

Nike SWOT Analysis

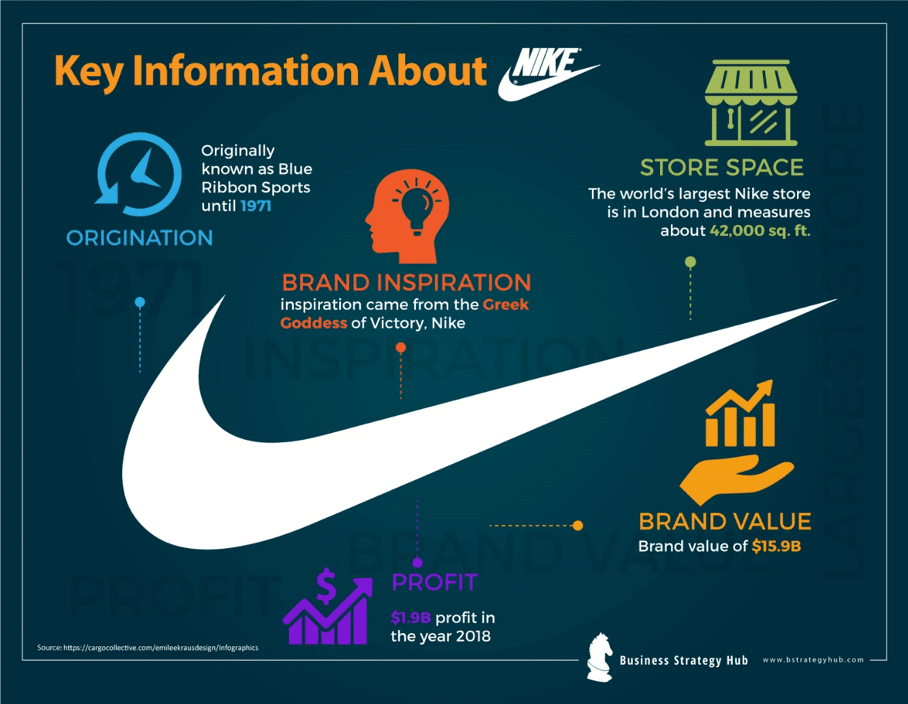
Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Nike. Nike is a multinational corporation based in the United States that designs, develops, and sells sports apparel, footwear, equipment, and accessories. The company was founded in 1964 by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight and was originally known as Blue Ribbon Sports. It officially became Nike in 1971, named after the Greek goddess of victory.
Nike is one of the world’s largest suppliers of athletic shoes and apparel and has a significant presence in the global market. The company’s product line includes a wide range of sports and fitness-related products, including running shoes, basketball shoes, football boots, apparel, and equipment. Nike also owns several subsidiary brands, including Converse and Hurley.
The company is known for its iconic “swoosh” logo and marketing campaigns featuring high-profile athletes such as Michael Jordan, Serena Williams, and Cristiano Ronaldo. Nike has also been involved in several controversies related to its labor practices, environmental impact, and marketing strategies, leading the company to make efforts to address these issues and improve its social and environmental responsibility.
Nike Business Model: Not a business but an inspiration

Here’s a SWOT analysis for Nike:
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Nike.
By the way, here is a course that will help you stand out in the world of strategy. The Strategic Thinking program for CxO by Cambridge Judge Business School maps your competitive advantage and teaches advanced techniques to formulate, evaluate, and execute winning strategies. Generate winning strategies and learn how to renew them in times of crisis for a competitive advantage.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
- Brand recognition : Nike is one of the most recognizable brands in the world, with its iconic “swoosh” logo and distinctive branding. The company’s marketing campaigns featuring high-profile athletes and celebrities have helped to build a strong association between the Nike brand and success, achievement, and performance.
- Innovation : Nike has a reputation for innovation and has been at the forefront of developing new product technologies and materials. The company’s commitment to research and development has helped it stay ahead of competitors and offer products at the cutting edge of sports performance.
- Product quality : Nike is known for producing high-quality products that are durable, comfortable, and perform well. The company’s products are designed to meet the needs of athletes and fitness enthusiasts of all levels, from beginners to professionals.
- Brand loyalty : Nike has a solid and loyal customer base, with many consumers identifying strongly with the Nike brand and its values. The company’s focus on creating products that inspire and enable people to achieve their goals has helped build a community of brand advocates passionate about the Nike brand.
Weaknesses:
- Reputation risks : Nike has faced several controversies over the years regarding its labor practices, environmental impact, and marketing strategies. These controversies have damaged the company’s reputation and potentially harmed its brand value.
- Dependence on third-party manufacturers : Nike outsources the production of its products to third-party manufacturers, which can create quality control and supply chain issues. This can impact the consistency and quality of Nike’s products.
- High pricing : Nike’s products are often priced higher than those of competitors, which can be a barrier for some consumers who are looking for more affordable options.
- Limited product range : While Nike offers a wide range of sports apparel, footwear, equipment, and accessories, its product range is still limited compared to some of its competitors, which may limit its appeal to some consumers.
- Increasing competition : The sports apparel and footwear industry is highly competitive, with many strong competitors vying for market share. The increasing competition could impact Nike’s sales and market position.
By the way, to communicate our strategy effectively within the team, we all need a robust collaboration platform. Miro is the leading visual collaboration platform. Build anything together on Miro. It’s free and as easy to use as a whiteboard , but endlessly more powerful. Do use the Miro platform for strong communication within your team.
Opportunities:
- Expansion into new markets : Nike has a strong presence in North America, Europe, and Asia, but there are still many untapped markets around the world where the company could expand. For example, Nike could focus on increasing its presence in emerging markets like Africa and Latin America.
- Growth in e-commerce : The evolution of e-commerce has opened up new opportunities for Nike to reach consumers worldwide. By investing in its online sales channels, Nike can reach more consumers and improve its overall sales performance.
- Increased focus on sustainability : As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is a growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. Nike has already tried to improve its sustainability practices, but significant room remains for growth.
- Partnerships and collaborations : Nike has a history of successful collaborations with high-profile athletes and celebrities. Nike can continue strengthening its brand and expanding its reach by forming strategic partnerships with influential figures and brands.
- Innovation and technology : Nike has a strong reputation for innovation and could continue to develop new technologies and materials to improve its products and stay ahead of competitors.
Overall, Nike has several opportunities to continue to grow and expand its brand in the global market. By focusing on these opportunities, the company can maintain its position as one of the world’s leading sports apparel and footwear brands.
Nike doesn’t sell shoes. It sells an idea with its marketing strategy!!
Nike is a global brand that faces several threats in the highly competitive sports apparel and footwear market. Some of the main threats to the Nike brand include the following:
- Intense competition : The sports apparel and footwear industry is highly competitive, with many strong competitors vying for market share. Nike faces competition from well-established brands like Adidas, Under Armour, and Puma, as well as new and emerging brands.
- Economic conditions : Economic downturns or global economic instability can impact consumer spending, hurting Nike’s sales and revenue.
- Counterfeit products : Nike is a popular brand, and as such, it is a target for counterfeiters who produce and sell fake Nike products. This can damage the Nike brand by diluting its reputation for quality and performance.
- Changing consumer preferences : Consumer preferences can shift quickly, and Nike must stay attuned to these changes to ensure that its products remain relevant and in demand.
- Supply chain disruptions : Nike relies on third-party manufacturers to produce its products, and any disruptions in the supply chain, such as factory closures or shipping delays, can impact its ability to deliver products to customers.
- Negative publicity : Any negative publicity related to labor practices, environmental impact, or other ethical issues can harm the Nike brand by damaging its reputation and turning off consumers.
Check out the SWOT Analysis of Global Businesses
Related posts.

SWOT Analysis of Digital Marketing

SWOT Analysis of an insurance company

SWOT Analysis of a Supply Chain

SWOT Analysis of a Human Resources (HR) department

SWOT Analysis of the call center industry in the US

Top 5 Software for SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis of a Sales Territory

SWOT Analysis of the ESG Framework
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Nike SWOT Analysis 2023

This SWOT analysis examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of Nike, Inc., a global footwear and apparel company, a champion brand builder whose slogans like “Just do it” have moved beyond advertising into popular expression.
This undisputed field titan has risen through emotional marketing, high-profile celebrity endorsements, sleek design concepts, and successful public relations campaigns to command over a third of the market share in an extremely competitive segment.
This report assesses both internal and external factors that impact Nike’s business environment while looking at its current and future potential.
Company Overview
Nike’s origins trace back to Blue Ribbon Sports, a company founded by Phil Knight, a track athlete, and his coach Bill Bowerman who was obsessed with improving the performance of his athletes through shoe design.
Knight, after graduating from the University of Oregon, attended Stanford’s MBA program, where he wrote a paper proposing that the manufacturing of running shoes be relocated from Germany to Japan, where labor was cheaper.
With a trip to Japan in 1962, Knight struck an agreement with a group of Japanese business owners to sell the country’s popular Tiger shoes in the United States. Bowerman backed Knight’s venture, entering into a 50-50 business agreement for possession of their new company, Blue Ribbon Sports, which was founded on 25 th of January 1964, in Eugene, Oregon US.
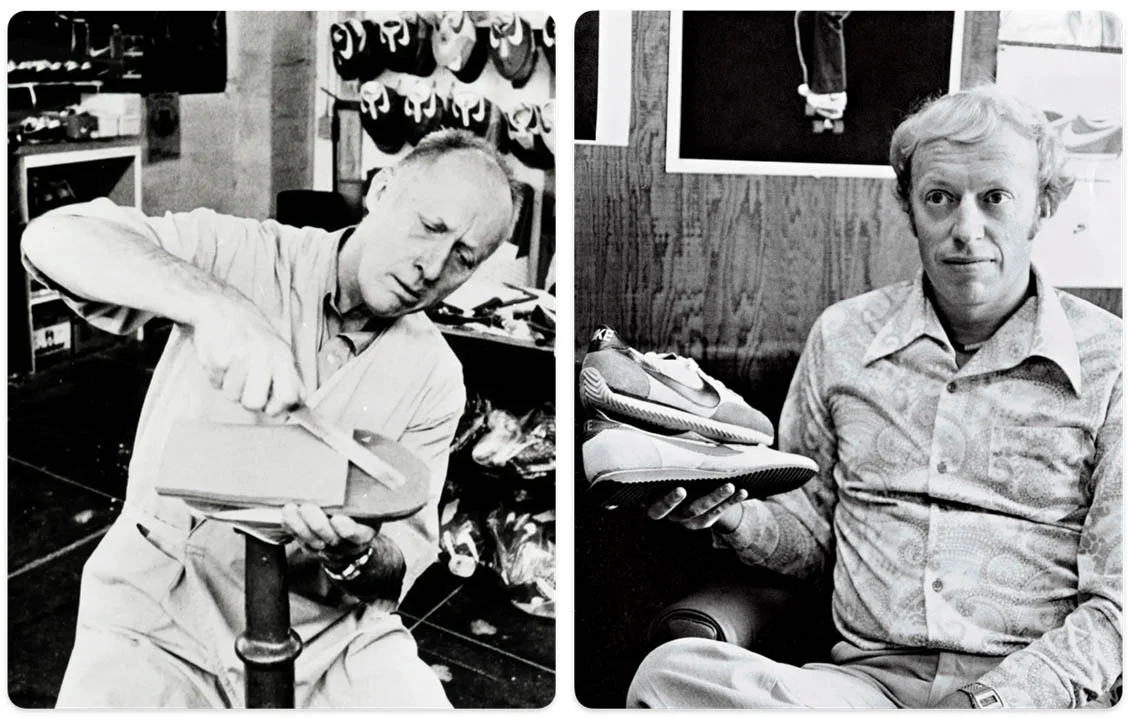

Knight started testing the waters for his imported shoes, initially selling them out of his vehicle when he returned to the United States. It quickly became clear that there was a market for these less expensive but still high-quality alternative options.
This was a time when Adidas and Puma were already established and dominated the market ( Puma was established in 1948, and Adidas in 1949 ).
Bowerman, ever inventive, proposed an improved shoe design to the Tiger shoe company, leading to the development of The Tiger Cortez which was released in 1967. It quickly became a hit due to its comfortable, durable, and stylish design. While a huge success, it was also a source of contention between Blue Ribbon and Tiger shoe company.
Tiger accused Blue Ribbon of selling duplicate Tiger Cortez Shoe with the name Nike which led to both companies going their separate ways. After the split, Blue Ribbon Sports rebranded itself as Nike and launched in the market.
Interestingly Nike’s logo, called the swoosh, was designed by Carolyn Davis, a design student, for a fee of $2 per hour, receiving $35 in total for the work. Knight reluctantly chose a swoosh, saying, “Well, I don’t love it, but perhaps it will grow on me”. Later in 1983, Davis received 500 shares of stock from Knight, estimated to be worth over $1 million today. [5]
Soon Knight released the waffle trainer shoes, a huge success for Nike, the first of many in the company’s early days, resulting in its 1980 IPO, which made Phil Knight a millionaire with shareholdings worth $178 million.

Today, Nike is a dominant global leader in the sports goods industry. It enjoys a robust brand value, extensive customer base, and diverse product portfolio. The company is engaged in the design, development, marketing, and sales of a broad range of athletic footwear, apparel, and equipment.
Nike offers a comprehensive range of performance equipment and accessories, including bags, socks, sports balls, eyewear, timepieces, digital devices, bats, gloves, protective equipment, and other specialized gear for sports activities. [2]
It also owns Converse, its subsidiary brand, headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, that designs, distributes, and licenses casual sneakers, apparel, and accessories under the Converse, Chuck Taylor, All Star, One Star, Star Chevron, and Jack Purcell trademarks.
Nike SWOT Summary
1. brand value.
In a digital age where intangible assets are the key drivers of value creation, technology patents, customer data, and brand value offer sustainable competitive advantages. Nike is in a pristine position to capitalize on this opportunity.
It is one of the most valuable brands in the world, and it is extremely popular across different geographies and ages, generating and benefiting from the casualization of fashion.
It is the highest-valued apparel brand in the world, with a valuation of $33.2 billion, according to Brand Finance. [7]

Interbrand [8] has ranked Nike at the 10 th position in 2022 with an estimated brand value of $ 50.3 billion, an 18 percent rise in brand value compared to the previous year.

Kantar [9] , the world’s leading data insights & consulting agency places Nike in the 13 th position with a brand value of $109 billion. This dominant position is underlined by the gigantic gap to the closest direct competitor Adidas which ranks 89 ($23 billion).
2. Robust and sustainable growth
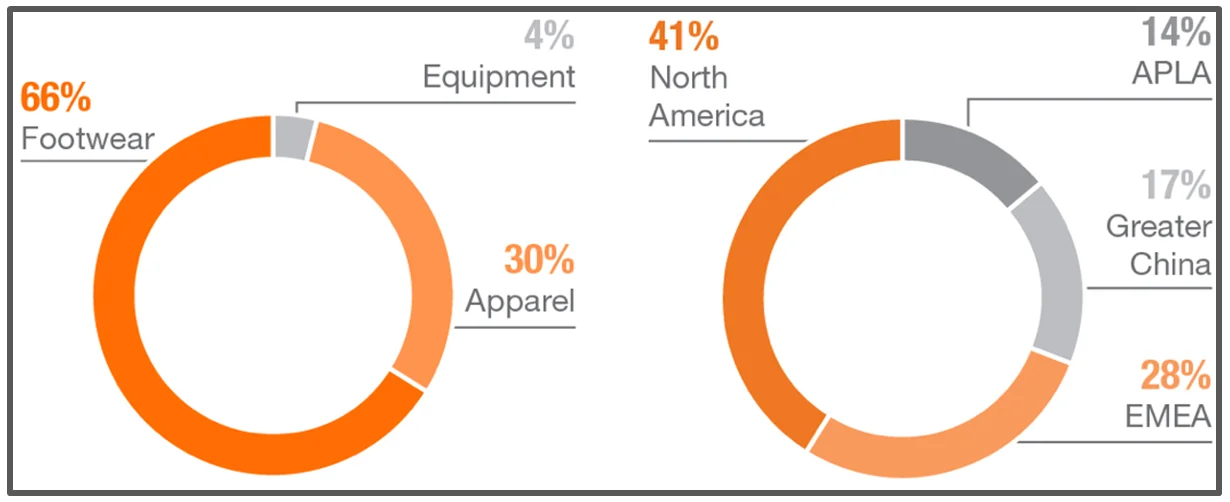
Nike generates its revenues from a portfolio of highly coveted products, which are organized into three categories: footwear, equipment, and apparel. The company’s revenue streams are geographically well-diversified, with close to 60% of sales from international markets reflecting a balanced global presence.
The sustained and consistent revenue growth of the company over the long term is a testament to its strong financial performance. This reflects Nike’s agility and resilience, which has proven to be adaptable to changing market conditions and challenges over time.
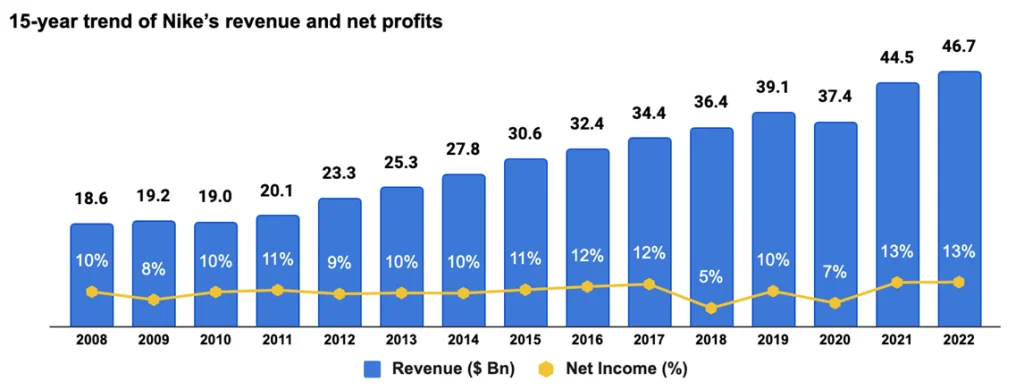
2018 income was lower due to the impact of the Tax Act, which offset strong revenue growth. 2020 income was affected due to the Pandemic’s adverse impact on input prices & supply chain. (Source: Nike financial reports).
During the pandemic, when companies chose to put their eCommerce marketing spend on hold, Nike identified it as a distinct opportunity and prioritized its digital direct-to-customer (D2C) sales. With consumers rapidly shifting towards online shopping, Nike’s digital sales soared 82% during the first quarter of fiscal year 2020 [10] . Nike’s growth in D2C sales since then has been rapid, resulting in better profitability in 2021 and 22.
3. Athlete endorsements and promotional campaigns
Based on research conducted by Nielsen Sports [11] , brand sponsorship in sporting events is one of the most effective advertising channels. The only channel that is considered more trustworthy is direct recommendations made by a close associate. Nike leads in this arena with over 650 sponsorships spanning more than 140 different leagues or associations [12] .
Nike’s brand has become synonymous with powerful athletes across all sports. It has demonstrated just how lucrative strategic sponsorship marketing can be.
Nike-sponsored athletes list includes basketball legend Michael Jordan to the best footballer Cristiano Ronaldo. Nike has spent heavily on athlete endorsements throughout the years, signing million-dollar deals with sports celebrities to advertise its products.
With the athletes spending their lives in front of cameras, these profitable collaborations allow Nike also enhances its appeal through the swoosh on the players’ sportswear.
Over the years, the brand has struck savvy endorsement partnerships that have grown a modest firm into a billion-dollar enterprise.
Nike’s 10 most notable athlete endorsements:
Nike’s athlete endorsements have proven to be very effective. For example, in 1984, Nike sold the deal to Jordan at a flat payment of $500,000 USD a year with the promise to allow him to create his own signature shoe. While Nike only projected that Michael’s Air Jordan 1 would only bring in $3 million USD over the course of four years, it brought close to $126 million in the first 12 months [15] .

Nike invests significant sums into its promotional campaigns each year. In 2022 alone, its advertising and promotion costs amounted to approximately 3.85 billion U.S. dollars.
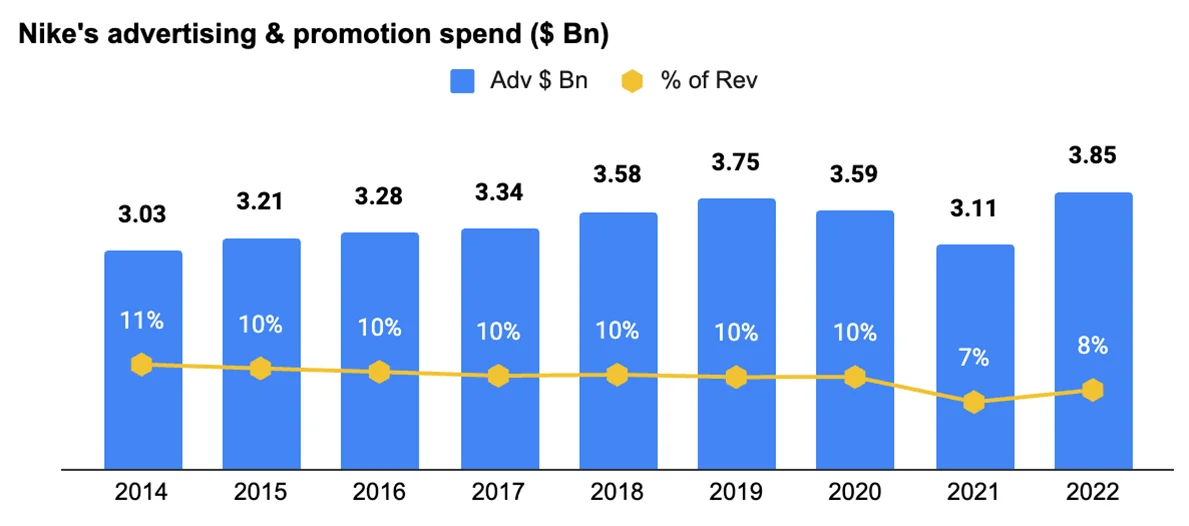
Results of Nike’s campaigns and marketing investments show. In a survey conducted in 2022, about 95 percent of online shoppers buying sports and outdoor goods in the US said they knew what Nike was. 60 percent of these respondents said they liked the brand, with a considerable share also stating that they used and will continue to use Nike products. [17]
4. Growing D2C Business
Aiming to deliver a more consistent experience and deeper connections with consumers, Nike has shifted away from wholesale partners toward its own distribution. The D2C sales contribution to Nike’s revenue is growing fast, particularly post the pandemic.
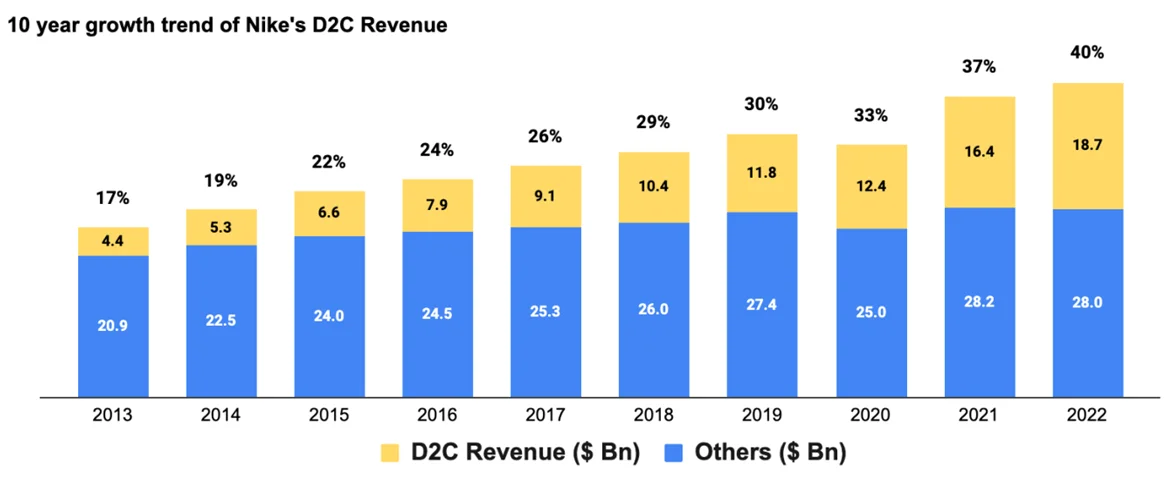
Nike first announced its Consumer Direct Offense (CDO) strategy in 2017 as a five-year plan to focus growth on 40 “strategic” retail partners and its own DTC. The strategy involved consolidating its retail partners and strengthening its eCommerce channels and launching new stores.

