
How To Make A Presentation Longer: Expert Tips & Tactics For Businesses
- By Herwin Jose
- April 10, 2024
Key Takeaways:
- Engage with your audience through audience participation and interaction on every slide.
- Extend your presentation by incorporating additional key points and expanding on main points.
- Add multimedia elements such as videos to enhance depth and engagement.
- Maximize audience participation through question and answer sessions and other interactive techniques.
- Master the art of delivery and timing to keep your audience engaged without rushing.
Have you ever wondered how to make your presentation more engaging and keep your audience captivated throughout?
Do you often find yourself needing a longer presentation to convey your key message effectively?
Look no further, as we delve into the best ways to extend the length of your presentation while keeping your audience engaged and informed. With these strategies at your disposal, you can confidently enhance your presentation, help your audience understand, and effectively convey your message. Let’s dive into each of these tactics in detail and explore how they can help you make a compelling and informative business presentation.
Understanding the Importance of Presentation Length
Before we dive into the techniques, it’s crucial to understand why the length of a presentation matters. The duration of your presentation can significantly impact its effectiveness and audience engagement. Finding the right balance between a concise delivery and providing sufficient information is key.
When a presentation is too short, it may leave your audience feeling unsatisfied or uninformed. On the other hand, an excessively long presentation can risk losing your audience’s attention and focus.
In general, the length of a presentation will depend on various factors, such as the purpose of your presentation, the complexity of the topic, and the preferences of your audience. Different types of presentations, whether it’s a pitch to potential investors or a training session for employees, may require different lengths to effectively convey the message.
Effectively lengthen a presentation doesn’t mean adding unnecessary content or filler material. It involves strategically expanding on key points, delivering the necessary information, and keeping your audience engaged throughout.
In the following sections, we will explore the best ways to make a powerpoint presentation longer without losing your audience’s interest. By employing these techniques, you’ll be able to enhance your presentation and deliver a memorable experience that keeps your audience fully engaged.
Make your presentation engaging by captivating your audience throughout

One of the key strategies to make a presentation longer is by continuously engaging your audience. It’s essential to keep them captivated and invested in your message. By incorporating techniques such as audience participation, effective use of every slide, and collaborating with a presentation design agency, you can create a more engaging and impactful presentation.
Audience participation is a powerful tool to keep your audience engaged. Encourage them to ask questions, share their thoughts, and actively participate in the discussion. This interaction not only enhances their understanding but also makes them feel involved in the presentation process.
Another way to make every slide count is to carefully craft your content. Each slide should have a clear purpose and contribute to the overall message. Use visuals, diagrams, and charts to convey information in a visually appealing and digestible manner.
Working with a presentation design agency can take your presentation to the next level. These professionals are experienced in creating visually stunning and engaging slides that will help you make a lasting impression on your audience. They can offer valuable insights and recommendations to make your presentation more engaging and effective.
Remember, the length of a presentation should not compromise its effectiveness. Creating an engaging presentation involves striking a balance between keeping your audience engaged and delivering your key points effectively. By incorporating these strategies within the presentation, you can lengthen your presentation without losing your audience’s attention.
Enhancing Your Presentation Structure
A well-structured presentation plays a crucial role in extending its duration without making it feel stretched. By incorporating additional key points and expanding on main points, you can effectively lengthen and enhance your presentation while maintaining a cohesive structure throughout.
Within the presentation, make sure to include key points that further support your main message. These key points not only provide more depth and clarity but also help extend your presentation by delving into relevant subtopics and providing additional insights.
Furthermore, throughout the presentation, consider expanding on your main points by providing examples, case studies, or real-world applications. This not only adds substance to your presentation but also reinforces your main ideas, keeping your audience engaged and interested.
Remember, an effective presentation is not just about increasing its length; it’s about delivering value and maintaining your audience’s attention. Therefore, ensure that each additional point or explanation you include is relevant to the overall topic and aligns with the purpose of your presentation.
By enhancing your presentation structure, you can create a cohesive and engaging experience that keeps your audience captivated from start to finish.
Using Multimedia to Add Depth and Engagement
Integrating multimedia elements into your presentation is one of the best ways to engage the audience and keep them engaged throughout. By adding videos, incorporating relevant visuals, and utilizing interactive elements, you can create a dynamic and captivating presentation experience.
Adding Videos
Videos are a powerful tool for engaging your audience. They can help you convey complex messages, provide real-life examples, and create an emotional connection with your viewers. When adding videos to your presentation, make sure they are relevant to your topic and enhance your main points. This will help your audience visualize concepts and ideas, making your presentation more memorable.
Incorporating Relevant Visuals
Visuals such as images, charts, and graphs can add depth and clarity to your presentation. They help your audience better understand and retain information by presenting data and concepts in a visually appealing way. Choose visuals that are directly related to your content and support your key messages. This will not only help your audience grasp the information more easily but also make your presentation visually engaging.
Utilizing Interactive Elements
Interactive elements can significantly enhance audience engagement in your presentation . Consider incorporating interactive quizzes or polls to encourage audience participation and make your presentation more interactive. This not only keeps your audience engaged but also allows them to actively contribute to the discussion and have a more personalized experience.
Overall, adding videos, incorporating relevant visuals, and utilizing interactive elements are some of the best ways to engage your audience and keep them engaged throughout your presentation. By using multimedia effectively, you can create a dynamic and memorable presentation that resonates with your audience.
Maximizing Audience Participation and Interaction

An engaged audience is essential for a successful presentation. By maximizing audience participation and interaction, you can keep your audience engaged and attentive throughout. Here are some techniques you can use to achieve this:
- Encourage Questions: Create an interactive environment by encouraging questions from the audience. This not only keeps them engaged but also allows for a deeper understanding of the topic.
- Q&A Sessions: Include dedicated question and answer sessions within your presentation. This gives the audience an opportunity to seek clarification and actively participate in the discussion.
- Interactive Activities: Incorporate interactive activities or exercises that require active participation from your audience. This could include group discussions, polls, or hands-on demonstrations.
- Engage with Visuals: Utilize visually engaging elements such as charts, graphs, and videos to capture and retain your audience’s attention. Visuals can help reinforce key points and make your presentation more memorable.
- Group Exercises: Divide your audience into smaller groups and assign them tasks or exercises related to your presentation. This fosters collaboration, stimulates discussion, and encourages active engagement.
Mastering the Art of Delivery and Timing
The way you deliver your presentation plays a crucial role in its length and audience engagement. To ensure a captivating delivery that keeps your audience engaged, consider the following tips and tricks:
- Take control of your voice: Your voice is a powerful tool for maintaining audience interest. Vary your tone, pitch, and volume to add depth and captivate your listeners.
- Include short pauses when making key points: Pauses not only give your audience time to absorb information but also create anticipation and emphasize important ideas.
- Shy away from repeating information: Repetition can be tedious for your audience and may contribute to a shorter presentation. Instead, focus on concise and impactful delivery, avoiding unnecessary repetition.
- Stay related to the topic: While it’s essential to provide comprehensive information, ensure that all your statements, examples, and anecdotes are directly related to your presentation topic. This will help you maintain focus and avoid unnecessary detours.
Expanding on Relevant Topics and Information

To effectively lengthen your presentation, it’s crucial to demonstrate your expertise and knowledge about the topic at hand. By fully embracing the subject matter, you can provide valuable and insightful information that helps your audience grasp complex concepts. Here are some techniques to enhance your presentation and make it more engaging:
Dive Deep into the Topic
- Conduct thorough research to become knowledgeable about the topic. This will allow you to provide in-depth information and answer audience questions confidently.
- Explore various angles and perspectives related to the topic. This will give your presentation depth and show your audience that you’ve considered different viewpoints.
Provide Relevant Examples and Case Studies
- Illustrate your points with real-life examples and case studies that demonstrate the practical application of the topic. This will make your presentation more relatable and help your audience connect with the information on a deeper level.
- Choose examples that are relevant to your audience’s industry or experiences. This will ensure that your presentation resonates with them and adds value to their understanding.
Use Visuals and Infographics
Incorporate visual elements, such as images, charts, and infographics, to enhance your presentation and make it visually appealing. Visuals can effectively convey complex information and help your audience grasp concepts more easily.
Pro Tip: When using visuals, ensure they are directly related to the topic and support your key messages. Avoid using irrelevant or distracting visuals that may confuse your audience.
Encourage Audience Interaction
- Include interactive elements in your presentation, such as polls, quizzes, or discussion points. This encourages audience participation and keeps them engaged throughout the presentation.
- Allocate time for questions and answers to address any queries or concerns your audience may have. This fosters a sense of involvement and demonstrates your expertise in the subject matter.
By expanding on the relevant topics and information in your presentation, you can effectively lengthen your speech without losing your audience’s attention. Remember to maintain a balance between depth and clarity, and cater to your audience’s level of knowledge and interest.
Leveraging Presentation Design and Templates
Utilizing professional presentation design and templates is a crucial element in enhancing the overall look and effectiveness of your business presentations. A well-designed and visually appealing presentation not only captures the attention of your audience but also helps keep them engaged throughout.
By partnering with a reputable presentation design agency, you can ensure that your presentations are created with a keen eye for detail and compelling visual aesthetics. These experts have the expertise to incorporate design choices that align with your brand identity and effectively convey your message.
When selecting templates for your presentations, opt for those that complement your content and enhance its impact. A carefully chosen template can make a significant difference in how your information is perceived, making it more engaging, memorable, and professional.
Visual elements such as high-quality images, charts, and graphs can also help convey complex data and information in a more digestible and visually appealing manner. When used strategically, these elements not only enhance the understanding of your audience but also prolong the duration of your presentation as they capture attention and encourage active participation.
“The right design and templates play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of a presentation. It’s like adding a touch of professionalism and visual allure to your content, making it more impactful and engaging.” – John Smith, Presentation Design Expert
Remember, an effective presentation is not just about the content but also about how it is visually presented. By leveraging presentation design and templates, you can elevate the overall quality of your presentations, capture and maintain your audience’s attention, and optimally optimize your presentation length without compromising engagement.
Some of the Benefits of Presentation Design and Templates includes,
- Increase audience engagement
- Creates a professional and polished look
- Elevate the overall impact of your message
- Enhance the understanding of complex information
- Optimize the length and flow of your presentation
In conclusion, implementing the strategies discussed in this article can effectively make your presentation longer without sacrificing audience engagement. By experimenting with different techniques and keeping your audience engaged, you can deliver a successful and impactful business presentation .
Engaging your audience throughout the presentation is key. Techniques such as incorporating audience participation, using every slide effectively, and working with a presentation design agency can help you make your presentation more engaging and lengthen its duration.
Furthermore, enhancing your presentation structure by expanding on key points and maintaining a cohesive flow will keep your audience captivated. Incorporating multimedia elements such as videos and interactive visuals can also add depth and engagement to your presentation.
Maximizing audience participation and interaction through Q&A sessions and creating an interactive environment will further extend your presentation. Mastering the art of delivery by taking control of your voice, including strategic pauses, and avoiding unnecessary repetition will help keep your audience engaged.
1. How can I make my presentation longer without losing audience engagement?
There are several techniques you can use to extend the length of your presentation while keeping your audience engaged. One strategy is to incorporate audience participation, such as asking questions or conducting interactive activities. Another approach is to ensure that every slide serves a purpose and effectively conveys key points. Additionally, you can consider adding multimedia elements like videos or relevant visuals to enhance audience involvement. By employing these strategies, you can lengthen your presentation without sacrificing audience engagement.
2. What is the ideal length for a presentation?
The ideal length for a presentation depends on various factors, such as the purpose of your presentation and the nature of your audience. Generally, shorter presentations of 10-20 minutes are suitable for delivering concise and focused messages. However, for more detailed or complex presentations, the duration can range from 30 minutes to an hour or longer. It’s essential to consider the attention span of your audience and ensure that your presentation is engaging and informative within the allotted time frame.
3. How can I engage my audience throughout the presentation?
Engaging your audience throughout the presentation is crucial to maintaining their attention and interest. One effective strategy is to encourage audience participation by asking questions or involving them in activities related to your topic. Another approach is to make each slide impactful by using visuals, graphs, or key points that capture their attention. Additionally, you can consider working with a presentation design agency to create visually appealing slides that enhance audience engagement. By employing these techniques, you can keep your audience engaged throughout your presentation.
4. How can I effectively lengthen my speech during a presentation?
To effectively lengthen your speech, you can incorporate various techniques. One approach is to take control of your voice by speaking slowly and emphasizing important points. You can also include short pauses strategically to allow your audience to reflect and absorb the information. Another technique is to expand on relevant topics and provide additional information that helps your audience fully embrace the topic. Additionally, you can utilize audience participation methods, such as question and answer sessions, to extend the duration of your speech. By implementing these strategies, you can effectively make a speech longer during a presentation.
5. How can I enhance my presentation by adding videos?
Adding videos to your presentation can be a powerful way to enhance audience engagement. You can incorporate relevant video clips that support your topic or provide additional information. Videos can help illustrate concepts, showcase product demonstrations, or share real-life examples. By integrating videos strategically, you can effectively convey your message, captivate your audience, and lengthen the overall duration of your presentation.
6. How can I make any presentation more engaging?
Making your presentation more engaging involves considering various factors. Firstly, ensure that your presentation design is visually appealing and complements the content. Utilize presentation templates and visual elements to enhance the overall look. Secondly, incorporate interactive elements such as audience participation, discussions, or activities that require their involvement. Thirdly, focus on the delivery by practicing your speech, using appropriate gestures and maintaining good eye contact with the audience. By implementing these strategies, you can increase audience engagement and make your presentation more impactful.
7. How long should a business presentation typically be?
The length of a business presentation can vary depending on the purpose and context. Generally, business presentations shouldn’t exceed 45-60 minutes, as that’s the average attention span of most audiences. However, it’s important to consider the complexity and depth of the information being presented. If you have a lot of detailed content to cover, it may be necessary to extend the duration up to 90 minutes. Regardless of the length, it’s crucial to ensure that your presentation is engaging, concise, and delivers your key message effectively.
8. How do you make a 10-minute presentation long?
Presenter, don’t be afraid to add some additional content to your presentation if you need to lengthen it. Whether you’re discussing more examples, going into further detail on certain points, or even adding in a personal anecdote, these can all help extend the time of your presentation. Instead of rushing through your many slides, take the opportunity to delve deeper into each point you’re making. This is a great strategy to use if you want your audience to walk away with a deeper understanding of the topic.
Why wait? Avail a complimentary 1-on-1 session with our presentation expert. See how other enterprise leaders are creating impactful presentations with us.
The 10 Slides, 20 Minutes and 30 Point Font Rule for Presentations
5 components of a successful elevator pitch presentation, 12 tips to prepare handouts in a presentation.
Presentation
- Written By Gregg Rosenzweig
- Updated: May 21, 2024
We’re here to help you choose the most appropriate content types to fulfill your content strategy. In this series, we’re breaking down the most popular content types to their basic fundamentals so you can start with a solid foundation — simple definitions, clarity on formats, and plenty of examples.
What is a Presentation?
A communication device that relays a topic to an audience in the form of a slide show, demonstration, lecture, or speech, where words and pictures complement each other.
Why should you think of presentations as content?
The beauty of content creation is that almost anything can become a compelling piece of content . It just depends on the creativity used to convert it and the story that brings it to life.
The long and short of it
Although the length of a presentation in terms of time can depend on the overall approach (Are you talking a lot? Are you referring to the screen in detail or not?), consider the number of informational content slides when tallying the overall presentation length. For instance, don’t include title slides in your tally when conveying length to a content creator.
A general guide to presentation length:
- Short Form (5 content slides)
- Standard Form (10 content slides)
- Long Form (20+ content slides)
Popular use cases for presentations…
Let’s consider TED Talks for a minute: one of the best examples (bar none) of how words, pictures, and a narrative can make people care about something they otherwise might not.
These “talks” pre-date podcasts and blend a compelling use of language and imagery in presentation format to spread ideas in unique ways.
TED Talks have been viewed a billion-plus times worldwide (and counting) and are worth considering when it comes to how you might use video-presentation content to connect with your customers in creative, cool, new ways.
Business types:
Any company that has a pitch deck, executive summary, sales presentation, or any kind of internal document can repurpose them into external-facing content pieces — without pain.
Presentation Examples – Short Form
Here are some short-form examples with curated to help inspire you.

