We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design

15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
By Krystle Wong , Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation & why is it important?
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

4. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
5. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
6. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
8. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

9. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo . But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s tools enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Ultimately, creating a memorable visual presentation isn’t just about throwing together pretty slides. It’s about mastering the art of making your message stick, captivating your audience and leaving a mark.
Lucky for you, Venngage simplifies the process of creating great presentations, empowering you to concentrate on delivering a compelling message. Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
Creating Effective Presentation Visuals
Connecting people with your message.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate.
Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids. He knew that slides are most effective when they tell a story rather than convey information, so his visuals were simple, elegant, and image-based. They complemented and reinforced his message, and they never competed with him for his audience's attention.
You don't have to be Steve Jobs to give a great presentation, but you do need great visuals. They convey a powerful message about your ideas and your brand, so it's essential to get them right. In this article, we'll look at how you can create effective presentation visuals – slides that connect your audience with your message.
Why Simplicity Speaks Volumes
The saying "A picture is worth a thousand words" is popular for a good reason: the human brain processes information more effectively when it is accompanied by images, or by short, memorable statements. This means that when you use simple, image-based slides to support your message, your audience can better grasp the information you're communicating.
However, many people use too many slides, or they build presentations around visual aids that are word-heavy or excessively complex.
These kinds of visual aids can negatively affect your presentation. Let's look at some examples:
- You're trying to convince the board to support a new product idea. Your slides are made up of graphs, numbers, and blocks of text from top to bottom, and board members spend most of their time reading the slides instead of listening to you. The result? You don't make a real connection, and your passion for the project is lost on them. They vote unanimously not to take the idea forward.
- You're pitching to a promising potential client. You spent a lot of time creating your slides, using many colors, animations, and fonts. However, the slides are so complex that your client has trouble understanding them. She leaves the presentation feeling overwhelmed and tired, and avoids using your firm because she fears, subconsciously, that dealing with your firm in the future could be similarly draining.
- You're giving a presentation to your department to highlight its good work. You want to feature everyone, so you make a slide detailing each person's accomplishments. Your department has dozens of people, so by the end, your team cares more about leaving than their results.
Now think about what happens when you use simple and engaging visuals. Instead of generating confusion or exhaustion, your slides create a positive connection with your audience. People might not remember exactly what you said, but they will remember a powerful image. They'll recall the positive emotions that they experienced during your presentation, and they'll start to associate your brand with clear, intelligent communication.
The results will be profound. You'll win new clients, convince colleagues to act on your ideas, and earn recognition for your team members' hard work. In short, you'll make positive impressions that will remain in people's minds long after the details of your presentation have faded.
Creating Great Visuals
Your visual aids have one job: to support your presentation . However, it takes considerable time, creativity, and effort to develop slides that do this well. Use the tips below to make the most of your preparation time.
1. Be Consistent
A common mistake is choosing different colors and fonts for each slide. This can confuse your audience and divert attention away from your message. Stay consistent with your slides, so that they form part of a seamless whole.
First, choose colors carefully, as color will affect your presentation's mood and tone. Also, think about the space that you'll be presenting in. If the room will be dark (with lights off), choose a darker background color, such as dark blue, black, or gray, with white or light-colored text. If the room will be light (with lights on or plenty of ambient light), choose a white or light-colored background, with black or dark-colored text.
You also need to match color with the tone and message of your presentation. Bright colors convey energy and excitement, while darker colors may seem more conservative and serious. Align the color palette you choose with your subject matter.
Microsoft® PowerPoint and Apple's Keynote are the most widely used presentation packages. They feature useful templates and tools, and most people are familiar with the layout of their presentations.
However, cloud-based presentation tools have features and templates that might be new to your audience, increasing the potential impact of your presentations.
2. Consider Culture
Before you create your visuals, make sure that you understand your audience. This is especially true if you're presenting to a culturally diverse group.
For example, not everyone reads from left to right, and people from some cultures may consider a particular color offensive or bad luck in business settings (look out for examples of this in our Managing Around the World articles). Additionally, jargon or slang may cause confusion with your audience.
When designing your visuals, use images and photographs that reflect the culture to which you're speaking. If you're presenting to a culturally diverse group, use pictures and images that reflect this diversity.
And keep graphics and phrases simple; remember, not everyone in the room will be a native English speaker. Whenever possible, use images to replace bullet points and sentences.
Our article on Cross-Cultural Communication has more tips for communicating with an ethnically diverse group.
3. Use Images Intelligently
When Steve Jobs unveiled the MacBook Air® , he needed to show just how small this new laptop was. The audience wasn't going to remember that it was 0.68 x 11.8 x 7.56 inches; those numbers don't create an emotional response. Instead, he showed them that the MacBook Air would fit easily into a standard manila envelope. This was a powerful way to show its size.
This kind of creativity is essential when choosing images. Your audience has probably seen plenty of bad clip-art and too many pictures of cross-cultural handshakes. Brainstorm creative, clever approaches with your imagery, and look for photographs or illustrations that tell a story in a less obvious way.
Thoughtful images will keep your audience engaged, reinforce your professionalism, and make a lasting impression.
4. Break Complex Data Down
When you have to communicate complex data or large chunks of information, avoid putting it all on one slide, as your audience may struggle to take in all of the details. Instead, either summarize the information, or split it up over several slides.
You can also use handouts to communicate complex information. Handouts allow your audience to look at data closely. This is especially important when you're presenting to analytical people, such as engineers, scientists, or finance professionals. They are trained to be skeptical about data, and a handout will give them a closer look. Once again, this kind of attention to the needs of your audience will highlight your professionalism and support your message.
5. Keep It Simple
Each slide should focus on one idea or concept. This allows your audience to grasp quickly what you want to communicate. Keep your text to a bare minimum (10 words or fewer if possible), and, where you can, use an image to convey a message rather than words: for example, consider using a graph instead of a list to show changing trends. Each slide should take three seconds or fewer to process. If it takes longer, the slide is probably too complex.
It can sometimes be helpful to follow a clear structure when creating your presentation; for example, if it is focused on a document or process with which audience members are familiar. This will help them make connections between your content and their existing knowledge.
Avoid bulleted lists whenever possible; they make it too easy to put several ideas on one slide, which can be overwhelming for your audience. If you do need to use bullets, don't use sentences; instead, simply list the fact, statistic, or idea you want to communicate. Then use your narrative to educate the audience about what these mean.
To simplify the wording on your slides further, highlight the key word in every sentence.
Next, look at the layout of your slides. Aim to use a plain background and plenty of blank space: this will help to focus audience members' eyes on your message. Avoid decorating slides with background pictures, logos or patterns that could distract attention.
Last, consider using blank slides when you need the audience's complete focus; a blank slide is equivalent to a pause, and it will add drama, tension, and focus to your words.
Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
First, take our interactive quiz, How Good Are Your Presentation Skills? to get an idea of how well you speak. Our articles on Delivering Great Presentations and Better Public Speaking contain tips and strategies that will help you communicate with clarity and intention.
When you practice your presentation, use your visuals. You should be able to glance at each slide and know exactly what you want to say.
If you're not confident in creating your own slides, think about outsourcing the task to a professional. This can be a smart option when a lot is at stake, or when you don't have the technical skills to create the type of presentation you want.
Consider using an outsourcing service such as Elance , Guru , or PeoplePerHour to find a suitable professional.
If you do, keep in mind that managing a freelancer requires a different approach from managing a regular staff member. Be clear about the project details, communicate your goals for the presentation, and set deadlines that give you plenty of time to revise and add as necessary.
Presentations that are too complex or lengthy can undermine your message. To create better visuals, do the following:
- Stay consistent.
- Consider culture.
- Use images intelligently.
- Break down complex data.
- Keep it simple.
If the stakes are high with your presentation and you don't feel confident with your technical skills, consider outsourcing slide preparation.
"iPhone," "Apple," "MacBook Air," and "Keynote" are trademarks of Apple Inc. (see www.apple.com ). "Microsoft" and "PowerPoint" are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation (see www.microsoft.com ). We have no association or connection with these organizations.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
The Art of Public Speaking
With Professor Steve Lucas
Great Presentations
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Management Skills

5 Phrases That Kill Collaboration
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How do i manage a hybrid team.
Adjusting your management style to a hybrid world
The Life Career Rainbow
Finding a Work-Life Balance That Suits You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Everyday leadership.
How Small Gestures Have Impact Employees and How They Let Anyone Become a Leader
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Pain Points

Engage your audience with powerful visual presentations.
Visual tools are critical to have in any presentation as they’re one of the key presentation aids that will help enhance your overall presentation .
We’ll give you tips on how to develop a sense of good presentation design whether you’re using PowerPoint, Prezi, Google Slides or any presentation software under the sun. The secret to creating a great presentation does not lie in a superior software, but understanding a few universal design concepts that can applied for all types of visual presentations.
Don’t be afraid to use a few presentation templates – there are ways to make the presentation ideas in those templates your own ideas and advance it in several different ways. Let’s make your next presentation on point and designed beautifully.
Presentations Are The Visual Communication Tool To Your Story

In the age of information, people remember facts faster through stories. Keep your bullet points and information short. You can use a rule of thumb to not put more than a paragraph and 3 points per slide to start.
Make your presentation the visual component of your story, but not something your audience has to read. Something that is short and succinct on screen will capture your audience’s attention and make sure they retain the main points of your message.
This does not mean incomplete slides. A common mistake presenters make is putting too little information on a slide in the name of simplicity when in fact they’re leaving out the main context.
A well designed visual presentation has a great story behind it and a well rehearsed voice telling it as well. Engaging the audience is also a great way to associate meaning or connection to the content of your slide decks. Ask questions and tell stories while showing off a great visual presentation! Think of writing the copy like writing for social media – you only have a certain amount of characters to use and a short audience attention span.
General Tips For Visual Presentations
Before you begin creating your presentation, you first need to know what makes effective presentations – storytelling. Such presentations target the audience’s emotions leading to a stronger connection to the audience member and the main point of the presentation.
Below are some storytelling tips for your slides, but remember to keep the presentation itself simple and practice makes perfect. And again, these are more for your spoken component that accompanies the visual component. These tips can be useful because they can be applied to all your presentations in general.
Step 1 is to ask yourself who your audience is and how to convey the key message you have in mind to them. Once you settle on your message, you can start designing your slides with that direction in mind.
You may wonder how to connect with an audience with your slides. Look to your own experiences, your own speaking style and tailor your message to what you know. Not many people want to hear others recite facts with no real meaning driving the story. Ask yourself, “Why does this matter to the audience and why should they care?”.
There is a lot of trust that can be built when the audience has a genuine connection to the presenter. Overall, if you have something that can solve a problem or teach someone complex things, that is enough to form a connection with your audience.
Think of the last app you used, the last email you read or perhaps the last business you purchased from. What was the content or visual elements that pulled you in?
Are you making a PowerPoint, Prezi or other form of visual presentation but it’s taking too much of your time? Enlist the help of Presentation Geeks and consider outsourcing your presentation design . Outsourcing your presentation slides allows you to free more of your time while still getting the results of an interesting presentation. You’ll have the support of expert slide designers who know what presentation visuals work and don’t work thanks to years of presentation feedback and background knowledge.
Color Design Tips For Presentation Slides
When designing your presentation, make sure you take into consideration the colors you’re using. We’ve listed a few background color combinations you might want to consider when developing the overall slide deck and the font to use.
Color Wheel Alignments:
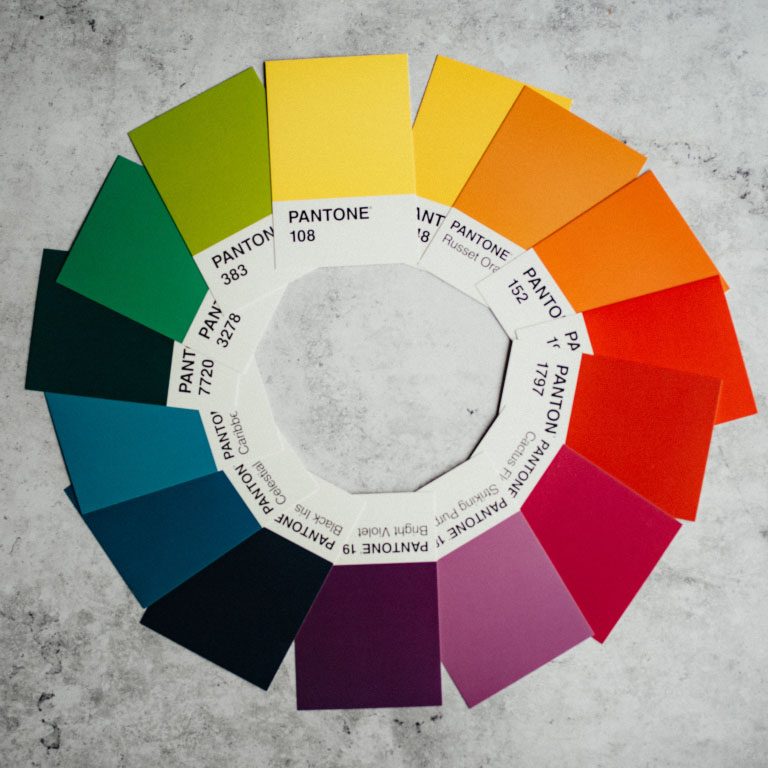

Primary Colors: Red, yellow, blue
Secondary Colors: Green, orange, purple
Tertiary Colors: Yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green & yellow-green
Analogous Colors: These are any three colors which are side by side on a color wheel. (Think green, lime green, yellow)
Complementary Colors: These are colors that are directly opposite of a color wheel. (Think green vs. purple, red vs. blue)
Monochromatic Colors: This is when you use one color and various shades or hues of it. It works well for minimal looks.
Color moods:
Red/Orange/Yellow: Generally these convey a sense of energy, are warm colors and catch your attention. Yellow is a happy warm color on one end and red is very striking and can warn of danger, and symbolizes importance, passion and sometimes violence.
Blue/Purple/Green: These colors are calming, reserved, elegant and often used for corporate slides. Think of how indigo blue is used for many large corporate entities. Green often is branded with earth or medical brands. Purple often conveys a sense of royalty, money and creativity.
Use The Power Of Photography Or Video

Pictures and videos are great visuals to incorporate into any presentation. Remember the saying, “A picture is worth a thousand words”? Well, it’s true! Photos help visualize complex information. You’ll often come across a lot of photos in research presentations as they help the audience understand examples better.
They can also save you from having to put a thousand thoughts into the PowerPoint presentation slide!
The first tip we can give to make a great visual presentation is to choose all your photos before you start. This way you can keep the consistency of the images across your slide deck and make sure they’re somewhat alike in terms of composition, mood and brand.
Use free stock photos
You don’t have to take the photos or videos yourself.
There are plenty of free resources and web pages for stock photos online – Unsplash , Pexels , Pixabay , Free Range , Creative Commons and some photos from Freepik are free to use with some accreditation.
Effective photo use
Make sure you pick an image that will focus on the main theme of the slide. One image is usually enough if the image choice is very relevant to the slide. If you have multiple photos, avoid poor or loose placement of photos all over the slide. Try to use a grid or gallery placement and it will immediately enhance the layout of the slide.
If you pick great images, making presentations can be faster. Instead of having to create an elaborate template with multiple elements, a photo with a couple of bullet points can go a long way in terms of capturing attention and making your presentation slides look professional. This is true on any presentation design platform – whether its PowerPoint, Google Slides, etc.

You can also embed videos whether they’re located on your computer, YouTube, Vimeo or other major video streaming sites. If you’re feeling nervous about your presentation or have a complex message that would be hard to condense in one slide, a video is a dynamic way of conveying your message in any type of presentation.
The Typography You Use Matters

Typography is how you will arrange and present the words in your presentation. An audience can engage when text is readable, functional and works well with the other elements in the presentation. Fonts and sizing are a good place to start establishing the tone of your presentation.
Overview of Font Choices
Elegant fonts often denote a sense of luxury or lifestyle tone. Use script fonts sparingly, but as titles they immediately give this polished and high-end look. This should not be used as body text or something lengthy to read. Think about if you sent an email in that text – it would be tedious to read. However, maybe if it were a title or a way to name email, the choice may be more correct.
Corporate fonts often are traditional, serif fonts or clean sans serif fonts that evoke a sense of trust and a clear message. Think of the fonts Lato, Helvetica or Arial – they’re go-to fonts that are easy to read, and work across many systems. This is especially helpful if you are working across teams when creating content or having to approve the content, idea or visuals.
Of course, you can incorporate more stylistic or playful fonts if you want to give your presentation a personal feel. Much like the scripted font, when used sparingly but in large titles, this choice of font can be very effective at conveying a certain personality.
Adding Symbols & Icons To Your Presentation

You can consolidate information by using symbols or icons to direct your eye to information such as an arrow symbol. What if you used a symbol instead of a bullet point? Think of symbols as anchors for the eye to quickly find information. You can collect symbols off free stock sites or use the built-in ones in PowerPoint that are free to use!
Depending on if your presentation is formal or informal , you may also want to consider adding emojis! Emojis are fun ways to express different emotions and can help connect with a younger demographic.
Overall Branding, Tone of Voice & Consistency

Another tool you may have at your disposal is if your brand, business or company has brand guidelines. It will be the guide and compass to your presentation’s information that goes within it. By keeping consistent you can achieve a polished look even if it looks very simple.
Use your business voice to communicate ideas and set the tone for your presentation. Are you in an investment banking business and want people to rely on the information given to you? That would inform perhaps using blues and purples, which are calmer colors and a cleaner look. Are you an influencer who’s buying power and spending choices matter to your audience? Maybe choosing bright colors with personal touches will make the connection. Are you designing an innovative app? Maybe more interactive slides would do the trick.
Use these questions to make sure your text and tone is consistent as this is a foundation of a well articulated brand or personal identity.
Consistent Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is how you will arrange objects and text in relation to one another to guide your user and not confuse the objects and how they should read them in your slides. Setting rules helps differentiate and prioritize what’s important in order.
Look at the difference between these two.
Snoop Dogg just launched a wine and it’s coming to Canada
Daily hive branded content | aug 11 2020, 6:30 am.
Australian winery 19 Crimes recently announced that its new Cali Red wine, created in collaboration with Entertainment Icon, entrepreneur, and hip-hop artist Snoop Dogg, will be hitting shelves across Canada later this summer.
The collaboration offers a refreshing take on celebrity partnerships as the apparent shared values and history between the brand and famous rapper make for a perfectly organic pairing.
Comment Name:
By browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. see our user agreement for the use of cookies..
You can see a clear distinction in the example below:
Think of hierarchy of a form of narration or story structure. Your eye goes to the title, then to the subtitle, then to the body copy in a logical manner. Where the eye travels is one of those things we don’t think about often. But you can also utilize eye lines in photos. Is your subject in the photo looking left or right? Consider placing text to where your subject is looking and see how effectively your eye travels to that text.
We’ll look at hierarchy strictly as sizing of words for now, but note you can establish hierarchy with type, white space, alignment, etc. As a general rule of thumb, you should have consistent sizing for your Header (or title slide / slide title), your subtitles and your body text. That’s it! If the sizing in your PowerPoint is consistent, your words will look uniform and clean. Everything will be much easier to read and the eye will be trained to move each slide.
Don’t Forget Your Own Style
Also don’t forget to incorporate your own style and what kind of visuals you like. Even if your early visuals may seem simple, build up that design muscle with the basics and design techniques that look clean and consistent.
You’ll find as you design these basics, you’ll probably start noticing other visuals and things you like in other mediums and presentations. Keep a note or screenshot the presentation that inspired you. Create a mood-board that you can refer to in the future for quick idea inspiration. Copying gets a bad rap, but learning how to design something you like even if it’s a clone copy will teach you many things about design. Build a collection of images that informs everything you do: for your color scheme, your designs, the cadence of images, etc.
That being said, you can also use free stock websites like Freepik for some design layouts inspiration. Creative Market is a paid website but the site offers a ton of design inspiration. This site has design templates for what’s currently in and trending. You can subscribe to an email newsletter on either site to get bite sized design influence each day that goes straight to your inbox.
However, don’t be afraid to try something new!
Once you get to a level of comfortable designing, these new ideas will be much easier to execute with the technical knowledge you amassed when you started. You could even try using a new app to design your ideas to keep your knowledge fresh! (Keep in mind that most online apps like SlideShare use cookies to improve functionality and performance.)
Ask your friends or people at your organization to give you feedback and critique, as that’s also crucial to honing your design skills. The people around you also represent different audiences!

The above image looks boring, right?
That’s because there are no visual elements!
Powerful visual presentations can engage audiences psychologically with both the presentation itself and the energy of the presenter. By understanding a few universal design concepts, you can begin your journey creating wonderful visual presentations and becoming a better presenter ! Thanks for reading this blog post, tell us your tips in the comments below.
Author: Content Team
Related posts.

FREE PROFESSIONAL RESOURCES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX.
Subscribe for free tips, resources, templates, ideas and more from our professional team of presentation designers.
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
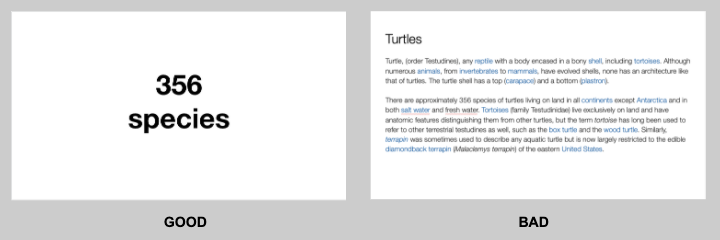
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
how to give the perfect presentation
Using visuals in your presentation, how to design memorable presentations.
Visuals can impact your presentation dramatically.These images, photos, objects, charts, diagrams, tables, graphs or illustrations have the potential to make or break your presentation. Used sloppily, they can damage your credibility and reputation. Designed wisely, they can strengthen your verbal message and enable you to achieve your objective. Why? Because a picture really is worth a thousand words.
According to research done by Professor Albert Mehrabian, a leading communications expert, we take in about 55% of visual information, versus only 7% of textual information. This means that whenever possible, you should use visuals such as photos, charts, graphs, and tables in your presentation. Also, eliminate sentences unless you are showing a quotation. Reduce the number of words or bullet points you use on your slides.They only distract your audience members and encourage them to read the slides, instead of listening to your words.
Hi-Tech or Low-Tech?
Today’s rapidly evolving technology enables us to add strong state-of-the-art audio-visual elements to our presentations. When planning a presentation before a huge audience, consult with your technical team (or, at least, your teenagers!) to come up with the best options. Yet, hi-tech technological components are not always the answer. In meeting rooms around the world, millions of people give presentations every day with or without the aid of laptops and powerpoint software. Remember the purpose of the visuals is to add interest and enhance your message. Yet, you are still the star, the primary focus. No amount of technology can cover up a poor performance.
Handling Equipment & Visuals
When you handle the equipment and visuals, you are still performing for your audience. Make sure you remain calm when using unfamiliar equipment or solving technical glitches. Remember the audience is watching and listening to the way you treat technicians and assistants. Speak respectfully to all who come up to help you. Practice, to ensure you can move confidently and seamlessly between your speech and your visuals, without fuss or delay. Rehearse the visual part of your presentation, just like other parts of your speech.
Benefits of Visuals
A study at the Wharton Research Centre also revealed that participants remembered 50% of the visual information, but only 5% of the bulleted points. Visuals can help you clarify points, reinforce your message, and create greater interest and enthusiasm for your subject. What’s more, visuals encourage audience interaction and provide a change from just hearing, to seeing and hearing.
As a presenter, you can be more relaxed and active when you show a slide. You may walk around, gesture, or point out key relationships in the information you are presenting graphically. Visuals take some of the attention off you and allow people to focus on your information. In this way, they are beneficial to you and your audience. According to research, audiences retain 10% of what was presented orally, 35% of what was presented visually alone, and 65% of what was presented visually and orally. The bottom line is that incorporating visuals can add to your bottom line.
Developing Visuals
Visuals include a variety of communication tools such as flip charts, overhead transparencies, slides, and videos. Powerpoint slide presentations are often the most popular, though not always what’s necessary. What you use depends on the size of your audience. If you are presenting for up to 50 people, you could use boards, flipcharts, overhead transparencies, handouts, and slides. If you are presenting for about 125 people, it is best to stick to overhead transparencies and slides. If you are presenting for 125 people or more, use slides alone.
When considering which type of visuals to use, take into account time and cost factors. Determine the number of times the slides can be used. Decide if professional development is necessary.
Plan a maximum of one transparency for every five minutes of your presentation. Don’t run after your visuals by trying to pack in too many in a short period of time. Let your visuals support your message and not the other way around.
If you are planning to develop your own visuals, keep the following points in mind:
- Emphasize only one thought or comparison on each slide. If you include more than one message, it may confuse your audience.
- Number your slides in case they get mixed up.
- Keep visuals brief and simple.
- Create visual material that is bold and easily seen from a distance.
Remember that research has shown that people remember most when there is only narration and graphics. In other words, they learn less when there is narration alone and they learn less when there is narration, graphics, and text. Check the effectiveness of your visuals by seeing if they can tell the story without added written information.
Environmental Influences
Lastly, remember that many of us are sleep-deprived. Try to keep some lights on during the presentation or it will be too easy for even the most well-intentioned audience members to doze off comfortably and miss all your hard work!
I put a lot of information on my slides. I need it so I won’t forget what to say, even though I’ve spoken English all my life. What can I do about that?
Start by reducing the number of words on the slides slowly. Soon, you will discover that it’s easier to speak when you don’t have to read every single word. Since you’re an English speaker, you only need a few key words to help you elaborate on the subject. Don’t get caught up in thinking you have to deliver the information only in a certain way. Accept the fact that each time you speak the words may be different but the message will come across just the same. I’m sure you can do it.
Ask a Question: Cancel reply
Ask only about topics covered on this page.
Your Question:
About Presentation Prep

Being able to speak in public can change your life! Presentation Prep is your complete, free guide to delivering speeches, lectures, and presentations more successfully and confidently. Whether you're a native English-speaker who suffers from public speaking anxiety, or a non-native speaker who needs guidelines for presenting to international audiences, this site will give you everything you need. Presentation Prep is written by Rebecca Ezekiel, an experienced corporate trainer who specializes in the areas of communications, presentations, and cross-cultural skills. Her online English language training videos are watched by millions of students worldwide.
- Storytelling Learning Journey
- Crafting Strategic Visual Stories
- Influencing with Visuals
- Presenting Data Visually
- Everyday Business Storytelling
- In-Person Training
- Virtual Training
- Resource Center
Easy Guide to Choosing the Right Presentation Visuals
Home / TPC Blog / Easy Guide to Choosing the Right Presentation Visuals

We live in a visual world. Billboards on the highway, TV commercials, and social media newsfeeds are constantly trying to sell us messages. But these visuals aren’t built merely to be colorful or pretty. Clever visuals are designed for a more strategic purpose – to get us to notice and respond to ideas.
This same logic directly applies to business communications: relevant visuals help our insights and recommendations be more easily understood, remembered, and acted on. Here’s a quick and easy guide to understanding how to make clear, powerful visuals in your presentation:
Why do visuals help us remember things?