In 2019, Nike ended a two-year pilot program with Amazon.com in a move that, according to Nike, allowed it to instead focus on “strong, distinctive partnerships” with other retailers. [20]
Nike has since been focusing on expanding its D2C operations while reducing its reliance on wholesale accounts. It ended its relationship with nine wholesale accounts in 2020, followed by another six in 2021. The brand has also cut off numerous smaller independents. [21]
Its D2C business brings higher margins and allows it to connect directly with customers.
This has enabled deeper insights into customer data for better customer experience. By going direct, Nike enjoys greater access to customers leading to better analytics allowing it to effectively market, merchandise, promote and launch new products to satisfy customers’ demands.
5. Going digital through strategic acquisitions
Nike has constructed a technology ecosystem to support its businesses, especially its transition into a D2C model. It has steadily invested in technology and distribution, acquiring start-ups with expertise in content creation to data analysis.
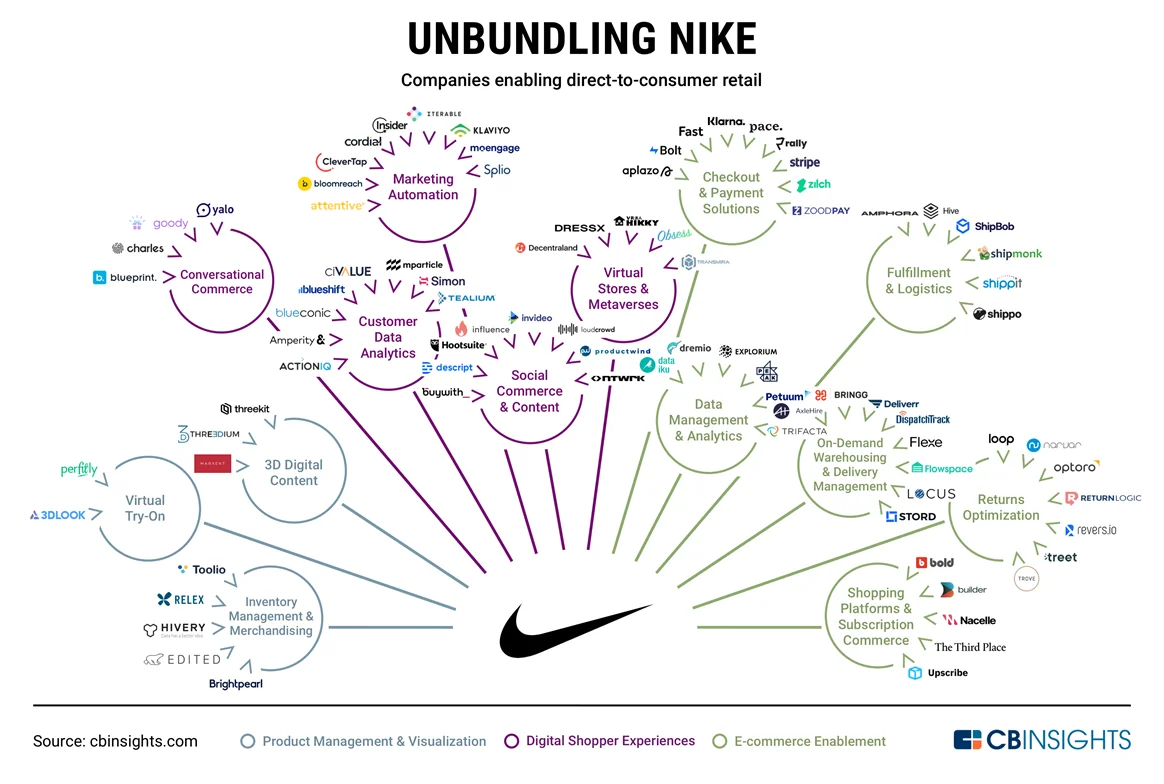
A look at how companies are unbundling Nike, from customer data platforms to fulfillment and logistics.
Source: cbinsights.com [22] . Note: The graphic is not exhaustive of space. Categories are not mutually exclusive.
In 2020, Nike announced the next phase of its former strategic plan (CDO). Named Consumer Direct Acceleration, this involved several initiatives:
- Creating a connected digital marketplace of the future, which focuses on developing a premium and seamless brand experience wherever customers shop.
- Operating under a more straightforward consumer construct of men’s, women’s, and kid’s categories.
- Aggressively invest in digital capabilities in their end-to-end technology foundation to accelerate digital transformation. This has included demand sensing, insight gathering, inventory management, and more.
Under this initiative, Nike has made several key acquisitions of technology startups to help boost its digital capabilities. A few of them are:
- Zodiac [23] , a predictive customer analytics platform that it acquired in 2018.
- Celect [24] , a demand-sensing firm based in Boston, that it acquired in 2019.
- Invertex [25] , a leading computer vision firm based in Tel Aviv, was acquired in 2018. According to its co-founder, “Invertex’s combination of powerful deep learning and augmented reality, combined with its 3-D body scanning technology and domain expertise, have created the world’s most accurate body-based match engine for footwear.”
- Datalogue [26] , a company that has built cutting-edge and proprietary machine-learning technology to automate data preparation and integration, was acquired in February 2021. This helped Nike integrate data from all sources, including the company’s app ecosystem, supply chain, and enterprise data, in a fast, seamless, easily accessible, and standardized platform.
Nike is also rapidly transitioning into headless e-commerce. Headless e-commerce is the decoupling of the front end (the “head”) or user interface (UI) and the back end of an e-commerce solution. This introduces flexibility and the ability to test and iterate quickly, allowing for more independence and customization potential.
With this, Nike has been able to provide a more personalized and mobile-first experience to its customers with interactive user experiences and optimized visuals for smaller screens.
6. A Culture of Innovation
Nike’s culture of innovation involves endless prototyping without constraints and testing without limits. The LeBron James Innovation Center at Nike World Headquarters celebrates and advances the company’s foundation of innovation. It unites over 700 staff from innovation teams previously spread across the Nike campus and is designed to foster the cross-pollination of ideas.
Inside the 700,000-square-foot building is a dedicated sports research facility named the Nike Sport Research Lab (NSRL) which positions Nike for future decades of game-changing products and experiences for all athletes.
The community working in the space allows for an intersecting mix of talent from biomechanics researchers and robotics experts to computational designers, to generate breakthroughs across the spectrum of play and movement.
Nike’s Sport Research Lab by Numbers:
It is here that Nike listens to the voice of the athletes, observing them in action while it prototypes, tests, and builds future products. The facility’s goal is to understand unique needs and opportunities, contextualize challenges and generate breakthroughs across the spectrum of play and movement in a variety of environments.

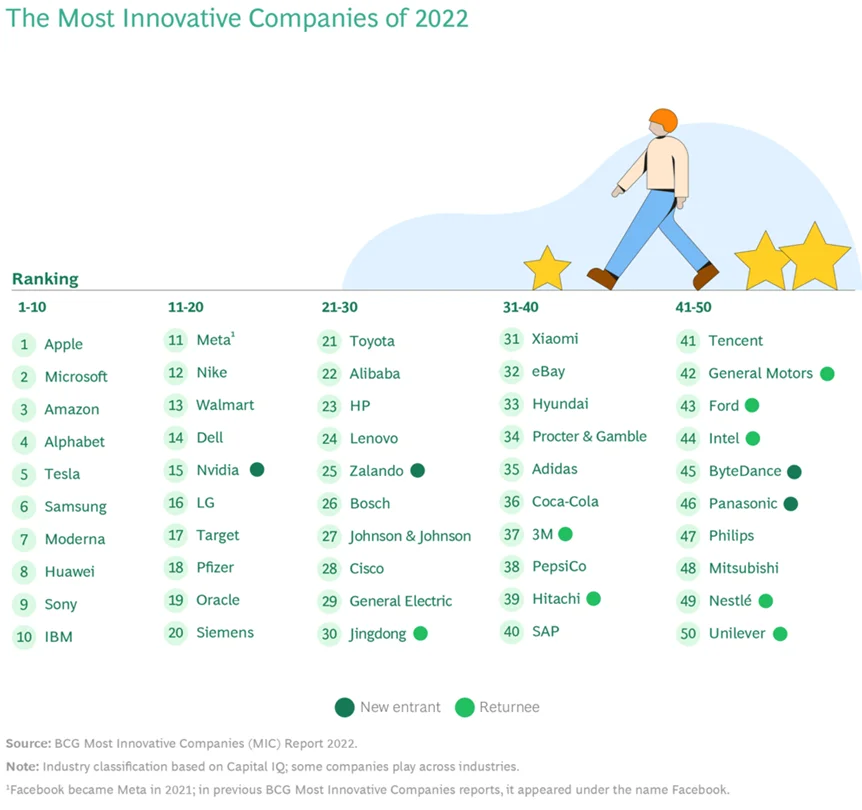
Nike is also among the most innovative companies in the world, ranking 12 th on the BCG’s 50 most innovative companies of 2022.
1. The stain of forced labor and poor working conditions
Nike, Inc. has been accused of using sweatshops and worker abuse to produce footwear and apparel in East Asia. It has been shamed in public for its labor practices to the point where it badly tarnished the company’s image and hurt sales.
This is an old issue that has been negatively impacting Nike’s reputation. Even in the 1990s, Nike was plagued with damning reports that its global supply chain was being supported by child labor in places like Cambodia and Pakistan, with minors stitching soccer balls and other products as many as seven days a week for up to 16 hours a day. [29]
In March 2020, a damning report [30] from the Australian Strategic Policy Institute revealed that the Chinese government was forcing hundreds of young Uyghur women to produce Nike shoes in the Taekwang factory in Laixi City.
In a more recent case, Nike has also been accused of breaching OECD Guidelines regarding the treatment of workers in its global supply chain following the Covid pandemic [31] . The case alleged that since the onset of the Covid pandemic in March 2020, garment workers in Nike’s supply chain have experienced layoffs and terminations, arbitrary pay cuts, unpaid wages for hours worked, and gender discrimination at an unprecedented scale.
The fact that Nike’s audits have failed to detect its supplier’s participation in forced labor programs undermines the public trust in its processes to uncover the truth. [32]
2. Inventory management issues
At the end of 2022, Nike staged a global fire sale to clear a huge inventory glut that it blamed on earlier ordering by retailers and faster-than-usual deliveries.
In 2023, the company has admitted that, despite strong demand, it will follow a policy of “aggressive markdowns” to clear inventories, likely impacting margins for the fiscal year.
Nike is exposed to the typical challenges faced by retailers running an omnichannel model in a world of chaos, where the customer, rather than the product, is the primary focus. Failure to accurately forecast consumer demand carries the risk of excess inventories or inventory shortages, resulting in decreased operating margins and reduced cash flows that could negatively impact Nike’s business.
Investors see Nike’s inventory problems are somewhat indicative of poor management. While the excess inventory is slowly dwindling, Nike has proven that supply chain disruptions can and will disturb its margins & inventory management [33] .
3. Involvement in Controversies
In November 2017, the Paradise Papers, a set of confidential electronic documents relating to offshore investment, revealed that Nike is among the corporations that used offshore companies to avoid taxes [1] .
In September 2018, Nike announced it had signed former American football quarterback Colin Kaepernick, noted for his controversial decision to kneel during the playing of the US national anthem, to a long-term advertising campaign [1] .
In October 2019, U.S. Vice President Mike Pence criticized Nike for its reaction to China’s treatment of protests in Hong Kong. He accused the company of “siding with the Chinese Communist Party and silencing free speech”. He stated that the brand “promotes itself as a so-called social-justice champion, but when it comes to Hong Kong, it prefers checking its social conscience at the door.” [1], [34] .
In January 2020, the World Athletics [35] issued new guidelines concerning shoes to be used in the Tokyo 2020 Olympics. These updates came in response to criticisms concerning technology in the Nike Vaporfly running shoes which stated that the shoes provided athletes with an unfair advantage and were a form of “Technology doping” [1] .
Controversies like these have the potential to undermine Nike’s brand value and negatively impact its business.
Opportunities
1. enhanced brand value and cost leadership through circularity.
According to World Economic Forum (WEF), the circular transformation of industries can unlock new value in a resource-constrained world. The transition towards a circular economy is estimated to represent a $4.5 trillion global growth opportunity by 2030 while helping to restore natural systems. [36]
The circular economy is a model of production and consumption, which involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials and products to the extent possible, thus extending the product lifecycle.
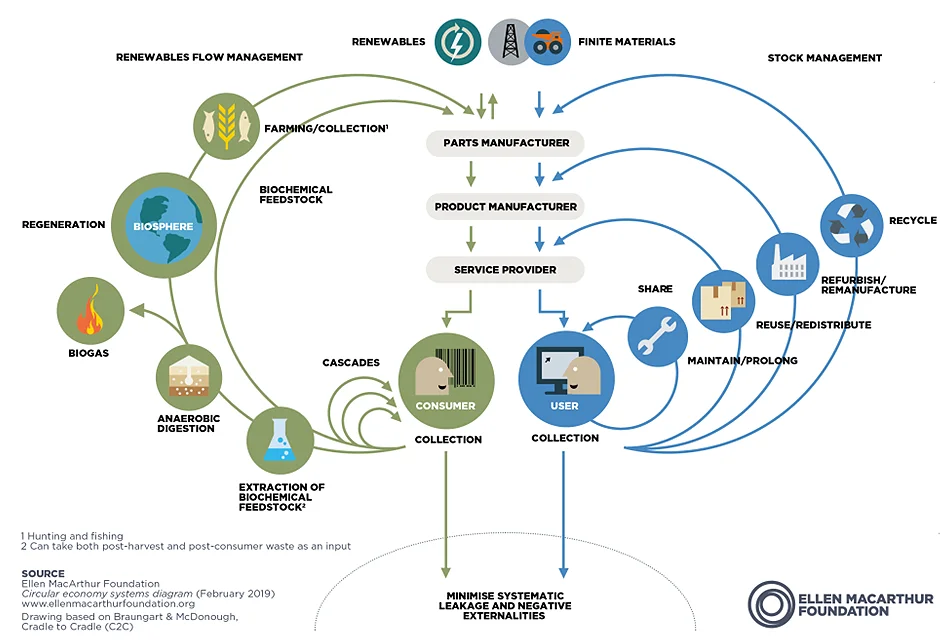
Nike’s circular vision is rooted in bold, science-based targets built on more than 30 years of exploring ways to reduce environmental impact. It aims to develop an industrial value chain with no beginning or end, closing the loop from product design all the way through the raw materials stage to manufacturing, shipping, retail, and product take-back.
Nike has been an early adaptor of Circular design principles.
For example, the company has created Flyleather [38] , a material made of recycled leather scrap once destined for the landfill, which is abrasion-resistant and 40% more lightweight than full-grain leather. It has developed a workbook that serves as its product design guideline based on ten key circularity principles [39] .
With these actions, Nike stands to benefit from a circular economy in several ways, such as:
- Reducing its environmental impact by using fewer resources, energy, and water, and emitting fewer greenhouse gases and toxic chemicals.
- Saving costs by reusing materials and components from waste streams and recycled products.
- Enhancing its brand reputation and customer loyalty by demonstrating its commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
- Driving innovation and creativity by exploring new design possibilities and solutions that are inspired by nature and biomimicry.
- Creating new business opportunities and revenue streams by offering products and services that are designed for circularity, such as repair, rental, resale, or remanufacturing.
2. Growing athleisure market
According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets [40] , the athleisure [41] market is expected to grow from $411 billion in 2021 to $793 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2021 to 2028.
Recent polling data from CivicScience found that Gen-Z, which represents most athleisure consumers, turned to Nike as its brand of choice.
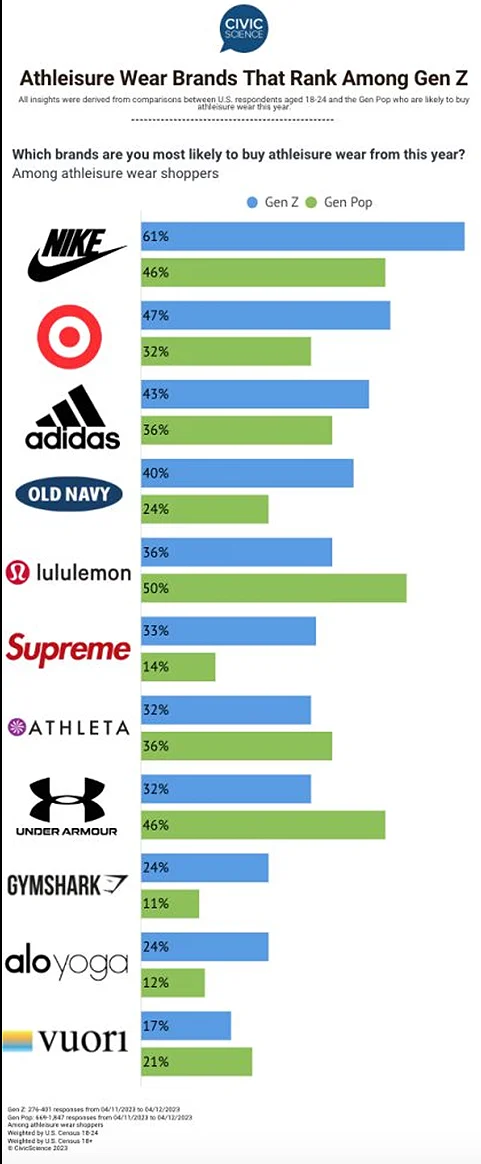
Post-pandemic, athleisure has quickly become popular because it appeals to several broad trends, such as the global shift toward consumers wearing more casual attire, the desire for comfortable clothing, and the increase in athletic activity among health-conscious consumers who need performance clothing for these activities.
This trend echoes even in emerging markets. For example, Global Consultancy Research and Markets pegged an estimated market size of $27.89 billion in 2022 for India’s sports equipment, footwear, and apparel market. It projects the market to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.82 percent reaching $40.64 billion by 2027 [43] .
Nike, with its global presence and dominant position in Athleisure, is well-positioned to leverage this growth.
3. Rise of the high-income middle class in emerging markets
Nike’s presence in China, as well as in the wider regions of Asia, Africa, and Latin America, indicates promising opportunities for expansion within emerging markets. With ongoing advancements and the steady rise of the middle class in underdeveloped areas, Nike is poised to expand its reach and attract a larger customer base.
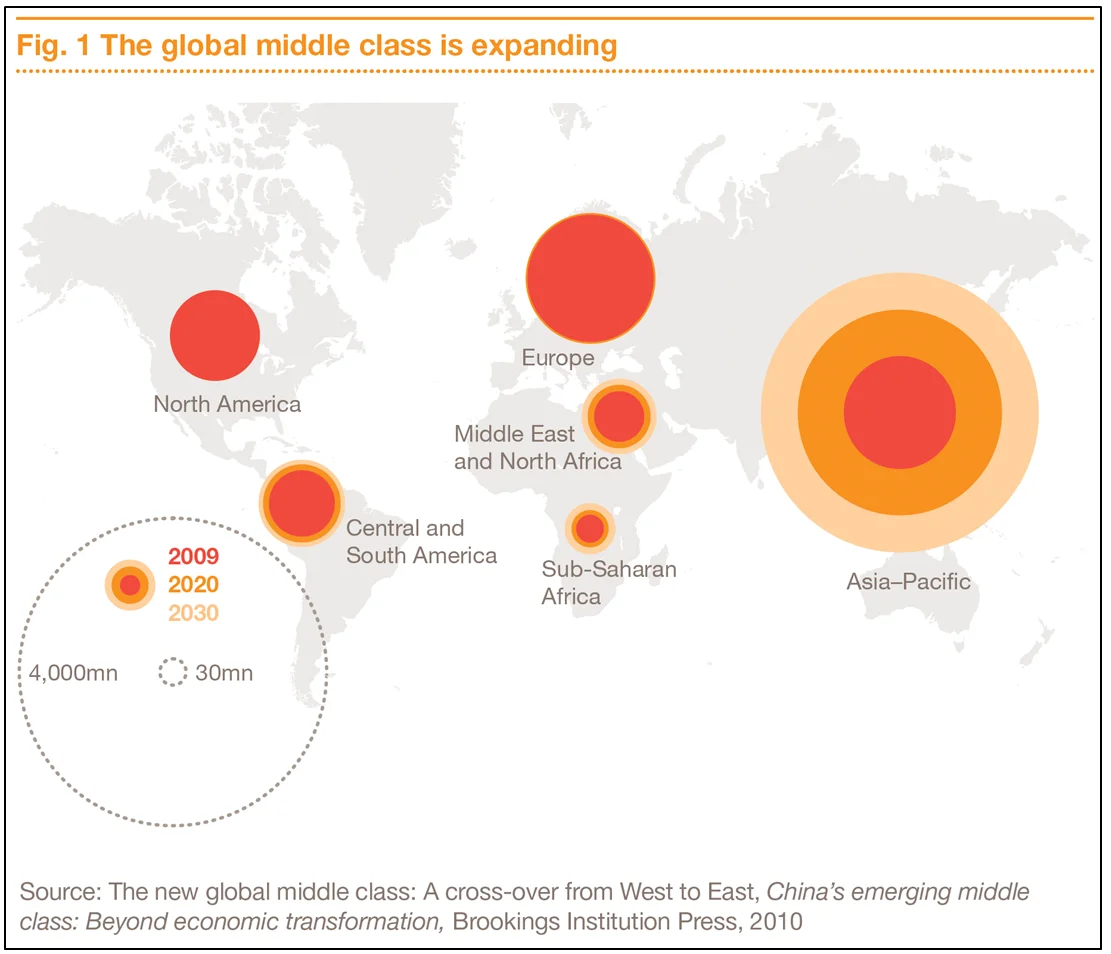
Nike’s sales will grow at an enticing rate, argues this report by seeking-alpha [33] while
projecting that more than 70% of Nike’s growth over the next five years may come from outside North America.
Unlike the growth by further saturating developed markets, this growth will be a more sustainable one.
4. Growth led by the virtualization of sports
According to a report by Deloitte [45] , the use of digital assets like non-fungible tokens (NFT), fan tokens, and blockchain-enabled tickets are evolving for sports.
Simple digital collectibles, originally seen as curiosities, are becoming advanced digital assets that can be used to improve fan engagement and loyalty and create new business models and even more new revenue streams.
In 2022, Nike launched its Web3 platform called .Swoosh (dot Swoosh) to offer Polygon-based NFT products [46] . Earlier in 2021, it acquired Web3 studio RTFKT [47] and released digital Nike sneakers as Ethereum NFTs.
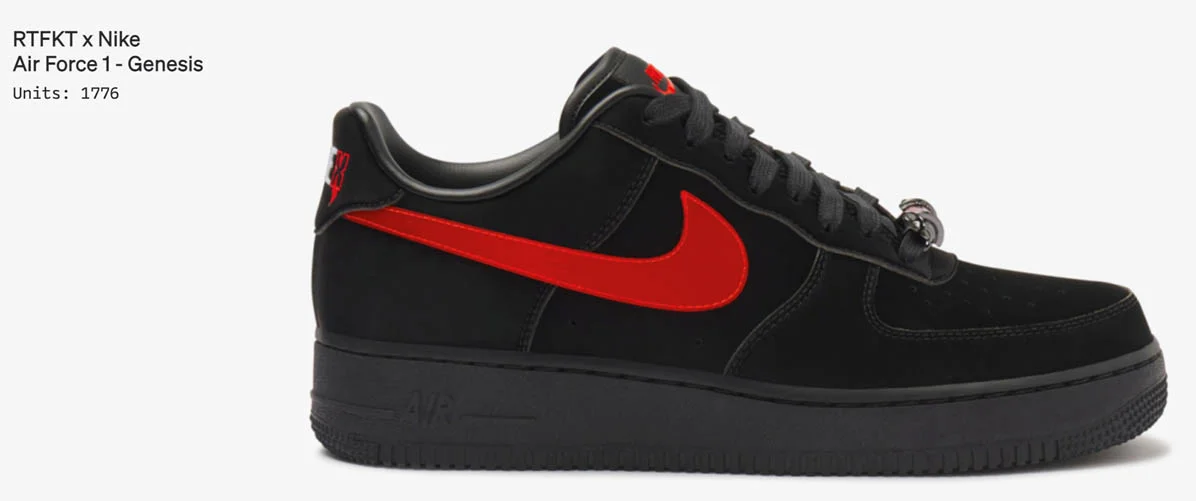

