
- Upload Ppt Presentation
- Upload Pdf Presentation
- Upload Infographics
- User Presentation
- Related Presentations


YOGA POSES AND TIPSFOR A FLAT BELLY
By: KhushbuSG Views: 1852

About Movement Disorders
By: KhushbuSG Views: 212

An Introduction to Pathology
By: KhushbuSG Views: 479

Running Injuries-Evaluation Treatment Prevention
By: KhushbuSG Views: 292

5 COMPONENTS OF FITNESS
By: KhushbuSG Views: 3822

Development of Imo Maritime Security Policy
By: kevinthompson56 Views: 1048

Models of Abnormal Behavior
By: KhushbuSG Views: 201

Common Adrenal Disorders In Children
By: yourdoctors Views: 545

Metabolism-Anabolism And Catabolism
By: FrankMarco Views: 566

Loneliness and Social Isolation
By: FrankMarco Views: 561

- About : Editor & Social Media Evangelist
- Occupation : Medical Professional
- Specialty : Other Health Professionals
- Country : India
- Website : http://blog.medicpresents.com/
HEALTH A TO Z
- Eye Disease
- Heart Attack
- Medications

Anatomy of Urinary System
Jan 04, 2020
720 likes | 900 Views
PAN 201. Anatomy of Urinary System. URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS. Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. Control blood volume and composition. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. Filter blood plasma, eliminate wastes Regulate blood volume, pressure Regulate fluid osmolarity

Share Presentation
- renal pyramids
- renal pelvis
- kidney anatomy
- proximal convoluted tubule
- blood vessels servicing kidney

