- Login / Register

‘Much will be said and promised over the next six weeks’
STEVE FORD, EDITOR
- You are here: Students

‘Making your personal development plan right for you’
06 February, 2019

Now in my final year of nursing, it is time for me and many other student nurses to write our final personal development plan.
A personal development plan (PDP) is something that you are supposed to write at the start of each year, detailing your goals for practice and theory and how you are going to achieve them.
I have found PDPs difficult to write, especially at the start of the year as all the modules are launching. My goal is to stay calm and not be overwhelmed by it all, as thinking about the end of the year seems impossible. But this is my final year writing PDPs and I have some tips to share.
Remember the PDP is for you
Although personal tutors at university will look at your PDPs, they are designed for you. The whole point of a PDP is to make it personal to you – not to write what you think your personal tutors wants to read.
The goals you want to set yourself should be things that you actually want to achieve. If the goal is personal to you, you are far more likely to put your energy into achieving it.
Make your PDP realistic
Being a student nurse is stressful and the last thing you need is to set yourself an unrealistic goal in either practice or theory – so be realistic.
Think about your current skillset and your goal. Then think about what needs to be done to get you to where you want to be and whether this will be realistic once you are juggling placement, university, family and friends.
Don’t make things hard for yourself as you can’t do everything at once. Consider all the little steps that will help you to get to where you want to be and take it each step at a time.
Talk to people about your PDP
If you’ve written about wanting a certain experience in practice within your PDP – for example spending time with a psychologist – then when you go into placement and have your initial interview, let them know about your burning interest to work with psychology or whatever you included in your PDP.
The same goes for theory. If you have written about being more critical in your assignments then speak with lecturers for advice on how you can do this.
PDPs are your goals for the year, so it is your responsibility to do things throughout the year that bring you closer to where you want to be.
Hannah Simpson is a third-year learning disability nursing student at De Montfort University
- Add to Bookmarks
Related articles
Have your say.
Sign in or Register a new account to join the discussion.
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
- MEDICAL ASSISSTANT
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
Personal development, planning and portfolios
Personal development plans • Post-registration education and practice • The knowledge and skills framework • Summary This chapter looks at your own personal and professional development. You will need to continue to prove over the course of your career that you have maintained your knowledge and competencies. You will also want to have a plan for growing into the kind of nurse you want to be. If you don’t plan, you won’t be ready when the opportunities you would like come up! First, some definitions to make this a bit easier: • KSF: knowledge and skills framework: under Agenda for Change, each job has a list of skills and knowledge that people in that job should have. The purpose of the KSF is to help you develop your knowledge and skill. • PDP: personal (or professional) development plan: a plan through which you undertake to improve your knowledge and skill. • PPP: personal professional portfolio: the portfolio of evidence that shows you have met your obligations under PREP. • PREP: post-registration education and practice: the NMC requires that you show you have maintained fitness to practise in between your registration renewals. PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT PLANS Personal development plans (PDPs) help you identify and carry out development that you will need. The areas of development can be very diverse. You might want to develop in any of a number of areas, for example by: • developing a new clinical skill • developing knowledge of a disease or medical problem • developing more assertiveness • taking a certain specialty course • gaining better IT skills. All of these things would be related to your practice as a nurse. The beauty of planning is that you can choose the areas you want to develop. As you probably have guessed, PDP and reflection are closely linked. As you reflect, you start to see what you need for development. The PDP then helps you work out how you are going to develop. Some other areas that might drive your development planning are government initiatives and policies, which are: • The National Service Frameworks, which require practitioners to give a certain level of care. • Essence of Care, which outlines certain standards. • The Department of Health, which puts out bulletins making recommendations about care and practice. • The Knowledge and Skills Framework under Agenda for Change. Your place of work will also offer training, courses and opportunities to further your education. Often, there are special initiatives to increase nursing knowledge or skill in certain areas. The professional press (books and journals) can also help you become aware of areas where you need to develop. For example, you might have read an article about catheter care in the Nursing Standard or Nursing Times , and it made you realise that you don’t have a good understanding of suprapubic catheterisations. You have recognised that this is a development need, as you care for patients with catheters. In addition, there are national nursing forums, specialty nursing groups and organisations such as the Royal College of Nursing that will put out material designed to help you recognise gaps and advance your practice. All of these things – reflection, policy, your employer, books and journals, and organisations – can give you ideas about how to develop your practice. They can also help you to develop that practice once you know what you want to do. But in order to get there, you need a plan. The plan starts by you looking inward and taking an inventory of what you already know, what you can build on, what is weak and what you think you need. Let’s use Oliver as an example: Oliver Thorpe is a new staff nurse on a ward for older people. He wants to become a clinical nurse specialist in a couple of years and perhaps do a Master’s degree in advanced practice. He has done some reading and observed the skills his more experienced colleagues have. He sits down and makes a list of things he needs. I need to learn about: 1. wound care – I don’t know what half the dressings do, or when to use them! 2. leg ulcer diagnosis and care 3. community assessment in general 4. making referrals 5. evidence-based practice, research and audit. Oliver has reflected on a number of things since he started in this post. He has identified that there are a few things he would like to improve: 1. I need to be more assertive. 2. I need to improve my time management skills. 3. I need to learn more about the documentation used by my team. Finally, Oliver knows from his team leader that he will be expected to use a new form: 1. I need to learn more about the single assessment process and SAP forms. As a new nurse, Oliver has identified nine areas in which he wants to develop himself and his practice. He decides to focus on just one area for now: wound care. Remember the nursing process (assess, plan, implement/intervention, evaluation) mentioned in Chapter 2? In the same way, Oliver has done his assessment and moves on to his plan. The first step of the plan is actually a transition between your assessment and your plan. In the initial stage, you are looking more in-depth at each of your assessed needs. It has two real purposes: to help keep you motivated because you really understand why you need this level of development, and to help you think out what you need to do to achieve goals. Your initial plan should be based on a basic formula: What? Why? Where? When? How? and Who? • What do I need to learn or do? What do I need for funding? • Why is it important for me to do this? • Where will I be once I have done this? • When are the classes/in-service training held? How soon do I need to do this? • How will I accomplish this and how much time will I need? (including a timeline for actions) • Who can help me to achieve this? Who might pay for this course/in-service training? Looking at his development needs for ‘wound care’, Oliver makes the following plan: Oliver is confident that this is a good basic plan. However, after speaking to his team leader, he also realises that ‘wound care’ is a much bigger topic than he realised. He and his team leader make a further list: • aetiology of wounds: acute and chronic wounds • anatomy and physiology of wounds and healing • wound-bed preparation • classes of wound-care product • wound-care techniques. For each of these, he develops another plan: One thing Oliver notices is that there isn’t a lot of information available on wound care and wound-care products in the team’s office, so he starts to build a team resource folder as he finds information for himself. After he has taken the wound-care course, Oliver realises that his team could use an audit of the patients’ wounds and the wound-care products being used. He asks his team leader for help and together they design an audit tool. He brings it to a team meeting and asks everyone to use it. Once he has all the information for the audit, Oliver and his team leader look at the findings. He finds that although most nurses use products in the way suggested by Tissue Viability (as specified in the policies given out in the wound-care course), in a few cases the dressings used don’t seem to make sense. The team leader reviews these cases and decides that a team update on wound care would be useful. Oliver is asked to prepare a brief presentation on his audit and the team leader offers help so that Oliver can do a presentation on what the results mean for the team. In May, Oliver reflects on all he has learned and meets with his team leader. The team leader is pleased with his progress and mentions that the team’s care has improved as a result of the audit. He agrees that the wound-care course at the University of Middle Earth would be very useful and approves Oliver’s study leave request. The team leader helps him sort out the funding. As part of his evaluation, Oliver put all his reflections, the certificate from the Tissue Viability course and the audit results in his PREP and KSF portfolios. He also looks back at the list of things he wanted to learn: 1. wound care – I don’t know what half the dressings do, or when to use them!
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- Research and evidence-based practice
- Clinical governance
- Professional accountability and the NMC
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Professional development planning framework for nurses and midwives
Professional development planning (PDP) is a continuous development process.
Having a professional development plan can help:
- nurses and midwives to make the best use of their skills
- with advancing the individual plans of the nurse/midwife
- with advancing the strategic goals of the organisation
The professional development planning (PDP) framework helps you create your professional development plan (PDP).
A Professional Development Plan (PDP) is a tool that supports the nurse or midwife to identify professional goals for the benefit of themselves, their service users and their workplace. Professional development planning is a continuous development process that facilitates nurses and midwives, to use their experience and skills, to identify their professional goals and the supports required to achieve their goals, and helps advance both their individual plans and service user needs.
In January 2020, the Chief Executive of the Health Service Executive (HSE) launched Performance Achievement (PA) as a mandatory process for all staff. Performance achievement is a supportive and developmentally based process that aims to ‘support staff to give of their best, be successful in their endeavours and develop their skills and careers within the health service’ (HSE 2020). Nurses and Midwives will use the Nurses and Midwives Professional Development Planning Framework for the HSE Performance Achievement process. View our short video here to find out more.
Benefits of having a PDP
When you create a professional development plan it will:
- support you to set professional long and short-term goals
- help to focus on your accomplishments, strengths and development needs
- ensure alignment of goals to NMBI code of professional conduct and ethics and other relevant policies and guidelines
- support organisational goals and objectives
- contribute to the delivery of safe quality care and improved patient experience
- help you to show that you as a nurse or midwife are maintaining your professional competence and development
Digital PDP
The digital PDP is available on the nursing and midwifery hub on HSELand.
There, you can create and maintain an online portfolio of your professional development.
See the HSELanD nursing and midwifery hub page for details on the process of registering with HSELanD and logging into HSELanD. Look for the purple professional development planning icon in the Nursing and Midwifery Hub.
Related topics Implementation Support Network Team Contact Details (PDF, size 352 KB, 3 pages) Professional Development Plan Framework (PDF, size 581.1 KB, 10 pages) Professional Development Plan Guide (PDF, size 700.3 KB, 19 pages)
Please accept functional cookies to use live chat
Read our cookies policy to find out more about cookies and how we use them.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare a...
How to prepare a personal development plan
- Related content
- Peer review
- Fiona Tasker , clinical teaching fellow, University of Bristol
- fionatasker{at}doctors.org.uk
Setting goals and gathering peer support are essential ingredients of a successful personal development plan, says Fiona Tasker
A personal development plan (PDP) will guide all doctors in their career, whatever grade they are at and whether they work in an acute or community setting. 1 PDPs help doctors become more self aware, enabling them to understand how to improve performance and develop new skills. All doctors should engage in this process, as it is now a key component of appraisals and revalidation. 2
A General Medical Council (GMC) survey found that 79% of respondents thought that their continuing professional development activity—of which PDPs are an essential part—over the past five years had helped them to improve the quality of care given to their patients. 3
An overview
When starting a PDP doctors should reflect on their learning and performance so that they can identify their developmental priorities. They should then plan how to deal with these needs for their current role as well as future aspirations. After undertaking a range of planned learning activities doctors must show that they have achieved their goals and reflect on how this benefits them and others. ⇓ 4

Personal development plan (PDP) cycle 4
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time bound (SMART) 5 goals is essential for your PDP as it is thought that low achievement of goals may relate to poor quality PDP planning. 6
Planning goals
When it comes to choosing goals, there are many ways of identifying strengths and development areas:
● Doctors should look at the GMC’s Good Medical Practice framework, which outlines the four domains that all doctors must demonstrate 7
● Those in a training programme should refer to the curriculum in their e-portfolio
● Qualitative feedback from colleagues using tools such as 360 degree assessments; feedback from patients, including details of complaints (if applicable); and feedback from consultants at previous appraisals
● Non-clinical aspects of practice, including audit/quality improvement, research, teaching, management, and leadership. For the leadership skill, review the Clinical Leadership Competency Framework. 8
Doctors should prioritise their goals, starting with essential learning needs. It is important to strike a balance between goals that are easily achievable and high aspirations. The number of goals to set will depend on personal choice and need and the resources available.
Example of objective one: To learn how to do a lumbar puncture by going on a clinical procedures course and watching colleagues perform this procedure. To ask colleagues to supervise me performing a lumbar puncture and then do a workplace based assessment. To complete this skill before my next interim review.
Example of objective two : To keep up to date with clinical practice by reading relevant journals once a week and reflecting on interesting articles in my e-portfolio. To continue to do this at this frequency up to the date of my job interview.
These objectives are well defined so they meet the specific criterion. They are measurable as they state how one will recognise when the goal has been achieved. They are also achievable. Example one is relevant for a doctor training in medicine, and example two is relevant for a doctor preparing for an interview.
A time scale should be set for completion of each goal, although some goals—such as example two—could be ongoing. A review date is important so that the goal can be adapted if necessary. So, in addition to reading journals, a doctor could perform evidence based reviews on relevant topics to keep up to date with clinical practice.
Achieving a goal
A PDP helps plan and show the achievement of continuing professional development. The GMC states that continuing professional development activities should maintain and improve the quality of care doctors give patients and the public and the standards of the teams and the services in which you work. 9
Doing a range of different continuing professional development activities to tackle a particular learning need is likely to be more effective than one-off events. 10 However, study days and study budgets are limited, so doctors should consider what they will gain from attending courses which award continuing professional development points as well as the impact it will have on clinical practice. The royal colleges and faculties provide guidance on the types of activity that would be most appropriate in particular specialties or general practice. 3
Potential ways of achieving goals include:
● Attending courses
● Attending regional/national/international conferences
● Completing e-learning modules
● Attending meetings—that is, multidisciplinary meetings, grand rounds
● Shadowing others
● Completing assessments—that is, workplace based assessments
● Discussions with seniors and colleagues for support and advice
● Learning from peers
● Collaborating with colleagues—that is, working on an audit project
● Completing a logbook of clinical cases/interesting cases.
