My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

Narrative Speech [With Topics and Examples]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.
Narrative Speech Topics

- Your Events, Life Lessons, Personal Experiences, Rituals and Your Identity.
The main point is that you are talking about yourself.
Your thoughts, feelings, ideas, views, opinions and events are the leading ladies in this special public speaking speech writing process.
In this article:
Your Life Lessons
Experiences, narrative speech writing tips, 10 fast showcases.
Here are example narrative speech topics you can share in a speech class or other public speaking assignment in high school, college education. Narrow the speech topics appropriately to the public speaking occasion rules with the specialized checklist I have composed with seven narrative speech writing tips .
The checks and tips also serve as hooks for to narrate a paragraph in an college essay.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
The backbone of my advice is: try to keep the story devoted and dedicated. If you find it hard to develop speech topics for narration purposes and you are a little bit overwhelmed, then try ten ways I’ve developed to find narrative speech topics .
Most students mark out an event in their speeches and essays. An event that stipulate a great step in life or an important moment that has impact on your prosperity or lifestyle from that particular period:
E.g. An accident or remarkable positive event that changed my life. The birth of my brother, sister or other relative and the impact on our household and family-life. My first day at high school or college. The decision I regret most at my school or in my professional job career. My day of graduation (If you have not yet graduated from an educational institution, describe your hardworking and your planning efforts to achieve the qualification). My first serious date with my boyfriend / girlfriend. A significant family event in the summer. A memorable vacation. A historical event that impressed me. The day I will move overseas. A milestone that seemed bad but turned out to be good. My heroic sports moment at the campus field.
Take personal growth and development as starting point. Widen the horizon of the audience to a greater extent with narrative speech topics on wisdom. Construct a life lesson yourself, based on a practical wisdom acquired by own experience, or one you have been be introduced to by someone else:
E.g. The influence of a special person on my behavior. How I have dealed with a difficult situation. What lessons I have learned through studying the genealogy of my family. A prejudice that involved me. An Eureka moment: you suddenly understood how something works in life you had been struggling with earlier. How you helped someonelse and what you learned from her or him, and from the situation.
For this kind of public speaking training begin with mentioning intuitively the emotions you feel (in senses and mind) and the greater perception of the circumstances that lead to apprehension of a precarious situation:
E.g. My most frustrating moment. How you handled in an emergency situation. How I break up with my love. A narrow escape. A moment when you did something that took a lot of courage. A time when you choose to go your own way and did not follow the crowd. How I stood up for my beliefs. The day you rebelled with a decision concerning you. How you cope with your nerves recently – think about fear of public speaking and how you mastered and controlled it in the end. What happened when you had a disagreement with your teacher or instructor in class, this triggering narrative speech idea is great for speech class, because everyone will recognize the situation.
This theoretic method is close related to the previous tips. However, there is one small but significant difference.
Let’s define rituals as a system of prescribed procedures or actions of a group to which you belong. In that case you have the perfect starters to speak out feelings .
Complement the ritual with your own feelings and random thoughts that bubble up when you are practicing the ritual:
E.g. How you usually prepare for a test at high school or for a personality interview or questionnaire. Your ritual before a sports game. Your ritual before going out with friends – make up codes, choosing your dress or outfit, total party looks. The routines you always follow under certain circumstances on your way to home. Church or other religious rituals you think are important to celebrate. Special meditative techniques you have learned from old masters in East Asia.
These examples are meant to accent the cultural and personal charateristics based on values, beliefs and principles.
What do you think is making life worth living? What shaped your personality? What are the psychological factors and environmental influences?
And state why and how you ground your decisions:
E.g. My act of heroism. The decisions my parents made for me when I was young – school choice, admission and finance. How curiosity brings me where I am now. I daydream of … A place that stands for my romantic moments – a table for two in a restaurant with a great view. My pet resembles my personal habits. A vivid childhood memory in which you can see how I would develop myself in the next ten to fifteen years. Samples of self-reliance in difficult conditions, empathy towards others in society, and your learning attitude and the learning curve.
Make a point by building to a climax at the end of your speech topic, whatever the narrative speech topics may be you want to apply in some sort of public speaking training environment. Build your way to the most intense point in the development or resolution of the subject you have chosen – culminate all facts as narrator to that end point in your verbal account.
Narrative speech tips for organizing and delivering a written description of past events, a story, lesson, moral, personal characteristic or experience you want to share.
- Select carefully the things you want to convey with your audience. Perhaps your public speaking assignment have a time limit. Check that out, and stick to it.This will force you to pick out one single significant story about yourself.And that is easier than you think when you take a closer look at my easy ways to find narrative topics.
- What do you want your audience to remember after the lapse?
- What is the special purpose, the breaking point, the ultimate goal, the smart lesson or the mysterious plot?
- Develop all the action and rising drama you need to visualize the plot of the story: the main events, leading character roles, the most relevant details, and write it in a sequence of steps. Translate those steps into dialogues.
- Organize all the text to speech in a strictly time ordered format. Make a story sequence. Relate a progression of events in a chronologically way.The audience will recognize this simple what I call a What Happened Speech Writing Outline, and can fully understand your goal. Another benefit: you will remember your key ideas better.It can help if you make a simple storyboard – arrange a series of pictures of the action scenes.
- Build in transition sentences, words or phrases, like the words then, after that, next, at this moment, etc. It helps to make a natural flow in your text.
- Rehearse your narrative speech in front of a friend and ask opinions. Practice and practice again. And return to my narrative speech topics gallore if you get lost in your efforts.Avoid to memorize your text to speech. When you are able to tell it in a reasonably extemp manner – everyone can follow you easily – it is okay.
- Finally, try to make eye contact with your listeners when you deliver this educational speech and apply my public speaking tips one by one of course.
- A good place to start finding a suitable narrative speech topic is brainstorming about a memorable moments in your life, a situation you had to cope with in your environment, a difficult setting or funny scene you had to talk your way out.
Try to catch it in one phrase: At X-mas I … and followed by a catchy anf active verb.
E.g. At X-mas I think … I want … I’m going … I was … I stated … I saw … .
After the task verb you can fill in every personal experience you want to share with your public speaking audience in a narration. These 40 speech topics for a storytelling structure can trigger your imagination further.
My most important advice is: stay close to yourself, open all your senses: sight, hearing, taste, and even smell and touch. Good for descibing the memorable moment, the intensity of it.
- A second way to dig up a narrative speech topic is thinking about a leading prophetic or predictive incident in the previous 10 years or in your chidhood. Something that illustrates very well why and how you became who you are right now.
E.g. Your character, moral beliefs, unorthodox manner of behaving or acting or you fight for freedom by not conforming to rules, special skills and qualities.
- The third way I like to communicate here with you is storytelling. Let yourself be triggered for a narrative speech story by incidents or a series of events behind a personal photograph or a video for example.
E.g. Creative writing on a photo of your grand-grandparents, of a pet, a horse, an exciting graduation party, a great architectural design.
- You also can find anecdotal or fictional storylines by highlighting a few of your typical behavior or human characteristics.
E.g. Are you a person that absorbs and acquires information and knowledge, likes to entertain other people or nothing at all? Or are you intellectually very capable in solving comprehensive mathematical calculations? Or are you just enjoying life as it is, and somewhat a live fast die young type?
Or a born organizer – than write speech topics about the last high school or college meeting you controlled and administered.
- The fifth method I would like to discuss is the like or not and why technique. Mark something you absolutely dislike or hate and announce in firm spoken language (still be polite) why. A narrative speech topic based on this procedure are giving insight in the way you look at things and what your references are in life.
It’s a bit like you make a comparison, but the difference is that you strongly defend your personal taste as narrator. It has a solid persuasive taste:
E.g. Speeches about drilling for oil in environmental not secure regions, for or against a Hollywood or Bollywood movie celebrity, our bankingsystem that runs out of trust of you the simple bank account consumer. Or your favorite television sitcom series.
- An exciting, interesting, inspiring or funny experience or event that changed your life is the next public speaking tip I like to reveal now.
E.g.? Staying weekends at your uncle’s farm shaped you as the hardworking person you are nowadays. A narrative speech topic in this category could also be about music lessons, practical jokes. Or troublesome events like divorce, or great adventures like trips at the ocean. Or even finding faith or a wedding happiness.
And what do you think of extreme sports tournaments?
- An important lesson you learned from someone you admire. This is a very classical narrative speech topic.
It tends to be a little bit philosophical, but if you tell you story people will recognize what you mean and compare that with their own stories and wisdom lessons.
Tell the story of a survivor of a traffic accident, and how you admire her or his recovery. Winners of awards, great songwriters, novelists, sportsheroes.
This list is almost exhaustive. Share the wisdom of their fails and achievements.
- The moment in your life you see the light, or that was very insightful. It seems a bit like my number six advice, but focus more on the greatness and happiness of that very moment. A moment’s insight is sometimes worth a life’s experience, American Judge Oliver Wendell Holmes have said.
Magnificent and breath-taking nature phenomenons, precious moments after a day of struggle, final decisions that replenish, lift your spirit.
- A fable or myth that has a moral lesson you try to live to.
Aesop Fables are a great source for a narrative speech topic idea structure. Think about The Dog and His Reflection, The Fox and The Grapes, and Belling the Cat. Talking about fairy tales as an inspiring source: what do you think of a personal story about the moral of The Emperor’s New Clothes?
- The relation between a brief series of important milestones in your life that mold your character is also possible – if catchy narrated storytelling of course :-).
First day of school, first kiss, Prom Night, your high school graduation, wedding, first job interview.
Christening Speeches
Pet Peeve Speech Topics
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Narrative Definition
What is narrative? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives, depending on how they use different narrative elements, such as tone or point of view . For example, an account of the American Civil War written from the perspective of a white slaveowner would make for a very different narrative than if it were written from the perspective of a historian, or a former slave.
Some additional key details about narrative:
- The words "narrative" and "story" are often used interchangeably, and with the casual meanings of the two terms that's fine. However, technically speaking, the two terms have related but different meanings.
- The word "narrative" is also frequently used as an adjective to describe something that tells a story, such as narrative poetry.
How to Pronounce Narrative
Here's how to pronounce narrative: nar -uh-tiv
Narrative vs. Story vs. Plot
In everyday speech, people often use the terms "narrative," "story," and "plot" interchangeably. However, when speaking more technically about literature these terms are not in fact identical.
- A story refers to a sequence of events. It can be thought of as the raw material out of which a narrative is crafted.
- A plot refers to the sequence of events, but with their causes and effects included. As the writer E.M. Forster put it, while "The King died and the Queen died" is a story (i.e., a sequence of events), "The King died, and then the Queen died of grief" is a plot.
- A narrative , by contrast, has a more broad-reaching definition: it includes not just the sequence of events and their cause and effect relationships, but also all of the decisions and techniques that impact how a story is told. A narrative is how a given sequence of events is recounted.
In order to fully understand narrative, it's important to keep in mind that most sequences of events can be recounted in many different ways. Each different account is a separate narrative. When deciding how to relay a set of facts or describe a sequence of events, a writer must ask themselves, among other things:
- Which events are most important?
- Where should I begin and end my narrative?
- Should I tell the events of the narrative in the order they occurred, or should I use flashbacks or other techniques to present the events in another order?
- Should I hold certain pieces of information back from the reader?
- What point of view should I use to tell the narrative?
The answers to these questions determine how the narrative is constructed, so they have a huge influence on the way a reader sees or understands what they're reading about. The same series of events might be read as happy or sad, boring or exciting—all depending on how the narrative is constructed. Analyzing a narrative just means examining how it is constructed and why it is constructed that way.
Narrative Elements
Narrative elements are the tools writers use to craft narratives. A great way to approach analyzing a narrative is to break it down into its different narrative elements, and then examine how the writer employs each one. The following is a summary of the main elements that a writer might use to build his or her narrative.
- For example, a story about a crime told from the perspective of the victim might be very different when told from the perspective of the criminal.
- For instance, F. Scott Fitzgerald and Ernest Hemingway were friends, and they wrote during the same era, but their writing is very different from one another because they have markedly different voices.
- For example, Jonathan Swift's essay " A Modest Proposal " satirizes the British government's callous indifference toward the famine in Ireland by sarcastically suggesting that cannibalism could solve the problem—but the essay would have a completely different meaning if it didn't have a sarcastic tone.
- For example, the first half of Charles Dickens' novel David Copperfield tells the story of the narrator David Copperfield's early childhood over the course of many chapters; about halfway through the novel, David quickly glosses over some embarrassing episodes from his teenage years (unfortunate fashion choices and foolish crushes); the second half of the novel tells the story of his adult life. The pacing give readers the sense that David's teen years weren't really that important. Instead, his childhood traumas, the challenges he faced as a young man, and the relationships he formed during both childhood and adulthood make up the most important elements of the novel.
- For example, Mary Shelley's novel Frankenstein uses three different "frames" to tell the story of Dr. Frankenstein and the creature he creates: the novel takes the form of letters written by Walton, an arctic explorer; Walton is recounting a story that Dr. Frankenstein told him; and as part of his story, Dr. Frankenstein recounts a story told to him by the creature.
- Linear vs. Nonlinear Narration: You may also hear the word narrative used to describe the order in which a sequence of events is recounted. In a linear narrative, the events of a story are described chronologically , in the order that they occurred. In a nonlinear narrative, events are described out of order, using flashbacks or flash-forwards, and then returning to the present. In some nonlinear narratives, like Ken Kesey's Sometimes a Great Notion , there is a clear sense of when the "present" is: the novel begins and ends with the character Viv sitting in a bar, looking at a photograph. The rest of the novel recounts (out of order) events that have happened in the distant and recent past. In other nonlinear narratives, it may be difficult to tell when the "present" is. For example, in Kurt Vonnegut's novel Slaughterhouse-Five , the character Billy Pilgrim, seems to move forward and backward in time as a result of post-traumatic stress. Billy is not always certain if he is experiencing memories, flashbacks, hallucinations, or actual time travel, and there are inconsistencies in the dates he gives throughout the book—all of which of course has a huge impact on how his stories are relayed to the reader.
Narrative as an Adjective
It's worth noting that the word "narrative" is also frequently used as an adjective to describe something that tells a story.
- Narrative Poetry: While some poetry describes an image, experience, or emotion without necessarily telling a story, narrative poetry is poetry that does tell a story. Narrative poems include epic poems like The Iliad , The Epic of Gilgamesh , and Beowulf . Other, shorter examples of narrative poetry include "Jabberwocky" by Lewis Carrol, "The Lady of Shalott" by Alfred Lord Tennyson, "The Goblin Market" by Christina Rossetti, and "The Glass Essay," by Anne Carson.
- Narrative Art: Similarly, the term "narrative art" refers to visual art that tells a story, either by capturing one scene in a longer story, or by presenting a series of images that tell a longer story when put together. Often, but not always, narrative art tells stories that are likely to be familiar to the viewer, such as stories from history, mythology, or religious teachings. Examples of narrative art include Michelangelo's painting on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel and the Pietà ; Paul Revere's engraving entitled The Bloody Massacre ; and Artemisia Gentileschi's painting Judith Slaying Holofernes .
Narrative Examples
Narrative in the book thief by markus zusak.
Zusak's novel, The Book Thief , is narrated by the figure of Death, who tells the story of Liesel, a girl growing up in Nazi Germany who loves books and befriends a Jewish man her family is hiding in their home. In the novel's prologue, Death says of Liesel:
Yes, often, I am reminded of her, and in one of my vast array of pockets, I have kept her story to retell. It is one of the small legion I carry, each one extraordinary in its own right. Each one an attempt—an immense leap of an attempt—to prove to me that you, and your human existence, are worth it.
Narrators do not always announce themselves, but Death introduces himself and explains that he sees himself as a storyteller and a repository of the stories of human lives. Choosing Death (rather than Leisel) as the novel's narrator allows Zusak to use Liesel's story to reflect on the power of stories and storytelling more generally.
Narrative in A Visit From the Goon Squad by Jennifer Egan
In A Visit From the Good Squad , Egan structures the narrative of her novel in an unconventional way: each chapter stands as a self-contained story, but as a whole, the individual episodes are interconnected in such a way that all the stories form a single cohesive narrative. For example, in Chapter 2, "The Gold Cure," we meet the character Bennie, a middle-aged music producer, and his assistant Sasha:
"It's incredible," Sasha said, "how there's just nothing there." Astounded, Bennie turned to her…Sasha was looking downtown, and he followed her eyes to the empty space where the Twin Towers had been.
Because there is an empty space where the Twin Towers had been, the reader knows that this dialogue is taking place some time after the September 11th, 2001 attack in which the World Trade Center was destroyed. Bennie appears again later in the novel, in Chapter 6, "X's and O's," which is set ten years prior to "The Gold Cure." "X's and O's" is narrated by Bennie's old friend, Scotty, who goes to visit Bennie at his office in Manhattan:
I looked down at the city. Its extravagance felt wasteful, like gushing oil or some other precious thing Bennie was hoarding for himself, using it up so no one else could get any. I thought: If I had a view like this to look down on every day, I would have the energy and inspiration to conquer the world. The trouble is, when you most need such a view, no one gives it to you.
Just as Sasha did in Chapter 2, Scotty stands with Bennie and looks out over Manhattan, and in both passages, there is a sense that Bennie fails to notice, appreciate, or find meaning in the view. But the reader wouldn't have the same experience if the story had been told in chronological order.
Narrative in Atonement by Ian McEwan
Ian McEwan's novel Atonement tells the story of Briony, a writer who, as a girl, sees something she doesn't understand and, based on this faulty understanding, makes a choice that ruins the lives of Celia, her sister, and Robbie, the man her sister loves. The first part of the novel appears to be told from the perspective of a third-person omniscient narrator; but once we reach the end of the book, we realize that we've read Briony's novel, which she has written as an act of atonement for her terrible mistake. Near the end of Atonement , Briony tells us:
I like to think that it isn’t weakness or evasion, but a final act of kindness, a stand against oblivion and despair, to let my lovers live and to unite them at the end. I gave them happiness, but I was not so self-serving as to let them forgive me. Not quite, not yet. If I had the power to conjure them at my birthday celebration…Robbie and Cecilia, still alive, sitting side by side in the library…
In Briony's novel, Celia and Robbie are eventually able to live together, and Briony visits them in an attempt to apologize; but in real life, we learn, Celia and Robbie died during World War II before they could see one another again, and before Briony could reconcile with them. By inviting the reader to imagine a happy ending, Briony effectively heightens the tragedy of the events that actually occurred. By choosing Briony as his narrator, and by framing the novel Briony wrote with her discussion of her own novel, McEwan is able to create multiple interlacing narratives, telling and retelling what happened and what might have been.
Narrative in Slaughterhouse-Five by Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut’s novel Slaughterhouse-Five tells the story of Billy Pilgrim, a World War II veteran who survived the bombing of Dresden, and has since “come unstuck in time.” The novel uses flashbacks and flash-forwards, and is narrated by an unreliable narrator who implies to the reader that the narrative he is telling may not be entirely true:
All this happened, more or less. The war parts, anyway, are pretty much true. One guy I knew really was shot in Dresden for taking a teapot that wasn’t his. Another guy I knew really did threaten to have his personal enemies killed by hired gunmen after the war. And so on. I’ve changed all the names.
The narrator’s equivocation in this passage suggests that even though the story he is telling may not be entirely factually accurate, he has attempted to create a narrative that captures important truths about the war and the bombing of Dresden. Or, maybe he just doesn’t remember all of the details of the events he is describing. In any case, the inconsistencies in dates and details in Slaughterhouse-Five give the reader the impression that crafting a single cohesive narrative out of the horrific experience of war may be too difficult a task—which in turn says something about the toll war takes on those who live through it.
What's the Function of Narrative in Literature?
When we use the word "narrative," we're pointing out that who tells a story and how that person tells the story influence how the reader understands the story's meaning. The question of what purpose narratives serve in literature is inseparable from the question of why people tell stories in general, and why writers use different narrative elements to shape their stories into compelling narratives. Narratives make it possible for writers to capture some of the nuances and complexities of human experience in the retelling of a sequence of events.
In literature and in life, narratives are everywhere, which is part of why they can be very challenging to discuss and analyze. Narrative reminds us that stories do not only exist; they are also made by someone, often for very specific reasons. And when you analyze narrative in literature, you take the time to ask yourself why a work of literature has been constructed in a certain way.
Other Helpful Narrative Resources
- Etymology: Merriam-Webster describes the origins and history of usage of the term "narrative."
- Narrative Theory: Ohio State University's "Project Narrative" offers an overview of narrative theory.
- History and Narrative: Read more about the similarities between historical and literary narratives in Hayden White's Metahistory: The Historical Imagination in 19th-Century Europe.
- Narrative Art: This article from Widewalls explores narrative art and discusses what kind of art doesn't tell stories.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1912 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,280 quotes across 1912 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Point of View
- End-Stopped Line
- Falling Action
- Dynamic Character
- Epanalepsis
- Verbal Irony
- Parallelism
- Foreshadowing
- Anachronism
- Protagonist
- Internal Rhyme
- Alliteration
- Colloquialism
- Round Character


Narrative Speech

Try to let this scenario ply out in your head. It is the first day of school. You see children running around the hallways and the canteen. You see the teachers in the faculty room taking their 15-minute break before the start of the school bell at 7:30 in the morning. You see the high school students doing typical teenager things (e.g. texting, putting make up on, chatting the day away, sleeping, doing their homework at the very last minute, etc…). As the bell begins to ring, the students start to sing the country’s national anthem followed by a patriotic oath to the country then, sometimes the school hymn. You may also see narrative writings .
- Speech Examples
- Informative Speech
As the students take their seats, the first period teacher walks in the classroom and begins to introduce herself as Ms. Katniss Everdeen. As she was just finishing doing her introductions, the principal made an announcement requesting all the students and faculty to assemble in the school’s multi-purpose room for welcoming remarks of the first day of school. After settling down, the principal walked up to the stage and said: “Here to talk about pursuing your dreams at a young age, I would like to introduce to you the speaker of today’s special talk. You may also see personal narrative essay .
May we please give a special round of applause to none other than Eleven herself from Stranger Things, Millie Bobbie Brown?”
We all wish our first day of school was like that… Oh well. Now considering that you are placed in her shoes and will be asked to talk about a similar topic to that, how would you go about it?
Narrative Speeches
But then, you remembered something. It is actually not that difficult since this speech is all about you, and how that experience allowed you to become a better version yourself. Personal narrative speeches give focus on a specific real life event that served as a turning point for the writer. Speeches are often given as an assignment or a project by the teacher. But in order to write a strong personal narrative about yourself, try to think of an idea that might pique the audience’s curiosity.
Just like every good speech, great books, and awesome movies, it must have an introduction, the middle events, the climax, and finally, the end of the story. Here is an example of a personal narrative that might be able to help you out in writing your own personal narrative. You may also see informative speech .
Basic Personal Narrative Outline Example

Size: 130 KB
Part 1. Brainstorming Ideas for the Narrative
Every good piece of literature or movie must always have a great idea to begin the story. Once you have an idea on what you would want to share with the audience, it makes things easier for you to explain as you just have to boil down to the specifics on what experiences can best go with the theme you are going to share. Listed below are some of the ways to brainstorm ideas:
Think of a memorable event or a moment in your life. Sure there are many moments and memories in your life that you have felt and experienced over the years. But there are only so few that have struck you to the depths of your soul that you cannot help but not forget that instance, even when you become old and gray. It does not have to be something major, it can even be as something simple as your first date with her and how you felt whenever she was with you. You may also see declamation speech .
For example, you can write about how your best friend stood up to you when you were getting bullied by a bunch of jerks in middle school or the time when you and your friends went to the club for the very first time and got wasted. You may also see launch speech .
Expand on an important conflict in your life. Everyone just loves watching drama. When you have found the perfect dramatic event to be included in your speech, include it in the speech and elaborate in detail. You may also see youth speech .
For example, you can write about the time your one and only best friend ditched you to start hanging out with those “plastic” losers and you were abandoned and treated like garbage afterwards by everyone in your class after your “best friend” spread some lies about you. You may also see graduation speech .
Think about a particular theme or idea. When deciding your speech, decide what the message you want to deliver the audience as a jumping off point for the narrative. Base your theme on your personal experiences that you would like to share. Once you have thought about it, ask yourself as to whether it has transformed you for the better or for the worst. Poverty, patience, sacrifice, and endurance are all good choices for a personal narrative. You may also see award speech .
For example, you may want to include in your experience on how a boy with no father or mother makes a living for himself by selling street food and how poverty has made you become more generous and thoughtful for others who are suffering on the streets. You may also see retirement speech .
Read examples of personal narrative. Finally, in order to write a good narrative, you must learn how others o it as well. To quote from the Jedi Master Yoda, he states: “You must unlearn what you have learned”. Very philosophical, but it is true. One cannot claim to know everything. And even if you did know everything, to learn something new, you must be open to change and new things in order to enhance and improve your skill. Here are some reading references you might want to glance at before starting:
- The Boys of My Youth by Jo Ann Beard
- Slouching Towards Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Me Talk Pretty One Day by David Sedaris
- The Lives section of The New York Times
David Becomes King Narrative Speech Outline Example

Size: 292 KB
Part 2. Writing the Personal Narrative
Now that you have brainstormed some ideas needed to start with your personal narrative, it is finally time to get to your computer and ignite the thought train full speed ahead.
Start with a hook. First impressions matter! If you have successfully bored out the audience in their chairs, then congratulations, only a few people are going to pay attention to what you have to say throughout the rest of your speech. Attention-grabbers often come in the form of a story, a quote, a personal experience. You may also see valedictorian speech .
For example, you can mention in the first line of your personal narrative: “I remember this one time when I accidentally slipped and fell down on the lake when I was fishing while everyone was staring at me.”
Set the scene with action. Every good story will not be complete without providing some background information and supporting details to the characters in your story.
Move chronologically through the events. When you begin your speech with your four year-old self accidentally drowning in a swimming pool just because he saw a slide and he wanted to get on it, do not immediately proceed to when you nine years old and you accidentally punched someone in the face because he was a jerk. It is important to set things in order as to avoid confusion between the timeline of your story. Finish explaining everything that occurred in event A before proceeding to event B and finally concluding with event C. You may also see acceptance speech .
Use sensory detail and description. They say it is important to show and not just simply to tell. Most speeches would allow visual aids or props to be presented at the front to give an audience a better idea on what the speaker is describing. But if not, then you must be able to use your imagination describing the object or event you have felt using the five senses. You may also see persuasive speech .
Finish with a moral or takeaway. Wrap your personal narrative up with a reflection or analysis of the transpired events. It is important that at the end of your speech, the audience is left with something to recall even if he forgets everything else. Allow them to leave the room with the moral and lessons that they have learned from your speech. You may also see elevator speech .
Speech 101 Narrative Speech Outline Example

Size: 75 KB
At the end of the day, speech writing is one challenge. The next challenge is on how you are going to deliver it in front of the audience. You may refer to these examples for guidance if ever you are still struggling with writing a narrative speech. With that, we would like to end here and wish you the best of luck in your speech writing journey!
Narrative Speech Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a narrative speech about a life-changing travel experience
2. Help me write a narrative speech on overcoming adversity
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- examples of narrative speech topics
Examples of narrative speech topics
125 strong ideas for effective personal storytelling speeches
By: Susan Dugdale
Narrative speech topics are topics especially designed to trigger telling a story.
And who doesn’t love being told a good story? They’re universally appreciated. It’s the oldest, most effective way of emphasizing a point, illustrating an idea or recounting an event.
For as long as there have been people in the world, there have been people telling them stories: storytellers.
What's on this page:
- 125 examples of narrative speech topics: - 40 'first' experiences , - 40 tell-a-story topics , - 35 personal story ideas
- How to best use this page
Choosing the right narrative speech topic
- How to get from topic to speech (with a printable speech outline to download)
A definition of the word 'narrative'
A personal story is a powerful story, the difference between an anecdote and a story.
- Additional resources for storytelling speeches

How to make best use of this page
Browse the topics and make a shortlist of any that appeal to you. (These are the ones that will immediately have you thinking of stories you could share.)
Make sure you download the printable narrative speech outline. Then take what you need from the other information. (If you've never given a narrative or storytelling speech before, read all of it!) It's here to help you put together the best speech you possibly can. ☺
Return to top
The most powerful stories to tell are personal. They’re the game changers, the significant events: meetings, accidents, cultural jolts, and life lessons that have made an impact.
They’re stories about family, our children, love, marriage, politics, education, work, living in society, philosophy, the natural world, ...
In telling these stories we reveal aspects of ourselves: sharing our innermost thoughts and feelings.
To give a good narrative speech, one that fully engages our audience we need to:
- choose a meaningful story with strong characters they can relate to in a situation they’ll recognize and identify with
- use vivid language enabling them to easily picture and feel what’s happening
A spoken or written account of connected events; a story: "a gripping narrative"
Word with similar meanings: account, story, tale, chronicle, history, description, record.
(Definition from Oxford Languages )
Because narrative speeches are often stories about ourselves we need to think carefully about what we share and with whom.
Some subjects are sensitive for many reasons. And what could be completely appropriate in one setting could be quite wrong in another.
As the giver of the speech, you’ll want to be clear about what you’re sharing and why.
Additionally, an emotional narrative speech exposing your own deeply felt and unresolved issues would be difficult for an audience to witness.
They’d want to help, send you to a therapist, leave... People do not want to feel embarrassed or uncomfortable on your behalf.
The right narrative topic idea is one you know your audience will want to hear, fits the speech purpose you’ve been given, and one you feel comfortable sharing.
Should you decide to use someone else's story for your speech be sure to acknowledge whose it is and where you got it from.
Getting from topic to speech
Once you’ve decided on your topic, the next step is developing a story outline. That involves carefully thinking through the sequence of the story, or what you’re going put in it, scene by scene and why, from beginning to end.
To help you do that easily I've put together a printable narrative speech outline. To download it click on the image below. (The pdf will open in a new window.)

