- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Theoretical Framework
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounded assumptions or predictions of behavior. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that summarizes concepts, ideas, and theories derived from prior research studies and which was synthesized in order to form a conceptual basis for your analysis and interpretation of meaning found within your research.
Abend, Gabriel. "The Meaning of Theory." Sociological Theory 26 (June 2008): 173–199; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (December 2018): 44-53; Swanson, Richard A. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines . San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers 2013; Varpio, Lara, Elise Paradis, Sebastian Uijtdehaage, and Meredith Young. "The Distinctions between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework." Academic Medicine 95 (July 2020): 989-994.
Importance of Theory and a Theoretical Framework
Theories can be unfamiliar to the beginning researcher because they are rarely applied in high school social studies curriculum and, as a result, can come across as unfamiliar and imprecise when first introduced as part of a writing assignment. However, in their most simplified form, a theory is simply a set of assumptions or predictions about something you think will happen based on existing evidence and that can be tested to see if those outcomes turn out to be true. Of course, it is slightly more deliberate than that, therefore, summarized from Kivunja (2018, p. 46), here are the essential characteristics of a theory.
- It is logical and coherent
- It has clear definitions of terms or variables, and has boundary conditions [i.e., it is not an open-ended statement]
- It has a domain where it applies
- It has clearly described relationships among variables
- It describes, explains, and makes specific predictions
- It comprises of concepts, themes, principles, and constructs
- It must have been based on empirical data [i.e., it is not a guess]
- It must have made claims that are subject to testing, been tested and verified
- It must be clear and concise
- Its assertions or predictions must be different and better than those in existing theories
- Its predictions must be general enough to be applicable to and understood within multiple contexts
- Its assertions or predictions are relevant, and if applied as predicted, will result in the predicted outcome
- The assertions and predictions are not immutable, but subject to revision and improvement as researchers use the theory to make sense of phenomena
- Its concepts and principles explain what is going on and why
- Its concepts and principles are substantive enough to enable us to predict a future
Given these characteristics, a theory can best be understood as the foundation from which you investigate assumptions or predictions derived from previous studies about the research problem, but in a way that leads to new knowledge and understanding as well as, in some cases, discovering how to improve the relevance of the theory itself or to argue that the theory is outdated and a new theory needs to be formulated based on new evidence.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
- The theoretical framework adds context around the theory itself based on how scholars had previously tested the theory in relation their overall research design [i.e., purpose of the study, methods of collecting data or information, methods of analysis, the time frame in which information is collected, study setting, and the methodological strategy used to conduct the research].
By virtue of its applicative nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges associated with a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Corvellec, Hervé, ed. What is Theory?: Answers from the Social and Cultural Sciences . Stockholm: Copenhagen Business School Press, 2013; Asher, Herbert B. Theory-Building and Data Analysis in the Social Sciences . Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1984; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (2018): 44-53; Omodan, Bunmi Isaiah. "A Model for Selecting Theoretical Framework through Epistemology of Research Paradigms." African Journal of Inter/Multidisciplinary Studies 4 (2022): 275-285; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Jarvis, Peter. The Practitioner-Researcher. Developing Theory from Practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1999.
Strategies for Developing the Theoretical Framework
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research problem. Identify the assumptions from which the author(s) addressed the problem.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
Structure and Writing Style
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, your work is expected to test the validity of that existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism Theory, which categorizes perceived differences among nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism Theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the disputed split between southern and northern Sudan that led to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Based upon the above example, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as an answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [i.e., justify the application of your choice of a particular theory and explain why alternative constructs were rejected. I could choose instead to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among ethnic conflict theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
Just as a research problem in your paper requires contextualization and background information, a theory requires a framework for understanding its application to the topic being investigated. When writing and revising this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks, concepts, models, or theories . As noted in the example above, there will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the theory you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory. Although the past tense can be used to describe the history of a theory or the role of key theorists, the construction of your theoretical framework is happening now.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory inadequately explains a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. "A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research." Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Weick, Karl E. “The Work of Theorizing.” In Theorizing in Social Science: The Context of Discovery . Richard Swedberg, editor. (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2014), pp. 177-194.
Writing Tip
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Other Disciplines
An increasingly important trend in the social and behavioral sciences is to think about and attempt to understand research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories developed within your particular discipline, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbents in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be more engaged in the research topic.
CohenMiller, A. S. and P. Elizabeth Pate. "A Model for Developing Interdisciplinary Research Theoretical Frameworks." The Qualitative Researcher 24 (2019): 1211-1226; Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Undertheorize!
Do not leave the theory hanging out there in the introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you describe should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the review of pertinent literature and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose supports analysis of the research problem or, if appropriate, how the theoretical framework was found to be inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.
Yet Another Writing Tip
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in newspapers and popular magazines and in non-academic settings. However, the difference between theory and hypothesis in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested assumptions that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory; critical race theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among a set of scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis. About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis. Slideshare presentation.
Still Yet Another Writing Tip
Be Prepared to Challenge the Validity of an Existing Theory
Theories are meant to be tested and their underlying assumptions challenged; they are not rigid or intransigent, but are meant to set forth general principles for explaining phenomena or predicting outcomes. Given this, testing theoretical assumptions is an important way that knowledge in any discipline develops and grows. If you're asked to apply an existing theory to a research problem, the analysis will likely include the expectation by your professor that you should offer modifications to the theory based on your research findings.
Indications that theoretical assumptions may need to be modified can include the following:
- Your findings suggest that the theory does not explain or account for current conditions or circumstances or the passage of time,
- The study reveals a finding that is incompatible with what the theory attempts to explain or predict, or
- Your analysis reveals that the theory overly generalizes behaviors or actions without taking into consideration specific factors revealed from your analysis [e.g., factors related to culture, nationality, history, gender, ethnicity, age, geographic location, legal norms or customs , religion, social class, socioeconomic status, etc.].
Philipsen, Kristian. "Theory Building: Using Abductive Search Strategies." In Collaborative Research Design: Working with Business for Meaningful Findings . Per Vagn Freytag and Louise Young, editors. (Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018), pp. 45-71; Shepherd, Dean A. and Roy Suddaby. "Theory Building: A Review and Integration." Journal of Management 43 (2017): 59-86.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 4:39 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis
Published on 8 July 2022 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review .
A strong theoretical framework gives your research direction, allowing you to convincingly interpret, explain, and generalise from your findings.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Sample problem statement and research questions, sample theoretical framework, your theoretical framework, frequently asked questions about sample theoretical frameworks.
Your theoretical framework is based on:
- Your problem statement
- Your research questions
- Your literature review
To investigate this problem, you have zeroed in on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
- Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
- Research question : How can the satisfaction of the boutique’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
The concepts of ‘customer loyalty’ and ‘customer satisfaction’ are clearly central to this study, along with their relationship to the likelihood that a customer will return. Your theoretical framework should define these concepts and discuss theories about the relationship between these variables.
Some sub-questions could include:
- What is the relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction?
- How satisfied and loyal are the boutique’s online customers currently?
- What factors affect the satisfaction and loyalty of the boutique’s online customers?
As the concepts of ‘loyalty’ and ‘customer satisfaction’ play a major role in the investigation and will later be measured, they are essential concepts to define within your theoretical framework .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Below is a simplified example showing how you can describe and compare theories. In this example, we focus on the concept of customer satisfaction introduced above.
Customer satisfaction
Thomassen (2003, p. 69) defines customer satisfaction as ‘the perception of the customer as a result of consciously or unconsciously comparing their experiences with their expectations’. Kotler and Keller (2008, p. 80) build on this definition, stating that customer satisfaction is determined by ‘the degree to which someone is happy or disappointed with the observed performance of a product in relation to his or her expectations’.
Performance that is below expectations leads to a dissatisfied customer, while performance that satisfies expectations produces satisfied customers (Kotler & Keller, 2003, p. 80).
The definition of Zeithaml and Bitner (2003, p. 86) is slightly different from that of Thomassen. They posit that ‘satisfaction is the consumer fulfillment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product of service itself, provides a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfillment.’ Zeithaml and Bitner’s emphasis is thus on obtaining a certain satisfaction in relation to purchasing.
Thomassen’s definition is the most relevant to the aims of this study, given the emphasis it places on unconscious perception. Although Zeithaml and Bitner, like Thomassen, say that customer satisfaction is a reaction to the experience gained, there is no distinction between conscious and unconscious comparisons in their definition.
The boutique claims in its mission statement that it wants to sell not only a product, but also a feeling. As a result, unconscious comparison will play an important role in the satisfaction of its customers. Thomassen’s definition is therefore more relevant.
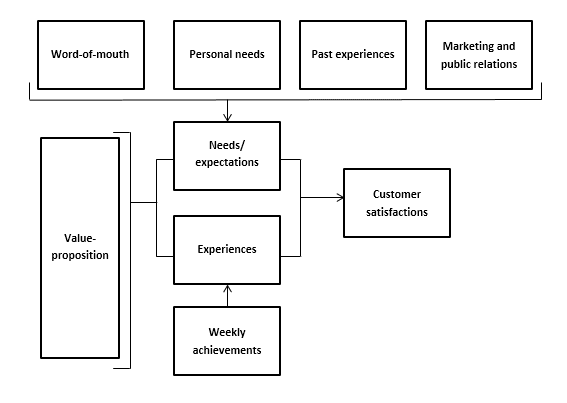
Thomassen’s Customer Satisfaction Model
According to Thomassen, both the so-called ‘value proposition’ and other influences have an impact on final customer satisfaction. In his satisfaction model (Fig. 1), Thomassen shows that word-of-mouth, personal needs, past experiences, and marketing and public relations determine customers’ needs and expectations.
These factors are compared to their experiences, with the interplay between expectations and experiences determining a customer’s satisfaction level. Thomassen’s model is important for this study as it allows us to determine both the extent to which the boutique’s customers are satisfied, as well as where improvements can be made.
Figure 1 Customer satisfaction creation
Of course, you could analyse the concepts more thoroughly and compare additional definitions to each other. You could also discuss the theories and ideas of key authors in greater detail and provide several models to illustrate different concepts.
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Vinz, S. (2022, October 10). Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/example-theoretical-framework/
Is this article helpful?
Sarah's academic background includes a Master of Arts in English, a Master of International Affairs degree, and a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science. She loves the challenge of finding the perfect formulation or wording and derives much satisfaction from helping students take their academic writing up a notch.
Other students also liked
What is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Introduction
Strategies for developing the theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Theoretical framework
The theoretical perspective provides the broader lens or orientation through which the researcher views the research topic and guides their overall understanding and approach. The theoretical framework, on the other hand, is a more specific and focused framework that connects the theoretical perspective to the data analysis strategy through pre-established theory.
A useful theoretical framework provides a structure for organizing and interpreting the data collected during the research study. Theoretical frameworks provide a specific lens through which the data is examined, allowing the researcher to identify recurring patterns, themes, and categories related to your research inquiry based on relevant theory.

Let's explore the idea of the theoretical framework in greater detail by exploring its place in qualitative research, particularly how it is generated and how it contributes to and guides your research study.
Theoretical framework vs. theoretical perspective
While these two terms may sound similar, they play very distinct roles in qualitative research . A theoretical perspective refers to the philosophical stance informing the methodology and thus provides a context for the research process. These perspectives could be rooted in various schools of thought like postmodernism, constructivism, or positivism, which fundamentally shape how researchers perceive reality and construct knowledge.
On the other hand, the theoretical framework represents the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. It presents a logical structure of connected concepts that help the researcher understand, explain, and predict how phenomena are interrelated. The theoretical framework can pull together various theories or ideas from different perspectives to provide a comprehensive approach to addressing the research problem.
Moreover, theoretical frameworks provide useful guidance as to which research methods are appropriate for your research project. If the theoretical framework you employ is relevant to individual perspectives and beliefs, then interviews may be more suitable for your research. On the other hand, if you are utilizing an existing theory about a certain social behavior, then ethnographic observations can help you more ably capture data from social interactions.
