Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., 8 easy ways to finish your homework faster.

How many times have you found yourself still staring at your textbook around midnight (or later!) even when you started your homework hours earlier? Those lost hours could be explained by Parkinson’s Law, which states, “Work expands to fill the time available for its completion.” In other words, if you give yourself all night to memorize those geometry formulas for your quiz tomorrow, you’ll inevitably find that a 30 minute task has somehow filled your entire evening.
We know that you have more homework than ever. But even with lots and lots to do, a few tweaks to your study routine could help you spend less time getting more accomplished. Here are 8 steps to make Parkinson’s Law work to your advantage:
1. Make a list
This should be a list of everything that has to be done that evening. And we mean, everything—from re-reading notes from this morning’s history class to quizzing yourself on Spanish vocabulary.
2. Estimate the time needed for each item on your list
You can be a little ruthless here. However long you think a task will take, try shaving off 5 or 10 minutes. But, be realistic. You won’t magically become a speed reader.
Free SAT Practice Tests & Events
Evaluate and improve your SAT score.
3. Gather all your gear
Collect EVERYTHING you will need for the homework you are working on (like your laptop for writing assignments and pencils for problem sets). Getting up for supplies takes you off course and makes it that much harder to get back to your homework.
The constant blings and beeps from your devices can make it impossible to focus on what you are working on. Switch off or silence your phones and tablets, or leave them in another room until it’s time to take a tech break.
Read More: How to Calculate Your GPA
5. Time yourself
Noting how much time something actually takes will help you estimate better and plan your next study session.
6. Stay on task
If you’re fact checking online, it can be so easy to surf on over to a completely unrelated site. A better strategy is to note what information you need to find online, and do it all at once at the end of the study session.
7. Take plenty of breaks
Most of us need a break between subjects or to break up long stretches of studying. Active breaks are a great way to keep your energy up. Tech breaks can be an awesome way to combat the fear of missing out that might strike while you are buried in your work, but they also tend to stretch much longer than originally intended. Stick to a break schedule of 10 minutes or so.
8. Reward yourself!
Finish early? If you had allocated 30 minutes for reading a biology chapter and it only took 20, you can apply those extra 10 minutes to a short break—or just move on to your next task. If you stay on track, you might breeze through your work quickly enough to catch up on some Netflix.
Our best piece of advice? Keep at it. The more you use this system, the easier it will become. You’ll be surprised by how much time you can shave off homework just by focusing and committing to a distraction-free study plan.
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
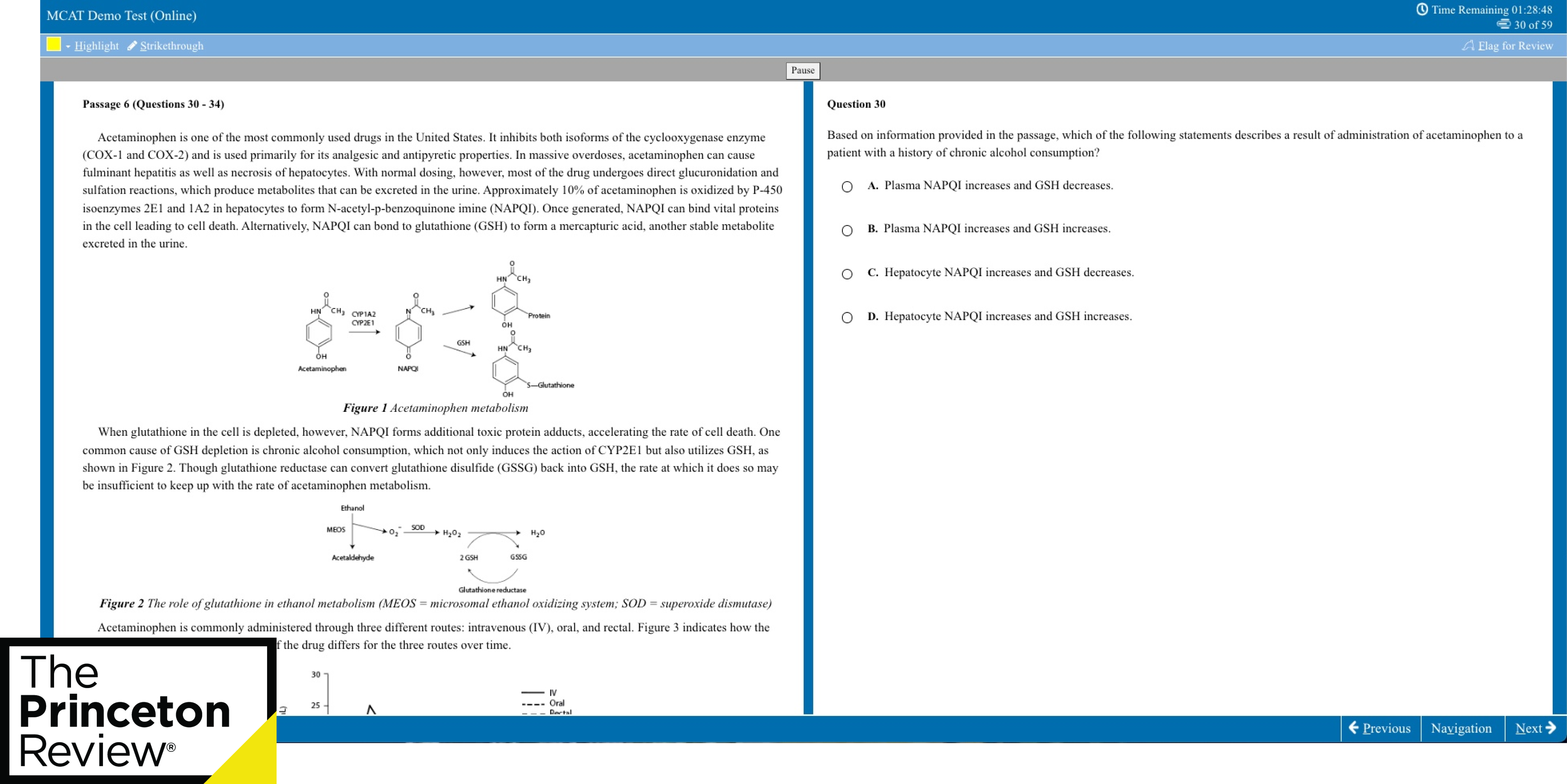
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Adolescence
How to Help a Teen Out of a Homework Hole
The more students fall behind in the pandemic, the less likely they are to feel that they can catch up.

By Lisa Damour
Pandemic school is taking its toll on students, especially teens. A recent study , conducted by NBC News and Challenge Success, a nonprofit affiliated with the Stanford Graduate School of Education, found that 50 percent more kids in high school report feeling disengaged from school this year than last. In December, Education Week reported that schools were seeing “ dramatic increases in the number of failing or near-failing grades ” on report cards.
A major symptom of school disengagement is not turning in homework, a problem that can easily snowball. The further students fall behind, the more overwhelmed they often become and the less likely they are to feel that they can catch up .
The good news is that finding out about missing homework is a first step to helping kids get back on track. You just need to keep a few considerations in mind.
Empathy will get you further than anger
At this point in the pandemic, finding out that your child has let schoolwork slide may trigger an angry response. Everyone is worn down by the demands of pandemic life and many parents are already operating on their last nerve . Getting mad, however, is likely to cause kids to adopt a defensive or minimizing stance. Instead, try to be compassionate. What students who have fallen behind need most are problem-solving partners who want to understand what they are going through.
If you’re having trouble summoning your empathy, bear in mind that there are many good reasons a student could fall off pace this year. For instance, Ned Johnson, a professional tutor and co-author of the book “The Self-Driven Child,” noted that most teens have very little experience managing email, which is now a main source of information for those in remote or hybrid arrangements. “We know how overwhelmed we as adults are by email. Imagine not being comfortable with it, and then suddenly getting everything — from Zoom links to assignments — that way.”
Some students learning remotely may also have unreliable broadband service; others may miss key information because their attention is split between the teacher on the screen and distractions at home.
“Many adults are having the exact same issues,” said Ellen Braaten, a psychologist and the executive director of the Learning and Emotional Assessment Program at Massachusetts General Hospital. “They are really productive when they can physically be at work, but may find themselves less attentive in the unstructured environment of working from home.”
Even teens who are attending school in person and using familiar systems for tracking assignments may be having a hard time managing their work now. The mental skills that help us stay organized — commonly called executive functioning — are being undermined by psychological stress, which is unusually high among today’s teens.
Work together to diagnose the problem
Finding out that your child is in academic trouble can tempt you to jump to solutions. It’s best, however, to properly diagnose the problem before trying to address it. Liz Katz, assistant head for school partnership at One Schoolhouse, an online supplemental school, suggested looking into the reasons students fall behind at school. Some don’t know what they’re supposed to be doing, others know and aren’t doing it, and still others “are doing their best and just can’t meet expectations.”
As you talk with a teenager about where things have gone off the rails, be kind, curious and collaborative. “This isn’t about you being in trouble or getting off the hook,” you might say. “It’s simply about figuring out what’s going wrong so we can solve the right problem.”
Students who are struggling to keep track of what’s expected of them may need to reach out to their teachers, either for clarification about specific assignments or for general guidance on where and when they should be looking for information about homework. As a parent or caregiver, you can coach them on how to approach their instructors. Start by pointing out that teachers are almost always eager to lend support to students who seek it. You can also offer to give feedback on a draft email to an instructor explaining where the student got lost and what they have already tried.
“For many students, the ability to ask for help is not fully formed,” said Ms. Katz, “or it can feel like an admission that they’ve done something wrong. Normalizing and praising self-advocacy is so important.”
For students who know what they’re supposed to do but aren’t doing it, other approaches make sense. They may be having a hard time sustaining motivation and need support on that front , or they may be swamped with commitments, such as caring for younger siblings, that make it impossible to complete their schoolwork. Here, parents and students will want to work together to make a realistic plan for addressing the biggest priorities in light of these circumstances. This might mean coming to an agreement about where the teen’s energies should be directed or exploring what additional support might be put in place.
In some cases, academic problems may be linked to issues with mental health. If there’s a question of whether a student is suffering from depression or anxiety; using drugs; or exhibiting any other significant emotional or behavioral concern, check in with the school counselor or family doctor for a proper assessment. Treatment should always take precedence over schoolwork. “If you’re depressed,” Dr. Braaten said, “no amount of executive function coaching is going to help, because that’s not the issue.”
Some students have subtle learning or attention disorders that became an issue only when school went online. Under regular conditions, said Mr. Johnson, instructors can notice when a student is tuning out and bring back his or her attention in a gentle way. Unfortunately, “Teachers really can’t do that effectively on Zoom.” If this is a concern, parents should consider checking in with teachers or their school’s learning support staff to get their read on the problem and advice for how to move forward.
Step back to see the big picture
“We all need to be easier on ourselves,” Dr. Braaten said, “and to sort through what students really need to do and what they don’t.” Well-meaning parents might hope to motivate students by emphasizing the importance of high grades, but that can make it harder for kids to recover from a substantial setback.
As students start to work their way back, give some thought to how comprehensive their turnaround needs to be. Do they really need to get equally high grades in every class? Could they instead direct their energy toward getting square with the courses they care about most? Could they work with their teachers to agree upon trimmed-down assignments for partial credit? According to Mr. Johnson, “Lowering expectations, for now , can actually help kids to get back on track.”
Dr. Braaten also noted that much of what students gain from school is not about content, but about learning how to solve problems. Engaging teens in constructive conversations to figure out how they fell behind can be an important lesson unto itself. “Having a 16-year-old who understands, ‘When I’m stressed, this is how I react,’” says Dr. Braaten, “may put us further ahead in the long run.”
In any school year, students learn a great deal beyond academic content. This year, more than most, might be one where students gain a deep understanding of how they respond when feeling overwhelmed and how to ask for help or rebound from setbacks — lessons that they will draw on long after the pandemic is gone.
Lisa Damour is a psychologist and the author of the New York Times best sellers “Untangled” and “Under Pressure.” Dr. Damour also co-hosts the podcast “Ask Lisa: The Psychology of Parenting.” More about Lisa Damour
Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
American academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league.
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.
Daniel Wong
11 Excuses for Not Doing Homework (And How to Stop Making Them)
July 5, 2022 By Daniel Wong 6 Comments

