

Business Plan Demand Analysis, Four Things to Consider
Small businesses and entrepreneurs use demand analysis to:
- Consider substitute products and services
- Get input from (potential) customers
- Determine what “drives” demand
- Understand what variables affect demand and to what degree
Demand analysis is about challenging your preconceived notions regarding your product/service. A stress test, if you will. A demand analysis will take your idea and start molding it into something that has even higher potential.
As an entrepreneur, you can’t be too stubborn. You have to be flexible. After going through this process, the hope is that you’ll come out the other end with an even more refined idea and a greater chance at success.
Market research and competitive analysis for a business plan
This is the second post on drafting a business plan for your startup. These posts are modeled after the SBA Business Guide .
Want to know how many people are included in your “customer avatar?” Read this post: BUSINESS PLAN DEMOGRAPHICS – DEFINING A TARGET MARKET
Business plan demand analysis of the total market
When first thinking about the market for your product/service, don’t define it too narrowly. Try to think of substitutions that you might not have otherwise considered. No, you might not compete directly with these substitute products, but the presence of substitute products will have an impact on your pricing and demand.
Pricing too high could push customers to these substitute products. Even if that pricing seems in line with your value proposition when compared to direct competitors. But, theoretically, the amount demanded changes (inversely) with the price. A higher price will push customers to consider alternatives. A lower price should result in a higher volume sold.
Further defining the market for my product
As I mentioned in my first business plan post on the topic of demographics, I am working alongside you. I have a prospective product that I would like to explore the viability of, and I am creating a business plan for this product as I write these posts. As a reminder, my potential product is an all-natural hair-thickening topical supplement.
Anyhow, in the previous post, I used “customer avatars” to roughly ascertain the size of my market. I think I was fairly liberal in that estimation. The three of my avatars that were the most detailed totaled approximately 5.2 million people. The avatar that was broader included 6.5 million people.
Want to know what a top-down and bottom-up analysis would say about your market size? Read this post: MARKET SIZE FOR A BUSINESS PLAN – 2 METHODS TO GAUGE IT
Substitute products
As mentioned above, I have to keep in mind that not all of these people will pursue hair loss treatment. Many, will just accept it as a normal part of aging. Others will choose to address the problem but will pursue an alternative treatment method to topical supplements. Some of these alternative treatment methods include:
- Biotin, vitamin D, Viviscal, Nutrafol, Finasteride (Propecia), collagen powder, nutriceuticals, Spironolactone (Aldactone)
- Toupees, hair fibers
- Laser treatments, microneedling, hair transplants, protein-rich plasma injection
- HairMax LaserComb, light treatment
In addition to substitutions, I have to consider the direct competition. The alternatives that are also topical. Those include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine), rosemary essential oil, pyrithione zinc shampoo, scalp tonic/serum
Obviously, there’s no shortage of alternatives to my prospective product. However, many of these treatments are ongoing and the potential exists for customers to combine them.
After listing these potential substitutions, it dawned on me that there are a couple of different classes of hair loss. I would probably target individuals that are in the early stages and are merely looking for help to slow down and, hopefully, somewhat reverse the initial effects of hair loss.
Another thing that dawned on me when researching substitutions is that it might be a mistake to only consider men when ascertaining the market for this product. Most of the results I found when searching “hair loss treatments” were articles targeted at women.
As I said, I’m taking this journey right along with you. So, I’m refining my idea and picking things up as I go along.
Gathering survey information for your business plan demand analysis
The next steps are mostly statistical. That might give you pause if numbers aren’t your thing.
I really do wish I could provide you with the handiest spreadsheet imaginable to manage the information you find. There are just too many variables, though. Different surveys asking different questions. Not to mention, every industry is going to address unrelated topics. I just couldn’t figure out how to make a one-size-fits-all tool.
What we’re going to do is compile whatever relevant statistical information we can get our hands-on, and interpret what we find. You can input this information into your own spreadsheet if you like
Statistical information, hopefully, can be obtained from a simple internet search. “[your topic/industry] survey results”, or something similar should yield some useful information. If you can’t find relevant info, then you might have to reach out to industry trade magazines or organizations.
As far as how much survey information to collect – there’s no clear answer. It depends, first and foremost, on the abundance of such information. If there is plenty available, then I guess I’d recommend collecting it until you’re tired of doing so. You can always circle back around and search for more specific results if you need to in the future.
What to focus on
Right now, focus on demographics information, substitute product information, and information about motivation (drivers).
This is where having it in a spreadsheet will come in handy. With the numbers in a spreadsheet, you can combine survey information and break it down as needed. Check out my example below to see what I mean.
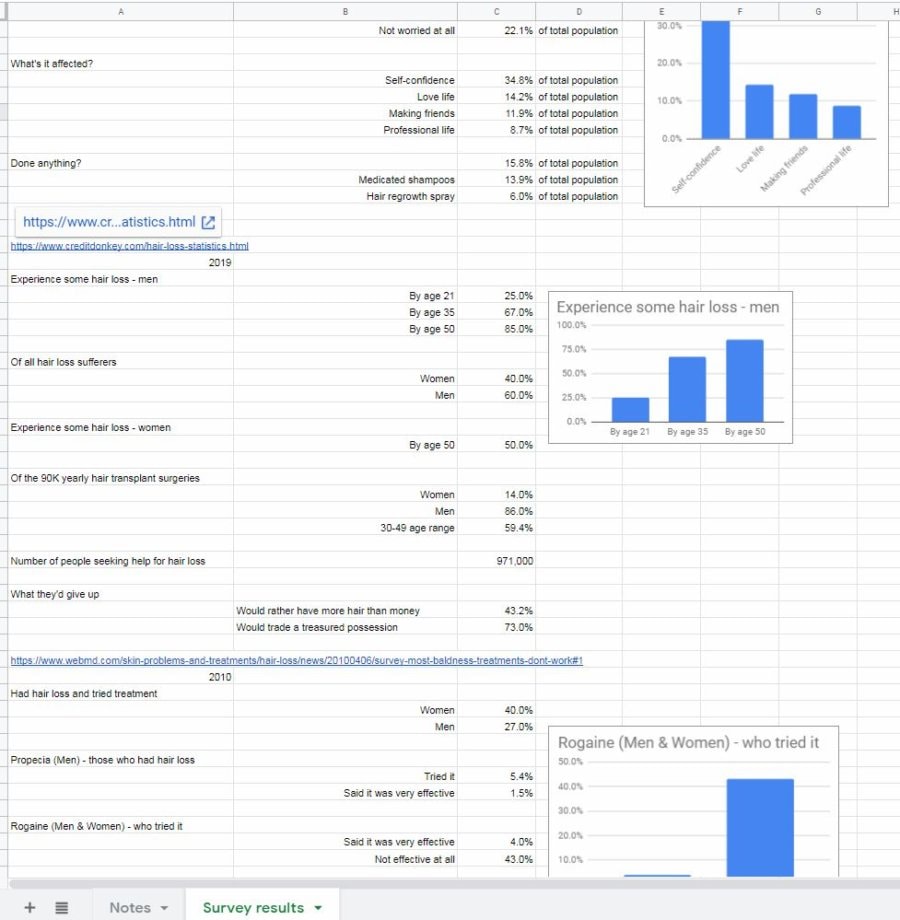
Survey information about my product
There was no shortage of survey results regarding hair loss. In fact, I grew tired of collecting information well before I was able to read it all.
I must admit, I learned something on this step. I learned that it probably makes more sense to do this research before creating customer avatars rather than after .
This research showed me that hair loss in women is a considerably more prevalent problem than I knew. So, I should definitely not exclude women when trying to calculate the size of my target market. Additionally, I learned a lot more about the age that hair loss starts to affect men and women. Not to mention, a lot of other interesting tidbits related to marketing and substitute products.
I simply typed the figures I found into the cells and tried to organize it in a somewhat easy-to-read format.
To make this information as useful as possible, I also included a link to the survey – in case I wanted to reference it again. Also, I thought it would be useful to make note of the year the survey was conducted. That way, I could note trends, if any existed.
Finally, to top it all off, I put in some charts. Charts can help to illustrate ideas in a way that numbers can’t, sometimes.
Now, I have a nice little foundation of data to build my business plan off of. I also know that there is plenty of other information out there if I want to delve further on a specific topic.
Divide total industry demand into its main components.
Now, you want to start to organize the information you found in a logical manner.
First, isolate the information related to demographics or that which otherwise describes your potential customers to you. You want to break this information up so that you can get an idea of what your potential customers might look like. You should, hopefully, begin to see customer “avatars” take shape.
Yes, I asked you to create avatars in the previous post. As I said above, that was probably premature. It would make more sense to create the avatars with this survey information, then use the census/demographic information to estimate the size of the market based on what you found.
Live and learn…
After you have the demographic information in good order, move on to the “solution” information – if available. This is information that specifies how customers are solving their problem(s) now.
If you’re lucky, this information will join seamlessly with the demographic information you organized above.
Start with the simplest questions (those with the fewest variables) and expound from there.
What if my survey data is inconsistent?
You might run into a situation where you have conflicting information. Or you might find yourself in the fortunate situation where different surveys seem to corroborate the same statistics.
If your information sources don’t jive, you have a couple of options. First, you can move forward with the information you deem to be the most trustworthy. Or, alternatively, you can average what you found. This works well if the differing results are relatively close together. Finally, you can choose to use the data source that is most recent – particularly if your industry is especially dynamic.
All of your numbers aren’t going to jive up perfectly. However, at this point, you are armed with a lot better information than when you started. Better information will ultimately lead to better decisions.
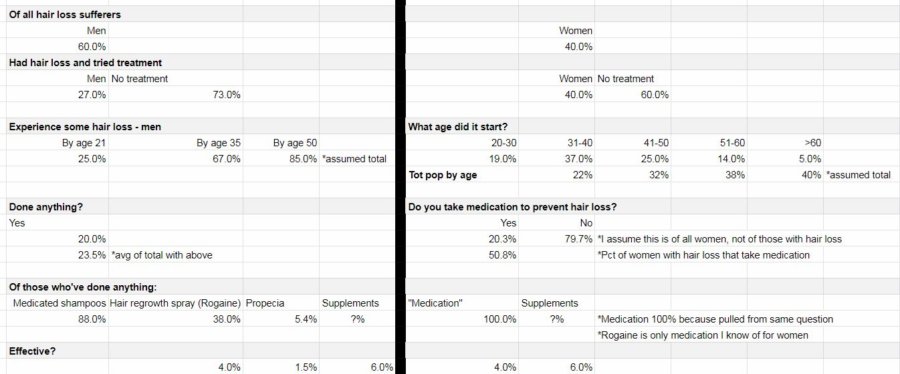
Industry components for my product
Demographics.
For my part, I like to start simple and divide my demographics based on the variable with the fewest options. In this case, the simplest variable only has two choices – men and women.
From there, I used information that I found regarding the percentage of men and women that have had hair loss and have tried treatments.
Next, I break things down further based on the age that men and women started experiencing hair loss. I was fortunate to find information for both genders.
That’s the extent of demographic information I was able to obtain. I would have liked to have found some information regarding income or socioeconomic status. If that information proves to be critical as I move forward with my business plan, I’ll have to circle back around to see if I can track it down.
Once I felt good about my (revised) customer avatars, I moved on to “solution” information.
Want to use data.census.gov to know how big your potential market is? Read this post: CENSUS DATA MARKET RESEARCH AT THE NEW DATA.CENSUS.GOV
Again, thanks to the abundance of information I was able to find, I found similar questions for both genders. The first question was the simplest. It asked if the person with hair loss had done anything to address the problem.
From there, I had a couple of survey questions that explored the alternatives that hair loss sufferers had tried in the past. Additionally, I found results that gave insight into how effective these alternatives were.
When all was said and done, I had the groundwork laid for the ability to know how many potential customers I might have, their demographics, what they have tried so far, and how well those alternatives had addressed the issue at hand.
Here’s what my worksheet looks like after sorting my information into industry components:
Business plan demand analysis of drivers
Hopefully, in your search for survey results, you came across some information that provided insight into the “why people buy” question.
In particular, we’re looking for drivers of sales here. Specifically, what circumstances compel a customer to buy your product/service (or a substitute)? Hint: people usually buy to solve a problem. To avoid pain, not seek pleasure. Or, so I’ve been told…
Insight into what compels your customers to buy will not only be valuable in the drafting of the remainder of the business plan but in all your marketing efforts once you are up and running.
The information about who your customers are (from the previous step), why they buy, and what steps they are currently taking to solve their problems (also from the previous step) will hopefully paint a clear picture for you. A picture that will guide you to a point where you can position your strengths in a manner that will help other people’s weaknesses.
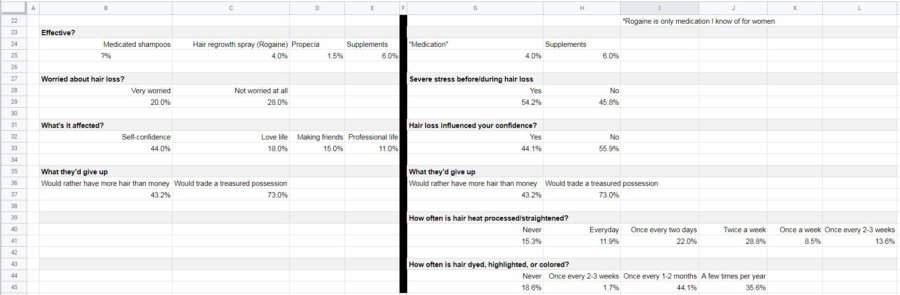
Understanding the drivers of demand for my product
Again, I was fortunate to have an abundance of survey information to draw from. A couple of my surveys not only touched on how hair loss made people feel but also on specific actions that they had taken before the hair loss started.
This information tells me an angle I can take when marketing my product, plus where a lot of my potential customers are going before they start to experience this problem. That place…the hairdresser.
Of course, that’s for women. Though there’s no rock-solid proof that it’s hairstyling that is contributing to hair loss in women, there is enough correlation to make a compelling case. For men, on the other hand, hair loss just seems to be the hand that most are dealt.
But, before we get into that, let’s look at some of the emotional drivers that might compel customers to purchase a topical hair loss supplement…
Drivers for men
On the “men” side I got information about how “worried” men were about hair loss. This told me that most men were, at least, “somewhat” worried about hair loss.
Beyond that, there was valuable information about how hair loss had affected them negatively.
Finally, the most valuable information, to me, was a question of what they would give up to solve this problem (men & women). The answers were encouraging for someone who was hoping to build a business in this industry. Almost half would rather have more hair than more money. Three quarters would give up a prized possession for more hair.
While I acknowledge that I’m not marketing a guaranteed cure to hair loss, that tells me that people are willing to try anything to fix this problem. As I know from my market segmentation analysis, supplementation works for about 1 in 17 people. Not great odds, by any means. But good enough, I hope, to at least try a new product. Especially when the ingredients are all-natural and offer no downside.
Drivers for women
About half had stress prior to experiencing hair loss. That’s a coin flip. It doesn’t mean that the hair loss was caused by the stress (though it surely didn’t help). But it provides insight into what women are feeling prior to and while they are experiencing this problem.
I also included the “What they’d give up” question on the women’s side of the analysis because my source for that information didn’t specify either gender. Plus, it seems feasible that women would feel the same or even stronger. It’s my opinion that society values female attractiveness above male attractiveness.
Finally, we get down to the brass tacks. A potential cause-and-effect situation for the problem I’m attempting to address. The number of women that are currently experiencing hair loss are also (possibly) straightening/heat processing or getting their hair colored on a semi-frequent basis.
This tells me that hairstyling might play a part in a lot of women’s hair loss (this goes back to the pressure to be attractive thing). Therefore, I should consider marketing my product in salons and other establishments that focus on women’s hair.
There’s still a lot of analysis to be done. But, two steps into the process of drafting my business plan, I feel a lot more confident about my understanding of the environment.
Here’s a look at my spreadsheet with the driver information included:
Business plan demand analysis of sensitivity
To this point, the goal has been to make assumptions and get answers. We want to have a better understanding of the environment in which our business will operate. Hopefully, you feel that you’ve accomplished that.
But, we don’t do ourselves any favors by lying to ourselves.
Well, yes. But probably not willingly.
You start off excited about your business idea. So excited that you decide to take the first step (something that the vast majority of people won’t do). You begin to write a business plan. You can feel your idea taking shape. You’ve already refined your idea a bit and feel that by the time this whole exercise is over, there’s no way you can fail. You’ve got momentum and your confidence keeps increasing.
That is all very good. Confidence is key. But, if everything looks rosy, you might be blind to a risk that could put your baby in jeopardy.
So, I don’t want to be a killjoy. But, for the sake of our businesses, let’s take a step back and play devil’s advocate. We need to ask ourselves some tough questions and challenge our assumptions. If we can rise to these challenges, and address them with confidence, our chances of success are that much greater.
Go back through your segmentation and demand drivers and think critically about this information. Some statistics might be a given, without much wiggle room. Others might be misrepresentative of reality. In these instances, tap into your inner cynic.
Make notes of what the worst-case scenario might look like. If you’re using a spreadsheet, like me, maybe use a different colored text. Address things like survey questions that might have been misinterpreted or alternative explanations for results.
Don’t get too down-and-out here and don’t dwell on this step too long. You don’t have to necessarily plan what you would do if these worst-case scenarios came to be. You just need to imagine them so that when the time comes for serious planning, you can take these risks into consideration.
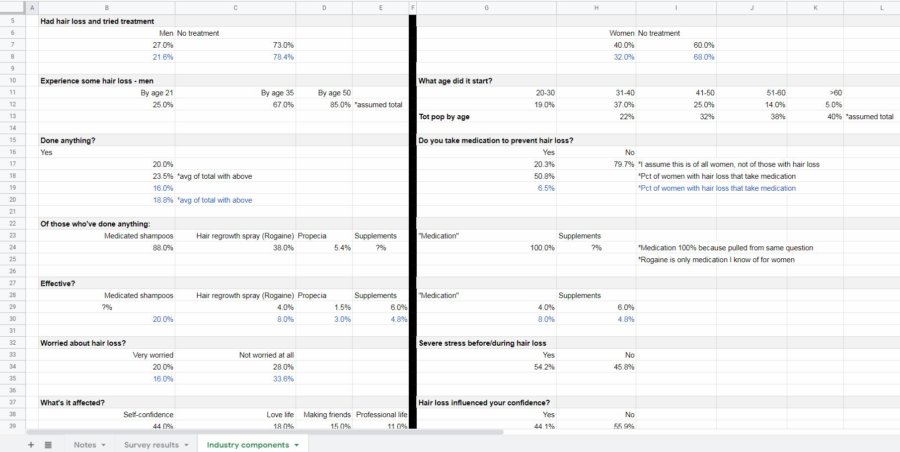
Demand sensitivity for my product
I think my categorization by demographics is pretty safe. It’s rather well established how many men and women experience hair loss. The only thing that I might tweak is the number of men and women who have had hair loss and tried treatment. I lowered those estimates by 20%. It could be that the respondents’ interpretation of “treatment” is to comb their hair a different way or to shave their heads rather than to buy a product to battle hair loss.
Furthermore, what if the number of people that have “done anything” is lower? What if I misinterpreted the question for women that asked: “Do you take medication to prevent hair loss?” Maybe it was 20% of women who actually had hair loss rather than all women? The effect of that would be dramatic.
What if the alternative treatments were more effective than I’ve been led to believe? It could be that the respondents only consider “effective” to be a restoration to a full, thick head of hair? Also, just because they consider them ineffective, it doesn’t mean that they’ll stop using them. They might think that all of their hair will fall out if they stop (which could work in my favor, though). Perhaps they were overly optimistic when it came to supplements? It could be that supplements gave them other benefits, but didn’t make their hair loss any worse – so they considered them “effective.”
Could it be that fewer men are really “(very) worried about hair loss” than I’m led to believe? Are more are “Not worried at all?” Plus, it might be that those who are only “somewhat worried” aren’t motivated to do anything about it.
As far as confidence (love life, making friends, professional life) goes, it might be that that hair loss is a contributor to low confidence, but not the primary driver. Maybe they’re overweight or socially awkward and that’s why they lack the confidence they desire?
As far as “what they’d give up” it could be that the respondents were primed by the hair loss questionnaire to be more self-conscious than they usually are. If it came down to it, perhaps not so many would be willing to part with valuables to solve this problem.
Finally, as far as hair styling being a cause of hair loss in women, it could be that I am wrong. Maybe hair styling has no effect on hair loss. Or, maybe women overestimate how often they heat process or color their hair. It only feels like every day/once every 2-3 weeks. When, in fact, they do it a lot less often.
Okay, that’s enough pessimism. It seems unlikely that every worst-case scenario would be true. But, there’s probably a mix in there between my initial interpretations and the not-so-great ones.
Want to back your business plan up with valuable data? Read this post: GOVERNMENT STATISTICS FOR MARKET RESEARCH VIA USA.GOV
This exercise should help me going forward to make realistic forecasts and assumptions. Which, in turn, should help me be proactive to some of the challenges I might face.
Here’s a final look at my spreadsheet with my worst-case notes in blue:
Business plan demand analysis
This step takes a little bit of thought and a decent amount of research. This is done to give you a deeper understanding of the market you hope to compete in and the customers you hope to sell to.
What other steps would you have taken to refine estimates of demand?
Do you think my demand sensitivity was rational? Or, was I taking it too easy on myself?
Join the conversation on Twitter!
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.