Later in this guide, we will also discuss conceptual frameworks , which help you visualize the essential concepts and data points in the context you are studying. For now, it is important to emphasize that these are all related but ultimately different ideas.
Example of a theoretical framework
Let's look at a simple example of a theoretical framework used to address a social science research problem. Consider a study examining the impact of social media on body image among adolescents. The theoretical perspective might be rooted in social constructivism, based on the assumption that our understanding of reality is shaped by social interactions and cultural context.
The theoretical framework, then, could draw on one or several theories to provide a comprehensive structure for examining this issue. For instance, it might combine elements of "social comparison theory" (which suggests that individuals determine their own social and personal worth based on how they stack up against others), "self-perception theory" (which posits that individuals develop their attitudes by observing their own behavior and concluding what attitudes must have caused it), and "cultivation theory" (which suggests that long-term immersion in a media environment leads to "cultivation", or adopting the attitudes and beliefs portrayed in the media).
This framework would provide the structure to understand how social media exposure influences adolescents' perceptions of their bodies, how they compare themselves to images seen on social media, and how these influences may shape their attitudes toward their own bodies.
Put your theories into focus with ATLAS.ti
Powerful data analysis to turn your data into insights and theory. Download a free trial today.
Other examples of theoretical frameworks
Let's briefly look at examples in other fields to put the idea of "theoretical framework" in greater context.
Political science
In a study investigating the influence of lobbying on legislative decisions, the theoretical framework could be rooted in the "pluralist theory" and "elite theory".
Pluralist theory views politics as a competition among groups, each one pressing for its preferred policies, while elite theory suggests that a small, cohesive elite group makes the most important decisions in society. The framework could combine these theories to examine the power dynamics in legislative decisions and the role of lobbying groups in influencing these outcomes.
Educational research
An educational research study aiming to understand the impact of parental involvement on children's academic success could employ a theoretical framework based on Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory and Epstein's theory of overlapping spheres of influence.

The ecological systems theory emphasizes the importance of multiple environmental systems on child development, while Epstein's theory focuses on the partnership between family, school, and community. The intersection of these theories allows for a comprehensive examination of parental involvement both in and outside of the school context.
Health services research
In a health services study exploring factors affecting patient adherence to medication regimes, the theoretical framework could draw from the health belief model and social cognitive theory.
The health belief model posits that people's beliefs about health problems, perceived benefits of action and barriers to action, and self-efficacy explain engagement in health-promoting behavior.
The social cognitive theory emphasizes the role of observational learning, social experience, and reciprocal determinism in behavior change. The framework combining these theories provides a holistic understanding of both personal and social influences on patient medication adherence.
Developing a theoretical framework involves a multi-step process that begins with a thorough literature review . This allows you to understand the existing theories and research related to your topic and identify gaps or unresolved puzzles that your study can address.
1. Identify key concepts: These might be the phenomena you are studying, the attributes of these phenomena, or the relationships between them. Identifying these can help you define the relevant data points to analyze.
2. Find relevant theories: Conduct a literature review to search for existing theories in academic research papers that relate to your key concepts. These theories might explain the phenomena you are studying, provide context for it, or suggest how the phenomena might be related. You can build off of one theory or multiple theories, but what is most important is that the theory is aligned with the concepts and research problem you are studying.
3. Map relationships: Outline how the theories you have found relate to one another and to your key concepts. This might involve drawing a diagram or writing a narrative that explains these relationships.
4. Refine the framework: As you conduct your research, refine your theoretical framework. This might involve adding new concepts or theories, removing concepts or theories that do not fit your data, or changing how you conceptualize the relationships between theories.
Remember, the theoretical framework is not set in stone. At the same time, it may start with existing knowledge, it is important to develop your own framework as you gather more data and gain a deeper understanding of your research topic and context.
In the end, a good theoretical framework guides your research question and methods so that you can ultimately generate new knowledge and theory that meaningfully contributes to the existing conversation around a topic.

Visualize your theories and analysis with ATLAS.ti
From literature review to research paper, ATLAS.ti makes the research process easier and more efficient. See how with a free trial.
Developing a Theoretical Framework and Rationale for a Research Proposal
- First Online: 01 January 2010
Cite this chapter

- Gregory M. Herek 4
7317 Accesses
4 Altmetric
It is useful to recall that our work as scientists will be at its best when it simultaneously tackles real-world problems and enriches our understanding of basic biological, psychological, or social processes. A good theory can help us do both. All empirical research is based on assumptions. Even purely “descriptive” or “exploratory” studies necessarily involve choices about the phenomena and variables to observe and the level of detail at which to observe them. Researchers planning an empirical study confront the challenges of making these assumptions explicit, examining them critically, and designing the investigation to yield data that permit those assumptions to be evaluated and modified appropriately. This is the process of theory construction. Unfortunately, although all research is based on theory, many grant proposals lack a well-developed theoretical rationale. The theoretical framework often remains implicit in the proposal without being formally articulated. Consequently, even though the application may be based on a good idea, it is conceptually weak and receives a poor priority/impact score. This chapter will give you a useful strategy for developing a clearly articulated theoretical framework for your research project and using it to write your entire research plan.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Arnold, E. M., Rice, E., Flannery, D., & Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2008). HIV disclosure among adults living with HIV. AIDS Care , 20 (1), 80–92.
Article Google Scholar
Capitanio, J. P., Abel, K., Mendoza, S. P., Blozis, S. A., McChesney, M. B., Cole, S. W., & Mason, W. A. (2008). Personality and serotonin transporter genotype interact with social context to affect immunity and viral set-point in simian immunodeficiency virus disease. Brain , Behavior, and Immunity , 22 (5), 676–689.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Cole, S. W. (2006). Social threat, personal identity, and physical health in closeted gay men. In A.M. Omoto & H.S. Kurtzman (Eds.), Sexual orientation and mental health: Examining identity and development in lesbian, gay, and bisexual people (pp. 245–267). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Google Scholar
Kurdek, L. A. (2008). Differences between partners from black and white heterosexual dating couples in a path model of relationship commitment. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships , 25 (1), 51–70.
Lewin, K. (1964). Problems of research in social psychology. In D. Cartwright (Ed.), Field theory in social science (pp. 155–169). New York: Harper and Row. (Original work published 1944).
O’Leary, A., Fisher, H. H., Purcell, D. W., Spikes, P. S., & Gomez, C. A. (2007). Correlates of risk patterns and race/ethnicity among HIV-positive men who have sex with men. AIDS and Behavior , 11 , 706–715.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Peplau, L. A., Garnets, L. D., Spalding, L. R., Conley, T. D., & Veniegas, R. C. (1998). A critique of Bem’s “Exotic Becomes Erotic” theory of sexual orientation. Psychological Review , 105 (2), 387–394.
Sears, D. O. (1986). College sophomores in the laboratory: Influences of a narrow data base on social psychology’s view of human nature. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 51 , 515–530.
Steward, W. T., Herek, G. M., Ramakrishna, J., Bharat, S., Chandy, S., Wrubel, J., & Ekstrand, M. L. (2008). HIV-related stigma: Adapting a theoretical framework for use in India. Social Science & Medicine , 67 (8), 1225–1235.
Stinchcombe, A. L. (1968). Constructing social theories . New York: Harcourt, Brace and World.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Preparation of this chapter was originally supported in part by a grant to the first author from the National Institute of Mental Health (K02 MH01455). The author gratefully acknowledges the assistance of Dr. William Woods, who gave insightful comments on an earlier draft.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, University of California at Davis (UCD), One Shields Avenue, Davis, CA, 95616, USA
Gregory M. Herek
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gregory M. Herek .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
National Institute of Mental Health, Executive Blvd. 6001, Bethesda, 20892-9641, Maryland, USA
Willo Pequegnat
Ellen Stover
Delafield Place, N.W. 1413, Washington, 20011, District of Columbia, USA
Cheryl Anne Boyce
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Herek, G.M. (2010). Developing a Theoretical Framework and Rationale for a Research Proposal. In: Pequegnat, W., Stover, E., Boyce, C. (eds) How to Write a Successful Research Grant Application. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1454-5_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1454-5_12
Published : 20 August 2010
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4419-1453-8
Online ISBN : 978-1-4419-1454-5
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Theoretical Framework: Research Writing Guide
In a thesis or dissertation, a theoretical framework is a section where the writer evaluates or discusses the most relevant theories to their study.
The purpose of this section is to:
- Define the key concepts
- Combine and evaluate relevant models and theories
- Explain expectations and assumptions that guide the project
The proper presentation of this information frames the research while justifying the approach taken by the writer. This section does this by showing the established ideas on which you ground your work.
Essentially, this section of a dissertation a foundation that supports the analysis that follows. It also allows the author to convincingly interpret their results and state or explain their relevance in a larger context.
When properly written, this section works like the software or buildings that provide critical support to the other aspects of the study. Writing a strong framework with a strong theoretical basis enhances investigations that lead to the achievement of specific study goals.
A well-written framework reduces a dreadful research topic into two basic concepts. These are:
- The study problem
- The rationale behind its investigation
When writing the framework section, focus on creating a piece that connects you with the existing knowledge via the guidance of relevant theories. Also, provide the basis of your hypothesis and your chosen research methods. A professional dissertation writer will help, if you’re in trouble.
What Is a Theoretical Framework?
- The Length of a Theoretical Framework
Theoretical or Conceptual Framework?
Types of theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework.
- Summary of a Theoretical Framework Sample
Just like the name suggests, this part of a dissertation or thesis is about theories. Researchers develop theories to draw connections, explain phenomena, and make predictions.
The simplest theoretical framework definition describes it as a collection of theories or interrelated concepts. It comprises concepts and their definitions, as well as, a reference to existing theory and scholarly literature that will be used in a particular study. Your content in this section of a thesis or dissertation must show your understanding of concepts and theories relevant to your research topic. It must also relate them to the considered broader field of knowledge.
- Some students confuse conceptual vs. theoretical framework. In some cases, learners use these terms interchangeably. But though these terms help readers understand the research problem while guiding the collection, as well as, analysis of information, they are different.
- According to the above definition of theoretical framework, it comprises concepts or theories relevant to a study. It highlights how the author will understand and investigate the research problem.
- On the other hand, a conceptual framework can include several formal theories partly or entirely, and other empirical findings and concepts from the field’s literature. The main difference between theoretical and conceptual framework is that the latter demonstrates the relationships among ideas and their relationship with the study.
- A conceptual framework is commonly used in qualitative research. Although some researchers use a theoretical framework in qualitative research, it is common in quantitative research. A conceptual framework is commonly used in qualitative research, especially in behavioral and social science studies.
The Length of a Theoretical Framework
The complexity and length of this section depend on the topic and study field. Some fields and topics have an obvious and well-established theoretical basis. Others need a more detailed justification and explanation.
Maybe you already know that you will apply a specific theory or several theories to your specific context. For instance, you may intend to use the social impact theory when conducting your market research. In that case, the main task is to discuss the main aspects of this theory and then convince the readers that it offers a solid basis that will enable you to answer the research question. It’s also crucial that you evaluate more theories, as long as, they are relevant to your study. Also, tell your readers why you’ve chosen that specific approach.
In some cases, authors draw on different theories and then combine ideas. This approach can lead to strong research. However, it may require more work because you have to implement the theories in your work.
Most theoretical framework examples range between three and five pages. However, no rules govern the length of this section of a dissertation. Nevertheless, try to keep yours within the range of 3-5 pages. This length is adequate for providing all the relevant information your reader wants to know about your chosen theories and assumptions.
Perhaps, you are torn between a theoretical and conceptual framework. Well, the best approach for deciding what to use in your paper is determining the kind of study you want to conduct. If you must use a theoretical framework in qualitative research, determine the theories you intend to use.
That’s because most types of theoretical framework in qualitative research are found in studies based on existing theories. For instance, you can use this framework when your study is based on motivation theory.
On the other hand, a conceptual framework is ideal for something you will develop based on a theory. Thus, you can use some or all concepts of this theory. Thus, you develop a conceptual framework to solve a problem for which you’re doing the study to find a solution.
