Law & Policy Policy

Resources for Journalists
- Food & Farming Media Network
- How to Pitch Us
- Freelance Charter
- Work With Us
Sentient Media
- Environmental Policy
- Code of Ethics
- Testimonials
Are Zoos Good or Bad for Animals? The Argument, Explained
Debates about the ethics of zoos abound — but when it comes to animal welfare, there are certainly more cons than pros.

Explainer • Entertainment • Policy

Words by Björn Ólafsson
For many people, zoos are the only chance they’ll have in their entire lives to see beautiful animals native to far-flung ecosystems — lions, elephants, pandas, lemurs — the list goes on. And they’re popular — over 181 million people visit a U.S. zoo every year . But zoos face criticism from animal welfare organizations and environmental activists for inhumane treatment of the animals they claim to protect. Zoos maintain that they are important aspects of conservation and education.
So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of zoos ? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of these controversial organizations.
What Are Some Pros and Cons of Zoos ?
First, not all zoos are created equal. While it is easy to imagine animal ethics as a binary of evil and moral, zoos can vary widely on how they treat their animals, how much space they are given and how the animals are obtained. Still, most zoos tend to have the same positives and negatives overall.
Arguments Against Zoos
Poor conditions for animals.
Animals Often Only Have Quite Limited Space
Many zoos’ enclosures are too small, especially for animal species that are used to roaming, flying or swimming large distances in the wild. For example, polar bears are used to home ranges of about 1,000 square kilometers in the wild — large swaths of land and ice they enjoy exploring . In zoos, they get a couple hundred square feet.
Zoos Are Crowded
In addition to limited space, many zoos cram in as many animals as possible into the enclosures. Many visitors prefer seeing animals up close, instead of peering at them from afar, hidden in their dens or nests. This encourages zoos to increase the number of animals per exhibit, increasing the likelihood of visitors seeing animals on the move near the boundaries of the enclosure.
Animals Are Trapped in Unnatural Environments
Anyone who has visited a zoo knows the exhibits are a far cry from the natural landscape they are trying to imitate. Nearly all zoo enclosures contain fences, glass or other barriers for visitors to look through, which are inherently artificial. And the natural-seeming landscapes can sometimes be made out of astroturf, concrete or plastic.
Confinement May Alter the Behavior of Animals
The lack of space, unnatural environments and crowded conditions can directly affect the behavior of animals ; most notably in the form of what’s known as “stereotypy.” Stereotypy is a condition in which non-human animals engage in repetitive behaviors with no apparent purpose, such as pacing for hours on end, wagging tails abnormally or picking their own fur.
The structure of zoos increases the likelihood of stereotypic behavior due to a lack of enrichment, mundane environments and boring, repetitive schedules. This prevalence of stereotypy in zoos even has its own name: “zoochosis,” or psychosis caused by zoos .
‘Surplus’ Animals Can Be Killed
After an animal has reproduced successfully and the zoo no longer requires the animal to maintain an exhibit, the animal is deemed “surplus.” At this point, the animal’s welfare is no longer profitable . Zoos can sell the animal to private owners (who may keep the animal in tiny cages for amusement or kill the animal for taxidermy purposes), sell the animal to other zoos or enclosures, or “euthanize” the animal.
Animals Are Often Mistreated
Animal mistreatment is much more than hitting or beating an animal. It also includes harmful training techniques, separation from family members and forcing animals to behave in abnormal ways.
In a report from World Animal Protection, three-fourths of zoos include human-animal interactions , many of which can be very stressful or physically harmful for animals. In some extreme cases, visitors rode on the backs of animals (causing injury) or encroached on the animals’ enclosure (causing stress).
Investigations into popular zoos sometimes reveal that caretakers don’t always clean the exhibits frequently , leaving the animals to live near their feces. The research also reveals many zookeepers hitting animals who “misbehave,” and not helping animals with injuries sustained in the enclosures. While not all animal caretakers behave this way, the reporting suggests many zoos around the world are lax with animal welfare.
Animals Don’t Like Being Visited
The mere presence of human beings can negatively affect wild animals, especially in massive crowds that are common at zoos. Being bombarded by the sounds, smells and appearances of swaths of humans can trigger the stress responses of some animals . Some studies show that the number of visitors correlates with the amount of stress hormones in many animal species.
Animals Struggle to Form Connections
Many animals are highly social creatures. Elephants, lions, pigs, cows and many more species are shown to have complex connections, hierarchies and relationships with members of their own kind — especially with friends and family. However, zoo animals rarely stay with the same herd or family for their entire lives. Instead, zoos opt to transfer, sell, buy or relocate animals throughout their lifespans, making it difficult for animals to form social connections . This lack of bonding can harm the animals emotionally.
Zoos Are for Humans, Not Animals
Most zoos are for-profit enterprises, meaning they have one goal in mind: maximizing revenue. It is easy to see how making more money can come at the expense of animal welfare. For example, a zoo is unlikely to fund an exhibit expansion if it isn’t cost-effective, regardless of its benefits for the animals inside. While many zookeepers form real bonds with their animal companions, the animals still exist under a for-profit, human-centered organization.
Zoos Promote Human Superiority
The aesthetic nature of zoos — animals in panopticon-like enclosures, viewed 24/7 by members of a different species — can reinforce human superiority. As moral philosopher Lori Gruen writes in her book, “visitors leave the zoo more convinced than ever of human superiority over the natural world.” Of course, zoos also reinforce the idea that humans have a right to take away animals’ freedom and bodily autonomy.
Zoos Don’t Always Help with Conservation — Some Wild Animals Have to Be Caught to Bring Them to Zoos
Many animals in zoos are born in captivity, but that’s not the case for all. Many animals are taken directly from the wild , often when they are babies, to make the transition to captivity a bit easier. At times, this is done in the name of conservation, or when a wild animal is very ill. But many zoos will take animals from the wild, or buy animals from unethical animal traders.
It’s Often Not Possible to Return Animals to the Wild
Releasing an animal into the wild isn’t always successful, especially if the animal has spent time in climates different from their native regions, like jungles, savannas or ice caps. Properly preparing animals for success in the wild is a multi-stage process that can require thousands of dollars — and it doesn’t always work . Captive-born predator species — disadvantaged by being born and raised in an artificial environment — only have a survival rate after being released into the wild of 33 percent , according to one study. As a result, re-release is not a priority for many zoos.
Zoos Are Poorly Regulated
While there exist many laws that protect animals, such as the Animal Welfare Act (AWA) and the Endangered Species Act , they only offer minimum protections . For example, the AWA excludes entire species of animals, like mice, farmed animals, birds and all cold-blooded animals. Its “minimum” standards of care usually ensure the animals’ safety, not their welfare or happiness. Many animal law experts say these regulations don’t go far enough .
What Are the Pros of Having Zoos?
They Can Be Important for Researchers
Biologists and zoologists can benefit from studying animals in zoos. Some breakthroughs in animal behavior and treatment, like why elephants swing their trunks or how gorillas develop heart disease, have been made possible because of zoos’ ease of access . However, not all animals behave the same in captivity as they do in the wild, so not all research is possible in zoos.
Zoos Are Educational — People May Behave “Eco-friendlier” After Going To the Zoo
Zoos can kickstart individuals’ interest in biodiversity, which is a critical aspect of environmental protection. Many zoos include calls to action in their exhibits, highlighting how endangered animals are being poached, driven away, or otherwise killed by human activity. This can inspire some people to behave more conscientiously. One limited survey found that 35 percent of eco-friendly people learned sustainable behavior from zoos . ‘
Zoos Can Help Educate Children About Animals
Zoos are a quintessential school experience for many young people. Children love learning about animals up-close in a safe environment — in fact, education is possibly the biggest advantage of modern zoos. Many programs, like school presentations, guided tours, informational exhibits, and talks with zookeepers can trigger a lifelong love of animals in children .
But zoos aren’t perfect in this regard. According to a study of zoo visitors in the UK, only 34 percent of children learned more about animals at zoos (the result was slightly better when the children were given a guided tour). Worse, children did not feel empowered to help with conservation efforts after visiting a zoo. This suggests that if zoos care about education, they need to more actively reach out to schoolchildren for empowerment and education.
Going to the Zoo Is Affordable
More ethical ways of engaging with animals without removing them from their natural habitats — like whale watching, safaris, hikes, or excursions — are usually expensive or inaccessible for many people. Zoos tend to be relatively cheap for the average family that wants to learn about animals.
Conservation
Zoos Can Protect Endangered Species from Extinction
Zoos often claim they can protect entire species from extinction through conservation programs that involve breeding more animals in captivity and then releasing them into the wild. This is especially important for endangered species like pandas.
While these conservation efforts are truly important, they don’t represent the majority of a zoo’s activities, nor are zoos leaders in conservation worldwide. At the National Zoo, for example, only one-fifth of animals are endangered . In North America, zoos only contribute about 14 percent of all animals reintroduced into the wild as part of a conservation program. Zoos also tend to focus on headline-grabbing endangered animals to bring in visitors, like pandas, elephants or tigers, as opposed to lesser-known but crucial species, like tamarins, kakapos or wombats.
Are Zoos Good or Bad for the Environment?
Zoos claim to support global biodiversity through conservation efforts like protecting endangered animals. This is somewhat true, although it varies greatly from zoo to zoo.
On the other hand, zoos are big polluters and use up lots of resources , especially energy and water . Aquariums in particular use tons and tons of water. Zoo animals also generate waste that may or may not be composted or disposed of correctly.
Should Zoos Exist or Be Banned?
Given the many ways that zoos are unethical to animals, the flawed attempts to contribute to conservation, and the positioning of humans as superior to animals, many animal ethicists believe zoos should not exist — or at least, not exist in their current form .
For example, animal philosopher Dale Jamieson says in his book Ethics on the Ark that zoos primarily “alleviate our sense of guilt for what we are doing to the planet, but they do little to help the animals we are driving to extinction.” He continues to argue that zoos exist for humans alone , and that it is very difficult to wave away the inherent immorality of depriving animals their liberty for the sake of human amusement.
Instead, private conservation programs can benefit endangered animals without showcasing them to the public. Animal sanctuaries, which are areas of land in which endangered and other animals are protected by humans, are also advantageous for both individual animals and global biodiversity .
Zoos do have advantages — fostering curiosity and education chief among them. But experts believe there are other ways of accomplishing these goals without resorting to zoos with tiny enclosures. Excursions, nature documentaries, safaris, local gardens, hikes, boat tours and other ways of interacting with nature don’t involve taking animals out of their natural habitats.
The Bottom Line
If you do choose to visit a zoo, opt for zoos that have certifications from independent animal welfare organizations. If you are interested in animal conservation, you’d be more impactful donating to a non-zoo animal protection organization instead. And if you do want to visit animals, consider an animal sanctuary or an ethical safari, where you can see animals in their native environments.
Independent Journalism Needs You
Björn Jóhann Ólafsson is a science writer and journalist who cares deeply about understanding the natural world and her inhabitants through stories and data. He reports on the environmental footprint of the meat industry, the alternative protein sector and cultural attitudes around food. His previous bylines include the EU Observer and Elemental. He lives in Spain with his two lovebirds.
Beagles Are Bred by the Thousands on Factory Farms, and It’s Perfectly Legal
Justice • 4 min read
More Law & Policy
New Supreme Court Case Threatens Legal Protections for Animals
Law & Policy • 7 min read
‘The Smell of Money’ Film Is Bringing Together Environmental and Food Justice Advocates
A new documentary chronicles the damage hog farm pollution has caused communities of Eastern North Carolina.
Justice • 5 min read
5 Ways Taxpayers Bail Out Factory Farms
The way we produce meat and dairy is responsible for all sorts of damage, and taxpayers end up footing the bill.
Law & Policy • 6 min read
New Climate Research Shows How Plants and Animals Face New Pressures in a Warming World
Climate • 6 min read
Why Plant-Based Burgers at Fast Food Chains Get So… Mushy
Diet • 8 min read
How Much Protein You Need to Be Healthy, Explained
Diet • 10 min read
Fish Feel Pain, Science Shows — But Humans Are Reluctant To Believe It
Science • 9 min read
Most Read Today
How zoos can save our animals