If you’re like many students, you’d rather take a nap, talk to your friends online, or play video games.
As you already know, finding reasons not to do your homework will prevent you from succeeding in school .
I’m sure you want to do well in school, and homework is definitely a part of that process.
In this article, I’ll go over 11 of the most common excuses for not doing homework and offer solutions to ensure that you stay engaged in school.
But first, make sure to download your free quick action guide…
FREE QUICK ACTION GUIDE:

Get your FREE copy of
12 Guaranteed Ways for Students to Improve Focus and Reduce Procrastination .
The guide has already been downloaded thousands of times, so don't miss out!
Excuse #1: You lack the required knowledge
Let your parents and teacher know if you’re taking a class and feel as if you lack the necessary skills or knowledge to complete the homework.
Ask your teacher for extra guidance so you don’t fall too far behind. See if your parents can find the time to help you, or you can look for a tutor.
Your teachers are there to help you develop the skills you need to do well in their classes.
You’re not alone in feeling that you lack the necessary skills, so don’t be too embarrassed to ask for assistance. You might even find some great study buddies who feel the same way.
Excuse #2: You lack confidence
Many students compare themselves to their peers, which can lead to a lack of confidence. When that happens, it’s easy to make excuses for not doing the homework.
But here’s what you need to know…
Everyone lacks confidence about something.
You might be good at math but need extra help with English. Perhaps you excel at geography but find biology confusing.
Give yourself a break.
If you lack confidence in your ability to learn a particular subject, get the support you need. Your teachers, parents, and even friends will help you out and give you a needed morale boost.
Excuse #3: Your home life is too hectic
The excuses for submitting assignments late are numerous, but one that I hear often is that it’s too busy or noisy at home to focus.
Finding a quiet space and using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones can help reduce distractions. This will make it easier for you to finish your homework.
If that doesn’t work, try finding an alternative location to do your work, like the library or a friend’s house.
You can also talk to your parents about it. They might not even be aware of all the interruptions that are preventing you from completing your schoolwork.
Excuse #4: You don’t know where to start
Feeling anxious and overwhelmed are often the main reasons that cause students to not know where to start on their homework.
If you ever feel this way, here’s what I suggest you do:
- Take a deep breath.
- Create a space where you can get organised.
- Make a list of all your assignments and deadlines.
- Work on one assignment at a time.
- Start with an easy assignment to get a quick win, or tackle the most challenging assignment to get it out of the way.
Excuse #5: You have poor study habits
Many students develop bad study habits over their years in school.
Not everyone learns the same way or at the same pace. As such, every student will have different study habits. If what you’re doing isn’t working, try a different approach.
If you’re trying to do your homework as soon as you get home from school but can’t focus, try having a snack and taking a power nap before getting to work instead.
If you’re staying up too late studying, set a rule for yourself that you’ll start doing your homework within one hour of getting home.
Establish a routine where you do your work at roughly the same time each day. Developing routines like this will improve your study habits , which will make you a more effective student.
Excuse #6: School isn’t important to you
A common misconception is that school isn’t important, that what you learn won’t be relevant once you leave school.
This isn’t completely true.
Of course, the education system can be improved. But the knowledge you acquire in school will help you to understand and appreciate the world better.
And the process of becoming a more effective student will lead you to develop traits like self-discipline and responsibility. These are the types of traits you’ll need in order to find success at any stage of life!
Excuse #7: You’re overloaded with after-school activities
I know it can be tough to balance schoolwork and extracurricular activities.
Maybe you’re on a sports team or you spend several hours each week volunteering.
Finding the right balance to ensure you have enough time for homework can be challenging.
When too many afterschool activities get in the way of completing your assignments on time, it’s time to review your schedule. Decide how you can prioritise the activities that are the most important.
You may need to put some activities on hold until you’re consistently staying on top of your schoolwork.
Speak with your coach, teachers, or parents about the ideas they have to help you manage your schedule more effectively.
Excuse #8: Studying is boring for you
If you find that doing your homework is uninteresting, it may be time for you to change your point of view.
I always encourage students to cultivate a growth mindset . This is a mindset where you focus more on the learning process instead of on getting good grades.
Rather than seeing a particular subject as boring, develop a sense of wonder. Decide that you’re going to be intellectually curious, and you’ll discover that we live in a fascinating world.
And while you’re on that journey, remember that the students who succeed in school find ways to get the work done even when they find the subject boring.
For example, if you don’t like math, consider that it isn’t just about numbers – it’s a way of thinking.
Reframing how you think about a subject will enable you to see it as more interesting. In turn, you’ll become a better student over time.
Excuse #9: Your teachers assign too much homework
Sometimes, it may seem like your teachers assign more homework than you can keep up with. You might even believe that what you’re required to do is unreasonable.
If you find yourself in this situation, take a moment to think about everything else you’re doing.
Are you managing your time well?
Are you struggling with a particular class?
Do you use memory techniques to enable you to learn faster ?
Instead of allowing homework to overwhelm you, try talking to your teacher, tutor, or parents to figure out the best way forward for you.
Excuse #10: You already have so much overdue homework
Procrastinating on your homework can lead to a significant pile-up of assignments. This will affect your confidence in being able to complete them.
What’s more, once you get a set of new assignments, you probably won’t know how to do them because you didn’t do the previous assignments.
This creates a vicious cycle where you tell yourself that there’s no point in completing your newly assigned homework because you still have the old ones to do.
When this happens, the likelihood of completing any of the work decreases.
If you’re in this situation, set a reasonable goal of keeping up with all the newly assigned homework while completing, say, one overdue assignment a day, or one overdue assignment every two days.
Excuse #11: You don’t believe you can get good grades
If you hate school, there’s a chance that it’s because you feel the pressure to be a straight-A student .
Here’s the good news: You don’t need to be perfect. After all, there’s no such thing as a perfect student.
But you do have to put in the effort and get the work done. The rest will then fall into place.
If you’re doing your best, you’re doing great! Celebrate your progress and keep moving forward.
Take it one step at a time, and don’t worry too much about what grades you’re getting at the moment.
In closing…
There are many possible reasons for you not to finish your homework.
No matter what those reasons are, it’s important to know that the people around you want to help you succeed.
From teachers to parents to coaches, you have a support network to provide solutions to almost any obstacle you face.
Identify the excuses listed in this article that are relevant to your situation, and apply the suggested solutions.
If you do that, you’ll become a better and happier student who makes far fewer excuses related to homework!
July 7, 2022 at 12:13 pm
Thank you so much for this article. These were the problems I was struggling with. Now that i know the solutions to it ,I’m sure I’ll do better than before.
July 7, 2022 at 1:05 pm
You’re very welcome.
July 7, 2022 at 6:20 pm
I pray that may Almighty God grant you long life, more knowledge, sound health, rest of mind, wealth and happiness, so that you can witness your good impact in this World 🌍. GOD has made you a useful tool for every students and parents that is actually seeking success.
July 7, 2022 at 7:42 pm
Thank you, God bless you too!
July 27, 2022 at 9:29 pm
Thank you so much for this. I have found a couple of solutions for excuses I’ve made in the past. I needed this.
July 27, 2022 at 9:42 pm
You’re welcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Mom-Tested Tips for Ending Homework Battles
Posted: August 27, 2023 | Last updated: August 27, 2023

Back-to-school season means a return to making lunches, signing field trip permission slips, planning for 127 different spirit day outfits, and having to face the prospect of taming the homework beast once again. Although some experts think homework shouldn't exist at all, the truth is that most kids will face reading logs, worksheets, and book reports at some point in the near future. For some kids (and their VERY lucky parents), getting homework done is a "no drama for their mama" situation.
For other kids, on the other hand, the struggle is all too real.
There are lots of reasons homework can become a battle, so we are super grateful for the advice of other moms who've figured out how to end those fights before they start. Read on for some genius tips, including knowing when to call it quits and when to get some help.
More from CafeMom: Utah Middle School Faces Backlash Over Forcing Kids To Eat Bugs for Assignment

Different Kids, Different Needs
"My best advice is to remember what works for one kid might not work for the other. My son has always wanted to come home and do homework right away so he can get it over with and have the rest of the day to play. I learned the hard way that it is MELTDOWN CITY if my daughter doesn’t get a snack and some play time before she has to do homework. Set them up for success by figuring out what time of the afternoon/evening is best for them." – Martha D., Iowa