At this point, you’re no longer asking, ‘what is theoretical framework?’ But, you most likely want to know the types of frameworks that you can consider for your research. Well, this framework provides a lens or a perspective via which you will examine your topic. And this perspective can be from any study field depending on your academic paper.
For instance, a nursing student can use a theoretical framework in nursing research as long as it defines the concepts while explaining the phenomena in question. However, learners can consider other categories and types of theoretical framework in research.
They include:
- Dynamic and sustainability framework
- Implementation results framework
- Theoretical domains validation framework
- Consolidated implementation research and theoretical domains framework
- Active research implementation framework
- Evaluation framework
The internet has many resources with examples of theoretical framework in qualitative research and quantitative research. Check them out before you use any framework in your research to know what it entails.
This article has already answered the question, ‘what is theoretical framework in research?’ It has also highlighted the types of this framework. But, how do you complete your theoretical framework research work?
Here is a guide for creating this framework for your research:
- Identify the main concepts : Start by picking the main terms of your research problem or research questions. Some concepts can have several definitions. Your framework should define what each concept means clearly. For instance, if concepts like “customer satisfaction” and “customer loyalty” are central to your study, define them and discuss theories that explain their relationship.
- Explain and evaluate relevant theories : Engage in an extensive literature review to find out the definition of the connections between theories and concepts by other researchers. As you compose your framework, focus on critically evaluating different approaches and comparing them. Establish the most appropriate definitions for your research after discussing different theories and models. Mention all important concepts that are connected to the theories that you discuss in your framework. Explain why you choose a well-established theory for your study and what makes it the most suitable for that purpose. If unsure about the best way to do this, check a theoretical framework example online first.
- Demonstrate how your study fits in : In addition to discussing theories by other people, your framework should demonstrate how your project will implement these ideas. That means you have to test whether your chosen theory holds in your specific context. Also, use this theory to interpret the findings of your study. It’s also crucial to challenge or critique the theory. What’s more, combine various theories in a unique or new way. If possible and relevant, use your framework to come up with your research hypothesis.
- Structure your framework : When writing a dissertation or a thesis paper, you can integrate your framework in the literature review chapter. However, you can have it as a separate section or chapter of your paper. If you will be dealing with several complex theories in your paper, have a separate chapter or section for the framework. Nevertheless, you don’t have to follow specific, fixed rules when it comes to structuring the research theoretical framework section. But, your framework should have a logical, clear structure. For instance, you can draw on your study problems or questions and then structure every section around a major concept or question.
These tips should guide you in writing a framework with the theories or concepts you intend to use in your thesis or dissertation. However, you can apply them differently depending on the nature of your study. For instance, a business paper framework may not be the same as a nursing theoretical framework because these are different study fields. However, the concept of creating this framework is the same.
Summary of a Theoretical Framework Sample
For some researchers, an ideal approach is to define theoretical framework. However, some researchers assume the reader already knows what this framework is all about. As such, they go straight to the details. Below is a summary of a theoretical framework in research example.
Company Y wants to resolve the problem of having many customers buy its products online without returning for subsequent purchases. As such, the company management is looking for ways to enhance customer loyalty, hoping that better customer satisfaction will lead to the achievement of this goal.
In your research, you have developed a problem statement, research question, and research question as follows:
- Research problem : Most online buyers do not come back for subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To boost customer loyalty hoping to increase revenue through online sales
- Research questions : How can company Y improve the satisfaction of online customers to enhance customer loyalty?
Your framework should focus on answering these questions:
- Is there a relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty?
- How loyal and satisfied are the online customers of company Y currently?
- What are some of the factors affecting the loyalty and satisfaction of the online customers of company Y?
Customer satisfaction and customer loyalty are major concepts that play a role in such a research paper. Therefore, they should be investigated and measured using theories or concepts that should be featured in the framework.
The information contained in this framework could be different from that of a theoretical framework nursing educators expect. That’s because this framework is meant for a business-oriented research paper. Nevertheless, the approach for writing both frameworks is the same.
The framework section of a thesis or dissertation paper clarifies implicit theories or concepts in a clearly defined manner. It also shows how they connect to the current research and why they are suitable for it. Your academic supervisor will most likely check this section first. Therefore, understanding its purpose and how to write it properly is very important.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Chapter 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
Designing the Theoretical Framework
Theoretical framework guide, making a theoretical framework, example framework, additional framework resources.
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
What is it?
- A foundational review of existing theories.
- Serves as a roadmap or blueprint for developing arguments and supporting research.
- Overview of the theory that the research is based on.
- Can be made up of theories, principles, and concepts.
What does it do?
- Explains the why and how of a particular phenomenon within a particular body of literature.
- Connects the research subject with the theory.
- Specifies the study’s scope; makes it more valuable and generalizable.
- Guides further actions like framing the research questions, developing the literature review, and data collection and analyses.
What should be in it?
- Theory or theories that the researcher considers relevant for their research, principles, and concepts.
- Theoretical Framework Guide Use this guide to determine the guiding framework for your theoretical dissertation research.
How to make a theoretical framework
- Specify research objectives.
- Note the prominent variables under the study.
- Explore and review the literature through keywords identified as prominent variables.
- Note the theories that contain these variables or the keywords.
- Review all selected theories again in the light of the study’s objectives, and the key variables identified.
- Search for alternative theoretical propositions in the literature that may challenge the ones already selected.
- Ensure that the framework aligns with the study’s objectives, problem statement, the main research question, methodology, data analysis, and the expected conclusion.
- Decide on the final framework and begin developing.
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation This link offers an example theoretical framework.
Some additional helpful resources in constructing a theoretical framework for study:
- https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework/
- https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework-example/
- https://www.projectguru.in/how-to-write-the-theoretical-framework-of-research/
Theoretical Framework Research
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). A theoretical framework provides the theoretical assumptions for the larger context of a study, and is the foundation or ‘lens’ by which a study is developed. This framework helps to ground the research focus understudy within theoretical underpinnings and to frame the inquiry for data analysis and interpretation. The application of theory in traditional theoretical research is to understand, explain, and predict phenomena (Swanson, 2013).
Casanave, C.P.,& Li,Y.(2015). Novices’ struggles with conceptual and theoretical framing in writing dissertations and papers for publication. Publications,3 (2),104-119.doi:10.3390/publications3020104
Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House. ” Administrative Issues Journal: Connecting Education, Practice, and Research, 4(2), 12–26
Swanson, R. (2013). Theory building in applied disciplines . San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
- << Previous: Conceptual Framework
- Next: Quantitative Research Questions >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- Hege Research Award
- Quaker Archives
- Art Gallery
- Student Support
- Teaching & Learning
- Reserving spaces
- Technology Lending
- Interlibrary Loan
- Course Reserves
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Poster Printing
- Virtual Reference
- Research Guides
- Off-campus access
- Digital Scholarship
- Guilford Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- Quaker Collections
- Digital Collections
- College Archives
- Underground Railroad
- Universities Studying Slavery
- Images & Exhibitions
Service Alert

Hege Library & Learning Technologies
Guide for Thesis Research
- Introduction to the Thesis Process
- Project Planning
- Literature Review
- Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology
- GC Honors Program Theses
- Thesis Submission Instructions This link opens in a new window
- Accessing Guilford Theses from 1898 to 2020 This link opens in a new window
Some Articles About Theory
The following are articles that may help you understand the importance of theory as a fundamental aspect of academic research.
- It's Just a Theory
- Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions
- Use of Theoretical Frameworks in Research
Why is theory important?

Theories reflect previous study and analysis that has been conducted in your field. They propose explanations for phenomena that occur in an area of study. Over time, theories are reexamined, refined, and sometimes discarded in favor of new ones, always with the purpose of providing ever more accurate explanations for the dynamics that operate in our world.
The following quote, taken from John Kuada's book Research Methodology: A Project Guide for University Students , helps to explain the importance of theory when developing a research project:
“Theory provides the language, the concepts, and assumptions that help researchers to make sense of the phenomenon that they seek to investigate. It enables researchers to connect the issues they are investigating to the existing body of knowledge in the area” (Kuada, 2012, p. 64).
A theory can help researchers make predictions about the phenomena they are setting out to study. They can be informative in terms of determining what variables should be observed, as well as how data should be collected, analyzed, and interpreted on the way to presenting and justifying conclusions.
As a researcher working on a project, it is essential that you be aware of theories that have gained prominence in your field. Think of scholarship as an ongoing conversation. As people publish ideas and develop theories, they help shape that conversation. When you do research and present your findings and ideas, you are joining in on those discussions. You become a contributor. Therefore, it is good to have a sense of what has been said before.
Identify major theories in your field. Be conscious of the fundamental concepts that have guided scholars in your area, and be aware of emerging perspectives and trends. Try to identify a theoretical base from which you can develop your arguments. This will greatly strengthen your positions when the time comes to present your thesis.
Resources About Theory and Theoretical Frameworks

- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Research Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 4:31 PM
- URL: https://library.guilford.edu/thesis-guide

Eureka! When I learnt how to write a theoretical framework
Feb 6, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Have you ever had a eureka moment? A moment where something that you’ve misunderstood for ages becomes crystal clear?
I did, about half way through my PhD.
Did I come up with a ground breaking discovery that would revolutionise my field? Did I develop a new theory that would change the way we think about the world?
I finally understood how to write a theoretical framework.
Sound silly? It isn’t.
During the one-on-one PhD coaching sessions I run, the issue of how to write a theory framework comes up more frequently than any other. The theoretical framework is important, but many people find it difficult. I know I struggled with it.
Then someone explained the theory framework to me in such a simple way. Here’s the eureka moment: The theoretical framework is like a toolbox.
Simple, right?
Let me explain. In the literature review you highlighted the problem that needs ‘fixing’. The theoretical framework – the ’toolbox’ – details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you’re using them) and concepts – the ’tools’ – that you will use to address or make sense of this problem.
So, your job in a theoretical framework chapter is to discuss in detail what the tools look like, how they behave, how they have been used before, how they relate to one another, how they are relevant to your aims and objectives and what the drawbacks are from using them. The methods chapter then discusses how you will use (operationalise) those tools.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
What is a theoretical framework?
In the literature review you highlighted the problem that needs ‘fixing’. The theoretical framework – the ’toolbox’ – details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you’re using them) and concepts – the ’tools’ – that you will use to address or make sense of this problem.
The list of potential explanations for why responses differ is enormous.
You could approach this question with a focus on, say, psychology, power, gender, economics, and so on. The best we can typically hope for – and this is particularly true in much of the social sciences – is an interpretation of the truth.
So – and this is important – we use theory to focus our attention on a small sub-set of all potential explanations, on one particular viewpoint.
Now I know I’m getting into messy epistemological and ontological waters here. I am an interpretivist, so I see theory as a ‘lens’ that you apply to make sense of the world. That’s the shape of my toolbox.
But, even if you’re a positivist you still pick and choose theoretical concepts and hypotheses from a range of available options; you just use them in a different way (rather than a lens, they become testable propositions, or measurement tools).
Without a theoretical framework we are left with a potentially endless choice of potential viewpoints, which would make our data collection and analysis and our discussion hugely chaotic.

Master your lit review & theory framework.
Learn what goes where (and why), and how it all fit together with this free, interactive guide to the PhD literature review and theory framework.
In other words, if we don’t know how to focus our attention, how we can present a coherent explanation?
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of the literature review. The purpose of the literature review, amongst other things, is to highlight gaps and shortcomings with the existing work in your field.
The theoretical framework details the perspective you will take to address that gap and shortcoming.
For example, in my doctoral research, my literature review focused on government responses to climate change and pointed out that there hadn’t been much discussion on local government.
The theoretical framework then made an informed decision to come at it from a particular theoretical perspective (institutional theory, if you’re interested) and then discussed what that theory looks like, highlighting the key concepts and ideas.
In your own research you will also need to make an informed decision about the particular theory you will employ to guide you through the rest of the research.
