only on segments of a text.
Paraphrasing is a way for you to start processing the information from your source . When you take a quote and put it into your own words, you are already working to better understand, and better explain, the information.
The more you can change the quote without changing the original meaning , the better. How can you make significant changes to a text without changing the meaning?
Here are a few paraphrasing techniques:
- Use synonyms of words
- Change the order of words
- Change the order of clauses in the sentences
- Move sentences around in a section
- Active – passive
- Positive – negative
- Statement-question
Let’s look at an example. Here is a direct quote from the article on orphans in Victorian literature:
“It is no accident that the most famous character in recent fiction – Harry Potter – is an orphan. The child wizard’s adventures are premised on the death of his parents and the responsibilities that he must therefore assume. If we look to classic children’s fiction we find a host of orphans” (Mullan).
Here is a possible paraphrase:
It’s not a mistake that a well-known protagonist in current fiction is an orphan: Harry Potter. His quests are due to his parents dying and tasks that he is now obligated to complete. You will see that orphans are common protagonists if you look at other classic fiction (Mullan).
What differences do you spot? There are synonyms. A few words were moved around. A few clauses were moved around. But do you see that the basic structure is very similar?
This kind of paraphrase might be flagged by a plagiarism checker. Don’t paraphrase like that.
Here is a better example:
What is the most well-known fact about beloved character, Harry Potter? That he’s an orphan – “the boy who lived”. In fact, it is only because his parents died that he was thrust into his hero’s journey. Throughout classic children’s literature, you’ll find many orphans as protagonists (Mullan).
Do you see that this paraphrase has more differences? The basic information is there, but the structure is quite different.
When you paraphrase, you are making choices: of how to restructure information, of how to organize and prioritize it. These choices reflect your voice in a way a direct quote cannot, since a direct quote is, by definition, someone else’s voice.
Which is better: Quoting or paraphrasing?
Although the purpose of both quoting and paraphrasing is to introduce the ideas of an external source, they are used for different reasons. It’s not that one is better than the other, but rather that quoting suits some purposes better, while paraphrasing is more suitable for others.
A direct quote is better when you feel the writer made the point perfectly and there is no reason to change a thing. If the writer has a strong voice and you want to preserve that, use a direct quote.
For example, no one should ever try to paraphrase John. F. Kenney’s famous line: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.”
However, think of direct quotes like a hot pepper: go ahead and sprinkle them around to add some spice to your paper, but… you might not want to overdo it.
Conversely, paraphrasing is useful when you want to bring in a longer section of a source into your piece, but you don’t have room for the full passage . A paraphrase doesn’t simplify the passage to an extreme level, like a summary would. Rather, it condenses the section of text into something more useful for your essay. It’s also appropriate to paraphrase when there are sentences within a passage that you want to leave out.
If you were to paraphrase the section of the article about Victorian orphans mentioned earlier, you might write something like this:
Considering the development of the novel, which portrayed everyday people making their way through life, using an orphan as a protagonist was effective. Orphans are characters that, by definition, need to find their way alone. The author can let the protagonist venture out into the world where the anything, good or bad, might happen (Mullan).
You’ll notice a couple of things here. One, there are no quotation marks, but there is still an in-text citation (the name in parentheses). A paraphrase lacks quotation marks because you aren’t directly quoting, but it still needs a citation because you are using a specific segment of the text. It is still someone else’s original idea and must be cited.
Secondly, if you look at the original quote, you’ll see that five lines of text are condensed into four and a half lines. Everything the author used has been changed.
A single paragraph of text has been explained in different words—which is the heart of paraphrasing.
What is summarizing?
Next, we come to summarizing. Summarizing is on a much larger scale than quoting or paraphrasing. While similar to paraphrasing in that you use your own words, a summary’s primary focus is on translating the main idea of an entire document or long section.
Summaries are useful because they allow you to mention entire chapters or articles—or longer works—in only a few sentences. However, summaries can be longer and more in-depth. They can actually include quotes and paraphrases. Keep in mind, though, that since a summary condenses information, look for the main points. Don’t include a lot of details in a summary.
In literary analysis essays, it is useful to include one body paragraph that summarizes the work you’re writing about. It might be helpful to quote or paraphrase specific lines that contribute to the main themes of such a work. Here is an example summarizing the article on orphans in Victorian literature:
In John Mullan’s article “Orphans in Fiction” on bl.uk.com, he reviews the use of orphans as protagonists in 19 th century Victorian literature. Mullan argues that orphans, without family attachments, are effective characters that can be “unleashed to discover the world.” This discovery process often leads orphans to expose dangerous aspects of society, while maintaining their innocence. As an example, Mullan examines how many female orphans wind up as governesses, demonstrating the usefulness of a main character that is obligated to find their own way.
This summary includes the main ideas of the article, one paraphrase, and one direct quote. A ten-paragraph article is summarized into one single paragraph.
As for giving source credit, since the author’s name and title of the source are stated at the beginning of the summary paragraph, you don’t need an in-text citation.
How do I know which one to use?
The fact is that writers use these three reference types (quoting, paraphrasing, summarizing) interchangeably. The key is to pay attention to your argument development. At some points, you will want concrete, firm evidence. Quotes are perfect for this.
At other times, you will want general support for an argument, but the text that includes such support is long-winded. A paraphrase is appropriate in this case.
Finally, sometimes you may need to mention an entire book or article because it is so full of evidence to support your points. In these cases, it is wise to take a few sentences or even a full paragraph to summarize the source.
No matter which type you use, you always need to cite your source on a References or Works Cited page at the end of the document. The MLA works cited entry for the text we’ve been using today looks like this:
Mullan, John. Orphans in Fiction” www.bl.uk/romantics-and-victorians/articles/orphans-in-fiction. Accessed 20. Oct. 2020
————–
See our related lesson with video: How to Quote and Paraphrase Evidence
Citation Guides
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- Citation Examples
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Page Numbers
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Bibliography
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- View MLA Guide
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
What is a Venn Diagram
What are your venn diagram needs.
Creating Venn diagrams is super simple and easy with our Venn diagram maker. Learn the essentials of Venn diagrams, along with their long history, versatile purposes and uses, examples and symbols, and steps to draw them.