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Ben Minteer

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, travel and tourism.
Today, many zoos promote the protection of biodiversity as a significant part of their mission. As conservation “arks” for endangered species and, increasingly, as leaders in field conservation projects such as the reintroduction of captive-born animals to the wild, they’re preparing to play an even more significant role in the effort to save species in this century .
It’s a task that’s never been more urgent. The recent Living Planet Index report authored by the World Wildlife Fund and the London Zoological Society paints a disturbing picture: globally, on average, vertebrate species populations have declined 52% since 1970. Over-exploitation, habitat destruction and alteration, global climate change, and other pressures have created conditions that scientists now suggest signal a sixth mass extinction episode for our planet. It’s an event rivaling the extinction of the dinosaurs.
The embrace of conservation by zoos, though, doesn’t always sit well with their own history. The modern American zoo that emerged in the late 19th century fancied itself as a center of natural history, education, and conservation, but zoos have also always been in the entertainment business. This priority has led many skeptics to question the idea that zoos can play a helpful conservation role in the coming decades.
Zoos also face a formidable set of practical constraints – namely space, capacity, resources, and in some cases, expertise – that will continue to bedevil their ability to make a dent in the extinction crisis. It’s also true that some of the most endangered animals are not the highly charismatic and exotic species that reliably attract zoo visitors. It’s a challenge that might pit zoos’ conservation priorities against their entertainment goals, and perhaps even their financial bottom line.
At the same time, wildlife protection does run deep in the history of zoos. The Bronx Zoo in New York, for example, led one of the earliest captive breeding and reintroduction efforts, helping to save the American bison from fading into oblivion more than a century ago. In the 1960s and 1970s, zoo conservation was energized by a burst of US federal policy-making focused on endangered species, especially the passage of the Endangered Species Act in 1973.
Many zoos went on to develop Species Survival Plans beginning in the 1980s, which coordinate breeding and population management programs for threatened and endangered animals among zoos worldwide. The goal is to create healthy and genetically diverse animal populations of these species across the zoo community, an effort that can ultimately aid the conservation of the species in the wild.
Reintroduction is a dicey business given the many biological and social factors that determine the viability of a population over time. Zoos’ track records here are mixed – but the successes are real. In addition to the bison, the California condor, the Arabian oryx, and the black-footed ferret have been saved due in part to the efforts of zoos .
For animal rights critics, however, these outcomes don’t offset what is seen as the basic injustice of keeping captive animals for human amusement. Earlier this year, the case of Marius the giraffe in the Copenhagen Zoo reignited the smoldering international debate over the ethics of zoos. A young and healthy giraffe considered a so-called surplus animal by the zoo managers, Marius was shot and his body was dissected before a public audience. The zoo argued that the decision was made on scientific grounds: Marius’s genes were well-represented in the zoo system and so he was said to have no remaining conservation value. Animal advocates countered that zoos’ noble conservation rhetoric masks a callousness toward the well-being of individual animals.
Whatever you think about the Copenhagen case – and it’s worth noting that the American Association of Zoos & Aquariums disagreed with it – debates about the ethics of zoos shouldn’t take place today without a serious discussion of our obligation to address global biodiversity decline. That includes thinking about how we influence the future of animals and ecosystems outside zoo walls with a thousand lifestyle decisions, from our consumer habits and energy consumption, to our transportation choices and what we put on our dinner plates. Take just one example, the mass production of palm oil. Widely used for cooking and commercial food production, its cultivation has resulted in severe habitat destruction and fragmentation in Indonesia. This in turn threatens the survival of orangutans in the wild.
There is a further challenge. As zoos become more engaged in conservation in the coming decades, the natural world will be further pressured and degraded by human activities. In many cases, nature preserves will likely require more human control than they have in the past in order to deliver the same conservation benefits. As a result, the boundary separating nature and zoo, the wild and the walled, will get even thinner . As it does, our understanding of what zoos are and what we want them to be – entertainment destinations, science centers, conservation arks, sustainability leaders – will also change. So will our idealized views of the wild as those places in nature that are independent of meaningful human influence and design.
Saying all this doesn’t let zoos off the hook when it comes to caring properly for animals in their charge. We should also expect them to actually deliver on the swelling conservation rhetoric, especially when their entertainment and recreation interests run up against their expanding vision for biodiversity protection. But it reminds us of the scope of the challenge.
To paraphrase Dr Seuss, we all run the zoo.
Published in collaboration with The Conversation
Author: Ben Minteer is Associate Professor of Environmental Ethics and Conservation at Arizona State University.
Image: Zeff, the Amur tiger at the Bronx Zoo in New York, 2003. REUTERS
Share this:
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Travel and Tourism .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

Turning tourism into development: Mitigating risks and leveraging heritage assets
Abeer Al Akel and Maimunah Mohd Sharif
February 15, 2024

Buses are key to fuelling Indian women's economic success. Here's why
Priya Singh
February 8, 2024

These are the world’s most powerful passports to have in 2024
Thea de Gallier
January 31, 2024