Achieving objectives
Reflection on learning and performance is a powerful learning tool, with the GMC stating that doctors must reflect on all aspects of their professional work. The Academy of Medical Royal Colleges has created a guide to aid the documentation on reflection on a variety of activities and events. 11
Most doctors in training programmes will have access to an e-portfolio, which can be used to record reflections. Alternatively, organisations including the royal colleges and faculties, specialist associations, and professional trade bodies may have an online portfolio or similar tools. 9 Methods to show that you have achieved your objectives(s) are:
● Reflection
● Certificates from courses or e-learning modules
● A record of the minutes and summary of learning points from a meeting
● Feedback from colleagues—that is, workplace based assessments, 360 degree assessments, peer group discussions
● Feedback from patients
● Winning awards/prizes
● Being able to perform a new skill/task
● Increased patient satisfaction, improved patient care measured via audit.
Protected time and peer support
A study of 14 general practitioners highlighted the problems in undertaking PDPs. They suggested that while PDPs were valued in principle, protected time is needed to complete them, as well as leadership and facilitation of this process. 12
Newby showed that peer groups are a practicable mechanism for generating PDPs. Participants at workshops reported that it was refreshing to take time out of their pressured working lives to reflect with colleagues on prioritising objectives and discussing how to achieve these. The author outlines factors for successful peer groups and PDPs. These include regular meetings at least every six months, which last two to three hours and have between three and eight participants, all of whom should have individual space to consider requirements. The meetings must be facilitated and structured with agreed “ground rules,” and there must be tangible outputs from the process. 13
Another study showed that a peer led approach opened up mutual conversations that also promoted and enhanced reflective learning. The role of the group facilitator was valued in helping to structure the sessions, and the authors have recommended the wider use of peers and mentors to help deaneries with educational planning. 14
The PDP is an important aspect of a doctor’s professional life and should be planned to meet patients’ needs as well as those of doctors. Doctors should choose goals that motivate them as this will provide the energy and drive to achieve them.
Planning and evaluating learning should be a continual process as circumstances change and plans may need to be modified. The final step is to reflect on how effective the PDP has been and whether there are areas that have not been tackled or have not worked. Reflection must drive learning, and a completed PDP should be a building block for future PDPs.
I thank Tom Roper, Brighton and Sussex Library and Knowledge Service, for the evidence search on personal development planning.
Competing interests: I have read and understood BMJ’s policy on declaration of interests and declare that I have no competing interests.
- ↵ Bullock K, Jamieson I. The effectiveness of personal development planning. The Curriculum Journal 1998 ; 9 : 63 -77. OpenUrl
- ↵ General Medical Council. Supporting information for appraisal and revalidation. GMC, 2012. www.gmc-uk.org/RT___Supporting_information_for_appraisal_and_revalidation___DC5485.pdf_55024594.pdf .
- ↵ General Medical Council. The GMC’s role in continuing professional development: Annexes. GMC, 2012. www.gmc-uk.org/static/documents/content/CPD-Annexes.pdf .
- ↵ Bryson D. The personal development planning cycle. Journal of Visual Communication in Medicine 2011 ; 34 : 177 -82. OpenUrl
- ↵ Doran GT. There’s a SMART way to write management’s goals and objective. Management Review 1981 ; 70 : 35 -36. OpenUrl
- ↵ Etherington C, Smith C, Wadhera M. Top tips on developing your personal development plan. BMJ Learning 2012 . http://learning.bmj.com/learning/module-intro/tips-personal-development-plan-pdp.html?locale=en_GB&moduleId=10037199 .
- ↵ General Medical Council. The Good medical practice framework for appraisal and revalidation. GMC, 2012 . www.gmc-uk.org/GMP_framework_for_appraisal_and_revalidation.pdf_41326960.pdf .
- ↵ NHS Leadership Academy. Clinical Leadership Competency Framework. NHS Institute for Innovation and Improvement. 2011. www.leadershipacademy.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/NHSLeadership-Leadership-Framework-Clinical-Leadership-Competency-Framework-CLCF.pdf .
- ↵ General Medical Council. Continuing professional development: Guidance for all doctors. GMC, 2012. www.gmc-uk.org/Continuing_professional_development___guidance_for_all_doctors_1114.pdf_56438625.pdf .
- ↵ Pyatt RS, Moore DE, Caldwell SC. Improving outcomes through an innovative continuing medical education partnership. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 1997 ; 17 : 239 -44. OpenUrl
- ↵ Academy of Medical Royal Colleges. Academy reflective template for revalidation. 2012. www.aomrc.org.uk/doc_view/9556-academy-reflective-template-for-revalidation .
- ↵ Ramsay R, Pitts P, While R, et al. Factors that helped and hindered undertaking practice professional development plans and personal development plans. Education for Primary Care 2003 ; 14 : 166 -177. OpenUrl
- ↵ Newby D. Personal development plans: Making them work, making them count. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment 2003 ; 9 : 5 -10. OpenUrl Abstract / FREE Full Text
- ↵ Main P, Curtis A, Pitts J, Irish B. A ‘mutually agreed statement of learning’ in general practice trainer appraisal: the place of peer appraisal by experienced course members. Education for Primary Care 2009 ; 20 : 104 -10. OpenUrl

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Professional Development Plans (PDPs)
Purpose of the pdp.
Students conceptualize a personalized blueprint for approaching their Walden doctoral studies and present it in a written Professional Development Plan (PDP) essay. Writing the essay allows students the opportunity to
- Reflect on their personal history, professional accomplishments, and future aspirations;
- Initiate a discussion with faculty about graduate study in general and the Walden program in particular;
- Articulate academic interests and set goals for their Walden educational experience; and
- Establish a personalized timeline for meeting degree requirements (i.e., the Program of Study form).
KAM-based PDPs also have the following goal:
- Identify themes for each KAM that support those interests and goals.
Students develop the PDP in close consultation with their Foundation course instructor/faculty mentor, who will review and approve the final document. (The Program of Study form is ultimately approved by the student's faculty chair.) Students are urged to review their PDP with their faculty mentor on an annual basis to assess their progress and growth. Students learn more about the PDP in the online Foundation course.
PDP Approval Process
Students submit the completed PDP to their Foundation course instructors electronically. Should a plan require revision, the course instructor returns it to the student with comments and feedback. When satisfied the plan meets the university's expectations, the course instructor forwards the PDP and the Program of Study form to the program's Student Success Advisors for initial review. He or she then forwards the PDP and the Program of Study form to the appropriate faculty chair for review.
The faculty chair may return the plan to the student and course instructor for revisions or approve it. Following approval by the faculty chair, the PDP is ratified in the Office of the Registrar.
Criteria for PDP Approval
A PDP will be considered for approval when all of the following criteria have been met:
- The PDP is well written and follows style and formatting guidelines in The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . (The use of the first person is permissible.)
- The content corresponds to the curriculum requirements of the university and the selected doctoral program, and to the student's specialization, if applicable.
- The content corresponds to the student's educational background and goals.
- The student has gained access to the necessary resources and exhibits the traits of an independent learner.
- The Plan of Study and the Program of Study form are complete.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Literature Review Matrix
- Next Page: Content and Structure of Course-Based PDPs
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Lifelong learning and nurses’ continuing professional development, a metasynthesis of the literature
Mandlenkosi mlambo.
1 Jersey General Hospital, St Helier, Jersey
2 Department of LIME, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Charlotte Silén
Cormac mcgrath.
3 Department of Education, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
Associated Data
The data in the study is comprised of previous research articles. A full list of articles is included in the Table Table3 3 .
Continuing professional development (CPD) is central to nurses’ lifelong learning and constitutes a vital aspect for keeping nurses’ knowledge and skills up-to-date. While we know about the need for nurses’ continuing professional development, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive continuing professional development. A metasynthesis of how nurses experience and view continuing professional development may provide a basis for planning future continuing professional development interventions more effectively and take advantage of examples from different contexts. The aim of this paper is to conduct such a metasynthesis, investigating the qualitative research on nurses’ experiences of continuing professional development.
A metasynthesis of the qualitative literature was conducted. A total of 25 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were reviewed.
We determined five overarching themes, Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. This metasynthesis highlights that nurses value continuing professional development and believe that it is fundamental to professionalism and lifelong learning. Moreover CPD is identified as important in improving patient care standards.
Conclusions
Based on the metasynthesis, we argue that access to continuing professional development could be made more attainable, realistic and relevant. Expediently, organizations should adequately fund and make continuing professional development accessible. In turn, nurses should continue to actively engage in continuing professional development to maintain high standards of nursing care through competent practice. This paper highlights the perceived benefits and challenges of continuing professional development that nurses face and offers advice and understanding in relation to continuing professional development. We believe that this metasynthesis contributes with insights and suggestions that would be valuable for nurses and policy makers and others who are involved in nurse education and continuing professional development.
Introduction
Health care professionals need to update their skills regularly and continuing education, or continued professional development (CPD) enables the renewal and updating of skills in health care settings. While we know about the need for CPD, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive CPD, and currently, there is no comprehensive global picture of how nurses view and experience CPD. A metasynthesis of the qualitative literature on nurses’ experiences of CPD may provide a basis for planning future CPD interventions more effectively and take advantage of examples from different contexts. This paper is organised in the following way; first we present the notion of CPD, we then use the United Kingdom, (UK) as a setting to offer an overview of the different mechanisms that exist in one specific health care setting, which may impact engagement with CPD. We acknowledge that similar mechanisms may exist in other health care settings and countries too, and identify the UK context, merely as a way to frame the paper. Subsequently, we conduct a metasynthesis of the qualitative literature addressing the topic of how CPD is experienced by nurses.
Continued professional development
This section aims to unpack the notion of CPD, which exists in different forms and is driven, in part, by top-down requirements, but also, bottom-up, from the needs of practitioners. Continuing professional development (CPD) programmes are central to nurses’ lifelong learning and are a vital aspect for keeping nurses’ knowledge and skills up-to-date. The requirement for nurses to participate in CPD differs between European countries and elsewhere in the world and can be mandatory or voluntary [ 1 , 2 ]. For example, CPD is mandatory in the U. K, Belgium, Spain, Australia and in some states in the United States of America, [ 2 – 4 ]. In these countries, nurses engage in CPD because it is a mandatory condition by nurse regulators for remaining registered to practice. However, in Sweden, Netherlands and Ireland nurses participate in CPD of their own volition [ 1 , 3 – 5 ]. Table 1 provides an overview of some of the European countries which provide mandatory and non-mandatory CPD.
Examples of mandatory and non-mandatory CPD in nursing in Europe (EFN, 2012)
In jurisdictions where CPD is mandatory, nurses engage in continuing education by participating in professional development that is relevant to their areas of practice. Mandatory CPD, refers to “… the process of ongoing education and development of healthcare professionals, from initial qualifying education and for the duration of professional life, in order to maintain competence to practice and increase professional proficiency and expertise” ([ 6 ], p.1). CPD can sometimes refer to a learning framework and activities of professional development which contribute to the continual professional effectiveness and competence [ 7 ]. Broadly, CPD is related to continuing education, and continual learning, both formal and informal, which results in the acquisition of knowledge and skills transfer by the practising nurse with the aim of maintaining licensure and competent practice [ 8 ]. Learners can utilise a mixed style approach to learning depending on the circumstances and context of the learning environment [ 9 – 11 ]. To succeed in providing comprehensive care for their patients, nurses need to utilise the best evidence available to them [ 12 – 14 ]. This requires different modes of learning and ways of knowledge acquisition and construction. To achieve this, nurses can engage in different approaches of acquiring knowledge through CPD, through formal learning, courses or workshops as well as workplace informal learning, through self-reflection, appraising literature for best evidence through journal clubs and giving feedback to each other [ 5 , 7 , 15 ]. Informal learning is often volitional and is largely initiated and controlled by individual nurses with the intention to develop their knowledge and skills [ 16 – 18 ]. Due to its unstructured and, at times, unintentional manner, such learning is often acquired during interactions with colleagues and patients [ 19 ]. One of the advantages of on-site learning, both formal and informal is that learners can utilise expertise which are already available on the ward [ 5 , 15 ]. On-site learning occurs often at the discretion and the willingness of managers to facilitate by providing time and space for learning to occur within the clinical areas. Even so, the fact remains that informal on-site learning is not an event but a continuous process, which draws from daily professional experiences. Lack of CPD trained nurses and ward needs, coupled with poor staffing levels, are cited as main barriers to informal workplace learning [ 5 , 15 ]. Evidence from CPD literature indicates that many nurses prefer informal work-based methods of learning, noting that most meaningful learning occurs through interactions with their colleagues [ 20 ]. From a study by Clarke [ 21 ], it was noted that nurses found informal learning methods such as supervision, attending team meetings/briefings, mentoring and observations to be important. Ultimately, whichever delivery method is used for CPD, continuous professional development extends the practitioner’s professional ability beyond pre-registration training, qualification and induction, thereby potentially enhancing the practitioner’s practice.
Continued professional development: the UK example
This next section aims to illustrate the different mechanisms that arise in one specific health care setting when implementing CPD on a national scale. We recognise that other mechanisms will exist in other contexts, and in places where CPD is not a formal requirement.