In one word: neuroscience. Neuroscientists have discovered that an idea expressed in visual form is processed 60,000 times faster than the same information either printed or spoken.
But visuals do more than just help us remember something – they spur action . Visuals trigger our right brain where we process emotion and feelings. And it’s emotion (even more than pure logic) that motivates us into action.
Why are visuals important in presentations?

To understand why getting visuals right is so important, ask yourself this one question: what is the purpose of any presentation? Or email ? Or proposal? Isn’t it to help decisions get made? Or move business conversations forward? Clear, simple visuals help our ideas be quickly interpreted and decisions get made faster because they humanize your ideas and infuse emotion (rather than relying on pure logic.) Conversely, distracting visuals slow decision-making down. Slower decisions mean slower business.
What are common mistakes for presentation visuals?

Visuals often go wrong when we lack either time or an overarching visual slide strategy (or both!). Business presenters are—understandably—always looking to save time, reuse, and repurpose existing slides. As a quick fix, we throw together slides from past decks, or borrow slides from a co-worker without giving thought to the intent of the message we are trying to communicate for the specific purpose (we call these “ Frankendecks .”)
Let’s face it: it’s easy to fall prey to bad visuals. Business presentations are essentially known for including too much text and data, while often using off-brand colors, fonts, and imagery (and let’s not forget about cheesy stock photography .)
On the other hand, even slides that are “pretty” aren’t always designed with a clear, easy-to-digest message, ultimately causing confusion rather than advancing the story we need to tell.
What are the visual elements that make a strong presentation?
There are five main ways to display information in presentations: photos, diagrams, data, text, and video.
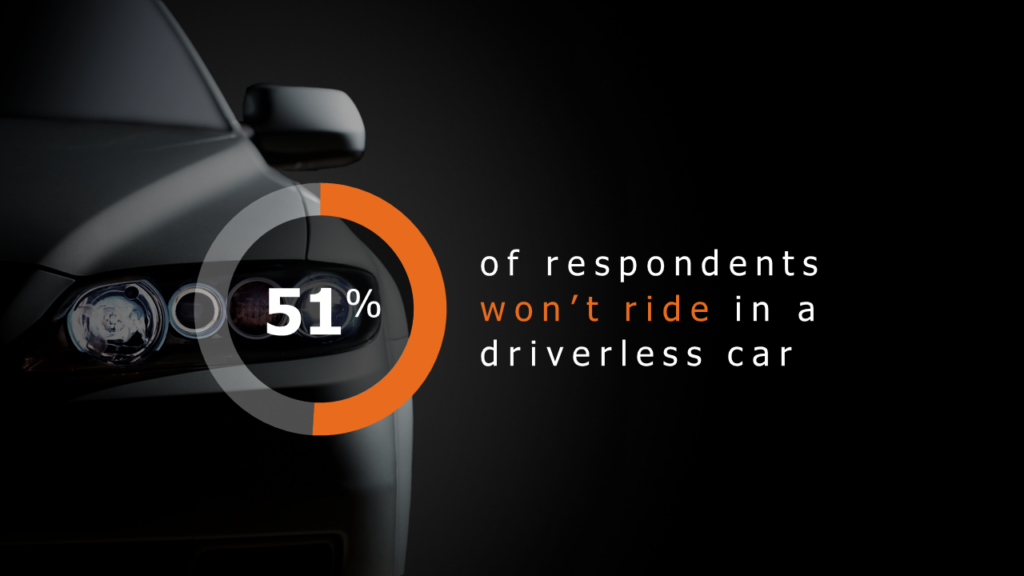
Photos are powerful. They’ll humanize your message help you connect your ideas to your audience on an emotional level. Photos can also build a mood or theme for your presentation.

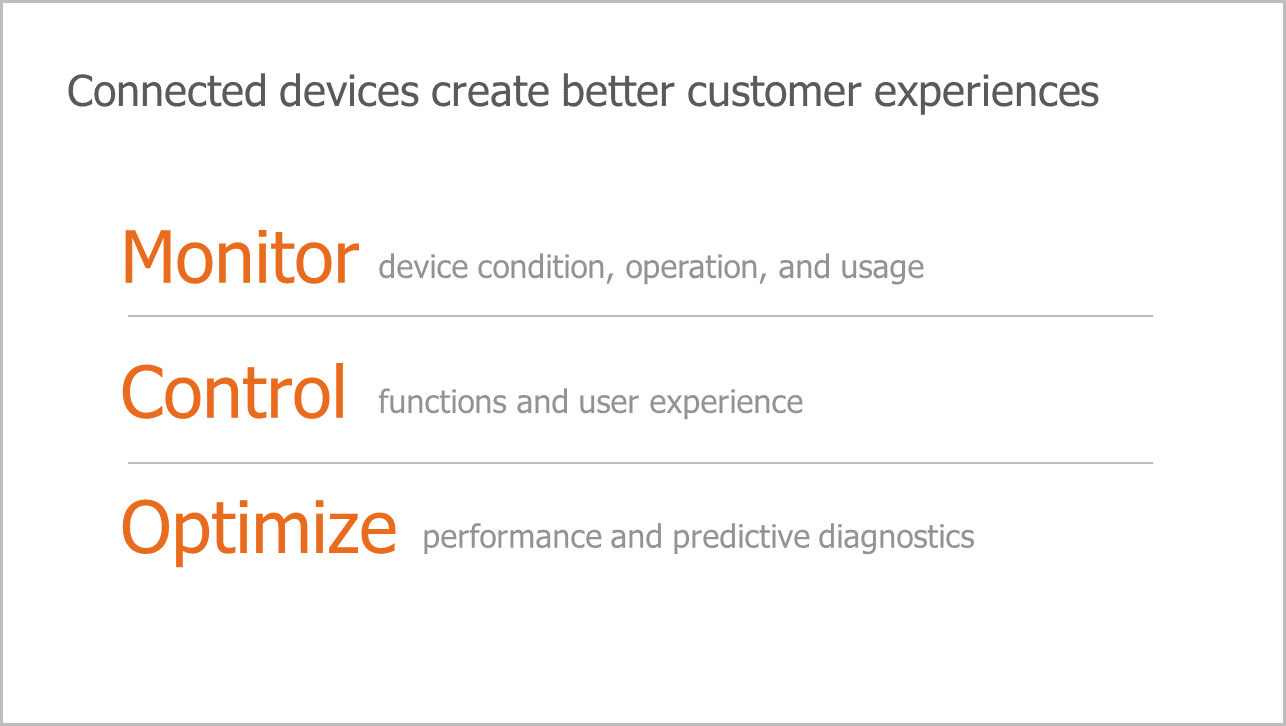
Diagrams help breakdown and ‘cluster’ information into digestible concepts. We often suggesting using shapes or icons to call-out key messages. An example of a diagram would be a timeline or an organizational chart.

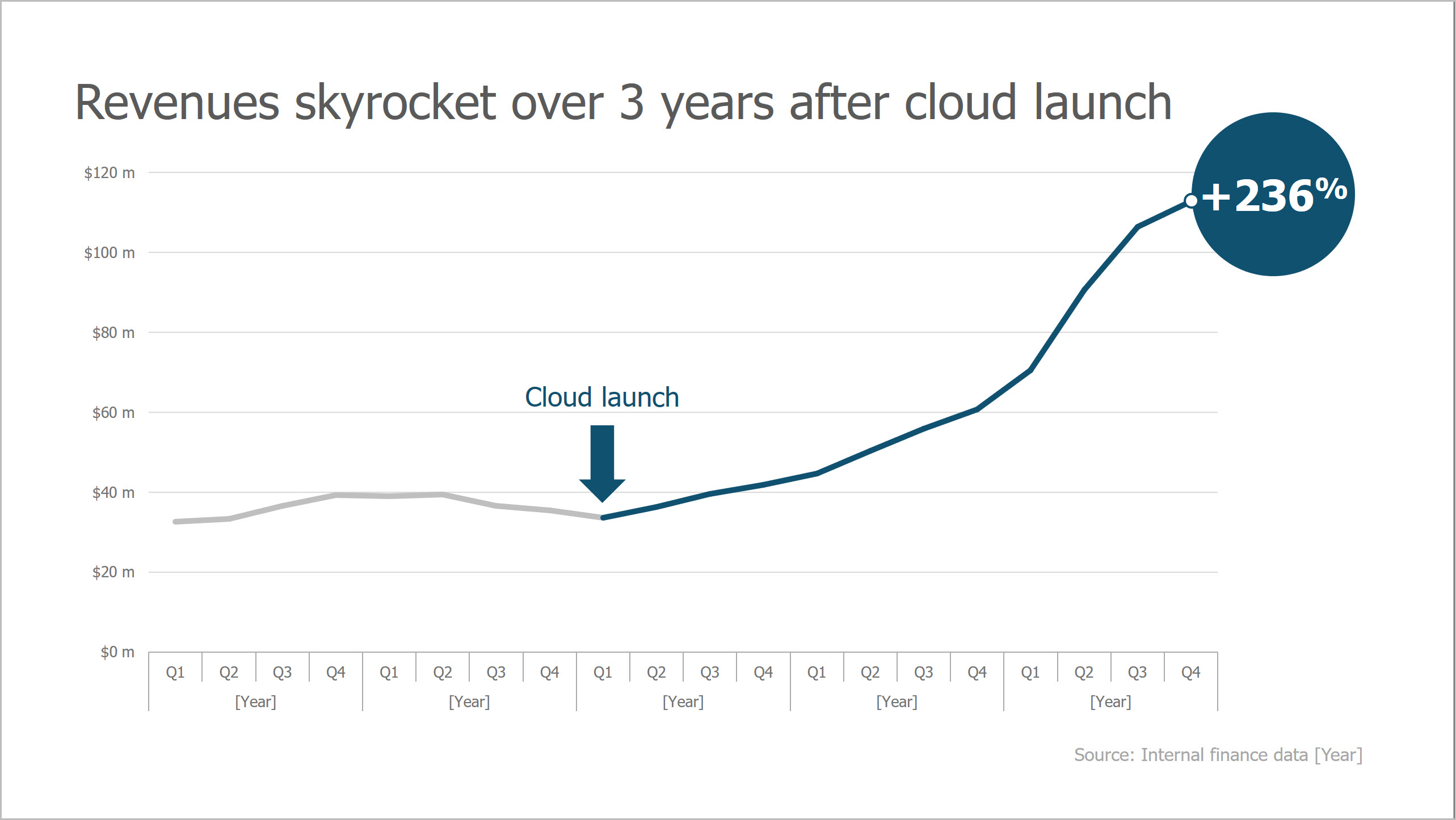
Data is most often presented in charts and tables. But sometimes, like in the case of the image below, only key data – that advances the story – is displayed. Also notice how the use of contrasting colors is used to draw the eye to the data point, and gray is used to subdue data that is simply there for context.
Text is the most common – and overused – visual we see in business presentations (hello bullets!). Text used sparingly with contrasting color and size, however, creates an easy-to-digest message.
Video is an excellent to way to change the pace, the voice, and the medium of a presentation. It’s usually a good idea to keep it brief and embedded straight into the slide deck. To ensure good flow to your visuals, it’s important that any change of medium – such as video – is seamlessly integrated.
Now that we’ve established how critical strong visuals are to business presentations…
Let’s get into some simple tips that will help jumpstart visual thinking the next time you open PowerPoint:
TIP 1: Callouts are Visual Eye-Candy
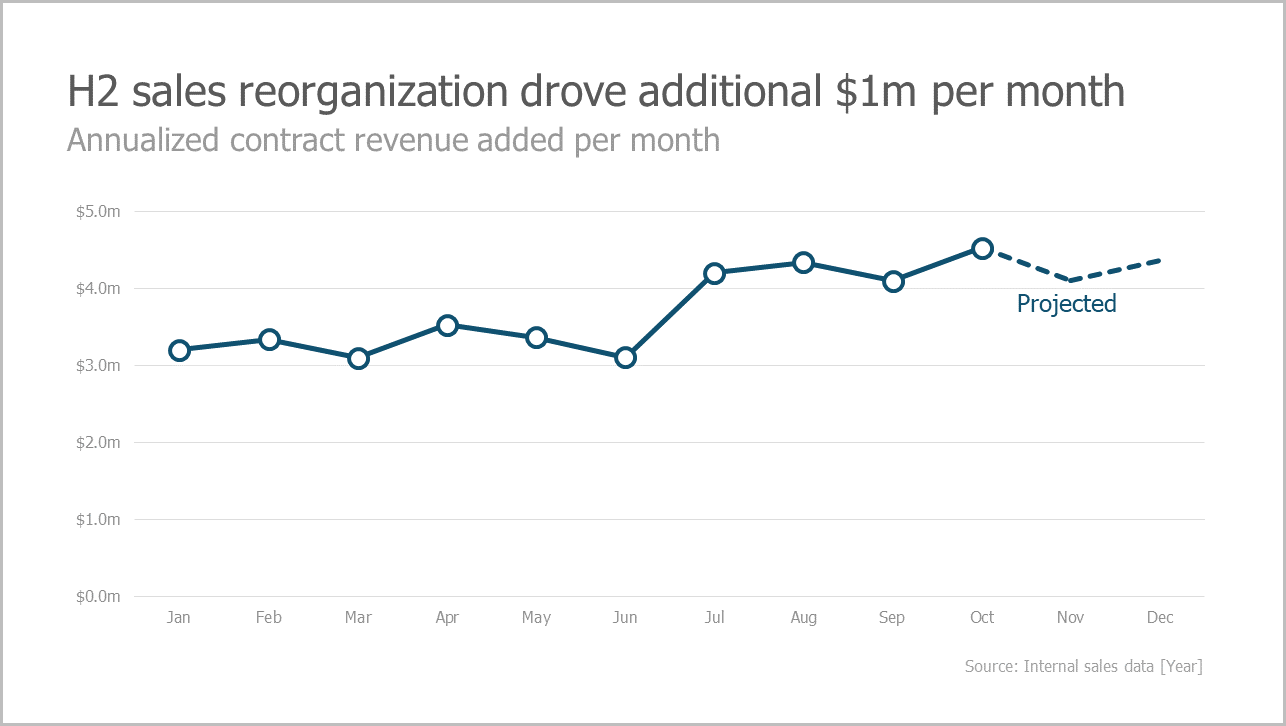
Callouts are one of the easiest and most potent data visualization techniques. By calling out key information with a contrasting color, size, or shape, you can easily highlight key points. This is a gift to your audience because with a simple visual ‘gesture’ you are helping them digest your message in one glance. This is one of the fastest ways to move your ideas forward.
TIP 2: Slide headlines refer to key visuals and help tell a story
Hands down , the best place to summarize the key message of your slide is in the headline (particularly if you are offering a lot of facts or data). Summing up your “big idea” in the slide title offers your audience the gift of clarity.
What’s more, slide headlines – like chapter headings – offer a logical outline to the overall story you are telling in your presentation. No data or facts are thrown in just because you have them. Everything should fit together logically.
TIP 3: Create a Landing Page for Easy Navigation
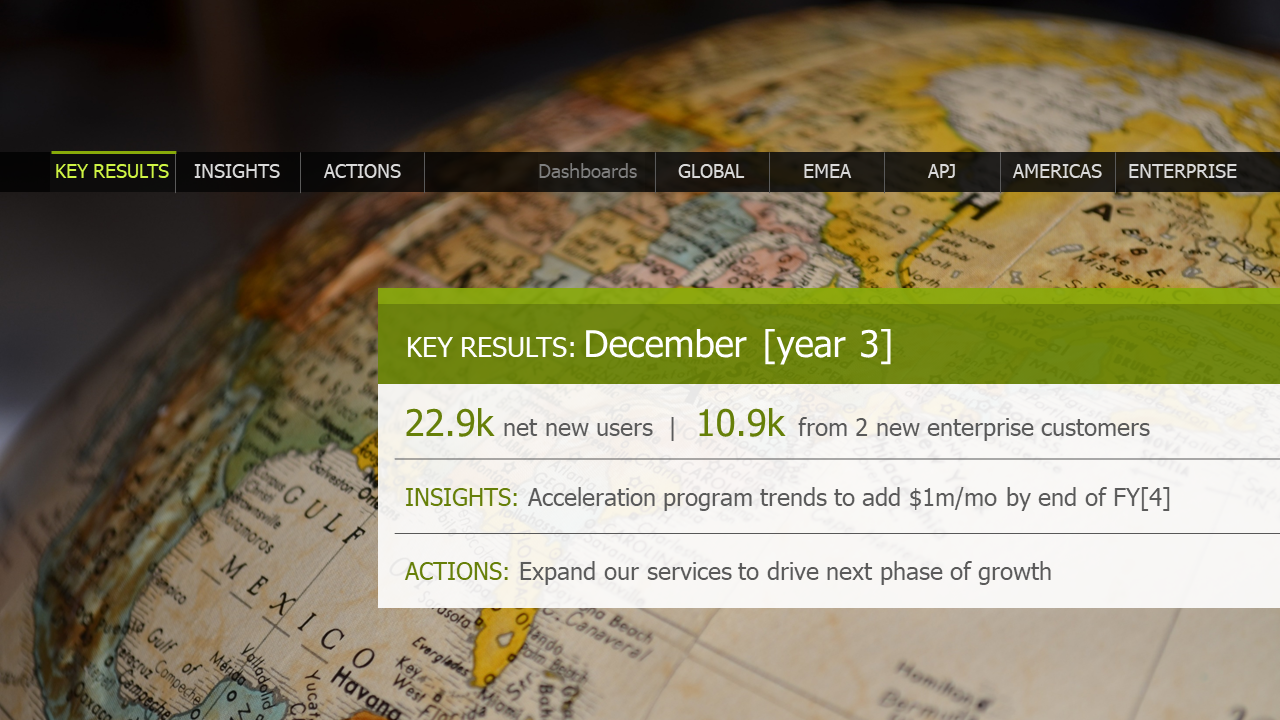
Not every presentation needs to be delivered in a linear format. As you can see from this slide, grouping your presentation into sections on a landing page gives an instant visual picture of everywhere you can go in this presentation.
Even better, each of the tabs on this landing page are portals to dive deeper into those sections, offering not only a visual orientation of your deck from start to finish but a way to jump around depending on your audience’s needs. This non-linear approach is particularly helpful for decks that are presented by someone else or being emailed.
Here are some additional questions we often get about creating memorable, authentic visuals for presentations…
Does Color Matter in Presentations?
So much has been written on the psychology of color and using it in presentations to incite emotion and convey ideas . So yes, red incites passion. And yellow conveys happiness. White is calm and neutral. Always consider color when planning your presentation. However, first and foremost, always select colors from your corporate palette to keep your visuals coordinated and brand-consistent.
How Do I Create Great Visuals Without Being a Graphic Designer?
Our best advice? Keep it simple. Clean, easy-to-interpret visuals are not only efficient to create, but keep the spotlight on your key message, rather than distract from it. Even a common list can be improved with basic icons or shapes. There are many easy, visual tactics that let you prioritize your ideas and offer an easy way to connect with and motivate your audience.
Looking for meaningful, authentic ways to visually express your ideas? We have loads of tips and resources for you. Stock photos don’t have to be cheesy – try adding search terms like “authentic,” “candid,” “context,” or “interactive” after the main search term to find real looking photos that aren’t posed or cliché. And while there’s no harm in trying free stock photo sites first, we’ve found that you often get what you pay for. Our favorite paid stock photos sites are iStock , Getty Images , Adobe Stock , and Shutterstock .
Alternatively, ditch photography altogether and try using icons to represent ideas. The Noun Project has millions of curated, editable icons created by people around the globe. And the best part? They’re all royalty free with attribution, or less than $40 per year for a subscription. Interested in learning best practices for transforming text- and data-heavy presentation slides into visuals that are easy to scan and highlight your key points? Our Influencing with Visuals workshop teaches teams how to organize ideas into visual messages that are clear, memorable, and (you guessed it) authentic.
Home Blog Design What is Visual Communication and How Can It Improve Your Presentations
What is Visual Communication and How Can It Improve Your Presentations
Look around; how is the world communicating with you? Is there music? Are your shoes pinching your heel? Are there a million visual triggers trying to get your attention? We don’t have a crystal ball to answer the first two questions, but the third is a definite YES. What’s behind it? It’s visual communication.
Visual communication is the magic behind all the visible things in the world that tell stories, share information, and attract interest. As a person who makes presentations, you own the power of visual communication to impact, inform and attract your audience with visuals. All you need is the knowledge and the tools to make it work.
In this guide, we’ll share essential facts you need to know about visual communication and how they can help improve your presentations.
Table of Contents
Visual Communication Strategy
Visual communication design.
- Why is Visual Communication Important for Presentations?
7 Types of Visual Communication Techniques in Presentation Design
- How to Use Visual Communication at Work Beyond Presentations
Final Words
What is visual communication.
Simply put, visual communication is the practice of communicating through the sense of sight. In a more profound sense, It democratizes communication in general because with visuals, there’s less need for language or translation.
But what does visual communication do? It tells stories through images, video, illustrations , and anything the audience can see.