These are the world’s 9 most powerful passports in 2024

South Korea is launching a special visa for K-pop lovers
- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- 2024 election
- TikTok’s fate
- Supreme Court
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
- Animal Welfare
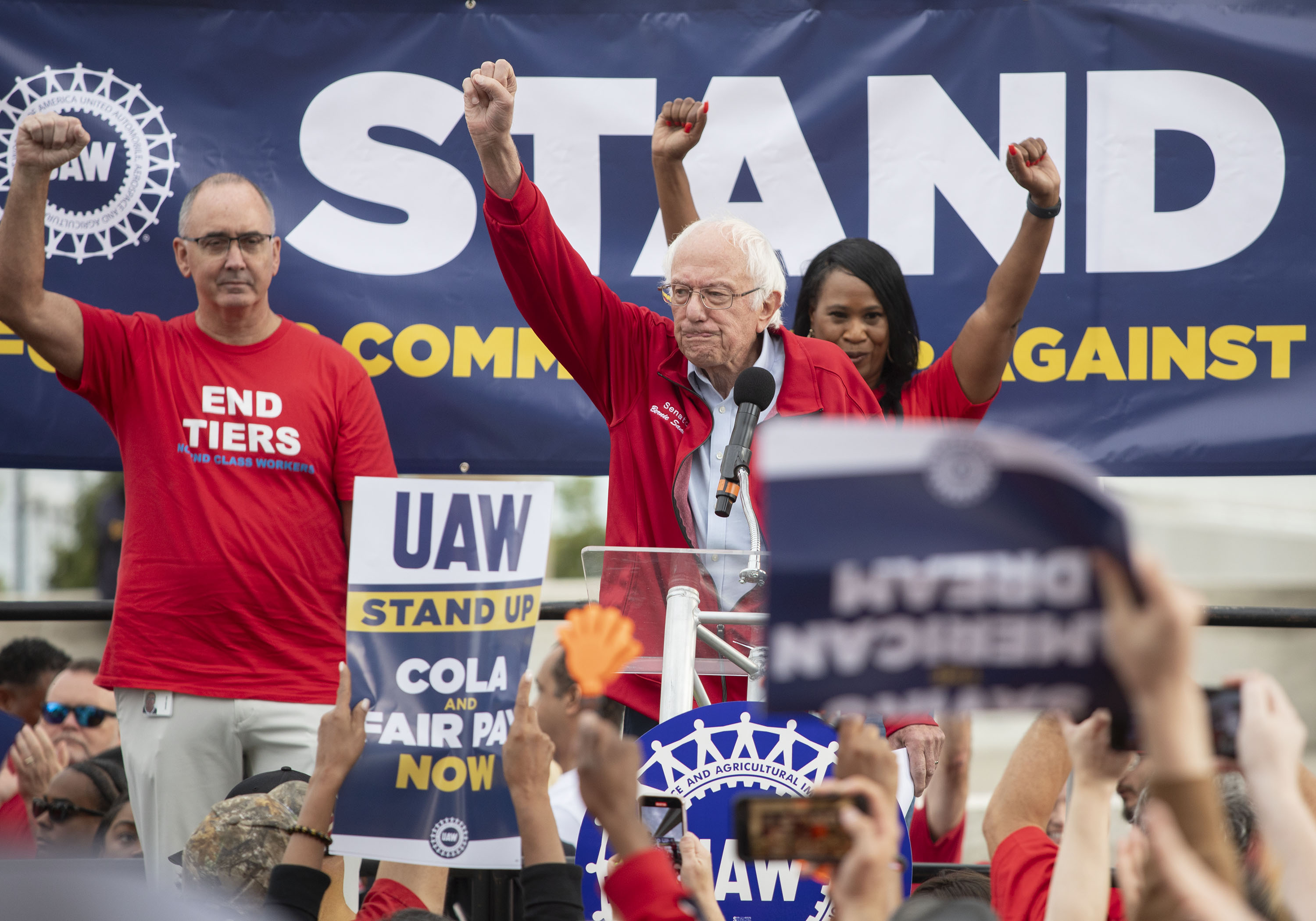
Zoos aren’t for animals. They’re for us.
Zoos say they’re leaders in protecting wildlife. But is it true?
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Zoos aren’t for animals. They’re for us.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/72751402/GettyImages_929335950__1_.0.jpg)
This week, a leading wildlife conservation group declared that zoos play an essential role in protecting wild species from extinction.
“Zoos, aquariums and botanic gardens are critical conservation partners, and their role should not be under-valued, under-recognized or misunderstood,” the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), a nonprofit that’s assessed extinction threat levels for more than 150,000 species, announced in a new position statement . “For anyone who questions the value of zoos in the modern age, IUCN’s position is clear — zoos are essential.”
It’s a bold statement from an authoritative voice on wildlife protection, but is it true? An examination of how zoos spend their money suggests that, despite branding themselves as champions of conservation, they devote far more resources to their main, original prerogative: confining animals for entertainment and profit.
Sign up for the Future Perfect newsletter
Twice a week, we’ll send you a roundup of the best ideas and solutions for tackling the world’s biggest challenges — and how to get better at doing good. Sign up here .
“The way that zoos have been trying to justify their existence for quite a few years now is pointing to conservation,” said Delcianna Winders, director of the Animal Law and Policy Institute at Vermont Law and Graduate School. “But the reality is that it’s really a very small fraction of their funding that is going to field conservation.” (Disclosure: This summer, I attended a media fellowship program at Vermont Law and Graduate School.)
In 2022, most of the 238 zoos and aquariums accredited by the nonprofit Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) spent a collective $252 million on field conservation — efforts to protect and preserve wildlife habitats. That’s serious money for the broader conservation movement.
“That puts them collectively among the world’s largest contributors to conservation,” Daniel Ashe, president and CEO of the AZA, told Vox. However, it’s just 5 percent of how much zoos and aquariums spent on operations and construction alone in 2018.
Similarly, an analysis of scientific papers published by AZA member institutions from 1993 to 2013 found that only 7 percent were related to biodiversity conservation.
Zoos argue that in addition to their conservation efforts in the field, their very existence contributes to species conservation. By breeding animals in captivity, and preserving their genetic material in “ biobanks ,” the argument goes, they’ve created a stock of animals — known as “insurance populations” — who could be released back into nature if wild populations dwindle to alarming levels.
Emma Marris, an environmental writer and author of Wild Souls: Freedom and Flourishing in the Non-Human World , wrote in a 2021 New York Times opinion piece that it’s “as if they might be called upon at any moment to release them, like Noah throwing open the doors to the ark, into a waiting wild habitat. But that day of release never quite seems to come.”
“I’m very skeptical that a lot of these captive breeding programs have any practical relevance to conserving species in their natural habitat, which, in my view, is the point of conservation,” said Mickey Pardo, a behavioral ecologist and postdoctoral research fellow at Colorado State University who studies elephants in the wild. The reason, Pardo says, is because reintroduction stemming from captive breeding programs is incredibly challenging and thus rare , and it’s not the primary goal of most captive breeding programs to begin with.
There are some exceptions , Marris notes, in which zoos have played a starring role in reintroducing threatened and endangered species to the wild, including the California condor, the Arabian oryx, and Black-footed ferrets, among others. Ashe told me zoos have played a role in dozens and dozens of reintroduction programs, though he didn’t have a specific number. It’s important work and should be celebrated, as should zoos’ contributions to field conservation. But, Pardo says, it doesn’t justify AZA-accredited zoos and aquariums keeping wild animals in captivity who are not part of any current reintroduction program nor likely to become part of one in the future.
Currently, AZA-accredited zoos and aquariums have about 780,000 animals .
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24998451/GettyImages_1179068808__1_.jpg)
Kira Mileham, IUCN’s global director of strategic partnerships, disagrees with the argument that field conservation is all that matters. Mileham told Vox captive breeding programs at zoos do more than just create insurance populations, and that they contribute to field conservation by providing opportunities for researchers to learn about species’ behavior, nutrition, veterinary needs, and more. Mileham added that zoos also play an important role in temporary rescue and “ head start ” efforts by, say, taking animals and/or their eggs that are facing a serious, temporary threat out of the wild, and then returning them when it’s safe.
Zoos undeniably do some good work for species conservation; however, that work can obscure their dark side: the suffering of animals in captivity.
Life at the zoo
Animals who, in their natural habitats, would travel great distances are resigned to living in film-set versions of lush rainforests and vast savannas while surrounded by city noise. As a result of the lack of stimulation and small environments, some animals will develop “stereotypic” behavior , in which they engage in repetitive motions that are rare in the wild.
Researchers call it “zoochosis,” a play on “psychosis,” though making enclosures a little nicer and providing “enrichment activities” to animals both help, as do pharmaceutical drugs .
There was Gus, the Central Park Zoo polar bear who would swim figure eights in his pool for sometimes up to 12 hours a day (his enclosure was just 0.00009 percent of his range in the wild), and Sukari , the giraffe at Roger Williams Park Zoo in Providence, Rhode Island, who for hours would lick steel cables, walls, and gates. Other animals pace, rock back and forth, and head-bob, or engage in self-harm, like pulling out their hair or biting themselves. There are many stories of escape attempts.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24998462/GettyImages_97330141.jpg)
Despite it all, AZA-accredited zoos keep acquiring more animals, either from other zoos, breeding them on their own, taking them from the wild (how 80 percent of animals at AZA-accredited aquariums are acquired, Ashe told me), as rescues, or from a number of other sources, such as private breeders and hunting ranches.
Mileham refutes the notion that many zoos are just acquiring animals at the expense of their welfare, however: “I don’t think [leading zoos] kind of flippantly trade off the welfare of species for the sake of having them in their facilities,” she said. And not every welfare matter is black and white, Mileham said. For instance, some animals in zoos might have come from areas with high levels of conflict with humans. “We can’t pretend that an animal in the wild always has a perfect life and has no welfare compromises just because they happen to not be in human care.”
Ashe assured me that “when you see animals at AZA member institutions, you’re seeing animals that are thriving there.” He went on to say, “I understand some people just don’t like the idea of any animal in a state of confinement, and in those cases, we just have a fundamental disagreement.”
When Marris asked Ashe about the constraints of captivity, Ashe largely shrugged the problem away, saying that, well, everyone has constraints put on them: “We are all captive in some regards to social and ethical and religious and other constraints on our life and our activities.”
I asked Ashe about this quote, and he said, “It’s factually true — we all live with constraint in our social life and we agree to constraint so we have social order.” He’s right, of course, that it’s true for humans, but there’s a glaring omission in his response: Animals can’t agree to the constraints we impose on them.
I can’t think of a more dissatisfying answer to the ethical dilemma of putting hundreds of thousands of wild animals behind glass. But it does reveal that the ideology undergirding earlier zoos and aquariums largely persists today — that animals are here for us, not with us.
Zoos: What are they good for?
Zoos justify their existence not just through conservation, but also by their educational work. Their actual impact in that domain, however, is likely minor.
The AZA says one of the “superpowers” of its 238 accredited zoos and aquariums is that they have “the opportunity to influence and inspire the 200 million people who visit every year.” On its face, it makes sense: If everyone could just see the beauty of the animal kingdom up close and learn about the plight of threatened species, they might be inspired to support or get involved in conservation work. Surely, zoos have that effect on some, but there’s no evidence it’s the case for many.
On the contrary , most people don’t read the educational plaques at zoos, and according to polls of zoo-goers, most go to spend time with friends or family — to enjoy themselves and be entertained, not to learn about animals and their needs. One study found the level of environmental concern reported by attendees before they entered the zoo was similar to those who were polled at the exits.
While the educational value of zoos is dubious, there’s certainly one message zoo-goers receive, if only implicitly: That it’s perfectly fine, even good , to put wild animals on display in tiny enclosures for the public’s leisure. In other words, animals — even if they’re suffering right in front of us — can be objects of entertainment.
“It’s rooted in this notion that yes, we have this privileged right to observe these animals at any cost to [them] or to their species more generally, and it’s deeply troubling,” Winders said.
The idea that we must exploit some animals in order to protect others creates a bizarre false choice, even when there are much more humane paths taken by others in the wildlife protection movement, like animal sanctuaries .
What a more humane zoo could look like
Animal sanctuaries are like zoos in that they’re large properties where animals live in captivity, but they differ in every other way. For one, animals in sanctuaries tend to have far more space than animals in zoos, and they’re there to live on their own terms, not to be put on display for an entrance fee. Some sanctuaries are not open to the public, while others conduct small tours or have much smaller attendance numbers than the typical zoo. (Beware, however, that many operations call themselves sanctuaries but in reality are more like petting zoos .)
The Wild Animal Sanctuary, a 45-minute drive from Denver, Colorado, provides a compelling example of how animals can better coexist with visitors. The 1,214-acre operation, home to rescued bears, tigers, lions, wolves, and other species, was closed to the public for its first 20 years. But in the early 2000s, it began to open up to visitors, who can only see the animals from the sanctuary’s observation decks and more than 1.5 miles of elevated walkways, causing less disturbance than zoo-goers.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24998391/Walkway_1.jpg)
Animals typically wind up in sanctuaries — the ethical kind, at least — because they were abandoned or injured, rather than bred, purchased, or taken from the wild. The Global Federation of Animal Sanctuaries, the animal sanctuary world’s equivalent to the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, takes the position that captive breeding is only permitted if it’s done for eventual reintroduction into the wild — unlike zoos, which largely breed animals as insurance populations and to keep a steady supply to put on display.
Some critics have called for zoos to phase out keeping animals from species that aren’t either critically endangered or extinct in the wild, or for which there’s no viable reintroduction program. Additionally, they argue, urban zoos should either close down or set limits on how many animals they keep.
I would add one more thing that zoos — and sanctuaries, for that matter — could do: Stop serving meat and dairy in their cafeterias. There’s the painfully obvious point that an institution whose mission is to protect animals probably shouldn’t sell animal meat . But there’s also this: One-third of Earth’s habitable land is devoted to cattle grazing and growing corn and soy to feed farmed animals, which has resulted in mass habitat loss for wildlife and crashing biodiversity levels. Meat production is the leading cause of global deforestation , and thus the leading threat to wildlife habitats.
Reforming zoos won’t be easy, and arguably, a lot of conservation dollars might vanish if zoos looked different. But it says something about the conservation movement, and us, if one of the best ways to raise funds for wild animals is to put them in captivity. I don’t have the answers for how the conservation movement could supercharge its funding in lieu of the significant amount of funding zoos provide, but I think it’s clear, as Marris puts it, that zoos are not worth the moral cost .
As our understanding of animal sentience and their capacity for suffering has grown, our economy has slowly adapted. Fashion designers are replacing leather and fur with animal-free textiles, meat companies are now selling plant-based nuggets and burgers, and in 2018, the traveling circus Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey announced it would stop using animals, such as lions, tigers, and bears, in its shows. Zoos, too, could reinvent themselves for a more enlightened age by focusing on what animals need, not what the public wants to do on a Saturday afternoon.
Will you help keep Vox free for all?
At Vox, we believe that clarity is power, and that power shouldn’t only be available to those who can afford to pay. That’s why we keep our work free. Millions rely on Vox’s clear, high-quality journalism to understand the forces shaping today’s world. Support our mission and help keep Vox free for all by making a financial contribution to Vox today.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Next Up In Future Perfect
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

Why is there so much lead in American food?

Multigenerational housing is coming back in a big way

You can’t afford to buy a house. Biden knows that.

Want a 32-hour workweek? Give workers more power.

The harrowing “Quiet on Set” allegations, explained

The chaplain who doesn’t believe in God
Search form
Are zoos a good thing.