Nike Air Force 1 Genesis collection, featuring a sleek design inspired by the SZN 1 Forging Event (Source: RTFKT [47] )
In 2023, the company unveiled its first .Swoosh NFT Digital Sneaker Drop named the “Our Force 1″ collection, potentially consisting of hundreds of thousands of virtual pairs of the brand’s iconic Air Force 1 sneaker [48] .
This blending of physical and digital experiences will move from proving concepts to creating new functionality and better experiences while opening doors to promising new opportunities for companies like Nike.
5. Growth in women’s sports and sportswear
Women’s professional sports had a record-breaking year in 2022, with levels of interest, attendance, viewership, media coverage, and investment reaching their peak. The segment is positioned to advance even further with a positive outlook in the coming years [45] .
This surge in awareness is expected to create increased opportunities in the women’s sports apparel and merchandise industry.
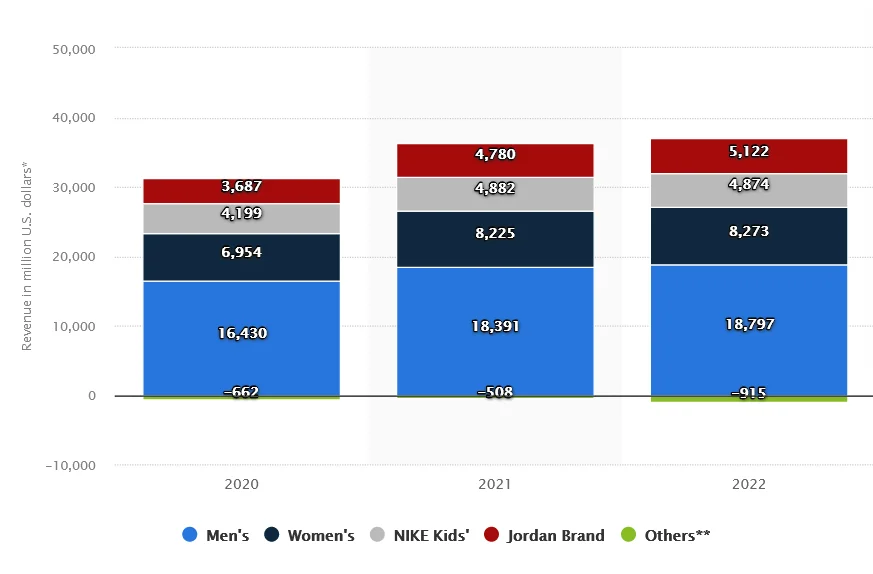
For years, the brand has made clear that selling more sports gear to women is a top priority.
With the pandemic accelerating Nike’s digital momentum, women’s apparel growth has been provided a boost.
Nike’s apps like Training Club and SNKRS, have led to the acquisition of millions of new members, particularly a significant number of women.
The company’s new strategic initiative appeals to a broader segment of the female market and takes advantage of the differences between women and men in how they conceive of sport and how they shop for clothing and shoes. Nike is changing the way it sells to, designs for, and communicates with women in order to double its sales to women by 2025.
1. Supply chain risks
Nike manages a global and vast supply chain that includes suppliers from around the world. Managing this supply chain is complex and challenging with potential risks and challenges that are sometimes beyond Nike’s control.
For example, Nike works with thousands of suppliers, many of whom are spread across the globe. Ensuring that its suppliers adhere to its standards is a challenge. This can get particularly difficult when dealing with suppliers in countries with different legal systems and cultural norms.
According to the company’s 2022 annual filings [2] , Nike relies on a concentrated source base of contract manufacturers to supply a significant portion of footwear products. It is supplied by 120 finished goods footwear contract factories located in 11 countries, out of which four footwear manufacturers accounted for over 10% of footwear production, each aggregating to ~58% of NIKE Brand footwear production.
If any of these primary footwear manufacturers failed to make timely shipments or did not meet quality standards or failed to deliver in accordance with Nike’s plans, it could have a materially adverse effect on the company’s operations.
Another challenge is the logistics and transportation. Nike’s products are sold in markets all over the world which requires the goods to be transported across many different borders. This can come with potential risks like an escalation in freight costs, shipping delays, natural disasters, and unfavorable transportation conditions.
Nike is also exposed to global risks like rapid currency exchange rate changes and international conflicts that could negatively impact its global business.
It must also adhere to customs regulations and border procedures in different countries while ensuring a seamless delivery.
2. The rise of counterfeit products
Nike is among the most counterfeited brand globally, according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development [50] .
The volume of international trade in counterfeit products was estimated to be $464 billion in 2019 – 2.5% of total international trade, according to the OECD iLibrary [51] .
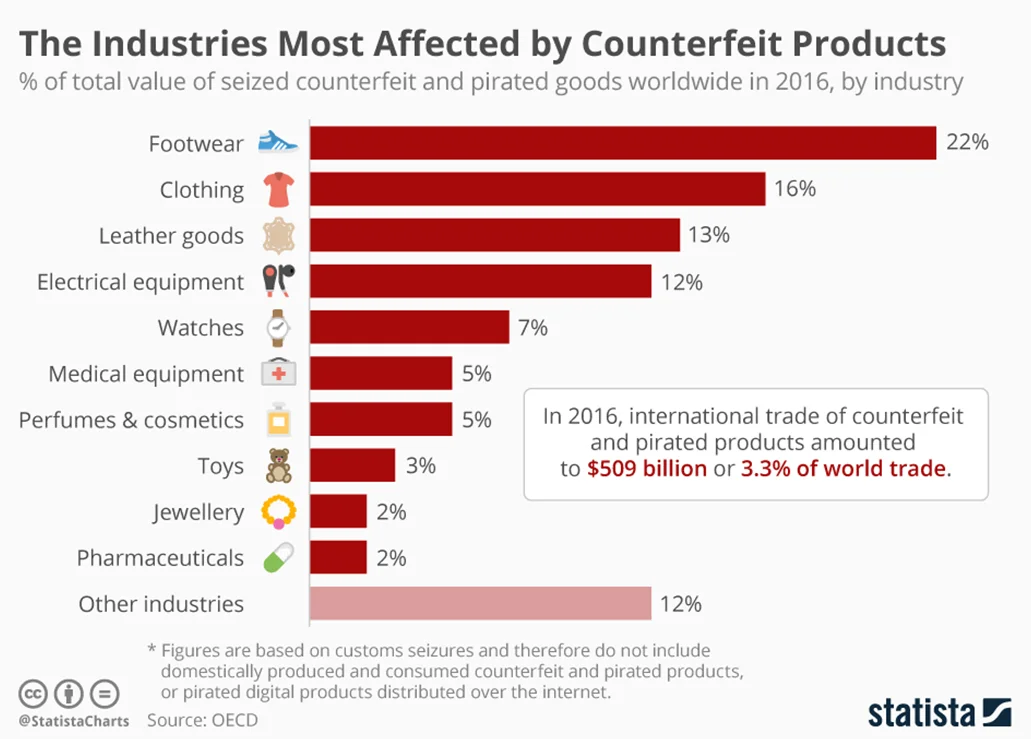
Footwear and clothing are among the most counterfeited goods which are also primary product categories for Nike.
Counterfeited products can have a negative impact on the company through diluted brand equity and lost revenues. Moreover, it is difficult for a consumer to differentiate between a fake and an original product judging by an image or the first impression. Eventually, these products easily wear out due to inferior materials and poor design with the potential to cause injury.
3. Threat of Lawsuits
According to the company’s 2022 Annual filings [2] , Nike is subject to a complex array of laws and regulations and litigation, and other legal and regulatory proceedings, which could have an adverse effect on its business, financial condition, and results of operations.
If the company’s employees, agents, suppliers, and other partners fail to comply with any of the laws or regulations, it could lead to fines, sanctions, or other penalties that could negatively affect our reputation, business, financial condition, and results of operations. Furthermore, laws, regulations, and policies and the interpretation of such can conflict among jurisdictions, and compliance in one jurisdiction may result in legal or reputational risks in another jurisdiction.
Nike is involved in various types of claims, lawsuits, regulatory proceedings, and government investigations relating to its business, products, and the actions of its employees and representatives, including contractual and employment relationships, product liability, antitrust, trademark rights, and a variety of other matters.
This also includes compliance risks, such as anti-bribery, anti-corruption, fraud, trade, environmental, competition, privacy, and other regulatory matters, which will continue to exist, and additional legal proceedings and other contingencies have and will continue to arise from time to time, which could adversely affect the company.
Additionally, regulation of certain transactions like non-fungible tokens (“NFTs”) and cryptocurrencies, which the company engages in, remains in an early stage and is subject to significant uncertainty.
According to the Violations tracker, Nike has paid a cumulative penalty of $17.7 million since the year 2000.
The company has also been involved in numerous lawsuits. In 2023, a long-running sexual harassment and gender discrimination lawsuit against Nike produced more than 5,000 pages of records, including surveys of female employees that allege sexist attitudes and behavior at the sportswear giant alongside corporate bullying and fears of retaliation [54] .
Besides litigation, Nike has over 20,000 active patents and is constantly engaged in patent wars with competition.
For example, in 2023, Nike filed a lawsuit against Lululemon alleging that their new shoe line infringes on Nike’s patent for Flyknit technology. In 2022, Adidas claimed that Nike’s Run Club, Training Club, and SNKRS mobile apps violated its patented technology and pressed for damages and an injunction against Nike.
4. Competition
While Nike has a broad economic moat due to its strong brand image and endorsements with the most valuable sports teams and athletes in the world, competition is evolving.
Players like Adidas, Puma, Anta Sports, ASICS, Li-Ning, Lululemon Athletica, Under Armour, VF Corporation, and Revolve, to name a few, have been constantly investing in product innovation, marketing, customer service, and brand endorsement to challenge Nike’s market share and profitability.
Some of these competitors are showing real promise, especially under challenging circumstances.
Lululemon, for example, has forged strong connections with its upscale, fitness-minded clientele, who are willing to pay what the products are worth. The company has managed to maintain higher gross margins compared to Nike, suggesting better operational efficiency.
In the third quarter of 2022, Revolve added more than 84,000 new active customers (a 34% increase year over year) while witnessing an increase in average order value by 16%. These signs point to an engaged and satisfied customer base that could continue to increase over time.
According to an article by The Motley Fool [55] , Lululemon and Revolve could emerge as significant competitors to Nike by 2032, presenting a notable threat to its market position.
With a strong brand value, a loyal customer base, and a diverse product portfolio, Nike is a global leader in the sports goods industry. The company’s history is deeply rooted in innovation, providing it with an economic moat over competition. It is agile in adapting to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
By leveraging its digital capabilities, direct-to-consumer strategy, and circular economy vision, Nike has unlocked new value and opportunities for its business.
To maintain its competitive edge and growth potential, Nike needs to continue its innovative journey and expand aggressively into emerging markets, especially targeting the high-income middle class, opportunities in the virtualization of sports and the growth in women’s sports and sportswear.
Just like athletics, in Nike’s line of business, excellence is perpetual, where “There is no finish line.”
1. “Nike, Inc..” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nike,_Inc. . Accessed 2 May 2023.
2. “2022 Annual Report – FORM 10-K.” Nike, https://investors.nike.com/investors/news-events-and-reports/ . Accessed 2 May 2023.
3. “Never Done Listening – Department of Nike Archives.” Nike, https://www.nike.com/in/a/never-done-listening . Accessed 2 May 2023.
4. “Life Advice from Phil Knight.” Mensjournal.com, https://www.mensjournal.com/entertainment/life-advice-from-phil-knight-w431388 . Accessed 2 May 2023.
5. “Why is Nike so Successful? Nike History | Nike Marketing Strategy.” ThinkWithNiche, https://www.thinkwithniche.com/blogs/details/why-is-nike-so-successful . Accessed 2 May 2023.
6. “History Of Nike: Blending Athletics With Timeless Fashion.” businessapac.com, https://www.businessapac.com/history-of-nike-athletics-fashion/ . Accessed 7 May 2023.
7. “Nike retains title as world’s most valuable apparel brand while luxury brands boom after COVID-19.” BrandFinance, https://brandfinance.com/press-releases/nike-retains-title-as-worlds-most-valuable-apparel-brand-while-luxury-brands-boom-after-covid-19 . Accessed 2 May 2023.
8. “Best Global Brands.” Interbrand, https://interbrand.com/best-global-brands/ . Accessed 2 May 2023.
9. “Kantar BrandZ Most Valuable Global Brands 2022.” Kantar, https://www.kantar.com/campaigns/brandz-downloads/kantar-brandz-most-valuable-global-brands-2022 . Accessed 2 May 2023.
10. “Nike’s online business is booming — ‘digital is here to stay,’ CEO says.” CNBC, https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/23/nikes-ceo-says-digital-is-here-to-stay-e-com-business-fuels-sales.html . Accessed 3 May 2023.
11. “Nielsen Releases 2022 Global Sports Marketing Report.” Nielsen, https://sponsorship.org/nielsen-releases-2022-global-sports-marketing-report/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
12. “Nike Increases Revenue & Continues to Spend on Sponsorships.” SPONSOR INSIGHTS, https://sponsorunited.com/nike-increases-revenue-continues-to-spend-on-sponsorships/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
13. “The Billion-Dollar Swoosh: Nike’s 10 Most Expensive Endorsements With Athletes.” TheRichest, https://www.therichest.com/rich-powerful/the-billion-dollar-swoosh-nikes-10-most-expensive-endorsements-with-athletes/ . Accessed 3 May 2023.
14. “How much money has Michael Jordan made from Nike? Contract details, revenue, net worth.” Sportingnews.com, https://www.sportingnews.com/us/nba/news/michael-jordan-made-nike-contract-revenue-net-worth/tahhp5y8wneeljjrdhqgpkg9 . Accessed 3 May 2023.
15. “Air Jordan.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Air_Jordan . Accessed 5 May 2023.
16. “Air Jordan: Most Valuable Sneaker.” Felix Richter, Statista, https://www.statista.com/chart/29726/most-expensive-sneakers-sold-at-auctions/ . Accessed 5 May 2023.
17. “Nike’s advertising and promotion costs from the financial years of 2014 to 2022.” Statista, https://www.statista.com/statistics/685734/nike-ad-spend/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
18. “Nike brand’s direct-to-consumer revenue worldwide from the fiscal years of 2009 to 2022.” Statista, https://www.statista.com/statistics/294512/nike-s-dtc-revenue-worldwide/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
19. “Nike debuts new store concept with Nike Style.” Retaildive.com, https://www.retaildive.com/news/nike-opens-new-store-concept-nike-style/627400/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
20. “Nike’s breakup with Amazon may lead other brands to call it quits: analysts.” S&P Global, https://www.spglobal.com/marketintelligence/en/news-insights/latest-news-headlines/nike-s-breakup-with-amazon-may-lead-other-brands-to-call-it-quits-analysts-56193375 . Accessed 4 May 2023.
21. “Nike says goodbye to more longtime wholesale partners.” RetailWire, https://retailwire.com/discussion/nike-says-goodbye-to-more-longtime-wholesale-partners/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
22. “Unbundling Nike: How Direct-To-Consumer Retail Is Being Disrupted.” Cbinsights.com, https://www.cbinsights.com/research/companies-unbundling-nike-dtc/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
23. “Nike’s purchase of analytics firm Zodiac highlights focus on customer lifetime value.” Zdnet.com, https://www.zdnet.com/article/nikes-purchase-of-analytics-firm-zodiac-highlights-focus-on-customer-lifetime-value/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
24. “Nike acquires A.I. platform Celect, hoping to better predict shopping behavior.” CNBC, https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/06/nike-acquires-ai-platform-celect-hoping-to-predict-shopping-behavior.html . Accessed 4 May 2023.
25. “Nike Acquires a Company in Israel That Specializes in 3-D Body Scanning.” Footwearnews.com, https://footwearnews.com/2018/focus/athletic-outdoor/nike-3d-scanning-acquisition-invertex-1202547874/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
26. “What Nike’s Datalogue deal says about the brand’s evolving approach to data-driven marketing.” Marketingdive.com, https://www.marketingdive.com/news/what-nikes-datalogue-deal-says-about-the-brands-evolving-approach-to-data/597104/ . Accessed 4 May 2023.
27. “Meet the LeBron James Innovation Center.” Nike, https://about.nike.com/en/newsroom/releases/inside-the-nike-sports-research-lab-lebron-james-innovation-center . Accessed 6 May 2023.
28. “Most Innovative Companies 2022.” BCG, https://www.bcg.com/publications/2022/innovation-in-climate-and-sustainability-will-lead-to-green-growth . Accessed 6 May 2023.
29. “Sweatshops Almost Killed Nike in the 1990s, Now There are Modern Slavery Laws.” Thefashionlaw.com, https://www.thefashionlaw.com/visibility-is-central-to-a-successful-supply-chain-heres-what-brands-need-to-know/ . Accessed 5 May 2023.
30. “Uyghurs for sale.” Australian Strategic Policy InstituteDownload 9.11 MB , https://www.aspi.org.au/report/uyghurs-sale . Accessed 5 May 2023.
31. “OECD Specific Instance: Twenty garment sector unions, Asia Floor Wage Alliance (AFWA) and Global Labor Justice – International Labor Rights Forum (GLJ-ILRF) vs. Nike.” globallaborjustice.org, https://globallaborjustice.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/OECD-Fact-Sheet-Nike.pdf . Accessed 5 May 2023.
32. “The China Challenge: The Stain of Forced Labor on Nike Shoes.” Discourse Magazine, https://www.discoursemagazine.com/economics/2022/01/05/the-china-challenge-the-stain-of-forced-labor-on-nike-shoes/ . Accessed 5 May 2023.
33. “Nike: Turning Cautiously Positive In The Long Term.” Seekingalpha, https://seekingalpha.com/article/4571788-nike-stock-turning-cautiously-positive-long-term-buy . Accessed 7 May 2023.
34. “Pence blasts Nike for pushing its ‘social-justice champion’ reputation while ‘checking its social conscience at the door’ by ignoring China’s actions in Hong Kong.” business insider, https://www.businessinsider.in/sports/news/pence-blasts-nike-for-pushing-its-social-justice-champion-reputation-while-checking-its-social-conscience-at-the-door-by-ignoring-chinas-actions-in-hong-kong/articleshow/71746443.cms . Accessed 6 May 2023.
35. “World Athletics.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Athletics . Accessed 6 May 2023.
36. “It’s time for the circular economy to go global – and you can help.” World Economic Forum, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/01/its-time-for-the-circular-economy-to-go-global-and-you-can-help/ . Accessed 6 May 2023.
37. “The butterfly diagram: visualising the circular economy.” ellenmacarthurfoundation.org, https://ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/circular-economy-diagram . Accessed 6 May 2023.
38. “Nike Flyleather.” Nike, https://www.nike.com/in/flyleather . Accessed 6 May 2023.
39. “Circularity.” Nike, https://www.nikecirculardesign.com/ . Accessed 6 May 2023.
40. “Global Athleisure Market Forecast Report 2021-2028 – Rising Trend of Sustainable Athleisure, Increased Demand from Millennials, Growing Penetration of e-Commerce – ResearchAndMarkets.com.” ResearchAndMarkets.com, https://apnews.com/article/covid-business-health-lifestyle-millennials-2ee76a101b8741e8866ab8fb50bf1bae . Accessed 6 May 2023.
41. “Athleisure.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Athleisure . Accessed 6 May 2023.
42. “Athleisure Wear Brands That Rank Among Gen Z – Nike Is No. 1.” civicscience.com, https://civicscience.com/ . Accessed 6 May 2023.
43. “INDIA’S ATHLEISURE AND SPORTSWEAR MARKET TO REACH $40.64 BILLION BY 2027: STUDY.” fashionatingworld.com, https://www.fashionatingworld.com/new1-2/india-s-athleisure-and-sportswear-market-to-reach-40-64-billion-by-2027-study . Accessed 6 May 2023.
44. “Global trend, local opportunity: the rise of the emerging middle classes.” PwC, https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/global-entertainment-media-outlook/assets/global-trend-local-opportunity.pdf . Accessed 7 May 2023.
45. “2023 sports industry outlook.” Deloitte, https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/technology-media-and-telecommunications/articles/sports-business-trends-disruption.html . Accessed 7 May 2023.
46. “Nike Launches .Swoosh Web3 Platform, With Polygon NFTs Due in 2023.” decrypt.co, https://decrypt.co/114494/nike-swoosh-web3-platform-polygon-nfts . Accessed 7 May 2023.
47. “Home Page.” RTFKT, https://rtfkt.com/ . Accessed 7 May 2023.
48. “Nike Unveils First .Swoosh NFT Digital Sneaker Drop.” decrypt.co, https://decrypt.co/137011/nike-unveils-first-swoosh-nft-collection-for-members . Accessed 7 May 2023.
49. “Nike’s wholesale equivalent revenues worldwide from the fiscal years of 2020 to 2022, by segment.” Statista, https://www.statista.com/statistics/888763/nikes-revenue-by-customer-segment-worldwide/ . Accessed 7 May 2023.
50. “Counterfeit consumer goods.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counterfeit_consumer_goods#Types . Accessed 5 May 2023.
51. “Global Trade in Fakes : A Worrying Threat.” Oecd-ilibrary.org, https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/74c81154-en/index.html?itemId=/content/publication/74c81154-en . Accessed 5 May 2023.
52. “The Industries Most Affected by Counterfeit Products.” Felix Richter, Statista, https://www.statista.com/chart/17410/counterfeit-and-pirated-products-by-category/ . Accessed 5 May 2023.
53. “Violation Tracker Current Parent Company Summary (Nike).” Violation Tracker, https://violationtracker.goodjobsfirst.org/parent/nike . Accessed 6 May 2023.
54. “Nike lawsuit records allege culture of sexism, bullying and fear of retaliation.” The Guardian, https://www.theguardian.com/business/2022/dec/20/nike-lawsuit-records-sexual-abuse-toxic-workplace-claim . Accessed 6 May 2023.
55. “2 Stocks That Could Be Worth More Than Nike by 2032.” The Motley Fool, https://www.fool.com/investing/2022/12/02/2-stocks-could-be-worth-more-than-nike-by-2032/ . Accessed 7 May 2023.
- SWOT Analysis of Walt Disney 2023
- SWOT Analysis of Blackberry 2023
- SWOT analysis of BMW 2023
- SWOT Analysis of eBay 2023
- SWOT Analysis of Dell 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Search 17293
- Search 64028
- Search 28448

Nike SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Nike
Company: Nike CEO: John Joseph Donahoe Founders: Phil Knight and Bill Bowerman Year founded: 1964 Headquarter: Beaverton, Oregon Employees (FY23): 83,700 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: NKE Revenue (FY23): US$51.21 Billion Profit | Net income (FY23): US$5.07 Billion
Products & Services: Apparel | Athleisure | Footwear | Sports Equipments | Accessories Competitors: Adidas | Under Armour | Allbirds | New Balance | Sketchers | Puma | Fila | ASICS | Lululemon | Fabletics | Victoria Secrets | Vans
Did you know? Nike swoosh logo is inspired by the Greek goddess of victory, Nike

Table of Contents
An Overview of Nike
Nike, Inc. is an American multinational corporation. Nike is headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon, USA . It was found by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight in the year 1964 . The company specializes in athletic wear, providing footwear, apparel, athletic equipment, and accessories.
Nike’s primary goal is to supply athletes with exceptional products and wearable that aids them in better sports performance . However, due to the success, Nike has gotten the company now provides athleisure wear as well. Currently, John Donahoe is the CEO of Nike.
SWOT Analysis of Nike
Here’s a detailed breakdown of Nike SWOT analysis.
Nike’s Strengths – Internal Strategic Factors
1. Strong Brand Awareness and Brand Value
Nike is one of the most recognizable brands in the world as its name alone is memorable, easy to pronounce, and very unique. Its swoosh symbol is easily recognized by everyone. According to Interbrand global brand ranking report, Nike is ranked at # 9 position with a brand value of $53.7 Billion .
2. Huge Customer base
Nike has millions of customer from around the world who loyally follow Nike’s trends, participate in Nike events, and even provide customer feedback. Due to its huge popularity, Nike’s market cap has grown to $142.2 billion as of March 2024.
3. America’s Favorite Sneaker Brand
Nike is the most popular and favorite sneaker brand in the U.S., according to a consumer insights survey by Statista.