"Homework was so awful with my son. Like, it was taking him almost two hours to do basically two 3rd grade workbook pages and 20 minutes of reading and I was yelling, he was crying. It felt like ‘wait, this shouldn’t be so hard’ and that was accurate.
"The homework challenge was the thing that kind of clued us in that there was something more going on. He eventually got diagnosed with a learning difference and ADHD, so I think my advice is to ask for help if the level of homework battle is just beyond normal." – Lara R., Colorado
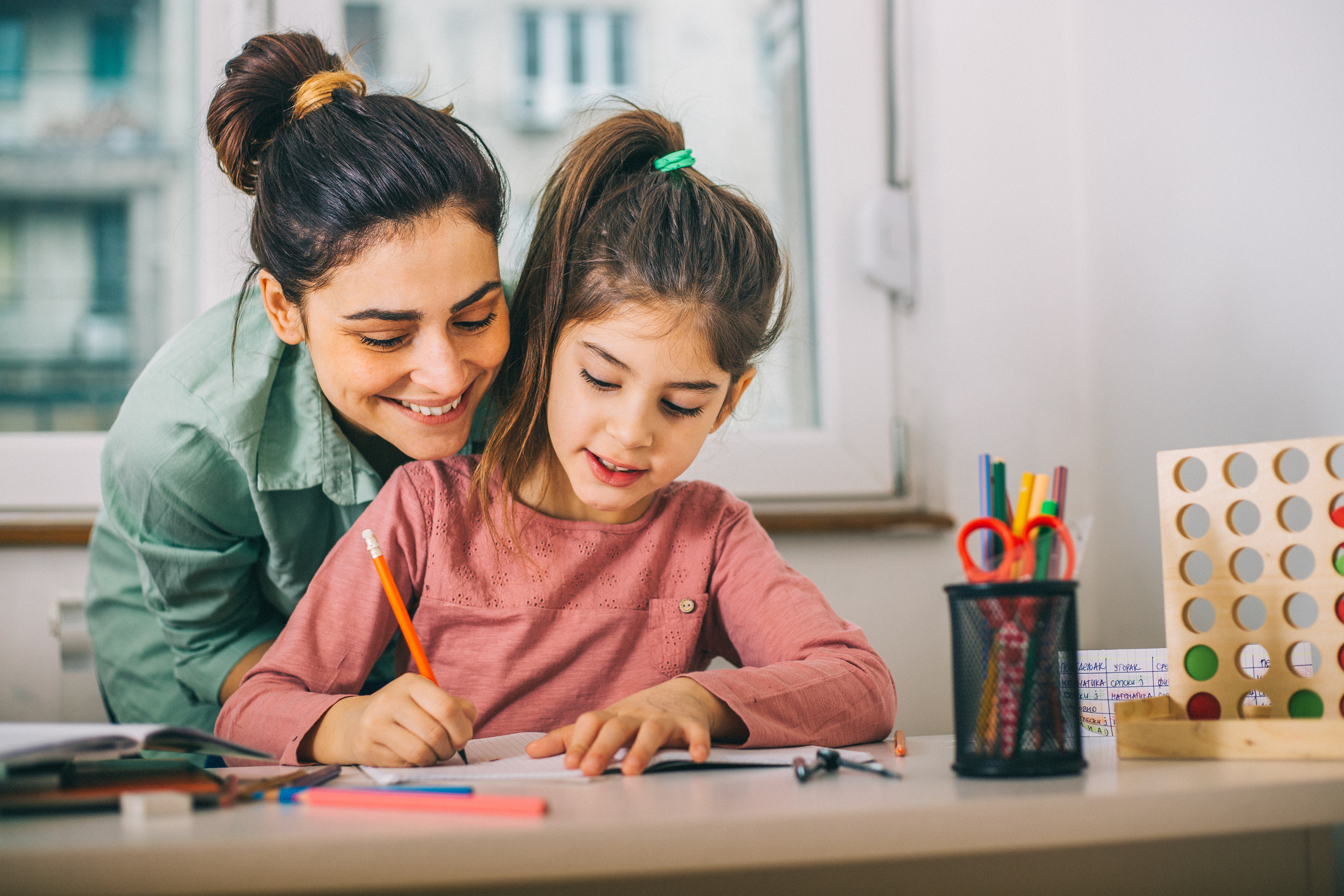

Make a Cozy Space
"I made a little homework nook in our kitchen with all the supplies they might need, comfortable chairs, and some snacks that they can help themselves to. I feel like it helps to have a welcoming space, and I usually make dinner when they are doing homework, so I can get that done but still be close by if they need help." – Jenny N., California

Watch the Screens
"Ugh. My kid’s school has them do homework on their school iPads, which I HATE. Last year it was taking my 2nd grade son forever to get his homework done and staying up too late, not getting chores done because ‘I still have homework, Mom!’.
"I eventually clued in to the fact that he was only spending like 40 minutes on homework and the rest of the time was screwing around on the iPad. Now he has to do his homework in the dining room, so I can see that he’s actually doing it. He gets done in less than an hour now." – KayCee C., Minnesota

Do the Hardest Thing First
"My suggestion is sort of basic, but it works for us: do the least fun/hardest thing first. Have a snack, do something relaxing, and then tackle the hard thing first when the brain is fresher. A lot less of battle when the worst is out of the way first." – Annie P., Arizona

Ditch the Log
"Can we just, as parents, band together and put an end to freaking reading logs? For whatever reason, all of our homework battles were around reading logs. As someone who loves reading, I hated seeing how much having to log it sucked the joy out of reading for my kids. So I just told my kids we’ll skip them.
They still read every day but not having to log it took the pressure off. It’s second grade! Who cares if they don’t turn in a reading log! Let that stuff go!" – Sasha W., Washington
More from CafeMom: Mom Puts Entire Family on 'Screen Detox' & Daughter Has Already Jumped 5 Reading Levels

"I’m strict about screen time (even for my high school kids) and our rule is simple: no screens until homework is done. We’ve done this since day one of having homework and the kids just know that we don’t budge on it. Consistency of expectations is the key!” – Laura W., Michigan

Homework Isn't Everything
"One of the things that helps our family is having a clear sense of how important homework is to us. The truth is that, with kids who are still in elementary school, it isn’t that important to us. Outside playtime, doing Legos, having fun with friends is more important to their development than homework is. So, I make it optional: they can do it when they want, if they want." – Blake E., Colorado

Always Start With a Snack
"My parenting lightbulb moment was realizing that fully 90% of my kid's post-school meltdowns (including homework ones) were because she was STARVING after school. I've started packing car snacks for her to eat on the way home and it makes everything easier once we get there." – Jamie J., Arizona

Be Realistic About Time
"Sometimes you have to give your kids permission to skip homework. Like, for us we are crazy busy on Wednesdays. We have soccer and church and there's just not time to do it. If I try to rush my 8 and 10 year olds to get homework done, everyone just gets stressed and cranky. I told their teachers that we just don't do homework on Wednesdays and they were fine with it. Saved so many tears!" - Melody D., Minnesota

Practice With a Planner
"Every Sunday, my son (he's 16) and I sit down and do his planner. He needs that extra support to help figure out how to break down doing bigger projects and how far in advance to start studying. Remember that teenage brains aren't fully developed! They don't just automatically know how to do tasks like this! Help them build the habit now so they are ready to do on their own in college." – Amy S., California
More from CafeMom: 5 Essential Conversations Moms Need To Have With Their Teens

Ask the Teacher
"When my first kid started getting homework, we were struggling. It was taking him at least two hours to get through all of it. In 1st grade! Of course there were awful meltdowns. I just assumed that was normal until I mentioned it to another mom and she was like 'uh, it should be taking like 15 minutes ..'
"I finally talked to his teacher and she confirmed that she'd never want him to be spending two hours a day on homework. We figured out some strategies around it and it got better. My advice: talk to the teacher if every home sesh is a struggle or if it is taking hours a day." – Kelly C., Indiana

"First, unless you are a single mom, don't act like a single mom! Dads need to help with the homework BS too! When we are gearing up for a homework fight, sometimes it's best if I tag out and he takes over. Some fresh parenting energy can help." – Olivia T., Rhode Island

Make Reading Fun
"For early grades, the bulk of their homework time is probably going to be reading, so finding ways to make that fun is clutch. We take reading outside or in the hammock, or even at a park just to mix it up." – Melissa H., Texas

Set a Timer
"With my ADHD kid, we do the 20-10-20 method and it helps reduce the tension a lot. He has to do 20 minutes of homework, gets a 10 minute break, and then another 20 minutes. We use a timer and he knows he can do whatever he needs to do in those 10 minutes. We say 'Anyone can do anything for 20 minutes' and I think that's true!" – Alice S., Minnesota
More for You
The most dangerous state to drive in in the US, according to data—plus, see where your state ranks
Full List Of Republicans Condemning Marjorie Taylor Greene
The 11 Rudest Things You Can Do In Someone Else’s House, According To Etiquette Experts
You could get in big trouble for throwing these items in trash
Rock Queens: Recognizing 25 Women Who Shaped the Music Industry
Should you avoid living in a 55-plus community? Here are 5 big problems with adult retirement communities in America
Map reveals best places to live in the US if nuclear war breaks out
How Much Beer You'd Have To Drink To Equal A Single Shot Of Liquor
Crimea Bridge Explosion Caused by Equivalent to 10 Tons of TNT: Russia
I’m 62 with no debt and a part-time job. My advisers say keep saving, but my kids say spend — do I go for a Roth 401(k)?
I Cut My Food Expenses In Half Using The Viral "6-To-1" Grocery Method — Here's How
I'm an interior designer. Here are 10 things in your living room you should get rid of.
New Chevrolet Corvette ZR1 Convertible Shows Its Face And Interior Early
The least expensive state to live in America. Plus, see the runners-up.
Donald Trump Lawyer May Have Committed 'Serious Ethical Violation'—Attorney
Here is the true value of having a fully paid-off home in America — especially when you're heading into retirement
14 Must-Try Experiences Every Woman Should Have
Taylor Swift Claims Record Top 14 Spots on Billboard Hot 100
Leaving These 13 Things by the Front Door Could Keep You Safe
The Mercedes E60 AMG Is Peak Benz
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Raising Kids
Yes, You Can Opt Your Kids Out of Homework—Here’s How
One mom says her kids haven't been doing homework for years. Here's how she opted them out and what experts say.
Guille Faingold / Stocksy
When Juliana Porter thinks about the feeling that homework induces, one word comes to mind: dread. With afternoon and evening time constraints, the North Carolina mom of three wants her kids to have some time to relax and unwind, so homework is often pushed until during or after dinnertime.
“The subject we’ve found to be the most challenging is math, in large part because strategies and ‘show your work’ are often required to get correct answers,” says Porter. “But as parents who are not in the class to learn new methods, we’re not able to help. Or we can help, but it’s not the correct method being taught and adds to our child’s confusion. These at-home cram sessions usually end in frustration for both child and parent.”
The Porter family’s experience isn’t unique. Research published in the Child & Youth Care Forum found more than 25% of parents and kids say homework “always or often interferes with family time and creates a power struggle,” while more than 36% of kids say homework sometimes forces them to get less sleep in grades 3 to 6. According to Stanford research , 56% of students surveyed say homework is a primary source of stress.
While many families do their best to help their children complete homework with as little frustration as possible, my family has chosen a different option: to simply skip it. And I don’t mean just skipping it on the nights it's difficult either. For four years, my family has totally opted out of homework, which I’ve learned doesn’t produce enough benefits for the stress it causes. And I want other parents to know that opting out of homework is an option for their kids, too.