The outline will guide you through each of the steps you need to complete. (Instructions are included.)
Rehearsal, rehearsal, rehearsal
Once your outline is done, your next task is rehearsing, and then rehearsing some more. You’ll want to know before you give the speech that it:
- makes sense and can be followed easily,
- grabs and holds the audience’s attention, is relevant to them,
- and easily fits the time you’ve been given.
Rehearsal lets you find out in a safe way where any glitches might be lurking and gives you an opportunity to fix them.
It also gives you time to really work at refining how you tell the story.
For instance, what happens if this part is said softly and slowly? Or if this bit is delivered more quickly, and that has a long pause after it?
And what about your body language? Are you conscious of what you’re actually doing as you speak? Do you ‘show’ with your body and how you use your voice, as well as ‘tell’ with your words?
The way you tell a story makes an enormous difference to how it is received. A good story can be ruined by poor delivery. If you make the time to practice, that’s largely avoidable.
- For more on how to rehearse – a step by step guide to rehearsing well
- For more on the vocal aspects of speech delivery
- For more on developing effective body language
Many people share an anecdote thinking they’re telling a story. They’re not. Although they have similarities, they are different.

An anecdote is a series of facts, a brief account of something that happened. It is delivered without interpretation or reflection. It’s a snapshot cut from a continuum: a slice of life. We’ve taken notice because it was interesting, strange, sad, amusing, attractive, eccentric...to us. It captured our attention in some way.
For example:
"Last night there was a gorgeous girl in the bar wearing a red dress. She ordered a brandy. After she finished her drink, she left."
In contrast, a story develops. It travels from its starting place, goes somewhere else where something happens, and finally arrives at a destination. A story has a beginning, a middle and an end. It moves. Things change.
Here’s the same anecdote example reworked as a very brief story. The person telling it is reminiscing, talking about the past to girl called Amy.
"Last night there was a girl in the bar wearing a red dress—so young, so gorgeous, so full of life. Seeing her whirled me back to us. You and me and that song. Our song: Lady in Red. “The lady in red is dancing with me, cheek to cheek. There's nobody here, it's just you and me. It's where I want to be.”
The complete and abrupt shift from present to past overwhelmed me. Thoughts, feelings, memories... At twenty-five and twenty-six we knew it all and had it all.
When I looked up, she’d finished her drink and gone. Oh, Amy! What did we do?"
Narrative speech topic ideas: 40 firsts
Often the first time we experience something creates deep lasting memories. These can be both very good and very bad which makes them an excellent foundation for a gripping speech.
We love listening to other people’s dramas, especially when they’ve gone through something significant and come out the other side strengthened – armed with new knowledge.

- The first time I stood up for myself.
- The first time I drove a car.
- The first time I rode a bike.
- The first time I fell in love.
- The first time I felt truly frightened.
- The first time I realised my family was different.
- The first time I understood I was different from other kids.
- My first day at a new school.
- The first time I felt truly proud of myself.
- My first date.
- My first job interview.
- The first time I realised no matter how hard I tried I was never going to please, or be liked, by everybody.
- How I got my first paid job.
- What I did with my first pay.
- My first pet.
- My first real fight- what it was about, and what I learned from it.
- The first time I tried hard to achieve something and failed.
- The first time I realised some people are not to be trusted.
- The first time I was away from home on my own.
- The first time I had to ask a stranger for help.
- The first time I experienced what it’s like to have someone close be either seriously ill or die
- The first time I was ill and was taken to hospital.
- The first time I felt utterly filled with happiness.
- The first time I was sincerely impressed and influenced by another person’s goodness.
- My first pin up hero.
- My childhood home – what I remember – the feelings and events I associate with it.
- The first time I realised the color of my skin, or the shape of my body, or my face, or my gender, or anything else about me, made a difference.
- The first time I tried to communicate with someone who did not speak my language.
- The first time I saw snow, the sea, climbed a mountain, camped out under the stars, walked a wilderness trail, caught a wave...
- The first time I visited another country where the language, customs and beliefs were vastly different to my own.
- The first time I understood and experienced the power of kindness.
- The first time I told a lie.
- The first time I understood how fortunate I was to be me.
- The first time I realised my goals and aspirations were attainable.
- The first time I realised having enough money to do whatever I wanted could not buy happiness.
- The first time I realised that some people were always going to be better at some things that I was.
- The first TV show/film/book I loved and why.
- The first time I really understood I was prejudiced.
- The first time someone stepped up for me – what that felt like, and what it changed.
- How first impressions of people and/or an event are not always right.
40 tell-a-story speech topics
Here's another 40 narrative speech suggestions. Give yourself time as go through them to consider suitability of the stories they trigger. Would what you're thinking of suit your audience? Does it fit your overall speech purpose?

- How I learned to stand up for my own beliefs.
- How my name influenced who I am.
- My favorite teacher – why, what did they do? How did that make you feel?
- When and how I learned being adult does not mean being grown up.
- Why winning is important to me.
- What terrified me as a child.
- How I learned to manage my anger.
- What people regularly assume about me and how that makes me feel.
- How having an animal to love made me a better human being.
- How humor defuses tension.
- What it feels like to rebel against authority, and why I do it.
- My learning break through.
- How I discovered what meant the most to me.
- How I learned my family was poor, rich, odd, ...
- When I fully realized the importance and power of community.
- What I learned through living through my parent’s divorce.
- My experience of being an outsider.
- My favorite way to unwind.
- A decision I made that I now regret and why.
- How goal setting has helped me achieve.
- My safe place.
- What being unfairly punished taught me about myself.
- Rituals that serve me well. For example, always cleaning my teeth a particular way, always sorting my clothes out for the following day before I go to bed, always making Christmas presents for my family, ...
- What money means to me and why.
- How being a parent fundamentally changed me,
- What being the underdog taught me.
- Why I chose my own path, and not the one my parents wanted for me,
- Why family celebrations are important to me.
- Why I adopted a child.
- What religion means to me.
- What marriage, friendship,... means to me.
- What needing to be helped has taught me.
- Why and how I support giving back to the community.
- Tricks I use to get myself to do things I know I should do but don’t really want to.
- What I do to manage fear or anxiety of public speaking.
- How I learned to stop biting my finger nails or stop some other behaviour driven by nervous anxiety.
- How I learned to stop feeling like my job in life was to make my parents or anybody else feel happy.
- What having a job as a young person taught me.
- The complications of being the favorite child in your family.
- The difficulties of having to choose between friends.
35 more narrative or personal story speech topics

- The time I made an assumption about a situation or a person and got it entirely wrong.
- What being totally and suddenly out of my depth in a situation felt like and the consequences.
- A lesson I learned the hard way that helped me become a better person. For example: over spending, driving too fast, drinking too much, being caught out in a lie...
- Important things I learned through keeping old people company.
- What I learned through losing a good friend
- What coming face to face with my own mortality taught me.
- How the language of kindness transcends language and cultural differences.
- What being ashamed of my own behaviour taught me.
- How I unknowingly broke local cultural customs while overseas and what happened
- How taking revenge for a wrong did not right it.
- The silliest unnecessary risk I’ve taken.
- How first impressions are not always right.
- How pretending to be strong (fake it until you make it) can work very well.
- What I really wanted my parents to do for me and they didn’t.
- How our clothing influences how other people perceive us.
- My earliest memories: what they were, how they made me feel.
- Why I became disillusioned about politics.
- Why I decided to go into politics.
- The influence of music on my life.
- A personal phobia and how it impacts on my life: fear of spiders, fear of the dark, fear of thunder...
- The impact of peer pressure on decision making.
- What I’ve learned about gratitude.
- How I lied in order to cover for a friend and what happened.
- My most embarrassing moment and how I survived it.
- The worst day of my life: what it taught me.
- How I know peer pressure can make us behave in ways we don’t really want to.
- How I learned to read people.
- Why saying thank you is important.
- Random acts of kindness and generosity.
- Being lost in a strange city.
- What I learned through genuinely apologizing for something I did.
- How the way a person speaks influences what we think about them.
- How a mentor changed my life.
- The most thrilling exciting thing I’ve done.
- How being a leader and being looked up to felt.
Other resources for narrative speeches
Pages on this site:
- 60 vocal variety and body language speech topics - speech ideas to encourage excellent storytelling
- Storytelling setups: what works & why - How to open or lead into a story
- How to effectively use a small story as part of a speech
- Tips and exercises for working with and improving body language
- Simple characterization techniques for compelling storytelling
- 9 aspects of vocal delivery - explanations, tips and exercises to improve your voice
- How to rehearse well - step by step guidance
Offsite storytelling speech resources
- 5 creative storytelling projects recommended by teachers, for everyone | (ted.com)
Toastmasters Project | Connect with storytelling – Level Three
- Connect with Storytelling – District One (district1toastmasters.org)
- 8300-Connect-with-Storytelling.pdf (toastmasters-lightning.org)
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
What is Narrative?
Narrative definition.
Narrative is the basis of storytelling. Narratives are oral or written accounts that connect related events or incidents for the purpose of entertaining, educating, communicating, sharing, and/or creating meaning for readers or listeners. Narratives can be found in novels, movies, plays, music, and even video games, and they are often referred to as storylines.
Use of Narrative in Literature
Writers use narrative in literature to present their stories. Narrative can be linear in which events are portrayed in a logical, often chronological, manner for relatively straightforward understanding on the part of readers. Narrative can also be nonlinear in which the reader must piece together the connections between events, characters , or action in the story . The literary devices and approaches that writers utilize to form their narrative styles combine to create varied, meaningful, innovative, and impactful works of literature.
History of Narration or Storytelling
Storytelling is an essential part of human nature. Man is the only creature that tells stories, and we have been telling stories and listening to them since the time we learned to speak. Storytelling began with oral traditions, and in such forms as myths , legends , fables , anecdotes , and ballads . These were told and retold, passed down from generation to generation, and they shared the knowledge and wisdom of early people.
The basic theme of various forms of story-telling were fear of natural forces, deeds of heroes , gods and goddesses, and to teach life lessons from others’ experiences. Biblical stories have the primary purpose of teaching spirituality. Most biblical stories were performed in churches to convey spiritual messages to the masses.
Narrative Examples in Everyday Life
Modern narratives have a broader function. After a close study of famous examples of modern narrative, we see that such narratives do not merely entertain, but serve as ways to communicate writers’ moral , cultural, and political perspectives .
Moreover, narratives have contributed to achieving educational objectives in our everyday life. Different forms of media enable people to express and record their real life stories, and to share their knowledge and their cultural values across the world. In addition, many documentaries on television adopt a narrative technique to communicate information in an interesting way.
Examples of Narrative in Literature
Example #1: animal farm (by george orwell).
Animal Farm , by George Orwell , is a modern narrative example known as a “political satire ,” which aims at expressing a writer’s political views. It uses animals on a farm to describe the overthrow of the last Russian Tsar, Nicholas II, and the Communist Revolution of Russia before WWII. The actions of the animals on the farm are used to expose the greed and corruption of the Revolution. It also describes how powerful people can change the ideology of a society.
Example #2: Faerie Queen (By Edmund Spenser)
Poetry written in the style of a narrative is known as “narrative verse .” Faerie Queen , by Edmund Spenser, is an example of such poetry. It narrates the adventures of the Red- Cross Knight in helping Lady Una rescue her parents from the evil Dagon. On a symbolic level it describes the mission of the Holiness as helping the Truth, fight Evil, and thus regain its rightful place in human hearts.
Example #3: The Withdrawing Room (By Charlotte Macleod)
Charlotte Macleod’s The Withdrawing Room is an example of a thriller or suspense narrative. Augustus Quiffen, a lodger at Sarah’s Brownstone home, is killed by falling under the train. It seems to be an accident until Mary Smith tells Sarah that it is a murder, but she is not sure of the identity of the murderer. Sarah and Max Bittersohn investigate the matter, and find that the killer has planned the death beforehand.
Example #4: Don Quixote (By Miguel de Cervantes)
Don Quixote , by Miguel de Cervantes, is a parody of romance narratives, which dealt with the adventures of a valiant knight. Unlike serious romances, in Don Quixote , the narrative takes a comical turn. We laugh at how Quixote was bestowed a knighthood in his battle with the giants [windmills]. We enjoy how the knight helps the Christian king against the army of a Moorish monarch [herd of sheep]. These and the rest of the incidents of the novel are written in the style of Spanish romances of the 16th century, in order to mock the idealism of knights in the contemporary romances.
Function of Narrative
Storytelling and listening to stories are part of human instinct. Therefore, writers employ narrative techniques in their works to attract readership. The readers are not only entertained, but also learn some underlying message from the narratives.
Moreover, a narrative is set in specific cultural contexts . Readers can get a deep insight of that culture, and develop an understanding toward it. Thus, narratives can act as a binding force in uniting humanity.
Related posts:
- Narrative Essay
- Narrative Poem
Post navigation
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Use Narrative
I. What is a Narrative?
A narrative is a story. The term can be used as a noun or an adjective. As a noun, narrative refers to the story being told. It is the account of events, experiences, and details. It also refers to the story-telling process. As an adjective, it describes the form or style of the story being told.
The adjective use of the word narrative has its roots in the Latin word, narrativus, which means “suited to narration.” The noun usage of the word appeared in the French language in the 15 th century and is defined as “a tale, story.”
Narrative is pronounced (năr′ə-tĭv), or “narr, uh, tive”.
II. Examples of Narrative
If you look at narrative when used as a noun, you will find many examples. Most things written in the first-person are narratives. A novel written from the point of view of the main character is a narrative. The essay you wrote, entitled “What I did on my summer vacation”, was a narrative. An article written by a blogger about his/her experience travelling across the United States on a bicycle would most likely be a narrative.
If you look at narrative when used as an adjective, you will find that it complements just about any form of writing or art. There are narrative poems, narrative works of visual art, narrative essays , or narrative dances. If you can make something tell a story, it is narrative.
III. Types of Narrative
Rather than there being “types” of narrative, narrative, itself, functions as an adjective, transforming other things. The narrative voice, or narrative style can be used to transform virtually anything into a story.
For example:
- Other forms of art can also be considered narratives. You can choreograph a narrative dance or paint a narrative series of pictures. The important element is that your creation tells a story.
- Autobiographies are, essentially, narrative. They are written in the first-person and describe the events of the story-teller’s life.
- Theatrical monologues are narrative. In a monologue, the character tells an intimate story, often addressing the audience, asking questions and seemingly seeking answers from them. In Hamlet’s famous monologue, that begins “To be or not to be,” he is seeking answers to the great philosophical questions of life and death. He is discussing them with himself and the audience, trying to puzzle them out and inviting the audience to do the same.
- Essays can also be narrative. An essay is a literary composition about a single subject. You have probably written many. A narrative essay is simply an essay written in a style that tells a story. They are often personal , anecdotal, and told from the writer’s point of view.
IV. The Importance of using Narrative
Everyone loves a story! Everyone has a story. Everyone wants to tell a story. Everyone can relate to a story. That is why it is important to use narratives.
Narrative is an engaging writing style. It immediately invites your audience into your world and offers them a chance to participate in the story you are telling. A reader can easily get wrapped up in a narrative. It is also a style that invites discussion and participation. By using it you tell your audience that this story is not over. They can take it home and think about it. They can retell it, add to it and change it.
Narratives are social. They are at the heart of how we communicate as social beings. If you look for definitions, descriptions, and discussions of what narratives are, you will find many references to the natural humanity of narratives. They are a part of who we are and how we share that with others.
Have you ever read an article that just bored you to tears? Maybe you thought it was “dry”. (Maybe you feel that way about this article?) There is a good chance the author did not make good use of narrative, and thus never managed to draw you in.
V. Examples of Narrative in Literature
Narratives can be found everywhere in literature. They appear in every style, form, and genre.
Fiction: Don Quixote, by Miguel de Cervantes is the tale of a man who is determined to be a knight. You may remember references to a madman on horseback fighting windmills? This is that book. It is a standard and classic example of a book written in the narrative voice.
Beloved , by Toni Morrison is the tale of an escaped slave, who remains haunted by things in her past. It is another more modern and ground-breaking narrative work.
The Hobbit, by J.R.R. Tolkien, that popular story about Bilbo Baggins, a fantasy creature called a hobbit who travels through Middle Earth and has unexpected adventures , is also a first-person narrative.
Nonfiction: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglas is the autobiography of a man who was a slave, an abolitionist, a writer and a newspaper editor. It is one of our country’s great historical works and it is written in the narrative voice.
VI. Examples of Narrative in Pop Culture
Narratives are everywhere in popular culture. In fact, popular culture is, in itself, an overarching narrative. It is the system of stories that weave in and out of one another to make up the story of the human race. Culture is open-ended and ever evolving, and that is what makes it a narrative. We participate in our own story, along with those around us, and make it up as we go along.
If we want to look at smaller examples, journalism and the news is an excellent form of narrative. Something happens and someone reports on it. Someone else picks up the story, adds a few details and comments, and publishes that. Then, someone else comes along, follows the same pattern, and the narrative continues.
Even more specifically, headlines have become increasingly narrative with the explosive popularity of social media. Writers try and draw in readers by inviting them into the discussion of a topic. In social media, you have just a few words, and maybe a picture, to interest your audience and get them to open your link. In order to do this, there is a trend to write narrative headlines such as these:
He opened the jar of peanut butter and what he saw will blow your mind.
She gave her toddler a crayon and you will never believe what happened next.
Blogs are also excellent examples of narratives as they include first-person accounts of experiences while inviting comment and conversation from readers.
Music is also a wonderful place to find narratives. People have an innate need to turn their stories in to songs. Turn on your stereo and you will find an endless number of narrative. American Pie by Don McLean is one of the great narrative musical creations in our country’s history. It is written in the first person and tells a cryptic story of the history of our music and a fatal plane crash.
A long long time ago I can still remember how That music used to make me smile And I knew if I had my chance That I could make those people dance And maybe they’d be happy for a while…
VII. Related Terms
Narrator : a person who tells a story or gives an account of something.
Story : a synonym to the word narrative. Some suggest that stories are closed ended with a beginning, middle and end, while narratives are larger open-ended discussions, comprised of stories, with listener participation.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write a Narrative Speech
Most people must give a narrative speech at some point in life. Speeches have a beginning, middle and an ending and speakers signal these speech segments by using short sentences for the main headings. A major consideration when writing the narrative includes deciding how to deliver the speech. An extemporaneous-style delivery of your narrative speech uses only a general outline of the body's main points and a few helpful notes, while manuscript delivery requires writing every word on paper and using this as a script during the delivery.
Select Your Topic
Topic selection for some speakers is the most difficult part of writing the narrative speech. Most people feel some stress when presenting a speech, so stick with the information you know best. This helps you remember while under the stress, even when giving a manuscript-style presentation. Experiences work well as narrative speeches, including interesting personal and life events and family traditions. An introduction about yourself also offers a short narrative topic. Some narrative presentations include a teachable moment or a moral for the listener, but this element is not necessary.
Do the Research
Speech research doesn't always require a trip to the library. Research for a narrative might include talking to family members to confirm important dates or refresh your memory about events for your speech. A narrative speech about an event in the life of another person should include traditional research at the library or using online resources. Keep quotations short, no more than one or two sentences, if you need to use a quote in your speech. Make a note of the source of the quotation and cite that in your speech, so your audience understands the quote belongs to another person.
Organize the Body
Organization helps the audience follow the main points of the speech and remember important parts of your presentation. A chronology, using a timeline for events, offers an easy organization pattern for a narrative speech. An event typically has a beginning, middle and end, and the chronological organization pattern fits the recommendations of the University of Pittsburgh Speaking in the Discipline Initiative by using no more than three separate categories for the body of the speech.
Develop an Introduction
Introductions grab attention, give the listeners a hint of the overall speech topic and offer a smooth transition to guide the audience into the body of the speech. However, the attention-getter should not distract the audience so that the introduction becomes the focus of the speech. A short quotation, anecdote, appropriate humor or fact about the topic of your narrative work well as an introduction. Test your introduction on some friends to make sure it grabs attention.
Write the Conclusion
The conclusion moves you from the front of the room as the speaker back to your seat and signals to the audience that your speech is over. A summary of your main points offers one way to end your presentation. More effective techniques combine that summary with a wrap-up quote, fact or anecdote that reminds your audience of your main topic. A restatement of the moral or lesson works well for a narrative speech with this message.
- Santa Rosa Junior College: Narrative Speech
- Mineral Area College Missouri: Narrative Speech
- Pace University: Narrative Chronology
- University of Pittsburgh: Public Speaking -- The Basics
- Los Gatos Union School District: Some Speech Note Card Tips
Lee Grayson has worked as a freelance writer since 2000. Her articles have appeared in publications for Oxford and Harvard University presses and research publishers, including Facts On File and ABC-CLIO. Grayson holds certificates from the University of California campuses at Irvine and San Diego.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
The Basics of Narrative Voice
3-minute read
- 8th August 2018
“Narrative” refers to how a story is told. A “narrative voice,” then, is a voice that tells a story. This makes it important for authors to understand the basics! In this post, therefore, we’re looking at key aspects of narrative voice.
Grammatical Person
One key element of narrative voice is point of view. This is reflected in the grammatical person used. In most narrative writing, this will either be first person or third person:
- First-person narration tells a story from the point of view of the narrator (i.e., using “I” or “we” pronouns). This will often be the main character in the story, but it could also be someone else recalling what they witnessed or a story they heard.
- In third-person narration , the narrator isn’t the main focus of the story. They may be part of the story, such as an onlooker giving their version of events. But a third-person narrator may also be the disembodied voice of the “author” telling the story. Either way, they refer to characters with third-person pronouns such as “he,” “she,” and “they,” but not “I” or “we.”
While not impossible, it is unusual to use the second person in narration . This is because it involves addressing the reader directly, as if you were telling a story about the person reading it!
What Does the Narrator Know?
A narrator can be either limited or omniscient. A limited narrator knows only what they would know within the bounds of the story (e.g., a character recounting their version of events). An omniscient narrator knows everything that is happening in the world of the story.
First-person narrators are usually limited since first-person narration is subjective. But third-person narrators can be either limited or omniscient depending on their relation to the story itself.
Narrative Reliability
Another element of narration is how trustworthy the narrative voice is. A reliable narrator provides a straightforward, credible account of events. An unreliable narrator , on the other hand, tells a story that should not be taken at face value. This may be because the narrator is lying, misinformed, or even insane. The point of this is to:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
- Make the reader question what they are being told
- Show the reader something about the narrator
For example, an unreliable narrator may be trying to persuade the reader to sympathize with an unsympathetic character, such as Patrick Bateman from American Psycho . Or it can be used to show us how the world appears to the narrator, such as in The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night-Time , where the story is told from the point of view of an autistic child.

