

Dell Value Chain Analysis
Value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. It is important to note that the pattern of Dell value chain management has been extensively imitated by other companies, including companies outside of consumer technology industry due to its evident contribution to the success of the company.
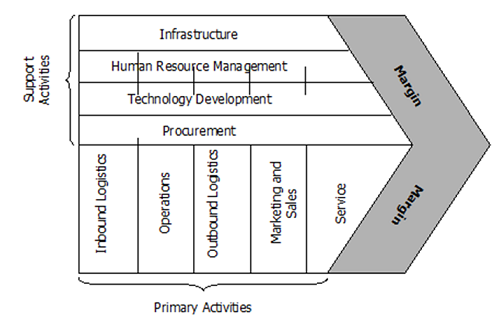
Figure 1 Value Chain Analysis
Inbound logistics . Dell works with more than 165,000 channel partners in inbound logistics and provides USD 125 million partner incentives and investments annually [1] . The company utilizes Just-in-Time (JIT) philosophy in dealing with inbound logistics. Thanks to this strategy, Dell is able to save on huge inventory costs and sustain cost leadership for the majority of its products and services. Customer orders are registered by Dell and its vendors simultaneously by an integrated system. Then, materials are shipped by suppliers within 2 hours and shortly received at Dell’s assembly unit due to geographical proximity (see Figure 2 below).
Operations . The main distinctive point between operations of Dell and its competitors relates to the fact that Dell is not a computer manufacturer; the company merely assembles parts manufactured by other companies. At the same time, high level of product customization is adapted as one of the bases of competitive advantage by the business. Therefore, operations mainly consist of three stages – assembly of stardard parts, installation of custom parts and testing product configurations (see Figure 2 below).
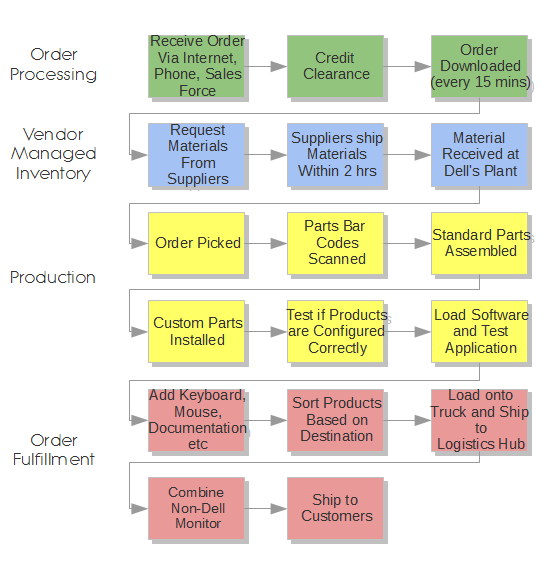
Figure 2 Dell’s value chain [2]
Outbound logistics consists of five stages as marked in red color in Figure 2 above. Thanks to the practice of mass customization, Dell is able to complete order fulfilment in a short duration of time. Generally, Dell completes customer shipments in a timely basis, staying committed to its promise of product customization as a result of cumulative advantages of part modularity, inventory program managed by vendors, demand management and mass customization.
Marketing and sales is acknowledged by Dell as a critically important primary activity and the company’s marketing strategy has changed since the company became private in August 2013. Specifically, Dell marketing management aims to associate the brand image with an entrepreneurial spirit by shifting attention to the fact that the company is no longer publicly listed, hence the management is freed from the need to track stock prices on a daily basis.
Service. Pre and post sales customer support can be specified as one of the solid bases of Dell’s competitive advantage. It has been noted that Dell’s employees “take 50,000 phone calls from customers every day and document and organize their comments, which are then distributed to managers” [3] . Also, there are 4300 Dell certified partners globally who assist with Dell solutions and services to customers [2] …
Dell Inc. Report contains more detailed discussion of Dell value chain analysis covering analysis of support activities. The report also comprises application of SWOT, PESTEL and Porter’s Five Forces Analyses on Dell , along with analysis of Dell’s marketing strategy and company’s approach towards Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).

[1] Annual Report (2015) Dell Inc.
[2] Source: Supply Chain Minded, Available at: http://supplychainminded.com/supply-chain-management-case-study-executives-guide/
[3] Farkaz, C. M. & Wetlaufer, S. (1996) “The Ways Chief Executive Officers Lead”, Harvard Business Review, Available at: https://hbr.org/1996/05/the-ways-chief-executive-officers-lead
[4] Annual Report (2015) Dell Inc.
- Skip to content.
- Jump to Page Footer.
Foreign Investment in 2024: Fueling Global Growth in Tight Markets
Join us as we share crucial insights into the anticipated shifts and emerging trends that will define the funding ecosystem in 2024.

Case study: Dell—Distribution and supply chain innovation
Read the highlights
- Cutting out the middleman can work very well.
- Forgoing the retail route can increase customer value.
- Re-examine & improve efficiency for process/operations.
- Use sales data and customer feedback to get ahead of the curve.
In 1983, 18-year-old Michael Dell left college to work full-time for the company he founded as a freshman, providing hard-drive upgrades to corporate customers. In a year’s time, Dell’s venture had $6 million in annual sales. In 1985, Dell changed his strategy to begin offering built-to-order computers. That year, the company generated $70 million in sales. Five years later, revenues had climbed to $500 million, and by the end of 2000, Dell’s revenues had topped an astounding $25 billion. The meteoric rise of Dell Computers was largely due to innovations in supply chain and manufacturing, but also due to the implementation of a novel distribution strategy. By carefully analyzing and making strategic changes in the personal computer value chain, and by seizing on emerging market trends, Dell Inc. grew to dominate the PC market in less time than it takes many companies to launch their first product.
No more middleman: Dell started out as a direct seller, first using a mail-order system, and then taking advantage of the Internet to develop an online sales platform. Well before use of the Internet went mainstream, Dell had begun integrating online order status updates and technical support into their customer-facing operations. By 1997, Dell’s Internet sales had reached an average of $4 million per day . While most other PCs were sold preconfigured and pre-assembled in retail stores, Dell offered superior customer choice in system configuration at a deeply discounted price, due to the cost-savings associated with cutting out the retail middleman. This move away from the traditional distribution model for PC sales played a large role in Dell’s formidable early growth. Additionally, an important side-benefit of the Internet-based direct sales model was that it generated a wealth of market data the company used to efficiently forecast demand trends and carry out effective segmentation strategies. This data drove the company’s product development efforts and allowed Dell to profit from information on the value drivers in each of its key customer segments.