Homework: How to Opt Out
If your child goes to an open admissions public school, opting out of homework can be something you consider. While it may be a particularly good choice if homework is causing major household stress, you don’t have to wait until your child is miserable to act if they (or you) would simply prefer to spend the time in other ways. There are no legal requirements that students complete work outside of school hours and, for many children, the actual determinants of homework outweigh the theoretical benefits.
To opt out, I send a note to each of my children's teachers at the beginning of the year letting them know that my child will not be completing homework, that their overall grade should not be impacted, and that they should not be penalized in any way for not turning in homework assignments.
I also let them know that we're committed to our kids' education, that we read together most evenings, and that, if my child is struggling or needs extra support in any subject, we're happy to brainstorm solutions to help them get the practice they need. Though no teachers have pushed back yet (and several have told us they wish they were not required to assign homework and that more families knew they could opt out), we have a small folder of research on the detriments of homework that we could share with an administrator if needed.
Opting out has worked well for our family but implicit bias might mean that other families don't receive the same neutral or positive reaction that our white family does.
"Many minoritized and historically marginalized families never consider opting out of homework, even when they know that it's not meaningful," says Sequoya Mungo, Ph.D. , an educational equity consultant and co-founder of BrownLight Inc. , a company helping to create positive diversity and inclusion results in educational, nonprofit, and corporate environments. "When white families make these types of educational choices, they are viewed as forward-thinking and seen as advocates for their children's education. Teachers and others often think that they're being proactive and identifying other enrichment opportunities for their kids. When non-middle class and non-white families opt out, the assumption is that parents don't value education and don't want to, or are unable to, help their kids with homework.”
According to Dr. Mungo, coming with research or policy can be helpful as even some school level administrators are unaware that opting out is within your rights as parents. “The more prepared you are, the more likely you are to not be met with pushback.”
Why Families May Want to Opt Out of Homework
Since homework is so prevalent, many assume it's vital, or at least important, to kids' academic growth. But the reality is murkier. "There's really no good evidence that homework completion positively impacts kids' academic growth or achievement," says Samantha Cleaver, Ph.D. , a reading interventionist and author of Raising an Active Reader: The Case for Reading Aloud to Engage Elementary School Youngsters .
A 2006 meta-analysis of homework and achievement found moderate correlation in middle school and little correlation in elementary school, while there was negative correlation (that is, more homework means less learning) in third grade and below.
While research shows homework can help high school kids improve grades, test results, and likelihood of going to college, the reality is academic pressures in the U.S. have increased over the last two decades, and so too has the amount of homework that kids are assigned. The National Education Association (NEA) recommends no more than 10 minutes of homework per night per grade level, but that's often not what's happening. According to a 2015 study, elementary school students are being assigned more than is recommended , sometimes almost triple the amount. And, often, even when educators are assigning homework they think falls in this window, it can take some students, particularly those who are “behind” already or who have learning disabilities, much more time to complete.
Excessive homework can negatively impact sleep, mental health, and stress levels. It’s also important to note homework is an issue of equity, since not every child has the same opportunities at home. "When kids are doing work in school, the classroom environment serves as somewhat of an equalizer,'' says Dr. Mungo. "Kids have access to the same teacher and generally the same resources within the classroom setting. At home, kids have different environments, different access to resources, and different levels of support." This means kids with less support and more challenges often end up getting lower grades or being penalized for not turning in work for reasons totally outside their control.
Making Change on Homework
Parents who don't want to be the only ones opting out can work to change the homework culture at their school. Consider reaching out to your principal about your homework concerns or connecting with other parents or the PTA to help build support for your cause.
And if you do opt out, don't be shy about letting other parents know that's what you've chosen to do. Sometimes just knowing there is an option and that others have opted out successfully can help families decide what's right for them.
What to Do With the Extra Time
When Porter thinks about what a life without homework would be like, she envisions a much more relaxed evening routine. “I imagine a scenario where my kids can do their after-school activities, read more, get outside, and generally just decompress from the daily eight-hour grind that is school with no more dread and no more crying,” she says.
If you opt out of homework and find your family with more time for other sorts of learning, leisure, or adventure, be thoughtful how you’ll structure your new routine and talk with your kids about the value of doing nothing, the importance of family time, or how to spend their time in ways that matter to them.
And if you want to be sure they're getting in some valuable post-school learning, consider repurposing your previous homework time to reading with your kids. "Reading aloud has benefits long after your kids can read on their own," says Dr. Cleaver. "Encourage them to choose books about subjects they're interested in, snuggle up together, and enjoy watching them learn through active reading."
But reading isn’t the only way to reap benefits. "There are lots of things that kids can do after school that will positively impact their growth and development that don't involve sitting down to do more of the work they've done at school,'' says Dr. Cleaver. "Time to decompress through play or relaxation isn't just fun, it actually helps kids' brains and bodies relax, making them more open to learning."
Related Articles

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 5 best homework help websites (free and paid).
Other High School , General Education

Listen: we know homework isn’t fun, but it is a good way to reinforce the ideas and concepts you’ve learned in class. But what if you’re really struggling with your homework assignments?
If you’ve looked online for a little extra help with your take-home assignments, you’ve probably stumbled across websites claiming to provide the homework help and answers students need to succeed . But can homework help sites really make a difference? And if so, which are the best homework help websites you can use?
Below, we answer these questions and more about homework help websites–free and paid. We’ll go over:
- The basics of homework help websites
- The cost of homework help websites
- The five best homework websites out there
- The pros and cons of using these websites for homework help
- The line between “learning” and “cheating” when using online homework help
- Tips for getting the most out of a homework help website
So let’s get started!

The Basics About Homework Help Websites–Free and Paid
Homework help websites are designed to help you complete your homework assignments, plain and simple.
What Makes a Homework Help Site Worth Using
Most of the best sites allow users to ask questions and then provide an answer (or multiple possible answers) and explanation in seconds. In some instances, you can even send a photo of a particular assignment or problem instead of typing the whole thing out!
Homework help sites also offer more than just help answering homework questions. Common services provided are Q&A with experts, educational videos, lectures, practice tests and quizzes, learning modules, math solving tools, and proofreading help. Homework help sites can also provide textbook solutions (i.e. answers to problems in tons of different textbooks your school might be using), one-on-one tutoring, and peer-to-peer platforms that allow you to discuss subjects you’re learning about with your fellow students.
And best of all, nearly all of them offer their services 24/7, including tutoring!
What You Should Should Look Out For
When it comes to homework help, there are lots–and we mean lots –of scam sites out there willing to prey on desperate students. Before you sign up for any service, make sure you read reviews to ensure you’re working with a legitimate company.
A word to the wise: the more a company advertises help that veers into the territory of cheating, the more likely it is to be a scam. The best homework help websites are going to help you learn the concepts you’ll need to successfully complete your homework on your own. (We’ll go over the difference between “homework help” and “cheating” a little later!)

You don't need a golden piggy bank to use homework help websites. Some provide low or no cost help for students like you!
How Expensive Are the Best Homework Help Websites?
First of all, just because a homework help site costs money doesn’t mean it’s a good service. Likewise, just because a homework help website is free doesn’t mean the help isn’t high quality. To find the best websites, you have to take a close look at the quality and types of information they provide!
When it comes to paid homework help services, the prices vary pretty widely depending on the amount of services you want to subscribe to. Subscriptions can cost anywhere from $2 to $150 dollars per month, with the most expensive services offering several hours of one-on-one tutoring with a subject expert per month.
The 5 Best Homework Help Websites
So, what is the best homework help website you can use? The answer is that it depends on what you need help with.
The best homework help websites are the ones that are reliable and help you learn the material. They don’t just provide answers to homework questions–they actually help you learn the material.
That’s why we’ve broken down our favorite websites into categories based on who they’re best for . For instance, the best website for people struggling with math might not work for someone who needs a little extra help with science, and vice versa.
Keep reading to find the best homework help website for you!
Best Free Homework Help Site: Khan Academy
- Price: Free!
- Best for: Practicing tough material
Not only is Khan Academy free, but it’s full of information and can be personalized to suit your needs. When you set up your account , you choose which courses you need to study, and Khan Academy sets up a personal dashboard of instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes –with both correct and incorrect answer explanations–so you can learn at your own pace.
As an added bonus, it covers more course topics than many other homework help sites, including several AP classes.
Runner Up: Brainly.com offers a free service that allows you to type in questions and get answers and explanations from experts. The downside is that you’re limited to two answers per question and have to watch ads.
Best Paid Homework Help Site: Chegg
- Price: $14.95 to $19.95 per month
- Best for: 24/7 homework assistance
This service has three main parts . The first is Chegg Study, which includes textbook solutions, Q&A with subject experts, flashcards, video explanations, a math solver, and writing help. The resources are thorough, and reviewers state that Chegg answers homework questions quickly and accurately no matter when you submit them.
Chegg also offers textbook rentals for students who need access to textbooks outside of their classroom. Finally, Chegg offers Internship and Career Advice for students who are preparing to graduate and may need a little extra help with the transition out of high school.
Another great feature Chegg provides is a selection of free articles geared towards helping with general life skills, like coping with stress and saving money. Chegg’s learning modules are comprehensive, and they feature solutions to the problems in tons of different textbooks in a wide variety of subjects.
Runner Up: Bartleby offers basically the same services as Chegg for $14.99 per month. The reason it didn’t rank as the best is based on customer reviews that say user questions aren’t answered quite as quickly on this site as on Chegg. Otherwise, this is also a solid choice!

Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath
- Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services)
- Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems
This site allows you to t ake a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept. Photomath also includes animated videos that break down mathematical concepts to help you better understand and remember them.
The basic service is free, but for an additional fee you can get extra study tools and learn additional strategies for solving common math problems.
Runner Up: KhanAcademy offers in-depth tutorials that cover complex math topics for free, but you won’t get the same tailored help (and answers!) that Photomath offers.
Best Site for English Homework Help: Princeton Review Academic Tutoring
- Price: $40 to $153 per month, depending on how many hours of tutoring you want
- Best for: Comprehensive and personalized reading and writing help
While sites like Grammarly and Sparknotes help you by either proofreading what you write via an algorithm or providing book summaries, Princeton Review’s tutors provide in-depth help with vocabulary, literature, essay writing and development, proofreading, and reading comprehension. And unlike other services, you’ll have the chance to work with a real person to get help.
The best part is that you can get on-demand English (and ESL) tutoring from experts 24/7. That means you can get help whenever you need it, even if you’re pulling an all-nighter!
This is by far the most expensive homework site on this list, so you’ll need to really think about what you need out of a homework help website before you commit. One added benefit is that the subscription covers over 80 other subjects, including AP classes, which can make it a good value if you need lots of help!

Best Site for STEM Homework Help: Studypool
- Best for: Science homework help
- Price: Varies; you’ll pay for each question you submit
When it comes to science homework help, there aren’t a ton of great resources out there. The best of the bunch is Studypool, and while it has great reviews, there are some downsides as well.
Let’s start with the good stuff. Studypool offers an interesting twist on the homework help formula. After you create a free account, you can submit your homework help questions, and tutors will submit bids to answer your questions. You’ll be able to select the tutor–and price point–that works for you, then you’ll pay to have your homework question answered. You can also pay a small fee to access notes, lectures, and other documents that top tutors have uploaded.
The downside to Studypool is that the pricing is not transparent . There’s no way to plan for how much your homework help will cost, especially if you have lots of questions! Additionally, it’s not clear how tutors are selected, so you’ll need to be cautious when you choose who you’d like to answer your homework questions.

What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Homework Help Sites?
Homework help websites can be a great resource if you’re struggling in a subject, or even if you just want to make sure that you’re really learning and understanding topics and ideas that you’re interested in. But, there are some possible drawbacks if you don’t use these sites responsibly.
We’ll go over the good–and the not-so-good–aspects of getting online homework help below.
3 Pros of Using Homework Help Websites
First, let’s take a look at the benefits.
#1: Better Grades Beyond Homework
This is a big one! Getting outside help with your studies can improve your understanding of concepts that you’re learning, which translates into better grades when you take tests or write essays.
Remember: homework is designed to help reinforce the concepts you learned in class. If you just get easy answers without learning the material behind the problems, you may not have the tools you need to be successful on your class exams…or even standardized tests you’ll need to take for college.
#2: Convenience
One of the main reasons that online homework help is appealing is because it’s flexible and convenient. You don’t have to go to a specific tutoring center while they’re open or stay after school to speak with your teacher. Instead, you can access helpful resources wherever you can access the internet, whenever you need them.
This is especially true if you tend to study at off hours because of your extracurriculars, work schedule, or family obligations. Sites that offer 24/7 tutoring can give you the extra help you need if you can’t access the free resources that are available at your school.
#3: Variety
Not everyone learns the same way. Maybe you’re more of a visual learner, but your teacher mostly does lectures. Or maybe you learn best by listening and taking notes, but you’re expected to learn something just from reading the textbook .
One of the best things about online homework help is that it comes in a variety of forms. The best homework help sites offer resources for all types of learners, including videos, practice activities, and even one-on-one discussions with real-life experts.
This variety can also be a good thing if you just don’t really resonate with the way a concept is being explained (looking at you, math textbooks!).