7 minute read
Want to make a Venn diagram of your own? Try Lucidchart. It's quick, easy, and completely free.
What is a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram uses overlapping circles or other shapes to illustrate the logical relationships between two or more sets of items. Often, they serve to graphically organize things, highlighting how the items are similar and different.
Venn diagrams, also called Set diagrams or Logic diagrams, are widely used in mathematics, statistics, logic, teaching, linguistics, computer science and business. Many people first encounter them in school as they study math or logic, since Venn diagrams became part of “new math” curricula in the 1960s. These may be simple diagrams involving two or three sets of a few elements, or they may become quite sophisticated, including 3D presentations, as they progress to six or seven sets and beyond. They are used to think through and depict how items relate to each within a particular “universe” or segment. Venn diagrams allow users to visualize data in clear, powerful ways, and therefore are commonly used in presentations and reports. They are closely related to Euler diagrams, which differ by omitting sets if no items exist in them. Venn diagrams show relationships even if a set is empty.
Venn diagram history
Venn diagrams are named after British logician John Venn. He wrote about them in an 1880 paper entitled “On the Diagrammatic and Mechanical Representation of Propositions and Reasonings” in the Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science.
But the roots of this type of diagram go back much further, at least 600 years. In the 1200s, philosopher and logician Ramon Llull (sometimes spelled Lull) of Majorca used a similar type of diagram, wrote author M.E. Baron in a 1969 article tracing their history. She also credited German mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibnitz with drawing similar diagrams in the late 1600s.
In the 1700s, Swiss mathematician Leonard Euler (pronounced Oy-ler) invented what came to be known as the Euler Diagram, the most direct forerunner of the Venn Diagram. In fact, John Venn referred to his own diagrams as Eulerian Circles, not Venn Diagrams. The term Venn Diagrams was first published by American philosopher Clarence Irving (C.I.) Lewis in his 1918 book, A Survey of Symbolic Logic.
Venn Diagrams continued to evolve over the past 60 years with advances by experts David W. Henderson, Peter Hamburger, Jerrold Griggs, Charles E. “Chip” Killian and Carla D. Savage. Their work concerned symmetric Venn Diagrams and their relationship to prime numbers, or numbers indivisible by other numbers except 1 and the number itself. One such symmetric diagram, based on prime number 7, is widely known in math circles as Victoria.
Other notable names in the development of Venn Diagrams are A.W.F. Edwards, Branko Grunbaum and Henry John Stephen Smith. Among other things, they changed the shapes in the diagrams to allow simpler depiction of Venn Diagrams at increasing numbers of sets.
Example Venn diagram
Say our universe is pets, and we want to compare which type of pet our family might agree on.
Set A contains my preferences: dog, bird, hamster.
Set B contains Family Member B’s preferences: dog, cat, fish.
Set C contains Family Member C’s preferences: dog, cat, turtle, snake.
The overlap, or intersection, of the three sets contains only dog. Looks like we’re getting a dog.
Of course, Venn diagrams can get a lot more involved than that, as they are used extensively in various fields.
Venn diagram purpose and benefits
To visually organize information, to compare two or more choices, to solve complex mathematical problems., to compare data sets,, to reason through the logic, venn diagram use cases, statistics and probability:, linguistics:, teaching reading comprehension:, computer science:, venn diagram glossary, on a lighter note: venn diagrams hit the small screen.
Not many diagrams have crossed over into popular culture, but the esteemed Venn diagram has.
Steps to draw and use a basic Venn diagram
- Determine your goal. What are you comparing, and why? This will help you to define your sets.
- Brainstorm and list the items in your sets, either on paper or with a platform like Lucidchart.
- Now, use your diagram to compare and contrast the sets. You may see things in new ways and be able to make observations, choices, arguments or decisions.
Additional Resources
- Venn Diagram Templates
- How to Create a Venn Diagram in PowerPoint
Lucidchart lets you create professional-looking Venn diagrams with easy-to-use software. With all editing taking place in the cloud, it’s easy to collaborate with colleagues on a Venn diagram. You can even import images and share your diagram digitally or via print.

Academic Integrity: Quoting, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
- Citing Sources
- How Do I Use NoodleTools
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Tips for Avoiding Plagiarism
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
- Paraphrasing
- Summarizing
- Common Knowledge
YOU SHOULD CITE WHEN:
- Referring to a source and stating someone else's opinions, thoughts, ideas, or research
- Using an image or media file that you did not create

WHEN REFERRING TO A SOURCE, YOU HAVE THREE OPTIONS FOR USING IT:
- Directly Quoting
- Summarizing
- Paraphrase
"Which option you should choose depends on how much of a source you are using, how you are using it, and what kind of paper you are writing, since different fields use sources in different ways." Grounds for Argument. When to Quote, Paraphrase, or Summarize a Source . Used under CC BY NC SA
YOU DO NOT NEED TO CITE:
- Your thoughts and your interpretations
- Common knowledge
Purdue OWL: Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
Harvard Guide to Using Sources: Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Quoting
WHAT IS A DIRECT QUOTATION:
"Must be identical to the original, using a narrow segment of the source. They must match the source document word for word and must be attributed to the original author." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- If summarizing or paraphrasing cannot capture the essence or meaning of the text
- To retain a specific or unique phrasing used by the source's author
- If you are analyzing the text itself (often in English or language classes)
BE ADVISED:
Most of the time when you cite a source, you want to summarize or paraphrase. Direct quotations should be used sparingly when the situation meets the criteria above. When you do use direct quotations:
- Do not take the quote out of context. The author's meaning should not change.
- Be sure to integrate multiple sources within your text. You don't want to have a paper or a passage that seems to have come only from one source, with little original text from you.
- Use transitions to make sure your quote adds to your paper without interrupting its flow.
HOW TO CITE A DIRECT QUOTATION:
- Place quotation marks around the entire word-for-word passage, whether it's a phrase or a sentence.
- Attribute with an in-text citation ; most citation styles request that you provide a page or paragraph number when directly citing.
- If your quotation is longer, check with your citation style guide to see if additional formatting is necessary (block quotations, for example).