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of the literature review. The purpose of the literature review, amongst other things, is to highlight gaps and shortcomings with the existing work in your field. The theoretical framework details the perspective you will take to address that gap and shortcoming.
So, the job of the theoretical framework isn’t to repeat the literature review . Instead, think of it as a separate, mini literature review , this time focusing on the theory you will employ. You don’t have to discuss every particular use and discussion of the theoretical position you employ. If you did, you’d quickly run out of space and time.
Remember, your examiners are likely to already be familiar with the theory, meaning that rather than discuss every possible thing that there is to discuss about it, you instead need to discuss how and why the theory has been adapted and adopted to the context of your research.
How to structure a theoretical framework
- You need to have a solid grasp of your aims and objectives. These define the space in which your research will sit and your goals when conducting it. You will need to briefly recap these when you start writing your theoretical framework, both to remind the reader and so that you can relate your theory to these overarching aims.
- What theory/theories are you using? Here you need to define and explain each theory you draw upon and, in doing so, discuss the leading proponents and applications. This shows that you understand the theory you are going to adopt.
- You then need to spend time critically arguing why you are adopting this particular theory. There are a lot of potential theories you could use. Why this one? Importantly, you should relate your choice to the discussions in the literature review and your aims and objectives.
- Can the theory/theories be broken down into different schools? Which one are you siding with and why?
- A theory contains a number of concepts. Which will you be drawing upon? Why these ones? Have you defined them properly? The way you approach this section will be influenced by your epistemological and ontological perspective and, thus, whether you use hypotheses or not. If you are using hypotheses, you need to state them as such.
- How do the concepts relate to your aims and objectives?
- Have you clearly stated your ontological and epistemological perspective?
- Are you the first to use this particular theory in this particular way? What benefits or drawbacks does that bring?
- Can you spot any drawbacks with applying this theory? Does it fail to account for a particular dimension of a phenomenon? Is it difficult to operationalize?
- How are your concepts related? Are you using them as hypotheses? Or as a model to make sense of the data? Somewhere in between? Be explicit about how they are all related and what you plan on doing with them.

The goal of writing up a theoretical framework is to tell the reader why you have chosen particular theories, how they relate to the gap in the literature, and how they relate to your aims and objectives.
A short (but necessary) note on ontology and epistemology
How do i choose theories and create my framework.
Unless you are using an inductive methodological approach (where you generate theory from the data), you will likely approach your fieldwork with a theoretical framework in mind. Which theory or theories you choose is, in part, down to your aims and objectives and whether there is a relevant theory available ‘off-the-shelf’ that is appropriate for your needs.
There are generally three strategies that researchers use to develop their theoretical frameworks:
- There may be theories in your field that have arisen on the basis of repeated observation and testing and which are widely accepted.
- Or, you might find that you need to select concepts from multiple theories and create a novel framework that is unique to your particular context.
- A growing and important trend in social research is to adopt an interdisciplinary perspective when trying to understand the social world. This can be achieved by looking beyond the dominant, well-established theories and thinking about how other theories, particularly those from other disciplines or sub-disciplines, can be used.
In any case, you must consider the following when selecting a theory:
- Identify your ontological and epistemological beliefs.
- List several theories that align with your epistemological position and which can aid your understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
- Engage in literature review around those theories, both to familiarise yourself with them but also to understand their relevance to your study.
- Ask yourself how each theory connects to your problem, aims & objectives.
- Select the theory or theories that provide more relevant tools for your thesis.
I have more than one theory. What do I do?
Often, you need to combine concepts, hypotheses or ideas from more than one theoretical school. Employing more than one theory is entirely legitimate. I did so in my PhD.
However, you need to consider a few key questions :
Are the theories you are bringing together epistemologically compatible?
Have you discussed each theory in the same level of detail to adequately explain the theory, your justification for its inclusion, its relation to the literature and its potential drawbacks?
What benefits does focusing on more than one theory bring? Perhaps one theory has shortcomings that the other addresses?
What downsides are there to employing more than one theory?
Has anyone else used this combination of theories before you?
The theoretical framework is a tricky section to write, largely because the choice available to you is huge.
But keep that toolbox metaphor in mind.
Each theory contains a number of tools. Your job in the theory framework is to take the tools you need for your project from the most relevant theory/theories and package them up into your own toolbox.
When you’re done, you should see that the theory framework offers:
- Structure, by detailing the key concepts, tools and, where relevant, hypotheses
- A way to connect to other research
- A coherent, joined up set of ideas that structure the writing and help to create an argumentative streak that can run throughout your thesis
- An approach that can be reused in additional contexts once you’re done
Along the way, you need to convince the reader that you’ve picked and applied the most appropriate tools possible, given your aims and objectives.
The theoretical framework frames the research. If you build that frame right, your research will shine. If you don’t then you’ll struggle.
If you need expert guidance to structure, plan or write your theory framework you can get in touch for a one-on-one coaching session . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.
Share this:
67 comments.
A great read. Quite some insight into my Phd journey. The conceptual framework?
Glad you found it useful. You having trouble with your conceptual framework?
This is enlightening. I was struggling with my Theoretical framework. I will apply the guidelines here and await feedback from my supervisor. Thanks
I’m glad you found the post useful. Thanks for your kind words.
I came across your posts while helping my wife with her work (I finished my PhD two years ago), and I keep thinking…hmmm the pain I went through to learn this… thank you for making it so easy for others…
Thanks for the kind words. I remember how difficult I found my own PhD, so my motivation is to make life easier for as many other PhD students as possible.
i need some more clear version to develop a theoretical framework. kindly contact me through email. thank you
Great insights. I have read through your thesis. You did a lot of quality work. I see the EM, Environmental Policy Capacity and the institutions theory all discussed. Really detailed and linked. Let me see how mine goes
I’ve sent you an email. I’d be glad to help.
This is very helpful because am really struggling to write my theoretical section. I have a question, I selected a framework but realised it has shortcomings, so I decided to include a model, but also I have another theory. All the three are confusing me how to structure them please I need your help. Thanks
Hi Carolyne,
Thanks for your email. Do you want to have a one-on-one coaching session with me? We’ll be able to get to the bottom of your confusion and clear up your theory problems once and for all. Click here for more details and to book yourself in.
Do you have a structured outline, similar to the overall diss outline, for the theoretical framework?
I sure do. You can find it here: https://www.thephdproofreaders.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Theoretical-Framework-Template_AW_20190208.pdf
What are the advantages of having a chapter on theoretical framework independent of the Literature Review chapter. Please assist.
Thanks for your comment. Whether or not you need a separate literature review and theory framework chapter depends on how distinct they are from one another and on how complex each chapter is. It may be the case that you need two chapters because to discuss both in one would make the chapter very large, complex and hard to follow. Also, it is often the case that the theory framework builds on and addresses gaps you’ve highlighted in your literature review, so for that reason it makes sense to keep them as two separate chapters.
But which one comes first? I thought theoretical framework comes earlier than literature review or is it in a proposal where it is structured that way?
Typically the lit review comes first, then the theory. The lit review makes the case for the research and the theory framework shows the approach you will take to conduct the research.
Thanks for the kind words 🙂
Dear Max, I am using multiple related concepts to frame my research. I am confused whether to dedicate a complete chapter to explain only these five concepts, or just operationalise them in one of the chapters. Again, is introducing these concepts early in my introductory chapter a good idea as it forms one of my research questions. This means I have answered the question in the introductory chapter
Thanks for your comment. Whether or not such concepts end up in your introduction/context discussion will depend in part on whether they are framing your research (as in, providing the background or context) or whether you’re using them to answer your research questions (in which case they’ll form part of your theory framework and will therefore come at a later stage).
Dear Max, I was searching how to structure Theoretical framework and came across your writing. Thank you for this, it is really helpful. I’m one of those phd students who struggles with Theoretical framework :/ I would appreciate your help if possible. Could you please outline, how can I reach you?
Thanks for your kind words. I’m glad you’re finding the phD Knowledge Base useful. You can reach me at max[at]thephdproofreaders.com
Speaks soon!
I’m so confused about my theoretical framework. Could you possibly help please?
Sure. Have you checked out the one-on-one PhD coaching service we offer? It sounds just that’s just what you need.
I couldn’t express how grateful I am. MAY YOU BE SHOWERED WITH BLESSINGS
Thanks! I’m glad you found the advice useful.
wow!!! thank you very much , I have been struggling to write my theoretical framework . thank you.
You’re welcome!
Dr. Max I am expecting to learn more on how to pick the right literatures, related to my theme. all of them seem very nice and informative. I am having hard time to select them. and also I have difficulties in starting the sentence of my Introduction. I am researching on “the impact of Prosperity gospel in Tanzanian mainline churches”. my topic is very popular and many has been said … I feel like I am saying what has been said .
Thanks for your comment. I wish you the best of luck.
Hi Max, Great read. Doing my MA Thesis after years away from academia has been a challenge to say the least. Your article provided clarity that I have been asking for/seeking elsewhere (supervision/consultant) for months. Wish I had of found it earlier but glad I came across it.
Thank you and all the best in these uncertain times.
Great! Glad you’re finding the resources useful. Good luck with the rest of the thesis.
Dear Max, thank you very much, many things got clear after reading this. I have a question, I am using political capability approach as my theoretical foundation which is part of RBW theory. So technically it is not a theory but just an approach, so does this indirectly mean that I am USING RBW Theory? Many Thanks
Hi – glad you found it useful. Without knowing more about your project I’m afraid I can’t advise about your choice of theory framework. Have you approached your supervisor with this question?
This is a very helpful article.
Glad you enjoyed it!
This has been one of the best articles that has clearly outlined the Theoretical framework. Kindly do a Youtibe video for auditory learners with real examples. It will greatly assist me especiall. I am glad I found this article.
Thanks for the kind words and for your feedback. I’ll take it on board for future guides.
Thanks so much for this which has helped me with a sticky bit as I move forward to discover new theoretical concepts from slightly outside my field that fit better than those I started out with. A part-time PhD has such a long life that it leaves too much room for changes and adaptations! A big thank you to Rebecca Baker on a Shut Up and Write Session who referred me to this!
I’m glad you found the guide useful. Thanks to you and to Rebecca Baker!
I found this post very helpful, thanks for sharing
Thanks for reading!
Thank you for this crisp advice on Theoretical framework. personally i have been experiencing difficulties selecting appropriate theory related to the study. However your advice was really beneficial. God bless you for your kindness towards us researchers.
Thanks for the kind words Roshni.
Thank you so much for sharing this information regarding the theoretical framework. I revisited my chapter and strengthened it based on the pointers you outlined here. This is a must read before drafting the chapter. Very helpful ?
Thanks for the kind words. I’m glad you found it useful.
This came just in time! I’m taking a research philosophy course and this week’s discussion is “Theory and Theoretical Frameworks”. I found this very helpful.
Great. I hope it helped deepen your understanding.
Thank you Dr Lempriere for this insightful article. I have just started my PhD journey and I found this article to be very useful and eye-opening.
Interesting and excellent read.
Thank you so very much for sharing your intellectual insights on this.
Hi this is really useful thank you. I have a question regarding one of my tools. I realise (quite late) that I am using one tool in a *generalised* way. I could put this another way – the context in which I found this tool constituted a more particular use of this more general tool, and I am seeking to retrieve it for a more general use. This opens the question – on what grounds am I employing a generalised form of this tool? What constraints govern this process of generalisation? Etc. I wish I’d dealt with this earlier… Do you have any thoughts on how I navigate this?
Hi – I’d love to give you advice, but without knowing more about your research and thesis any advice I would give wouldn’t be qualified. Sorry I can’t be of more help.
I loved your explanation, but what if you ARE doing an inductive project?
I found your article very useful, thank you! I am currently building a Foucauldian theoretical framework through which to discuss a phenomena (“Karens”).
Do you any academic articles which I can use to justify using the interpretavist approach (using theory as a lens)? I cant find anything through my searches.
Hi – sorry, we don’t I’m afraid.