4. Aimed For Sustainability
Nike’s CEO Mark Parker has addressed that they will continue to acknowledge the environmental issues in the communities. The CEO ensures that Nike will help to contribute in finding a solution against these environmental issues.
5. Iconic Relationships
Nike’s long-term partnership with Michael Jordan has proved to be beneficial in terms of sales for the company. Their collaboration resulted in “ Air Jordan 1 Shoes ”. Additionally, Nike teamed up with the famous basketball player to help design the “Air Jordan 1 Shoes”.
6. Side Brands
Nike’s ability to maintain and enhance its side brands such as converse and Hurley have enabled it to enjoy unparalleled success for decades.
7. Low Manufacturing Cost
Most of Nike’s footwear is manufactured in foreign countries. In the fiscal year 2023, Vietnam produced 50% , Indonesia produced 27% , and China produced 18% of total Nike’s footwear. Other operations are in Argentina, Brazil, India, Italy, and Mexico.
8. In-house Professionals
Nike has a professional team that designs its shoes and other athletic accessories. Nike believes their business has flourished due to their thorough research, design, and development efforts.
9. Superior Marketing Capabilities
Nike has excellent marketing campaigns. The brand heavily relies on demand creation expense , which includes advertisement, promotion, endorsement contracts, media print and complimentary products. In the fiscal year 2021, 2022 and 2023, Nike spent $3.1 billion, $3.8 billion, and 4.06 billion respectively. The brand has successfully utilized social media and marketing campaigns to target more customers .
10. Black Community Support
The brand has excellent marketing campaigns and released “ Don’t Do It ” ad campaign in support of Black communities against racism.
11. High Market Share
Nike is a market leader in footwear industry . Nike has captured approximately 39% of the global athletic footwear market and 13% of global athletic apparel market.

Nike’s Weaknesses – Internal Strategic Factors
1. Poor Labor Conditions in Foreign Countries
In the last 20 years, Nike has been consistently targeted regarding their poor labor conditions. These issues include forced labor, child labor, low wages, and horrific working conditions that were deemed “ unsafe ”.
2. Retailers Have a Stronger Hold
Nike’s retail sector makes Nike weak due to its sensitivity against pricing. 56% of Nike products are sold directly to wholesalers or retailers . With retailers serving as their core customers, Nike does not put up a fight against their pricing structures whatsoever.

3. Pending Debts
Although Nike’s income statements prove to be prosperous, a quick glance at their balance sheet could paint a different picture. Nike is still facing financial threats. As of FY23, Nike’s total long term debt was $8.9 billion
4. Lawsuits
- Recently, a former employee accused Nike of discrimination based on his Croatian origin.
- Four former female Nike employees filed a class-action lawsuit against the company in August 2018. According to these women, Nike has a toxic company culture for women. The women filed their case against the sportswear company claiming that the company violated the Equal Pay Act . The women said the company engaged in systematic gender pay bias where men were paid more than women for the same amount of work.
5. Lack of Diversification
Nike’s over-dependence on sporting footwear and apparel or lack of diversification is a major weakness. During the pandemic, major sporting events were canceled or postponed. If there is a similar crisis in the future, Nike’s losses can be catastrophic.

6. Contradicting Strategies
Nike pledged to shift all its facilities to 100% renewable energy with net-zero carbon emissions under the “ Move to Zero ” scheme. While the strategy is great and welcomed, it contradicts Nike’s strategy that favors innovation over sustainability. This creates the perception that Nike is not committed to addressing climate change and its pledge is just a marketing stunt.
7. Dependency on North America especially US Market
Even after having established itself globally, Nike still relies on the U.S Market in terms of sales and revenue. In the fiscal year 2023, about 44 % of Nike’s sales came from the North America , while the rest of 56% came globally. Despite its fame, Nike depends on the U.S for substantial sales and growth.

8. Sexual Harassment
Former female employees also pointed out that sexual harassment and misconduct was very common in the company. The New York Times conducted interviews with 50 former and present Nike employees to investigate the company culture. Through the interviews, it was established that Nike did have a toxic working environment, where sexual misconduct was rampant.
Multiple female employees reported that they had complained to the HR but saw no action being taken from their part. The women were left devastated and felt unsafe while working at Nike. Some even left their jobs. The entire controversy has significantly affected the company’s image.
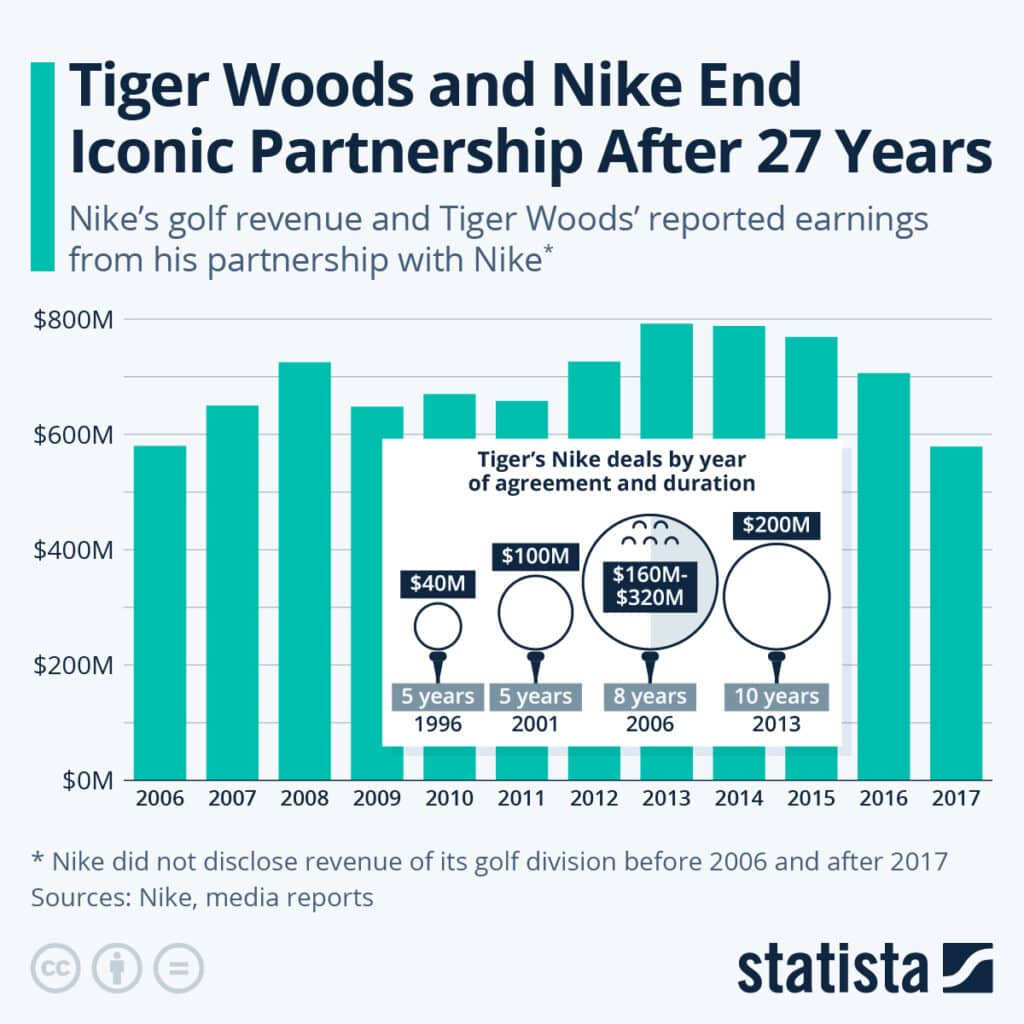
9. End of Iconic Tiger Woods & Nike Partnership
Tiger Woods’ 27-year Nike partnership has come to an end. In a world where brands compete to bring the most sought-after celebrity for their brand endorsements, Nike has lost a golf legend .
Woods was the face of Nike Golf brand, and Nike Golf’s revenue ranged from approximately $600 – 800M from fiscal 2006-2017. Experts believe Nike has more to lose in the long term after cutting ties with Woods.
Nike’s Opportunities – External Strategic Factors
1. Emerging Markets
Although Nike already has a presence in many foreign countries, there is still plenty of opportunities for Nike. This is because emerging markets like India, China, and Brazil are gradually flourishing.
2. Innovative Products
Although Nike has produced many products, there is still a lot to innovate. Nike has extended its reach in technology in association with fitness and health. Products like wearable technology that monitors physical activities, is the first step in building innovative technology products . Combining technology with athletic wear can prove to be beneficial as it is an aspect of the fashion industry that still hasn’t been explored much.
3. Efficient Integration
The supply and production of Nike’s products depend on independent manufacturers. The brand can either acquire a few of these or make some of its own for a more efficient and streamlined supply chain.
4. Cutting ties with big retailers
Nike has decided to cut ties with some of the biggest multi-brand retailers and wholesale partners. According to the report , Nike will no longer work with wholesale retailers such as Zapoo’s , Dillard’s , Fred Meyer , Bob’s Stores , etc. The step is taken for better product positioning and greater customer experience.
5. Acquired Artificial Intelligence Start-up
With its vast financial resources, Nike can acquire small or medium companies or startups. It recently acquired predictive analytics platform – Celect to expand its online sales capabilities and predict customer’s shopping behavior.
6. Merges with the Metaverse
Recently, Nike acquired RTFKT, a digital shoe-making company . Yes, you heard that right, the company designs shoes, but for the virtual stratosphere only. However, RTFKT also claimed that it partnered with FEWOCiOUS (a young artist) to sell real shoes along with their digital versions. Nike is banking on the opportunity to market their digital shoes on the Metaverse , where players can use their Metamask wallets to purchase different types of in-game merchandize.
7. Exiting From Wholesale Distribution
Recently, Nike announced it’s going to be exiting the wholesale distribution market in the U.S. The company plans to only market its products at Nike stores , app , and websites . According to Nike, the move away from distributors is going to help them double their profit margins . Moreover, Nike will also have the opportunity to spearhead the customer shopping experience as well as control prices .
8. Nike to End Use Of Kangaroo Leather For Its Shoes
Nike has announced a significant move that will please both animal rights activists and consumers. The athletic apparel giant will no longer use kangaroo skins in their shoes, ending a controversial practice. The decision comes after Puma made a similar move weeks ago.
Instead of kangaroo leather, Nike will use synthetic material in its new line of Tiempo football boots, the Tiempo Legend Elite, set to launch this summer. The company also ended its partnership with its sole kangaroo leather supplier in 2021, reflecting its commitment to more sustainable and ethical practices.
9. Consumer Direct Strategy
Nike has accelerated the consumer-direct strategy, which means shifting its focus to digital business and subsequently closing physical stores. In fiscal year 2023, 44 % of its Nike revenue comes from online sales. Clearly, the pandemic is shaping up how Nike interacts with its customers.

Nike’s Threats – External Strategic Factors
1. Counterfeit Products
Counterfeit products can significantly affect the revenue and reputation of Nike. The company deals globally and the risk of counterfeit products has become higher. A number of merchandisers and retailers offer counterfeit Nike products at lower prices.
The low-priced products are made from low-quality materials but still have the Nike label. This can tarnish the image of the brand as the customers might feel that Nike has started producing low quality products.
2. Increased Competition
Although, Nike is a dominating the athletic industry, competition, and new emerging brands (On, Hoka etc.) are still potential threats to the company. Due to high competition, Nike has to spend more money on marketing and advertising to differentiate itself.
Nike spent $4.06 Billion specifically on marketing and demand generation in fiscal year 2023. To overpower competition, Nike’s safest bet is to design innovative products that are tailored according to the needs of athletes.
3. Marketing Budget Pressure
Companies like Under Armour , Adidas and Lululemon are spending more on marketing and advertising campaigns, increasing the pressure on Nike.
4. Currency Foreign Exchange Risks
Since the brand operates globally, it is affected by fluctuating foreign exchange rates. Nike reports its financial earnings in U.S dollars. This affects its revenue as the U.S dollar is exposed to volatility against other financial currencies.
5. Patent Disputes
Regardless of whether a company is wrong or right, patent disputes are hotly and fiercely contested in the public domain and expose some dirty secrets about sides in the dispute. Nike and Adidas have been engaged in a fierce patent disputes over Primeknit and Flyknit shoes in U.S. and German courts.
6. Economic Uncertainty
Regardless of the industry, all companies are susceptible to the negative effects of a global recession . During lockdown, Nike had reported a decline in sales and sales can drop further in the future if the recession strikes as hard as predicted by experts.
7. Trade Tensions
Nike depends on different markets across the world evidenced by the recent increase in its stocks rallied by an increase in sales in China . With China and the US as its biggest markets, a large chunk of Nike’s sales will be threatened if the trade tensions between the two giants escalate.
8. Patent Conflict towards Adidas Primeknit Shoes
In an appeal to a U.S. agency, Nike filed a complaint that Adidas has been infringing on the company’s Flyknit shoe technology patent. The company also stated that the German shoe manufacturer had used Nike’s Flyknit tech in 49 shoe designs (which uses Primeknit tech).
However, according to an Adidas representative , the company will fight these claims and stated that Adidas has started using their Primeknit technology after numerous years of research and development.
9. Risk to Kangaroo Population
Nike has been accused of putting the Australian kangaroo population at risk of extinction. The leading athletic brand uses kangaroo skin to manufacture leather football shoes . Animal rights activists and advocates have urged Nike to rethink its strategies and to use plant-based alternatives . So far, Nike hasn’t responded to these allegations.
10. Nike Faces A Wave Of Retail And Warehouse Thefts
Nike experiences a surge in theft crimes throughout its supply chain, including warehouse and train thefts. According to the National Retail Foundation, retail theft has become a massive problem in the United States, with an estimated cost of $95 billion.
The company has reported that thieves are stealing from shelves and vehicles. This forced Nike to close a popular outlet store in its hometown of Portland. In addition, two suspects were arrested in Memphis for stealing Nike merchandise worth about $60,000 from five rail cars. Despite having 369 stores across the United States, including outlets and Converse stores, Nike finds it hard to prevent theft along its entire supply chain.
11. Nike Sues Lululemon Over Patent Infringement
Nike has filed a complaint in Manhattan federal court against Canadian athletic apparel company, Lululemon, alleging patent infringement of at least four footwear products.
Nike claims that Lululemon’s Blissfeel, Chargefeel Mid, Chargefeel Low, and Strongfeel footwear have caused economic harm and irreparable injury to the company.
Although this isn’t the first time Nike sued Lululemon for patent infringement, the recent complaint alleges that three patents have been infringed, including one addressing the performance of footwear when force is applied. While the company seeks unspecified damages, Lululemon has yet to comment on the matter.
12. Decline in Demand for Classic Shoe Brands
Nike faces tough competition with running shoe competitors like On , Hoka , and New Balance. The analyst believes that the company’s heavy reliance on classic shoes like Air Jordan and Pegasus led to complacency , and it needs to catch up on innovation . There is declining interest in wearing Air Jordan sneakers, and they are not as cool anymore .
Nike plans to scale back classics and introduce new products to attract customers from rival brands.

Final Thoughts
The fiscal year 2023 proved to be successful for Nike. Although the brand is still in debt, the next few years look promising. Nike has grown exponentially in the last decade.
From releasing new product lines to building new brands, to outsourcing, and establishing a global presence alone is an extraordinary achievement.
Through this SWOT analysis of Nike, you will be able to understand the business model of the brand .
References & more information
Xu, V. Your favorite Nikes might be made from forced labor. Here’s why . The Washington Post.
- Cara Salpini. Nike is on track to make $50 billion this year. How much is that, really? Retail Dive
- Interbrand – Best Global Brands
A management consultant and entrepreneur. S.K. Gupta understands how to create and implement business strategies. He is passionate about analyzing and writing about businesses.
28 comments
Cancel reply.
This article was very interesting. Thank you. The article was enlightening.
Dorrene, Thanks for your positive feedback, I am glad you liked it.
It’s to easy to understand and explain to others.. Thanks it will help me my upcoming presentation. 😃
Thank you Gargi, I have been through business school not so long ago, so I can totally relate to you. I am guessing the presentation is for school?
No. I m persuing MBA integrated..
Great, All the best for your MBA!
Lot of clarity in the format – the SWOT is explained.
Using for my management program – Leadership & People Management. It’s a great help. Thanks.
Hi Choo Patrick,
I am glad you liked our analysis. Thank you !
i want to know the publisher of this analysis
Hi Ap, here are the details
Date of Publish : Dec 17, 2018 Author : SG
Quick and to the point. Good read. Thank You
Oasis, I am glad you liked it !
who wrote this article ? can i know the name? very grateful analysis.
Thanks Taku, I am glad you liked our analysis. – SG
why is there no reference?
Hi Divya, Most of the information is from Nike’s annual report and few points have embedded hyperlinks for references.
top analysis
THIS HELPED ME A LOT!
Hey, who is the author of this report and what year was it finalized. I need this info for citations.
Hey Justin,
Author: S.K Gupta First published: December 17, 2018 Last updated: Oct 06, 2020
Hey! loved it, read it in my class!
Hi Aden, Glad you loved it, happy reading !
Hey this was super helpful for a school project. Thank you.
Thanks Nicholas for the feedback, glad to see it was helpful. Happy Reading 🙂
I really love your work thank you this was so helpful to help me help another person but not me thank you for this thank you.
Dear Mr. Gupta , Thanks for publishing this excel report about Nike, do you have the latest BCG matrix about Nike’s product. If yes, can you share to me me on my below email
Hi Ahmed, Glad you liked Nike swot analysis, Unfortunately, we don’t have the latest BCG matrix on Nike.
You may also like

Disney SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Disney
Company: Walt Disney CEO: Robert Chapek Year founded: 1923 Headquarter: Burbank, California, USA Number of Employees (2022): 220,000 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: DIS Market Cap (Feb...

Amazon SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Amazon
...

Ford SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Ford
Company: Ford Motor Company CEO : James Duncan Farley Jr. Year founded : 1903 Headquarter : Dearborn, Michigan, USA Number of Employees (FY 2022): 173,000 Public or Private: Public Ticker...
Microsoft SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Microsoft
Company: Microsoft CEO: Satya Nadella Year founded: 1975 Headquarter: Redmond, Washington, USA Number of Employees (2022): 221,000 Public or Private: Public Ticker Symbol: MSFT Market...

CVS SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: CVS CEO: Karen S. Lynch Founder: Stanley Goldstein, Sidney Goldstein, and Ralph Hoagland Year founded: 1963 Headquarter: Woonsocket, Rhode Island, United States Employees (2021): 295,000 Type: Public Ticker...

Starbucks SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Starbucks
Company: Starbucks CEO: Laxman Narasimhan Year founded : 1971 Headquarter : Seattle, USA Number of Employees (FY2023): 381,000 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: SBUX Market Cap (Apr 2024): $98.33 Billion Annual Revenue...

Burger King SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Burger King
Company: Burger King Corporation CEO: Jose Cil Founder: Jim McLamore and David Edgerton. Year founded: 1953 Headquarters: Miami, Florida, U.S.A. Employees: 35,000+ Annual Revenue (FY2019): US$1.78...

H&M SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of H&M
Written by Brianna Parker | Last updated: Jan 14, 2024 Company: Hennes & Mauritz AB (H&M) CEO: Helena Helmersson Founder: Erling Persson Year founded: October 4, 1947 Headquarters: Stockholm, Sweden Employees...