WHAT IS A PARAPHRASE:
"A paraphrase is a detailed restatement in your own words of a written or sometimes spoken source material. Apart from the changes in organization, wording, and sentence structure, the paraphrase should be nearly identical in meaning to the original passage. It should also be near the same length as the original passage and present the details of the original." University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
Paraphrasing is "your own rendition of essential information and ideas expressed by someone else, presented in a new form." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing

- "When the wording is less important than the meaning of the source" University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
- If a summary would not provide enough specific details
HOW TO CITE A PARAPHRASE:
- Attribute with an in-text citation; some citation styles request that you provide a page or paragragh number whenever available.
- When paraphrasing, you must change both the sentence structure and language of the original text. Therefore, since you will be changing the text, you do NOT need quotation marks around your paraphrase.
Includes 6 steps to effective paraphrasing and examples.
WHAT IS A SUMMARY:
"Involves putting the main idea(s) into your own words, including only the main point(s).... Summaries are significantly shorter than the original and take a broad overview of the source material." Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (2012). Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
"Similar to paraphrasing, summarizing involves using your own words and writing style to express another author's ideas. Unlike the paraphrase, which presents important details, the summary presents only the most important ideas of the passage." University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.). Decide when to Quote, Paraphrase & Summarize.
- To provide necessary background information for your audience
- When broad, concise information will suffice
HOW TO CITE A SUMMARY:
- You should not be using any word-for-word quotations or language unique to the source, so you do NOT need quotation marks around your summary.
COMMON KNOWLEDGE:
It doesn't necessarily mean that most people would know it offhand. And sometimes it's a judgment call because what seems like common knowledge to one person isn't to another. Here are good rules of thumb:
- If you can find the same information in multiple places, stated in relatively the same way, it's common knowledge (Generally, it is said that you should find the information three to five sources)
- If most people are aware of this fact, or if it's general reference, it's common knowledge
CAUTION: Opinions and unique terminology/phrasing do not qualify as common knowledge.

- << Previous: Tips for Avoiding Plagiarism
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 12:30 PM
- URL: https://libguides.middlesex.mass.edu/academicintegrity

- Admissions Essays
- Books and Manuscripts
- Business Proofreading and Editing
- Dissertations
- Editing Tools
- Personal Statements
- Professional Writing
- Proofreading and Editing
- Thesis Proposals
- Uncategorized
- Working From Home
- Writing Fiction
- Writing Guides
Differences in a Paraphrase, Summary, and Précis

Get 400 words proofread and edited for free
Look up “paraphrase,” “summary,” and “précis” in the dictionary, and you’re going to find a lot of overlapping ideas, but the uses of these terms (especially in academic writing) have quite well-defined boundaries.
All these terms deal with the idea that you’re reading something someone else wrote and then putting it in different terms while maintaining the meaning. But these similarities come to an end when you consider the different purposes for these tasks.
Let’s Start with the Paraphrase
A paraphrase is specifically different from a quote. To qualify, it must relay all the same information but in different words.
Not seeing how this is different from the others? Think about the purpose. A paraphrase reveals that you know what is being said and can rephrase it in words of your own choosing. You are proving you “get it.”
Get a free sample proofread and edit for your document. Two professional proofreaders will proofread and edit your document.
A paraphrase thus has no space limits. Indeed, a paraphrase might be much longer than the original text. One paraphrase of, “To be, or not to be / That is the question,” is: “I am asking myself whether I should decide to go on living, or kill myself, and this may be ‘the question’ in terms of all existence. Should humanity bother to keep on going or just snuff it?”
A paraphrase may also be much shorter. One paraphrase of:
Now therefore, while the youthful hue Sits on thy skin like morning dew, And while thy willing soul transpires At every pore with instant fires, Now let us sport us while we may, And now, like amorous birds of prey, Rather at once our time devour Than languish in his slow-chapped power,
would be: “Hey, let’s have sex before we get all old and stuff.”
Of course, that second paraphrase might not get you a good grade in English Lit.
A Summary Is a Whole Different Deal
A summary is generally understood to be of something long enough to benefit from a summary. There’s no real summary for, “I am going to the store.” (A paraphrase would be, “The speaker is traveling to the shop.”) A summary is understood to be smaller than the original and may use some of the same words.
A summary also does not have to be complete. A summary of MLK’s “I Have a Dream” speech can just be, “White and Black people should try to get along better.” A paraphrase of the speech would have to cover all the bases.

A summary’s purpose is not to interpret meaning so much as to relay information, so the pressure is off to make sure the words are different. We might even throw in a quote or two. Think of summarizing a movie you just saw for a friend. You might do a line of dialogue like, “To the pain!” or “Excuse me while I whip this out.”
A Précis Is for You
“Précis” is just an academic term for “summary,” and you might never be assigned to do one, but it’s a handy thing. The purpose here is to remind yourself of what the original said.
Let’s say you’re reading a bunch of books and articles that might be important for a test, and you decide just taking a few notes isn’t enough. You can write a précis with the idea that you’ll read it again later to refresh your memory. A précis might then include details about the article beyond the text, such as that this is the first time a certain procedure was successful or that this approach to writing code was useful for a while but is now obsolete.
If you do a precise for the primary sources for your discipline, you’ll have that as a resource not only for tests, but also for papers you might want to write: sort of your own version of CliffsNotes (Coles Notes for you Canadians, York Notes for you Brits). Because you do them yourself, they are geared toward your interests and your style of thinking.
So, while the main idea is the same, the different purposes of these ways of summing things up require different skills. (Note that that final line there is a summary for the purpose of a conclusion. Ain’t I a tricky one?)
Julia H. (except for the poem, which is Andrew M.)

Get a Free Sample
We will get your free sample back in three to six hours!
We proofread documents 24/7 Support 888-833-8385

Customer Service
Get in touch.
ProofreadingPal LLC 105 Iowa Ave., Ste. 214 Iowa City, IA 52240
Call Us 888-833-8385
Live Customer Support Hours Sun.–Thur. 8 a.m. to midnight CT Fri. and Sat. 8 a.m. to 6 p.m. CT
Submit Documents 24/7
© 2010 - 2020 ProofreadingPal LLC - All Rights Reserved.