Presentation Transcript
PAN 201 Anatomy of Urinary System
URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS • Kidneys (2) • Ureters (2) • Urinary bladder • Urethra
KIDNEY FUNCTIONS • Control blood volume and composition
KIDNEY FUNCTIONS • Filter blood plasma, eliminate wastes • Regulate blood volume, pressure • Regulate fluid osmolarity • Secrete renin • Secrete erythropoietin (EPO) • Regulate PCO2, Acid-Base balance • Synthesize calcitriol (Vitamin D) • Detoxify free radicals, drugs • Gluconeogenesis
EXCRETION Removal of wastes • Respiratory system • CO2, water • Integumentary system • Water, salts, lactic acid, urea • Digestive system • Water, salts, CO2, lipids, bile pigments, cholesterol, etc. • Urinary system • Metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs, hormones, salts, H+, water
KIDNEY ANATOMY Protected by three connective tissue layers • Renal fascia • Attaches to abdominal wall • Adipose capsule • Fat cushioning kidney • Renal capsule • Fibrous sac • Protects from trauma and infection
KIDNEY ANATOMY Gross anatomy • Renal sinus • Renal parenchyma
KIDNEY ANATOMY Renal sinus • Surrounded by renal parenchyma • Contains blood & lymph vessels, nerves, urine-collecting structures
KIDNEY ANATOMY Renal parenchyma • Glandular tissue • Forms urine • Two zones • Outer cortex • Inner medulla
KIDNEY ANATOMY Renal parenchyma • Renal pyramids • Extensions of cortex (renal columns) divide medulla into 6 – 10 renal pyramids • Pyramid + overlying cortex = Lobe • Point of pyramid = Papilla • Papilla nested in cup (minor calyx) • 2 – 3 minor calices Major calyx • 2 – 3 major calices Renal pelvis • Renal pelvis Ureter
KIDNEY ANATOMY: NEPHRONS Nephrons • Functional units of kidney • ~1.2 million per kidney • Three main parts • Blood vessels • Renal corpuscle • Renal tubule
NEPHRONS Blood vessels servicing kidney • Supplied by renal artery • ~21% or cardiac output • (Mass in only ~ 0.4%) • Afferent arterioles • Capillary cluster (glomerulus)
NEPHRONS Blood vessels servicing kidney • Glomerulus • Fenestrated capillaries • Capillary filtration in glomerulus initiates urine production • Filtrate lacks cells & proteins • Drained by efferent arteriole • Peritubular capillaries • Renal vein
NEPHRONS Renal corpuscle • Glomerulus plus capsule • Glomerulus enclosed in two-layered glomerular capsule • “Bowman’s capsule” • Fluid filters from glomerular capillaries • “Glomerular filtrate” • Fluid collects in capsular space • Fluid flows into renal tubule
NEPHRONS Renal tubule • Leads from glomerular capsule • Ends at tip of medullary pyramid • ~3 cm long • Four major regions • Proximal convoluted tubule • Nephron loop • Distal convoluted tubule • Collecting duct
NEPHRONS Renal tubule • Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) • Arises from glomerular capsule • Longest, most coiled region • Prominent microvilli • Function in absorption • Much contact with peritubular capillaries
NEPHRONS Renal tubule • Nephron loop (“Loop of Henle”) • “U” – shaped, distal to PCT • Descending and ascending limbs • Thick segments • Active transport of salts • High metabolism, many mitochondria • Thin segments • Permeable to water • Low metabolism
NEPHRONS Renal tubule • Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) • Coiled, distal to nephron loop • Shorter than PCT • Less coiled than PCT • Very few microvilli • Contacts afferent and efferent arterioles (regulation imparted) • Contact with peritubular capillaries
NEPHRONS Renal tubules • Collecting duct • DCTs of several nephrons empty into a collecting duct • Passes into medulla • Several merge into papillary duct (~30 per papilla) • Drain into minor calyx
URINE FORMATION Overview • Blood plasma Urine • Four steps • Glomerular filtration • Tubular reabsorption • Tubular secretion • Water conservation
URINE STORAGE Ureters • Carry urine from kidneys to urinary bladder via peristalsis • Rhythmic contraction of smooth muscle • Enter bladder from below • Pressure from full bladder compresses ureters and prevents backflow
Arterial Supply • Ureter is supplied by multiple arteries throughout its course • From above downward, these are:: • Renal artery • Gonadal artery • Common iliac artery • Internal iliac artery 1 2 3 4
URINE STORAGE Ureters • Small diameter • A 25 – 30 cm long muscular tube transporting urine from kidney to urinary bladder. • Begins as a continuation of renal pelvis. • Easily obstructed or injured by kidney stones (renal calculi)
URINE STORAGE Urinary bladder • Muscular sac • Wrinkles termed rugae • Openings of ureters common site for bladder infection
Urinary Bladder • Located immediately behind the pubic symphysis • Shape and relations vary according to the amount of urine it contains • An empty bladder: • In adults, is entirely a pelvic organ; as it fills, rises up into the hypogastric region. • In young children, it projects above the pelvic inlet
An empty bladder is pyramidal in shape having: • Anapex • Abase (posterior surface) • Asuperiorsurface • Twoinfrolateral surfaces • Aneck
Apex • Directed forward • Lies behind the upper margin of the symphysis pubis • Is connected to umbilicus by the median umbilical ligament (remnant of urachus)
Base or Posterior surface • Triangular in shape • Upper part covered by peritoneum • Lower part related to: • In males: vas deferentia and seminal vesicles • In females: vagina
Female pelvis Male pelvis Superior surface Completely covered by peritoneum. Related to the coils of ileum or sigmoid colon in males and to uterus in females
Infrolateral surfaces: • Related in front to the retro pubic pad of fat & the pubic bones • Posteriorlylie in contact with the obturatorinternus above and levatorani below Retropubic fat • Accommodates distention of bladder • Continuous with anterior abdominal wall. • Rupture of bladder results in escape of urine to anterior abdominal wall
Neck: • Lies inferiorly, and is the most fixed part of the bladder • Is related to lower border of symphysis pubis • In male, rests on the upper surface of prostate. Here, the smooth muscle fibers of the bladder are continuous with those of the prostate • The circular muscle fibers thickened to form the sphincter vesicae
Interior of the Urinary Bladder • Mucous membrane thrown into folds except in the triangular region in the base of bladder, between the openings of the two ureters and the urethra. This region is called the ‘trigone’.Here The mucous membrane is always smooth even when the bladder is empty • Uvula vesicae, a small elevation located just behind the urethral orifice, It is produced by the median lobe of prostate.
Blood & Nerve Supply • The nerves form the vesical nerve plexus that contains: • Sympathetic fibers derived mainly fromL1,2 • Parasympathetic fibers derived from pelvic splanchnic nerves S2,3,4 • Sensory fibers from the bladder are visceral and transmit pain sensation resulting from overdistention Arterial supply: from internal iliac artery Venous drainage: into internal iliac vein Lymphatics:into internal iliac lymph nodes
The normal capacity of bladder is about 300-500ml. • As bladder fills, the superior surface bulges upward into abdominal cavity. • The peritoneal lining is peeled off the lower part of anterior abdominal wall and thebladder comes into direct contact with the anterior abdominal wall
URINE ELIMINATION Urethra • Conveys urine from body • Internal urethral sphincter • Retains urine in bladder • Smooth muscle, involuntary • External urethral sphincter • Provides voluntary control over voiding of urine
URINE ELIMINATION Urethra • 3 – 4 cm long in females • Bound by connective tissue to anterior wall of vagina • Urethral orifice exits body between vaginal orifice and clitoris
URINE ELIMINATION Urethra • ~18 cm long in males • Prostatic urethra • ~2.5 cm long, urinary bladder prostate • Membranous urethra • ~0.5 cm, passes through floor of pelvic cavity • Penile urethra • ~15 cm long, passes through penis
- More by User