Presentation Examples – Standard Form

Presentation Examples – Long Form

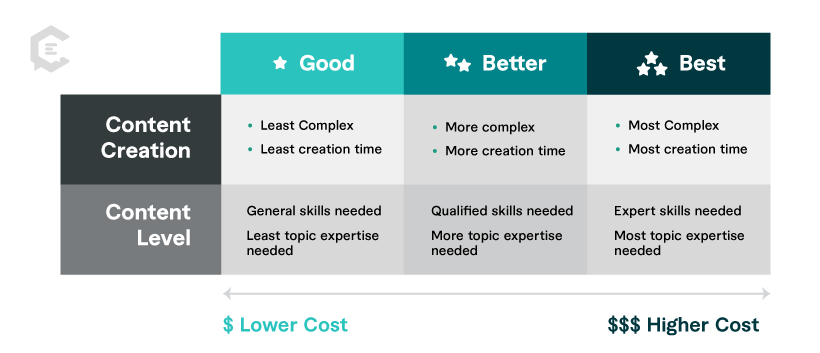
Understanding Content Quality in Examples
Our team has rated content type examples in three degrees of quality ( Good, Better, Best ) to help you better gauge resources needed for your content plan.
In general, the degrees of content quality correspond to our three content levels ( General, Qualified, Expert ) based on the criteria below. Remember though, multiple variables determine the cost, completion time, or content level for any content piece with a perceived degree of quality.
How to Get Exceptional Content That Elevates
If you want to impress your clients, co-workers, or leadership team with your next presentation or product demonstration, to might want to consider working with proven content creators.
At ClearVoice, we have a Talent Network of 4000+ professionals across 200+ industries. That means we can find creators with the exact skill sets and expertise you need to create content that gets results.
Talk to a content specialist today to start the conversation.
Stay in the know.
We will keep you up-to-date with all the content marketing news and resources. You will be a content expert in no time. Sign up for our free newsletter.
Elevate Your Content Game
Transform your marketing with a consistent stream of high-quality content for your brand.

You May Also Like...

ClearVoice Content Roadmap: The Product

Diverse Voices: Exploring the Various Roles of Content Writers

An Introduction to the ClearVoice Content Roadmap
- Content Production
- Build Your SEO
- Amplify Your Content
- For Agencies
Why ClearVoice
- Talent Network
- How It Works
- Freelance For Us
- Statement on AI
- Talk to a Specialist
Get Insights In Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Intellectual Property Claims
- Data Collection Preferences
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
presentation
Definition of presentation
- fairing [ British ]
- freebee
- largess
Examples of presentation in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'presentation.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
15th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing presentation
- breech presentation
Dictionary Entries Near presentation
present arms
presentation copy
Cite this Entry
“Presentation.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/presentation. Accessed 23 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of presentation, medical definition, medical definition of presentation, more from merriam-webster on presentation.
Nglish: Translation of presentation for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of presentation for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about presentation
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, flower etymologies for your spring garden, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

Presentation Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
Featured In
Table of contents, unraveling the presentation definition, what is a presentation, historical roots: from latin to modern day, types and formats of presentations, enhancing presentation skills: a guide, presentation in the digital age: multimedia and keynote, the art of visual aids: graphs and more, presentation in different languages, presentation in literature and culture, effective presentation: tips and techniques, incorporating quizzes and group activities, presentation in educational contexts, synonyms and related terms, the thesaurus and vocabulary expansion, historical and specialized types of presentations, presentation in business: introducing a new product, word of the day: presentation, key points and summarization, cultural influences and adaptations, the role of technology, eye contact and body language, the art of storytelling, innovation and new products, speechify studio.
Unraveling the Presentation DefinitionPresentation - a word frequently used in English, Spanish, Latin, French, and Arabic contexts, but what does it exactly...
Presentation - a word frequently used in English, Spanish, Latin, French, and Arabic contexts, but what does it exactly mean? In this article, we delve into the definition of presentation , exploring its various facets and applications in different fields.
The Essence of Presentation: A Definition
A presentation is the act of presenting information or ideas to a group of people in a structured and deliberate manner, often with the aid of visual aids like PowerPoint, Keynote, or multimedia tools.
Presentations are a ubiquitous part of the professional, educational, and social landscape. The act of presenting, essentially communicating information and ideas to a group of people, has evolved significantly over time. This article explores the definition of a presentation, its various formats, the skills required to make it effective, and the nuances of a great presentation, all while weaving in an eclectic mix of keywords.
The Evolution from 'Praesentātiō' to 'Presentation'
In its essence, a presentation is the act of presenting or displaying information or ideas to an audience. The Oxford English Dictionary defines it as "the action or process of presenting something to someone." In Latin, the term stems from 'praesentātiō', denoting the action of placing before or showing. This definition has broadened in modern English to encompass various methods of showcasing information, whether it's a business pitch, an academic lecture, or introducing a new product.
The term has its origins in Latin ('praesentātiō'), evolving through various languages like French and British English, symbolizing the act of presenting, displaying, or giving something to others.
Diverse Formats for Different Needs
Presentations can vary in formats - from formal PowerPoint presentations to informal Prez (an informal abbreviation of presentation) discussions, each tailored to suit specific requirements.
Mastering the Art of Presentation
Presentations come in various formats, from the traditional speech to more contemporary multimedia showcases. PowerPoint, a widely used tool, allows the integration of text, images, and graphs to create visually appealing slides. Similarly, Apple's Keynote offers tools for creating impactful multimedia presentations. The inclusion of visual aids, like graphs and charts, enhances comprehension and retention. For those interested in learning Spanish, Arabic, or French, incorporating these languages in presentations can broaden audience reach.
Effective presentation skills involve a blend of clear communication, eye contact , engaging visual aids , and a confident delivery. These skills are crucial in both business and educational settings.
Embracing Technology for Impactful Presentations
In the era of digital communication, tools like multimedia presentations and Apple's Keynote software have become indispensable for creating dynamic and interactive presentations.
Using Graphs and Visuals Effectively
Effective presentations often include graphs and other visual aids to convey complex information in an easily digestible format, enhancing the audience's understanding.
A Multilingual Perspective
The concept of presentation transcends languages, from English to Arabic , each offering unique nuances in the art of presenting.
Presentation Copy and Beyond
The term also appears in literary contexts, such as a "presentation copy" of a book, and in cultural scenarios like a "breech presentation" in childbirth, where the baby is positioned to exit the birth canal feet first.
Crafting an Impactful Presentation
An effective presentation is more than just delivering facts; it involves engaging storytelling, structured key points , and the ability to connect with the audience.
To deliver an effective presentation, certain skills are paramount. English, being a global lingua franca, is often the preferred language for presentations. However, the ability to present in multiple languages, like Spanish or French, can be a significant advantage.
Eye contact is a crucial skill, establishing a connection with the audience and making the presentation more engaging. Additionally, the ability to read the room and adjust the presentation accordingly is vital.
Interactive elements like quizzes can transform a presentation from a monologue into a dynamic group activity. They encourage participation and can be especially effective in educational settings. Quizzes can also be used in business presentations to gauge audience understanding or to introduce a new product.
Learning Through Presentations
In educational settings, presentations are used as a tool for teaching and assessment, often involving quizzes and interactive sessions to enhance learning.
Exploring Synonyms and the Thesaurus
The thesaurus offers a range of synonyms for 'presentation,' such as exhibition, demonstration, and display, each with slightly different connotations.
Utilizing a thesaurus can enrich presentation language, offering synonyms and example sentences to clarify points. The 'word of the day' concept, often found in English learning resources, can be an interesting addition to presentations, especially in multilingual contexts.
The term 'presentation' also has specialized meanings. In historical contexts, a 'presentation copy' refers to a book or manuscript gifted by the author. In obstetrics, 'breech presentation' denotes a situation where the baby is positioned to exit the birth canal feet or buttocks first. Understanding these specialized definitions enriches the overall grasp of the term.
The Role of Presentation in Business
In business contexts, presentations are crucial for scenarios like introducing a new product , persuading investors, or communicating with stakeholders.
Expanding Vocabulary with 'Presentation'
In language learning, 'presentation' can be a word of the day , helping learners understand its usage through example sentences and pronunciation (notated as /ˌprez.ənˈteɪ.ʃən/ in English).
An effective presentation distills complex information into key points, making it easier for the audience to remember the most important takeaways. Summarization skills are critical in achieving this clarity.
The concept of presentations varies across cultures. In Arabic-speaking countries, the style of presentation might differ significantly from that in English-speaking contexts. The benefice of understanding cultural nuances cannot be overstated, as it can significantly impact the effectiveness of a presentation.
Technology, particularly multimedia, plays a pivotal role in modern presentations. From PowerPoint slides to advanced software like Keynote, the use of technology has revolutionized the way information is presented. The integration of videos, sound, and interactive elements makes presentations more engaging and memorable.
In delivering a presentation, non-verbal cues like eye contact and body language are as important as the spoken content. Maintaining eye contact with the audience establishes a connection and keeps them engaged. Similarly, confident body language can convey authority and enthusiasm.
A great presentation often resembles storytelling. It's not just about relaying facts; it's about weaving a narrative that resonates with the audience. This involves understanding the audience's needs and interests and tailoring the content accordingly.
Presentations are often the first introduction of a new product to the market. The effectiveness of these presentations can make or break the product's success. Highlighting the unique features and benefits in a clear, compelling manner is crucial.
The Power of Presentation
Presentations are a powerful tool for communication and education. Whether in a formal business setting or an informal educational environment, mastering the art of presentation can lead to more effective and impactful communication.
1. Oxford English Dictionary
2. Merriam-Webster Thesaurus
3. Apple Keynote User Guide
4. Presentation Techniques in Educational Literature
Pricing: Free to try
Speechify Studio is a comprehensive creative AI suite for individuals and teams. Create stunning AI videos from text prompts, add voice overs, create AI avatars, dub videos into multiple languages, slides, and more! All projects can be used for personal or commercial content.
Top Features : Templates, text to video, real-time editing, resizing, transcription, video marketing tools.
Speechify is clearly the best option for your generated avatar videos. With seamless integration with all the products, Speechify Studio is perfect for teams of all sizes.
## Frequently Asked Questions About Presentations
### What is in a presentation?
A presentation typically includes a combination of spoken words and visual aids such as PowerPoint slides, graphs, or multimedia elements. It's an organized way to convey information or ideas to a group of people.
### What is meant by giving a presentation?
Giving a presentation refers to the act of presenting information or ideas to an audience. This act, known in various languages including English, Spanish, and French as 'presentation' (or 'praesentātiō' in Latin), involves communication skills, visual aids, and sometimes interactive elements like quizzes.
### What makes a good presentation?
A good presentation effectively communicates key points, engages the audience through eye contact and clear speech (often practiced as a 'word of the day' in English classes), uses visual aids like graphs, and is well-structured. Effective presentation skills are crucial for this.
### What are the types of presentation?
There are various types of presentations, including formal business presentations (often using PowerPoint or Keynote), educational lectures, sales pitches for a new product, and informal talks. Each type uses different formats and approaches.
### What are the 4 parts of a presentation?
The four main parts of a presentation are the introduction, the main body, the conclusion, and the Q&A session. Each part plays a vital role in delivering an effective presentation.
### What are the three things that a good presentation should do?
A good presentation should inform, engage, and persuade or inspire the audience. It's about more than just delivering facts; it's an act of communication that can change perspectives or encourage action.
### How is a presentation linked with multimedia?
Presentations often use multimedia elements like videos, audio clips, and animated graphs to enhance the viewer's understanding and engagement. Multimedia tools like PowerPoint and Keynote are widely used in creating dynamic presentations.
### How long should a presentation be?
The length of a presentation can vary, but it's typically between 15 to 30 minutes. The duration depends on the context and the amount of information to be covered. It's important to keep presentations concise to maintain the audience's attention.
These answers incorporate various aspects of presentations, including their definition, formats, and the skills required, in multiple languages and contexts, as seen in resources like Oxford dictionaries and thesaurus.
AI Maker: Everything you need to know!
ChatGPT 5 Release Date and What to Expect