Virtual integration: On the manufacturing side, the company pursued an aggressive strategy of “virtual integration.” Dell required a highly reliable supply of top-quality PC components, but management did not want to integrate backward to become its own parts manufacturer. Instead, the company sought to develop long-term relationships with select, name-brand PC component manufacturers. Dell also required its key suppliers to establish inventory hubs near its own assembly plants. This allowed the company to communicate with supplier inventory hubs in real time for the delivery of a precise number of required components on short notice. This “just-in-time,” low-inventory strategy reduced the time it took for Dell to bring new PC models to market and resulted in significant cost advantages over the traditional stored-inventory method. This was particularly powerful in a market where old inventory quickly fell into obsolescence. Dell openly shared its production schedules, sales forecasts and plans for new products with its suppliers. This strategic closeness with supplier partners allowed Dell to reap the benefits of vertical integration, without requiring the company to invest billions setting up its own manufacturing operations in-house.
Innovation on the assembly floor: In 1997, Dell reorganized its assembly processes. Rather than having long assembly lines with each worker repeatedly performing a single task, Dell instituted “manufacturing cells.” These “cells” grouped workers together around a workstation where they assembled entire PCs according to customer specifications. Cell manufacturing doubled the company’s manufacturing productivity per square foot of assembly space, and reduced assembly times by 75%. Dell combined operational and process innovation with a revolutionary distribution model to generate tremendous cost-savings and unprecedented customer value in the PC market. The following are some key lessons from the story of Dell’s incredible rise:
1. Disintermediation (cutting out the middleman): Deleting a player in the distribution chain is a risky move, but can result in a substantial reduction in operating costs and dramatically improved margins. Some companies that have surged ahead after they eliminated an element in the traditional industry distribution chain include:
- Expedia (the online travel site that can beat the rates of almost any travel agency, while giving customers more choice and more detailed information on their vacation destination)
- ModCloth (a trendy virtual boutique with no bricks-and-mortar retail outlets to drive up costs)
- PropertyGuys.com (offers a DIY kit for homeowners who want to sell their houses themselves)
- iTunes (an online music purchasing platform that won’t have you sifting through a jumble of jewel cases at your local HMV)
- Amazon.com (an online sales platform that allows small-scale buyers and sellers to access a broad audience without the need for an expensive storefront or a custom website)
- Netflix (the no-late-fees online video rental company that will ship your chosen video rentals right to your door)
2. Enhancing customer value: Forgoing the retail route allowed Dell to simultaneously improve margins while offering consumers a better price on their PCs. This move also gave customers a chance to configure PCs according to their specific computing needs. The dramatic improvement in customer value that resulted from Dell’s unique distribution strategy propelled the company to a leading market position.
3. Process and operations innovation: Michael Dell recognized that “the way things had always been done” wasn’t the best or most efficient way to run things at his company. There are countless examples where someone took a new look at a company process and realized that there was a much better way to get things done. It is always worth re-examining process-based work to see if a change could improve efficiency. This is equally true whether you’re a company of five or 500.
4. Let data do the driving: Harnessing the easily accessible sales and customer feedback data that resulted from online sales allowed Dell to stay ahead of the demand curve in the rapidly evolving PC market. Similarly, sales and feedback data were helpful in discovering new ways to enhance customer value in each of Dell’s key customer segments. Whether your company is large or small, it is essential to keep tabs on metrics that could reveal emerging trends, changing attitudes, and other important opportunities for your company.
See additional learning materials for distribution .
Summary: Dell combined operational and process innovation with a revolutionary distribution model to generate tremendous cost-savings and unprecedented customer value in the PC market.
Read next: customer discovery: identifying effective distribution channels for your startup.
Strickland, T. (1999). Strategic Management, Concepts and Cases . McGraw Hill College Division: New York.
Customer discovery: Identifying effective distribution channels for your startup
Should startups build distribution channels or sell products directly, sign up for our monthly startup resources newsletter about building high-growth companies..
- Enter your email *
You may unsubscribe at any time. To find out more, please visit our Privacy Policy .

How Dell’s strategy transformed it from a doomed player to leading the data revolution
Table of contents, here’s what you’ll learn from dell's strategy study:.
- How to sustain your company’s growth beyond its initial success.
- How a sober bet for the future fuels your conviction to win.
- How to think long-term and not sacrifice your future for short-term benefits.
Dell Technologies is a multinational technology company that designs, develops, and sells a wide range of products and services, including personal computers (PCs), servers, data storage devices, network switches, software, and cloud solutions.
The general public owns 58% of Dell Technologies, while private equity firms and institutions own the rest. Michael Dell is the founder, chairman, and current CEO.

Dell's market share and key statistics:
- Brand value of $26,5 billion
- Net Worth of $28.7 billion as of Jan 13, 2023
- Annual revenue of $105.3 billion for 2022
- Total number of employees: 133.000
- Total assets worldwide: $93 billion in 2022
{{cta('e9abffcd-5522-40c9-be83-0e844633a49a')}}
Humble beginnings: How did Dell start?
The story of every company starts with the story of its founder.
Usually, a great company has a great founder story behind it. And Dell Technologies certainly has one. Michael Dell’s story goes hand in hand with the story of the company he founded. By understanding the story of Michael, we can understand the company’s initial advantages and opportunities it pursued.
And like every great tech company story, Dell’s story starts in a college dorm room.
From stamps to startups: Michael Dell's early years and the birth of Dell
Michael Dell founded the company in college, but his entrepreneurial journey started much earlier.
He had an early interest in technology and business, and by the age of 12, he was already buying and selling stamps and coins to make extra money. As a teenager, he worked summer jobs where he learned by trial and error how demand and supply worked, how to be efficient, how to segment the market, and determine the most profitable persona to sell.
By the time he graduated from high school, he had saved up enough money to buy his own BMW and his first personal computer, an Apple and later an IBM.