The Vocative Comma Is Important, People! · September 25, 2022
8 Tips to Make Your Writing Sound More Formal · August 29, 2022
Worlde Tips and Tricks · March 10, 2022
Worlde Tips and Tricks · February 25, 2022
Top 4 Misspelled Words · November 5, 2021
How to Capitalize Medicine · October 1, 2021
How to Capitalize Medicine · August 18, 2021
4 Fixes for Comment Boxes in MS Word · January 17, 2021
How to Avoid Wordiness · July 15, 2020
Write an Effective Blog Post · June 9, 2020
Proofreading Services Rates · April 19, 2020
How to Make Your Writing More Inclusive · March 5, 2020
How to Make Your Writing More Inclusive · February 27, 2020
Guide to Olde English · December 27, 2019
Guide to Olde English · December 26, 2019
Common Apostrophe Errors · December 19, 2019
Guide to Olde English · December 18, 2019
Capitalization in APA, Chicago, MLA, and AP · August 27, 2019
Avoiding Common Capitalization Errors · July 31, 2019
Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A Venn diagram is a great tool for brainstorming and creating a comparison between two or more objects, events, or people. You can use this as a first step to creating an outline for a compare and contrast essay .
Simply draw two (or three) large circles and give each circle a title, reflecting each object, trait, or person you are comparing.
Inside the intersection of the two circles (overlapping area), write all the traits that the objects have in common. You will refer to these traits when you compare similar characteristics.
In the areas outside the overlapping section, you will write all of the traits that are specific to that particular object or person.
Creating an Outline for Your Essay Using a Venn Diagram
From the Venn diagram above, you can create an easy outline for your paper. Here is the beginning of an essay outline:
1. Both dogs and cats make great pets.
- Both animals can be very entertaining
- Each is loving in its own way
- Each can live inside or outside the house
2. Both have drawbacks, as well.
- They can damage property
- Both can be costly
- Both require time and attention
3. Cats can be easier to care for.
- Leaving for a day
4. Dogs can be better companions.
- Going to the park
- Going for walks
- Will enjoy my company
As you can see, outlining is much easier when you have a visual aid to help you with the brainstorming process.
More Uses for Venn Diagrams
Besides its usefulness for planning essays, Venn Diagrams can be used for thinking through many other problems both at school and at home. For example:
- Planning a Budget: Create three circles for What I Want, What I Need, and What I Can Afford.
- Setting Priorities: Create circles for different types of priorities: School, Chores, Friends, TV, along with a circle for What I Have Time for This Week.
- Choosing Activities: Create circles for different types of activities: What I'm Committed to, What I'd Like to Try, and What I Have Time for Each Week.
- Comparing People's Qualities: Create circles for the different qualities you're comparing (ethical, friendly, good looking, wealthy, etc.), and then add names to each circle. Which overlap?
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Brainstorming Techniques for Students
- 101 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- 7 Active Reading Strategies for Students
- Writing Cause and Effect Essays for English Learners
- Using Graphic Organizers for Special Education
- Discover Ideas Through Brainstorming
- Vocabulary Chart ESL Lesson Plan
- Miss Nelson Is Missing Lesson Plan
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- Second Grade Map Project Ideas
- 20 Book Activities to Try With Grades 3-5
- Learning Styles: Holistic or Global Learning
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- 10 Tips for the SAT Essay
Know the Difference: Quoting, Paraphrasing and Summarizing

An important part of any academic discussion is citations. It highlights the existing works on a particular topic, enabling readers to track relevant research 1 to develop their arguments. Though the function of citation is simple, the learning process of correctly citing other articles can be challenging. There is an increased possibility of plagiarism if you incorporate others’ work or ideas without full or correct acknowledgment. As a research student or early researcher, you will come across rules for paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting in your research articles. These are essential strategies for citing existing research work to support or challenge your writings or arguments. You’ll use a combination of these in your assignments, dissertation, or research papers, so understanding their differences is important.
In simple terms, the difference between these three terms lies in the proximity of your writing to the source writing, but their use could be hindered for the following reasons. 2
- Low linguistic ability: limit the power to define, summarize, evaluate, and contrast existing literature.
- Unfamiliarity with the language of citations: repeat citation patterns, integrate references incorrectly, or misplace reporting verbs.
- Lack of awareness of the importance of referencing: Under referencing
This article compares and discusses paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting to help you become more comfortable with their usage.
Quoting involves using a direct quotation , where you quote the author verbatim to define or describe specific concepts. Use double quotation marks at the beginning and end of the quote, and use the exact words from the original text. It is important to cite the original source and name the author, or else your work could be considered plagiarized as there is software that easily detects this. Also, it is better to avoid long passages as direct quotes; limit them to one or two sentences. Another point to remember is to limit their instances in your paper. Use words/phrases such as stated , in the words of , etc., to indicate that you are using the author’s exact words. Discuss its meaning or add more information as needed so that the quotes fit logically in your writing.
Paraphrasing
Unlike quoting, paraphrasing involves rewriting the text; the aim is to explain the original and relevant idea in one’s own words as a basis to build an argument. You can avoid words such as mentioned or stated for paraphrased text, but cite the source to ensure the reader knows that you are borrowing ideas. Paraphrasing can be challenging to most ESL students as it requires a good command of paraphrasing and considerable time and effort in choosing the right active or passive verbs to introduce a paraphrase. 3 A common mistake to avoid is swapping words in the original sentence with their synonyms.
In academic writing, the preference is towards paraphrasing because it shows your understanding of the literature and allows you to present relevant evidence to your readers. Also, as it incorporates your own academic voice, you can avoid getting flagged by plagiarism detection tools, such as Turnitin.
Tips for effective paraphrasing
- Reformulate the sentence by changing the voice from active to passive or starting from a different point.
- Use quality sources to support your ideas.
- Remove irrelevant information from the source text.
- Combine information from multiple sentences.
- Use synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning.
Summarizing
When summarizing, you describe the original text without analyzing it. Your aim is to give your readers a broad overview of a subject. It involves placing the main ideas or points in your own words. Since your focus is on providing a general overview of the topic, summaries are often provided in the introductory paragraph. But remember to cite the summarized ideas.