Surely, this is a great lesson offered. How I pray I had your email, I would love to learn more from you. Thank you
Been struggling with my Phd and literature review . This has been very helpful. Is it possible for you to share your email so i can engage more with you and get some insights and help
Really really helpful guide, I am so grateful to you for providing this! It is helping me immensely in developing my own framework, a task which previously seemed scary, confusing and impossible!
Thanks for this. It is very useful. So should I first write my Lit review and then only the theoretical framework? TIA
Thanks! It’s hard to say without knowing more about your project, I’m afraid!
Thank you for the wonderful work. I want to know if theoretical frame work can presented in a diagram form
You’re welcome! Yes, your theory framework can be presented visually. It’s a great way of showing the framework in a clean, simplified way. It also serves as a useful reference guide for people to easily refer back to if they want to remind themselves of what your theory framework looks like.
I found your article highly informative. I recently enrolled for my PhD and my supervisor asked me to submit my Research outline. Does the outline have to have that detailed Theoretical framework. Again how best can I choose the theoretical framework suitable for my topic. If I may have a list of Theoretical frameworks I will be happy. I will also be grateful to have a direct contact with you.
A great insight into how to write a theoretical framework, simple and jargon free, the article makes the purpose and the method of writing the chapter explicit. Thank you.
That’s so kind of you Sethu. I’m glad you found it useful.
i WOULD LIKE TO KNOW WHAT IS THE IDEAL PLACE TO SITUATE THE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK WITHIN THE LITERATURE REVIEW? Peter Nemaenzhe
The theory/conceptual framework is often its own chapter between the lit review and methods. Sometimes though you can include it in the literature review, but I would suggest including it towards the end. I.e. do the lit review first, then introduce the theory framework.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Theoretical Framework
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge, within the limits of the critical bounding assumptions. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework introduces and describes the theory which explains why the research problem under study exists.
Importance of Theory
A theoretical framework consists of concepts, together with their definitions, and existing theory/theories that are used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that will relate it to the broader fields of knowledge in the class you are taking.
The theoretical framework is not something that is found readily available in the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research literature for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways .
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to move from simply describing a phenomenon observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you to identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest. It alerts you to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
By virtue of its application nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges of a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Drafting an Argument . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Strategies for Developing the Theoretical Framework
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm on what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, what factors contribute to the presumed effect?
- Review related literature to find answers to your research question.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review the key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory or theories that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint (framework) that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered, understanding concepts and variables according to the given definitions, and building knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To the end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.*
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Way of telling us that certain facts among the accumulated knowledge are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
*Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
Structure and Writing Style
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, you are expected to test the validity of an existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism theory, which categorizes perceived differences between nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the growing split between southern and northern Sudan that may likely lead to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Given this, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as the answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [I could choose to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among Ethnic Conflict Theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
In writing this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks , concepts, models, or theories . There will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the framework you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitiations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory does not explain a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research. Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Writing Tip
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Elsewhere
A growing and increasingly important trend in the social sciences is to think about and attempt to understand specific research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories you've read about in a particular class, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbants in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be fully engaged in the research topic.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Undertheorize!
Never leave the theory hanging out there in the Introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you introduce should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the analysis and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose fit the research problem, or if appropriate, was inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.
Still Another Writing Tip
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in everyday use. However, the difference between them in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested hypotheses that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis . About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis . Slideshare presentation.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 4: Theoretical frameworks for qualitative research
Tess Tsindos
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Describe qualitative frameworks.
- Explain why frameworks are used in qualitative research.
- Identify various frameworks used in qualitative research.
What is a Framework?
A framework is a set of broad concepts or principles used to guide research. As described by Varpio and colleagues 1 , a framework is a logically developed and connected set of concepts and premises – developed from one or more theories – that a researcher uses as a scaffold for their study. The researcher must define any concepts and theories that will provide the grounding for the research and link them through logical connections, and must relate these concepts to the study that is being carried out. In using a particular theory to guide their study, the researcher needs to ensure that the theoretical framework is reflected in the work in which they are engaged.
It is important to acknowledge that the terms ‘theories’ ( see Chapter 3 ), ‘frameworks’ and ‘paradigms’ are sometimes used interchangeably. However, there are differences between these concepts. To complicate matters further, theoretical frameworks and conceptual frameworks are also used. In addition, quantitative and qualitative researchers usually start from different standpoints in terms of theories and frameworks.
A diagram by Varpio and colleagues demonstrates the similarities and differences between theories and frameworks, and how they influence research approaches. 1(p991) The diagram displays the objectivist or deductive approach to research on the left-hand side. Note how the conceptual framework is first finalised before any research is commenced, and it involves the articulation of hypotheses that are to be tested using the data collected. This is often referred to as a top-down approach and/or a general (theory or framework) to a specific (data) approach.
The diagram displays the subjectivist or inductive approach to research on the right-hand side. Note how data is collected first, and through data analysis, a tentative framework is proposed. The framework is then firmed up as new insights are gained from the data analysis. This is referred to as a specific (data) to general (theory and framework) approach .
Why d o w e u se f rameworks?
A framework helps guide the questions used to elicit your data collection. A framework is not prescriptive, but it needs to be suitable for the research question(s), setting and participants. Therefore, the researcher might use different frameworks to guide different research studies.
A framework informs the study’s recruitment and sampling, and informs, guides or structures how data is collected and analysed. For example, a framework concerned with health systems will assist the researcher to analyse the data in a certain way, while a framework concerned with psychological development will have very different ways of approaching the analysis of data. This is due to the differences underpinning the concepts and premises concerned with investigating health systems, compared to the study of psychological development. The framework adopted also guides emerging interpretations of the data and helps in comparing and contrasting data across participants, cases and studies.
Some examples of foundational frameworks used to guide qualitative research in health services and public health:
- The Behaviour Change Wheel 2
- Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) 3
- Theoretical framework of acceptability 4
- Normalization Process Theory 5
- Candidacy Framework 6
- Aboriginal social determinants of health 7(p8)
- Social determinants of health 8
- Social model of health 9,10
- Systems theory 11
- Biopsychosocial model 12
- Discipline-specific models
- Disease-specific frameworks
E xamples of f rameworks
In Table 4.1, citations of published papers are included to demonstrate how the particular framework helps to ‘frame’ the research question and the interpretation of results.
Table 4.1. Frameworks and references
As discussed in Chapter 3, qualitative research is not an absolute science. While not all research may need a framework or theory (particularly descriptive studies, outlined in Chapter 5), the use of a framework or theory can help to position the research questions, research processes and conclusions and implications within the relevant research paradigm. Theories and frameworks also help to bring to focus areas of the research problem that may not have been considered.
- Varpio L, Paradis E, Uijtdehaage S, Young M. The distinctions between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework. Acad Med . 2020;95(7):989-994. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000003075
- Michie S, van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci . 2011;6:42. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-6-42
- CFIR Research Team. Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR). Center for Clinical Management Research. 2023. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://cfirguide.org/
- Sekhon M, Cartwright M, Francis JJ. Acceptability of healthcare interventions: an overview of reviews and development of a theoretical framework. BMC Health Serv Res . 2017;17:88. doi:10.1186/s12913-017-2031-8
- Murray E, Treweek S, Pope C, et al. Normalisation process theory: a framework for developing, evaluating and implementing complex interventions. BMC Med . 2010;8:63. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-8-63
- Tookey S, Renzi C, Waller J, von Wagner C, Whitaker KL. Using the candidacy framework to understand how doctor-patient interactions influence perceived eligibility to seek help for cancer alarm symptoms: a qualitative interview study. BMC Health Serv Res . 2018;18(1):937. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3730-5
- Lyon P. Aboriginal Health in Aboriginal Hands: Community-Controlled Comprehensive Primary Health Care @ Central Australian Aboriginal Congress; 2016. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://nacchocommunique.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/cphc-congress-final-report.pdf
- Solar O., Irwin A. A Conceptual Framework for Action on the Social Determinants of Health: Social Determinants of Health Discussion Paper 2 (Policy and Practice); 2010. Accessed February 22, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241500852
- Yuill C, Crinson I, Duncan E. Key Concepts in Health Studies . SAGE Publications; 2010.
- Germov J. Imagining health problems as social issues. In: Germov J, ed. Second Opinion: An Introduction to Health Sociology . Oxford University Press; 2014.
- Laszlo A, Krippner S. Systems theories: their origins, foundations, and development. In: Jordan JS, ed. Advances in Psychology . Science Direct; 1998:47-74.