Visual communication sits at the top of the list of effective communication strategies and designs for all industries and fields. It’s in all the conversations about marketing, community building, and the future of work. If your presentation design still hasn’t embraced the need to thrive on visual communication, it’s time to fix that.
A visual communication strategy is key to a presentation’s overall mood and message. To create a visual communication strategy, follow the same steps as any communication strategy, and develop them simultaneously.
To give you an idea of the scope of influence of a visual communication strategy, consider all the advertisements you see regularly. Regarding the most successful ones, their visual qualities have been minutely strategized to inspire emotional reactions from you.
Do you want to get reactions when making your presentations ? Use a visual communication strategy to create an overarching visual quality for your presentations’ slides.
FYI: Professionals building visual communication strategies include; brand specialists, marketing strategists, content designers, UX/UI designers, publicists, art curators, and anyone that understands how important planning and strategy are for every project.
Once a visual communication strategy is in place, it’s time to take care of the visual communication design. This is the actionable part of the process; the strategy is the plan, and the design is the creation.
Visual communication design is essential for your presentations. You’re telling a story with your information, and visual techniques will help you add interest. Even a text section can have visual communication techniques applied. For example, the font, spacing, and layout.
Your visual communication strategy will help you choose the proper visual layout, data visualizations, and graphics for the presentation slides.
Why Is Visual Communication Important for Presentations?
If you aren’t aware, storytelling is a massive factor in effective presentation design. To achieve it, you can’t depend on text content; you need visuals to support the information and create connections with the viewer. On a presentation slide, what’s better? A bullet point list or an infographic widget composition? The answer to this question would be the most visual option, in this case, the infographics .
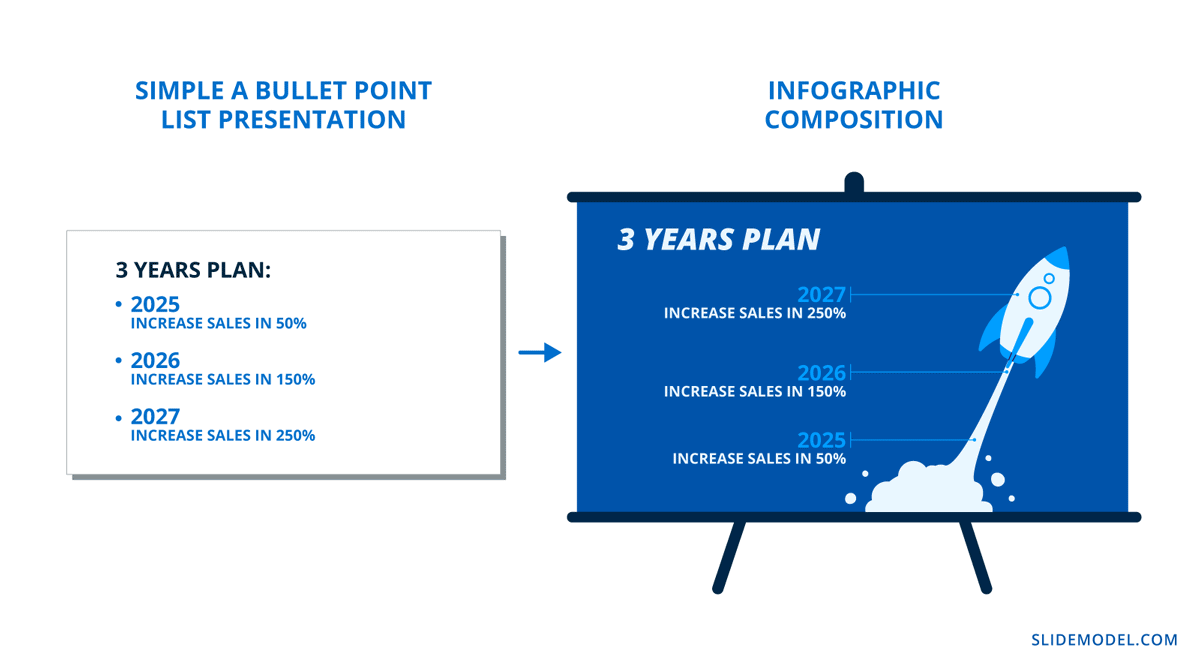
Surely you’ve heard of “Death by PowerPoint.” It’s the perfect example of how visual communication influences the audience. In this case, how can it go wrong and get undesired effects? Humans create emotional and memorable connections with everything they see. As soon as a presentation proves to be a drab PowerPoint, your audience clocks out and checks their phone.
Thankfully, visual communication harnesses many benefits for your presentation designs:
- Ideas and concepts are easier to understand and transmit in visual form.
- Visuals deliver information faster and more directly.
- A good visual communication strategy is attention-grabbing and engaging.
- Visual elements and characteristics make an impact on the viewer.
- A strong visual component improves the credibility of the message.
Visual communication is vital in presenting a slide deck to an audience. Your outfit, body language, and poise all matter. The audience isn’t just looking at your presentation; they’re looking at you. Take the time to expand your presenting skills by practicing, trying new things, and improving your confidence.
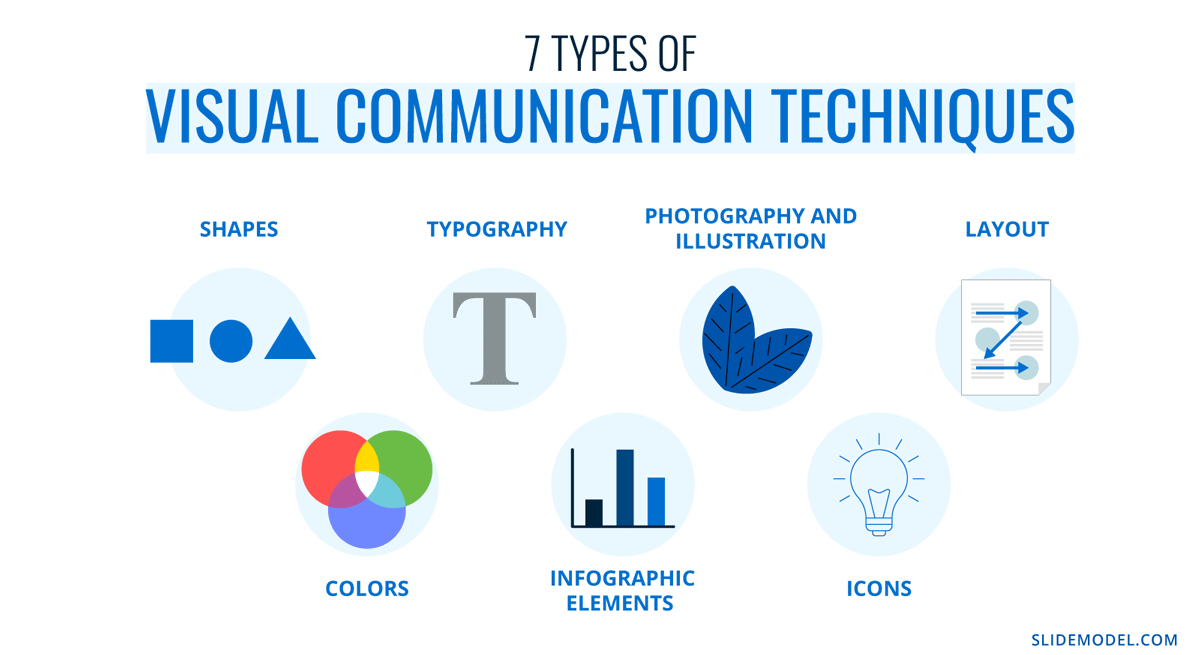
Visual communication techniques are the puzzle pieces of successful content. They are so important that there are psychological applications for all of them.
Here’s a quick list to give you an idea of their importance.
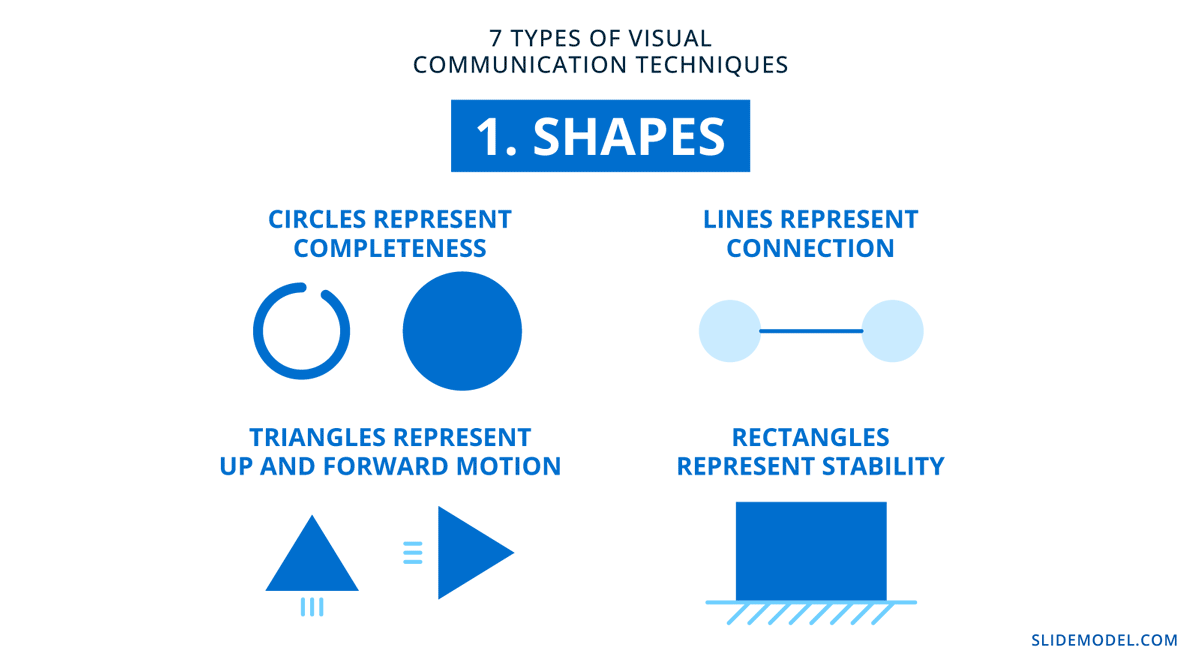
1. Shapes
Shapes have subliminal, subconscious, and even cultural perceptions. The shapes you choose to include across the slides will set the tone for the entire presentation. For example, circles represent completeness, triangles represent up and forward motion, lines represent connection, and rectangles represent stability.
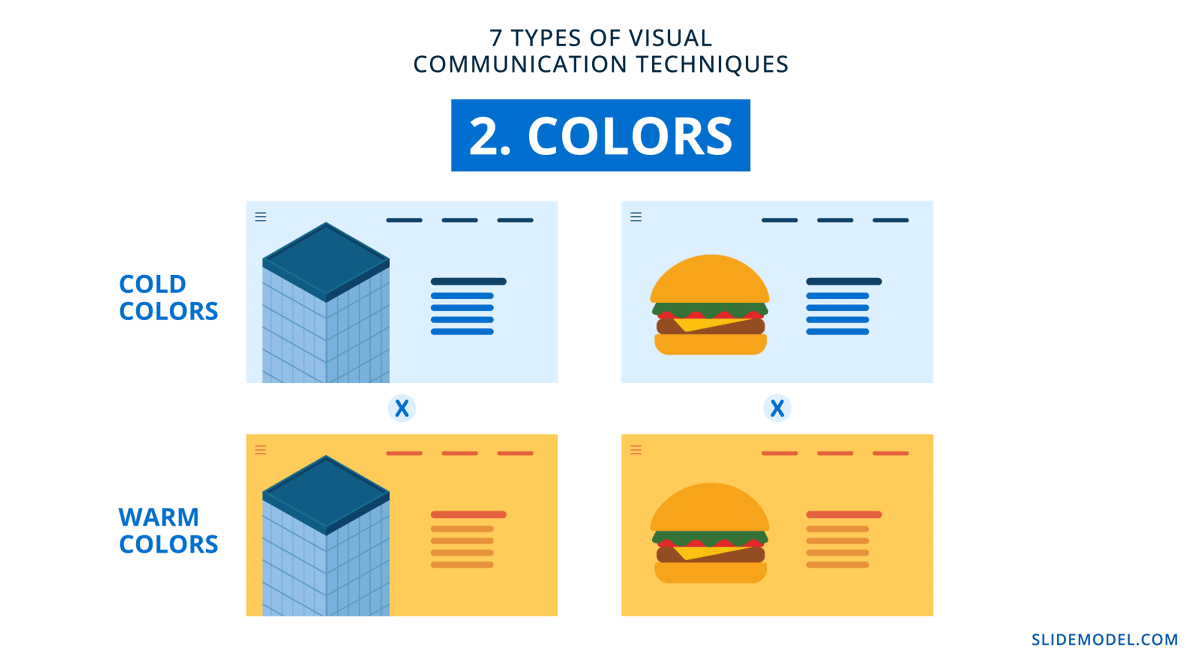
2. Colors
In design, colors are the trigger for emotion in content and visualization. Each color has a meaning and an association. Combining colors to create palettes is a practice in mood and emotional communication through vision. If a presentation is all blue and gray, it feels corporate, a vibrant color combination feels happy and inspiring. Muted and desaturated colors feel calm and inviting.
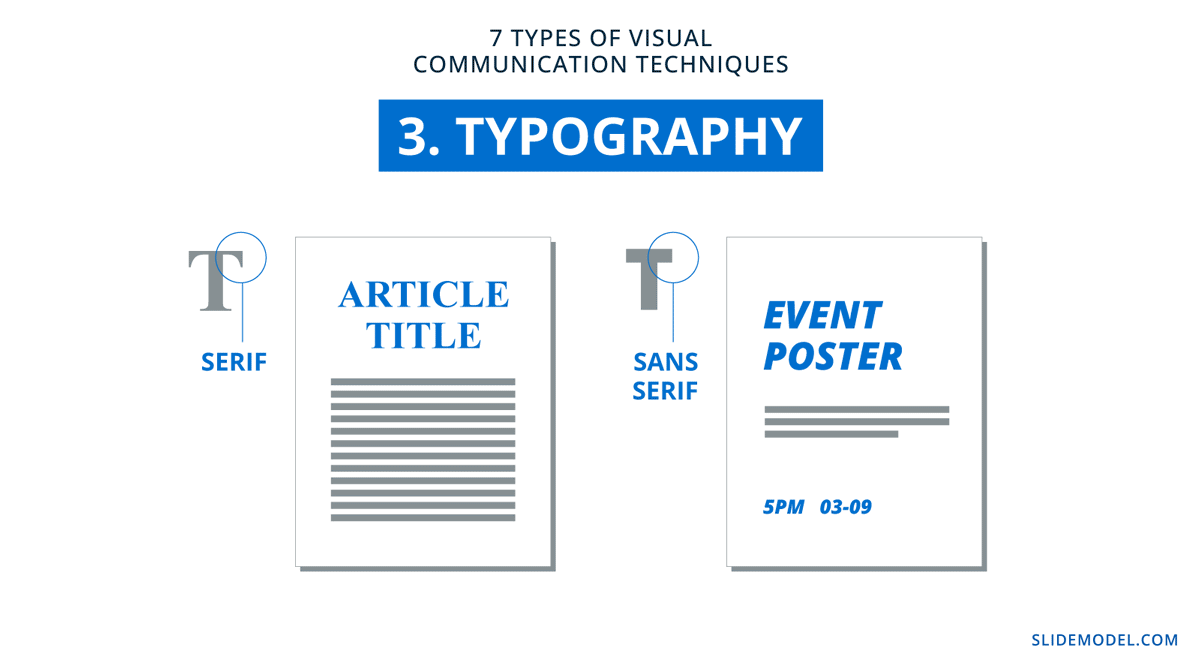
3. Typography
The way letters look brings a sense of meaning from content to the eyes—from text to visual. There are two main font types; serif and sans serif. Serifs are more serious, while sans serifs are friendlier and easygoing. On top of that, each type has a personality that emanates through the content. The visual style of the typography in your presentation must match energetically with the tone and message of both visual and textual content.
4. Infographic elements
Infographics are the poster boy for visual communication. Data visualization and information design are at the core of data stories and exciting business communication. Data viz graphics simplify complex ideas that can take up lots of text space in a presentation slide. Your regular charts and graphs can fall through the cracks if you don’t add a good dose of visual communication strategy and design.
5. Photography and Illustration
Photography and illustration are classic tools for storytelling. Every slide can be easily turned into a pictorial presentation to tell your story, and you have the power to structure it how you want. Be wary of stock photography; overused images will negatively affect your presentation. Custom imagery adds integrity and uniqueness that only a visual communication strategy can achieve.
When using icons in your presentation templates , remember to keep a visual unity between them. Icons can also tell a story from slide to slide in your presentation. Stay consistent in terms of style, color, size, and positioning.

7. Layout & Visual Hierarchy
Viewers use their eyes to see, read and understand your content. When the layout is designed in a way that helps them absorb the information subconsciously, engagement is seamless. It’s as simple as following visual hierarchy and placing elements in the viewer’s line of sight in a Z or F reading pattern.
How To Use Visual Communication At Work Beyond Presentations
Visual communication doesn’t stop at presentations. There are countless other ways to incorporate visual communication at work. Here’s a—not complete—list of the design practices that embody visual communication.
- Infographics
- Visual guides
- Flowcharts and processes
- Employee training
- Internal communication
- Work attire
- Body autonomy
If someone can see it and understand it, it can be communicated visually. Take advantage of that and harness the power of perception, association, and emotional response.
In visual communication, it’s important to remember that first impressions matter. Your presentations and the message they deliver depending on the value of the visuals throughout the slides. Discover more techniques for improving your presentations in the SlideModel blog . Learn how to incorporate SlideModel templates into your PowerPoint slide decks and leave your audiences satisfied and informed.

Like this article? Please share
Design, Presentation Approaches, Presentation Skills Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Filed under Design • February 9th, 2024
How To Apply the 7×7 Rule in PowerPoint
Avoid dull or unclear presentation slides by implementing the 7×7 rule in PowerPoint presentation design. Check it out here.
Leave a Reply

7 Types of Visual Presentations

When it comes to delivering a presentation, visuals can be extremely helpful in getting your point across. There are many types of visual presentations that can be used to communicate your message.
This blog post will discuss seven different types of visual presentations and when they might be appropriate to use. We will also provide examples of each kind of presentation. Let’s get started!
What are Visual Presentations?
3. whiteboards, 5. infographics, 7. paper handouts, which one is right for you.
Visual presentations are a visual aid that can be used in both business and academia to help explain concepts or topics that might otherwise be difficult for an audience member to understand without seeing them firsthand.
In addition, visuals allow the presenter to provide more information than just words alone would do on their own because they provide context and give the audience something concrete to look at while listening.
There are many types of visual presentations, but we will focus on seven of the most common ones here. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand when each would be appropriate to use.
Slides are the most common type of visual aid. You can use slides to demonstrate your point and make it easier for the audience to follow along with what you’re saying. They are also pretty easy to prepare.
For example, a slide that shows how much money was spent on advertising last year might be useful in an annual meeting where everyone’s attention span is short or they don’t want to take the time to read a long report.
Graphs and charts are other types of visual presentation that can be used to show trends or compare data.
For example, you might use a graph to illustrate how your company’s revenue has increased or decreased over the past five years. Or, you could use a chart to compare the number of sales your company has made this year compared to last year.
Whiteboards are a great way to explain something in detail, as they allow you to draw pictures and write on them. For example, if your company is thinking about designing a new website but needs some ideas first, then using whiteboards would help everyone get their thoughts out.
One issue about using whiteboards is that they cannot be easily saved and shared with others. Moreover, as you need to write manually, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Videos are another type of visual aid that can be used to demonstrate a concept or show how something works. It’s beneficial when you want to show live instances of your products or services through movements.
For example, if you’re selling cars, then showing them driving around would help people get an idea of what they look like in action (and not just sitting still on a lot).
The downside to using videos is that creating one from scratch can be time-consuming and expensive, so this isn’t always feasible. In addition, videos can be challenging to follow if they are not properly edited.
Infographics are visual presentations that use images and text to convey information. They can be used in many ways, from illustrating trends or comparing data points graphically; to explaining complex concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.
Infographics are especially handy when trying to illustrate a point based on a massive number of data. For example, if you wanted to show how much data your company has collected over the past year, you could use an infographic.
Posters are used primarily in academic settings because they allow students to display their research findings at conferences or other events where the audiences are present.
For example, if someone were presenting on the use of social media in politics, they might create a poster with an image of the political landscape and then use text to explain how social media is being used.
Posters can be created using software or hand-drawing, but they should always be designed with legibility.
Paper handouts are visual aids that can be used to supplement slides or other visuals.
They can be especially useful if you want to provide the audience with additional information that isn’t easily conveyed in a slide or chart.
For example, you might use paper handouts to give the audience more details about the data shown in a graph or provide them with a list of your company’s products and services.
Now that you know about the different types of visuals, how do you decide which one is right for your presentation?
Well, it depends on what you’re trying to accomplish. If you want to make your presentation more interesting and engaging, then using slides or videos might be a good option.
However, if you need to show complex data or explain a concept in detail, charts, whiteboards, or infographics might be better.
In the end, it’s crucial to pick the right type of visual that will help you communicate your message most effectively.
While there are many different types of visual presentations, the seven we’ve outlined in this blog post should give you a good place to start when creating your own visual presentation.
Keep in mind the tone and purpose of your presentation as you select which type will work best for you. And always be sure to test out your visuals on a small audience before presenting them to a larger group. Happy presenting!
Related Posts:


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.2 Incorporating Effective Visuals into a Presentation
Learning objectives.
- Recognize the characteristics of effective visual aids.
- Analyze different types of visual aids and appropriate ways to use them.
- Determine how to create original visual aids and how to locate visual aids created by others.
Good communication is a multisensory experience. Children first learning how to read often gravitate toward books with engaging pictures. As adults, we graduate to denser books without pictures, yet we still visualize ideas to help us understand the text. Advertisers favor visual media—television, magazines, and billboards—because they are the best way to hook an audience. Websites rely on color, graphics, icons, and a clear system of visual organization to engage Internet surfers.
Bringing visuals into a presentation adds color, literally and figuratively. There is an art to doing it well. This section covers how to use different kinds of visual aids effectively.
Using Visual Aids: The Basics
Good writers make conscious choices. They understand their purpose and audience. Every decision they make on the page, from organizing an essay to choosing a word with just the right connotations, is made with their purpose and audience in mind.
The same principle applies to visual communication. As a presenter, you choose the following:
- When to show images or video for maximum impact
- Which images will best produce the effect you want
- When to present information using a table, chart, or other graphic
- How much text to include in slides or informational graphics
- How to organize graphics so they present information clearly
Your goal is to use visual media to support and enhance your presentation. At the same time, you must make sure these media do not distract your audience or interfere with getting your point across. Your ideas, not your visuals, should be the focus.
As you develop the visual side of your presentation, you will follow a process much like the process you follow when you write. You will brainstorm ideas, form an organizational plan, develop drafts, and then refine and edit your work. The following sections provide guidelines to help you make good decisions throughout the process.
What Makes Visual Aids Effective?
To help you get a sense of what makes visual media work, think about what does not work. Try to recall occasions when you have witnessed the following visual media failures:
- Websites crammed with so many images, flashing phrases, and clashing colors that they are almost unreadable
- Assembly instructions with illustrations or diagrams that are impossible to follow
- Photographs that are obviously (and badly) altered with photo-editing software
- Distracting typos or other errors in signs, advertisements, or headlines
- Tables, charts, or graphs with tiny, dense text or missing labels
In each case, the problem is that the media creator did not think carefully enough about the purpose and audience. The purpose of images, color, or flashing text on a website is to attract attention. Overusing these elements defeats the purpose because the viewer may become overwhelmed or distracted. Tables, charts, and graphs are intended to simplify complex information, but without clear labels and legible text, they will confuse the audience.
In contrast, effective visual elements are chosen or created with the purpose and audience in mind. Although a photo shoot for a magazine article might result in dozens of images, editors choose those few that work best with the article. Web designers and video game creators have an audience test their products before they are released, to ensure that people will understand how to use them. Understanding the function of different visual aids will help you use them with purpose.
Types of Visual Aids
Visual aids fall into two main categories—images and informational graphics. Images include photographs, illustrations and clip art, and video footage. Informational graphics include tables, charts, bar graphs, and line graphs.
These visual aids serve two purposes: to add emotional impact to your presentation and to organize information more clearly. With that in mind, read to find out how specific types of visual aids achieve those purposes.
Photographs
A striking photograph can capture your audience’s attention far more successfully than words can. Consider including photographs at the beginning or end of your presentation to emphasize your main ideas or to accompany a particularly important point in the body of your presentation. Remember that, as with other types of graphics, less is often more. Two or three well-chosen photographs are more effective than a dozen mediocre ones.
When you choose photographs, ask yourself these questions:
- What purpose does this image serve? Will it surprise the audience? Will it provoke a strong emotional response? Does it support an important point?
- Will this photograph be more effective if shown with only a caption, or does it need additional text?
- Will the audience understand what is happening in the photograph? Is the meaning immediately evident, or does the photo need some context?
- Would editing the image make it more effective? Consider using image-editing software to crop the photo, change the brightness, or make other cosmetic changes. (Do not go overboard, though. A slightly imperfect but authentic image is preferable to one that has been obviously altered.)
To illustrate the sense of helplessness people felt in the midst of tragedy, a student could use a photograph that shows fear, weariness, or defeat on the face of the photograph’s subject.
Figure 14.3

Neil Moralee – On The Scrap Heap . – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Illustrations
Illustrations, such as editorial or political cartoons, serve much the same purpose as photographs. Because an illustration does not capture a moment in time the way a photo does, it may have less impact. However, depending on your topic and the effect you want to achieve, illustrations can still be very useful. Use the same criteria for choosing photographs to help you choose illustrations.
Figure 14.4