Tata Motors SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: Tata Motors Limited Founder: Jamsetji Ratanji Dadabhoy Tata Year founded: 1945 Executive Director: Girish Wagh Headquarter: Mumbai Employees: 73,608 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: TTM Annual Revenue (FY22): 2.7...
General Motors SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of General Motors
Company: General Motors Company CEO: Mary T. Barra Founder: William C. Durant Year founded: September 16, 1908 Headquarters: Detroit, Michigan, United States Employees (Dec 2019): 164,000 Ticker Symbol:...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns Westin Hotels & Resorts?
- Who Owns Truist Bank?
- Who Owns Alfa Romeo?
- Who Owns Burt’s Bees?
- Top 15 Ruggable Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Ticketmaster Competitors and Alternatives
- Who owns Kidz Bop?
- Top 20 Zapier Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Boxabl Competitors and Alternatives
- Who Owns High Noon?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
- Strategic Management
- SWOT Analysis of Nike
Opportunities
related articles.
- SWOT Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of Google
- SWOT Analysis of Starbucks
- SWOT Analysis of Amazon
- SWOT Analysis of IKEA
- SWOT Analysis of Microsoft
- Competitor Analysis
- What is Competitive Advantage ?
- Porter’s Five Forces Model
View All Articles
Authorship/Referencing - About the Author(s)
The article is Written and Reviewed by Management Study Guide Content Team . MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider . To Know more, click on About Us . The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link(s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.
- Strategic Management - Introduction
- Strategy - Definition and Features
- Components of a Strategy Statement
- Vision & Mission Statements
- Strategic Management Process
- Environmental Scanning
- Strategy Formulation
- Strategy Implementation
- Strategy Formulation vs Implementation
- Strategy Evaluation
- Strategic Decisions
- Benefits of Strategic Management
- Business Policy
- SWOT Analysis of Blackberry
- Personal SWOT Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of China Mobile
- Human, Social, and Intellectual Capital as a Means of Competitive Advantage
- Blue Ocean Strategy and its Implications for Businesses
- Overfished Ocean Strategy: How to Drive Growth and Attain Profitability
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of the Airlines Industry in the United States
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of Samsung
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of Virgin Atlantic
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of China Mobile
- Strategic Leadership
- Some Pitfalls to be Avoided
- Corporate Governance
- Business Ethics
- Social Responsibilities of Managers
- Core Competencies
- Core Competency Theory of Strategy
- Ansoff Matrix
- Routes to Strategic Growth
- Diversification as a Viable Corporate Strategy
- 5 Configurations of Strategic Management
- Role of Planning, Plans and Planners
- Reasons for Avoiding Strategic Planning
- Strategic Management for the Millennials
- Strategizing for the Future
- PESTLE Analysis of the Global Aviation Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of Starbucks
- PESTLE Analysis of Samsung
- SWOT Analysis of Unilever
- Business Strategies to Beat the Downturn
- Analysis of Amazon’s Corporate Strategy
- How Amazon Can Improve its Corporate Strategy
- Cutting Costs Strategically
- Actualizing Business as Usual Strategies for Mission Critical Organizations and Functions
- Why Indian Firms Must Strive for Strategic Autonomy in Their Geoeconomic Strategies
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
PESTLE Analysis
Insights and resources on business analysis tools
SWOT Analysis of Nike (2024 Updated)
Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 by Jim Makos Filed Under: SWOT Analysis , Companies , SWOT Examples
In this article, we’ll conduct a SWOT analysis of Nike, where we look at the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats influencing Nike’s business. In combination with our PESTLE analysis of Nike , today’s analysis will give us a balanced insight into Nike’s future possibilities and help us better understand its current and future business decisions.
Nike is truly a leader in the footwear and sports apparel markets. In the fiscal year 2024, Nike reported a notable financial performance. Revenues reached $13.4 billion on a quarterly basis, marking a modest but welcome 1% increase on a YoY basis. Meanwhile, earnings per share beat expectations significantly ($0.98 vs $0.69 expected). Nike’s popular catchphrase “Just Do It” and powerful celebrity endorsements continue to make the sportswear giant a household name across much of the world.
What is a SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis reveals the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of an organization. It’s a strategic planning tool used in business and project management.
With that in mind, today’s SWOT analysis of Nike will:
- start with the strengths that underscore Nike’s dominance in the global sportswear market
- move to the weaknesses that present hurdles to its growth and efficiency
- discuss the opportunities that the evolving sports and fitness world offers, and
- reveal the threats in an industry known for its fierce competitiveness and rapid innovation
By examining these influences, we will also investigate what’s achievable in the spheres of sports, lifestyle branding, and athletic technology. In the meantime, I’ve written everything you need to know about SWOT here .
Nike SWOT Analysis
Nike strengths (internal factors).
Did you know that Phil Knight, the co-founder of Nike, was talked out of naming the company “Dimension 6” in favor of Nike?
Now that you know let’s start the SWOT analysis of Nike with the brand’s strengths, the first section of every SWOT . Needless to say, the most important strengths are Nike’s powerful brand and low product cost.
- Strong Core Brand : The Nike brand itself is one of the strongest — if not the strongest — names in the entire sportswear industry . Across much of the world, Nike is one of the first companies to come to the public’s mind when they think of hip, sporty footwear. Overall, this extremely powerful core brand is one of Nike’s biggest strengths, and you can bet that helps them rake in billions in additional revenue every year. Its iconic “Swoosh” logo and “Just Do It” slogan are known globally, contributing to its strong brand presence.
- Global Reach: Nike’s products are available worldwide through retail stores and online platforms. This vast distribution network is surely a strength as it ensures that a global customer will have access to its products.
- Diverse Brand Portfolio : Although the Nike brand itself is incredibly strong, the company has a diverse brand portfolio beyond that. Most notably, this brand portfolio includes Converse as well as dozens of other Nike-centric sub-brands such as Nike Shox, Nike Blazers, and Nike Tiempo. This suggests that Nike has its foundations well spread across the footwear industry, allowing it to painlessly weather changes in preference.
- Low Product Cost: Since many of Nike’s products are manufactured in developing Southeast Asian countries such as Indonesia and Thailand , Nike has extremely low labor costs. What’s more, Nike also uses relatively inexpensive materials for many of its shoes. Together, these two factors — labor cost and material cost — allow Nike to manufacture its footwear for extremely low prices.
- Innovative Products: Nike is renowned for its innovation in product design and technology. From the Dri-FIT technology to the Air Max DN shoe announced in March 2024 , Nike has introduced groundbreaking products. This has allowed Nike to set trends in the sportswear industry.
- Endorsements and Sponsorships: Nike has a long history of sponsoring high-profile athletes and sports teams. From Michael Jordan to Serena Williams and agreements with teams like FC Barcelona, these partnerships have solidified Nike’s position as a key player in the sports world. In 2024, Nike took the place of Adidas as the sponsor of the German football team, ending a 77-year-old partnership !
Nike Weaknesses (Internal Factors)
Did you know that the Swoosh outlines the “swooshing” sound you might hear as an athlete speeds past, adding an auditory dimension to the brand’s identity?
Now that you know, we move to the second type of internal factors affecting the company in our SWOT Analysis of Nike.
As you’d expect, Nike does indeed have some weaknesses. It’s dependent on the US market, its manufacturers, and the footwear industry.
- Dependence on the US Market: In 2018 , over 40% of Nike’s revenue came from the US market. This increased to 43% in 2023 . As you can imagine, this demonstrates a huge dependence on the US market as part of Nike’s business model. If American tax or legal policies were to change, in any way affecting Nike’s ability to sell on the US market , that would significantly hurt the sportswear giant’s profits.
- Controversies and Negative Publicity: Over the years, Nike has faced several controversies related to labor practices and working conditions. Allegations of poor working environments and exploitation in factories have led to negative publicity. Although Nike has taken steps to address these issues, such controversies can tarnish the brand’s image and consumer perception. In 2023, Nike critics launched a ‘ burn bra challenge ‘ and railed against its treatment of female athletes.
- Outsourced Manufacturing: Despite the low cost associated with manufacturing products abroad, there are indeed downsides to doing so. For one, manufacturing abroad requires you either to set up dedicated manufacturing operating in your chosen country or to outsource your work to existing manufacturers. Nike has chosen to do the latter, which means that their products aren’t always top quality.
- Footwear Focus: Although Nike is relatively diversified within the footwear industry itself, Nike has not diversified itself much across other industries. Although the footwear industry is probably here to stay, Nike may consider broadening their horizons.
- Intense Competition: The sportswear and athletic footwear markets are highly competitive. Nike competes with major global brands like Adidas, Under Armour, and Puma, among others. This competition pressures Nike to continually innovate and invest in marketing to maintain its market position, which can strain resources and affect profitability.
Nike Opportunities (External Factors)
Did you know that the very first NikeTown, which opened in Oregon in 1990, was not just a retail store but a sort of museum and interactive experience, pioneering a retail concept that many brands have since tried to emulate?
Now that you know, we move to the third section of today’s SWOT Analysis of Nike.
Nike has a growing market in all senses, thanks to healthier consumers and wealthier countries. This presents a few new opportunities.
- Growing Market: There are only more and more people in this world, and many of them (especially in developed countries) are becoming gradually more active. Together, these two factors compound to create a constantly growing footwear market. If played correctly, Nike should be able to capture much of the business of this growing market, allowing the company to further grow its profits.
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with fashion designers, celebrities, and other brands can open up new markets and demographics for Nike. Limited edition releases and exclusive collaborations can generate buzz and attract customers looking for unique products.
- Emerging Markets: As countries across the world become wealthier and wealthier, citizens in developing countries have more disposable income. In areas such as South East Asia, growing disposable incomes present an opportunity for new markets in which to sell products. If Nike is able to market themselves in these emerging markets, they could grow their reach and reduce dependence on the US market.
- Sustainability and Eco-friendly Products: In many Western countries, there is a growing trend of knowing where products have come from and how the environment and workers have been treated. This presents another opportunity for Nike. If they are able to brand themselves as a responsible manufacturer of sportswear goods, they may be able to increase their market penetration among more ethically and environmentally conscious consumers.
- Women’s Athletic Wear and Casual Sportswear: The women’s athletic wear market and the casual sportswear (or “athleisure”) segment are growing rapidly. Nike can further develop and market products specifically designed for women, tapping into this expanding market segment to drive sales.
- Focus on Health and Wellness Trends: The global emphasis on health and wellness, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, presents an opportunity for Nike. It can position itself as a partner in consumers’ fitness and wellness journeys. Offering products and services that support a healthy lifestyle, such as fitness apps or community events, can enhance brand loyalty and customer engagement.
Nike Threats (External Factors)
Did you know that in 1985, Nike created a special pair of Air Jordan 1s for Michael Jordan to wear during the Grammy Awards that made it easier for Jordan to play the guitar during his performance?
Now that you know, it’s time to talk about the final part of the SWOT Analysis of Nike. For threats, Nike has to look in all directions: tax, market competition, and product counterfeiting.
- Global Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns, fluctuations in currency exchange rates, and trade disputes can significantly affect Nike’s sales and profitability. As a global company, Nike is exposed to the risk of economic instability in key markets, which can lead to decreased consumer spending and disruptions in the supply chain.
- Tax Clampdowns: Like many other big companies, Nike has its tax strategies optimized down to the dollar. This has for many years allowed Nike to avoid paying large amounts of tax, even on its billion dollar profits. However, there is growing controversy about the amount of leeway large organizations are afforded when it comes to tax matters, and their freedom to pay low amounts of tax may one day come to a close. This would afford Nike significantly smaller net profits.
- Competition: Nike is competing in the fiercely competitive sports apparel market, with other big names such as Adidas, PUMA, and Reebok ready to pounce on any new opportunities. As such, Nike needs to tread extremely carefully to ensure it isn’t replaced by one of these, or — somewhat less dramatically — doesn’t lose out on potential revenue.
- Counterfeiting: Like many valuable branded goods, Nike apparel is subject to large amounts of counterfeiting. Counterfeit Nike goods are available everywhere — even on the internet. Nike needs to develop a strategy to ensure that the counterfeiting of their goods doesn’t affect their core business model, perhaps by taking legal action against counterfeiters or with a clever marketing campaign that encourages consumers to buy the real thing.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Consumer tastes and preferences in the sportswear and footwear industries are constantly evolving. A failure to anticipate or quickly respond to these changes can result in lost sales and inventory surplus.
Recommendations: Taking action based on the SWOT Analysis of Nike
Nike is a giant organization competing in a tough market, but it’s doing incredibly well. With its extremely powerful brand and low costs, Nike has been able to net several billions of dollars on an annual basis. Unfortunately, Nike is very much dependent on the US market and is little diversified beyond the footwear and sports apparel markets. Nike needs to watch out for threats associated with these weaknesses, and others such as tax clampdowns or counterfeiting. Thankfully, Nike has several opportunities for growing its business, including making the most of the rapidly expanding sportswear market.
Based on the SWOT analysis of Nike, here are actionable recommendations for Nike to bolster its strengths, address its weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats:
- Enhance E-commerce and Digital Engagement: Invest further in digital platforms and e-commerce to strengthen direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales channels. They should be enhancing the online shopping experience, leveraging AI for personalized marketing, and utilizing social media for engaging storytelling to attract more customers online.
- Expand Sustainable Product Lines: Continue to expand the range of sustainable and environmentally friendly products.
- Accelerate Expansion in Emerging Markets: Focus on expanding presence in emerging markets with high growth potential.
- Innovate Through Technology: Continue to lead in innovation by investing in research and development (R&D) for new materials, product designs, and technological advancements in wearable technology.
- Address and Communicate on Ethical Practices: Proactively address labor practices and working conditions in the supply chain. Implementing transparent reporting and third-party audits can build trust and improve public perception. Engaging in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives can further demonstrate Nike’s commitment to ethical practices.
- Foster Inclusive and Diverse Branding: Ensure branding and product lines are inclusive, catering to a diverse range of consumers in terms of gender, body type, and cultural background. Inclusive marketing and product diversity can broaden Nike’s appeal and strengthen its global brand image.
Time to wrap up our SWOT analysis of Nike, by checking out previous SWOT analyses we’ve conducted for Nike’s competitors:
- SWOT Analysis of Adidas
- SWOT Analysis of PUMA
- SWOT Analysis of Under Armour
- SWOT Analysis of Lululemon

Nike Swot Analysis As Of 2024 [Detailed View]
Nike started as a distributor for the Japanese shoe company Onitsuka Tiger. Today, it is the world’s largest supplier of athletic shoes and apparel and a significant producer of sports goods.
In this SWOT analysis of Nike, we delve into the company’s core attributes, analyzing how its strengths have made it a market leader, addressing its weaknesses, exploring potential opportunities for growth, and acknowledging the challenges it faces to maintain its reputation in the highly competitive sportswear industry.
Let’s uncover the strategic insights that have shaped Nike’s journey to success, what factors affect its business model, and see how it thrives in the ever-changing world of sports shoes and clothing.
Table of Contents
Company Profile
- Started in 1964
- Founders : Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight
- CEO : John Donahoe
- Headquarters : Beaverton, Oregon, United States
- Number of employees : 83,700+
- Annual Revenue : $51.22 billion+
- Gross Profit : $22.29 billion+
- Market Capitalization : $170 billion+
How Did It All Start?
Nike’s origin can be traced back to the early 1960s when Phil Knight (a student at Stanford University and a middle-distance runner) had an idea of importing low-cost, high-quality shoes from Japan to the United States.
He reached Bill Bowerman (a track-and-field coach at the University of Oregon) with his proposal, and they both agreed to start a distribution business.
They travel to Japan to meet with Onitsuka Tiger, a Japanese shoe company (now called ASICS). They negotiated a deal to become an exclusive distributor of Onitsuka Tiger shoes in the United States.
In January 1964, the two men formed a company named “Blue Ribbon Sports” and started selling Onitsuka Tiger shoes at track meets and events. In 1966, they opened their first store in Portland, Oregon.
However, the turning point for the company came in 1971 when Blue Ribbon Sports decided to open its own line of footwear items. To align with this change, Knight and Bowerman rebranded the company and registered it as “Nike Inc.”
Since then, the company has witnessed impressive growth. Over the decades, Nike has introduced creative design and launched innovative footwear products that appeal to athletes and sports enthusiasts.
Today, Nike is one of the world’s most recognizable brands. It employs more than 83,700 people, which includes a strong research and development team that is always looking for ways to improve its products.
In terms of market capitalization, Nike is among the 50 largest companies in the world.
Mission Statement and Vision Statement
Nike focuses on bringing inspiration and innovation to each athlete in the world. They believe that everyone has the potential to be an athlete, regardless of their physical abilities or skill levels.
Nike’s vision is to maximize human potential through all possible means. Their vision statement reflects their commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology and inspiring people to reach their potential in fitness, sports, and beyond.
Quick Summary of Nike’s SWOT Analysis
1. Strong Brand Identity
Known for its strong association with sportswear products and athletic performance, Nike consistently ranks high in several brand value rankings. It has an estimated brand value of $31.3 billion .
Nike’s “smoosh” logo is instantly recognizable — its simple and memorable design has become synonymous with the brand’s identity.
2. Extensive Product Portfolio
Nike’s vast product portfolio caters to a wide range of athletic and lifestyle needs. It includes footwear, equipment, apparel, and accessories designed for various sports and activities.
The Nike Pro line, for example, focuses on performance-grade training apparel. These Pro products are designed for athletes engaging in intense training and competition.
Jordan Brand, Converse, and Hurley International are some of the key parts of Nike’s product portfolio.
Nike also collaborates with popular athletes, designers, and other brands to develop special collections and limited-edition releases. Such collaborations often create significant buzz and generate demand among consumers
3. Vast Distribution Network
Nike reaches consumers in over 190 countries. Its large distribution network consists of three main channels:
- Wholesale : Nike sells its products to wholesalers, who then sell them to retailers. The wholesale distribution channel accounts for about 80% of sales.
- Direct to consumers : Nike has its own retail stores and online platform to sell products directly to consumers. It accounts for nearly 20% of sales.
- Global brand divisions : Nike’s global brand divisions sell products to retailers in specific regions, ensuring that their products are available in all substantial markets.
Nike’s strategic approach to distribution has been a key part of the company’s success. It has allowed the company to get its products to consumers quickly and efficiently.
4. Focus on Innovation
The company actively invests in research and development and introduces new technologies and materials to enhance performance and comfort for athletes.
For instance, Nike’s Flyknit technology uses strong yet lightweight strands of yarn and different types of knit patterns to create a breathable and comfortable shoe.
Nike has over 26,000 patents globally, out of which about 20,500 are active. The majority of these have been filed and granted in the United States, followed by China and Europe.
5. Strong Online Presence
In addition to 1,050+ retail stores worldwide, Nike has a robust eCommerce platform. The company sells its products directly to consumers through its website and mobile application.
Their online store , which attracts more than 141 million visitors per month, offers a convenient way to browse and buy products from the comfort of your home.
The company also leverages social media platforms to market its products and engage with consumers directly. It has over 302 million and 5.2 million followers on Instagram and Twitter.
6. Good Profit Margins
Nike’s profit margin has remained consistently high over the past few years. In 2023, its gross profit margin was 43.52%, its operating profit margin was 11.5%, and its net profit margin was 9.9%
These impressive profit margins have allowed the company to invest heavily in marketing and R&D, and maintain its position as one of the leading brands in the athletic footwear industry.
7. Direct-to-Consumer Strategy
The company has been investing in a direct-to-consumer strategy for many years. They have opened new retail stores, launched new mobile apps (for both iOS and Android), and expanded their online store. They have also been focusing on data analytics and personalization technology.
This strategy has several advantages. For example, it
- Allows Nike to develop a closer relationship with customers,
- Collect data about customer preferences and offer a personalized shopping experience using this data, and
- Capture more profit from sales.
8. Celebrity Endorsements
Nike has collaborated with numerous athletes and professional players from various fields to create impactful marketing campaigns. Some of their most famous endorsers include:
- Michael Jordan : He has been with Nike since 1984. The collaboration led to the creation of the well-known Air Jordan line of basketball shoes, which revolutionized the sneaker industry.
- Cristiano Ronaldo : He has been a prominent face of Nike’s football-related campaigns since 2003.
- LeBron James : He has been with Nike since 2003. The LeBron James signature shoe line and related apparel have been extremely popular among basketball fans.
- Serena Williams : She has been the face of the NikeCourt line of tennis apparel and shoes since 2003.
9. Sponsorship and Partnerships
Nike sponsors numerous sports leagues, events, and teams across the world. This helps in increasing brand visibility and fostering strong connections with the athletic community.
For example, Nike is the official provider of NFL jerseys and on-field gear. This partnership with the NFL gives the company significant exposure during football games.
Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign is one of the world’s most popular campaigns. First introduced in 1988, it has become synonymous with the Nike brand and its core values of motivation, determination, and athletic achievement.
In 2022, Nike spent $3.85 billion on advertising and promotion . That same year, the company generated $46.71 billion in global revenue.
10. High Market Share
Nike has held a significant market share in the athletic footwear (38.23%) and apparel industry (16.2%), and it is increasing gradually year over year.
This shows Nike’s ongoing influence in the industry, despite increasing sales for competitors.
11. Sustainable Initiatives
The company has been actively working on sustainable efforts, focusing on reducing its water and energy use and utilizing environmentally friendly materials such as recycled polyester and organic cotton.
By 2025, Nike aims to
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 0.5 million tons
- Divert 100% of waste from landfills within its extended supply chain
- Reduce freshwater usage by 25% (per kilogram of textiles produced)
12. Experienced Management Team
Nike’s leaders deeply understand the athletic footwear industry and have a proven track record of success.
For example, John Hoke III (currently the Chief Design Officer) joined Nike in 1992. He now leads the entire design team that includes over 1,000 products and graphic designers, fashion designers, industrial designers, as well as architects and digital content designers.
1. Counterfeit Products
The company has been dealing with counterfeit products for decades. These fake products are often made of inferior materials and can pose a safety hazard to consumers.
Nike shoes are among the most counterfeited goods in the world. In fact, a whopping 88% of the sneakers on the list of the 25 most counterfeited footwear brands are Nike shoes.
Air Jordan 1 Retro High OG Dark Mocha is one of the most counterfeited sneakers. While its replica costs about $130, the legitimate ones sell for more than $500 on resale sites.
2. High Product Costs
Nike’s products are quite expensive compared to its competitors. Its average price for a pair of sneakers is $110, compared to $85 for a pair of Adidas sneakers and $70 for Under Armour sneakers.
High costs limit the accessibility of Nike products to price-conscious consumers, especially in price-sensitive markets.
3. Dependency on Third-Party Manufacturers
Nike does not own any factories, and it outsources all of its manufacturing to third-party suppliers and contract manufacturers located in various countries.
While this is a common practice in the apparel industry, it may lead to supply chain disruptions, quality control challenges, and reputational risks.
Any negative issues arising from the actions of suppliers (like environmental controversies or labor violations) could reflect poorly on Nike’s brand image, even if Nike is not directly responsible for those actions.
4. Product Overexposure
Product overexposure refers to the risk of saturating the market with too many product variations. It can make the brand seem less exclusive.
Also, too many Nike sneakers and their slight variations could end up competing against each other for sales. This may lead to cannibalization, where sales of one item eat into the sales of another, eventually affecting overall profitability.
5. Controversies and Labor Issues
Nike has faced many controversies and labor issues over the years, including sweatshop allegations in the early 1990s, child labor accusations in the mid-1990s, human rights abuses in the mid-2000s, and factory conditions and safety concerns in the past few years.
While the company has taken several initiatives to resolve those issues (such as increased transparency, auditing of manufacturing factories, and partnering with firms focused on labor rights and sustainability), it still faces scrutiny from labor rights advocates and consumers regarding the ongoing labor issues in its supply chain.
6. Product Recalls
The company has recalled several products over the years due to quality issues and safety concerns. Some of their most notable product recalls are
- In 2019, Nike recalled their special edition of Air Max 1 featuring the Betsy Ross flag design due to racial connotations associated with the flag.
- In 2014, Nike recalled the LeBron Zoom Soldier 8 Shoe after receiving complaints about the strap coming loose during use.
- In 2014, Nike recalled the first-generation FuelBand fitness tracker due to its inaccurate tracking measurements.
7. Regional Market Differences
Nike operates in over 190 countries, and each region has its unique market dynamics and unique consumer preferences regarding fashion, sports, and athletic styles.
In addition to these regional differences, Nike has to deal with climate and seasonal variations as well as economic conditions that impact consumers’ purchasing power and buying behaviors.
8. Overreliance on footwear
Nike’s footwear products account for most of the company’s overall revenue. In 2022, Nike generated $29.14 billion in revenue from footwear items, which represents about 66% of the company’s total revenue.
The overreliance on footwear items has been a cause for concern for many investors. This is because
- The footwear industry is cyclical, which means Nike’s revenue and profits can be volatile
- The industry is highly competitive
- The industry is becoming increasingly commoditized, making it more difficult for brands to differentiate their products
9. Average customer service
Nike has a mixed reputation for its customer service — while some customers have encountered negative experiences, others have had more satisfactory or decent encounters.
Nevertheless, the company has often been criticized for its poor customer service. Consumers have complained about long wait times, a lack of responsiveness to complaints, and difficulty getting in touch with their representatives.
OPPORTUNITIES
1. international expansion.
The company can expand into new markets, such as Asia and Africa. Since these markets are growing rapidly, there is a large potential for Nike to increase its sales.
Nike generates over $7.5 billion and $5.9 billion from Greater China and Asia Pacific regions. Considering the growth in these markets and Nike’s popularity, the company can easily grow its sales at a CAGR of over 9%.
2. Direct-to-Consumer Sales
The company can leverage DTC sales to strengthen its brand, develop deeper relationships with consumers, and increase profit margins. It should continue investing in eCommerce platforms, apps, and loyalty programs to offer a seamless and personalized shopping experience.
In the fiscal year 2023, Nike’s digital sales grew 17% in North America and 24% in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
3. Growing Athleisure Trend
The global athleisure market is expected to exceed $330 billion by 2030. Nike can capitalize on this growing athleisure trend by adapting its product offerings and marketing strategies to cater to the preferences of customers who seek both style and comfort in their everyday wear.
The company can introduce new lines of athleisure wear that seamlessly blend athletic functionality with fashion-forward designs, such as versatile hoodies, joggers, and casual sneakers.
4. Women’s Market
The women’s sportswear market has seen significant growth in the past, and the trend is likely to continue in the coming years. It is estimated that the women’s activewear market will reach $269 billion by 2029.
Nike can implement targeted strategies that cater to the unique preferences and needs of these customer segments.
5. Health and Wellness Trend
The company can capitalize on increasing fitness and active lifestyle product demand. As people become more health-conscious and prioritize physical well-being, Nike can establish itself as a brand that not only offers performance-oriented sportswear but also actively promotes a comprehensive approach to health and wellness.
It can collaborate with health and wellness experts, fitness trainers, nutritionists, and mindfulness coaches who can add credibility to Nike’s offerings and offer customers guidance and valuable resources on their wellness journeys.
6. Enter the Subscription Business
Introducing athleisure subscription services can be a great opportunity to increase customer loyalty and drive repeat purchases.
These services offer convenience to consumers who want to regularly update their wardrobes without the hassle of shopping. Nike can curate personalized shipments based on individuals’ styles and preferences.
Regular shipments would build anticipation and excitement among subscribers. Plus, this would lead to recurring revenue streams and increased predictability and stability in Nike’s revenue.
7. Acquisitions and Strategic Alliances
Nike can target startups and partnerships that align with its core business objectives and complement its existing product offerings. The company has already made dozens of acquisitions and formed strategic alliances in the past. The most notable ones include
- Acquisition of Hurley International in 2002
- Acquisition of Converse Inc. for $305 Million in 2003
- Strategic Alliance with Apple to launch the Nike+iPod in 2006
- Acquisition of Zodiac (data analytics firm) in 2018 to enhance its direct-to-consumer strategy
Read: 33 Biggest and Most Expensive Tech Acquisitions Of All Time