Demand Analysis: Meaning and Types

Demystifying Demand Analysis: Unveiling the Secrets of Market Research
In today's fierce business terrain, grasping customer demand is pertinent to excellence. Demand analysis plays a crucial role in assisting businesses to make informed decisions, chart out efficient marketing strategies, and optimize their product offerings. By searching deep into market trends, consumer behavior, and preferences, demand analysis equips companies to align their supply with the ever-transforming demands of their target audience. Here, we will traverse the concept of demand analysis, its importance, and how it can be leveraged to amass a competitive edge.
What is Demand Analysis?
Demand analysis is the method of accessing the desire and purchasing power of consumers for a specific product or service within a given market. It comprises inspecting different factors that shape demand, such as consumer demographics, economic conditions, pricing, competitors, and market trends. By comprehending the demand for a product or service, businesses can make informed decisions about production, pricing, marketing, and distribution.
Significance of Demand Analysis
Market Opportunity Identification: Demand analysis aids businesses figure out unexploited market opportunities by assessing consumer needs, inclinations, and behaviors. It offers worthy insights into market gaps, emerging trends, and unmet customer requirements, permitting companies to construct new products or modify current ones to fulfill those needs.
Forecasting and Planning: Precise demand forecasting is instrumental for successful production planning, inventory management, and resource distribution. By examining historical data, market trends, and customer behavior, demand analysis empowers businesses to forecast future demand patterns, anticipate market fluctuations, and make informed decisions about production capacity and timing.
Pricing and Revenue Management: Apprehending consumer demand assists businesses decipher optimal pricing strategies. By gauging price elasticity, competitive pricing, and perceived value, demand analysis permits companies to set prices that align with customer expectations while enhancing profitability. It helps in revenue management by identifying opportunities for dynamic pricing and promotional activities.
Marketing Strategy Development: Effective marketing campaigns are based on an extensive understanding of customer requirements. Demand analysis offers invaluable insights into target market segments, letting businesses customize their marketing messages, channels, and promotions accordingly. It helps identify the most successful marketing channels and optimize marketing budgets for the most impact.
Methods of Demand Analysis
Surveys and Questionnaires: Organizing surveys and questionnaires is a famous technique to collect direct feedback from consumers. By asking targeted questions, businesses can amass data on consumer preferences, buying habits, and opinions, providing insights for demand analysis.
Data Analysis: Using available data sources, like sales records, customer databases, and market research reports, businesses can conduct statistical analysis techniques to detect demand patterns, trends, and correlations. Data analysis tools and software can aid in procuring meaningful insights from large datasets.
Focus Groups and Interviews: Organizing focus groups or executing interviews with target customers can offer qualitative insights into consumer preferences, motivations, and opinions. This method offers a chance for in-depth deliberations and exploration of underlying parameters shaping demand.
Online Analytics: Capitalising on web analytics tools and social media monitoring, businesses can assess online consumer behavior, involvement, and sentiment. Tracking website traffic, search trends, and social media conversations can unveil valuable insights about consumer preferences and demand.
Demand analysis is an integral component of market research that enables businesses to decipher and accustom to changing consumer needs. Companies can acquire valuable insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and preferences by using varied research methods and evaluating relevant data. This know-how enables them to make data-driven decisions regarding production, pricing, marketing , and innovation. In an ever-evolving business landscape, demand analysis provides the base for strategic planning, helping businesses flourish and stay ahead of their rivals.
Demand Distinctions: Exploring Different Types of Demand in Demand Analysis
In the arena of business and economics, demand is a core concept that propels the production, pricing, and marketing strategies of companies. However, demand is not a monolithic entity; it manifests in various shapes, each with its own features and ramifications. Understanding the different kinds of demand is imperative for executing effective demand analysis, facilitating businesses to tailor their approaches based on particular market dynamics. Here, we will explore the distinctions between different kinds of demand and how demand analysis plays a crucial role in deciphering consumer preferences and behaviors.
Types of Demand in Demand Analysis
Primary Demand: Primary demand symbolizes the overall demand for a product or service category within a specific market. It refers to the aspiration and purchasing power of consumers for a specific category of product, irrespective of brand or particular attributes. For instance, the primary demand for smartphones spans the over-arching desire for smartphones as a technology, regardless of individual brand preferences. Evaluating primary demand lets businesses identify growth opportunities and market potential within a specific industry.
Derived Demand: Derived demand originates when the demand for a specific product or service is directly shaped by the demand for another allied product or service. It often occurs in business-to-business (B2B) contexts, where the demand for components, raw materials, or intermediate goods is derived from the demand for the final product. For example, the demand for automobile tires is derived from the demand for cars. Knowing derived demand is paramount for suppliers and manufacturers to align their production and distribution strategies accordingly.
Composite Demand: Composite demand exists when a product or service demands a multitude of purposes. It comprises catering to varied consumer segments with varying needs and preferences. An example of composite demand is milk, which is consumed as a beverage, used in cooking, and serves as an ingredient in various food products. Analyzing composite demand lets businesses identify market segments and accordingly sketch their marketing and distribution strategies to address diverse consumer needs.
Seasonal Demand: Seasonal demand refers to shifting demand patterns owing to seasonal or periodic parameters. It is characterized by distinctive peaks and troughs in demand throughout the year. Seasonal demand is widespread in industries such as fashion, tourism, and agriculture. By analyzing seasonal demand, businesses can generalize and plan for fluctuations, adjust production and inventory levels, and produce targeted marketing campaigns during peak seasons.
Price Elastic Demand: Price elastic demand refers to the sensitivity of consumer demand to changes in price. When demand is price elastic, a small change in price leads to a proportionally larger change in demand. Whereas, when demand is price inelastic, changes in price have a comparatively smaller impact on demand. Understanding price elasticity helps businesses investigate optimal pricing strategies, predict revenue, and assess the potential effect of price changes on consumer demand.
Demand analysis is a pivotal tool that pushes businesses to understand consumer preferences, anticipate market trends, and make informed decisions across different business functions. By realizing and analyzing the different kinds of demand, companies can tailor their strategies to meet specific market dynamics effectively. Whether it is primary demand, derived demand, composite demand, seasonal demand, or price elastic demand, each type offers valuable insights that can influence product development, pricing, marketing, and supply chain management approaches.
Unveiling the Exceptional Demand Curve: Analyzing Demand Patterns for Informed Decision-Making
Demand analysis forms the bedrock of successful decision-making for businesses. By acknowledging consumer preferences, behaviors, and purchasing power, companies can align their strategies to meet market demands. The exceptional demand curve is a concept within demand analysis that throws light on unique demand patterns and their implications. Here, we will explore the exceptional demand curve, its importance in demand analysis, and how it aids businesses in making informed decisions to achieve success in the marketplace.
The Exceptional Demand Curve: A Unique Perspective
The exceptional demand curve challenges the traditional notion of a linear demand curve, which illustrates the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. Unlike the typical downward-sloping demand curve, the exceptional demand curve exhibits unique patterns due to specific factors or market conditions that defy conventional expectations. These factors can cause demand to digress from the usual price-demand relationship, resulting in exceptional demand patterns.
Understanding Exceptional Demand Patterns
Veblen Goods: Veblen goods are a kind of exceptional demand pattern where consumers perceive higher-priced goods as more desirable. The demand for these goods rises as their prices rise, contradicting the law of demand. The Veblen effect occurs when consumers link high prices with luxury, exclusivity, or social stature, leading to higher demand as prices increase.
Giffen Goods: Giffen goods symbolize a rare exception where the demand for a product rises as its price rises, in spite of consumers having a lower income. This situation occurs when a product is regarded as a staple or essential, and its price increase compels consumers to allocate a larger chunk of their restrained budget to that particular item, resulting in higher demand.
Snob Effect: The snob effect alludes to a demand pattern where consumers seek products or services to distinguish themselves from others. In this case, consumers demand goods precisely because they are unique or exclusive. As demand for the product increases, its desirability disappears, leading to a downward-sloping exceptional demand curve.
Bandwagon Effect: The bandwagon effect is the opposite of the snob effect. Consumers are driven by the desire to conform and be part of a trend or social group. As more people adopt a particular product or trend, its demand increases, producing an upward-sloping exceptional demand curve.
Utilizing Demand Analysis for Exceptional Demand Pattern
Demand analysis plays an instrumental role in figuring out and deciphering extraordinary demand patterns. By employing different research methods, businesses can gather data on consumer preferences, organize market surveys, assess historical sales records, and leverage economic indicators. These insights let businesses assess market dynamics, identify exceptional demand patterns, and make informed decisions.
Implications for Business Decision-Making
Understanding exceptional demand patterns has important implications for businesses. By acknowledging the existence of Veblen goods, Giffen goods, snob effects, or bandwagon effects, companies can tailor their strategies accordingly:
Pricing Strategies: Exceptional demand patterns challenge conventional pricing models. For Veblen goods, a higher price may be significant to maintain the notion of luxury. Giffen goods may warrant strategic pricing to ensure affordability. Businesses need to adapt pricing strategies to leverage these demand patterns effectively.
Product Differentiation: The snob effect and bandwagon effect stress the significance of product positioning and branding. Companies can leverage these effects to generate an emotion of exclusivity or appeal to the longing for social conformity. By stressing the unique characteristics or restricted availability of a product, businesses can tap into the snob effect. Conversely, leveraging the bandwagon effect comprises highlighting the popularity and widespread adoption of a product to attract consumers.
Marketing and Promotion: Exceptional demand patterns need tailored marketing and promotional strategies. For Veblen goods, marketing efforts should center on highlighting the luxury and status linked with the product. Giffen Goods may mandate targeted promotions that stress affordability and value. The snob effect and bandwagon effect can be harnessed through strategic influencer marketing, social proof, and creating a sense of community around the product.
Product Development and Innovation: Recognizing extraordinary demand patterns can propel product development and innovation. For example, understanding the Veblen effect may prompt businesses to produce high-end variations of their products to cater to luxury-seeking consumers. Identifying Giffen goods can inspire companies to develop cost-effective alternatives that meet essential needs.
Market Segmentation: Exceptional demand patterns often showcase unique consumer segments with distinctive preferences and behaviors. Businesses can leverage these patterns to identify and target specific customer segments more effectively. By tailoring marketing messages and product offerings to these segments, companies can leverage extraordinary demand and maximize their market share.
Exceptional demand patterns, represented by the exceptional demand curve, challenge conventional assumptions about price-demand relationships. By knowing and analyzing these patterns, businesses can make informed decisions in domains such as pricing, product differentiation, marketing, and innovation. Recognizing the existence of Veblen goods, Giffen goods, snob effects, and bandwagon effects empowers companies to customize their strategies and tap into consumer behavior more successfully. Demand analysis plays a crucial role in uncovering these exceptional demand patterns and providing valuable insights for businesses seeking a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Exploring the Chief Characteristics of the Law of Demand: Insights for Effective Demand Analysis
The law of demand is a foundational principle in economics that underlies the correlation between the price and quantity demanded of a product or service. Understanding the chief features of the law of demand is critical for businesses carrying out demand analysis. By delving into these characteristics, companies can acquire valuable insights into consumer behavior and make informed decisions regarding pricing, marketing, and resource allocation. Here, we will explore the primary characteristics of the law of demand and its relevance in demand analysis.
Chief Characteristics of the Law of Demand
Inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
The essential characteristic of the law of demand is the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. According to this principle, when the price of a product or service rises, the quantity demanded by consumers decreases, and vice versa. This behavior occurs due to the substitution effect and income effect. As the price rises, consumers tend to seek alternatives or substitutes, reducing their demand for the higher-priced item. Additionally, a higher price can reduce consumers' purchasing power, leading to a decrease in overall demand.
Ceteris Paribus Assumption
The law of demand assumes that all other factors influencing demand remain constant, except for the price of the product or service in question. This assumption, known as ceteris paribus, lets economists and businesses isolate the effect of price changes on demand. In reality, however, different factors, such as consumer income, tastes and preferences, availability of substitutes, and market trends, can shape demand. While demand analysis regards these factors, the law of demand centers specifically on the relation between price and quantity demanded, assuming other factors remain constant.
Individual and Market Demand
The law of demand is applicable to both individual consumers and the overall market. At the individual level, consumers make choices dependent on their own choices, income, and needs. When aggregated, these individual demand curves produce the market demand curve, which represents the combined behavior of all consumers in the market. The law of demand holds true at both levels, indicating that as the price of a product increases, individuals and the market, as a whole, will demand less of that product.
Diminishing Marginal Utility
Another characteristic linked with the law of demand is the concept of diminishing marginal utility. Marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction or benefit derived from consuming one more unit of a product. According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, as individuals consume more units of a product, the additional satisfaction they get from each additional unit diminishes. This diminishing marginal utility contributes to the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. As the price decreases, consumers can afford to consume more units, increasing their overall satisfaction.
Relevance of the Law of Demand in Demand Analysis
Understanding the key characteristics of the law of demand is quintessential for businesses conducting demand analysis. By recognizing the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, companies can:
Price Products Strategically: The law of demand stresses the significance of pricing strategies. By assessing demand elasticity and consumer responsiveness to price changes, businesses can determine optimal price points to maximize revenue and profitability.
Forecast Demand: The law of demand offers an edifice for demand forecasting. By considering the relation between price and quantity demanded, businesses can anticipate how changes in price will affect future demand patterns, enabling effective production planning and inventory management. By understanding the price elasticity of demand, companies can forecast how changes in price will affect the quantity demanded. This information is invaluable for managing inventory levels, and production capacity, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
Evaluate Pricing and Promotional Strategies: The law of demand helps businesses assess the effectiveness of their pricing and promotional strategies. By analyzing the price-demand relationship, companies can analyze the effect of price changes or promotional campaigns on consumer behavior. This knowledge facilitates businesses to make data-driven decisions about adjusting prices, offering discounts, or executing targeted marketing campaigns to drive demand.
Understand Consumer Behaviour: The law of demand offers insights into consumer behavior and decision-making processes. By recognizing the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, businesses can acquire deeper know-how of consumer preferences, purchasing power, and sensitivity to price changes. This understanding helps companies tailor their products, marketing messages, and distribution channels to better meet customer needs and maximize sales.
Identify Market Opportunities and Competitive Advantages: Demand analysis, premised on the law of demand, lets businesses identify market opportunities and acquire a competitive edge. By assessing price-demand relationships, companies can figure out underpriced or overpriced products in the market. This knowledge enables businesses to adjust their pricing strategies and leverage gaps in the market, effectively positioning themselves against competitors.
Optimize Resource Allocation: The law of demand assists businesses in optimizing resource distribution. By understanding the price-demand relation, companies can allocate resources more efficiently, emphasizing products or services with higher demand elasticity and profit potential. This optimization can result in improved operational efficiency, cost management , and overall business performance.
The law of demand acts as a guiding principle in demand analysis, offering businesses valuable insights into consumer behavior and market dynamics. By acknowledging the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, companies can strategically price their products, forecast demand, evaluate pricing and promotional strategies, understand consumer behavior, identify market opportunities, and optimize resource allocation. Incorporating the chief characteristics of the law of demand into demand analysis empowers businesses to make informed decisions, meet consumer needs effectively, and achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Post A comment
Recent posts.
.jpg)
FMS Executive MBA: All you need to know.
.jpg)
Executive MBA for Working Professionals in India: Top 20 Colleges.

LPU Online MBA: Fees, Eligibility, & Everything you need to know.

MCA Vs MBA: Which one is the right course for me?.
.png)
MBA in Marketing Management: Best Courses to choose from.
- Executive Certificates
- Colleges in India
- Top MBA colleges in cities
- Product Management
- MBA for Working Professionals
- Strategy & Leadership
Related Blog
You don't have to struggle alone, you've got our assistance and help.

What are General Management Course?

Your Guide to a Transformative Finance Leadership

Mastering Your Strategy: The Art of Implementing a
- Marketing Strategy
- Five Forces
- Business Lists
- Competitors
- Marketing and Strategy ›
Demand Analysis - Meaning, Importance, Steps, Parameters & Example
What is demand analysis.
Demand analysis is a research done to estimate or find out the customer demand for a product or service in a particular market. Demand analysis is one of the important consideration for a variety of business decisions like determining sales forecasting, pricing products/services, marketing and advertisement spending, manufacturing decisions, expansion planning etc. Demand analysis covers both future and retrospective analysis so that they can analyze the demand better and understand the product/service's past success and failure too.
Importance of Demand Analysis
For a new company, the analysis can tell whether a substantial demand exists for the product/service and given the other information like number of competitors, size of competitors, industry growth etc. It helps to decide if the company could enter the market and generate enough returns to sustain and advance its business.
Demand analysis helps in identifying key business areas where demand is highest and areas which needs attention as very low demand indicates different problems like either the customers are not aware of the product/service and more focus must be in advertisement and promotion or the customer needs are not met by current product/service and improvements are needed or competitors have sprung up with better offerings etc.
With the rise of AI (Artificial Intelligence) in recent years, demand analysis has become much more accurate and can very accurately be used to predict future demands and trends. AI models can be trained on multiple parameters and data points to arrive at tangible and actionable demand analysis.
- Demand Based Pricing
- Demand-Backward Pricing
Steps in the Demand Analysis
Demand analysis process needs to be done in a structured manner for a particular market and affects the business strategy and decisions. Some of the steps which are to be followed for the analyzing the demand are:
1. Market Selection
Demand is linked to a market. Without knowing the market properly, demand cannot be analyzed. Every business would be operating in a single or multiple markets but it should be clearly known. The first step is understanding the market and knowing the demand trends for the particular product or service.
2. Product/Service category analysis
Next step would be to make sure which product or service is being used to analyze the demand. A company may be having a product portfolio of 20 products. Total demand would not give a picture at an individual level. It may happen that demand is huge for 5 categories and low for the rest of 15 but still overall demand is high. For analysis, the product category has to be selected. e.g. if a company is selling smart devices it needs to select phones or the tablets only for its purpose.
3. Understanding Business Parameters
Demand is never constant across a single year or a time. A less demand in a particular month may not be a sign of an issue with the product line but it may be that due to climate change, the demand of an item like an air conditioner may go low but it may again rise in summer season.
4. Understanding the competitors and partner trends
For an accurate demand analysis, we also need to see what our partners, vendors and suppliers are predicting in the market as they are also in the same market and product category. Also competitors performance and past sales can help us analyze the demand correctly.
Demand Analysis Parameters
The key drivers while determining demand are:
1. Product's own price
Price of the product plays an important role in demand analysis. If the price is high as compared to competitors or what the customer can pay, the demand would be affected.
It can be low or high depending upon the price point of the product or service.
2. Customer income
They buying power of customer would definitely impact the demand of a product. If the product or service is offered at a price point more than the affordability of a customer group then the demand would be low hence customer income needs to be analyzed for demand.
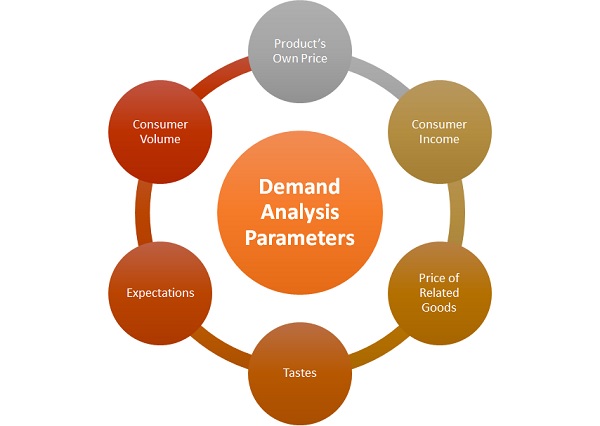
3. Price of competitor goods
As we discussed in the first 2 points about price and buying power, competitor's price adds to the equation and can affect the demand of product/service. If competitor is priced lower then the demand of that particular product would be more and vice versa. It can be different scenario in case of luxury of niche products.
4. Tastes & requirements of the customer
Consumer behavior has be to taken into account. The product or service has to align with the customer's preferences else there would be no demand for the product.
5. Expectations
Sometimes the customer has expectations from a new or existing product based on the overall industry landscape. e.g. if every competitor in the market is offering free warranty service but one company doesn't then most likely it would not be able to meet the customer expectations.
6. Number of customers in the market
The potential market is an important parameter for demand analysis as the customers drive the demand. if the customers are too low then even though the first 5 points are in favor still the demand would never rise as the customer base is too small for a viable business.
Demand Analysis Example
Below is the demand analysis for US restaurant industry (Source: Dun & Bradstreet)
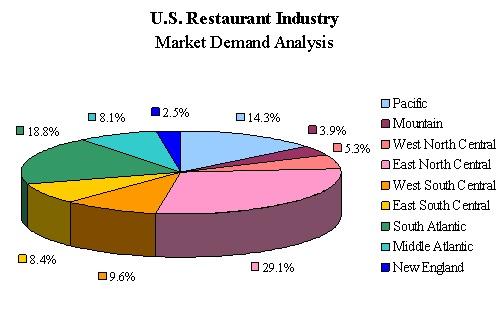
It shows that market activity is highest in East North Central area. The figures are arrived by tracking the annual sales in each region. So for offering a particular product in this market, a company needs to analyze if they can do business in multiple sub-markets with decent demand or focus on sub markets or areas with high demand. Both aspects are part of demand analysis to be done by the company based on product or service parameters.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Demand Analysis along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team . It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
- Sales Management
- Market Segmentation
- Brand Equity
- Positioning
- Selling Concept
- Marketing & Strategy Terms
- Human Resources (HR) Terms
- Operations & SCM Terms
- IT & Systems Terms
- Statistics Terms
What is MBA Skool? About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
- Operations & SCM
- Human Resources
Quizzes & Skills
- Management Quizzes
- Skills Tests
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
- Inventory Costs
- Sales Quota
- Quality Control
- Training and Development
- Capacity Management
- Work Life Balance
- More Definitions
All Business Sections
- Business Concepts
- SWOT Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Mix
- PESTLE Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Top Brand Lists
Write for Us
- Submit Content
- Privacy Policy
- Contribute Content
- Web Stories
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

- What is Customer Segmentation
- Customer Journey Maps
- Visualizing Buyer Personas
- Improving Customer Support Processes
- Guide to Viral Videos
- Marketing Mix
- Ansoff Matrix
- BCG Matrix Template
- Brand Wheel
- Agile Templates
- Chore Chart Templates
- Cost Management Techniques
- Dependency Mapping
- Event Planning
- Expense Report Templates
- Improving Project Estimation Accuracy
- Power Influence Grid
- Progress Report
- Project Evaluation
- Project Management Methodologies
- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirement Gathering Process
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Stakeholder Engagement Model
- Stakeholder Identification
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Stakeholder-theory
- Team Alignment Map
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- User Story Guide
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Critical Success Factors
- Deadline Management
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
Understanding Demand Management
In business, it’s crucial to understand and meet customer demand to succeed. Demand management involves strategies to understand and shape what customers want. This guide explores its importance, basic principles, and strategies for businesses aiming to do well in today’s fast-changing market.
What is Demand Management?
Demand management is a critical component in the strategic alignment of supply with customer expectations. It involves a series of processes designed to manage and forecast customer demand to optimize the balance between supply and demand. This management process not only helps in reducing operational bottlenecks but also enhances organizational agility.
Within a business context, demand management refers to the systematic process of forecasting, planning, and controlling customer demand to maximize operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Managing Demand, Supply and Customer Expectations
Understanding demand management means looking at things like customer behavior, market trends, supply chains, the economy, and rules. This understanding helps predict demand, allocate resources, and make decisions, making it easier to adapt to changes in demand, manage inventory well, and take advantage of opportunities for growth.
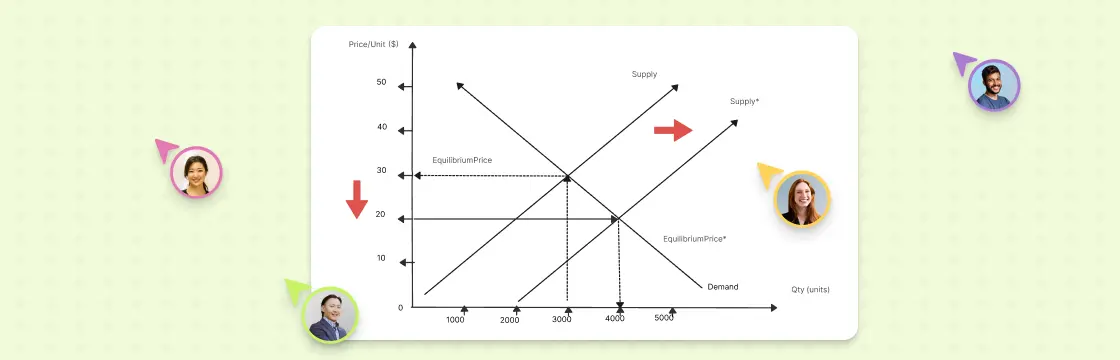
Supply & Demand
Supply and demand is a simple concept in economics. It’s about how much of something is available (supply) and how much people want it (demand). When there’s more supply than demand, prices go down. When there’s less supply than demand, prices go up. The balance between supply and demand determines the price and quantity of a product or service. When they’re equal, it’s called the equilibrium point. At this point, the market works efficiently, and neither buyers nor sellers have a reason to change their behavior. You can easily visualy the supply and demand with a supply & demand graph template .
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Demand management focuses on the customer, aiming to predict and meet demand with the right products and services. Key areas of emphasis include better customer service, more accurate forecasting, and reduced costs.
Specific objectives of customer-centric demand management include:
Improved customer service: Understanding customer needs and behaviors leads to higher satisfaction and better service. Demand management is crucial for businesses to meet customer needs without having too much or too little inventory, which keeps them competitive and keeps customers loyal. Accurate forecasting and managing customer demand help prevent disruptions in the supply chain and problems with operations.
Enhanced forecasting accuracy: Using predictive analytics helps make better decisions and improves supply chain management.
Cost reduction: Improved forecasting optimizes inventory investments and minimizes safety stock levels, saving money. Effective demand management helps you avoid excessive carrying costs, wasted product and the expense of last-minute orders, rush deliveries, refunds and extra staff. If you know what’s coming, you can stock and staff appropriately, maximizing your revenue.
- Product innovation: Develop new customer-appropriate products and refine them based on feedback for ongoing improvement.
- Efficient planning: Balance demand and supply to minimize surpluses using reliable data. Being agile, or quickly adjusting to changes in demand, is very important in fast-moving markets. Effective demand management helps with this, allowing businesses to succeed in changing environments.
The ultimate goals of demand management are increased sales growth and strong profit margins. It serves as a crucial decision support tool for business leaders, contributing to both strategic initiatives and day-to-day operations.
Key Differences: Demand Management VS Demand, Capacity & Supply Planning
Understanding the factors between demand management, demand planning, and capacity planning is crucial for optimizing business operations. Each plays a distinct role in the broader scope of organizational efficiency and resource allocation. Demand management matches supply with demand, while demand planning predicts what customers will want. Capacity planning makes sure there are enough resources for operations.
Demand Management vs. Demand Planning
Demand management aligns what a business needs with what it can supply, thinking about both present and future needs to stay sustainable. Meanwhile, demand planning is more about predicting and meeting customer demand using past data and market analysis.
Demand Management vs. Capacity Planning
Demand management ensures efficient demand fulfillment, while capacity planning guarantees that the organization has enough resources to meet those demands. It’s all about optimizing resource allocation for operational excellence. Integrating demand management with capacity planning helps businesses meet current demands and scale operations effectively. A comprehensive guide to capacity planning. provides further insights into how these strategies can be effectively implemented.
Demand Management vs Supply Planning
Demand management predicts what customers will want. Supply planning figures out how to meet that demand without overspending or sacrificing service quality. It ensures your plans are realistic by considering production, inventory, and logistics.
By understanding these key differences and how they complement each other, businesses can better manage and plan their resources, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational bottlenecks. For more detailed strategies on resource allocation, see 11 resource planning templates for smooth project execution.
Demand Management Examples Within Industries
Demand management involves predicting and fulfilling customer needs efficiently. It’s about using data to forecast how much of a product or service people will want and then making sure you can meet that demand without wasting resources. This applies across different industries, from retail to healthcare, where businesses adjust their plans and operations based on what customers are likely to want.
Retail: Predicting trends and adjusting inventory to avoid excess stock.
Manufacturing: Planning production and resources based on demand forecasts to reduce costs.
Hospitality: Adjusting prices and capacity to maximize revenue and occupancy rates.
Transportation: Optimizing shipping and logistics to reduce costs and transit times.
Healthcare: Allocating resources efficiently based on patient demand to enhance satisfaction.
Technology: Forecasting demand for products and adjusting offerings and strategies accordingly.
Energy: Balancing supply and demand to maintain stability and reduce costs with smart grid technologies.
5 Steps to Effective Demand Management
Effective demand management is crucial for matching business operations with market needs and customer expectations. By following these five steps closely, organizations can improve how they work and better respond to changes in the market.
Analyze Historical Data and Current Market: Start by analyzing historical data and studying current market trends, competitor actions, and economic signals to understand past performance and real-time conditions affecting demand. Visualize research data analysis using Creately.
Forecast Future Demand: Utilize data analysis and market research to predict future demand levels accurately based on the insights gained from historical data and current market analysis.
Develop Flexible Demand Strategies: Create flexible plans to handle expected demand by adjusting operations, marketing tactics, or product offerings as needed, considering both past data and current market conditions.
Integrate Demand Forecasts into Business Planning: Incorporate demand forecasts into overall business planning to align all departments towards common goals, optimizing resource usage and operational efficiency.
Coordinate Demand with Supply Planning and Process Optimization: Connect demand management with supply planning to ensure the supply chain can quickly adapt to changes in demand. Conclude the demand management cycle by evaluating and refining the process to establish the most effective system tailored to the business’s specific requirements. Map out your supply chain to garner deeper insights using effective supply chain management tools
Upon completion of the demand management lifecycle, it is important to initiate a new cycle with a focus on optimization. A thorough evaluation of how the demand management process can be refined to establish the most effective system tailored to the specific requirements of the business is needed. It is essential to acknowledge that the demand management process is dynamic and should adapt and evolve together with the evolving needs of the business.
Advantages of Demand Management
Advantages of demand management refer to the benefits or positive outcomes achieved through effectively forecasting, anticipating, and fulfilling customer demand for products or services. These advantages may include:
Right Inventory Levels: Demand management keeps inventory in line with what customers want, avoiding too much or too little stock.
Happier Customers: Meeting demand accurately makes customers happy, encouraging them to come back and spread positive feedback.
Efficiency Boost: Demand management streamlines production and resources, cutting waste and making operations smoother.
Saving Money: Avoiding excess inventory and supply chain issues saves money on storage, shipping, and holding costs.
Smarter Decisions: Insights from demand management help businesses plan production, buying, and resources better, leading to better overall decisions.
Adaptability: Businesses that manage demand well can quickly adjust to changes in the market and customer preferences, staying competitive.
Maximized Revenue: Matching production and stock with demand means businesses can make the most money by selling what customers want when they want it.
Stronger Supply Chain: Accurate forecasting and management keep the supply chain running smoothly, preventing disruptions and ensuring operations continue.
Good Reputation: Meeting demand consistently builds trust with customers, boosting the brand’s image and reputation. Read Creately’s guide on how to create a winning brand strategy to learn further.
Competitive Edge: Excelling in demand management gives businesses a leg up over rivals by anticipating trends, using resources efficiently, and providing great customer experiences.
Demand Management Challenges
Demand management comes with its fair share of challenges and difficulties that organizations face in effectively predicting, influencing, and fulfilling customer demand.
Forecasting Accuracy: Predicting future demand accurately is hard due to changing trends and customer preferences.
Data Quality and Availability: Reliable forecasts rely on accurate data, which may not always be available.
Supply Chain Complexity: Managing demand across multiple suppliers and locations can be complex.
Seasonality and Market Dynamics: Demand varies seasonally, and markets change rapidly.
Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels is tricky to avoid overstocking or understocking. Read more on techniques to optimize inventory management.
Demand Volatility: Demand can be unpredictable, especially with changing consumer preferences.
Alignment with Business Goals: Ensuring demand strategies align with business objectives is crucial.
Resource Allocation: Allocating resources effectively to meet demand while controlling costs can be challenging.
Demand-Supply Mismatches: Mismatches between demand and supply can lead to issues like stock outs or excess inventory.
Technology and Tools: Implementing the right tools for forecasting and management can be complex and costly.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of robust data analytics, effective communication across departments, strategic planning, and continuous improvement in demand management processes.
Difficulties of Demand Management
Difficulties of demand management refer to the potential drawbacks or challenges associated with forecasting, anticipating, and fulfilling customer demand for products or services. These may include:
Inventory Issues: Poor forecasting can cause too much or too little inventory, wasting money or missing sales opportunities.
Supply Chain Problems: Wrong predictions can disrupt production, supplier relationships, and upset customers.
Wasted Resources: Mismanagement can lead to inefficient production, causing unnecessary costs and reducing profits.
Higher Expenses: Bad demand management can increase costs for rush orders, shipping, and storage, cutting into profits.
Unhappy Customers: Inconsistent supply due to mismanagement can upset customers, harming the brand and loyalty. Explore Creately’s guide on improving customer service processes.
Missed Sales: Failing to meet demand means lost sales and losing out to competitors who do.
Complexity and Errors: Dealing with complicated factors like market trends and customer behavior can lead to mistakes in forecasting.
Resource Balancing Challenges: It’s hard to balance resources for fluctuating demand, leading to waste or shortages.
Lack of Adaptability: Being too rigid in managing demand can make it difficult to respond quickly to market changes, affecting competitiveness.
External Vulnerability: Demand management depends on outside factors like the economy and regulations, leaving the organization vulnerable to forces beyond its control.
Demand Management Best Practices
Managing demand better is really important for staying competitive and agile in today’s fast-moving markets. By always working to improve and using advanced technologies, businesses can work more efficiently and react faster to changes in the market.
Improve Forecasting Accuracy: Utilize advanced analytics and predictive modeling, incorporating real-time data for dynamic adjustments.
Ensure Data Quality: Invest in robust data management systems and validation processes to enhance accuracy and reliability.
Simplify Supply Chain: Streamline processes and foster collaboration with suppliers to improve visibility and coordination.
Adapt to Market Dynamics: Develop flexible strategies to adjust to seasonal variations and market shifts, monitoring trends closely.
Optimize Inventory: Use techniques like just-in-time inventory and tracking systems to minimize stockouts and excess inventory.
Address Demand Volatility: Implement agile planning processes and contingency plans to respond to unexpected demand fluctuations.
Align with Business Goals: Ensure demand objectives align with overall business goals, fostering cross-functional collaboration.
Optimize Resource Allocation: Implement tools and processes for efficient resource allocation, identifying areas for improvement.
Leverage Technology: Invest in advanced forecasting tools and provide training for effective utilization.
Listen to Customers: Incorporate customer feedback to refine strategies and predict future trends.
Adopt AI and Machine Learning: Implement AI and machine learning for predictive analysis and automation. Understand AI and explore possibilites in this comprehensive guide by Creately.
Maintain Flexibility: Stay agile to adapt quickly to changes in demand or supply chain issues.
Utilizing Creately for Demand Management
Demand management involves forecasting, planning, and controlling the demand for products or services to ensure that an organization meets its customers' needs efficiently. Using Creately, you can create various visualizations and diagrams to help with demand management processes. Here’s how you can use Creately for demand management:
Demand Forecasting Diagrams: Create diagrams illustrating the demand forecasting process. This might include techniques like time series analysis, regression analysis, or qualitative methods. Use Creately’s diagramming tools, shape libraries and templates to represent these techniques visually, making it easier to understand for stakeholders.
Supply and Demand Graphs: Visualize supply and demand curves to understand market equilibrium and fluctuations in demand. Creately provides tools to draw graphs easily, allowing you to analyze how changes in factors such as price, consumer preferences, or external influences affect demand.
Inventory Management Flowcharts: Design flowcharts showing inventory management processes, including ordering, storage, and distribution. Creately’s templates and shapes can help you map out these processes step by step, identifying potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Explore creately’s inventory management templates.
Capacity Planning Diagrams: Use Creately to create capacity planning diagrams, illustrating how demand fluctuates over time and how resources are allocated to meet that demand. This can include workforce planning, production scheduling, and resource allocation strategies.
Scenario Planning Maps: Develop scenario planning maps to anticipate and prepare for different demand scenarios, such as seasonal fluctuations or changes in consumer behavior. Creately allows you to create multiple scenarios and compare their potential impacts on demand and operations.
Collaborative Planning Boards: Utilize Creately’s real-time collaboration features to engage stakeholders in demand planning sessions. Create planning boards where team members can contribute ideas, identify risks, and propose strategies to manage demand effectively.
Dashboard Visualization: Create interactive dashboards using Creately’s features to monitor key demand metrics in real-time. Creately’s tools have the ability to bring data on to the canvas and give them structure for better analysis. Dashboards can include charts, graphs, and KPIs that provide insights into demand patterns, customer preferences, and market trends.
Demand management is important for matching supply with what customers want, making operations run smoothly and keeping customers happy. It involves predicting, planning, and controlling customer demand to balance supply and demand, reducing problems and making the business more flexible. In changing economic times, things like how people buy and market trends affect demand a lot, so it’s important to forecast accurately and make smart decisions. Demand management is different from demand planning and capacity planning because it focuses on strategic planning, forecasting, and using resources wisely.
To improve efficiency and react faster, businesses should look at past data, study the market, predict future demand, and use those predictions to plan their business and supply better. To make demand management better, it’s important to always be looking for ways to improve, use data to make better decisions, listen to customers, and use new technology. This helps businesses stay competitive and flexible.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Heroshe is a content specialist at Creately. He is passionate about art, music & travel.
A step-by-step guide to product demand analysis in 2023
2020 showed us: even the steady sales of toilet paper can’t be taken for granted. Sudden surges or drops in demand happen across all product categories, from soap to software.
What is a product demand analysis?
Why conduct a product demand analysis, what are the types of product demand, how to conduct a product demand analysis in 5 steps, product demand analysis examples, product demand analysis best practices, picking the right market research tools.
But if you become an expert at product demand analysis, those highs and lows don’t catch you by surprise as often. In this guide, you’ll learn the foundations of product demand analysis for the marketplace of tomorrow.