Not so fast. There are cons to homework help websites, too. Get to know them below!
3 Cons of Using Homework Help Websites
Now, let’s take a look at the drawbacks of online homework help.
#1: Unreliable Info
This can be a real problem. In addition to all the really good homework help sites, there are a whole lot of disreputable or unreliable sites out there. The fact of the matter is that some homework help sites don’t necessarily hire people who are experts in the subjects they’re talking about. In those cases, you may not be getting the accurate, up-to-date, and thorough information you need.
Additionally, even the great sites may not be able to answer all of your homework questions. This is especially true if the site uses an algorithm or chatbot to help students…or if you’re enrolled in an advanced or college-level course. In these cases, working with your teacher or school-provided tutors are probably your best option.
#2: No Clarification
This depends on the service you use, of course. But the majority of them provide free or low-cost help through pre-recorded videos. Watching videos or reading info online can definitely help you with your homework… but you can’t ask questions or get immediate feedback if you need it .
#3: Potential For Scamming
Like we mentioned earlier, there are a lot of homework help websites out there, and lots of them are scams. The review comments we read covered everything from outdated or wrong information, to misleading claims about the help provided, to not allowing people to cancel their service after signing up.
No matter which site you choose to use, make sure you research and read reviews before you sign up–especially if it’s a paid service!

When Does “Help” Become “Cheating”?
Admittedly, whether using homework help websites constitutes cheating is a bit of a grey area. For instance, is it “help” when a friend reads your essay for history class and corrects your grammar, or is it “cheating”? The truth is, not everyone agrees on when “help” crosses the line into “cheating .” When in doubt, it can be a good idea to check with your teacher to see what they think about a particular type of help you want to get.
That said, a general rule of thumb to keep in mind is to make sure that the assignment you turn in for credit is authentically yours . It needs to demonstrate your own thoughts and your own current abilities. Remember: the point of every homework assignment is to 1) help you learn something, and 2) show what you’ve learned.
So if a service answers questions or writes essays for you, there’s a good chance using it constitutes cheating.
Here’s an example that might help clarify the difference for you. Brainstorming essay ideas with others or looking online for inspiration is “help” as long as you write the essay yourself. Having someone read it and give you feedback about what you need to change is also help, provided you’re the one that makes the changes later.
But copying all or part of an essay you find online or having someone write (or rewrite) the whole thing for you would be “cheating.” The same is true for other subjects. Ultimately, if you’re not generating your own work or your own answers, it’s probably cheating.

5 Tips for Finding the Best Homework Help Websites for You
Now that you know some of our favorite homework help websites, free and paid, you can start doing some additional research on your own to decide which services might work best for you! Here are some top tips for choosing a homework help website.
Tip 1: Decide How You Learn Best
Before you decide which site or sites you’re going to use for homework help, y ou should figure out what kind of learning style works for you the most. Are you a visual learner? Then choose a site that uses lots of videos to help explain concepts. If you know you learn best by actually doing tasks, choose a site that provides lots of practice exercises.
Tip 2: Determine Which Subjects You Need Help With
Just because a homework help site is good overall doesn’t mean that it’s equally good for every subject. If you only need help in math, choose a site that specializes in that area. But if history is where you’re struggling, a site that specializes in math won’t be much help. So make sure to choose a site that you know provides high-quality help in the areas you need it most.
Tip 3: Decide How Much One-On-One Help You Need
This is really about cost-effectiveness. If you learn well on your own by reading and watching videos, a free site like Khan Academy is a good choice. But if you need actual tutoring, or to be able to ask questions and get personalized answers from experts, a paid site that provides that kind of service may be a better option.
Tip 4: Set a Budget
If you decide you want to go with a paid homework help website, set a budget first . The prices for sites vary wildly, and the cost to use them can add up quick.
Tip 5: Read the Reviews
Finally, it’s always a good idea to read actual reviews written by the people using these homework sites. You’ll learn the good, the bad, and the ugly of what the users’ experiences have been. This is especially true if you intend to subscribe to a paid service. You’ll want to make sure that users think it’s worth the price overall!