Humor Blog – Political Cartoon about Budget Cuts – CC BY 2.0.
The style of an illustration or photograph affects viewers just as the content does. Keep this in mind if you are working with the stock images available in office software programs. Many of these images have a comical tone. This may be fine for some topics—for instance, a presentation on television shows for children. However, if you need to project a more serious tone, make sure you choose images to suit that purpose. Many free (or reasonably priced) image banks are available online.
Video Footage
Even more than photographs, video footage can create a sense of immediacy, especially if your video includes sound. Showing a brief video clip can help your audience feel as if they are present at an important event, connect with a person being interviewed, or better understand a process. Again, ask yourself the following questions to ensure you are using the footage well:
- What purpose does this video serve? (Never rely on video clips just to fill time.)
- How much footage should be shown to achieve your purpose?
- What will need to be explained, before or after showing the video, to ensure that your audience understands its significance?
- Will it be necessary to edit the video to stay within time requirements or to focus on the most important parts?
Informational graphics, such as tables, charts, and graphs, do not provoke the same response that images do. Nevertheless, these graphics can have a powerful impact. Their primary purpose is to organize and simplify information.
Tables are effective when you must classify information and organize it in categories. Tables are an especially good choice when you are presenting qualitative data that are not strictly numerical. Table 14.1 “Example of Qualitative Data Table” was created for a presentation discussing the subprime mortgage crisis. It presents information about people who have held powerful positions both in the government and at one of the investment banking firms involved in the subprime mortgage market.
Table 14.1 Example of Qualitative Data Table
Sources: http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/news/%3Bkw=%5B3351,11459%5D ; http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/19/business/19gold.html ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/p/henry_m_jr_paulson/index.html?inline=nyt-per ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/r/robert_e_rubin/index.html?inline=nyt-per , http://www.nytimes.com/2002/12/13/us/man-in-the-news-economic-adviser-from-other-side-of-the-deficit-stephen-friedman.html ; http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/342086.stm .
If you are working with numerical information, consider whether a pie chart, bar graph, or line graph might be an effective way to present the content. A table can help you organize numerical information, but it is not the most effective way to emphasize contrasting data or to show changes over time.
Pie charts are useful for showing numerical information in percentages. For example, you can use a pie chart to represent presidential election results by showing what percentage of voters voted for the Democratic presidential candidate, the Republican candidate, and candidates from other political parties.
Figure 14.5
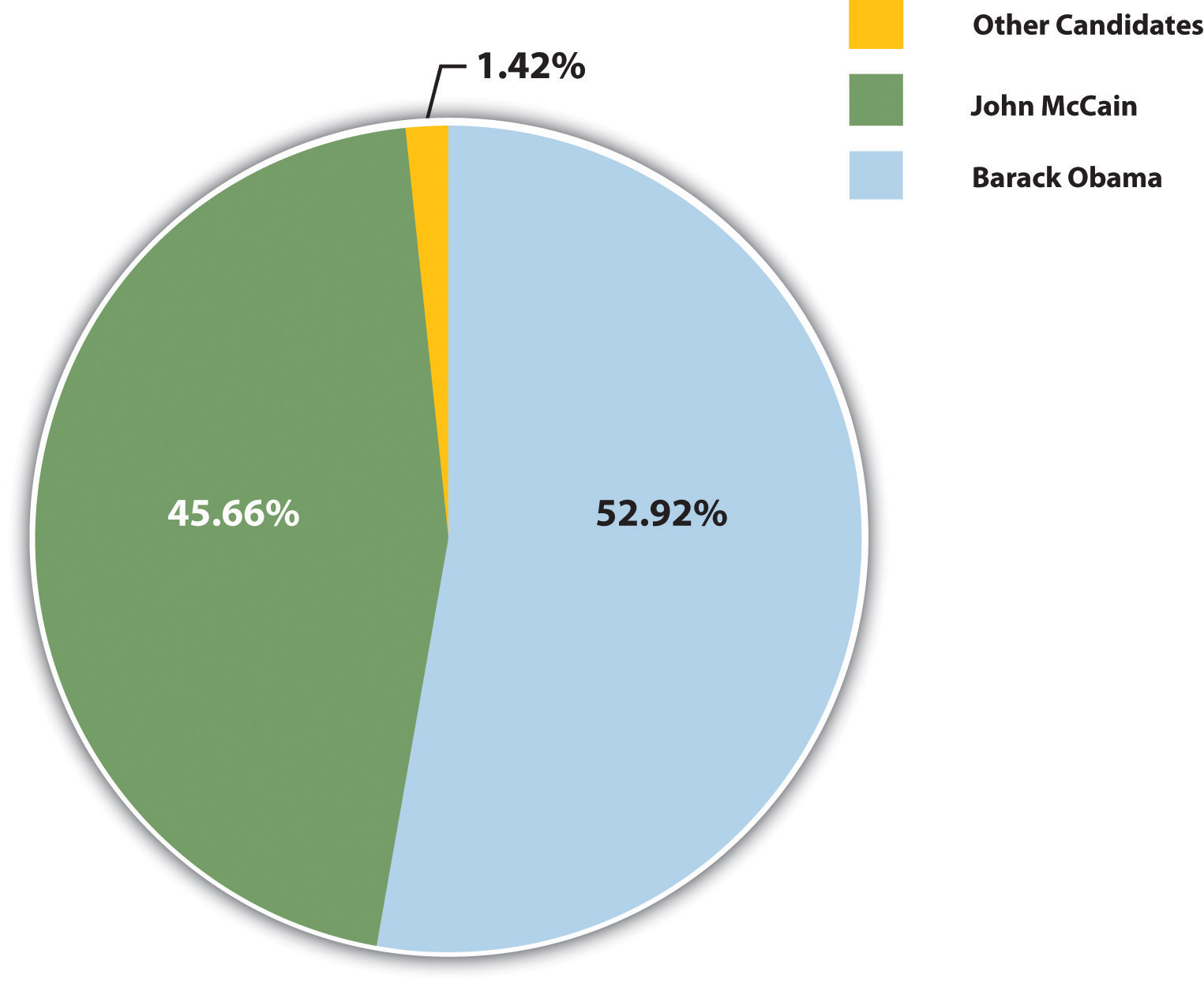
Source: http://www.fec.gov/pubrec/fe2008/2008presgeresults.pdf
Bar graphs work well when you want to show similarities and differences in numerical data. Horizontal or vertical bars help viewers compare data from different groups, different time periods, and so forth. For instance, the bar graph in Figure 14.6 allows the viewer to compare data on the five countries that have won the most Olympic medals since the modern games began in 1924: Norway, the United States, the former Soviet Union, Germany, and Austria. Bar graphs can effectively show trends or patterns in data as well.
Figure 14.6
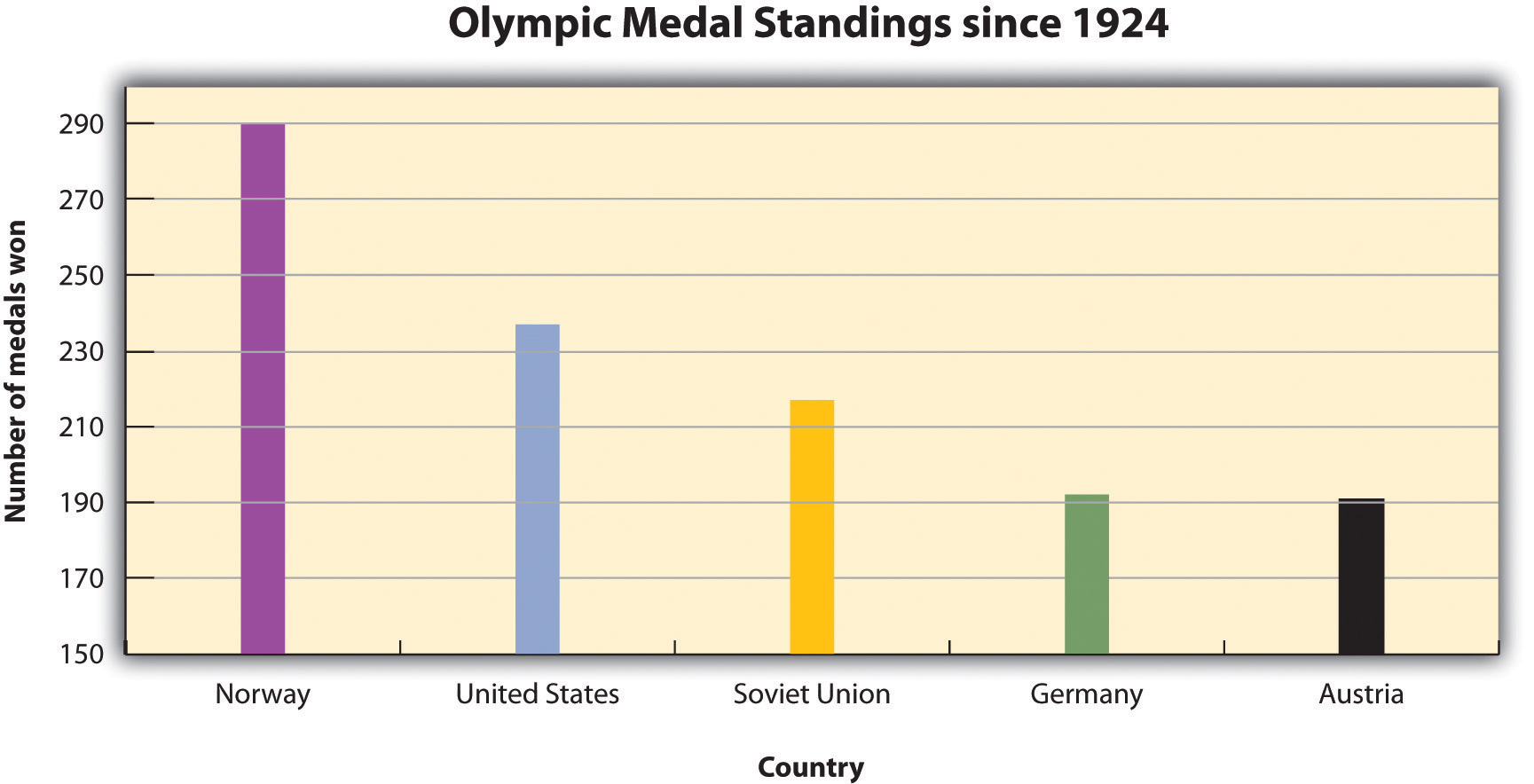
Source: http://www.nbcolympics.com/medals/all-time-standings/index.html
Line Graphs
Like bar graphs, line graphs show trends in data. Line graphs are usually used to show trends in data over time. For example, the line graph in Figure 14.7 shows changes in the Dow Jones Industrial Average—an economic index based on trading information about thirty large, US-based public companies. This graph shows where the Dow closed at the end of each business day over a period of five days.
Figure 14.7
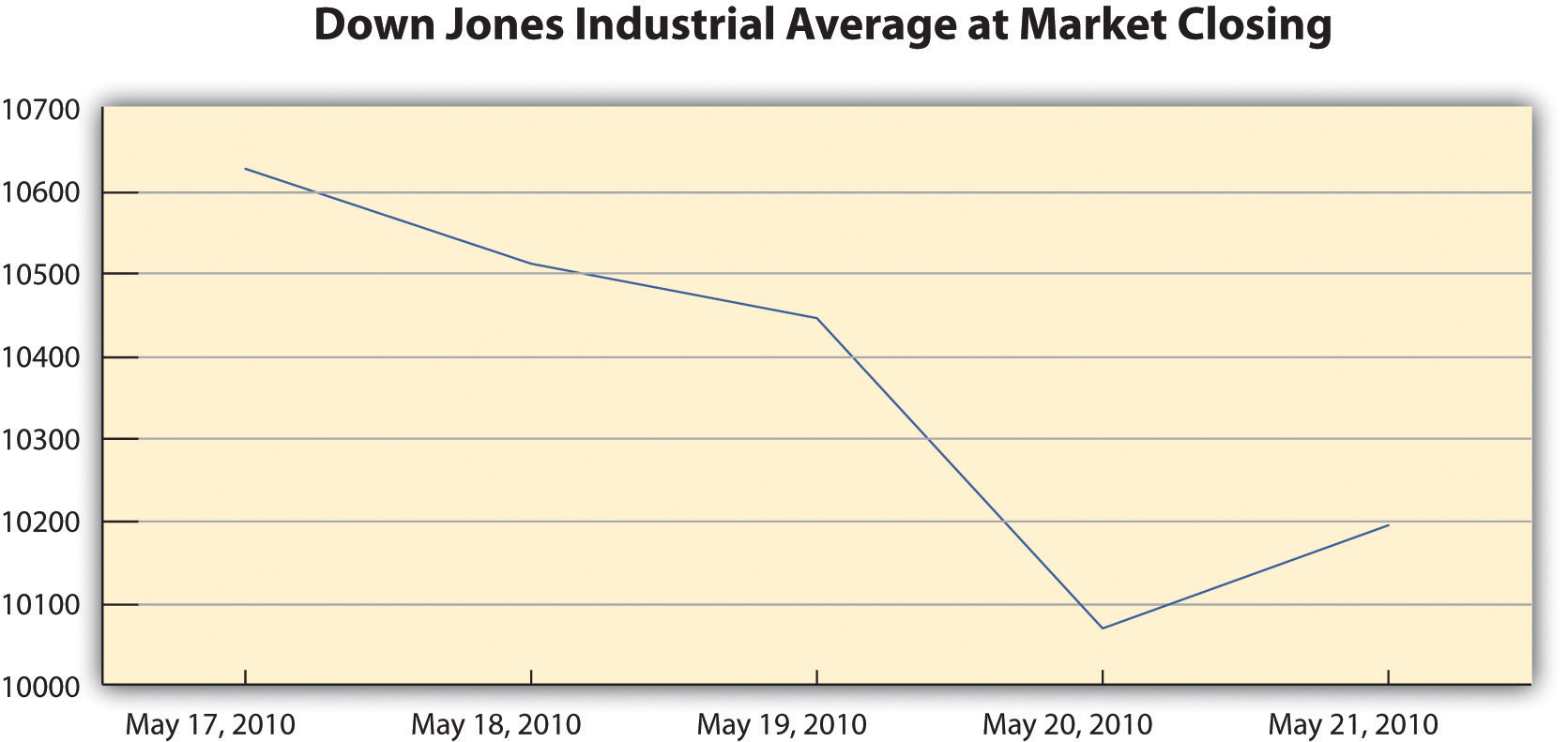
Source: http://www.google.com/finance/historical?cid=983582&startdate=May+17%2C+2010&enddate=May+21%2C+2010
In this exercise, you will begin to refine your ideas for incorporating media into your presentation. Complete the following steps on your own sheet of paper.
- Revisit the list you brainstormed for Note 14.12 “Exercise 3” in Chapter 14 “Creating Presentations: Sharing Your Ideas” , Section 14.1 “Organizing a Visual Presentation” and the annotated outline you developed for Note 14.17 “Exercise 4” .
- Analyze the two different types of visual aids: images and informational graphics. Identify at least two places in your presentation where you might incorporate visual aids.
- Evaluate the purpose of the visual aid. Does it create emotional impact, or does it organize information? Is the visual effective?
- Determine whether you will be able to create the visual aid yourself or will need to find it.
Creating Original Visual Aids
You will include original visual aids in your presentation to add interest, present complex information or data more clearly, or appeal to your audience’s emotions. You may wish to create some visual aids by hand—for instance, by mounting photographs on poster board for display. More likely, however, you will use computer-generated graphics.
Computer-generated visual aids are easy to create once you learn how to use certain office software. They also offer greater versatility. You can print hard copies and display them large or include them in a handout for your audience. Or, if you are working with presentation software, you can simply insert the graphics in your slides.
Regardless of how you proceed, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Create visual aids with purpose. Think carefully about how they will enhance your message, and choose a form that is appropriate for your content.
- Strive for quality. You do not need the skills of a professional photographer or designer, but do take time to make sure your visual aids are neat, attractive, and legible. Proofread for errors, too.
Using Software to Create Visual Aids
You can use standard office software to create simple graphics easily. The following guidelines describe how to work with word-processing software and presentation software.
Working with Photographs
Most personal computers come equipped with some basic image-editing software, and many people choose to purchase more advanced programs as well. You can upload photographs from a digital camera (or in some cases, a cell phone) or scan and upload printed photographs. The images can then be edited and incorporated into your presentation. Be sure to save all of your images in one folder for easy access.
Creating Tables
To create a table within a word-processing document consult your software program’s help feature or an online tutorial. Once you have created the table, you can edit and make any additional changes. Be sure that the table has no more than six to seven rows or columns because you do not want to compromise the size of the text or the readability. Aligning with precision will help your table look less crowded. Also, the row and column titles should spell out their contents.
Creating Graphs
Figure 14.8
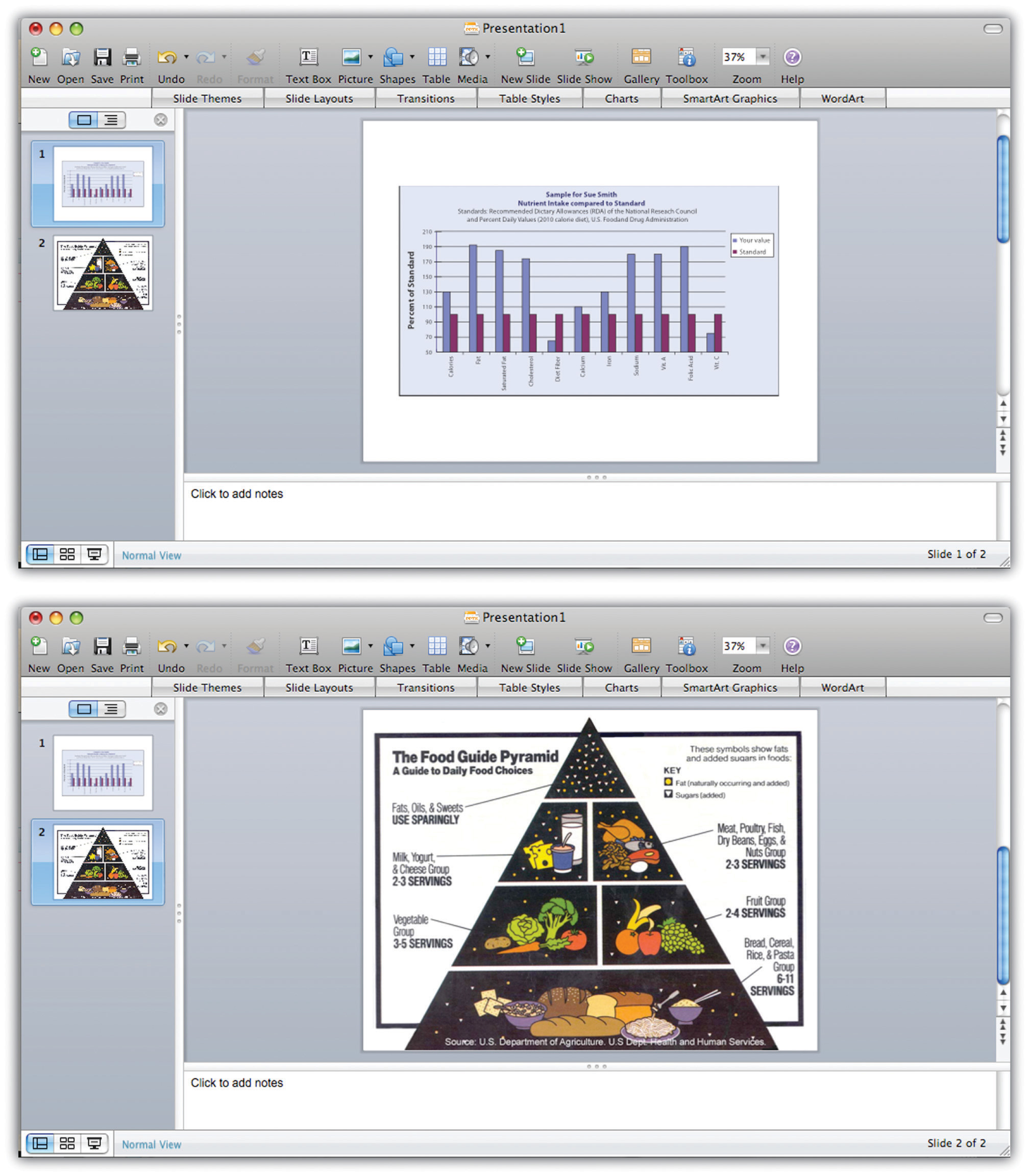
Pie charts and bar and line graphs can also be created using standard office software. Although you can create these graphics within a document, you will need to work with both your word-processing application and your spreadsheet application to do so. The graph should visually explain the data using colors, titles, and labels. The use of color will help the audience distinguish information; however, avoid colors that are hard on the eyes, such as lime green or hot pink. The title should clearly state what the graph explains. Lastly, avoid using acronyms in the titles and other labels.
Creating Graphics in an Electronic Presentation
If you plan to work only with hard copy graphics during your presentation, you may choose to create them as word-processing documents. However, if you are using presentation software, you will need to choose one of the following options:
- Create your graphics using the presentation software program.
- Create your graphics within another program and import them.
Standard office presentation software allows you to create informational graphics in much the same way you would create them within a word-processing application. Keep the formatting palette, a menu option that allows you to customize the graphic, open while you use the software. The formatting menu provides options for inserting other types of graphics, such as pictures and video. You may insert pictures from an image bank available within the program, or insert images or video from your own desktop files. Shape your use of multimedia in accordance with the message your presentation is trying to convey, the purpose, and your audience.
Creating Visual Aids by Hand
Most of the time, using computer-generated graphics is more efficient than creating them by hand. Using office software programs helps give your graphics a polished appearance while also teaching you skills that are useful in a variety of jobs. However, it may make sense to use hand-created visual aids in some cases—for instance, when showing a 3-D model would be effective. If you follow this route, be sure to devote extra time to making sure your visual aids are neat, legible, and professional.
Flip charts are inexpensive and quick visual aids used during face-to-face presentations. The flip chart can be prepared before, as well as during, the presentation. Each sheet of paper should contain one theme, idea, or sketch and must be penned in large letters to be seen by audience members farthest away from the speaker.
Writing Captions
Any media you incorporate should include a caption or other explanatory text. A caption is a brief, one- to two-sentence description or explanation of a visual image. Make sure your captions are clear, accurate, and to the point. Use full sentences when you write them.
Captions should always be used with photographs, and in some cases, they can be useful for clarifying informational graphics, which represent qualitative data visually. However, informational graphics may not require a caption if the title and labels are sufficiently clear. For other visual media, such as video footage, providing explanatory text before or after the footage will suffice. The important thing is to make sure you always include some explanation of the media.
In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing.
- Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas that you can create. ( Note: If you are using software to develop a slideshow presentation, count this as one of your self-created visual aids. Include at least one other self-created visual aid, such as an original photograph, within your slideshow.)
- Get creative! Take your photographs, construct a 3-D model, create informational graphics, or work on your presentation slides. Develop good working drafts.
- After you have completed drafts of your visual aids, set them aside for a while. Then revisit them with a critical eye. First, check any text included with the graphic. Make sure your facts are correct, your words are clear and concise, and your language is free of errors.
- Next, evaluate how well your aids work visually. Are they large enough to be seen and read from a distance? Are captions and labels easy to find? Are photographs of reasonably high quality? Ask someone else for feedback, too.
- Begin making any needed changes. As you proceed through the rest of this section, continue to revisit your work to improve it as needed.
Collaboration
Please share the first version of your visual aids with a classmate. Examine what they have produced. On a separate piece of paper, note both the elements that catch your attention and those that would benefit from clarification. Return and compare notes.
Testing and Evaluating Visual Aids
Regardless of how you create your visual aids, be sure to test-drive them before you deliver your presentation. Edit and proofread them, and if possible, show them to someone who can give you objective feedback. Use the following checklist.
Checklist 14.1
Visual Aid Evaluation Checklist
- Visual aids are clearly integrated with the content of the presentation
- Photographs and illustrations suit the overall tone of the presentation
- Images and text are large and clear enough for the viewer to see or read
- Images are shown with explanatory text or a caption
- Informational graphics include clear, easy-to-read labels and headings
- Text within informational graphics is easy to read (Watch out for wordiness and crowded text or a font that is too small and hard to read.)
- Formatting choices (color, different fonts, etc.) organize information effectively
- Any text within graphics is free of errors
- Hyperlinks within slides function properly
- Display text for hyperlinks is concise and informative (Never paste a link into a slide without modifying the display text.)
Writing at Work
Office software includes many options for personalizing a presentation. For instance, you can choose or create a theme and color scheme, modify how one slide transitions to the next, or even include sound effects. With so many options, students and employees sometimes get carried away. The result can seem amateurish and detract from, rather than enhance, your presentation.
Remember, you are delivering a presentation, not producing a movie. Use the customization options to help give your presentations a consistent, polished, appearance. However, do not let these special effects detract from the substance of your slides.
Using Existing Visual Media
Depending on your topic, you may be able to find images and other graphics you can use instead of creating your own. For instance, you might use photographs from a reputable news source or informational graphics created by a government agency. If you plan to use visual aids created by others, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Set a purpose before you begin your search. You will search more efficiently if you start with a general idea of what you are looking for—a line graph of unemployment rates for the past twelve months, for example, or a video clip of the most recent State of the Union address.
- Filter out visual aids that are not relevant. You may come across eye-catching graphics and be tempted to use them even if they are only loosely related to your topic, simply because they are attention getting. Resist the temptation. If the graphic is not clearly connected to your point, it does not belong in your presentation.
- Read carefully. In addition to reading labels, headings, and captions, read any text that accompanies the visual. Make sure you understand the visual in its original context. For informational graphics, make sure you understand exactly what information is being represented. (This may seem obvious, but it is easy to misread graphic information. Take the time to examine it carefully.)
- Evaluate sources carefully and record source information. When you look for visual media to complement your presentation, you are conducting research. Apply the same standards you used for your research paper. Choose reliable sources, such as reputable news organizations, government and nonprofit organizations, and educational institutions. Verify data in additional sources. Finally, be sure to document all source information as you proceed.
Searching Efficiently for Visual Media
You will probably find it most efficient to use the Internet to search for visual aids. Many students begin by typing keywords into a search engine to locate related images. However, this search technique is not necessarily efficient, for several reasons:
- It often pulls up hundreds or even thousands of images, which may be only loosely related to your search terms.
- It can sometimes be difficult to understand the image in its original context.
- It can be hard to find copyright information about how you may use the image.
A more efficient strategy is to identify a few sources that are likely to have what you are looking for, and then search within those sites. For instance, if you need a table showing average life expectancy in different countries, you might begin with the website of the World Health Organization. If you hope to find images related to current events, news publications are an obvious choice. The Library of Congress website includes many media related to American history, culture, and politics.
Searching this way has the following advantages:
- You will often find what you are looking for faster because you are not wasting time scrolling through many irrelevant results.
- If you have chosen your sources well, you can be reasonably certain that you are getting accurate, up-to-date information.
- Images and informational graphics produced by reputable sources are likely to be high quality—easy to read and well designed.
If you do choose to use a search engine to help you locate visual media, make sure you use it wisely. Begin with a clear idea of what you are looking for. Use the advanced search settings to narrow your search. When you locate a relevant image, do not download it immediately. Read the page or site to make sure you understand the image in context. Finally, read the site’s copyright or terms of use policy—usually found at the bottom of the home page—to make sure you may use the material.
If you are unable to find what you are looking for on the Internet consider using print sources of visual media. You may choose to mount these for display or scan them and incorporate the files into an electronic presentation. (Scanning printed pages may lower the quality of the image. However, if you are skilled at using photo-editing software, you may be able to improve the quality of the scanned image.)
Inserting Hyperlinks in an Electronic Presentation
If you are working with images, audio, or video footage available online, you may wish to insert a link within your presentation. Then, during your presentation, you can simply click the link to open the website in a separate window and toggle between windows to return to your presentation slides.
To insert a hyperlink within your presentation, click on insert in the toolbar and then select hyperlink from the menu. Doing so will open a dialogue box where you can paste your link and modify the accompanying display text shown on your slide.
Copyright and Fair Use
Before you download (or scan) any visual media, make sure you have the right to use it. Most websites state their copyright and terms of use policy on their home page. In general, you may not use other people’s visual media for any commercial purpose without contacting the copyright holder to obtain permission and pay any specified fees.
Copyright restrictions are somewhat more ambiguous when you wish to download visual media for educational uses. Some educational uses of copyrighted materials are generally considered fair use —meaning that it is legally and ethically acceptable to use the material in your work. However, do not assume that because you are using the media for an educational purpose, you are automatically in the clear. Make sure your work meets the guidelines in the following checklist. If it does, you can be reasonably confident that it would be considered fair use in a court of law and always give credit to the source.
Checklist 14.2
Media Fair Use Checklist
- You are using the media for educational purposes only.
- You will make the work available only for a short period and to a limited audience. For instance, showing a copyrighted image in a classroom presentation is acceptable. Posting a presentation with copyrighted images online is problematic. In addition, avoid any uses that would allow other people to easily access and reproduce the work.
- You have used only as much of the work as needed for your purposes. For video and audio footage, limit your use to no more than 10 percent of the media—five minutes of an hour-long television show, for example. Image use is harder to quantify, but you should avoid using many images from the same source.
- You are using the media to support your own ideas, not replace them. Your use should include some commentary or place the media in context. It should be a supporting player in your presentation—not the star of the show.
- You have obtained the material legally. Purchase the media if necessary rather than using illegally pirated material.
- Your use of the media will not affect the copyright holder or benefit you financially.
By following these guidelines, you are respecting the copyright holder’s right to control the distribution of the work and to profit from it.
In some fields, such as teaching, job applicants often submit a professional portfolio to a prospective employer. Recent college graduates may include relevant course work in their portfolios or in applications to graduate school. What should you do if your course work uses copyrighted visual media?
This use of media is acceptable according to fair use guidelines. Even though you are using the work for your personal professional advancement, it is not considered an infringement on copyright as long as you follow the additional guidelines listed in the previous checklist.
Crediting Sources
As you conduct your research, make sure you document sources as you proceed. Follow the guidelines when you download images, video, or other media from the Internet or capture media from other sources. Keep track of where you accessed the media and where you can find additional information about it. You may also provide a references page at the end of the presentation to cite not only media and images but also the information in the text of your presentation. See Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” for more information on creating a reference page.
Write captions or other explanatory text for visual media created by others, just as you would for media you created. Doing so helps keep your audience informed. It also helps ensure that you are following fair use guidelines by presenting the media with your commentary, interpretation, or analysis. In your caption or elsewhere in your presentation, note the source of any media you did not create yourself. You do not need to provide a full bibliographical citation, but do give credit where it is due.
In this exercise, you will locate visual aids created by others and continue developing the work you began earlier. Complete these steps.
1. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas for which it would make more sense to find the visual aid than to create it yourself. 2. Use the search tips provided in this section to locate at least two visual aids from reputable sources that you can use. Prepare them for your presentation by adding clarifying text as needed. Be sure to credit your source. 3. Incorporate the visual aids you created in Note 14.26 “Exercise 2” and Note 14.32 “Exercise 3” into your presentation. This may involve preparing physical copies for display or inserting graphic files into an electronic presentation.
4. Take some time now to review how you will integrate the visual and verbal components of your presentation.
- If you are working with presentation software, refine your slides. Make sure the visual approach is consistent and suits your topic. Give your text a final proofread.
- If you are not using presentation software, review the annotated outline you created in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Update it as needed to reflect your current plan. Also, determine how you will physically set up your visual aids.
Key Takeaways
- Visual aids are most effective when they are chosen with the purpose and audience in mind. They serve to add emotional impact to a presentation and to organize information more clearly.
- Visual aids should always be clearly related to the presenter’s ideas. Captions, labels, and other explanatory text help make the connection clear for the audience.
- Like writing, developing the visual components of a presentation is a process. It involves generating ideas, working with them in a draft format, and then revising and editing one’s work.
- Visual aids can be divided into two broad categories—image-based media and informational graphics.
- Widely available software programs make it relatively easy to create visual aids electronically, such as photo images, charts, and graphs.
- When using visual aids created by others, it is important to apply good research skills, follow guidelines for fair use, and credit sources appropriately.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Are looking for custom service?
- Presentation Design
- Report Design
- Brochure Design
- Infographic Design
- Illustration Design
- Package Design
- Exhibition Design
- Print Design
- Logo Design
- Video Animation
- Motion Graphics
Visuals in Presentations
The Importance of Visuals in Presentations
Emily Bryce
17 April 2023