With a product demand analysis, you try to get an accurate estimate of future sales of your product. It’s a way of understanding how competition, seasons and other relevant events affect the sales of a certain product.
Product demand analysis can be done at various times – even for products that aren’t for sale yet. It’s not only based on past sales, demand can also be predicted based on changes in society, technological advancements and environmental changes.
So yes, there are a lot of factors weighing in, and nobody can predict the future down to the last chocolate bar being sold. But gauging product demand is crucial for building a future-proof business. Here’s why.
The goals of your product demand analysis depend very much on at what stage your business or product is in.
Validating ideas and financial planning
You could be doing exploratory market research and trying to find out if there’s a big enough market for you to enter with your product. And if there is, could you enter at a price point high enough to make your idea worth pursuing?
Buying materials from suppliers
Product demand analysis is also important for businesses who heavily rely on secondary manufacturers or resources from external sources. Will you be able to get the necessary materials in time?
Save money and work more efficiently
Saving money could also be one of the goals of performing a product demand analysis. Knowing when your product will be popular will help you better allocate your budget and manpower. Knowing when demand will be higher will help you plan the budget and timing for marketing campaigns, but also make sure you have enough employees on the work floor to handle the extra orders.
Track product demand with our audience of 125 million
Attest makes any product demand analysis easy. Unlock new sources of growth and find out what product features your key customers want.
Product demand isn’t as straightforward as you’d think. Products and categories are connected to each other, and sometimes demand comes from where you were least expecting it. Here are the most important types of product demand with examples.
- Direct demand: the simplest form of product demand is the demand for a final product. For instance, how many people are planning to buy a new smart TV.
- Indirect Demand is the demand for a product that is used to produce another product. Are you still following? A simple example is the rising demand for, let’s say, standing desks. The wood of the table would be the product that is in higher indirect demand, due to the popularity of the end product.
- Joint demand occurs when two products have a direct and positive correlation in demand. If people start buying more paint, they will start buying more canvases.
- Composite demand is the demand for products that can be used in more ways than one. For materials like the wood earlier, it’s important to know that it’s not just in demand for stand-up desks. It could also be used for millions of other products.
- Latent demand is the demand for a product that consumers can’t satisfy. There are three scenarios in which this happens:
1. The consumer doesn’t have the means to buy the product. They want it, but they can’t afford it.
2. The product that consumers want isn’t available.
3. The consumer doesn’t know the product exists or doesn’t know a certain product fulfils their needs.
When conducting your product demand analysis, it’s important to distinguish between these types of demand, but also to see the connections where possible. You might be able to benefit from composite or joint demand, while never having looked into that option.
Product demand analysis shouldn’t be wild guessing: it’s building a solid foundation of knowledge and structuring your research on top of that- and it’s a fundamental part of market research for new product development . Here are the steps:
- Define your market
- Assess the maturity of the market business cycle
Identify your market niche
Calculate market growth potential.
- Evaluate the competition
Define your market
Who could you be selling to, how much do those people have to spend, and who are they currently giving their money to? Those are crucial questions to ask when defining your market.
Defining your market shouldn’t just be done in words, by explaining personas or target audiences – the numbers are crucial to this.
Depending on the goal of your product demand analysis, you could also look at secondary markets for this part of your research. There might be some ground you could cover in markets where your product would be used by people who are not in your primary target audience.
Assess the maturity of the market and business cycle
Some products seem to have an endless life cycle. The oldest beer brewery has been around since 1040, and we’re still drinking it – even though many other alternatives have entered the market. But there are also breweries that have gone bankrupt. What’s up with that?
The market and business life cycle are two important things to analyse. First of all, you want to get an idea of how steady the market is. Will you be entering a market that is in the growth phase, is it mature and stable, or is it heading towards decline?
The same should be done for your business: how mature is it? It’s important to make this a part of your product demand analysis. If your market is growing but you can’t keep up, how will you deliver enough products to actually be profitable?
Your market niche is the sweet spot of where there’s potential to enter and where you would be able to deliver. Not only in terms of physical products or practical services, it should also be a match when it comes to values and USPs. Consumers aren’t just looking for products, they are looking for brands they connect with.
When doing a product market analysis, it’s important that you are specific and don’t paint a better picture by looking at the entire market, or too large a part of it. Eventually, you will have to choose a targeted message that will not speak to everyone in the market: keep this in mind when defining the real size of your market.
Find your niche fast with Attest
Our consumer segmentation filters and built-in audience of over 125 million people make finding your niche easy.
Now you have the data on the current situation: time to look into the future. To do that, we’ll start by going to the past.
How has the market share been divided among your competitors ever since the market came to exist? What events and products affected these changes in the division? What was happening in related or similar markets in the same time period?
Based on this information you can try to pinpoint patterns and find opportunities for growth in the future. Also keep societal factors in mind, like wages and costs of other possibly related products, and changes in tax.
Evaluate the competition
Chances are, your competitors are also performing some kind of product demand analysis while you are too. Maybe they also have a new product in mind that they want to launch, or they’re trying to increase their market share another way.
Look at how they went about their previous product launches and how this was received by your target market. How were the sales numbers? What could you learn from them?
You can keep an eye on what’s being said by and about your competitors using smart competitor tracking tools .
Is it magic? Is it witchcraft? Is it espionage? No, it’s artificial intelligence.
One of the kings in product demand analysis is undoubtedly Amazon. How do they have that tiny screw in the right colour available for next day delivery, when all hardware stores in your area are out of stock?
A lot of it is thanks to artificial intelligence, and an exquisite product demand analysis. Amazon has mastered the craft of balancing human intelligence with human tasks. Product demand analysis on the scale they are doing would simply take too long to do manually, so where possible they let AI do the heavy lifting. In the background, their team is figuring out the details that make their supply chain so impressive.
The team knows not only what products to have in stock, but also where. In 2013, they got a patent for ‘anticipatory shipping’. This technique helped them to get a product to the closest warehouse to you, even before you actually hit ‘buy now’.
Other parts of their product demand analysis are more common sense. Certain local products will only get stocked in relevant regions, and they look beyond the obvious seasonal changes. Sunscreen is important in summer, yes, but also in winter in places where, for example, families go on skiing holidays.
How do you actually gather all that information we mentioned above? Let’s look at some tools and best practices that will help you get the most relevant and actionable insights regarding product demand predictions.
Product demand surveys
To accurately estimate the demand for your product through a survey, it’s crucial that you ask the right questions. Think about how precise you would want people to answer, what data you need. Is it just numbers, or also about days or months? Will you ask them about alternative buying reasons for your product?
Set a clear goal for your product demand survey and build the questions based on that, so you won’t miss a single piece of information.
Another crucial element is defining quality respondents. Your product demand analysis survey should only be sent to people who match the criteria of actual buyers. This way you prevent getting data on latent demand, from people who would buy, but don’t actually have the money.
Ask the right questions with the right survey
With templates for market analysis plus on-demand support from our research experts, we’re here to help you gather continuous product demand data, fast.
Experiments with price and offer
Some markets are unpredictable, mostly because they are new. If after your initial product demand analysis you find that the numbers are a tiny bit lower than you’d hoped for, try analysing what happens if you tweak your offer.
You can experiment with different price points, package deals or bundles, or other types of promotions. You can also try finding partnerships or products that go well with yours to create more demand, even if it’s just secondary. This could be especially helpful if you are just entering a new market, and you want to ride on the success of another product.
Consumer trends
To identify consumer trends, you can use tools such as Google Trends, look into frequent Amazon searches and keep an eye on trending topics on social media.
With social listening tools, you can keep track of what people are saying about a certain product or brand, which will help you get data on what’s trending. Joining online communities or Facebook groups that are relevant to your market is also a great way to stay up to date on what’s happening.
Don’t forget to also look into popular topics in specific regions if that’s relevant for you. When looking at specific keywords, you can get incredibly precise data that will drive your decision-making process forward.
Still feel like product demand analysis is just a guessing game? With the right market research tools , you’ll see that getting accurate data is more a science than an art. Here are four of our favourite tools for market research that could help you getting your product demand analysis right:
- Attest : we had to! With our quick, easy-to-use market research platform you can find those hyper-relevant consumers and ask them those burning questions about their buying behaviour.
- Social Mention : to keep an eye on consumer trends, we highly recommend using social mention. This is a social listening tool that will give you first-hand data on what’s being said about your market across different platforms, without you having to monitor them manually.
- Heartbeat.ai : if you know that people are talking about your market, it’s also important to know what they’re saying. Just because a lot of people are talking about Blockbuster, doesn’t mean DVD rental is back in the picture. They’re just making memes. With heartbeat.ai, you can automatically analyse the tone of online conversations.
Love these tools? So do we. If you’re looking for more of this, check out our entire article with 6 of our favourite tools for market research .
Track product demand with Attest
Learn how your customers think, act and buy to give them the products they want. With an audience of over 125 million people in 59 countries, our data gives you an accurate picture of your product demand.

VP Customer Success
Sam joined Attest in 2019 and leads the Customer Research Team. Sam and her team support brands through their market research journey, helping them carry out effective research and uncover insights to unlock new areas for growth.
Related articles
11 customer profiling tools to understand your market, consumer profiling, how to conduct a brand tracking study, brand tracking, 7 brand intelligence software to collect insights, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
- Unlocking Insights: Understanding Demand Analysis ...
Unlocking Insights: Understanding Demand Analysis in Retail
March 12, 2024

Do you know that customer experience is the biggest competitive advantage for 81% of marketers ? In fact, ensuring good customer experience is increasingly becoming difficult. However, it doesn’t have to be when businesses strive to understand customer needs and market trends. That’s what demand analysis in retail is all about. It attempts to decode the target market, where a business can successfully launch its products and gain profit margin.
Sounds simple as it may, it involves considerable expertise, skill and data-analysis. Translating the data into concrete business decisions is yet another task. We will explore those details in this blog. Keep readint to get an idea about retail demand analysis, the process, best practices, and challenges in demand analysis.
5. Competitor Analysis
Demand analysis meaning.
Businesses that enter new markets have to evaluate customer needs, market sentiments, competitors, and target markets for making several decisions. It is known as demand analysis. It is a crucial and calibrated step to assess target markets and how they can gain maximum profitability.
Demand analysis reveals concrete data regarding customer demands, and buyer personals. Based on the data, companies make decisions on budget allocation, production planning, marketing and advertising, product pricing and innovation, etc. Demand analysis varies depending on the type of product, maturity of a business, capital, and resources.
The Importance of Demand Analysis in Retail
- Business success depends on identifying and satisfying customer needs.
- Analysing consumer behaviour is crucial for holding appropriate inventory levels.
- Demand analysis provides essential insights for decision-making processes: budget decisions, marketing and advertising costs.
- Demand forecast requires demand analysis for better outcomes.
- Businesses can decide product pricing based on consumer demand trends.
- With the help of demand analysis, companies can set up production planning.
- Demand analysis serves as a foundational element in business strategy.
- It guides effective lead generation by giving insight into customer needs.
- It gives a view into new markets to release products or services.
- Demand analysis helps in effective inventory control.
Steps in Demand Analysis
1. market research.
The first and foremost thing businesses attempting demand analysis is to dive deep into the target markets. Market surveys are the most used traditional method to understand consumer needs. Survey your customers about the new product and find out how satisfied they are. If consumers express dissatisfaction, it is time to develop on the product or bring something new.
While consumer surveys are common for market research, use a variety of methods like interviews, focus groups, public events, observations, experiments, and secondary data analysis. It ensures the credibility of collection data.
Interestingly, most companies analyse just 12% of their gathered data . They miss out on 88% of potential opportunities and threats. Effective use of data is one of the biggest competitive advantages out there. So, not just gather data, but act on it.
Create concrete buyer personas in numbers. It will also reveal opportunities in secondary markets where the audience might need your product or service.
2. Evaluate the Business Cycle
After market research, the focus must become internal i.e. evaluating the business cycle and maturity. There are three stages in a business cycle: Emerging stage when there is high demand but low supply, Plateau stage when the supply meets the demand, and declining stage where demand is going down.
In other words, some products seem to have a lifetime cycle, while others have short. For example, the oldest beer brew has been popular in the market since 1040. But some breweries have gone bankrupt.
Analyse the market and business life cycle to measure stability. Determine if the market is growing, stable, or declining. Similarly, assess your business’s maturity level. Integrate this into product demand analysis. If the market grows but you can’t match it, consider how to sustain profitability.
3. Aiming at a Product Niche
When doing a product demand analysis, it is crucial to be specific. Avoid painting a better picture by considering the entire market or a bigger part of the market. Customers are not just looking at the quality, pricing and unique features of a product. They are looking for brands they can connect with. Brands that share personal values and motivations along with the product needs.
So identifying a niche and tailoring a product for that niche wins the game. It also helps customers differentiate your products from that of competitors.
4. Define the USP
After knowing the markets, it is time to differentiate yourself from them. Businesses must develop products or services with an aim to solve customer problems rather than make profits. It automatically increases demand.
Identify trends and seek growth opportunities ahead. Consider societal aspects such as wages, costs of related products, and tax adjustments.
Start by identifying the market competitors and their market share. It also gives insights into market demand by highlighting the best selling products, how they’re winning the sales game, and increasing market shares. You can also understand what new products they are launching and how.
But, it also depends on which stage of the business cycle you are in. For emerging brands, there will be few competitors. As your business matures, the competition will be tough.
Challenges in Demand Analysis
- Understanding the consumer behaviour, preferences, and costs involves complexity. From employing different market research methods to accuracy of data, demand analysis requires skilled expertise.
- Time consumption is another challenge as gathering data can be lengthy. Depending on the response time of the customers, it can take unsustainably longer.
- Demand analysis often relies on subjective judgement rather than concrete data. So translating it into business decisions is cumbersome and tricky.
Data-driven decisions often require sophisticated technologies like AI, analytics, and ML. It is capital-intensive. On the other hand, with help of such technologies, businesses can make decisions 5X faster .
Best Practices in Demand Analysis
Regularity: Consumer needs and market sentiments change rapidly in today’s world. That is why businesses must conduct demand analysis regularly to gain updated information. Depending on the product type, conduct the demand analysis at least once a month.
Variety in Data-collection Methods: Use a variety of data collection methods for maintaining accuracy and consistency.
Comprehensive Data Collection: Gather data from all market segments to understand consumer response. It helps make informed marketing decisions for your products and services.
Thorough Analysis: After achieving data collection, thorough analysis is required to narrow down the essential data and eliminate fallible data.
Data-driven Decisions: While expert opinions are crucial, always depend on data-driven decisions before consulting them. There is no place for guess work.
Related read: Methods of Demand Forecasting
Entering retail markets without demanding analysis is shooting in the dark. It is a very unsustainable way to enter target markets. Given the volatility of markets and increasing consumer awareness, businesses that want to stay longer must focus on detailed demand analysis. Without that, they’re staking business reputation and brand value in the long-run.
What is demand analysis in economics?
Demand analysis is research done by companies to understand customer interest in a product. It helps them decide if they can enter the market and make a profit.
What are different types of retail demand analysis?
There are four types of demand analysis: Market demand analysis, product demand analysis, consumer demand analysis, and organisational demand analysis.
What are the consequences of ignoring market analysis?
Mismatch between inventory levels and customer demand, resulting in excess stock or shortages. Ineffective pricing strategies, missing market opportunities or driving away customers. Inefficient production planning, leading to higher costs or inability to meet demand. Poor marketing and sales efforts due to lack of understanding customer needs. Decreased profitability, customer dissatisfaction, and loss of market share.
How often should retail businesses conduct demand analysis?
Retail businesses should do demand analysis often. It helps keep pace with changing consumer needs and market trends. The recommended frequency for demand analysis varies by product type. Do it at least once a month to keep the information fresh for smart decisions.
Supercharge your fulfilment with WareIQ now, contact our team.