How to use quotations, paraphrases, and summaries
- Place all exact source words in quotation marks immediately.
- When summarizing or paraphrasing, the following strategies can be adopted to avoid looking at the source material and reduce the influence of the source text in your version:
- Read the text multiple times. This will help you understand the author’s main ideas and explain them to others.
- Write down the main phrases and ideas. This should be done without looking at the original sentence.
- Write in sentence form. Develop the summary or paraphrase based on your understanding of the source text.
- Compare with the original work. Rewrite your work if words/phrases are the same as in the original work or if the structure is very similar.
The following is an example of a good paraphrase. It has the same ideas as the source text (quoted on the left) but with different wording and sentence structure.
Ways to avoid accidental plagiarism
- Use citations: Give credit where it is due.
- Organize and develop your own idea: Work out a balance between the ideas from other sources and your original ideas. Your writing should have originality and be concise.
- Use plagiarism checkers: There are a number of good plagiarism checker tools available online. Many online check tools also correct grammar errors, sentence structures, word choices, and subject-specific phrasing.
Developing your paraphrasing and summarizing skills will take time. So, it is important that you set aside a lot of time to practice these skills to perfect your writing.
- Hunter, J. (2006). The importance of citation. URL: http://web grinnell edu/Dean/Tutorial/EUS/IC pdf (1204 2007) .
- Elizalde Esain, A. (2017). English for Academic Purposes: The Challenge of Paraphrasing.
- McKeown, K. (1983). Paraphrasing questions using given and new information. American Journal of Computational Linguistics , 9 (1), 1-10.
- Bachman, L. F. (1990). Fundamental considerations in language testing . Oxford University Press.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How and When to Use Active or Passive Voice in Research Papers
- What does ‘et al.’ mean and How to Use ‘et al.’ in a Research Paper
3 Easy Ways for Researchers to Improve Their Academic Vocabulary
- 7 Common Writing Mistakes to Avoid in Your Research Paper
A Comparative Analysis of 5 AI Editing Tools for Researchers
You may also like, publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for..., how to make your thesis supervision work for..., how to paraphrase research papers effectively, 4 types of transition words for research papers , paraphrasing in academic writing: answering top author queries, how to write a conclusion for research papers..., ethical research practices for research with human subjects.
Venn Diagram
About this Interactive
Related resources.
This interactive tool allows students to create Venn diagrams that contain two or three overlapping circles. Students identify and record concepts that can be placed in one of the circles or in the overlapping areas, allowing them to organize their information logically. Students may view and edit their draft diagrams, then print the finished diagrams for reference. In some cases, the Venn diagram tool has been customized to complement a specific lesson or activity.
- Lesson Plans
- Calendar Activities
- Strategy Guides
- Student Interactives
Students compare the sinking of the Edmund Fitzgerald with the song, "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald," then create their own poetry about a historical event.
Students often find poetry frustrating and meaningless. By helping students think critically about the differences between poetry and prose, this introduction sets the stage for different strategies for comprehending poetic texts.
Students build their understanding of the terms compare and contrast by participating in class discussions, using Internet resources, working collaboratively, and by visually representing information in a Venn diagram.
Through a classroom game and resource handouts, students learn about the techniques used in persuasive oral arguments and apply them to independent persuasive writing activities.
Students research, evaluate, and synthesize information about the Harlem Renaissance from varied resources, create an exhibit, and highlight connections across disciplines (i.e., art, music, and poetry) using a Venn diagram.
Cinderella without castles, coaches, or ball gowns? Students use versions of Cinderella to explore how the setting of a storytime, place, and cultureaffects the characters and plot.
A little understanding can go a long way. After learning about difficulties that Palestinian youths face, students will write a letter to an official discussing these issues.
Following the model of N. Scott Momaday's The Way To Rainy Mountain , students write three-voice narratives based on Kiowa folktales, an interview with an Elder, and personal connections to theme.
In this lesson, kindergarten students manipulate hula hoops and real objects, as they use Venn diagrams to problem solve, explore, and record information to share with others.
Students explore picture books to identify the characteristics of four types of conflict. They then write about a conflict they have experienced and compare it to a conflict from literature.
This lesson uses clips from The Matrix and other dystopian movies to introduce students to the characteristics found in dystopian works, such as Brave New World , Fahrenheit 451 , and 1984 .
After exploring The Odyssey and a contemporary epic, students choose paired characters from the texts, complete a graphic organizer, and place their characters in hypothetical contemporary situations.
Students compose a multigenre paper, modeled after the Delany sister's autobiography, Having Our Say , that includes the autobiographical narrative essay as well as an informational nonfiction piece.
Students will be introduced to persuasive techniques used in advertising, analyze advertising, and explore the concepts of demographics, marketing for a specific audience, and dynamic advertising.
This step-by-step literature response template for use with read-alouds asks students to use drawing and writing to respond to increasingly-complex prompts which address literary elements as well as personal connections.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
1.3 Understanding Venn Diagrams
Learning objectives.
After completing this section, you should be able to:
- Utilize a universal set with two sets to interpret a Venn diagram.
- Utilize a universal set with two sets to create a Venn diagram.
- Determine the complement of a set.
Have you ever ordered a new dresser or bookcase that required assembly? When your package arrives you excitedly open it and spread out the pieces. Then you check the assembly guide and verify that you have all the parts required to assemble your new dresser. Now, the work begins. Luckily for you, the assembly guide includes step-by-step instructions with images that show you how to put together your product. If you are really lucky, the manufacturer may even provide a URL or QR code connecting you to an online video that demonstrates the complete assembly process. We can likely all agree that assembly instructions are much easier to follow when they include images or videos, rather than just written directions. The same goes for the relationships between sets.
Interpreting Venn Diagrams
Venn diagrams are the graphical tools or pictures that we use to visualize and understand relationships between sets. Venn diagrams are named after the mathematician John Venn, who first popularized their use in the 1880s. When we use a Venn diagram to visualize the relationships between sets, the entire set of data under consideration is drawn as a rectangle, and subsets of this set are drawn as circles completely contained within the rectangle. The entire set of data under consideration is known as the universal set .