Urinary System
Urinary System . Chapter 26. Urinary System. Essential Homeostatic system Maintains & Regulates body’s internal environment Coordinates activities of digestive, cardiovascular, respiratory, and urinary systems Blood volume Blood composition Mechanism for homeostasis Blood filtration.
1.17k views • 46 slides

APPLIED ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
APPLIED ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM . Functional Anatomy and Physiology Kidney size = 11-14cm Located retro - peritoneally on either side of vertebral column, Extends from T12 to L3. Left kidney is slightly higher than Right.
1.4k views • 20 slides

Anatomy of Lower Urinary Tract
Anatomy of Lower Urinary Tract. Hann-Chorng Kuo Department of Urology Buddhist Tzu Chi General Hospital. Embryology of Lower Urinary Tract. Cloaca Procodeum- ectodermal depression in hindgut Cloacal membrane Cloaca separates to urogenital sinus and rectum
2.16k views • 52 slides

Urinary System- Anatomy and Physiology
Urinary System- Anatomy and Physiology. Zoe McCarthy. Urinary System in Context. Urinary System in Context. Functions of the Urinary system. 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood pH
901 views • 20 slides

Anatomy and Physiology The Urinary System Chapter 18
Anatomy and Physiology The Urinary System Chapter 18. Community Education Mr. Kestner. Information. The urinary system, also known as the excretory system , is responsible for removing certain wastes and excess water from the body It also maintains the body’s acid-base balance
385 views • 14 slides

Urinary System. Chapter 13 A&P1 Tutor: Eleshia Howell. The urinary system is the main excretory system, removing the majority of physiological wastes. It consists of the following structures: Kidneys x 2 Ureters x 2 Urinary bladder Urethra
1.06k views • 59 slides

ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. OBJECTIVES. Identify the main functions of the urinary system Learn the organs of the urinary system and describe their physical characteristics Describe the microscopic structure of the kidney and learn the function of the nephron
2.26k views • 39 slides
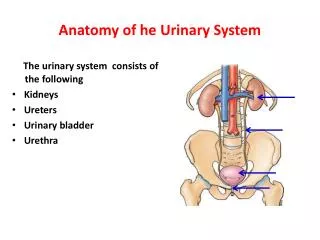
Anatomy of he Urinary System
Anatomy of he Urinary System. The urinary system consists of the following Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra. The Kidney. Bean-shaped organ It lies on the posterior abdominal wall at the side of vertebral column It measures 4x2x1 inches
3.05k views • 30 slides

Urinary System. Identify the primary function of the urinary system. . filter blood to remove waste products to maintain normal pH. State the location and function of each of the structures of the urinary system:. kidneys
482 views • 29 slides

Exercise 26 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary System
Exercise 26 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary System. Gross Anatomy of the Human Urinary System. Renal capsule a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a thick layer of adipose tissue . It provides some protection from trauma and damage . Organs of the Urinary System.
1.12k views • 47 slides

Urinary System. Urinary System Structure Urine Formation Regulating Urine Formation. 10.1 Urinary System Structure. Kidneys Nephrons Capillary Beds. Kidneys. The kidneys lie in the lower, dorsal part of the abdominal cavity
676 views • 54 slides
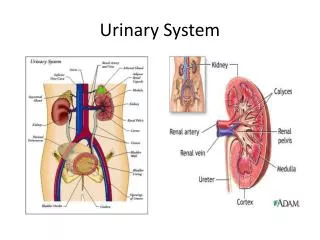
Urinary System. The Urinary System. Kidney. Every vertebrate has a pair of kidneys Three major parts of the kidney are: 1. Cortex - outer part of kidney - contains the glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, and blood supply to the nephron unit 2. Medulla - middle of the kidney
1.38k views • 20 slides