What’s Next?
If you want to get good grades on your homework, it’s a good idea to learn how to tackle it strategically. Our expert tips will help you get the most out of each assignment…and boost your grades in the process.
Doing well on homework assignments is just one part of getting good grades. We’ll teach you everything you need to know about getting great grades in high school in this article.
Of course, test grades can make or break your GPA, too. Here are 17 expert tips that’ll help you get the most out of your study prep before you take an exam.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Feeling Unmotivated? Here’s How to Get Out of the Rut
A conversation Harvard Business School’s Boris Groysberg and Robin Abrahams on shifting your mindset and energy at work.
- Apple Podcasts
Worker disengagement is on the rise around the world. Even those of us who generally like our jobs sometimes find it hard to muster energy and focus. So what’s the key to regaining motivation? Harvard Business School professor Boris Groysberg and research associate Robin Abrahams share a four part process to help you get your groove back: detachment, empathy, action and reframing. They offer simple tips like thinking in the third person, helping others, and gamification to help get back on track. Groysberg and Abrahams are the authors of the HBR article “Advice for the Unmotivated.”
ALISON BEARD: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Alison Beard.
Okay, let’s all be honest with each other for a minute. Yes, if you’re listening to this podcast, you’re probably someone who cares a lot about your work and career. I hope you can tell that I care a lot about mine too. But there will come days, maybe even months or years when we just aren’t feeling it. We’ve lost motivation, we’re burnt out, we’re just bored. We’re going through the motions of our jobs, but not enjoying them or excelling in the ways that we could be. This happens from the front lines to the C-suite.
Most of the advice about how to address the problem is directed at managers and organizations: how they can get us more engaged. But is it possible for us to snap ourselves out of these ruts?
Our guests today say it is, and they’ve developed a four-step process for doing so. They’re here to walk us through it. Robin Abrahams is a Research Associate Harvard Business School and Boris Groysberg is a Professor at HBS. Together, they wrote the HBR article, Advice for the Unmotivated. Robin, Boris, welcome.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Thank you. It’s good to be here.
BORIS GROYSBERG: Thank you for having us, Alison.
ALISON BEARD: Let’s start with the problem, which I think that you initially called “The Working Dead” when we were working on the article together. How do you know when you slipped into this kind of disengagement? How do you measure it or quantify it?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: You can’t really quantify it because you know it when you’re there. In the words of William Kahn, who was the person who wrote the first article about disengagement, it’s a withdrawal of the self. You’re just not yourself at work. That’s why we called it The Working Dead, because you do feel like a zombie. You’re not putting forth physical, emotional, cognitive energy. You’re kind of going through the motions. You’re operating on your limbic system a lot of the time.
BORIS GROYSBERG: One executive described it, “I was giving work my time, but I did not give it my heart.” The second one was, “I was feeling empty and frustrated like I was running in a race without a finish line.”
ALISON BEARD: In terms of the responses that you got from reaching out to HBR readers and executive education participants, do you see this happening at every level of the organization?
BORIS GROYSBERG: I guess most interesting things in our research, that we can clearly see this happening at a frontline level of organization. A number of people have told us, “Look, the higher up you are, the less you should feel disengaged.” We have so far had conversations with about 20 plus CEOs. I mean, people who are actually running their own businesses. Disengagement reaches out as high as that group of people as well. So it feels to us it’s present at every level. It plays out in a different way, but it’s certainly present in every level.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: The reason that people get disengaged from their work is because the demands of the job, be it emotional, physical, cognitive, time, logistics, overwhelm their personal resources, the support they’re getting, the amount of time they have, the knowledge they have, et cetera. That can happen at any level of the workplace. Also over the past three years, I would say demands have increased in almost every area of life. Resources are generally not keeping up for a lot of people.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah, I think we’re all keenly aware of that. What about the problem of not necessarily burnout, but boredom, particularly mid-career when you’ve been doing the same job for a long time and can go through the emotions and still be competent?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: If it’s feeling like a problem, then it is a problem. To some extent, this is very much, are you subjectively experiencing this as, “Oh, I have to go into the office again.” Or is it more like, “I’ve got this part of my life handled.” If you’re feeling it as a problem, then I would think it’s, especially these kinds of cases of just boredom, I kind of like the job, but I’m not entirely sure all of that, that our article is really especially well suited to address.
BORIS GROYSBERG: A few years ago, we did a piece on boredom. Some of the dynamics are actually somewhat different. The challenge with disengagement is that many people who are actually disengaged act on that disengagement. Disengagement is kind of costing the person who is disengaged as well as the organization that is employing that person. If you look at this, and I think you mentioned this in introduction, most of the advice and the research has been done like: How can we make Google a better place to work? How can we make John Smith or Jan Smith a better manager?
When we talk about engagement or disengagement, the focus has always been on organization and a manager. Can we make an organization? What are the practices that organization should employ and what can managers do? What Robin and I have experienced over the last few years as doing this project is imagine you are working for an organization that is not doing it, or for a manager that should not be managing. A lot of time we basically say, “Well, you should just leave and get another job.” Many people cannot leave, and so is there anything that you can do to any situation that engagement is not that prevalent to keep yourself more engaged or to keep yourself less disengaged?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: But it really is, I think you hit it, a lot of our advice is very much geared around don’t make your situation worse. Because when people kind of hit an exhausted state, when they hit burnout, they will frequently act out. They’ll pull themselves back even further. They dig themselves into a little doom spiral of learned helplessness, and we’re wanting to arrest that cycle for folks.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah, absolutely. Because you drift into an area where the disengagement isn’t just a bad feeling you have personally, but something that is destroying team culture, that’s diminishing your performance, that eventually might hurt your career.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: That’s diminishing your ability to make wise decisions about what to do with your situation.
ALISON BEARD: Let’s dig into the process. Why don’t you first give us a quick overview of the four steps?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: We call it the DEAR Method for Detachment, Empathy, Action, and Reframing. We did not just put them in that order to make the cool little acronym. It actually sort of works sequentially that people first need to detach from their emotional reactions and give themselves a little bit of distance to develop empathy, kindness for oneself and others that can then lead to appropriate actions to reassert your sense of agency that you can do something in the world, to reframing thinking logically about what is my situation? Is it the job? Is it me? Can I conceive of things in a different way?
ALISON BEARD: Do you see this as sort of a short-term immediate intervention every time you feel yourself disengaging? Or is it more about changing your mindset and behavior for the long-term so that you’re less likely to fall into that state?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: I think both. A number of the things that we’ve advised, if I’m just having a particularly bad day at a job where I’m not… I mean, you don’t go in feeling “Yay, go team,” 100% every single day. Nobody’s like that. Even in a minor slump, I mean, one thing I tend to like to do is if I just feel like I’m not getting anywhere on my work, clean out the office refrigerator because everybody loves it. It puts everyone else slightly in your debt, and you can see the results of what you’ve done. A lot of times just that, having a genuine human connection with a colleague or customer, can be enough to get you over a puddle, but these processes can also be used to help you get across a river.
BORIS GROYSBERG: Also, some of the practices that we describe are just good practices for a long-term career.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: True.
BORIS GROYSBERG: We talk about exercising and self-care. I think there’s a short-term impact of those practices. You mentioned that when you were reading, you were connecting to the ideas of the people. There are days when you just feel you are disengaged. Whatever that is, even though you might enjoy what you do and so on. I think there’s a short-term impact of those strategies, and I think some of them, if you practice them, would help you to build a sustainable long-term career as well.
ALISON BEARD: Detachment is the first step, but it seems like an odd one for people who are already feeling detached. What exactly do you mean and why is it helpful?
BORIS GROYSBERG: It is probably when people ask us, it’s I think out of the four, we keep getting this, “Wow, this is really counterintuitive.” But if you think about why you need this detachment, if you want to disengage a motivated state, having some distance and having some perspective, might be really, really uncomfortable, but long-term can provide you with some ideas or some strategies of how to get re-engaged again.
I mean, we heard stories from people enrolling to take some classes in a different city, taking time off to immerse themselves in something new, to get energized. I still remember a quote from somebody who goes, “The course gave me a lot of new ideas. I found myself feeling eager to start implementing them.” Learning something new can motivate you and get you re-excited about your work.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: But the detachment isn’t just about detaching and finding things outside the work. It’s really about getting a little bit of distance, not from the work per se, but from your own emotions. So things like meditation, exercise, just getting out of doors, feeling your body can help you calm down, get in touch with your feelings a little bit, and get that distance that you need to make the right choices and not be stuck in a kind of flight or fight mode, or “I can’t do anything. Everything’s just terrible.” It will be forever to get yourself out of that emotional reactive pattern. If you weren’t in an emotionally reactive pattern, you wouldn’t have gotten disengaged and burnt out to begin with.
ALISON BEARD: One of the interesting tips was to try to talk to yourself in the third person. Give me an example of how I might get myself motivated to edit a 6,000 word article when I’m just not feeling it by talking to myself in the third person.
BORIS GROYSBERG: Robin and I practice this from time to time.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: I’m not sure that it would motivate you for that. It’s more a question of if you’re trying to decide, oh gosh, do I even want to be in a job where I have to edit 6,000 word articles? Think about it as if it were honestly an HBS business case. Alison Beard woke up that spring morning wondering if she wanted to be here. You think through and you just sort of put yourself as a little protagonist because come on, it is always easier to solve other people’s problems than your own, right? So you think about yourself in the third person, and believe it or not, it will sort of trick your brain into thinking of it as someone else’s problems.
ALISON BEARD: Right. Yeah, what would I tell my best friend to do in this situation?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Exactly. Exactly.
ALISON BEARD: Okay, so the second step is empathy. What’s the advice on this front?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Empathy is very much a sort of two pronged thing. People often first think of it in terms of kindness, sympathy, I feel your pain. But there’s also the cognitive aspect of it, just like I feel your pain. Why did that happen to you? Let’s analyze this. Let’s try to think through other people’s points of view. Both of those are important to sort of re-energizing yourself. It’s also important to have empathy for yourself, have a degree of kindness towards yourself.
One thing that is very characteristic of people who are disengaged or burnt out is that they tend to act like automatons and treat other people in a dehumanizing manner as well. They don’t see the humanity. And to break out of that, to try to make those human connections, honestly fake it until you make it. But having emotional connections with people at work, it can be very crucial.
BORIS GROYSBERG: That’s why if you think about some of the kind of advice that we gave is, I mean, looking for friends and helping others. There’s two executives, their perspective really stand out in my mind. One, she talked about asking questions, looking for one-on-one conversations with employees at time of low motivation. Her quote was, “When I speak with my team, it makes me challenge. I have at hand feel less daunting. The mountain to climb is still there, but the conversation make me feel less alone in climbing.”
People look for those relations. Interesting enough, people reach out to their former mentors and coaches, and maybe if there’s one piece, and it’s kind of indirectly in that bucket, but if I have to add maybe one piece to it that we kind of missed, and I should give credit to a colleague Gamze Yucalglu is kind of practicing gratitude.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Yes, that’s a good one.
BORIS GROYSBERG: It was mentioned a few times. One of the executives said, “I remind myself of things I’m grateful about. This instantly changes my perspective.” That’s kind of like the gratitude practice. If I had to add one more, that’s the one that we probably need.
ALISON BEARD: I think the self-compassion piece is really important too, because I know I find myself when I’m not feeling motivated, getting mad at myself or feeling guilty for not being motivated.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: This is another way that the thinking of yourself in the third person can help, because you wouldn’t be like that lazy, terrible Alison did this and that. You’d be more neutral about it. You take away that voice in your own head.
One of the really fun findings that I discovered when I was looking at the psychological research on all of this is that people who are suffering burnout at work feel better when they help others than when they themselves receive help. If you can do something for another person, you feel powerful, you feel good, you feel like you have a reason to be in this world.
ALISON BEARD: That totally resonates with me. I find that sort of what I do when I’m feeling unmotivated and then also guilty about feeling unmotivated, I will reach out to one of my best work friends, and we might commiserate a little bit, but then I find myself that I’m helping with his problems and he’s talking to me about not feeling bad about my problem. So sort of it’s that empathetic, virtuous circle happening.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS:
Exactly. And even in far worse situations than any workplace really, like POW camps and natural disasters. Boris and I studied a bit about survival psychology during the pandemic, and this is what has enabled people who go through horrific experiences like that without psychological damage, do it because they have connections with other people. You can get through almost anything if you can connect to the people that you’re going through it with.
ALISON BEARD: Okay. So the next step is action, which that actually seems the hardest because the whole point is that we don’t feel that we have the energy or motivation to do anything. You mentioned earlier cleaning out the office refrigerator. What other kind of actions might help?
BORIS GROYSBERG: It’s actually one of the hardest things when you are disengaged, is to take action. Maybe somewhere along the way we provide advice to people, say, look at small things first, tackle the little stuff, the one that you can concentrate on and get things done. Invest in outside activities. A number of people that we interviewed talked about just even simply doing daily to-do lists for both for business and the personal stuff, and setting up specific goals in the morning and then the exercise of crossing things off. Then one person said crossing things off felt like real progress.
Once you do it, you also have to celebrate those small accomplishments and it allows you to be at least feel a little bit more motivating.
ALISON BEARD: I make little boxes that I can do check marks in because that actually feels like happier than crossing things out.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: I mean, we’ve all done the thing where you do the thing and then you write it down on your to-do list, so we can check it off. That’s not just me, right?
ALISON BEARD: 100% I do that.
BORIS GROYSBERG: That would be the three of us. Yeah.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Well, I’m going to take a slightly different tack on this, which is disengaged employees, by and large already are taking action. They’re just frequently taking unhelpful action. They are more likely to drink, use drugs, sleep, watch television, passive internet use on the job, playing pranks on coworkers. These are all dangers of disengagement. The reason – I told you this thing was sequential – the reason that we put emotional detachment, and then empathy first is to kind of get your head in the right space so that the action you take is the appropriate action, because people who are disengaged are often taking inappropriate actions that are just going to make their situation worse.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. So apart from tackling little tasks, are there any other types of actions you recommend?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: One of the best, and surprisingly, is to invest yourself in something that is not your job, to develop a hobby, some kind of outside activity. There’s been some recent articles published that were really interesting where the assumption going in was that, oh, if somebody has a side hustle or a volunteer commitment, then they’re going to be less engaged at their job. And in fact, it was not the case at all. That sense of agency, empowerment, connection that you get from those other things transfer into the workplace and can make even a job that’s not particularly meaningful, feel meaningful and fulfilling.
BORIS GROYSBERG: If you do the D and the E, the first two steps, it might open up your eyes to see there are some pieces, parts of your jobs or maybe kind of something that – other jobs that exist in organization that you can do that really relates to your strength and can reenergize you as well. So looking for those. I’m talking about special projects, but not the special projects that nobody cares about, but the real special projects that almost enrich your job. We heard it from a number of people when they did the D and the E, it allowed them to see some things in an organization and pick some things that were slightly outside of their work incorporated into their jobs, and that was kind of enough to get them reengaged back at work.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: The curiosity part of the empathy as you’re connecting with people, you’re talking to them about what are their experiences, what’s their area of expertise, will frequently give you some kind of path to moving forward. But if you go into these situations without some emotional detachment and some empathy, you’re just going to be flailing around.
ALISON BEARD: Okay, so finally the last step, reframing. Why is that helpful and how can people practically do it?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Reframing is once you’ve sort of reestablished, as it were, your humanity through empathy, through getting some distance on your own emotions, through taking some action and feeling like you can take meaningful action, reframing is kind of the one where you ask yourself, “Okay, what about the situation though? Is there a different way I can think of my job that will make it more fulfilling? Can I restructure it in some way?” Maybe the answer is yes, and you’ll have a better vision of how to do that. Maybe the answer is no, and then you do need to be moving on, but you’ll have a sense of what you want to be moving on to.
BORIS GROYSBERG: We provide three strategies for people. Examine your work identity, consider how other benefit from your work. But the one that I always… This speaks to me because I think about it a lot in my own work and in my own job is looking at the big picture. There are a number of different ways to get to that. We have an example of somebody who in the energy business. That person joined the leadership program when one of the exercises were to define his core values. Then what he did is got in the habit of asking himself daily what he’s doing today towards those type of core values and prioritize a lot of daily tasks around that.
He claimed that this has been tremendously helpful. So examining your values, why you do this for. And so that would be one. Another person talked about going to dinner with his sister, make him realize what’s in life, health, family, and that he was depleting a lot of his energy on short-term problems that really didn’t matter. This kind of looking at the big picture and also trying to understand what really matters to you is kind really important part of-
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: I feel a kind of idea floating around that people should always find their jobs intrinsically meaningful. Not everybody does. Not everybody gets jobs that are engaging. How do those people get through it? And the main way they do is by thinking about, this is what the job is providing to me. I’m providing for my family, I’m saving for my education, I’m doing this. It enables me to live in this community and do these things. It’s really okay if the job is kind of a means to an end.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah, I think that makes sense.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: There’s been a lot of research on the extent to which when people are doing unpleasant, boring tasks, repetitive physical labor or repetitive clerical labor, or studying long boring things, thinking about what they’re doing it for, what life outcomes they’re doing it for, really does help them get through it.
ALISON BEARD: What happens if you try all of these strategies and you still feel unmotivated? Is it a sign that you need to talk to your manager, that you do need to leave your job?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: It might be a sign that you need to talk to your doctor. I’m not being sarcastic. I mean, there’s a lot of reasons that a person might really feel unable to pull themselves out of it. But yeah, there may be a point at which you do all of these things and then you look around and you’re like, oh, the problem is the situation.
BORIS GROYSBERG: I think if you think about engagement and you think about what’s controllable versus not, you look at research on engagement. There are differences by countries. There are differences by industries. There are even some differences between functions.
Those are things that are not really controllable. If you take a step back and say, “What is controllable?” The controllable thing is the organization you work for, hopefully over a period of time.
The controllable thing that the manager you work for. I always say, if you work for a bad company and you work for a bad manager, you are in hell. If you work for a great company and you work for a great manager, you are in heaven. But many of us are working for a great company and a bad manager or a great manager in a bad company. In those cases, if it’s a company’s great, bad managers, think about job rotations. Even if you’re going to take a lateral assignment, you will feel better. If your manager is the one who creating disengagement, moving to another manager would help you.
If it’s an organization, then not everybody has a chance to move. But you should seriously consider if you should switch organizations. By the way, a lot of people do for a lower compensation. Because what you have is if you can’t change the organization, if you cannot change the manager and you cannot change yourself, those are the three levers that’s available to you.
If you are unable to create engagement energy in yourself, you got to look at other things that you can control. Those are the three yourself, the person that you work for, and maybe the company that you work as well. We don’t advocate for turnover, but there comes the time that says I should be doing something else for somebody else.
ALISON BEARD: Yeah. I’m going to shout-out two players on the Boston Celtics who just took less lucrative contracts to continue to play for the Celtics because they obviously felt they had a good coach at a good organization, which makes me as a fan very happy.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: That’s a perfect example, yeah. And people will make a better choice if they’ve gone through these steps. They won’t run from, instead of to, they won’t resign in a harmful way that blows up their career and possibly who knows what else. They will make better choices if they’ve gone through all four of the steps first.
ALISON BEARD: Do either of you have a specific story about struggling with motivation and how you use this framework or a piece of the framework to get out of that rut?
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: I would say for me, one thing that has always protected me for years now against that kind of loss of motivation is I do invest myself in a lot of activities outside of work. I do theater. I wrote a play that’s going to be produced next year. I’m involved to some extent in my husband’s business. All of those things, it’s like if I’m having a bad day in one area, I can maybe make it up in another. Even if that’s not, I’m learning perspectives in one world that I can put into another, like, oh, this is really interesting. This also applies to this problem that I’m having over here. And so it kind of keeps everything fresh as well as keeping my network of weak ties and people that I don’t know that well active so that I can learn more things, discover new opportunities. Those things can really help inoculate you against that loss of motivation.
ALISON BEARD: Robin, Boris, it was really a pleasure working on this piece with you. I know that it helped me regain my motivation, which I really appreciated, and I hope it’s going to help others. Thanks for talking to me today.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: Thank you so much.
BORIS GROYSBERG: Thank you very much, Alison.
ALISON BEARD: That’s Research Associate Robin Abrahams and Professor Boris Groysberg, both of Harvard Business School. Together, they wrote the HBR article, Advice for the Unmotivated.
We have more episodes and more podcasts to help you manage your team, your organization, and your career. Find them at HBR.org/podcasts or search HBR in Apple Podcast, Spotify or wherever you listen.
Thanks to our team, senior producer Mary Dooe, associate producer Hannah Bates, audio product manager Ian Fox, and senior production specialist, Rob Eckhardt. And thanks to you for listening to the HBR IdeaCast . We’ll be back with a new episode on Tuesday. I’m Alison Beard.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about personal resilience.
- Managing yourself
- Motivating people
- Mindfulness
Partner Center
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- School Stuff
How to Excuse Yourself from Unfinished Homework
Last Updated: December 13, 2023
This article was co-authored by Alicia Oglesby . Alicia Oglesby is a Professional School Counselor and the Director of School and College Counseling at Bishop McNamara High School outside of Washington DC. With over ten years of experience in counseling, Alicia specializes in academic advising, social-emotional skills, and career counseling. Alicia holds a BS in Psychology from Howard University and a Master’s in Clinical Counseling and Applied Psychology from Chestnut Hill College. She also studied Race and Mental Health at Virginia Tech. Alicia holds Professional School Counseling Certifications in both Washington DC and Pennsylvania. She has created a college counseling program in its entirety and developed five programs focused on application workshops, parent information workshops, essay writing collaborative, peer-reviewed application activities, and financial aid literacy events. This article has been viewed 890,010 times.
Ideally, you will always be ready for class and have your homework completed. Sometimes, however, life gets in the way and you aren’t prepared. There are several methods for developing an excuse to give your teacher for why you don’t have your homework ready, ranging from honest to deceptive.
Inventing an Elaborate Excuse