But he was curious about the inner workings of these machines and, to his parents' horror, he took them apart, learning about the different components and how they worked together. He soon made a crucial discovery. IBM DIDN’T manufacture its own parts. Instead, it sourced them from other companies. This sparked an idea in Michael's mind - he could build his own PCs using the same components but at a lower cost and higher quality.
That idea didn’t come out of the blue.

Michael Dell was constantly educating himself on computers, how to build them, how they worked, and how to code. He followed all computer magazines at the time and attended every event in his neighborhood to network and learn the latest about the industry. In high school, he was already an expert, modifying his own PC and, once the word spread, customizing the PCs of professionals.
His first customers were friends and acquaintances who were impressed by his knowledge and expertise. Michael quickly realized that there was a demand for customized computers that were not available in the market. He began assembling machines with increased storage capacity and memory at a fraction of the cost of buying from big brands like IBM.
Doctors and lawyers were among his early customers, and word-of-mouth about Michael's high-quality and affordable PCs spread quickly.
He eliminated the middleman by buying components directly and assembling the machines himself, which allowed him to offer lower prices and better performance. By the end of his first year in college, Michael had a vendor's license, he was winning bids against established companies in the industry, and he incorporated his first company, “ Dell Computer Corporation .”
Dell’s direct-to-consumer strategy & how its corporate culture was formed
The company was growing frightfully fast, forcing the team to constantly change and evolve its processes.
Before the company had its second birthday, they had moved to bigger offices three times to accommodate its increased inventory, growing telephone needs, and physical or electronic systems. However, the company was still a high-risk venture and had a small capacity for expensive mistakes.
In those early days, the challenges Dell faced formed its processes and the core traits of its culture that are present to this day:
- Practicality and reduced bureaucracy. They did some things unconventionally, like having salespeople set up their own computers. That way, they gained first-hand knowledge of the technology and the customer’s pain problems (customers and salespeople were uneducated on the technology, so they shared the same problems).
- A “can-do” and “I’ll-pitch-in” attitude. Employees took substantial liberties with their “responsibilities.” Engineers would help with the overloaded manufacturing line, everyone would answer phone calls, salespeople would fulfill orders while taking new ones, etc.
- A sense of making a difference. Money was tight, so Dell employees wouldn’t mind solving secondary “needs” with cheap solutions like using cardboard boxes to throw their trash because they didn’t have trash cans.
- Direct relationships with the customers. Maybe one of the most important aspects of Dell’s culture and strategy. The company was talking at the same time with prospects and current customers on the phone. That way, it got first-hand feedback on what the market was currently asking for and was enjoying or not enjoying. That gave birth to Dell’s “Direct Model.”

The company went to great lengths to build and maintain the direct model because it was one of its most important sources of competitive advantage. Where other companies had to guess what to build next, Dell was already on it because their customers were telling them.
There were clear advantages to the Direct model:
- Closed feedback loop. Dell was talking directly to prospects – no dealer costs – and had no need for inventory. Lower costs = lower prices = more customers. And with every new customer, Dell had another finger on the pulse of the market.
- A single salesforce. Focused solely on the end customer. There was no need to have salespeople to sell to dealers and then additional salespeople to sell to the customer.
- Specialization in sales. Dell sold to large corporations, and smaller customers, like SMBs, educational institutions, and individual consumers. But selling to these two different buyers, large corporations and SMBs, was incomparable. So, the company had different salespeople for different customer segments and thus offering the best customer support and experience.
But the model wasn’t without its disadvantages:
- The model wasn’t irreplicable. Dell was making IBM-compatible PCs and selling them directly to customers. This model wasn’t hard to replicate, and the market’s conditions favored the birth of competitors with the same model.
- Lack of credibility. It’s hard to make a $5,000 sale when the customer has never heard of you and you lack a physical store.
- Incompatibility. Dell’s PC had to be compatible with IBM’s. But they had multiple suppliers for their components and sometimes those components were incompatible. Designing high-quality machines that were outperforming and compatible with IBM’s was a challenge.
But these disadvantages didn’t stop the team. The company doubled down on customer support and service and developed a strong reputation around them. It advertised a 30-day money-back guarantee and educated its suppliers to make components based on Dell designs. They even started their first R&D attempts that gave them a 12-MHz that was faster than IBM’s latest model, cheaper, and got them on the cover of the most prestigious magazine in the industry, the PC Week .
Dell’s strategy was so effective that phone calls started coming in, urging them to accept capital and go public.
Only three years after the company’s birth in a college dorm room, Dell went public, raising $30 million with a market valuation of $85 million.
Key Takeaway #1: Build a coherent strategy beyond your initial differentiator to sustain growth
Most companies enjoy initial success due to an untapped opportunity in the market, from addressing a niche market to exploiting the weaknesses of major players.
But no company succeeds at growing beyond the limits of the initial opportunity if it doesn’t evolve and expand its competitive advantage. So when evaluating your next move, ask yourself:
- What is our current competitive advantage?
- How easily can our competition replicate it?
- How can we make it harder (if we can)?
- How can we expand our capabilities to strengthen our current competitive advantage?
- How can we develop new competitive advantages?
- What are the market trends and how can we adapt/take advantage of them before others?
The occasional bold move doesn’t hurt, either.
Recommended reading: 6 Competitive Analysis Frameworks: How to Leave Your Competition In the Dust
How Dell’s privatization led to a strategic triumph
In the first decade of the new millennium, the PC business was growing rapidly.
Computing power followed Moore’s Law and innovation cycles in hardware were less than 12 months long. At the same time, a new generation of software was spreading and the World Wide Web was expanding globally. Being a part of a growing industry, like the PC business back then, was lucrative. So naturally, many companies did well.
Dell was one of them. In 2000, the company became the world’s largest seller of PCs, having enjoyed a decade of skyrocketing sales.
However, in 2011, things changed. The PC global sales reached their peak and the next year was the first of an 8-year streak of decline that lasted until the pandemic hit.
That decline impacted Dell severely.
Navigating decline: Dell's strategy for a shrinking market
Dell was in deep trouble at the start of the previous decade:
- It had lost its position as a top PC seller in the US to its main competitor, HP.
- It came third in the global PC market share, behind HP and ACER.
Many believed that it was a dying company that would perish like Kodak or Motorola.