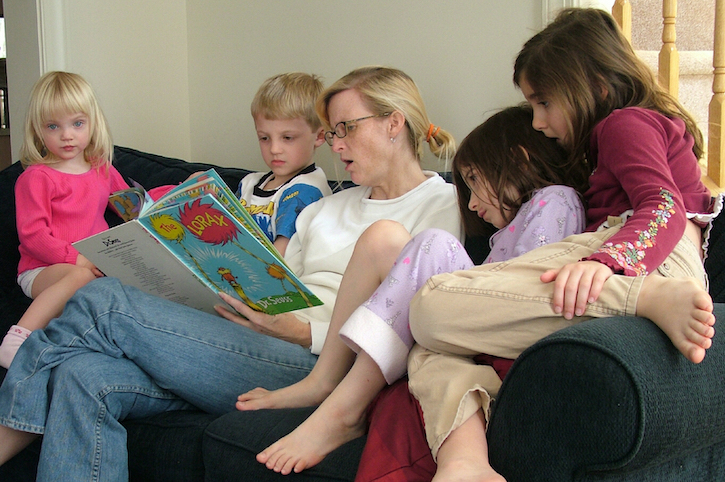
How do you feel about keeping animals in zoos? Read both sides of the argument to help you decide.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then read the text and do the other exercises.
Preparation
Zoos are hugely popular attractions for adults and children alike. But are they actually a good thing?
Critics of zoos would argue that animals often suffer physically and mentally by being enclosed. Even the best artificial environments can't come close to matching the space, diversity, and freedom that animals have in their natural habitats. This deprivation causes many zoo animals to become stressed or mentally ill. Capturing animals in the wild also causes much suffering by splitting up families. Some zoos make animals behave unnaturally: for example, marine parks often force dolphins and whales to perform tricks. These mammals may die decades earlier than their wild relatives, and some even try to commit suicide.
On the other hand, by bringing people and animals together, zoos have the potential to educate the public about conservation issues and inspire people to protect animals and their habitats. Some zoos provide a safe environment for animals which have been mistreated in circuses, or pets which have been abandoned. Zoos also carry out important research into subjects like animal behaviour and how to treat illnesses.
One of the most important modern functions of zoos is supporting international breeding programmes, particularly for endangered species. In the wild, some of the rarest species have difficulty in finding mates and breeding, and they might also be threatened by poachers, loss of their habitat and predators. A good zoo will enable these species to live and breed in a secure environment. In addition, as numbers of some wild species drop, there is an increased danger of populations becoming too genetically similar. Breeding programmes provide a safeguard: zoo-bred animals can be released into the wild to increase genetic diversity.
However, opponents of zoos say that the vast majority of captive breeding programmes do not release animals back into the wild. Surplus animals are sold not only to other zoos but also to circuses or hunting ranches in the US or South Africa, where some people are willing to pay a lot of money for the chance to kill an animal in a fenced enclosure. Often, these animals are familiar with humans and have very little chance of escaping.
So, are zoos good for animals or not? Perhaps it all depends on how well individual zoos are managed, and the benefits of zoos can surely outweigh their harmful effects. However, it is understandable that many people believe imprisoning animals for any reason is simply wrong.
Check your understanding: true or false
Check your vocabulary: gap fill, worksheets and downloads.
What do you think about zoos? Are they a good thing, or is it cruel to keep animals in captivity?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Pros and cons of zoos: Should animals be kept in zoos?

Source: This image was created for netivist.org. If you want to use it you simply need to attribute it by linking to this page or to https://netivist.org . Thanks
Animal cruelty or protection? Learn about the pros and cons of zoos and join our debate and poll: Should there be zoos? Should animals be kept in captivity? Vote and explain your view on whether zoos are necessary or should be banned.
Should animals be kept in zoos?
Over 181 million people visit zoos and aquariums every year in the United States, and 25 million in the United Kingdom. Zoos have more visitors than the combined attendance of the four major sports leagues ( NFL , NBA , MLB and NHL ). Despite their immense popularity , zoos have become increasingly controversial institutions. An increasing number of animal rights advocates and animal protection organizations are questioning the role of zoos in modern societies. The shocking evidence of animal abuse in some circuses , dolphinariums and zoos have pushed many environmental and wildlife activist groups to campaign for the closure of many of the institutions that keep wild animals in captivity.
To the question "should animals be kept in captivity?" the initial reaction of most people is rejection. Why should animals be kept in zoos? In an ideal world that would not be necessary, wild animals would roam freely in their natural habitats and we, humans, would find ways to observe them and learn about them without disrupting their lives. However, today on Earth due to population growth and urbanization many animal species are endangered and most people have very few opportunities to observe and learn from animals.
Jane Goodall , the famous British primatologist and one of the most important experts in chimpanzees in the world, has defended the role of zoos in helping us understand and preserve the life of wild animals (see video below). On the other hand, organizations such as PETA (People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals), Animal Aid and Born Free have initiated campaigns for the closure of zoos, arguing that most zoos deprive animals from their most basic needs and that animal abuse and suffering should not be a source of entertainment.
Do you think that zoos are an effective way to increase awareness about animal life? Do they really help preserve endangered species or it is more a business and a cruel source of entertainment? Is keeping animals in captivity a good way to ensure their future? Let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of zoos before we make up our minds.
Watch this video with Jane Goodall on the role of zoos in saving animals
Pros and cons of zoos
These are the most common arguments in favor and against zoos.
Pros of zoos
- After the famous wildlife conservationist Geral Durrell opened a zoo in Jersey in 1959, zoos all over the world have embraced the mission of saving endangered species in the world. Zoos are not like the exotic animal menageries from the middle ages. They want to provide entertainment but they are greatly concerned with the protection of animals and their natural habitats. Zoos help raising awareness and funding for wildlife initiatives and research projects.
- Animals are not always caged in zoos. Edinburgh was the first British zoo to follow the idea of displaying animals without bars. The Chester and Whipsnade zoological parks where the first two non-urban zoos without cages and larger enclosures. They opened in 1931. In the 1960s The drive-through safari parks became very popular. Ever since there has been an increasing public concern about animal welfare in zoos.
- Zoos are monitored and follow strict regulation in most developed countries. There is less room for animal cruelty in zoos than ever before in history.
- Most people working in zoos are true animal lovers. Veterinary doctors, zoologist, voluntary staff, etc. chose to work in zoos because they like animals, and wanted to work closely with them and help them thrive.
- Education is another positive feature of zoos. Many children and adults in cities can only see wild animals in TV or the Internet. Zoos offer them the unique experience of contemplating real animals. They can smell them, see how they move and listen their sounds. This is a much more vivid and enriching experience than the one you can get through a screen. Thanks to zoos kids and adult develop empathy toward animals.
- Zoos are key for research . Being able to observe and study animals is crucial if we want to contribute to help them and repair the ecosystems. They also help redice human-animal conflicts and better understand the needs and psychology of animals. Zoos serve as laboratories to learn more about how to fight animal diseases and develop effective animal anaesthetics and other treatments to help more animals in the future.
- Another pro of zoos is their role in animal reproduction. Zoos study animal breeding and thanks to them many wild animals in captivity can reproduce. This is particularly important in the case of endangered species. Due to the low density of the population of some animals in their natural ecosystems they struggle to find partners. Some populations in the wild are weakened by endogamy too. In zoos vets and biologist help to prevent inbreeding.
Cons of zoos
- Animal cruelty in zoos continues to be extremely common. There are continuous cases of animals abused by visitors and zoo workers. Many of them are reported every week in the media, however, the large majority are kept secret and those responsible are never held accountable or punished.
- Animals in captivity are deprived of many things that are important to them, as a result they become lonely and bored. Many of them suffer from "zoochosis" , a psychological condition characterized by repetitive and obsessive behaviors including vomiting, excessive grooming, coprophagia and self-mutilation.
- Most animals in zoos still live in small enclosures and cages . There are Safari Parks and large zoos in which animals have more space and live in an enviroment slightly more similar to their natural habitat .however, the large majority of zoos in the world are much smaller and have less economic means than the big zoos we often see in the media such as the San Diego Zoo, the Berlin Zoological Garden, the San Louis Zoo, etc.
- In zoos many animals sicken and die because they contract diseases from other animals and species. Zoos usually group animals from many different parts of the world with very distinct immunological systems. People also have been sickened from diseases contracted from animals in zoos.
- Many zoos do little for research or animal protection. They are simply businesses run with the sole purpose of making money . Their concern for animals is secondary. Cost efficiency often means they move animal welfare down in the list of priorities.
- Zoos and aquariums have incentivized the illegal hunt of animals . Historically poachers have hunted and sold wild animals for zoos all over the world. Although this practice is increasingly prosecuted in most countries, there are still small zoos and aquariums which acquire their animals without paying much attention to their origin.
- From an ethical point of view zoos are also questionable. Zoos are a typical form of family entertainment, but associating leisure and fun with the contemplation of animals in captivity can send the wrong signals to our children. Zoos can be construed as a sadistic pleasure .
Do you think zoos are necessary? Do the cons of zoos outweight their benefits? Should we boycott or ban zoos? Vote and join our debate (see below)
Watch this video on "zoochosis" and the living conditions of animals in captivity
Vote to see result and collect 1 XP. Your vote is anonymous. If you change your mind, you can change your vote simply by clicking on another option.
Voting results
New to netivist?
Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free. You will not receive any promotional materials from third parties.
Or sign in with your favourite Social Network:
Join the debate
In order to join the debate you must be logged in.
Already have an account on netivist? Just login . New to netivist? Create your account for free .
Report Abuse and Offensive language
Was there any kind of offensive or inappropriate language used in this comment.
If you feel this user's conduct is unappropriate, please report this comment and our moderaters will review its content and deal with this matter as soon as possible.
NOTE: Your account might be penalized should we not find any wrongdoing by this user. Only use this feature if you are certain this user has infringed netivist's Terms of Service .
Our moderators will now review this comment and act accordingly. If it contains abusive or inappropriate language its author will be penalized.
Posting Comment
Your comment is being posted. This might take a few seconds, please wait.
Error Posting Comment
error.
We are having trouble saving your comment. Please try again .
Most Voted Debates
Start a Debate
Would you like to create a debate and share it with the netivist community? We will help you do it!
Found a technical issue?

Are you experiencing any technical problem with netivist? Please let us know!
Help netivist
Help netivist continue running free!
Please consider making a small donation today. This will allow us to keep netivist alive and available to a wide audience and to keep on introducing new debates and features to improve your experience.

- What is netivist?
- Entertainment
- Top Debates
- Top Campaigns
- Provide Feedback

Follow us on social media:

Share by Email
There was an error...
Email successfully sent to:

Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free You will not recive any promotional materials from third parties
Join netivist
Already have a netivist account?
If you already created your netivist account, please log in using the button below.
If you are new to netivist, please create your account for free and start collecting your netivist points!
You just leveled up!
Congrats you just reached a new level on Netivist. Keep up the good work.