Combining These Elements in Narrative Voice
You can combine the elements above in various ways. As mentioned, for example, a third person narrator can be either limited or omniscient. You can also use different narrative voices in different parts of a story.
Try experimenting with telling your story in different ways. They key is finding a voice that works for you. To work out what type of narration to use:
- Think about what you want to reader to feel and think as they read
- Consider how you want the reader to relate to the narrator
- Work out what type of voice will let you achieve this
Whatever you choose to do, though, remember that narrative voice is an essential part of storytelling.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
What Is a Narrative? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Narrative definition.
Narrative (NAIR-uh-tihv) is a spoken or written account of related events conveyed using certain literary techniques and devices. Narratives are seen throughout written works and other media, including prose , verse, movies and television shows, theater , music, video games, and podcasts.
The word narrative derives from the Middle French narrative and originates with the Late Latin narrare , which means “to tell, relate, recount, explain.” It was first used in English in the 1560s to indicate “a tale, a story, a connected account of the particulars of an event or series of incidents.”
The History of Narrative Storytelling
For as long as human civilization has existed, people have been recounting narratives. The ways that narratives are expressed and transmitted to an audience has evolved through the centuries, but the essential impulse—to tell a story—has remained unchanged.
Storytelling began with the oral tradition. Myths , legends, fables, ballads, and folktales were performed aloud to entertain and inform an audience. These narratives were memorized using mnemonic devices such as oral-formulaic composition, which utilizes repetition of the same phrases that fit into specific metrical conditions. The canonical spiritual works of world religions—such as Buddhism, Hinduism, Judaism, Islam, and Catholicism—have roots in the oral tradition, as do epic poems like Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey , the Norse Eddas and Sagas, the Mesopotamian Epic of Gilgamesh , and the Anglo-Saxon Beowulf .
As written languages developed, they were used to transcribe narratives from the oral tradition. Some of the earliest written narratives are the Sumerian stories in the Epic of Gilgamesh , which dates back to 2250–2000 BCE. With the advent of handwritten manuscripts and wood block-printed texts, written narratives continued in almost every culture in the Eastern and Western worlds. In the 15th century, Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the printing press allowed the precise and rapid creation of metal moveable type in large quantities, thus making printed texts more readily available and affordable.
Although both oral and written narratives have always focused on themes like love, adventure, heroes, life lessons, and supernatural and divine forces, modern narratives have evolved to include genres such as Westerns, science fiction , espionage, and mysteries /police procedurals. The popularity of different narratives depends on cultural context and often waxes and wanes based on interests and concerns of the era.
The Elements of Narrative
To build a narrative, writers rely on several other literary elements, including but not limited to characterization, conflict, frame stories, linear vs. nonlinear narration, pacing, point of view, and tone.
Characterization
This literary technique introduces and develops a story’s character(s). There are two types of characterization: direct/explicit and indirect/implicit. Direct characterization is when the narrator tells the audience specific details about a character; this information can also be provided by another character in the story. Indirect characterization is when the audience must deduce aspects of a character for themselves by observing the character’s thought process, physical description, behavior, or dialogue.
The opposition of forces or people, which creates dramatic action, is a narrative’s conflict. There are two categories of conflict: internal and external. Internal conflict exists only as man vs. self—when a character experiences opposing emotions or desires simultaneously. External conflict, on the other hand, can exist in five different forms: man vs. man, man vs. mature, man vs. society, man vs. technology, and man vs. the supernatural. When employing any of these, the narrative’s conflict constitutes a protagonist’s struggle against forces outside themselves.
Frame Story
This is a literary form where one all-encompassing story contains one or more related stories. This technique unifies the stories’ narratives by providing smooth transitions and an overall theme. Frame stories can be found in Homer’s epic poem The Odyssey , Geoffrey Chaucer’s The Canterbury Tales , Ovid’s Metamorphoses , and Giovanni Boccaccio’s Decameron .
Linear vs. Nonlinear Narration
The order in which events are told is another way to build narrative. If an author chooses to recount events in a chronological order, then their narrative is linear. If the narrative is told out of sequence, it’s nonlinear. The advantage of linear narration is that it’s easier for the reader to understand, and it builds tension as the narrative progresses through the natural rise and fall of the central conflict. Nonlinear narration, on the other hand, adds aesthetic interest to a written work and builds emotional resonance for readers.
The rate at which a story develops, or its pace, is controlled through elements like the length of scenes, depth of description, and intensity and frequency of action. Genre often affects pacing as certain types of writing require a faster pace (like action-adventures, horror, espionage, and crime thrillers) while others need a slow, extended pace (such as historical dramas or sweeping family sagas).
Point of View
The narrator or speaker provides a story’s point of view; as such, the reader only experiences events as the narrator sees and describes them. There are three main types of point of view: first person, where everything is narrated from one single character using the pronouns I, me , and mine; second person, which is written as if the reader is a character and uses the pronouns you and your; and third person, which is told from an authorial point of view outside the story and uses the pronouns she / her, he / his, and they / them/ theirs.
This indicates the general character or attitude of a piece. There are as many types of tone as there are attitudes and emotions. A piece of writing can be cheerful or depressing; romantic or sincere; elegiac or optimistic. Even an objectively written news article maintains a tone—in that case, the tone is neutral.
Narrative Poetry
Narrative is not restricted to fiction, nonfiction, and theater. Although some poems focus on an image, an emotion, an idea, or a mood, other poems tell a story. When a poem focuses on recounting a series of events, it is called a narrative poem .
The epic poems The Iliad , The Odyssey, The Epic of Gilgamesh, The Aeneid , The Kalevala, and Beowulf are all narrative poems, as are other longer poetic works, such as The Canterbury Tales, Metamorphosis, and The Rime of the Ancient Mariner. There are shorter narrative poems as well, such as Alfred Lord Tennyson’s “ The Lady of Shalott ,” Edgar Allan Poe’s “ The Raven ,” and Alfred Noyes “ The Highwayman .”
Why Writers Employ Narrative
Writers use narrative because it keeps audience members engaged. A strong narrative can heighten characterization and augment the emotional or aesthetic elements of a work. It is human nature to want to know “what happens next,” so readers are inclined to follow the full narrative arc once it begins. A compelling narrative will keep the audience consistently engaged and interested.
Narrative’s Relationship to Story and Plot
Although people often use the words narrative , story , and plot interchangeably, they are not the same thing.
Story refers to a series of events related in their chronological order. Plot indicates a series of events that are arranged deliberately to reveal emotional, thematic, or dramatic significance. This means the plot also conveys the causes, effects, and meanings of events. According to E. M. Forster’s Aspects of the Novel , the sentence “The king died and then the queen died” is a story, whereas the sentence “The king died and then the queen died of grief” is a plot.
Narrative, on the other hand, includes the sequence of events (the story), the causes, effects, and meaning of these events (plot), and the techniques and decisions employed by the author that determine how these events are recounted to the audience.
One way to remember these distinctions is to think of what each provides. The story is what happens, the plot includes the whys and significance of what happens, and the narrative is how what happens is recounted.
Examples of Narrative in Literature
1. Samuel Taylor Coleridge, The Rime of the Ancient Mariner
Coleridge’s long narrative poem opens with the Ancient Mariner stopping the Wedding-Guest, who is with two companions, in the street:
It is an ancient Mariner,
And he stoppeth one of three….
He holds him with his glittering eye—
The Wedding-Guest stood still,
And listens like a three years’ child:
The Mariner hath his will.
Although the Wedding-Guest wishes to continue on his way, he is unable to resist the compelling story of the Mariner’s ill-fated journey and inexplicable sin of killing an albatross. Coleridge utilizes the narrative technique of a frame story to contain the Mariner’s tale within the larger experience of the Wedding Guest who listens—and learns—from the Mariner.
2. Anthony Burgess, A Clockwork Orange
Burgess’s novel is told by a first-person narrator. Alex, a hardened young criminal, relates the nefarious doings of himself and his “droogs” with great delight, peppering his memories with a distinctive slang:
There was me, that is Alex, and my three droogs, that is Pete, Georgie,
and Dim, Dim being relly dim, and we sat in the Korova Milkbar making up
our rassoodocks what to do with the evening, a flip dark chill winter bastard
though dry. The Korova Milkbar was a milk-plus mesto, and you may, O my
brothers, have forgotten what these mestos were like, things changing so
skorry these days and everybody very quick to forget, newspapers not being
read much neither.
Alex’s use of invented slang and run-on sentences lends greater depth to Burgess’s characterization and forces the readers to experience the narrative’s sequence of events alongside Alex, rather than having any objective distance from them.
3. Louise Erdrich, Love Medicine
Erdrich’s award-winning novel, which chronicles the lives of several indigenous families across six decades, opens with third person point of view:
The morning before Easter Sunday, June Kashpaw was walking down the clogged main street of oil boomtown Williston, North Dakota, killing time before the noon bus arrived that would take her home.
While this chapter is written in the third person, most chapters are told from other characters’ first person point of view. Erdrich’s episodic, nonlinear approach heightens characterization and allows her to create a vast panoply of voices, bringing fully to life a number of Chippewa living on an Ojibwa reservation.
4. Toni Morrison, The Bluest Eye
Morrison’s debut novel also shifts points of view with its narrative structure. It begins with lines drawn from the Dick and Jane early reading primers, moves to first-person narration, then continues with a third person narrator as the narrative jumps back in time to the Great Migration.
In the novel’s final section, the point of view reverts to Claudia MacTeer’s first-person narration as she explains how complicit the community was in the unfortunate events that befell Pecola Breedlove:
All of us—all who knew her—felt so wholesome after we cleaned ourselves on her. We were so beautiful when we stood astride her ugliness. Her simplicity decorated us, her guilt sanctified us, her pain made us glow with health, her awkwardness made us think we had a sense of humor. Her inarticulateness made us believe we were eloquent. Her poverty kept us generous. Even her waking dreams we used—to silence our own nightmares. And she let us, and thereby deserved our contempt.
Morrison’s nonlinear narrative,with its shifting points of view, creates a fragmented effect, which reflects both the dissolution of Pecola’s sanity as the book progresses and the way her community failed to sustain her.
5. Katherine Boo, Behind the Beautiful Forevers
Boo’s award-winning nonfiction examination of poverty in Mumbai begins with a Prologue. She sets the scene by introducing some of the people whose lives she will follow:
Midnight was closing in, the one-legged woman was grievously burned, and the Mumbai police were coming for Abdul and his father. In a slum hut by the international airport, Abdul’s parents came to a decision with an uncharacteristic economy of words. The father, a sick man, would wait inside the trash-strewn, tin-roofed shack where the family of eleven resided. He’d go quietly when arrested. Abdul, the household earner, was the one who had to flee.
Boo uses third person narration and a neutral tone . These choices allow her to maintain a sense of journalistic objectivity, which is necessary for this type of nonfiction work. Her nuanced characterization and detailed description throughout the book add to readers’ ability to trust her knowledge and breadth of research.
Further Resources on Narrative
Project Gutenberg has an extensive list of narrative techniques.
Ohio State University’s “ Project Narrative ” is a wonderful source for information about narrative theory.
Amit Majmudar published a great round up of “ old-school narrative poems ” on the Kenyon Review website.
Related Terms
- Narrative Poem
Definition and Examples of Narratives in Writing
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
The definition of narrative is a piece of writing that tells a story, and it is one of four classical rhetorical modes or ways that writers use to present information. The others include an exposition, which explains and analyzes an idea or set of ideas; an argument, which attempts to persuade the reader to a particular point of view; and a description, a written form of a visual experience.
Key Takeaways: Narrative Definition
- A narrative is a form of writing that tells a story.
- Narratives can be essays, fairy tales, movies, and jokes.
- Narratives have five elements: plot, setting, character, conflict, and theme.
- Writers use narrator style, chronological order, a point of view, and other strategies to tell a story.
Telling stories is an ancient art that started long before humans invented writing. People tell stories when they gossip, tell jokes, or reminisce about the past. Written forms of narration include most forms of writing: personal essays, fairy tales, short stories, novels, plays, screenplays, autobiographies, histories, even news stories have a narrative. Narratives may be a sequence of events in chronological order or an imagined tale with flashbacks or multiple timelines.
Narrative Elements
Every narrative has five elements that define and shape the narrative: plot, setting, character , conflict , and theme. These elements are rarely stated in a story; they are revealed to the readers in the story in subtle or not-so-subtle ways, but the writer needs to understand the elements to assemble her story. Here's an example from "The Martian," a novel by Andy Weir that was made into a film:
- The plot is the thread of events that occur in a story. Weir's plot is about a man who gets accidentally abandoned on the surface of Mars.
- The setting is the location of the events in time and place. "The Martian" is set on Mars in the not-too-distant future.
- The characters are the people in the story who drive the plot, are impacted by the plot, or may even be bystanders to the plot. The characters in "The Martian" include Mark Watney, his shipmates, the people at NASA resolving the issue, and even his parents who are only mentioned in the story but still are impacted by the situation and in turn impact Mark's decisions.
- The conflict is the problem that is being resolved. Plots need a moment of tension, which involves some difficulty that requires resolution. The conflict in "The Martian" is that Watney needs to figure out how to survive and eventually leave the planet's surface.
- Most important and least explicit is the theme . What is the moral of the story? What does the writer intend the reader to understand? There are arguably several themes in "The Martian": the ability of humans to overcome problems, the stodginess of bureaucrats, the willingness of scientists to overcome political differences, the dangers of space travel, and the power of flexibility as a scientific method.
Setting Tone and Mood
In addition to structural elements, narratives have several styles that help move the plot along or serve to involve the reader. Writers define space and time in a descriptive narrative, and how they choose to define those characteristics can convey a specific mood or tone.
For example, chronological choices can affect the reader's impressions. Past events always occur in strict chronological order, but writers can choose to mix that up, show events out of sequence, or the same event several times experienced by different characters or described by different narrators. In Gabriel García Márquez's novel "Chronicle of a Death Foretold," the same few hours are experienced in sequence from the viewpoint of several different characters. García Márquez uses that to illustrate the peculiar almost magical inability of the townspeople to stop a murder they know is going to happen.
The choice of a narrator is another way that writers set the tone of a piece. Is the narrator someone who experienced the events as a participant, or one who witnessed the events but wasn't an active participant? Is that narrator an omniscient undefined person who knows everything about the plot including its ending, or is he confused and uncertain about the events underway? Is the narrator a reliable witness or lying to themselves or the reader? In the novel "Gone Girl," by Gillian Flynn, the reader is forced to constantly revise her opinion as to the honesty and guilt of the husband Nick and his missing wife. In "Lolita" by Vladimir Nabokov, the narrator is Humbert Humbert, a pedophile who constantly justifies his actions despite the damage that Nabokov illustrates he's doing.
Point of View
Establishing a point of view for a narrator allows the writer to filter the events through a particular character. The most common point of view in fiction is the omniscient (all-knowing) narrator who has access to all the thoughts and experiences of each of her characters. Omniscient narrators are almost always written in the third person and do not usually have a role in the storyline. The Harry Potter novels, for example, are all written in third person; that narrator knows everything about everybody but is unknown to us.
The other extreme is a story with a first-person point of view in which the narrator is a character within that story, relating events as they see them and with no visibility into other character motivations. Charlotte Bronte's "Jane Eyre" is an example of this: Jane relates her experiences of the mysterious Mr. Rochester to us directly, not revealing the full explanation until "Reader, I married him."
Points of view can also be effectively shifted throughout a piece—in her novel "Keys to the Street," Ruth Rendell used limited third-person narratives from the point of view of five different characters, enabling the reader to assemble a coherent whole out of what first appears to be unrelated stories.
Other Strategies
Writers also use the grammatical strategies of tense (past, present, future), person (first person, second person, third person), number (singular, plural) and voice (active, passive). Writing in the present tense is unsettling—the narrators have no idea what will happen next—while past tense can build in some foreshadowing. Many recent novels use the present tense, including "The Martian." A writer sometimes personalizes the narrator of a story as a specific person for a specific purpose: The narrator can only see and report on what happens to him or her. In "Moby Dick," the entire story is told by the narrator Ishmael, who relates the tragedy of the mad Captain Ahab, and is situated as the moral center.
E.B. White, writing columns in 1935's "New Yorker" magazine, often used the plural or "editorial we" to add a humorous universality and a slow pace to his writing.
"The barber was cutting our hair, and our eyes were closed—as they are so likely to be... Deep in a world of our own, we heard, from far away, a voice saying goodbye. It was a customer of the shop, leaving. 'Goodbye,' he said to the barbers. 'Goodbye,' echoed the barbers. And without ever returning to consciousness, or opening our eyes, or thinking, we joined in. 'Goodbye,' we said, before we could catch ourselves."—E.B. White "Sadness of Parting."
In contrast, sportswriter Roger Angell (White's stepson) epitomizes sports writing, with a quick, active voice, and straight chronological snap:
"In September 1986, during an unmomentous Giants-Braves game out at Candlestick Park, Bob Brenly, playing third base for San Francisco, made an error on a routine ground ball in the top of the fourth inning. Four batters later, he kicked away another chance and then, scrambling after the ball, threw wildly past home in an attempt to nail a runner there: two errors on the same play. A few moments after that, he managed another boot, thus becoming only the fourth player since the turn of the century to rack up four errors in one inning."—Roger Angell. "La Vida."
- A Guide to All Types of Narration, With Examples
- Understanding Point of View in Literature
- Point of View in Grammar and Composition
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- Third-Person Point of View
- How to Summarize a Plot
- Organizational Strategies for Using Chronological Order in Writing
- Introduction to Magical Realism
- What Are the Parts of a Short Story? (How to Write Them)
- 5 Easy Activities for Teaching Point of View
- What Is Narrative Therapy? Definition and Techniques
- What Is Narrative Poetry? Definition and Examples
- What Is a Novel? Definition and Characteristics
- How a Narrative Arc Structures a Story
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?

How to Write an Outline for a Narrative Speech
How to write an essay with a thesis statement.
A narrative speech relates the story of an event, whether from the speaker’s life or from that of someone she knows. Usually organized chronologically, narrative speeches are often given to entertain or teach the listener. In writing an effective narrative speech, start with an outline to help focus on the purpose of the speech, organize the events discussed in the speech and create a final draft .
A Statement of Purpose
Identify the purpose of your speech, such as imparting a moral or making the audience feel good. This step is necessary and saves revision, because you know where the speech is going from the beginning. It also ensures that nothing necessary is left out. Identifying your purpose can be as simple as writing a one-sentence statement at the top of the outline . Keep the statement of purpose in view and refer back to it or refine it if needed.
Your Attention Please
Grab the audience’s attention and preview the topic of the speech in the introduction. Include a hook or attention-getter, the thesis and a preview of the narrative in this order; establish credibility after the hook if you think it's important. In your outline, the introduction is Roman numeral “I,” and each part receives a capital letter under it -- A: Hook, B: Establish Credibility, C: Thesis, D: Preview. Capture the main idea of each part in one sentence, saving the details for the post-outline writing stage.
A Full Body
Ensure no essential narrative parts are missing by organizing the story carefully in the body. Outline this part of the speech in a straightforward manner by including the most important points in chronological order , adding extraneous information as necessary. Write the body as Roman numeral “II” and give each body point its own capital letter. Add numbers underneath the letters for supporting information. Use full sentences and save minute details for the writing stage.
Thank You, Ladies and Gentlemen
An abrupt stop at the end of the narrative will confuse or frustrate the audience. Use the conclusion to wrap up the speech, reminding the audience of the takeaway, if any. Include three main points: a signal that the speech is nearly finished, a summary of the story and a thesis review . Add Roman numeral “III” for the conclusion, then one capital letter for each point — A: Signal, B: Summary, C: Thesis Review. Capture the essential information in one sentence for each. When finished, review the purpose of the speech to ensure that the outline is in accordance.
Related Articles

How to Write an Excellent Self Introduction Speech Really Quick

How to Write APA Papers in Narrative Style

How to Write a Speech Essay
How to write a rebuttal speech.

How to Write a Good Closing Argument

Activities for Writing Introductions & Conclusions

How to Write a Letter to First Lady Michelle Obama

How to Use a Summarization for APA Format
- Purdue OWL: Narrative Essays
- Wittenberg University: Organizing Your Presentation -- Basic Outline Format
Melissa Harr is a writer and knitting pattern designer with a range of publication credits. Her latest work includes blogging for Smudge Yarns, judging fiction for Ink & Insights 2015 and creating patterns for I Like Knitting magazine. Harr holds a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Illinois at Chicago and a CELTA.

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:
TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
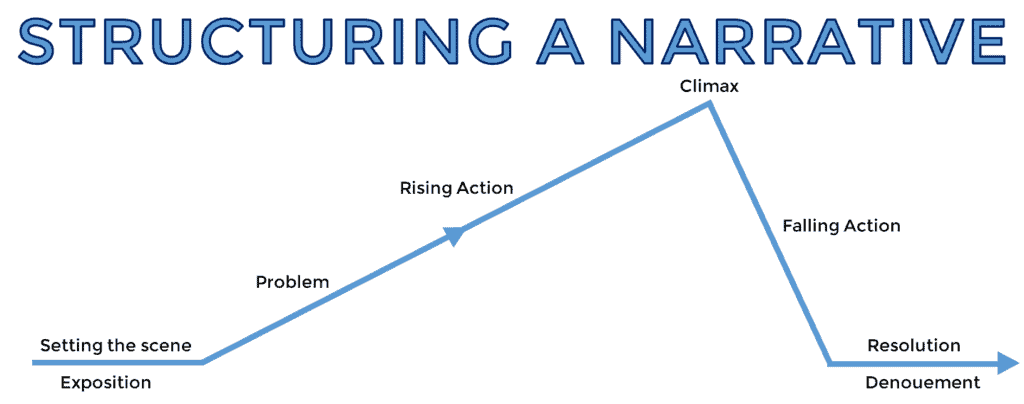
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE

Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.

Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- African Literatures
- Asian Literatures
- British and Irish Literatures
- Latin American and Caribbean Literatures
- North American Literatures
- Oceanic Literatures
- Slavic and Eastern European Literatures
- West Asian Literatures, including Middle East
- Western European Literatures
- Ancient Literatures (before 500)
- Middle Ages and Renaissance (500-1600)
- Enlightenment and Early Modern (1600-1800)
- 19th Century (1800-1900)
- 20th and 21st Century (1900-present)
- Children’s Literature
- Cultural Studies
- Film, TV, and Media
- Literary Theory
- Non-Fiction and Life Writing
- Print Culture and Digital Humanities
- Theater and Drama
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Narrative theory.
- Didier Coste Didier Coste Universite Bordeaux Montaigne
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190201098.013.116
- Published online: 28 June 2017
The narrative mode of world-representation and world-building is omnipresent and far exceeds the domain of literature. Since literature is not necessarily narrative and narrative not necessarily literary, the study of narrative in a literary context must confront narrative and literature in a dual way: How does the presence of narrative affect literature? And how does literariness affect narrative? The basic terminology needs to be clarified by comparing English with the vocabulary of other natural languages. No consensus has been reached, even in the West, on the nature of narrative discourse.
The entire history of poetics shows that, before the middle of the 20th century, little attention was paid to the narrative components of literary texts qua narrative—that is, insofar as the same narrative elements could equally be found in non-aestheticized uses of verbal and non-verbal languages. Aristotelian poetics, based on the mimesis of human action, keeps its grip on narrative theory. The post-Aristotelian triad separated more sharply the lyric from the epic and dramatic genres, but modern narrative theories, mostly based on the study of folk tales and the novel, have still failed to unify the field of literary narrative, or have done it artificially, dissolving narrative discourse into the undifferentiated experience of human life in linear time.
The Western “rise of the novel,” in Ian Watt’s sense, and its worldwide expansion, turned the question of fiction, not that of narrativity, into the main focus of narrative studies. Later, the emergence of formalism and semiotics and the “linguistic turn” of the social sciences pushed the narrative analysis of literary texts in the opposite direction, with all of its efforts bearing on minimal, supposedly deeper units and simple concatenations. The permanent, unresolved conflict between an analytical and constructivist view grounded in individual events and a holistic view concerned with story-worlds and storytelling leaves mostly unattended such fundamental questions as how narrative is used by literature and literature by narrative for their own ends.
Literary narrativity must be thoroughly reconsidered. A critical, transdisciplinary theory should submit to both logical and empirical trial—on a large number of varied samples—and narrative analyses that would take into account the following concepts used to forge methodological tools: discrimination (between the functions of discourse genres and between pragmatic roles in literary communication); combination rules (whether linear or not); levels (as spatial placing, as interdependence and hierarchical authority); scale and spatiotemporal framing and backgrounding , especially the (dominant) time concepts in a particular cultural context. The preconditions for analysis begin by investigating the relation between aesthetic emotions and narrative in other cultural domains than the West and the English-speaking world.
Literary narrativity and social values concur to link the rhetorical manipulation of narrative with its aestheticization. The pleasure and fear of cognition combine with strategies of delusion to either acquiesce to the effects of time and violence or resist them; routine and rupture are alternatively foregrounded, according to needs.
- literary aesthetics
- narrativity
- reader response
- spatiotemporal framing
If we can agree on the common transcultural intuition that literature is another name for verbal art, we will also readily accept that many and indeed most other channels of communication, expression, and information can and do “tell stories,” or at least contain fragments of narrative discourse. The visual arts and instrumental music also often use their non-verbal means to convey narrative meaning beside the symbolic value or emotional significance brought about by formal features. There is no need for a title to perceive that a pietà , a crucifixion, or a Rape of the Sabine Women iconically refer to a particular event, real or imaginary, just like bullet marks on a wall refer to a shooting indexically, in Charles Sanders Peirce’s terms. Some instrumental music (Ludwig van Beethoven’s Eroica , a military march) and elaborate Maori war cries refer emotionally and or symbolically to the narratable event or collection of events of war. Should we examine verbal communication, oral or written, with no detectable intended aesthetic manipulation and little or no aesthetic added value (when a policeman reports on his night patrols in the morning, when a technician tells you how your computer system crashed), we will equally find that they more often than not tell complete or fragmented stories, or at least propose elements to put to work some kind of narrative program, a more or less open coded pattern that can be played with interactively; such everyday acts of verbal communication are frequently motivated by the narrative drive of the sender or its presupposition in the receiver and simultaneously point to it.
Verbal art may be considered as another anthropological universal. We can easily speculate that it began with the first rhyme, the first pun, the first chanting modulation—in other words, that it was nearly coetaneous with the appearance of articulate speech in homo sapiens sapiens . But rhymes, puns, chanting rhythms are not narrative acts: they can indirectly, through symbolism and sensorial association, evoke, announce, or recall a narrative without formulating one any more than the hand imprints of the prehistoric Cueva de las Manos . We could even say that they may run counter to the narrative potential of the text, like the recurring couplets of a ballad or an insistent leitmotiv in narrative (“program”) music. Repetition establishes constants; it can smother events. Lyric, argumentative discourse, critical commentaries, the questioning, speculative discourse of the essay can be implicitly or explicitly motivated by a subjacent or projected narrative; they can be interspersed with narrative utterances and even sequences without conveying any properly narrative meaning by themselves. The same applies to descriptions that, taken together, can combine and contrast to stimulate or generate the production of narrative but, taken separately, present by definition a static, tabular vision of the world of reference, not a dynamic one.
The logical asymmetry of narrative and verbal art must not be offset by the quantitative prevalence of the former in the latter, from comedy and tragedy to modern drama and film scripts, from myth and epic to the novel and artful historical narratives, from hagiography to autobiography, from fairy tales to fantasy, from anecdote and fable to concise hyperrealist fiction. Even if the use of narrative discourse is the most ordinary and widespread expression of human awareness of life and its transience, of the will to be part of its dynamics, verbal art develops other means to the same effect and also in order to resist transience and refuse to participate in dynamics it cannot control. Synchronic history would be one example of this resistance. Mysticism is not only a quest; it is fascinated by the absent presence of God or the beloved; it does not always lead to silence; it can manifest itself in repetition, verbosity, and verbiage that blur or even destroy any possible kind of narrativity. Incantation and enchantment are part of an arsenal to fight the corrosive action of perceived linear time. Verbal art is sometimes bent on deflecting or turning its back on the sense of mortality involved in narrative just as it can celebrate and enhance the eventfulness of life; it can use devices such as the regular return of certain signifiers and structures in order to conjure up a cyclic notion of time (eternal return), as well as disruptive devices in order to highlight the wonder of birth, innovation, and metamorphosis.
The fundamental disconnection of narrative and literature is often not recognized by Western theorists, mainly because the novel became the dominant genre there between the 17th and 19th centuries and has conquered the rest of the world in the last one hundred and fifty years. This disconnection makes it an obligation to denaturalize, investigate, describe, and sometimes question the workings of narrative in literature and the role of aestheticization in narratives (like those of historiography, cosmology, or biology) that do not a priori require an aesthetic supplement to fulfill their cognitive, social, political, and ethical purposes.
Straightening the Terminological Maze
Since the infancy of modern narratologies, the very notion of “narrative” has never been a consensual object of study. From their reputedly “classical” formalist and structuralist development to the huge diversification of the so-called “post-classical” phase and beyond, with the rise of cognitive theories and the impact of neuroscience, “the appropriation of narratological frameworks by non-literary disciplines often results in the dilution of the narratological basis, in a loss of precision, and the metaphoric use of narratological terminology.” 1 In fact, literary disciplines, bending toward “fiction,” are largely responsible for this tension, and the definitions of “narrative,” whether literary or not, vary enormously. They often remain contradictory in themselves and incompatible with those used in other fields of knowledge and practice: linguistic definitions are not shared by law or business. This severe lack of consensus implies that any description of literary narrative results from difficult preliminary theoretical choices heavily influenced by historical circumstances and particular philosophical and ideological positions. In the West and through the global expansion of Western rationalization, such discrepancies may find their origin partly in the persistent authority of Aristotelian poetics. According to it, the enunciative factor, the impersonation or not of the acts of speech that construct a story by the actors of the same sharply divides epic from drama (tragedy or comedy). The tragic mode of drama has curiously provided the prevalent paradigm to analyze and interpret the structures of narrative genres, such as the tale, the short story, and the novel, that use one or more external narrators and thus, if we follow Aristotle, belong to epos , not drama. Aristotle denies poetic and even narrative interest to historia , the plain factual recounting of verifiable events in the world as it is or was; therefore, fiction, in the narrow sense of the representation of possible human action, has come to stand as the most significant type of literary narrative, cut off by a more or less high partition from other narrative texts, on the one hand, and indiscriminately packed with non-narrative fiction (such as imaginary descriptions) on the other hand. The classical Indian aesthetics of rasa , although it concentrated, like Aristotelian poetics, on performed narratives, has had a unifying effect across the arts, but, since it seems to be more concerned with a hierarchic value system of human emotions and the techniques of their representation than with the nature of events and their sequence, it brings closer narrative and non-narrative texts instead of separating clearly the representation of a static world from katha , or the mimesis of an evolutive world. This does not mean that “narrative” should forever remain something completely elusive or that the immense modern investment of the human sciences (from sociology, anthropology, history, and law to the science of literature through linguistics) in its theory, analysis, and interpretation is a futile, wasted effort. It rather means that we should henceforth abstain from talking of “narrative” in any vague or all-embracing sense; instead, we should select and test the approaches that will prove most productive in the critical study and appreciation of literary phenomena. If, for instance, a certain approach helps us to make more sense of complex, borderline generic formations such as the lyrical novel, the prose poem, personal and literary diaries or notebooks, the anecdote, the Hadiths or the Upanishads, if it contributes to enhancing our enjoyment of literary and non-literary expressions alike, bringing enough genres under one roof while maintaining and justifying their functional specificities, we will deem it, for now, appropriate to literary studies and reader education.
The Word “Narrative”
The word “narrative,” in contemporary English, can be either adjective or substantive, as in the expressions “narrative poetry” or “a vivid narrative.” Without any surface determinant, the noun “narrative” further objectifies and universalizes the characteristics contained in the acceptation of the adjective when we say, for example (no matter whether it is true or false): “Narrative is present in every speech act.” “Narrative,” in this case, becomes the concept of the set or sets of features that allow us to call some texts or acts of communication “narrative,” and names the open corpus of all the extant, recorded, or possible/potential texts or acts of communication that do or would manifest “narrative features.”
The identity of signifiers between the English adjective and the two aspects (grammatically determined and not determined) of the noun entails a particular way of apprehending the narrative phenomenon. What this way might be, we can begin to infer from a comparison between the lexical uses outlined in contemporary educated English and those found in other states of the English language and in other languages. Suffice it to note the asymmetry of French and English in this respect: in French, even though the adjective “ narratif” could be nominalized like any other similar adjective, this potential nominalization has not been actualized: although the English and French adjectives “narrative” and “ narratif” are fully equivalent, we translate the English noun “narrative” as “ récit .” This substantive etymologically evokes memory, repetition, quotation, a posteriori telling; it refers more to the oral, written, or visual text of narratives through which the telling is done than to the teller of the tale, who is not necessarily a “ récitant ”—especially in modern times—and is technically tagged “ narrateur ” or would be called a “ conteur ” in an older or an oral context. This fact is all the more important in view of the impact of French or French-inspired structuralism on the worldwide development of narratology and its early insistence on dismissing the figure of the author from this field of study.
Comparison with other languages would show that the terminology in the semantic field of “narrative” is culturally and historically determined and therefore generates large numbers of “untranslatables” in Barbara Cassin’s sense. The semantic field of “narrative” is covered and divided differently in each language, which does not make it easy for us to speak of “narrative” from the standpoint of modern English while purporting to discuss it as an anthropological universal. If the Arabic word qissa covers virtually any kind of story, anecdotal stories or records of matters of the Minor Way ( xiaodao ), considered as “fiction” because they did not carry a relevant moral message, seem to be separated from other narrative genres in pre-Ming China.
The use of the same signifier, in English, for the adjective and the concrete and conceptual nouns, and the presence of the same Latin etymon in a large spectrum of the semantic field (with “narrate,” “narrator,” “narration”) involve a serious risk of considering narrative phenomena as naturally unified in space, time, and the logic at work. The Proto-Indo-European root gno , unconsciously shared with “know,” can also perpetuate a confusion of informing and knowledge acquisition in general with narration and its reception. Overlooking heterogeneity is as dangerous as denying the possibility of anthropological universals.
The Word “Literature”
Contemporary uses of the words “literature” and “literary” are fraught with difficulties at least as great as those of “narrative.” The variation of social and philosophical values in the present context of fragmented cultural globalization and acts of resistance to these variations contributes to this vagueness. Where people of widely different backgrounds and persuasion, in different languages, could readily agree that (a) “Peter and Mary got married yesterday” is a narrative utterance, even the closest friends and collaborators might well disagree on whether the above sentence, or, alternately, (b) “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously,” can be literary at all. An affirmative answer, for the first example, would always depend on a relaxation of exogenous and/or inbuilt aesthetic criteria; with the second example, it would depend on the relaxation of the principle of non-contradiction in the name of an aesthetics of surprise or an anti-rationalist stance. One could say that literariness is subject to much wider socio-cultural and historical variations than narrativity. From the standpoint of the early 21st-century West, the criteria and inclusiveness of verbal art (as opposed to verbal non-art and non-verbal art) might perhaps be reduced to four phases for didactic purposes.
In Greek- and Latin-dominant poetics—more Aristotelian than Platonic—and their afterlife, “poetry” or “poesie” would cover the artful verbal (written and oral) imitation of human action in the two large genres (drama and epic) acknowledged by Aristotle, with the necessary addition of the lyric, not considered extensively in Aristotle’s Poetics . From the low Middle Ages onward, with the development of European vernacular languages in writing, with the first traces of secularization and individualization of art, and with the nostalgia and revival of classical know-how, the belles-lettres gradually separated from popular verbal art, tending to include rhetorical and didactic genres (sermon, discourse, eulogy, apology, essay, etc.) in the field. The novel use of the word “literature” in the 18th century did little more than legitimate a process of integration of written narrative fiction that had begun in the 13th century and had seen successively the transformation of the popular tale into the short story, the gentrification of the novel (including the “romance” as supposed sub-genre), and the defense of the epic in prose as a noble art form. “Literature” (or “poetry”), verbal art—although it had always been opposed or sometimes hated and despised since the times of Plato—had on the whole steadily accumulated a huge capital of prestige by the first half of the 19th century . “Literature,” mostly in its narrative guise, had come to embrace almost all domains of knowledge and expression, except those that made use of specific formal languages rather than natural languages. The fourth phase, of which we have generally become intensely aware only from the late 20th century , had already begun in the second half of the 19th century , under the combined pressure of scientific faith and growing distrust of “the word” associated with manipulation, propaganda, exploitation, war-mongering, and genocide.
The formation of a concept of literariness no longer tied to questions of moral and social value coincided with and probably contributed to the accelerated rise of a disinterested and above all non-mimetic vision of literature. Roman Jakobson’s “poetic function,” for example, conveniently condoned a renewed sharp separation between high and low, abstract and concrete, pure and pragmatic uses of aestheticization, favoring self-reflexive poetry or the formal structures of narrative over any “referential” semantic contents or conative intention and effect. The polysemy criterion of Mircea Marghescou anticipated a post-communist attitude at odds with the actual or imagined demands of the city; 2 Roland Barthes’s “readerly” regime, reception aesthetics, and reader-oriented criticism, as well as the demise of the author and the foregrounding of the unconscious, all tended to turn literature into a playground for language games. The denunciation of universals by many postcolonial and “decolonial” theorists, together with the postmodern deconstruction of a coherent logos and the bewildering changes in the human perception of time and practice of memory—all these factors combined to support the idea that literature, at least as we had known it in our lifetimes, was indeed coming to an end. If we are to talk of literature at all, were it to accept or rejoice that it is no more, it is nevertheless a logical necessity to either describe “what was literature” or define what it could be in a differently configured world. It would be meaningless to declare dead a concept that was always empty. Moreover, there are too many traces and records of it—whether official, secret, or unacknowledged—in ordinary language and our everyday lives not to attempt to propose some ample but not vague working definition of what is literary in literary communication. It is a basic requirement here when the current corpus of what passes for “literature” is more dominantly narrative than ever, thus tightly, if unduly, conjoining two universals.
“Literature” must not be equated with the sum of supposedly literary genres any more than “narrative” with the sum of genres conventionally labelled “narrative” in any one cultural context. The fact that, before, during and after the rise of structural narratologies, the theory of literary narrative was always rooted in the study of a limited number of emblematic genres, such as the epic and the fable in the neoclassical period, the fairy tale 3 and then the novel 4 in the long structuralist period, or historiography, comics, and digital games more recently, 5 never stopped generating as many conceptual distortions as useful insights. The diversity of historically inscribed genre-based theories should, on the contrary, motivate us to work our way toward features that have a chance to be anthropologically, transculturally, and transhistorically shared.
Here, then, an act of literary communication is any cooperative speech sequence that fulfills three minimal conditions: (a) its effectiveness depends on intertextual linkage at least as much as on its internal coherence and its reference to a non-textual world; (b) the resolution of ambiguities and the reduction of tropes and other figures leave a positive surplus to the act of communication; (c) this act of communication actually generates or has the potential to generate some kind of aesthetic satisfaction in the empirical or virtual participant subjects. Literariness, thus broadly defined, can be historically modulated; it is not a static, immutable property of some classes of “texts” that other classes would not possess, but its existence does not depend on particular historical circumstances or on a grand evolutionist narrative of progressive achievement or rise and decay.
A Brief Narrative of the Poetics of Narrative
The word “poetics” rather than “theory” is preferred: first of all, narrative meaning and resonance are held to be the result of a making, a collaborative fabrication, not a given of a “text” as it stands in its own space, as early textual structuralism saw it, or a ready-made code or pattern that would reside in the minds of both receiver and sender and could be called upon, activated at will without undergoing important modifications, as some cognitivist views, like those popularized by Jonathan Gottschall would have it. 6 Second, a poetics has a normative aspect that a theory lacks: until the second half of the 20th century , all concepts of literary narrative were largely motivated by a quest for moral and/or aesthetic added value, even when they purported to be amoral or immoral and cultivated ugliness or negligence. In fact, the demand for such values or their deliberate denial still weighs upon most contemporary theories of narrative. Even though Lubomir Doležel validly argued that a change of paradigm in Western poetics, 7 from an anatomical, taxonomic view to a morphological, organicist one, emerged in the Romantic period, it is obvious it has been and is still, two centuries later, at pains to replace the earlier one.
The Aristotelian Conundrum
Aristotle’s Poetics remains, after twenty-four centuries, by far the single most influential treatise of its type in the West and, by colonial extension, worldwide. What were the motivations of such a persistent impact in spite of the Judeo-Christian revelation and revolution, when a very different attitude to the Book was now carried by the three monotheisms, when divine authorship and its truth-value imposed a unique, linear master narrative of the history of mankind always already pre-written by God? The Enlightenment; the destabilizing, iconoclastic avant-gardes; the formalist, structuralist, pragmatist, cognitivist, and deconstructionist perturbations of the basic Aristotelian tenets have also proven unable to uproot them. Whether this inexpugnable resistance is due to an ever-renewed tragic vision of life that neither eschatological monotheism nor radical skepticism could seriously alter, or whether it was propitiated by the foundational character of the Poetics , by an incompleteness that gave rise to a number of equally plausible interpretations, or on the contrary by the often schematic pronouncements it makes, pre-figuring a culture of manifestos, its system is still at the heart of contemporary narrative theories that do not refer to it at all.
“Imitation is natural to man from childhood, one of his advantages over the lower animals being this, that he is the most imitative creature in the world, and learns at first by imitation. And it is also natural for all to delight in works of imitation.” 8 If man is a born imitator, if this is one of his key defining features, his dignity and his limit, he can imitate good or evil and his innate imitation skills must be guided: the main function of art, itself imitative qua human, will be to guide imitative behavior by the receiver. And the role of poetics will be to guide art—for which a description and an evaluation are necessary. Evaluation selects the best objects and the most adequate manner within each kind of means/vehicles. But Aristotle, in these lessons, considers only the art or set of arts that uses language as its means, independently of music or meter, prose or verse, a subset that still lacked a name. We could say that this field delimitation is the one in which the notions of “poetry” and later “literature” originate. The focus is not on the materiality of the signifier but on the process of signification and how it achieves the goals of mimesis in the minds and hearts of the receivers, influencing their view of themselves in the world and therefore their actions.
“The objects the imitator represents are actions, with agents who are necessarily either good men or bad.” 9 “Action” ( praxis ) or actions, “human affairs” ( pragmata ), are at the core of Aristotelian poetics. The mimesis of human actions is for Aristotle at once the shared and the sole determinant feature and primary purpose of all the arts, considered themselves at all levels as “makings of,” practicing a technique to pursue a goal. Regarding “narrative,” this choice has wide-ranging philosophical implications and hermeneutic consequences that will always complicate and sometimes hamper the task of contemporary narrative theory. On the one hand, it potentially unifies all the arts under the common denominator of narrative, allowing and even encouraging inter-artistic and trans-medial comparison; on the other hand, it excludes from the artistic domain and aesthetic enjoyment, in an unjustifiable way according to our modern view and practice, any act of expression and/or imitation that is either conceptual or merely descriptive or yet refers to natural, non-human events. Unless the making of a house, a decorative frieze, or a symphony is taken as imitation of human action, which is certainly not the primary purpose, an architectural realization, a landscaped garden, or a piece of non-imitative music are not objects of art.
Second, but more important, if non-human events such as meteors, geological, astronomical, physical events at large, or the life events of animals and plants are not valid objects of representation by literary language (unless they serve as metaphors of human actions, as in some parallels and allegories), a radical dichotomy is maintained between human nature and culture, on one side, and nature (what there is or what might be without mankind or discounting man’s action on it) on the other; we could even wonder whether this severance of man from the rest of the universe is not constitutive of the tragic condition that motivates for Aristotle the highest form or genre of “poetry.” Catharsis would serve as the fantasized healing of the repressed but active subconscious separation.
Third, the confusion of event with (human) action limits the scope of narrative discourse to its transactive level (A acts on B, there is an agent and a patient), making strangely irrelevant to poetry/literature those events and processes that involve only one (human) entity without any necessary and knowable action on its part, such as being born, growing, falling in love, becoming sick, old or stupid, and dying. Moreover, all human events that occur without the intervention of a third human party would have to be caused by the action of one part or side of a human being on another part or side of the same: the human, causal, and transactive Aristotelian notion of event paradoxically implies the universal responsibility of a subject that is at the same time inevitably fractured. Freudian psychoanalysis could be seen in this light as an attempt not only to explain and overcome the tragic burden, but to open up the Western poetics of narrative to alternate stories in which responsibility is measurable and the purgation of guilt is not the only answer.
Fourth, if the restriction of literary (meaningful) narrative to the telling of human action implies a tight bond to ethos , to character (as a quasi-person), there can be no proper narrative without the continuity demanded and provided by individual human lives and consciousnesses and their continuous interactions: the unity of argument or story line and its successiveness, conveniently reflected by textual unity and/or unity of performance (“the work”), the careful disposition of parts, the clear framing of the whole, all point at a narrativity that depends on the role of the narrator (in epic) or the concerted conjunction of players (in drama). Fragmentation, unsolved riddles, the breaking up of a spatiotemporal continuum, precisely what an event does as such according to most narrative theories, would appear as detrimental to narrativity.
Finally, since faithfully, neutrally imitating uninterpreted past human action, as in historia , would be useless from a moral and social point of view that actively concerns itself with the present and the future, the Aristotelian literary narrative is bound to embrace at least a certain degree of fictional world-making: this narrative, whether it is based on historically recorded facts, on supposed facts, or on myths and the imagination, needs fiction as much as faction, and its storytelling implies a willing suspension of disbelief, a “let us suppose that,” virtually experiencing “what it’s like.” 10 Planning a future is always, after all, a conspiracy.
It is no great surprise then that, although Aristotle’s Poetics focused on drama, it could still easily fit the semiotics of tale and the theory of the novel, as long as they could be forcibly reduced to some form of compositional and referential unity (a storyline and a story-world), and as long as their perceived purpose could be held as at least partly social, ethical, educative, and therapeutic. But, when these two conditions appeared increasingly difficult to fulfill with the formal contortions, the self-referentiality, and the proclaimed disengagement of a not so large but widely publicized and very visible fraction of 20th-century experimental writing—narrative by default—some literary theorists with an interest in narrative were forced to discard post-modern, non-“prototypical” narratives from their investigative scope, assuming also that a lower “consciousness factor” lessened the narrative experience. 11 They are doubly wrong when they treat the French nouveau roman, American metafiction, or other unconventional 20th-century prose forms as alien to the representation of consciousness, and when they think that its conventional representation, as in the “psychological” novel, enhances narrativity. From Homer to James Joyce and beyond, the contours of literary narrative cannot be drawn by story fetishism. Literary narrative uses it and questions it at once, as it swings between defamilarization and re-familiarization. 12
Problems in Contemporary Western Narrative Theory
A comparative history of modern and contemporary narrative theory remains to be written. It could certainly not be linear and its findings would doubtless be somewhat puzzling, but many of these difficulties have to do with four persistent, rarely challenged beliefs: (a) that narrative discourse and “story” or “plot” are coextensive; (b) that narrative is a kind of “language” and it has some sort of universal “grammar” or “logic”; (c) that narratives, especially literary ones, are necessarily about humans and human kind; (d) that narrative interest is provided by anomalous, unexpected events, developments, and resolutions rather than by the repetition and confirmation of standard schemata. These beliefs impose undue limitations on the theory of literary narrative.
Event, Change, and Action
The notion of “action” is related to the philosophy of action or ethics, and it is etymologically cognate to those of “author” and “actor.” It assigns an identifiable origin to the telling of the tale and also to the events told, or at least it manifests the relevance of origin and launches a regressive quest of origins that has no reason to stop or pause unless an all-powerful, all-embracing deity makes the search redundant, since every event then belongs to a self-caused world. The only difference between author and actor being that between a gesture that will be repeated and the imitation/the serious or playful repetition of this gesture, “action” tightly binds the authorial figure with character, and those two with a reader or receiver who will identify with them and re-enact what was acted by the character in the presented world. Since, additionally, one cannot just act but has to act, retroactively or proactively, on something or someone, all the elements of plot (sequentiality; connectivity; interactivity; plurality of actants; actual or potential causality; directionality, i.e., time-oriented events with a finality) are already given by the notion of action. This troubles any narratology that wishes to distinguish deeper and more elementary levels, steps or stages of meaning formation from the articulations that operate at the levels of story ( fabula ) and textual actualization ( szuzhet ). Eliminating all stratification, as did Philip Sturgess, is conducive to erasing the very specificity of the texts we commonly perceive and classify as distinctly narrative together with the difference between action and mere event or process (the difference between “John starts watering the garden” and “it starts raining” or “Marcel becomes a novelist”). 13
J.A. García Landa rewrote “action” ( acción ) as “event” ( acontecimiento ) in his early forays into narrative theory; he also rewrote “action” as a collective, holistic noun, always already sequential. 14 In his later work, he fortunately denounces the illusion produced by “hindsight bias,” renamed by him “narrative fallacy”: “The configuration effected by narrative is imaginatively projected backwards and transformed into the reified structure of experience before it is narrated—and before it unfolds, actually.” 15 Nevertheless, when the same author, together with Sturgess and many others, insists on an “inherently retrospective logic of narrative,” he still collapses the post hoc of the narrated with the propter hoc of narration. A concept of narrative logic, unavowedly placed under the aegis of “action,” conflates prior narration and its pre-formation in the mind of the narrator/author with the narrated as it is concretized by the receiver. As a result, one could not take at face value the narrative present tense, let alone the use of the future: “And then the blade (of the guillotine) falls,” or “The just will be rewarded on the Day of Judgment” do not, we contend, use these verb tenses “to mask the inherent retrospectivity of narration.” 16 Indeed, the present and future tenses of testimonial, forecasting, and prophetic narratives are more effectively narrative because they point at an event as it is happening or in its promising or threatening imminence, while the past is past, as people say, and past, preterit events exist only in the form of inert traces, inscriptions, states, however hard we try to make them come to life. 17
Narrative discourse, in its most general sense, is the discourse of change, not action; it provides a transitive view of the world. 18 Daniel Punday is eager to add a spatial dimension, one of movement, to what he sees as limited to change in time in Didier Coste’s definition of narrative meaning. 19 But, if “ sic transit gloria mundi ” could be the blasé motto of narrative discourse, then the spatial dimension is ipso facto already present in the inevitable metaphors of “passing,” “going to,” and “going through” (the Catalan language strangely uses the auxiliary verb “va” for its narrative preterit). None of these conceptual features is a priori dependent upon the supposedly logical priority of narration over the narrated, but they are not intrinsically textual either: “Far from being dependent on universal, context-free structures and traits, narrativity is largely tied to pragmatic, functional, contextual, generic and cultural circumstances.” 20 Without effacing the ontological distinction between stasis and change, what counts as event or process, what is construed as change in the elaboration of narrative meaning, certainly depends on the play of foregrounding and backgrounding.
Narration and Narrated
In his foreword to Raphael Baroni’s La Tension narrative , Jean-Louis Schaeffer states, perhaps slightly hastily, that narrative theory, after a peak in the so-called “structuralist period,” had fallen into dire disgrace in the final two decades of the 20th century , since the findings of structural narratology were held by some as definitive and obvious, while, for others, “theory” itself had become a dirty word and the very idea of a general narratology chimerical. 21 Schaeffer’s vision is probably too influenced by his focus on the French and Francophone scene. Bibliographies of narrative theory in other languages (English, German, Spanish, Portuguese) show that there was a steady flow of important books and collections in the new discipline all along those twenty years. 22 What is true is that there happened a marked shift away from “deep structures” à la A. J. Greimas toward the modalities of narration and the question of fictionality, and away from intra-textual considerations toward intertextual hermeneutics, pragmatics, reader-oriented criticism, and cognitive or psychological approaches. Not all of this research has had the same impact on the discipline. Some of the newer “post-structural” research enriched the bases provided by formalist-structuralist theories, corrected their rigidities and blunders, brought enlightening inflections. But, curiously, the development of enunciative stylistics, the study of embedded and mosaic composition, metalepsis, overwriting, pastiche, parody, and metafiction did not significantly help to strengthen the non-porous, epistemic, and pragmatic border between narration and narrated.
In a glossary entry for “Narration, narrative act,” Monika Fludernik defines these (for her) synonymous expressions as follows: “The telling of a story by a narrator, who may address a narratee. The narrative act, which corresponds to Gérard Genette’s level of narration , forms the communicative framework of the narrative.” 23 Here, at first sight, a clear-cut distinction seems to be drawn between narration as act and narrated as object produced. But many ambiguities and potentially risky presuppositions derived from the central role given to experientiality mar the simple definition:
What is told is a “story,” something sequential, coherent, presumably with a beginning, a middle, and an ending—“first things first,” as Aristotle would say—implying once again that there is a pre-formed story to be told, that “telling” is primarily “re-counting,” a repetition with or without variations. Why not, if this is what happens when a child asks Grandma to tell him the story of Snow White and the Seven Dwarves, or when I was eyewitness to a cat and dog fight and I shaped the scene into an anecdote that I will re-cite to my neighbor—and much literature relies on these rituals? But a story can never be transmitted whole and intact by the narrative act, or the narrator would be reduced to the status of a robotic tape recorder. Even the story of Snow White owes its existence, like a Rorschach test, to its myriad collaborative reconstructions by the millions of receivers it has accumulated in the course of time. “Narration” should be understood as the enunciation of a discourse or parole from which it is inferred that a story might be constructed. The “narrated” is not a story, but a program to build one in agreement or disagreement with the intentions that are deemed to underlie the text in which narrative discourse is used. The juxtaposition, in one textual frame, of two incompatible descriptions—like the before and after pictures in weight-watching advertisements—is both a program of the sort and an incentive to activate it.
If the formula “narration is the telling of a story by a narrator” is not an empty tautology, it implies that the narrator is not just a role, function, or device but that he/she is a quasi-person who should be and is usually perceived as a character active in the narrative of narrating: “According to Ansgar Nünning ( 2001 ), this narrative act is often portrayed in such a lively manner that it constitutes a ‘secondary mimesis’ of the act of narration: the narrational process itself and the figure of the narrator seem to be part of a second fictional world, that of the narrator as s/he tells the story.” 24 Autobiography and autofiction are ready examples to support this remark. Such a superimposition of “stories,” even when it is a mere projective fantasy, can be profitable to complicate literary narratives and enrich their hermeneutic ambiguities, but it can also be circular and drastically reductive, if the story of narration is expected to explain the narrated contents and their form. The most banal readings of autobiographical narratives, those destabilized by Marcel Proust and autofiction , offer arch-examples of circular reasoning in this respect. We could call this convenient naiveté the “narrational fallacy,” one so successfully exploited by self-reflexive narratives of all times, fictional or not, from Don Quixote and Tristram Shandy to critical accounts of the latest terrorist attack.
It is therefore of crucial importance to avoid using the adjective “narrative” indiscriminately for phenomena and structures that pertain to narration, focalization, presented world, and gloss. In order to describe the relations between two or several narrating instances within a narrative, the unfortunate expression “narrative levels” should be replaced by “narration levels” or “narrating levels” or, better, by “narrational levels.” 25
Narrative and Narrativization/Denarrativization
If “narrative” is so pervasive in the human world that it is finally our only way of making sense of the world and of ourselves, if we are redefined no longer as mimetic (imitative) animals but as narrating animals, if speech is narrative in essence, and if we are ipso facto more human and more alive when we are more “narrative,” “tale-men” like Ulysses, there is no point in distinguishing “narrative” acts of communication from any other act of speech. Moreover, a tall tale would be more “graphic” than a sound, precise description, and the curse on the “accursed kings” a better explanation of their evil behavior than the anarchy that marked the coexistence of late feudalism with the budding nation-states of Europe.
In other words, we would deprive ourselves of the higher understanding of social and personal phenomena accrued by the two opposite mental gestures of narrativization and denarrativization, and their various modalities, depending on the shape, nature, and dimensions of time that condition these processes. Let us consider, for instance, one of the most famous among the many still renderings of the “death of the lovers” final scene from the Greek legend of Hero and Leander, a painting by Paul Rubens, c. 1604 (figure 1 ).