Today, nurses in the U.K. are required to engage in continuous learning in order to maintain competence as a means of keeping their licensure with their professional body, the Nursing & Midwifery Council (NMC) [ 22 ]. Since the 1980s, UK nurses and other allied health care professionals such as physiotherapists and occupational therapists have been required to engage in continuous professional development [ 23 ]. A justification for CPD has been the need to maintain professional registration to practice. For registered nurses in the UK, the requirement to engage in CPD came to the fore of continuing education in 1995. It was introduced by the then licensing body, the United Kingdom Central Council for Nursing, Midwifery and Health Visiting (UKCC) as post registration education and practice (PREP) [ 24 ]. Further to that, the Agenda for Change Reforms in 2003 introduced a system for linking pay and career progression to competency called the National Health Service Knowledge and Skills Framework [ 25 ]. The framework is linked to the individual nurse’s ability to demonstrate that they possess the necessary knowledge and skills to get promoted and be remunerated accordingly [ 25 ]. In the UK, further reforms to CPD were introduced in 2012 through the introduction of the Health Education England (HEE) in England [ 27 ]. Its mandate was to equip the NHS (National Health Service) workforce, including nurses with appropriate knowledge and skills to deliver high standard care to patients. The HEE’s role was to support workforce development by providing funding largely for nurses’ CPD. In 2016, PREP was replaced with revalidation, which still requires nurses to attend 35 h of CPD every 3 years [ 24 , 26 ]. Revalidation is the process through with nurses and midwives continue as registrants with the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) [ 25 ]. However, comprehensive HEE budget cuts have had a negative effect on nurse CPD initiatives [ 27 ]. CPD funding in UK was cut from 205 million pounds in 2015–16 to 83 million in 2017–18 [ 28 , 29 ]. Consequently, nurses have struggled to fulfil revalidation requirements due to some authorities freezing access and refusing to give nurses time to attend CPD activities [ 27 ].
This previous section offers an insight into different push-pull mechanisms, in the UK alone. Statutory requirements are underpinned by the need for nurses to maintain and develop the knowledge and skills to meet the expected competence standards of practice in response to expanding nursing roles and global trends. Our experience suggests that local governing bodies may enforce similar measures in contexts where CPD measure are not formalised. Nurses may find themselves caught between a patchwork of statutory requirements and a need to develop their skills and knowledge. Consequently, while we know about the need for nurses’ continuing professional development, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive continuing professional development. Therefore we propose that a metasynthesis of the qualitative literature could be a part of forming such a comprehensive view and use the following three questions to examine the literature What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?, What are the conditions necessary for CPD?, and, What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?
In this study, a metasynthesis was used to investigate the qualitative literature [ 30 , 31 ]. Metasynthesis is a form of systematic review method used to review qualitative studies in order to develop theory, to explore and understand phenomena or generate new knowledge, thereby creating meaning from that knowledge [ 32 – 36 ]. In this review, we present a metasynthesis based on the interpretation of qualitative results from topically related qualitative reports. In doing so we strive towards theoretical development, which according to Zimmer refers to the synthesis of findings into a product that is ‘thickly descriptive, and comprehensive’ and thus more complete than any of the constituent studies alone ( [ 30 ] p.313).
The results from metasynthesis studies may be used to underpin and inform healthcare policy, nursing practice and patient care. Furthermore, such information can be utilised by health care professionals involved in nursing education to inform planning and designing of training and educational programs. A number of steps are taken when conducting a metasynthesis [ 36 ] and involve;
a) bringing together a multidisciplinary team, in our case the team of three people includes two skilled medical education professional researchers with extensive experience in qualitative studies, including systematic reviews, moreover these two authors have more than 40 years of comprehensive experience of CPD in health care settings, two of the team are registered nurses and afford the team key insights into the context of nursing CPD, the team is spread across three institutions in two countries, finally, the team consisted of a search engine expert,
b) defining inclusive but manageable research questions, see the questions above;
c) conducting the systematic search, in our case this was conducted by the search engine expert, see Table 2 for the search criteria,
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review
d) quality assessment of the studies, this was done using the CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) criteria, weighting three levels (not met, partially met, totally met) where assessment was done by all three authors see Table 4 , e) extracting data from the studies, see Table 3 ,
Summary of articles with location cohort data collection method
Quality assessment according to modified CASP criteria
e) data analysis, which is explained in more detail below, and.
f) expressing the details of the synthesis which is done in the findings sections below.
Search strategy
A comprehensive systematic search of literature was subsequently conducted on Medline (OVID), PubMed and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Web of Science (Clarivate) and ERIC (ProQuest). The literature search was conducted by a librarian. The literature search was conducted in December 2019 and was limited to articles published in English from 2010 to 2019. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the literature search were established and are presented below in Table Table2. 2 . The inclusion criteria comprise of articles from empirical studies (using qualitative methods), discussing nurse continuing learning and education, professional development, lifelong learning, CPD, motivation and barriers.
Data analysis
A total of 1675 records were identified, and following de-duplication, 1395 articles remained. All 1395 articles were screened. Articles had to address nurses’ CPD and continuing education, using qualitative oriented methods. After the first screening 72 articles remained. These articles were divided into three batches and were divided among the researchers. Each author read one batch to further identify if the articles were to be included. For each batch, a second author read the articles, meaning all articles were read by at least two authors. Any remaining ambiguities were discussed and resolved among the team. Figure 1 is a summary of the literature search and screening and Table Table3 3 presents an overview of each study with its citation, location, cohort size and data collection method. 25 articles were identified for the final metasynthesis. All authors read the final 25 articles. Quality assessment using CASP criteria as outlined by Lachal et al., [ 36 ] is reported in Table Table4. 4 . In the quality assessment we assess the following components; Was there a clear statement of the aims of the research?, Is a qualitative methodology appropriate?, Was the research design appropriate to address the aims of the research?, Was the recruitment strategy appropriate to the aims of the research?, Were the data collected in a way that addressed the research issue?, Has the relationship between researcher and participants been adequately considered and reported?, Have ethical issues been taken into consideration?, Is there a clear statement of findings? We also introduce the question of whether the texts are available in Open Access form or not. We introduce this question, as we believe the outcomes on research on nurses’ perceptions and experiences of CPD is potentially important for their practice, and access via Open Access channels could act as a quality dimension. However, without access to the data and the process of interpretation we choose not to assess; How valuable is the research?, Was the data analysis sufficiently rigorous?

Overview of the steps in the literature screening
For the final analysis enabling the synthesis of the studies in this metasynthesis the articles were read carefully, findings related to the research questions; What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?, what are the conditions necessary for CPD? And what are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?, were identified. In the next step of the analysis, study findings were examined using constant comparative analysis. The findings and conceptual categories were coded, compared, and sorted, focusing on conditions, strategies, and consequences. Finally, the synthesis, the interpretation of the findings, were described as themes, and these were revised several times until a coherent whole was formed [ 30 , 36 – 38 ] Before the final description of the synthesized themes, all the three authors discussed the content of the themes until consensus concerning credibility was reached.
From the metasynthesis we present five overarching themes, Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. Each theme is further explained below with references to the relevant literature.
Organisational culture shapes the conditions
Organisational culture played an important role towards the professional development of staff. Organisational commitment and support to personal and professional development of its staff was seen as an indication that staff were valued [ 5 , 15 ] Moreover, CPD initiatives contributed to attracting and retaining staff [ 39 ]. Additionally, a culture that was flexible and adaptable to change was perceived by some participants to be favourable towards CPD [ 40 – 42 ]. Flexibility extends to matters such as CPD availability, and also location, but related also to creating opportunities in the work schedule for the nurses to participate [ 43 ]. Other organisational factors such as funding for CPD programs, staff access of CPD learning, role of management in staff CPD, manageable nursing workloads, the design & delivery of CPD activities, communication and collaboration between CPD providers and management are specifically organisational factors seen as crucial to effective staff development [ 44 , 45 ]. Developing a strategy for CPD was also acknowledged as a key element of organisational culture as a way of enabling participation [ 46 ]. In a similar fashion, it was argued that the organisation needs to be focussed on incremental, but constant development of practices, and here CPD was seen to play a key role [ 47 ]. This sentiment was expressed elsewhere too, but from a re-skilling, or keeping up-to-date perspective, where the organisation is seen to have great importance [ 48 , 49 ]. The value of partnerships and shared understanding between managers and nurses as key enabling factors was identified in several studies [ 46 , 50 ]. In a related fashion, Jantzen argues that organisations should actively avoid fragmentation of CPD initiatives [ 51 ]. As more CPD training is digitised IT/ICT (information communication technology) skills were seen as key to successful CPD implementation [ 46 , 52 ]. It was acknowledged that the transformation to online learning does not only affect nurses, it involves change for the whole department [ 52 ].
Supportive environment as a prerequisite
An environment that supports learning was seen as a necessary prerequisite for CPD. Conditions had to include, flexible off-duty patterns to allow time for staff to study, availability of workplace learning, workloads were not excessive and CPD was fully funded or a shared responsibility between employer and staff [ 46 , 52 ]. Other indicators of a supportive environment included staff access to different CPD activities relevant to their career goals, while at the same time meeting organisational goals and where staff felt free to study openly and not secretively [ 15 , 41 ]. Moreover, the development of local and contextual CPD was seen as something that supported and made participation possible [ 43 , 53 , 54 ]. Participants indicated that nurses required financial support and practical support in the form of adequate time to participate in CPD activities and suitable staff cover when colleagues were away attending CPD activities [ 47 ]. Jantzen et al. [ 51 ] suggest there are three catalysts in a supportive environment; mentors, workplace camaraderie and a highly functional workplace team. Moral support or encouragement was identified in more than one study, where it was articulated that learners want to know there is an appreciation for the time and dedication needed to engage in CPD [ 44 , 46 , 50 ]. The value of learning from other health professionals other than nurses, in the day-to-day work was highlighted for professional development [ 54 ]. Similarly, the sense of a supportive environment with a strong team spirit is communicated elsewhere [ 39 ]. Explicit support is noted in several studies; support for novice nurses [ 39 ] but also the importance of explicit managerial support [ 55 ]. Conversely, in one study, respondents noted that there was less support for experienced or late career nurses [ 56 ].
Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values
The value and importance of CPD was discussed in many of the studies. In some, CPD was perceived to be key in defining nurse professionalism [ 6 , 15 , 40 , 47 , 49 ]. Engaging in CPD was also viewed by new nurse graduates as an important element of their individual professionalisation in nursing [ 6 , 15 , 40 ]. In addition, CPD was perceived to be important for enhancing and up or re-skilling, keeping knowledge and skills up-to-date, considering that nursing practice has become more evidence based [ 6 , 43 , 46 , 51 , 54 , 56 ]. Furthermore, nurses stated that CPD was important for maintaining licensure, and felt that the responsibility for enrolling and participating in CPD activities was with the individual nurse, not with the employing organisations [ 53 ]. On the other hand, participants felt more motivated to learn if they could easily access CPD programs, if they felt supported and if there were a variety of CPD activities on offer. Here, bedside and informal learning was emphasized as important [ 57 ]. Similarly, contextualising learning and placing it in close proximity to practice was seen to enhance motivation and engagement [ 42 ]. CPD was also viewed as a way to start networking with other peers [ 44 ]. In one study, a competency framework was introduced, here participants felt that such a framework could help them reflect on their own practice and, as it provides a systematic approach to assessing a patient, look at their own strengths and weaknesses [ 58 ]. Such competency frameworks help to harness scarce training more effectively and encourage individuals to take more responsibility for their own development [ 58 ].
Participants’ attitudes towards CPD funding were mixed, with some stating that funding for CPD was the employer’s responsibility, while others felt that the individual practitioner was responsible or that the burden ought to be shared between the organisation and the nurse [ 5 , 15 , 40 ].
Nurses’ perceptions of barriers
Poor staffing levels, heavy workloads, lack of funding, lack of study time and anti-intellectualism were some of the perceived barriers to CPD brought out by this review. Participants in the studies reviewed felt that a lack of organisational support, especially from their managers, was an indication that the organisation did not take professional development of its staff seriously [ 46 ]. Some respondents reasoned that an anti-academic culture and lack of relevant CPD programs was further indication of this [ 5 , 15 , 40 ]. Seeing a connection to patient care was identified as a strong driver and nurses identified that CPD initiatives would be filtered out unless there was such a clear connection to patient care [ 43 , 51 ].
Additionally, some studies indicated that as role models, managers had to show interest in their own CPD, in order to motivate other nurses. In other words, the manager’s knowledge of CPD activities was reflected by their attitude towards work-based study, acceptance of staff who studied openly, the way the manager prioritised funding support and managed staff shift schedules to allow study release time [ 5 , 39 , 54 , 56 ]. Fatigue was identified as a major barrier. For example in Jho et al. [ 53 ], in a context of mandated CPD, respondents felt tired due to the heavy nursing workload in conjunction with CPD. Lack of strategy, and financial initiatives in terms of money, or time off to study was also acknowledged as a barrier [ 5 , 39 , 54 , 56 ]. Lack of transparent career trajectories were also acknowledged as an area of concern [ 44 ].
Other barriers, or de-motivating factors were identified; difficulties in attending CPD and keeping a life-work balance [ 48 ]. Barriers included: formal CPD courses away from the clinical areas were perceived to lack in authenticity [ 47 , 49 ] and a mis-match in expectations and outputs, where nurses viewed themselves as agents of change, but where the organisation was unable to offer means to capitalise on this perception and desire to bring about change [ 50 , 59 ]. As much as competency frameworks were viewed positively in offering a sense of direction, a divergent view was that they were limiting or created set boundaries that participants experienced as limited, for example, if used as prescriptive, hindering nurses to define their own learning needs [ 58 ]. Lack of IT competence was also perceived as a barrier [ 52 ] with more CPD being conducted online.