Together we can make a difference
Follow us and don't miss out on the latest debates!
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer
Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?
Please try again

Update: Our award-winning video series Above the Noise took a fresh look at the pros and cons of zoos. Students can watch the video to get a primer on the facts then write their own responses on KQED Learn.
This post is part of KQED’s Do Now U project. Do Now U is a weekly activity for students and the public to engage and respond to current issues using social media. Do Now U aims to build civic engagement and digital literacy for learners of all ages. This post was written by Sophia Buscher and Victoria Staudenraus , students at St. Mary’s College of California , in partnership with the Lindsay Wildlife Experience .
Featured Media Resource: VIDEO: Zoo Conservation Raise Debate (CNN) Hear opposing thoughts from a field biologist at the University of York and the president of the Born Free Foundation about keeping animals in zoos for conservation purposes.
Do you think animals should be kept in zoos? #DoNowUZoo
How to Do Now
To respond to the Do Now U, you can comment below or post your response on Twitter. Just be sure to include #DoNowUZoo and @KQEDedspace in your posts.
Learn More about Animals in Zoos
Although wild animals have been held captive for thousands of years, the first modern zoo opened in 1763 in Paris, France. As people became more interested in science and natural history, zoos served as a way to display and study animals. Today, zoos provide opportunities for public education and entertainment, as well as scientific research and conservation. There are about 2,800 licensed animal exhibitors throughout the U.S., which include zoos, circuses, petting farms, wildlife and marine mammal parks, and some sanctuaries. Out of these, 233 are accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA). The AZA “ holds animal exhibitors to high standards of animal care, science and conservation ” in the United States and all over the world. Even though many animal exhibitors are still considered zoos, they have not met the requirements of the AZA and, therefore, have not been accredited.
Proponents of zoos point to the fact that they educate the general public, are beneficial for scientific research, and work toward conservation efforts and captive breeding. At the San Francisco Zoo, there are educational programs for children ages 1-17. From camps, to mobile programs that bring smaller animals to schools, to family activities that look at local wildlife near the zoo, the public is able to get hands-on education about animals they may not be able to meet and learn about otherwise. The Lindsay Wildlife Experience in Walnut Creek, California, offers similar experiences to connect locals with wildlife and educate people on how they can do small things to help benefit wildlife in urban areas. Zoos can also be beneficial for scientific research. Studies are sometimes better able to be completed in zoos because of the controlled environment of a zoo. Lastly, zoos help endangered populations by using captive breeding and release. The AZA’s Species Survival Plan Program is a long-term plan that incorporates conservation breeding, preservation of habitat, education and research to support the survival of threatened and endangered species. Many zoos also work on local conservation efforts to maintain local wildlife populations.
On the other hand, many would say that wild animals should not be held in captivity. It has been argued that captive breeding isn’t always effective, zoos do not provide natural habitats, and that zoos put unnecessary stress on animals. Some studies have shown that reintroduced animals have high mortality rates because they are poorly adapted and lack the skills needed to survive in the wild. Since an animal’s well-being is dependent on their environment, some contend that zoos do not provide healthy habitats for animals. Enclosures–even when designed to mimic an animal’s natural habitat–are still not really natural. And, zoos can’t really provide the space that large or wide-ranging animals, like elephants, are used to. Due in part to unnatural enclosures, animals in zoos are under stress . Animals are often bored and, as a result, some become aggressive and can lash out at other animals or zookeepers. In a study done on 40 chimpanzees in six different zoos, all of the chimps exhibited behavior their counterparts in nature did not. Some of these behaviors included rocking back and forth, tearing out their hair, self-mutilation, and the drinking of their urine. This behavior is not seen in their wild counterparts suggesting that being in the zoo is causing these chimps to develop mental illness due to stress.
What do you think? Should animals be kept in zoos? Why or why not?
More Resources
Video: DNews The Pros & Cons of Zoos Hear about some of the benefits zoos and some of negative effects that they have on animals.
Video: BBC Horizon: Should We Close Our Zoos? This clip briefly examines the history of zoos, and questions experts and professionals about keeping animals in small enclosures.
Audio: WNYC A Passionate Call to Leave Animals Alone and Zoos Behind Not everyone enjoys their visit to the zoo. Hear why Tim Zimmerman believes we should reconsider our arguments for keeping zoos open. He offers an alternative to traditional zoos that can make both animals and human visitors happy.
Article: The Washington Post At Zoos, Not Every Resident is a Spring Chicken From protecting elderly animals to preserving endangered species, read more about the benefits of holding animals in captivity.
Find best practices for using Do Now, using Twitter for teaching , and using other digital tools .
KQED Do Now U is a bi-weekly activity in collaboration with SENCER . SENCER is a community of transformation that consists of educators and administrators in the higher and informal education sectors. SENCER aims to create an intelligent, educated, and empowered citizenry through advancing knowledge in the STEM fields and beyond. SENCER courses show students the direct connections between subject content and the real world issues they care about, and invite students to use these connections to solve today’s most pressing problems.
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.
April 15, 2009
How Do Zoos Help Endangered Animals?
There are more to zoos than putting animals on display
Dear EarthTalk: Do zoos have serious programs to save endangered species, besides putting a few captives on display for everyone to see? -- Kelly Traw, Seattle, WA
Most zoos are not only great places to get up close to wildlife, but many are also doing their part to bolster dwindling populations of animals still living free in the wild. To wit, dozens of zoos across North America participate in the Association of Zoos and Aquarium’s (AZA’s) Species Survival Plan (SSP) Program, which aims to manage the breeding of specific endangered species in order to help maintain healthy and self-sustaining populations that are both genetically diverse and demographically stable.
The end goal of many SSPs is the reintroduction of captive-raised endangered species into their native wild habitats. According to the AZA, SSPs and related programs have helped bring black-footed ferrets, California condors, red wolves and several other endangered species back from the brink of extinction over the last three decades. Zoos also use SSPs as research tools to better understand wildlife biology and population dynamics, and to raise awareness and funds to support field projects and habitat protection for specific species. AZA now administers some 113 different SSPs covering 181 individual species.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
To be selected as the focus of an SSP, a species must be endangered or threatened in the wild. Also, many SSP species are “flagship species,” meaning that they are well-known to people and engender strong feelings for their preservation and the protection of their habitat. The AZA approves new SSP programs if various internal advisory committees deem the species in question to be needy of the help and if sufficient numbers of researchers at various zoos or aquariums can dedicate time and resources to the cause.
AZA’s Maryland-based Conservation and Science Department administers the worldwide SSP program, generating master plans for specific species and coordinating research, transfer and reintroductions. Part of this process involves designing a “family tree” of particular managed populations in order to achieve maximum genetic diversity and demographic stability. AZA also makes breeding and other management recommendations with consideration given to the logistics and feasibility of transfers between institutions as well as maintenance of natural social groupings. In some cases, master plans may recommend not to breed specific animals, so as to avoid having captive populations outgrow available holding spaces.
While success stories abound, most wildlife biologists consider SSP programs to be works in progress. AZA zoos have been instrumental, for instance, in establishing a stable population of bongos, a threatened forest antelope native to Africa, through captive breeding programs under the SSP program. Many of these captive-bred bongos have subsequently been released into the wild and have helped bolster dwindling population numbers accordingly.
Of course, for every success story there are dozens of other examples where results have been less satisfying . SSP programs for lowland gorillas, Andean condors, giant pandas and snow leopards, among others, have not had such clear success, but remain part of the larger conservation picture for the species in question and the regions they inhabit.
CONTACTS : AZA’s Conservation & Science Program, www.aza.org/Conscience .
EarthTalk is produced by E/The Environmental Magazine. SEND YOUR ENVIRONMENTAL QUESTIONS TO: EarthTalk , P.O. Box 5098, Westport, CT 06881; [email protected] . Read past columns at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalk/archives.php . EarthTalk is now a book! Details and order information at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalkbook .
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- Find Student Housing
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
In this IELTS Zoo Essay you have to discuss whether you think zoos are cruel and should be shut down or whether they are useful as they protect some wild animals.
Essays on zoos have appeared in the IELTS test before and this was a question that was recently in the test.
Some people think that zoos are all cruel and should be closed down. Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals.
Discuss both opinions and give your own opinion.
Understanding the Question
You must always read the question carefully and note if there is anything restricting the topic.
You have to discuss both sides of the argument and with this zoo essay question it would be very easy to read it and then simply write about the benefits and drawbacks of zoos.
But look at this bit carefully:
- Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals .
One of the arguments is specifically about protecting animals. So when you discuss the second argument you must be careful not to just write generally about the advantage of zoos.
You have to focus on how they may protect wild animals . So when you brainstorm your ideas for the zoo essay, you should be thinking about:
- why animals need protecting and
- how zoos can help with this

And in your other body paragraph you would need to explain why they are also seen as cruel.
And of course you must remember to give your own opinion. In this essay, the author makes it clear at the beginning that they support the closing down of zoos.
The opinion you decide on though is of course your choice.
Zoo Essay Sample
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Zoo Essay Model Answer
Zoos remain popular places for people to visit for entertainment and to learn about wild animals. Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals and so should be kept open, I believe that the cruelty that animals suffer outweighs this benefit, and that they should be shut down.
These days, animals are under threat from humans in many ways, seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed through the cutting down of rain forests, or through poaching. Following on from this, the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals that are under threat. The reason is that they are in a safe environment managed by trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after and can produce offspring. There are examples of successes in this respect, such as with Pandas, which have been endangered for many years but have been protected.
However, there are more convincing arguments for why zoos should be shut down. Firstly, even though some species are under threat, there are lots of animals which do not fall into this category and who are there just for the entertainment of visitors. While it may be fun and educational to see them, animals are not meant to be caged, and their distress can often be seen in the way many of them pace back and forwards all day. Not only this, if the prime reason of zoos is to protect animals, this could be done in other environments such as wild life parks where the animals have more freedom.
In conclusion, animals should be protected but this does not have to be in zoos. Zoos are cruel to animals, not similar enough to their natural habitat, and they should be closed down.
(299 Words)
Band scores are given for task response, coherence and cohesion, lexis (vocabulary) and grammatical range and accuracy.
This zoo essay would get a good score for task response as it fully answers the question by discussing both opinions and giving a personal opinion. Ideas are also well explained, extended and supported.

It would get a good score for coherence and cohesion as it is organised coherently and logically and is easy to follow. The introduction introduces the topic then there is a thesis statement.
One body paragraph discusses one side of the argument, and the other discusses the other side. The second body paragraph is also the writers opinion, and this is summarised again in the conclusion
.There is some interesting vocabulary and phrases. For example:
- sanctuary for endangered animals
- under threat from humans
- habitats are being destroyed
- produce offspring
- successes in this respect
- not meant to be caged
- natural habitat
There are also some good complex grammatical constructions and the grammar is precise. For example, the red words show that some of these are adverbial clauses , noun clauses and relative clauses :
- Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals...
- ...seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed...
- ...the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals who are under threat.
- ...trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after...
- Pandas who have been endangered...
- ... even though some species are under threat...
- ... While it may be fun and educational...
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Discuss Two Opinion Essays:

Formal and Informal Education Essay: What age should it start?
This formal and informal education essay is about whether it is best for children to begin their formal education at school when they are 7 rather than much younger.

Childcare Essay: Should family or carers look after young children?
Childcare Essay: In the essay you have to discuss two sides of an argument. The first is that it is better if pre-school children are looked after at home with relatives such as grandparents. The second opinion is that children should be looked after at childcare centres.