Cliff Weitzman
Cliff Weitzman is a dyslexia advocate and the CEO and founder of Speechify, the #1 text-to-speech app in the world, totaling over 100,000 5-star reviews and ranking first place in the App Store for the News & Magazines category. In 2017, Weitzman was named to the Forbes 30 under 30 list for his work making the internet more accessible to people with learning disabilities. Cliff Weitzman has been featured in EdSurge, Inc., PC Mag, Entrepreneur, Mashable, among other leading outlets.
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
What is a Presentation?
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The formal presentation of information is divided into two broad categories: Presentation Skills and Personal Presentation .
These two aspects are interwoven and can be described as the preparation, presentation and practice of verbal and non-verbal communication.
This article describes what a presentation is and defines some of the key terms associated with presentation skills.
Many people feel terrified when asked to make their first public talk. Some of these initial fears can be reduced by good preparation that also lays the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
A Presentation Is...
A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team.
A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other ‘speaking engagements’ such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across in a video conference.
To be effective, step-by-step preparation and the method and means of presenting the information should be carefully considered.
A presentation requires you to get a message across to the listeners and will often contain a ' persuasive ' element. It may, for example, be a talk about the positive work of your organisation, what you could offer an employer, or why you should receive additional funding for a project.
The Key Elements of a Presentation
Making a presentation is a way of communicating your thoughts and ideas to an audience and many of our articles on communication are also relevant here, see: What is Communication? for more.
Consider the following key components of a presentation:
Ask yourself the following questions to develop a full understanding of the context of the presentation.
When and where will you deliver your presentation?
There is a world of difference between a small room with natural light and an informal setting, and a huge lecture room, lit with stage lights. The two require quite different presentations, and different techniques.
Will it be in a setting you are familiar with, or somewhere new?
If somewhere new, it would be worth trying to visit it in advance, or at least arriving early, to familiarise yourself with the room.
Will the presentation be within a formal or less formal setting?
A work setting will, more or less by definition, be more formal, but there are also various degrees of formality within that.
Will the presentation be to a small group or a large crowd?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a new audience, you will have to build rapport quickly and effectively, to get them on your side.
What equipment and technology will be available to you, and what will you be expected to use?
In particular, you will need to ask about microphones and whether you will be expected to stand in one place, or move around.
What is the audience expecting to learn from you and your presentation?
Check how you will be ‘billed’ to give you clues as to what information needs to be included in your presentation.
All these aspects will change the presentation. For more on this, see our page on Deciding the Presentation Method .
The role of the presenter is to communicate with the audience and control the presentation.
Remember, though, that this may also include handing over the control to your audience, especially if you want some kind of interaction.
You may wish to have a look at our page on Facilitation Skills for more.
The audience receives the presenter’s message(s).
However, this reception will be filtered through and affected by such things as the listener’s own experience, knowledge and personal sense of values.
See our page: Barriers to Effective Communication to learn why communication can fail.
The message or messages are delivered by the presenter to the audience.
The message is delivered not just by the spoken word ( verbal communication ) but can be augmented by techniques such as voice projection, body language, gestures, eye contact ( non-verbal communication ), and visual aids.
The message will also be affected by the audience’s expectations. For example, if you have been billed as speaking on one particular topic, and you choose to speak on another, the audience is unlikely to take your message on board even if you present very well . They will judge your presentation a failure, because you have not met their expectations.
The audience’s reaction and therefore the success of the presentation will largely depend upon whether you, as presenter, effectively communicated your message, and whether it met their expectations.
As a presenter, you don’t control the audience’s expectations. What you can do is find out what they have been told about you by the conference organisers, and what they are expecting to hear. Only if you know that can you be confident of delivering something that will meet expectations.
See our page: Effective Speaking for more information.
How will the presentation be delivered?
Presentations are usually delivered direct to an audience. However, there may be occasions where they are delivered from a distance over the Internet using video conferencing systems, such as Skype.
It is also important to remember that if your talk is recorded and posted on the internet, then people may be able to access it for several years. This will mean that your contemporaneous references should be kept to a minimum.
Impediments
Many factors can influence the effectiveness of how your message is communicated to the audience.
For example background noise or other distractions, an overly warm or cool room, or the time of day and state of audience alertness can all influence your audience’s level of concentration.
As presenter, you have to be prepared to cope with any such problems and try to keep your audience focussed on your message.
Our page: Barriers to Communication explains these factors in more depth.
Continue to read through our Presentation Skills articles for an overview of how to prepare and structure a presentation, and how to manage notes and/or illustrations at any speaking event.
Continue to: Preparing for a Presentation Deciding the Presentation Method
See also: Writing Your Presentation | Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves | Dealing with Questions Learn Better Presentation Skills with TED Talks

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center

The Definitive Guide to Longer Presentations
In many situations, short and succinct presentations are the norm. A five-minute pitch, a 15-minute conference talk, or a brief classroom lecture can be incredibly effective. However, there are times when a longer presentation is not just beneficial but necessary. This can be the case when you have a complex topic to cover, a multifaceted message to convey, or an audience that expects a deep dive into your subject matter.
With that being said, longer presentations can lead to audience fatigue. When audience members become disengaged, they may lose interest and stop paying attention to your content.
So, can we extend a presentation while also ensuring audience engagement? How do we design presentations that are not just highly informative but also captivating? If you were wondering the same, you have come to the right page! Whether you’re a business professional, an educator, a public speaker, or someone who simply wants to share their ideas effectively through long-form presentations, you will find the tips and advice shared in this article useful in making your presentations longer without losing your audience’s attention.
But before we dive in, let’s first identify the scenarios in which a longer presentation is justified and also look at some common pitfalls of longer presentations (and ways to avoid them).
When is a Long Presentation Justified?
Extended presentations are valuable when you need to provide in-depth analysis, offer comprehensive solutions, or explore a multifaceted issue. In fact, a longer presentation is very much warranted in situations where the subject matter, audience, or goals demand a more in-depth and comprehensive exploration. With the help of such presentations, you can engage with your audience on a deeper level, providing a rich learning experience and enabling a thorough examination of your ideas.
Here are some common situations where a longer presentation is justified:
Complex Topics: When dealing with complex, multifaceted subjects that require thorough explanations, a longer presentation allows you to delve into the details, provide context, and ensure the audience gains a comprehensive understanding.
In-Depth Training: Training sessions, workshops, or educational seminars often require longer presentations to cover the curriculum extensively. This is especially true for technical or skill-based training programs.
Research and Analysis: Presentations based on extensive research or data analysis often need more time to present findings, methodology, and implications comprehensively.
Strategic Planning: Longer presentations are essential in corporate or organisational settings when discussing strategic plans, objectives, and business strategies. They require detailed explanations and discussions.
Policy and Legislative Matters: Government or policy-related presentations often require longer durations to discuss proposed legislation, regulations, or policy changes in detail, as well as address questions from stakeholders.
Innovation and New Technologies: Presentations on cutting-edge technologies or innovative solutions may demand additional time for explaining intricacies, applications, and potential disruptions.
Scientific and Academic Conferences: Longer presentations are common in scientific and academic conferences, where researchers and scholars present their findings and discuss them with peers.
Public Health and Safety: Information related to public health, safety, or emergency procedures necessitates longer presentations to ensure clarity and compliance with guidelines.
Comprehensive Marketing and Sales: Sales and marketing presentations for complex products or services may require a longer duration to address features, benefits, and customer questions.
Community Engagement: Presentations involving community issues, development projects, or local initiatives often require more time for public engagement and thorough discussions
Historical and Cultural Topics: Presentations about historical events, cultural practices, or traditions may demand a longer duration to provide background, context, and in-depth exploration.
In-Depth Workshops and Seminars: Workshops and seminars focused on skill development, personal growth, or leadership often require more time to provide hands-on experiences and interactive learning.
Government and Policy Briefings: Government officials often need longer presentations to brief stakeholders, agencies, or the public on policy proposals, legislative changes, or key government initiatives.
Strategic Decision-Making: Longer presentations are essential for board meetings, executive presentations, and decision-making discussions where strategic choices and their implications are under consideration.
Product Launches and Demonstrations: Product launches or demonstrations may need longer presentations to showcase features, benefits, and usage scenarios, as well as to answer questions from potential customers.
Educational Institutions: In academic settings, lectures, thesis defences, or educational sessions may require extended presentations to ensure a comprehensive transfer of knowledge.
Public Awareness and Advocacy: Presentations related to social issues, advocacy, and public awareness campaigns often need longer durations to effectively communicate the importance of the cause and potential actions.
Policy Debates: In debates related to policy or controversial topics, longer presentations allow for more thorough arguments and counterarguments.
Crisis Management and Response: Longer presentations are necessary for crisis response plans, as they require detailed explanations, response protocols, and communication strategies.
Market Research and Analysis: Business presentations that focus on market research, consumer behaviour, or industry analysis may require additional time to cover data, insights, and strategic implications in depth.
In these situations, a longer presentation ensures that the audience receives a comprehensive and well-rounded understanding of the subject matter, making it a necessary choice for effective communication and engagement.
What Are The Common Pitfalls of Longer Presentations?
While longer presentations can be valuable in certain situations, they also come with common pitfalls that presenters should be aware of and work to avoid. Some of these pitfalls include:
Loss of Audience Engagement: Longer presentations can lead to audience fatigue. When audience members become disengaged, they may lose interest and stop paying attention to your content.
Information Overload: Presenters risk overwhelming their audience with excessive information. Too much data or content can make it difficult for the audience to absorb and retain key points.
Lack of Clarity: Extended presentations can suffer from a lack of clarity if the presenter doesn’t structure the content well or if they go off on tangents. This can confuse the audience and dilute the message
Ineffective Time Management: Managing time in longer presentations is crucial. If a presenter doesn’t allocate enough time to different sections or overruns, the presentation can feel rushed at the end, leaving the audience with unanswered questions.
Loss of Focus: Longer presentations might lose focus as the presenter tries to cover too many subtopics. This can dilute the main message and make it challenging for the audience to identify key takeaways.
Audience Fatigue: As presentations extend beyond a certain duration, audience fatigue sets in. The longer the presentation, the more likely it is that audience members will start to lose interest and become restless
Decreased Retention: Longer presentations can lead to decreased information retention. The human brain has limits to how much information it can absorb and remember in a single sitting, so extended presentations may result in lower retention rates.
Repetition: To fill time in a longer presentation, presenters may inadvertently repeat points, which can frustrate the audience and diminish the overall quality of the presentation.
Ineffective Visuals: When presenters use visuals, such as slides, they must ensure that these visuals are engaging and relevant. In longer presentations, there’s a risk of using too many or poorly designed visuals, which can hinder understanding and engagement.
Inadequate Interaction: Longer presentations may lack audience interaction, which can lead to reduced engagement. Failing to involve the audience through questions, discussions, or activities can make the presentation feel like a one-way lecture.
Overloading with Data: When dealing with data-heavy content, it’s vital to present the data effectively. Longer presentations run the risk of inundating the audience with data without clear explanations or insights.
Complex Language and Jargon: Presenters might use complex language or industry-specific jargon in longer presentations, which can alienate or confuse the audience, especially if they are not experts in the subject matter.
Poor Storytelling: In a longer presentation, storytelling is still essential. If the presenter fails to incorporate relevant stories or anecdotes effectively, the content can become dry and uninspiring.
Lack of a Clear Roadmap: Longer presentations need a clear structure and roadmap. If the presenter fails to provide a sense of direction and organisation, the audience may feel lost.
Ineffective Visual Design: Longer presentations often rely on visuals for support. If these visuals are poorly designed or cluttered, they can detract from the presentation’s effectiveness.
Failure to Address Questions: In longer presentations, there may be time for audience questions. Failing to address questions effectively or dismissing them can lead to audience dissatisfaction.
Overestimating the Audience’s Attention Span: Presenters should be cautious not to overestimate the audience’s attention span. Even in longer presentations, breaks, interactive elements, or format changes are necessary to keep the audience engaged.
Lack of Adaptation: A longer presentation may necessitate adjustments based on the audience’s reactions and needs. Presenters should be prepared to adapt the content on the fly to maintain audience interest and engagement.
To avoid these common pitfalls, it’s essential to plan longer presentations meticulously, keeping the audience’s needs, attention span, and overall goals of the presentation in mind. Now that you are aware of the common mistakes most presenters make with longer presentations, let’s have a look at some of the best ways to avoid them.
Important Things to Keep in Mind When Creating Longer Presentations
Creating longer presentations requires careful planning and execution to ensure that your message remains engaging and effective throughout the extended duration. Here are important things to keep in mind when crafting longer presentations:
Understand Your Audience: Know your audience’s expectations, interests, and prior knowledge. Tailor your content to meet their needs and level of expertise.
Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of your presentation. What do you want to achieve, inform, or persuade your audience about?
Structure Your Content: Organise your presentation with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Create a logical flow that guides the audience through the content.
Use a Strong Opening: Start with an attention-grabbing introduction. Engage the audience from the beginning with a compelling story, a thought-provoking question, or a surprising fact
Focus on Key Messages: Identify the core messages you want to convey and keep them at the forefront throughout the presentation. Avoid going off on tangents.
Engage with Stories and Examples: Incorporate real-life stories, examples, and anecdotes to illustrate your points and make the content relatable.
Interactive Elements: Include interactive elements like questions, polls, group discussions, and activities to keep the audience engaged and participating.
Visual Aids: Use well-designed slides and visuals to complement your message. Visuals should enhance understanding, not overwhelm with information.
Practice and Rehearse: Practice your presentation multiple times to ensure a smooth and confident delivery. This also helps you manage time effectively
Time Management: Allocate appropriate time to each section and stick to your schedule. Be prepared to adjust if you notice you’re running behind or ahead of schedule
Clarity and Simplicity: Use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon or overly technical terms that might confuse your audience.
Transitions: Pay attention to smooth transitions between different sections of your presentation. Use transitional phrases to guide the audience
Audience Engagement: Continually assess the audience’s engagement levels. Adjust your delivery or content if you sense the audience is disengaging.
Incorporate Variety: Change the pace, tone, and style of your presentation to maintain interest. Break up monotonous segments with stories, questions, or multimedia.
Use Multimedia Wisely: Integrate multimedia (videos, images, and audio) when it enhances your message, but avoid overloading the presentation with too many elements.
Reinforce Key Points: Periodically summarise key points to reinforce the main message. This helps the audience remember the core takeaways.
Anticipate Questions: Prepare for common questions the audience might have and address them proactively in your presentation.
Feedback and Adaptation: Be open to feedback during the presentation. Adjust your approach based on the audience’s reactions and questions.
Confidence and Passion: Project confidence and enthusiasm about your topic. Your enthusiasm can be contagious and keep the audience engaged.
Effective Closure: End your presentation with a strong conclusion that summarises the main points and leaves a lasting impression on the audience.
Provide Additional Resources: Offer handouts, links, or references for those interested in diving deeper into the topic.
Continuous Learning: Reflect on each presentation and seek feedback to improve your skills for future presentations.
Remember that longer presentations require more attention to detail, but with proper planning and a focus on audience engagement, you can make them both informative and captivating. Adapt your approach to the specific needs and preferences of your audience while ensuring that your key message remains central throughout the presentation.
Now that we know when it’s best to create a long-form presentation, the challenges that may arise when you create such a presentation and how to best avoid such challenges, let’s have a look at the various ways you can make your presentation longer.
How to Make Your Presentation Longer?
If you need to make your presentation longer while keeping it engaging and informative, consider these strategies:
Expand on Key Points
To make your presentation longer, you can delve deeper into your key points or main arguments. This involves providing more comprehensive information, examples, and evidence for each point. Use specific case studies, anecdotes, or research findings to illustrate and support your main ideas. Take the time to explain the intricacies and nuances of each key point, helping your audience gain a more profound understanding of the subject matter.
Incorporate Case Studies
Case studies offer a practical and in-depth view of how your topic relates to the real world. By including well-researched and relevant case studies, you can extend your presentation and demonstrate the practical applications of your ideas. Analyse these cases thoroughly, highlighting the challenges, solutions, and outcomes to provide a richer context for your audience.
Introduce Expert Opinions
To add depth and authority to your presentation, incorporate expert opinions. Quote well-known experts, researchers, or thought leaders in your field who have expressed viewpoints related to your topic. This lends credibility to your presentation and allows you to explore different perspectives and approaches.
Present Counterarguments
Expanding on counterarguments or alternative viewpoints involves providing a detailed exploration of these opposing perspectives. Explain the reasons behind these counterarguments and offer a well-reasoned response. By engaging in a thorough discussion of counterarguments, you encourage critical thinking and offer a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Use More Visuals
Visuals, such as charts, graphs, images, and diagrams, can help convey complex information more effectively. You can extend your presentation by including additional visuals that provide a deeper insight into your subject. Ensure that each visual is carefully chosen and directly supports the content you’re presenting.
Explore Subtopics
Breaking down your main topic into subtopics is an excellent way to extend your presentation. Each subtopic can be explored in depth, allowing you to provide a comprehensive overview of the subject matter. By dedicating a portion of your presentation to each subtopic, you can ensure that the audience gains a thorough understanding of the entire topic.
Tell More Stories
Storytelling is a powerful tool for engagement. By sharing more stories, anecdotes, and examples, you can make your presentation longer while keeping it relatable and memorable. Personal stories or stories related to your topic can effectively illustrate your main points and connect with your audience on an emotional level.
Engage in Deeper Analysis
To extend your presentation, engage in a deeper analysis of your data, trends, or implications. Dive into the details, examine patterns, and consider the implications of the information you’re presenting. A thorough analysis can help your audience grasp the complexities and nuances of your subject.
Incorporate Audience Interaction
Engage your audience by incorporating interactive elements. Encourage questions, discussions, and participation to make your presentation longer while involving the audience. Interactive sessions allow the audience to apply the knowledge you’ve shared and can lead to deeper exploration of the topic.
Use Audience Polls
Incorporating audience polls or surveys can extend your presentation while actively involving the audience. Pose questions related to your topic and allow the audience to participate. Share the poll results and discuss the implications to encourage deeper exploration.
Utilise Extended Q&A Sessions
Dedicate more time to answering audience questions to make your presentation longer. Encourage an extended Q&A session to explore topics in greater depth. Engaging in open dialogues with the audience can lead to insightful discussions.
Include Expert Interviews
If possible, conduct or include interviews with experts in your field. Expert interviews offer a unique and valuable perspective, adding depth and credibility to your presentation. These insights can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the topic, making your presentation more informative.
Explore Different Perspectives
Extend your presentation by presenting various perspectives on the topic. By discussing contrasting viewpoints and different angles, you provide a more comprehensive view of the subject matter. Encourage critical thinking and analysis among your audience
Create More Examples
Generate additional examples, scenarios, and use cases that illustrate the practical applications of your ideas. Providing multiple instances where your concepts are applied can help the audience connect theory to practice and make your presentation more thorough.
Reinforce Key Point
Periodically reinforce your key points throughout the presentation. Summarise important takeaways and revisit the main message to ensure that the audience retains the core concepts. Repetition can help reinforce understanding.
Engage in Group Activities
Incorporate group activities or discussions that require audience participation. These activities can be used to delve deeper into specific aspects of your presentation. Encourage group discussions or problem-solving exercises to make your content more interactive and extensive.
Discuss Current Events
Incorporating current events and news into your presentation keeps the content relevant and relatable to the audience. To expand on this, discuss the context and significance of these current events as they relate to your topic. Consider how recent developments have influenced the subject matter, and explore potential future impacts. This not only prolongs the presentation but also highlights the real-time relevance of the subject, making it more engaging and informative.
Collaborate with Guest Speakers
Collaborating with guest speakers or experts can enhance your presentation by offering diverse perspectives and insights. To extend this collaboration, encourage an in-depth discussion with these guest speakers, allowing them to share their experiences and expertise. By doing so, you create a more interactive and informative presentation with a broader range of viewpoints.
Connect with Personal Experiences
Sharing personal experiences related to the topic adds authenticity and depth to your presentation. Expanding on these personal insights can involve a deeper exploration of the challenges faced, lessons learned, and the practical implications of your experiences. By offering a more comprehensive look at your personal journey, you connect with the audience on a deeper level.
Visualise Future Possibilities
Extending your presentation by visualising future possibilities or potential scenarios adds a forward-looking dimension to your content. Provide detailed discussions of the various paths and choices that could shape the future of your topic. Explore the long-term implications of these choices and highlight potential opportunities and challenges. By offering a more comprehensive exploration of future possibilities, you enable the audience to envision the subject’s future evolution.
Address Common Misconceptions
Identifying and addressing common misconceptions related to your topic involves providing detailed explanations that debunk these myths. Explain the origins of these misconceptions, clarify the correct information, and offer a well-informed response to these misconceptions. By providing a comprehensive exploration of common misconceptions, you ensure the audience gains a deeper and more accurate understanding of the subject matter.
Engage in Panel Discussions
Organising panel discussions with multiple experts or stakeholders offers diverse perspectives and insights. Expanding on panel discussions can involve facilitating in-depth conversations, allowing panellists to share their experiences and engage in meaningful debates. By offering a more comprehensive panel discussion, you create an interactive and informative presentation with a wide range of viewpoints.
Use Demonstrations
Incorporating live demonstrations or simulations into your presentation engages the audience in a hands-on learning experience. Expanding on demonstrations involves offering a detailed walkthrough of the demonstration, explaining the steps and intricacies involved. By providing a deeper exploration of the practical application of your ideas, you make your content more tangible and actionable, ensuring the audience gains a thorough understanding.
Final Thoughts
By using the tips and advice shared in this article, you can create longer presentations that inform, inspire, and captivate your audience, whilst also avoiding the common pitfalls that most presenters face when it comes to delivering extended presentations.
However, if you’re inspired to work with experts in crafting your upcoming presentation and preparing for it in the best way possible, look no further. At Presentation Experts, we specialise in not just presentation design, but also presentation skills development . Whether you’re seeking support in crafting a compelling presentation, refining your storytelling techniques, or acquiring the skills to keep your audience captivated during extended presentations, we’ve got you covered.
To learn more about our services, contact us today!