Perceived impact on practice as a core value
The impact of CPD on nursing practice was perceived as important and valuable in different ways. The impact could be both direct and indirect depending on the organisational culture [ 41 , 45 ]. This mixed perception could be due to the complex nature of health care organisations which can make knowledge sharing difficult [ 45 ] and that some CPD learning was done secretly, results of which were difficult to evaluate [ 41 ]. In the case where a competency framework was studied, participants felt that using the competency framework helped them organise their work and their thought processes [ 58 ]. A common sentiment was that CPD would benefit health care organisation through the provision and enhancement of practitioners’ knowledge and skills [ 46 ]. Sentiments articulating expectations of an impact of CPD could also be seen elsewhere too [ 52 , 55 , 56 , 60 ]. Moreover, CPD is expected to rely on better communication between managers and nurses as a way of informing each other about needs and means of fulfilling those needs [ 48 ]. Direct impact was realised through improved interprofessional collaboration and the idea that new methods could be directly translated into practice [ 47 ]. Others however, raised concerns that CPD programmes or courses may not translate into new practices [ 50 ]. This sentiment was echoed elsewhere too, where a need to situate CPD in close proximity of patients was seen as important for CPD to impact practice [ 49 ] While indirect impact happened through dissemination of knowledge and skills from CPD learning to other nurses at ward level, arguments were put forward that there will be no difference to practice unless organisational processes support and evaluate its effect on practice [ 46 ]. Participants reported that their professional confidence was enhanced, they felt they could challenge medical decisions and the status quo [ 41 ]. Furthermore, participants felt that CPD enhanced their professional knowledge and skills for better patient care through improved care standards, how they communicated and collaborated with other professionals. Participants also believed that learning increased their chances for career progression and reduced work-related anxiety because of enhanced knowledge [ 40 , 41 ].
The aim of this paper is to conduct a metasynthesis investigating the qualitative research on nurses’ experiences of continued professional development. As a result, this metasynthesis revealed a number of overarching themes, which synthesize the findings of previous qualitative oriented research during the period 2010–2019. 2010 was chosen to include the last 10 years of CPD research. The themes are; Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. The themes put focus on important issues that were recurrently put forward by the nurses in the studies reviewed. However, the themes are not isolated from each other, rather, the content of the themes is interrelated. Some of the themes mainly mirror an overarching perspective at the organisational level of health care, while other themes describe the nurses’ experiences and needs on a personal level. The following discussion explores the above themes in relation to the three questions posed earlier; what is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge? What are the conditions necessary for CPD? What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD? While we acknowledge that the questions and themes overlap, we have endeavoured to frame the discussion around the three research questions individually.
What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?
Nurses reported that CPD raises professional standards through competencies gained, thereby increasing professional performance with positive benefits for patients, organisations and individual nurses [ 40 ]. These outcomes were seen most prominently in the themes Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. Closely aligned to CPD are the nurses’ clinical effectiveness and competence. Maintaining both requires nurses to keep their practice up-to-date highlighting the importance of CPD for nurses. The knowledge and skills gained by nurses through CPD advances the professional status of nursing, which was an idea that was prevalent in some of the studies in this review [ 15 , 40 , 47 , 50 ], but is also illustrated elsewhere in the literature [ 8 , 21 ]. Nurses acknowledged that expectations of professional accountability meant that standards of practice ought to be kept high in order to pass public scrutiny [ 15 , 40 ]. Furthermore, skills acquired through CPD, such as the ability to conduct systematic peer-reviews [ 45 ] and appraise literature for best evidence, provide nurses with essential professional competencies, embeds values such as caring behaviours, influences beliefs and attitudes which in turn shape nurses’ professional conduct [ 61 ]. As such CPD is seen as a tool for nurses to update their skills, and in doing so deliver safe and high-quality health care. As revealed in this review, nurses were willing to fully fund or part-fund their CPD as long as CPD programs were captivating, easily accessible, there was fair allocation of study time and their efforts towards CPD were recognised. The latter implies that nurses want time and space to transfer their CPD learning into practice and for their CPD to be recorded [ 5 , 45 ]. The belief is that, consequently, patient care will improve with positive impact from organisational change [ 15 , 45 ]. However, it is clear that the organisation is key in making CPD work for nurses. The issues brought up in the theme organisational culture shapes the conditions is thus very important in stimulating nurses to engage in CPD. The nurses’ attitudes and motivation to engage in CPD also depends on a supportive environment and engagement may in turn influence the organisational culture.
What are the conditions necessary for CPD?
A disconnect could be seen in relation to the conditions for CPD, where access to CPD training came to the fore as problematic in some of the studies. Nurses had to travel long distances to attend courses [ 15 , 62 , 63 ]. To avoid these challenges, nurses settle for CPD as long as it fulfils mandatory requirements for registration [ 53 ]. If intentions of CPD are to provide a basis for the continual updating of skills, then authentic learning as an expected outcome is seen as a prerequisite for nurses to engage in CPD, whether it occurs at the bedside, at a training facility or through an IT mediated interaction. This calls for accessible CPD, improved design and delivery methods for all nurses [ 52 ]. Nurses’ experiences described in the themes Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, show that structural and moral support are both important. Structural support in the form of availability, time to engage in CPD, as well as clear expected outcomes [ 46 , 49 ], but also moral support in the form of an understanding management and environment, and also peers and leaders who themselves also prioritise CPD [ 58 ]. Organisational support and commitment towards CPD should mean allocation of study time, support of nurses who study privately, by creating space for knowledge and skills integration and managing poor cultural practices that hinder open study. Funding is seen as a key factor across many of the studies, both in terms of enabling nurses to participate, but also as a way of acknowledging nurses who engage in CPD. Further studies may need to look more closely at how nurses perceive different aspects of funding. For nurses’ lifelong learning to endure, CPD programs need to be more accessible and kept interesting by making them more relevant to nurses’ practice contexts. Here the importance of the organisation for creating a CPD conducive environment is emphasized [ 46 , 51 , 52 ]. As role models, managers need to lead by example and engage in CPD themselves, but also demonstrate explicit support. They also need to influence policy to create environments conducive to CPD. If funding situations do not improve, work-based CPD learning could be one of the alternative ways of CPD delivery for nurses. To promote CPD engagement and cost reduction, eLearning approaches could be utilised for education and training. However, poor IT skills among nurses, but also within organisations continues to be a potential weakness [ 52 ]. A challenge remains here in enabling nurses to get recognition from informal on-site learning [ 16 – 18 ], where elements of meta-cognitive reflection can be used to acknowledge nurses’ continued professional development.
What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?
In some of the literature reviewed, participants lamented their current conditions for CPD, and identified clear barriers and challenges in the form of concerns related to lack of funding for CPD, staffing levels, time allocation for study, lack of organisational support because of negative cultural practices, CPD design & delivery and limited choice of CPD activities. This is articulated within the themes: Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers [ 2 , 11 , 34 , 41 ] . However, studies did not explore the views of nurses on recruitment and retention and its impact on accessing a variety of CPD activities. Evidence from this review indicates that modernising healthcare and simultaneously cutting CPD funding for nurses could lead to a limited number of nurses attaining the skills and competences needed for the modernisation process. In view of the understaffing that is reported elsewhere [ 5 , 15 ], we identify a cause for concern. These perceived barriers may undermine nurses’ professional development [ 23 , 59 ]. Moreover, the findings presented here revealed that nurses face a number of challenges in relation to their CPD participation. The challenges include limited CPD activities to choose from, poor CPD delivery methods, negative organisational culture practices such as anti-intellectualism and lack of support. As a result, nurses were less motivated to participate in CPD training [ 57 ].
It is clear from the review, that IT concerns are becoming more and more prominent, given that more CPD programmes are being offered through digital platforms [ 47 ]. This is a concern for both the individual nurses, but also their organisations. On concerns regarding CPD delivery methods, nurses indicated that they preferred different styles. With these concerns comes the view that learners learn in different ways depending on the context and subject of study [ 61 , 62 ]. This supports the notion that individuals have different learning preferences [ 61 ], where some adult learners learn better in a structured and teacher guided context, while others prefer self-direction.
Limitations
The search was conducted by an experienced search engine expert. Even so, we may still have been unsuccessful in finding all the relevant articles. The study was focussed on qualitative studies, which means that studies using predominantly quantitative or mixed methods were not included, but could hold important insights. In the introduction to the study we used the UK as an example for how CPD might be regulated. However, we have conducted a comprehensive search of the literature and our analysis was not conducted with a UK-centric perspective. While each study needs to be understood in terms of local rules and regulations, the similarities in the findings are striking.
The metasynthesis indicates that differences exist between the nurses’ CPD needs and expectations and organisations’ approaches to nurses’ professional development. The review lays bare a disconnect between the rhetoric of identifying CPD as a way to enhance nurses’ skills, and the reality of CPD interventions, where nurses do not feel support within their organisations or from their immediate supervisors. The review also revealed that CPD is an important element of nursing practice and nurses’ lifelong learning. Furthermore, it suggests that nurses are motivated to take part in CPD to enhance their knowledge, improve skills and keep up- to -date with recent evidence. While evidence from this review indicates that nurses believe that CPD has a positive impact on patient care, there is lack of contemporary research to qualify this claim and there is limited evidence from this review to support this assumption. However, evidence from the review suggests and confirms, that the greatest barriers for CPD in nursing are a lack of funding and time to participate in CPD activities, which are clearly related to organisation structure. It is difficult to envisage how such conditions could be conducive for nurse CPD to flourish. Such perceived barriers undermine nurses’ efforts to keep knowledge and skills up-to-date and provide better patient care while meeting the ever-changing needs and expectations of their patients. This is further exacerbated by negative organisational cultural practices and lack of knowledge on how to facilitate, design and deliver CPD for their staff. We conclude that policy makers and relevant stakeholders need to put in place strategies to support nurse CPD in long term and in doing so tear down the barriers of CPD.

Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Gun Brit Knutssön, at Karolinska Institutet’s University Library, Stockholm, Sweden for the systematic search.
Abbreviations
Authors’ contributions.
MM, CS and CMG designed the study. MM, CS and CMG defined the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the search. MM, CS and CMG conducted an equal share of the analysis work. Versions of the manuscripts were shared, revised and written by all three authors. All authors have read and approved the submitted manuscript.
Open Access funding provided by Stockholm University.
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
Ethical vetting in Sweden is conducted by a central and national committee, the Swedish Ethical Review Authority. Review articles where research is not conducted on humans, or animals does not require ethical vetting as per Swedish Ethical Review Act (SFS 2003:460).
Not Applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Our range of over 180 online courses are fully accredited, trusted by more than 3 million learners and ideal for training you and your team.
- Food Hygiene
- Health and Safety
- Safeguarding
- Asbestos Awareness
- Fire Safety
- Mental Health
- Health and Social Care
- Business Essentials
- Team training

Welcome to the Hub, the company blog from High Speed Training.
Select a topic to find the most up to date, practical information and resources produced by our experts to support you in your professional life.
- Health & Safety
A Personal Development Plan (PDP) Guide & Template
What is a personal development plan.
Personal development is an ongoing process that drives you to improve your knowledge, skills and experience, so that you can achieve your goals. A personal development plan (or PDP) is a method of focussing your goals into achievable steps, which helps you keep track of your personal development.
Download Free PDP Example/Template
Why Should I Create a Personal Development Plan?
Your plan may be aimed at your education, career or personal goal, or a mixture of all three – that is up to you to determine. Whatever the case may be, a good plan will provide you with a clear sense of focus. It helps you map out a path towards your goals, strategise a plan to achieve them, record the actionable steps you will take, and set a timeframe for completing them. Focussing your goals into a PDP helps you maintain your vision, keep on track to achieve your targets, and reflect on your progress.
Simply put, a PDP can help you build a clear understanding of what you want to achieve and how you are going to achieve it.
Interested in Learning More?
Let us help with your personal development goals this year. Choose from a wide range of business essentials courses , whether it be Leadership and Management , Starting a Business , or Coaching and Mentoring . You could have your CPD recognised certificate in a matter of hours!
A clear plan can also support your positive mental wellbeing and improve your level of satisfaction. It can provide a sense of direction, purposefulness and a feeling of success as you start to fulfil your potential. All of these can have very positive impacts on your mental health.
Therefore, discovering what your goals are, getting organised and giving yourself a sense of direction can be incredibly beneficial. This article will give you an understanding of how to write a personal development plan, as well as provide you with a handy template to support your development journey.
How to Write a Personal Development Plan
There are seven steps to writing a PDP:
- Set yourself goals.
- Prioritise those goals.
- Set yourself deadlines for when you want to achieve them.
- Recognise threats and opportunities.
- Develop your skills or increase your knowledge.
- Use your support network.
- Measure your progress.

1. Set Yourself Goals
The first step is to set yourself goals . Think about what you want to achieve, whether that’s within a few weeks, within a year, or over your lifetime.
Deciding what you want is not only the first step in planning, it’s also the hardest. Once you’ve figured out what you want to do, that goal will provide clear direction and a structure for your resulting plan.
At this stage, your goals will feel big. You might be wondering how you are ever going to achieve them. Don’t worry – the next step is to prioritise and turn those goals into smaller, actionable steps that will support you on your way to achieving them.
2. Prioritising Your Goals
Now that you have your goals, the next stage is to break them down into smaller steps. When doing this, it’s important that your goals are SMART:
- Specific. Avoid large, ambiguous steps. These won’t support you on your way to achieving your goals. Insted, make sure that your goals are specific and clearly highlight the skill, knowledge or experience you want to develop.