Related Posts

What Is POD? Understanding Its Full Form and Impact on Modern Logistics
In the intricate web of modern logistics, where the seamless movement of goods is imperative for businesses to thrive, Proof of Delivery (POD) stands as a beacon of reliability. Defined as conclusive evidence of successful delivery, POD holds paramount importance in both shipping and logistics realms. This pivotal document serves as a testament to the completion of the delivery process, assuring both senders and recipients alike. In the dynamic landscape of e-commerce, where speed and accuracy are non-negotiable, understanding what is POD and its intricacies essential for businesses aiming to stay ahead of the curve. As we delve deeper into the world of logistics, it becomes evident that POD is more than just an acronym; it embodies the essence of accountability and transparency in supply chain operations. From its full form to its impact on modern logistics, this article aims to unravel the layers of POD, shedding light on its significance and implications for businesses navigating the complex terrain of shipping and delivery. Join us on this journey as we explore the nuances of POD, from its inception to its evolution in the digital age, and discover how this seemingly simple document has revolutionised the way we perceive and manage logistics operations. What Is POD? Proof of Delivery (POD) serves as a critical document in the logistics ecosystem, offering tangible evidence that a shipment has been successfully delivered to its intended recipient. It bridges the gap between the sender and the recipient, confirming that the goods or services have reached their final destination. Typically, a POD includes vital information such as the recipient's name, signature, delivery date and time, description of the delivered items, and any relevant remarks or notes. This documentation acts as legal proof of the completion of the delivery process, safeguarding both parties against disputes or discrepancies. The acronym "POD" stands for "Proof of Delivery," encapsulating the essence of its purpose. It signifies the conclusive evidence required to validate the successful receipt of goods or services by the intended recipient. In essence, POD serves as a testament to the completion of the delivery journey, providing peace of mind to both senders and recipients. Whether it's a physical signature on a paper document or an electronic confirmation through a digital platform, the underlying principle remains the same: to establish irrefutable proof that the shipment has been received in good order. Importance of POD in Logistics Enhanced Tracking and Accountability In logistics operations, where the movement of goods involves multiple parties and stages, tracking becomes paramount. POD serves as a linchpin in this process, providing a clear trail of each shipment's journey. By capturing essential details such as the time and location of delivery, the recipient's signature, and any additional remarks, POD enhances tracking capabilities, enabling businesses to monitor the progress of their shipments in real-time. This transparency not only facilitates efficient inventory management but also fosters accountability throughout the supply chain. With POD in place, businesses can pinpoint the exact whereabouts of their shipments at any given moment, enabling them to proactively address any delays or issues that may arise, thus ensuring timely delivery to customers. Reduced Disputes and Errors In the realm of logistics, where the slightest error or miscommunication can lead to costly disputes, POD serves as a beacon of clarity and certainty. By providing irrefutable proof of delivery, complete with recipient signatures and timestamps, POD minimises the risk of misunderstandings or disputes regarding the status of shipments. This not only streamlines the resolution process but also cultivates trust and confidence among all stakeholders involved. Moreover, by documenting the condition of goods upon delivery, POD helps mitigate the risk of errors or discrepancies, ensuring that customers receive their orders accurately and in good condition. In essence, POD acts as a shield against potential disputes and errors, safeguarding the interests of both businesses and customers alike. POD in Modern Logistics Digitalisation of POD In recent years, the advent of digital technologies has revolutionised the way POD is managed and processed in the logistics industry. Traditional paper-based methods are being phased out in favour of electronic proof of delivery systems, which offer a host of benefits. These digital solutions streamline the entire POD process, from capturing signatures electronically to providing real-time updates on delivery status. By digitising POD, businesses can eliminate the need for manual paperwork, reduce the risk of errors, and improve operational efficiency. Moreover, digital POD systems often integrate seamlessly with other logistics management software, allowing for centralised tracking and management of all delivery-related data. Integration with E-commerce Platforms The rise of e-commerce has necessitated the integration of POD systems with online retail platforms, creating a seamless end-to-end delivery experience for customers. Modern e-commerce platforms often come equipped with built-in POD functionalities, allowing customers to track their orders in real time and receive instant notifications upon delivery. This integration not only enhances the overall customer experience but also provides businesses with valuable insights into their delivery performance. By leveraging data from POD systems, e-commerce companies can optimise their delivery processes, minimise transit times, and improve customer satisfaction levels. In essence, the integration of POD with e-commerce platforms represents a paradigm shift in the way logistics operations are managed and executed in the digital age. POD Documentation and Number POD Document The POD document serves as the official record of a successful delivery transaction, capturing vital information that verifies the completion of the delivery process. Typically, a POD document includes details such as the recipient's name, signature, delivery date and time, description of the delivered items, and any relevant remarks or notes. This documentation acts as tangible proof of delivery, assuring both senders and recipients that the goods or services have been received in good order. In addition to its legal significance, the POD document also serves as a valuable tool for record-keeping and audit purposes, enabling businesses to track and monitor their delivery transactions effectively. Understanding the POD Number Each POD is assigned a unique identifier known as the POD number, which serves as a tracking reference for the delivery transaction. This alphanumeric code helps businesses identify and trace individual shipments within their logistics systems, providing them with valuable insights into the movement of goods. The POD number plays a crucial role in streamlining logistics operations, allowing businesses to track the status of their shipments, generate delivery reports, and reconcile delivery records with customers' orders. By leveraging the POD number, companies can ensure transparency and accountability throughout the delivery process, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Best Practices for Successful Implementation of POD Systems 1. Integration with Supply Chain Management Systems Businesses can maximise the benefits of POD by integrating it with their existing supply chain management systems. By linking POD data with inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management systems, companies can streamline their operations and gain valuable insights into their logistics performance. This integration allows for seamless coordination between different departments and stakeholders, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. 2. Customisation and Flexibility Businesses must choose a POD solution that offers customisation and flexibility to meet their specific needs. Whether it's capturing additional data fields, configuring delivery notifications, or integrating with third-party software, a customisable POD system can adapt to evolving business requirements and enhance overall effectiveness. By tailoring the POD process to suit their unique workflows, businesses can optimise efficiency and achieve better outcomes in their logistics operations. 3. Training and Support Implementing a new POD system requires proper training and support for employees to ensure smooth adoption and usage. Companies should invest in comprehensive training programs to familiarise staff with the new system's features and functionalities. Additionally, ongoing technical support and troubleshooting assistance are crucial for addressing any issues or concerns that may arise during implementation or day-to-day operations. By empowering employees with the necessary knowledge and support, businesses can maximise the benefits of their POD solution and drive success in their logistics endeavours. Conclusion In the fast-paced realm of logistics, Proof of Delivery (POD) stands as a testament to reliability and efficiency. From its role in verifying deliveries to its integration with digital technologies, POD plays a crucial role in modern supply chains. By embracing digitalisation and best practices for implementation, businesses can harness the power of POD to streamline operations and enhance customer satisfaction. As we look to the future, the journey of POD continues, shaping the way we perceive and manage logistics in an ever-changing world. FAQs About POD What is the significance of POD in shipping and logistics?POD holds immense significance in shipping and logistics as it serves as tangible evidence of successful delivery, enhances tracking capabilities, and reduces disputes and errors in the delivery process.How does digitalisation impact the POD process?The digitalisation of the POD process enables real-time tracking, instant access to delivery confirmations, and seamless integration with e-commerce platforms, thereby improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.What information is included in a typical POD document?A typical POD document includes details such as the recipient's name and signature, delivery date and time, description of delivered items, and any relevant notes or remarks.How does POD help in reducing disputes and errors in delivery?By clearly documenting the delivery process, including recipient signatures and timestamps, POD minimises the risk of misunderstandings or false claims, thereby reducing disputes and errors.What role does the POD number play in logistics?The POD number serves as a unique identifier for each delivery transaction, enabling tracking and traceability throughout the supply chain and ensuring accountability at every stage.How does POD contribute to the overall efficiency of logistics operations?POD streamlines the delivery process, enhances tracking capabilities, and integrates seamlessly with e-commerce platforms, thereby improving the efficiency of logistics operations and enhancing the overall customer experience.
May 16, 2024

Understanding the SLA Full Form and Its Importance in Logistics and Fulfilment
In the ever-changing domain of logistics and fulfilment, the concept of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) stands as a cornerstone, ensuring that service providers meet the expected performance standards. Understanding the SLA full form—Service Level Agreement—and its significance is crucial for businesses seeking to optimise their supply chain operations and enhance customer satisfaction. SLAs are not merely contractual obligations but are strategic tools that can dramatically influence the efficiency and reliability of supply chain services. This article delves into the essence of SLAs, exploring their meaning, implementation in logistics, the basis for their formulation, and their pivotal role in streamlining business processes. By dissecting how SLAs function within the logistics and fulfilment sectors, we can uncover their potential to boost operational transparency and foster stronger partnerships between service providers and their clients. The insights provided here aim to equip businesses with the knowledge to leverage SLAs for improved service delivery and operational excellence. What Is the Meaning of SLA? The term "SLA" stands for "Service Level Agreement," a fundamental concept in many service-oriented industries, including logistics and fulfilment. An SLA is essentially a contract between a service provider and a client that specifies the performance standards the provider is expected to meet and the penalties for failing to meet those standards. SLAs are designed to establish clear, measurable guidelines that ensure both parties have the exact expectations regarding the quality, scope, and timing of the service delivered. SLAs often include metrics by which services are measured, the duties and responsibilities of both the service provider and the client, and the protocol for addressing and resolving service issues. This may encompass aspects such as response time, accuracy of service, and availability rates, among others. The primary objective of Service Level Agreement is to create a mutual understanding between service providers and clients, facilitating a transparent framework that supports both accountability and quality assurance in the delivery of services. What Is SLA in Logistics? In the context of logistics, an SLA (Service Level Agreement) serves as a critical framework that defines the level of service expected from a logistics provider. This agreement outlines specific metrics that are crucial to the success of logistics operations, such as delivery times, shipment accuracy, and goods handling. For businesses, SLAs in logistics ensure that the logistics providers adhere to agreed-upon standards, which can significantly influence the efficiency of the supply chain, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance. SLAs in logistics typically cover several key performance indicators (KPIs): Delivery Time: The time it takes for goods to be delivered from point A to point B, which should meet or exceed the timeframe specified in the Service Level Agreement. Order Accuracy: Ensuring that the right products are delivered in the correct quantity and condition. Damage Rate: The percentage of shipments that arrive damaged should be minimised as stipulated in the Service Level Agreement. Availability and Uptime: The extent to which logistics facilities, like warehouses and distribution centres, are operational and accessible. By clearly defining these and other metrics, Service Level Agreement help streamline logistics processes, reduce disputes between service providers and clients, and enhance the overall reliability and trust in the logistics services provided. What Basis SLA Is Decided in Logistics? In logistics, the decision-making process for establishing the specifics of an SLA (Service Level Agreement) is influenced by a multitude of factors that cater to the operational priorities and strategic objectives of both the service provider and the client. Here are some key considerations that typically influence the formation of an SLA in logistics: 1. Business Objectives Understanding the client's business goals is crucial. SLAs are often aligned to support overarching business strategies, such as improving customer satisfaction, reducing time to market, or enhancing product availability. 2. Service Requirements The specific needs related to the logistics services—such as same-day delivery, international shipping capabilities, or special handling (like refrigeration for perishable products)—dictate the parameters of the Service Level Agreement. 3. Performance Metrics These are critical and based on measurable outcomes, such as delivery times, accuracy rates, inventory management efficiency, and response times for resolving issues. 4. Historical Performance Data Past performance can guide the setting of realistic and achievable service levels. Both parties might review previous delivery records, incident reports, and customer feedback to set informed targets. 5. Risk Management The Service level agreement must consider potential risks and mitigation strategies. This includes assessing the likelihood of supply chain disruptions, logistic failures, and even geopolitical issues that could impact service delivery. 6. Technology and Infrastructure The logistics provider's technological and infrastructure capabilities also play a decisive role. Advanced tracking systems, automated warehouses, and robust transportation networks enable higher service levels. 7. Regulatory Compliance Compliance with local and international laws must be factored into the Service level agreement to avoid legal penalties and ensure smooth operations, especially in global logistics. 8. Cost Considerations Finally, the economic aspect of service delivery is crucial. The Service Level Agreement must balance optimal service levels with the cost implications for both parties to ensure a sustainable business relationship. By considering these factors, both logistics providers and their clients can develop an Service Level Agreement that is both ambitious in its service quality goals and realistic in terms of execution capabilities, thereby ensuring mutual benefits and long-term cooperation. How Does SLA Help Businesses Streamline Processes? Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are instrumental in helping businesses streamline their logistics and operational processes. By defining explicit service standards and expectations, Service level agreement facilitate a number of improvements in business efficiency and effectiveness: 1. Enhanced Performance Monitoring SLAs establish clear performance benchmarks that enable businesses to monitor service delivery continuously. This constant evaluation helps identify performance gaps and areas for improvement, ensuring that logistics operations align with business objectives. 2. Increased Accountability With specific metrics and penalties outlined in the SLA, logistics providers are held accountable for their performance. This ensures that they maintain the necessary focus and dedication to meeting their contractual obligations, thereby reducing the likelihood of service disruptions. 3. Improved Risk Management SLAs compel both parties to consider and plan for potential risks. By proactively addressing possible issues that could impact service levels, businesses can devise effective strategies and contingency plans, minimising the impact of disruptions on operations. 4. Better Resource Allocation SLAs help businesses optimise resource allocation by outlining precise service expectations. Understanding the required service levels allows companies to allocate the right amount of resources, such as manpower and technology, to meet these demands efficiently. 5. Stronger Relationships with Service Providers Clear and transparent Service level agreements foster a healthier relationship between businesses and logistics providers. With both parties clearly understanding their roles, responsibilities, and expectations, communication improves, leading to more collaborative problem-solving and innovation. 6. Scalability and Flexibility SLAs can be revised and adapted as business needs evolve. This flexibility allows businesses to scale their logistics operations up or down based on market demands, seasonal peaks, and other changing conditions without sacrificing service quality. 7. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction Ultimately, well-managed SLAs lead to more reliable and efficient service delivery. This reliability translates into better customer experiences, as end-users receive their products on time and in good condition, thereby boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty. SLAs are not just administrative tools but strategic enablers that help businesses optimise their logistics operations, adapt to changing environments, and deliver superior service to their customers. Through careful planning and effective implementation of SLAs, companies can achieve operational excellence and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Conclusion Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in logistics are more than just contractual necessities; they are pivotal instruments that help shape the efficiency and reliability of supply chain operations. By establishing clear, measurable standards for service delivery, SLAs enable businesses to enhance operational control, improve accountability, and foster stronger, more transparent relationships with service providers. These agreements are essential in helping companies mitigate risks, manage resources effectively, and achieve consistency in service quality, which is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced market. Moreover, Service Level Agreement are integral to driving customer satisfaction. They ensure that logistics providers meet the expectations of the businesses they serve, thereby directly impacting the end customer's experience. In an era where customer loyalty can significantly influence a company's success, effective SLAs can be a decisive factor in attracting and retaining customers. Ultimately, the strategic implementation of well-crafted SLAs is crucial for any business aiming to optimise its logistics operations and enhance its market presence. FAQs About SLA in Logistics What is a Service Level Agreement (SLA)?A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a contract between a service provider and a customer that outlines the agreed-upon level of service expected. It defines the scope, quality, and responsibilities of the service being provided.Why are SLAs important in business?SLAs are crucial in business as they establish clear expectations between the service provider and the customer. They help set performance benchmarks, ensure accountability, and maintain customer satisfaction.What are the key components of an SLA?The critical components of an SLA include:Service descriptionMetrics for measuring performanceResponsibilities of the service provider and the customerConsequences for not meeting agreed-upon standardsProcedures for monitoring and reporting performanceHow are SLAs beneficial for both parties involved?SLAs benefit both parties involved by:Providing transparency and clarity regarding service expectations.Establishing accountability for meeting performance standards.Improving communication between the service provider and the customer.Facilitating resolution processes in case of service disruptions or failures.What are the different types of SLAs?There are various types of SLAs, including:Service-based SLAs: Focus on specific services provided.Customer-based SLAs: Tailored to the needs and requirements of individual customers.Multilevel SLAs: Hierarchical SLAs that address different levels of service.How are SLAs measured and monitored?SLAs are measured and monitored using predefined metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Regular monitoring involves tracking performance, analysing data, and addressing any deviations from agreed-upon standards.What happens if the service provider fails to meet SLA targets?If the service provider fails to meet SLA targets, it may result in penalties or financial compensation as outlined in the SLA agreement. Additionally, corrective actions may be implemented to address the underlying issues and prevent future failures.Can SLAs be modified or updated?Yes, SLAs can be modified or updated based on changing business requirements or evolving customer needs. However, any modifications should be agreed upon by both parties and documented in writing to ensure clarity and transparency.
May 15, 2024

Footwear Brands: How to Manage Returns Effectively With Wareiq’s Returns QC Solution
In the footwear industry, post-purchase experience plays a pivotal role in determining a brand's success and customer loyalty. As e-commerce continues to grow, so does the volume of returns, presenting a dual challenge of maintaining high customer satisfaction while managing logistical efficiencies. For footwear brands, managing returns effectively is not just about handling unwanted or unsatisfactory products; it involves a comprehensive strategy that encompasses customer service, logistics, quality control, and financial implications. Effective returns management can significantly impact customer retention and profitability. A smooth, transparent returns process enhances customer trust and promotes a positive brand image. However, ineffective returns strategies can lead to increased operational costs, inventory mismanagement, and damaged customer relationships. This article will explore the intricacies of returns management for footwear brands, emphasising the need for robust systems and innovative solutions like WareIQ's Returns QC solution, which optimises this complex process through technology-driven efficiency and quality control. By addressing these challenges head-on, footwear brands can transform returns management from a cost centre into a strategic advantage, ultimately driving greater customer loyalty and sustainable growth. Challenges Faced by Footwear Brands in Managing Returns Footwear brands face several distinct challenges when managing returns, each adding layers of complexity to their operations: 1. High Return Rates Footwear often experiences higher return rates compared to other products, primarily due to sizing issues, colour mismatches, or style dissatisfaction. This high volume of returns puts a strain on logistical operations and customer service. 2. Quality and Condition Assessments Returns in the footwear industry require rigorous inspection to ensure the products are in resellable condition. This involves checking for wear and tear, verifying packaging integrity, and ensuring that all parts and accessories are returned. Such detailed assessments require time and resources, complicating the logistics workflow. 3. Logistical Complexities Managing the logistics of returned items includes organising reverse shipping, handling, and restocking. Each step must be coordinated efficiently to minimise costs and time delays, which can be challenging, especially when dealing with high volumes of returns. 4. Financial Impact The costs associated with processing returns are significant. They include shipping costs, handling fees, and the potential loss of revenue from products that cannot be resold. Furthermore, frequent returns can lead to increased scrutiny from payment processors and banks, potentially resulting in higher fees or penalties for the brand. 5. Customer Expectations Today’s consumers expect a seamless return process. They demand easy-to-understand and accessible return policies, quick turnaround times, and flexible return options. Meeting these expectations is crucial for customer satisfaction and loyalty but can be difficult to manage alongside the need to control costs and maintain operational efficiency. 6. Sustainability Concerns With a growing focus on environmental impact, footwear brands must consider the sustainability of their returns process. This includes minimising waste associated with packaging and damaged goods and finding ways to recycle or refurbish products wherever possible. Addressing these challenges requires a thoughtful approach that balances customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial health. Strategies for managing these issues effectively are critical for maintaining competitiveness in the footwear market. Strategies for Effective Returns Management To address the challenges associated with returns and create a streamlined process, footwear brands can employ several strategic approaches: 1. Clear and Concise Return Policies Establish transparent and easily understandable return policies that clearly state the terms and conditions of returns. This reduces confusion and helps manage customer expectations, potentially reducing the volume of unnecessary returns. 2. Invest in Technology Utilise advanced logistics and inventory management systems to automate and optimise the returns process. Technologies such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode scanning can help track products efficiently, reduce errors, and speed up the processing time. 3. Enhanced Quality Control Implement rigorous quality control measures at the point of return to ensure products are in the appropriate condition for resale. This helps maintain product integrity and reduces the financial burden of unsellable returns. 4. Customer Communication and Feedback Develop a robust system for communication and feedback throughout the returns process. Keep customers informed with updates via emails or SMS about the status of their return. Also, feedback should be gathered to understand why products are being returned and used to reduce future returns. 5. Flexible Return Options To enhance customer convenience, offer multiple return options, such as in-store returns, locker drop-offs, or postal returns. Providing a variety of options can improve the customer experience and potentially reduce the cost of handling returns. 6. Staff Training and Development Ensure that all personnel involved in the returns process are well-trained and understand the importance of efficient and customer-friendly service. This includes training in handling procedures, customer service skills, and the use of any relevant technology. 7. Analyse Data to Identify Trends Analyse return data regularly to identify patterns or trends in product returns. This can help identify specific issues with certain products or sizes, which can then be addressed through design improvements or better product descriptions. 8. Sustainable Practices Adopt environmentally friendly practices in the returns process by minimising packaging use, encouraging customers to consolidate returns, and finding ways to refurbish or recycle unsellable returns. Implementing these strategies improves the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the returns process and enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, creating a competitive advantage in the dynamic footwear market and repeat business. WareIQ's Returns QC Solution for Footwear Brands To address the complexities of returns management in the footwear industry, WareIQ offers a specialised Returns QC (Quality Control) solution that is tailored to meet the specific needs of footwear brands. This innovative solution incorporates several key features designed to streamline the returns process, ensure product quality, and enhance customer satisfaction: 1. Automated Returns Processing WareIQ’s solution automates many aspects of the returns process, from initiation to final disposition. This automation includes the generation of return labels, tracking of return shipments, and updates to inventory levels. Automation helps reduce human error and speeds up the processing time, making the returns process more efficient. 2. Integrated Quality Control Central to WareIQ's offering is its robust quality control system that inspects returned items to ensure they meet the brand’s standards for resale. This system uses advanced scanning and imaging technologies to assess the condition of the footwear, ensuring that only items in appropriate condition are restocked. 3. Real-Time Data and Analytics WareIQ provides real-time analytics that allows brands to monitor and analyse return rates, reasons for returns, and customer feedback. This data is invaluable for making informed decisions about product improvements, inventory management, and customer service strategies. 4. Customisation Options Recognising that each footwear brand has unique challenges and requirements, WareIQ’s Returns QC solution offers customisable options to address specific logistical and operational needs. This flexibility ensures that brands can optimise the solution to better suit their business models and customer base. 5. Seamless Integration The solution seamlessly integrates with existing logistics and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, ensuring that information flows smoothly between returns processing and other business functions. This integration helps maintain data integrity and provides a holistic view of inventory and operations. 6. Enhanced Customer Experience By streamlining the returns process and ensuring that customers receive timely refunds or exchanges, WareIQ's solution helps improve the overall customer experience. Transparent communication throughout the returns process keeps customers informed and helps build trust and loyalty. By leveraging WareIQ's Returns QC solution, footwear brands can not only handle returns more effectively but also turn the challenge of high return rates into an opportunity for enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Case Studies: Footwear Brands Leveraging WareIQ's Returns QC Solution Several footwear brands have adopted WareIQ's Returns QC solution to address their challenges with returns management. These case studies highlight the effectiveness of the solution in transforming their returns process, enhancing customer satisfaction, and improving operational efficiency: 1. Brand A A prominent sports footwear brand faced high return rates primarily due to sizing issues and customer expectations not being met. After integrating WareIQ’s Returns QC solution, Brand A reported a 25% reduction in return rates within the first six months. The automated quality checks helped maintain the integrity of returned items, ensuring that nearly 95% of returns were restocked and resold, thereby significantly reducing waste and improving profitability. 2. Brand B A luxury footwear brand struggled with managing the returns of high-value items, which required meticulous quality control to maintain brand standards. The introduction of WareIQ’s customised quality control system allowed Brand B to enhance its product reassessment process, increasing customer satisfaction by ensuring that customers received products in pristine condition. This also elevated the brand's reputation for quality and customer service. 3. Brand C Faced with logistical challenges with reverse shipping and restocking, Brand D leveraged WareIQ’s integration capabilities to synchronise their ERP systems with the Returns QC solution. This enabled real-time data flow and analytics, which improved inventory management and reduced return processing times by 40%. 4. Brand D This rapidly growing online footwear retailer used WareIQ’s analytics tools to gain insights into the reasons behind returns. The data collected led to changes in product descriptions and sizing information on their e-commerce platform, which reduced return rates by 20% and enhanced customer trust and retention. Conclusion Effective returns management is pivotal for the success and sustainability of footwear brands in today's market. As demonstrated by the integration of WareIQ's Returns QC solution across various brands, this approach can significantly improve operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. The solution's ability to automate processing, ensure rigorous quality control, and provide valuable data analytics transforms a traditionally cumbersome and cost-heavy process into a strategic asset. By embracing advanced technology solutions like WareIQ's Returns QC, footwear brands can effectively address the myriad challenges associated with high return rates. This not only supports a positive customer experience—encouraging loyalty and repeat purchases—but also aligns with broader business objectives such as sustainability and profitability. As the footwear market continues to evolve, the brands that will thrive are those that leverage innovative technologies to enhance their returns management processes, turning potential setbacks into opportunities for growth and customer engagement. Frequently Asked Questions What are the typical return rates for footwear brands online?Online footwear brands often experience return rates between 20% and 30%, primarily due to sizing issues and customer expectations not being met. This rate can vary widely depending on the type of footwear, the brand's target demographic, and the effectiveness of its sizing guides and product descriptions.How does WareIQ's Returns QC solution enhance customer satisfaction?WareIQ's Returns QC solution enhances customer satisfaction by streamlining the returns process, ensuring faster processing times, and maintaining communication with the customer throughout the process. This transparency and efficiency directly improve the customer's experience and perception of the brand.Can WareIQ's solution integrate with existing logistics systems?Yes, WareIQ's Returns QC solution is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing logistics and inventory management systems, providing a cohesive and efficient workflow. This integration helps maintain data accuracy, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances overall operational efficiency.What are the cost benefits of implementing WareIQ's Returns QC solution for a footwear brand?Implementing WareIQ's solution can significantly reduce the costs associated with handling and processing returns by automating many of the labour-intensive steps involved. Additionally, the improved efficiency can reduce the turnaround time for getting products back into inventory and available for sale, minimising the financial impact of returns.How does real-time analytics from WareIQ help manage footwear returns?Real-time analytics provide footwear brands with insights into return patterns and reasons, aiding in better stock management and preventive measures for high-return products. This data allows brands to make informed decisions about product adjustments, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements.What measures does WareIQ's solution include to prevent fraudulent returns?WareIQ incorporates verification checks and quality control assessments to identify and reduce fraudulent returns, ensuring that only legitimate returns are processed and restocked. This helps protect revenue and maintains the integrity of the brand’s inventory.
May 14, 2024
WareIQ has helped 400+ top online brands across categories get quick access to:
- Pan-India network of fulfillment centers
- National, regional & hyperlocal shipping partners
- Team of experts for managing fulfillment operations and customer experience seamlessly
- Smart tech platform to manage all logistics operations, integrated with all leading D2C, Marketplaces & B2B channels
Connect with our team to know more!