How to Avoid Using Filler Words in Your Presentationn
A guide to slide count in presentationsn, 6 essential presentation skills for pitching successn, a guide to crafting powerful endings in presentationsn, what can our clients tell us about social media usen, a comprehensive guide to presentation openingn, a guide to relaxing before your presentationn.

How to Avoid Using Filler Words in Your Presentation

A Guide to Slide Count in Presentations

6 Essential Presentation Skills for Pitching Success
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Oral Presentations
Presentation basics, key elements of good presentations.
There are three key elements of good presentations: Content, Organization, Delivery. Your audience needs interesting and appropriate content in order to pay attention, especially at the start of a presentation. Logical organization helps retain your audience’s attention – they need to be able to follow your train of thought and predict where you are going with your ideas. Delivery also is important, as your own engagement with the information helps your audience engage.
Content deals with the substance of your presentation. Your ideas and information should be original and significant. Use accepted and relevant sources in your research, and reference those sources as needed. Offer a clear analysis that’s comprehensive and concise at the same time – strive for the right amount of information for your audience’s needs and the allotted presentation time. Make sure that your content is relevant to your audience, so that they understand immediately why they should pay attention to your presentation.
Garr Reynolds, in his book Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery , identifies characteristics of presentation content that create what he calls SUCCES(s): [1]
- Simplicity – reduce information to key points and essential meanings
- Unexpectedness – pose questions, offer interesting statistics, “make the audience aware that they have a gap in their knowledge and then fill that gap”
- Concreteness – use specific language, provide real-life examples
- Credibility – use sources, facts, statistics to back up your content; deliver information confidently; know your information well
- Emotions – engage your audience to feel something about your content
- Stories – use examples and illustrations to create a “story element” to the presentation
Finally, to make your content effective, repeat key information throughout your presentation. A memory research pioneer, German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, found that we forget approximately 50 percent of new information within 18 minutes, with retention falling to 35 percent after a week. However, Ebbinghaus also discovered that repetition of the new information at key intervals can change this trajectory, a discovery known as the spacing effect. The lesson for presenters: work repetition into your presentation content.
Organization
Good organization requires a clear beginning, middle, and end. Link your ideas logically throughout the presentation to lead to an ending that resolves the problem or summarizes the situation you presented at the start. If you’re presenting based on a formal report or proposal, you may want to follow the order of the longer written document, but you don’t have to; as long as you include main ideas, it’s up to you to determine your presentation’s organization based on your audience and purpose. Strive for clear transitions between individual points, slides, and topics.

Delivery involves a range of factors from body language and word choice to vocal variety. A good presenter has a passion for the subject and an ability to convey and perhaps elicit that emotion in the audience. Audience engagement through eye contact, facial expression, gestures, and/or vocal tone contributes to an effective presentation. Delivery also deals with the confidence and professionalism with which you deliver the presentation. Hesitations, “ums,” and other types of vocal fumbling will distract your audience, while a clear, confident presentation helps to engage them.
Content, organization, and delivery work together and are equally important aspects of presentations.
The following two videos provide basic tips for creating effective presentations in terms of content, organization, and delivery. As you view them, consider their similarity of information and dissimilarity in presentation style. What can you infer about the presenter and intended audience of each presentation? Which video resonates more fully with you personally, and why? In terms of conveying information to a general audience, which video do you think is most effective, and why?
Planning Presentations
As you can see based on the video examples, presentations always require a situational analysis in the planning stage. Identify your audience, purpose, context, and all of the communication variables that you need to consider in order to make choices that will result in an effective presentation for your purpose and audience. For example, your purpose – the one, main idea that you want to convey through your presentation – can influence your content, organization, delivery, and overall approach. Identifying your audience can help you with what may be the most critical aspect of your presentation, making your information relevant to your audience. Analyzing communication variables for your presentation also will help you determine if you need supplemental materials or handouts, how to arrange a room for an in-person presentation, how best to structure a virtual presentation, and more.
Even if you are creating a presentation based on a formal report or proposal for which you have already done a situational analysis, do another situational analysis for your presentation, as your audience, organization, language, and overall approach may differ based on the different communication mode.
Planning Online Presentations
In addition to doing a situational analysis, online presentations may require some additional planning time in terms of how you present information. A real-time, in-person audience may pay attention to your presentation simply because you are present, and you may be able to adapt your presentation to audience reaction. However, it’s more difficult to capture the attention of a virtual audience, either real-time or asynchronous, so online presentations need to be thought through very deliberately in terms of their content, organization, look, and approach.
The following video, while written for online instructors, nonetheless offers important points to consider for any type of virtual, online presentation.
Understanding Presentation Audiences
Audiences are egocentric, meaning that they operate under the principle of WIIFM: what’s in it for them. Don’t expect your audience to meet you where you are; meet them where they are and then take them where you want to go together. According to Lucas, audiences “pay closest attention to messages that affect their own values, beliefs, and well being. Listeners approach speeches with one question uppermost in mind: ‘Why is this important to me?’ … What do these psychological principles mean to you as a speaker? First, they mean that your listeners will hear and judge what you say on the basis of what they already know and believe. Second, they mean you must relate your message to your listeners–show how it pertains to them, explain why they should care about it as much as you do.” [2]
Also, audiences have relatively short attention spans, and often decide whether or not to give you their attention within the first minute or so of a presentation. Various research studies indicate a five – twenty minute attention span for any type of presentation (note that results of studies vary). An article titled “ Neuroscience Proves You Should Follow TED’s 18-Minute Rule to Win Your Pitch ” discusses the concept of “cognitve backlog,” or the idea that the more information you provide, the more information your audience will tune out and not remember. [3]

These audience characteristics lay the groundwork for presentation strategies identified in the videos, strategies such as starting with and continuing a story, engaging attention with an interesting statistic, and more. The point to remember is that you need to make conscious, reasoned decisions about ways to engage your audience. Keeping audience attention span and egocentrism in mind, strive for the following presentation basics:
- Conciseness
- Connection with audience
Expectations for Presentations
The 10/20/30 rule, generally attributed to venture capitalist Guy Kawasaki, is a good guideline to help you achieve a “just right” balance in your presentations. Geared for entrepreneurs pitching their business, his advice is a discipline that would improve the quality—and, effectiveness—of most presentations. In brief, 10/20/30 translates to a maximum of 10 slides, a maximum of 20 minutes and a minimum of 30 point font. [4]
While this rule is a good starting point, it does not overrule your audience analysis or understanding of your purpose. Sometimes, you may need more slides or have a more involved purpose—like training people in new software or presenting the results of a research study—that takes more than 30 minutes to address. In that case, go with what your audience needs and what will make your presentation most effective. The concept behind the 10/20/30 rule—to make new learning easy for your audience to take in, process and remember—should still be your guide even if you don’t follow the rule exactly.
One last way to gauge presentations is to consider most audiences’ expectations for good presentations:
- main ideas are compelling and relevant
- information is organized with a clear beginning, middle, and end; audience can follow where the ideas are leading
- delivery shows the presenter’s enthusiasm and engagement
- visuals apply good design practices
- presentation length is appropriate for audience, purpose, and context
The following video summarizes characteristics that create effective presentations.
[1] Reynolds, Garr. (2012) Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery. 2nd ed. New Riders, Pearson Education. Information from pages 78- 81. http://ptgmedia.pearsoncmg.com/images/9780321811981/samplepages/0321811984.pdf
[2] Lucas, Stephen E. (2020) The Art of Public Speaking (13th edition).
[3] Gallo, Carmine. “Neuroscience Proves You Should Follow TED’s 18-Minute Rule to Win Your Pitch.” Inc. , https://www.inc.com/theupsstore/small-biz-ings.html
[4] Kawasaki, Guy. The 10/20/30 Rule of PowerPoint . December 2005. ↵
- Presentation Basics, original material and material adapted from Business Communication Skills for Managers, see attributions below. Authored by : Susan Oaks. Project : Communications for Professionals. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Making a Presentation for a Meeting. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/making-a-presentation-for-a-meeting/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- image of professional making a presentation. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/agreement-brainstorming-business-3408113/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- video Create an Effective Business Presentation. Authored by : Nick Morgan. Provided by : Harvard Business Review. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTRt0zkD73M . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video How to Give a Great Presentation - 7 Presentation Skills and Tips to Leave an Impression. Provided by : Practical Psychology. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MnIPpUiTcRc . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Teaching Tip: Designing Online Lectures and Recorded Presentations. Authored by : Greg Steinke and Jill Zimmerman. Provided by : CCAPS Teaching Tips, University of Minnesota. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GCAaRZJFJAU . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of businesswoman presenting to an audience. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/analyzing-audience-board-3565815/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Visual Aids. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/visual-aids/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- video Five Simple Rules for Creating World Changing Presentations. Authored by : Nancy Duarte. Provided by : Duarte Inc.. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hT9GGmundag . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video

Privacy Policy
The 8 Types of Presentation Styles: Which Category Do You Fall Into?
Updated: December 16, 2020
Published: September 24, 2018
Types of Presentations
- Visual Style
- Freeform Style
- Instructor Style
- Coach Style
- Storytelling Style
- Connector Style
- Lessig Style
- Takahashi Style
Everyone on the internet has an opinion on how to give the “perfect” presentation.