Urinary System. Ashley Morgade, Nick Perez, Kayla Lopez, TJ ”APPLE HEAD ” Martin MRS. HILL IS YOUR #1 FAN…… LOVE AND MISS YOU ALL 4 TH PERIOD ! . Urinary System. The urinary system which is also called the renal system is the system that stores, produces, and eliminates urine.
435 views • 26 slides

Urinary System. I. Introduction . A. Organs/Structure Kidneys Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra. Introduction. Function Removes waste material from blood Primary organ responsible for monitoring blood composition. II. Kidneys. Function
437 views • 36 slides

Urinary System. A. Functions 1. maintain blood homeostasis 2. elimination of waste B. Structures 1. kidneys A) reddish-brown & bean-shaped. Urinary System. B) lie in superior lumbar region of the posterior abdominal wall (T 12 to L 3 ) C) External Anatomy
663 views • 49 slides

Urinary System. By: Emily Bonilla. What is the Urinary System?. The Urinary System is composed of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, sphincter, and the urethra. It is what makes you pee. Kidneys:. The shape of the bean. They are purplish-brownish. They are behind your ribs.
201 views • 9 slides
Exercise 26 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary System. Gross Anatomy of the Human Urinary System. Renal capsule a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a thick layer of adipose tissue. It provides some protection from trauma and damage . Organs of the Urinary System.
501 views • 28 slides
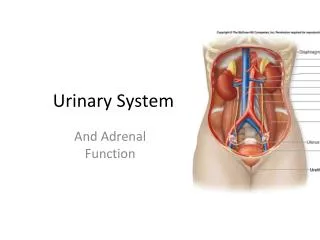
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function. Overview. Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function. Functions of the Kidney. Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition of blood Gluconeogenesis Produce hormones renin and erythropoietin
696 views • 31 slides

Urinary System. Functions of the Urinary System. Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood Blood pressure Red blood cell production Activation of vitamin D.
494 views • 38 slides

The Urinary System Dept. of Anatomy Luzhou Medical College
The Urinary System Dept. of Anatomy Luzhou Medical College. Edited by professor Xiao. The Urinary System. Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra
1.15k views • 42 slides

Anatomy of the Urinary System
Anatomy of the Urinary System. Structures. Kidneys: located under back muscles, behind parietal peritoneum, above the waistline, right slightly lower than left Internal structure: Cortex: outer layer Medulla: inner portion Pyramids: triangular sections of medulla. Kidney…con’t
480 views • 27 slides