As humans, we are naturally drawn to visual elements. We process images much faster than we do text. This is why incorporating visuals in presentations is crucial in effectively conveying your message to your audience. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of visuals in presentations and how they can enhance your message.

1. Visuals make information more memorable
One of the main reasons why visuals are important in presentations is because they make information more memorable. People are more likely to remember an image than a block of text. According to research, people remember up to 80% of what they see, compared to only 20% of what they read.
When you incorporate visuals in your presentation, you’re not only making it easier for your audience to remember your message, but you’re also making it more engaging. This is especially important if you’re presenting complex data or statistics. By using charts, graphs, and other visual aids, you can help your audience understand and remember the information you’re presenting.
2. Visuals help you connect with your audience
Visuals can also help you connect with your audience on a more emotional level. When you use images, videos, or other visual elements, you can tap into your audience’s emotions and help them relate to your message. This is especially important if you’re presenting to a diverse audience with different backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives.
By incorporating visuals that are relevant and relatable to your audience, you can build trust and credibility. This can help you establish a stronger connection with your audience and make it more likely that they’ll remember your message.
3. Visuals make your presentation more engaging
Another benefit of using visuals in presentations is that they make your presentation more engaging. When you use visuals, you can break up the monotony of a text-heavy presentation and capture your audience’s attention.
Visuals can also help you pace your presentation and keep your audience engaged throughout. You can use visuals to transition between topics, illustrate key points, or simply provide a visual break for your audience.
4. Visuals help you communicate complex information
Visuals can also be incredibly helpful when you need to communicate complex information. When you’re presenting data, statistics, or other technical information, it can be difficult to convey your message in a way that is both accurate and understandable.
By using visuals like charts, graphs, and info-graphics, you can help your audience understand complex information more easily. Visuals can help you illustrate key points, highlight trends, and make data more accessible and understandable for your audience.
5. Visuals help you stand out from the crowd
Finally, using visuals in your presentations can help you stand out from the crowd. In today’s fast-paced world, attention spans are short, and audiences are easily distracted. By using visuals, you can create a presentation that is more engaging, memorable, and impactful than a text-heavy presentation.
Visuals can also help you differentiate yourself from other presenters who may be presenting on similar topics. By using visuals that are unique and relevant to your message, you can create a presentation that is more memorable and distinctive.
In conclusion, visuals are incredibly important in presentations. They can help you make your message more memorable, connect with your audience on an emotional level, make your presentation more engaging, communicate complex information, and stand out from the crowd.
If you’re looking to enhance your presentations, consider incorporating more visuals. You can use images, videos, charts, graphs, infographics, or other visual aids to make your message more impactful and memorable. By using visuals effectively, you can create a presentation that resonates with your audience and leaves a lasting impression.
Stay Updated
Join our exclusive subscribers list to receive the latest design trends, industry updates and digital world insights in your inbox.
You can read our privacy policy here .
Related Posts

The Power of Storytelling in Presentations

The Do’s and Don’ts of Presentation Design

How to Use Videos in Your Presentations

How to Create a Powerful Opening for Your Presentation

My Presentation Designer is a brand of Out of Box Ltd. which is a registered company in England and Wales under company no. 06937876 and VAT ID GB381889149 .
Copyright © 2015-2023 • My Presentation Designer • All rights reserved.
2024’s Must-See Visual Presentation Examples to Power Up Your Deck
Anh Vu • 28 Feb 2024 • 6 min read
Keep on reading because these visual presentation examples will blow your boring decks away! For many people, delivering a presentation is a daunting project, even before it turns to hybrid and virtual displays due to the pandemic. To avoid the Death By PowerPoint phenomenon, it is time to adopt new techniques to make your presentations more visual and impressive.
This article tries to encourage you to think outside of the slide by providing essential elements of a successful visual presentation, especially for the new presenter and those who want to save time, money, and effort for the upcoming presentation deadline.
Table of Contents
What is a visual presentation.
- Types of Visual Presentation Examples
How to Create a Visual Presentation
- What Makes a Good Presentation Visual?
Frequently Asked Questions
How ahaslides supports a good visual presentation.
As mentioned before, you need a presentation tool to make your presentation more visual and engaging. The art of leveraging visual elements is all intended visual aids make sense and kick off audiences’ imagination, curiosity, and interest from the entire presentation.
The easiest way to create interaction between the presenter and the audience is by asking for rhetorical and thought-provoking quizzes and quick surveys during the presentation. AhaSlides , with a range of live polls, interactive questions, image questions, creative fonts, and integration with streaming platforms can help you to make a good visual presentation in just a second.
- Types of Presentation
- College Presentation
- Creative Presentation Ideas
- AhaSlides Free Public Templates

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
So, what are the visual presentation examples? When providing as much information as possible, many presenters think that text-heavy slides may help, but by contrast, they may lead to distraction. As we explore the characteristics of good presentations, illustrations and graphics play an important role in delivering compelling content and turning complex concepts more clearly, precisely, and instantly to understand. A visual presentation is the adoption of a range of visual aids on presentation to ensure information is easier to understand and memorize.
In addition, visual aids can also help to keep presenters on track, which can be used as a cue for reviving a train of thought. They build better interaction and communication between presenters and the audience, making them notice more deeply what you are saying.
Types of Visual Presentation Examples
Some possible visual presentations include infographics , charts, diagrams, posters, flipcharts, whiteboards, and video presentation examples.
An infographic is a collection of different graphic visual presentations to represent information, data, or knowledge intended more visually quickly and clearly to grab the audience’s attention.
To illustrate quantitative data effectively, it is important to make use of graphs and charts. For both business use and research use, graphs and charts can show multiple and complex data in a way that is easy to understand and memory.
When it comes to presenting information systematically and logically, you can use diagrams. A diagram is a powerful tool for effective communication and brainstorming processes. It also is time-saving for people to read and collect information.
A poster, especially a research project poster, provides brief and concrete information about a research paper straightforwardly. The audiences can grab all important data knowledge and findings through posters.
A flipchart and whiteboard are the most basic presentation aids and work best to supplement lecture slides. Excellent whiteboard and flipchart composite of well-chosen words, and clear diagram will help to explain complex concepts.
A video presentation is not a new concept, it is a great way to spread ideas lively and quickly attract the audience’s attention. The advantages of a video presentation lie in its animation and illustration concepts, fascinating sound effects, and user-friendliness.
In addition, we can add many types of visual aids in the presentations as long as they can give shapes and form words or thoughts into visual content. Most popular visual aids include graphs, statistics, charts, and diagrams that should be noted in your mind. These elements combined with verbal are a great way to engage the listeners’ imagination and also emphasize vital points more memorable.

It is simply to create more visual presentations than you think. With the development of technology and the internet, you can find visual presentation examples and templates for a second. PowerPoint is a good start, but there are a variety of quality alternatives, such as AhaSlides , Keynote, and Prezi.
When it comes to designing an effective visual presentation, you may identify some key steps beforehand:
Visual Presentation Examples – Focus on Your Topic
Firstly, you need to determine your purpose and understand your audience’s needs. If you are going to present in a seminar with your audience of scientists, engineers, business owners… They are likely to care about data under simple charts and graphs, which explain the results or trends. Or if you are going to give a lecture for secondary students, your slides should be something fun and interesting, with more colourful pictures and interactive questions.
Visual Presentation Examples – Animation and Transition
When you want to add a bit of excitement to a slideshow and help to keep the listener more engaged, you use animation and transition. These functions help to shift the focus of audiences between elements on slides. When the transition style and setting are set right, it can help to give fluidity and professionalism to a slideshow.
Visual Presentation Examples – Devices for Interactivity
One of the approaches that improve communication between audiences and the use of visual aids is using technology assistance. You don’t want to take too much time to create well-designed visual aids while ensuring your presentation is impressive, so why not leverage a presentation app like AhaSlides ? It properly encourages participant engagement with interactive visual features and templates and is time-saving. With its help, you can design your presentation either formally or informally depending on your interest.
Visual Presentation Examples – Give an Eye-catching Title
Believe it or not, the title is essential to attracting audiences at first sight. Though don’t “read the book by its cover”, you still can put your thoughts into a unique title that conveys the topic while piquing the viewer’s interest.
Visual Presentation Examples – Play a Short Video
Creative video presentation ideas are always important. “Videos evoke emotional responses”, it will be a mistake if you don’t leverage short videos with sound to reel in and captivate the audience’s attention. You can put the video at the beginning of the presentation as a brief introduction to your topic, or you can play it as a supplement to explain difficult concepts.
Visual Presentation Examples – Use a Prop or Creative Visual Aid to Inject Humour
It is challenging to keep your audience interested and engaged with your audience from the whole presentation. It is why to add a prop or creative visual aid to pull your audience’s focus on what you say. Here are some ideas to cover it:
- Use neon colour and duotones
- Tell a personal story
- Show a shocking heading
- Use isometric illustrations
- Go vertical
Visual Presentation Examples – Rehearsal and Get Feedback
It is an important step to make your visual presentation really work out. You won’t know any unexpected mirrors may come out on D-day if you don’t make the rehearsal and get feedback from a reliable source. If they say that your visual image is in bad-quality, the data is overwhelming, or the pictures are misunderstood, you can have an alternative plan in advance.

What Makes a Good Visual Presentation?
Incorporate visual or audio media appropriately. Ensure you arrange and integrate suitable data presentation in your slides or videos. You can read the guidelines for visual aids applications in the following:
- Choose a readable text size about the slide room and text spacing in about 5-7 doubted-spaced.
- Use consistent colour for overall presentation, visual aids work better in white yellow and blue backgrounds.
- Take care of data presentation, and avoid oversimplification or too much detail.
- Keep the data shown minimum and highlight really important data points only.
- Choose font carefully, keep in mind that lowercase is easier to read than uppercase
- Don’t mix fonts.
- Printed text is easier to read than handwritten text.
- Use the visual to emphasize punctuation in your verbal presentation.
- Say no to poor-quality images or videos.
- Visual elements need to be strategic and relevant.
What well-designed visual aids should have?
To make an effective visual aid, you must follow principles of design, including contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity.
Why is it important to keep visual aids simple?
Simple ads help to keep things clear and understandable, so the message can be communicated effectively.
What is the purpose of visual aids in the classroom?
To encourage the learning process and make it easier and more interesting so students would want to engage in lessons more.

More from AhaSlides

10 Tips to achieve Visual Consistency in Presentations
Ralf (IconUncle)
When creating presentations, visual consistency plays a crucial role in conveying your message effectively and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. Consistency in design helps maintain coherence, improves understanding, and enhances the overall impact of your presentation. Whether you’re presenting to clients, colleagues, or a broader audience, follow these ten tips to achieve visual consistency and elevate the quality of your presentations.
1. Choose a Theme and Stick to It
Selecting a consistent theme for your presentation lays the foundation for visual consistency. This involves choosing a color scheme, font styles, and layout elements that align with your topic and brand. Once you’ve settled on a theme, make sure to maintain it throughout the entire presentation to create a harmonious and polished look.
2. Standardize Fonts and Typography
Using a variety of fonts can create confusion and distract your audience. Instead, opt for two or three complementary fonts—one for headings and the other(s) for body text. Ensure they are easy to read, especially from a distance. Stick with these chosen fonts throughout the presentation to maintain a consistent visual identity.
3. Create a Master Slide
Most presentation software allows you to create master slides, which act as templates for all your slides. Design a master slide that includes your chosen theme elements, such as the background, logo , and page numbers. Utilize this master slide consistently for all your presentation slides to maintain a cohesive appearance. (Press ALT+CMND+1 on Mac to Access Slide Master in PowerPoint)
4. Align Elements and Use Grids
Visual consistency is also about arranging elements in an organized manner. Employ grids and guidelines to align text boxes, images, and other content on your slides. Keeping elements consistent in their positioning will create a polished and professional look.
5. Limit Color Palette
Using too many colors can overwhelm your audience and undermine visual consistency. Stick to a limited color palette that complements your theme and brand. Avoid using clashing colors and ensure your color choices are consistent across all slides. Find great color combinations on Adobe Color .
6. Use High-Quality Images
Incorporating relevant and high-quality images can enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Ensure that the images you use are consistent in style, resolution, and quality. Avoid mixing different image types as this may lead to visual dissonance.
7. Maintain Slide Layout Consistency
Consistent slide layouts contribute to a smoother flow and improve the audience’s ability to follow your presentation. Use the same layout structure for slides that serve similar purposes. For example, keep title slides consistent, as well as content slides, and any other slide types you might use.
8. Visual consistency through hierarchy
Creating a clear visual hierarchy helps your audience focus on the most important elements. Use size, color, and placement to emphasize key points, headings, or data. This will guide your audience through the presentation in a logical and coherent manner.
9. Limit Animations and Transitions
While animations and transitions can add interest to your presentation, excessive use of them can be distracting and disrupt visual consistency. Stick to simple and consistent animations that complement your content without overshadowing it.
10. Use a visual consistent icon library
Icons from stock portals often have different styles because they come from different designers. IconUncle gives you access to thousands of icons in a consistent visual style, which helps you create professional presentations. Get started with the free vector icons .
The consistency of visual design principles. why is this important?
Visual consistency in presentations is a critical aspect of delivering your message effectively. By following these ten tips, you can create a visually appealing and coherent presentation that captivates your audience and leaves a lasting impression. Remember, a consistent design not only enhances the aesthetics but also helps convey your ideas with clarity and impact. So, next time you prepare a presentation, keep these tips in mind to achieve visual consistency and take your presentations to the next level.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Visual Aids In Presentations: The Complete Guide
@danishd This is a sample bio. You can change it from WordPress Dashboard, Users → Biographical Info. Biographical Info
Published Date : August 21, 2020
Reading Time :
A picture, they say, is worth a thousand words. Using visual aids in presentations helps you pass a lot of information in a relatively shorter time. With the right visual aids, you can create the desired impact that you want your presentation to make on your audience. Learning how to use visual aids effectively will boost the quality of your presentations. We discuss some of the top visual aids in our recent YouTube video :
Visual Aid Definition
What are visual aids? Simply put, visual aids are things that your listening can look at while you give your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Visual aid appeals to the audience’s vision more than any other sensory organ.
Why use visuals for presentations?
There is no such thing as a perfect Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, there are ways to make a presentation closer to perfection. What are they? Simple: Visual aids. Visual aids can bring life back into a tedious Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , and they take less time to come up with than long notes. This article discusses how you can use visual aids effectively and conquer an audience. Before that, we discuss how visuals can help you achieve a better presentation.
They help you structure your work.
Using the right types of visual aids can help you create a perfect picture of what you want your audience to see in your presentations. Instead of struggling to condense a lot of information into a long text, you can present your information in one straightforward image or video and save yourself the stress.
It is easier to engage the audience.
An excellent visual setup can help elicit audience interest and sometimes their input in the presentation. When the audience is engaged, they tend to be more interested in the presenter’s work. Also, an interactive audience can boost your morale and encourage you.
You save time on your presentation.
When presenting, time is of the essence. So, you can effectively reduce your presentation time if you have useful visual aids and use them properly. Would you prefer to go on and on for minutes about a topic when you can cut your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech down by inserting a few images or videos?
What are visual aids?
A visual aid is any material that gives shape and form to words or thoughts. Types of visual aids include physical samples, models, handouts, pictures, videos, infographics, etc. Visual aids have come a long way, including digital tools such as overhead projectors, PowerPoint presentations, and interactive boards.
Different Types Of Creative Visual Aid Ideas To Awe Your Audience
Have you ever been tasked with making a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or a presentation but don’t know how to make it truly remarkable? Well, visual aid is your answer.
Giving a presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is hard. You have to strike a balance between persuading or informing your audience while also maintaining their attention. The fear of your audience slipping away is very real. And a visual aid can help.
We surveyed the Orai community to vote for their preferred visual aid. Here are the top ten creative visual aid ideas that you could use in your next presentation:
Videos emerged as the clear winner in all our surveys. We ran these surveys on all our social handles and contacted successful speakers. 27.14% of all respondents prefer visual aids because they are easy to understand, can be paused during a presentation, and can trigger all sorts of emotions. That being said, it is also very tough to create good videos. However, more and more tools are available to help you create amazing videos without professional help.
Hans Rosling’s TED talk, titled ‘the best stats you have ever seen,’ is one of the best speeches. He uses video for the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s entirety while not diverting the audience’s attention away from him. He does all this while also bringing out some optimism for the world’s future. We highly recommend this TED talk to learn how to use videos effectively as a visual aid and inject some positivity into your lives during these trying times.
2. Demonstrations
Demonstrations, also known as demos, are undoubtedly among the most effective visual aids for communication. You can use demonstrations in two ways. One as a hook to captivate your audience. Prof. Walter Lewin was famous for using demonstrations as a hook during lectures. In his most famous lecture, he puts his life in danger by releasing a heavy pendulum to show that a pendulum’s period remains constant despite the mass.
Demonstrations can also be used to show how some things are done or work. We use demonstrations to showcase how Orai works and how you can use them to improve your speaking skills.
18.57% voted for demonstrations because they are unique, interactive, up close, and have a personal touch.
3. Roleplays
Jokes aside, why do you think comedy shows are memorable? You guessed it right. Roleplays! Role – play is any speaking activity when you put yourself into somebody else’s shoes or stay in your shoes but put yourself into an imaginary situation!
Nothing is more boring than a comedian delivering lines straight from a joke book. Legendary comedians like George Carlin, Kevin Hart, Chris Rock, and Bill Burr use roleplays effectively and make a mundane joke genuinely memorable.
Jokes aside, you can use roleplays in business presentations and speeches. Use real-life stories or examples in your role plays to make them authentic.
15.71% of the survey respondents voted for roleplays because they are very close to real life and do not take the audience’s attention away from the speaker.
With 12.86% of the votes, Props is number 4. A prop is any concrete object used to deliver a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Props add another dimension to our Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and help the listeners visualize abstract concepts like vision, milestones, targets, and expectations. It ties verbal to visual. Introducing a prop into your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation should not seem forced. Use them sparingly to highlight your address’s most critical points or stories.
People voted for props because they feel 3D visualization is more useful than 2D visualization. Props will make your presentations stand out because few people use them today.
When we sent out the survey to the Orai community and some highly successful speakers, we were sure that slides/presentations would come out on top. However, we were surprised by the results. With 12.86% votes, slides are number five on our list.
Presentations are effortless to create and, therefore, the most commonly used visual aid in business communications. Today, dozens of software programs are available to help you make beautiful presentations. Microsoft PowerPoint is the pioneer in the space and holds a significant market share.
Whatever is your preferred software, you need to keep your audience at the center while making presentations.
People described the ease of creation and the ability to incorporate other visual aids when asked why they chose presentations as their top visual aid.
The inclusion of Audio in this list can appear controversial. But it got a significant vote share in our survey and cannot be ignored. Audio can add a new dimension to your presentations where the audience is hearing your voice and other sound cues that can trigger various emotional responses. Especially when coupled with other visual aids, audio can be a powerful tool for making impactful presentations.
Vote share:
Audio aid is number six, with 4.29% of the votes.
7. Handouts
What is a handout.
A handout is a structured view of your presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that you can distribute to the audience.
What are the benefits of a handout?
Like how this blog gives more information than our YouTube video on the different visual aids, handouts can be used to furnish more information than your discourse itself. They give your audience something to take away after your presentation, making you and your presentation more memorable.
Are you going to be speaking about something overly technical? Then handouts are your friends. Handouts are also an opportunity to facilitate follow-ups if you specify your contact details.
Handouts are tied with whiteboards and got 2.86% of the votes in our survey.
8. Physical & Online Whiteboards
What is a whiteboard.
Traditionally, whiteboards are white, shiny, and smooth boards on which texts and diagrams are made using non-permanent markers. It is widely used in professional presentations, Brainstorming <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:132">A collaborative process to generate ideas freely and spontaneously, fostering creative thinking and problem-solving.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73">Develop a wide range of innovative ideas without judgment or criticism.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:60">Overcome creative blocks and stimulate fresh perspectives.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:67">Encourage participation and engagement from diverse team members.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0">Build upon and combine individual ideas to reach breakthrough solutions.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:96"><strong>Openness:</strong> All ideas are welcomed, regardless of their initial feasibility or practicality.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:109"><strong>Quantity over quality:</strong> Focus on generating as many ideas as possible, even if they seem unconventional.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:93"><strong>Spontaneity:</strong> Encourage quick thinking and rapid-fire suggestions without overanalyzing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:114"><strong>Building upon ideas:</strong> Combine, adapt, and improve upon existing ideas to generate even more unique solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Positive environment:</strong> Maintain a supportive atmosphere where participants feel comfortable sharing their thoughts freely.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:13"><strong>Benefits:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:68">Sparks creativity and innovation, leading to unexpected solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95">Encourages participation and team building, fostering collaboration and a sense of ownership.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:78">It breaks down communication barriers and allows diverse perspectives to shine.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0">It helps identify potential flaws and roadblocks early in the ideation process.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:16"><strong>Application:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-32:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:69">Idea generation for new products, projects, or marketing campaigns.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:78">Problem-solving for existing challenges or obstacles within an organization.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-32:0">Developing communication strategies or messaging frameworks.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="33:1-33:38"><strong>Brainstorming for Public Speaking:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="35:1-38:0"> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-35:86">Use brainstorming with your team to research and develop <strong>public speaking topics</strong>.</li> <li data-sourcepos="36:1-36:122">Generate creative ideas for introductions, transitions, and conclusions in your <strong>professional speaking</strong> presentations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="37:1-38:0">Brainstorm innovative ways to incorporate storytelling, humor, or visuals into your speeches.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190">While brainstorming offers numerous advantages, it's crucial to have a strong facilitator, clear objectives, and a follow-up process to evaluate and refine the generated ideas.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/brainstorming/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">brainstorming sessions, and group discussions. Post-COVID, more and more companies are moving to online whiteboards. Online whiteboards are software that provides a space where individuals across the globe can collaborate online. Many companies have moved beyond the whiteboard and started using online whiteboards for meetings and discussions.
What are the benefits of a whiteboard?
A whiteboard helps listeners better visualize thoughts, concepts, and ideas. It is also a better alternative to the blackboard for a smaller audience as it is tidier and easier to use. Online whiteboards can be used instead of traditional whiteboards without being limited by space constraints. Online whiteboards will transform virtual meetings into a collaborative experience.
With 2.86% of the votes, whiteboards stand at eight on our list.
9. Blackboard
What is a blackboard.
A blackboard (aka chalkboard) is a surface on which texts or diagrams are made using chalk made from calcium sulfate or calcium carbonate. Blackboards are typically used in classrooms for large groups of students.
What are the benefits of blackboards?
Blackboard is one of the foremost and most popular teaching aids. Blackboard is useful for teaching as it helps instructors move from easy to complex topics in an organized manner. Diagrams, symbols, charts, and drawings can be introduced in discourse to bring life to rather dull topics. Blackboards are highly interactive, where the teacher and students can participate during a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
With 1.43% of the vote share, the blackboard stands at the bottom, along with flipcharts.
10. Flipchart
What is a flipchart.
Flipcharts consist of a pad of large sheets of paper bound together. It is typically fixed to the upper edge of a whiteboard or canvas. Flipcharts are easy to create and inexpensive fit for small groups of people.
What are the benefits of presenting using a flipchart?
Nowadays, everybody seems only interested in making presentations powered by computer-generated slide decks. However, the flip chart has its charm. Since most presentations consist of less than ten people, flip charts can be a refreshing change to the standard slide deck. Moreover, flipchart does not require electricity. No electricity and no software means fewer of those last-minute hick-ups.
Flipchart got 1.43% of the vote and shared the bottom position with its counterpart, which we will discuss in the next section.
Master the art of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , practice with Orai
How to make an informative speech with visual aids in presentations
If you have a presentation coming up soon, you can follow the instructions below to learn how you can take advantage of visual aids:
Determine your overall objective
The aim of your presentations depends on you, what information is being presented, and your audience. The motivational speaker and the classroom teacher may approach the same types of visual aids differently due to differences in overall objectives. For instance, if you aim to inspire and remind your audience of salient points, a poster template should serve well; infographics work well when trying to show relationships between complex information. A chart will be quite effective if you seek to explain a given data set.
Choose appropriate visual aids in presentations.
After identifying the overall aim of your presentation, you have to match it with the right visual aids example. Will a graph, picture, or video suffice?
If you use the PowerPoint Presenter, focus mainly on the media that best conveys your message. Make sure that the notes you add are bold and brief. Try to keep your sentence in one line of text.
Prepare thoroughly
You will spend some time preparing your visual aids before the day of your presentation. It is good to allow yourself enough time to prepare so you can perfect your work accordingly. Take note of when, where, and how you will use your visual aids. If you discover some inconsistencies, you can compensate for them by adjusting your choice or using visual aids in presentations.
After you have a final draft of your visual aids, run a series of sessions with them. Let your friends or colleagues be your audience and ask for their honest feedback. Make appropriate adjustments where necessary.
During presentation
First, you need to be comfortable and confident. A neat and appropriate dress should boost your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence . Follow the tips below during presentations.
- Keep your face on your audience. It may help to look a little above their heads while presenting.
- Only point to or take the visual aid when needed. When you do, explain what you mean immediately.
- Do not read texts on your visual aids verbatim.
- Once a visual aid has served its purpose, you should keep it away from your audience’s view.
If you need more help boosting your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence , we have written a detailed piece on how to conquer your fear of speaking in front of people.
What is the importance of using visuals in giving a presentation?
Visual aids in presentations are invaluable to you and the audience you hope to enlighten. They make the job easier for you, and the audience leaves feeling like they learned something. Apart from their time-saving abilities, here are some reasons why you need to incorporate visual aids in your presentations:
- Visual aids can help your audience retain the information long-term.
- The human brain processes images faster than text, so visuals make us understand things faster.
- Using visual aids makes your presentations more enjoyable, interactive, and memorable.
- Visual aids help your audience connect and relate with you better
- Presentations with visual aids are less likely to be misunderstood or misrepresented. They are usually easier to understand and leave little room for confusion
- Visual designs help stimulate cognition and they are great for people with learning disabilities.
- Visual aids act as key cards and pointers for the presenter and help you keep track of what you’re saying
What are the ideas for speech topics using visual aids?
- Use a picture or image that closely represents the topic. A one-hundred-dollar note can suggest topics revolving around money and finances.
- Use a chart showing trends or statistics that your audience finds appealing. You can use popular sayings or quotes to generate topics your audience can relate to.
- Newspaper headlines on related issues can be good starters for opinion-based topics.
Why is the use of color important in presentations, according to research?
Color plays a crucial role in presentations, boosting audience engagement with its ability to enhance motivation and create visually appealing visuals. By understanding color theory and using shades thoughtfully, presenters can ensure their work is professional and organized and accessible to a diverse audience, considering color blindness and cultural associations.
What are the key points to consider when using visual aids in a presentation?
Ensure effective and engaging visuals in your presentation by considering the space, practicing beforehand, utilizing and limiting color strategically (considering color blindness), and maintaining consistency throughout your presentation.
What are some tips for using objects or artifacts as visual aids in presentations?
Objects in presentations can captivate your audience! Choose relevant objects for demonstrations or explanations. In small groups, pass the object around but manage time. For larger audiences, move it around for clear visibility. Reveal the object at the right moment with context and explanation. If demonstrating, use deliberate movements and explain each step clearly to keep them engaged.
What are some tips for using visual aids to engage the audience and maintain their interest?
Capture and keep your audience’s attention with impactful visuals! Ensure clear visibility, maintain eye contact, and use visuals to complement your spoken words, not replace them. Explain each visual promptly and remove it seamlessly when finished to refocus attention on your message.
How can visual aids be tailored to suit the audience and make the presentation more effective?
Craft impactful presentations by tailoring visuals to your audience and goals. Choose relevant and resonant visuals, be it a graph, picture, or video, accompanied by clear, concise notes. Prepare thoroughly, refining visuals and considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback to fine-tune for optimal audience connection.
How should one prepare and use visual aids effectively during a presentation?
Prepare polished visuals beforehand, considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback. During your presentation, prioritize Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity , avoid overwhelming the audience, and use visuals purposefully to enhance, not replace, your message. Practice beforehand and maintain audience engagement through confident delivery.
The visual aid definition is very clear on how much impact using visual aids in Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking has on an audience. With a great selection of visual aids, you can transform your presentations into a pleasant experience that you and your audience will always look forward to.
Become a confident speaker. Practice with Orai and get feedback on your tone, tempo, Conciseness <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:326">In the realm of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>conciseness</strong> refers to the ability to express your message clearly and effectively using the fewest possible words. It's about conveying your ideas precisely, avoiding unnecessary details and rambling while maintaining your message's essence and impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:33"><strong>Benefits for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:137"><strong>Engaged audience:</strong> A concise speech keeps your audience focused and prevents them from losing interest due to excessive information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:117"><strong>Increased clarity:</strong> By removing unnecessary clutter, your core message becomes clearer and easier to understand.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:137"><strong>Enhanced credibility:</strong> Concise communication projects professionalism and efficiency, making you appear more confident and prepared.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Knowing you have a clear and concise message can help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by minimizing the pressure to fill time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:35"><strong>Challenges for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:126"><strong>Striking a balance:</strong> Knowing where to draw the line between conciseness and omitting important information can be tricky.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:115"><strong>Avoiding oversimplification:</strong> Complex topics may require elaboration to ensure clarity and understanding.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Overcoming natural tendencies:</strong> Some speakers naturally use more words than others, requiring a conscious effort to be concise.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:41"><strong>Strategies for Achieving Conciseness:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="20:1-25:0"> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-20:92"><strong>Identify your core message:</strong> What is your audience's main point to remember?</li> <li data-sourcepos="21:1-21:128"><strong>Prioritize and eliminate:</strong> Analyze your content and remove any information not directly supporting your core message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:133"><strong>Use strong verbs and active voice:</strong> This makes your sentences more impactful and avoids passive constructions that can be wordy.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:109"><strong>Simplify your language:</strong> Avoid jargon and technical terms unless they are essential and clearly defined.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-25:0"><strong>Practice and refine:</strong> Rehearse your speech aloud and identify areas where you can tighten your wording or eliminate redundancies.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="26:1-26:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="28:1-31:0"> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-28:93"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Engaging narratives can convey complex ideas concisely and memorably.</li> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:110"><strong>Focus on the visuals:</strong> Powerful visuals can support your message without extensive explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-31:0"><strong>Embrace silence:</strong> Pausing deliberately can emphasize key points and give your audience time to absorb your message.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Conciseness</strong> is a powerful tool for <strong>public speakers</strong>. By eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on your core message, you can create a more engaging, impactful, and memorable presentation for your audience. This can also help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by reducing the pressure to fill time and enabling you to focus on delivering your message with clarity and confidence.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/conciseness/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">conciseness , and Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence .
You might also like
2023 complete guide to presentation templates 📊, how to improve your speaking skills: 50 experts reveal their secrets [in..., quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