One group champions visual aids, another thinks visual aids are a threat to society as we know it. One expert preaches the benefits of speaking loudly, while another believes the softer you speak the more your audience pays attention. And don’t even try to find coordinating opinions on whether you should start your presentation with a story, quote, statistic, or question.
But what if there wasn’t just one “right” way to give a presentation? What if there were several? Below, I’ve outlined eight types of presentation styles. They’re used by famous speakers like Steve Jobs and Al Gore -- and none of them are wrong.
Check out each one and decide which will be most effective for you.
![presentation long definition → Free Download: 10 PowerPoint Presentation Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/2d0b5298-2daa-4812-b2d4-fa65cd354a8e.png)
Types of Presentation Styles
1. visual style.
What it is: If you’re a firm believer slides simply exist to complement your talking points, this style is for you. With this speaking style, you might need to work a little harder to get your audience engaged, but the dividends can be huge for strong public speakers, visionaries, and storytellers.
When to use it: This style is helpful when speaking to a large audience with broad interests. It’s also great for when you need to throw together slides quickly.
Visual style presenter: Steve Jobs
2. Freeform Style
What it is: This impromptu style of presenting doesn’t require slides. Instead, the speaker relies on strong stories to illustrate each point. This style works best for those who have a short presentation time and are extremely familiar with their talking points.
When to use it: Elevator pitches, networking events, and impromptu meetings are all scenarios in which to use a freeform style of speaking. You’ll appear less rehearsed and more conversational than if you were to pause in the middle of a happy hour to pull up your presentation on a tablet.
Freeform style presenter: Sir Ken Robinson
3. Instructor Style
What it is: This presentation style allows you to deliver complex messages using figures of speech, metaphors, and lots of content -- just like your teachers and professors of old. Your decks should be built in logical order to aid your presentation, and you should use high-impact visuals to support your ideas and keep the audience engaged.
When to use it: If you’re not a comfortable presenter or are unfamiliar with your subject matter (i.e., your product was recently updated and you’re not familiar with the finer points), try instructor-style presenting.
Instructor style presenter: Al Gore

4. Coach Style
What it is: Energetic and charismatic speakers gravitate towards this style of presenting. It allows them to connect and engage with their audience using role play and listener interaction.
When to use it: Use this presentation style when you’re speaking at a conference or presenting to an audience who needs to be put at ease. For example, this style would work well if you were speaking to a group of executives who need to be sold on the idea of what your company does rather than the details of how you do it.
Coach style presenter: Linda Edgecombe
5. Storytelling Style
What it is: In this style, the speaker relies on anecdotes and examples to connect with their audience. Stories bring your learning points to life, and the TED’s Commandments never let you down: Let your emotions out and tell your story in an honest way.
When to use it: Avoid this style if you’re in the discovery phase of the sales process. You want to keep the conversation about your prospect instead of circling every point or question back to you or a similar client. This style is great for conference speaking, networking events, and sales presentations where you have adequate time to tell your stories without taking minutes away from questions.
Storytelling style presenter: Jill Bolte Taylor
6. Connector Style
What it is: In this style, presenters connect with their audience by showing how they’re similar to their listeners. Connectors usually enjoy freeform Q&A and use gestures when they speak. They also highly encourage audience reaction and feedback to what they’re saying.
When to use it: Use this style of presenting early in the sales process as you’re learning about your prospect’s pain points, challenges, and goals. This type of speaking sets your listener at ease, elicits feedback on how you’re doing in real time, and is more of a dialogue than a one-sided presentation
Connector style presenter: Connie Dieken
7. Lessig Style
What it is: The Lessig Style was created by Lawrence Lessig , a professor of law and leadership at Harvard Law School. This presentation style requires the presenter to pass through each slide within 15 seconds. When text is used in a slide, it’s typically synchronized with the presenter’s spoken words.
When to use it: This method of presentation is great for large crowds -- and it allows the speaker to use a balance of text and image to convey their message. The rapid pace and rhythm of the slide progression keeps audiences focused, engaged, and less likely to snooze.
Lessig style presenter: Lawrence Lessig
8. Takahashi Style
What it is: This method features large, bold text on minimal slides. It was devised by Masayoshi Takahashi , who found himself creating slides without access to a presentation design tool or PowerPoint. The main word is the focal point of the slide, and phrases, used sparingly, are short and concise.
When to use it: If you find yourself in Takahashi’s shoes -- without presentation design software -- this method is for you. This style works well for short presentations that pack a memorable punch.
Takahashi style presenter: Masayoshi Takahashi
Slides from one of Takahashi’s presentations:
Whether you’re speaking on a conference stage or giving a sales presentation , you can find a method that works best for you and your audience. With the right style, you’ll capture attention, engage listeners, and effectively share your message. You can even ask an AI presentation maker tool to create presentations for you in your preferred style
![presentation long definition Blog - Beautiful PowerPoint Presentation Template [List-Based]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/013286c0-2cc2-45f8-a6db-c71dad0835b8.png)
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![presentation long definition 10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales-deck.jpg)
10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]

15 Sales Presentation Techniques That Will Help You Close More Deals Today

9 Ways to End Your Sales Presentation With a Bang

7 Apps That Help Salespeople Become Even Better Speakers

7 Secrets of a Winning Capabilities Presentation

Insight Selling: The 8-Slide Framework for a Better Pitch

The Best Work-Appropriate GIFs to Use in Your Next Sales Slide Deck
![presentation long definition How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-make-a-business-presentation.jpg)
How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]

How to Handle Difficult Sales Calls Like a Pro

Technology Give You the Middle Finger in a Demo? 7 Reactions to Avoid
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
Written by: Krystle Wong Aug 11, 2023

From persuasive pitches that influence opinions to instructional demonstrations that teach skills, the different types of presentations serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences.
Presentations that are tailored to its objectives and audiences are more engaging and memorable. They capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
Don’t worry if you’re no designer — Whether you need data-driven visuals, persuasive graphics or engaging design elements, Venngage can empower you to craft presentations that stand out and effectively convey your message.
Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface, extensive presentation template library and customizable design options make it a valuable tool for creating slides that align with your specific goals and target audience.
Click to jump ahead:
8 Different types of presentations every presenter must know
How do i choose the right type of presentation for my topic or audience, types of presentation faq, 5 steps to create a presentation with venngage .

When it comes to presentations, versatility is the name of the game. Having a variety of presentation styles up your sleeve can make a world of difference in keeping your audience engaged. Here are 8 essential presentation types that every presenter should be well-acquainted with:
1. Informative presentation
Ever sat through a presentation that left you feeling enlightened? That’s the power of an informative presentation.
This presentation style is all about sharing knowledge and shedding light on a particular topic. Whether you’re diving into the depths of quantum physics or explaining the intricacies of the latest social media trends, informative presentations aim to increase the audience’s understanding.
When delivering an informative presentation, simplify complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples. Organize your content logically, starting with the basics and gradually delving deeper and always remember to keep jargon to a minimum and encourage questions for clarity.
Academic presentations and research presentations are great examples of informative presentations. An effective academic presentation involves having clear structure, credible evidence, engaging delivery and supporting visuals. Provide context to emphasize the topic’s significance, practice to perfect timing, and be ready to address anticipated questions.
2. Persuasive presentation
If you’ve ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you’ve experienced a persuasive presentation .
This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective. Expect to encounter solid evidence, logical reasoning and a dash of emotional appeal.
With persuasive presentations, it’s important to know your audience inside out and tailor your message to their interests and concerns. Craft a compelling narrative with a strong opening, a solid argument and a memorable closing. Additionally, use visuals strategically to enhance your points.
Examples of persuasive presentations include presentations for environmental conservations, policy change, social issues and more. Here are some engaging presentation templates you can use to get started with:

3. Demonstration or how-to presentation
A Demonstration or How-To Presentation is a type of presentation where the speaker showcases a process, technique, or procedure step by step, providing the audience with clear instructions on how to replicate the demonstrated action.
A demonstrative presentation is particularly useful when teaching practical skills or showing how something is done in a hands-on manner.
These presentations are commonly used in various settings, including educational workshops, training sessions, cooking classes, DIY tutorials, technology demonstrations and more. Designing creative slides for your how-to presentations can heighten engagement and foster better information retention.
Speakers can also consider breaking down the process into manageable steps, using visual aids, props and sometimes even live demonstrations to illustrate each step. The key is to provide clear and concise instructions, engage the audience with interactive elements and address any questions that may arise during the presentation.

4. Training or instructional presentation
Training presentations are geared towards imparting practical skills, procedures or concepts — think of this as the more focused cousin of the demonstration presentation.
Whether you’re teaching a group of new employees the ins and outs of a software or enlightening budding chefs on the art of soufflé-making, training presentations are all about turning novices into experts.
To maximize the impact of your training or instructional presentation, break down complex concepts into digestible segments. Consider using real-life examples to illustrate each point and create a connection.
You can also create an interactive presentation by incorporating elements like quizzes or group activities to reinforce understanding.
5. Sales presentation
Sales presentations are one of the many types of business presentations and the bread and butter of businesses looking to woo potential clients or customers. With a sprinkle of charm and a dash of persuasion, these presentations showcase products, services or ideas with one end goal in mind: sealing the deal.
A successful sales presentation often has key characteristics such as a clear value proposition, strong storytelling, confidence and a compelling call to action. Hence, when presenting to your clients or stakeholders, focus on benefits rather than just features.
Anticipate and address potential objections before they arise and use storytelling to showcase how your offering solves a specific problem for your audience. Utilizing visual aids is also a great way to make your points stand out and stay memorable.
A sales presentation can be used to promote service offerings, product launches or even consultancy proposals that outline the expertise and industry experience of a business. Here are some template examples you can use for your next sales presentation:

6. Pitch presentation
Pitch presentations are your ticket to garnering the interest and support of potential investors, partners or stakeholders. Think of your pitch deck as your chance to paint a vivid picture of your business idea or proposal and secure the resources you need to bring it to life.
Business presentations aside, individuals can also create a portfolio presentation to showcase their skills, experience and achievements to potential clients, employers or investors.
Craft a concise and compelling narrative. Clearly define the problem your idea solves and how it stands out in the market. Anticipate questions and practice your answers. Project confidence and passion for your idea.
7. Motivational or inspirational presentation
Feeling the need for a morale boost? That’s where motivational presentations step in. These talks are designed to uplift and inspire, often featuring personal anecdotes, heartwarming stories and a generous serving of encouragement.
Form a connection with your audience by sharing personal stories that resonate with your message. Use a storytelling style with relatable anecdotes and powerful metaphors to create an emotional connection. Keep the energy high and wrap up your inspirational presentations with a clear call to action.
Inspirational talks and leadership presentations aside, a motivational or inspirational presentation can also be a simple presentation aimed at boosting confidence, a motivational speech focused on embracing change and more.
8. Status or progress report presentation
Projects and businesses are like living organisms, constantly evolving and changing. Status or progress report presentations keep everyone in the loop by providing updates on achievements, challenges and future plans. It’s like a GPS for your team, ensuring everyone stays on track.
Be transparent about achievements, challenges and future plans. Utilize infographics, charts and diagrams to present your data visually and simplify information. By visually representing data, it becomes easier to identify trends, make predictions and strategize based on evidence.

Now that you’ve learned about the different types of presentation methods and how to use them, you’re on the right track to creating a good presentation that can boost your confidence and enhance your presentation skills .
Selecting the most suitable presentation style is akin to choosing the right outfit for an occasion – it greatly influences how your message is perceived. Here’s a more detailed guide to help you make that crucial decision:
1. Define your objectives
Begin by clarifying your presentation’s goals. Are you aiming to educate, persuade, motivate, train or perhaps sell a concept? Your objectives will guide you to the most suitable presentation type.
For instance, if you’re aiming to inform, an informative presentation would be a natural fit. On the other hand, a persuasive presentation suits the goal of swaying opinions.
2. Know your audience
Regardless if you’re giving an in-person or a virtual presentation — delve into the characteristics of your audience. Consider factors like their expertise level, familiarity with the topic, interests and expectations.
If your audience consists of professionals in your field, a more technical presentation might be suitable. However, if your audience is diverse and includes newcomers, an approachable and engaging style might work better.

3. Analyze your content
Reflect on the content you intend to present. Is it data-heavy, rich in personal stories or focused on practical skills? Different presentation styles serve different content types.
For data-driven content, an informative or instructional presentation might work best. For emotional stories, a motivational presentation could be a compelling choice.
4. Consider time constraints
Evaluate the time you have at your disposal. If your presentation needs to be concise due to time limitations, opt for a presentation style that allows you to convey your key points effectively within the available timeframe. A pitch presentation, for example, often requires delivering impactful information within a short span.
5. Leverage visuals
Visual aids are powerful tools in presentations. Consider whether your content would benefit from visual representation. If your PowerPoint presentations involve step-by-step instructions or demonstrations, a how-to presentation with clear visuals would be advantageous. Conversely, if your content is more conceptual, a motivational presentation could rely more on spoken words.