Urinary System. Chapter 26. Urinary Components. Functions of Urinary System 1. Kidney Functions 2. Urine transport 3. Urine storage. 4. Excretion. Urinary System – Kidney Functions. 1. Regulate blood ionic composition. 2. Regulate blood pH. 3. Regulate blood volume.
953 views • 36 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Anatomy of Urinary system simplified for Nursing students. Health & Medicine. 1 of 42. Download Now. Download to read offline. Urinary System Anatomy - ppt - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
1) urea (a nitrogenous waste produced in the liver from the breakdown of protein. It is the main component of urine) ; 2) uric acid (usually produced from breakdown of DNA or RNA) and. 3) creatinine (waste product of muscle action). All of these compounds have nitrogen as a major component. The kidneys are more than excretory organs.
The urinary system consists of 4 major organs; the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and the urethra.Together these organs act to filter blood, remove waste products, create urine and transport urine out from the body. The urinary system is also called the excretory system, because held within the urine are the various excreted products, including by-products such as urea and uric acid, drugs ...
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until urination. During urination, the bladder contracts and the urethra carries the urine out of the body.
The urinary system (or urinary tract) works as your body's filtration system. When your urinary system removes toxins and wastes from your body, it comes out as pee (urine). To be able to pee, your body must pass this waste through a series of organs, ducts and tubes. If there's a problem at any step in this process, it can affect if you ...
The urinary system removes them by filtering and cleansing the blood as it passes through the kidneys. Another vital function is the regulation of the volume, acidity, salinity, concentration, and chemical composition of blood, lymph, and other body fluids. Under hormonal control, the kidneys continually monitor what they release into the urine ...
The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra. The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it needs, waste products are left behind in the bowel and in the blood. The kidney and urinary systems help the body to eliminate ...
It begins at the neck of the urinary bladder by the internal urethral orifice (or internal urinary meatus). It opens into the vestibule of vagina by the external urethral orifice (or external urinary meatus). It has two parts: 1. intramural part (corresponds with the neck of bladder); 2. perineal part (which pierces the perineum).
Definition. The urinary system produces, stores, and excretes urine via a filtration mechanism in which potentially harmful molecules are removed from the body. It also plays a crucial role in water homeostasis, electrolyte and acid-base balance, and red blood cell production.The human urinary tract is comprised of two kidneys, two ureters, one ...
What we'll talk about... Components of the urinary system. The kidney performs several critical functions. Nephrons filter blood and reabsorb solutes and water. The kidney contains two types of nephrons to filter blood and regulate electrolyte concentration and pH. Arcuate arteries define the border between cortex and medulla in the kidney.
General anatomy of urinary system ppt. The urinary system, also known as the renal system or urinary tract, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate ...
The urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra, plays a crucial role in filtering and eliminating waste products from the blood, maintaining electrolyte balance, and regulating fluid levels in the body.Additionally, it contributes to blood pressure regulation and the production of hormones involved in red blood cell production and calcium metabolism.
Slide 5-. The urinary system is the main excretory system and consists of the following structures: 2 kidneys, which secrete urine. 2ureters that convey the urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. the urinary bladder, which collects and stores urine. the urethra through which urine leaves the body.
PK !ÌÑ•/ " [Content_Types].xml ¢ ( Ę]o›0 †ï'í? ßNÁ¡Ûºv éÅ>®öQ©Ý ðà@¼ Û² ¬ù÷;@šQD—¦Žå›HÆœó>Ç ûå,®î 'lÀX®dN²tN …*¹¬sòãöóì‚$Ö1Y2¡$äd -\-_¾XÜn5Ø £¥ÍÉÊ9ýžR[¬ a6U $ÎTÊ4ÌáÐÔT³â7« žÍçç´PÒ t3×æ ËÅG¨ØZ¸äÓ ^îI~i¨Iò¡¿±ÕÊ oÚ Ý Œ1 ì(†i-xÁ VG7² 'ÍvT)Fv÷Ø ×ö ¢"i…væ!ÔPàñ ...
THE URINARY SYSTEM. FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM 1. Excretion - removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts, and excess water from blood 2. Maintain acid-base balance 3. Secrete waste products in the form of urine Eliminate urine from blodder KIDNEYS 2 bean shaped organs that are about 4 inches long by 2-3 inches wide by 1 inch thick.
THE URINARY SYSTEM NIKITA SHARMA LECTURER BECON. 2. KIDNEYS The kidneys lie on the posterior abdominal wall, one on each side of the vertebral column, behind the peritoneum and below the diaphragm. They extend from the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra to the 3rd lumbar vertebra, receiving some protection from the lower rib cage. The right ...
Presentation Transcript. The Urinary System • Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra • Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra • Filter the blood and return most of water and solutes to the bloodstream. Overview of Kidney Functions • Regulation of blood ionic composition ...
Slide 2-. The urinary system: its functions and its organs The urinary system, also referred to as the genitourinary system (abbreviation GU), is responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood and removing them from the body. It is also responsible for adjusting water and electrolyte levels as well as maintaining a correct pH.
4 Structure and Function Structure and Function The Urinary System Also called the excretory system Maintains water balance Removes waste products from the blood by excreting them in the urine. Slide 5-. 5 Kidneys Structure and Function Kidneys The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the retroperitoneal portion of the abdominal cavity on ...
27 likes • 23,866 views. A. abhay joshi. The urinary system, components, the urine formation process, The gross structure of the kidney, Microscope structure of the kidney, Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System. Read more. Education. 1 of 30. The urinary system - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
This medical PowerPoint presentation is about the urinary system, also known as the renal system. The urinary system is responsible for producing, storing, and eliminating urine from the body. It consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in the back of the abdomen.
Presentation Transcript. PAN 201 Anatomy of Urinary System. URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS • Kidneys (2) • Ureters (2) • Urinary bladder • Urethra. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS • Control blood volume and composition. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS • Filter blood plasma, eliminate wastes • Regulate blood volume, pressure • Regulate fluid osmolarity • Secrete ...
53 likes • 4,370 views. D. deepaingawale21. Urinary System. Health & Medicine. 1 of 52. Download Now. Download to read offline. Urinary system - Download as a PDF or view online for free.