- Tips & Tricks
- PowerPoint Templates
- Training Programs
- Free E-Courses
Visual Presentations – The Right and Wrong Way
Home > Presentation Concepts > Presentation Ideas > Visual Presentations
Presenting visually is not just about cute pictures on your slides. Learn the real difference between ‘beautiful slides’ and ‘effective visual slides’ in a business presentation.
Recent trend in presentation skills:
Presentations have come a long way in the last few years. With the growing popularity of presentation sharing sites like Slideshare, we see two clear trends emerging:
- More and more presenters are realizing the value of visuals in presentations
- Many of them confuse cute or philosophical photos slides with effective presentations
As a result, slides like these are being worshiped for their design excellence.

Another typical slide looks like this:

The slides are so beautiful that the point of the presentation is forgotten by the audience. Such presentations may get you raving fans on Slideshare and lots of readers on your blogs. But, they just don’t cut it when it comes to a business presentation. That requires a different approach to presentations.
We believe that an effective presentation in business is something that helps you convey your message clearly and effectively. Period.
Here is a simple rule that differentiates ‘beautiful slides’ and ‘effective visual slides’:
In a ‘beautiful slide’ – picture is the hero. In an ‘effective visual slide’ – Message is the hero.
Let us evaluate 3 different set of slides with different objectives. One conveys a fact, another conveys a concept and the third conveys an emotion.
Presentation visual to convey facts:
Here is a beautiful slide that talks about the seriousness of tobacco related deaths.

The hero in this slide is the picture.
The picture is so intense that it takes away the attention from the presenter. Audience gets so busy admiring the image, that the message is lost.
Consider this alternative representation of the same information:

The hero in this slide is the message.
The attention of the audience is retained on the subject in hand. The image puts the numbers in context.
Visual presentation to convey a concept:
Here is a ‘beautiful slide’ that represents the 3 step process in creating presentations.

The hero of the slide is the picture.
A photo of two pretty executives celebrating success might look relevant to the subject of presentations. But, the picture dominates the slide without adding any specific clarity to the message. So, the slide is ineffective.
Consider this alternative:

The hero here is the message.
The 3 steps in creating a presentation are clearly illustrated without taking the attention away from the message and the presenter. We have used simple visual diagrams to make the point.
Visual presentation to convey emotions:
Here is a ‘beautiful slide’ that talks about the inadequacy of basic healthcare facilities in India.

The hero is the picture.
An image plays a significant role in triggering emotions. When you want your audience to feel your message, it is a good idea to use full bleed images. But, in this particular slide, the choice of image is not strong enough. The image illustrates the words and leaves the feeling out.
Consider this alternative which considers the emotions:

The hero is still the picture.
But, the picture does the intended job. It captures the feeling of helplessness.
Evaluating business presentations…
The next time you see a slide with a picture on it, find the hero: Is it the picture or is it the message? In an effective visual slide, message is always the hero. However, if the objective is to express feelings, the picture should play the dominant role.
If a picture is used to express feelings, find if the picture illustrates the words or captures the feelings. If it captures the right feelings, the slide is visually effective.
Go ahead and evaluate your favorite slides with new eyes.
To express ideas in an effective way using visuals is not easy. Learn a simple 3-step process to convey your ideas visually with…
Visual Presentations eBook.
It teaches you our proprietary approach to creating diagrams with examples and exercises meant for business presenters.

Get Your copy of Visual Presentations here and change the way you present…
Return to Top of Visual Presentations Right and Wrong Way Page
Share these tips & tutorials
Get 25 creative powerpoint ideas mini course & members-only tips & offers. sign up for free below:.
Videography & Photography on demand
10 reasons why you need good presentation visuals Getting your message across with the best visual content
Presentation visuals are one of the most compelling parts of a presentation. Some presenters underestimate the importance of a visual presentation and decide to only speak, or use text slides to back up what they’re saying.
This is a huge mistake – effective visual presentations can have a massive positive impact on your viewers. Almost all information transmitted to the brain is visual (see below), which underlines the effectiveness of visuals in a good presentation.
Here, we will go over the top 10 benefits of using visual content to help you deliver an engaging and memorable presentation.
1. Visuals save you time in preparing your presentation
We understand that creating a great presentation is a demanding and time-consuming process! Why spend hours transcribing your notes onto a PowerPoint presentation when you could use effective visuals that communicate your message better and save you a lot of preparation time? Besides, it’s unlikely audience members will be trying to read a lot of text as they will be focussing on what you are saying. And if they are reading large text slides, they will your speaking. Visuals make it easy for your listeners to follow along and hear you at the same time.
2. Visuals make your presentation more interesting
Everyone has had a bad presentation experience, and it might be said that we’re all suffering from PowerPoint presentation fatigue, to an extent. To avoid casting your audience’s mind back to the experience of fighting to stay awake in a particularly dry university lecture, use photography and video content to keep them hooked. Visuals used correctly can make your presentation a lively and engaging affair.

3. Visuals grab the audience’s attention
The bottom line is, visuals are more likely to grab your audience’s attention. Presentations can be difficult to follow, especially when the information being presented is unfamiliar or challenging. According to the Visual Teaching Alliance , visuals transmit information faster than spoken or written words; we can get the sense of a visual scene in less than 1/10 of a second, and visuals are processed 60,000 times faster in the brain than text. With people processing images at lightning speed, it is a mistake to miss out on visuals in your presentation.
4. Visuals help the audience to understand your presentation
Not only is visual content attention-grabbing, but it is a powerful tool for helping your audience to understand your content. The majority of us are visual learners. According to Forbes, 65% of us are visual learners . Considering that much of public speaking is conjuring an image in the audience’s mind by painting a picture with your words – why not cut out the middle man, and use a literal image? Visuals are much more likely to be effective in communicating your message, given that 90% of information transmitted to the brain is visual .
5. The audience is more likely to remember the content with visuals
The average person only remembers about a fifth of what they hear, and visual aids can improve learning by 400% . Furthermore, a study conducted by Georgia State University found that imagery is an effective way to enhance memory . If you want your audience to remember your presentation once it’s finished, use visual content to embed the information in their mind.
6. Visuals make you an effective communicator
Not everyone is skilled in the art of oratory and that’s okay. You don’t need to have elocution lessons to deliver the perfect presentation. Public speaking is just one element of presentations. as we have already seen, visual content is incredibly important in helping you deliver your speech. If public speaking isn’t your best asset, we have some good news for you. Photographs, infographics, and videos can all be used to help deliver your message and make an engaging and informative presentation.
7. Visuals can be emotive
Sometimes you can describe an emotive scene to someone, and they can acknowledge the emotions but they don’t feel them. Seeing an image is much more evocative than hearing someone describe it. Sometimes, the emotions just don’t register until you can see them with your own eyes. If you want to get your audience to feel something, use photos and videos to make your audience members feel happy, excited, amused, empathetic, sad, or inspired.
8. Visual presentations are more inclusive
Many presenters fall into the trap of assuming everyone in the audience thinks in the same way. When we assume everyone thinks the same way as us, we are discounting the fact that audiences are linguistically diverse, culturally diverse, and neuro-diverse. Because not everyone operates at the same level of comprehension, some of your speech is likely to go over the heads of members of your audience. To help deliver a useful and engaging presentation for everyone, use effective visuals which are more likely to get through to them.

9. Impressive visuals increase your credibility
Using polished, well-constructed photos, videos and infographics is a sure-fire way to increase your credibility. Linking to someone else’s YouTube video or using a generic stock photo doesn’t rouse the same admiration and respect as using your custom-made visual content. Professionally made visuals upgrade the overall look and feel of your presentation as well as sending a message of professionalism and trustworthiness in you and your brand.
10. Unique visuals make your presentation stand out
If you want to deliver a truly memorable and unique presentation you cannot use the same tired formula. One of the best ways to enhance your presentation to an outstanding quality is to use unique visuals. Custom photography and videography allow you complete creative control over your presentation, which means it will be unique to you and your cause. For maximum personalisation, create your visual content the way you see fit.
We hope you enjoyed our top 10 reasons why you need good presentation visuals!
Splento has experienced experts in visual content; get in touch today if you require any visual content creation , or even if you just have a query.
Contact Splento if you are in need of:
Event Photography and Videography
Professional Headshots
eCommerce Photography and Videography
From Dreams to Reality: Book a Photoshoot and Capture the Magic Unlock the magic of your moments with our guide on booking a photoshoot. Discover tips, planning advice, and the lasting impact of professional photos
Love at first sight: how a ‘dating photographer london’ can transform your profile unlock the secret to a standout online dating profile with our expert tips on hiring a dating photographer in london. elevate your love quest today.

This will close in 0 seconds

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Presentations > 5 reasons to use visual aids for speeches and presentations
5 reasons to use visual aids for speeches and presentations
A whopping 65 percent of humans are visual learners . This makes sense, considering the brain processes visual information about 60,000 times faster than text.
It also explains why it’s so important for speakers to incorporate compelling visual aids into their presentations . Impactful visuals help us communicate our ideas and messaging more effectively—no matter what type of audience we are trying to reach.

Here are 5 facts that drill home the importance of visual aids when it comes to delivering a memorable presentation or speech.

Grow a business
Use free apps and tools from microsoft for your small business and side gig.
1. Presentation visuals grab an audience’s attention—and keep it
Human beings are naturally curious creatures but we have a short attention span—and it’s gotten worse in our current era of information overload and non-stop scrolling. When listening to a speech or presentation, audience interest peaks around the 10-minute mark and then drops precipitously depending on the content and communication style of the speaker. (A Ben Stein soundalike drolling on about duality quantum algorithms? Godspeed.) That’s why so many experts insist on capping lectures at 15 to 20 minutes or mixing up the format with 20-minute blocks. Interesting visual aids can help you do that.
They spark interest when the brain is feeling fatigued, making it easier to receive and process complex information. Think of each new visual or animation as little shots of adrenaline—capturing the waning attention of an audience and re-energizing the room. This can be especially effective when embedding picture polls, or visuals that require audience members to pull out their phones and interact with the content you’ve presented.
2. Presentation visuals make complex ideas easier to understand
Not everyone computes information at the same speed. Infographics make data-heavy presentations more digestible—breaking statistics and other figures or timelines into bite-sized chunks. They’re also more persuasive. According to a study conducted at the Wharton School of Business, 67 percent of audience members were more convinced by the content of a verbal presentation with accompanying visuals versus 50 percent with a verbal-only presentation.
3. Presentation visuals build emotional bridges with the audience
They say a picture is worth a thousand words—it’s cliché but true. Images make viewers feel things that words cannot and give presenters a way to connect with their audience on a more visceral level. (Yes, even if your audience is a bunch of humorless academics.) Instead of listing off dull facts about global warming, pop in a few slides depicting recent floods or forest fires to drive home your point. Powerful imagery, including 3D effects and visually appealing templates , resonate with audiences and makes them care more deeply about what you’re saying.
4. Presentation visuals help audiences retain information
Researchers have found that people who are asked to recall information after a three-day period retained just 10 percent of what they heard during an oral presentation, 35 percent from a visual presentation, and 65 percent from an oral presentation with visuals. You’ve worked too hard preparing your address to have the audience walk away remembering only a tiny fraction of what you said. Embracing visuals will improve the odds by six times.
5. Presentation visuals keep your speech on track
Peppering your presentation with visual aids will help you organize your talking points, avoid off-topic rambling, and even jog your memory if you get hit with a bout of stage fright.
But remember: While thoughtful visuals will make a speech or presentation much stronger, they won’t save you if you show up unprepared. The purpose of a visual aid is to engage the audience, boost their understanding of your content, ignite an emotional response, and help you convey important messaging—but it is never a substitute for preparation .

Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

How to password protect your PowerPoint presentations
Learn how to password protect your PowerPoint presentations and secure your valuable files.

Choosing the Right Font For Your PowerPoint Presentation
Make your presentation look great by choosing the best font for PowerPoint. We'll highlight some of the best fonts and why you should use them over others.

Tips and tricks for managing up
Whether you have the best boss in the world or find your manager challenging to work with, your relationship with them does not have to be one-sided.