Figure 1. Peter Paul Rubens, Flemish, 1577–1640, Hero and Leander , c. 1604.
Its general structure is characterized by a circular or rather elliptical convolution of the figures, the visible shape of a whirlwind or a maelstrom, caught at a particular moment, but not situated in linear time and endless in principle. The decorative and erotic/anatomical values, typical of baroque art, are complemented by the presence, obscure but close to the few sunrays—a source of light often encountered in Christian devotional painting—of two tiny figures that seem to be flying above the main scene but are also embedded in a secondary marine landscape, under clouds shaped like eagle wings. These figures, whatever they are supposed to represent, contribute to an allegorical interpretation of the painting. If it were only for the livid, presumably dead male body floating on the surface of the sea and surrounded by very lively, full-fleshed Nereids, we could be satisfied with reading the scene as one more representation of “death and the young man,” the fragility of human lives exemplified and exalted by the age and beauty of the young deceased adult. But one human figure, on the far right side, departs from the overall structure and conventions in two remarkable ways: it is partly clad, in a red robe, and it is upside down, falling from nowhere toward the rocks or the foamy waves underneath; we cannot tell. This figure breaks the unity and permanence of the whole. We have to question it in the specific terms of “What is happening?”—“What happened?”—“What will happen next?”—“How will it end?” This figure therefore constitutes what we could call a “narrative prompter.” It is a readerly way of seeing what Amy Golahny already noted about Rubens’s innovations: “Rubens enhanced the dramatic content of his literary and pictorial sources—achieving a marked synthesis of action and expressiveness—by juxtaposing the two deaths and by giving such prominence to the nereids.” 26
In another painting, Romantic this time, by William Etty, first exhibited in 1829 , the naked, lifeless, livid body of a young man is stretched on a rocky ledge, the abrupt shore of a stormy sea. 27 A young woman, over him, upside down, embraces his torso and presumably touches his neck with her lips. Beside its somber and hesitant eroticism, beside the absence of warm colors and the shocking encounter of dominant verticality with the narrow horizontality of the sea horizon, and other formal and symbolic features that generate a whole set of emotions—sadness, admiration, fear, and compassion—in the beholder, the situation depicted is one that cannot last forever in human time, and it cannot have frozen a long time ago. The traumatic moment needs to be motivated in order to transcend trauma and achieve catharsis or at least some sort of moral recovery, and it also wants to be prolonged and/or transformed into an actualizable not-yet. This is when we narrativize our vision of the painting, supposing prior events and events to come without which the present of the scene would not be a present, could not be embedded in our experiential lifetime. We will say that the young man has drowned in the sea a short while before the moment depicted, that the young woman who expresses extreme grief may not survive the death of the young man she loved. The long title given by William Etty to his painting, “Hero, Having Thrown herself from the Tower at the Sight of Leander Drowned, Dies on his Body,” does half of the narrativizing. But it is the paradoxical stillness of the painting itself that accomplishes implicitly the eventual denarrativization without which the events would remain gratuitous in the ethical realm of legend and myth. The immobility of the bodies in their perfect pose, beyond any movement and defying any alteration, tells us silently that “the lovers are now united for ever (in death as they were in life).” The chain of events also needs to be denarrativized in order to transcend transience and abolish precedence and successiveness so that narrative meaning can eventually be transformed into moral law and injunction.
In a silent movie, the 1920 version of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde , we can see successively a figure with similar features acting good, then bad, then good again: if we say that they are the same person, we also see this person as changing, transforming, time and again; we narrativize the filmic text. But, if we say that they cannot possibly be one and the same, that there are two different characters to carry out good deeds and crimes, we have two parallel, contrasting portraits, but no change; we de-narrativize the sequentiality of the movie. And, if we hesitate between these two interpretations, endlessly oscillating between ontological identity and non-identity of the two human figures, we relativize the notion of change itself as we are tempted to refuse to choose between the different meanings generated by a linear, a circular, or a spiral vision of time. Italo Calvino has played very cleverly with successive narrativization, de-narrativization, and re-narrativization in his moral tale The Cloven Viscount .
As Jan Alber noted very aptly, Hayden White and Monika Fludernik agree that the general purpose of narrativization (“giving narrative form to a discourse”) is to facilitate “a better understanding of the represented phenomena.” 28 For White, it is a manipulation of the reader with ulterior motives—the reader is always in need of coherence, reassured by a causal chain. Fludernik argues on the contrary that “experientiality both subsumes and marginalizes plot.” 29 Her “natural” vision of narrativization, that, out of basic necessity, “applies one specific macro-frame, namely that of narrativity , to a text,” aligns once more with Aristotelian thought, and fails to see how the denarrativization of possible plots, by synchronic historiography, lyrical poetry, or even the final stasis of happy and tragic endings, fulfills the equally basic human need of resisting the tear and wear of linear time and confronting mortality with the inscription of permanence: the image of Charles Bovary sitting dead on the bench at the far end of the garden is not there just for the sake of narrative coherence, but because his clumsy love of Emma is now liberated, as it enters the non-time of metaphor. 30
Narrative Mimesis: Fiction or Non-fiction?
In the West and elsewhere, the theory of narrative and narratology (the study of narratives) at large originates in a poetics of fiction, understood as the art of “as if” and the mimesis of possible worlds based on human experience and the supposed spiritual, psychological, and physical nature of man. David Gorman notes, sadly and quite rightly, that “throughout the history of literary study, the overwhelming majority of narratives of interest to critics have been fictional; indeed, the terms fiction and narrative seem often to be used as synonyms.” 31 In spite of this initial warning, though, this author proceeds as if there were a necessary link between “narrative,” “fiction,” and “literature.” But the consequences of the reification of “fiction” are disastrous for the understanding of the phenomenon of narrative. For sure, “possible worlds,” in the sense of Pavel, Ryan, or Doležel, are crafted by the human mind; they are no longer transcendent, metaphysical objects to be discovered as they were for Gottfried Leibniz, but it does not mean that they are representations of a human world. 32 A man-made tool, including computers, is first of all a tool before it can symbolize, let alone represent, the human mind and the human condition. An encounter with the non-human has always been what happens most strikingly to humans in realist narratives as well as in fantasy. Denying the narrativity of social realism, chronicles, or scientific cosmologies, as does Herman among others, bars us from understanding the full richness of the games literary narratives play with time and being. 33
With or without boundaries between fact and fiction, three assumptions are made by most theorists who place the question of fictionality at the center of both literary and narrative theory:
Fictionality depends on the intentionality of the human/anthropomorphic sender of the message, typically a non-deceptive intention to convey meaning through the fabrication of something inexistent as if it existed. This is in apparent contradiction with Lavocat’s contention that fictionality (or “fiction”—she uses the two words interchangeably) boosts the hermeneutic drive of the receiver by creating an obstacle to the automatic, straightforward transmission of information based on a strong belief in the referentiality of the message, thus de-automatizing literal comprehension. 34 In this case, the most efficient booster of interpretation should be our wariness about the sincerity and truthfulness of the sender. As far as narrative is concerned, though, Hayden White’s rhetorical approach is the most convincing at a basic level: the narrativization of the relation between discrete objects consists in supposing an ontological continuity of these objects through (linear) time, so that discrepancies of one or more features of these objects can be interpreted as events. Narrative as such could therefore be seen as a special metonymic operation that substitutes contiguity in time to spatial contiguity, while fictionalization, indifferent to the time factor, is more akin to metaphor.
The second assumption is that since human beings experience their lives as narratives, narrative discourse is the most natural or spontaneous tool to convey meaning. This idea is a generalization of a notion acquired through the analysis of myths and fairy tales and is generally supported by both psychoanalysis and causal history, based therefore on a deterministic rule of origin: a tribe is a community by kinship, a church is a community of worshippers of the same creator and the same prophet/founder; members of the community identify with a story of themselves that was already told/written before the event. But literary narratives, from the very beginning, are different from sacred texts; they are not only the repetition of a myriad-times-told tale; their looseness turns them into a breeding ground of emergence, of the unexpected. In each embodiment of a preformed story there must appear elements that are at variance with this original story; the tension between portrait and change, between different or even antagonistic spatiotemporal coordinates, opens the playing field of possibilities that is constitutive of literariness, even for Aristotle. Narrative, insofar as it leaves these options open, can serve literariness. If it does, it is not past-oriented: you cannot change the past. If fiction was that which “makes exist what does not exist,” or was “presenting as existent what is non-existent,” it could not be differentiated from lie or error. We must sever all a priori dependence, all supposedly “natural” or experiential links between fictionality, literariness, and narrativity in order to observe their interplay and the added value that this interplay can bring to human communication. To take one obvious example, look at what happens in a modern Western secular context to canonical literary narratives such as Hellenistic romances, Hamlet , Don Quixote , Great Expectations, Mrs Dalloway , or Waiting for Godot . Each of these narratives gives an unforeseen twist to temporality.
The third assumption equates the difference between fiction and non-fiction to the opposition between referentiality and non-referentiality, referentiality being taken here in the sense of pointing at something that “exists,” that belongs to the sphere of “the real.” In the framework of a reflection about literary narrative, we will provisionally leave aside the relevance of “fiction” in communication through media other than natural languages. The reduction of “referentiality” to an empirical or scientific notion of the real is highly detrimental to a historical apprehension of both narrativity and the fluctuating ontological status of the objects involved in events. If we understand fictionality as polyreference to two or more universes characterized by incompatible features, such as sacred and profane, real and imaginary, virtual and actual, or concrete and conceptual, etc., panfictionality theory does not run against the ethical “Auschwitz test.” 35 It is not liable to accusations of negationism, as Lavocat is prone to hint. 36 Nevertheless, we have to accept that, where narrative is concerned, the principle of panfictionality generates the risk of substituting pseudo-cognitive events to material events, the story of the discovery of a “hidden truth” to the story of what happened or probably happened. Since narrative meaning is not a natural given but cooperatively constructed, negotiated, narrative truth is not a given; it can only be established through an argumentative dialog.
The future remaining generally more hidden, less knowable than the past, grand predictive narratives (apocalyptic, millenarist, or on the contrary, eutopian, idealistic projections) are a privileged terrain for preferring the neatness of a narrative Gestalt to the incoherence produced by lawless chance.
Narrative Versus Non-narrative in Literature
When Genette affirmed that there was no difference of ontological status between narrative and description, he could be held partly responsible for later developments of narrative theory that would self-defeatingly hollow out the narrative specificity of certain texts. But literature uses narrative in order to fulfill its aesthetic, ethical, and political purposes, and narrative uses literature to fulfill its own political agenda, conservative or revolutionary, communitarian, cosmopolitan, or disruptive, in particular traditions and at specific cultural moments. Storytelling is of all times, but non-narrative discourses can counter it as much as they can support it.
Narrative As a Genre of Discourse
Narrative discourse is the whole set of what is said and thought, in a cooperative or conflictive fashion, when the world of reference is seen as actually or potentially transitive, subject to change. This set of communicational transactions is the locus of narrativity.
“The degree of narrativity of a given narrative depends partly on the extent to which that narrative fulfills a receiver’s desire by representing oriented temporal wholes …” 37 Discourses can be called narrative when they manifest their participant minds’ desire or acceptation of a world view according to which existents are subject to change at one or several points of a linear temporal continuum. Although story-logic adepts 38 minimalize their role in the construction of narrative meaning or experientiality and sometimes risk confusing narrational speech events with change in the presented world, 39 events—i.e., the manifestation and perception of change—are unanimously held to be the nucleus of narrative discourse, as maintained by Genette. 40 Reis also comes to this conclusion in his commentary of Van Dijk. 41 No narrative is ever self-contained; it neither can nor has to represent a temporal whole: a closed temporal whole would cut off the temporal continuum that is the possibility condition of events. Many narratologists, confusing narrative with plot, demand a sequence or series of correlated events to label a text “narrative,” but, if all these events were locked into a closed temporal whole, with no before or after, they would amount to a static world-description, uniformly valid for a certain duration, as in synchronic historiography. Narrative discourse, as the eventful or processual discourse of change, operates in specific contradistinction with various kinds of non-narrative discourses.
Figure 2. Coste’s ( 1989 ) transformational tree, from Narrative as Communication , University of Minnesota Press, 49.
Consider one of the narrative statements presented in figure 2 , “Peter died.” It reconciles in terms of an “event” the contradictory descriptions “Peter is alive” + “Peter is dead” by indicating that they describe the entity “Peter” at two discrete moments on a linear time axis. This kind of narrative is not or is little interested in action and causality; its point is not concerned with who or what killed Peter. Such narratives are more about time (and space) than about agents. The statement “John killed Peter” combines two non-contradictory but otherwise unlinked non-transactive narrative statements: “John became a murderer (or: turned out to be a murderer)” and “Peter died.” Obviously, one key locus of narrative interest, or narrative tension, is the grey zone between the two narrative levels of discourse whose analytical complexity already invites us to indulge in multiple, or even endless, interpretation, with its accompanying emotions (hence, very probably, the temptation to equate literature with the thrill of narrative discourse). 42 More intricate and more aesthetically and cognitively exciting yet is the game played by those literary narratives of process, of becoming—the Bildungsromanen of Henry James and Marcel Proust—or of decay and decline (Franz Kafka) that hesitate deliberately between mere sequentiality (chance) and a deterministic system of causality.
Narrative discourse, whose precondition is the relevance of linear time to its meaning and significance, should not only be analyzed in this respect but also contrasted with other genres of discourse, such as argumentation, commentary, and the lyric, that have little to do with linear time or at least try to negate it through strategies of effacement and dismantling of linearity. For instance, two aspects usually studied are the prevalent question of enunciation (who speaks?) and that of the presence or absence of narrative discourse and narrative programs among the lyric: “the more a poem foregrounds vocal effects, … the more powerful the image of voicing, oral articulation, … the less we find ourselves dealing with the voice of a person.” 43 In other words, the more lyrical a poem is, the less it relies on “character,” which is still a way of making out the lyric from narrative in Aristotelian, actional, and anthropomorphic terms. Thus, along the lines of a case grammar, narrative would rather be dominated by the nominative and the accusative, while the lyric would foreground the vocative and the dative, since it is primarily concerned with calling what it names to existence and presence and seducing whoever it addresses with free offerings that would hopefully generate counter-gifts. In the European 18th century , the critique of a futile rhetoric of ornament in the lyric was followed by the Romantic surge of the expressive function: the speaking subject, in a dramatic revolutionary context, became a kind of narrator as he told his transience in an accelerated time stream.
Units and Concatenation
The quarrel of minimal units.
When Prince defined a “narrative statement” as “an elementary constituent of discourse independent of the particular medium of narrative manifestation,” adding that “the discourse can be said to state the story through a connected set of narrative statements,” he seemed to accept a commonsense constructivist view of stories. 44 But the issue becomes immediately blurred by the subdivision of narrative statements into “process statements (in the mode of Do or Happen ) and stasis statements (in the mode of is ),” implying that stasis statements are also narrative. 45 True, a text certainly does not need to contain any explicit “process statement” for us to construe its meaningfulness qua narrative; when we are told somewhere that Julien Sorel climbs a ladder to court Mme de Rénal, and, somewhere else in the same volume, that his severed head lies in the lap of Mathilde, the principle of non-contradiction requires that we situate the two stasis statements at different points along a linear temporal axis. Even if both statements were in the present tense and the second were textually placed before the first, we would have to bind them in linear time and choose between the event of death, if we do not believe in miracles, or resurrection, if we believe in them. When contradictory “stasis statements” alternate randomly, the formation of consistent, safe narrative meaning is impeded by apparent textual incoherence and the lack of allegiance to a linear notion of time. The nouveau roman as well as fantasy, surrealist texts, and magical realism have often played with the juxtaposition of incompatible “stasis statements” in this way: an excellent example is found in Alain Robbe-Grillet’s Les Gommes ( The Erasers ), whose Spanish translation was published under the title La doble muerte del professor Dupont (Prof. Dupont’s Double Death). But the narrative drive, however unfulfilled, remains the motor of reading; its presupposition and its astute deception oblige the reader to pay attention to the dispositio of signifiers where another kind of aesthetic enjoyment will take root.
Unlike Revaz, we should therefore remain attentive at once to the rhetorical uses of narrativization/denarrativization and to the frame in which minimal narrative (or non-narrative) units are considered. 46 Both Barthes and Genette were intuitively right when they proposed that a (coherent) narrative of any size could be seen as an expansion of a single process statement (the famous “Ulysses returns to Ithaca” for The Odyssey , or “Marcel becomes a writer” for Remembrance of Things Past ), but they erred in two ways: such minimal narrative or “process” statements, nowhere to be found in the texts under scrutiny, should also be considered as condensations or summaries of many narrative and non-narrative statements rather than minimal units similar to “Zorro has just arrived.” 47 A minimal(ist) narrative ( “recit minimal” ) must be viewed as a self-contained or self-framing act of narrative communication, but minimal units are building blocks that may fit or not in a frame drawn to satisfy our anthropological needs for continuity and coherence. Narrative syntax, in the etymological sense of “syn-tax,” is the articulation of minimal narrative units in the textual, experiential, and diegetic spatiotemporal frames required to obtain coherence, sequentiality, and, eventually, sometimes, causality.
Kinds of Narrative Syntax
Narrative syntax is far from being uniform; it does not espouse a single model: for example, “states” and “events” can be textually juxtaposed (in close succession) without necessarily inferring a referential relationship between them in the presented world, or they can appear far apart and be construed by narrative memory as bearing a necessary causal relationship—without which their co-presence in a text (in a set of acts of communication that constitute a whole) could not be justified. When we read or hear that “a bird soared, the bathtub overflowed, a dart was shot,” asyndetic parataxis does not operate in the same way as in “John met Mary, Peter threw a tantrum.” If, to put it in Laurence Sterne’s own words, “Great wits jump,” they can do it in two very different ways, either jumping to the side, in order not to be crushed by the tragic demands of narrative determinism (this is when digressions occur and at times multiply), or jumping to conclusions: if we discover, after any number of pages, that “Peter threw a tantrum” and his anger cannot be explained by anything else, we might promptly relate it to the earlier statement that “John met Mary,” inferring for example that jealous Peter was secretly in love with his virtual friend Mary, but, contrary to John, never had a chance to meet this remote screen princess in real life … In classical detective stories, clues, true or false, emerge retrospectively, hindsight fabricates past omissions and dissimulation on the background of which otherwise far-fetched causal links, newly forged, shine all the more strikingly. To quote Sterne again: “It is the nature of an hypothesis, when once a man has conceived it, that it assimilates every thing to itself, as proper nourishment … This is of great use.”
Not only is narrative syntax diverse with regard to parataxis, hypotaxis, and their more or less strict separation and/or their more or less complex combination, but it can be put to widely different uses, employed as a decoy or turned into a tremendously powerful hermeneutic and heuristic machine. Whatever these uses, deceptive or enlightening, narrative syntax is one of the main means of production of aesthetic emotions in literary narratives. Loose syntactic links, those of simple verbal consecution, often require considerable effort on the part of the interpretative community and the individual receiver at the time of putting two and two together; their fatigue and frustration may lead to an entropic or a chaotic perception of the presented world and of language itself that is not infrequent in Samuel Beckett’s works or in American metafiction but was already found in the medieval Story of the Grail by Chrétien de Troyes—not only because it is unfinished. The wasted effort to achieve narrative coherence must be compensated by another kind of reward, an aesthetic reward. Conversely, with conspiracy theories as well as tragedy, the prevalence of tight syntactic links, a high degree of indexicality (owing to the systematic use of appropriate shifters, for example) will easily lead to the notion that everything fits all too well, that nothing happens by chance, that the fatal issue (or the happy ending, why not?) were literally bound to happen, and modern aesthetic sensibility—touchy about subjective freedom—can be hurt by the authoritarian resonance of an apparently implacable, deterministic logic.
Roles in Literary Narrative Communication
Without extrapolating the roles of anthropomorphic entities (author, narrator, character, receiver) from narrative to all literary communication or reducing these roles in narrative communication to their common denominator with other forms of literary communication, it is desirable to examine them at least in one of two ways: as virtual positions filled, when possible, by actual agents, or as empirical behavioral sets (groups of actions) conceptually projected as quasi-subjects. Actual authors, storytellers, receivers and commentators, members of interpretative communities are not only the effective human beings who carry out certain roles without which narrative meaning or significance would not happen or would not be traded and transformed into world descriptions or supports of ethical and political values. They are also those who watch their own images in the narrative text, draw them from the manipulation it exerts upon them and forge flattering or disparaging self-portraits from its interpretation. Considering that the nucleus of “narrative” is a statement of change (in the world of reference), with the status of “event” if it fulfils some particular additional conditions—of relevance, irreversibility and (perhaps) unexpectedness 48 —narrative effect consists not only in breaking a temporal continuum but also in disrupting a principle of identity or consistency. The most characteristic and striking events that can affect an entity or a character, such as birth, metamorphosis, death, name change, kinship and relationship mutations, point at the paradox of narrative: they radically alter a subject at the most fundamental semantic levels (descriptive, definitional, or even ontological—“she/he has become unrecognizable,” “she is not the same,” “she is no more”)—while at the same time identifying the altered subject as the one to whom “it” happened to become other or another. The eventness of narrative defeats our need for coherence, persistence, and stable definitions in the first place; it makes us shout “What?” or exclaim “Wow!” orally or using digital emoticons and stickers, but, at the same time, it is our readiest recourse to restore coherence, the easiest prosthesis of identity. The difficult path from trauma to reconciliation, from time as killer to time as healer, with its many setbacks, cannot be trodden by a lone subject; it requires complex games of projection and introjection, identification and dissociation; it wants a dialogical, conversational cooperation that is at once polemical and geared toward conflict-solving through negotiation and role playing. Following the track opened by The Epic of Gilgamesh , Homer’s Odyssey , Don Quixote , and Proust’s Remembrance of Things Past are among the most magnificent and increasingly self-conscious illustrations of how narrative struggles with its own paradoxical assumption that the subject can only manifest itself in the alterations that make it different from itself. All the theories of narrative that assign to the teller (the enunciative instance, author, narrator, or “unmediated” performer) the entire intentional responsibility of narrativity are blind to the necessary cooperation of participants in the narrative act of communication. Their collaboration consists not only in playing their respective nominal roles (“the author writes, the reader reads”) but in trying out or impersonating all the other roles: the author reads, the teller listens, the reader writes, etc. Understanding and coming to terms have a cost. The double-edged economy of narrative communication is thus similar to the oscillation between defamiliarization and refamiliarization adumbrated by Russian formalism and Victor Shklovsky. “The better a story is, the more text-like and meme-studded, the more cognitive labour it paradoxically requires, not only from tellers , but also from the hearers who become totally engaged in the process of drawing out its multifarious implicatures. This seems … certainly true of the high literary texts of a culture, where not only individuals but institutions make it their business to obsessively interpret.” 49 The same theorist pursues: “My further … contention is that the pleasure we take in retrieving perlocutionary effects … from stories, remains observable in the most ordinary of our conversational anecdotes.” This approach comes with two very important implications. First, the visibly complex narratives of high literary culture—like Joyce’s Ulysses —can and should be distinguished from simple conversational anecdotes that they do not just amplify or load with ornament, but there is no difference of nature between supposedly natural and unnatural narratives: high narratives do not necessarily proceed from low ones, or vice versa. Instead, the production of narrative significance always engages the same cooperative processes. Aesthetic and cognitive pleasure, pathos and gnosis , are intimately linked in the training of emotional intelligence, “which is to say, our skills at interpreting, simulating, and responding to emotions.” 50 The protracted debate between a merely semantic, denotational concept of narrativity and a relative, gradational notion has to do with the separation or not of sense and intensity but also with framing, contextualization, models, intertextuality, and intermediality.
Absolute or Scalar Narrativity
“Narrative designates the quality of being narrative, the set of properties characterizing narratives and distinguishing them from non-narratives … It also designates the set of optional features that make narratives more prototypically narrative-like, more immediately identified, processed and interpreted as narratives. In the first acceptation, narrativity … is usually considered a matter of kind … In the second acceptation, narrativity is a matter of degree …” 51 According to these definitions, narrativity would depend on substantive features or properties that presumably pertain to a text in which they are somehow inscribed (or missing), features ready to be recognized by a reader before he can consider, process, and interpret the said text as (a) narrative.
At the level of elementary units (sentences or even simple clauses), the presence or absence of a predicate of change is certainly decisive. Out of context, the receiver has no choice but to perceive “John came over” as narrative and “John is a boy” as non-narrative, just like a “no smoking” or “no parking” sign posted anywhere must be understood as injunctive, if they are understood at all. When the text exceeds the single sentence or clause in extension and complexity, or when a single sentence needs context to be disambiguated, interpretation is required prior to the attribution of narrative meaning. This attribution depends on framing and selection, on the readiness, desire or fear of the individual or collective receiver: the interpretative communities to which they belong will play a key role. Narrativity, then, is no longer just a matter of verifiable presence or absence of certain features in the text but a matter of intersubjective negotiation. In this sense, there would be three rather than two modes of existence of narrativity, in literature as elsewhere: the absolute and scalar modes described by Prince, but also an optional mode that occurs when we ask: “Did something happen, or what?” or when we deny the eventness of something that did happen in the world of reference, calling it a “non-event” or commenting in a jaded tone: “nothing new under the sun.” Narratives with an open ending—those, like The Magus by John Fowles, that maintain cliffhanging suspense intact until the last word inclusively, or indefinitely, suspended searches like unresolved criminal cases or filiation quests—can by no means be deemed less narrative as a whole than a conventional love romance that in the end happily marries the suitable boy with the suitable girl. Even the disjointed structures, the elusive endings, and the probabilistic futurity of so-called post-modern literary narratives have generally not met with an appropriate revision of narrative theory.
Questioning whether we are dealing with a static world (describable once and for all for the duration of its existence), with one that is in process (becoming, growing, blossoming, or aging, shrinking, and vanishing), or open to change is an essential aspect of narrative communication. Audet, quoted by Porter Abbott, makes an important point when he proposes a notion of “eventness” (not “eventfulness”) “where the tension between a before and an after seems to generate a virtuality, that of a story to come.” 52 If narrative tenses are most commonly of the accomplished past, the orientation of narrative discourse as one genre of discourse among others, or as a mode among others, is turned toward the future , the possible but not-yet. 53 Past counterfactuals, for example, mediate analogically with possible things to come. Again for the same reason, many forms of the disnarrated (“John did not come,” “Mary would not wait for John,” “Mary did not realize that John was always late,” etc.) or juxtaposed incompatible descriptions are indeed more narrative, that is more prone to induce narrative meaning than chronological lists of events (“George W. Bush was elected president, then Barack Obama was elected president, then Obama was re-elected for a second term, etc.”). The former phenomena are pro-narrative; they imply a narrative program; they call for projective narrative thinking to make sense of them. Conversely, consistent cumulative eventfulness will automatically tend toward a static worldview: a character portrait (“as eternity changes him into himself”); descriptions; physical and moral laws (“natural disasters occur whenever man neglects his duty to the divinity”). Beyond the paradox of emplotment, but similarly to its effects, the heuristic value of narrative is equally threatened by its accumulative quest of mimetic exhaustivity: “It has often been said that narrative somehow banishes chance. Leland Monk says this in his study of chance in the British novel, that ‘chance is that which cannot be represented in narrative’ despite the manifest efforts to do so in the novel of the late Victorian and modern period.” 54 Totalization, therefore, is equally “catastrophic for the categories of choice and freedom, … even while the efforts to represent free choice have produced some of the most important developments in modern narrative technique.” 55 Narrative theory should now follow the example of such developments; it must not forfeit the unexpected to satisfy the foreseeable.
This is why a distinction between quantitative and hierarchic dominance of narrative discourse remains useful. With quantitative dominance, in narratives of adventure, travelogues, picaresque romances, surreal and fantasy narratives, biographies rich in varied experience, national histories full of Sturm und Drang , something new happens all the time (discoveries and encounters, victories and defeats, gains or losses, mysteries and explanations …). In vast architectonic epics (John Milton’s Paradise Lost and Paradise Regained , Sri Aurobindo’s Savitri ) or elongated Bildungsromanen ( Great Expectations , Remembrance of Things Past ), a comparatively small number of major incidents are highlighted, but all descriptions, non-events, imperceptible changes eventually converge toward the formation of a single and simple summary (“Mankind was—or will be—saved,” “Marcel becomes a writer”). Since the genre of the classical, realist short story or nouvelle (not the anecdote or the folk tale) has a vocation to concentrate on a single story line and only one or a few protagonists and must at once provide enough context to make sense of the key event or process, it will often combine the quantitative and hierarchic or qualitative dominance of narrativity, as in Stefan Zweig’s works—or Guy de Maupassant’s or Henry James’s.
But literary genres like those just evoked are not abstract, transhistorical kinds; they are deeply rooted in historically inscribed, cultural conditions of production, transmission, and reception that orient the production of aesthetic and ideological value without which narrative interest would be reduced to an empty game.
Toward an Aesthetics of Literary Narrative
When a narrative is judged to be “well formed,” its emplotment, the progression of action, the spacing and collocation of incidents (events), correspond to certain narrative patterns that recall canonical/patrimonial literary, historical, sacred, or mythical narratives stored in the collective cultural memory of a civilization and/or a natural language. This aesthetic judgment bears specifically on literary narratives as narratives. Other aesthetic aspects, such as rhetorical and stylistic ornament or the lack thereof, enunciative devices like prosopopeia, or a lyrical (vocative) mode of address, may either reinforce narrativity or run counter to it. Both ornament and the well-formedness of literary narrative have been the object of many attacks over the centuries in the West, especially in certain periods, such as the baroque, the avant-gardes, and postmodernity: we will examine these attacks and their effects under the rubric of “dissident aesthetics.” Finally, we shall confront the Western tradition of narrative aesthetics with one non-Western tradition that still keeps a hold and a creative impact on contemporary literary narrative production.
Well-formedness; or the Legacy of Beauty
Even after successive ur-narratives, foundational fictions, master-narratives, and grand historical narratives all started to crumble under the combined fire of the sciences (each with its own field restrictions and limited purpose), the defeats of utopias, the experience of disaster, and the rebellion of the masses, a global narrative vision of the world (in the sense of trying to read it as a single coherent story) keeps creeping back, recalling all the losses suffered with the death of the king, the death of God and the death of empire. Ancient mythical, religious, and genealogical narratives (or their substitutes generated by and for market economy), democracy or human self-rule, the theory of evolution, and physical cosmologies share a sense that a lost order, or one that never was, must be restored or established in the end. Once the epic and even the novel were all but stripped of their credibility and relevance, the object of nostos could no longer be a fatherland; it became the art of narrative itself, in which the deepest truth and the utmost beauty were one and the same ( anagnoresis and catharsis hand in hand). But, as the human subject, now a self-made man, no longer preexists its representation, this art in turn is also threatened to be dislocated from the mimesis of action to the mimesis of mimesis.
From the beginning of the 20th century , reactions to this state of affairs have been very diverse; they are all manifested in dominant narrative theories concurrently with the steady production of mainstream literary narrative and the prosification of the lyric. Early structural and formalist narratologies dealt preferentially with simple, popular, traditional types of narrative (Vladimir Propp’s Morphology of the Folk-Tale , 1928 ; Andreas Jolles’s Einfache Formen , 1930 ) or with the short story (Algirdas Julien Greimas’s, Maupassant: La sémiotique du texte , 1976 ). French structuralism, in its softer, more flexible version, with Genette’s Narrative Discourse ( Figures III ) ( 1972 ) after Roland Barthes’s S/Z ( 1970 ), multiplied grids and codes to deal with the underlying structures of complex and ambiguous works. It is striking that the choice by Genette of Proust’s magnum opus to nourish, develop, and test his reading grids applies to a monument with a “good shape,” beginning with the evocation of a preterit habit and ending with salvation (the promise of the recovery of a past wasted because it had not been processed and recorded). The many characters, scenes and incidents in La Recherche appear in this light as so many single-minded moments and objects of a long struggle to retrieve (the memory of) the time lost and therefore become a writer. The condensation of the narrative skeleton into a single backbone (“Marcel becomes a writer”) and the imposition of a hierarchy between the red thread of a life story and its fleshing out with details (the level of “écriture”), was attacked by some early reviewers of Genette’s work, approved by others. 56 Both blame and praise were motivated by Genette’s openly anti-aestheticist attitude at the time. His structural method of description, like other methods introduced in the 20th century (literary psychoanalysis, sociocriticism), was an easy target for the “old” critics prone to accusing the “new” ones of ignoring the differential value of high literary language, the impact of stylistic complexities and ornament. In fact, we can now realize that Genette, his supporters, and his detractors alike had it all wrong in this respect: the aesthetic criterion was left intact but it found the quality of Proust’s monument in its overall design, in its engineering rather than in the refinement of the stained glass work of the “cathedral.”
Other major and massive narrative fictions of the first half of the 20th century , such as James Joyce’s Ulysses or Robert Musil’s Man without Qualities , were not favored by “classical” structural narratology because they did not fulfill the conditions of a successful account imposed by its methods: the outline of Ulysses purports to reproduce that of The Odyssey , but it shockingly combines the complex narrational levels and episodic elements of the epic of nostos with the unities of time and place of classical tragedy, the end product having to be read consequently as a critical, deconstructive parody of the demands of classical narrative aesthetics; Musil’s work, as a “story of ideas” and an errant quest for sense without any likely place to look for it, departs in too many respects from the goal-oriented Aristotelian notion of mimesis of actions; it was unfinishable in its principle and remained unfinished. Theorists were bound to leave most so-called postmodern and postcolonial literary narratives out of their field of inquiry, labelling them anti-narrative, if not non-narrative, or they tried rather obscurely to design specific, dissident narrative theories in order to accommodate the new dissident narrative aesthetics and the parallel oppositional tradition (Rabelais, Cervantes, Swift, Sterne, not The Faery Queene or Pilgrim’s Progress or even Robinson Crusoe ) on which the “new narrative” drew heavily to try and secure a place in the canon while at the same time finding in it “room for maneuver.” 57
Dissident Aesthetics
Dissident narrative aesthetics follows many different strategies of estrangement, disturbance, and renewal: foregrounding banality or accident, blurring the ontological statutory difference between objects and events, minimalism, maximalism, self-reflexivity, abstraction, fragmentation, rejection of the principle of non-contradiction, open choice between universes of reference, straining distortion or cutting up of linear time, warped frames, relative or irreversible spaces, etc. These strategies can operate at all “levels” or at any step of narrative communication, one of them can be hegemonic, or they can subtly complement each other to alter and rethink the values borne by “well-formed,” readerly, straightforward, easily recognizable narratives. An unreliable narrator (the liar, the uncontrollable chatterbox, the amnesiac, the mentally deficient, the taciturn and secretive calculating mind) will afford a ready justification for gaps and ellipses, digression, repetition, incoherence, inconclusiveness, over-information and disinformation. Conversely, ironic uses of the disnarrated, denial, and absurd maxims can build the figure of an all-powerful, manipulative author that may draw the receiver’s attention to the unconfessed manipulation carried out by whatever apparently clean narrativization of any represented world. Here, we can only sketch out a few examples of how dissident narrative aesthetics operates and how a self-labelled “postmodern narrative theory” tries to account for the varied operations of dissident narrative aesthetics. 58 Seemingly contradictory labels for the same work alert us to the high ideological stakes of tampering with the traditional ingredients of narrative significance: When Raymond Carver’s short stories are alternately or simultaneously labelled “minimalist” or “hyperrealist,” is a stock paradox like “less, sometimes, is more” sufficient to sweep off the etymological and conceptual contradiction between these terms? In the worlds of Carver’s short stories, very little happens; what is expected to happen according to the conventions of tragedy, romance, or drama fails to happen, and what does happen is reduced to triviality since it eventually does not achieve the status of story point. If we ask “so what?” the apparently pointless narrative will only echo back: “… what? … what?” The minimalist foregrounding of the trivial and/or the hyperrealist leveling out of the trivial and the non-trivial underscore the arbitrariness of the dispositio of events and the artificiality or utter lack of a causal system, the ideologically determined manipulation of literary as well as historical narratives at large.
Another interesting case is that of the comical, nihilistic, or absurdist narratives of untellability that abound in Western literature from the 18th century onward but have proliferated after WWII, with the nouveau roman, American and non-American metafiction, and Borgesian aporetic constructs. As Mark Currie remarks, “it would be misleading to describe new directions in literary theory as the cause of fictional change. There is a chicken-and-egg problem with fictional and a more general linguistic self-consciousness.” 59 If theory is not the motor of practice, or vice versa, their changes nevertheless share the same external, socioeconomic, political, or epistemological causes. The progressive but not smooth secularization of philosophical thought was concomitant with the discovery of the autonomous, exorbitant power of language and its dysfunctionality: our stories were no longer always already written by the sure hand of God, language was no longer a precious gift, the instrument of revelation, a tool meant to inform, tell the truth, and pass fair judgments; it could no longer even name mystery; its power of seduction and delusion was now other and proportionate to its inability to truly represent, to say things as they are or even as they might be, to tell (count) events as they happen(ed) or even as they might happen. When the authorship of our life stories was finally transferred to human responsibility without the means to forge a new language, fictional (and historical) literary narratives had to face the inadequacy of language, its vagaries, its constitutive incapacity to stick to experience, its usurpation of experience itself. Hence, in Tristram Shandy , the narrator’s questioning of the irresponsible behavior of his parents when they authored him, and the resolution not to do the same as the author of the book of his life. There is always an irony: the resulting theoretical fiction ponders its possible defects so thoroughly that it has to be content with describing and exemplifying the impossibility of a proper or prototypical narrative (traditionally: a mimesis of actions). The adventure (or the misadventure) of narration, as a substitute for the narrative of adventure, to use Jean Ricardou’s 60 famous chiasm once again, manifests a deep distrust of the narrative condensation of phenomena, of its facile seduction, of the relevance and accuracy of “narrative intelligence.” Theoretical fictions and metahistories deconstruct and kill narrative seduction, which may be a good thing for the critical mind and a bad one for the senses.
Are there any alternatives to this quandary? Could we find them in post-colonial narratives, and do non-Western works have a local narrative poetics of their own to rely on?
A Different, Non-Western Aesthetics? Rasa, Katha, and Narrative Emotions
Beyond implicitly recalling the principle of anthropological unity, hardcore structural semantics has little to bring to the narrative comprehension of a world increasingly divided by its push for globalization and its resistance to it. In particular, any narratology that fails to take into account the different and often complex sets of time concepts that prevail in any one culture, or its current and historical system of universes of reference, is bound to err grossly even at the elementary level of the definition and identification of narrative discourse and what it stands for.
Because some languages may foreground aspect rather than tense in verb phrases, and some cultures prefer relative to absolute dating, because some prefer to measure distances in time of transport and others in length units, we can no longer accept the diktat that the preterit or “simple past” is, generally speaking, both the natural and dominant narrative tense. Rejecting the hegemony of any one locally anchored notion of narrative does not amount to a dangerous first step toward radical cultural relativism, but to recognizing a systemic variety of contrastive processes by which narrative communication operates as a factor of negotiation—identity and consent, differentiation and dissent. While “West” and “non-West” or “North” and “Global South” may not refer to anything more than historically restricted cartographies of power and values, the objects and methods of narratology have, by definition, an anthropological dimension that makes them responsible to both the unity and diversity of humankind.
Narrative, as we already knew before Benedict Anderson, is heavily involved in the socio-historical processes of colonization and freedom struggles, globalization and resistance. Inevitably it is also, as testimony and as interpreted retelling, at the heart of discourses produced by the social sciences and/or the humanities about these modern cultural and political phenomena. In his suggestive but cautious advocacy of a “postcolonial narratology,” Gerald Prince states that “just as it endeavors to trace explicitly the definitional boundaries of narrative … , narratology tries to account for narrative diversity (for what allows narratives to differ from one another qua narratives).” 61 He insists that categories of time, tense, space, and person should be investigated across cultures. Nevertheless, no sustained effort has yet been made to relate postcolonial or non-Western practices and poetics of literary narrative communication to their respective aesthetic traditions or linguistic conceptualizations.
Indian aesthetics and poetics can be located at a safe and measurable but obvious distance from the Western (Aristotelian) tradition, with which it shares Indo-European linguistic structures and the centrality of the dramatic and epic modes of representation but not the same hierarchy of emotions or time concepts. At first sight, the combination of rasa (flavor, emotion, mood) and dhvani (suggestion) 62 that appears to be prevailing in long eras of Indian aesthetic thought in the past (although with marked variations of status) and has made a forceful comeback since the middle of the 20th century is much more closely associated with music, dance, and the performing arts, especially stage drama, than it is with verbal narrative, or narrative qua narrative. One contemporary theorist goes as far as saying that “in Indian aesthetics, the moral function of art has never been given a primary place as in the West (e.g., Plato, Aristotle et al .). Bharata in Natya Sastra … justifies dance, which fulfills the simple function of being beautiful, for leading us to delight.” 63 And again: “Morality has never been the main issue. One might find this strange. But … the rasa experience is a kind of delight that transcends ordinary levels of reality … Nonetheless [with] santa rasa … rasa experience does serve a moral function—it helps one overcome one’s worldly desires and achieve transcendence to a higher level.” 64 There are however, even in ritual practices, forms of katha that are told with an avowed moral, didactic purpose, and there are prayers, forms of puja (worship), that require the story of the prayer to be told in order to make the devotion efficient.
When Priyadarshi Patnaik applies rasa theory to Western narrative literature, he tends to denarrativize it, or at least to substitute a mimesis of mind events for a mimesis of actions. 65 This is particularly obvious in his choice of Albert Camus’s Myth of Sisyphus and its proposed interpretation, 66 according to which purity of mind and detachment through the experience of emotions and their universalization lead to santa , the rasa of bliss: “he is superior to his destiny and stronger than his rock,” writes Camus. The presentation of Sisyphus accepting his absurd destiny as a victory is not a narrative reading; a narrative reading would show that, by eternally repeating the same useless action, Sisyphus at best defines himself and depicts his (our) world as totally iterative, unchanging.
If we take it for granted that the essence of Indian art (verbal or of any other kind) lies in a total identification of the receiver with the work of art, be it a monument or a performance, “frozen at a moment of time for posterity [or] live for the moment in specific duration,” 67 and that it always and only moves outward in expanding circles from the still center so as to return to it, we would find it difficult to accommodate in this aesthetics any of the constitutive elements of what we have called narrative communication and narrative significance so far. Furthermore, Kapila Vatsyayan insists that “neither character nor plot is important in itself. They are interwebbed as a labyrinth and drama is always cyclic in nature.” 68
When one cares to demonstrate the autonomy of Indian narrative by listing aspects, such as interiorization, serialization, fantasization, cyclicalization, allegorization, anonymization, elasticization of time, etc. 69 —some of which are supposed to be present in all Indian narratives but all being in principle absent from Western narratives unless they were influenced by the former—there is nothing much left to compare, and the anthropological notion of narrative itself is dismembered. But, as Amya Dev observes pointedly, a closer analysis would probably show “that there is more in common between the Indian itihasa [epic] and the Homeric epic than not.” 70 He explains immediately that he cannot “fully understand the distinction … between temporal and spatial narrative. All narrative to my mind is an excursion in time.” Amya Dev had detected that the nationalist effort of dedicated Sanskritists to free the roots of Indian poetics from any proximity or affinity with the West is counterproductive insofar as it enforces a radical discontinuity between Vedic and medieval narratives, on the one hand, and modern narratives, on the other, while continuities exist and should be found, also in the permanent hybridity of all cultures, India included. Sri Aurobindo’s successful fusion of Milton, Ramayana , and modernist narrative poetry in Savitri is a striking piece of evidence to support Amya Dev’s views. Paniker, while acknowledging the deficiencies of Indian “critical discourse on fiction [that] was somewhat stillborn in the Indian tradition,” takes the notion of narrative for granted and limits himself to proposing a typology. 71 However, several of the listed features, such as serialization, provide very vivid insights into universal functions of the more participative narratives, from African griot epics to interactive digital stories. We might suggest that anthropological continuities of narrative functions across cultural spaces and historical times could be found in a non-dualistic or a minima a dialectical relationship between body and mind that are shared by Greek tragedy and the ever-revisited tragicomedy of Shakuntala , in which the key events of abandonment, encounter, loss, and recognition are all present and bodily inscribed, however differently they are ordered and with whatever different outcomes.
When Rukmini Bhaya Nair dismantles the metaphysics of the one and ineffable event presented by Maurice Blanchot in The Writing of the Disaster as “the ultimate experience, because it is indescribable,” she confirms the necessity of reintroducing affect and individuation in historical telling: “Numbers make history … But in order to render emotion, you need the individual mode, which can only be literary and artistic. That is the paradox.” 72 Handling this paradox is exactly what has made the modern Western novel since Cervantes possible. Rather than a free-floating postcolonial narratology, this is a good example of a hybrid, glocal narrative theory, one that reintroduces traditional Indian aesthetics along with carrying out sophisticated discourse analysis and displaying a self-reflexive awareness of the theorist’s inscription as a historical (narrated) subject in argumentative dialogue. Such a narratology, fundamentally based on conversational, other-directed oral enunciation, skillfully avoids the shortcomings of both the sublime on the horizon of European romantic thinking—or on that of the suprasensuous achievement of unity in Indian philosophy—and the postmodern sacralization of antinarrative open-endedness. Narrative can easily be another opium of the people, but, if we make out its variations from the constant pleasure generated by its experience, it is also one of the best sites to investigate the verbal ways of telling and showing how self-conscious bodies change and move in space-time—that is, how to cope with the inner and mutual otherness of humans and their worlds. In Salman Rushdie’s Satanic Verses , the book itself metamorphoses all the time as its characters do. Genre shifting and distortions mutually correlated with narrated contents is a shared property of all but the simplest formulaic literary narratives. “Narrative is a moderately historical concept … While narrative reflects particular historical conditions in how it became an object of study and in how it is given cultural meaning at different moments, it nonetheless describes a type of discourse that transcends a number of specific historical manifestations …” 73
Perspectives
Narrative discourse or communication is about the world as it changes, about things that move and people who travel and are perceived differently as they change location. It is a way of registering past and present novelty and imagining, simulating, planning, or calculating novelty to come, for the sake of decision-making, of action and reaction, and also to experience and ponder the pain and pleasure of being alive. But patterns of change and novelty repeat themselves, identities are acquired through repetition of these patterns schematized as typical origins, destinations, and itineraries, so that change can be perceived or constructed anew. For these purposes, there are recurrent modes of telling without which a compelling complicity could not develop and generate a measure of consent on what happens, on how things go, tightening the links that forge and stabilize (narrative) communities for some time. When people start telling themselves different stories, when they start telling them differently (in writing instead of orally, or vice versa, in a monological or in a dialogical mode, in a chorus or taking turns of speech, etc.), the contours of the community itself change and there may or may not be someone left to tell this story. From cosmogonic myths to the storytelling of advertising and propaganda, narratives and narrations are always in a tension between scandal and banality. The verbal arts have several functions within the social, psychological, ideological, and political inevitability of narratives: they help memorize and naturalize them, strengthening the community; they manipulate them rhetorically, turning into an event something that has always been there—we call this a discovery—or turning an emerging phenomenon into a non-event—a revolution being seen as a return to a previous state of things. Thanks to “poetic license,” grammatical loopholes and language anomalies, artful narratives devise parallel worlds, possible or impossible, against which what is held as the real takes its specific shape; and they produce the pleasure, guilty or not, of seriously playing the emotions of the other, combining empathy with distinction, projection with introjection. But all art, narrative or not, must negotiate its way with and between the pleasure principle and the reality principle. Literary narratives are neither natural nor unnatural; they do not belong to the id any more than to the superego. “Identifying narrative as the fictional par excellence ” generates more problems than it can solve. 74
Even when an aesthetics of emotions aims at doing away with change and difference altogether, an affective narratology will always help understand why literary narrative is the privileged playfield of the anthropological game between desire and delusion, between estrangement and recognition. The claim that “story structures are fundamentally shaped and oriented by our emotion systems,” 75 if it was supported by strong evidence and eventually proved to be true, should nonetheless be complemented by an in-depth investigation of the moving frontiers and the grey zones of narrative communication. For example, if there is no such thing as a narrator-less story, one that “tells itself,” and if no story can ever exist in “real time,” since stories always rely, even in orature, on their own deferral, any narrative will still form an odd couple with its narration. The narrative of narration, cooperatively constructed by the receiver who needs to retrace the origin of information and track down the steps of its expression, may seem to duplicate the narrated; it may overlap with it or entertain a polemic, absurd, or aporetical relation with it, but in every case, the relative porosity of narration and narrated is put to test: What happens when a reputed liar recounts only historically recorded “facts”? How does the lyric generally shun narration? How does an extended metaphor, or an initially argumentative digression, almost always slip into a narrative?
Cognitivism—the many facets of the cognitive sciences in the last fifty years—has made much, perhaps too much, of “narrative” without taking into account these fuzzy borders and grey zones that play an even greater role in literary narratives than in “ordinary” (i.e., merely referential, informative) narrative communication. Jerome Bruner says that a story occurs “when you encounter an exception to the ordinary.” 76 The intuition may be right in standard conversational situations: I will not tell my family the details of my road trip if it went smoothly, but I will tell once and again how an accident occurred, how the clutch of the car suddenly broke or I saw an elephant at the gas station. But literary, aestheticized verbal creativity will often (in traditional societies as much as in modernity) make the exactly opposite move, called ostranenie by the Russian formalists, especially Shklovsky: when banality becomes oppressive, when you need to expose its terror, you invent a story to animate it. In fact, it is exactly what realism, from the picaresque or before down to Dickens, Balzac, Zola, or Premchand, has always done. Symmetrically, in times of great plague, millennial fears, or disruptive sociopolitical changes, narrative literature will need to develop reassuring tales of ordinariness.
When Daniel Dennett gloats over the stupidity of “someone, a benighted literary critic, perhaps, who doesn’t understand that fiction is fiction,” arguing that “with regard to any actual man, living or dead, the question of whether or not he has or had a mole on his left shoulder blade has an answer,” his brand of rationalism superbly ignores that the “actuality” of “Aristotle” (the man) is only inferable in a similar fashion to that of the original Eve, that no living person will ever be able to experience Aristotle’s bodily presence any better than that of those other paper creatures called Ophelia, Catherine Linton, Emma Bovary, or Molly Bloom. 77 Dennett’s axiom ignores that narrative is not about having or not having a property or feature, but about acquiring or losing it. Literary narrative intelligence remains the best safeguard against the so-called “narrative paradigm” that posits an all-embracing maxim where narrative is any verbal and nonverbal interpretation arranged logically to generate a meaning. 78 Literary intelligence teaches us that narrative, as it plays with what was not but now is and with what now is but may not be later, is as much a device used to dissimulate an unchanging nature of things as it helps come to terms with an ever-changing world, enjoying the benefits of emotional education in the process.
Further Reading
- Alber, Jan , and Fludernik, Monika , eds. Postclassical Narratology: Approaches and Analyses . Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 2010.
- Auerbach, Erich . Mimesis: The Representation of Reality in Western Literature . Rev. ed. Translated by Willard R. Trask , with a new introduction by Edward B. Said. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2013.
- Boyd, Bryan . On the Origin of Stories: Evolution, Cognition, and Fiction . Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2009.
- Bres, Jacques . La Narrativité . Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium: Duculot, 1994.
- Chatman, Seymour . Story and Discourse: Narrative Structure in Fiction and Film . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1978.
- García Landa, José Ángel . Narrative Theory . Zaragoza: University of Zaragoza, 2005.
- Herman, David . Storytelling and the Sciences of Mind . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2013.
- Herman, David , ed. Narratologies: New Perspectives on Narrative Analysis . Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1999.
- Herman, David , et al., eds. Narrative Theory: Core Concepts and Critical Debates . Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 2012.
- Hillis Miller, J. Reading Narrative . Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1998.
- Hühn, Peter , et al., eds. Handbook of Narratology . Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 2009.
- Hühn, Peter , et al., eds. The Living Handbook of Narratology . Hamburg University.
- Jahn, Manfred . Narratology: A Guide to the Theory of Narrative . Version 1.8. English Department, University of Cologne, 2005.
- Keen, Suzanne . Narrative Form . 2d ed. Basingstoke, U.K.: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015.
- Phelan, James . Narrative as Rhetoric: Technique, Audiences, Ethics, Ideology . Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1996.
- Phelan, James , and Peter J. Rabinowitz , eds. A Companion to Narrative Theory . Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2008.
- Polkinghorne, Donald E. Narrative Knowing and the Human Sciences . Albany: State University of New York Press, 1988.
- Porter Abbott, H. The Cambridge Introduction to Narrative . 2d ed. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 2008.
- Rabinowitz, Peter J. Before Reading: Narrative Conventions and the Politics of Interpretation . Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1987.
- Ribière, Mireille , and Jan Baetens , eds. Time, Narrative & the Fixed Image/Temps, narration & image fixe . Faux Titre 208. Amsterdam: Rodopi, 2001.
- Ricoeur, Paul . Time and Narrative . vol. 3. Translated by Kathleen Blamey and David Pellauer . Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1990.
- Scholes, Robert , and Robert Kellogg . The Nature of Narrative . New York: Oxford University Press, 1966.
- Stanzel, F. K. A Theory of Narrative . Translated by Charlotte Goedsche . Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 1986.
- Worth, Sarah E. “Narrative Understanding and Understanding Narrative.” Contemporary Aesthetics 2 (2004).
1. Monika Fludernik , “Histories of Narrative Theory (II): From Structuralism to the Present,” in A Companion to Narrative Theory , eds. James Phelan and Peter J. Rabinowitz (Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2008).
2. Mircea Marghescou , Le Concept de littérarité: Critique de la métalittérature (Paris: Éditions Kimé, 2009).
3. Vladimir Propp , Morphology of the Folktale (Austin: University of Texas Press, 1968).
4. Gérard Genette , Figures III , Poétique (Paris: Éditions du Seuil, 1972), trans. Jane E. Lewin as Narrative Discourse (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1980).
5. Françoise Lavocat , Fait et fiction: Pour une frontière , Poétique (Paris: Éditions du Seuil, 2016).
6. Jonathan Gottschall , The Storytelling Animal: How Stories Make Us Human (Boston: Mariner, 2012).
7. Lubomír Doležel , Occidental Poetics: Tradition and Progress (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1990); and David Herman , “Histories of Narrative Theory (I): A Genealogy of Early Developments,” in A Companion to Narrative Theory , eds. James Phelan and Peter J. Rabinowitz (Oxford: Blackwell, 2005), 19–35.
8. Aristotle , “Poetics,” in The Complete Works of Aristotle: The Revised Oxford Translation , ed. Jonathan Barnes , vol. 2 of Bollingen Series 71 (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1984), 2317–2318.
9. Aristotle, Complete Works , 2317.
10. David Herman , Basic Elements of Narrative (Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2009), 137–160.
11. Herman, Basic Elements , 139.
12. Victor Shklovsky , Bowstring: On the Dissimilarity of the Similar , trans. Shushan Avagyan (Champaign, IL: Dalkey Archive Press, 2011).
13. Philip J. M. Sturgess , Narrativity: Theory and Practice (Oxford: Clarendon, 1992).
14. José Ángel García Landa , Acción, relato, discurso: Estructura de la ficción narrative (Salamanca: Ediciones Universidad de Salamanca, 1996), 19.
15. José Ángel García Landa , “Narrating Narrating: Twisting the Twice-Told Tale,” in Theorizing Narrativity , eds. John Pier and José Ángel García Landa , Narratologia (Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 2008), 419–451.
16. Suzanne Fleischman , Tense and Narrativity: From Medieval Performance to Modern Fiction (London: Routledge, 1990), 131, quoted in García Landa, “Narrating Narrating,” 431.
17. Jean-Paul Engélibert , Apocalypses sans royaume: Politique des fictions de la fin du monde, XXe–XXIe siècles (Paris: Classiques Garnier, 2013), 121–134.
18. Didier Coste , “Narrative as Communication,” Theory and History of Literature , 64 (1989): 4.
19. Daniel Punday , Narrative Bodies: Toward a Corporeal Narratology (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003), 189–190.
20. José Ángel García Landa , “Emergent Narrativity,” in Linguistic Interaction In/& Specific Discourses , eds. Marta Conejero , Micaela Muñoz , and Beatriz Penas (València: Editorial de la Universitat Politècnica de València, 2010), 109–117.
21. Raphaël Baroni , La Tension narrative: Suspense, curiosité et surprise , Poétique (Paris: Éditions du Seuil, 2007), 11.
22. Monika Fludernik , An Introduction to Narratology (New York: Routledge, 2009), 171–182.
23. Fludernik, Introduction to Narratology , 157.
24. Ansgar Nünning , “Mimesis des Erzählens: Prolegomena zu einer Wirkungsästhetik, Typologie und Funktiongeschichre des Akts des Erzählens und der Metanarration,” in Erzählen und Erzählentheorie in 20 Jahehundert: Festschrift für Wilhelm Füger , ed. Joerg Helbig (Heidelberg: Winter, 2001), 13–47, quoted by Fludernik, An Introduction to Narratology , 157.
25. Didier Coste and John Pier , “Narrative Levels,” in Handbook of Narratology , eds. Peter Hühn et al. (Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 2009), 294.
26. Amy Golahny , “Rubens’ ‘Hero and Leander’ and its Poetic Progeny,” Yale University Art Gallery Bulletin (1990): 21–37.
27. William Etty , Hero, Having Thrown Herself from the Tower at the Sight of Leander Drowned, Dies on his Body , 1829, oil on canvas, The Tate, London. Reference no. T12265.
28. Gerald Prince , “Narrativity,” in Routledge Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory , eds. David Herman , Manfred Jahn , and Marie-Laure Ryan (London: Routledge, 2005), 386–387; Jan Alber, “Narrativisation,” in Encyclopedia of Narrative Theory , eds. Herman et al., 386–387.
29. Monika Fludernik , Towards a “Natural” Narratology (London: Routledge, 1996), 311.
30. Fludernik, Towards a “Natural” Narratology , 34.
31. Prince, “Narrativity,” 163.
32. Lubomír Doležel , Heterocosmica: Fiction and Possible Worlds (Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1998), 14; Marie-Laure Ryan , Possible Worlds, Artificial Intelligence and Narrative Theory (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1991), 29; and Thomas Pavel , Fictional Worlds (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1986), 50.
33. Herman, Basic Elements of Narrative , 137–160.
34. Françoise Lavocat, “ Pour une herméneutique spécialisée de la fiction ,” in “Pourquoi l’interprétation?,” Fabula-LhT14 (2015).
35. Coste, “Narrative as Communication,” 108.
36. Lavocat, Fait et fiction .
37. Gerald Prince , Dictionary of Narratology (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1987), 64.
38. David Herman , Story Logic: Problems and Possibilities of Narrative (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2002), 27–51.
39. Herman, Story Logic , 40–41.
40. Gérard Genette , Narrative Discourse Revisited (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1988), 19.
41. Carlos Reis and Ana Cristina M. Lopes , Dicionário de narratologia (Coimbra: Almedina, 2002), 277, quoted in Teun A. Van Dijk and Walter Kintsch , Strategies of Discourse Comprehension (New York: Academic Press, 1983), 154.
42. Charles Grivel , Production de l’intérêt Romanesque (The Hague: Mouton, 1973); Raphaël Baroni , La Tension narrative: Suspense, curiosité et surprise , Poétique (Paris: Éditions du Seuil, 2007), 11.
43. Jonathan Culler , Theory of the Lyric (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2015), 176.
44. Prince, Dictionary of Narratology , 63.
45. Prince , Dictionary of Narratology , 63–64.
46. Françoise Revaz , Introduction à la narratologie: Action et Narration (Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium: De Boeck/Duculot, 2009).
47. Roland Barthes , “Introduction à l’analyse structurale des récits,” Communications 1 (1966): 1–27, trans. Lionel Duisit as “An Introduction to the Structural Analysis of Narrative,” in On Narrative and Narratives, New Literary History 6.2 (Winter 1975): 4, 237–272, quoted in Genette, Figures III , 75.
48. Wolf Schmid , Narratology: An Introduction , trans. Alexander Starritt (Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 2010), 8–21.
49. Rukmini Bhaya Nair , Narrative Gravity: Conversation, Cognition, Culture (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2002), 181.
50. Patrick Colm Hogan , Affective Narratology: The Emotional Structure of Stories (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2011), 77, 245.
51. Prince, “Narrativity,” 387.
52. René Audet , “Narrativity: Away from Story, Close to Eventness,” in Narrativity: How Visual Arts, Cinema and Literature are Telling the World Today , eds. René Audet et al. (Paris: Dis Voir, 2007), 7–35, quoted in H. Porter Abbott , “Narrativity,” in Handbook of Narratology , eds. Peter Hühn et al., Narratologia (Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, 2009), 309–328.
53. Porter Abbott, “Narrativity,” 323.
54. Mark Currie , The Unexpected: Narrative Temporality and the Philosophy of Surprise (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2013), 148.
55. Currie, The Unexpected , 148.
56. Jean-Louis Bachellier , “La poétique lézardée: Figures III , de Gérard Genette,” Littérature 12.4 (1973): 107–113.
57. Ross Chambers , Room for Maneuver: Reading Oppositional Narrative (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1991).
58. Mark Currie , Postmodern Narrative Theory , Transitions (New York: St. Martin’s Press, 1998), 54.
59. Currie, Postmodern Narrative Theory , 54.
60. Jean Ricardou , Pour une théorie du Nouveau Roman , Tel Quel (Paris: Éditions du Seuil, 1971).
61. Prince, “Narrativity,” 374.
62. Dhanajay Singh , “ Dhvani as a Method of Interpreting Texts,” in Sabda: Text and Interpretation in Indian Thought , eds. Santosh K. Sareen and Makarand Paranjape (New Delhi: Mantra Books, 2004), 258–26; and Surendra Sheodas Barlingay , A Modern Introduction to Indian Aesthetic Theory: The Development from Bharata to Jagannatha (New Delhi: DK Printworld, 2007).
63. Priyadarshi Patnaik , Rasa in Aesthetics: An Application of Rasa Theory to Modern Western Literature (New Delhi: DK Printworld, 1997), 48–49.
64. Patnaik, Rasa in Aesthetics , 49.
65. Patnaik, Rasa in Aesthetics , 48–49.
66. Patnaik, Rasa in Aesthetics , 186–188.
67. Kapila Vatsyayan , Bharata: The Natyasastra (New Delhi: Sahitya Akademi, 1996), 110.
68. Vatsyayan, Bharata , 110.
69. K. Ayyappa Paniker , Indian Narratology (New Delhi: Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts in association with Sterling Publishers, 2003), 1–7.
70. Amya Dev, review of Indian Narratology , by K. Ayyappa Paniker, Indian Literature 47.6 (2003): 214–217.
71. Paniker, Indian Narratology , 1–17.
72. Bhaya Nair, Narrative Gravity , 305, 208.
73. Daniel Punday , Narrative Bodies: Toward a Corporeal Narratology (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003), 185.
74. Fludernik, Towards a “Natural” Narratology , 36.
75. Hogan, Affective Narratology , 1.
76. Jerome Bruner , Acts of Meaning (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1990), 46, quoted in Hogan, Affective Narratology , 77.
77. Daniel C. Dennett , “The Self as a Center of Narrative Gravity,” in Self and Consciousness: Multiple Perspectives , eds. S. Kessel et al. (Hillsdale, NJ: Psychology Press, 1992), 103–114.
78. Walter R. Fisher , Human Communication as Narration: Toward a Philosophy of Reason, Value and Action (Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, 1987).
Related Articles
- Affect Studies
- Aesthetics and Form in Charles Darwin's Writings
- Form and Formalism
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Literature. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 20 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216
Character limit 500 /500
Narrative Voice | Definition, Properties & Examples
- February 3, 2024
Table of Contents:
Definition: what is narrative voice, properties of narrative voice, 1. point of view, types of narrative writing, nonlinear narrative, descriptive narrative, viewpoint narrative, examples of narrative voice.
- First-Person Voice - "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee
- Second-Person Voice – "Bright Lights, Big City" by Jay McInerney
- Third-Person Voice – "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling
- Unreliable Voice - "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger
The craft of storytelling is not limited to the elements such as characters, plot, and setting. One of the most important yet dramatically understated elements in strong narrative writing is voice.
The means through which a narrative is narrated has been referred to aptly as “narrative voice.” This can greatly bias that story’s reception and change how readers interpret characters and situations. It can even affect understanding at all levels, up to undermining comprehension.
This article focuses on narrative voice, features, types, and how it is utilized.
In literary terms, the narrative voice is the character or entity via whom a reader relives the plot. It is the point of view in which the events in a story are recounted. Although voice is often confused with the author’s words, narrative voice does not necessarily belong to the same source.
Narrative ghost writers might use a character in the story (first and second-person narratives) or an external entity not directly involved in the narrative plot line (third person).
The following characteristics often define narrative voice.
Who is telling the story determines the point of view. There can be first-person (I, we) where one of the characters tells a story. It can be second-person (you), directed at the readers, and third-person narrator who accounts for given events.
The narrative voice’s tone affects how readers react emotionally to this story. It might be happy, sad, gloomy, sarcastic, sober, or any other emotion. The narrator’s voice, therefore, determines the tone or mood of an entire story.
3- Reliability
The trustworthiness of a narrative voice refers to its reliability. A truthful narrator gives facts and reliable information. Nevertheless, an untrustworthy narrator brings in ambiguity, and the reader must determine between truth and a lie.
4- Degree of Omniscience
Omniscience establishes how much the narrator knows. An omniscient narrator knows everything about these characters and events. In contrast, a limited narrator can know only as much as one character does or has very little knowledge of the series.
Narrative pieces span different literary forms such as historical writings, Horror Fiction Writing , short stories, epics, and ballads. Yet, regardless of their format, narrative writing services emphasize that narratives predominantly fall into four primary categories.
- Descriptive
In this type of narrative, the narrator follows an order of events. The fictional or non-fictional story unfolds from start to finish.
- Linear Narrative
Linear narrative style can be identified in Bildungsroman (or coming-of-age novels). Popular examples of linear narratives include ‘The Catcher in the Rye’ by J.D Salinger, Mark Twain’s “The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn,” and Charles Dickens’ Last but not Least.’
The other forms of writing that follow a narrative style include historical pieces, biographies, and autobiographies. Linear narration is evident in the movie ‘Moana.’ It begins with Moana as a young girl growing up to be fully acquainted with her culture and responsibilities towards the tribe.
This style is well-suited to the theme and plot. You notice that Moana is always attracted to the ocean, determines what her life means, and crosses the sea to rescue people from destruction.
A nonlinear narrative does not tell the story chronologically. This is the type of story that has flashbacks. It goes back and forth from some point. This style of narration prevails in most suspense thriller novels and movies. Other lighter themes are also shown in this way.
Other novels which employ the nonlinear narrative include ‘Wuthering Heights’ by Emily Bronte, ‘The Sound and the Fury’ by William Faulkner, among others.
In this mode of narration, the audience is made to see and feel what world the characters live in. A descriptive narrative includes words and word groups that create images in readers’ minds.
Descriptive narrative is demonstrated in works such as ‘The Perks of Being a Wallflower’ by Stephen Chbosky, The Song of Achilles by Madeline Miller, and Arundhati Roy’s The God Small Things.
Most of you may have watched ‘Avatar’ and ‘Avatar: Way of the Water’. Both movies use the descriptive technique. The Avatar world is represented so the viewers form an identity with characters and surroundings.
A viewpoint narrative is a kind of literature where there exists either the first, second or third-person narrator. The change in pronoun use depends on who narrates these happenings. The most dominant point-of-view narratives are the first-person narrative and third-person narrative. The First-person point of view is used in writing autobiographies and third-person for presidential biographies .
First-person narratives include John Green’s ‘The Fault in Our Stars’ and Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird.’
Third-person narratives include such novels as ‘Little Women’ by Louisa May Alcott and ‘Beloved’ by Toni Morrison. The second-person narrative does not have as many books compared to the first and third-person narratives.
Nevertheless, others are beautifully presented. The novels Ghost Light’ by Joseph O’Connor and ‘If on a Winter’s Night, a Traveler’ by Italo Calvino are written in the second-person narrative. Read these novels and see the impact different perspectives have on the reader.
The first-person narrator of the movie, ‘The Life of Pi,’ is Piscine Molitor Patel (Pi). Bagheera, the panther in ‘The Jungle Book,’ tells about how Mowgli joined the wolves and what is happening. This can be referred to as a third-person narrative structure.
Let’s look at some examples to appreciate the concept of narrative voice.
First-Person Voice – “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
Harper Lee’s seminal work uses the first-person narrative voice, with young Scout Finch as the narrator. This choice gives readers a child’s perspective of the events unfolding during a racially charged trial in 1930s Alabama.
For instance, Scout’s innocent voice and naive understanding of the complex social issues contribute enormously to the novel’s emotional resonance.
Excerpt: “Until I feared losing it, I never loved to read. One does not love breathing.”
Second-Person Voice – “Bright Lights, Big City” by Jay McInerney
Jay McInerney’s novel breaks traditional norms by using a second-person narrative. The authorial choices in employing ‘you’ create an intimate, engaging storytelling style, pulling the reader directly into the story.
Excerpt: “You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning.”
Third-Person Voice – “Harry Potter” series by J.K. Rowling
J.K. Rowling uses the third-person limited narrative voice in the Harry Potter series. Though an external entity narrates, the voice closely follows Harry Potter, helping readers identify and empathize with him.
Excerpt: “Harry — yer a wizard.”
Unreliable Voice – “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
An example of an unreliable narrative voice can be seen in J.D. Salinger’s “The Catcher in the Rye.” Holden Caulfield, the narrator, distorts reality, often stretches the truth, and has a strongly biased viewpoint, leaving readers to piece the real story themselves.
Excerpt: “I’m the most terrific liar you ever saw. It’s awful.”
The narrative voice is a silent yet incontrovertible element of any narrative. It allows the story writers to control how events unfold and characters emerge.
We hope that with this article now, you understand what narrative writing is and what types are there.
limited Time offer
50% off on all services.
REDEEM YOUR COUPON: VHBA50
Recommended Blogs
How famous do you have to be to get a wikipedia page, how does wikipedia make money: a detailed guide, how to write a bio for a conference – 8 easy steps, hire book authors & publishers at discounted rates looking for a book author or publisher contact us for a free consultation and get 30% off your first project..
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10 The Power of Story: The Secret Ingredient to Making Any Speech Memorable