6. Align with the setting
Take the presentation environment into account. Are you presenting in a formal business setting, a casual workshop or a conference? Your setting can influence the level of formality and interactivity in your presentation. For instance, a demonstration presentation might be ideal for a hands-on workshop, while a persuasive presentation is great for conferences.
7. Gauge audience interaction
Determine the level of audience engagement you want. Interactive presentations work well for training sessions, workshops and small group settings, while informative or persuasive presentations might be more one-sided.
8. Flexibility
Stay open to adjusting your presentation style on the fly. Sometimes, unexpected factors might require a change of presentation style. Be prepared to adjust on the spot if audience engagement or reactions indicate that a different approach would be more effective.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach, and the best type of presentation may vary depending on the specific situation and your unique communication goals. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the most effective presentation type to successfully engage and communicate with your audience.
To save time, use a presentation software or check out these presentation design and presentation background guides to create a presentation that stands out.
What are some effective ways to begin and end a presentation?
Capture your audience’s attention from the start of your presentation by using a surprising statistic, a compelling story or a thought-provoking question related to your topic.
To conclude your presentation , summarize your main points, reinforce your key message and leave a lasting impression with a powerful call to action or a memorable quote that resonates with your presentation’s theme.
How can I make my presentation more engaging and interactive?
To create an engaging and interactive presentation for your audience, incorporate visual elements such as images, graphs and videos to illustrate your points visually. Share relatable anecdotes or real-life examples to create a connection with your audience.
You can also integrate interactive elements like live polls, open-ended questions or small group discussions to encourage participation and keep your audience actively engaged throughout your presentation.
Which types of presentations require special markings
Some presentation types require special markings such as how sales presentations require persuasive techniques like emphasizing benefits, addressing objections and using compelling visuals to showcase products or services.
Demonstrations and how-to presentations on the other hand require clear markings for each step, ensuring the audience can follow along seamlessly.
That aside, pitch presentations require highlighting unique selling points, market potential and the competitive edge of your idea, making it stand out to potential investors or partners.
Need some inspiration on how to make a presentation that will captivate an audience? Here are 120+ presentation ideas to help you get started.
Creating a stunning and impactful presentation with Venngage is a breeze. Whether you’re crafting a business pitch, a training presentation or any other type of presentation, follow these five steps to create a professional presentation that stands out:
- Sign up and log in to Venngage to access the editor.
- Choose a presentation template that matches your topic or style.
- Customize content, colors, fonts, and background to personalize your presentation.
- Add images, icons, and charts to enhancevisual style and clarity.
- Save, export, and share your presentation as PDF or PNG files, or use Venngage’s Presentation Mode for online showcasing.
In the realm of presentations, understanding the different types of presentation formats is like having a versatile set of tools that empower you to craft compelling narratives for every occasion.
Remember, the key to a successful presentation lies not only in the content you deliver but also in the way you connect with your audience. Whether you’re informing, persuading or entertaining, tailoring your approach to the specific type of presentation you’re delivering can make all the difference.
Presentations are a powerful tool, and with practice and dedication (and a little help from Venngage), you’ll find yourself becoming a presentation pro in no time. Now, let’s get started and customize your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.17(12); 2021 Dec

Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides
Kristen m. naegle.
Biomedical Engineering and the Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
Introduction
The “presentation slide” is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what is spoken about that slide. Multiple slides are strung together to tell the larger story of the presentation. While there have been excellent 10 simple rules on giving entire presentations [ 1 , 2 ], there was an absence in the fine details of how to design a slide for optimal effect—such as the design elements that allow slides to convey meaningful information, to keep the audience engaged and informed, and to deliver the information intended and in the time frame allowed. As all research presentations seek to teach, effective slide design borrows from the same principles as effective teaching, including the consideration of cognitive processing your audience is relying on to organize, process, and retain information. This is written for anyone who needs to prepare slides from any length scale and for most purposes of conveying research to broad audiences. The rules are broken into 3 primary areas. Rules 1 to 5 are about optimizing the scope of each slide. Rules 6 to 8 are about principles around designing elements of the slide. Rules 9 to 10 are about preparing for your presentation, with the slides as the central focus of that preparation.
Rule 1: Include only one idea per slide
Each slide should have one central objective to deliver—the main idea or question [ 3 – 5 ]. Often, this means breaking complex ideas down into manageable pieces (see Fig 1 , where “background” information has been split into 2 key concepts). In another example, if you are presenting a complex computational approach in a large flow diagram, introduce it in smaller units, building it up until you finish with the entire diagram. The progressive buildup of complex information means that audiences are prepared to understand the whole picture, once you have dedicated time to each of the parts. You can accomplish the buildup of components in several ways—for example, using presentation software to cover/uncover information. Personally, I choose to create separate slides for each piece of information content I introduce—where the final slide has the entire diagram, and I use cropping or a cover on duplicated slides that come before to hide what I’m not yet ready to include. I use this method in order to ensure that each slide in my deck truly presents one specific idea (the new content) and the amount of the new information on that slide can be described in 1 minute (Rule 2), but it comes with the trade-off—a change to the format of one of the slides in the series often means changes to all slides.

Top left: A background slide that describes the background material on a project from my lab. The slide was created using a PowerPoint Design Template, which had to be modified to increase default text sizes for this figure (i.e., the default text sizes are even worse than shown here). Bottom row: The 2 new slides that break up the content into 2 explicit ideas about the background, using a central graphic. In the first slide, the graphic is an explicit example of the SH2 domain of PI3-kinase interacting with a phosphorylation site (Y754) on the PDGFR to describe the important details of what an SH2 domain and phosphotyrosine ligand are and how they interact. I use that same graphic in the second slide to generalize all binding events and include redundant text to drive home the central message (a lot of possible interactions might occur in the human proteome, more than we can currently measure). Top right highlights which rules were used to move from the original slide to the new slide. Specific changes as highlighted by Rule 7 include increasing contrast by changing the background color, increasing font size, changing to sans serif fonts, and removing all capital text and underlining (using bold to draw attention). PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide
When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged. During practice, if you find yourself spending more than a minute on a slide, there’s too much for that one slide—it’s time to break up the content into multiple slides or even remove information that is not wholly central to the story you are trying to tell. Reduce, reduce, reduce, until you get to a single message, clearly described, which takes less than 1 minute to present.
Rule 3: Make use of your heading
When each slide conveys only one message, use the heading of that slide to write exactly the message you are trying to deliver. Instead of titling the slide “Results,” try “CTNND1 is central to metastasis” or “False-positive rates are highly sample specific.” Use this landmark signpost to ensure that all the content on that slide is related exactly to the heading and only the heading. Think of the slide heading as the introductory or concluding sentence of a paragraph and the slide content the rest of the paragraph that supports the main point of the paragraph. An audience member should be able to follow along with you in the “paragraph” and come to the same conclusion sentence as your header at the end of the slide.
Rule 4: Include only essential points
While you are speaking, audience members’ eyes and minds will be wandering over your slide. If you have a comment, detail, or figure on a slide, have a plan to explicitly identify and talk about it. If you don’t think it’s important enough to spend time on, then don’t have it on your slide. This is especially important when faculty are present. I often tell students that thesis committee members are like cats: If you put a shiny bauble in front of them, they’ll go after it. Be sure to only put the shiny baubles on slides that you want them to focus on. Putting together a thesis meeting for only faculty is really an exercise in herding cats (if you have cats, you know this is no easy feat). Clear and concise slide design will go a long way in helping you corral those easily distracted faculty members.
Rule 5: Give credit, where credit is due
An exception to Rule 4 is to include proper citations or references to work on your slide. When adding citations, names of other researchers, or other types of credit, use a consistent style and method for adding this information to your slides. Your audience will then be able to easily partition this information from the other content. A common mistake people make is to think “I’ll add that reference later,” but I highly recommend you put the proper reference on the slide at the time you make it, before you forget where it came from. Finally, in certain kinds of presentations, credits can make it clear who did the work. For the faculty members heading labs, it is an effective way to connect your audience with the personnel in the lab who did the work, which is a great career booster for that person. For graduate students, it is an effective way to delineate your contribution to the work, especially in meetings where the goal is to establish your credentials for meeting the rigors of a PhD checkpoint.
Rule 6: Use graphics effectively
As a rule, you should almost never have slides that only contain text. Build your slides around good visualizations. It is a visual presentation after all, and as they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. However, on the flip side, don’t muddy the point of the slide by putting too many complex graphics on a single slide. A multipanel figure that you might include in a manuscript should often be broken into 1 panel per slide (see Rule 1 ). One way to ensure that you use the graphics effectively is to make a point to introduce the figure and its elements to the audience verbally, especially for data figures. For example, you might say the following: “This graph here shows the measured false-positive rate for an experiment and each point is a replicate of the experiment, the graph demonstrates …” If you have put too much on one slide to present in 1 minute (see Rule 2 ), then the complexity or number of the visualizations is too much for just one slide.
Rule 7: Design to avoid cognitive overload
The type of slide elements, the number of them, and how you present them all impact the ability for the audience to intake, organize, and remember the content. For example, a frequent mistake in slide design is to include full sentences, but reading and verbal processing use the same cognitive channels—therefore, an audience member can either read the slide, listen to you, or do some part of both (each poorly), as a result of cognitive overload [ 4 ]. The visual channel is separate, allowing images/videos to be processed with auditory information without cognitive overload [ 6 ] (Rule 6). As presentations are an exercise in listening, and not reading, do what you can to optimize the ability of the audience to listen. Use words sparingly as “guide posts” to you and the audience about major points of the slide. In fact, you can add short text fragments, redundant with the verbal component of the presentation, which has been shown to improve retention [ 7 ] (see Fig 1 for an example of redundant text that avoids cognitive overload). Be careful in the selection of a slide template to minimize accidentally adding elements that the audience must process, but are unimportant. David JP Phillips argues (and effectively demonstrates in his TEDx talk [ 5 ]) that the human brain can easily interpret 6 elements and more than that requires a 500% increase in human cognition load—so keep the total number of elements on the slide to 6 or less. Finally, in addition to the use of short text, white space, and the effective use of graphics/images, you can improve ease of cognitive processing further by considering color choices and font type and size. Here are a few suggestions for improving the experience for your audience, highlighting the importance of these elements for some specific groups:
- Use high contrast colors and simple backgrounds with low to no color—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment.
- Use sans serif fonts and large font sizes (including figure legends), avoid italics, underlining (use bold font instead for emphasis), and all capital letters—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment [ 8 ].
- Use color combinations and palettes that can be understood by those with different forms of color blindness [ 9 ]. There are excellent tools available to identify colors to use and ways to simulate your presentation or figures as they might be seen by a person with color blindness (easily found by a web search).
- In this increasing world of virtual presentation tools, consider practicing your talk with a closed captioning system capture your words. Use this to identify how to improve your speaking pace, volume, and annunciation to improve understanding by all members of your audience, but especially those with a hearing impairment.
Rule 8: Design the slide so that a distracted person gets the main takeaway
It is very difficult to stay focused on a presentation, especially if it is long or if it is part of a longer series of talks at a conference. Audience members may get distracted by an important email, or they may start dreaming of lunch. So, it’s important to look at your slide and ask “If they heard nothing I said, will they understand the key concept of this slide?” The other rules are set up to help with this, including clarity of the single point of the slide (Rule 1), titling it with a major conclusion (Rule 3), and the use of figures (Rule 6) and short text redundant to your verbal description (Rule 7). However, with each slide, step back and ask whether its main conclusion is conveyed, even if someone didn’t hear your accompanying dialog. Importantly, ask if the information on the slide is at the right level of abstraction. For example, do you have too many details about the experiment, which hides the conclusion of the experiment (i.e., breaking Rule 1)? If you are worried about not having enough details, keep a slide at the end of your slide deck (after your conclusions and acknowledgments) with the more detailed information that you can refer to during a question and answer period.
Rule 9: Iteratively improve slide design through practice
Well-designed slides that follow the first 8 rules are intended to help you deliver the message you intend and in the amount of time you intend to deliver it in. The best way to ensure that you nailed slide design for your presentation is to practice, typically a lot. The most important aspects of practicing a new presentation, with an eye toward slide design, are the following 2 key points: (1) practice to ensure that you hit, each time through, the most important points (for example, the text guide posts you left yourself and the title of the slide); and (2) practice to ensure that as you conclude the end of one slide, it leads directly to the next slide. Slide transitions, what you say as you end one slide and begin the next, are important to keeping the flow of the “story.” Practice is when I discover that the order of my presentation is poor or that I left myself too few guideposts to remember what was coming next. Additionally, during practice, the most frequent things I have to improve relate to Rule 2 (the slide takes too long to present, usually because I broke Rule 1, and I’m delivering too much information for one slide), Rule 4 (I have a nonessential detail on the slide), and Rule 5 (I forgot to give a key reference). The very best type of practice is in front of an audience (for example, your lab or peers), where, with fresh perspectives, they can help you identify places for improving slide content, design, and connections across the entirety of your talk.
Rule 10: Design to mitigate the impact of technical disasters
The real presentation almost never goes as we planned in our heads or during our practice. Maybe the speaker before you went over time and now you need to adjust. Maybe the computer the organizer is having you use won’t show your video. Maybe your internet is poor on the day you are giving a virtual presentation at a conference. Technical problems are routinely part of the practice of sharing your work through presentations. Hence, you can design your slides to limit the impact certain kinds of technical disasters create and also prepare alternate approaches. Here are just a few examples of the preparation you can do that will take you a long way toward avoiding a complete fiasco:
- Save your presentation as a PDF—if the version of Keynote or PowerPoint on a host computer cause issues, you still have a functional copy that has a higher guarantee of compatibility.
- In using videos, create a backup slide with screen shots of key results. For example, if I have a video of cell migration, I’ll be sure to have a copy of the start and end of the video, in case the video doesn’t play. Even if the video worked, you can pause on this backup slide and take the time to highlight the key results in words if someone could not see or understand the video.
- Avoid animations, such as figures or text that flash/fly-in/etc. Surveys suggest that no one likes movement in presentations [ 3 , 4 ]. There is likely a cognitive underpinning to the almost universal distaste of pointless animations that relates to the idea proposed by Kosslyn and colleagues that animations are salient perceptual units that captures direct attention [ 4 ]. Although perceptual salience can be used to draw attention to and improve retention of specific points, if you use this approach for unnecessary/unimportant things (like animation of your bullet point text, fly-ins of figures, etc.), then you will distract your audience from the important content. Finally, animations cause additional processing burdens for people with visual impairments [ 10 ] and create opportunities for technical disasters if the software on the host system is not compatible with your planned animation.
Conclusions
These rules are just a start in creating more engaging presentations that increase audience retention of your material. However, there are wonderful resources on continuing on the journey of becoming an amazing public speaker, which includes understanding the psychology and neuroscience behind human perception and learning. For example, as highlighted in Rule 7, David JP Phillips has a wonderful TEDx talk on the subject [ 5 ], and “PowerPoint presentation flaws and failures: A psychological analysis,” by Kosslyn and colleagues is deeply detailed about a number of aspects of human cognition and presentation style [ 4 ]. There are many books on the topic, including the popular “Presentation Zen” by Garr Reynolds [ 11 ]. Finally, although briefly touched on here, the visualization of data is an entire topic of its own that is worth perfecting for both written and oral presentations of work, with fantastic resources like Edward Tufte’s “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” [ 12 ] or the article “Visualization of Biomedical Data” by O’Donoghue and colleagues [ 13 ].
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the countless presenters, colleagues, students, and mentors from which I have learned a great deal from on effective presentations. Also, a thank you to the wonderful resources published by organizations on how to increase inclusivity. A special thanks to Dr. Jason Papin and Dr. Michael Guertin on early feedback of this editorial.
Funding Statement
The author received no specific funding for this work.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Business Jargons
A Business Encyclopedia
Presentation
Definition : A presentation is a form of communication in which the speaker conveys information to the audience. In an organization presentations are used in various scenarios like talking to a group, addressing a meeting, demonstrating or introducing a new product, or briefing a team. It involves presenting a particular subject or issue or new ideas/thoughts to a group of people.
It is considered as the most effective form of communication because of two main reasons:
- Use of non-verbal cues.
- Facilitates instant feedback.