Market research
Demand analysis: what it is and how to do it

TRY OUT NOW
Demand analysis is a comprehensive process that focuses on evaluating and understanding the factors that influence the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase in a given market and over a given period of time .
This approach examines in depth elements such as price, income, consumer preferences, economic conditions, and other external factors that may influence the relationship between supply and demand for a product or service.
Using demand analysis, companies can make informed decisions about pricing strategies, market positioning and product development to anticipate and meet changing consumer needs.
- 1 Types of demand
- 2.1 Identification of key variables
- 2.2 Demand curve
- 2.3 Elasticity of demand
- 2.4 Factors affecting demand
- 2.5 Predicting demand
- 3.1 Step 1: Define the subject of the investigation
- 3.2 Step 2: Collect market data
- 3.3 Step 3: Identify the influencing factors
- 3.4 Step 4: Determine the elasticity of demand
- 3.5 Step 5: Demand Curve Analysis
- 3.6 Step 6: Assess the competition
- 3.7 Step 7: Examine past demand
- 3.8 Step 8: Using Predictive Models
- 3.9 Step 9: Conduct market research
- 3.10 Step 10: Summary of results
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 1:1 Live Online Presentation: QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
- 6 Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
Types of demand
There are different types of demand that can be classified according to different criteria. These categories help analysts and companies better understand how fluctuations in various variables can affect demand for products or services in the market.
- Completely inelastic demand: Quantity demanded does not change in response to changes in price. It is a scenario in which consumers are willing to purchase a fixed quantity of the good or service, regardless of its price.
- Inelastic demand : The quantity demanded changes less than the price. Essential goods or services often have inelastic demand because consumers are willing to pay a higher price for these necessary products.
- Elastic demand: The quantity demanded changes more than the price. This is usually the case for goods or services that are considered somewhat optional or for which there are readily available substitutes.
- Cross demand : This refers to the relationship between the demand for a good and the price of a related good. An increase in the price of one good can affect the demand for another related good.
- Complementary demand: This occurs when the demand for one good is positively related to the demand for another good. For example, the demand for cars and the demand for gasoline are complementary.
- Competing Demand: Occurs when two or more products compete to satisfy a similar consumer need. Price changes for one product can affect demand for the other.
- Derived demand: Mainly refers to goods or services that are necessary for the use of another product. For example, the demand for cars is derived from the demand for tires.
- Seasonal demand: It is subject to predictable fluctuations at different times of the year. Examples include the demand for winter clothing or toys before the Christmas season.
- Luxury demand : This refers to goods and services whose demand increases as consumers' income increases. These products are often perceived as luxurious and not essential to life.
Factors affecting demand analysis
Demand analysis provides critical information to businesses by understanding the forces that influence consumers' purchasing decisions. In this way, they can effectively adapt their business strategies to meet the needs of the market and maintain a competitive advantage.
This process examines the factors that influence the demand for a product or service in the market.
A more detailed description can be found below:
Identification of key variables
- Price : Demand analysis first examines how the quantity demanded of a product or service changes in response to price changes.
- Income : The availability of consumers' income directly affects the demand for products and services. It examines how changes in income can influence purchasing decisions.
Demand curve
- The relationship between price and quantity demanded is usually represented by a demand curve. This curve shows how quantity demanded changes when price changes and other factors remain constant.
Elasticity of demand
- Elasticity of demand measures the sensitivity of the quantity demanded to changes in price. Elastic demand means that the quantity demanded is very sensitive to price changes, while inelastic demand suggests that the quantity demanded is less sensitive to price changes.
Factors affecting demand
- External factors: Changes in economic conditions, cultural trends, technology, government regulations and others can significantly impact demand.
- Substitution and supplementary products : The availability of substitute or complementary products can influence the demand for a particular good or service.
Predicting demand
- Demand analysis can be used to try to predict future trends and purchasing behavior. This is important for companies to plan their production, marketing and pricing strategies.
How do you conduct a demand analysis?
Conducting demand analysis can be a structured and useful process to understand consumer behavior and make informed decisions. Here are step-by-step instructions on how to easily conduct a demand analysis:
Step 1: Define the subject of the investigation
Clearly identify the product or service you are analyzing. Define its main characteristics and position in the market.
Step 2: Collect market data
Gather information about the market where your product or service is offered. This may include demographic data, economic and social data, and information about competitors.
Step 3: Identify the influencing factors
Identify the factors that influence demand for your product or service. These may include price, income, consumer tastes and preferences, economic conditions, etc.
Step 4: Determine the elasticity of demand
Determine whether demand is elastic, inelastic, or uniform by determining how the quantity demanded changes as price changes. You can use the elasticity of demand formula:
Elasticity= % change in quantity demanded.
% Price change
Step 5: Demand Curve Analysis
Based on the data collected, draw a demand curve. This allows you to illustrate how the quantity demanded changes as prices change.
Step 6: Assess the competition
Analyze how competitors' behavior can affect demand for your product. Consider the presence of substitutes and complementary products.
Step 7: Examine past demand
Review historical sales data and demand patterns. This can provide valuable information about seasonality and trends over time.
Step 8: Using Predictive Models
Apply forecasting models to anticipate changes in future demand. You can use techniques such as regression analysis, time series or opinion polls.
Step 9: Conduct market research
If necessary, conduct surveys or interviews to get direct feedback from consumers. This can provide detailed insights into their preferences and purchasing behavior.
Step 10: Summary of results
Summarize the results and use the information to make strategic decisions. Consider adjustments related to marketing, pricing, sales, or even the product itself.
Remember, the key is to use accurate and relevant data. This ongoing analysis allows you to adapt to changes in the market and better meet consumer needs.
In summary, demand analysis helps you understand the factors that influence consumers' purchasing decisions, from price to individual preferences. By assessing elasticity, constructing demand curves, and considering elements such as competition and seasonality, companies can make informed strategic decisions.
Demand analysis not only provides an in-depth understanding of market dynamics, but also serves as a guide for adapting strategies, anticipating change, and ultimately driving sustainable success in an ever-changing business environment.
QuestionPro has a number of tools that allow you to collect information to properly analyse various aspects of your business. Create a free account or request a demo so we can understand your needs and offer you the best solution.
1:1 live online presentation: QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
Arrange an individual appointment and discover our market research software.
Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
Do you have any questions about the content of this blog? Simply contact us via contact form . We look forward to a dialogue with you! You too can test QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge and without risk in depth!
Test the agile market research and experience management platform for qualitative and quantitative data collection and data analysis from QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge
FURTHER KEYWORDS
Market research | Market research software | Analysis dashboard
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
KEYWORDS OF THIS BLOG POST
Demand analysis | demand | analysis | Market research

FURTHER INFORMATION
- Conduct quantitative and qualitative market research with QuestionPro (Qual & Quant)
- Market research: examples, tips, data collection, data analysis, software for carrying out and presenting the results
- The big QuestionPro-Guide on the subject of customer surveys: definition, development, methods, examples, evaluation, template for import.
- Customer Experience Management: Tips, Tools, Best Practices
- Reputation management: tips, software, app
- Sentiment analyses and semantic text analysis based on artificial intelligence
- All information about the experience management platform QuestionPro
- Conducting employee surveys: A specialist article from QuestionPro
PRESS RELEASES
Solving your most complex planning challenges

Explore Industry Research
What do Gartner, Forrester, and IDC have in common? They all named Anaplan a planning leader.
Your success is the heart of our success

Hear from our customers at Anaplan Connect 2024
Join us for a day of connected inspiration from your industry-leading peers who have found the answer in agile, connected enterprise planning.
Transform how you see, plan and lead your business
Get started today.
Explore on-demand demos to discover how our modeling and planning capabilities are designed to meet the specific and unique needs of your business.
Transform how you see, plan, and lead your business
We’d love to find out how we can help you
Events, training, and content for your planning journey

Visit our blog and newsroom
Your hub for Anaplan updates, insights, perspectives, and innovations.
Powerful partnerships to drive your digital transformation and deliver game-changing strategies.
Solutions for your business, your industry, from the world’s leading alliances.
- wrappers --> Supply Chain
What is demand planning?
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
The platform for orchestrating performance.

Learn the basics of effective demand planning to improve the accuracy of your forecasts, align inventory levels, and enhance profitability.
Demand planning is the supply chain management process of forecasting demand so products can be reliably delivered and customers remain satisfied. Effective demand planning can improve the accuracy of revenue forecasts, align inventory levels with peaks and troughs in demand, and enhance profitability for a particular channel or product.
Demand planners keep an eye on internal and external factors that could impact demand, such as labor force issues, natural disasters, weather patterns, and news events or other influences. Gathering information from all possible sources is the best way to generate an accurate forecast and ensure integration with the supply forecast to efficiently meet customer demand.
The importance of demand planning
The market can shift on a dime and demand plans needs to move at the speed of the changing market. If demand plans can’t be adjusted with agility, companies could end up with stock-outs and unhappy customers, or warehouses full of unused inventory, unhappy finance managers, and millions of dollars in wasted capital.
In an ideal world, demand planners must stay ahead of the market instead of merely reacting to it, and make decisions based on near real-time market data, rather than solely on historical data. That’s not always possible, but with the advent of cloud-based planning platforms, it’s closer to reality than ever before.
Check out our on-demand demo to see how a cloud-based demand planning solution will enable you to sense, shape, and orchestrate demand with a holistic view of data and trends.
Elements of the demand planning processes
Let’s take a look at a few of the processes involved in demand planning.
Trade promotion management:
Trade promotions are marketing tactics (most often in retail companies) that focus on generating in-store demand through discounts, giveaways, in-store promotions, and other similar techniques. Trade promotion management is designed to help brands stand out from their competition through highly coordinated promotion activities and builds stronger connections with retailers.
Trade promotion planners seek to plan collaboratively at detailed and aggregated levels so they can adjust products, campaigns, and promotions without long delays, aligning an optional trade promotion spending plan that incorporates end signals from distributors and customers across all time periods, products, and geography.
Top-down and bottom-up trade promotion management and analysis includes profit and loss data, creating insights around promotion spending. It also tracks and identifies which promotions don’t optimize margins due to ineffective trade promotion spending and poor brand growth from trade promotions and creates maximum ROI using a broad range of data.
Product portfolio management:
Product portfolio management is the process of managing every facet of the product lifecycle, from new product introduction to end-of-life planning. The goal of product portfolio management is to maintain a high-level view of the entire portfolio and reveal where product lines are interconnected and interdependent.
Product portfolio management includes planning for fitting new products into the existing product portfolio, understanding how introducing those new products will affect other products (cannibalization), and the analysis of attachment rates (how the sales of one product affects the sales of another). Planners involved in product portfolio management are heavily involved in scenario planning to ensure that they’re aware of each product line’s effect on the other product lines to optimize the product mix, maximize profitability across product lines, and increase global market share.
When new products are launched, it’s important to know how the new products will affect the global planning strategy, the cost of introducing that new product, and the revenue and profits that will be generated by the new products. Using intelligent product portfolio management techniques, feasibility models are connected to ideation processes, scenario-based profitability models are generated, and the process of taking a product from idea to commercialization is accelerated.
When this process is collaborative, a real-time granular forecast model can identify how different market segments across geographies might purchase this new product and at what price. In a collaborative system, new product introduction links sales and supply chain, resulting in key connections to sales and operations planning (S&OP) processes, production planning, and allocation planning.
Statistical forecasting:
Statistical forecasting in demand planning leverages historical data to generate supply chain forecasts using various advanced statistical algorithms. In demand planning, it’s essential to have data-backed forecasts to avoid stock-outs or overstocks and ensure that customers are satisfied.
There are multiple aspects to how statistical forecasting makes demand planning more effective. Demand planners can analyze many algorithms and decide which forecast is most accurate by reviewing each model’s accuracy and bias measures. Then they can choose from the best model for each product and product family.
And when a forecasting dashboard is part of the equation, it becomes easier to customize forecast algorithm assumptions and measure accuracy with techniques like mean absolute percentage error. With statistical forecasting, demand planners can quickly identify outliers and exclusions based on user-defined parameters, including standard deviation or the inter-quartile range.
Seasonality has a major impact on demand planning. Retailers have many factors to sort through to ensure that they’re prepared for various seasonal events. Will they be ready for the holiday shopping rush? What if weather patterns shift and all those winter coats they’ve stocked aren’t purchased? With statistical forecasting in demand planning, these questions are easy to answer because multiple statistical simulations can be run, including models to forecast the impact of intermittent demand, multi-linear regression forecast quantity, price, attach rates, and discounts.
The skills demand planners need
Demand planning is undergoing large-scale radical change with an emphasis on digital transformation. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are already beginning to make an impact on how demand planners operate.
Algorithmic “touchless” supply chains that weave in the power of big data, blockchain, robotics, and 3D printing may soon be the rule rather than the exception. Demand planning of the future will be always on, dynamic, and non-linear. The power to react quickly and make value-based decisions is essential to staying ahead of the market.
To lead the way into a transformative future, demand planners need to combine technical and business knowledge with collaboration and communication skills. The ability to influence department leaders that partner with demand planning is key, as well as the skills to interact intelligently with leaders across the organization because supply chain initiatives often reach across business units. Strong business acumen is a must-have — you’ll be more effective working with your counterparts in finance, sales, and marketing if you can speak their language.
The effective demand planning leader of tomorrow is tech-savvy and comfortable working alongside the world of machines. Some have said AI won’t replace managers, but managers who work with AI will replace managers who don’t. This highlights the transformation taking place in supply chain management: Humanity is essential but so is technology. It’s not a paradox — it’s the new normal. The new demand planning leader is digitally dexterous and also skilled with people.
The already many-faceted role of a demand planning leader is changing. To thrive in this new world, demand planning professionals must grow their capacities in collaboration, communication, and leadership, and pair those skills with in-depth technical knowledge if they want to become and stay a powerful force for the future of demand planning.
Digital demand management
The future of demand planning is what Supply Chain Brain calls “digital demand management” (DDM). It’s centered around implementing demand-driven structures, frameworks, and digital enterprise architectures. Multiple groups connect to facilitate a seamless exchange of information, ideas, and solutions that are synchronized with the omnichannel buying habits of consumers.
Even in our personal buying habits, the competitive demand landscape has changed radically in the past few years. There are rapidly emerging digital markets, new competitors, and faster market changes that can threaten the extinction of any enterprise that doesn’t adapt. DDM makes complex data comprehensible, actionable, predictive, and prescriptive because it provides a real-time synchronized knowledge base that permits improved customer focus.
The development of DDM starts by challenging traditional linear thinking across supply chains. The old linear thinking accepted the inevitability of forecast cycles that are weeks or months old, poor visibility into SKU locations, and the inability to address ongoing variability that disturbs traditional network and inventory optimization systems. Linear decision-making adds unnecessary time and causes potentially false demand signal amplification.
The essential change is to replace traditional functional metrics with DDM, fostering collaborative execution across the entire supply chain. The resulting demand management organization enables a business to be simultaneously planned dynamically in real time, both horizontally and vertically, enabling true digital collaboration.
DDM requires a new planning model that enables causal and external factor analysis, along with a process-control approach to smart digital network management. The beauty of DDM is that it works within a range of pre-defined acceptable variability. Using real-time DDM forecasts — based on standard deviations along with the range of consumer behaviors that are likely to occur — participants can agree to ranges of performance, commitment horizons (periods of risk), and exception conditions. The result is a beneficial digital collaboration that enables next-generation demand planning.
Watch our Demand Planning demo

LONDON--( BUSINESS WIRE )--A well-known market intelligence company, Infiniti Research, has announced the completion of their recent article on evaluating the importance of demand analysis for your business. The article provides comprehensive insights on why demand analysis is vital for modern businesses and the key steps involved in an ideal demand analysis strategy.
Demand analysis is the process of understanding the customer demand for a product or service in a target market. Companies use demand analysis techniques to determine if they can successfully enter a market and generate expected profits to expand their business operations. It also gives a better understanding of the high-demand markets for the company’s offerings, using which businesses can determine the viability of investing in each of these markets.
Identifying market opportunities and meeting the market demand can prove to be challenging without the right expertise. Request a Free Brochure to learn how experts at Infiniti Research can assist you with smart solutions that cater to dynamic business needs.
Steps in market demand analysis
Market identification
one of the first steps in market demand is to identify the target market for the company’s products or services. Surveys or customer feedbacks can be leveraged to determine the current customer satisfaction levels. Any comments indicating dissatisfaction can be taken into consideration for planning improvements that will eventually enhance customer satisfaction.
Get one step ahead of your peers in the market with intelligent and agile business solutions. Request a free proposal to know how our solutions can help you achieve this!
Business cycle
After identifying the potential markets, the next step is to assess the stage of the business cycle that each market is undergoing. A business cycle ideally comprises of three stages: emerging, plateau and declining. Markets that are in the emerging stage show higher consumer demand and low supply of current products or services. The plateau stage depicts the break-even level of the market, where the supply of goods meets the current market demand. A declining stage indicates lagging consumer demand for the company’s goods or services.
Product Niche
Once the market and their respective business cycles have been reviewed, companies must develop products or tailor their services to meet a specific niche in the market. Products must be differentiated from the peers in the market so that they meet the specific needs of consumers, and thereby create higher demand for the company’s goods or services.
Evaluate competition
A crucial factor of demand analysis is determining the number of competitors in the market and their current market share. Markets in the emerging stage of the business cycle tend to have fewer competitors. This translates to a higher profit margin for your company.
Request for more information and know how we can help you create robust market intelligence strategies that will give you a first-mover advantage in the market.
About Infiniti Research
Established in 2003, Infiniti Research is a leading market intelligence company providing smart solutions to address your business challenges. Infiniti Research studies markets in more than 100 countries to help analyze competitive activity, see beyond market disruptions, and develop intelligent business strategies. To know more, visit: https://www.infinitiresearch.com/about-us
Infiniti Research Anirban Choudhury Marketing Manager US: +1 844 778 0600 UK: +44 203 893 3400 https://www.infinitiresearch.com/contact-us

Release Summary
Infiniti Research has announced the completion of their recent article on evaluating the importance of demand analysis for your business.
- #MarketIntelligence
- #demandmanagement
- #demandandsupply
- #demandanalysis
- #CompetitiveIntelligence
Social Media Profiles
- Infiniti Research
- Infiniti Research Ltd.
Supply & Demand Analysis
- Small Business
- Advertising & Marketing
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
The Concept of Supply & Its Uses in Business
What happens to price when supply decreases, relationship between level of prices and demand.
- What Can Make a Demand Curve Shift?
- What Is the Market Analysis of a Supply and Demand Curve?
A demand and supply analysis is a vital tool used in economics to inform business decisions. When it is done accurately after considering factors such as trends and seasons, a supply and demand analysis can anticipate the effects of market shifts.
What Is Demand and Supply Analysis?
At the core of a supply and demand analysis are two laws: the law of demand and the law of supply. According to The Business Professor , the law of demand stipulates that the quantity of demanded goods and services lowers with the rise of prices. Conversely, the law of supply stipulates that the number of goods and services supplied increases with a rise in price.
Britannica explains that a supply and demand analysis indicates the relationship between the quantity producers want to sell at various price points and the quantity consumers will buy. Including a demand and supply analysis in a business plan is one of the best tools business owners can use to predict their next moves. By analyzing various factors that affect supply and demand, businesses can predict the amount of product they should produce at a particular price point to yield the most profit.
How to Interpret Supply and Demand
In a graph, the demand curve is represented by a downward curve based on the relationship between what consumers want and what they can pay. As prices rise, demand decreases. If consumers cannot afford a product, they won’t be interested in buying it. When plotted on a graph with price on the vertical axis and demanded quantity on the horizontal axis, the demand curve slopes downward as price increases and quantity decreases. The steepness of the curve depends on the current influences on demand.
In a supply analysis, the supply curve is plotted onto the same graph – with prices on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal – as an upward sloping curve. Based on the number of goods produced, the supply curve factors in input resources, labor, technology and regulations to accumulate its data.
The equilibrium is the point where the two curves meet. This point indicates where the market balances and the quantity supplied matches the demand. Businesses can adjust their prices or supply to find the equilibrium point and use workforce planning to meet an upcoming predicted demand.
Supply and Demand Influences
Many factors influence supply and demand trends. Five common factors that influence demand are consumer preference, income level, substitute prices, complementary goods and future expectations.
Many products become popular based on trends; However, trends don’t last forever. As consumer preferences shift, demand for formerly popular products will likely decrease. Similar to trends, future expectations also influence buyer habits. For example, if the consumer expects prices to decrease, they may wait to purchase later, such as buying holiday decorations after the holiday season has ended.
However, complementary goods, which are items that are traditionally bought together, affect demand differently. If one item becomes cheaper, such as pancake mix, the demand for maple syrup is more likely to increase. Production costs, technology advances, the number of suppliers and government regulations can all affect supply trends. For example, advances in technology can influence supply by cutting costs in the production chain, making it cheaper to produce more product.
- The Business Professor: Demand-Supply Analysis - Explained
- Britannica: Supply and Demand
Danielle Smyth is a writer and content marketer from upstate New York. She has been writing on business-related topics for nearly 10 years. She owns her own content marketing agency, Wordsmyth Creative Content Marketing, and she works with a number of small businesses to develop B2B content for their websites, social media accounts, and marketing materials. In addition to this content, she has written business-related articles for sites like Sweet Frivolity, Alliance Worldwide Investigative Group, Bloom Co and Spent.
Related Articles
The imposition of taxes and supply & demand, difference between a demand function and a demand curve, explain elasticity of supply in economic terms, what happens to the equilibrium price when quantity of supply & demand shifts upward, effects of technology on supply and demand curves, differences between aggregate demand curve and market curve, how does an excise tax change the quantity demanded, dependent demand vs. independent demand, how to make supply & demand figures in excel, most popular.
- 1 The Imposition of Taxes and Supply & Demand
- 2 Difference Between a Demand Function and a Demand Curve
- 3 Explain Elasticity of Supply in Economic Terms
- 4 What Happens to the Equilibrium Price When Quantity of Supply & Demand Shifts Upward?
A Five-Step Approach to Effective Demand Planning Implementation

Good handling of market demand data is one of the most vital concepts in any supply chain. The correct management of demand information can greatly influence the level of integration and responsiveness and has a direct impact on customer service and inventory levels. If customer demand is the activating element in the supply chain, it’s quite clear that a multi-step operational supply chain management process to create reliable demand forecasts can play an active role in improving supply chain effectiveness. But how to create powerful demand planning implementation? The five-step approach outlined below provides guidance.
How to Create a Demand Planning Process
Start with a demand analysis.
It’s an old saying: ‘garbage in, garbage out’. Any forecasting process starts with analyzing and understanding your sales history and cleaning up your dataset. In addition to the typical data cleansing tasks, it’s also important to establish a focus for the forecasting process: which items do we need to review?
Doing a customer-product segmentation prior to the demand planning implementation is a great help in this respect. Additionally, opting for a separate forecast for the recurring items and promotional, project or tender items will sharpen your focus. High-volume, fast-moving items that can be forecasted accurately based on statistics should be left to the automated forecast of the demand planning tool. However, you should always incorporate an exception-based review list.
Rely on a quantitative baseline forecast
Statistics should always be your starting point rather than the finishing post. This not only makes life easier for Sales but also helps to remove bias from the forecast because people have a natural tendency to over-forecast. Furthermore, it will free up extra time for your sales team to focus on lumpy and erratic figures.
At the same time, you should be very careful with statistical forecasting . In general, the forecast statistics are too complex and often poorly understood. If you have an effective process and a good tool, statistical forecasting can easily generate 30-40% more efficiency. If the results applied incorrectly, however, the only outcome will be frustration. So look for a knowledgeable partner who can help you select the right level of complexity for your business and ensure you benefit from improved performance as a result.
Strive for a collaborative demand planning implementation process
We can’t overemphasize the importance of gaining extra input for the statistical forecast from the right people, both from within the company and from key customers and distributors. Demand can be influenced by a myriad of factors, and way more than any statistical model can currently handle, so, statistics alone can’t do the job!
You have to rely on a collaborative process within and beyond company, boundaries to receive the additional, crucial demand information such as about product launches, substitutions, and end-of-life products, for instance. Other types of relevant information include promotions, price changes, and marketing campaigns, and projects and tenders could also be a disruptive factor in your supply chain. This extra demand information is typically managed via reviewing lists. Besides these, it can be very useful to ask your sales team to validate the statistical forecast, which is often easier to do on an aggregated level.
But it doesn’t end with your sales team’s contribution. You should stop trying to guess what your most valuable and important customers will buy. Instead, go and talk to them and set up a collaborative forecast approach. Do the same for your other important channel partners too.
Invest in performance management
The numbers tell the tale! In return for all your efforts to improve the forecast, you should also be able to measure your progress. Reducing the forecast error will improve service while lowering cost and inventory, so it’s worth ensuring that the forecast accuracy is monitored effectively.
In a typical situation, Supply Chain will generate the statistical forecast, Marketing or Product Management will add information about promotional campaigns, new product launches, and end-of-life products, and Sales will add customer data. Ensure that your tool enables you to check the added value of each of the different forecast versions and include a feedback cycle.
At the very least, follow up on these three key metrics: the mean percentage error, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and the stability of the forecast accuracy.
Hold a demand review meeting
The final step in demand planning implementation should be a demand review meeting, led by the demand manager or the S&OP manager. Supply Chain is the only department that can be regarded as being ‘neutral’ with regards to Sales, Operations, and Finance and hence is in the best position to chair demand review meetings.
Some tips and tricks for a successful demand review meeting include: avoid getting into discussions about the data, don’t allow the S&OP forecast to differ from the financial one, shift the discussion onto values instead of volumes, keep the meeting brief and powerful, and prepare scenarios in the case of uncertainty. This will all help you to build consensus and ensure a high-quality forecast in the S&OP process!
Share This Article.
About the author: prof. dr. bram desmet.

Related Posts

What the Economic Outlook Means for Demand Planning

Avoiding the Assumption of Normal Distribution in Safety Stock Calculations

Arkieva Named Challenger in 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Supply Chain Planning Solutions

Unwrapped: What You’ll Take Away from the 2024 Gartner Supply Chain Symposium

The Latest R in Sustainability: Reshoring

Unpacking S&P Global’s 2024 Supply Chain Industry Outlook
Pin it on pinterest.