Ideas are not really alive if they are confined to one person’s mind.
Nancy Duarte, Speech coach and author
We love stories because they are engaging, they ignite the imagination, and they have the potential to teach us something. You have likely sat around a campfire or the dinner table telling stories? That is because stories are the primary way we understand the world causing communication scholar Rhetorical scholar Walter Fisher to call us homo narrans–storytelling humans. Not only is storytelling important in conversation, but it is also important to speechmaking. It is no surprise then, that when researchers looked at 500 TED Talks, they found of the TED talks that go viral, 65% included personal stories.
Professional speakers, college students, politicians, business leaders, and teachers are all beginning to understand the benefits of telling stories in speeches. Increasingly, business leaders are encouraged to move away from the old model of sharing the vision and the mission to a new model of telling the story of the business. Academic literature points out that teachers who use stories can help students understand and recall information. For years, politicians have been coached to include a story in their speeches. They do it because it works, and it is bound in science.
In short, people don’t pay attention to boring things. The story is one way to engage and help ideas come alive. Cognitive psychologist Daniel Willingham says, “The human mind seems exquisitely tuned to understand and remember stories—so much that psychologists sometimes refer to stories as ‘psychologically privileged,’ meaning that they are treated differently in memory than other types of material.”
The goal of public speaking is to plant an idea into the minds of your listeners and the most effective way to accomplish that is through a story. I want to share with you three major principles about storytelling and give you concrete ways to incorporate them into your own storytelling.
- Stories, when told properly, will ignite both the reason center and the emotion center of your audience’s brains making them not only more effective in the moment but also more memorable in long run.
- Stories activate the little voices in the audience’s heads and help them think creatively about problems. This activation encourages audiences to act on the idea as opposed to just being passive listeners.
- The best way to tell a story is to connect it to a message, offer concrete details, and follow a predetermined plotline.
(Editorial note: One of the advantages of digital textbooks is I can add videos. In my opinion, the best way to learn about how to write a good story is to see numerous examples of good stories in action. I have provided you with numerous videos illustrating how the story is used in business, used in law, used in entertainment, and used in education so that you can see the many applications. This chapter is different from standard textbooks on the subject because it includes more examples than text. You will only get deep learning if you take the time to watch the video clips.)
Tell me the fact and I’ll learn. Tell me the truth and I’ll believe. But tell me a story and it will live in my heart forever.
–Ancient proverb
Stories Engage the Audience and Make a Point
In under four minutes, Mark Bezos, tells a memorable story. He makes us laugh, allows us to see the situation, and then uses all the emotion and visualization he has created to make a powerful point. A good story draws us in and helps us connect with the person and their idea.
The brain doesn’t pay attention to boring things.
– John Medina, author of Brain Rules
Stories Help Ideas Stick
Stories are sticky. A well-told story “sticks” to our brains and attaches to our emotions. A speaker can tell a story in such a way that the audience “sees” the story in their mind’s eye and “feels” the emotions of the story. In some situations, an audience may become so involved in the story they “react” by making facial expressions or gasping in surprise. By “seeing the story” and physically reacting to the story, the audience is moved from a passive listener to an active participant.
Think about college teachers you have had who told stories as part of their lectures. Did it help you to listen? Did it help you to learn? Chances are it did. Researchers Kromka and Goodby put it to the test on one hundred ninety-four undergraduate students. One group listened to a lecture that included a lesson with a story, while others just heard the lesson’s key points. Students that heard the narrative had more sustained attention to the lecture and they did better on a test of short-term recall. The stories helped them remember the material, but there was an added benefit. The students who heard the narrative liked the teacher more and were more likely to take another course from the instructor in the future.
One of the top TED Talks of all time is My Stroke of Insigh t by Jill Bolte Taylor. In this talk, she weaves a story so engaging that the audience is afraid to blink because they might miss what happens next. Watch as she tells you about the “morning of the stroke.”
On the morning of the stroke, I woke up to a pounding pain behind my left eye. And it was the kind of caustic pain that you get when you bite into ice cream. And it just gripped me — and then it released me. And then it just gripped me — and then it released me. And it was very unusual for me to ever experience any kind of pain, so I thought, “OK, I’ll just start my normal routine.” So I got up and I jumped onto my cardio glider, which is a full-body, full-exercise machine. And I’m jamming away on this thing, and I’m realizing that my hands look like primitive claws grasping onto the bar. And I thought, “That’s very peculiar.” And I looked down at my body and I thought, “Whoa, I’m a weird-looking thing.” And it was as though my consciousness had shifted away from my normal perception of reality, where I’m the person on the machine having the experience, to some esoteric space where I’m witnessing myself having this experience. Jill Bolte Taylor
I’d like to illustrate to you the connection between thinking and doing.
- Imagine you are looking at the Eiffel tower.
- Think of two words that start with “b.”
- Think of two words that start with “p.”
- Imagine that I am cutting a lemon in half and then squeezing the juice in a glass.
- Imagine fingernails running down a chalkboard.
When imagining the Eiffel tower, most people’s eyes scan up.
When thinking of the words that begin with “b” and “p”, most people will mouth the words.
When imagining the lemon, many people will salivate.
When imagining fingernails on a chalkboard, many people will tighten their facial muscles.
We respond physically because a connection exists between our imagination and our physical response. When we say things in our speech that cause a physical response, the audience becomes actively engaged with our talk.
Stories Help the Audience Become Emotionally Engaged
“Emotions are the condiments of speech,” according to speech coach Nancy Duarte. They add spice and flavor to your talk. Emotions such as passion, vulnerability, excitement, and fear are particularly powerful. Researchers at Ohio State have a word for that sense of being carried away into the world of a story. They call it transportation. Their research demonstrated that people can get so immersed in a story they hardly notice the world around them. Audiences can be transported by stories as facts and stories as fiction. Narrative transportation theory proposes that when people lose themselves their intentions and attitudes may change to align with the characters in the story. As speakers, our goal should be to help our audience get lost in the story. Sometimes that means telling our own stories, sometimes it means telling the stories of others, and other times telling a hypothetical story.
You’ve probably heard of an fMRI. It’s the machine that measures blood flow to the brain. Scientists used fMRI machines to measure what happened when someone is telling a story and when someone is listening to that story. What they found is exciting. When they compared the speaker’s brain to the listener’s brains, they noticed the brains were lighting up in the same places. When the speaker described something emotional, the audience was feeling the emotion and the emotional centers of their brains were lighting up. Princeton researcher, Uri Hanson calls this brain synching, “neural coupling.”
Consider a study at Emory University that noticed differences in how brains respond to texture words, “she had a rough day” versus non-texture words “she had a bad day.” The texture words activated sensory parts of the brain. When telling a story, find creative and tactile descriptions to engage your audience.
Texture Words Nontexture words He is a smooth talker He is persuasive The logic was fuzzy The logic was vague She is sharp-witted She is quick-witted She gave a slick performance She gave a stellar performance She is soft-hearted She is kind-hearted
Imagine you pull up to a flashing red stoplight at an intersection. Seeing it in your mind activates the visual part of your brain. Now, imagine a loved one giving you a pat on the back. Once you imagine it, your tactile center will light up. This is quite powerful when you think about it. When you hear a story, you don’t just hear it, but you feel it , visualize it, and simulate it.
Dopamine, oxytocin, and endorphins are what David Philips calls the “angel’s cocktail.” He suggests speakers should intentionally create stories to activate each of these hormones. By telling a story in which you build suspense, you increase dopamine which increases focus, memory, and motivation. Telling a story in which the audience can empathize with a character increases oxytocin, the bonding hormone which is known to increase generosity and trust. Finally, making people laugh can activate feel-good endorphins which help people feel more relaxed, more creative, and more focused.
Because of neural coupling (our brain waves synching) and transportation (getting lost in a story), the audience members begin to see the world of the person in the story. Because of hormonal changes, they feel their situation and can empathize. A thoughtfully crafted story has the power to help the audience believe in a cause and care about the outcome.