- Measureable. You need to be able to monitor and reflect on your progress. Therefore, your goals need to be measurable, such as by setting a goal to develop your SEO knowledge with a measurable target of growing your website traffic by a set, defined percentage.
- Attainable. Your goals need to be achievable and realistic. You need to think about if it is something you can realistically achieve with the time and resources you have. If not, you will likely be setting yourself up for failure.
- Relevant. It’s important to keep your overall goal in mind and make sure that every step you take is supporting you to achieve it. You don’t want to be spending time doing things that don’t get you where you want to go.
- Time-bound. Set yourself key targets to achieve and deadlines in which to achieve them. This will help you stay focussed on achieving your goals. However, it’s important to make sure you are realistic in what you can achieve in any given period. Don’t try to achieve everything all at once. It’s unrealistic and you won’t be setting yourself up well to achieve them. Remember that personal development is a journey – your PD plan can continue to grow and develop as you take those steps towards your goals.
Once you have your goals, you’ll need to prioritise them.
In your PDP, you should be setting yourself mini goals to make the big ones happen.
For example, if you wish to pursue a career in academia as a senior lecturer and then a professor, a necessary step to succeeding in this goal is to achieve a PhD. So that would be one of your long-term goals. You then need to break it down into steps, such as:
- Learn about the PhD application process.
- Find a suitable university and supervisor for a PhD.
- Look at routes for funding.
- Find studentships to apply for or apply to your university of choice.
- Write and submit your PhD application.
3. Set Yourself Deadlines
Knowing when you want to achieve a goal is crucial, and picturing your future is an important source of motivation and inspiration.
Having goals and a set deadline will drive your motivation to achieve them. For example, if your goal is to buy a home, knowing when you want to achieve it will help you calculate exactly how much money you need to save each year in order to get your deposit. The same is true for your skills, knowledge and experience development. As mentioned above, setting realistic and time-bound goals are essential to achieving them.
One good way to understand more about achieving your goals is to speak to those who have previously trodden a similar path. Learning about their experiences can help you understand key barriers to, or methods of, success that may also be applicable to your PDP.

4. Recognise Threats and Opportunities
When considering your goals, you should identify your own strengths, consider areas of weakness you can develop, look at the opportunities available to support you in achieving your goals, and any threats that may hinder you in your progress. This is called a SWOT analysis. Note that these threats may be external or they may be core skills that you can develop as part of your PDP.
For example, a lack of motivation could hinder your plans to apply for a PhD. However, once you’ve identified your tendency to procrastinate or lose focus, you can put in place methods that will keep you motivated.
There are also going to be things that you could do, and connections with people or resources you could take advantage of, that will help you on your way. These are your opportunities that you should commit to doing.
For example, if there’s a conference coming up, take advantage of that. Go along and network, stay up to date on the latest knowledge, or even present a paper. These are all opportunities that could help you achieve your goals.
5. Develop Yourself
Once you have an idea of what could help or hinder you, this is when you can capitalise on those opportunities you recognised. Make an action plan about how you’ll make that progress.
Whatever it is that hinders you, there’s a way to stop it. Your plan is the first step to making sure you stay on track.
So, why not take a look at how to upskill yourself , develop transferable skills in today’s rapidly changing jobs market, or even discover an online learning opportunity .
6. Use Your Support Network
The next thing you need to realise is that:
You don’t have to do everything by yourself.
And you shouldn’t. The support network around you is a valuable asset, so use it and don’t underestimate it.
In your PDP, list the people who can help you. This could be a financial advisor, a friend, or a colleague. People are often so happy to help you, more than you might realise.

7. Measure Progress
After you’ve achieved some progress, whether it’s big or small, take time to reflect on how far you’ve come.
Recognising what has gone well is an effective way to bolster your motivation and remain dedicated.
And after a setback, this is another time to take stock.
Wallowing – briefly – is a good way to feel what you need to without holding on to it. Holding onto sadness, anger or frustration, however, will only deter you. These emotions will take you nowhere and will only hinder you.
You should also spend a little time figuring out why it went wrong. Can you identify a skills or knowledge gap?
If you can, then you can get yourself back on track by focussing on your next step. This will reignite your sense of purpose and help you regain control, which is integral to making progress.
Continue to reflect on your progress. You can gain significant insight from your reflections and this can help you grow. Remember that you should update your plan where necessary. Don’t overload it at any one time but, once you have achieved your small steps, reflect and then update your plan to focus on your next move.
Free Personal Development Plan Example & Template
In this article, we have discussed how you can create your own personal development plan, so you should now feel ready to start considering your goals and developing your own plan. To help you produce an effective personal development plan, we have created an editable template that you can use. Take a look at our example PDP, and download your free template below:
Further Resources:
- How to Upskill Yourself
- What are Personal Development Goals for Work?
- Using Key Phrases in Performance Reviews & Appraisals
- Resilience Quiz
- Resilience in the Workplace: What are the Benefits and How Can Businesses Develop It?
- How to Stand Out in a Virtual Interview: Preparation Tips
- What is CPD? A Guide to Continuing Professional Development
- Writing A Professional Development Plan – Example & Template
- Business Essentials Courses

Post Author

Her favourite article is Five Top Learning and Development Trends for 2020
You may also like

- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 14 April 2021
Lifelong learning and nurses’ continuing professional development, a metasynthesis of the literature
- Mandlenkosi Mlambo 1 , 2 ,
- Charlotte Silén 2 &
- Cormac McGrath 2 , 3
BMC Nursing volume 20 , Article number: 62 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
231k Accesses
150 Citations
22 Altmetric
Metrics details
Continuing professional development (CPD) is central to nurses’ lifelong learning and constitutes a vital aspect for keeping nurses’ knowledge and skills up-to-date. While we know about the need for nurses’ continuing professional development, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive continuing professional development. A metasynthesis of how nurses experience and view continuing professional development may provide a basis for planning future continuing professional development interventions more effectively and take advantage of examples from different contexts. The aim of this paper is to conduct such a metasynthesis, investigating the qualitative research on nurses’ experiences of continuing professional development.
A metasynthesis of the qualitative literature was conducted. A total of 25 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were reviewed.
We determined five overarching themes, Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. This metasynthesis highlights that nurses value continuing professional development and believe that it is fundamental to professionalism and lifelong learning. Moreover CPD is identified as important in improving patient care standards.
Conclusions
Based on the metasynthesis, we argue that access to continuing professional development could be made more attainable, realistic and relevant. Expediently, organizations should adequately fund and make continuing professional development accessible. In turn, nurses should continue to actively engage in continuing professional development to maintain high standards of nursing care through competent practice. This paper highlights the perceived benefits and challenges of continuing professional development that nurses face and offers advice and understanding in relation to continuing professional development. We believe that this metasynthesis contributes with insights and suggestions that would be valuable for nurses and policy makers and others who are involved in nurse education and continuing professional development.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Health care professionals need to update their skills regularly and continuing education, or continued professional development (CPD) enables the renewal and updating of skills in health care settings. While we know about the need for CPD, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive CPD, and currently, there is no comprehensive global picture of how nurses view and experience CPD. A metasynthesis of the qualitative literature on nurses’ experiences of CPD may provide a basis for planning future CPD interventions more effectively and take advantage of examples from different contexts. This paper is organised in the following way; first we present the notion of CPD, we then use the United Kingdom, (UK) as a setting to offer an overview of the different mechanisms that exist in one specific health care setting, which may impact engagement with CPD. We acknowledge that similar mechanisms may exist in other health care settings and countries too, and identify the UK context, merely as a way to frame the paper. Subsequently, we conduct a metasynthesis of the qualitative literature addressing the topic of how CPD is experienced by nurses.
Continued professional development
This section aims to unpack the notion of CPD, which exists in different forms and is driven, in part, by top-down requirements, but also, bottom-up, from the needs of practitioners. Continuing professional development (CPD) programmes are central to nurses’ lifelong learning and are a vital aspect for keeping nurses’ knowledge and skills up-to-date. The requirement for nurses to participate in CPD differs between European countries and elsewhere in the world and can be mandatory or voluntary [ 1 , 2 ]. For example, CPD is mandatory in the U. K, Belgium, Spain, Australia and in some states in the United States of America, [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. In these countries, nurses engage in CPD because it is a mandatory condition by nurse regulators for remaining registered to practice. However, in Sweden, Netherlands and Ireland nurses participate in CPD of their own volition [ 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Table 1 provides an overview of some of the European countries which provide mandatory and non-mandatory CPD.
In jurisdictions where CPD is mandatory, nurses engage in continuing education by participating in professional development that is relevant to their areas of practice. Mandatory CPD, refers to “… the process of ongoing education and development of healthcare professionals, from initial qualifying education and for the duration of professional life, in order to maintain competence to practice and increase professional proficiency and expertise” ([ 6 ], p.1). CPD can sometimes refer to a learning framework and activities of professional development which contribute to the continual professional effectiveness and competence [ 7 ]. Broadly, CPD is related to continuing education, and continual learning, both formal and informal, which results in the acquisition of knowledge and skills transfer by the practising nurse with the aim of maintaining licensure and competent practice [ 8 ]. Learners can utilise a mixed style approach to learning depending on the circumstances and context of the learning environment [ 9 , 10 , 11 ]. To succeed in providing comprehensive care for their patients, nurses need to utilise the best evidence available to them [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. This requires different modes of learning and ways of knowledge acquisition and construction. To achieve this, nurses can engage in different approaches of acquiring knowledge through CPD, through formal learning, courses or workshops as well as workplace informal learning, through self-reflection, appraising literature for best evidence through journal clubs and giving feedback to each other [ 5 , 7 , 15 ]. Informal learning is often volitional and is largely initiated and controlled by individual nurses with the intention to develop their knowledge and skills [ 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Due to its unstructured and, at times, unintentional manner, such learning is often acquired during interactions with colleagues and patients [ 19 ]. One of the advantages of on-site learning, both formal and informal is that learners can utilise expertise which are already available on the ward [ 5 , 15 ]. On-site learning occurs often at the discretion and the willingness of managers to facilitate by providing time and space for learning to occur within the clinical areas. Even so, the fact remains that informal on-site learning is not an event but a continuous process, which draws from daily professional experiences. Lack of CPD trained nurses and ward needs, coupled with poor staffing levels, are cited as main barriers to informal workplace learning [ 5 , 15 ]. Evidence from CPD literature indicates that many nurses prefer informal work-based methods of learning, noting that most meaningful learning occurs through interactions with their colleagues [ 20 ]. From a study by Clarke [ 21 ], it was noted that nurses found informal learning methods such as supervision, attending team meetings/briefings, mentoring and observations to be important. Ultimately, whichever delivery method is used for CPD, continuous professional development extends the practitioner’s professional ability beyond pre-registration training, qualification and induction, thereby potentially enhancing the practitioner’s practice.
Continued professional development: the UK example
This next section aims to illustrate the different mechanisms that arise in one specific health care setting when implementing CPD on a national scale. We recognise that other mechanisms will exist in other contexts, and in places where CPD is not a formal requirement.
Today, nurses in the U.K. are required to engage in continuous learning in order to maintain competence as a means of keeping their licensure with their professional body, the Nursing & Midwifery Council (NMC) [ 22 ]. Since the 1980s, UK nurses and other allied health care professionals such as physiotherapists and occupational therapists have been required to engage in continuous professional development [ 23 ]. A justification for CPD has been the need to maintain professional registration to practice. For registered nurses in the UK, the requirement to engage in CPD came to the fore of continuing education in 1995. It was introduced by the then licensing body, the United Kingdom Central Council for Nursing, Midwifery and Health Visiting (UKCC) as post registration education and practice (PREP) [ 24 ]. Further to that, the Agenda for Change Reforms in 2003 introduced a system for linking pay and career progression to competency called the National Health Service Knowledge and Skills Framework [ 25 ]. The framework is linked to the individual nurse’s ability to demonstrate that they possess the necessary knowledge and skills to get promoted and be remunerated accordingly [ 25 ]. In the UK, further reforms to CPD were introduced in 2012 through the introduction of the Health Education England (HEE) in England [ 27 ]. Its mandate was to equip the NHS (National Health Service) workforce, including nurses with appropriate knowledge and skills to deliver high standard care to patients. The HEE’s role was to support workforce development by providing funding largely for nurses’ CPD. In 2016, PREP was replaced with revalidation, which still requires nurses to attend 35 h of CPD every 3 years [ 24 , 26 ]. Revalidation is the process through with nurses and midwives continue as registrants with the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) [ 25 ]. However, comprehensive HEE budget cuts have had a negative effect on nurse CPD initiatives [ 27 ]. CPD funding in UK was cut from 205 million pounds in 2015–16 to 83 million in 2017–18 [ 28 , 29 ]. Consequently, nurses have struggled to fulfil revalidation requirements due to some authorities freezing access and refusing to give nurses time to attend CPD activities [ 27 ].
This previous section offers an insight into different push-pull mechanisms, in the UK alone. Statutory requirements are underpinned by the need for nurses to maintain and develop the knowledge and skills to meet the expected competence standards of practice in response to expanding nursing roles and global trends. Our experience suggests that local governing bodies may enforce similar measures in contexts where CPD measure are not formalised. Nurses may find themselves caught between a patchwork of statutory requirements and a need to develop their skills and knowledge. Consequently, while we know about the need for nurses’ continuing professional development, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive continuing professional development. Therefore we propose that a metasynthesis of the qualitative literature could be a part of forming such a comprehensive view and use the following three questions to examine the literature What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?, What are the conditions necessary for CPD?, and, What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?