Business Presentations are a tool to influence people toward an intended thought or action.
Parts of Presentation

- Introduction : It is meant to make the listeners ready to receive the message and draw their interest. For that, the speaker can narrate some story or a humorous piece of joke, an interesting fact, a question, stating a problem, and so forth. They can also use some surprising statistics.
- Body : It is the essence of the presentation. It requires the sequencing of facts in a logical order. This is the part where the speaker explains the topic and relevant information. It has to be critically arranged, as the audience must be able to grasp what the speaker presents.
- Conclusion : It needs to be short and precise. It should sum up or outline the key points that you have presented. It could also contain what the audience should have gained out of the presentation.
Purpose of Presentation
- To inform : Organizations can use presentations to inform the audience about new schemes, products or proposals. The aim is to inform the new entrant about the policies and procedures of the organization.
- To persuade : Presentations are also given to persuade the audience to take the intended action.
- To build goodwill : They can also help in building a good reputation
Factors Affecting Presentation

Audience Analysis
Communication environment, personal appearance, use of visuals, opening and closing presentation, organization of presentation, language and words, voice quality, body language, answering questions, a word from business jargons.
Presentation is a mode of conveying information to a selected group of people live. An ideal presentation is one that identifies and matches the needs, interests and understanding level of the audience. It also represents the facts, and figures in the form of tables, charts, and graphs and uses multiple colours.
Related terms:
- Verbal Communication
- Visual Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Communication
- 7 C’s of Communication
Reader Interactions
Abbas khan says
October 2, 2022 at 11:33 pm
Thank you so much for providing us with brief info related to the presentation.
Farhan says
February 23, 2023 at 9:45 am
yusra shah says
July 3, 2023 at 2:04 am
it was helpful👍
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Adverse Childhood Experiences
- Risk and Protective Factors
- Program: Essentials for Childhood: Preventing Adverse Childhood Experiences through Data to Action
- Adverse childhood experiences can have long-term impacts on health, opportunity and well-being.
- Adverse childhood experiences are common and some groups experience them more than others.

What are adverse childhood experiences?
Adverse childhood experiences, or ACEs, are potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood (0-17 years). Examples include: 1
- Experiencing violence, abuse, or neglect.
- Witnessing violence in the home or community.
- Having a family member attempt or die by suicide.
Also included are aspects of the child’s environment that can undermine their sense of safety, stability, and bonding. Examples can include growing up in a household with: 1
- Substance use problems.
- Mental health problems.
- Instability due to parental separation.
- Instability due to household members being in jail or prison.
The examples above are not a complete list of adverse experiences. Many other traumatic experiences could impact health and well-being. This can include not having enough food to eat, experiencing homelessness or unstable housing, or experiencing discrimination. 2 3 4 5 6
Quick facts and stats
ACEs are common. About 64% of adults in the United States reported they had experienced at least one type of ACE before age 18. Nearly one in six (17.3%) adults reported they had experienced four or more types of ACEs. 7
Preventing ACEs could potentially reduce many health conditions. Estimates show up to 1.9 million heart disease cases and 21 million depression cases potentially could have been avoided by preventing ACEs. 1
Some people are at greater risk of experiencing one or more ACEs than others. While all children are at risk of ACEs, numerous studies show inequities in such experiences. These inequalities are linked to the historical, social, and economic environments in which some families live. 5 6 ACEs were highest among females, non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native adults, and adults who are unemployed or unable to work. 7
ACEs are costly. ACEs-related health consequences cost an estimated economic burden of $748 billion annually in Bermuda, Canada, and the United States. 8
ACEs can have lasting effects on health and well-being in childhood and life opportunities well into adulthood. 9 Life opportunities include things like education and job potential. These experiences can increase the risks of injury, sexually transmitted infections, and involvement in sex trafficking. They can also increase risks for maternal and child health problems including teen pregnancy, pregnancy complications, and fetal death. Also included are a range of chronic diseases and leading causes of death, such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and suicide. 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
ACEs and associated social determinants of health, such as living in under-resourced or racially segregated neighborhoods, can cause toxic stress. Toxic stress, or extended or prolonged stress, from ACEs can negatively affect children’s brain development, immune systems, and stress-response systems. These changes can affect children’s attention, decision-making, and learning. 18
Children growing up with toxic stress may have difficulty forming healthy and stable relationships. They may also have unstable work histories as adults and struggle with finances, jobs, and depression throughout life. 18 These effects can also be passed on to their own children. 19 20 21 Some children may face further exposure to toxic stress from historical and ongoing traumas. These historical and ongoing traumas refer to experiences of racial discrimination or the impacts of poverty resulting from limited educational and economic opportunities. 1 6
Adverse childhood experiences can be prevented. Certain factors may increase or decrease the risk of experiencing adverse childhood experiences.
Preventing adverse childhood experiences requires understanding and addressing the factors that put people at risk for or protect them from violence.
Creating safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments for all children can prevent ACEs and help all children reach their full potential. We all have a role to play.
- Merrick MT, Ford DC, Ports KA, et al. Vital Signs: Estimated Proportion of Adult Health Problems Attributable to Adverse Childhood Experiences and Implications for Prevention — 25 States, 2015–2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:999-1005. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6844e1 .
- Cain KS, Meyer SC, Cummer E, Patel KK, Casacchia NJ, Montez K, Palakshappa D, Brown CL. Association of Food Insecurity with Mental Health Outcomes in Parents and Children. Science Direct. 2022; 22:7; 1105-1114. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2022.04.010 .
- Smith-Grant J, Kilmer G, Brener N, Robin L, Underwood M. Risk Behaviors and Experiences Among Youth Experiencing Homelessness—Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 23 U.S. States and 11 Local School Districts. Journal of Community Health. 2022; 47: 324-333.
- Experiencing discrimination: Early Childhood Adversity, Toxic Stress, and the Impacts of Racism on the Foundations of Health | Annual Review of Public Health https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-090419-101940 .
- Sedlak A, Mettenburg J, Basena M, et al. Fourth national incidence study of child abuse and neglect (NIS-4): Report to Congress. Executive Summary. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health an Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.; 2010.
- Font S, Maguire-Jack K. Pathways from childhood abuse and other adversities to adult health risks: The role of adult socioeconomic conditions. Child Abuse Negl. 2016;51:390-399.
- Swedo EA, Aslam MV, Dahlberg LL, et al. Prevalence of Adverse Childhood Experiences Among U.S. Adults — Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2011–2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:707–715. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7226a2 .
- Bellis, MA, et al. Life Course Health Consequences and Associated Annual Costs of Adverse Childhood Experiences Across Europe and North America: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Public Health 2019.
- Adverse Childhood Experiences During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Associations with Poor Mental Health and Suicidal Behaviors Among High School Students — Adolescent Behaviors and Experiences Survey, United States, January–June 2021 | MMWR
- Hillis SD, Anda RF, Dube SR, Felitti VJ, Marchbanks PA, Marks JS. The association between adverse childhood experiences and adolescent pregnancy, long-term psychosocial consequences, and fetal death. Pediatrics. 2004 Feb;113(2):320-7.
- Miller ES, Fleming O, Ekpe EE, Grobman WA, Heard-Garris N. Association Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2021;138(5):770-776. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004570 .
- Sulaiman S, Premji SS, Tavangar F, et al. Total Adverse Childhood Experiences and Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review. Matern Child Health J . 2021;25(10):1581-1594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-021-03176-6 .
- Ciciolla L, Shreffler KM, Tiemeyer S. Maternal Childhood Adversity as a Risk for Perinatal Complications and NICU Hospitalization. Journal of Pediatric Psychology . 2021;46(7):801-813. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsab027 .
- Mersky JP, Lee CP. Adverse childhood experiences and poor birth outcomes in a diverse, low-income sample. BMC pregnancy and childbirth. 2019;19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2560-8 .
- Reid JA, Baglivio MT, Piquero AR, Greenwald MA, Epps N. No youth left behind to human trafficking: Exploring profiles of risk. American journal of orthopsychiatry. 2019;89(6):704.
- Diamond-Welch B, Kosloski AE. Adverse childhood experiences and propensity to participate in the commercialized sex market. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2020 Jun 1;104:104468.
- Shonkoff, J. P., Garner, A. S., Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, Committee on Early Childhood, Adoption, and Dependent Care, & Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics (2012). The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics, 129(1), e232–e246. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2663
- Narayan AJ, Kalstabakken AW, Labella MH, Nerenberg LS, Monn AR, Masten AS. Intergenerational continuity of adverse childhood experiences in homeless families: unpacking exposure to maltreatment versus family dysfunction. Am J Orthopsych. 2017;87(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000133 .
- Schofield TJ, Donnellan MB, Merrick MT, Ports KA, Klevens J, Leeb R. Intergenerational continuity in adverse childhood experiences and rural community environments. Am J Public Health. 2018;108(9):1148-1152. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2018.304598 .
- Schofield TJ, Lee RD, Merrick MT. Safe, stable, nurturing relationships as a moderator of intergenerational continuity of child maltreatment: a meta-analysis. J Adolesc Health. 2013;53(4 Suppl):S32-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.05.004 .
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
ACEs can have a tremendous impact on lifelong health and opportunity. CDC works to understand ACEs and prevent them.
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
liquid reality —
Google unveils veo, a high-definition ai video generator that may rival sora, google's video-synthesis model creates minute-long 1080p videos from written prompts..
Benj Edwards - May 15, 2024 8:51 pm UTC

On Tuesday at Google I/O 2024, Google announced Veo , a new AI video-synthesis model that can create HD videos from text, image, or video prompts, similar to OpenAI's Sora . It can generate 1080p videos lasting over a minute and edit videos from written instructions, but it has not yet been released for broad use.
Further Reading
Veo reportedly includes the ability to edit existing videos using text commands, maintain visual consistency across frames, and generate video sequences lasting up to and beyond 60 seconds from a single prompt or a series of prompts that form a narrative. The company says it can generate detailed scenes and apply cinematic effects such as time-lapses, aerial shots, and various visual styles
Since the launch of DALL-E 2 in April 2022, we've seen a parade of new image synthesis and video synthesis models that aim to allow anyone who can type a written description to create a detailed image or video. While neither technology has been fully refined, both AI image and video generators have been steadily growing more capable.
In February, we covered a preview of OpenAI's Sora video generator, which many at the time believed represented the best AI video synthesis the industry could offer. It impressed Tyler Perry enough that he put his film studio expansions on hold. However, so far, OpenAI has not provided general access to the tool—instead, it has limited its use to a select group of testers.
Now, Google's Veo appears at first glance to be capable of video-generation feats similar to Sora. We have not tried it ourselves, so we can only go by the cherry-picked demonstration videos the company has provided on its website . That means anyone viewing them should take Google's claims with a huge grain of salt, because the generation results may not be typical.
Veo's example videos include a cowboy riding a horse, a fast-tracking shot down a suburban street, kebabs roasting on a grill, a time-lapse of a sunflower opening, and more. Conspicuously absent are any detailed depictions of humans, which have historically been tricky for AI image and video models to generate without obvious deformations.
Google says that Veo builds upon the company's previous video-generation models, including Generative Query Network (GQN), DVD-GAN, Imagen-Video , Phenaki , WALT, VideoPoet, and Lumiere . To enhance quality and efficiency, Veo's training data includes more detailed video captions, and it utilizes compressed "latent" video representations. To improve Veo's video-generation quality, Google included more detailed captions for the videos used to train Veo, allowing the AI to interpret prompts more accurately.
Veo also seems notable in that it supports filmmaking commands: "When given both an input video and editing command, like adding kayaks to an aerial shot of a coastline, Veo can apply this command to the initial video and create a new, edited video," the company says.
While the demos seem impressive at first glance (especially compared to Will Smith eating spaghetti ), Google acknowledges AI video-generation is difficult. "Maintaining visual consistency can be a challenge for video generation models," the company writes. "Characters, objects, or even entire scenes can flicker, jump, or morph unexpectedly between frames, disrupting the viewing experience."
Google has tried to mitigate those drawbacks with "cutting-edge latent diffusion transformers," which is basically meaningless marketing talk without specifics. But the company is confident enough in the model that it is working with actor Donald Glover and his studio, Gilga, to create an AI-generated demonstration film that will debut soon.
Initially, Veo will be accessible to select creators through VideoFX , a new experimental tool available on Google's AI Test Kitchen website, labs.google. Creators can join a waitlist for VideoFX to potentially gain access to Veo's features in the coming weeks. Google plans to integrate some of Veo's capabilities into YouTube Shorts and other products in the future.
There's no word yet about where Google got the training data for Veo (if we had to guess, YouTube was likely involved). But Google states that it is taking a "responsible" approach with Veo. According to the company, "Videos created by Veo are watermarked using SynthID , our cutting-edge tool for watermarking and identifying AI-generated content, and passed through safety filters and memorization checking processes that help mitigate privacy, copyright, and bias risks."
reader comments
Channel ars technica.
Watch HGSE's Presentation of Diplomas and Certificates 2024
- Posted May 23, 2024
- By News editor
Following the University Ceremonies in Harvard Yard, HGSE diplomas and certificates are awarded to all graduates (both doctoral and master's) on stage in Radcliffe Yard. Dean Long will give her address; graduates will be individually presented with degrees and will walk across the stage.
Live stream begins Thursday, May 23, at 1:45 p.m.
For more information on Commencement 2024, visit: https://www.gse.harvard.edu/commencement .