The PC market was shrinking and some experts were saying it was the beginning of its end. Dell was expected to be among the first casualties. The truth was that the PC industry wasn’t dying, but it was evolving – it was losing some of its traits and gaining new ones. The difference is subtle but also key. In a competitive arena, every alert player is aware of the market changes: declining sales, emerging trends, and other important facts. But how each player interprets them determines whether they’ll formulate a winning strategy or not.
The more substantial the changes, the more important the interpretation.

In 2012, the fact was that the PC business was declining. Every major player could see it with a single glance at their balance sheet. In Dell's case, the decline was even direr since its PC sales were down by double digits. The company desperately needed to turn things around. And only a bold strategic move could do that.
The company tried to bounce back up with some obvious but desperate moves:
- The introduction of the Streak “phablet.” An embarrassing attempt at creating a new product category between tablets and smartphones. Its design was bulky and its Android software unsuitable for the device, while its purpose was unclear to the consumer.
- Making Windows 8 its default operating system. Dell and Microsoft have been longtime partners, to the benefit of both companies. Unfortunately, their growing interdependence meant that when one failed, it dragged the other one down. Windows 8 failure dragged down Dell and further decreased its PC market share.
- Attempts to enter the tablet and smartphone markets: the “Venue” debacle. Dell was always viewed as a PC company, not a technology company, making it harder to expand to new categories. Its first smartphone, the Venue , ran on Windows Mobile and it never got any traction. As a result, the company abandoned the categories and, even today, it has less than negligible presence in these markets.
But where people saw a vulnerable company, Michael Dell saw an opportunity.
He had an assumption, a vision attached to it, and a plan to make it a reality. But he had no way to execute it with the company’s organizational structure at the time.
The obstacles to implementing Dell's competitive strategy
Dell’s strategy was to go on the offensive. He wanted the company to be highly aggressive by:
- Becoming competitive in the PC business again.
- Expanding its services and software solutions.
- Increasing its sales capacity.
Dell aimed to achieve these goals by investing heavily in R&D, gaining tighter control over its PC and server prices, and expanding its sales workforce. The idea was to fund new business capabilities in the software and services space from Dell's PC segment. That was a bold plan that involved a lot of changes and, thus, a lot of risks.
Dell’s strategy was essentially a business transformation proposal.
And although a lot of public companies have successfully gone through a transformation, none did it in such a short period of time without sacrificing the short-term faith of its shareholders. And that was exactly the problem.
The strategy was inherently risky – like every good strategy is – as it promised capital expenditure and an immediate decrease in profitability due to increased operating expenses. Things shareholders hate. And if shareholders aren’t happy with the company’s near-term returns, they start selling their shares, and the company loses its value and a good portion of its funding capabilities.
Short-term risk = lower share prices = less funding for the company
Thus, the strategy was impossible to execute without the support of the shareholders. So the company had only two options: gain the support of the shareholders or go private.
Dell chose to go private.
Dell's game-changing decision was based on a strategic bet
For a gigantic public company with a market cap of nearly $20 billion, going private is a tough decision and a complicated process.
But it was an unavoidable preliminary for the successful execution of Michael Dell’s plan. And the first step was to convince the board of the necessity of the transformation. After announcing his idea, the board started discussions with experts to evaluate the move, i.e. top consulting agencies and other independent third parties.
JP Morgan , Boston Consulting Group, Evercore, and Debevoise were some of the names involved. And they all shared the same view:
- The PC is dying.
- Funding a business transformation from a declining business is a bad idea (despite such successful attempts from IBM and BMW in the past).
The experts had a lot of facts and strong arguments to support their case. However, all of them were based on a single assumption: tablets and smartphones will replace the dying PC . The growth in those categories would entail a decline in the PC business. They believed the PC was about to be cannibalized.
Dell’s CEO disagreed. What was his assumption?
He believed that tablets and smartphones wouldn’t take away from PCs but rather add to it. He believed that the PC’s central role in productivity and business wasn’t going to be dethroned by the new shiny toys. People would buy and use tablets and smartphones, but PCs would remain their primary productivity tool.
And he would bet Dell’s future on it.
But he had to convince the board of directors first. At the start, conversations were happening in secret and things were moving slowly but steadily. But when the idea was leaked, two new problems presented themselves.
The first was Carl Icahn, who contested for the ownership of Dell. Carl Icahn is a self-proclaimed “activist investor” but others call him a “corporate raider.” The closer the go-private initiative was to happen, the more Carl Icahn fought for it. And he used every improper tool and method he could muster. The battle that followed between Carl and Michael delayed the deal and almost derailed it.
The second was Dell’s customers’ hesitation in doing business with the company. The rumors about the go-private initiative left the customers wondering about the future of Dell and doubted whether any kind of investment in it was worth it. They were suspending purchases and all Dell’s leadership could say was, “We don’t comment on rumors and speculations.”
The press had also concluded that the go-private initiative was a declaration of Michael Dell’s incompetence and a desperate attempt to keep Wall Street’s eyes away from its demise.
History would prove them wrong and crown Michael Dell victorious.
A new chapter: How Dell's go-private move set the stage for future success
The deal happened.
In February 2013, Michael Dell and the investment firm of Silver Lake took Dell private in a leveraged buyout of $24.4 billion, at $13.65 a share.
Despite all the time that passed until Dell could fully execute its strategy, the company didn’t remain idle. It had made several calculated moves to significantly reduce its dependence on the declining PC market before the deal conversations ever happened.
From 2007 to 2012, Dell spent north of $12.40 billion in key acquisitions to increase its enterprise software and hardware solutions, including cloud data storage and management. The acquisitions focused on areas like:
- Data storage
- Systems management
- Data management in healthcare
- Cutting edge software
The company had already started severing the connection between its financial health and its PC market share many years ahead of its privatization.
But after the buyout, it went all in. Speed and agility became its prominent advantages. Dell became, nearly overnight, a hungry, quick, and ready-to-attack-its-prey jackal. Whenever a new opportunity arose and people asked for resources to pursue it, leadership committed double the resources and said, "Go faster!"
For example, SMBs (small and medium businesses) presented a gigantic opportunity. So the company increased its sales workforce, retrained its existing salespeople, and hit endless SMB doors. They would enter a business selling their low-margin PCs and simultaneously become their trusted advisor on all things tech. Then they sold their whole portfolio of solutions.