In this study, a metasynthesis was used to investigate the qualitative literature [ 30 , 31 ]. Metasynthesis is a form of systematic review method used to review qualitative studies in order to develop theory, to explore and understand phenomena or generate new knowledge, thereby creating meaning from that knowledge [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ]. In this review, we present a metasynthesis based on the interpretation of qualitative results from topically related qualitative reports. In doing so we strive towards theoretical development, which according to Zimmer refers to the synthesis of findings into a product that is ‘thickly descriptive, and comprehensive’ and thus more complete than any of the constituent studies alone ( [ 30 ] p.313).
The results from metasynthesis studies may be used to underpin and inform healthcare policy, nursing practice and patient care. Furthermore, such information can be utilised by health care professionals involved in nursing education to inform planning and designing of training and educational programs. A number of steps are taken when conducting a metasynthesis [ 36 ] and involve;
a) bringing together a multidisciplinary team, in our case the team of three people includes two skilled medical education professional researchers with extensive experience in qualitative studies, including systematic reviews, moreover these two authors have more than 40 years of comprehensive experience of CPD in health care settings, two of the team are registered nurses and afford the team key insights into the context of nursing CPD, the team is spread across three institutions in two countries, finally, the team consisted of a search engine expert,
b) defining inclusive but manageable research questions, see the questions above;
c) conducting the systematic search, in our case this was conducted by the search engine expert, see Table 2 for the search criteria,
d) quality assessment of the studies, this was done using the CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) criteria, weighting three levels (not met, partially met, totally met) where assessment was done by all three authors see Table 4 , e) extracting data from the studies, see Table 3 ,
e) data analysis, which is explained in more detail below, and.
f) expressing the details of the synthesis which is done in the findings sections below.
Search strategy
A comprehensive systematic search of literature was subsequently conducted on Medline (OVID), PubMed and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Web of Science (Clarivate) and ERIC (ProQuest). The literature search was conducted by a librarian. The literature search was conducted in December 2019 and was limited to articles published in English from 2010 to 2019. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the literature search were established and are presented below in Table 2 . The inclusion criteria comprise of articles from empirical studies (using qualitative methods), discussing nurse continuing learning and education, professional development, lifelong learning, CPD, motivation and barriers.
Data analysis
A total of 1675 records were identified, and following de-duplication, 1395 articles remained. All 1395 articles were screened. Articles had to address nurses’ CPD and continuing education, using qualitative oriented methods. After the first screening 72 articles remained. These articles were divided into three batches and were divided among the researchers. Each author read one batch to further identify if the articles were to be included. For each batch, a second author read the articles, meaning all articles were read by at least two authors. Any remaining ambiguities were discussed and resolved among the team. Figure 1 is a summary of the literature search and screening and Table 3 presents an overview of each study with its citation, location, cohort size and data collection method. 25 articles were identified for the final metasynthesis. All authors read the final 25 articles. Quality assessment using CASP criteria as outlined by Lachal et al., [ 36 ] is reported in Table 4 . In the quality assessment we assess the following components; Was there a clear statement of the aims of the research?, Is a qualitative methodology appropriate?, Was the research design appropriate to address the aims of the research?, Was the recruitment strategy appropriate to the aims of the research?, Were the data collected in a way that addressed the research issue?, Has the relationship between researcher and participants been adequately considered and reported?, Have ethical issues been taken into consideration?, Is there a clear statement of findings? We also introduce the question of whether the texts are available in Open Access form or not. We introduce this question, as we believe the outcomes on research on nurses’ perceptions and experiences of CPD is potentially important for their practice, and access via Open Access channels could act as a quality dimension. However, without access to the data and the process of interpretation we choose not to assess; How valuable is the research?, Was the data analysis sufficiently rigorous?
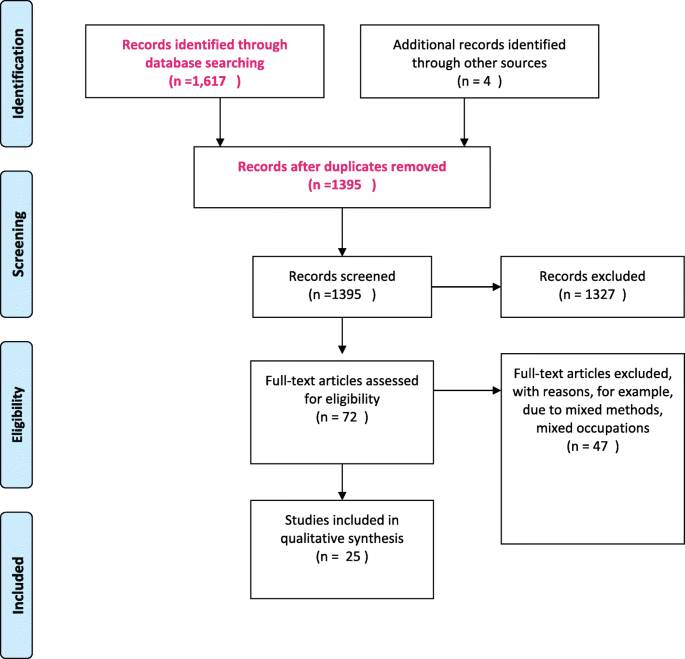
Overview of the steps in the literature screening
For the final analysis enabling the synthesis of the studies in this metasynthesis the articles were read carefully, findings related to the research questions; What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?, what are the conditions necessary for CPD? And what are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?, were identified. In the next step of the analysis, study findings were examined using constant comparative analysis. The findings and conceptual categories were coded, compared, and sorted, focusing on conditions, strategies, and consequences. Finally, the synthesis, the interpretation of the findings, were described as themes, and these were revised several times until a coherent whole was formed [ 30 , 36 , 37 , 38 ] Before the final description of the synthesized themes, all the three authors discussed the content of the themes until consensus concerning credibility was reached.
From the metasynthesis we present five overarching themes, Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. Each theme is further explained below with references to the relevant literature.
Organisational culture shapes the conditions
Organisational culture played an important role towards the professional development of staff. Organisational commitment and support to personal and professional development of its staff was seen as an indication that staff were valued [ 5 , 15 ] Moreover, CPD initiatives contributed to attracting and retaining staff [ 39 ]. Additionally, a culture that was flexible and adaptable to change was perceived by some participants to be favourable towards CPD [ 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Flexibility extends to matters such as CPD availability, and also location, but related also to creating opportunities in the work schedule for the nurses to participate [ 43 ]. Other organisational factors such as funding for CPD programs, staff access of CPD learning, role of management in staff CPD, manageable nursing workloads, the design & delivery of CPD activities, communication and collaboration between CPD providers and management are specifically organisational factors seen as crucial to effective staff development [ 44 , 45 ]. Developing a strategy for CPD was also acknowledged as a key element of organisational culture as a way of enabling participation [ 46 ]. In a similar fashion, it was argued that the organisation needs to be focussed on incremental, but constant development of practices, and here CPD was seen to play a key role [ 47 ]. This sentiment was expressed elsewhere too, but from a re-skilling, or keeping up-to-date perspective, where the organisation is seen to have great importance [ 48 , 49 ]. The value of partnerships and shared understanding between managers and nurses as key enabling factors was identified in several studies [ 46 , 50 ]. In a related fashion, Jantzen argues that organisations should actively avoid fragmentation of CPD initiatives [ 51 ]. As more CPD training is digitised IT/ICT (information communication technology) skills were seen as key to successful CPD implementation [ 46 , 52 ]. It was acknowledged that the transformation to online learning does not only affect nurses, it involves change for the whole department [ 52 ].
Supportive environment as a prerequisite
An environment that supports learning was seen as a necessary prerequisite for CPD. Conditions had to include, flexible off-duty patterns to allow time for staff to study, availability of workplace learning, workloads were not excessive and CPD was fully funded or a shared responsibility between employer and staff [ 46 , 52 ]. Other indicators of a supportive environment included staff access to different CPD activities relevant to their career goals, while at the same time meeting organisational goals and where staff felt free to study openly and not secretively [ 15 , 41 ]. Moreover, the development of local and contextual CPD was seen as something that supported and made participation possible [ 43 , 53 , 54 ]. Participants indicated that nurses required financial support and practical support in the form of adequate time to participate in CPD activities and suitable staff cover when colleagues were away attending CPD activities [ 47 ]. Jantzen et al. [ 51 ] suggest there are three catalysts in a supportive environment; mentors, workplace camaraderie and a highly functional workplace team. Moral support or encouragement was identified in more than one study, where it was articulated that learners want to know there is an appreciation for the time and dedication needed to engage in CPD [ 44 , 46 , 50 ]. The value of learning from other health professionals other than nurses, in the day-to-day work was highlighted for professional development [ 54 ]. Similarly, the sense of a supportive environment with a strong team spirit is communicated elsewhere [ 39 ]. Explicit support is noted in several studies; support for novice nurses [ 39 ] but also the importance of explicit managerial support [ 55 ]. Conversely, in one study, respondents noted that there was less support for experienced or late career nurses [ 56 ].
Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values
The value and importance of CPD was discussed in many of the studies. In some, CPD was perceived to be key in defining nurse professionalism [ 6 , 15 , 40 , 47 , 49 ]. Engaging in CPD was also viewed by new nurse graduates as an important element of their individual professionalisation in nursing [ 6 , 15 , 40 ]. In addition, CPD was perceived to be important for enhancing and up or re-skilling, keeping knowledge and skills up-to-date, considering that nursing practice has become more evidence based [ 6 , 43 , 46 , 51 , 54 , 56 ]. Furthermore, nurses stated that CPD was important for maintaining licensure, and felt that the responsibility for enrolling and participating in CPD activities was with the individual nurse, not with the employing organisations [ 53 ]. On the other hand, participants felt more motivated to learn if they could easily access CPD programs, if they felt supported and if there were a variety of CPD activities on offer. Here, bedside and informal learning was emphasized as important [ 57 ]. Similarly, contextualising learning and placing it in close proximity to practice was seen to enhance motivation and engagement [ 42 ]. CPD was also viewed as a way to start networking with other peers [ 44 ]. In one study, a competency framework was introduced, here participants felt that such a framework could help them reflect on their own practice and, as it provides a systematic approach to assessing a patient, look at their own strengths and weaknesses [ 58 ]. Such competency frameworks help to harness scarce training more effectively and encourage individuals to take more responsibility for their own development [ 58 ].
Participants’ attitudes towards CPD funding were mixed, with some stating that funding for CPD was the employer’s responsibility, while others felt that the individual practitioner was responsible or that the burden ought to be shared between the organisation and the nurse [ 5 , 15 , 40 ].
Nurses’ perceptions of barriers
Poor staffing levels, heavy workloads, lack of funding, lack of study time and anti-intellectualism were some of the perceived barriers to CPD brought out by this review. Participants in the studies reviewed felt that a lack of organisational support, especially from their managers, was an indication that the organisation did not take professional development of its staff seriously [ 46 ]. Some respondents reasoned that an anti-academic culture and lack of relevant CPD programs was further indication of this [ 5 , 15 , 40 ]. Seeing a connection to patient care was identified as a strong driver and nurses identified that CPD initiatives would be filtered out unless there was such a clear connection to patient care [ 43 , 51 ].
Additionally, some studies indicated that as role models, managers had to show interest in their own CPD, in order to motivate other nurses. In other words, the manager’s knowledge of CPD activities was reflected by their attitude towards work-based study, acceptance of staff who studied openly, the way the manager prioritised funding support and managed staff shift schedules to allow study release time [ 5 , 39 , 54 , 56 ]. Fatigue was identified as a major barrier. For example in Jho et al. [ 53 ], in a context of mandated CPD, respondents felt tired due to the heavy nursing workload in conjunction with CPD. Lack of strategy, and financial initiatives in terms of money, or time off to study was also acknowledged as a barrier [ 5 , 39 , 54 , 56 ]. Lack of transparent career trajectories were also acknowledged as an area of concern [ 44 ].
Other barriers, or de-motivating factors were identified; difficulties in attending CPD and keeping a life-work balance [ 48 ]. Barriers included: formal CPD courses away from the clinical areas were perceived to lack in authenticity [ 47 , 49 ] and a mis-match in expectations and outputs, where nurses viewed themselves as agents of change, but where the organisation was unable to offer means to capitalise on this perception and desire to bring about change [ 50 , 59 ]. As much as competency frameworks were viewed positively in offering a sense of direction, a divergent view was that they were limiting or created set boundaries that participants experienced as limited, for example, if used as prescriptive, hindering nurses to define their own learning needs [ 58 ]. Lack of IT competence was also perceived as a barrier [ 52 ] with more CPD being conducted online.