The latest research, perspectives, and highlights from the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Paxton, Maheshwari-Kanoria to Receive 2024 Alumni Council Awards
Alums will be honored for their educational contributions at HGSE Convocation

Creating Spaces for Growth and Equity
Keshav Bhatt and Helena Martinez Bravo will be honored with the Intellectual Contribution Award for the Human Development and Education Program

Improving the Teacher Workforce
With her research work, doctoral marshal Mary Laski, Ph.D.'24, is trying to make teaching in K–12 schools more sustainable and attractive

FERC Takes on Long-Term Planning with Historic Transmission Rule
FERC acted today to ensure the transmission grid can meet the nation’s growing demand for reliable electricity with a new rule that outlines how to plan and pay for facilities that regions of the country will need to keep the lights on and power the American economy through the 21st Century.
Today’s rule, Order No. 1920, marks the first time in more than a decade that FERC has addressed regional transmission policy – and the first time the Commission has ever squarely addressed the need for long-term transmission planning.
“Our country is facing an unprecedented surge in demand for affordable electricity while confronting extreme weather threats to the reliability of our grid and trying to stay one step ahead of the massive technological changes we are seeing in our society,” FERC Chairman Willie Phillips said. “Our nation needs a new foundation to get badly needed new transmission planned, paid for and built. With this new rule, that starts today.”
The grid rule adopts specific requirements for transmission providers to conduct long-term planning for regional transmission facilities and determine how to pay for them. It reflects tens of thousands of pages of comments, filed over the course of the past three years, from hundreds of stakeholders representing all sectors of the electric power industry, advocacy groups and state and other government entities.
The rule requires transmission operators to conduct and periodically update long-term transmission planning over a 20-year time horizon to anticipate future needs. It also provides for cost-effective expansion of transmission that is being replaced, when needed, known as “right-sizing” transmission facilities. And it expressly provides for the states’ pivotal role throughout the process of planning, selecting, and determining how to pay for transmission lines.
“We need to seize this moment,” Chairman Phillips said. “Over the last dozen years, FERC has worked on five after-action reports on lessons learned from extreme weather events that caused outages that cost hundreds of lives and millions of dollars. We must get beyond these after-action reports and start planning to maintain a reliable grid that powers our entire way of life. The grid cannot wait. Our communities cannot wait. Our nation cannot wait.”
Latest News
Extra | ferc insight | volume 4.5, sunshine notice | may 2024 commission meeting, innovations and efficiencies in generator interconnection workshop.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Asking for a Trend
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Tonix pharmaceuticals to deliver an oral presentation and present two posters at the american society of clinical psychopharmacology (ascp) annual meeting.
Oral Presentation of Tonmya™ (TNX-102 SL) for Fibromyalgia; NDA preparation in progress
Posters Highlighting Other TNX-102 SL Programs In Clinical Development; Long COVID and Acute Stress Disorder
CHATHAM, N.J., May 22, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. (Nasdaq: TNXP) (Tonix or the Company), a fully-integrated biopharmaceutical company with marketed products and a pipeline of development candidates, today announced that the Company will deliver an oral presentation and present two posters at the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology (ASCP) Annual Meeting being held May 28-31, 2024 at the Loews Miami Beach Hotel in Miami Beach, Fla.
The oral presentation will detail findings of studies of Tonmya (TNX-102 SL, sublingual cyclobenzaprine HCl) in fibromyalgia. One poster will describe the Phase 2 proof of concept study of TNX-102 SL in fibromyalgia-type Long COVID. The second poster will describe the upcoming investigator-initiated Phase 2 trial of TNX-102 SL in treating acute stress disorder and preventing posttraumatic stress disorder after motor vehicle collision, which will be conducted by the University of North Carolina, the sponsor of the study.
TNX-102 SL is a centrally acting, non-opioid medication, which is trade named Tonmya™ for the management of fibromyalgia. As previously announced, the second statistically significant Phase 3 study of Tonmya, RESILIENT, met its pre-specified primary endpoint, significantly reducing daily pain compared to placebo in participants with fibromyalgia (p=0.00005). Statistically significant and clinically meaningful results (p=0.001 or better) were also seen in all key secondary endpoints related to improving sleep quality, reducing fatigue, and improving overall fibromyalgia symptoms and function.
Tonix plans to submit a New Drug Application (NDA) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the second half of 2024 for Tonmya for the management of fibromyalgia and has scheduled a Type B pre-NDA meeting with FDA for the second quarter of 2024.
Copies of the Company’s presentation and posters will be available under the Scientific Presentations tab of the Tonix website at www.tonixpharma.com following the conference. Additional meeting information can be found on the ASCP website here .
Oral Presentation Details
Poster Presentation Details
Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. *
Tonix is a fully-integrated biopharmaceutical company focused on developing, licensing and commercializing therapeutics to treat and prevent human disease and alleviate suffering. Tonix’s development portfolio is focused on central nervous system (CNS) disorders. Tonix’s priority is to submit a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA in the second half of 2024 for Tonmya 1 , a product candidate for which two statistically significant Phase 3 studies have been completed for the management of fibromyalgia. TNX-102 SL is also being developed to treat acute stress reaction as well as fibromyalgia-type Long COVID. Tonix’s CNS portfolio includes TNX-1300 (cocaine esterase), a biologic designed to treat cocaine intoxication that has Breakthrough Therapy designation. Tonix’s immunology development portfolio consists of biologics to address organ transplant rejection, autoimmunity and cancer, including TNX-1500, which is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CD40-ligand (CD40L or CD154) being developed for the prevention of allograft rejection and for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Tonix also has product candidates in development in the areas of rare disease and infectious disease. Tonix Medicines, our commercial subsidiary, markets Zembrace ® SymTouch ® (sumatriptan injection) 3 mg and Tosymra ® (sumatriptan nasal spray) 10 mg for the treatment of acute migraine with or without aura in adults.
*Tonix’s product development candidates are investigational new drugs or biologics and have not been approved for any indication.
1 Tonmya™ is conditionally accepted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as the tradename for TNX-102 SL for the management of fibromyalgia. Tonmya has not been approved for any indication.
Zembrace SymTouch and Tosymra are registered trademarks of Tonix Medicines. All other marks are property of their respective owners.
This press release and further information about Tonix can be found at www.tonixpharma.com .
Forward Looking Statements
Certain statements in this press release are forward-looking within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by the use of forward-looking words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “forecast,” “estimate,” “expect,” and “intend,” among others. These forward-looking statements are based on Tonix's current expectations and actual results could differ materially. There are a number of factors that could cause actual events to differ materially from those indicated by such forward-looking statements. These factors include, but are not limited to, risks related to the failure to obtain FDA clearances or approvals and noncompliance with FDA regulations; risks related to the failure to successfully market any of our products; risks related to the timing and progress of clinical development of our product candidates; our need for additional financing; uncertainties of patent protection and litigation; uncertainties of government or third party payor reimbursement; limited research and development efforts and dependence upon third parties; and substantial competition. As with any pharmaceutical under development, there are significant risks in the development, regulatory approval and commercialization of new products. Tonix does not undertake an obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statement. Investors should read the risk factors set forth in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on April 1, 2024, and periodic reports filed with the SEC on or after the date thereof. All of Tonix's forward-looking statements are expressly qualified by all such risk factors and other cautionary statements. The information set forth herein speaks only as of the date thereof.
Investor Contact
Jessica Morris Tonix Pharmaceuticals [email protected] (862) 904-8182
Peter Vozzo ICR Westwicke [email protected] (443) 213-0505
Media Contact
Katie Dodge LaVoieHealthScience [email protected] (978) 360-3151
Sunak has gambled on election date knowing success under any definition is hard
The prime minister has called an election with a story to tell about the economy. But there was a real - perhaps existential - question about how long Sunak could continue to hold it together.

Deputy political editor @SamCoatesSky
Wednesday 22 May 2024 22:37, UK

Rishi Sunak has made the calculation that 4 July is, if not the best election date for the Conservatives, then the least worst.
Firstly, he thinks there is a story to tell on the economy - albeit one that is not without peril.
Britain is out of recession, while inflation today is statistically within "normal" levels.
Politics Live: Sunak ditches jacket for first election rally - as he asks 'who do you trust?'
Secondly, it's likely a plane will possibly take off for the Rwanda within the election campaign. While this will be branded a success, it avoids the judgement on the true purpose of the policy - to stop the boats.
Thirdly, I understand it was no longer possible to have a budget or further fiscal statement after the big promise to increase military spending to 2.5% by 2030.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player

One Tory source told me that the moment they saw that, they knew there wouldn't be further tax cuts and an election would be sooner rather than later.
More on General Election 2024

And they're off... what has the first day of the election campaign told us?

Two ministers and deputy speaker Eleanor Laing join ranks of Tory MPs not standing in general election

'It's on - what will the 2024 election be like?'
Related Topics:
- General Election 2024
- Rishi Sunak
But more than that, there was a real - perhaps existential - question about how long Sunak could continue to hold it together.
Read More: General election called for 4 July What happens now an election has been called? Find your new constituency and how it's changed

There are revolts in parliament looming - on abortion, on smoking and on shorter prison sentencing. This potentially avoids some of those.
He was also facing questions whether he would have to do a reshuffle after Chris Heaton Harris, Northern Ireland Secretary, announced his departure at the next election. Precedent that should have prompted a reshuffle - perhaps this has avoided that.

There are also claims - that might never be proved one way or another - that more and more Tories wanted him gone and he could have been tiptoeing closer to a vote of no confidence. Only Sir Graham Brady may know the truth of this.
All of that is now in the past. Sunak has gambled, knowing success under any definition is hard.
Related Topics
Trump, Biden spar over whether Trump's 30-second pause was intentional or a 'glitch'
Former President Donald Trump suddenly stopped talking for more than 30 seconds during a speech at the National Rifle Association’s annual meeting in Dallas, Texas over the weekend, leading the Biden campaign to capitalize on the speculation about whether his Republican opponent is fit for office.
The presumptive Republican presidential nominee addressed gun owners after receiving the association’s endorsement, stoking fears of the Biden administration “coming for your guns.” Trump’s critics were quick to attack him, saying he froze during his speech and is unfit for office. His supporters said he paused for dramatic effect.
The campaigns’ sparring was the latest in a back-and-forth about both candidates’ ages and mental competency . Biden is 81 and Trump is 77.
More: Trump trial live updates: Michael Cohen is back on the stand for more cross-examination
Biden supporters say Trump “glitched”
The Biden-Harris HQ account on X, formerly Twitter, posted a 44-second clip showcasing Trump’s more than 30-second pause, criticizing his speech as “bizarre” and “slur-filled.”
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
An account called “Biden’s Wins,” with more than 362,000 followers, reposted the video saying, “Donald Trump just glitched out and froze at his rally tonight. He is clearly unfit for office. Retweet so every American knows Trump is senile.”
The Biden-Harris HQ account attacked Trump’s entire address, alleging the dramatic music playing in the background during Trump’s pause is a song favored by QAnon .
The Biden-Harris campaign’s post-Saturday was the second time it appeared to attack Trump’s competency over the weekend. On Friday, the account called Trump “feeble” after his podium shifted when he leaned on it at an event in St. Paul, Minnesota .
Sign up for Your Vote: Text USA TODAY reporters and the elections team by joining our SMS service.
Trump says glitch story is “made up”
Social media users speculated Trump’s pause was due to a problem with his teleprompter, but Trump said that was not the case.
Trump said that the 30-second “period of silence” is a standard part of his speeches and that the Biden-Harris campaign was to blame for the “fake story” that he froze in a post on Truth Social .
“The reason they came up with this Disinformation is that Biden freezes all the time, can’t put two sentences together, and can rarely find his way off the stage without help,” Trump wrote. “Donald Trump doesn’t freeze!”
During his address Saturday, Trump promised to undo gun regulations passed during the Biden administration.
“In my second term, we will roll back every Biden attack on the Second Amendment,” Trump said. “Starting the minute that crooked Joe shuffles his way out of the White House.”
Rachel Barber is a 2024 election fellow at USA TODAY, focusing on politics and education. Follow her on X, formerly Twitter, as @rachelbarber_

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Engage with your audience through audience participation and interaction on every slide. Extend your presentation by incorporating additional key points and expanding on main points. Add multimedia elements such as videos to enhance depth and engagement. Maximize audience participation through question and answer sessions and other interactive ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
A general guide to presentation length: Short Form (5 content slides) Standard Form (10 content slides) Long Form (20+ content slides) Popular use cases for presentations… Let's consider TED Talks for a minute: one of the best examples (bar none) of how words, pictures, and a narrative can make people care about something they otherwise ...
presentation: [noun] the act of presenting. the act, power, or privilege especially of a patron of applying to the bishop or ordinary for instituting someone into a benefice.
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
In its essence, a presentation is the act of presenting or displaying information or ideas to an audience. The Oxford English Dictionary defines it as "the action or process of presenting something to someone." In Latin, the term stems from 'praesentātiō', denoting the action of placing before or showing.
PRESENTATION meaning: 1. a talk giving information about something: 2. an occasion when prizes, qualifications, etc. are…. Learn more.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new ...
A Presentation Is... A presentation is a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. A presentation can also be used as a broad term that encompasses other 'speaking engagements' such as making a speech at a wedding, or getting a point across ...
When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences. As an ...
Extending your presentation by visualising future possibilities or potential scenarios adds a forward-looking dimension to your content. Provide detailed discussions of the various paths and choices that could shape the future of your topic. Explore the long-term implications of these choices and highlight potential opportunities and challenges.
A presentation conveys information from a speaker to an audience. Presentations are typically demonstrations, introduction, lecture, or speech meant to inform, persuade, inspire, motivate, build goodwill, or present a new idea/product. [1] Presentations usually require preparation, organization, event planning, writing, use of visual aids ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Credibility - use sources, facts, statistics to back up your content; deliver information confidently; know your information well. Emotions - engage your audience to feel something about your content. Stories - use examples and illustrations to create a "story element" to the presentation. Finally, to make your content effective ...
[countable] a meeting at which something, especially a new product or idea, or piece of work, is shown to a group of people presentation on/about somebody/something The sales manager will give a presentation on the new products.; Several speakers will be making short presentations.; The conference will begin with a keynote presentation by a leading industry figure.
3. Instructor Style. What it is: This presentation style allows you to deliver complex messages using figures of speech, metaphors, and lots of content -- just like your teachers and professors of old. Your decks should be built in logical order to aid your presentation, and you should use high-impact visuals to support your ideas and keep the audience engaged.
An engaging start to your presentation helps you quickly build rapport and connect with your audience's emotions. A hook to begin your presentation may include a surprising statistic or fact, interesting quotation, relevant question, joke or story. Whatever hook you choose, it's important to ensure that it clearly connects to your content. 4.
Start with a presentation template. Use the 20/30 rule when designing presentations. Prioritize visual appeal in design. The importance of organization. Form a brand identity. The power of color in brand identity. Emphasize data with charts, graphics and infographics. Utilize icons to add dynamics to your presentation.
2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
The "presentation slide" is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what ...
Definition: A presentation is a form of communication in which the speaker conveys information to the audience. In an organization presentations are used in various scenarios like talking to a group, addressing a meeting, demonstrating or introducing a new product, or briefing a team. It involves presenting a particular subject or issue or new ideas/thoughts to a group of people.
Toxic stress, or extended or prolonged stress, from ACEs can negatively affect children's brain development, immune systems, and stress-response systems. These changes can affect children's attention, decision-making, and learning. 18. Children growing up with toxic stress may have difficulty forming healthy and stable relationships.
93. On Tuesday at Google I/O 2024, Google announced Veo, a new AI video-synthesis model that can create HD videos from text, image, or video prompts, similar to OpenAI's Sora. It can generate ...
00:00. HGSE Presentation of Diplomas and Certificates 2024. Following the University Ceremonies in Harvard Yard, HGSE diplomas and certificates are awarded to all graduates (both doctoral and master's) on stage in Radcliffe Yard. Dean Long will give her address; graduates will be individually presented with degrees and will walk across the stage.
The rule requires transmission operators to conduct and periodically update long-term transmission planning over a 20-year time horizon to anticipate future needs. It also provides for cost-effective expansion of transmission that is being replaced, when needed, known as "right-sizing" transmission facilities.
Oral Presentation of Tonmya™ (TNX-102 SL) for Fibromyalgia; NDA preparation in progress Posters Highlighting Other TNX-102 SL Programs In Clinical Development; Long COVID and Acute Stress ...
The prime minister has called an election with a story to tell about the economy. But there was a real - perhaps existential - question about how long Sunak could continue to hold it together.
Trump said that the 30-second "period of silence" is a standard part of his speeches and that the Biden-Harris campaign was to blame for the "fake story" that he froze in a post on Truth ...