Consider the statement: All trees are plants. This statement expresses the relationship between the set of all plants and the set of all trees. Because every tree is a plant, the set of trees is a subset of the set of plants. To represent this relationship using a Venn diagram, the set of plants will be our universal set and the set of trees will be the subset. Recall that this relationship is expressed symbolically as: Trees ⊂ Plants . Trees ⊂ Plants . To create a Venn diagram, first we draw a rectangle and label the universal set “ U = Plants . U = Plants . ” Then we draw a circle within the universal set and label it with the word “Trees.”
This section will introduce how to interpret and construct Venn diagrams. In future sections, as we expand our knowledge of relationships between sets, we will also develop our knowledge and use of Venn diagrams to explore how multiple sets can be combined to form new sets.
Example 1.18
Interpreting the relationship between sets in a venn diagram.
Write the relationship between the sets in the following Venn diagram, in words and symbolically.
The set of terriers is a subset of the universal set of dogs. In other words, the Venn diagram depicts the relationship that all terriers are dogs. This is expressed symbolically as T ⊂ U . T ⊂ U .
Your Turn 1.18
So far, the only relationship we have been considering between two sets is the subset relationship, but sets can be related in other ways. Lions and tigers are both different types of cats, but no lions are tigers, and no tigers are lions. Because the set of all lions and the set of all tigers do not have any members in common, we call these two sets disjoint sets , or non-overlapping sets.
Two sets A A and B B are disjoint sets if they do not share any elements in common. That is, if a a is a member of set A A , then a a is not a member of set B B . If b b is a member of set B B , then b b is not a member of set A A . To represent the relationship between the set of all cats and the sets of lions and tigers using a Venn diagram, we draw the universal set of cats as a rectangle and then draw a circle for the set of lions and a separate circle for the set of tigers within the rectangle, ensuring that the two circles representing the set of lions and the set of tigers do not touch or overlap in any way.
Example 1.19
Describing the relationship between sets.
Describe the relationship between the sets in the following Venn diagram.
The set of triangles and the set of squares are two disjoint subsets of the universal set of two-dimensional figures. The set of triangles does not share any elements in common with the set of squares. No triangles are squares and no squares are triangles, but both squares and triangles are 2D figures.
Your Turn 1.19
Creating venn diagrams.
The main purpose of a Venn diagram is to help you visualize the relationship between sets. As such, it is necessary to be able to draw Venn diagrams from a written or symbolic description of the relationship between sets.
To create a Venn diagram:
- Draw a rectangle to represent the universal set, and label it U = set name U = set name .
- Draw a circle within the rectangle to represent a subset of the universal set and label it with the set name.
If there are multiple disjoint subsets of the universal set, their separate circles should not touch or overlap.
Example 1.20
Drawing a venn diagram to represent the relationship between two sets.
Draw a Venn diagram to represent the relationship between each of the sets.
- All rectangles are parallelograms.
- All women are people.
- The set of rectangles is a subset of the set of parallelograms. First, draw a rectangle to represent the universal set and label it with U = Parallelograms U = Parallelograms , then draw a circle completely within the rectangle, and label it with the name of the set it represents, R = Rectangles R = Rectangles .
In this example, both letters and names are used to represent the sets involved, but this is not necessary. You may use either letters or names alone, as long as the relationship is clearly depicted in the diagram, as shown below.
- The universal set is the set of people, and the set of all women is a subset of the set of people.
Your Turn 1.20
Example 1.21, drawing a venn diagram to represent the relationship between three sets.
All bicycles and all cars have wheels, but no bicycle is a car. Draw a Venn diagram to represent this relationship.
Step 1: The set of bicycles and the set of cars are both subsets of the set of things with wheels. The universal set is the set of things with wheels, so we first draw a rectangle and label it with U = Things with Wheels U = Things with Wheels .
Step 2: Because the set of bicycles and the set of cars do not share any elements in common, these two sets are disjoint and must be drawn as two circles that do not touch or overlap with the universal set.
Your Turn 1.21
The complement of a set.
Recall that if set A A is a proper subset of set U U , the universal set (written symbolically as A ⊂ U A ⊂ U ), then there is at least one element in set U U that is not in set A A . The set of all the elements in the universal set U U that are not in the subset A A is called the complement of set A A , A ' A ' . In set builder notation this is written symbolically as: A ' = { x ∈ U | x ∉ A } . A ' = { x ∈ U | x ∉ A } . The symbol ∈ ∈ is used to represent the phrase, “is a member of,” and the symbol ∉ ∉ is used to represent the phrase, “is not a member of.” In the Venn diagram below, the complement of set A A is the region that lies outside the circle and inside the rectangle. The universal set U U includes all of the elements in set A A and all of the elements in the complement of set A A , and nothing else.
Consider the set of digit numbers. Let this be our universal set, U = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 } . U = { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 } . Now, let set A A be the subset of U U consisting of all the prime numbers in set U U , A = { 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 } . A = { 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 } . The complement of set A A is A ' = { 0 , 1 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 9 } . A ' = { 0 , 1 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 9 } . The following Venn diagram represents this relationship graphically.
Example 1.22
Finding the complement of a set.
For both of the questions below, A A is a proper subset of U U .
- Given the universal set U = { Billie Eilish, Donald Glover, Bruno Mars, Adele, Ed Sheeran} U = { Billie Eilish, Donald Glover, Bruno Mars, Adele, Ed Sheeran} and set A = { Donald Glover, Bruno Mars, Ed Sheeran} A = { Donald Glover, Bruno Mars, Ed Sheeran} , find A ' . A ' .
- Given the universal set U = { d|d is a dog } U = { d|d is a dog } and B = { b ∈ U|b is a beagle } B = { b ∈ U|b is a beagle } , find B ' . B ' .
- The complement of set A A is the set of all elements in the universal set U U that are not in set A . A . A ' = { Billie Eilish, Adele } A ' = { Billie Eilish, Adele } .
- The complement of set B B is the set of all dogs that are not beagles. All members of set B ′ B ′ are in the universal set because they are dogs, but they are not in set B , B , because they are not beagles. This relationship can be expressed in set build notation as follows: B ′ = { All dogs that are not beagles .} B ′ = { All dogs that are not beagles .} , B ′ = { d ∈ U | d is not a beagle .} B ′ = { d ∈ U | d is not a beagle .} , or B ′ = { d ∈ U | d ∉ B } . B ′ = { d ∈ U | d ∉ B } .