- > Economics
A Guide to Demand and Supply Analysis
- Yashoda Gandhi
- Feb 15, 2022

Introduction
The study of how buyers and sellers interact to determine transaction prices and quantities is known as demand and supply analysis. As we'll see, prices reflect both the value of the next (or marginal) unit to the buyer and the cost to the seller of that unit.
The most basic set of microeconomic tools in private enterprise market economies, which are the primary concern of investment analysis , is demand and supply analysis.
Consumers (or households) and firms are the two types of private economic units classified by microeconomics. The theory of the consumer and the theory of the firm are two branches of study based on these two groups.
The consumer theory is concerned with utility-maximizing individuals' consumption (demand for goods and services) (those who make decisions to maximise satisfaction from current and future consumption).
The firm theory is concerned with profit-maximizing firms' provision of goods and services. The consumer and firm theories are important because they help us understand the underlying principles of demand and supply. The theory of the consumer and the theory of the firm will be the focus of subsequent readings.
What is Supply and demand analysis ?
Two laws are at the heart of a supply and demand analysis: the law of demand and the law of supply. According to The Business Professor , the law of demand states that as prices rise, the quantity of desired goods and services decreases. The law of supply, on the other hand, states that as prices rise, so does the number of goods and services available.
A technical assessment of securities based on factors influencing supply and demand for a specific security or for securities in general. The purpose of the supply-demand analysis is to see if there is or will be an imbalance between supply and demand for securities.
For instance, if a security's supply is expected to exceed demand, the security should be sold or avoided because its price is likely to fall. New stock offerings, government borrowing, pension fund contributions, mutual fund cash balances, and a variety of other similar factors are all factored into the supply-demand analysis.
Also Read | Factors affecting the supply of a product
When to apply Supply and demand analysis ?
With a few exceptions, the law of demand states that as the price of a good or service rises, so does the quantity demanded. The law of supply states that as a supplier's price rises, so does the quantity supplied. Demand is often a downward sloping curve in the price-quantity plane, whereas supply is an upward sloping curve.
The market equilibrium is defined as the intersection of the supply and demand curves, which determines the equilibrium levels of price and quantity of a particular good (or service) in the economy. Excess demand describes a situation in which the current demand for a good (or service) in the economy exceeds the equilibrium quantity.
In a similar vein, excess supply is defined. Changes in supply and demand (and thus the equilibrium price and quantity) of any good or service can be influenced by a variety of factors, including policy changes, unexpected economic shocks, business cycle fluctuations such as a recession or a boom, or even simply over time (long run versus short run).
It also depends on the market's characteristics (whether the market is perfectly competitive or monopolistic etc.). The study of supply and demand, or simply 'Demand-Supply Analysis,' could be applied to all of the above. (source)
Supply-demand analysis tool
A comprehensive strategic planning approach includes supply and demand analysis. Because the market and consumer habits are rapidly changing, it's all about making sure you're always responding in the best way possible to the needs of the customers you're trying to serve.
This tool will give you a solid foundation for a supply and demand analysis, which can then be used to inform a more comprehensive strategic planning process.
The Supply/Demand Analysis feature is a chart that is directly embedded in the scenario. The graph shows the supply and demand planning data over time in a combined view.
The supply data is shown as a stacked bar graph, with the area stacked vertically according to the building or lease. The demand data is shown as a line graph that is superimposed on the bars. This graph depicts how an organization's space or area supply compares to its demands.
You can use this tool to interactively analyse scenario options to match forecasted business demand to portfolio space supply over time. The graphical analysis tool can assist you with the following:
Visually identify supply-demand gaps that necessitate action planning to meet demand or maximise portfolio utilisation.
Consider what-if supply-side scenarios for lease contract options, new building expansions, and portfolio consolidations.
Examine the effects of demand-side changes in order to match supply or close gaps.
Also Read | 11 Types of Economic Theory
Importance of demand and supply analysis
Demand analysis.
For a new business, the analysis can determine whether there is a significant demand for the product/service, as well as other information such as the number of competitors, size of competitors, industry growth, and so on. It aids in determining whether a company can enter a market and generate sufficient returns to sustain and grow its operations.
Demand analysis aids in identifying key business areas with the highest demand and areas that require attention, as low demand can indicate a variety of issues, such as customers not being aware of the product/service, which necessitates increased advertising and promotion, or customer needs not being met by current product/service, which necessitates improvements, or competitors have sprung up with better offerings, among other things.
Supply analysis
Supply analysis aids manufacturers in determining the impact of changes in production and policies on the increase or decrease in finished goods supply.
For example, newer upcoming technology can aid in the production of more goods in the same amount of time. The results of the analysis can be used to determine whether or not this new technology should be adopted.
Is there a demand for more products if this technology can help produce more? What effect will it have on the current labour market, and how will it affect supply?
Another example is the impact of market wage increases on supply. The cost of labour will rise, and with it, the cost of goods will rise as well.
If the supply must be maintained at the same level, the costs must be maintained at the same level, and if the supply must be maintained at the same level, the supply must be reduced, driving up prices if the demand remains constant. These are some of the questions that supply analysis aims to address.
Also Read | What is Scarcity in Economics?
Demand analysis parameters
Price of similar products.
As we discussed in the first two points about price and purchasing power, the price of a competitor's product or service enters the equation and can influence demand. If a competitor's price is lower, demand for that product will be higher, and vice versa. In the case of luxury or niche products, the situation may be different.
Customer preferences and requirements
Consumer behaviour must be taken into consideration. The product or service must match the preferences of the customer; otherwise, there will be no demand for it.
Price set by the product itself
In demand analysis, the product's price is very important. Demand will be affected if the price is too high in comparison to competitors or what the customer can afford. It can be low or high, depending on the product or service's price point.
Profits from customers
Customer purchasing power has a significant impact on product demand. If a product or service is offered at a price point that is higher than a customer group's affordability, demand will be low, so customer income must be considered.
Customers in the market
Customers drive demand, so the potential market is an important parameter for demand analysis. If the customer base is too small for a viable business, even if the first five points are favourable, demand will never rise because the customer base is too small.
Expectations
Based on the overall industry landscape, the customer may have expectations for a new or existing product. For example, if every competitor in the market provides free warranty service but one company does not, that company is unlikely to meet customer expectations. (source)
Example of demand-supply analysis in tariffs
A tariff is a tax imposed on goods from other countries that are sold in the United States. Assume that foreign-made automobiles are subject to a 10% tax.
Who would be the ones to bear the brunt of this tax? Assume that a Japanese car and a similar American car both sell for $25,000 in the United States.
According to the source , with the ten per cent tax ($2,500) on Japanese cars, the Japanese company wants to raise the price to $27,500. The tariff will be imposed on Japanese automobile manufacturers.
A tariff on a foreign product with very elastic demand is referred to as an optimal tariff in technical terms. In the United States, the price of a foreign product rises very slowly.
Also Read | Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Scope of Managerial Economics
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Different Types of Research Methods
Latest Comments
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Business Jargons
A Business Encyclopedia
Demand Analysis
Definition: The Demand Analysis is a process whereby the management makes decisions with respect to the production, cost allocation, advertising, inventory holding, pricing, etc. Although, how much a firm produces depends on its production capacity but how much it must endeavor to produce depends on the potential demand for its product.
Thus, the marketer is required to analyze properly the demand for its product in the market and must hold inventory accordingly. Such as if there is a potential demand in the future, then the firm should hold more inventories and in case there is no demand, then the production remains unwarranted, and hence, lesser inventories are held.
There is a possibility that production might exceed the demand, then the marketer must use alternative ways such as better advertisements to create a new demand.
The demand shows the relationship between two economic variables, the price of the product and the quantity of product that a consumer is willing to buy for a given period of time, other things being equal.
Features/Characteristics of Demand
The following are the main features or characteristics of demand that the marketer must keep in mind while analyzing the demand for its product:
- The demand is the specific quantity that a consumer is willing to purchase. Thus, it is expressed in numbers .
- The demand must mean the demand per unit of time , per month, per week, per day.
- The demand is always at a price, e. any change in the price of a commodity will bring about a certain change in its quantity demanded.
- The demand is always in a market , a place where a set of buyers and sellers meet. The market needs not to be a geographical area.
Thus, demand plays a crucial role in the success of any business enterprise. And it must be remembered that demand is always at a price and a particular time period in which it is created. Such as demand for woolen clothes will be more in winters than in any other season. Hence, demand analysis is always done in terms of the price and the relevant time period.
Related terms:
- Market Demand
- Types of Demand
- Law of Demand
- Elasticity of Demand
- Types of Price Elasticity of Demand
Reader Interactions
messay leulesged says
August 2, 2021 at 11:51 am
I have learned very well about demand analysis. Thank you
CHANDANA says
August 12, 2021 at 10:55 am
GOOD EXPLANATION
Komal Jha says
October 24, 2021 at 11:34 am
Very good explanation
Mathivathani.M says
October 8, 2022 at 9:01 pm
Good explanation
NIKITA SAINI says
November 3, 2023 at 7:59 pm
very well explained
Ritik Jaiswal says
November 5, 2023 at 11:23 am
Very well explained.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Demand Management: Process, Importance and Tools

The relationship between supply and demand is Economics 101. Whether a business is manufacturing or managing a warehouse, understanding demand management goes a long way to ensure that stock levels are always balanced with customer needs.
This requires first an understanding of demand management and how it benefits business. Next, we’ll outline the demand management process to learn how to implement this planning methodology and how software can facilitate that process.
What Is Demand Management?
Demand management is the process of managing customer needs for a product that a company sells. It’s a planning methodology that tries to forecast what a customer will want, when they’ll want it and the logistics of getting that product to them. By planning, companies can identify and avoid potential problems, such as bottlenecks in production or the supply chain and market volatility.
In manufacturing , demand management comes after supply chain management, such as managing procurement and suppliers, but before portfolio management. Demand management is cross-functional as it crosses many disciplines, from consumer demand, supply teams and inventory to marketing and customer service.
One way to look at demand management is as a bridge between the marketplace and a company’s internal operations. That is, demand management works to create interactions between operations and marketing with the goal of being able to develop actions that align the fluctuations of the market with a company’s strategy, production capacity and customer needs.
Managing production is key to demand management and project management software is essential to that process. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with resource allocation features to keep teams working at capacity. Use the team page or the color-coded workload chart to monitor your team’s allocation. If some are over- or underallocated, the team’s workload can be balanced quickly to keep them as productive as needed to meet demand. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
What Is the Importance of Demand Management for Businesses?
Understanding customer demand will benefit any business that manufactures or sells products. Demand management is a crucial part of any business strategy so they have stock on hand to meet customer needs. Here are some other reasons that illustrate the importance of demand management for businesses.
Helps Organizations Establish their Production Budget
Demand management allows companies to analyze and predict changes and trends in market demand. This leads to a reduction in costs due to overproduction or stockouts. It also informs the production budget to make sure that there are enough funds to meet demand but not add unnecessary costs through excess inventory, labor, etc.
Allows Businesses to Meet Customer Demand
Knowing what customers want allows for better planning of delivering it to them. If there’s a spike in customer demand or if customer demand is waning, production planning must follow suit or suffer a loss in business or the cost of carrying unwanted inventory. Demand management allows for a better gauge of customer demand.
Prevents Excess Inventory and Overproduction
As stated above, excess inventory is costly. All that product must be stored, which leads to money spent on items that aren’t being sold. Ideally, a company wants a warehouse full of inventory that will move due to a balance between what’s in stock and the customer demand. Demand management is a way to achieve that balance.
Helps With Supply Chain Planning
Supply chain planning is all about optimizing the manufacturing and delivery of goods. It starts with raw materials, moves to finished products and ends with customers. A clear picture of customer demand will inform these steps, from knowing how much raw material is needed to the quantity of items produced, etc. Demand management, then, is an integral part of this process and helps a business spend only what it needs.
Informs Workforce Planning
Demand management helps managers understand the current and future workforce requirements, which allows them to plan better. The managers better understand customer demand, which leads to knowing how to allocate resources to meet that demand by having the right people with the right skills.
Demand Management Process
Demand management helps businesses to oversee and manage customer demand. To do this, though, requires a process. The demand management process includes knowing what customers want and the steps necessary to fulfill those needs. To plan for current and future demand requires following these six steps in the demand management process.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is the process of predicting customer needs for a business’ products. That demand determines what adjustments need to be made or if new offerings should be added. Estimating what customers want and how much of each item they’ll want isn’t an exact science. To get an accurate estimate, businesses use many methods, some qualitative and other quantitative. Data, software and analytics are all used in this process, but predictions should always be hedged by noting their strengths and weaknesses.
Demand Planning
Once the forecast is clear, the planning begins. Demand planning is part of the demand management process that enables a business to plan to meet the demand forecast through the production of its products. This is also part of the larger supply chain process and requires an understanding of horizon (timeline for the demand plan), frequency (how often the plan is updated) and granularity (level of detail in the plan). This allows for the creation of a demand plan that meets customer needs.
Demand Modeling
One way to make a more accurate demand forecast and, therefore, have a better demand plan is through demand modeling. Demand modeling uses predictive analysis to understand customer behavior. It looks at things such as the propensity of a customer to purchase a product and how the propensity changes based on things like the price of that product. Historical data is also used to better understand the customers’ behavior.
Demand Capacity
Demand capacity is a ratio that compares the production that a company makes with the demand coming from its customers. When manufacturing, businesses measure demand capacity to make sure they have the production capacity levels that allow them to meet the demand for their products. Calculating this uses several sources, such as sales records, customer feedback, inventory levels, production reports or service logs.
Demand Sensing
Another way to predict customer demand is with demand sensing, which uses real-time data and analytics to understand and predict what a customer will want, when they’ll want it and how much they’ll want. This is done by reviewing sales history, inventory levels and customer behavior, point-of-sale systems, online sales platforms and customer surveys. While not perfect, demand sensing can reduce forecast error by up to 50 percent and increase accuracy by up to 20 percent.
Demand Shaping
Demand shaping is a supply chain strategy that uses tactics such as price and promotion incentives, product substitutions and cost modifications to lure customers to buy specific products. Through these means, a business can influence demand for a certain item to match its planned supply.
What Does a Demand Manager Do?
The person responsible for the demand management process is a demand manager or demand planning manager a professional tasked with overseeing the daily operations of the demand planning team, who analyzes customer and vendor demand to create and refine their forecasts.
Demand managers are responsible for reviewing purchase history, sales history and the marketing strategies businesses use to promote products and stimulate growth. They also evaluate their effectiveness and respond accordingly to improve.
To do this, the demand manager will come up with effective forecast models based on industry trends and demand patterns. They’ll implement solutions to improve the accuracy of demand forecasting, as well. They are highly analytical and have a deep knowledge of advanced mathematical and forecasting policies.
How to Manage Production With ProjectManager
Demand management has a great influence on production. It tells manufacturers how much of a product customers want so they can produce just the right amount or as close to that number as possible. This saves money on labor, storage and more. However, demand management can’t help create a more effective production plan, but project management software can. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software with multiple project views to plan production activities, schedule resources and track labor costs to ensure that manufacturing goes according to budget.
Plan Production Activities
Managers can plan their production activities on robust Gantt charts that link all four types of task dependencies to avoid delays. Once the schedule is made, resources allocated and costs determined, set a baseline to capture that plan so it can be compared to actual progress and costs during production. Real-time dashboards capture key performance indicators (KPIs) on easy-to-use graphs and charts for a high-level overview of production. There are also customizable kanban boards with columns that reflect the production cycle and cards that track costs, progress and schedule resources. Use kanban to manage order fulfillment, too.
Track Labor Costs With Timesheets
Keeping a close eye on labor costs helps manage production costs. Employees can use timesheets that automatically add their hours and are securely sealed once sent to a manager to review and pass onto payroll. While this streamlines the payroll process, it’s only part of what timesheets can do. Timesheets capture labor costs and let managers see how far each team member is in terms of completing their assigned tasks. This allows managers to calculate whether the production is progressing as planned or if resources need to be allocated to get back on track.
Stakeholders can stay up to date with production by using one of the multiple project views to track progress, such as the calendar view, which is more a high-level overview of the production cycle. But there are also customizable reports on project status, portfolio, variance and much more. All can be filtered to show only the data stakeholders want to see and shared with them across formats.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or on the factory floor. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams from companies, such as Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver success. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
Evaluating the Importance of Demand Analysis for Your Business
What is demand analysis.
Demand analysis involves understanding the customer demand for a product or service in a particular market. Companies use demand analysis techniques to determine if they can successfully enter a market and generate expected profits to advance their business operations. It also gives a better understanding of the high-demand markets for the company’s offerings, giving them a fair idea on which markets to invest in. Demand analysis is one of the most important considerations for a variety of business decisions including sales forecasting, pricing products/services, marketing and advertisement spending, manufacturing decisions, and expansion planning.
Identifying market opportunities and meeting the market demand can prove to be challenging without appropriate expertise. Request a free brochure to learn how experts at Infiniti Research can assist you with smart solutions that cater to dynamic business needs.
Key factors affecting demand analysis

Common steps in market demand analysis
While there may be several methods of market demand analysis that varies according to the complexity of operations in the business, we have curated some of the commonly used steps for demand analysis:
Market identification
Identifying the specific and target market for the company’s products or services is one of the first market demand analysis steps. Surveys or customer feedbacks can be used to determine the current customer satisfaction levels. Comments indicating dissatisfaction can lead to improvements that will eventually enhance customer satisfaction. Although companies usually identify markets close to their current product line, new industries may be tested for business expansion possibilities.
Business cycle
After identifying the potential markets, the next step is to assess the stage of the business cycle in which that particular market is. A business cycle ideally comprises of three stages: emerging, plateau and declining. Markets that are in the emerging stage indicate higher consumer demand and low supply of current products or services. The plateau stage depicts the break-even level of the market, where the supply of goods meets the current market demand. A declining stage indicates lagging consumer demand for the company’s goods or services.
Request a free proposal for more insights into our market intelligence solutions and learn how we can help enhance your business outcomes.
Product Niche
Once the market and their respective business cycles have been reviewed, companies will need to develop products or tailor their services to meet a specific niche in the market. Products must be differentiated from other peers in the market, so that they meet a specific need of consumer demand, creating higher demand for their product or service. It is also advisable to conduct tests in sample markets to determine which of the potential product styles is most preferred by consumers. Companies can also develop their goods in order to prevent competitors from easily duplicating their products or business strategies.
Evaluate competition
A crucial factor of demand analysis is determining the number of competitors in the market and their current market share. Markets in the emerging stage of the business cycle tend to have fewer competitors. This translates to a higher profit margin for your company. Once a market becomes saturated with competing companies and products, fewer profits are achieved and companies will begin to lose money. As markets enter the declining business cycle, companies must conduct a new market demand analysis to find more profitable markets.
GET MORE INFO on our demand analysis solutions for business.
We help our clients make smarter decisions to achieve rapid business growth
Our strength lies in the unrivaled diversity of our international market research teams, innovative research methodologies, and unique viewpoints that merge seamlessly to offer customized solutions for your every business requirement.
Recent Posts

Competitive Intelligence Impact: Streamlining Your Responsibilities

Strategies for Success: Market Research Intelligence in Manufacturing

Financial Evolution: AI’s Impact on Customer Intelligence
Manage settings.

Demand planning is a supply chain management process that enables a company to project future demand and successfully customize company output—be it products or services—according to those projections. It is the linchpin of an effective supply chain, which makes it doubly important to business.
Demand planning seeks to achieve and maintain an effectively lean supply equilibrium, one in which store inventories contain just as many products as demand dictates, but no more. Finding that perfect balance that exists between sufficiency and surplus can prove especially tricky. And although maintaining that balance is a major concern of demand planning, so is the constant effort to help shape demand through an effective use of promotions.
Effective demand planning typically requires the use of demand forecasting techniques to accurately predict demand trends, and carries added benefits, such as heightened company efficiency and increased customer satisfaction.
Discover the power of integrating a data lakehouse strategy into your data architecture, including enhancements to scale AI and cost optimization opportunities.
Register for the guide for data leaders
Demand planning is the linchpin of an effective supply chain, serving two essential functions — which makes it doubly important to business.
First, there always exists the fundamental drive to protect the sale and ensure that expected revenues are generated. But retailers can’t sell what they don’t have in stock. And it doesn’t take long for today’s consumers to develop a lasting impression of a company, and whether it can meet supply demand. Demand planning works to see that retailers have exactly the right amount of inventory at the right place to avoid stock-outs and remain prepared for that next sale.
But protecting sales isn’t enough anymore. It’s also about running businesses more efficiently. Demand planning assists with efficiency, by helping manage inventory space smarter. Why should companies invest in more physical space than they need? Demand planning can help businesses avoid the perils of overstocking — such as increased inventory carrying costs and financial situations that require the use of product discounts or other temporary measures to alleviate overstocking by selling inventory as quickly as possible.
Demand planning and forecasting is more crucial than ever, especially since so many outside forces — such as weather events, economic trends and global emergencies — can end up shaping and reshaping demand.
Effective demand management requires a comprehensive understanding of products and their respective lifecycles. Product portfolio management offers this, detailing a product’s complete lifecycle, from its origins until its eventual phase-out. And since many product lines are interdependent, product portfolio management shows you how shifting demand can affect “neighboring” products.
Working from the traditional concept that past history is usually the best predictor of future performance, statistical forecasting uses complex algorithms to analyze historical data and develop supply chain forecasts. The mathematics of statistical forecasting methods is advanced and the exacting process demands accurate data (including from outliers, exclusions or assumptions).
Demand sensing uses a combination of new sources of data, such as weather, infectious disease trends, government data and more, with historical trend data and applies AI to detect disruptions and demand influences in near real-time.
Survival in the retail jungle depends on sparking the interest of potential customers. Trade promotions and other marketing strategies use special events (such as discount prices or in-store giveaways) to spike consumer demand. Trade promotion management works to ensure that such opportunities are properly executed and deliver all expected benefits.
Organizations vary widely in how they approach the demand planning process, but there is a general set of steps that businesses typically follow. Those steps include:
- Organizing and preparing data.
- Making a preliminary forecast.
- Integrating market data.
- Reconciling bottom-up and top-down forecasts.
- Developing a final forecast.
- Using analytics to monitor project performance.
In addition to establishing a precise set of implementation steps, successful companies usually engage in the following best practices for demand planning:
In order to process complex projections, effective demand planning requires ample amounts of data. Smart companies rely on metrics reports that help them prepare their data through increasingly sophisticated data mining and aggregation techniques.
There are numerous options when choosing demand planning software, but companies should try to be selective, based on their unique needs. Goal: Find a solution refined enough to reflect the subtleties of demand forecasting methods yet robust enough to handle reporting tasks.
Experienced demand planners typically begin their process by using descriptive analytics data to develop a testing baseline. Next, they shape the actual plan, devoting personnel and resources to cultivate and refine that plan, and then work on the exact implementation steps.
To be sure, the future is digital — and so is the outlook for demand planning. As demand forecasting in supply chain management becomes increasingly sophisticated because of advances in machine learning, companies will reap substantial benefits, such as being able to receive precise, real-time inventory updates and forecasts.
These continuing advances are drawing companies closer to the ideal promoted through demand planning. If an enterprise stocks just enough inventory to satisfy customer demand and withstand temporary market fluctuations, it’s able to run more efficiently and profitably thanks to its lean inventory strategy.
Your business is always evolving, which is why you need continuous intelligent planning.
Discover how to streamline the planning process for supply chain plans that are synchronized and responsive.
Get a single view of your inventory — from raw material availability and supplier orders all the way to customer delivery.
View all upcoming IBM events, such as THINK, Supply Chain Academy and more.
Predict outcomes with flexible AI-infused forecasting and analyze what-if scenarios in real-time. IBM Planning Analytics is an integrated business planning solution that turns raw data into actionable insights. Deploy as you need, on-premises or on cloud.

- Business Plans
- Limited Company
- Self Employed
- Bank Accounts
Business Plan (3) – Market Analysis, Demand Analysis
- October 11, 2020
- Business Plan Guide
In Part 3 of our 8-Part Guide to Writing a Business Plan we look at Market Analysis and Demand Analysis.
3. Market Analysis
In this chapter you will define:
- Geographical area
- Consumer behaviour
- Market segmentation
3.1 The market is the people or organisations that will participate in the buying and selling processes of the products or services or use these products or services.
3.2 The geographical area refers to a type or range of products in a defined geographical zone, for example, the car market in the USA or the cosmetic market in the UK.
3.3 Once you have defined the market and the geographical area you need to summarise the needs and behaviour of the consumers. Who are they? Why do they need the product or service?
3.4 Different groups of customers will have different requirements. The market for any product can be split into individual segments, where each segment describes customers with similar requirements, tastes, characteristics, interests, or lifestyles. Segmentation indicates gaps in the market and highlights requirements of different types of users, enabling products to be positioned to meet those needs.
- If you do not know your market, you can not create a viable plan, so do your homework.
- Think about the behaviour and habits of each of the segments.
- Identify consumer needs that the competition does not cater for, and make sure that these are highlighted clearly in the customer requirements.
4. Demand Analysis
In this section you are going to make a numerical evaluation of the market and the segments of the market that you have defined in the following areas:
- Potential demand
- Actual demand
- Future demand
- Evolution of demand
4.1 The potential demand is the maximum the consumers could buy in a determined period of time.
4.2 Actual demand is the demand for the product or service this year or the previous year if the data is not available. It is possible to obtain sales data on a national or regional level from many different sources. If there is no data available you need to make estimates using other methods.
4.3 To establish future demand, estimate the increase in demand for the next year as a percentage of actual demand. For example the market for video games will go up by 10% in the next year. You can also make estimate for the medium and long term, 3-5 years would give you information to provide for and create future strategies.
4.4 To see the potential evolution of demand make a graph of historical sales in your sector, using this you can see the market trends and define the phases of the product life cycle. Using the actual, potential and future demand figures and applying them to the market segments previously identified by geographical region, objectives can be created as detailed later.
- Do not commit the error of being over optimistic with demand forecasts.
- Define the life cycle of your product or service, apply this to future demand.
- The launch phase of many products is slow; sometimes it is better to enter a market after others when the demand has already been created.
Go to Part 4 – Environmental, Company and Competition Analysis
Go to the Guide to Writing a Business Plan Index
More Bytestart Guides

Super Market Research
Latest Industry News and Competitor Analysis
Octene Manufacturing Plant Report 2024: Business Plan, Market Demand Analysis, Cost and Economics
IMARC Group’s report titled “ Octene Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue ” provides a comprehensive guide for establishing an octene manufacturing plant. The report covers various aspects, ranging from a broad market overview to intricate details like unit operations, raw material and utility requirements, infrastructure necessities, machinery requirements, manpower needs, packaging and transportation requirements, and more.
In addition to the operational aspects, the report also provides in-depth insights into octene manufacturing process, project economics, encompassing vital aspects such as capital investments, project funding, operating expenses, income and expenditure projections, fixed and variable costs, direct and indirect expenses, expected ROI, net present value (NPV), profit and loss account, and thorough financial analysis, among other crucial metrics. With this comprehensive roadmap, entrepreneurs and stakeholders can make informed decisions and venture into a successful octene manufacturing unit.
Customization Available:
- Plant Location
- Plant Capacity
- Machinery- Automatic/ Semi-automatic/ Manual
- List of Machinery Provider
Octene is a significant alpha-olefin widely used in various industrial applications, notably in the synthesis of polyethylene, lubricants, and chemical intermediates. As an unsaturated hydrocarbon, it is highly versatile in chemical reactions, making it essential for producing high-strength and flexible plastics. Different types of octene, characterized by the position of the double bond in their carbon chain, cater to specific industry needs, enhancing properties like durability and chemical resistance in end products. Its high reactivity facilitates efficient polymerization processes and imparts desirable qualities to polymers, such as improved tensile strength and impact resistance, underscoring its importance in modern manufacturing.
The global market for octene is primarily driven by strong demand in the polyethylene industry, where it is used as a comonomer to produce linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). This polymer’s extensive use in films, packaging materials, and containers supports market growth, propelled by the expanding packaging industry and increasing consumption of flexible, high-quality plastic products. Additionally, the growing automotive sector boosts demand for octene, as it is used in manufacturing high-performance synthetic lubricants and elastomers, crucial for modern automotive components. The rise in industrialization and urbanization further fuels the need for advanced materials and chemicals, supporting infrastructure, automotive, and consumer goods development.
Emerging market trends include technological advancements in catalysis and polymerization processes, which enhance the efficiency and environmental sustainability of octene production. The shift towards greener manufacturing practices and the growing demand for sustainable materials are prompting companies to invest in developing bio-based octene, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints. Additionally, there is a growing focus on the circular economy, driving innovations in recycling technologies and the reuse of polyethylene products. These trends, coupled with stringent environmental regulations, are steering the industry towards sustainable growth and influencing the strategic development of key market players.
Request for a Sample Report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/octene-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Key Insights Covered the Octene Plant Report
Market Coverage:
- Market Trends
- Market Breakup by Segment
- Market Breakup by Region
- Price Analysis
- Impact of COVID-19
- Market Forecast
Key Aspects Required for Setting Up a Octene Plant
Detailed Process Flow:
- Product Overview
- Unit Operations Involved
- Mass Balance and Raw Material Requirements
- Quality Assurance Criteria
- Technical Tests
Project Details, Requirements and Costs Involved:
- Land, Location and Site Development
- Plant Layout
- Machinery Requirements and Costs
- Raw Material Requirements and Costs
- Packaging Requirements and Costs
- Transportation Requirements and Costs
- Utility Requirements and Costs
- Human Resource Requirements and Costs
Project Economics:
- Capital Investments
- Operating Costs
- Expenditure Projections
- Revenue Projections
- Taxation and Depreciation
- Profit Projections
- Financial Analysis
Ask Analyst for Customization: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=11453&flag=C
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the octene market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the market segmentation of the global octene market?
- What is the regional breakup of the global octene market?
- What are the price trends of various feedstocks in the octene industry?
- What is the structure of the octene industry and who are the key players?
- What are the various unit operations involved in an octene manufacturing plant?
- What is the total size of land required for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What is the layout of an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the machinery requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the raw material requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the packaging requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the transportation requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the utility requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the human resource requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the infrastructure costs for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the capital costs for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the operating costs for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What should be the pricing mechanism of the final product?
- What will be the income and expenditures for an octene manufacturing plant?
- What is the time required to break even?
- What are the profit projections for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the key success and risk factors in the octene industry?
- What are the key regulatory procedures and requirements for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
- What are the key certifications required for setting up an octene manufacturing plant?
IMARC Group is a leading market research company that offers management strategy and market research worldwide. We partner with clients in all sectors and regions to identify their highest-value opportunities, address their most critical challenges, and transform their businesses.
IMARC Group’s information products include major market, scientific, economic and technological developments for business leaders in pharmaceutical, industrial, and high technology organizations. Market forecasts and industry analysis for biotechnology, advanced materials, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, travel and tourism, nanotechnology and novel processing methods are at the top of the company’s expertise.
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: [email protected]
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-631-791-1145 | United Kingdom: +44-753-713-2163
Related Articles
Sunglasses market size 2023 | global share, growth, top brands, research report by 2028.
The latest research study “Sunglasses Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2023-2028” by IMARC Group, finds that the global sunglasses market size reached US$ 36.4 Billion in 2022. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 49.3 Billion by 2028, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5% during 2023-2028. What […]

Global Functional Water Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth, Analysis, Key Players, Report, Forecast 2023-2028
The ‘Global Functional Water Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth, Analysis, Key Players, Report and Forecast 2023-2028’ by Expert Market Research gives an extensive outlook of the global functional water market, assessing the market on the basis of its segments like product type, ingredient, packaging, distribution channels, and major regions. The key highlights of the report include: […]
Packaged Sweets Market in India 2023: Industry Demand, Business Trends 2028
IMARC Group, a leading market research company, has recently releases report titled “Packaged Sweets Market in India: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2023-2028.” The study provides a detailed analysis of the industry, including the India packaged sweets market size, share, trends, and growth forecasts. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Macy's lifts annual profit forecast as new CEO's revamp takes root
- Medium Text

- Company Macy's Inc Follow
- Company Bloomingdale's Inc Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Anuja Bharat Mistry and Ananya Mariam Rajesh in Bengaluru; Editing by Sriraj Kalluvila
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Ananya as the U.S. Consumer and Retail Sector Specialist covers breaking and business news on major firms including Walmart, Nike, Procter & Gamble, PepsiCo and Coca-Cola among other U.S. listed Cruises, Apparel Makers, Discount Stores, Beverages, Second-hand Retailers, Restaurants, Luxury companies. She writes long-form initiative stories supported by data sets explaining the current consumer demand trends in the U.S. and the impact of macroeconomic conditions on retailers and companies. As a sector lead, she mentors and trains newer members of the team bringing them up to speed with sector knowledge.