- Engel GL. From biomedical to biopsychosocial: being scientific in the human domain. Psychosomatics . 1997;38(6):521-528. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(97)71396-3
- Schmidtke KA, Drinkwater KG. A cross-sectional survey assessing the influence of theoretically informed behavioural factors on hand hygiene across seven countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1432. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11491-4
- Graham-Wisener L, Nelson A, Byrne A, et al. Understanding public attitudes to death talk and advance care planning in Northern Ireland using health behaviour change theory: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:906. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13319-1
- Walker R, Quong S, Olivier P, Wu L, Xie J, Boyle J. Empowerment for behaviour change through social connections: a qualitative exploration of women’s preferences in preconception health promotion in the state of Victoria, Australia. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1642. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-14028-5
- Ayton DR, Barker AL, Morello RT, et al. Barriers and enablers to the implementation of the 6-PACK falls prevention program: a pre-implementation study in hospitals participating in a cluster randomised controlled trial. PLOS ONE . 2017;12(2):e0171932. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171932
- Pratt R, Xiong S, Kmiecik A, et al. The implementation of a smoking cessation and alcohol abstinence intervention for people experiencing homelessness. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1260. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13563-5
- Bossert J, Mahler C, Boltenhagen U, et al. Protocol for the process evaluation of a counselling intervention designed to educate cancer patients on complementary and integrative health care and promote interprofessional collaboration in this area (the CCC-Integrativ study). PLOS ONE . 2022;17(5):e0268091. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0268091
- Lwin KS, Bhandari AKC, Nguyen PT, et al. Factors influencing implementation of health-promoting interventions at workplaces: protocol for a scoping review. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275887. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275887
- Wilhelm AK, Schwedhelm M, Bigelow M, et al. Evaluation of a school-based participatory intervention to improve school environments using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1615. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11644-5
- Timm L, Annerstedt KS, Ahlgren JÁ, et al. Application of the Theoretical Framework of Acceptability to assess a telephone-facilitated health coaching intervention for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275576. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275576
- Laing L, Salema N-E, Jeffries M, et al. Understanding factors that could influence patient acceptability of the use of the PINCER intervention in primary care: a qualitative exploration using the Theoretical Framework of Acceptability. PLOS ONE . 2022;17(10):e0275633. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275633
- Renko E, Knittle K, Palsola M, Lintunen T, Hankonen N. Acceptability, reach and implementation of a training to enhance teachers’ skills in physical activity promotion. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1568. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09653-x
- Alexander SM, Agaba A, Campbell JI, et al. A qualitative study of the acceptability of remote electronic bednet use monitoring in Uganda. BMC Public Health . 2022;22:1010. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-13393
- May C, Rapley T, Mair FS, et al. Normalization Process Theory On-line Users’ Manual, Toolkit and NoMAD instrument. 2015. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://normalization-process-theory.northumbria.ac.uk/
- Davis S. Ready for prime time? Using Normalization Process Theory to evaluate implementation success of personal health records designed for decision making. Front Digit Health . 2020;2:575951. doi:10.3389/fdgth.2020.575951
- Durand M-A, Lamouroux A, Redmond NM, et al. Impact of a health literacy intervention combining general practitioner training and a consumer facing intervention to improve colorectal cancer screening in underserved areas: protocol for a multicentric cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health . 2021;21:1684. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11565
- Jones SE, Hamilton S, Bell R, Araújo-Soares V, White M. Acceptability of a cessation intervention for pregnant smokers: a qualitative study guided by Normalization Process Theory. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1512. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09608-2
- Ziegler E, Valaitis R, Yost J, Carter N, Risdon C. “Primary care is primary care”: use of Normalization Process Theory to explore the implementation of primary care services for transgender individuals in Ontario. PLOS ONE . 2019;14(4):e0215873. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0215873
- Mackenzie M, Conway E, Hastings A, Munro M, O’Donnell C. Is ‘candidacy’ a useful concept for understanding journeys through public services? A critical interpretive literature synthesis. Soc Policy Adm . 2013;47(7):806-825. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9515.2012.00864.x
- Adeagbo O, Herbst C, Blandford A, et al. Exploring people’s candidacy for mobile health–supported HIV testing and care services in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: qualitative study. J Med Internet Res . 2019;21(11):e15681. doi:10.2196/15681
- Mackenzie M, Turner F, Platt S, et al. What is the ‘problem’ that outreach work seeks to address and how might it be tackled? Seeking theory in a primary health prevention programme. BMC Health Serv Res . 2011;11:350. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-350
- Liberati E, Richards N, Parker J, et al. Qualitative study of candidacy and access to secondary mental health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114711. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2022.114711
- Pearson O, Schwartzkopff K, Dawson A, et al. Aboriginal community controlled health organisations address health equity through action on the social determinants of health of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples in Australia. BMC Public Health . 2020;20:1859. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09943-4
- Freeman T, Baum F, Lawless A, et al. Revisiting the ability of Australian primary healthcare services to respond to health inequity. Aust J Prim Health . 2016;22(4):332-338. doi:10.1071/PY14180
- Couzos S. Towards a National Primary Health Care Strategy: Fulfilling Aboriginal Peoples Aspirations to Close the Gap . National Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Organisation. 2009. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/35080/
- Napier AD, Ancarno C, Butler B, et al. Culture and health. Lancet . 2014;384(9954):1607-1639. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61603-2
- WHO. COVID-19 and the Social Determinants of Health and Health Equity: Evidence Brief . 2021. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240038387
- WHO. Social Determinants of Health . 2023. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/social-determinants-of-health#tab=tab_1
- McCrae JS, Robinson JAL, Spain AK, Byers K, Axelrod JL. The Mitigating Toxic Stress study design: approaches to developmental evaluation of pediatric health care innovations addressing social determinants of health and toxic stress. BMC Health Serv Res . 2021;21:71. doi:10.1186/s12913-021-06057-4
- Hosseinpoor AR, Stewart Williams J, Jann B, et al. Social determinants of sex differences in disability among older adults: a multi-country decomposition analysis using the World Health Survey. Int J Equity Health . 2012;11:52. doi:10.1186/1475-9276-11-52
- Kabore A, Afriyie-Gyawu E, Awua J, et al. Social ecological factors affecting substance abuse in Ghana (West Africa) using photovoice. Pan Afr Med J . 2019;34:214. doi:10.11604/pamj.2019.34.214.12851
- Bíró É, Vincze F, Mátyás G, Kósa K. Recursive path model for health literacy: the effect of social support and geographical residence. Front Public Health . 2021;9. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.724995
- Yuan B, Zhang T, Li J. Family support and transport cost: understanding health service among older people from the perspective of social-ecological model. Arch Public Health . 2022;80:173. doi:10.1186/s13690-022-00923-1
- Mahmoodi Z, Karimlou M, Sajjadi H, Dejman M, Vameghi M, Dolatian M. A communicative model of mothers’ lifestyles during pregnancy with low birth weight based on social determinants of health: a path analysis. Oman Med J . 2017 ;32(4):306-314. doi:10.5001/omj.2017.59
- Vella SA, Schweickle MJ, Sutcliffe J, Liddelow C, Swann C. A systems theory of mental health in recreational sport. Int J Environ Res Public Health . 2022;19(21):14244. doi:10.3390/ijerph192114244
- Henning S. The wellness of airline cabin attendants: A systems theory perspective. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure . 2015;4(1):1-11. Accessed February 15, 2023. http://www.ajhtl.com/archive.html
- Sutphin ST, McDonough S, Schrenkel A. The role of formal theory in social work research: formalizing family systems theory. Adv Soc Work . 2013;14(2):501-517. doi:10.18060/7942
- Colla R, Williams P, Oades LG, Camacho-Morles J. “A new hope” for positive psychology: a dynamic systems reconceptualization of hope theory. Front Psychol . 2022;13. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809053
- Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–136. doi:10.1126/science.847460
- Wade DT, HalliganPW. The biopsychosocial model of illness: a model whose time has come. Clin Rehabi l. 2017;31(8):995–1004. doi:10.1177/0269215517709890
- Ip L, Smith A, Papachristou I, Tolani E. 3 Dimensions for Long Term Conditions – creating a sustainable bio-psycho-social approach to healthcare. J Integr Care . 2019;19(4):5. doi:10.5334/ijic.s3005
- FrameWorks Institute. A Matter of Life and Death: Explaining the Wider Determinants of Health in the UK . FrameWorks Institute; 2022. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.frameworksinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/FWI-30-uk-health-brief-v3a.pdf
- Zemed A, Nigussie Chala K, Azeze Eriku G, Yalew Aschalew A. Health-related quality of life and associated factors among patients with stroke at tertiary level hospitals in Ethiopia. PLOS ONE . 2021;16(3):e0248481. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248481
- Finch E, Foster M, Cruwys T, et al. Meeting unmet needs following minor stroke: the SUN randomised controlled trial protocol. BMC Health Serv Res . 2019;19:894. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4746-1
Qualitative Research – a practical guide for health and social care researchers and practitioners Copyright © 2023 by Tess Tsindos is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 2
- Integration of a theoretical framework into your research study
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Roberta Heale 1 ,
- Helen Noble 2
- 1 Laurentian University , School of Nursing , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- 2 Queens University Belfast , School of Nursing and Midwifery , Belfast , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Roberta Heale, School of Nursing, Laurentian University, Ramsey Lake Road, Sudbury, P3E2C6, Canada; rheale{at}laurentian.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2019-103077
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Often the most difficult part of a research study is preparing the proposal based around a theoretical or philosophical framework. Graduate students ‘…express confusion, a lack of knowledge, and frustration with the challenge of choosing a theoretical framework and understanding how to apply it’. 1 However, the importance in understanding and applying a theoretical framework in research cannot be overestimated.
The choice of a theoretical framework for a research study is often a reflection of the researcher’s ontological (nature of being) and epistemological (theory of knowledge) perspective. We will not delve into these concepts, or personal philosophy in this article. Rather we will focus on how a theoretical framework can be integrated into research.
The theoretical framework is a blueprint for your research project 1 and serves several purposes. It informs the problem you have identified, the purpose and significance of your research demonstrating how your research fits with what is already known (relationship to existing theory and research). This provides a basis for your research questions, the literature review and the methodology and analysis that you choose. 1 Evidence of your chosen theoretical framework should be visible in every aspect of your research and should demonstrate the contribution of this research to knowledge. 2
What is a theory?
A theory is an explanation of a concept or an abstract idea of a phenomenon. An example of a theory is Bandura’s middle range theory of self-efficacy, 3 or the level of confidence one has in achieving a goal. Self-efficacy determines the coping behaviours that a person will exhibit when facing obstacles. Those who have high self-efficacy are likely to apply adequate effort leading to successful outcomes, while those with low self-efficacy are more likely to give up earlier and ultimately fail. Any research that is exploring concepts related to self-efficacy or the ability to manage difficult life situations might apply Bandura’s theoretical framework to their study.
Using a theoretical framework in a research study
Example 1: the big five theoretical framework.
The first example includes research which integrates the ‘Big Five’, a theoretical framework that includes concepts related to teamwork. These include team leadership, mutual performance monitoring, backup behaviour, adaptability and team orientation. 4 In order to conduct research incorporating a theoretical framework, the concepts need to be defined according to a frame of reference. This provides a means to understand the theoretical framework as it relates to a specific context and provides a mechanism for measurement of the concepts.
In this example, the concepts of the Big Five were given a conceptual definition, that provided a broad meaning and then an operational definition, which was more concrete. 4 From here, a survey was developed that reflected the operational definitions related to teamwork in nursing: the Nursing Teamwork Survey (NTS). 5 In this case, the concepts used in the theoretical framework, the Big Five, were the used to develop a survey specific to teamwork in nursing.
The NTS was used in research of nurses at one hospital in northeastern Ontario. Survey questions were grouped into subscales for analysis, that reflected the concepts of the Big Five. 6 For example, one finding of this study was that the nurses from the surgical unit rated the items in the subscale of ’team leadership' (one of the concepts in the Big Five) significantly lower than in the other units. The researchers looked back to the definition of this concept in the Big Five in their interpretation of the findings. Since the definition included a person(s) who has the leadership skills to facilitate teamwork among the nurses on the unit, the conclusion in this study was that the surgical unit lacked a mentor, or facilitator for teamwork. In this way, the theory of teamwork was presented through a set of concepts in a theoretical framework. The Theoretical Framework (TF)was the foundation for development of a survey related to a specific context, used to measure each of the concepts within the TF. Then, the analysis and results circled back to the concepts within the TF and provided a guide for the discussion and conclusions arising from the research.
Example 2: the Health Decisions Model
In another study which explored adherence to intravenous chemotherapy in African-American and Caucasian Women with early stage breast cancer, an adapted version of the Health Decisions Model (HDM) was used as the theoretical basis for the study. 7 The HDM, a revised version of the Health Belief Model, incorporates some aspects of the Health Belief Model and factors relating to patient preferences. 8 The HDM consists of six interrelated constituents that might predict how well a person adheres to a health decision. These include sociodemographic, social interaction, experience, knowledge, general and specific health beliefs and patient preferences, and are clearly defined. The HDM model was used to explore factors which might influence adherence to chemotherapy in women with breast cancer. Sociodemographic, social interaction, knowledge, personal experience and specific health beliefs were used as predictors of adherence to chemotherapy.
The findings were reported using the theoretical framework to discuss results. The study found that delay to treatment, health insurance, depression and symptom severity were predictors to starting chemotherapy which could potentially be adapted with clinical interventions. The findings from the study contribute to the existing body of literature related to cancer nursing.
Example 3: the nursing role effectiveness model
In this final example, research was conducted to determine the nursing processes that were associated with unexpected intensive care unit admissions. 9 The framework was the Nursing Role Effectiveness Model. In this theoretical framework, the concepts within Donabedian’s Quality Framework of Structure, Process and Outcome were each defined according to nursing practice. 10 11 Processes defined in the Nursing Role Effectiveness Model were used to identify the nursing process variables that were measured in the study.
A theoretical framework should be logically presented and represent the concepts, variables and relationships related to your research study, in order to clearly identify what will be examined, described or measured. It involves reading the literature and identifying a research question(s) while clearly defining and identifying the existing relationship between concepts and theories (related to your research questions[s] in the literature). You must then identify what you will examine or explore in relation to the concepts of the theoretical framework. Once you present your findings using the theoretical framework you will be able to articulate how your study relates to and may potentially advance your chosen theory and add to knowledge.
- Kalisch BJ ,
- Parent M , et al
- Strickland OL ,
- Dalton JA , et al
- Eraker SA ,
- Kirscht JP ,
- Lightfoot N , et al
- Harrison MB ,
- Laschinger H , et al
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Patient and public involvement Not required.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Theoretical Research: Definition, Methods + Examples

Research is the careful study of a particular research problem or concern using the scientific method. A theory is essential for any research project because it gives it direction and helps prove or disprove something. Theoretical basis helps us figure out how things work and why we do certain things.
Theoretical research lets you examine and discuss a research object using philosophical ideas and abstract theoretical structures.
In theoretical research, you can’t look at the research object directly. With the help of research literature, your research aims to define and sketch out the chosen topic’s conceptual models, explanations, and structures.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
This blog will cover theoretical research and why it is essential. In addition to that, we are going to go over some examples.
What is the theoretical research?
Theoretical research is the systematic examination of a set of beliefs and assumptions.
It aims to learn more about a subject and help us understand it better. The information gathered in this way is not used for anything in particular because this kind of research aims to learn more.