Time and time, when faced with the task of persuading a group of managers to get enthusiastic about a major change, storytelling was the only thing that worked. Steve Denning, the Leaders Guide to Storytelling
Stories Inspire Action
The conventional view has always been when you speak, you try to get the listeners to pay attention to you. The way you get them to pay attention is to keep the little voice inside their heads quiet. If it stays quiet, then your message will get through. Stephen Denning in The Leader’s Guide to Storytelling suggests an alternative view. He challenges speakers to tell stories to work in harmony with the voices in people’s heads. He says that you don’t want your audience to ignore their voice; you want to tell a story in a way that awakens their little voice to tell its own story. You awaken their voice and then you give it something to do. He advocates using stories as springboards to help the audience think about situations so they can begin to mentally solve problems. In this way, you are not speaking to an audience but rather you are inviting the audience to participate with you.
Consider this story told by Jim Ferrell about the local garbage man and how it engages you and creates both mental images and new ideas.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c_phMQY_3S8&fbclid=IwAR1zogB-TdWyNOD9Wib6mVWNdSzuNQ4yJ3cc6rj_Wa38PokqwhUpEPgvX8Q
Stories Help the Ideas Stick in a Way that the Audience Remembers and Understands
Steven Covey, considered one of the twenty-five most influential people by Time Magazine, teaches on business, leadership, and family. In his books and seminars, he uses stories to help the audience remember his lessons. In this video, Green and Clean, he uses a story to help the audience understand servant leadership. As you watch, ask yourself if you will remember this story and the lesson that it offers?
Stories Help Win Law Cases–Example of a Story Analogy
Gerry Spence is considered one of the winningest lawyers and he credits his ability to tell stories to his success. In this video clip, you can see him in action as he tells this jury the story of the old man and the bird. Imagine yourself as a member of the jury, how might this affect you?
“Here’s the story of the bird that some of you wanted to hear again. This is one I’ve used many, many times. It’s a nice method by which you can transfer responsibility for your client to the jury. Ladies and gentlemen, I am about to leave you, but before I leave you I’d like to tell you a story about a wise old man and a smart-alec boy. The smart-alec boy had a plan, he wanted to show up the wise old man, to make a fool of him. The smart-alec boy had caught a bird in the forest. He had him in his hands. The little bird’s tail was sticking out. The bird is alive in his hands. The plan was this: He would go up to the old man and he would say, “Old man, what do I have in my hands?” The old man would say, “You have a bird, my son.” Then the boy would say, “Oldman, is the bird alive or is it dead?” If the old man said that the bird was dead, he would open up his hands and the bird would fly off free, off into the trees, alive, happy. But if the old man said the bird was alive, he would crush it and crush it in his hands and say, “See, old man, the bird is dead.” So, he walked up to the old man and said, “Old man, what do I have in my hands?” The old man said, “You have a bird, my son.” He said, “Old man, is the bird alive or is it dead?” And the old man said, “The bird is in your hands, my son.” Ladies and gentlemen of the jury my client is in yours.” Gerry Spence
Stories Help People Engage With Topics
Alan Alda founded the Alan Alda Center for Communicating Science because he wanted to help scientists learn how to best communicate what they know to a lay audience. In this video clip, he shares his lesson on using stories to draw in an audience.
Example from a Corporate Trainer
The Leader Who Withheld Their Story by Robert “Bob” Kienzle
Our communication training firm was hired to conduct a storytelling workshop for a major client. I quickly realized a major problem: the leader refused to tell a story in the storytelling workshop. We brought the water to the horse and the horse wouldn’t drink. Read the full story of Bob explaining how he taught one of his corporate clients to use storytelling.
Story Changes the Brain Chemistry in Listeners
Paul Zak told audience members a story and then measured the chemicals their bodies released during this story. His conclusion is that story changes brain chemistry and makes individuals more empathetic. In this case, they were more likely to donate money to charity. Watch this video as Zak talks about a universal story structure that includes exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and denouement.
Stories Can Have Drawbacks
While storytelling can be used positively, it can have drawbacks. A story can be more memorable than the point. If the audience remembers your story without the purpose of the story, you missed it. In the teacher’s study mentioned before, students had better short-term recall when the teacher told a narrative. The study also reported that listening to stories increased student cognitive load and some students basically used up their “brainpower” to remembering extraneous information instead of the lesson. The lesson here is to make sure the story reinforces a point and to make sure that the point is clear.
Because stories draw people in emotionally, there can be ethical challenges. Is it ethical to tug at an audience’s heartstrings to get them to donate money? How about giving you money? Speakers need to consider the ethical obligation to consider the impact of the story. Stories tap into emotions and create lasting memories. Stories told with the wrong motives can be manipulative.
The Formula for a Good Story
Tension-release.
So now you see the clear advantage in telling a story, let’s talk about the formula for a good story. A good story should help the audience see the events in their mind’s eye. Your story should play out like a movie in their head. This movie happens because you help them see the setting, characters, and details. To be fully engaged, the audience must feel some sort of tension.
The formula is tension and release.
The best stories create tension or conflict and then in some way resolve conflict. In persuasion, a story can create tension that can be released only by acting on the persuasion. Haven defines a story as “A character-based narration of a character’s struggles to overcome obstacles and reach an important goal.” Notice the focus on struggle and overcoming the struggle. Once you decide on the story that you want to tell, work on helping the audience feel the tension and release.
If the point of life is the same as the point of a story, the point of life is character transformation. If I got any comfort as I set out on my first story, it was that in nearly every story, the protagonist is transformed. He’s a jerk at the beginning and nice at the end, or a coward at the beginning and brave at the end. If the character doesn’t change, the story hasn’t happened yet. And if story is derived from real life, if story is just condensed version of life then life itself may be designed to change us so that we evolve from one kind of person to another. Donald Miller, A Million Miles in a Thousand Years: What I Learned While Editing My Life.
Dale Carnegie’s formula for storytelling includes three parts: Incident, action, and benefit. In the incident phase, the storyteller shares a vivid personal experience relevant to the point. Next, they give the action phrase, and they share the specific action that was taken. Finally, the speaker tells the benefit of taking the action. It still fits the tension-release formula, it just expands it to make sure that the speaker clearly lets the audience know what conclusion they are supposed to draw.
Dave Lieber illustrates this tension and release in his opening story and explains how it works. (You have to watch only the first five minutes to get the point, but I warn you it is hard to stop listening once he has you hooked) According to Dave Lieber, the formula is to meet the character; there is a low part in the story; the hero pushes up against the villain and overcomes.
Good stories represent a change
One part of the tension-release model is how the character changes. Matthew Dick Moth storytelling champion suggests that stories, where no change took place in the storyteller, are just anecdotes, romps, drinking stories, or vacation stories, but they leave no real lasting impression.
The story of how you’re an amazing person who did an amazing thing and ended up in an amazing place is not a story, it is a recipe for a douchebag. The story of how you are a pathetic person who did a pathetic thing and remained pathetic, is also not a story, it is a recipe for a sadsack. You should represent a change in behavior, a change in heart, a change in attitude. It can be a small change or a very large change. A story cannot simply be a series of remarkable events. You must start out as one version of yourself and end as something new. The change can be infinitesimal. It need not reflect an improvement in yourself or your character, but change must happen. Matthew Dick. I once was this, but now I am this I once thought this, but now I think this I once felt this, but now I feel this. I once was hopeful, but now I am not I once was lost, but now I am found I once was happy, but now I am sad I once was sad, but now I am happy I once was uncertain, but now I know I once was angry, but now I am grateful I once was afraid, but now I am fearless I once doubted, but now I believe
Stories Often Follow Common Plots
According to Heath and Heath of Made to Stick , there are common story plots. Each of these can be used in most speech types and can be adapted to the tension-release model.
Challenge Plot
- Underdog story
- Rags-to-riches story
- Willpower over adversity
Challenge plots work because they inspire us to act.
- To take on challenges
- To work harder
Connection Plot
- Focusing on relationships
- Making and developing friendships
- Discovering and growing in love
Connection plots work because they inspire us in social ways.
- To love others
- To help others
- To be more tolerant of others
Creativity Plot
- Making a mental breakthrough
- Solving a longstanding puzzle
- Attacking a problem in an innovative way
Creativity plots work because they inspire us to do something differently.
- To be creative
- To experiment
- To try something new
Elements to a Good Story
For the audience to experience the tension and release, they must be invested in the story. Good stories help the audience see the setting, know the characters, and feel the action.
Think of the setting as a basket to hold your story. If you start with the basket, the audience has a place to hold all the other details you give them. For this reason, many storytellers begin by describing the setting.
2. Characters
When you describe how the characters look or how they felt, we can see them as if we are watching them in a movie. The trick is to tell enough details we can create a mental picture of the character without giving so much information that we get bogged down.
When you describe the action that is taking place, the audience begins to feel the action. If you describe something sad that happened, the audience will feel the sadness. If you describe something exciting that happened to you or a character, the audience will feel that excitement.
Watch the first two minutes of this video and notice how Matthew starts with the setting and the characters and you can see the events unfold. You can see the action take place in your mind’s eye and you become invested in his story.
Flavor Crystals–The Little Extras
As a child, I used to love breath mints that would have blue flecks in them. They were called flavor crystals and they were there as little taste surprises that would enhance the flavor. You can enhance your story with little flavor crystals–little details that make it more interesting. Flavor crystals are those extra details that will impact your audience.
Ruben Gonzalez and Olympic Champion luger is a motivational speaker. As you watch this video clip, notice how he incorporates details in his story so we can see what’s happening.
Make Sure Your Story is Relatable
When you pick your story, make sure that you pick themes others can relate to in some way. Watch World Champion Presiyan Vasilev and notice how he uses little examples that everyone can relate to, like how you always get a flat tire when you are dressed up.
Why do flat tires always happen when you’re dressed up? Is there something collapsed in your life? Your knowledge may be limited. Your skills may be rusty. But no doubt, you will be changed when you reach out.
Do This: Keep a Story Log Notetaking Challenge Matthew Dicks suggests sitting down every day and asking yourself, “What happened today that is storyworthy?” Keep a notebook and write down a few ideas every day. The Magical Science of Storytelling TED Speaker David Philips has a similar suggestion. He encourages people to not only write down your stories but you index them based on the emotional reaction you wanting to get.
Theory Application
Literary theorist Kenneth Burke asks us to think of life as a drama where people are actors on a stage. What is their motivation for what they do and what they say? He offered five strategies for viewing life that he called dramatistic pentad.
- Act: What happened? What is the action? What is going on? What action; what thoughts?
- Scene: Where is the action happening? What is the background situation?
- Agent: Who is involved in the action? What are their roles?
- Agency: How do the agents act? By what means do they act?
- Purpose: Why do the agents act? What do they want?
How does all this relate to telling a story in a speech? The first thing you can do is to use this list when brainstorming how to fully develop your story. You can also use it as a way to evaluate the completeness of your story. The third way to use it is as a tool to evaluate your audience and how they view life. Why do they do what they do and what do they need to hear in order to be inspired, motivated, or persuaded?
In this TED Talk, My Invention that Made Peace with Lions, Richard Turere makes the audience wonder how a problem like lions killing livestock can possibly be solved. Richard draws us into his story and makes us want to know how a young boy could solve such a large problem. Watch this video and see if you can apply each of Burke’s Five Items.
Key Takeaways
Remember This!
- A story is a powerful tool because it engages the audience on not just a logical but also an emotional level.
- Good stories offer a setting, a description of the characters, and add enough detail for the audience to see the story take place in their mind’s eye. The action of a story should be told in a way that the audience can see the events unfold in their mind’s eye.
- Good stories have tension and release.
- Good stories have characters and situations that demonstrate a change.
Please share your feedback, suggestions, corrections, and ideas.
I want to hear from you.
Do you have an activity to include? Did you notice a typo that I should correct? Are you planning to use this as a resource and do you want me to know about it? Do you want to tell me something that really helped you?
Click here to share your feedback.
Bonus Features
There is so much information on this topic, that I struggled with what to include and what to leave out or put as optional. Here are a few videos that I like to think of as the BONUS FEATURES. In addition, there is a supplemental chapter on story that includes more videos and activities.
The Magical Science of Storytelling
David Philips uses stories to illustrate how storytelling can activate what he calls the angel’s cocktail: dopamine, oxytocin, and endorphins.
Angel’s Cocktail
- What it does: Increases focus, motivation, memory.
- How to do it: Build suspense, launch a cliffhanger, create a cycle of waiting and expecting.
- What it does: Increases generosity, trust, bonding.
- How to do it: Create empathy for whatever character you build.
- What it does: Increases creativity and focus and people become more relaxed.
- How to do it: Make people laugh.
The Structure of Story
Nancy Duarte studied hundreds of speeches and found the same storytelling technique. In her TED talk, she provides this chart. It is a story that is easy to digest, remember and retell.
Figure 1: Nancy Duarte-Persuasive Story Pattern
INSERT VIDEO: NANCE DUARTE THE SECRET STRUCTURE OF GREAT TALKS
https://www.ted.com/talks/nancy_duarte_the_secret_structure_of_great_talks?language=en
Examples of Storytelling
- Storytelling in a Eulogy: Brook Shield’s Eulogy to Michael Jackson: https://youtu.be/vpjVgF5JDq8
- Storytelling in Business: Steve Denning Discovered the Power of Leadership: https://youtu.be/qiVBcD5M3yc
- Storytelling and Education: Speak Less, Expect More. Matthew Dicks: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sK2P2NEIXUE
Alda, A. (2017). If I understood you, would I have this look on my face? Random House.
Alda, A. (2017). Knowing how to tell a good story is like having mind control. Big Think. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r4k6Gm4tlXw Standard YouTube License.
Bezos, M. (2011). A life lesson from a volunteer firefighter. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.ted.com/talks/mark_bezos_a_life_lesson_from_a_volunteer_firefighter?utm_campaign=tedspread&utm_medium=referral&utm_source=tedcomshare Standard YouTube License.
Bolte-Taylor, J.92008). My Stroke of Insight. Ted Talk. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.ted.com/talks/jill_bolte_taylor_my_stroke_of_insight?language=en Standard YouTube License.
Braddock, K., Dillard, J. P. (25 February 2016). Meta-analytic evidence for the persuasive effect of narratives on beliefs, attitudes, intentions, and behaviors. Communication Monographs, 83 (4), 446–467. doi:10.1080/03637751.2015.1128555. S2CID 146978687.
Brooks, D. (2019). The lies our culture tells us about what matters–and a better way to live. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.ted.com/talks/david_brooks_the_lies_our_culture_tells_us_about_what_matters_and_a_better_way_to_live?language=en Standard Youtube License.
Burke, K. (1945). A grammar of motive s. Berkeley: U of California Press.
Carnegie, D. (2017). The art of storytelling. Dale Carnegie & Associates ebook.
Covey, S. (2017). Green and Clean. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z8MylQ_VPUI Standard YouTube License.
Dahlstrom, M,F. (2014). Using narratives and storytelling to communicate science with nonexpert audiences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(4), 13614–13620. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1320645111
Denning, S. (2005). The leader’s guide to storytelling: Mastering the art and discipline of business narrative. John Wiley and Son.
Denning, S. (2001). The springboard: How storytelling ignites action in knowledge-era organizations. Taylor & Francis.
Dicks, M. (2018). Storyworthy: Engage, teach, persuade, and change your life through the power of storytelling. New World.
Dicks, M. (2016). This is Gonna Suck. Moth Mainstage. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N3J4Q5c1C1w Standard YouTube License.
Duarte, N. (n.d.) Fifteen Science-Based Public Speaking Tips to be a Master Speaker, The Science of People. https://www.scienceofpeople.com/public-speaking-tips/ .
Ferrell, J. (2017). An outward mindset for an inward world. Jim Ferrell Keynote. The Arbinger Institute. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c_phMQY_3S8 Standard YouTube License.
Fisher, W.R. (2009). Narration as a human communication paradigm: The case of public moral argument. Communication Monograph s, 51 (1), 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637758409390180
Fisher, W.R. (1985). The Narrative Paradigm: In the Beginning, Journal of Communication , 35(4), 74-89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.1985.tb02974.x
Gallo, C. (2016). I’ve analyzed 500 TED Talks, and this is the one rule you should follow when you give a presentation. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/ted-talk-rules-for-presentations-2016-3
Gershon, N, & Page, W. (2001). What storytelling can do for information visualization. Communication of the ACM, 44, 31–37. https://doi.org/10.1145/381641.381653
Gonzales, R. (2011). Three-time Olympian, peak performance expert. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qqMOrjsRUT4. Standard YouTube License.
Green, M. C., & Brock, T. C. (2000). The role of transportation in the persuasiveness of public narratives. Journal of personality and social psychology , 79 (5), 701–721. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.79.5.701
Green, S. J., Grorud-Colvert, K. & Mannix, H. (2018). Uniting science and stories: Perspectives on the value of storytelling for communicating science. Facets, 3 (1). https://doi.org/10.1139/facets-2016-0079
Hasson, U., Ghazanfar, A.A., Galantucci, B., Garrod S, & Keysers C. (2012). Brain-to-brain coupling: a mechanism for creating and sharing a social world. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16 (2), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.12.007
Haven, K. (2007). Story proof: The science behind the startling power of story. Kendall Haven.
Heath, C & Heath, D. (2008). Made to Stick. Random House.
Homo Narrans: Story-Telling in Mass Culture and Everyday Life. (1985). Journal of Communication , 35 (3) https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.1985.tb02973.x
Kromka, S. M. & Goodboy, A. K. (2019) Classroom storytelling: Using instructor narratives to increase student recall, affect, and attention, Communication Education, 68:1, 20-43. DOI: 10.1080/03634523.2018.1529330
Lacey, S., Stilla, R., & Sathian, K. (2012). Metaphorically feeling: comprehending textural metaphors activates somatosensory cortex. Brain and language , 120 (3), 416–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2011.12.016
Lieber, D. (2013). The power of storytelling to change the world. TEDtalk. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Bo3dpVb5jw Standard YouTube License.
Miller, D. (1994). A million miles in a thousand years: How I learned to live a better story. Thomas Nelson.
Philips, D. (2017). The magical science of storytelling. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nj-hdQMa3uA Standard YouTube License.
Reynolds, G. (2014). Why storytelling matters TED. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YbV3b-l1sZs Standard YouTube License.
Simmons, A. (2001). The story factor: Inspiration, influence, and persuasion through the art of storytelling. Basic Books.
Spencer, G. (1995). How to argue and win every time . St. Martin.
Spence, G. (2018). Persuasive storytelling for lawyers by Alan Howard. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rzdoR2PJqYg Standard YouTube License
Turere, T. (2013). My invention that made peace with lions. TED. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RAoo–SeUIk Standard YouTube License.
Willingham, D. T. (2009). Why Don’t Students Like School?: A cognitive scientist answers questions about how the mind works and what it means for the classroom . Jossey-Bass.
Zac, P.J. (2014). Why your brain loves good storytelling. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2014/10/why-your-brain-loves-good-storytelling
Zac, P.J. (2012). Empathy, neurochemistry, and the dramatic arc: Paul Zac and the future of storytelling. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q1a7tiA1Qzo Standard YouTube License.
Media Attributions
- Sitting around a campfire © Ball Park Brand is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Voices in your head is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Formula for a story © Lynn Meade is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Persuasive Story Pattern
Advanced Public Speaking Copyright © 2021 by Lynn Meade is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Create a free profile to get unlimited access to exclusive videos, sweepstakes, and more!
Ciara Miller Slams Questions About Her Relationship Progress with West: "I'm Not His"
"I don't like the narrative," the Summer House cast member said while talking about one aspect of her romance with West Wilson.