Your Turn 1.22
Check your understanding, section 1.3 exercises.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/contemporary-mathematics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Donna Kirk
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Contemporary Mathematics
- Publication date: Mar 22, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/contemporary-mathematics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/contemporary-mathematics/pages/1-3-understanding-venn-diagrams
© Dec 21, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Use and Create a Venn Diagram to Help Write Compare and Contrast Essays
- R. Elizabeth C. Kitchen
- Categories : Help with writing assignments paragraphs, essays, outlines & more
- Tags : Homework help & study guides
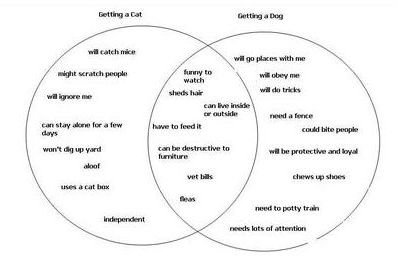
Creating a Venn Diagram
When using a Venn diagram to write a compare and contrast essay, first draw two large circles. These two circles should overlap each other. Assign a title to each circle that represents each idea you are comparing. In the overlapping area, write all of the things that the two ideas, people, or objects have in common. These will be what you refer to when you are comparing these ideas in the essay. In the areas that are not overlapping, write all of the differences, or contrasts, between the two ideas, objects, or people.
Creating an Outline from Your Diagram
An example of the beginning of the outline for a compare and contrast essay should be similar to:
1. Both turtles and cats make good pets.
- a. Both of these animals are entertaining.
- b. Both animals are relatively easy to care for.
- c. Both animals are inexpensive to adopt and to care for.
2. Both turtles and cats have drawbacks.
- a. Both animals will need to have a cage (turtles) or a litter box (cats) that needs to be cleaned.
- b. Both animals require attention and time.
- c. Both animals can be costly in terms of veterinary care.
3. Cats can be easier to care for.
- a. They can feed themselves as long as their food bowl remains filled.
- b. Cats can be left alone for a day or two.
4. Turtles are less messy.
- a. Turtles live in an aquarium.
- b. Turtles do not need a litter box.
Writing the Compare and Contrast Essay
A compare and contrast essay will ultimately follow this basic format:
- Introduction and Thesis Statement (one paragraph).
- Topic One (at least one paragraph, can be more, discussing just one of the ideas, people, or objects being discussed in great detail).
- Topic Two (will follow the same guidelines as topic one).
- Topic One and Topic Two Together (analyze both topics together, can be one or more paragraphs).
- Conclusion (sum up the compare and contrast essay, should generalize the thesis and should reaffirm the thesis).
The first paragraph of the essay will be an introductory paragraph. It will also include the essay’s thesis statement. The first paragraph should present the first comparison from the Venn diagram, the second paragraph should present the second comparison from the Venn diagram, and the third paragraph should present the third comparison from the Venn diagram. If there are more comparisons on the Venn diagram, more paragraphs can be added. The fourth paragraph should present the first contrast from the Venn diagram. The fifth paragraph should present the second contrast from the Venn diagram. The sixth paragraph should present the third contrast from the Venn diagram. Like the comparison, more contrast paragraphs can be added. The eighth paragraph should present the comparisons and contrasts together. The ninth paragraph should present the conclusion, generalization of the thesis, and reaffirmation of the thesis.
Tips and Tricks
The Venn diagram should ideally contain three comparisons and three contrasts. However, it must contain at least two comparisons and two contrasts. When drawing the Venn diagram, the circles should be very large, so that all information fits within them and within their overlap. Once all of the information is written within the Venn diagram, it is a good idea to make each circle a different color, as well as the overlap area. Using three colors to “separate” the information makes a Venn diagram easier to read.

OASIS: Writing Center
Video transcripts, paraphrasing strategies: comparing paraphrasing and quoting.
Last updated 5/6/2020
Visual: Screen opens to a background image with a person typing on a laptop and a notebook and pencil, along with the Walden University Writing Center logo. The title Walden University Writing Center and tagline “Your writing, grammar, and APA experts” appears on the screen. The screen changes to show the series title “Paraphrasing Sources" and the video title "Comparing Paraphrasing & Quoting.”
Audio: Guitar music.
Visual: Slide changes to a mostly gray slide with the heading: "Paraphrasing: One form of evidence." Below the heading are two blue circles comparing quotation and paraphrase:
- Identical to original
- Narrow (1+ lines)
- Quotation marks
- Author, year, page/paragraph #
- Your own words & sentence structure
- Shorter than original
- Author/year
Audio: A quotation is where the wording you’re using is identical to the original source. You are using, word for word, the exact same thing that the original source said. In a paraphrase, you are going to change your wording, change the sentence structure, and still keep the same information, but you're going to put it into your own words.
There is a little bit of a difference in citation between a quotation and a paraphrase. When you cite a quotation, you use quotation marks, you use the author, the year, and then a page number or paragraph number. In a paraphrase, you give the author and the year, and you can choose to give a page number, but it is not required.
One thing to keep in mind between paraphrasing and quoting is that we really want to be wary of using direct quotations too often. When you use a direct quotation, you're parroting someone else's information, kind of like a little parrot copies and imitates people's words. That is in essence what we're doing. When we use a direct quotation, we're not using our own words, we're using someone else's. It can be helpful to use someone else's words, but to do that often shows we're not critically engaging with the information. We're not really diving in and fully understanding it. I could copy and paste multiple quotations out of a source, but if I don't explain them, integrate them, or use them in any sort of way, why would anyone want to read my work? I’m simply repeating what someone else has already said. Be aware that quotations can be helpful, but you do really want to be wary of using them too often.
Paraphrases, however, are always going to be stronger. When you can take information and put it into your own words, it really shows that you are critically using that text. You're understanding it and are able to rearticulate it in a new and a fresh way.
So those are some differences and similarities in how to cite quotations and paraphrases, but also keep in mind that in academic writing, in general, we prefer writers use paraphrases over quotations.