All professionals, like biologists, chemists, engineers, architects, philosophers, writers, sociologists, historians, etc., can do theoretical research. No matter what field you work in, theoretical research is the foundation for new ideas.
It tries to answer basic questions about people, which is why this kind of research is used in every field of knowledge.
For example , a researcher starts with the idea that we need to understand the world around us. To do this, he begins with a hypothesis and tests it through experiments that will help him develop new ideas.
What is the theoretical framework?
A theoretical framework is a critical component in research that provides a structured foundation for investigating a specific topic or problem. It encompasses a set of interconnected theories, existing theories, and concepts that guide the entire research process.
The theoretical framework introduces a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Also, the theoretical framework strengthens the research’s validity and specifies the key elements that will be explored. Furthermore, it connects different ideas and theories, forming a cohesive structure that underpins the research endeavor.
A complete theoretical framework consists of a network of theories, existing theories, and concepts that collectively shape the direction of a research study.
The theoretical framework is the fundamental principle that will be explored, strengthens the research’s credibility by aligning it with established knowledge, specifies the variables under investigation, and connects different aspects of the research to create a unified approach.
Theoretical frameworks are the intellectual scaffolding upon which the research is constructed. It is the lens through which researchers view their subject, guiding their choice of methodologies, data collection, analysis, and interpretation. By incorporating existing theory, and established concepts, a theoretical framework not only grounds the research but also provides a coherent roadmap for exploring the intricacies of the chosen topic.
Benefits of theoretical research
Theoretical research yields a wealth of benefits across various fields, from social sciences to human resource development and political science. Here’s a breakdown of these benefits while incorporating the requested topics:
Predictive power
Theoretical models are the cornerstone of theoretical research. They grant us predictive power, enabling us to forecast intricate behaviors within complex systems, like societal interactions. In political science, for instance, a theoretical model helps anticipate potential outcomes of policy changes.
Understanding human behavior
Drawing from key social science theories, it assists us in deciphering human behavior and societal dynamics. For instance, in the context of human resource development, theories related to motivation and psychology provide insights into how to effectively manage a diverse workforce.
Optimizing workforce
In the realm of human resource development, insights gleaned from theoretical research, along with the research methods knowledge base, help create targeted training programs. By understanding various learning methodologies and psychological factors, organizations can optimize workforce training for better results.
Building on foundations
It doesn’t exist in isolation; it builds upon existing theories. For instance, within the human resource development handbook, theoretical research expands established concepts, refining their applicability to contemporary organizational challenges.
Ethical policy formulation
Within political science, theoretical research isn’t confined to governance structures. It extends to ethical considerations, aiding policymakers in creating policies that balance the collective good with individual rights, ensuring just and fair governance.
Rigorous investigations
Theoretical research underscores the importance of research methods knowledge base. This knowledge equips researchers in theory-building research methods and other fields to design robust research methodologies, yielding accurate data and credible insights.
Long-term impact
Theoretical research leaves a lasting impact. The theoretical models and insights from key social science theories provide enduring frameworks for subsequent research, contributing to the cumulative growth of knowledge in these fields.
Innovation and practical applications
It doesn’t merely remain theoretical. It inspires innovation and practical applications. By merging insights from diverse theories and fields, practitioners in human resource development devise innovative strategies to foster employee growth and well-being.
Theoretical research method
Researchers follow so many methods when doing research. There are two types of theoretical research methods.
- Scientific methods
- Social science method
Let’s explore them below:

Scientific method
Scientific methods have some important points that you should know. Let’s figure them out below:
- Observation: Any part you want to explain can be found through observation. It helps define the area of research.
- Hypothesis: The hypothesis is the idea put into words, which helps us figure out what we see.
- Experimentation: Hypotheses are tested through experiments to see if they are true. These experiments are different for each research.
- Theory: When we create a theory, we do it because we believe it will explain hypotheses of higher probability.
- Conclusions: Conclusions are the learnings we derive from our investigation.
Social science methods
There are different methods for social science theoretical research. It consists of polls, documentation, and statistical analysis.
- Polls: It is a process whereby the researcher uses a topic-specific questionnaire to gather data. No changes are made to the environment or the phenomenon where the polls are conducted to get the most accurate results. QuestionPro live polls are a great way to get live audiences involved and engaged.
- Documentation: Documentation is a helpful and valuable technique that helps the researcher learn more about the subject. It means visiting libraries or other specialized places, like documentation centers, to look at the existing bibliography. With the documentation, you can find out what came before the investigated topic and what other investigations have found. This step is important because it shows whether or not similar investigations have been done before and what the results were.
- Statistic analysis : Statistics is a branch of math that looks at random events and differences. It follows the rules that are established by probability. It’s used a lot in sociology and language research.
Examples of theoretical research
We talked about theoretical study methods in the previous part. We’ll give you some examples to help you understand it better.
Example 1: Theoretical research into the health benefits of hemp
The plant’s active principles are extracted and evaluated, and by studying their components, it is possible to determine what they contain and whether they can potentially serve as a medication.
Example 2: Linguistics research
Investigate to determine how many people in the Basque Country speak Basque. Surveys can be used to determine the number of native Basque speakers and those who speak Basque as a second language.
Example 3: Philosophical research
Research politics and ethics as they are presented in the writings of Hanna Arendt from a theoretical perspective.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
From our above discussion, we learned about theoretical research and its methods and gave some examples. It explains things and leads to more knowledge for the sake of knowledge. This kind of research tries to find out more about a thing or an idea, but the results may take time to be helpful in the real world.
This research is sometimes called basic research. Theoretical research is an important process that gives researchers valuable data with insight.
QuestionPro is a strong platform for managing your data. You can conduct simple surveys to more complex research using QuestionPro survey software.
At QuestionPro, we give researchers tools for collecting data, such as our survey software and a library of insights for any long-term study. Contact our expert team to find out more about it.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 20 Employee Engagement Software Solutions
May 3, 2024

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024

Top 12 Employee Pulse Survey Tools Unlocking Insights in 2024
May 1, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
How to Use a Conceptual Framework for Better Research
A conceptual framework in research is not just a tool but a vital roadmap that guides the entire research process. It integrates various theories, assumptions, and beliefs to provide a structured approach to research. By defining a conceptual framework, researchers can focus their inquiries and clarify their hypotheses, leading to more effective and meaningful research outcomes.
What is a Conceptual Framework?
A conceptual framework is essentially an analytical tool that combines concepts and sets them within an appropriate theoretical structure. It serves as a lens through which researchers view the complexities of the real world. The importance of a conceptual framework lies in its ability to serve as a guide, helping researchers to not only visualize but also systematically approach their study.
Key Components and to be Analyzed During Research
- Theories: These are the underlying principles that guide the hypotheses and assumptions of the research.
- Assumptions: These are the accepted truths that are not tested within the scope of the research but are essential for framing the study.
- Beliefs: These often reflect the subjective viewpoints that may influence the interpretation of data.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Together, these components help to define the conceptual framework that directs the research towards its ultimate goal. This structured approach not only improves clarity but also enhances the validity and reliability of the research outcomes. By using a conceptual framework, researchers can avoid common pitfalls and focus on essential variables and relationships.
For practical examples and to see how different frameworks can be applied in various research scenarios, you can Explore Conceptual Framework Examples .
Different Types of Conceptual Frameworks Used in Research
Understanding the various types of conceptual frameworks is crucial for researchers aiming to align their studies with the most effective structure. Conceptual frameworks in research vary primarily between theoretical and operational frameworks, each serving distinct purposes and suiting different research methodologies.
Theoretical vs Operational Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks are built upon existing theories and literature, providing a broad and abstract understanding of the research topic. They help in forming the basis of the study by linking the research to already established scholarly works. On the other hand, operational frameworks are more practical, focusing on how the study’s theories will be tested through specific procedures and variables.
- Theoretical frameworks are ideal for exploratory studies and can help in understanding complex phenomena.
- Operational frameworks suit studies requiring precise measurement and data analysis.
Choosing the Right Framework
Selecting the appropriate conceptual framework is pivotal for the success of a research project. It involves matching the research questions with the framework that best addresses the methodological needs of the study. For instance, a theoretical framework might be chosen for studies that aim to generate new theories, while an operational framework would be better suited for testing specific hypotheses.
Benefits of choosing the right framework include enhanced clarity, better alignment with research goals, and improved validity of research outcomes. Tools like Table Chart Maker can be instrumental in visually comparing the strengths and weaknesses of different frameworks, aiding in this crucial decision-making process.
Real-World Examples of Conceptual Frameworks in Research
Understanding the practical application of conceptual frameworks in research can significantly enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your studies. Here, we explore several real-world case studies that demonstrate the pivotal role of conceptual frameworks in achieving robust research conclusions.
- Healthcare Research: In a study examining the impact of lifestyle choices on chronic diseases, researchers used a conceptual framework to link dietary habits, exercise, and genetic predispositions. This framework helped in identifying key variables and their interrelations, leading to more targeted interventions.
- Educational Development: Educational theorists often employ conceptual frameworks to explore the dynamics between teaching methods and student learning outcomes. One notable study mapped out the influences of digital tools on learning engagement, providing insights that shaped educational policies.
- Environmental Policy: Conceptual frameworks have been crucial in environmental research, particularly in studies on climate change adaptation. By framing the relationships between human activity, ecological changes, and policy responses, researchers have been able to propose more effective sustainability strategies.
Adapting conceptual frameworks based on evolving research data is also critical. As new information becomes available, it’s essential to revisit and adjust the framework to maintain its relevance and accuracy, ensuring that the research remains aligned with real-world conditions.
For those looking to visualize and better comprehend their research frameworks, Graphic Organizers for Conceptual Frameworks can be an invaluable tool. These organizers help in structuring and presenting research findings clearly, enhancing both the process and the presentation of your research.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your Own Conceptual Framework
Creating a conceptual framework is a critical step in structuring your research to ensure clarity and focus. This guide will walk you through the process of building a robust framework, from identifying key concepts to refining your approach as your research evolves.
Building Blocks of a Conceptual Framework
- Identify and Define Main Concepts and Variables: Start by clearly identifying the main concepts, variables, and their relationships that will form the basis of your research. This could include defining key terms and establishing the scope of your study.
- Develop a Hypothesis or Primary Research Question: Formulate a central hypothesis or question that guides the direction of your research. This will serve as the foundation upon which your conceptual framework is built.
- Link Theories and Concepts Logically: Connect your identified concepts and variables with existing theories to create a coherent structure. This logical linking helps in forming a strong theoretical base for your research.
Visualizing and Refining Your Framework
Using visual tools can significantly enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your conceptual framework. Decision Tree Templates for Conceptual Frameworks can be particularly useful in mapping out the relationships between variables and hypotheses.
Map Your Framework: Utilize tools like Creately’s visual canvas to diagram your framework. This visual representation helps in identifying gaps or overlaps in your framework and provides a clear overview of your research structure.