And the morale of employees was off the charts. Leadership kept their promises on the changes and provided all the support their people needed to execute the plan.
In addition, people started viewing PC and smartphones as complementary, just as Dell expected.
Was Michael Dell’s bet a good one? Well…
45% of Dell’s revenue was generated from PC sales, but 80% or more of its profits were generated by its new solutions. Eight years after the privatization, the value of their equity had increased more than 625% and their enterprise value reached $100 billion.
We’re pretty confident that’s a yes.
Key Takeaway #2: Successful strategic bets require a sober conviction
Markets change and evolve all the time. The difference between players that emerge prosperous and those that struggle to fit in the new order of things isn’t the unique access to data.
No. Every alert player in your competitive zone has more or less the same access to market trends and changes. The difference lies in what you envision the future to be. That’s your bet.
That’s what a winning corporate strategy needs. And because bets are inherently risky, you require two things to place a successful bet:
- Sobriety to envision what the future of your industry will look like.
- Conviction to pursue that vision relentlessly.

Steering towards success: Dell's current strategy and the EMC merger
Michael Dell had foreseen the evolution of the technology industry since the 2000s.
Not the specifics, but the trend of PCs and hardware becoming less relevant – or at least less profitable – and software, the cloud, and back-end taking the front seat. He realized (from very early on) that servers and storage management would become a huge concern for large enterprises building (or upgrading) their IT infrastructure.
Dell anticipated the market’s needs by making a simple observation: the quantity of data in the world expanded exponentially and the traditional way of data management would require server performance that wasn’t physically possible to achieve. But he knew there was a solution underway: virtualization – software that mimics the computer, creating virtual mainframes within the physical mainframe.
That’s why the company had started investing in these technologies since 2001.
Achieving synergy: Dell's competitive strategy and the merger with EMC and VMware
Dell, EMC, and VMware are three major players in the technology industry with distinct but complementary offerings.
EMC had a successful product in networked information storage systems, i.e. a database management system for enterprises.
VMware was pioneering in virtualization, allowing users to run multiple operating systems on the same device.
Dell had an established distribution network and a series of back-end solutions that could expand and fit well with the former technologies.
The relationship between these three companies started in 2001. Dell and EMC entered a strategic alliance to rule a market of $100 billion worth by 2005.
%20(1).jpg)
For EMC, the alliance was a one-stone-three-birds initiative. First, it offered a lucrative distribution channel to customers their competitors were already targeting. Second, it ensured Dell wouldn’t partner with a competitor. And third, it reduced its supply costs for components.
For Dell, it also had a threefold benefit. First, It added high-performing products to a rapidly growing business. Second, it gave it an important customer – EMC was using Dell’s servers. And third, it allowed Dell to infiltrate deeper into enterprise data centers.
A strategic alliance that gave both Dell and EMC a competitive edge.
Then EMC bought VMware. That gave the company massive capabilities around cloud infrastructure services ending up being a very lucrative move. Dell, which had invested in VMware back in 2002, saw a massive opportunity to acquire the new EMC.
So Dell and EMC first began discussions of a potential partnership back in 2008, but the idea was ultimately shelved due to the financial crisis. However, in 2014, Dell revisited the idea as both companies had grown and become leaders in their respective industries.
Dell saw the potential for a merger as the two companies' services would bring significant value to their customers when combined. EMC's CEO, Joe Tucci, agreed with this assessment, but they still had to convince EMC's board. EMC was publicly held while Dell was private, and as soon as the idea was on the table, Dell found itself competing with two other interested parties, Cisco Systems and HP. In fact, HP nearly succeeded in acquiring EMC.
It failed due to a financial disagreement. So Dell jumped on the opportunity.
By then, EMC had grown tremendously and had eliminated any short- to mid-term potential start-up disruptors by acquiring them. EMC’s three businesses were uniquely complementary to Dell’s solutions:
- EMC Information structure , a leader in the data storage system market.
- VMware , the undisputed leader in virtualization.
- Pivotal , a start-up with a platform to develop cloud software.
However, the acquisition was a tough process. EMC had grown to a market cap of over $60 billion. It was impossible for Dell to fund an acquisition. Instead, the two companies merged.
The merger happened through a complex but effective financial plan, and the synergies created by the combined company increased revenue significantly. A year after the merger was initiated, the added revenue was well above expectations. This allowed Dell to pay down a significant portion of its debt and improve its financial standing and investment rating. The success of the merger led the company to simplify its structure and align the interests of the stakeholders of the three companies.
In 2018, Dell went public again as a very different entity than its first IPO, uniquely equipped to lead the 5-S sectors: services, software, storage, servers, and security.
What is Dell’s business strategy’s primary focus today?
Dell aspires to become a leading player in the data era by providing a wide range of solutions, products, and services.
Excluding VMware, Dell is divided into two main business segments supported by its financial subsidiary:
- The Infrastructure Solutions Group ISG helps customers with their digital transformation by providing multi-cloud and big data solutions that are built on modern data center infrastructure. These solutions are designed to work in multi-cloud environments and can handle workloads in public and private clouds as well as on-premise.
- The Client Solutions Group CSG focuses on providing solutions for clients such as laptops, desktops, and other end-user devices.
- Dell Financial Services DFS supports Dell businesses by providing financial options and services to customers according to the company’s flexible consumption models. Through DFS, the company tries to tailor its financial options to each customer’s way of consuming Dell’s solutions.
Dell's core offerings include servers, storage solutions, virtualization software, and networking solutions. The company is constantly investing in research and development, sales and other key areas to improve its products and solutions and to drive long-term growth.
Its primary strategic priorities are:
- Improving and modernizing its current offerings in the markets it operates in.
- Expanding into new growth areas such as Edge computing, telecommunications, data management, and as-a-service consumption models.
And its plan involves several key initiatives :
- Developing its flexible consumption models and as-a-Service options to customers to meet their financial needs and expectations.
- Building momentum in recurring revenue streams through multi-year agreements.
- Investing in R&D to develop scalable technology solutions and incorporating AI and machine-learning technology. Since its Fiscal year 2020, the R&D budget is consistently at least $2.5 billion. Most of it goes towards developing the software that powers its solutions.
- Collaborating with a global network of technology companies for product development and integration of new technologies.
- Investing in early-stage, privately-held companies through Dell Technologies Capital.