8. Fitness Technology Integration
Nike’s products can be integrated with fitness tracking technology to tap into the growing market for fitness enthusiasts and strengthen customer engagement.
The company has already been doing that for years. They have developed the Nike Training Club app , a comprehensive fitness platform that provides a wide range of workouts, personalized training plans, and guided exercises.
They have also integrated adaptive fit technology into footwear, allowing wearers to adjust fit and comfort through a mobile app. The Nike Adapt line, for example, features self-lacing technology, offering a personalized fit for athletes during different activities.
Nike has partnered with tech companies to develop products that can effectively enhance athletic performance. These include GPS running watches, heart rate monitors, and smartwatches with fitness tracking functions.
By continuously improving these fitness apps and connected products, Nike can stay at the forefront of the sportswear and fitness industry.
9. Focus on Sustainability
According to a study conducted by Boston Consulting Group, about 83% of consumers believe that companies have a responsibility to address climate change. The World Economic Forum found that about 71% of consumers are concerned about the environmental impact of their purchases.
As consumer demand for sustainable items grows, Nike’s emphasis on sustainability can further strengthen its brand reputation and competitiveness in the sportswear industry.
10. Invest in research and development
Nike has a long history of investing in R&D to drive innovation and stay ahead of the competition. These investments have led to new technologies like Flyknit and Zoom Air.
The general areas where Nike has focuses its R&D efforts include:
- Footwear technologies, including cushioning systems, sole materials, and performance-enhancing features
- Apparel innovations like advanced fabrics, designs, and manufacturing technique
- Digital commerce and data analytics to analyze trends and customer preferences
- Sustainable materials and manufacturing processes
The company also explores emerging technologies (like 3D printing, AR, and VR) to explore new possibilities in product design, customization, and customer experiences.
1. Political Instability In Some Countries
Like many multinational companies, Nike may face challenges associated with political instability in some countries. Political instability may arise from government changes, geopolitical tensions, economic crises, civil unrest, or unexpected events.
For example, the Hong Kong protests in 2019 disrupted Nike’s sales and operations in the area. In 2014, there were reports of a factory strike in Vietnam that affected Nike’s supply chain.
2. Economic Fluctuations
Economic downturns can impact consumer spending on non-essential items like sportswear. This can ultimately hurt Nike’s sales and profits.
Recessions, like the one that happened in 2008, increase unemployment rates. This makes it more difficult for Nike to find workers, which can lead to production delays and higher costs.
3. Trade Wars
Trade wars between the United States and other countries (especially China and Europe) could disrupt Nike’s supply chain and decrease its profit margins. It could also result in Nike losing its market share to foreign competitors.
For instance, the 2018-19 US-China trade war led to increased tariffs on Nike’s footwear and accessories. This impacted the company’s profitability and made its products less competitive.
This is because the imposition of tariffs and trade barriers on imported goods can significantly increase companies’ production and distribution costs.
4. Changing Consumer Preferences
Rapid changes in consumer preferences and fashion trends can lead to shifts in demand for specific product categories or styles, potentially leaving Nike with reduced sales or excess inventory.
For example, the trend for athleisure wear has grown in recent years, and this has resulted in increased competition for Nike from brands that specialize in athleisure wear, such as Under Armour and Lululemon.
Also, the growth of eCommerce platforms has made it easy for customers to shop for sportswear products from various brands. This has pressured Nike to invest in online e-commerce technologies and compete on price and convenience.
5. Patent Disputes
Nike has been involved in numerous patent disputes over the decades. These disputes are complex and lengthy legal processes, and the outcomes can have significant implications.
In some cases, patent disputes may lead to licensing agreements, settlements, paying damages, or ceasing the use of patented technology. Some of the most notable cases are:
- Nike vs. Adidas (2012) : Nike sued Adidas for patent infringement of its Flywire technology.
- Nike vs. Skechers (2018) : Nike sued Skechers for patent infringement of its Air Zoom technology.
- Converse vs. Competitors : Converse, a subsidiary of Nike, has been involved in numerous legal disputes with competitors over its Chuck Taylor All-Star sneakers.
6. Negative Publicity or Controversies
The company has been involved in numerous controversies over the years, including child labor concerns, sweatshop allegations, and the Betsy Ross flag controversy .
Nike has also faced criticism for its sustainability practices and environmental impact. Concerns have been raised about its carbon footprint, waste generation, and use of certain materials.
In today’s modern era, controversies or negative incidents can quickly go viral on social media platforms, potentially damaging Nike’s brand value and causing a public relations crisis.
7. Cybersecurity Threats
Like all brands with a significant online presence, Nike is susceptible to cybersecurity threats, including data breaches, DDoS attacks, malware, and social engineering attacks.
Read: 14 Different Types of Computer Viruses
8. Intense Competition
Nike operates in a highly competitive market. Its top competitors are:
With over 17,000 stories in 170+ countries, Adidas has a strong presence in the soccer market. While Nike has the edge over Adidas in terms of market share and revenue ($51.21 billion vs. $23.43 billion in annual revenue), Adidas is a strong competitor and is not far behind.
Under Armour
Under Armour is growing rapidly and is gaining market share. It focuses primarily on performance apparel, including moisture-wicking fabrics, compression wear, and other technologies developed to enhance athletic performance. As of 2023, its annual revenue is approximately $5.9 billion .
Puma has been successful in marketing itself to millennials and young adults, particularly those interested in street culture and fashion. It has also been repositioning itself as a luxury brand by launching a number of high-end products. Last year, Puma’s sales reached nearly $9.35 billion .
Reebok is focusing on its strengths, such as its heritage and association with fitness. The company has launched retro sneakers, partnered with celebrities, and expanded its market in China and India to grow its revenue. It is well-positioned to continue to grow and give tough competition to Nike (especially in developing regions).
Additional Analysis
Nike’s growth timeline .
1964 : Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight founded Blue Ribbon Sports in Portland, Oregon
1972 : The company changes its name to Nike, Inc
1972 : The company unveils its first Nike-branded shoes, Nike Cortez, at the US Olympics Trials
1980 : Nike goes public
1984 : Nike launches Air Jordan Line in collaboration with Michael Jordan.
1988 : Nike introduces its iconic “Just Do It” slogan
Early 1990s : The company expands its product offering to include sports apparel, accessories, and equipment
1996 : Nike launches its first online store
2003 : Nike acquires Converse for $305 million
2006 : The company collaborates with Apple to develop the Nike+iPod Sport Kit
2012 : Nike introduces a proprietary Flyknit technology, setting new standards in athletic footwear design
2015 : Nike introduces the Women’s division, focusing on female sportswear and athleisure products
2018 : Nike introduces the self-lacing Adapt BB basketball shoe
2020 : The company launches the “Move to Zero” sustainability campaign aiming to reduce the environmental impact of its products and operations
2021 : Nike’s market capitalization reaches $280 billion for the first time
2023 : Nike launches first localized app in China
How owns Nike?
Nike is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange, which means its ownership is distributed among various institutional investors, mutual funds, asset management firms, and individual shareholders.
The largest shareholder of Nike is its co-founder, Phil Knight , who owns about 22% of the company through various entities. The largest institutional investors are The Vanguard Group (with a 7.1% ownership share) and BlackRock (with a 5.5% ownership share).
Financial Analysis
Nike’s financial performance has been quite strong over the past few years. It has been growing its revenue and profits at a steady pace.
The company’s profit margin hovers between 11% and 13%, and its debt levels are relatively low.
Although Nike faces numerous external risks (such as economic slowdown, trade war, and continuously changing consumer trends), it has proven itself in all market phases. The company has a strong track record of innovation and growth, and it’s set up for continued success in the future.
Product Failure
Like any large and innovative company, Nike has had its share of product launches that didn’t meet customers’ expectations. The most notable failed products or product lines in Nike’s history include
- Nike Shox : Introduced in 2000, these shoes featured a spring-loaded cushioning system
- Nike SB Koston 1 : It was a signature skateboarding shoe endorsed by professional skateboarder Eric Koston
- Nike FuelBand : Launched in 2012, this wearable fitness tracker failed to grab customers’ attention
- Nike Free : These shoes were criticized for being too minimalist and uncomfortable
- Nike Air Pippen II : Endorsed by NBA star Scottie Pippen, these shoes didn’t become as popular as expected
Global footwear market
The global footwear market size is expected to exceed $725 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.9% from 2023 to 2032.
The major factors behind this growth include the growing population, rising disposable income (especially in developing countries), advancements in footwear technology, and increasing demand for comfortable and stylish footwear options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Nike benefits from its strong brand recognition, extensive product offerings, and strategic partnership and sponsorship. Its commitment to research and development leads to innovative products that cater to athletes’ evolving needs and preferences.
The brand is synonymous with performance, quality, and style.
It has countless opportunities for growth, such as expanding into international markets, capitalizing on growing athleisure trends, and integrating existing products with fitness tracking technology.
The company also faces numerous threats and challenges, including economic fluctuations, trade wars, patent disputes, and ever-changing consumer preferences.
33 Small Business Ideas For Teens
Amazon Swot Analysis [Detailed View]
What Is Financial Analytics? Tools & Services
Varun Kumar
I am a professional technology and business research analyst with more than a decade of experience in the field. My main areas of expertise include software technologies, business strategies, competitive analysis, and staying up-to-date with market trends.
I hold a Master's degree in computer science from GGSIPU University. If you'd like to learn more about my latest projects and insights, please don't hesitate to reach out to me via email at [email protected] .
Related articles

19 Largest Banks In The World By Total Assets | 2024 Edition

14 Aviation Startups to Watch In 2024
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

BUSINESS STRATEGY, CORPORATE STRATEGY, SWOT ANALYSIS & SWOT MATRAX REPORT: BUSINESS STRATEGY CASE STUDY: NIKE INC

Business strategy has been concern for many managers and investors, in order for any organization to be successful in its missions and vision, organization should establish and implementing the best strategy that can conform to all organization's corporate and business levels. As famous scholar has already said ''business without strategy is like a ship without compass''. Nevertheless, this report discusses the background of Nike Corporation, mission and vision statement of the company, the company's SWOT analysis in the form of Matrix, the corporation's competitive Profile matrix, External factor evaluation matrix, Internal factor evaluation matrix, the report also identifies and evaluates Nike's current corporate and business level, finally the this report recommends the best strategy that Nike should pursuit in order to be successful in the athletic market. Nike Corporation is being chosen because there are no corporations that operate officially here in Mogadishu, Somalia and what is more, data availability is relatively difficulty.
Related Papers
theido mokhara
Madeeha Kanwal
Strategy is about the most crucial and key issues for the future of organizations. Strategy is also important to explore several strategic options, investigating each one carefully before making strategic choices. The study incorporates a rigorous and systematic effort to uncover the strategies and its impact on the company's performance by analysing case studies, articles and the annual report of Nike Inc. and Adidas Inc. The study attempts to find out the relevance of the strategies adopted by these companies, which are globally successful athletic apparel companies in the context of Bahrain. The findings of the study highlight Nike's strategies which focus on innovation and emphasis on its research and development department, provision of premium pricing for its customers, broad differentiation strategy, market Segmentation Strategy and Closed-Loop strategy. The Adidas strategies focus on the broad differentiation, innovation, trying to produce new products, services and processes in order to cope up with the competition. It embraces a multi-brand strategy, emphasis on expanding activities in the emerging markets, continuously improving infrastructure, processes and systems, foster a culture of challenging convention and embracing change, foster a corporate culture of performance, passion, integrity and diversity. These strategies coupled with its resources and unique capabilities form the basis of sustainable competitive advantage for both the companies. INTRODUCTION: The strategy is a path towards achieving the optimum goals of individuals, groups and organizations. In addition, it leads to a best use of companies' available resources and it also guides the company to stay in a business successfully and continuous improvements for its processes. The definition of strategy could be differ from one author to another, but the most common definition is that the strategy is long term plans and approaches towards the intended visions and objectives. It is a general framework that specified the organizations' plans, policies and approaches to meets its objectives, goals and end results. The way an organization used to shape its strategies could be differentiate from other organizations in order to make its products unique and remarkable. Globally, companies formulate their strategies based on their visions and reaching the satisfaction of customer's needs, requirements and expectations. Subsequently, they use those strategies as a baseline to compare their actual performance with planned ones, to evaluate the end results and ensuring the continuing organizational excellence. There are many kinds of strategies that are pursued by the companies; Such as cost leadership, differentiation and the focus strategies (Porter, 1985), services strategies, growth strategies. Based on the goals, the companies form those strategies and they rank them upon the priorities. It is more than important for any organization to put strategies and not any strategies; the correct strategies which are formulated after a long time of studying and after numerous number of brainstorming among the top management members. Therefore, those strategies then to be implemented by converting the organization's plans and policies into real actions through the best use of available resources such as: human resources, budgets and technological advance; in order to enhance the organization's performance, productivity and sustainability.
Fariaz Fahad
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Ciência e Tecnologia
Aparecida Cristina Laureano Flôr da Rosa
O presente artigo analisou a relação entre os fenômenos Educação Financeira e a Teoria da Tecnologia Social em resposta a pergunta: como poderia ser trabalhada a Educação Financeira considerando os conhecimentos da Tecnologia Social? A discussão apresentada deriva de uma pesquisa de caráter qualitativo bibliográfico e constitui um estudo teórico-reflexivo. Os resultados sinalizaram que a Teoria da Tecnologia Social pode contribuir significativamente para a Educação Financeira, fomentando metodologias que: valorizem o indivíduo e seu contexto; incorporem uma visão ampliada das finanças em relação às dimensões ambiental e social; tenham como ponto de partida a necessidade do educando; entre outros aspectos.
We analyzed data with the highest vertical resolution for Pacific bluefin tuna to determine whether step-lengths obtained from the data provided evidence of a power or an exponential distribution. The test involved a maximum likelihood estimation and the Akaike information criterion. When dealing with empirical data sets, fitting a distribution to the tail of the data only is customary, and thus data below a specified value, , are not included. We address the importance of these truncated data and show the difficulty in distinguishing patterns between power and exponential distributions, even during a rigorous statistical analysis. We conclude that this phenomenon is dependent on the resolution of the depth sensors used. Furthermore, to identify the process describing actual paths, we constructed two types of one-dimensional random walks, Brownian random walks and Levy walks, to test which model provided better fit to actual paths. The step-length in each model is based on estimated...
International journal of home science
Sunita Tripathi
Disability is a curse for all. Disabled women in particular face greater challenge for their very survival. Disabled women face several kinds of discrimination and reduced access to education, employment and other socioeconomic opportunities. Disabled women stand at a disadvantageous position in society. Their status is not only inferior to that of men, disabled women also face gender bias from their male counterparts. The objective of the present study is to examine the socio economic status of disabled women. The study was conducted in three districts of Uttar Pradesh. The sample consisted of 300 disabled women. Personal interview technique was used for data collection. Various government schemes for the betterment and upliftments for disabled women have failed to bring desired result. Majority of disabled women living in extremely pathetic condition belong to lowest strata of the society. Among different types of disabilities the prevalence of locomotors disability was highest, f...
Revista de Toxicología
Francisco Soler
DOAJ Directory of Open Access Journals, SPARC Europe Award 2009 English. ... Author: M. Hermoso de Mendoza ; F. Soler Rodríguez ; D. Hernández Moreno ; ME Gallego Rodríguez ; A. López Beceiro ; M. Pérez López. Abstract: Journal: Revista de Toxicología. ...
Romain Aeberhardt
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics
Bruno CONDAMIN
Klesis - Revue philosophique
Thierry Ménissier
RELATED PAPERS
amélie pierre
Journal of the Endocrine Society
TIRTH PATEL
Hazen Russell
Broder Merkel
Food Chemistry
Svein Knutsen
Catalysis Science & Technology
Marcelo Domine
Erika Gasperikova
Journal of Kerbala for Agricultural Sciences
Dr. Firas Al-Samarai
Anique Ducharme
Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy
Pere-Joan Cardona
Ciro Monteiro
Andi Riansyah
Sociedade & Natureza
Luciana Medeiros
Clinical Cancer Research
Scott Lucia
European Heart Journal Supplements
DOMENICO CARRETTA
Endocrine Abstracts
Maria Costa
Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry
Anajulia Gonzalez
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
📕 Studying HQ
Nike analysis: a comprehensive guide for business students, dr. wilson mn.
- June 28, 2023
- Business StudyingHq , Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
If you are studying business, you need to learn how to do a company analysis. Nike is a great company to use as a case study for this kind of analysis. In this guide on Nike Analysis, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about Nike, including its history, mission, products, market position, and main rivals.
Nike is one of the largest companies in the world that makes athletic shoes and clothes. Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight started it in 1964 as Blue Ribbon Sports. In 1971, the name was changed to Nike. Nike is a global brand that can be found in more than 190 countries around the world .
Understanding company analysis is important for business students because it lets them figure out a company’s strengths and weaknesses, find possible opportunities and threats, and learn more about how the company works and what strategies it uses. By looking at a successful company like Nike, students can learn a lot about how to do marketing, come up with new ideas, and be good corporate citizens.
What You'll Learn
Company Profile
A. company history.
Nike was founded in 1964 by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight, who were both track and field coaches at the University of Oregon. Originally named Blue Ribbon Sports, the company initially operated as a distributor for the Japanese shoemaker Onitsuka Tiger (now ASICS). In 1971, the company officially became Nike and began designing and manufacturing its own shoes.
Over the years, Nike has become synonymous with athletic footwear and apparel, and its iconic “swoosh” logo is recognized around the world. The company has grown through a combination of innovative product design , savvy marketing, and strategic partnerships with athletes and sports teams.
B. Vision, Mission, and Core Values
Nike’s mission is to “bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete* in the world.” The company’s vision is to “remain the most authentic, connected, and distinctive brand.” Nike’s core values include innovation, sustainability, and diversity and inclusion.
C. Products and Services
Nike produces a wide range of athletic footwear and apparel for various sports, including basketball, football, soccer, and running. The company also offers accessories such as bags, socks, and hats. In addition to its core products, Nike has expanded into other areas, such as digital fitness tracking and smart clothing.
D. Industry and Market Position
Nike operates in the highly competitive athletic footwear and apparel industry, which includes companies such as Adidas, Under Armour, and Puma. Despite intense competition, Nike has maintained a dominant market position and is consistently ranked as one of the most valuable brands in the world.
One of Nike’s key strengths is its ability to innovate and stay ahead of trends in the industry. The company is known for its cutting-edge product design and technology , such as its Flyknit shoes and Nike+ digital platform. Nike has also been recognized for its commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices .
E. Key Competitors
Nike’s key competitors include Adidas , Under Armour, Puma, and New Balance. Adidas is Nike’s biggest rival, and the two companies often compete head-to-head for market share in key categories such as basketball and soccer footwear.
SWOT Analysis
To gain a deeper understanding of Nike’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, we’ll conduct a SWOT analysis .
A. Strengths
Nike’s strengths include:
- Strong brand recognition and reputation
- Innovative product design and technology
- Extensive distribution network
- Effective marketing and advertising campaigns
- Commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices
B. Weaknesses
Nike’s weaknesses include:
- Dependence on a few key product categories , such as basketball footwear
- Vulnerability to economic downturns and shifts in consumer preferences
- Criticism for labor practices and working conditions in overseas factories
C. Opportunities
Nike’s opportunities include:
- Expansion into new markets, such as China and India
- Expansion into new product categories, such as smart clothing and wearable technology
- Growth potential in the women’s athletic apparel market
Nike’s threats include:
- Intense competition from rivals, particularly Adidas
- Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates
- Increasing scrutiny of environmental and social impacts of athletic footwear and apparel manufacturing
Noteworthy Research Papers on Nike
There have been several noteworthy research papers published on Nike over the years. Here are a few that provide valuable insights into the company’s operations and strategies:
A. Noteworthy Research Papers on Nike
- “ Nike’s Global Women’s Fitness Business: Driving Strategic Integration and Operational Efficiency ” by Michael E. Porter and Elizabeth Kind (2018). This paper examines Nike’s approach to the women’s athletic apparel market and its strategies for driving growth and profitability.
- “ Nike’s Sustainable Innovation Journey: New Frontiers in Nike’s Business Model Innovation ” by Stefan Gold and Florian Lüdeke-Freund (2019). This paper explores Nike’s sustainability initiatives and how they have been integrated into the company’s business model .
- “ Nike’s Global Labor Practices: A Case Study in Supplier Relationship Management ” by Richard M. Locke and Fei Qin (2007). This paper provides a critical analysis of Nike’s labor practices and supply chain management , and offers recommendations for improvement.
- The impact of Nike’s marketing and advertising on consumer behavior
- Nike’s approach to innovation and product design in the athletic footwear and apparel industry
- Nike’s supply chain management practices and efforts to improve labor conditions in overseas factories
- The impact of Nike’s sustainability initiatives on its brand reputation and financial performance
- The competitive landscape of the athletic footwear and apparel industry and Nike’s strategies for maintaining market leadership
Essay Titles on Nike
- “The Evolution of Nike: From Blue Ribbon Sports to Global Athletic Brand”
- “Marketing Strategies of Nike: How the Swoosh Became a Global Icon
- An Analysis of Nike’s Sustainable Business Practices
- “Nike’s Impact on the Athletic Footwear and Apparel Industry”
- “The Role of Innovation in Nike’s Success”
- Nike’s Approach to Corporate Social Responsibility”
- “The Power of Branding: How Nike Built a Global Empire”
- “A Critical Look at Nike’s Labor Practices and Supply Chain Management”
- “Nike’s Investment in Women’s Sports: A Strategic Move or a Social Responsibility?”
- “The Nike-Adidas Rivalry: A Battle for Athletic Footwear Supremacy”
Research Topics on Nike
- The impact of Nike’s marketing campaigns on consumer behavior
- Nike’s partnerships with athletes and sports teams and their impact on brand image and sales
- The role of digital technology in Nike’s marketing and distribution strategies
- Nike’s expansion into new markets and product categories and their potential for growth and profitability
- An analysis of Nike’s financial performance and its position in the global market
- Nike’s response to criticism and controversy, such as the Colin Kaepernick ad campaign and allegations of labor abuses in its supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions on Nike
1. when was nike founded.
Nike was founded in 1964 as Blue Ribbon Sports, before officially becoming Nike in 1971.
2. Who are the founders of Nike?
Nike was founded by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight.
3. What does Nike’s “swoosh” logo represent?
The “swoosh” logo was designed by Carolyn Davidson in 1971 and represents the wing of the Greek goddess Nike, who was the goddess of victory.
4. What is Nike’s mission statement?
Nike’s mission statement is to “bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete* in the world.
5. What are Nike’s core values?
Nike’s core values include innovation, sustainability, and diversity and inclusion.
6. What products does Nike sell?
Nike sells a wide range of athletic footwear and apparel for various sports, including basketball, football, soccer, and running. The company also offers accessories such as bags, socks, and hats.
7. Who are Nike’s key competitors?
Nike’s key competitors include Adidas, Under Armour, Puma, and New Balance.
8. Where is Nike headquartered?
Nike is headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon, USA.
9. How many employees does Nike have?
As of 2021, Nike has approximately 75,000 employees worldwide.
10. What is Nike’s stance on sustainability?
Nike has made a commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices, and has set ambitious goals for reducing its environmental impact and promoting social responsibility. The company has launched initiatives such as the “Move to Zero” campaign, which aims to create zero waste and carbon emissions in its supply chain by 2030.
In summary, Nike is a global brand with a rich history , a dominant market position, and a commitment to innovation, sustainability, and corporate social responsibility. Through our analysis of Nike’s company profile , SWOT analysis, research papers, essay titles, and frequently asked questions, we have gained valuable insights into the company’s operations, strategies, and impact on the athletic footwear and apparel industry.
For business students, understanding how to conduct a company analysis is a critical skill to develop. By studying successful companies like Nike and conducting in-depth research on their operations, strategies, and impact, students can learn valuable lessons on best practices for marketing, innovation, and social responsibility. They can also gain insights into the competitive landscape of the global market and develop the analytical skills necessary to make informed business decisions.
Further Reading
Recommended sources on nike:.
- “ Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of Nike ” by Phil Knight
- “ Just Do It: The Nike Spirit in the Corporate World ” by Donald Katz
- “ The Nike Controversy ” by Ballinger, J.
- “ Sustainability at Nike ” by Andrew Winston
- “T he Power of Nike’s Brand Image ” by Emily Delbridge
External links to reputable sources:
- Nike’s official website
- Nike’s sustainability report
- Nike’s investor relations page
- Forbes article on Nike’s marketing strategy
- Harvard Business Review case study on Nike’s digital strategy
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

SWOT Analysis Nike, Inc.
Would you like a lesson on SWOT analysis?
- Nike is a very competitive organization. Phil Knight (Founder and CEO) is often quoted as saying that ‘Business is war without bullets.’ Nike has a healthy dislike of is competitors. At the Atlanta Olympics, Reebok went to the expense of sponsoring the games. Nike did not. However Nike sponsored the top athletes and gained valuable coverage.
- Nike is exposed to the international nature of trade. It buys and sells in different currencies and so costs and margins are not stable over long periods of time. Such an exposure could mean that Nike may be manufacturing and/or selling at a loss. This is an issue that faces all global brands .
- The market for sports shoes and garments is very competitive. The model developed by Phil Knight in his Stamford Business School days (high value branded product manufactured at a low cost) is now commonly used and to an extent is no longer a basis for sustainable competitive advantage. Competitors are developing alternative brands to take away Nike’s market share.
- As discussed above in weaknesses, the retail sector is becoming price competitive. This ultimately means that consumers are shopping around for a better deal. So if one store charges a price for a pair of sports shoes, the consumer could go to the store along the street to compare prices for the exactly the same item, and buy the cheaper of the two. Such consumer price sensitivity is a potential external threat to Nike.
‘If you have a body, you are an athlete’ – Bill Bowerman said this a couple of decades ago. The guy was right. It defines how he viewed the world, and it defines how Nike pursues its destiny. Ours is a language of sports, a universally understood lexicon of passion and competition. A lot has happened at Nike in the 30 years. Read more…
Disclaimer: This case study has been compiled from information freely available from public sources. It is merely intended to be used for educational purposes only.
- Nike has no factories. It does not tie up cash in buildings and manufacturing workers. This makes a very lean organization. Nike is strong at research and development, as is evidenced by its evolving and innovative product range. They then manufacture wherever they can produce high quality product at the lowest possible price. If prices rise, and products can be made more cheaply elsewhere (to the same or better specification), Nike will move production.
- Nike is a global brand . It is the number one sports brand in the World. Its famous ‘Swoosh’ is instantly recognisable, and Phil Knight even has it tattooed on his ankle.
Weaknesses.
- The organization does have a diversified range of sports products. However, the income of the business is still heavily dependent upon its share of the footwear market. This may leave it vulnerable if for any reason its market share erodes.
- The retail sector is very price sensitive. Nike does have its own retailer in Nike Town. However, most of its income is derived from selling into retailers. Retailers tend to offer a very similar experience to the consumer. Can you tell one sports retailer from another? So margins tend to get squeezed as retailers try to pass some of the low price competition pressure onto Nike.
Opportunities.
- Product development offers Nike many opportunities. The brand is fiercely defended by its owners whom truly believe that Nike is not a fashion brand . However, like it or not, consumers that wear Nike product do not always buy it to participate in sport. Some would argue that in youth culture especially, Nike is a fashion brand . This creates its own opportunities, since product could become unfashionable before it wears out i.e. consumers need to replace shoes.
- There is also the opportunity to develop products such as sport wear, sunglasses and jewellery. Such high value items do tend to have associated with them, high profits.
- The business could also be developed internationally, building upon its strong global brand recognition. There are many markets that have the disposable income to spend on high value sports goods. For example, emerging markets such as China and India have a new richer generation of consumers. There are also global marketing events that can be utilised to support the brand such as the World Cup (soccer) and The Olympics.