Business Chevron

SingTel annual profit more than halves on $2.3 bln impairment hit
Singapore Telecommunications' annual net profit more than halved on Thursday, hit by a previously announced S$3.1 billion ($2.30 billion) impairment charge, most of which relates to its Australian unit Optus.

- Thursday, May 23, 2024

© 2023 - Businessday NG. All Rights Reserved.
UPVC Windows Manufacturing Plant Setup Report 2024: Business Plan, Market Demand Analysis, Cost and Economics
Press release from: imarc group.

Permanent link to this press release:
You can edit or delete your press release UPVC Windows Manufacturing Plant Setup Report 2024: Business Plan, Market Demand Analysis, Cost and Economics here
Delete press release Edit press release
More Releases from IMARC Group

All 5 Releases
More Releases for UPVC
- Categories Advertising, Media Consulting, Marketing Research Arts & Culture Associations & Organizations Business, Economy, Finances, Banking & Insurance Energy & Environment Fashion, Lifestyle, Trends Health & Medicine Industry, Real Estate & Construction IT, New Media & Software Leisure, Entertainment, Miscellaneous Logistics & Transport Media & Telecommunications Politics, Law & Society Science & Education Sports Tourism, Cars, Traffic RSS-Newsfeeds
- Order Credits
- About Us About / FAQ Newsletter Terms & Conditions Privacy Policy Imprint
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
News updates from May 14: Anglo American to break itself up; Powell hints at rates staying high
Today’s top headlines:
Anglo American to break itself up after rejecting BHP bid
Powell hints at rates staying high as fed continues inflation fight, citi executive in charge of implementing bank’s restructuring plan exits, home depot sales weaken due to soft spending on diy projects, aws chief quits as amazon’s cloud business focuses on ai race.

- News updates from May 14: Anglo American to break itself up; Powell hints at rates staying high on x (opens in a new window)
- News updates from May 14: Anglo American to break itself up; Powell hints at rates staying high on facebook (opens in a new window)
- News updates from May 14: Anglo American to break itself up; Powell hints at rates staying high on linkedin (opens in a new window)
- News updates from May 14: Anglo American to break itself up; Powell hints at rates staying high on whatsapp (opens in a new window)
Edited by Jaren Kerr , Alexandra White , Peter Wells , Nora Redmond , Maxine Kelly , Jonathan Wheatley , Oliver Ralph , William Sandlund and George Russell
Harry Dempsey in London
Anglo American has unveiled sweeping plans to break itself up in a bid to defend itself from a £34bn takeover approach by mining industry leader BHP.
The 107-year-old company said it would divest or demerge its platinum, diamond producing De Beers, steelmaking coal and nickel units, narrowing its portfolio down to copper, iron ore and fertiliser.
Anglo said that it would also radically pull back and delay spending on Woodsmith, which is a risky bet on a huge underground mine in the UK that would produce a new kind of unproven fertiliser.
Chief executive Duncan Wanblad said that “these actions represent the most radical changes to Anglo American in decades”.
Anglo American rejected a second improved £34bn takeover offer from BHP on Monday, under which it would have to divest its platinum and iron ore businesses based in South Africa.
Read more here .
- Share $ Anglo American to break itself up after rejecting BHP bid on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Anglo American to break itself up after rejecting BHP bid on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Anglo American to break itself up after rejecting BHP bid on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Stephen Gandel in New York
Fed’s Barr optimistic about buy-in after ‘material’ revisions to Basel bank rules
The Federal Reserve’s top banking regulator said he expects regulators to revise a set of controversial bank rules, dubbed the Basel III endgame, that were proposed last year, and has been met with strong opposition from banks and other industry groups.
Michael Barr, the Fed’s vice-chair for supervision, said he was still optimistic, following “material” revisions, that broad consensus could be reached on the rules, which would require banks to hold capital against loans, potentially cutting into their profit margins and limiting their ability to lend.
Barr’s comments on the bank rules were part of the written testimony the Fed official submitted ahead of Wednesday’s planned House Financial Services Committee hearing that will feature himself along with other bank regulators.
- Share $ Fed’s Barr optimistic about buy-in after ‘material’ revisions to Basel bank rules on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Fed’s Barr optimistic about buy-in after ‘material’ revisions to Basel bank rules on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Fed’s Barr optimistic about buy-in after ‘material’ revisions to Basel bank rules on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Ian Johnston in London and Oliver Barnes in New York
Novo Nordisk to test weight-loss drugs’ effect on alcohol use and liver disease
Novo Nordisk is trialling its weight-loss drugs to explore if they can reduce alcohol intake and treat alcoholic liver disease, as it seeks to expand the uses of the blockbuster treatments.
The Danish pharmaceutical company has started recruitment for a mid-stage trial looking at whether an estimated 240 patients using semaglutide, the active ingredient in Wegovy, and cagrilintide, an ingredient in another Novo Nordisk drug in development for weight loss, can treat liver damage and reduce alcohol use in participants with alcoholic liver disease.
Novo Nordisk is already assessing semaglutide’s effects in liver disease linked to obesity — metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis — but this is the first study to assess the effectiveness of the new generation of weight-loss treatments on alcoholic liver disease, which kills more than 30,000 Americans a year.
Read more here
- Share $ Novo Nordisk to test weight-loss drugs’ effect on alcohol use and liver disease on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Novo Nordisk to test weight-loss drugs’ effect on alcohol use and liver disease on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Novo Nordisk to test weight-loss drugs’ effect on alcohol use and liver disease on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Jaren Kerr in New York
Nasdaq Composite closes at record high ahead of key US inflation report
The Nasdaq Composite closed at a record high, helped by an afternoon rally in Big Tech groups.
The tech-heavy index added 0.8 per cent on Tuesday, surpassing its previous peak from a month ago. Every “Magnificent Seven” stock rose, with Tesla’s 3.3 per cent gain the best performance among the group.
The S&P 500 finished 0.5 per cent higher to hit its highest closing level since the end of March. The small-cap focused Russell 2000 rose 1.1 per cent, closing at its highest level since April 1.
The advance comes ahead of a closely watched US inflation report that will be released on Wednesday morning. Economists expect there was a slight decline in price growth in April.
“If we see a slowdown in US growth and inflation, Fed easing expectations could be pulled forward,” said Karl Schamotta, chief market strategist at Corpay. Economists put the chances of a September interest rate cut in the US at 50 per cent, according to an LSEG poll.
- Share $ Nasdaq Composite closes at record high ahead of key US inflation report on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Nasdaq Composite closes at record high ahead of key US inflation report on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Nasdaq Composite closes at record high ahead of key US inflation report on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Ciara Nugent in Buenos Aires
Argentina’s monthly inflation rate returns to single-digit territory
Argentina’s monthly inflation rate has fallen into single-digit territory for the first time in six months.
Prices rose 8.8 per cent in April, the country’s statistics agency said on Tuesday. That is down from a peak of 25.5 per cent in December, following President Javier Milei’s sharp devaluation of the peso’s official exchange rate.
The country’s Libertarian leader has made taming Argentina’s price pressures — among the worst in the world — his top priority since taking office in December. His main tool has been steep cuts to government spending, which has allowed the central bank to halt money printing that the previous left-leaning government relied on.
The annual inflation rate continues to rise, though, and reached 289.4 per cent in April — the highest since 1991.
- Share $ Argentina’s monthly inflation rate returns to single-digit territory on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Argentina’s monthly inflation rate returns to single-digit territory on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Argentina’s monthly inflation rate returns to single-digit territory on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Joshua Franklin in New York
‘This is Bill. Bill Hwang’: US jury hears founder’s call to Archegos lenders
Bill Hwang told panicked Wall Street investment banks that his family office Archegos needed up to three weeks to “make everyone whole” shortly before the fund collapsed in 2021, which ended up costing his lenders more than $10bn.
On the second day of Hwang’s trial for fraud and market manipulation, the jury in New York heard portions of a call he held three years ago with six investment banks that were on the hook for billions of dollars as the value of Archegos’s investments plummeted.
The audio recording was a rare insight into the dealings of Hwang, who kept a low profile on Wall Street and worked hard to mask his trading strategy and the positions taken by Archegos, which managed his personal fortune.
- Share $ ‘This is Bill. Bill Hwang’: US jury hears founder’s call to Archegos lenders on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ ‘This is Bill. Bill Hwang’: US jury hears founder’s call to Archegos lenders on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ ‘This is Bill. Bill Hwang’: US jury hears founder’s call to Archegos lenders on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
US stocks edge higher after Powell remarks and producer price data
US stocks edged higher as investors assessed remarks from Federal Reserve chair Jay Powell, weighed the latest producer price data and prepared for Wednesday’s inflation report.
The S&P 500 was up 0.2 per cent in Tuesday afternoon trading. The tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite was up 0.6 per cent, with every Magnificent Seven stock except Amazon moved higher as the e-commerce group announced the head of its profitable web services arm is stepping down .
Treasuries endured choppy but muted trading earlier in the day as US producer prices rose more than forecast in April, but March’s figures were revised lower.
Later in the morning, Powell suggested US interest rates would have to stay high in the face of sticky inflation.
The yield on the two-year Treasury was down 0.04 percentage points at 4.82 per cent.
- Share $ US stocks edge higher after Powell remarks and producer price data on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US stocks edge higher after Powell remarks and producer price data on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US stocks edge higher after Powell remarks and producer price data on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Oil heads for 2-month low as traders weigh demand outlook

Oil prices were on track to settle at their lowest level since March, as analysts weigh the outlook for global demand.
Brent crude, the international benchmark, was down 1.4 per cent at $82.18 a barrel. That puts it on course for its lowest settlement price since March 12, although it had briefly fallen below $82 a barrel during intraday trading late last week.
Rising US inventories, which have hit an 11-month high, and concerns over the global demand outlook have played a part in the pullback for oil prices since the start of May.
“Crude is reacting to the outlook for future demand growth,” said David Morrison, analyst at Trade Nation. “This has been tempered recently as the prospect of sharp US rate cuts this year has been dialled back... At the same time, there’s uncertainty over the state of China’s economy.”
- Share $ Oil heads for 2-month low as traders weigh demand outlook on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Oil heads for 2-month low as traders weigh demand outlook on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Oil heads for 2-month low as traders weigh demand outlook on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Titi Cole, Citigroup’s top executive in charge of implementing its sweeping restructuring plan , and one of the most senior Black women in finance, is leaving the bank.
The exit, which was announced Tuesday in an internal memo, comes as Citi continues to implement its reorganisation. The overhaul has resulted in about 7,000 job cuts at the bank, but is planned to eliminate a further 13,000 positions in the next two years.
A source with knowledge of the departure said it had nothing to do with the restructuring and that Cole had been planning for some time to leave the bank and work for a non-profit.
Cole joined Citi in 2020, and was promoted to head of legacy franchises in early 2022, taking on the task of managing Citi’s exit from consumer banking in more than a dozen countries.
- Share $ Citi executive in charge of implementing bank’s restructuring plan exits on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Citi executive in charge of implementing bank’s restructuring plan exits on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Citi executive in charge of implementing bank’s restructuring plan exits on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Andrew England, Middle East editor
Iran open to ‘serious dialogue’, says UN nuclear chief
Iran has shown a willingness to engage in “serious dialogue” with the UN’s nuclear watchdog for the first time in more than a year, according to the agency’s head, in a sign Tehran is seeking to ease tensions with the US.
Rafael Grossi, director-general of the International Atomic Energy Agency, told the Financial Times that Tehran and the watchdog, which have endured fraught relations for months, could be entering a “different phase” after he held talks in Iran.
Tehran appears willing to discuss “concrete” issues, he said.
The apparent shift in tone was prompted by an invitation from Iran’s nuclear chief Mohammad Eslami for Grossi to attend talks in the Islamic republic.
- Share $ Iran open to ‘serious dialogue’, says UN nuclear chief on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Iran open to ‘serious dialogue’, says UN nuclear chief on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Iran open to ‘serious dialogue’, says UN nuclear chief on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Claire Bushey in Chicago
Boeing deliveries of 737 Max fall to lowest since September
Boeing has made the fewest deliveries of its 737 Max since last year as quality problems at the aircraft maker force a slowdown in production.
Just 16 Maxes were delivered to airlines and lessors last month, the company said on Tuesday, dropping from 24 in March and the fewest since last September.
The decline comes as Boeing reels from an accident in January, when a door panel blew out from a 737 Max operated by Alaska Airlines shortly after take-off. While no passengers were seriously injured, the episode sparked multiple investigations by US authorities .
- Share $ Boeing deliveries of 737 Max fall to lowest since September on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Boeing deliveries of 737 Max fall to lowest since September on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Boeing deliveries of 737 Max fall to lowest since September on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Rafe Uddin in London
UK stocks push higher as traders weigh rate outlook
UK stocks rose on Tuesday to close up slightly as investors swallowed stronger than expected wage growth figures but remained divided over whether an interest rate cut would take place in June.
The FTSE 100 and domestically focused FTSE 250 gained 0.2 per cent and 0.3 per cent after data published earlier in the day showed annual growth in weekly wages remained steady at 5.7 per cent, 0.2 percentage points higher than expected.
Swap markets have priced in roughly a 50 per cent probability that the Bank of England will cut rates in June.
The region-wide Stoxx Europe 600 ended the day up 0.2 per cent and France’s Cac 40 rose 0.2 per cent. Germany’s Dax was down 0.1 per cent.
- Share $ UK stocks push higher as traders weigh rate outlook on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ UK stocks push higher as traders weigh rate outlook on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ UK stocks push higher as traders weigh rate outlook on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Rachel Millard in London
Plug Power shares jump on US funding for hydrogen plants
Shares in hydrogen developer Plug Power leapt as it secured a conditional loan guarantee worth up to $1.66bn from the US government.
The company’s US-listed shares climbed 32 per cent in late-morning trade on Tuesday after opening about 70 per cent higher. The government support will help the New York-based company develop six “green hydrogen” plants in the US.
The financing marks a reversal in Plug Power’s fortunes. In November, it warned of “substantial doubt” in its ability to stay afloat without raising additional money.
Andy Marsh, chief executive, said the loan guarantee will help grow the company’s network and the “clean hydrogen industry in the United States”.
- Share $ Plug Power shares jump on US funding for hydrogen plants on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Plug Power shares jump on US funding for hydrogen plants on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Plug Power shares jump on US funding for hydrogen plants on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
James Politi in Washington
Powell says Fed rate rise a ‘very small probability’
Jay Powell, chair of the Federal Reserve, said the US central bank was looking at “keeping policy at the current rate for a longer time than had been thought” but it was not likely the “next move” would be to increase interest rates.
“By many, many measures, the policy rate is restrictive,” Powell said during a panel in Amsterdam. He added “time will tell” whether it was “sufficiently restrictive” but there was only a “very small probability” the Fed would be forced to increase interest rates.
- Share $ Powell says Fed rate rise a ‘very small probability’ on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Powell says Fed rate rise a ‘very small probability’ on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Powell says Fed rate rise a ‘very small probability’ on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Laura Onita in London
Tesco chief’s pay more than doubles to £10mn
The pay of Tesco’s chief executive has more than doubled to almost £10mn for the past year.
Ken Murphy’s pay package reached £9.9mn, largely thanks to performance-linked bonuses of £8.2mn, compared with total pay of £4.4mn the previous year.
The UK’s largest supermarket chain said in its annual report on Tuesday that the significant year-on-year increase in remuneration was down to “strong performance against stretching targets over a challenging period”.
Supermarkets have had to contend with high inflation and customers tightening their belts amid the cost of living squeeze over the past two years.
Tesco’s share price has risen about 20 per cent since Murphy joined the retailer in October 2020.
- Share $ Tesco chief’s pay more than doubles to £10mn on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Tesco chief’s pay more than doubles to £10mn on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Tesco chief’s pay more than doubles to £10mn on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Jay Powell said the Federal Reserve would have to be “patient and let restrictive policy do its work” — suggesting interest rates would have to stay high in the face of higher than expected inflation data.
Speaking on a panel in Amsterdam, Powell said the US economy had been “performing very well lately” but the first months of 2024 had been notable for the “lack of progress” when it came to bringing inflation down to the Fed’s 2 per cent target.
- Share $ Powell hints at rates staying high as Fed continues inflation fight on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Powell hints at rates staying high as Fed continues inflation fight on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Powell hints at rates staying high as Fed continues inflation fight on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
US stocks steady after strong inflation data
US equities opened steady as investors took stock following stronger than expected producer inflation data.
The benchmark S&P 500 was flat in early trading in New York, while the tech-dominated Nasdaq Composite was up 0.1 per cent.
Wholesale inflation increased 0.5 per cent last month, the US labour department said on Tuesday, surpassing analysts’ expectations by 0.2 percentage points.
- Share $ US stocks steady after strong inflation data on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US stocks steady after strong inflation data on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US stocks steady after strong inflation data on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Camilla Hodgson in London
Adam Selipsky, the head of Amazon’s closely watched cloud business, is stepping down and will be succeeded by a company veteran who will help steer the company in its race to compete in artificial intelligence.
The chief executive of Amazon Web Services will “move on to his next challenge” on June 3, the company said on Tuesday, with Matt Garman, currently senior vice-president of sales, marketing and global services at AWS, taking over the role.
“Matt has an unusually strong set of skills and experiences for his new role . . . in the 18 years he’s been in AWS, he’s been one of the better learners I’ve encountered,” Amazon’s chief executive Andy Jassy said.
- Share $ AWS chief quits as Amazon’s cloud business focuses on AI race on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ AWS chief quits as Amazon’s cloud business focuses on AI race on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ AWS chief quits as Amazon’s cloud business focuses on AI race on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
George Steer in London
GameStop and AMC shares surge for second day in ‘meme stock’ revival
Shares in video game retailer GameStop and cinema group AMC Entertainment surged for a second consecutive session on Tuesday, extending a ferocious “meme stock” rally that was sparked this week by the re-emergence of a popular day trader.
GameStop and AMC jumped 63 per cent and 78 per cent, respectively, in early trading in New York, building on 73 per cent and 77 per cent gains on Monday. Trading in GameStop was briefly halted for volatility three times in the first 20 minutes of Tuesday trading.
The sharp moves higher come after bandanna-wearing trader Keith Gill — known as “Roaring Kitty” — who was at the heart of a rally driven by an army of retail traders during the pandemic, appeared to resurface on Sunday after a three-year hiatus from social media site X.
- Share $ GameStop and AMC shares surge for second day in ‘meme stock’ revival on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ GameStop and AMC shares surge for second day in ‘meme stock’ revival on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ GameStop and AMC shares surge for second day in ‘meme stock’ revival on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
BHP chief says Anglo American break-up a ‘variant’ of its takeover vision
BHP chief executive Mike Henry called Anglo American’s break-up strategy a “variant” of its own vision for the company as part of its £34bn takeover offer, as he instructed investors to judge whether they are confident in the ability of the leadership at his rival to deliver on a break-up.
“What we see today is some variant on the approach we’ve brought forward, which involves spinning out one of the assets, which I think is a pretty clear indicator it’s doable,” he said at an industry conference in Miami just moments after Anglo chief executive Duncan Wanblad had laid out his defence strategy to overhaul the mining group.
“It’s ultimately for shareholders to judge,” Henry added.
BHP has until next Wednesday to decide whether to make a formal bid for Anglo American.
- Share $ BHP chief says Anglo American break-up a ‘variant’ of its takeover vision on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ BHP chief says Anglo American break-up a ‘variant’ of its takeover vision on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ BHP chief says Anglo American break-up a ‘variant’ of its takeover vision on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Alexandra White in New York
US producer prices rise to highest level in a year
US wholesale inflation rose more than expected in April to the highest annualised gain in 12 months, in a sign that the Federal Reserve has more work to do to combat price growth.
The producer price index, a leading indicator of inflation, increased 0.5 per cent last month, the labour department said on Tuesday, surpassing analysts’ expectations for a 0.3 per cent gain. The annualised rate rose 2.2 per cent, up from March’s downwardly revised reading of a 1.8 per cent. That was the highest level since April 2023.
Core PPI, which strips out volatile food and energy prices, rose 0.5 per cent last month, pushing up the annualised rate of price pressures to 2.4 per cent from a downwardly revised annualised reading of 2.1 per cent.
- Share $ US producer prices rise to highest level in a year on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US producer prices rise to highest level in a year on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US producer prices rise to highest level in a year on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
US Treasuries sell off as producer prices rise more than expected
Treasury yields climbed after monthly US producer price inflation edged markedly higher than expected in a sign that sticky inflation could stall possible Fed rate cuts.
Figures published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics on Tuesday showed that wholesale inflation increased 0.5 per cent month on month in April, compared with analyst expectations of 0.3 per cent.
The yield on the benchmark 10-year US Treasury was up 0.01 percentage points. Yields move inversely to prices. Futures tracking the benchmark S&P 500 and the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite were down 0.1 per cent and 0.3 per cent, respectively, ahead of the opening bell in New York.
- Share $ US Treasuries sell off as producer prices rise more than expected on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US Treasuries sell off as producer prices rise more than expected on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US Treasuries sell off as producer prices rise more than expected on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Polina Ivanova in Berlin
Russia’s new defence minister vows more efficient military spending
Russia’s new defence minister Andrey Belousov said that better equipping the Russian armed forces would be his priority, with a focus on optimising military spending and making state contracts more efficient.
Speaking for the first time since President Vladimir Putin put forward his candidacy on Sunday, Belousov said he would also focus on integrating the economy of the armed forces with the wider national economy, and improving oversight of military construction contracts.
“Everything that is effective in the country should be put to work to achieve victory,” said Belousov, whose candidacy for the post is expected to be ratified on Tuesday by the upper house of Russia’s parliament.
- Share $ Russia’s new defence minister vows more efficient military spending on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Russia’s new defence minister vows more efficient military spending on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Russia’s new defence minister vows more efficient military spending on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Home Depot missed sales estimates in the first quarter due to a delayed start to spring weather and continued softness in big-ticket discretionary categories.
The US do-it-yourself retailer reported net sales declined 2.3 per cent to $36.4bn in the three months that ended on April 28, missing analysts’ estimates for $36.6bn.
Customers continued to pull back spending amid persistent high inflation. The number of transactions and the average amount spent per visit declined 1 and 1.3 per cent, respectively, compared with the same period last year.
Home Depot earned $3.63 a share, beating analyst expectations for $3.59 a share.
- Share $ Home Depot sales weaken due to soft spending on DIY projects on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Home Depot sales weaken due to soft spending on DIY projects on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Home Depot sales weaken due to soft spending on DIY projects on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Ryan McMorrow in Beijing
Alibaba profits fall as it spends heavily to claw back market share
Alibaba’s profits fell in the first quarter as the Chinese ecommerce giant ramped up spending in a bid to claw back market share from surging rivals such as PDD Holdings.
Adjusted net income fell 11 per cent from a year earlier to Rmb24bn ($3.3bn) during the quarter. Revenues rose 7 per cent from a year earlier to Rmb222bn.
Free cash flow plummeted 52 per cent as the company spent heavily on cloud infrastructure.
Alibaba said it would pay a dividend and continue share repurchases, as it attempts to appease shareholders following a fall in its share price of about 75 per cent from its 2020 peak.
Even so, its New York-listed shares fell 5 per cent in pre-market trading.
- Share $ Alibaba profits fall as it spends heavily to claw back market share on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Alibaba profits fall as it spends heavily to claw back market share on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Alibaba profits fall as it spends heavily to claw back market share on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
John Paul Rathbone in London
China an ‘increasing’ cyber risk to UK, says GCHQ chief
China poses a “genuine and increasing cyber risk to the UK”, the head of British spy agency GCHQ said on Tuesday, adding that while Russia and Iran were also an “immediate threat . . . China is the ‘epoch-defining’ challenge”.
Anne Keast-Butler’s remarks come amid a slew of alleged China-related espionage activity in the UK — including a suspected cyber attack that was reported last week and which targeted the records of thousands of British military personnel.
Keast-Butler said the cyber threat from Russia was “acute and globally pervasive” and that Iran was also “aggressive” in cyber space. But the head of the UK’s intelligence communications agency stressed that China was GCHQ’s top priority.
- Share $ China an ‘increasing’ cyber risk to UK, says GCHQ chief on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ China an ‘increasing’ cyber risk to UK, says GCHQ chief on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ China an ‘increasing’ cyber risk to UK, says GCHQ chief on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Alexandra White in New York and George Steer in London
GameStop surges 90% in pre-market trading
GameStop shares showed signs of repeating Monday’s gains, surging 90 per cent in pre-market trading, extending Monday’s 74 per cent rise after investors cheered the apparent return of the day trader who was at the centre of the “meme stock” craze in 2021.
The social media account of Keith Gill, known under the alias “Roaring Kitty”, appeared to come back to life on Sunday evening after he posted a meme of a man leaning forward in his chair.
Trading volume on Monday was almost 15 times the 20-day average, according to Bloomberg data. GameStop now trades at more than 3,000 times its estimated earnings per share for the coming year.
Shares in AMC Entertainment and BlackBerry also surged 85.93 per cent and 28.06 per cent, respectively, in pre-market trading.
- Share $ GameStop surges 90% in pre-market trading on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ GameStop surges 90% in pre-market trading on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ GameStop surges 90% in pre-market trading on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Lukanyo Mnyanda in London
South African minister backs Anglo American break-up plan
South Africa’s mining minister has backed Anglo American’s break-up plan over the £34bn takeover offer from rival BHP.
Speaking to the Financial Times, Gwede Mantashe said: “I am happy with the rejection of the BHP deal and I hope it will continue, then Anglo can restructure itself to optimise value for shareholders.”
- Share $ South African minister backs Anglo American break-up plan on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ South African minister backs Anglo American break-up plan on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ South African minister backs Anglo American break-up plan on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
What to watch in North America today
Home Depot: Investors will be keen to learn how demand for home improvement products held up in the first three months of the year amid persistent inflation and high mortgage rates. Earlier this year, the do-it-yourself retailer struck an $18bn deal to acquire speciality building products supplier SRS Distribution as part of a renewed push into the professional contractor market. Home Depot is forecast to report earnings declined 6 per cent to $3.59 a share year on year on revenues that dipped 1.6 per cent to $36.6bn, according to analysts polled by LSEG.
Wholesale inflation: The US producer price index, which tracks prices businesses receive for their goods, is forecast to have edged higher in April — increasing 2.2 per cent from a year ago, up from 2.1 per cent in March. The core reading, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, is forecast to remain flat at 2.4 per cent.
Fedspeak: Fed chair Jay Powell will participate in a moderated discussion in Amsterdam with Klaas Knot, president of the Netherlands’ central bank. Fed governor Lisa Cook will speak on growth and change at community development institutions at an event hosted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
- Share $ What to watch in North America today on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in North America today on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in North America today on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Arjun Neil Alim in London
Leapmotor to sell EVs beyond China in Stellantis tie-up
Stellantis will distribute and manufacture electric vehicles made by Chinese automaker Leapmotor outside China, starting in Europe later this year, in the latest sign of how legacy carmakers are adapting to the new generation of Chinese competitors.
The European carmaker, which manufactures Jeeps in the US and Fiat cars in Europe, invested €1.5bn in Leapmotor for about 20 per cent equity last year. On Tuesday the two companies announced a joint venture, Leapmotor International, through which Leapmotor models will be sold outside China.
“We have a cost competitiveness in China that we will leverage in the European market,” said Stellantis chief executive Carlos Tavares. “With Leapmotor we will bring more affordable EVs to market . . . speed is of the essence.”
- Share $ Leapmotor to sell EVs beyond China in Stellantis tie-up on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Leapmotor to sell EVs beyond China in Stellantis tie-up on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Leapmotor to sell EVs beyond China in Stellantis tie-up on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Ellie Olcott in Hong Kong
Tencent profits surge on ad revenues as gaming sales struggle
Profits at China’s most valuable listed company surged by almost two-thirds in the first quarter, as it ramped up monetisation in its advertising and wealth management businesses.
Tencent said net income rose 62 per cent to Rmb42bn ($5.8bn) in the three months to the end of March, even as revenues grew just 6 per cent from a year earlier, the slowest pace since 2022, to Rmb159.5bn, in line with estimates.
The country’s largest gaming developer has struggled to find new blockbuster titles to replace ageing games.
Tencent’s share price is up more than 30 per cent this year, as investors show signs of selectively returning to Chinese tech stocks after years of battered valuations.
- Share $ Tencent profits surge on ad revenues as gaming sales struggle on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Tencent profits surge on ad revenues as gaming sales struggle on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Tencent profits surge on ad revenues as gaming sales struggle on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Maxine Kelly in London
Risers and fallers in Europe
Big share price moves in Europe today include German food delivery platform Delivery Hero, German chemicals company Brenntag and Dublin-based gambling group Flutter:
Delivery Hero: Shares in the German food delivery business soared 20 per cent on Tuesday after it announced Uber would take a minority stake in the company and acquire its Taiwan-based Foodpanda business.