Although Dell has a coherent strategy to achieve its objectives, competition isn’t idle nor trivial in the core competitive arenas. The company faces a significant risk that includes:
- Failure to achieve intended benefits regarding the VMware spin-off.
- Competition providing products and services that are cheaper and perform better.
- Delays in products, components, or software deliveries from single-source or limited-source suppliers.
- Inability to effectively execute its business strategy (transitioning sales capabilities, expanding solutions capabilities through acquisitions, etc.) and implement its cost efficiency measures.
The technological advances are rapid, and players are in a constant race to innovate not only on the technologies they provide but on their business models and all of their services and solutions. Emerging players and strategic relationships between competitors could easily shift the competitive landscape before the company finds a way to react.
Key Takeaway #3: When making transformational decisions, prioritize thinking long-term
A major acquisition, or a merger, between industry leaders is a bet on the industry’s future.
If you believe in the bet long-term, don’t sacrifice a good move for short-term returns, as HP did with EMC. Instead, do your due diligence in the consideration phase:
- Consider real alternatives.
- Understand deeply how the capabilities of both companies will be improved.
- Validate your assumptions with current market needs and trends.
- Move faster than the competition.
Why is Dell so successful?
One of the key reasons Dell has been so successful is Michael Dell’s intuition and strategic instinct.
He demonstrated a consistent ability to take an accurate pulse of the market, make a winning bet and chase it relentlessly by performing a business transformation. Additionally, Dell never lost one of its core strategic strengths: building strong relationships with its customers by providing excellent customer support and tailored solutions to meet their unique needs. The company has also been successful in streamlining its operations and supply chain, which has allowed it to offer competitive prices and high-quality products.
Dell puts the customer first and makes strategic pivots with perfect timing.
How Dell’s vision guides its steps
According to Dell’s annual report, its vision is:
“To become the most essential technology company for the data era. We seek to address our customers’ evolving needs and their broader digital
transformation objectives as they embrace today’s hybrid multi-cloud environment.”
And their two strategic priorities, growing core offerings and pursuing new opportunities, are their roadmap to achieving it.
Growth by numbers
Dell – From Direct Sales to Channel Strategy
October 10, 2011
This management case study briefly discusses Dell’s channel strategy and partner program introduced to recapture its lost market leader position. The case further highlights how Dell has successfully transformed itself from its direct-sales-only mantra to building a successful reseller network within three years.
Case Contents
Introduction.
- Dell’s unique ‘direct build-to-order’ sales model
- Dell’s Transformation over the years
- The 80s – PCs by mail
- The 90s – Extending Direct sales, user-customized systems & JIT
- The 2000s – Moving towards a broad-based IT company
- Dell – Quick Facts
- Michael Dell – Leading from the front
- Dell’s Channel Strategy
- White Box program
- Partner Program – Dell PartnerDirect
- Three tiers in Dell PartnerDirect
- Bibliography
- Exhibit 1 – How Dell’s direct build-to-order’ sales model worked
- Exhibit 2 – Five key elements in Dell’s successful Direct Model
- Exhibit 3 – Dell – Business Segments
- Exhibit 4 – Dell Historical Timeline
- Exhibit 5 – Requirements for Dell PartnerDirect program
- Exhibit 6 – Dell PartnerDirect Timeline – Dec 2007 to 2008
- Exhibit 7 – Dell – Product Lines and Brands
- Exhibit 8 – Dell Inc. – Historical Stock Chart
- Exhibit 9 – Dell Inc. – Historical Income Statement
- Exhibit 10 – Dell’s market share in Q1 2009 versus other PC makers
Sample Page of case study
[quote]”We don’t think about the channel as a second thought – it’s integrated into everything we are doing. Every new offering and capability has partners in mind.” – Michael Dell in September 2011. [/quote]
[quote]“Our channel business continues to grow, continues to prosper, and we continue to attract new partners and grow our install base, and become a bigger and bigger part of the Dell portfolio.” – Davis, Dell’s global channel chief in 2011. [/quote]
In January 2007, Dell had lost its No. 1 position in worldwide PC shipments to Hewlett-Packard Company (HP). In 2011, Dell reported the largest revenue increase in the company’s history when it reported its results for financial year 2011. Within three years, Dell had successfully transformed itself from its direct-sales-only mantra to building a successful reseller network.
Dell has probably witnessed more changes in its business model than many other companies have. Dell is now engaging more with channel strategy and is on a channel-hiring blitz seeking ways to improve working with channel partners. Dell is making bigger investments in the channel with new innovative channel sales initiatives. The Dell channel business now amounts to about 33 percent of the company’s $62 billion in annual sales in 2011.

- Business User
- IT Professional
- Microsoft 365
- Microsoft Copilot
- Microsoft Copilot for Microsoft 365
- Microsoft Copilot for Sales
- Microsoft Copilot for Small and Medium Business
- Microsoft Adoption Score
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Microsoft Lists
- Microsoft Loop
- Microsoft Mesh
- Microsoft Planner
- Microsoft Power Platform
- Microsoft Search
- Classic Microsoft Teams
- New Microsoft Teams
- Microsoft Teams Premium
- Microsoft Teams Phone
- Microsoft Security
- Microsoft Syntex
- Microsoft Viva
- Outlook mobile
- SharePoint Premium
- Champion Management Platform
- Extensibility Look Book Gallery
- Microsoft 365 Archive
- Microsoft 365 Backup
- Microsoft 365 Learning Pathways
- Microsoft Intelligent Document Processing
- Microsoft Teams App Templates
- New Employee Onboarding Solution Accelerator
- Partner Solution Gallery
- Sample Solution Gallery
- SharePoint eSignature
- SharePoint look book
- Accessibility
- Adoption guides
- Azure Adoption Framework
- Case Studies
- Employee experience
- FastTrack for Microsoft 365
- Frontline workers
- Guidance for virtual events
- Microsoft 365 Roadmap
- Meetings and webinars in Microsoft Teams
- Modern Collaboration Architecture (MOCA)
- Podcasts & Shows
- Remote learning in education
- Skype for Business to Microsoft Teams upgrade
- Streamline end user training
- AI learning hub
- Become a Service Adoption Specialist
- Coffee in the Cloud tutorials
- Developer training
- End user training
- IT Pro training
- Microsoft 365 Champion Program
- Microsoft Learn
- Modern Work Customer Hub (Microsoft Copilot customer training)
- Office Quick Start guides
- Community Events
- Community Tenant
- Global Community Initiative
- Microsoft Community Hub
- Student Ambassador Community
- Release notes
Home / Case Studies / Dell Technologies
Dell Technologies unlocks new connections and streamlines work with Microsoft Viva Topics
Published on March 1, 2023

Dell Technologies
Among one of the world’s leading technology companies, Dell Technologies is committed to transforming business, shaping the future of innovation, and driving human progress. With more than 158,000 employees, the organization has a vast amount of organizational knowledge and content that its tens of thousands of salespeople around the world consider vital. Dell Technologies turned to Microsoft Viva Topics, a knowledge platform that uses AI to bring knowledge and content directly to employees in the Microsoft 365 apps where they already work.