- Crumple and tear a paper assignment. Then you can tell the teacher that it flew out the window and got run over or trampled on.
- Smear dirt and water on your assignment and claim it fell in a puddle. Make sure to write a few words (bonus points if it relates to the homework assignment) so that it looks believable.
- Spill something dark (like juice or ink) on the assignment so that it is illegible.

- For instance, if you have to save work to a USB drive, you can claim to have a problem with the file.
- If you are asked to email or otherwise electronically send a homework file, you can “accidentally” send a different assignment, or the “wrong” draft (which could have just your name and the first part of the assignment, for instance). You might even be able to purchase corrupted files.
- Be aware that your teachers can be tech-savvy and know all of these tricks, so you might have to get creative. [2] X Research source

Buying Time and Stretching the Truth

- If the missed homework is for a class late in the day, you might be able to do the work before school, during another class, or during lunch or a break.
- You can hand in the wrong assignment—such as one from another class—or an old one from the same class. By the time your teacher notices the mistake, you will be able to complete the real homework, or just turn it in the next day and say you are sorry about the mix-up.
- Copy answers from a friend so you have something to turn in. Make sure your friend is ok with helping. This also only works for assignments where it is expected that students will have the same or similar answers. In some schools, even copying something like homework can merit a suspension. Remember to evaluate the situation and make a good decision as to whether or not you will copy homework off of a peer.

- A dangerous move, you can forge a note from a parent explaining why you couldn't do your homework.
- If you decide to forge one, be warned that your teacher might know it’s a fake. If you are caught, you face punishment from both your parents and teacher.
Telling the Truth

- You might say something like "I am really sorry, but I got behind on things and wasn't able to finish my homework. Could I be excused just this once? I'll turn it in tomorrow and I won't be late again."
- Keep things simple and direct, rather than annoying your teacher with long, rambling excuses.

- This means saying something like: "I know there's no excuse, and I accept full responsibility. I should have done my work. I'm sorry that I'm not prepared, and it won't happen again."
- Doing so will display maturity and your teacher might respect your honesty.

- Perhaps you are overworked and stressed (this is especially persuasive at exam time).
- If circumstances beyond your control, like an illness or death in the family, have prevented you from doing your work, say so.
- You can also explain that you didn’t understand the assignment, or struggled with it, or felt rushed, and needed to give it more time.

- Your teacher is more likely to accept the excuse if you don’t spring it on him or her at the last minute.
- You might also be able to ask for an extension so that you can turn the homework in later.
- Know your teacher’s personality, and how flexible and forgiving he or she is. When you talk to your teacher, look sad, serious, agitated, etc. depending on your excuse.
Community Q&A
- The best approach is to try to do your work on time rather than be tempted by an excuse. Don’t attempt to make excuses too often. This way, when you actually need to use one, your teacher is more likely to accept it. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Turn in your work, even if you have to make an excuse and submit it late. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
- If you are able to do any of your homework, even a small amount or poor quality work, consider turning it in anyway. Having something prepared can be better than having nothing, and sometimes teachers will give you partial credit for partial work. You can also explain to your teacher that you would like to do a better job and turn it in later, if you want. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 1

- Be prepared to face the consequences if you get caught for using a deceptive excuse. Talk to your teacher in a mature way, explaining that you have a problem with procrastination, or feel overworked, or struggled with the assignment, etc. Thanks Helpful 50 Not Helpful 7
- Try not to lie, a bad conscious can easily come from repetitive lying. Thanks Helpful 40 Not Helpful 10
- If you get caught lying, it may lead to severe consequences with your teacher and parent/guardian. Thanks Helpful 21 Not Helpful 7
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2012/08/30/british-lecturer-compiles-best-student-excuses
- ↑ https://chronicle.com/blogs/wiredcampus/the-computer-ate-my-homework-how-to-detect-fake-techno-excuses-2/7207
About This Article

To excuse yourself from unfinished homework, try to make your excuse as believable as possible, like saying you were sick last night. If your homework was on a computer, claim your laptop crashed or your files were corrupted. Another thing you can try is handing in an old assignment. Then, do your actual homework before your teacher realizes. When they ask you about it, say that you accidentally handed in the wrong homework, and then give them the homework that was actually due. Even if you think you have a good excuse, your teacher’s probably heard it a dozen times before, so consider being honest with them and apologizing for falling behind. For example, say, “I’m sorry, but I wasn’t able to finish my homework this week. I had a lot of things to deal with. Is it okay if I turn it in tomorrow?” If you decide to be honest, try to tell your teacher at the beginning of class or even earlier in the day, which will make your excuse more realistic. For more tips, including how to pretend you lost your homework, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 12, 2016
Did this article help you?
Isabella Jayne
Oct 3, 2017
Feb 27, 2017
Feb 25, 2017
Sep 13, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
9 Tips for Finding the Best OB-GYN for You
Your women’s health specialist plays a big role in health and wellness. Whether you’re going to an obstetrician-gynecologist for a preventive screening, birth control advice, pregnancy care or to get help for a menopausal issue, you need an OB-GYN who can respond to your changing needs. Here's how to find someone who is a good fit for you.
How to Find the Best OB-GYN for You
An obstetrician-gynecologist, or OB-GYN for short, is a doctor who specializes in women's health and reproduction and can take care of you for both general gynecological needs as well as childbirth.