Animal Rights Essay: Should animals be exploited for humans?
Animal Rights Essay for IELTS: Learn how to write an essay where you have to discuss two opinions. People who believe in animal rights think that they should not be treated cruelly, for example in experiments or for sport.

IELTS Writing Example: What are the aims of a university education?
IELTS writing example essays. This is an essay on the aims of university education. In this essay, two opposing opinions need to be discussed. It is important to understand how to answer this type of question in the IELTS exam.

Extraterrestrial Life Essay: Should we look for life on other planets?
This extraterrestrial life essay is an IELTS opinion essay where you have to discuss both sides of an issue then give your own opinion.

IELTS Essay Becoming Independent
This IELTS essay discussed whether people are becoming more independent than they were in the past. This is a question that has come up a few times in the test. This is discussion type essay as you have to discuss both sides of an argument and come to a conclusion.

Child Development Essay: What factors influence a child's development?
Child Development Essay for IELTS. The essay is about the factors that affect the way that children develop. It provides you with a model answer and comments on the response to help you know how to improve your band score.
Sources for Stories Essay: Should parents read to their children?
This sources for stories essay asks for your opinion on the best way for children to get stories. Is it from parents reading to them or other ways?

IELTS Essays: What is the best way to reduce crime?
IELTS essays online with comments by an IELTS instructor - A writing sample on the topic of reducing crime.

Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay
Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay- Model answer for IELTS. Who has had the most influence on our world? In this essay you have to discuss both sides.

Diet and Health Essay: Who is responsible for diet and health?
Diet and Health Essay for IELTS: This model examines the extent to which individuals or governments should be responsible for health. Read a model answer and useful comments about the essay which will help you to improve your IELTS Score.

Donating Money to Charity Essay: Where should the money go?
Donating Money to Charity Essay: IELTS model answer to an essay on the topic of giving locally or to national and international charities.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Student Housing
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
Alternatives to the IELTS Exam
Mar 22, 24 12:32 PM
Common Questions about the IELTS Speaking Test
Mar 09, 24 05:28 AM
IELTS Computer Delivered Practice Tests Plus Band Score
Mar 01, 24 02:38 AM

Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
Are Zoos Ethical? Arguments for and Against Keeping Animals in Zoos
Zoos, if done right, could be a good thing for the animals and the public—yet many so-called zoos get it terribly wrong.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dorislin2-77cc0f7bb4a34be3ba4644a99f6e6a89.jpeg)
- University of Southern California
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Betsy-Petrick-4x5-70cf94b5a1934c9199bddce1f2457f37.jpg)
- Ohio Wesleyan University
- Brandeis University
- Northeastern University
- Animal Rights
- Endangered Species
A Brief History of Zoos
Arguments for zoos, arguments against zoos, the last word on zoos.
A zoo is a place where captive animals are put on display for humans to see. While early zoos (shortened from zoological parks) concentrated on displaying as many unusual creatures as possible—often in small, cramped conditions—the focus of most modern zoos is conservation and education. While zoo advocates and conservationists argue that zoos save endangered species and educate the public, many animal rights activists believe the cost of confining animals outweighs the benefits, and that the violation of the rights of individual animals—even in efforts to fend off extinction—cannot be justified.
Humans have kept wild animals for thousands of years. The first efforts to keep wild animals for non-utilitarian uses began about 2500 BCE, when rulers in Mesopotamia, Egypt kept collections in enclosed pens. Modern zoos began to evolve during the 18th century and the Age of Enlightenment, when scientific interest in zoology, as well as the study of animal behavior and anatomy, came to the fore.
Early zoos were a dismal affair. Animals were kept in small enclosures with little if any, greenery. With a scant understanding of what the various animals needed, many perished relatively quickly. In accredited U.S. zoos (and elsewhere) things are better now, fortunately. Primates, for example, have gone from barren cages with little furniture to naturalistic and sometimes semi-free-ranging designs. But is it enough?
- By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species.
- Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe environment, where they are protected from poachers, habitat loss, starvation, and predators.
- Many zoos have breeding programs for endangered species. In the wild, these individuals might have trouble finding mates and breeding, and species could become extinct.
- Some zoos have conservation programs around the world that use the zoo's expertise and funding to help protect wildlife against poaching and other threats.
- Reputable zoos accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums are held to high standards for the treatment of their resident animals. According to AZA, its accreditation guarantees that the organization has undergone strict evaluation by recognized experts to ensure the highest standards of "animal management and care, including living environments, social groupings, health, and nutrition."
- A good zoo provides an enriched habitat in which the animals are never bored, are well cared for, and have plenty of space.
- Seeing an animal in person is a much more personal and more memorable experience than seeing that animal in a nature documentary and is more likely to foster an empathetic attitude toward animals.
- Some zoos help rehabilitate wildlife and take in exotic pets that people no longer want or are no longer able to care for.
- Both accredited and unaccredited animal exhibitors are regulated by the federal Animal Welfare Act, which establishes standards for animal care.
- From an animal rights standpoint, humans do not have a right to breed, capture, and confine other animals— even if those species are endangered . Being a member of an endangered species doesn't mean the individual animals should be afforded fewer rights.
- Animals in captivity suffer from boredom, stress, and confinement. No pen—no matter how humane—or drive-through safari can compare to the freedom of the wild.
- Intergenerational bonds are broken when individuals are sold or traded to other zoos.
- Baby animals bring in visitors and money, but this incentive to breed new baby animals leads to overpopulation. Surplus animals are sold not only to other zoos, but also to circuses and hunting facilities. Some zoos simply kill their surplus animals outright.
- Some captive breeding programs do not release animals back into the wild. The offspring may be forever part of the chain of zoos, circuses, and petting zoos.
- Removing individual specimens from the wild further endangers the wild population because the remaining individuals will be less genetically diverse and may have greater difficulty finding mates. Maintaining species diversity within captive breeding facilities is also a challenge.
- If people want to see wild animals in real life, they can observe wildlife in the wild or visit a sanctuary. (A true sanctuary does not buy, sell, or breed animals, but instead takes in unwanted exotic pets, surplus animals from zoos, or injured wildlife that can no longer survive in the wild.)
- The federal Animal Welfare Act establishes only the most minimal standards for cage size, shelter, health care, ventilation, fencing, food, and water. For example, enclosures must provide "sufficient space to allow each animal to make normal postural and social adjustments with adequate freedom of movement. Inadequate space may be indicated by evidence of malnutrition, poor condition, debility, stress, or abnormal behavior patterns." Violations often result in a slap on the wrist and the exhibitor is given a deadline to correct the violation. Even a long history of inadequate care and AWA violations, such as the history of Tony the Truck Stop Tiger, does not necessarily ensure abused animals will be freed.
- Animals sometimes escape their enclosures, endangering themselves as well as people. Likewise, people ignore warnings or accidentally get too close to animals, leading to horrific outcomes. For example, Harambe, a 17-year-old western lowland gorilla, was shot in 2016 when a toddler accidentally fell into his enclosure at the Cincinnati Zoo. While the child survived and was not badly injured, the gorilla was killed outright.
- Petting zoos have been linked with numerous incidents of diseases including E. coli infection, cryptosporidiosis, salmonellosis, and dermatomycosis (ringworm).
In making a case for or against zoos, both sides argue that they're saving animals. Whether or not zoos benefit the animal community, they certainly do make money. As long as there is demand for them, zoos will continue to exist.
Since zoos are likely an inevitability, the best way to move forward is to ensure that zoo conditions are the best possible for the animals that live in captivity and that individuals who violate animal care health and safety sanctions are not only duly punished but denied any future access to animals.
One day we may look back at zoos and marvel at their barbarity. Or, one day we may look back at zoos and be grateful for the species they saved from extinction. Of these two scenarios, only time will tell.
Hosey, Geoff, et al. Zoo Animals: Behaviour, Management, and Welfare . Oxford University Press. 2013.
Hosey, G. (2023). The History of Primates in Zoos . In: Robinson, L.M., Weiss, A. (eds) Nonhuman Primate Welfare. Springer, Cham.
“ Species Survival Plan Programs .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums.
“ Accreditation Basics .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums .
“ Animal Welfare Act and Animal Welfare Regulations .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Meagher, Rebecca K., Georgia J. Mason. “ Environmental Enrichment Reduces Signs of Boredom in Caged Mink .” PLoS ONE , vol. 7, 2012, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049180
Kleiman, Devra G., et al. Wild Mammals In Captivity: Principles And Techniques For Zoo Management, Second Edition . University of Chicago Press. 2010.
Gunasekera, Crystal Allen. “ The Ethics of Killing “Surplus” Zoo Animals .” Journal of Animal Ethics , vol. 8, 2018, doi:10.5406/janimalethics.8.1.0093
Brichieri-Colombi, Typhenn A., et al. “ Limited Contributions of Released Animals from Zoos to North American Conservation Translocations .” Conservation Biology , vol. 33, 2019, pp. 33-39., doi:10.1111/cobi.13160
Krasnec, Michelle O., et al. “ Mating Systems in Sexual Animals .” Nature Education Knowledge, vol. 3, no. 10, 2012, p. 72.
“ 9 CFR § 3.128 - Space Requirements .” Cornell University Legal Information Institute .
“ Animal Welfare Act Enforcement .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Conrad, Cheyenne C. Conrad et al. " Farm Fairs and Petting Zoos: A Review of Animal Contact as a Source of Zoonotic Enteric Disease ." Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, vol. 14, 2017, pp. 59-73., doi:10.1089/fpd.2016.2185
- How Animal Rights Activists View Zoos Keeping Endangered Species
- Zoos and Endangered Species Conservation
- What's Wrong With Aquariums?
- What's the Difference Between a Zoo and a Sanctuary?
- Animal Cruelty in Circuses
- What Will Happen to the Animals If Everyone Goes Vegan
- Pet Tiger Seen Roaming in Houston Is Now in a Sanctuary
- Expedia Stops Selling Tickets to Dolphin and Whale Shows
- 10 Women Who Changed the Way We See Nature
- Responses to Top Arguments Against Animal Rights
- 8 Fascinating Facts About the Axolotl
- Rescuer Saves and Rehabs Hundreds of Wild Animals in Peru
- 18 Famous Animal Conservationists
- Why Animal Rights Activists Are Against the AKC
- 9 Uncanny Facts About Crows
- 8 Things You Didn't Know About Boa Constrictors
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
Are Zoos Immoral?
A guest opinion essay argues that modern zoos are harmful to the health and well-being of animals. Do you agree? Is it time to rethink the zoo, and perhaps even end them?