When Sandra Murtagh, Vice President of Global Sales Learning and Development at Dell Technologies, and Karen Butcher, Head of the Global Sales Learning and Development Transformation Office at Dell Technologies, launched a transformation office within the Dell learning and development organization, the goal was to orient the sales function toward the future. “We’re always thinking about what’s next,” says Butcher. “How can we make the learning experience better? How can we make life easier for our sellers?”
They focused on delivering great experiences and integrating their learning platform with Microsoft Teams, where sellers will be able to access training content at the moment of need. Viva Topics emerged as the next logical step. “Moving forward, we want to integrate more and more information in convenient places for sellers,” says Butcher. “That’s exactly what we’ve started to do with Viva Topics.”
The sales learning and development organization at Dell recognized AI as the most effective way to gather and present large amounts of information. “We’re using Viva Topics because it’s an AI-driven curation engine that pulls together both content and people associated with topics,” says Bruce Sánchez, Global Lead for Sales Learning and Development Technology at Dell Technologies. And because Viva Topics will extend to partner apps, employees will gain a full picture of information gathered from Microsoft sources and beyond. “We’re always on the lookout for partner integrations,” adds Srikanth Ramaswamy, Global Lead for Modern Content and Collaboration Services, Dell Digital Team Member Experience at Dell Technologies. After the success of the pilot testing phase, Dell has recently expanded the use of Viva Topics and embraced a full-scale rollout across its global sales force.
Turning to Viva Topics to uncover knowledge from within the apps they use every day leads Dell sales employees to forge new connections with colleagues. “That’s probably one of the biggest benefits we’re experiencing,” says Murtagh. “Historically, we relied on legacy relationships, but with the combination of Microsoft Teams and Viva Topics, we’re opening up collaboration and relationships across all our functions.”
The ability to effortlessly create connections is a boon for a global, highly dispersed sales force. “Dell has championed working from home for many years,” says Butcher. “And today, a hybrid approach is at the forefront of our organization.” Creating a flexible, highly mobile experience for sellers is one way the sales learning and development organization supports the hybrid approach for Dell’s sales team. “The ability to easily search for and uncover content natively in Teams and other applications was a big hit,” Butcher continues. “Especially because people have the same experience on mobile devices and desktops, no matter where they work from.”
“We’ve made Viva Topics a big part of our reimagination of what work looks like for our sellers.”
As the sales learning and development organization expands its use of Viva Topics, it’s also exploring other Microsoft Viva modules, including Microsoft Viva Connections, Microsoft Viva Sales, and Microsoft Viva Insights. It’s an exciting moment. “I’ve been with Dell for 26 years,” says Murtagh. “Where we are now in terms of knowledge management and learning is a massive flip from where we were in the past. We’ve made Viva Topics a big part of our reimagination of what work looks like for our sellers.”
Share this page
- Share on Microsoft Teams
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn

- Guidelines to Write Experiences
- Write Interview Experience
- Write Work Experience
- Write Admission Experience
- Write Campus Experience
- Write Engineering Experience
- Write Coaching Experience
- Write Professional Degree Experience
- Write Govt. Exam Experiences
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 6 (On-Campus)
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 5 (For Platform Software Engineer)
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 2 (On-Campus for Dell International R&D)
- DELL Interview Experience for Platform Engineer
- Dell Bangalore Interview Experience For SDE (On-campus)
- Dell R&D interview experience
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 3 (On-Campus for Dell International R&D)
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 4 (On-Campus)
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 7 (On-Campus)
- Dell Interview Experience | Set 8 (On-Campus)
- Dell EMC Drive Interview Experience
- Dell Technologies Interview Experience for SDE-2 Intern + FTE
- Dell EMC R&D Center Interview Experience for Software Engineer (Off-Campus)
- DELL EMC Interview Experience (On-Campus)
- DELL EMC Interview Experience for Remote Systems Engineer
- Dell Interview Experience for Software Engineer
- Reliance Interview Experience
- Teradata Interview Experience | Set 5 (On-Campus)
- Oyo Rooms Interview Experience | Set 9
DELL Interview | Set 1 (On-Campus)
Pattern : written + 2TECH + 1 HR(But for me 1Tech + 2HR) Type : Online Cgpa criteria : NO Written Exam Modules : 60 questions 70 min (no -ve marking) Aptitude questions were time taking, OS, Data structure, Database and Computer Networks
Tips: Try to read gate material from geeksforgeeks. many of the questions and concepts are from it.
“Be individual and solve them”
Shortlisting Information :
If you can answer at least 40 questions, you’ll get shortlisted. They shortlisted 15 candidates for interviews and also they called 8-10 waiting list candidates for interviews.
My Interview Experience: Round 1 : (35 min) 1. code of Inorder recursive and non recursive 2. Questions on sorting like best algorithm if u consider (no. of swaps, no. of comparisons etc) 3. Sorting words in a large file. 4. T9 Dictionary(most important question of many companies). 5. Insertion sort code (they look for each every corner cases,so better check ur code with all types of test cases and then ask the interviewer to review it ) 6. course projects.
Then he asked to wait for second round.
By that time, those guys(DELL interviewers) have decided to take only 10 members and they already have the count and they were calling the selected candidates and congratulating them and for my friend they have specified the field and under whom he would be working. As the count have been reached, those guys are not interested in me, they would like to take my interview just for formal. I understood the scenario and i should create an special impression about me to get selected and increase their count.