Nike in 2024: Detailed SWOT Analysis with a Complimentary PowerPoint Template
Download Nike's 2024 SWOT Analysis: Comprehensive insights and free PowerPoint template. Key strategies, opportunities, and challenges revealed.

StrategyPunk
Introduction to the post.
Welcome readers! The iconic Nike swoosh is one of the most recognizable logos in the world.
This post will conduct an in-depth SWOT analysis of Nike in 2024 . Nike is the world's largest supplier of athletic shoes and apparel. We'll examine Nike's internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.
To make this analysis useful, we have also created a free, editable SWOT analysis PowerPoint template that summarizes the key takeaways.
Let's dive right in!
Introduction to Nike
Nike, Inc. is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon. It was founded in 1964 as Blue Ribbon Sports by Bill Bowerman, a track-and-field coach, and his former student Phil Knight.
Nike is the world's most extensive athletic footwear and apparel brand today. Its swoosh logo is one of the most recognizable brand symbols globally.
Nike employs over 75,000 people worldwide and manufactures athletic footwear, apparel, equipment, accessories, and services. It caters to various sports, including running, basketball, football, training, and more.
Some key facts about Nike:
- Founded: 1964
- CEO: John Donahoe
- Headquarters: Beaverton, Oregon
- Annual revenue (2023): $51.1 billion
- Net income (2023): $6.7 billion
Next, look at Nike's history and how it became the sportswear empire it is today.
A Brief Look at the History of Nike
Nike's journey began in 1964 when University of Oregon track athlete Phil Knight and his coach Bill Bowerman set up Blue Ribbon Sports. They started by importing running shoes from Japan's Onitsuka Tiger (now known as ASICS).
In 1971, Blue Ribbon Sports started making its footwear line, now marked with its famous "Swoosh" logo. The brand was renamed Nike in 1978, named after the Greek goddess of victory.
Nike's early innovations in footwear technology, like the 1979 introduction of the Nike Air cushioning system, helped establish Nike as a leader in athletic footwear innovation. Its shoes were lighter, faster, and provided better shock absorption.
In the 1980s and 90s, Nike signed endorsement deals with celebrity athletes like Michael Jordan and Tiger Woods. The Air Jordan brand of basketball shoes brought Nike colossal success.
Nike also expanded aggressively overseas, mainly focusing on China's untapped market. Today, over half of Nike's sales come from outside North America.
Nike has continued to innovate over the decades with advanced proprietary technologies like Flyknit, Dri-FIT moisture-wicking fabric, and Nike+ digital ecosystem.
This focus on constant innovation and endorsement deals with top athletes have made Nike the most valuable sports brand in the world.
Financials of Nike 2023
In fiscal year 2023 (June 2022 to May 2023), Nike delivered strong financial results despite global economic challenges:
- Annual revenue grew 6% year-over-year to $51.1 billion
- Net income rose 6% to $6.7 billion
- Nike Direct sales (online + retail stores) were up 14% over 2022
- Earnings per share came in at $4.30, up 7%
Nike's revenues have grown at an average rate of over 5% annually in the past five years. In that timeframe, its net profit margins have remained steady between 14-15%.
About 42% of Nike's sales come directly from Nike retail stores and nike.com. The rest is from wholesale customers like department stores and sporting goods retailers.
Geographically, North America remains Nike's largest market, accounting for over 40% of sales. However, significant growth areas are China, Europe/Middle East/Africa (EMEA), and the Asia Pacific/Latin America (APLA) regions.
After reviewing Nike's recent financial performance, let's move on to an in-depth SWOT analysis for 2024.
In-depth SWOT Analysis of Nike 2024
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
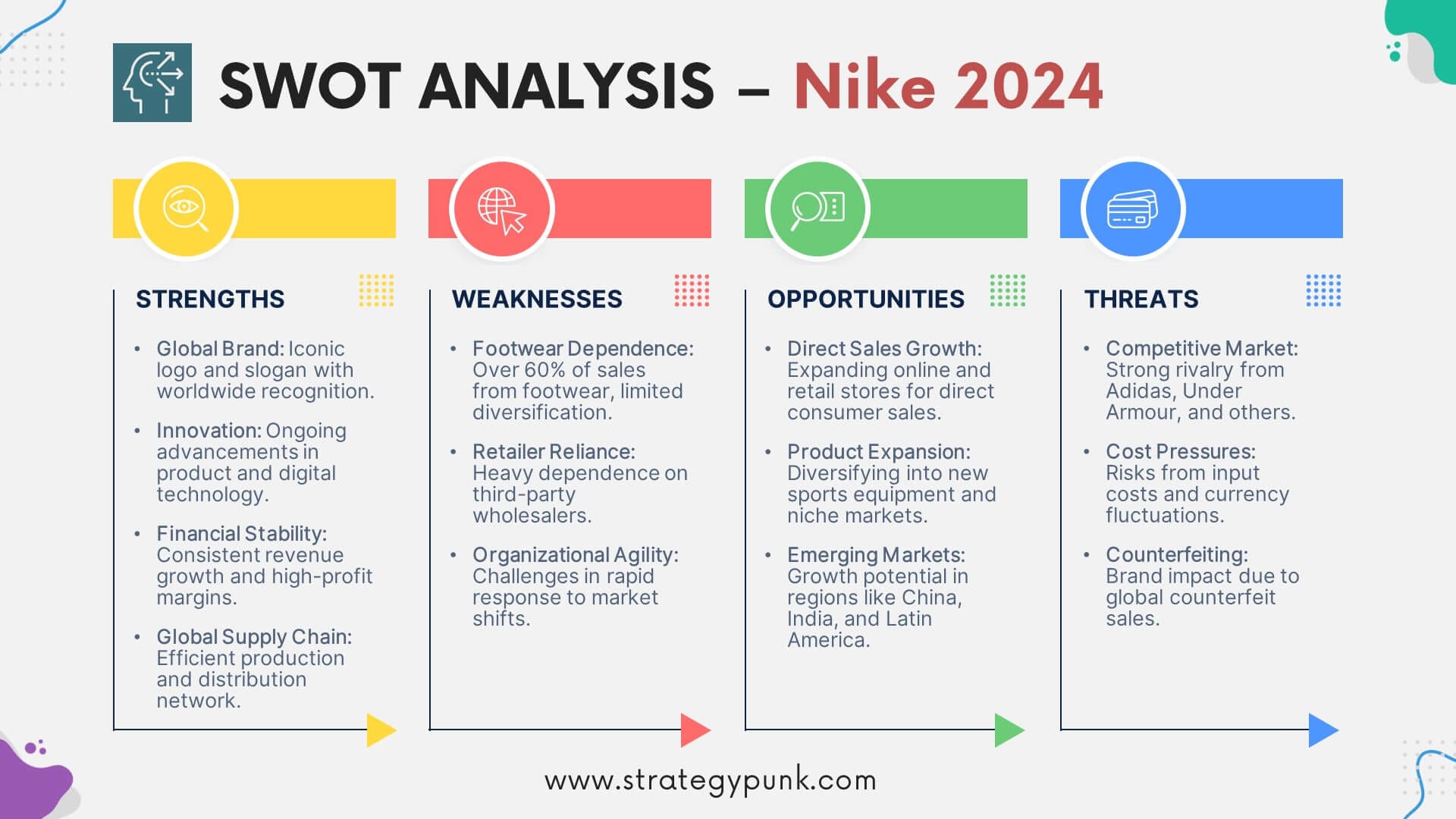
It is a structured framework to evaluate a company's strategic position by looking at internal and external factors.
Nike’s Strengths
Nike's key strengths are:
Global Brand Recognition : Nike's Swoosh logo and "Just Do It" slogan are recognized globally. It has built powerful brand awareness through decades of quality products and marketing.
Innovation Capabilities : Nike has continually innovated in product design, proprietary technology, and digital experiences. Its R&D infrastructure helps sustain the innovation pipeline.
Financial Performance : Nike has delivered consistent revenue and earnings growth historically. Its vertically integrated business model and high-margin Nike Direct sales underpin profitability.
Global Production & Distribution : Nike has well-established outsourced manufacturing capabilities and a solid global distribution infrastructure, ensuring efficient worldwide supply.
Nike’s Weaknesses
Some weaknesses Nike needs to manage are:
Over-reliance on Footwear : Footwear makes up over 60% of Nike's sales. It needs to diversify into apparel and accessories to drive sales growth.
Third-Party Retail Dependence : About 60% of Nike's sales come from wholesalers. As direct-to-consumer channels grow, managing third-party retail relationships is vital.
Lack of Agility : As a large company, Nike lacks the agility to respond quickly to market changes. It needs to streamline its structure and decision-making to become more nimble.
Nike’s Opportunities
Nike can capitalize on the following key opportunities:
Direct-to-Consumer Expansion : Nike can accelerate its online and retail store expansion to grow higher-margin direct sales.
New Products & Categories : Nike has growth headroom to expand into related categories like sports equipment and gear and launch new brands targeting niche consumers.
Emerging Markets : Nike has significant untapped growth potential in emerging markets like China, India, the Middle East, and Latin America through its localization strategy.
Nike’s Threats
Some threats Nike faces are:
Intensifying Competition : Rivals like Adidas, Under Armour, Lululemon, and local players are competing aggressively and eroding market share.
Margin Pressures : Input cost inflation, wholesale discounting demands, and foreign exchange fluctuations may compress Nike's healthy margins.
Counterfeits : Counterfeit Nike products illegally sold globally can negatively impact brand image and sales. Nike continues its brand protection efforts against counterfeiting.
Nike SWOT Analysis Summary
Internal factors.
Nike's substantial brand equity, innovation capacity, and financial track record are critical internal strategic advantages.
However, over-dependence on footwear and third-party distribution pose risks requiring mitigation focus.
External Factors
Favorable industry growth trends, emerging market expansion potential, and direct sales growth avenues are significant opportunities for Nike. However, competition pressures, margin headwinds, and counterfeiting risks need to be managed through targeted strategies.
Nike can retain its sportswear industry leadership by leveraging its strengths, overcoming weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and countering threats. However, it will require strategic clarity and effective execution.
Frequently Asked Questions
related to to SWOTAnalysis Nike
What are Nike’s most significant strengths?
Nike’s strengths are its robust global brand recognition, product development capabilities, extensive distribution network, and consistent financial results.
What are the major threats facing Nike?
Critical threats Nike faces are intensifying competition from brands like Adidas and Under Armour, counterfeiting its trademarks, and potential consumer spending declines in an economic recession.
What opportunities can fuel Nike's future growth?
Significant opportunities to spur Nike’s growth include expanding digital and e-commerce sales, entering developing markets, and showcasing sustainability credentials to attract socially-conscious shoppers.
What is Nike's competitive strategy?
Nike's competitive strategy is centered on product differentiation. It aims to offer athletic shoes and apparel with cutting-edge styles, technologies, and performance that stand out from rivals. Nike also invests heavily in signing endorsement deals with top athletes to enhance its aspirational and "cool" brand image.
How does Nike's marketing support its business strategy?
Nike's marketing reinforces its product differentiation strategy. Advertising campaigns spotlight product innovations and link Nike to elite athletic performance. Sponsorships of superstars like LeBron James and emotional storytelling around sports tap into consumers' passions. The goal is to strengthen Nike's brand prestige and premium positioning.
What sustainability initiatives has Nike undertaken?
Key sustainability initiatives for Nike include using recycled polyester and leather, eliminating virgin plastic in apparel, implementing renewable energy in owned facilities, and setting targets to cut carbon emissions across its supply chain. The Nike Grind program also recycles old athletic shoes into material for surfaces like running tracks and playgrounds.
How can sustainability provide Nike strategic benefits?
Sustainability can enhance Nike's branding among environmentally-conscious younger consumers who increasingly favor responsible companies. It also makes supply chains more resilient against climate disruptions and criticism regarding labor policies and waste. Furthermore, greener manufacturing can reduce costs over the long run as energy and material expenses decline.
Have there been any notable acquisitions in Nike's history?
Major past acquisitions fueled Nike's growth, including purchasing surf-inspired footwear brand Hurley International in 2002 and sports technology firm Celect in 2019. Both deals obtained Nike valuable intellectual property and innovative product designs. The Select takeover also bolstered Nike's data analytics capabilities for demand forecasting and inventory optimization.
Could Nike acquire other companies in the future?
Nike could acquire more petite sports apparel and accessories brands catering to specific consumer niches like yoga, cycling, or outdoor adventure. It might also pursue data analytics firms to improve its digital sales platforms and supply chain resilience. However, Nike already possesses a formidable scale, so it seems less inclined toward transformational mergers and more inclined toward expanding organically.
Nike SWOT Analysis PowerPoint Template
free and fully editable PPT template
A SWOT analysis evaluates the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats impacting a company.
This free editable PowerPoint template provides a SWOT analysis framework to evaluate Nike's internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.

Download this pre-made SWOT analysis template to evaluate Nike's business strategy and document your SWOT conclusions. Customize it easily with your content.
Nike SWOT Analysis PDF Template
Discover more.
Clickworthy Resources
SWOT Analysis: Free PowerPoint Template
This PowerPoint slide deck contains five different layouts to complete a SWOT analysis.

New! SWOT Framework & Free PPT Template - 2024 Edition
Dive into the 2024 Edition of our SWOT Analysis guide, complete with a free PowerPoint template. This resource covers the essentials of conducting a SWOT analysis, its benefits, and practical application tips, including a case study on Mercedes Benz.
Primark SWOT Analysis: Free PPT Template and In-Depth Insights 2024
Explore Primark's 2024 SWOT Analysis with our free PowerPoint template. Gain key insights into strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Download now for a comprehensive analysis.

Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Download our free PPT template for in-depth PESTLE insights into Nestlé's global strategy. Learn more today!
PESTLE Analysis: Decoding Reddit's Landscape (Free PPT)
Decode Reddit's global influence with our free PowerPoint PESTLE Analysis. Explore the hub of vibrant discussions and ideas.
Navigating the Terrain: A PESTLE Analysis of Lululemon (Free PowerPoint)
Explore Lululemon's business terrain with our free PESTLE analysis PowerPoint. Instant access!
The Art of Strategic Leadership: 5 Keys to Success by Willie Peterson
Explore Willie Peterson's 5 crucial strategies for strategic leadership. Master learning, customer focus, and effective storytelling.

- Search by theme
- Search by keyword
- Plagiarism checker
- Document production & correction
- Publish my documents
Consult more than 14968 documents with no limitation. Our subscription options
Can't find what you are looking for? Order a tailor-made document!
- Marketing & branding
- Sport marketing
SWOT Analysis - Nike
Nike SWOT Analysis, Nike, SWOT Analysis , Puma, Adidas, New Balance, Asics, sport , sports shoes, sportswear
Nike originated in the 1960s, it started as a collaboration between Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight, and shoes were then sold under the name "Blue Ribbon Sports". The company name changed to "Nike" in 1978 : the name Nike reflects a Greek goddess that symbolises victory. The vision behind the company is to bring inspiration and innovation to athletes globally. Nike continually seek to produce, design and develop products to enhance athletic performance. Their desire is to produce products that initiate true performance and technological advantages to help athletes progress in their desired sport. Nike finds it important that if you have a body, you are an athlete. Nike is the brand for everyone and this is emphasised in their "Just Do It" slogan. Their headquarters are situated in the United States but they have stores worldwide and employs over 40,000 people.
- Presentation of Nike
- The sporting goods market
- Opportunities
[...] The sporting goods market ● Nike promote a highly competitive sports apparel, footwear and accessories industry ● They compete with other large number of players, such as Puma, Adidas, New Balance and Asics ● The sportswear and accessories industry are exposed to continuous changes in consumer needs and technology ● Nike needs to ensure they are able to quickly adapt to changes or it will immediately lose its market share by staying focused on their audience and product lines ● When they compare the results to their competitors, Nike recorded a total increase in sales in their 2nd quarter of 2020 of 10% year-on- year ● Nike believes that the growing competition from new entrants and existing competition in emerging markets are focusing on unique market segments and continually improving their product quality ● A major threat and competitor to Nike are Adidas ● Adidas are in a similar strong position and have the second-largest market share - 21% for Nike and for Adidas in 2017 in the footwear market ● Adidas is a German brand created in 1949 which designs and manufactures athletic shoes, clothing and accessories ● The main slogan of the marketing strategy for Adidas is: "Impossible is nothing," which aims to show that no matter who you are, you are capable of following your dreams as nothing is impossible ● Puma is another German multinational company founded in 1924 and is the third-largest competitor for Nike ● Puma brand is based on the values that make an athlete excel ● New Balance, an American company founded in 1906 is another one of Nike's competitors ● They manufacture mainly in the United States and United Kingdom and as a result has made their shoes more expensive ● Another competitor to Nike is Japanese brand Asics which was established in 1949 ● Its name translates to “Healthy Soul in a Healthy Body” ● According to an article in the newspaper Les Echos (April 2017), “The distribution of sporting goods is growing by per year worldwide. [...]
[...] ) with $ 6.6 billion in direct sales, Nike ranks fifth worldwide and Adidas (with $ 4.6 billion) sixth. With double-digit growth rates.” As of 2018 Nike's market share was at II. [...]
[...] Nike Swot Analysis A SWOT analysis is a useful way to identify the external and internal factors that influence Nike ● Nike's logo, the so-called swoosh has been a large part of the brand's strength ● People identify the Nike logo without the brand name ● This allows them to be able to identify it as Nike, which shows the power of the brand and design of the logo ● Nike have a good Research and Development department which puts them ahead of technology ● Although they are highly innovative, they do have weaknesses ● Nike has a large range of sportswear and shoes but relies mostly still on shoe sales ● The enormous advertising costs mean they invest a lot of money into marketing ● The marketing strategy works but does come at a very high cost ● Although Nike is seen as an elite sports brand, more people are enjoying the products and choose to wear them as they are fashionable ● Playing in a highly competitive sports industry market, Nike is able to easily expand to emerging markets ● The famous Nike name and “swoosh” logo allows them to target countries where the passion for sport is high ● Brazil, Russia and China are all massive sports enthusiast countries ● Nike need to ensure they are able to adapt to constant consumer needs and desires in a highly competitive market so they do not lose market share ● The world's economic status and a country's economic downturns can affect the consumer goods industries ● During the recent credit crisis that many countries face, the market for Nike's products suffer and can make it weaker A. [...]
[...] Nike and Adidas compete with the brands. ( . [...]
[...] Weaknesses ● Nike have been faced with controversies surrounding their exploitation of cheap labour ● There were alleged reports of them using child labour in Pakistan and Cambodia ● This has negatively impacted the company especially considering their production and factories are in developing countries ● Although they have a diverse range of products, their product line is still limited and they rely mostly on their sports shoes sales ● Their global growth is somewhat limited too as other retailers provide a very similar product experience ● Nike are also faced with pricing issues in developing countries where imitations are available ● Their patent protection is also an issue and contributes to these difficulties ● John Donahoe has been elected as the new CEO of Nike after numerous changes in leadership since Phil Knight's resignation in 2005 C. [...]
- Number of pages 5 pages
- Language English
- Format .doc
- Publication date 29/08/2020
- Read 1 times
- Updated on 13/10/2020
APA Style reference
Online reading
Content validated
Most consulted
- Porter's Five Forces - Zoom
- PESTEL Analysis - Zoom
- SWOT Analysis - Zoom
- Porter's diamond 5 forces : Stellantis, an automotive company
- PESTEL Analysis - Shein
Most recent
- How to measure the value of a professional football player through a financial valuation model?
- PESTEL Analysis - Lafuma
- Mega-Sport Events: Impact on Women Opportunities in Sponsorship and Their Brand Image
- Asics' history, marketing and strategy
- Porter's five forces, PESTEL and SWOT analysis - Puma France

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Nike’s Mission Statement & Vision Statement (An Analysis)