Different Types of Fonts And How to Choose One
There are so many different types of fonts available. Do you know how to choose a font? Our guide will highlight types of fonts and the best time to use them.
Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories

Presentation Training Institute
A division of bold new directions training, what is the importance of using visuals when giving a presentation.
While preparation and delivery are critical components of a successful presentation, the visuals you use throughout your presentation are equally important. Science and research suggest that nearly 75% of learning occurs through sight, which is why visuals are a necessary tool for effective presentations. When used properly, visual aids can help your audience connect to the topic and understand it’s message. There are many types of visual aids including slideshows, videos, handouts, and props, all of which can help reinforce your main message. Here are a few reasons why visuals play such a significant role in presentations.
Enhance Your Presentation Listening to a speaker talk for a lengthy period of time is enough to put anyone to sleep. Visuals help to add that extra element of interest to the presentation. No matter the topic, you can always make it more interesting with visuals. Visual aids help to grab the audiences’ attention by enabling them to see colorful representations of your message.
Maintain Audience Attention In a world where just about everyone has a cell phone or tablet with them at all times, it can be extremely difficult to capture and maintain people’s attention. With the swipe of a finger they can be checking emails, browsing the web, or checking sports scores so it’s incredibly important to do everything you can to capture their attention. High quality visuals can significantly increase the chances of your audience paying attention to you rather than staring at their phone.
Images Help People Understand When you throw mountains of text at your audience, it can be nearly impossible for them to understand the material. Images are important because they help to clarify your points. Our brains process images much faster than text, meaning that the best way to help your audience understand the material is through visual aids.
Visuals Help with Long-Term Memory Visual images make a long-lasting impression on our minds, increasing the chances that your audience will remember the information. Research shows that the combination of visuals along with text increases one’s ability to remember the information for a longer period of time. If you want audiences to remember your material long after your presentation ends, it’s best to incorporate some good visuals.
Visuals Can Inspire The ultimate goal of any presentation is to inspire your audience. You want them to take something away from your presentation and actually do something with the information you give them. Visuals resonate with people in a way that text and words alone cannot. Great visuals have the power to move people and inspire them.
Katalist Storytelling Studio
Use ai to turn your scripts into visual stories with customizable scenes, characters, and props.
Translating your TikTok concept into a frame-by-frame visual for your team is beyond your skill set. ( “I can definitely draw...stick figures.” )
Even after browsing through hundreds of stock photos and trying your luck at Midjourney, your idea might never see the light of day.
What if there was an AI platform that could turn any script into high-quality visual stories that look and feel cinematic?
Introducing Katalist Storytelling Studio .
At-a-glance
- Content creators
- Marketing agencies
- Videographers
Alternative to
- Adobe Photoshop
- GDPR-compliant
Katalist Storytelling Studio is an AI-powered platform that turns scripts into visual stories without complicated prompts.
Katalist Storytelling Studio lets you choose from two visual styles : ”sketch” for simple details or “cinematic” for realistic, movie-like visuals.
From there, simply upload the script and let the AI whip up consistent characters, scenes, and activities —no prompting required!
Your AI sidekick will be able to create a storyboard with multiple frames to bring all your creative ideas to life.
Let AI turn your script into a visual story with characters, scenes, and activities.
Katalist Storytelling Studio can detect the main characters and assign them an AI-generated actor from the character library.
That means you’ll get consistent characters in each frame without having to fiddle with generation parameters.
Your first draft will be in tip-top shape! But if you want to adjust anything, you can edit characters and scenes directly in the frame .
Cast AI-generated actors to represent the main characters in your script.
You’ll be able to tweak the setting of any scene , including a modern office, city subway, local cafe, and a bustling cityscape.
It’s easy to change a character’s location and control their limbs , so you can fine-tune the story until it matches your vision.
And thanks to generative fill, you can add props or objects anywhere to get the perfect shot for every frame.
Change the scene, modify the poses, and add props to fine-tune your vision.
When you’re done, turn the visual story into an interactive presentation and share it as a link through Slack and email.
No matter what changes you’ve made to your script or visual story, this platform keeps your link up-to-date —so you never have to reshare it.
Katalist Storytelling Studio also lets export your visual story as a PowerPoint, ZIP file, or MP4 for more flexibility.
Turn your visual story into an interactive presentation and share it with your team.
Ditch the stick figures! Katalist Storytelling Studio can turn all your scripts into visual stories with customizable scenes, characters, and props.
Create visual stories with AI.
Get lifetime access to Katalist Storytelling Studio today!
Plans & features
Deal terms & conditions.
- Lifetime access to Katalist Storytelling Studio
- All future Pro Individual (Tier 1) or Studio (Tier 2+) Plan updates
- If Plan name changes, deal will be mapped to the new Plan name with all accompanying updates
- No codes, no stacking—just choose the plan that’s right for you
- You must activate your license within 60 days of purchase
- Ability to upgrade between 3 license tiers while the deal is available
- Ability to downgrade between 3 license tiers within 60 days of purchase
- GDPR compliant
- Only for new Katalist Storytelling Studio users who do not have existing accounts
60 day money-back guarantee. Try it out for 2 months to make sure it's right for you!
Features included in all plans
- AI storyboard generation
- Import via CSV, Word, or PowerPoint presentation
- Adjust framing, angle, character pose, composition, props, and scene
- Automatic prompt engineering
- 32 character library (all current and future characters)
All our deals are time-sensitive! Make sure you don't miss any of our awesome limited-time offers.
- Search Menu
- Advance Articles
- Supplements
- Breast Cancer
- Cancer Diagnostics and Molecular Pathology
- Community Outreach
- Endocrinology
- Gastrointestinal Cancer
- Genitourinary Cancer
- Geriatric Oncology
- Global Health and Cancer
- Gynecologic Oncology
- Head and Neck Cancers
- Health Outcomes and Economics of Cancer Care
- Hematologic Malignancies
- Hepatobiliary
- Immuno-Oncology
- Lung Cancer
- Medical Ethics
- Melanoma and Cutaneous Malignancies
- Neuro-Oncology
- New Drug Development and Clinical Pharmacology
- Pediatric Oncology
- Radiation Oncology
- Browse content in Regulatory Issues
- Regulatory Issues: FDA
- Regulatory Issues: EMA
- Symptom Management and Supportive Care
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why Publish With Us?
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Young Investigator Award
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Reprints, ePrints, Supplements
- About The Oncologist
- About the Society for Translational Oncology
- Editorial Board
- Discussions with Don S. Dizon
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, ocular adverse events associated with mek inhibitors, screening for ocular toxicity during mek inhibitor therapy, report of cases with ocular toxicity, conflict of interest, author contributions, data availability, ocular effects of mek inhibitor therapy: literature review, clinical presentation, and best practices for mitigation.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Karen W Jeng-Miller, Miles A Miller, Jeffrey S Heier, Ocular Effects of MEK Inhibitor Therapy: Literature Review, Clinical Presentation, and Best Practices for Mitigation, The Oncologist , 2024;, oyae014, https://doi.org/10.1093/oncolo/oyae014
- Permissions Icon Permissions
MEK signaling pathway targeting has emerged as a valuable addition to the options available for the treatment of advanced cancers including melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Ophthalmologic monitoring of patients taking part in clinical trials of MEK inhibitors has shown that while ocular effects are common, generally emerging during the first days to weeks of treatment, the majority are either asymptomatic or have minimal visual impact and are benign, resolving without intervention or the need to reduce or stop MEK inhibitor therapy. However rare cases of serious, potentially vision-threatening ocular toxicities have been reported during MEK inhibitor therapy. There is currently no recommendation for routine ophthalmologic screening or monitoring of patients with advanced cancer who are initiating MEK inhibitor therapy. However, baseline ophthalmologic examination may be useful for all patients initiating MEK inhibitor therapy to allow the differentiation of preexisting pathology versus the development of MEK inhibitor-associated retinopathy in the event of the emergence of symptomatic ocular events. Regular ophthalmologic examination may be appropriate for patients at increased risk for ocular events, such as patients with a history of ocular inflammation, infection, or underlying macular/retinal disease. All patients reporting visual disturbance should be referred for prompt ophthalmologic review to determine the potential seriousness of any underlying abnormalities and whether there is a need for treatment modification or specific intervention. Understanding the potential consequences of ocular toxicities is of particular importance in the context of decision-making for the continuation of potentially life-prolonging medications such as MEK inhibitors.
Ocular toxicities are a known class effect of MEK inhibitor therapy. The majority of symptomatic ocular toxicities are likely to resolve without clinical sequelae or the need for the interruption or cessation of potentially life-prolonging MEK inhibitor therapy. However, the potential for vision-threatening ocular toxicities associated with MEK inhibitor therapy, while small, suggests a need for ophthalmologic examination before treatment is initiated. Examination of patients at risk for such events, including those with a history of ocular inflammation, infection, or underlying macular/retinal disease, should be routine practice with MEK inhibitor therapy.
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway plays a critical role in cellular signaling and contributes to the regulation of a variety of processes including cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, motility, and angiogenesis. 1 , 2 The fundamental components of the pathway consist of the Ras small GTPases, which recruit and activate the downstream kinases RAF and MEK (MAP kinases) that in turn trigger the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) proteins. 3 Activated ERKs can either translocate to the cell nucleus, with implications for gene expression, or remain in the cell cytoplasm where they interact with a variety of substrates. 1 , 3 The subcellular location of ERK proteins can determine their role in regulating diverse cell functions. 4 , 5 Through variations in the individual components, this basic pathway structure enables cells to detect extracellular signals and respond by driving or inhibiting diverse cellular functions.
Aberrant MAPK signaling is implicated in the development and progression of >40% of all human cancers, including melanoma, colorectal, non-small cell lung, thyroid, pancreatic, breast, and endometrial cancers. 2 , 3 , 6 For this reason, the MAPK pathway has been subject to intense investigation in order to better understand the pathophysiologic basis of human carcinogenesis as well as for the development of novel therapies.
Agents targeting the MEK components of the MAPK signaling cascade have been investigated for the treatment of various tumor types in recent years, with promising results. 1 Seven MEK enzymes (MEK1-7) have been identified so far that operate within 4 distinct MAPK signaling pathways and selectively activate downstream substrates of the signaling cascade. 1 Inhibitors targeting MEK1 and MEK2 have received the most attention, with several, including trametinib, cobimetinib, binimetinib, and selumetinib, 7-10 approved for clinical use. Trametinib is approved for the treatment of unresectable/metastatic melanoma (with a BRAF V600 mutation), advanced non-small cell lung cancer (with a BRAF V600 mutation), and advanced anaplastic thyroid cancer (with a BRAF V600 mutation), all in combination with the BRAF-targeted kinase inhibitor dabrafenib. The MEK1/2-targeted inhibitors cobimetinib (in combination with the BRAF-targeted vemurafenib) and binimetinib (in combination with the BRAF-targeted encorafenib) are approved for the treatment of adults with BRAF V600-mutant unresectable or metastatic melanoma, and the MEK1/2-targeted inhibitor selumetinib is approved for the treatment of pediatric neurofibromatosis type 1. These agents have been shown to decrease tumor burden and prolong progression-free and overall survival. 11-15 However, as with most targeted therapies, MEK inhibitors are associated with adverse events. For this class, the predominant adverse events include papulopustular exanthema, serous retinal detachments, musculoskeletal events, hypertension, and decreased ventricular ejection fraction. 16 While most such events are mild or moderate in intensity and time-limited, vigilance for their emergence and appropriate interventions to ameliorate their effects is an important part of the management of patients receiving targeted therapy.
Serious ocular adverse events have emerged as a rare but important consequence of MEK inhibitor therapy, thus requiring early ophthalmic screening and subsequent surveillance. 17 , 18 Here we review the ocular adverse events associated with MEK inhibitor therapy for advanced cancers, with a particular focus on MEK inhibitor-associated retinopathy (MEKAR), and share clinical experience and best practice approaches to their management.
Ocular adverse effects related to MEK inhibitors are mostly concentrated in the retina. These effects include clinical findings of chorioretinopathy and serous retinal detachment, which, if symptomatic, present with symptoms of blurred vision, halos around lights, and colorful spots in the vision. 11 , 17 , 19-21 Although many patients with ocular adverse effects are asymptomatic or have only mild symptoms, some of these effects can have vision-threatening potential. 17 Therefore, these side effects are important for practitioners to be aware of as MEK inhibitor usage increases.
MEKAR is characterized by the presence of subretinal fluid resulting in the self-limiting serous detachment of the neurosensory retina. 19 , 22 , 23 The pathophysiologic basis of MEKAR is, as yet, not completely understood, but appears to be caused by acute toxic effects on the retinal pigment epithelium and resultant dysfunction by inhibition of the MAPK pathway that lies downstream of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR). 24 The FGFR binds a neurotrophic factor that is essential for maintenance, repair, and survival of the retinal pigment epithelium. MEK inhibition causes increased permeability of the retinal pigment epithelium and subsequent accumulation of subretinal fluid via upregulation of aquaporin 1, a membrane water channel essential in the permeability of the retinal pigment epithelium. 25 , 26
Indirect evidence suggests local disruption of the blood-retinal barrier may also be involved in MEKAR. In mice, genetic Erk1/2 ablation systemically disrupts the integrity of quiescent endothelium; in rats, treatment with the MEK inhibitor PD0325901 causes evidence of retinal endothelial damage; and in rabbits, PD0325901 treatment can elicit retinal vein occlusion. 27 , 28 Microglia are tissue-resident macrophages of the retina that maintain physiologic blood-retinal barrier integrity, and trametinib can induce macrophages to produce factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), that signal locally with neighboring cells. 29 Despite possible roles for perivascular signaling, MEKAR does not present with neovascularization expected from chronic VEGF-driven angiogenesis.
MEKAR has been estimated to occur in up to 90% of patients receiving MEK inhibitor therapy, although the majority of cases are apparently asymptomatic and resolve without the need for intervention or compromising the therapeutic dose of cancer-directed therapy. 19 , 23 , 30 Clinical trial data show a high incidence of MEKAR among treated patients but also indicate that only a minority of patients have symptomatic MEKAR. For most of these patients, the events are self-limiting and resolve without the need for intervention or dose adjustment. 14 , 18 , 31 , 32
There is currently no recommendation for the routine ocular screening of patients undergoing MEK inhibitor therapy. Previous MEK inhibitor studies recommended ocular screening of patients based on incidences of ocular adverse events observed; some ocular adverse events, such as conjunctivitis, were detected as part of routine physical examination of patients, while others, including retinopathy, required ophthalmologic examination. 17 A baseline ophthalmologic evaluation, including visual acuity and fundoscopy, may be useful for all patients initiating MEK inhibitor therapy. 17 A baseline exam will allow differentiation of preexisting pathology from MEKAR. This distinction may be important in the case of symptomatic pathology and may impact treatment. For instance, if symptomatic disease is due to MEK therapy, dose modification or hold may be necessary. However, if symptoms are due to underlying disease progression, for instance, worsening of an epiretinal membrane, there is no need or benefit to changing MEK therapy. Regular screening should be considered for patients who may be at increased risk for ocular toxicities, such as those with underlying macular disease which could make recognition of ocular toxicities difficult. For patients reporting visual disturbance, prompt ophthalmology referral is appropriate. A baseline ophthalmologic examination, including visual acuity, slit-lamp and dilated funduscopic examination, and optical coherence tomography imaging, establishes a baseline and may uncover any underlying conditions that could confound the detection of MEKAR and its subsequent management.
Presentation 1: Mild Asymptomatic
Describe/discuss: Asymptomatic ocular toxicities associated with MEK inhibitor therapy have been detected among patients participating in clinical trials who have undergone regular ophthalmologic examination. Visual acuity changes may be apparent on examination even when vision changes are not reported by the patient ( Table 1 ). Retinal lesions may be observable on examination and optical coherence tomography may reveal changes such as subretinal fluid both in subfoveal and extrafoveal locations. In the case of a patient receiving MEK inhibitor therapy for metastatic ovarian cancer, such lesions were apparent on optical coherence tomography 2 weeks after initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy. 33 In our experience, subretinal fluid can be present even as early as a few hours after initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy. In this case, treatment was continued because the changes were not considered to be vision-threatening, and the lesions had almost completely resolved by 4 weeks after MEK inhibitor therapy initiation without the need for dose reduction or treatment interruption. In instances similar to this presentation, observation is recommended. It is not recommended that the systemic treatment be discontinued. Repeat ocular examination in 4 weeks is appropriate, sooner if any vision changes should arise.
Clinical presentations observed with ocular toxicity.
Presentation 2: Mild Symptomatic
Describe/discuss: Mild or transient visual symptoms, such as blurred vision, reported by patients may indicate ocular toxicities and warrant ophthalmologic investigation ( Table 1 ). The emergence of blurred vision may be associated with serous retinal detachment (detectable on optical coherence tomography) as well as uveitis. 34 Such was the case for 2 patients receiving MEK inhibitor therapy for metastatic cancer. 34 For both patients, neurosensory subfoveal retinal detachment was detected on optical coherence tomography. For both patients, the abnormality resolved after 1 week; 1 patient required no change to MEK inhibitor dosage and the other patient required a dose reduction. The decision to decrease the dose or dose hold is largely based upon the degree of the patient’s symptoms. If mild, and not impacting daily functioning, continuing the current dose is reasonable, but with closer follow-up to ensure visual stability. Repeat ophthalmologic examination in 2-4 weeks, or sooner if symptoms increase, is appropriate.
Presentation 3: Moderate With Visual Symptoms
Describe/discuss: Patient-reported blurred vision may indicate more concerning underlying ocular effects during MEK inhibitor therapy including macular edema requiring additional intervention 33 ( Table 1 ). The case reported by Duncan et al highlights the potential for such events to occur later during the course of MEK inhibitor therapy. In this case, the patient reported the emergence of blurred vision 8 months after the initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy. Retinal examination and optical coherence tomography revealed cystoid macular edema of the left eye. The patient had no history of diabetes, uveitis, macular degeneration, eye surgery, vein occlusions, or any other etiology for the disease. The patient’s macular edema was treated with prednisolone acetate 1% (Pred Forte) and ketorolac (Acular) topical drops with complete resolution after 6 weeks. Ongoing treatment with anti-inflammatory eye drops was required to prevent recurrence; however, this is uncommon with MEKAR and it may have been secondary to an unrecognized, unrelated etiology. It should be noted that cystoid macular edema is an uncommon occurrence with MEK inhibitor therapy and may have been secondary to an unrecognized, unrelated etiology. 33 However, in the case of moderate symptoms impacting the patients’ daily activities, dose reduction or dose holding is common. The retinopathy often resolves quickly, typically within 1 to several weeks, allowing resumption of MEK therapy. If the dose was held, then resumption at a lower dose is frequently used. If the dose was reduced, observation for further retinopathy, and retinopathy does not recur, increasing the dose slowly may be tried.
Presentation 4: Severe With Visual Symptoms
Describe/discuss: More severe ocular toxicities may also emerge during MEK inhibitor therapy and can be associated with vision loss and pain. Such was the case for a patient receiving MEK inhibitor therapy for metastatic melanoma who experienced vision loss, pain, and foreign body sensation in both eyes 3 months after the initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy 35 ( Table 1 ). The patient reported no prior medication, relevant illnesses, or allergies. A uveitis work-up, including blood test and computer tomography, was negative. Serous retinal detachment of the fovea was revealed on fundoscopy and optical coherence tomography. MEK inhibitor therapy was stopped immediately, although anterior uveitis developed 2 weeks later requiring treatment with topical corticosteroids and subsequently periocular triamcinolone acetonide injection. 35 In our opinion, it is unlikely that the uveitis was associated with MEK inhibitor therapy. Association with ocular inflammation has been documented, albeit with a limited sample size, in the phase III coBRIM study (4/5 patients with a history of ocular inflammation developed symptomatic retinopathy among 247 patients treated with cobimetinib + vemurafenib). 31 For this patient, MEK inhibitor therapy was initiated again after 6 months, and although serous retinal detachment was detected again, no inflammatory process or uveitis emerged. 35 With severe ocular symptoms, it is reasonable to trial cessation of the medicine to observe if there is a swift resolution of the symptoms. Like in cases of moderate toxicity, the retinopathy often resolves swiftly allowing for re-introduction of the MEK inhibitor therapy. Close follow-up is advised and dose escalation trials may be attempted over time.
Ocular toxicities are listed as adverse effects for all currently approved MEK inhibitors and monitoring requirements and recommendations for discontinuation of treatment for non-resolution of symptomatic events are included for cobimetinib, trametinib, binimetinib, and selumetinib. 7-10 Ophthalmologic evaluations are recommended for all patients, including those receiving binimetinib, who report visual disturbance. 7 , 8 , 10 While the incidence of retinal vein occlusion is low among patients receiving MEK inhibitor therapy, retinal vein occlusion is a serious adverse event and, in such cases, systemic evaluation to rule out other risk factors may be considered. 36 Prescribing information dictates to permanently discontinue MEK inhibitor therapy if retinal vein occlusion is confirmed. 7 , 36 Retinal vein occlusion is the second most common retinal vascular disease in the US behind diabetic retinopathy, and patients with cancer are at higher risk given their hypercoagulable state. 37 , 38 In our clinical experience, we have rarely, if ever, treated retinal vein occlusion in our MEK inhibitor patients that could be directly attributed to MEK inhibitor therapy. Based on clinical trial data, the prevalence of retinal vein occlusion in patients receiving MEK inhibitor therapy is 0.5%, which is higher than the 0.1% prevalence in the general population. 36 The increased incidence could be related to MEK inhibitor therapy, but it could also be secondary to confounding factors such as hyperviscosity related to their underlying disease. Retinal pigment epithelial detachment is more frequently observed, and regular ophthalmologic examinations upon initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy are warranted. 7 , 8 , 10
Registrational phase II and prospective observational studies conducted for cobimetinib and binimetinib provided valuable insights into the prevalence, course, and long-term sequelae of MEKAR in patients with advanced cancers. In the phase III coBRIM study among patients with BRAF- mutated melanoma receiving treatment with cobimetinib + vemurafenib ( n = 247) or vemurafenib alone ( n = 246), 86 cases of serous subretinal fluid were reported among 69 patients, 62 in the cobimetinib group and 7 in the vemurafenib group. 18 Despite this apparently high incidence of serous retinopathy among patients treated with cobimetinib, cases were generally asymptomatic or mild and resolved without the need for dose modification or other intervention. 18 More recent data from the coBRIM study have provided additional insights into the ocular adverse events associated with this agent. 31 Among the total cohort, 72 patients (29%) developed retinopathy. Although most cases were asymptomatic, 33 patients (13%) developed symptomatic retinopathy. The most prominent risk factor for retinopathy was a history of ocular disease, including ocular inflammation. For patients with a history of ocular inflammation, infection, or significant irritation of the eye, 4 out of 5 developed symptomatic retinopathy during treatment. 31
MEKAR has also been reported in clinical trials among patients treated with binimetinib. 14 , 32 These events appear early, often within the first few hours or days of treatment, and are usually mild and transient, resolving without the need for intervention or dose modification. In the phase III COLUMBUS study, in which patients with BRAF -mutant melanoma received encorafenib + binimetinib ( n = 192), encorafenib alone ( n = 192), or vemurafenib alone ( n = 186), all patients were required to undergo regular ophthalmologic examination due to signals from previous MEK inhibitor studies, and patients were closely monitored for serous retinopathy in those receiving binimetinib via frequent routine eye assessments. 14 , 32 The incidence of serous retinopathy in the combination arm of the study was 20%, with the majority (87% of all events in this group) being grade 1 or grade 2. 32 Dose interruption or adjustment was required for 11 patients, with no patient requiring discontinuation of the study drug for the resolution of this event. The majority of events were classed as recovered (82%) or recovering (3%), suggesting a general reversibility of serous retinopathy when associated with binimetinib treatment. 32
Beyond the registrational studies for binimetinib, the emergence of serous retinopathy was evaluated in a prospective, observational, cohort-based, cross-sectional study of 30 patients with cutaneous melanoma and 5 patients with uveal melanoma treated with binimetinib or a combination of binimetinib and the protein kinase C inhibitor sotrastaurin. 21 Optical coherence tomography revealed accumulation of subretinal fluid (indicating MEKAR) among 77% of patients with cutaneous melanoma and 60% of those with uveal melanoma, affecting the fovea in 85% of cases. 21 Six patients were evaluated for the presence of autoantibodies against retinal pigment epithelium proteins, and their presence was confirmed in all 6 patients, suggesting that autoantibody formation in addition to drug-related toxicity may play a role in binimetinib-associated serous retinopathy. 21 In a separate prospective, observational study in a cohort of 32 patients with advanced cutaneous melanoma, treatment with binimetinib as a single agent or in combination with RAF inhibitors induced transient retinopathy with multiple bilateral lesions in some patients. 30 Patients underwent regular ophthalmologic examinations that revealed grade 1-2 retinopathies in 13/20 patients receiving binimetinib monotherapy and 6/12 patients receiving combination therapy. Patients reported mild and short-lived visual disturbances and the increase in central retinal thickness observed during the initial weeks of treatment markedly decreased during continued treatment. 30 A longer-term (up to 2 years) evaluation of MEKAR in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving treatment with binimetinib found that although almost all patients showed signs of MEKAR during the initial weeks of treatment, the retinopathy resolved over time without any reported functional deficits in vision or changes in the structural integrity of the retina. 30
Routine ophthalmologic evaluations of patients taking part in the registrational trials for trametinib in melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer were not conducted, so the incidence of MEKAR in trametinib-treated patients is unknown. 7 There is limited information on ocular adverse events during treatment with selumetinib. In the phase II registrational SPRINT study that evaluated selumetinib in 74 patients in pediatric care with neurofibromatosis type 1, ocular adverse events were reported in 15% of patients and resolved in 82% of cases. 10
Routine ophthalmologic examination is not required for patients initiating MEK inhibitor therapy, but it can be helpful in differentiating underlying pretreatment retinal pathology from MEKAR, and subsequently, impacting the type of treatment used to improve vision. However, the potential for ocular side effects, for which the outcome and course are still unknown, suggests that an initial ophthalmologic examination is warranted to enable clinicians to recognize MEKAR from underlying disease. This would allow for clinically directed recommendations regarding dose modification, treatment, and additional regular ophthalmologic monitoring. Further understanding of ocular effects associated with MEK inhibitor therapy is needed to better understand the evolution and appropriate management of these adverse events, identify patients most at risk, and prevent unnecessary interruption of therapy for asymptomatic or self-limiting MEKAR.
A current challenge in the evaluation of the true prevalence of potentially vision-threatening ocular events relates to the variability of ocular toxicity report descriptions. For example, in clinical trials, the term serous retinopathy may encompass retinal detachment, chorioretinitis, chorioretinopathy, cystoid macular edema, macular retinal pigment epithelium detachment, retinal pigment epithelium detachment, macular detachment, macular edema, retinal disorder, retinal exudates, retinal edema, retinal pigment epitheliopathy, retinopathy, and subretinal fluid. 18 , 32 Moreover, version 4.0 of the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) does not include a specific severity grading for serous retinopathy 18 and there are limited data available to relate the severity of the event with either the likelihood of visual disturbance or longer-term visual impairment. 21
There are many etiologies in clinical practice for the presence of subretinal fluid. In addition to clinical examination, ancillary imaging studies such as optical coherence tomography, fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green, and optical coherence tomography angiography are useful in determining the root pathophysiology of the retinopathy. Unlike more common etiologies of subretinal fluid, such as exudative choroidal neovascular membrane or central serous retinopathy, MEK inhibitor-associated subretinal fluid has a distinct fluorescein angiography pattern that does not display leakage. From this, it appears to be a distinct entity from the abovementioned retinopathies. From observational studies, it is known that these lesions fluctuate and resolve upon cessation of the medication. As a result, it is hypothesized that the mechanism of action of MEK inhibitor-associated retinopathy is through disruption of the retinal pigment epithelium resulting in impaired function and subsequent exudation. 20 Given this clinical knowledge, management should begin with observation and should not immediately involve therapies such as anti-VEGF injections unless choroidal neovascularization is detected.
In conclusion, an overview of the available literature, clinical presentations, and key learnings from our clinical experience highlight best practices for managing MEK inhibitor-associated ocular toxicity. Patients should undergo regular ophthalmologic evaluations, beginning prior to initiation of MEK inhibitor therapy. For the majority of patients, dose interruption or reduction will not be required because the events are generally mild and self-limiting.
This publication was sponsored by Array BioPharma. Array BioPharma was acquired by Pfizer in July 2019. Medical writing/editorial support were was provided by Tracey Lonergan, PhD, at Caudex, New York, and was funded by Pfizer.
Karen W. Jeng-Miller indicated no financial relationships. Miles A. Miller reported research funding from Roche/Genentech and intellectual property with Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Massachusetts General Hospital. Jeffrey S. Heier reported consulting/advisory roles with 4DMT, AbbVie/Regenxbio, Adverum, Affamed, AGTC, Akouos, Allegro, Allgenesis, Annexon, Apellis, Asclepix, Aviceda, BioCryst, Biovisics, Boehringer Ingleheim, Caeregen, Cognition, Daiichi Sankyo, DTx, Frontera, Genentech/Roche, Iveric, Janssen R&D, jCyte, Kriya, Nanoscope, NGM, Notal Vision, Novartis, Ocular Therapeutix, Ocuphire, OcuTerra, Osanni Bio, Outlook Therapeutics, Perceive, Ray Therapeutics, Regeneron, RetinAI, RevOpsis, Sanofi, Stealth, Thea, Unity, Vanotech, Visgenx, Xequel; and ownership interests in Adverum, Aldeyra, Allegro, Aviceda, Caeregen, jCyte, Ocuphire, Ocular Therapeutix, RevOpsis, Vinci, Vitranu.
Conception/design: K.W.J.-M., J.S.H. Collection and/or assembly of data: K.W.J.-M., J.S.H. Data analysis and interpretation: All authors. Manuscript writing and final approval of manuscript: All authors.
No new data were generated or analyzed in support of this research.
Akinleye A , Furqan M , Mukhi N , Ravella P , Liu D. MEK and the inhibitors: from bench to bedside . J Hematol Oncol. 2013 ; 6 : 27 . https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-6-27
De Luca A , Maiello MR , D’Alessio A , Pergameno M , Normanno N. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches . Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 ; 16 ( Suppl 2 ): S17 - S27 . https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2011.639361
Yuan J , Dong X , Yap J , Hu J. The MAPK and AMPK signalings: interplay and implication in targeted cancer therapy . J Hematol Oncol. 2020 ; 13 ( 1 ): 113 . https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00949-4
Maik-Rachline G , Hacohen-Lev-Ran A , Seger R. Nuclear ERK: mechanism of translocation, substrates, and role in cancer . Int J Mol Sci. 2019 ; 20 ( 5 ): 1194 . https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051194
Tomasovic A , Brand T , Schanbacher C , et al. . Interference with ERK-dimerization at the nucleocytosolic interface targets pathological ERK1/2 signaling without cardiotoxic side-effects . Nat Commun. 2020 ; 11 ( 1 ): 1733 . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15505-4
Crispo F , Notarangelo T , Pietrafesa M , et al. . BRAF inhibitors in thyroid cancer: clinical impact, mechanisms of resistance and future perspectives . Cancers (Basel). 2019 ; 11 ( 9 ): 1388 . https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091388
Novartis . MEKINIST® (Trametinib) Prescribing Information . Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation ; 2020 . Accessed March 30, 2021 . https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/204114s016lbl.pdf
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Genentech Inc . COTELLIC® (Cobimetinib) Prescribing Information . Genentech USA, Inc., A Member of the Roche Group ; 2018 . Accessed March 30, 2021 . https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206192s002lbl.pdf
Array BioPharma Inc . MEKTOVI® (binimetinib) prescribing information . 2019 . Accessed March 30, 2021 . https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/210498s001lbl.pdf
KOSELUGO (selumetinib) . AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP . 2020 . Accessed September 2020 . https://www.azpicentral.com/koselugo/koselugo.pdf#page=1
Alves C , Ribeiro I , Penedones A , Mendes D , Batel Marques F. Risk of ophthalmic adverse effects in patients treated with MEK inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Ophthalmic Res. 2017 ; 57 ( 1 ): 60 - 69 . https://doi.org/10.1159/000446845
Ascierto PA , Schadendorf D , Berking C , et al. . MEK162 for patients with advanced melanoma harbouring NRAS or Val600 BRAF mutations: a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 study . Lancet Oncol. 2013 ; 14 ( 3 ): 249 - 256 . https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70024-X
Flaherty KT , Infante JR , Daud A , et al. . Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations . N Engl J Med. 2012 ; 367 ( 18 ): 1694 - 1703 . https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1210093
Dummer R , Ascierto PA , Gogas HJ , et al. . Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial . Lancet Oncol. 2018 ; 19 ( 5 ): 603 - 615 . https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30142-6
Kopetz S , Grothey A , Van Cutsem E , et al. BEACON CRC: a randomized, 3-arm, phase 3 study of encorafenib and cetuximab with or without binimetinib vs. choice of either irinotecan or FOLFIRI plus cetuximab in BRAF V600E–mutant metastatic colorectal cancer . Paper presented at: ESMO 21st World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer; 2019 ; Barcelona, Spain.
Heinzerling L , Eigentler TK , Fluck M , et al. . Tolerability of BRAF/MEK inhibitor combinations: adverse event evaluation and management . ESMO Open. 2019 ; 4 ( 3 ): e000491 . https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000491
Agustoni F , Platania M , Vitali M , et al. . Emerging toxicities in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: ocular disorders . Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 ; 40 ( 1 ): 197 - 203 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.05.005
de la Cruz-Merino L , Di Guardo L , Grob JJ , et al. . Clinical features of serous retinopathy observed with cobimetinib in patients with BRAF-mutated melanoma treated in the randomized coBRIM study . J Transl Med. 2017 ; 15 ( 1 ): 146 . https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1246-0
Mendez-Martinez S , Calvo P , Ruiz-Moreno O , et al. . Ocular adverse events associated with MEK inhibitors . Retina. 2019 ; 39 ( 8 ): 1435 - 1450 . https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0000000000002451
Stjepanovic N , Velazquez-Martin JP , Bedard PL. Ocular toxicities of MEK inhibitors and other targeted therapies . Ann Oncol. 2016 ; 27 ( 6 ): 998 - 1005 . https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw100
van Dijk EH , van Herpen CM , Marinkovic M , et al. . Serous retinopathy associated with mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition (binimetinib) for metastatic cutaneous and uveal melanoma . Ophthalmology. 2015 ; 122 ( 9 ): 1907 - 1916 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.05.027
Francis JH , Habib LA , Abramson DH , et al. . Clinical and morphologic characteristics of MEK inhibitor-associated retinopathy: differences from central serous chorioretinopathy . Ophthalmology. 2017 ; 124 ( 12 ): 1788 - 1798 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.05.038
Weber ML , Liang MC , Flaherty KT , Heier JS. Subretinal fluid associated with MEK inhibitor use in the treatment of systemic cancer . JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016 ; 134 ( 8 ): 855 - 862 . https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2016.0090
van der Noll R , Leijen S , Neuteboom GH , Beijnen JH , Schellens JHM. Effect of inhibition of the FGFR-MAPK signaling pathway on the development of ocular toxicities . Cancer Treat Rev. 2013 ; 39 ( 6 ): 664 - 672 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.01.003
Jiang Q , Cao C , Lu S , et al. . MEK/ERK pathway mediates UVB-induced AQP1 downregulation and water permeability impairment in human retinal pigment epithelial cells . Int J Mol Med. 2009 ; 23 ( 6 ): 771 - 777 . https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm_00000191
Stamer WD , Bok D , Hu J , Jaffe GJ , McKay BS. Aquaporin-1 channels in human retinal pigment epithelium: role in transepithelial water movement . Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 ; 44 ( 6 ): 2803 - 2808 . https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.03-0001
Huang W , Yang AH , Matsumoto D , et al. . PD0325901, a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor, produces ocular toxicity in a rabbit animal model of retinal vein occlusion . J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 ; 25 ( 6 ): 519 - 530 . https://doi.org/10.1089/jop.2009.0060
Ricard N , Scott RP , Booth CJ , et al. . Endothelial ERK1/2 signaling maintains integrity of the quiescent endothelium . J Exp Med. 2019 ; 216 ( 8 ): 1874 - 1890 . https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20182151
Wang SJ , Li R , Ng TSC , et al. . Efficient blockade of locally reciprocated tumor-macrophage signaling using a TAM-avid nanotherapy . Sci Adv. 2020 ; 6 ( 21 ): eaaz8521 . https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz8521
Urner-Bloch U , Urner M , Stieger P , et al. . Transient MEK inhibitor-associated retinopathy in metastatic melanoma . Ann Oncol. 2014 ; 25 ( 7 ): 1437 - 1441 . https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu169
Booth AEC , Hopkins AM , Rowland A , et al. . Risk factors for MEK-associated retinopathy in patients with advanced melanoma treated with combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor therapy . Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 ; 12 : 1758835920944359 . https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920944359
Gogas HJ , Flaherty KT , Dummer R , et al. . Adverse events associated with encorafenib plus binimetinib in the COLUMBUS study: incidence, course and management . Eur J Cancer. 2019 ; 119 : 97 - 106 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.07.016
Duncan KE , Chang LY , Patronas M. MEK inhibitors: a new class of chemotherapeutic agents with ocular toxicity . Eye (Lond). 2015 ; 29 ( 8 ): 1003 - 1012 . https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2015.82
McCannel TA , Chmielowski B , Finn RS , et al. . Bilateral subfoveal neurosensory retinal detachment associated with MEK inhibitor use for metastatic cancer . JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014 ; 132 ( 8 ): 1005 - 1009 . https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.976
Sarny S , Neumayer M , Kofler J , El-Shabrawi Y. Ocular toxicity due to trametinib and dabrafenib . BMC Ophthalmol. 2017 ; 17 ( 1 ): 146 . https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-017-0541-0
Francis JH , Diamond EL , Chi P , et al. . MEK inhibitor-associated central retinal vein occlusion associated with hyperhomocysteinemia and MTHFR variants . Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2020 ; 6 ( 3 ): 159 - 163 . https://doi.org/10.1159/000501155
Toft-Petersen AP , Muttuvelu DV , Heegaard S , Torp-Pedersen C. Correlation between retinal vein occlusion and cancer - a nationwide Danish cohort study . Acta Ophthalmol . 2018 ; 96 ( 8 ): 800 - 803 . https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.13860
Kida T. Mystery of retinal vein occlusion: vasoactivity of the vein and possible involvement of endothelin-1 . Biomed Res Int. 2017 ; 2017 : 4816527 . https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4816527
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations

- Online ISSN 1549-490X
- Print ISSN 1083-7159
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Introducing .NET Smart Components – AI-powered UI controls
Daniel Roth
March 20th, 2024 23 16
New advances in AI promise to revolutionize how we interact with and use software. But adding AI features into existing software can be challenging. That’s why we built the new .NET Smart Components, a set of genuinely useful AI-powered UI components that you can quickly and easily add to .NET apps. You don’t have to spend weeks of dev time redesigning your UX or researching machine learning and prompt engineering. .NET Smart Components are prebuilt end-to-end AI features that you can drop into your existing app UIs to make your users more productive.
The .NET Smart Components are an experiment and are initially available for Blazor, MVC, and Razor Pages with .NET 6 and later. We expect to provide components for other .NET UI frameworks as well, like .NET MAUI, WPF, and Windows Forms, but first we’re interested in your feedback on how useful these components are and what additional capabilities you’d like to see added.
Watch Steve Sanderson demonstrate what the .NET Smart Components can do:
What’s included
The .NET Smart Components currently include the following smart features:
Smart Paste
Smart Paste fills out forms automatically using data from the user’s clipboard with the click of a button. You can use this with any existing form in your web app. This helps users add data from external sources without re-typing.
Learn more: Smart Paste docs
Smart TextArea
An intelligent upgrade to the traditional textarea. You can configure how it should autocomplete whole sentences using your own preferred tone, policies, URLs, and so on. This helps users type faster and not have to remember URLs etc.
Learn more: Smart TextArea docs
Smart ComboBox
Upgrades the traditional combobox by making suggestions based on semantic matching. This helps users find what they’re looking for.
Learn more: Smart ComboBox docs
Running the samples
You can try out the .NET Smart Components with Blazor or MVC/RazorPages using the .NET Smart Components sample apps on GitHub.
To get started with the .NET Smart Components sample apps:
Download and install the .NET SDK if you don’t already have it installed.
Clone or download the .NET Smart Components sample repo from GitHub: https://aka.ms/smartcomponents.
Deploy an Azure OpenAI backend if you don’t already have one, and then edit the RepoSharedConfig.json file at the root of the solution to add your API key, deployment name, and endpoint URL.
RepoSharedConfig.json
Run either ExampleBlazorApp or ExampleMvcRazorPagesApp to see the .NET Smart Components in action.
Add to an existing app
Once you’re ready, you can add .NET Smart Components to your existing Blazor, MVC, or Razor Pages apps by following these guides:
- Get started with .NET Smart Components and Blazor
- Get started with .NET Smart Components and MVC or Razor Pages
Feedback and support
The .NET Smart Components are currently experimental and not officially supported. We want to hear from you whether these components are useful and how we can improve them to best meet your app development needs. Please take a moment to share your thoughts and feedback with us by filling out our short .NET Smart Components survey . You can also report issues and suggest improvements by creating an issue on GitHub.
Thank you for trying out the .NET Smart Components!
Daniel Roth Principal Product Manager, ASP.NET
23 comments
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Log in to join the discussion or edit/delete existing comments.
Looks promising. But without source code it isn’t of much use if you want to combine the smart features with third party UI libraries.
Hi Samuel. We expect to make the source available once we establish there is sufficient interest. We’ve already received this request from others on GitHub, so can go ahead and add your 👍 on the original post of this issue: https://github.com/dotnet-smartcomponents/smartcomponents/issues/13 .
I would question the AI part of this functionality, not every if statement is AI. and the smart paste makes me shudder in fear, because of privacy concern. that my paste content gets uploaded to server, and analyzed.
Thanks for sharing this feedback! Please note these components aren’t just doing simple if statements – they’re leveraging AI services to augment the user experience.
As for privacy, these components are intended to be used as part of forms that would submit to your server anyway. The data also gets sent to Azure OpenAI, which has a strict privacy policy that you can read about here: https://learn.microsoft.com/legal/cognitive-services/openai/data-privacy .
Did you have to type all this answer, or did you use a smart component? 😉
How can I run it on the WPF or WinUI framework?
As was pointed out
are initially available for Blazor, MVC, and Razor Pages with .NET 6 and later. We expect to provide components for other .NET UI frameworks as well, like .NET MAUI, WPF, and Windows Forms, but first we’re interested in your feedback on how useful these components are and what additional capabilities you’d like to see added.
Does it also work with an API key from openai.com, at least for playing around with it?
Hi Alex. Yup, you can instructions on how to use an OpenAI API key here: https://github.com/dotnet-smartcomponents/smartcomponents/blob/main/docs/configure-openai-backend.md
Nice idea! I wonder if this could have been implemented as a browser extension that can work on any site.
Looks interesting but as the OpenAI backend is still by request only and only available to organisations (not individuals) with an Azure subscription it’s usefulness as something to even try out is rather limited
You can alternatively use an OpenAI API key. Instructions here: https://github.com/dotnet-smartcomponents/smartcomponents/blob/main/docs/configure-openai-backend.md
Fantastic application of existing technology to solve real-world problems! Amazing.
Why just web pages and blazor? How about with MAUI and WinUI?
Hi Ken. We wanted to get feedback from the community first on how useful these components are before we expand them to other UI frameworks. If you’d like to use these components with a particular UI framework, please let us know on our GitHub issue tracker: https://github.com/dotnet-smartcomponents/smartcomponents/issues .
That looks great. One question: I don’t want to keep the API Key in the appsettings.Development.json because the source code, including this json, is public on GitHub. So is there a way for me to get it from environment variable and register it in the Program.cs (I’m using Blazor Web Server)?
Or am I overthinking, as there may be no threat model to require me to secure the API Key?
Please refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/app-secrets?view=aspnetcore-8.0 for more info about storing your secrets during development.
Thank you. Just want to report that it works on Azure with the Environment Variables keys as SmartComponents__ApiKey and SmartComponents__DeploymentName.
I keep getting errors when running either of the apps and I believe it points too when I put in my account in place of YOUR_ACCOUNT. And not recognizing my DeploymentName.
Hi Karen. If you’re using Azure OpenAI, you should be able to get the endpoint URL from the Azure portal when you browse to your Azure OpenAI resource. To get the deployment name, make sure you actually create a deployment using the Azure AI Studio and then use the name from that deployment. You can get to the Azure AI Studio from your Azure OpenAI resource in the Azure portal.

Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- Undergraduate Admission
- Graduate Admission
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Communications
- Health Sciences and Human Performance
- Humanities and Sciences
- Music, Theatre, and Dance
- IC Resources
- Office of the President
- Ithaca College at a Glance
- Awards and Accolades
- Five-Year Strategic Plan
- Public Health
- Directories
- Course Catalog
- Undergraduate
2023-24 Diversity Scholar Presentation: Caroline Charles
Curating black archives as community practice.
On April 5thfrom 5-7pm in Clark Lounge, Caroline Charles will discuss her research on Black visual archives and how it intersects with her involvement in two public-facing archival projects in her hometown of Syracuse, NY--A Love Supreme: Black Cultural Expression and Political Activism of the 1960s and 1970san exhibition in Syracuse University Libraries Special Collections Research Center and the Turning the Lens Collective’s Family Pictures Syracuse Project. She will discuss the process of curation, the importance of collaboration in the archives, and how these practices can be activated alongside local communities.
Appetizers and drinks will be provided. All are encouraged to attend.
Individuals with disabilities requiring accommodations should contact Mack Rovenolt at [email protected] or 607-274-7011. We ask that requests for accommodations be made as soon as possible.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Center for Latin American Visual Studies | Department of Art and Art History | University of Texas at Austin

March 26, 2024 , Filed Under: Uncategorized
Schedule of 2024 ISLAA Forum Participant Dissertation Presentations
DISSERTATION PRESENTATIONS
Friday, April 5
9AM-12:15PM + 2PM-4:30PM
DFA 2.204
Open to the public
SESSION I
Each presentation followed by discussion
9:05 Lynne Lee
Rice University
Black Art in White Narratives: Early Afro-Brazilian Art History at the Crossroads of Science and Aesthetics
9:40 Juan Gabriel Ramírez Bolivar
Institute of Fine Arts, New York University
The Idea of Hispanoamérica in the Visual Culture of Mexico and Colombia (1920-1940)
10:15 COFFEE BREAK, Dean’s Patio in DFA
10:45 Joseph Shaikewitz
Incongruent, Incomprehensible: Trans Femme Visualities in Latin America, 1900–1960
11:20 Alhelí Harvey
University of Texas at Austin
Experiencing Enchantment: A Cultural Ecology of Place in New Mexico
12:00 LUNCH BREAK
SESSION II
2:05 Lucía Laumann
Universidad Nacional de San Martín/CONICET
Las grabadoras. Formación gráfica, prácticas y derroteros institucionales de las mujeres en Buenos Aires a mediados de siglo XX
2:40 Lucy Quezada
Shaping the Official Field: Art and Power during the Civilian-Military Dictatorships of Argentina, Brazil, and Chile
3:15 COFFEE BREAK, Dean’s Patio in DFA
3:45 Jennifer Leite Sales
The Experimental: Reimaging Art and Pedagogy in 1970s Brazil
4:30 Letícia Cobra Lima
University of California, Santa Barbara
Assembling the Body: Sculpture in Argentina, Brazil, and Colombia, 1960-1996
5:00 RECEPTION, Dean’s Patio in DFA
Electronic: Email UT CLAVIS
Department of Art and Art History
1 University Station
D1300 Austin, TX

- Center Leadership
- Current Students
- Visiting Students & Scholars
- Recent Alumni
- Events and Exhibitions
- The Permanent Seminar in Latin American Art
- Visiting Lecturers
- Critical Interventions and Collaborations
- ISLAA Forum
- Publications
- Getty Foundation Connecting Art History Seminars (2012-2020)
- International Emerging Scholars Forums (2009-2012)
- ISLAA Forum 2024
- Research Resources
- Graduate Student Funding
- Study Trips
- Giving to CLAVIS

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience. Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals.
Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate. Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids.
General Tips For Visual Presentations. Before you begin creating your presentation, you first need to know what makes effective presentations - storytelling. Such presentations target the audience's emotions leading to a stronger connection to the audience member and the main point of the presentation.
The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says "any slide with more than 10 words is a document.". If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
1. Use stock photos for your presentation slides. When I'm giving a presentation training workshop, I ask people what types of visuals they should avoid, and a lot of them say "stock photos!" I see where they're coming from. The term "stock photo" has become synonymous with "cheesy stock photo of white people smiling at the camera."
Rehearse the visual part of your presentation, just like other parts of your speech. Benefits of Visuals. A study at the Wharton Research Centre also revealed that participants remembered 50% of the visual information, but only 5% of the bulleted points. Visuals can help you clarify points, reinforce your message, and create greater interest ...
Text is the most common - and overused - visual we see in business presentations (hello bullets!). Text used sparingly with contrasting color and size, however, creates an easy-to-digest message. Video Video is an excellent to way to change the pace, the voice, and the medium of a presentation.
Visual communication is the magic behind all the visible things in the world that tell stories, share information, and attract interest. As a person who makes presentations, you own the power of visual communication to impact, inform and attract your audience with visuals. All you need is the knowledge and the tools to make it work.
There are many types of visual presentations, but we will focus on seven of the most common ones here. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to understand when each would be appropriate to use. 1. Slides. Slides are the most common type of visual aid. You can use slides to demonstrate your point and make it easier ...
Exercise 2. In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 "Exercise 1".
5 ways to boost your visual power. For you to start getting these benefits, some simple tricks can boost your visuals and, with them, your message. Here are the 5 main ways you can make presentations more engaging and memorable. 1. Speak your words — don't write them on your slides.
1. Visuals make information more memorable. One of the main reasons why visuals are important in presentations is because they make information more memorable. People are more likely to remember an image than a block of text. According to research, people remember up to 80% of what they see, compared to only 20% of what they read.
1. Charts and Graphs. Charts and graphs are a form of presentation aid used to visually compare statistics and figures. These are some of the most used forms of visual aids in the business world. Listening to long strings of numbers can be a challenging task.
Some possible visual presentations include infographics, charts, diagrams, posters, flipcharts, whiteboards, and video presentation examples. An infographic is a collection of different graphic visual presentations to represent information, data, or knowledge intended more visually quickly and clearly to grab the audience's attention.
6. Use High-Quality Images. Incorporating relevant and high-quality images can enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Ensure that the images you use are consistent in style, resolution, and quality. Avoid mixing different image types as this may lead to visual dissonance. 7.
Top Visual Aids In Presentations | Use These To Impress Your Audience. Watch on. The best stats you've ever seen | Hans Rosling. Watch on. Trust in Physics. Watch on. George Carlin -Child Worship. Watch on. Using visual aids in presentations helps you pass the right information in a relatively shorter time.
Here is a simple rule that differentiates 'beautiful slides' and 'effective visual slides': In a 'beautiful slide' - picture is the hero. In an 'effective visual slide' - Message is the hero. Let us evaluate 3 different set of slides with different objectives. One conveys a fact, another conveys a concept and the third ...
Visual storytelling refers to the use of compelling visuals, such as images, infographics, charts, and videos, to convey information and engage the audience during presentations. It goes beyond simply presenting facts and data by incorporating narrative elements and visual cues to create a more immersive and memorable experience.
Effective visual presentations can be accomplished if you use the right visual aids. To help you ace your next presentation, in this post we will be going through the top 5 types of visuals for a presentation. In addition to the visual presentation examples, we will provide some helpful visual presentation tips to make your presentation a ...
Presentation visuals are one of the most compelling parts of a presentation. Some presenters underestimate the importance of a visual presentation and decide to only speak, or use text slides to back up what they're saying. This is a huge mistake - effective visual presentations can have a massive positive impact on your viewers.
It's not enough to just copy and paste your data into a presentation slide. Luckily, PowerPoint has a lot of smart data visualization tools! You just need to put in your data, and PowerPoint will work it up for you. 1. Collect your data. First things first, and that is to have all your information ready.
5. Presentation visuals keep your speech on track. Peppering your presentation with visual aids will help you organize your talking points, avoid off-topic rambling, and even jog your memory if you get hit with a bout of stage fright. But remember: While thoughtful visuals will make a speech or presentation much stronger, they won't save you ...
While preparation and delivery are critical components of a successful presentation, the visuals you use throughout your presentation are equally. Call Us: 1-800-501-1245 ... which is why visuals are a necessary tool for effective presentations. When used properly, visual aids can help your audience connect to the topic and understand it's ...
Turn your visual story into an interactive presentation and share it with your team. Ditch the stick figures! Katalist Storytelling Studio can turn all your scripts into visual stories with customizable scenes, characters, and props. Create visual stories with AI. Get lifetime access to Katalist Storytelling Studio today!
Presentation 4: Severe With Visual Symptoms Describe/discuss: More severe ocular toxicities may also emerge during MEK inhibitor therapy and can be associated with vision loss and pain. Such was the case for a patient receiving MEK inhibitor therapy for metastatic melanoma who experienced vision loss, pain, and foreign body sensation in both ...
NET Smart Components are prebuilt end-to-end AI features that you can drop into your existing app UIs to make your users more productive. The .NET Smart Components are an experiment and are initially available for Blazor, MVC, and Razor Pages with .NET 6 and later.
Visual aids were of high quality and easily visible Content of the visual aids was pertinent to the topic Additional Notes: ... Presentation pace was consistent and appropriate (not too fast or too s low) Presenter displayed enthusiasm while presenting
Individuals with disabilities requiring accommodations should contact Mack Rovenolt at [email protected] or 607-274-7011. We ask that requests for accommodations be made as soon as possible. Curating Black Archives as Community Practice On April 5thfrom 5-7pm in Clark Lounge, Caroline Charles will discuss her research on Black visual archives and ...
Each presentation followed by discussion 9:05 Lynne Lee Rice University Black Art in White Narratives: Early Afro-Brazilian Art History at the Crossroads of Science and Aesthetics 9:40 Juan Gabriel Ramírez Bolivar Institute of Fine Arts, New York University The Idea of Hispanoamérica in the Visual Culture of Mexico and Colombia (1920-1940)