By Jeremy Engle
Do you like going to the zoo? Do you have a favorite?
Have you ever stopped to consider the possible harmful effects zoos might have on the animals?
In “ Modern Zoos Are Not Worth the Moral Cost ,” Emma Marris, an environmental writer, asks the reader to reconsider the value of zoos and the effects of captivity on the animals we visit:
After being captives of the pandemic for more than a year, we have begun experiencing the pleasures of simple outings: dining al fresco, shopping with a friend, taking a stroll through the zoo. As we snap a selfie by the sea lions for the first time in so long, it seems worth asking, after our collective ordeal, whether our pleasure in seeing wild animals up close is worth the price of their captivity. Throughout history, men have accumulated large and fierce animals to advertise their might and prestige. Power-mad men from Henry III to Saddam Hussein’s son Uday to the drug kingpin Pablo Escobar to Charlemagne all tried to underscore their strength by keeping terrifying beasts captive. William Randolph Hearst created his own private zoo with lions, tigers, leopards and more at Hearst Castle. It is these boastful collections of animals, these autocratic menageries, from which the modern zoo, with its didactic plaques and $15 hot dogs, springs.
Ms. Marris describes how the “educational day out” model of zoos endured until the late 20th century, when zoos began actively rebranding themselves as serious contributors to conservation, functioning as “ambassadors” for their species and teaching humans to care about wildlife.
However, she writes, while species such as the Arabian oryx, the California condor and Black-footed ferrets were saved from extinction by the concerted efforts of zoos, these popular public institutions remain largely about entertainment and family outings:
A fine day out with the family might itself be justification enough for the existence of zoos if the zoo animals are all happy to be there. Alas, there’s plenty of heartbreaking evidence that many are not. In many modern zoos, animals are well cared for, healthy and probably, for many species, content. Zookeepers are not mustache-twirling villains. They are kind people, bonded to their charges and immersed in the culture of the zoo, in which they are the good guys. But many animals clearly show us that they do not enjoy captivity. When confined they rock, pull their hair and engage in other tics. Captive tigers pace back and forth, and in a 2014 study, researchers found that “the time devoted to pacing by a species in captivity is best predicted by the daily distances traveled in nature by the wild specimens.” It is almost as if they feel driven to patrol their territory, to hunt, to move, to walk a certain number of steps, as if they have a Fitbit in their brains. The researchers divided the odd behaviors of captive animals into two categories: “impulsive/compulsive behaviors,” including coprophagy (eating feces), regurgitation, self-biting and mutilation, exaggerated aggressiveness and infanticide, and “stereotypies,” which are endlessly repeated movements. Elephants bob their heads over and over. Chimps pull out their own hair. Giraffes endlessly flick their tongues. Bears and cats pace. Some studies have shown that as many as 80 percent of zoo carnivores, 64 percent of zoo chimps and 85 percent of zoo elephants have displayed compulsive behaviors or stereotypies. Elephants are particularly unhappy in zoos, given their great size, social nature and cognitive complexity. Many suffer from arthritis and other joint problems from standing on hard surfaces; elephants kept alone become desperately lonely; and all zoo elephants suffer mentally from being cooped up in tiny yards while their free-ranging cousins walk up to 50 miles a day. Zoo elephants tend to die young. At least 20 zoos in the United States have already ended their elephant exhibits in part because of ethical concerns about keeping the species captive.
Ms. Marris concludes her essay with some ways to reimagine and transform the zoo:
What if zoos stopped breeding all their animals, with the possible exception of any endangered species with a real chance of being released back into the wild? What if they sent all the animals that need really large areas or lots of freedom and socialization to refuges? With their apes, elephants, big cats, and other large and smart species gone, they could expand enclosures for the rest of the animals, concentrating on keeping them lavishly happy until their natural deaths. Eventually, the only animals on display would be a few ancient holdovers from the old menageries, animals in active conservation breeding programs and perhaps a few rescues. Such zoos might even be merged with sanctuaries, places that take wild animals that because of injury or a lifetime of captivity cannot live in the wild. Existing refuges often do allow visitors, but their facilities are really arranged for the animals, not for the people. These refuge-zoos could become places where animals live. Display would be incidental.
Students, read the entire article , then tell us:
Do you like going to the zoo? Do you have a favorite one? Tell us about a memorable experience you had at a zoo.
What impact have zoos had on you? Have they helped you to develop what some zoos call a “conservation ethic?” Do you look at the animals with a “sense of empathy for the individual animal, as well as the wild populations of that animal,” as Dan Ashe, a former director of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hopes? Have zoos made you care more about conservation or take any action to support it?
What is your reaction to Ms. Marris’s essay? Which details on the harmful effects of captivity on animals, such as the physical and emotional toll on elephants, stand out? What do they make you think or feel?
How persuasive is Ms. Marris’s argument? Are zoos immoral or wrong? Is our pleasure in seeing wild animals up close worth the price of their captivity? What do you see as the benefits and harms of zoos, both for the human visitors and the animals who live in them?
What do you think of Ms. Marris’s recommendations for transforming the zoo? Do you think her idea of the “refuge-zoo,” a place where animals live and displays are incidental, is a good one? What other ideas do you have to improve or reform the modern zoo?
Do you think you will visit zoos in the future? Why or why not?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides
Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos (Argumentative Essay)
Should animals be kept in zoos.
The debate of whether or not confining of animals is right in zoos is a popular one that attracts both opponents and proponents. The increased interests in science and natural history saw the introduction of zoos in 1763, which facilitated up close animal studies and would provide a chance for entertaining and educating the public. Nevertheless, confining the animals into small spaces in unnatural habitats, the constant staring from people and loss of their freedom makes zoos the worst homes for animals.
Zoos provide unnatural habitats for the animals. Animals are naturally born and bred to live and die in wilderness habitats. However, despite the numerous efforts and good intentions by zoo management, it is impossible to provide the perfect environment for various animals. For instance, animals like the wilder beasts live in groups that migrate over long distances while elephants on average walk for over 50 km a day in packs. However, zoos can only provide minimal acres of land for the animals to walk about thereby making the environments unnatural and uncomfortable for the animals.
Zoos are a premise of captivity for animals that makes them crazy. Imprisoning of animals in small cages housed in poorly managed zoos that fail to meet the necessary standards, averts them from behaving naturally. As a result, suffer from zoochosis condition, which elicits stress, strange behavior of hurting themselves due to frustration and boredom; they become inactive and increasingly pace around. Moreover, the animals adopt aggressive behavior that results in them lashing out and injuring or killing people.
Zoos are not educational. Zoos operate on the premise that they provide an opportunity for the public to learn about animals. However, this is untrue, as keeping animals in confined and unnatural environments tend to alter their natural behavior, character, and responses. Thus, persons visiting the zoos observe the altered behavior marred by boredom, stress, and loneliness. Moreover, keeping animals in zoos teach people that it is okay to lock up and make animals miserable for their personal gain. Therefore, by gaining pleasure and entertainment from making animals suffer is a horrible lesson to learn.
Proponents of keeping animals in zoos argue that zoos offer the best forms of protection for animals. According to them, animals receive protection from poaching and predators that are out to kill them. Additionally, by engaging in breeding programs, zoos believe they protect various species from becoming extinct, therefore, making them positive institutions to exist. However, this is untrue as some zoos keep the animals in deplorable environments whey they lack food and adequate medical care. Moreover, based on research, endangered animals living in zoos are only about five species and only a few species undergo breeding.
Proponents also believe that zoos provide the opportunity for people to see a wide array of animals while benefiting children with lessons about the environment and animals. Nevertheless, this is not the case as zoos only house few species of animals as compared to those an individual can observe in the wild. Also, zoos expose animals to neglect and stress that alter their behavior hence impeding true learning for children.
In conclusion, animals just as humans enjoy rights to freedom, protection from abuse, stress, neglect and lack of privacy. There is no denying that zoo violates all these rights by introducing them to unnatural habitats and caging the animals. Hence, in promoting health and happiness of the animals, animals should not be kept in zoos.
Our academic writers are animal lovers, so you can trust them and buy essay papers about animals in our essay writing service.

The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals Essay
Introduction, stress and boredom, no right to protection and safety, ‘surplus’ animals, works cited.
Albert Einstein once said: “Our task must be to free ourselves by widening our circle of compassion to embrace all living creatures and the whole of nature and its beauty” (Popova). This statement may be understood if one considers people’s usual efforts to support animals and nature. Deforestation, water pollution, and other processes harm the environment and all living creatures because humans only have compassion for themselves, not for nature as a whole. Zoos are daily examples of people’s indifference and cruelty towards other species. Although zoos are often seen as significant in today’s society, they are actually a way of imprisoning animals while harming them in doing so. This opinion is proved by the fact that living creatures in captivity suffer from boredom and stress, cannot protect themselves or escape danger, and are killed instantly if considered to be ‘surplus’ individuals.
The first argument against zoos to discuss is the lack of interesting activities, joy, and ways to get rid of stress that animals can access in the wild. Such circumstances make living creatures in captivity stressed, bored, and confined. First, according to Bashaw et al., who examined behavior patterns of captivated and wild tigers and lions, animals in zoos tend to be more pessimistic, passive, and indifferent (95). Bashaw et al. notice that “in captivity, they spend the most time on exhibit sleeping or pacing,” not being able to hunt or socialize properly, and the way most zoos are projected also contributes to animals’ boredom and reduced activity (95). Thus, chain-link fencing may be a source of uncontrolled sensory contact for many animals, interfering with their behavior patterns.
Further, it is well-known that humans experiencing deprivation are at risk of developing various mental issues, like anxiety or depression, and losing their interest in life. The same happens to many captivated animals: “Elephants, orcas and other animals with large brains are likely to react in similar ways to life in a severely stressful environment” (Jacobs). Moreover, the term ‘zoochosis’ describes how living creatures in zoos perform unhealthy activities like swaying, rocking, self-mutilation, and others. It happens because they are held in captivity without any possibility of being engaged in common for their actions.
The second argument that highlights unethical zoo practices refers to the fact that animals are deprived of any opportunity to protect themselves or escape danger. One may wonder what kind of danger animals in a zoo can be exposed to in the first place. Unfortunately, most cases are related to humans’ foolishness and irresponsibility: for example, many zoos are unable or unwilling to make sure that no contact between animals and visiting people is possible.
As service providers, zoos have an obligation to keep people and animals safe, but their protection mostly covers the former. For instance, if a person accidentally falls into an animal’s enclosure, even a not curious or aggressive animal can be killed by the zoo staff in order to save the person. One terrible story of a gorilla named Harambe being murdered after a boy fell in its cage is told by Gambone. Unfortunately, since “we prioritize the entertainment or even the education of humans first, rather than the needs, especially the need for freedom, of self-aware, autonomous nonhuman beings like Harambe, they will continue to die” (Gambone). In situations like this, the creature cannot defend itself or escape. Moreover, with inadequate behavior of visitors, the animal may try to attack for self-defense but will also suffer.
Finally, there is also a shocking and unethical practice when zoos get rid of animals that are considered excess or ‘surplus.’ Statistics are terrifying: according to Bekoff, “European zoos kill as many as 5,000 healthy animals every year” merely because these individuals are no longer useful, pretty, or profitable. This inhumane practice again proves the need to apply stricter control over zoos or eliminate such places. When zoos need more room for younger animals to attract more visitors or reproductive animals to become more profitable, they terminate healthy individuals and may sometimes even make it a show in front of the audience (Shuchat). In other words, these terminations are not euthanasia but actual murders because there is no mercy in them (Bekoff). This practice also demonstrates that animals are considered property that can be thrown away when no longer needed.
To draw a conclusion, one may say that zoos are not a significant and ethical part of the modern world but places where animals are imprisoned and deprived of their rights. In the wild, different species have more opportunities to engage in their common activities, and in captivity, they suffer from boredom, stress, and depression. Moreover, animals in zoos are valued and protected less than visitors, and they cannot even escape when facing danger. In cases when they try to defend themselves, animals merely get killed. Finally, there are also situations when they are cruelly murdered because of being considered ‘surplus.’ Therefore, it is recommended that people get more information about the zoos they visit and avoid such unethical places.
Bashaw, Meredith J., et al. “Environmental Effects on the Behavior of Zoo-Housed Lions and Tigers, with a Case Study of the Effects of a Visual Barrier on Pacing.” Journal of Applied Animal Welfare Science , vol. 10, no. 2, 2007, pp. 95-109.
Bekoff, Mark. “ Zoothanasia: The Cruel Practice of Killing Healthy Zoo Animals .” Salon, Web.
Gambone, Emily. “ Why We Fight for Nonhuman Rights: Harambe’s Story .” Nonhuman Rights Project, Web.
Jacobs, Bob. “The Neural Cruelty of Captivity: Keeping Large Mammals in Zoos and Aquariums Damages Their Brains.” AP News , Web.
Popova, Maria. “ Einstein on Widening Our Circles of Compassion .” The Marginalia , Web.
Shuchat, Shimon. “ Honoring Animals Purposely Killed by Zoos on World Zoothanasia Day .” In Defense of Animals , Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 9). The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-harm-that-zoos-do-to-animals/
"The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals." IvyPanda , 9 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/the-harm-that-zoos-do-to-animals/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals'. 9 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-harm-that-zoos-do-to-animals/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-harm-that-zoos-do-to-animals/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Harm That Zoos Do to Animals." January 9, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-harm-that-zoos-do-to-animals/.
- Zoos: Cruel or Educational?
- The Future for Zoos and Aquariums Bibliography
- Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?
- Setting Up a Safari Zoo in the UAE
- The Role of Zoos in Endangered Species Protection
- The Australia Zoo Rescue Unit Project
- Negotiating About Pandas for San Diego Zoo
- The Effectiveness of Sustainable Practices, Plans, Programs and Initiatives Implemented by Australian Zoo
- The Analysis of Siamangs’ Behavior in a Zoo Setting
- Negotiating: Pandas in San Diego Zoo Case
- Happy Cows Case: People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals
- The Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Kitties
- Animal Testing in Medicine and Industry
- Wearing Clothes Made of Animal Fur
- Animal Sentience: Impact on Animal Welfare Movement

Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Students are often asked to write an essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Introduction.
Zoos are places where people can see different animals from around the world. Some people believe zoos are good for animals, but others think they are not. This essay will discuss both sides of this issue.
Zoos for Education
Zoos can be helpful for teaching. They let people, especially kids, learn about different animals. They can see how animals behave and live. This can make people care more about animals and want to protect them.
Animal Safety
Zoos can keep animals safe. Some animals are in danger in the wild because of people or other animals. Zoos can protect these animals and help them to live longer.
Against Animal Freedom
On the other side, zoos can limit animals’ freedom. Animals in zoos don’t get to live like they would in the wild. They can’t hunt, roam, or do other things they would normally do. This can make them sad or sick.
In conclusion, zoos have both good and bad points. They can teach people about animals and protect them. But they can also limit animals’ freedom. It’s important to think about these points when talking about zoos.
250 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Zoos are places where people can see animals from all over the world. They have been around for many years. But, is it right to keep animals in zoos? This is a big question that people have different views on.
Reasons for Zoos
One reason people think zoos are good is because they help protect animals. Some animals are in danger of disappearing forever. Zoos can keep these animals safe and help them have babies, so they don’t disappear.
Zoos also help us learn about animals. By watching animals in zoos, scientists can learn how they live, what they eat, and how they behave. This information can help protect animals in the wild.
Reasons Against Zoos
On the other hand, some people think zoos are bad for animals. They believe animals should live in the wild, not in cages. In the wild, animals can roam free, hunt for food, and live with other animals. In zoos, they can’t do these things.
Some people also worry that zoos don’t give animals enough space. Animals in the wild have a lot of room to move around. But in zoos, they often live in small cages or enclosures.
So, should animals be kept in zoos? It’s a tough question. Zoos can help protect and study animals, but they can also limit their freedom and space. It’s important to make sure that if we have zoos, they are as good as possible for the animals that live there.
500 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Zoos are places where people can see a variety of animals from all over the world. But should animals be kept in zoos? This question has sparked many debates. There are both good and bad points about zoos. Let’s explore these points.
Learning Opportunity
One of the main reasons why zoos exist is for education. Zoos give us a chance to see animals that we would never see otherwise. They teach us about different species, their habits, and their habitats. This can inspire people, especially children, to care more about animals and nature. It can also help them to understand the importance of conservation.
Conservation Efforts
Zoos play a big role in protecting endangered species. Some animals are at risk of disappearing forever because of hunting, habitat loss, and climate change. Zoos can provide a safe place for these animals to live. They can also help to increase their numbers through breeding programs. This can be a lifeline for species that are struggling to survive in the wild.
Quality of Life
On the other side, many people argue that zoos are not good for animals. They believe that animals should be free to live in their natural habitats. Zoos often can’t provide the same amount of space and freedom that animals would have in the wild. This can lead to stress and boredom for the animals. It can also cause health problems.
Is There a Better Way?
Some people suggest that there might be better ways to protect animals and educate people. Wildlife parks and sanctuaries, for example, often provide more space for animals. They also focus on preserving natural habitats. This could be a better option for many species.
In conclusion, there are both pros and cons to keeping animals in zoos. Zoos provide valuable learning opportunities and can help to protect endangered species. But they can also limit the quality of life for animals. It’s important for us to keep asking this question and looking for the best ways to care for all creatures. After all, every animal deserves to live a life that is happy and healthy.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Shopping With My Mother
- Essay on Shopping With Friends
- Essay on Shopping Mall
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
Children love learning about animals up-close in a safe environment — in fact, education is possibly the biggest advantage of modern zoos. Many programs, like school presentations, guided tours, informational exhibits, and talks with zookeepers can trigger a lifelong love of animals in children. But zoos aren't perfect in this regard.
For animal rights critics, however, these outcomes don't offset what is seen as the basic injustice of keeping captive animals for human amusement. Earlier this year, the case of Marius the giraffe in the Copenhagen Zoo reignited the smoldering international debate over the ethics of zoos. A young and healthy giraffe considered a so-called ...
Mileham added that zoos also play an important role in temporary rescue and " head start " efforts by, say, taking animals and/or their eggs that are facing a serious, temporary threat out of ...
Zoos keep an safe environment for the animals and they help with mating and safety for the Endangered species. Without zoos soo many species wouldnt exist right now. ... Zoos should be banned: a for and against essay Throughout the past few years, many people have been debating on whether zoos are actually relevant in this day and age ...
Pros and cons of zoos. These are the most common arguments in favor and against zoos. Pros of zoos. After the famous wildlife conservationist Geral Durrell opened a zoo in Jersey in 1959, zoos all over the world have embraced the mission of saving endangered species in the world. Zoos are not like the exotic animal menageries from the middle ages.
Zoo animals are sort of like ambassadors for their counterparts in the wild. Zoos also contribute to scientific research. "Zoo" is short for zoological park, and zoology is the scientific study of animal biology and behavior. In addition, zoos work really hard to save animals that are threatened in the wild. Zoos can take at-risk animals ...
And, zoos can't really provide the space that large or wide-ranging animals, like elephants, are used to. Due in part to unnatural enclosures, animals in zoos are under stress. Animals are often bored and, as a result, some become aggressive and can lash out at other animals or zookeepers. In a study done on 40 chimpanzees in six different ...
The end goal of many SSPs is the reintroduction of captive-raised endangered species into their native wild habitats. According to the AZA, SSPs and related programs have helped bring black-footed ...
1. Regardless, zoos are essential for the preservation and cultivation of endangered species. 2. There are countless animals ranging from various big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, and other sub-species), to pandas, rhinoceros, gorillas, pangolins and many more that depend on zoos for protection and safe breeding grounds. 3.
Animals despise being captives in zoos. No matter how you "enhance" enclosures, they do not allow for freedom, a natural diet or adequate exercise. Animals end up stressed and unhealthy or ...
A 2008 study of 206 zoo visitors by some members of the same team showed that while 42 percent said that the "main purpose" of the zoo was "to teach visitors about animals and conservation ...
In Egypt, tourists can visit the archeological site of Nehken, where the remains of old mummified captive animals, like hippos, an elephant, and baboons, lie. But the modern zoo industry in the U.S., of course, started many centuries later — in late 1800s Philadelphia. Since then, the business of keeping animals captive has exploded.
In this IELTS Zoo Essay you have to discuss whether you think zoos are cruel and should be shut down or whether they are useful as they protect some wild animals. Essays on zoos have appeared in the IELTS test before and this was a question that was recently in the test. Some people think that zoos are all cruel and should be closed down.
Arguments for Zoos. By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species. Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe ...
Giraffes endlessly flick their tongues. Bears and cats pace. Some studies have shown that as many as 80 percent of zoo carnivores, 64 percent of zoo chimps and 85 percent of zoo elephants have ...
A trip to the zoo is sure to be a memorable one for people of all ages. 3. Provides a Safe Haven for Displaced Animals. Zoos keep animals safe when they lose their natural homes because of human activity. By keeping these animals safe in captivity, zoos help ensure they will not disappear entirely from the planet.
However, this is untrue, as keeping animals in confined and unnatural environments tend to alter their natural behavior, character, and responses. Thus, persons visiting the zoos observe the altered behavior marred by boredom, stress, and loneliness. Moreover, keeping animals in zoos teach people that it is okay to lock up and make animals ...
The World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA) is like an "umbrella" that protects the "zoos and aquariums" but not the "animals" (Marino, Bradshaw, & Malamud, 2009). In other words, these regulations are just like a choice for bosses of zoos. It will not be a threaten for them if they choose not to follow it, which truly ...
To be more detailed, these 30 species are difficult to re-introduced into the wild (Zimmerman, 2015). It clearly turns out fact that the effect of "conserving" animals in zoos is poor. Not only the proportion of protecting near-extinct animals is small, but the effect of it is also worse than we imagine. In this case, the necessity of zoos ...
As service providers, zoos have an obligation to keep people and animals safe, but their protection mostly covers the former. For instance, if a person accidentally falls into an animal's enclosure, even a not curious or aggressive animal can be killed by the zoo staff in order to save the person. ... This essay, "The Harm That Zoos Do to ...
Students are often asked to write an essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... Animal Safety. Zoos can keep animals safe. Some animals are in danger in the wild because of people or other animals.
The zoo's job is to keep animals safe in an enclosed area from the outside where there are many dangers and well away from poachers, so the animals can produce more babies effectively in a well constructed habitat where the can grow up and increase numbers. ... Essay on Should Animals Be Kept in the Zoo? Some people agree that animals should ...