Round 2 : (30 min Tech + HR) Interviewer was the best guy among the other interviewers i met till now. Awesome experience with him. I felt like I was speaking to my friend and some times we were cracking jokes on each other.
Basic HR questions 1. Tell me about yourself 2. +ve’s and -ve’s 3. Explanation of Course Projects(discussion oriented went for 20 min) 4. Show me an example that you are good at team work. 5. course projects 6. Finally he asked me to say about DELL as much as i know? But really speaking, I don’t know anything more about the company information.But i said only one sentence “DELL, The main weapon of most of the Computer Science students over here and every where.”
By that one sentence he was impressed more and he gave me one best complement.
“You have good narrating and management skills. You can be recruited into HR management and can come to you campus again next year to recruit your juniors”. It was an awesome feeling when he said that sentence.
Round 3: (5 min) I said that I was placed in INTEL and want to join INTEL. He said he was impressed with my frankness and ended the interview over there.
Source: http://amarnath-iitd-placement-experience.blogspot.in/2013/12/dell-interview-experience-2013.html
Please Login to comment...
- Experiences
- Interview Experiences
- 10 Best HuggingChat Alternatives and Competitors
- Best Free Android Apps for Podcast Listening
- Google AI Model: Predicts Floods 7 Days in Advance
- Who is Devika AI? India's 'AI coder', an alternative to Devin AI
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Your Browser is Out of Date
Nytro.ai uses technology that works best in other browsers. For a full experience use one of the browsers below

Case Studies
Demonstrable examples of Dell Technologies capabilities within the realm of Converged Core for Telecom.

Communication Service Provider Builds 5G with Nokia, VMware, and Dell Technologies
This Tier 1 CSP drastically reduced the time and cost to update and manage their 5G standalone core infrastructure with validated integrated telecom solutions by Nokia, VMware, and Dell Technologies.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Dell Technologies Pre Sales Engineer Interview Questions. Updated Aug 20, 2023. Search job titles. Find Interviews ... Second round is a case study round where a problem statement is given and we have to prepare solution and ppts. Next will be interviews and HR be final. ... Passion for Pre sales. 1 Answer. Be the first to find this interview ...
First round was communication based. They give some topics and you have to talk about it for 2 minutes .They will check our confidence, flow of narration and how well we can talk in given time period. Second round is a case study round where a problem statement is given and we have to prepare solution and ppts. Next will be interviews and HR be ...
2 Dell Technologies Pre Sales Analyst interview questions and 3 interview reviews. Free interview details posted anonymously by Dell Technologies interview candidates.
September 3, 2015. Value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. It is important to note that the pattern of Dell value chain management has been extensively ...
By 1997, Dell's Internet sales had reached an average of $4 million per day. While most other PCs were sold preconfigured and pre-assembled in retail stores, Dell offered superior customer choice in system configuration at a deeply discounted price, due to the cost-savings associated with cutting out the retail middleman.
By 1997, Dell's Internet sales had reached an average of $4 million per day. While most other PCs were sold preconfigured and pre-assembled in retail stores, Dell offered superior customer ...
In 2012, the fact was that the PC business was declining. Every major player could see it with a single glance at their balance sheet. In Dell's case, the decline was even direr since its PC sales were down by double digits. The company desperately needed to turn things around. And only a bold strategic move could do that.
Efficient computing — accelerating systems science research. The School of Systems Science at Beijing Normal University uses Dell EMC PowerEdge MX modular infrastructure to conduct systems science research. The solution has increased research computing capacity by a factor of more than 100. With rapidly expanding student and business needs ...
Dell - From Direct Sales to Channel Strategy. October 10, 2011. This management case study briefly discusses Dell's channel strategy and partner program introduced to recapture its lost market leader position. The case further highlights how Dell has successfully transformed itself from its direct-sales-only mantra to building a successful ...
Dell EMC Converged Platform Helps ProMedica Roll Out Epic EHR. To replace outdated systems and costly IT sprawl, ProMedica reduced its number of data centers by two-thirds and eliminated unplanned downtime by deploying converged infrastructure from Dell Technologies. Case studies depicting successful installations of Dell VxBlock Systems.
Summary. Among one of the world's leading technology companies, Dell Technologies is committed to transforming business, shaping the future of innovation, and driving human progress. With more than 158,000 employees, the organization has a vast amount of organizational knowledge and content that its tens of thousands of salespeople around the ...
a $500,000 opportunity.". Tech Data also helped a medium-sized reseller who wanted to start selling storage and servers in the government, construction and healthcare verticals. Within three months, the reseller closed. a $77,000 storage deal, while meeting its existing business goals. a unified team," says Attinella.
Dell's sales and marketing. ... which are user- to-user support postings where topics range from support to pre-purchase or enthusiast discussions. There are millions of members with tens of thousands of discussions and accepted solutions each week. ... (2008); Dell case study; Online Marketing Masterclass, presented at the Royal Institute of ...
They shortlisted 15 candidates for interviews and also they called 8-10 waiting list candidates for interviews. My Interview Experience: Round 1 : (35 min) 1. code of Inorder recursive and non recursive. 2. Questions on sorting like best algorithm if u consider (no. of swaps, no. of comparisons etc) 3. Sorting words in a large file.
Case studies related to Dell Technologies solutions for SAP. Product page Video - Turn operations into outcomes with 4-socket servers. SAP HANA. SAP. html. Customer stories. Read about customer success stories with Dell Technologies solutions for SAP. Intel.
Case Study Locked. Reference Rating 4.7 / 5.0. Customer References 23 total. About. CRITICALSTART is leading the way in Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services. Their Trusted Behavior Registry reviews every alert to determine if it was generated by known-good behavior versus unknown behaviors that need to be investigated by their analysts.
Case Studies. Demonstrable examples of Dell Technologies capabilities within the realm of Converged Core for Telecom. This Tier 1 CSP drastically reduced the time and cost to update and manage their 5G standalone core infrastructure with validated integrated telecom solutions by Nokia, VMware, and Dell Technologies. Demonstrable examples of ...
IT procurement options for global organizations. Dell Premier provides a single platform for global purchasing, reporting, and order status; allowing for multi-country, multi-currency commerce. With Premier global procurement, organizations benefit from: Globally consistent pricing and standards. Localized currency & product options.