Getty Images
These specialists play an important role in the care of women throughout their lives, not just during pregnancy. The American Pregnancy Association, a national organization that promotes pregnancy wellness, reports that OB-GYNs are medical doctors who specialize "in the management of pregnancy, labor and birth. They also receive specialized education in the area of the female reproductive system and surgical care. Much of their education focuses on the detection and management of obstetrical and gynecological problems."
Your gynecologist, OB-GYN or women’s health specialist screens you for diseases, helps you plan a family – whether that means assisting with or preventing pregnancies – troubleshoots below-the-belt problems and more. You may see an OB-GYN for routine gynecological care, such as pelvic exams, breast exams and Pap smears, as well as for infertility, abnormal bleeding, cancer, endometriosis , fibroids , menopause issues and many other women's health concerns. And whatever the reason for the visit, at the end of the day, there’s a good chance this person will throw on gloves, spread your legs and dive headfirst toward a very private part of your body . Because you’ll be discussing your most intimate and personal health issues with this doctor, you’ll want to find someone with experience who you can trust.
So how can you find the right doctor for you? "It's actually a very complicated question," says Dr. Jonathan Schaffir, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus. This is because many factors may play into your decision, ranging from convenience and the doctor's subspecialty to cultural preference and the doctor's bedside manner.
9 Tips For Finding the Best OB-GYN
How do you find that OB-GYN who will truly get you? Who will celebrate with you in joy, comfort you in sorrow, answer all your pregnancy and perimenopause questions, hold your hand when needed – and get up close and personal without making it weird?
You discuss a lot of important and sensitive topics with your OB-GYN. Ideally, they should be able to deliver good and bad news as deftly as they deliver a baby. But your doctor also needs to have the ability to operate in an expert and occasionally emergent fashion if the need should arise.
How do you find this unicorn of a physician who you may spend a lot of time with during very significant milestones in your life? Here are are few aspects to consider:
1. Who Accepts Your Health Insurance Plan?
One place to start, Schaffir says, is by looking at local doctors who accept your health insurance plan. Choosing an OB-GYN in-network usually means your insurance will cover more of their services. This can help you better understand your coverage options and avoid unexpected surprises down the line.
2. OB or GYN or OB-GYN?
Are you planning on becoming pregnant? Or are having children not part of your life plan?
First, determine whether you specifically need an obstetrician, a gynecologist or both (an OB-GYN). An obstetrician specializes in all stages of pregnancy. A gynecologist, on the other hand, specializes in all aspects of women’s health.
Women who neither are pregnant nor plan to have children should decide how to choose a gynecologist. However, women who are currently pregnant or planning to become pregnant will want to find out how to choose an obstetrician. As OB-GYNs, many doctors specialize in both areas, but be sure to double-check before making an appointment.
3. Do Your Homework
William Parker , clinical professor of OB-GYN at the UCLA School of Medicine in Santa Monica, also suggests looking online at websites that show information such as credentials, specialties, years in practice, patient reviews, education and more. Try the doctor finder tool from U.S. News , which includes location, insurance covered, patient reviews and more.
4. Do You Have Specific Health Concerns or Special Needs?
Schaffir also recommends considering whether you have any special needs or other health concerns.
"If you are a reasonably healthy woman without a lot of high-risk factors, you could likely see anyone and have a great experience. But if you do have medical conditions that would make your pregnancy high-risk, or a previous pregnancy with some complication, then it's important to seek out a provider who has some expertise and comfort in dealing with those particular problems. That should be a big factor in choosing a provider."
If you have specific concerns or conditions, they'll likely fall under one of gynecology's numerous subspecialties, which range from infertility troubles to cancer to pelvic floor disorders and more. Bring up your concerns with your gynecologist or OB-GYN, and they may send you to a specialist. For example, say you have urinary incontinence issues . Your doctor may refer you to a specialist in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. Each doctor has their own strengths.
If your regular gynecologist wants to be the primary source for solving your problem – say they want to perform the surgery that helps solve your incontinence – ask a few questions to make sure they are the best for the job. Find out how many of these kinds of surgeries they perform in a month and how many of them have been for women with your specific problem. Also ask if there are ever complications with the procedures, and if so, what they've been.
"That's your right to ask those kinds of questions," says Parker. "You're looking out for one person, and that's yourself. You want the best care you can get." It might turn out that, indeed, your gynecologist is the perfect person to handle your specialized concerns. But, in addition to the questioning, it doesn't hurt to ask your primary care physician for a specialist referral, and do some online searching, too.
Dr. Kecia Gaither, director of Perinatal Services at NYC Health + Hospitals/Lincoln in the Bronx, agrees that factoring in any other health concerns should be "the first question to consider" when selecting a doctor. Pregnant women with comorbid medical conditions, like diabetes, will "require a subspecialist – a maternal fetal medicine specialist, as opposed to a generalist."
5. Is Gender Important to You?
You should think carefully about whether you'd be more comfortable being seen by a male doctor or a female doctor. Some women do prefer being seen by a doctor of the same gender. Some cultural or religious backgrounds will direct a woman to a female doctor. If you’d prefer to be cared for by a female gynecologist, factor that into your choice. But also consider which provider will give you the highest level of care and who is available, convenient and in network.
Gaither recommends thinking about your expectations for the relationship you'll have with your OB-GYN.
While all doctors should be respectful and compassionate, those qualities can be particularly important for the professionals peeking between your legs. Sex, STDs , family planning, fears and, not to mention, your overall health – try discussing these topics with someone who seems uninterested, judgmental or short on time.
A good doctor will engage in a dialogue. Expect your doctor to listen well, take your questions and concerns seriously and explain his or her advice and actions. For example, if you're 40 years old and, at the appointment, tell your doctor you're weary of a mammogram , they should explain the pros, cons and guidelines of the screening.
6. Do You and Your OB-GYN Share the Same Values?
Make sure you and your doctor share the same values. Consider this: If you're going to the gynecologist seeking contraception and, upon discussing it at the appointment, discover that your doctor does not believe in birth control – red flag!
"My style of communication is direct. I show pictures. I explain the 'whys' and 'hows' and give a logical rationale using non-medical words of how a disease affects (the patient's) pregnancy," and how the patient can facilitate a more healthful pregnancy. But not every patient likes to hear that she might have to work at the pregnancy or change certain behaviors, and some may be fearful or in denial, all of which can lead to a negative assessment of the provider.
Consider the following criteria:
- How does your doctor view pain management ?
- How open is your doctor to alternative medicine?
- How does your doctor view access to reliable birth control?
- Will your doctor perform a vaginal birth after C-section ?
- Will your doctor perform an abortion if you need one?
7. Come Prepared to Your First Meeting
When you head into that first meeting, Gaither recommends coming in armed with information about "your medical and surgical histories. It's not wise to withhold information that may be pertinent to your physician establishing a health care plan." Also have a list of questions to ask and a list of your medications so your physician can have this information. "And know your family history," Gaither says.
8. If You're Expecting or Trying to Conceive
If you’re expecting, trying to conceive or planning for pregnancy in the near future, choosing the women’s health expert to trust with your care is a big decision. You can choose to work with an OB-GYN during your pregnancy or you can choose a midwife for pregnancy care.
Some women already have a maternity hospital in mind, so they try to find a good OB-GYN or midwife at the location where they want to deliver. Others start with an OB-GYN or midwife they like and then see if there’s a location for delivering near them. Both ways work, but regardless of what method you choose, make sure that hospitals affiliated with your OB-GYN or midwife have their own excellent reputation, have high neonatal standards and are covered by your insurance. Look at U.S. News's ratings for Best Maternity Hospitals .
9. If You Have a Good Health Provider, Stick With Them
When you find a good provider , hang on to them.
"I think continuity is always great," across multiple pregnancies, Schaffir says, because then you can build a relationship with a doctor "who knows you and is familiar with your history. I think that helps with your care." For his part, he says "it's very rewarding to have patients that I come to know and forge a relationship with and get to see them through multiple pregnancies. That's one of the most rewarding parts of being an obstetrician."
Hospital Bag Checklist for Mom

Tags: doctors , patient advice , obstetrics and gynecology , women's health
Most Popular
Patient Advice

health disclaimer »
Disclaimer and a note about your health », you may also like, finding the best orthopedic surgeon.
Elaine K. Howley May 3, 2024
Does Medicare Cover Ozempic?
Paul Wynn May 2, 2024

Is Mifepristone Safe?
Payton Sy May 1, 2024

Health Screening Tests Women Should Have
Angela Haupt and Gretel Schueller May 1, 2024

Doctors That Women Should See
Vanessa Caceres and Gretel Schueller May 1, 2024

Early Miscarriage Symptoms
Claire Wolters April 30, 2024

11 Tips for Your First Mammogram
Elaine K. Howley April 29, 2024

Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, Osteopenia
Payton Sy April 29, 2024

Key Medicare Enrollment Deadlines
Joanne Kaldy and Vanessa Caceres April 26, 2024

LASIK Eye Surgery
Mariya Greeley and Elaine K. Howley April 26, 2024


IMAGES
COMMENTS
2. Look up the answers online or in the back of the book. Many textbooks have all or half of the answers listed in the back of the book (especially math books). Your teacher may have found the worksheets or questions online, too, so search for the answers online. 3. Act like you did the homework, but forgot it at home.
Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes? Should we get rid of homework? In " The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, " published ...
You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you've got SAT studying to do. It's just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you're reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time. 5.
1. Take a break now and then. You might think that tearing through all of your homework tasks from start to finish is the fastest way to do it. If you have a ton of homework, however, you'll probably get burnt out if you don't take a break every now and then. At least every two hours, take a 15 minute breather.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
For high schoolers, Cooper's research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Evaluate and improve your SAT score. 3. Gather all your gear. Collect EVERYTHING you will need for the homework you are working on (like your laptop for writing assignments and pencils for problem sets). Getting up for supplies takes you off course and makes it that much harder to get back to your homework. 4.
The good news is that finding out about missing homework is a first step to helping kids get back on track. You just need to keep a few considerations in mind. Empathy will get you further than anger
Here are 10 tips to help your child learn how to make homework less stressful. 1. Stick to a Schedule. Help your child plan out his or her time, scheduling time for homework, chores, activities, and sleep. Keep this schedule handy so your child knows what he or she should be working on, and when. 2.
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework, points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't ...
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
If you're finding that homework is becoming an issue at home, check out this article to learn how to tackle them before they get out of hand. Con 1: Too Much Homework Can Negatively Affect Students . You'll often hear from students that they're stressed out by schoolwork. Stress becomes even more apparent as students get into higher grade ...
Using a homework contract can help your child set realistic goals. Encourage "thinking out loud." Get tips for helping grade-schoolers do schoolwork on their own. Sometimes, homework challenges don't go away despite your best efforts. Look for signs that kids may have too much homework. And learn how to talk with teachers about concerns.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the " 10-minute homework guideline "—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students' needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
Excuse #1: You lack the required knowledge. Let your parents and teacher know if you're taking a class and feel as if you lack the necessary skills or knowledge to complete the homework. Ask your teacher for extra guidance so you don't fall too far behind. See if your parents can find the time to help you, or you can look for a tutor.
Back-to-school season means a return to making lunches, signing field trip permission slips, planning for 127 different spirit day outfits, and having to face the prospect of taming the homework ...
2. Eliminate as many distractions as possible. Put your phone away, get away from your computer, and make your environment as quiet as possible. Giving homework your undivided attention will actually make it easier, because your mind won't be balancing different tasks at the same time.
Homework: How to Opt Out . If your child goes to an open admissions public school, opting out of homework can be something you consider. While it may be a particularly good choice if homework is ...
Best Site for Math Homework Help: Photomath. Price: Free (or $59.99 per year for premium services) Best for: Explaining solutions to math problems. This site allows you to take a picture of a math problem, and instantly pulls up a step-by-step solution, as well as a detailed explanation of the concept.
ROBIN ABRAHAMS: The reason that people get disengaged from their work is because the demands of the job, be it emotional, physical, cognitive, time, logistics, overwhelm their personal resources ...
3. Ask a parent to write an excuse for you. A dangerous move, you can forge a note from a parent explaining why you couldn't do your homework. If you decide to forge one, be warned that your teacher might know it's a fake. If you are caught, you face punishment from both your parents and teacher. Method 3.
Do Your Homework. William Parker ... You want the best care you can get." It might turn out that, indeed, your gynecologist is the perfect person to handle your specialized concerns. But, ...