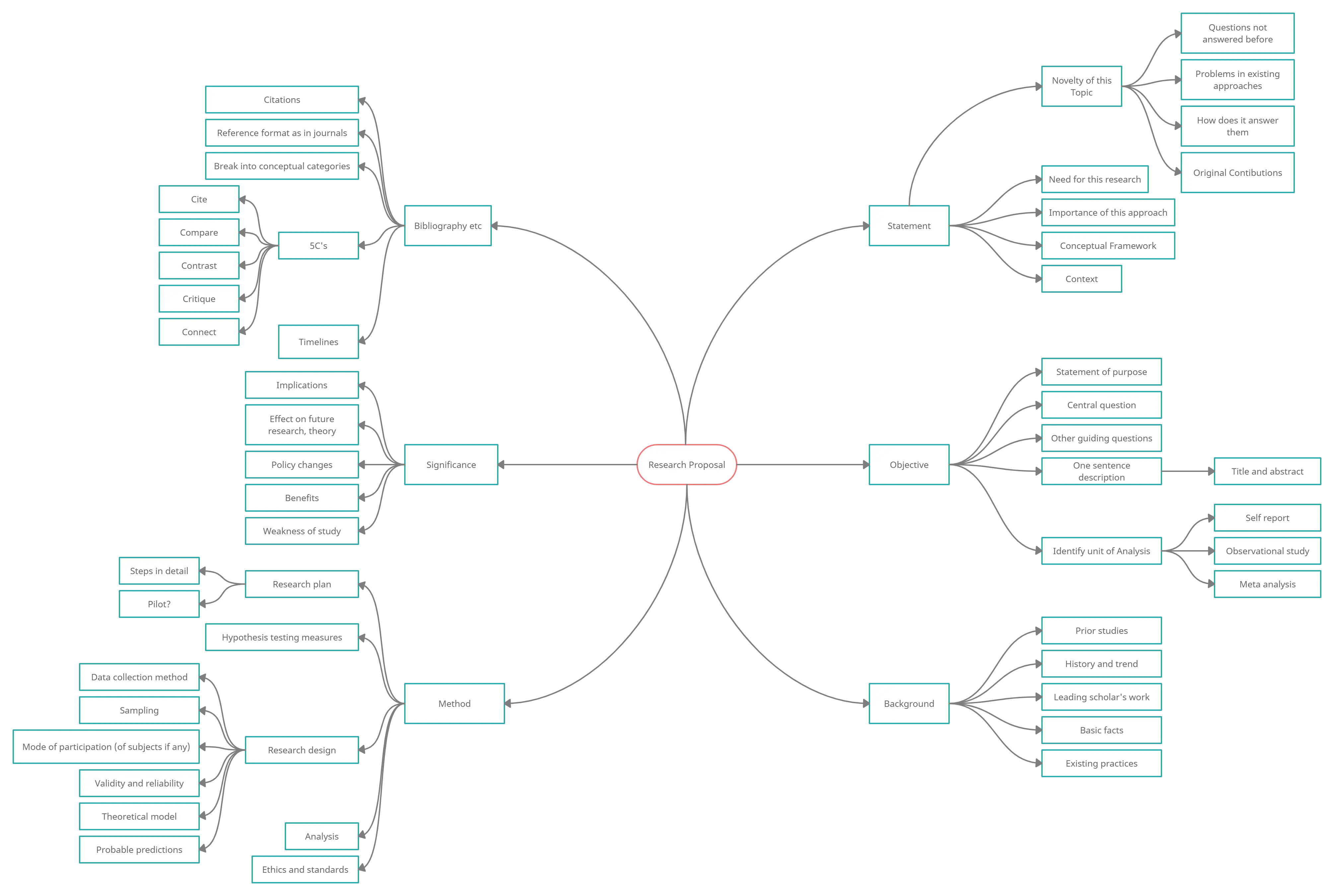
Analyze and Refine: As your research progresses, continuously evaluate and refine your framework. Adjustments may be necessary as new data comes to light or as initial assumptions are challenged.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your conceptual framework is not only well-defined but also adaptable to the changing dynamics of your research.
Practical Tips for Utilizing Conceptual Frameworks in Research
Effectively utilizing a conceptual framework in research not only streamlines the process but also enhances the clarity and coherence of your findings. Here are some practical tips to maximize the use of conceptual frameworks in your research endeavors.
- Setting Clear Research Goals: Begin by defining precise objectives that are aligned with your research questions. This clarity will guide your entire research process, ensuring that every step you take is purposeful and directly contributes to your overall study aims. \
- Maintaining Focus and Coherence: Throughout the research, consistently refer back to your conceptual framework to maintain focus. This will help in keeping your research aligned with the initial goals and prevent deviations that could dilute the effectiveness of your findings.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Use your conceptual framework as a lens through which to view and interpret data. This approach ensures that the data analysis is not only systematic but also meaningful in the context of your research objectives. For more insights, explore Research Data Analysis Methods .
- Presenting Research Findings: When it comes time to present your findings, structure your presentation around the conceptual framework . This will help your audience understand the logical flow of your research and how each part contributes to the whole.
- Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Be vigilant about common errors such as overcomplicating the framework or misaligning the research methods with the framework’s structure. Keeping it simple and aligned ensures that the framework effectively supports your research.
By adhering to these tips and utilizing tools like 7 Essential Visual Tools for Social Work Assessment , researchers can ensure that their conceptual frameworks are not only robust but also practically applicable in their studies.
How Creately Enhances the Creation and Use of Conceptual Frameworks
Creating a robust conceptual framework is pivotal for effective research, and Creately’s suite of visual tools offers unparalleled support in this endeavor. By leveraging Creately’s features, researchers can visualize, organize, and analyze their research frameworks more efficiently.
- Visual Mapping of Research Plans: Creately’s infinite visual canvas allows researchers to map out their entire research plan visually. This helps in understanding the complex relationships between different research variables and theories, enhancing the clarity and effectiveness of the research process.
- Brainstorming with Mind Maps: Using Mind Mapping Software , researchers can generate and organize ideas dynamically. Creately’s intelligent formatting helps in brainstorming sessions, making it easier to explore multiple topics or delve deeply into specific concepts.
- Centralized Data Management: Creately enables the importation of data from multiple sources, which can be integrated into the visual research framework. This centralization aids in maintaining a cohesive and comprehensive overview of all research elements, ensuring that no critical information is overlooked.
- Communication and Collaboration: The platform supports real-time collaboration, allowing teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location. This feature is crucial for research teams spread across different geographies, facilitating effective communication and iterative feedback throughout the research process.
Moreover, the ability t Explore Conceptual Framework Examples directly within Creately inspires researchers by providing practical templates and examples that can be customized to suit specific research needs. This not only saves time but also enhances the quality of the conceptual framework developed.
In conclusion, Creately’s tools for creating and managing conceptual frameworks are indispensable for researchers aiming to achieve clear, structured, and impactful research outcomes.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
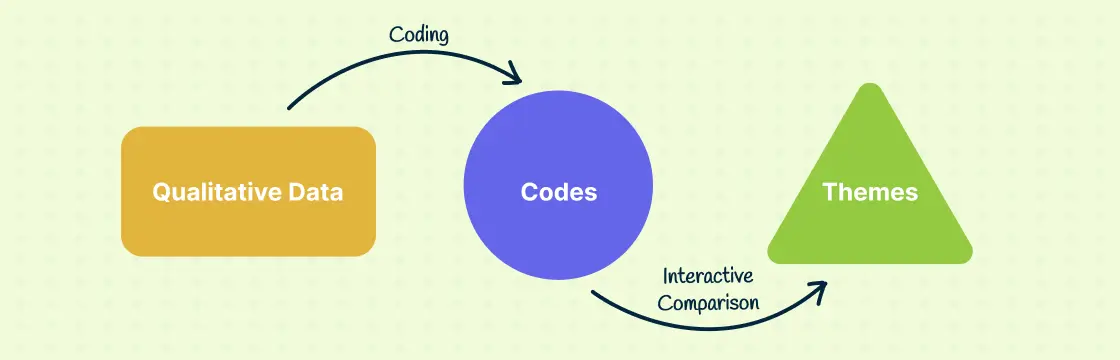
Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn what a theoretical framework is, why it is important, and how to write it for your research. See examples of different types of theoretical frameworks and tips to develop your own.
Learn what a theoretical framework is, why you need it, and how to write one for your research paper, thesis, or dissertation. Follow the three steps to identify key concepts, evaluate and explain relevant theories, and show how your research fits into existing research.
Theoretical Framework. Definition: Theoretical framework refers to a set of concepts, theories, ideas, and assumptions that serve as a foundation for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It provides a conceptual framework that helps researchers to design and conduct their research, as well as to analyze and interpret their findings.
A theoretical framework is a review of existing theories that supports your research and justifies your approach. Learn how to identify your key concepts, evaluate and explain relevant theories, and show how your research fits into existing research.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways: An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically. The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
To learn more about the definition and goal of a theoretical framework, check out our step-by-step guide to writing a theoretical framework. Other interesting articles If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go ...
Abstract. Theoretical frameworks can be confounding. They are supposed to be very important, but it is not always clear what they are or why you need them. Using ideas from Chaps. 1 and 2, we describe them as local theories that are custom-designed for your study. Although they might use parts of larger well-known theories, they are created by ...
Your theoretical framework is based on: A new boutique downtown is struggling with the fact that many of their online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases. This is a big issue for the otherwise fast-growing shop.Management wants to increase customer loyalty. They believe that improved customer satisfaction will play a major role ...
Theoretical framework. The theoretical perspective provides the broader lens or orientation through which the researcher views the research topic and guides their overall understanding and approach. The theoretical framework, on the other hand, is a more specific and focused framework that connects the theoretical perspective to the data analysis strategy through pre-established theory.
The task of developing a theoretical framework starts with asking a research question, proceeds through the task of identifying key variables and the relationships among them, and results in a plan for empirically observing those variables and relationships. Theory construction is always an iterative process.
significance, and the research questions. The theoretical framework provides a grounding base, or an anchor, for the literature review, and most importantly, the methods and analysis. Lysaght (2011) highlighted the necessity of identifying one's theoretical framework for a dissertation study:
It takes time to understand the relevant research, identify a theoretical framework that provides important insights into the study, and formulate a conceptual framework that organizes the finding. In the research process, there is often a constant back and forth among these elements as the study evolves. ... Writing literature reviews: A guide ...
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). A theoretical framework provides the theoretical assumptions for the larger context of a study, and is the foundation or 'lens' by which a study is developed. This framework helps to ground the research focus ...
In a thesis or dissertation, a theoretical framework is a section where the writer evaluates or discusses the most relevant theories to their study. The purpose of this section is to: Define the key concepts. Combine and evaluate relevant models and theories. Explain expectations and assumptions that guide the project.
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). A theoretical framework provides the theoretical assumptions for the larger context of a study, and is the foundation or 'lens' by which a study is developed. This framework helps to ground the research focus ...
Resources About Theory and Theoretical Frameworks. Challenging Ideas: Theory and Empirical Research in the Social Sciences and humanities Edited by Maren Lytje, Torben K. Nielsen, and Martin Ottovay Jørgensen. Call Number: Ebook, click link to view. ISBN: 9781443887373. Publication Date: 2015.
The theoretical framework - the 'toolbox' - details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you're using them) and concepts - the 'tools' - that you will use to address or make sense of this problem. The list of potential explanations for why responses differ is enormous. You could approach this question with a focus on ...
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory, in which case, you are expected to test the validity of an existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena.Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism theory, which categorizes perceived differences between nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey ...
What is a Framework? A framework is a set of broad concepts or principles used to guide research. As described by Varpio and colleagues 1, a framework is a logically developed and connected set of concepts and premises - developed from one or more theories - that a researcher uses as a scaffold for their study.The researcher must define any concepts and theories that will provide the ...
This lesson will help you finish writing your theoretical framework in one hour. Tips and list of commonly used theories are included. #theory#research#thesi...
Often the most difficult part of a research study is preparing the proposal based around a theoretical or philosophical framework. Graduate students '…express confusion, a lack of knowledge, and frustration with the challenge of choosing a theoretical framework and understanding how to apply it'.1 However, the importance in understanding and applying a theoretical framework in research ...
A theoretical framework is a critical component in research that provides a structured foundation for investigating a specific topic or problem. It encompasses a set of interconnected theories, existing theories, and concepts that guide the entire research process. The theoretical framework introduces a comprehensive understanding of the ...
Developing a conceptual framework in research. Step 1: Choose your research question. Step 2: Select your independent and dependent variables. Step 3: Visualize your cause-and-effect relationship. Step 4: Identify other influencing variables. Frequently asked questions about conceptual models.
Theoretical vs Operational Frameworks. Theoretical frameworks are built upon existing theories and literature, providing a broad and abstract understanding of the research topic. They help in forming the basis of the study by linking the research to already established scholarly works. On the other hand, operational frameworks are more ...
Theoretical Framework Part 2 [How to Write Theoretical Framework] #research #thesis #dissertation #researchpaper代写 #researcher #researchpaper #researchstudy #researchwriting #researchlife....