Nike’s mission statement and vision statement determine business goals and strategic direction for the company’s competitive position as the leading athletic shoes and apparel business in the global market. A company’s mission statement defines the fundamental objectives of the business, especially in terms of its purpose. In this company analysis case, Nike’s mission statement prompts the business to support the endeavors of athletes. On the other hand, a company’s vision statement provides a target future condition of the business. Nike’s vision statement focuses on brand strength and development. The company applies these corporate statements as guides for the evolution of its business, leading to the creation of business strengths and competitive advantages, like a strong brand image, as determined in the SWOT analysis of Nike Inc . Through the evolution and effective implementation of its mission statement and vision statement, the company supports its market position as a leading producer of sports footwear, apparel, and equipment.
Adhering to its vision statement and mission statement, Nike Inc. aims for leadership in the international market, while counteracting competition. The Five Forces analysis of Nike shows that competitive rivalry imposes a strong force against the company and its industry environment. The mission and vision statements compel the company’s strategic management to develop policies for competitiveness against other firms, such as Adidas, Puma , ASICS, and Under Armour. These firms make the global sporting goods market a challenging business environment.
Nike’s Mission Statement
Nike’s mission is “ to bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world. ” This mission considers the psychological and utilitarian aspects of how the sportswear company satisfies its customers. The following main components are in Nike’s mission statement:
- Inspiration
- Every athlete in the world
The company states that everybody is an athlete, based on Nike founder Bill Bowerman’s statement, “If you have a body, you are an athlete.” In this context, the mission statement represents the company’s strategic goal of reaching every person on earth because everybody is considered an athlete and, thus, a customer. As a leading manufacturer of sports shoes, apparel, and equipment, Nike Inc. inspires people to adopt a “winner mindset”, which is covered in the “inspiration” component of the mission statement. The company’s “Just Do It” slogan represents this inspirational goal. Also, Nike’s mission statement emphasizes innovation. This component is applied through the organization’s strategy of continuous improvement of products through new technologies, as included in Nike’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies . The “every athlete in the world” component indicates that the company’s mission statement pushes the business to target every person in the world. As noted, the company considers every person an athlete. Thus, based on this mission, Nike’s products are designed to attract and satisfy a wide variety of market segments globally.
Nike’s Vision Statement
Nike’s vision is “ to remain the most authentic, connected, and distinctive brand. ” The business continues to apply this vision statement for its long-term strategic goal of keeping its market dominance and business growth. The sportswear company focuses on developing its brand. The following are the notable keywords in Nike’s vision statement:
- Most authentic
- Most connected
- Most distinctive
Nike’s vision statement uses the word “remain,” which indicates that the company already considers its brand as the most authentic, connected, and distinctive in the global market for sporting goods and related products. The “authentic” component of the corporate vision statement shows that the business organization aims to make its sports and leisure products deliver high performance to satisfy consumers. On the other hand, the “connected” component is about ensuring customers’ personal connection with the brand. Nike’s marketing mix or 4P supports the creation and maintenance of such connection with customers. The company also maintains a “distinctive” quality by delivering the best possible products to the sporting goods market. This vision statement regards Nike Inc. as a leader in the industry, while pushing the business to further separate itself from competitors. A notable point about the company and its vision statement is that it also develops connections with consumers through its separate vision for corporate social responsibility: “to help NIKE, Inc. and our consumers thrive in a sustainable economy where people, profit and planet are in balance.” This CSR vision serves as a basis for Nike’s corporate social responsibility (CSR), ESG, and stakeholder management strategy .
Assessment & Recommendations – Nike’s Mission & Vision
Nike’s mission statement outlines the general strategic direction of the business. The statement includes such information as the company’s customers (everybody), the target market (global), and part of the philosophy of the sporting goods business. This corporate statement has strong points, based on conventions in writing ideal mission statements. However, Nike’s mission statement is philosophical and does not include specifics about the kind of products offered to consumers and the nature of relevant business processes. In this regard, it is appropriate to recommend that the company specify the nature of its products. For example, Nike can improve its mission statement by illustrating that its products are in the athletic and leisure footwear, apparel, and equipment industry. Also, stating that business processes are within the scope of the design and manufacture of such products can make the corporate mission statement more accurate in guiding Nike’s operations, employees, and business partners, including suppliers.
Nike’s vision statement is about keeping brand leadership in the global industry. The athletic goods company considers its brand as one of the major strengths of the business and points out that it has already achieved the top brand position. In this regard, Nike’s vision statement is satisfactory in terms of having the characteristics of ideal vision statements. For example, the company’s vision statement is concise, clear, inspiring, and challenging in focusing on maintaining brand leadership. The statement is also future-oriented, considering that Nike Inc. highlights keeping its brand’s leading position as a strategic aim for future business development.
- About Nike, Inc.
- Fitzsimmons, A. B., Qin, Y. S., & Heffron, E. R. (2022). Purpose vs mission vs vision: Persuasive appeals and components in corporate statements. Journal of Communication Management, 26 (2), 207-219.
- Lüthy, A. (2023). From the Mission Statement to Value-Oriented Corporate Management. In Value-Oriented Leadership in Theory and Practice: Concepts-Study Results-Practical Insights (pp. 79-93). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Nike, Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Nike, Inc. – Investor Relations .
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Consumer Goods Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Nike Inc.’s Global Sourcing Analysis Case Study
Introduction, market segmentation and positioning strategies, customer analysis, marketing mix: 4ps, alternative solutions, recommendation, exhibit 1: the apparel commodity chain.
Nike’s current position as one of the biggest companies in sportswear and athleisure clothing continues to be challenged by both competitors and changing consumer principles. The issue of ethical and high-quality sourcing is one of the most significant concerns that Nike has. The balance between sustainability and cost is a factor that the company has spent years measuring and adjusting. After the company expanded and began delivering more substantial quantities of products to different continents, its relationship with other members of the supply chain also changed. The pressure to produce goods and meet customer demands increased due to the firm’s social responsibility.
Currently, Nike faces several significant problems in the sphere of global sourcing, but all of them are related to one root concern that the company has to address. The demand for Nike products, in particular, and athleisure clothing, in general, continues to increase, and Nike has to perfect its supply chain to deliver the goods. However, its process, from designing a product to selling it to the customer, is long and inflexible, and the slow speed of all operations also makes Nike vulnerable to sudden demand shifts. The search for new suppliers and manufacturers also exposes Nike’s burden of finding ethical and reliable partners. The purpose of this report is to analyze the current position of Nike in the market of sportswear and athleisure and see how it can address such problems as unsustainable sourcing, slow product cycle, and growing demand.
Environmental Analysis
Nike operates on a global scale and sources the majority of its materials and labor from overseas. Therefore, it is highly dependent on changes in the political climate. Taxation, labor laws, and manufacturing regulations are among the primary factors that determine Nike’s access to some suppliers as well as its financial contribution to certain countries. Moreover, sales are also regulated by taxation, and such differences can influence Nike’s exports.
Nike produces a wide range of clothing and accessories, some of which can be considered luxury items, while others are closer to the category of essentials or goods for everyday use. Therefore, it is vital for Nike to consider the economy of countries to which it markets the products, noting their capability and stability. For instance, Nike has successfully penetrated the US market and similar areas with high buying power and stable consumer demand.
The popularity of sports and fitness is one of the trends that Nike can use to increase the demand for its products. At the present moment, the trend for athleisure is dominating not only the segment of sports clothing but the markets of fashion and luxury clothing. Thus, the present social influences are favorable for Nike and its competitors. However, the increase in demand also challenges Nike to increase its quality and meet the demand while also outselling rivaling companies. It is also apparent that the increase in people’s ethical concerns is a trend that the business has to acknowledge and address.
Technological
Innovation in the field of sports clothing is needed in both the quality, design, material of the goods, and the process of their manufacturing. The increase in computerization is one of the steps that the supply chain is implementing to change business operations. Furthermore, as the speed of innovation increases rapidly, Nike’s lack of participation can endanger the status of the company. The increasing role of e-commerce and portable devices (smartphones, smartwatches, fitness bracelets) contributes to the profits of companies such as Nike but raises the demand for new lines.
The regulation of labor standards in different countries puts significant pressure on Nike to monitor the environment in which supply chain employees work. The previous scandals about poor working conditions, exploitation, underpayment, and child labor urge the firm to continuously strengthen its standards for choosing suppliers. Another concern is Nike’s legal control of copyrighted designs and marketing campaigns. Here, the possible legal constraint is the need to follow popular trends while creating unique goods and preventing the production of replicas.
Environmental
As noted above, the idea of conscious consumption is gaining attention among consumers. Thus, Nike has to maintain its commitment to sustainability and enhance the quality of the manufacturing process. The change in climate is a problem that can be detrimental to sales and production, and it serves as both an opportunity and a threat to the company. Nike’s current focus on ethical production has to be expanded further.
Competition structure
Nike faces competition in several markets since it produces a variety of shoes, clothing, and accessory types. The first and main rival is Adidas – a business that also focuses on sportswear and athleisure clothing. Adidas is the second, after Nike, in sales of sneakers, and the company’s clothing lines target a similar client base. Notably, both companies have sizable contracts with athletes and sports teams. Other firms also compete in the same segment, namely Puma and Reebok. As Nike also markets to consumers interested in athleisure clothing, such competitors as Under Armour have to be considered. The contracts with famous celebrities and athletes allow such brands to gain recognition and increase customer loyalty. As a whole, Nike faces intense competition for all product categories, as the number of established and developing brands is significant.
Nike possesses many strengths supported by the long history and current popularity of the brand. First of all, Nike’s logo remains one of the most recognizable symbols on the market – the “swoosh” symbol is connected in customers’ minds to sports shoes and world-class athletes such as LeBron James and Serena Williams. In fact, its celebrity partnerships increase the exposure of the brand and its status as a seller of popular goods. Second, as Nike offers not only shoes but athleisure clothing and professional sports equipment, the company has a broad appeal to several demographics. The supply chain of the business shows that Nike operates through multiple retail channels, diversifying the products’ route from plants to customers (Exhibit 1). Nike’s low cost of manufacturing, based on its selection of manufacturers, is paralleled by its innovative research and development (R&D) departments’ ideas. Finally, Nike is an international brand, which widens its reach to clients all over the world.
However, Nike also has some weaknesses that affect its performance. The long process from the design of a product to its presentation to customers makes the company’s production inflexible. The company’s representatives demonstrate that the company may spend several months creating a shoe. As a result, Nike cannot correctly predict customer demand, trends, weather changes, and other outside factors that may influence sales. Furthermore, Nike continues to encounter unstable suppliers who may have poor working conditions or other violations of Nike’s sustainability and worker protection standards. Nike also relies heavily on the US market as a dominating location of interest, while other markets are not as explored. The ability of retailers to manipulate prices, as evident in the case of Nike’s late delivery of shoes, can significantly lower Nike’s profits. Additionally, the history of previous scandals still affects the brand and limits its outreach to some client groups.
One of the opportunities that Nike can explore is to further build its international presence in the markets of athleisure and professional sportswear. Annual global sports events, for example, are a suitable place to get new contracts, advertise, and raise customer awareness. The shift to increasing the brand’s reliance on other countries may provide additional stable channels of revenue. Moreover, as Nike had a strong R&D department, the company can invest in the creation of new products such as wearable devices, sunglasses, jewelry, and other goods. As athleisure is becoming widely recognized as a fashionable trend, Nike may collaborate with designers and brands to create exclusive lines and limited editions for a sector of customers to enjoy. Another opportunity lies in the supply chain- Nike can integrate some suppliers, taking more responsibility for the quality and environment of facilities.
Nike faces several threats related to the market, customers’ perceptions, and economic instability. As Nike is a famous brand, the possibility of fakes and design stealing among competitors is high. Replicas of Nike shoes sold at lower prices can appeal to some individuals and lower the sales of the brand. Apart from that, the competition in the segment of sports shoes is rising – companies use aggressive advertising campaigns and struggle to establish relationships with teams, athletes, and celebrities. In the supply chain, Nike’s position as an ethical company can always be undermined by new news of human rights violations, unfair labor practices, and other social crises. Lastly, as Nike operates globally, it is vulnerable to any currency exchange rate fluctuation and political conflicts between countries. Table 1 combines the central points in the SWOT analysis of Nike.
Table 1. Nike SWOT Analysis – Key Points.
The abundance of product categories implies Nike’s need to segment the market into several groups. First of all, Nike’s advertising reveals targeting based on demographic qualities. Children, teenagers, young adults, and adults are the main categories to whom Nike offers its products. The main segments are teenagers and young adults since these groups are often the most active in sports, both recreationally and professionally. Nike presents different lines and marketing campaigns for men and women, signifying gender segmentation. While clothing products may be in the same line, their colors and sizes differ according to gender.
Nike’s goods are also separated according to their style, utility, and technological advancement. Some lines are made to target groups interested in athleisure – fashion-based clothing, smaller brands such as Converse, and items for everyday wear. In contrast, other products are marketed as athletic – they are segmented according to the activity, including running, basketball, football, tennis, and others. Finally, Nike also presents separate groups of products with innovative materials and ideas as well as vintage designs. As an outcome, Nike’s market segmentation is sophisticated, and the company reaches a wide variety of customer bases.
To understand the positioning strategy of Nike, one has to analyze who it targets. Among the main characteristics of target groups, young age, urban living, high- and middle-income, and interest in sports are the most distinguishable. Therefore, the brand uses a mix of high price, high quality, and product attributes approaches to formulate the position of the company. For instance, Nike’s focus on athleticism shifts the focus from products to their underlying meaning – a person wearing Nike is an aspiring or established athlete. Here, the inspirational message is embedded with the functionality of the goods, and Nike’s goal is to inspire and assist. Thus, Nike positions itself both in professional and amateur sports categories – athletes are offered goods based on their quality, while other people are being marketed as a tool for achieving sports-related goals.
It should be noted that, by positioning the brand as global and ubiquitous, Nike gains access to many market segments. While running is a significant activity that Nike focuses on due to its history with running shoes, the brand also has an established position in basketball and tennis, working with major athletes from these sports. As a result, Nike’s technological advancements are also appealing to different people, and their positioning can be further expanded to new areas of physical activity. Additionally, with the latest popularity of athleisure, the brand’s choice of a younger demographic is a benefit to maintaining a status for being both high-quality and fashionable.
As described above, Nike’s segmentation allows it to appeal to multiple groups simultaneously. Nonetheless, one can further describe the three main targets that the brand considers as the primary client categories. The first group is young athletes – Nike’s image of an inspirational brand based on partnerships with major athletes is key to attracting young aspiring sportspersons to consider Nike’s shoes and clothing. Second, Nike markets to women, both in professional and athleisure segments. Although men’s clothing continues to take up a significant part of Nike’s lines, women’s increasing role in sports and advocacy for health change aligns with Nike’s marketing. Finally, runners are another group that gets more attention than other athletes due to Nike’s participation in various projects.
However, customer analysis shows that other characteristics may define Nike’s clientele. The income of people mentioned in the previous analysis cannot be overlooked, as Nike’s pricing is often approached with the premium strategy. Thus, Nike’s consumers have high incomes to match the prices that Nike sets. Furthermore, the focus on residents of urban areas is tied to Nike’s collaboration with major athletic teams and its preference for athleisure and professional training. It is clear that Nike’s customers have to respond to such influencers as famous athletes who are also winners and leaders of sports competitions. Nike’s proposition to its customers, therefore, is to bridge the gap between these ideals of performance and customers’ physical abilities. To establish a connection with clients and deliver this message, Nike uses short inspirational quotes and direct calls to action.
The range of goods offered by Nike is wide, but the company focuses on athletic shoes, clothing, and accessories. The category of shoes is the pillar of Nike’s activity – historically, shoes have been the main products that Nike sold. However, now, the brand’s selection of footwear is much larger than before, as it sells sneakers, hiking and outdoor boots, shoes for professional basketball, football, and tennis players, running shoes, and many other varieties. In addition, the company also designs footwear not directly related to sports, including flip-flops and sandals. The second category, clothing, is also divided according to its purpose. While some items are marketed as specific for physical activity, others are now viewed as a part of everyday outfits. Finally, Nike sells equipment and accessories – the list ranges from golf clubs to water bottles.
Nike applies several strategies to its products, using both value-based and premium pricing for its goods. Some lines of footwear and clothing are created with technological advancements or specific characteristics, making premium pricing a viable option in the market. For instance, as Nike presents itself as the best company for running gear and sportswear, prices for the latest models and gadgets may be higher than those of competitors. In other categories, Nike pays more attention to the market’s trends, using the price of the materials and the final product to establish the worth of each item. As a whole, this combination of approaches allows Nike to market to a broad audience.
As mentioned in the previous analyses, Nike distributes its products through several channels. These include specialty stores, department stores, discount chains, and various outlets (Exhibit 1). Additionally, Nike has an online-based store with the ability to deliver goods to customers internationally. Retail stores are the foundation of Nike’s selling strategy since they make goods easily accessible to consumers. Nike’s products are often sold alongside its competitors, which requires the brand to pay increased attention to marketing, presentation, and pricing. Moreover, the capabilities of e-commerce allow Nike to distribute its new lines without having to think about its relationships with other members of the supply chain. The brand’s outlet stores also provide Nike with more opportunities to collect customer data.
As a major international company, Nike utilizes many approaches to marketing. The need to maintain a strong brand image identified in the SWOT analysis put additional pressure on Nike to engage its consumer base. First of all, Nike continues to work with traditional media, advertising its products on television and in print. Second, Nike uses online advertising, sharing campaigns with celebrities and ordinary people. Direct marketing is a strategy that the company uses when working with sports teams, organizations, and event representatives. Sales staff engages in personal selling, persuading customers to choose certain products. Moreover, Nike contributes to public events through sponsorship and endorsements. Finally, discounts and special offers sometimes are applied to Nike’s products, depending on the location and season.
To reiterate, Nike is facing such issues as a long and inflexible process of developing new products, unreliable suppliers, and the growing demand for products burdened with the increased environmental and social awareness. The analysis shows that Nike has succeeded in creating a sound brand image that has a high recognition and commitment scale. Nonetheless, the public’s attention to ethical manufacturing and the growing number of competitors endanger the top position of the company. One may suggest a number of strategies that would address the problems related to global sourcing.
The first alternative is to restructure the supply chain to engage suppliers in producing goods for their respective regions. Currently, the majority of manufacturing plants are concentrated in a small number of countries, and almost all goods are created in and shipped from one region. This system results in several problems – transportation and shipping are complicated and unsustainable, Nike’s relationship with companies is not involved, and it is challenging for the company to establish ethical standards for its suppliers adequately. The proposed change is to refocus on some other regions that will shorten the time of travel and open new areas for new supplier relationships.
Nike has already examined the potential of South and Central America, finding that the placement of its plants in these regions would shorten the time of delivery. Therefore, it would also affect Nike’s flexibility in responding to new trends and customer demand fluctuations. The benefits of this proposition lie in the diversification of Nike’s key locations, thus making its planning more adjustable to the market. Nonetheless, Nike will have to completely reform its approach to pricing, find new suppliers and train them according to its standards, and engage more resources to maintain the quality of goods and the state of plants’ working environment.
The second alternative does not call for relocation but encourages Nike to improve its ethical standards further. While the current system places much focus on workers’ conditions, it does not increase workers’ safety and comfort actively. The brand puts this responsibility on suppliers, monitoring their compliance and changing orders when necessary. This strategy does not engage Nike in the process of changing the practices of these manufacturers.
As evident in the case, many suppliers comply only for a short period of time or fall back into harmful practices with time. To combat such an inability to follow standards, Nike can pursue several options. One approach is to make the position of Nike more demanding and uplift the voices of workers by providing them with a direct channel of communicating concerns. The other is to participate in the enforcement of guidelines, creating training programs, and resourcing staff and employee awareness.
The proposed strategies of increasing Nike’s participation in suppliers change programs, if successful, will allow Nike more control over the quality of goods and the environment in which employees have to work. The main benefit of this solution is the improved ethical position of suppliers. By taking on specific responsibilities, Nike will also be able to raise clients’ awareness about the ethical policies of the company, which may positively affect customer interest. This approach has drawbacks, mainly related to the use of financial resources and staff. Training projects and higher engagement require sufficient funding and available personnel. Moreover, some suppliers may protest the increased intervention from the outside, withdrawing from contracts. Finally, this strategy is unlikely to reduce the time of development for Nike, keeping its processes inflexible and vulnerable.
Using the information about the company as well as its analysis, one may recommend Nike to pursue the first discussed alternative strategy – to restructure the supply chain. The relocation of manufacturers to move them closer to customers can bring many benefits to the company, but only if Nike continues to enforce its sustainable and ethical principles in choosing and monitoring suppliers. The environmental analysis of the brand shows that Nike is highly dependent on retailers’ decisions, customer trends, and economic relationships between countries. Therefore, making transportation of the goods more accessible can positively influence the resource flow in the business. If the process shortens the time during which a product is designed, manufactured, and delivered to the customer, it will also allow Nike to respond adequately to retailers’ demands and crises.
Moreover, this step will provide Nike with a marketing opportunity and distinguish it from its competitors as a pioneer in making steps towards sustainability. As the SWOT analysis indicates, the threat of competition will increase, and Nike has to take additional steps to maintain its place as the leader of sportswear and athleisure goods. The proposed alternative also aligns with the opportunities presented in the SWOT analysis – the relocation may open up new markets and collaboration projects.
This approach would require Nike to review its possibilities and contracts with the existing manufacturers, deciding which of them adhere to the standards. Nonetheless, it will be a chance for the partners to show that they are the best for working with Nike in terms of quality, speed, sustainability, and working environment. Overall, Nike should not disregard an option of making communication between employees in the supply chain and the brand more transparent. By integrating several solutions in multiple steps, Nike can move forward towards high-quality global sourcing without sacrificing its image and the relationship with its suppliers.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, June 11). Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-global-sourcing-analysis/
"Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis." IvyPanda , 11 June 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-global-sourcing-analysis/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis'. 11 June.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis." June 11, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-global-sourcing-analysis/.
1. IvyPanda . "Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis." June 11, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-global-sourcing-analysis/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis." June 11, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-global-sourcing-analysis/.
- Brief Description of Nike Inc: Is Nike a Monopoly?
- Nike Company's Marketing Strategy
- Views on Nike Brand
- Lego Company’s Performance Management
- Netflix Company's Global Success and Opportunities
- Subway Company's Strategic Analysis and Business Policies
- Petrobras Company's Incidents and Investment Potential
- Google Incorporation's Development

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nike Inc. SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) & recommendations are discussed in this sports shoes business management case study. ... Brand activism, the relation and impact on consumer perception: A case study on Nike advertising. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 12(4), 30-42. Nike, Inc.'s E-commerce ...
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture's success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT ...
Last updated: August 30, 2023 by Ovidijus Jurevicius. This SWOT analysis examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of Nike, Inc., a global footwear and apparel company, a champion brand builder whose slogans like "Just do it" have moved beyond advertising into popular expression. This undisputed field titan has risen ...
The company is undoubtedly successful in these areas, being the most valuable sports apparel company in the world, with a net worth of $189.5 billion in 2023. It is also indisputably one of the most successful brands in the world, with a brand value of $33 billion. Nike directly employs over 79,000 people and indirectly employs countless others ...
An Overview of Nike. Nike, Inc. is an American multinational corporation. Nike is headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon, USA. It was found by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight in the year 1964. The company specializes in athletic wear, providing footwear, apparel, athletic equipment, and accessories. Nike's primary goal is to supply athletes with ...
Nike is a global brand that is synonymous with quality and excellence. This article analyses the company using the SWOT Methodology. The key theme in this article is that Nike is currently at a stage where it has to either diversify into other segments or risk placing all its eggs in one basket. The SWOT Analysis is a useful methodological tool to analyze companies and arrive at a logical ...
SWOT Analysis of Nike. SWOT represents strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and SWOT analysis can then be used to evaluate these four components of your enterprise. One can use SWOT Analysis to form the foremost of what the organization has, for the organization's best advantage and to scale back the probabilities of failure, by ...
In the fiscal year 2024, Nike reported a notable financial performance. Revenues reached $13.4 billion on a quarterly basis, marking a modest but welcome 1% increase on a YoY basis. Meanwhile, earnings per share beat expectations significantly ($0.98 vs $0.69 expected).
Since these markets are growing rapidly, there is a large potential for Nike to increase its sales. Nike generates over $7.5 billion and $5.9 billion from Greater China and Asia Pacific regions. Considering the growth in these markets and Nike's popularity, the company can easily grow its sales at a CAGR of over 9%.
Nike Financials. Nike generated $51.22 billion in revenue in 2023 and over $5 billion in net profits, compared to over $46.71 billion in revenue and $6.05 billion in profits for 2022. Nike Mission Statement. Nike's vision is "To bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world.".
business strategy, corporate strategy, swot analysis & swot matrax report: business strategy case study: nike inc Ali JILIOW Business strategy has been concern for many managers and investors, in order for any organization to be successful in its missions and vision, organization should establish and implementing the best strategy that can ...
The Five Forces analysis model relates these external factors to the weak force of suppliers on Nike's business environment. On the other hand, the moderate number of suppliers equates to their moderate bargaining power over sporting goods businesses. The combination of these factors leads to the weak bargaining power of Nike's suppliers.
Sheets, the total liability of the company is 23,287. million dollars, thus, the liability asset ratio is 74.3% [1]. In comparison with other companies in the sporting. goods industry, such as ...
Do you want to know about Nike's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats? Are you looking for a video to learn about them? Do you want to know why ...
Nike is a great company to use as a case study for this kind of analysis. In this guide on Nike Analysis, we'll tell you everything you need to know about Nike, including its history, mission, products, market position, and main rivals. Nike is one of the largest companies in the world that makes athletic shoes and clothes. Bill Bowerman and ...
Nike SWOT is one of 50+ FREE examples of SWOT analysis on Marketing Teacher. Nike SWOT is one of 50+ FREE examples of SWOT analysis on Marketing Teacher. Search ... This case study has been compiled from information freely available from public sources. It is merely intended to be used for educational purposes only.
Final Case Study Analyzing Nike's AFI Framework Jena M. Sidle, Sport Business Management MGT4260: Strategic Management (ONLF22) Ohio Christian University Prof. Vicki Clark Dec. 19, 2022. ... If Nike management applies the SWOT analysis and my diagnosis is correct, I believe Nike should innovate its marketing approach by changing how it uses ...
Introduction to the post. Welcome readers! The iconic Nike swoosh is one of the most recognizable logos in the world. This post will conduct an in-depth SWOT analysis of Nike in 2024. Nike is the world's largest supplier of athletic shoes and apparel. We'll examine Nike's internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.
Case study, 5 pages, sport marketing published on 29 August 2020: SWOT Analysis - Nike. This document was updated on the 13/10/2020
Nike's Mission Statement. Nike's mission is " to bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world. " This mission considers the psychological and utilitarian aspects of how the sportswear company satisfies its customers. The following main components are in Nike's mission statement: Inspiration. Innovation.
Read in detail: https://myassignmenthelp.com/case-study/nike-swot-pest-analysis-case-study.htmlThe success story of Nike is worth a listen for anyone who's i...
Case Study Pages 13 Words 3599 Subjects Business Company Analysis Topics Nike Language 🇺🇸 English Date of foundation January 25, 1964 ... Table 1 combines the central points in the SWOT analysis of Nike. Table 1. Nike SWOT Analysis - Key Points. Remember! This is just a sample . You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers .
Read in detail here: https://myassignmenthelp.com/case-study/nike-swot-pest-analysis-case-study.htmlGet Case Study sample on Nike SWOT analysis 2013 and Nike...