Visual: The screen changes to an ending slide with slide a background image with a person typing on a laptop and a notebook and pencil, along with the Walden University Writing Center logo. The email address [email protected] appears on the screen.
- Previous Page: Paraphrasing Sources: What Is Paraphrasing?
- Next Page: Paraphrasing Strategies: Paraphrasing Strategies
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary: The article discusses paraphrasing vs. summarizing by explaining the two concepts. It specifies when you should use paraphrasing and when you should summarize a piece of text and describes the process of each. It ends with examples of both paraphrasing and summarizing to provide a better understanding to the reader.
Key Takeaways: Summarizing vs Paraphrasing. How They Are Similar: Paraphrasing and summarizing are both writing techniques that allow us to use other people's ideas without direct copying. How They Are Different: Paraphrasing involves rewording text to create new written content with the same meaning as the original. On the other hand, summarizing condenses the text to an overview of the ...
Oppositely, the main difference between quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing is that quoting is done word for word from the original work. Both paraphrasing and summarizing only touch on the key points and are written with some variation from the initial author's work, usually in the style and tone of the new author.
Paraphrasing and summarizing both offer a way to use someone else's idea as your own in your writing. Paraphrasing transforms the writing into your own words but keeps the same basic length and idea in writing. Summarizing condenses the writing into its main points. Both paraphrasing and summarizing require proper citation because the idea ...
Paraphrasing. Paraphrasing is when you restate someone else's words, but not word for word. Example (original quote): "It's risky trusting employees as much as we do. Giving them as much freedom as we do. But it's essential in creative companies where you have much greater risk from lack of innovation.".
Display a blank T-chart or Venn diagram. Have your students read through the objective textbook summary and personal summary. As a class, compare and contrast the two summaries for content and writing style. Fill in the T-chart or Venn diagram with your students' observations.
A direct quote should be enclosed in quotation marks. Expressing a short passage in your own words. Paraphrasing involves completely rewriting the passage while retaining the meaning. Expressing a longer excerpt in your own words. Summarizing involves conveying the main ideas and main points of the source material.
Research guides: PSYD22: Socialization Processes : Paraphrasing, Summarizing, Quoting
Paraphrasing is usually expected in research and argumentative essays. These type of papers benefit from paraphrasing because it shows that you understand the source and are therefore a reliable voice on that source. Paraphrasing can make the evidence more straightforward. Another reason to paraphrase is to adjust your tone for your audience.
Quoting, paraphrasing and summarizing are similar in that they allow a writer to incorporate another writer's work into his or her own work. However, they are different in the methods of application. Quotation s are identical in every way to the original. To quote a source, write out the exact words in the original document and put those words ...
What is summarizing? Next, we come to summarizing. Summarizing is on a much larger scale than quoting or paraphrasing. While similar to paraphrasing in that you use your own words, a summary's primary focus is on translating the main idea of an entire document or long section. Summaries are useful because they allow you to mention entire chapters or articles—or longer works—in only a few ...
A Venn diagram uses overlapping circles or other shapes to illustrate the logical relationships between two or more sets of items. Often, they serve to graphically organize things, highlighting how the items are similar and different. Venn diagrams, also called Set diagrams or Logic diagrams, are widely used in mathematics, statistics, logic ...
A summary is mostly used to explain the main idea of the content or give an overview of the article. It is also used when your supervisor or teacher asks about the idea you want to convey. Major Differences Between Paraphrasing and Summarizing. The primary difference between paraphrasing and summarizing is in functionalities.
Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing "Similar to paraphrasing, summarizing involves using your own words and writing style to express another author's ideas. Unlike the paraphrase, which presents important details, the summary presents only the most important ideas of the passage." University of Houston-Victoria Student Success Center (n.d.).
A summary is generally understood to be of something long enough to benefit from a summary. There's no real summary for, "I am going to the store." (A paraphrase would be, "The speaker is traveling to the shop.") A summary is understood to be smaller than the original and may use some of the same words. A summary also does not have to ...
Summarizing, Paraphrasing, Direct Quoting paraphrasing summarizing involves putting passage from source into your own words. is about the same length as the. ... M4 Activity 2 [Venn Diagram] Summarizing, Paraphrasing, Direct Quoting. Course. Pagbasa at Pagsulat sa Akademikong Filipino (FIL101) 66 Documents.
A Venn diagram is a great tool for brainstorming and creating a comparison between two or more objects, events, or people. You can use this as a first step to creating an outline for a compare and contrast essay . Simply draw two (or three) large circles and give each circle a title, reflecting each object, trait, or person you are comparing.
Develop the summary or paraphrase based on your understanding of the source text. Compare with the original work. Rewrite your work if words/phrases are the same as in the original work or if the structure is very similar. The following is an example of a good paraphrase. It has the same ideas as the source text (quoted on the left) but with ...
Overview. This interactive tool allows students to create Venn diagrams that contain two or three overlapping circles. Students identify and record concepts that can be placed in one of the circles or in the overlapping areas, allowing them to organize their information logically. Students may view and edit their draft diagrams, then print the ...
To create a Venn diagram, first we draw a rectangle and label the universal set " U = Plants. " Then we draw a circle within the universal set and label it with the word "Trees.". Figure 1.7. This section will introduce how to interpret and construct Venn diagrams. In future sections, as we expand our knowledge of relationships between ...
When using a Venn diagram to write a compare and contrast essay, first draw two large circles. These two circles should overlap each other. Assign a title to each circle that represents each idea you are comparing. In the overlapping area, write all of the things that the two ideas, people, or objects have in common.
The screen changes to show the series title "Paraphrasing Sources" and the video title "Comparing Paraphrasing & Quoting." Audio: Guitar music. Visual: Slide changes to a mostly gray slide with the heading: "Paraphrasing: One form of evidence." Below the heading are two blue circles comparing quotation and paraphrase: Quotation. Identical ...
In comparing summarizing, paraphrasing, and direct quoting, we can use a Venn diagram to illustrate their similarities and differences. The similarities they all share include the fact that they all involve the use of other people's ideas to support your own arguments and that they all require citation to avoid plagiarism.