Brenntag: Shares in the German chemicals distribution company led losses on the region-wide Stoxx 600 index, dropping 8 per cent after it reported first-quarter earnings that came in below analysts’ expectations and lowered its full-year guidance.
Flutter: Shares in the owner of the Paddy Power and Betfair gambling brands slipped 3.3 per cent after it held its profit guidance steady despite reporting a surge in quarterly core profit of 46 per cent to $514mn. Earlier this month Flutter’s shareholders voted to move its primary listing to the US.
- Share $ Risers and fallers in Europe on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Risers and fallers in Europe on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Risers and fallers in Europe on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Max Seddon in Riga
Russia arrests second defence official on bribery charges
Russia has jailed a senior military officer in a possible sign President Vladimir Putin may be clearing house after replacing longtime defence minister Sergei Shoigu.
Yuri Kuznetsov, a lieutenant general in charge of the defence ministry’s personnel department, faces up to 15 years in prison on bribery charges, Russian investigators said on Tuesday, according to Interfax. He was arrested on Monday and the court ordered that he be held in jail for two months awaiting trial.
Kuznetsov is the second senior defence official to be arrested in recent weeks. Similar charges against Timur Ivanov, a deputy minister, last month were widely interpreted as a move to weaken Shoigu.
- Share $ Russia arrests second defence official on bribery charges on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Russia arrests second defence official on bribery charges on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Russia arrests second defence official on bribery charges on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Joe Leahy and Wenjie Ding in Beijing
Vladimir Putin to visit Beijing this week

Russian President Vladimir Putin will visit Beijing on Thursday and Friday, Chinese state media reported.
The state visit will mark the 43rd time Putin will have met President Xi Jinping and comes as China is playing an increasing role in supporting Russia’s economy following its full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
- Share $ Vladimir Putin to visit Beijing this week on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Vladimir Putin to visit Beijing this week on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Vladimir Putin to visit Beijing this week on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
UK stocks tick down as traders weigh impact of wage data
UK stocks were down slightly in early trading as stronger than expected wage growth signalled that interest rates could remain higher for longer.
The FTSE 100 fell 0.1 per cent after the Office for National Statistics posted data showing that annual growth in average weekly wages remained steady at 5.7 per cent in the three months to March, slightly above expectations of 5.5 per cent.
Swap markets indicate roughly a 50 per cent probability that the Bank of England will cut rates in June.
The region-wide Stoxx Europe 600 and France’s Cac 40 were up 0.1 per cent. Germany’s Dax was flat.
- Share $ UK stocks tick down as traders weigh impact of wage data on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ UK stocks tick down as traders weigh impact of wage data on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ UK stocks tick down as traders weigh impact of wage data on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Ofgem to lift ban on cheaper energy deals to lure new customers
British household energy suppliers are set to regain the ability to offer cheaper deals to entice new customers, marking a potential return of households shopping around for the best deal.
Energy regulator Ofgem banned so-called “acquisition-only” tariffs as wholesale gas and electricity prices soared during the energy crisis of 2022 and 2023, in order to protect consumers and suppliers. It confirmed in February it would remove the ban and on Tuesday said it was “minded to” do so from October, although the timing remains under consultation. Ofgem said retaining the ban was “not compelling for either market stability or price protection measures”.
- Share $ Ofgem to lift ban on cheaper energy deals to lure new customers on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Ofgem to lift ban on cheaper energy deals to lure new customers on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Ofgem to lift ban on cheaper energy deals to lure new customers on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Eri Sugiura in London
Flutter’s US bet pays off as profits surge 46%
Paddy Power and Betfair owner Flutter’s core profit surged 46 per cent in the first quarter to $514mn, shrugging off unfavourable US sports results in late March.
The world’s largest online betting company said its US business turned a profit of $26mn from a loss of $53mn a year ago, driven by its FanDuel brand increasing its market share.
This month, Flutter shareholders voted to move the group’s primary listing from London to New York, which will take effect on May 31.
- Share $ Flutter’s US bet pays off as profits surge 46% on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Flutter’s US bet pays off as profits surge 46% on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Flutter’s US bet pays off as profits surge 46% on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Kathrin Hille in Taipei
Foxconn reports 72% jump in quarterly profits
Foxconn reported a 72 per cent jump in net profit for the first quarter of 2024 compared with the same period last year due to strong demand for servers.
The increase to NT$22bn ($678.5mn) in quarterly profits reflects the benefits of strong growth in generative AI for the entire electronics industry, but the figure still missed analysts’ expectations.
Revenues for the quarter decreased by 9 per cent to NT$1.3tn, Foxconn said. Foxconn is the world’s largest contract electronics manufacturer and assembles gadgets from smartphones to electric cars and also makes many components.
- Share $ Foxconn reports 72% jump in quarterly profits on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Foxconn reports 72% jump in quarterly profits on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Foxconn reports 72% jump in quarterly profits on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Nora Redmond in London
Demand for top end holidays boosts On The Beach
Online travel agent On The Beach said that forward bookings for this summer are running 22 per cent ahead of last year, as consumer enthusiasm for travel gathers momentum.
Chief executive Shaun Morton predicted that the company would have its “biggest summer ever”, with sales of top end holidays performing particularly strongly. A recent partnership deal with Ryanair had been “encouraging”, he added.
The company on Tuesday reported pre-tax profits of £4.3mn for the first half of its financial year, up from break even in the same period last year.
- Share $ Demand for top end holidays boosts On The Beach on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Demand for top end holidays boosts On The Beach on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Demand for top end holidays boosts On The Beach on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Yasemin Craggs Mersinoglu
Vodafone reports rise in profits as boss Della Valle pushes turnaround
Vodafone reported a rise in fourth quarter revenue as it met its 2024 guidance, as chief executive Margherita Della Valle continues her attempts to turn around the UK-based telecoms group.
The FTSE 100 company posted a 7.1 per cent rise in organic group service revenue, a key measure that includes sales from contracts, network use and roaming, in the three months to 31 March.
Since Della Valle took over, Vodafone has announced the sale of its Spanish and Italian businesses — which have been treated as discontinued operations — and a merger of its domestic operations with CK Hutchison’s Three UK.
Della Valle said: “Much more still needs to be done in the year ahead . . . to simplify our operations throughout the group.”
- Share $ Vodafone reports rise in profits as boss Della Valle pushes turnaround on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Vodafone reports rise in profits as boss Della Valle pushes turnaround on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Vodafone reports rise in profits as boss Della Valle pushes turnaround on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Delphine Strauss in London
Strong UK wage growth puts pressure on BoE
UK wage growth remained persistently strong in the three months to March despite a slowing jobs market, giving hawks on the Bank of England’s monetary policy committee fresh grounds to wait for firmer signs of inflationary pressures easing before cutting interest rates.
The Office for National Statistics said annual growth in average weekly wages, including bonuses, remained steady at 5.7 per cent in the three months to March, compared with analysts’ expectation of a slowdown to 5.5 per cent.
Strength in earnings came against a backdrop of a softening jobs market in which vacancies continued a long-running decline, payrolled employment was virtually flat and the number of people claiming jobless benefits edged up.
- Share $ Strong UK wage growth puts pressure on BoE on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Strong UK wage growth puts pressure on BoE on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Strong UK wage growth puts pressure on BoE on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
William Sandlund in Hong Kong
Markets update: Chinese tech companies lead gains in Asia
Chinese tech companies with stock listings in Hong Kong outperformed the broader Asian region on Tuesday as investors awaited earnings announcements from Alibaba and Tencent.
Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Tech index, which includes many large-cap mainland Chinese tech companies, rose 1.1 per cent — well ahead of the city’s benchmark Hang Seng index, which shed 0.1 per cent.
Equity markets in the broader Asia region were muted. Traders are likely waiting for remarks from Federal Reserve chair Jay Powell on Tuesday, along with the release of inflation data, for clues as to when the US central bank will begin lowering interest rates.
- Share $ Markets update: Chinese tech companies lead gains in Asia on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Markets update: Chinese tech companies lead gains in Asia on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Markets update: Chinese tech companies lead gains in Asia on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Yasemin Craggs Mersinoglu in London
Uber takes stake in Delivery Hero and buys Foodpanda in Taiwan
Delivery Hero has announced Uber is taking a minority stake in the online food delivery group and is to acquire its Foodpanda business in Taiwan.
The Berlin-based company on Tuesday said the share purchase agreement for the sale of Foodpanda in Taiwan amounted to $950mn on a cash and debt free basis, subject to certain adjustments.
Delivery Hero added its management board resolved on a $300mn capital increase against cash contributions by issuing new shares. A wholly owned subsidiary of Uber had agreed to subscribe for them, representing about 2.98 per cent of the company’s share capital.
- Share $ Uber takes stake in Delivery Hero and buys Foodpanda in Taiwan on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Uber takes stake in Delivery Hero and buys Foodpanda in Taiwan on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Uber takes stake in Delivery Hero and buys Foodpanda in Taiwan on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Blinken arrives in Ukraine amid Russian offensive
US secretary of state Antony Blinken has arrived in Kyiv amid a Russian offensive in Ukraine’s north-eastern Kharkiv region.
Blinken’s visit is the first by a senior US official to Ukraine since Congress approved military aid to the country following a protracted delay. He will meet President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and other senior leaders to discuss the war, US aid and Ukraine’s economy.
Blinken will emphasise Washington’s “commitment to Ukraine’s sovereignty, territorial integrity, and democracy in the face of Russia’s ongoing aggression”, the state department said.
- Share $ Blinken arrives in Ukraine amid Russian offensive on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Blinken arrives in Ukraine amid Russian offensive on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Blinken arrives in Ukraine amid Russian offensive on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Jonathan Wheatley in London
What to watch in Europe today
Events: US secretary of state Antony Blinken is due to arrive in Ukraine to meet senior officials. EU finance ministers will gather in Brussels. The 77th Cannes Film Festival begins.
Economic indicators: Germany releases consumer price inflation data for April and the ZEW economic sentiment survey for May. The UK releases labour market data for March.
Central bankers: Federal Reserve chair Jay Powell is in Amsterdam to join Klaas Knot, president of the Dutch central bank, at the Foreign Bankers’ Association. Bank of England chief economist Huw Pill answers online questions for accounting body ICAEW.
Corporate updates: One day after rejecting an improved offer from rival miner BHP, Anglo American is due to present a detailed update for investors on the accelerated delivery of its standalone strategy. Results are due from UK household electrical goods retailer Currys, Greggs, the flourishing seller of sausage rolls and other baked goods, Bayer, Virgin Money and Vodafone.
- Share $ What to watch in Europe today on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in Europe today on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in Europe today on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Markets update: Hong Kong stocks rise as Japanese bonds sell off
Hong Kong equities rose on Tuesday morning, with Chinese property developers and tech companies leading gains.
The city’s benchmark Hang Seng index rose 0.9 per cent while the Hang Seng mainland China properties index added 2.2 per cent and the Hang Seng tech index jumped 2.1 per cent.
Asian currencies weakened against the dollar, with South Korea’s leading losses as it slid 0.3 per cent to Won1,370.11.
Yields on Japanese government bonds rose as traders priced in sooner than expected rate increases from the Bank of Japan and a slowdown in the central bank’s bond buying programme.
- Share $ Markets update: Hong Kong stocks rise as Japanese bonds sell off on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Markets update: Hong Kong stocks rise as Japanese bonds sell off on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Markets update: Hong Kong stocks rise as Japanese bonds sell off on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
What to watch in Asia today
Events: The Australian government announces its budget for 2024-25. Pakistan Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif starts an official visit to China.
Economic indicators: Japan publishes its producer price index and machine tool order figures for April. India announces wholesale prices for the same month.
Corporate updates: Tencent, Sony, Alibaba and Foxconn report earnings.
- Share $ What to watch in Asia today on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in Asia today on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ What to watch in Asia today on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Amanda Chu in New York
US adopts new rules on power line rollout as electricity demand rises
The top US energy regulator adopted sweeping new rules to reform the country’s buildout of long-distance power lines as rising electricity demand, including from artificial intelligence, poses a threat to domestic grid reliability.
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission on Monday voted 2-1 in a partisan split to require operators to craft plans for long-term transmission construction and cost allocation, representing the largest overhaul of transmission rules since 2011.
US transmission buildout trickled to a record low last year, just as the country faces growing power demand for the first time in two decades and the increasing need to transmit clean energy from remote areas of generation to consumers.
- Share $ US adopts new rules on power line rollout as electricity demand rises on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US adopts new rules on power line rollout as electricity demand rises on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ US adopts new rules on power line rollout as electricity demand rises on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
S&P 500 retreats from 6-week high as inflation data looms
The S&P 500 retreated from a six-week high, starting on the back foot a week in which investors will receive the latest readings on the state of the US consumer via inflation data and results from major retailers.
Wall Street’s benchmark index ended Monday fractionally lower, with financial stocks the worst-performing sector on the day. The tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite added 0.3 per cent, with four of the Magnificent Seven stocks rising. The small-cap focused Russell 2000 rose 0.1 per cent.
Treasury prices rose, pushing the yield on the two-year note slightly lower to 4.87 per cent, and the yield on the 10-year note down 0.02 percentage points at 4.49 per cent.
- Share $ S&P 500 retreats from 6-week high as inflation data looms on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ S&P 500 retreats from 6-week high as inflation data looms on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ S&P 500 retreats from 6-week high as inflation data looms on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
Demetri Sevastopulo in Washington
Biden orders Chinese crypto-miner to sell land near US military base

The White House has ordered a Chinese group that runs a crypto-mining operation in Wyoming to sell the land where it keeps its servers because the facility is next to a base that houses US nuclear ballistic missiles.
President Joe Biden ordered MineOne Partners and its partners to sell the land next to Warren Air Force Base in Wyoming within 120 days.
The White House said the company, a British Virgin Islands group majority owned by Chinese nationals , had not informed the US government about the sensitive transaction.
Biden said MineOne’s equipment included foreign-sourced technology that posed a national security risk to the US.
- Share $ Biden orders Chinese crypto-miner to sell land near US military base on X (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Biden orders Chinese crypto-miner to sell land near US military base on Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Share $ Biden orders Chinese crypto-miner to sell land near US military base on LinkedIn (opens in a new window)
International Edition

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business plan demand analysis of drivers. Hopefully, in your search for survey results, you came across some information that provided insight into the "why people buy" question. In particular, we're looking for drivers of sales here. Specifically, what circumstances compel a customer to buy your product/service (or a substitute)?
In an ever-evolving business landscape, demand analysis provides the base for strategic planning, helping businesses flourish and stay ahead of their rivals. ... By analyzing seasonal demand, businesses can generalize and plan for fluctuations, adjust production and inventory levels, and produce targeted marketing campaigns during peak seasons.
Demand analysis is a research done to estimate or find out the customer demand for a product or service in a particular market. Demand analysis is one of the important consideration for a variety of business decisions like determining sales forecasting, pricing products/services, marketing and advertisement spending, manufacturing decisions, expansion planning etc. Demand analysis covers both ...
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
Demand management aligns what a business needs with what it can supply, thinking about both present and future needs to stay sustainable. Meanwhile, demand planning is more about predicting and meeting customer demand using past data and market analysis. Demand Management vs. Capacity Planning
2. The product that consumers want isn't available. 3. The consumer doesn't know the product exists or doesn't know a certain product fulfils their needs. When conducting your product demand analysis, it's important to distinguish between these types of demand, but also to see the connections where possible.
Demand Analysis Meaning. Businesses that enter new markets have to evaluate customer needs, market sentiments, competitors, and target markets for making several decisions. It is known as demand analysis. It is a crucial and calibrated step to assess target markets and how they can gain maximum profitability.
3.1 Step 1: Define the subject of the investigation. 3.2 Step 2: Collect market data. 3.3 Step 3: Identify the influencing factors. 3.4 Step 4: Determine the elasticity of demand. 3.5 Step 5: Demand Curve Analysis. 3.6 Step 6: Assess the competition. 3.7 Step 7: Examine past demand. 3.8 Step 8: Using Predictive Models.
Demand planning is a type of financial forecasting that businesses can use to predict the future demand for the products and services they sell. It's a way of looking ahead and figuring out how much your customers and future may order from your company in the weeks, months, and years to come. Everyone has seen the results of demand planning ...
Demand planning is the supply chain management process of forecasting demand so products can be reliably delivered and customers remain satisfied. Effective demand planning can improve the accuracy of revenue forecasts, align inventory levels with peaks and troughs in demand, and enhance profitability for a particular channel or product.
LONDON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--A well-known market intelligence company, Infiniti Research, has announced the completion of their recent article on evaluating the importance of demand analysis for your ...
Including a demand and supply analysis in a business plan is one of the best tools business owners can use to predict their next moves. By analyzing various factors that affect supply and demand ...
What is it? This tool will provide you with a solid basis for analyzing supply and demand as part of strategic planning. It will help you confirm whether your business still meets the needs of your target clients in the best way possible.
Hold a demand review meeting. The final step in demand planning implementation should be a demand review meeting, led by the demand manager or the S&OP manager. Supply Chain is the only department that can be regarded as being 'neutral' with regards to Sales, Operations, and Finance and hence is in the best position to chair demand review ...
Demand analysis . For a new business, the analysis can determine whether there is a significant demand for the product/service, as well as other information such as the number of competitors, size of competitors, industry growth, and so on. It aids in determining whether a company can enter a market and generate sufficient returns to sustain ...
Demand Analysis. Definition: The Demand Analysis is a process whereby the management makes decisions with respect to the production, cost allocation, advertising, inventory holding, pricing, etc. Although, how much a firm produces depends on its production capacity but how much it must endeavor to produce depends on the potential demand for its ...
A demand plan can be simply defined as an action plan that coordinates the efforts of multiple departments in an organization so that ... Demand forecasting is the first step of the demand planning process. It consists of the analysis of business data to estimate customer demand and create a demand forecast. To create an effective ...
The demand and supply analysis focuses on the demand for a product or service and maximum production-distribution capabilities. It highlights the gap between the market's requirements and the fulfillment of goods and services. This analysis is based on the law of demand and the law of supply. The law of demand explains that the demand for ...
Demand planning is a cross-functional process that helps businesses meet customer demand for products while minimizing excess inventory and avoiding supply chain disruptions. It can increase profitability and customer satisfaction and lead to efficiency gains. Demand planning should be a continuous process that's ingrained in your business.
Use competitive analysis to find a market advantage. Competitive analysis helps you learn from businesses competing for your potential customers. This is key to defining a competitive edge that creates sustainable revenue. Your competitive analysis should identify your competition by product line or service and market segment.
Demand planning is part of the demand management process that enables a business to plan to meet the demand forecast through the production of its products. This is also part of the larger supply chain process and requires an understanding of horizon (timeline for the demand plan), frequency (how often the plan is updated) and granularity ...
Demand analysis involves understanding the customer demand for a product or service in a particular market. Companies use demand analysis techniques to determine if they can successfully enter a market and generate expected profits to advance their business operations. It also gives a better understanding of the high-demand markets for the ...
Predict outcomes with flexible AI-infused forecasting and analyze what-if scenarios in real-time. IBM Planning Analytics is an integrated business planning solution that turns raw data into actionable insights. Deploy as you need, on-premises or on cloud. Demand planning is the process of aligning product availability with anticipated demand.
In Part 3 of our 8-Part Guide to Writing a Business Plan we look at Market Analysis and Demand Analysis.. 3. Market Analysis. In this chapter you will define: The market; Geographical area; Consumer behaviour; Market segmentation; 3.1 The market is the people or organisations that will participate in the buying and selling processes of the products or services or use these products or services.
Here's how to answer these questions. 1) Define your target audience. There is no single way to do a demand analysis. The demand analysis you carry out will depend on the kind of market, the size, and the target or target audience. For this, it can be beneficial to carry out surveys and interviews that help you know your current clients ...
IMARC Group's report titled "Octene Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue" provides a comprehensive guide for establishing an octene manufacturing plant. The report covers various aspects, ranging from a broad market overview to intricate details like unit operations, raw material and ...
Macy's expects fiscal 2024 net sales of between $22.3 billion and $22.9 billion, compared to its prior forecast of $22.2 billion to $22.9 billion. The company posted first-quarter adjusted profit ...
The Nigeria Labour Congress (NLC) and Trade Union Congress (TUC) are demanding that the country's minimum wage be increased by 1,950 percent from N30,000 to N615,000. The Union says it arrived at the minimum wage recommendation after painstakingly computing the monthly cost of living of Nigerian workers, with food, transportation taking a ...
UPVC Windows Manufacturing Plant Setup Report 2024: Business Plan, Market Demand Analysis, Cost and Economics. 05-21-2024 12:57 PM CET | Business, Economy, Finances, Banking & Insurance. Press ...
Flutter: Shares in the owner of the Paddy Power and Betfair gambling brands slipped 3.3 per cent after it held its profit guidance steady despite reporting a surge in quarterly core profit of 46 ...