Perceived impact on practice as a core value
The impact of CPD on nursing practice was perceived as important and valuable in different ways. The impact could be both direct and indirect depending on the organisational culture [ 41 , 45 ]. This mixed perception could be due to the complex nature of health care organisations which can make knowledge sharing difficult [ 45 ] and that some CPD learning was done secretly, results of which were difficult to evaluate [ 41 ]. In the case where a competency framework was studied, participants felt that using the competency framework helped them organise their work and their thought processes [ 58 ]. A common sentiment was that CPD would benefit health care organisation through the provision and enhancement of practitioners’ knowledge and skills [ 46 ]. Sentiments articulating expectations of an impact of CPD could also be seen elsewhere too [ 52 , 55 , 56 , 60 ]. Moreover, CPD is expected to rely on better communication between managers and nurses as a way of informing each other about needs and means of fulfilling those needs [ 48 ]. Direct impact was realised through improved interprofessional collaboration and the idea that new methods could be directly translated into practice [ 47 ]. Others however, raised concerns that CPD programmes or courses may not translate into new practices [ 50 ]. This sentiment was echoed elsewhere too, where a need to situate CPD in close proximity of patients was seen as important for CPD to impact practice [ 49 ] While indirect impact happened through dissemination of knowledge and skills from CPD learning to other nurses at ward level, arguments were put forward that there will be no difference to practice unless organisational processes support and evaluate its effect on practice [ 46 ]. Participants reported that their professional confidence was enhanced, they felt they could challenge medical decisions and the status quo [ 41 ]. Furthermore, participants felt that CPD enhanced their professional knowledge and skills for better patient care through improved care standards, how they communicated and collaborated with other professionals. Participants also believed that learning increased their chances for career progression and reduced work-related anxiety because of enhanced knowledge [ 40 , 41 ].
The aim of this paper is to conduct a metasynthesis investigating the qualitative research on nurses’ experiences of continued professional development. As a result, this metasynthesis revealed a number of overarching themes, which synthesize the findings of previous qualitative oriented research during the period 2010–2019. 2010 was chosen to include the last 10 years of CPD research. The themes are; Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. The themes put focus on important issues that were recurrently put forward by the nurses in the studies reviewed. However, the themes are not isolated from each other, rather, the content of the themes is interrelated. Some of the themes mainly mirror an overarching perspective at the organisational level of health care, while other themes describe the nurses’ experiences and needs on a personal level. The following discussion explores the above themes in relation to the three questions posed earlier; what is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge? What are the conditions necessary for CPD? What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD? While we acknowledge that the questions and themes overlap, we have endeavoured to frame the discussion around the three research questions individually.
What is the reported value of CPD for nurses’ lifelong learning and its impact on nursing knowledge?
Nurses reported that CPD raises professional standards through competencies gained, thereby increasing professional performance with positive benefits for patients, organisations and individual nurses [ 40 ]. These outcomes were seen most prominently in the themes Attitudes and motivation reflect nurse’s professional values, and Perceived impact on practice as a core value. Closely aligned to CPD are the nurses’ clinical effectiveness and competence. Maintaining both requires nurses to keep their practice up-to-date highlighting the importance of CPD for nurses. The knowledge and skills gained by nurses through CPD advances the professional status of nursing, which was an idea that was prevalent in some of the studies in this review [ 15 , 40 , 47 , 50 ], but is also illustrated elsewhere in the literature [ 8 , 21 ]. Nurses acknowledged that expectations of professional accountability meant that standards of practice ought to be kept high in order to pass public scrutiny [ 15 , 40 ]. Furthermore, skills acquired through CPD, such as the ability to conduct systematic peer-reviews [ 45 ] and appraise literature for best evidence, provide nurses with essential professional competencies, embeds values such as caring behaviours, influences beliefs and attitudes which in turn shape nurses’ professional conduct [ 61 ]. As such CPD is seen as a tool for nurses to update their skills, and in doing so deliver safe and high-quality health care. As revealed in this review, nurses were willing to fully fund or part-fund their CPD as long as CPD programs were captivating, easily accessible, there was fair allocation of study time and their efforts towards CPD were recognised. The latter implies that nurses want time and space to transfer their CPD learning into practice and for their CPD to be recorded [ 5 , 45 ]. The belief is that, consequently, patient care will improve with positive impact from organisational change [ 15 , 45 ]. However, it is clear that the organisation is key in making CPD work for nurses. The issues brought up in the theme organisational culture shapes the conditions is thus very important in stimulating nurses to engage in CPD. The nurses’ attitudes and motivation to engage in CPD also depends on a supportive environment and engagement may in turn influence the organisational culture.
What are the conditions necessary for CPD?
A disconnect could be seen in relation to the conditions for CPD, where access to CPD training came to the fore as problematic in some of the studies. Nurses had to travel long distances to attend courses [ 15 , 62 , 63 ]. To avoid these challenges, nurses settle for CPD as long as it fulfils mandatory requirements for registration [ 53 ]. If intentions of CPD are to provide a basis for the continual updating of skills, then authentic learning as an expected outcome is seen as a prerequisite for nurses to engage in CPD, whether it occurs at the bedside, at a training facility or through an IT mediated interaction. This calls for accessible CPD, improved design and delivery methods for all nurses [ 52 ]. Nurses’ experiences described in the themes Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, show that structural and moral support are both important. Structural support in the form of availability, time to engage in CPD, as well as clear expected outcomes [ 46 , 49 ], but also moral support in the form of an understanding management and environment, and also peers and leaders who themselves also prioritise CPD [ 58 ]. Organisational support and commitment towards CPD should mean allocation of study time, support of nurses who study privately, by creating space for knowledge and skills integration and managing poor cultural practices that hinder open study. Funding is seen as a key factor across many of the studies, both in terms of enabling nurses to participate, but also as a way of acknowledging nurses who engage in CPD. Further studies may need to look more closely at how nurses perceive different aspects of funding. For nurses’ lifelong learning to endure, CPD programs need to be more accessible and kept interesting by making them more relevant to nurses’ practice contexts. Here the importance of the organisation for creating a CPD conducive environment is emphasized [ 46 , 51 , 52 ]. As role models, managers need to lead by example and engage in CPD themselves, but also demonstrate explicit support. They also need to influence policy to create environments conducive to CPD. If funding situations do not improve, work-based CPD learning could be one of the alternative ways of CPD delivery for nurses. To promote CPD engagement and cost reduction, eLearning approaches could be utilised for education and training. However, poor IT skills among nurses, but also within organisations continues to be a potential weakness [ 52 ]. A challenge remains here in enabling nurses to get recognition from informal on-site learning [ 16 , 17 , 18 ], where elements of meta-cognitive reflection can be used to acknowledge nurses’ continued professional development.
What are the challenges faced by nurses when engaging in CPD?
In some of the literature reviewed, participants lamented their current conditions for CPD, and identified clear barriers and challenges in the form of concerns related to lack of funding for CPD, staffing levels, time allocation for study, lack of organisational support because of negative cultural practices, CPD design & delivery and limited choice of CPD activities. This is articulated within the themes: Organisational culture shapes the conditions, Supportive environment as a prerequisite, Nurses’ perceptions of barriers [ 2 , 11 , 34 , 41 ] . However, studies did not explore the views of nurses on recruitment and retention and its impact on accessing a variety of CPD activities. Evidence from this review indicates that modernising healthcare and simultaneously cutting CPD funding for nurses could lead to a limited number of nurses attaining the skills and competences needed for the modernisation process. In view of the understaffing that is reported elsewhere [ 5 , 15 ], we identify a cause for concern. These perceived barriers may undermine nurses’ professional development [ 23 , 59 ]. Moreover, the findings presented here revealed that nurses face a number of challenges in relation to their CPD participation. The challenges include limited CPD activities to choose from, poor CPD delivery methods, negative organisational culture practices such as anti-intellectualism and lack of support. As a result, nurses were less motivated to participate in CPD training [ 57 ].
It is clear from the review, that IT concerns are becoming more and more prominent, given that more CPD programmes are being offered through digital platforms [ 47 ]. This is a concern for both the individual nurses, but also their organisations. On concerns regarding CPD delivery methods, nurses indicated that they preferred different styles. With these concerns comes the view that learners learn in different ways depending on the context and subject of study [ 61 , 62 ]. This supports the notion that individuals have different learning preferences [ 61 ], where some adult learners learn better in a structured and teacher guided context, while others prefer self-direction.
Limitations
The search was conducted by an experienced search engine expert. Even so, we may still have been unsuccessful in finding all the relevant articles. The study was focussed on qualitative studies, which means that studies using predominantly quantitative or mixed methods were not included, but could hold important insights. In the introduction to the study we used the UK as an example for how CPD might be regulated. However, we have conducted a comprehensive search of the literature and our analysis was not conducted with a UK-centric perspective. While each study needs to be understood in terms of local rules and regulations, the similarities in the findings are striking.
The metasynthesis indicates that differences exist between the nurses’ CPD needs and expectations and organisations’ approaches to nurses’ professional development. The review lays bare a disconnect between the rhetoric of identifying CPD as a way to enhance nurses’ skills, and the reality of CPD interventions, where nurses do not feel support within their organisations or from their immediate supervisors. The review also revealed that CPD is an important element of nursing practice and nurses’ lifelong learning. Furthermore, it suggests that nurses are motivated to take part in CPD to enhance their knowledge, improve skills and keep up- to -date with recent evidence. While evidence from this review indicates that nurses believe that CPD has a positive impact on patient care, there is lack of contemporary research to qualify this claim and there is limited evidence from this review to support this assumption. However, evidence from the review suggests and confirms, that the greatest barriers for CPD in nursing are a lack of funding and time to participate in CPD activities, which are clearly related to organisation structure. It is difficult to envisage how such conditions could be conducive for nurse CPD to flourish. Such perceived barriers undermine nurses’ efforts to keep knowledge and skills up-to-date and provide better patient care while meeting the ever-changing needs and expectations of their patients. This is further exacerbated by negative organisational cultural practices and lack of knowledge on how to facilitate, design and deliver CPD for their staff. We conclude that policy makers and relevant stakeholders need to put in place strategies to support nurse CPD in long term and in doing so tear down the barriers of CPD.
Availability of data and materials
The data in the study is comprised of previous research articles. A full list of articles is included in the Table 3 .
Abbreviations
Continued Professional Development
United Kingdom Central Council for Nursing, Midwifery and Health Visiting
Post registration education and practice
Nursing & Midwifery Council
Health Education England
National Health Service
Pool IA, Poell RF, Berings MGMC, Ten Cate O. Motives and activities for continuing professional development: An exploration of their relationships by integrating literature and interview data. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;38:22–8 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med12&NEWS=N&AN=26833276.
Article Google Scholar
Ross K, Barr J, Stevens J. Mandatory continuing professional development requirements: what does this mean for Australian nurses. BMC Nurs. 2013;12(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6955-12-9 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brekelmans G, Poell RF, van Wijk K. Factors influencing continuing professional development. Eur J Train Dev. 2013;37(3):313–25 DOI: 10.1108/03090591311312769.
James A, Francis K. Mandatory continuing professional education: what is the prognosis? Collegian. 2011;18(3):131–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colegn.2011.03.001 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Govranos M, Newton JM. Exploring ward nurses’ perceptions of continuing education in clinical settings. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(4):655–60 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med10&NEWS=N&AN=23891123.
Pool IA, Poell RF, Berings M, ten Cate O. Motives and activities for continuing professional development: an exploration of their relationships by integrating literature and interview data. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;38:22–8 DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.01.004.
Gallagher L. Continuing education in nursing: a concept analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2007;27(5):466–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2006.08.007 .
Hegney D, Tuckett A, Parker D, Robert E. Access to and support for continuing professional education amongst Queensland nurses: 2004 and 2007. Nurse Educ Today. 2010;30(2):142–9 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med7&NEWS=N&AN=19646799.
Astin F, Closs SJ, Hughes N. The self-reported learning style preferences of female Macmillan clinical nurse specialists. Nurse Educ Today. 2006;26(6):475–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2005.12.007 .
Frankel A. Nurses’ learning styles: promoting better integration of theory into practice. Nurs Times. 2009;105(2):24–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
Vinales JJ. The learning environment and learning styles: a guide for mentors. Br J Nurs. 2015;24(8):454–7. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2015.24.8.454 .
Bradshaw W. Importance of nursing leadership in advancing evidence-based nursing practice. Neonatal Netw. 2010;29(2):117–22. https://doi.org/10.1891/0730-0832.29.2.117 .
Baumann SL. The limitations of evidenced-based practice. Nurs Sci Q. 2010;23(3):226–30. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894318410371833 .
Barker J. Evidence-based practice for nurses: SAGE publications. Sage; 2013.
Google Scholar
Brekelmans G, Poell RF, van Wijk K. Factors influencing continuing professional development: a Delphi study among nursing experts. Eur J Train Dev. 2013;37(3):313–25. Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/docview/1413415361?accountid=11794 . https://doi.org/10.1108/03090591311312769 .
Noe RA, Tews MJ, Marand AD. Individual differences and informal learning in the workplace. J Vocat Behav. 2013;83(3):327–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2013.06.009 .
van Rijn MB, Yang H, Sanders K. Understanding employees’ informal workplace learning: the joint influence of career motivation and self-construal. Career Dev Int. 2013;18(6):610-28. https://doi.org/10.1108/CDI-12-2012-0124 .
Tews MJ, Michel JW, Noe RA. Does fun promote learning? The relationship between fun in the workplace and informal learning. J Vocat Behav. 2017;98:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2016.09.006 .
Lammintakanen J, Kivinen T. Continuing professional development in nursing: does age matter? J Work Learn. 2012;24(1):34–47. Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/docview/964181952?accountid=11794 . https://doi.org/10.1108/13665621211191096 .
Zaleska KJ, De Menezes LM. Human resources development practices and their association with employee attitudes: between traditional and new careers. Hum Relations. 2007;60(7):987–1017. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018726707081155 .
Clarke N. Workplace learning environment and its relationship with learning outcomes in healthcare organizations. Hum Resour Dev Int. 2005;8(2):185–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/13678860500100228 .
Griffith R, Tengnah C. Law and professional issues in nursing (second ed.). Exeter: Learning Matters; 2020.
Ryan J. Continuing professional development along the continuum of lifelong learning. Nurse Educ Today. 2003;23(7):498–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-6917(03)00074-1 .