Ciara Miller is hitting back at commentary surrounding the pace of her romance with West Wilson.
How to Watch
Watch Summer House on Bravo Thursdays at 9/8c and next day on Peacock . Catch up on the Bravo app .
On Season 8, Episode 9 of Summer House , which aired on April 18, West turned to Paige DeSorbo and Amanda Batula for advice about his relationship with Ciara as related to their sex life — or lack thereof .
"I mean, obviously, we're, like, more than friends at this point," West shared in an interview during the episode. "But after so long, does it become like, there's gotta be a reason for it? She told me she's never dated anyone younger than 35 or something. Not only am I, like, seven years younger than everyone she's dated, but I also just don't have a job. It is a little in the back of my head for sure."
In the Summer House Season 8 After Show video above, West notes that although he had questions about why he and Ciara weren't having sex, he wasn't exactly surprised by it.
"Everyone is very forward about, like, 'Ciara is very traditional. You're gonna have to f-cking work for it. It'll take a long time,'" he says. "But also, she told me that."
Paige and Amanda React to West's "Awkward" Concern About His Relationship with Ciara
"And I obviously didn't want to be the dude who reads like, 'Please f-ck me,'" he continues. "Like, that's the last kind of guy you want to be."
Here's What You May Have Missed on Bravo:
Paige Hits Back at Questions About Her Future with Craig: "It's Gonna Be on My Terms"
Austen Kroll Sent West Wilson *This* DM After He "Called Him Out" on the After Show
Amanda Batula Shuts Down "Misconception" That Her Parents "Run" Her Finances: "I'm an Adult"
Ciara Miller slams "narrative" surrounding her sex life with West Wilson

As Ciara explains in the video, she is bothered by the conversation surrounding her physical intimacy with West.
"I don't like the narrative of, like, I'm withholding something from him," she says. "That implies that he's not getting something that's his. I'm not his. It's my body. He's not entitled to my body. He's not entitled to have sex with me. It's a f-cking privilege to have sex with me."
On Summer House Season 8, Episode 7, Ciara explained to Jesse Solomon and Danielle Olivera that she was "not trying to rush into anything" with West.
"I kind of like that we're taking it slow," she said. "We'll have sex when I'm ready."
Press play on the video above to watch Ciara, West, Paige, Amanda, Danielle, and Jesse talk about the subject in the Summer House Season 8 After Show.
- Ciara Miller
- West Wilson
Summer House
- Relationships
Related Stories

Amanda Weighs In on Carl and Linday's Relationship

Ciara Miller, Paige DeSorbo, and Gabby Prescod's “Icks” Will Make You LOL

Taylor Shares an Update on Her Friendship with Kyle

Tom Schwartz & Sophia Reveal Just How Serious They Are

Kelly Shares New Details on Her "Perfect Wedding Dress"

Ciara Weighs in on Austen and West's Friendship

See Kenya Moore and Cynthia Bailey Reunite (PHOTO)

Did West Wilson Ever Get a Job in Sports Journalism?

Brittany Cartwright Addresses *Those* Carl Radke Rumors

Katie Reveals "Wild” Info About Laura-Leigh and Lukas Gage

Garcelle Regrets *This* About Her Divorce

Check Out Candiace Dillard Bassett's Engagement Ring

Latest Videos
![Danielle Olivera Gets Honest with Paige DeSorbo: “You Are Giving [Craig Conover] Nothing” Danielle Olivera Gets Honest with Paige DeSorbo: “You Are Giving [Craig Conover] Nothing”](https://www.bravotv.com/sites/bravo/files/styles/16_9_medium/public/media_mpx/thumbnails/bravo-video.nbcuni.com/image/NBCU_Bravo/900/222/SH809_1_proxy_SD_thumb_2.jpg?itok=SZnTLw6D)
Danielle Olivera Gets Honest with Paige DeSorbo: “You Are Giving [Craig Conover] Nothing”

Lindsay Hubbard Was Relieved to Have Some Alone Time While Carl Radke Was Out of Town

West Wilson Asks Paige DeSorbo and Amanda Batula for Advice About Ciara Miller
Recommended for you.

We Have a Major Update on Tom, Katie, and Katie

Kyle Says She Will Spend Christmas with Mauricio

Kim Richards Just Shocked Kyle with a New Update
The 13 Best Movies That Adapt Shakespeare's 'Hamlet,' Ranked According to IMDb
"To adapt, or not to adapt... that is the question."
Read update
It seems that movie fans are like Depeche Mode when it comes to Hamlet movies, because they just can't get enough. Hamlet adaptations go back to the silent era, meaning that this timeless story of revenge and tragedy has been popular with film audiences for over a century at this point. Of all the movies based on Hamlet , IMDb is a great way to find the best, with the average ratings from users on the site ultimately showing what the best Hamlet movie is.
Hamlet is up there with the likes of Macbeth and Romeo and Juliet as one of William Shakespeare 's most famous plays. It's an epic, violent tragedy that takes multiple hours to act out in full, thanks to having a large cast of engaging characters who are all involved in its story about family conflict, betrayal, and death (so, so much death).
Its popularity also means it's got more film adaptations than most Shakespeare plays. The following 10 are among the most well-known movies that either adapt Hamlet or feature plots heavily inspired by the iconic play's narrative. They're ranked below by their average rating on IMDb, and collectively show how applicable the story of Hamlet is to various genres, periods in history, and cultures.
Updated on May 23, 2023, by Jeremy Urquhart:
13 'hamlet' (2000).
IMDb Rating: 5.9/10
It's ironic that this adaptation of Hamlet aimed to update the story into a modern-day New York City setting, yet by being so clearly set around the turn of the millennium, it's ended up "aging" worse than most adaptations that are set centuries ago. In the film's defense, those behind it likely didn't know how fast technology was going to advance, and how quickly Blockbuster was going to become obsolete (in the film, it's where Hamlet has his "To be or not to be" soliloquy).
It makes it an accidental period piece in hindsight, but at least it stands out as far as adaptations go. For anyone who loves late 90s/early 2000s aesthetics and/or Ethan Hawke , it's probably one take on the iconic play that's worth a watch.
Watch on Paramount+
12 'The Banquet' (2006)
IMDb Rating: 6.4/10
The Banquet is a Chinese film that loosely adapts Hamlet into a historical setting that's also slightly fantastical. The story here takes place more than 1000 years ago, and is kicked off with the actions of a murderous uncle, but ultimately builds to an extensive (and violent) banquet where numerous characters collide.
The plot might be familiar to those who know Hamlet well, but the fact that The Banquet adds martial arts into the mix makes it unique, given that's something that couldn't exactly be done on stage. Overall, it's a solid addition to the ever-growing list of Hamlet movies that manages to add something new to the mix.
Watch on Hoopla
11 'Strange Brew' (1983)
IMDb Rating: 6.6/10
There are plenty of cult classic 1980s sci-fi movies that have taken some time to find an audience, usually because they're a little offbeat. Strange Brew could definitely count itself as one of those films, as it's perhaps one of the most aggressively Canadian movies of all time, features comedy and sci-fi elements, and has a story loosely inspired by Hamlet .
It revolves around a brewery, and sees two hosers (an informal Canadian term for "losers") get a job there, and end up in a plot to help a young woman regain ownership of it from a mysterious brewmaster who's also her uncle. It's very silly and unlikely to appeal to a wide audience, but it has its fans, and stands as a unique take on the classic play.
10 'Hamlet' (1990)
IMDb Rating: 6.7/10
Hamlet (1990) is notable for starring Mel Gibson as the Prince of Denmark, but can also be singled out as the one where the title character has a terrible haircut. Otherwise, it sort of blends into the crowd when it comes to Hamlet adaptations, seeing as it plays things straight when it comes to adapting the original text, and forgoes adding any genres besides basic "drama" to the mix.
It was far from director Franco Zeffirelli 's first Shakespeare adaptation, as he'd previously directed The Taming of The Shrew in 1967 and Romeo and Juliet in 1968. The latter of those is particularly well-regarded for being one of the best film adaptations of a Shakespeare play, and even if Zeffirelli's Hamlet is still seen as decent, it couldn't quite measure up to 1968's Romeo and Juliet .
9 'Hamlet' (1921)
IMDb Rating: 7.0/10
1921's Hamlet is one of the oldest known film versions of the play, and more significantly, is still watchable. There are plenty of films from the 1920s and earlier that have been lost to time, meaning those interested in old cinema can only imagine what they would have looked like.
This take on Hamlet also stands out from the crowd because it changes Hamlet from prince to princess, with the title character needing to pass as a man for much of the film's runtime. Naturally, this leads to various plot elements being changed, too, adding another level to the film and making it surprisingly unpredictable in the process, even though all the characters - and the core premise - are found in the original play.
8 'The Northman' (2022)
IMDb Rating: 7.1/10
If there's one thing that The Northman does exceptionally well, it's highlighting the cyclical nature of revenge and the way violence can continue to inspire more violence until there's no one left to be violent. Speaking of violence: the movie has a ton of it.
Interestingly, The Northman might not quite be an adaptation of Hamlet , given it's based on the Scandinavian legend of Amleth, which itself inspired Hamlet . However, given Hamlet's ultimately overshadowed its predecessor, The Northman does end up feeling like another take on that familiar story, but thankfully contains a few surprises for those who think they know the original text well (plus a good deal more action than most Hamlet movies).
Watch on Prime Video
7 'Rosencrantz & Guildenstern Are Dead' (1990)
IMDb Rating: 7.3/10
Rosencrantz & Guildenstern re-frames Hamlet to focus on two of its minor characters who tend to be cut out of most film adaptations. Those two characters are none other than Rosencrantz and Guildenstern, and they spend much of the movie having philosophical conversations about their existence and lack of purpose in life in a way that's consistently very meta.
It's an odd movie, and its sense of humor isn't going to be for everyone. Also, for as clever as the premise is, the whole thing is fairly one-note and repetitive, considering it's almost two hours long. At least it's unique and undoubtedly entertaining in parts, and benefits hugely from having Tim Roth and Gary Oldman in the titular roles.
6 'Hamlet' (1948)
IMDb Rating: 7.6/10
1948's Hamlet is the only direct Shakespeare adaptation to have won Best Picture. Sure, West Side Story (1961) also won the top prize at the Oscars, but that's based on a musical that drastically modernized Romeo and Juliet. And while 1998's Shakespeare in Love is (loosely) about the man itself, it's not an adaptation of one of his plays.
In essence, this take on Hamlet is a direct, simple, and perfectly efficient one. It trims the play down to a still fairly epic 2.5 hours, and showcases Laurence Olivier at the height of his powers as both an actor and director. It might not stand out now, 75 years later, but it was an undoubtedly impressive film for its time.
Watch on Max
5 'Hamlet' (1996)
IMDb Rating: 7.8/10
Kenneth Branagh 's Hamlet is easily the longest, with the 1996 film clocking in at just over four hours . It would be difficult to feasibly make an adaptation longer without adding material, given this version is notable for adapting the entire play to the big screen.
This results in a movie that might well be too long and exhausting for some viewers, but the epic scope achieved through such an ambitious adaptation of the play is undeniable. For Shakespeare purists out there, there's a good chance this would have to rank as one of the very best films based on one of his works, given it leaves nothing on the cutting room floor.
4 'The Bad Sleep Well' (1960)
IMDb Rating: 8.0/10
The Bad Sleep Well is one of many underrated Akira Kurosawa movies that gets buried under the likes of more popular movies like Seven Samurai , Ran , and Yojimbo . As far as adaptations go, it's fairly loose, having less in common with its source material than Kurosawa's 1957 take on Macbeth ( Throne of Blood ) did.
It transports things to mid-20th century Japan, and follows a young man who seeks revenge on a powerful industrialist who he holds responsible for his father's death. Murder, madness, and human corruption are explored in both Hamlet and The Bad Sleep Well , and the film captures the spirit of the source material well, even if numerous aspects of the plot itself are quite different.
Watch on The Criterion Channel
3 'Haider' (2014)
Haider is a must-see Indian film that takes the story of Hamlet and sets it in Kashmir during the 1990s. At 160 minutes long, it's one of the longest adaptations of Hamlet out there, and one of the most explosive, unwilling to shy away from the violent consequences of its protagonist's quest for revenge after his father dies in mysterious circumstances.
Even though it's one of the most recent Hamlet adaptations, it's already among the highest-rated, with an 8.0/10 on IMDb and a similarly impressive 88% rating from critics on Rotten Tomatoes . Just like the title character himself, it seems like nothing will stop Hamlet's persistent rampage throughout pop culture.
Watch on Netflix
2 'Hamlet' (1964)
IMDb Rating: 8.2/10
One of the highest-rated versions of Hamlet according to IMDb ratings is this 1964 adaptation from the Soviet Union. It's not quite as widely seen as many of the better-known adaptations, but those who are familiar with it seem to hold it in high regard, and it was recognized by the BAFTAs and the Golden Globes upon release, too.
There's not a great deal else to say about it. It's another strong adaptation of a great play, and of the direct adaptations, is also one of the shortest (even though it still runs for about two hours and 20 minutes).
1 'The Lion King' (1994)
IMDb Rating: 8.5/10
While the idea of adapting Hamlet into a family-friendly Disney movie might sound absurd on paper, it led to one of the most acclaimed animated movies of all time. And yes, though The Lion King is far from a direct adaptation, it does feature the protagonist's father being murdered by a treacherous uncle, with the protagonist then setting out to avenge the killing and right the injustice that was committed.
Thankfully, things end much better here for the main character, Simba, than things usually do for characters based on Hamlet. And even if that means The Lion King isn't nearly as dark as most versions of Hamlet , at the same time, most animated Disney movies aren't nearly as dark as The Lion King .
Watch on Disney+
NEXT: The Best Shakespeare Film Adaptations, Ranked

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Narrative Speech Topics. Narrative speech topics list with public speaking ideas for a storytelling training I have categorized them in: Your Events, Life Lessons, Personal Experiences, Rituals and Your Identity. The main point is that you are talking about yourself. Your thoughts, feelings, ideas, views, opinions and events are the leading ...
The word "narrative" is also frequently used as an adjective to describe something that tells a story, such as narrative poetry. How to Pronounce Narrative. Here's how to pronounce narrative: nar-uh-tiv. Narrative vs. Story vs. Plot. In everyday speech, people often use the terms "narrative," "story," and "plot" interchangeably.
Wrap your personal narrative up with a reflection or analysis of the transpired events. It is important that at the end of your speech, the audience is left with something to recall even if he forgets everything else. Allow them to leave the room with the moral and lessons that they have learned from your speech. You may also see elevator speech.
125 examples of narrative speech topics: - 40 'first' experiences, - 40 tell-a-story topics, - 35 personal story ideas. How to best use this page. Choosing the right narrative speech topic. How to get from topic to speech (with a printable speech outline to download) A definition of the word 'narrative'. A personal story is a powerful story.
Narrative Essay Topics . Choosing the topic for your essay may be the hardest part. What you're looking for is a particular incident that you can recount in a well-developed and clearly organized essay or speech. We have a few ideas to help you brainstorm topics. They're quite broad, but something will surely spark an idea.
Narrative is the basis of storytelling. Narratives are oral or written accounts that connect related events or incidents for the purpose of entertaining, educating, communicating, sharing, and/or creating meaning for readers or listeners. Narratives can be found in novels, movies, plays, music, and even video games, and they are often referred ...
A narrative is a story. The term can be used as a noun or an adjective. As a noun, narrative refers to the story being told. It is the account of events, experiences, and details. It also refers to the story-telling process. As an adjective, it describes the form or style of the story being told. The adjective use of the word narrative has its ...
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
A narrative speech about an event in the life of another person should include traditional research at the library or using online resources. Keep quotations short, no more than one or two sentences, if you need to use a quote in your speech. Make a note of the source of the quotation and cite that in your speech, so your audience understands ...
One key element of narrative voice is point of view. This is reflected in the grammatical person used. In most narrative writing, this will either be first person or third person: First-person narration tells a story from the point of view of the narrator (i.e., using "I" or "we" pronouns). This will often be the main character in the ...
Narrative Definition. Narrative (NAIR-uh-tihv) is a spoken or written account of related events conveyed using certain literary techniques and devices. Narratives are seen throughout written works and other media, including prose, verse, movies and television shows, theater, music, video games, and podcasts. The word narrative derives from the ...
Examples of Narration. For examples of different styles of narration, check out the following: The Battle of the Ants by Henry David Thoreau (first person, nonfiction) In writing or speech, narration is the process of recounting a sequence of events, real or imagined. It is used in any style and genre of writing.
A narrative is a form of writing that tells a story. Narratives can be essays, fairy tales, movies, and jokes. Narratives have five elements: plot, setting, character, conflict, and theme. Writers use narrator style, chronological order, a point of view, and other strategies to tell a story. Telling stories is an ancient art that started long ...
In writing an effective narrative speech, start with an outline to help focus on the purpose of the speech, organize the events discussed in the speech and create a final draft. A Statement of Purpose. Identify the purpose of your speech, such as imparting a moral or making the audience feel good. This step is necessary and saves revision ...
NARRATIVE FEATURES. LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience's minds as they read. PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.. DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
The individual elements of different narrative techniques can be broken down into six distinct categories: Character. Perspective. Plot. Setting. Style. Theme. Each of these plays an important role in developing a story — taking the writer's message and presenting it to their audience in a deliberate way.
Narrative As a Genre of Discourse. Narrative discourse is the whole set of what is said and thought, in a cooperative or conflictive fashion, when the world of reference is seen as actually or potentially transitive, subject to change. This set of communicational transactions is the locus of narrativity.
Examples of Narrative Voice. First-Person Voice - "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee. Second-Person Voice - "Bright Lights, Big City" by Jay McInerney. Third-Person Voice - "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling. Unreliable Voice - "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger. Conclusion.
Students that heard the narrative had more sustained attention to the lecture and they did better on a test of short-term recall. The stories helped them remember the material, but there was an added benefit. The students who heard the narrative liked the teacher more and were more likely to take another course from the instructor in the future.
Narrative intervention is one of the most powerful approaches to language intervention that school-based speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can use. We define narrative intervention as any language intervention that involves children telling or retelling stories that have specific language-related features purposefully targeted by the ...
Narrative voice is the perspective the story is told from. The writer chooses a narrative voice carefully, as it can have an important effect on the story and the reader's response.
This is where narrative voice comes in. Narrative voice refers to the perspective or point of view from which a story is told. It is the voice of the narrator, the person or entity who is telling the story. Narrative voice can have a big impact on the overall tone and mood of a story, and can also affect the reader's level of immersion and ...
22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11.2DS), the most frequent microdeletion syndrome in humans, is related to a high risk of developing neurodevelopmental disorders. About 95% of patients with 22q11.2DS have speech and language impairments. Global articulation, story generation, and verbal memory tests were applied to compare articulatory characteristics of speech sounds, spontaneous language ...
As Ciara explains in the video, she is bothered by the conversation surrounding her physical intimacy with West. "I don't like the narrative of, like, I'm withholding something from him," she says.
5 likes, 0 comments - relawandigital_tasminghamid01_April 19, 2024 on : "#RELAWANDIGITALTASMINGHAMID #thenext #Walukotaparepare When the election approaches, that's where the narrative war begins, including fake news and hate speech, and it's time for us to fight it @tasminghamid @teman.sampai.mati @dedyhamiid @de_artmand ".
6 'Hamlet' (1948) IMDb Rating: 7.6/10. 1948's Hamlet is the only direct Shakespeare adaptation to have won Best Picture. Sure, West Side Story (1961) also won the top prize at the Oscars, but that ...
Catch the top stories of the day on ANC's 'Top Story' (18 April 2024)