Rowe JA. Accountability: a fundamental component of nursing practice. Br J Nurs. 2000;9(9):549–52. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2000.9.9.6289 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Gould D, Berridge E-J, Kelly D. The National Health Service Knowledge and skills framework and its implications for continuing professional development in nursing. Nurse Educ Today. 2007;27(1):26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2006.02.006 .
Griffith R. Nursing professionalism and NMC revalidation. Br J Card Nurs. 2016;11(7):344–5. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjca.2016.11.7.344 .
Buchan J, Charlesworth A, Gershlick B, Seccombe I. A critical moment: NHS staffing trends, retention and attrition. London: Health Foundation; 2019.
House of Commons Health Committee. The nursing workforce, second report of session 2017–19. London: House of Commons; 2018. https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201719/cmselect/cmhealth/353/353.pdf
Royal College of Nursing. Improving continuing professional development: how reps can make a difference in the workplace. London: Royal College of Nursing; 2018. https://www.rcn.org.uk/professional-development/publications/pub-007215
Zimmer L. Qualitative meta-synthesis: a question of dialoguing with texts. J Adv Nurs. 2006;53(3):311–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03721.x .
Finlayson KW, Dixon A. Qualitative meta-synthesis: a guide for the novice. Nurse Res. 2008;15(2):59-71.
Walsh D, Downe S. Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2005;50(2):204–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03380.x .
Finfgeld-Connett D. Generalizability and transferability of meta-synthesis research findings. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(2):246–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05250.x .
Suri H. Purposeful sampling in qualitative research synthesis. Qual Res J. 2011;11(2):63–75. https://doi.org/10.3316/QRJ1102063 .
Korhonen A, Hakulinen-Viitanen T, Jylhä V, Holopainen A. Meta-synthesis and evidence-based health care–a method for systematic review. Scand J Caring Sci. 2013;27(4):1027–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/scs.12003 .
Lachal J, Revah-Levy A, Orri M, Moro MR. Metasynthesis: an original method to synthesize qualitative literature in psychiatry. Front psychiatry. 2017;8:269. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00269 .
Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Finding the findings in qualitative studies. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2002;34(3):213–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2002.00213.x .
Barroso J, Powell-Cope GM. Metasynthesis of qualitative research on living with HIV infection. Qual Health Res. 2000;10(3):340–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/104973200129118480 .
Goudreau J, Pepin J, Larue C, Dubois S, Descôteaux R, Lavoie P, et al. A competency-based approach to nurses’ continuing education for clinical reasoning and leadership through reflective practice in a care situation. Nurse Educ Pract. 2015;15(6):572–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2015.10.013 .
Balls P. What are the factors that affect band 5 nurses’ career development and progression? Nurs Times. 2010;106(15):10–3.
Tame SL. Secret study: a new concept in continuing professional education. Nurse Educ Today. 2011;31(5):482–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.09.007 .
Cleary M, Horsfall J, O’Hara-Aarons M, Jackson D, Hunt GE. The views of mental health nurses on continuing professional development. J Clin Nurs. 2011;20(23–24):3561–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2011.03745.x .
Cleary M, Horsfall J, O’Hara-Aarons M, Jackson D, Hunt GE. The views of mental health nurses on continuing professional development. J Clin Nurs. 2011;20(23–24):3561–6 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med7&NEWS=N&AN=21722221.
Shrestha GK, Bhandari N, Singh B. Nurses’ views on need for professional development in Nepal. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2010;49(179):209–15 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med7&NEWS=N&AN=22049825.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lee N-J. An evaluation of CPD learning and impact upon positive practice change. Nurse Educ Today. 2011;31(4):390–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.07.012 .
Draper J, Clark L. Managers’ role in maximising investment in continuing professional education. Nurs Manag. 2016;22(9):30–6 Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=112667810&site=ehost-live .
Averlid G. Norwegian Nurse Anesthetist Perceptions of Professional Development and the Influence of Production Pressure. AANA J. 2017;85(5):345–51 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=prem&NEWS=N&AN=31566534.
Pool IA, Poell RF, Berings MGMC, ten Cate O. Strategies for continuing professional development among younger, middle-aged, and older nurses: a biographical approach. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52(5):939–50 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med11&NEWS=N&AN=25766265.
Pool I, Poell R, ten Cate O. Nurses’ and managers’ perceptions of continuing professional development for older and younger nurses: a focus group study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50(1):34–43 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med9&NEWS=N&AN=22944285.
Clark E, Draper J, Rogers J. Illuminating the process: enhancing the impact of continuing professional education on practice. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;35(2):388–94. Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=103880632&site=ehost-live . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2014.10.014 .
Jantzen D. Refining nursing practice through workplace learning: A grounded theory. J Clin Nurs. 2019;28(13–14):2565–76 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=30807678.
Green JK, Huntington AD. Online professional development for digitally differentiated nurses: An action research perspective. Nurse Educ Pract. 2017;22:55–62 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medc1&NEWS=N&AN=27940391.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Jho MY, Kang Y. Perceptions of Continuing Nursing Education in Korea. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2016;47(12):566–72 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med12&NEWS=N&AN=27893920.
Kyrkjebø D, Søvde BE, Råholm M-B. Nursing competence in the municipal health service: can professional development be accommodated? Nor J Clin Nurs Sykepl Forsk. 2017;12:64027. Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=126914658&site=ehost-live .
Ennis G, Happell B, Reid-Searl K. Enabling professional development in mental health nursing: the role of clinical leadership. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2015;22(8):616–22 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med11&NEWS=N&AN=26010165.
Price S, Reichert C. The Importance of Continuing Professional Development to Career Satisfaction and Patient Care: Meeting the Needs of Novice to Mid- to Late-Career Nurses throughout Their Career Span. Adm Sci. 2017;7(2):17.
Thurgate C. Supporting those who work and learn: A phenomenological research study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;61:83–8 Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=127701702&site=ehost-live .
Stanford PE. How can a competency framework for advanced practice support care? Br J Nurs. 2016;25(20):1117–22 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med12&NEWS=N&AN=27834515.
Gray M, Rowe J, Barnes M. Continuing professional development and changed re-registration requirements: midwives’ reflections. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(5):860–5 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med10&NEWS=N&AN=24219922.
Goudreau J, Pepin J, Larue C, Dubois S, Descôteaux R, Lavoie P, et al. A competency-based approach to nurses’ continuing education for clinical reasoning and leadership through reflective practice in a care situation. Nurse Educ Pract. 2015;15(6):572–8. Available from: http://proxy.kib.ki.se/login?url=http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=111488515&site=ehost-live . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2015.10.013 .
Hayes C. Approaches to continuing professional development: putting theory into practice. Br J Nurs. 2016;25(15):860–4. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2016.25.15.860 .
Fitzgerald CE, Townsend RP. Assessing the continuing education needs and preferences of rural nurses. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2012;43(9):420–7 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med8&NEWS=N&AN=22715876.
Katsikitis M, McAllister M, Sharman R, Raith L, Faithfull-Byrne A, Priaulx R. Continuing professional development in nursing in Australia: current awareness, practice and future directions. Contemp Nurse. 2013;45(1):33–45 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi? T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med9&NEWS=N&AN=24099224.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Gun Brit Knutssön, at Karolinska Institutet’s University Library, Stockholm, Sweden for the systematic search.
Open Access funding provided by Stockholm University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Jersey General Hospital, St Helier, Jersey
Mandlenkosi Mlambo
Department of LIME, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Mandlenkosi Mlambo, Charlotte Silén & Cormac McGrath
Department of Education, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
Cormac McGrath
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MM, CS and CMG designed the study. MM, CS and CMG defined the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the search. MM, CS and CMG conducted an equal share of the analysis work. Versions of the manuscripts were shared, revised and written by all three authors. All authors have read and approved the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cormac McGrath .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical vetting in Sweden is conducted by a central and national committee, the Swedish Ethical Review Authority. Review articles where research is not conducted on humans, or animals does not require ethical vetting as per Swedish Ethical Review Act (SFS 2003:460).
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
Additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mlambo, M., Silén, C. & McGrath, C. Lifelong learning and nurses’ continuing professional development, a metasynthesis of the literature. BMC Nurs 20 , 62 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00579-2
Download citation
Received : 03 November 2020
Accepted : 31 March 2021
Published : 14 April 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00579-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Articulate personal goals and evaluate progress towards their achievement. Encourage a positive attitude towards work throughout life. 1.1.1 What is Professional development plan: A professional development plan is a set of guidelines used to improve or redirect a career. It improves self-knowledge and identity, develop talents and potential ...
A personal development plan (PDP) is something that you are supposed to write at the start of each year, detailing your goals for practice and theory and how you are going to achieve them. I have found PDPs difficult to write, especially at the start of the year as all the modules are launching. My goal is to stay calm and not be overwhelmed by ...
Reflective essay of personal and professional development. Info: 3303 words (13 pages) Nursing Essay. Published: 10th Dec 2020. Reference this. Tagged: professional development. Share this: Facebook Twitter Reddit LinkedIn WhatsApp. This assignment is a critical analysis and reflection of my continuing personal and professional development ...
Creating A Personal Development Plan To Improve Professionalism Nursing Essay. Info: 2721 words (11 pages) Nursing Essay. Published: 11th Feb 2020. Reference this. Personal Development Planning is a structured and supported process undertaken by an individual to reflect upon their own learning, performance and/or achievement and to plan for ...
The purpose of the KSF is to help you develop your knowledge and skill. • PDP: personal (or professional) development plan: a plan through which you undertake to improve your knowledge and skill. • PPP: personal professional portfolio: the portfolio of evidence that shows you have met your obligations under PREP.
A professional development plan (PDP) is a tool that helps you identify your goals, strengths, gaps, and actions to advance your nursing career. It can also help you align your personal and ...
Examine the achieved outcomes and impact. Set the direction for the future. 9. The nursing professional development practitioner's primary role as a leader requires: an operational position, rather than a staff position. alignment of educational operations with organizational goals and needs.
Look for the purple professional development planning icon in the Nursing and Midwifery Hub. Related topics. Implementation Support Network Team Contact Details (PDF, size 352 KB, 3 pages) Professional Development Plan Framework (PDF, size 581.1 KB, 10 pages) Professional Development Plan Guide (PDF, size 700.3 KB, 19 pages)
Professional development as a nursing practice specialty is defined by standards based on research and is critical to quality patient and organizational outcomes. The specialty of nursing professional development (NPD) has evolved over the years. The first educational focus in nursing started with the establishment of the first national nursing organization, the American Society of ...
Achieving a goal. A PDP helps plan and show the achievement of continuing professional development. The GMC states that continuing professional development activities should maintain and improve the quality of care doctors give patients and the public and the standards of the teams and the services in which you work.9 Doing a range of different continuing professional development activities to ...
PDP in place for remaining 4 years of my cycle to cover 35 hrs verifiable I have left. Mixed (NHS and private) general practice, part time. • Perform reception role when needed; • Perform sterilisation role when needed. • General population; • Large ethnic and cultural diversity. Personal development plan Learning or Maintenance need
Purpose of the PDP. Students conceptualize a personalized blueprint for approaching their Walden doctoral studies and present it in a written Professional Development Plan (PDP) essay. Writing the essay allows students the opportunity to. Establish a personalized timeline for meeting degree requirements (i.e., the Program of Study form).
It is defined as "The nursing professional development (NPD) practitioner integrates scholarship, evidence, and research findings into practice" (p. 104). There is often confusion between quality improvement, evidence-based practice, and research. A seminal article by Shirey and colleagues. [2] differentiated these three topics.
In turn, nurses should continue to actively engage in continuing professional development to maintain high standards of nursing care through competent practice. This paper highlights the perceived benefits and challenges of continuing professional development that nurses face and offers advice and understanding in relation to continuing ...
Professional Development. 5 26. I welcome feedback for my improvement. 4 27. I want to know where I stand & am headed to. 4 28. I value learning & advancement. 5 29. I surely need to assess my plans in line with my objectives. 4 30. I need to discern to what extent my plans have been achieved. Legal Issues. 4 31. I am a law-abiding person. 4 32.
Personal development is an ongoing process that drives you to improve your knowledge, skills and experience, so that you can achieve your goals. A personal development plan (or PDP) is a method of focussing your goals into achievable steps, which helps you keep track of your personal development. Download Free PDP Example/Template.
A professional development plan is a visual S.M.A.R.T goals outline that includes one's interests and dislikes, values and skills, strengths and professional experience. It is an overall snapshot of how one's education, work experience, goals, and personality align with a desired job role.
Continuing professional development (CPD) is central to nurses' lifelong learning and constitutes a vital aspect for keeping nurses' knowledge and skills up-to-date. While we know about the need for nurses' continuing professional development, less is known about how nurses experience and perceive continuing professional development. A metasynthesis of how nurses experience and view ...
In 1938, it was granted town status. [citation needed]Administrative and municipal status. Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Elektrostal Urban Okrug.
Elektrostal. Elektrostal ( Russian: Электроста́ль) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is 58 kilometers (36 mi) east of Moscow. As of 2010, 155,196 people lived there.
Moscow Oblast ( Russian: Моско́вская о́бласть, Moskovskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia. It is located in western Russia, and it completely surrounds Moscow. The oblast has no capital, and oblast officials reside in Moscow or in other cities within the oblast. [1] As of 2015, the oblast has a population of 7,231,068 ...
In order to enhance knowledge, skills, values and attitudes needed for a safe and effective nursing practice, this reflective piece aims to demonstrate the author's commitment to the need for professional development contribution and personal supervision activities. Through leadership, peer support, supervision and teaching this account will ...
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts.A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License.