25% OFF ALL FRAMES OFFER ENDING SOON PROMO CODE: GRAD25
Enter GRAD25 to get 25% OFF

Start Building My Frame
Suggestions:
- Try fewer words; use "Jefferson" instead of "Jefferson High School" or "Thomas" instead of "St. Thomas".
- If you are still not able to find your school or group, please contact Customer Service .
Please note : If your school or group has closed, you will not be able to locate it on our website.

2/28/2024 By University Frames
- 10 Effective Class Presentation Tips for College Students
Giving a presentation to your classmates can be a bit challenging, especially if you are new to visual or oral presentations or fear public speaking.
However, class presentations foster an excellent opportunity for students to enhance their public speaking skills while broadening their perception and understanding of a particular subject matter.
Also, the presentation provides a platform for students to connect with peers, professionals, and potential employers.
By showcasing their skills and knowledge, they can build relationships and establish themselves as a better performer in their field.
While presentation helps students to expand their horizons of knowledge and skills, beginners may be slightly concerned about where to start and how to master it.
Worry not! Here, we discuss the best presentation tips for students for a flawless delivery of the subject.
10 Handy Presentation Tips for College Students
Effective delivery of a presentation requires efficient presentation techniques and exceptional presentation abilities.
The following tips for presenting in class help students strengthen their public speaking skills, empowering them to effectively communicate their message or information to the audience.
1. Overcome Presentation Anxiety
While it is quite common to feel anxious before the presentation, it won’t allow you to deliver a presentation confidently.
There are several reasons why students fear public speaking, including, worrying about committing a mistake, lack of experience, losing control, or what if their audience dislikes their speech.
Nevertheless, don’t worry, as you can overcome your presentation anxieties with the following techniques:
- Prepare and practice your topic thoroughly.
- Just focus on the message you want to convey to your audience.
- Be open to feedback and criticism from others.
- Have a mindset that you are going to make it.
- Practice deep breathing to keep your mind calm and composed.
2. Learn the Art of Public Speaking
Learning and getting used to public speaking can help students feel more confident and comfortable in delivering their message to the audience.
Also, it helps them to structure their thoughts and use perfect language to convey their content crisp and clean while engaging their audience.
There are several ways for students to learn public speaking skills, including:
- Online platforms and courses
- Local resources (community clubs, associations, etc.)
- Public speaking workshops
- Watching experienced public speakers and observing their techniques
Also Read: 17 Best Advice for College Students from Experts .
3. Craft Compelling Content
A robust opening statement sets the tone for the entire student presentation, helping you grab your audience’s attention.
Ensure to develop a clear, concise, and thoughtful opening statement that talks about what the presentation is about and how it helps everyone out there.
Moving on, your body content is the heart of your presentation, and that is what is going to keep your audience in the loop while conveying your ideas and thoughts.
So, it should be well-structured, engaging, and easy to follow. Here’s how you can devise engaging content:
- Create a strong opening and ending statement with a powerful quote, thought-provoking question, or intriguing scenario.
- Clearly and precisely define your topic and its significance.
- Conduct in-depth research that is backed with statistical data or real-time stories.
- Organize your content with slides and images.
4. Add Engaging Visuals
Rather than constantly scrolling the loads of information, it is better to use visuals to engage your audience while helping them comprehend and retain complex matters and building emotional connections with them.
Tips for slideshow presentations:
- Use simple yet high-quality images.
- Add contrast and pleasing colors to make your slides look good.
- Incorporate snippets to support your visuals.
- Keep your slides consistent in terms of layout and design.
- Choose easy-to-follow fonts and numbers.
- Add data, icons, and infographics for illustration.
5. Balance Information and Entertainment
Adding humor to a presentation is a way to engage and connect with your audience more personally.
It can help relieve tension, break the silence/drowsy state of mind, and make complex or dry information more perceivable during class presentation.
Also, it helps keep your presentation memorable for a long time. Here is how you can add humor to your presentation:
- Know your audience and tailor your humor accordingly.
- Use humorous analogies, cartoons, catchphrases, or your own experiences.
- Try not to hurt others while using humor.
- You can make fun of everyday situations or activities, so people can relate with them.
6. Time Management in Class Presentation
Time management is one of the best tips for presenting in class. Starting and finishing your presentation in a predefined time frame is important.
It helps you to convey your message precisely and effectively without disrupting the flow of the presentation and making it difficult for the audience to follow along.
To manage your class presentation time, here are some presentation tips for students:
- Practice beforehand to know the required time.
- If you are going beyond the allotted time, cut short your content, delivering the most important points.
- Use visuals to quickly deliver messages.
- Use a timer to know that you are nearing the end.
7. Real-Life Examples
Listening to successful presentations helps you learn new techniques and gain insights on how to give better presentations. You can take note of key elements used, gestures followed, and eye contact made.
Also, you can study the agenda of the presentation, like how it is structured, what topics are discussed, how properly visuals and icons are used, etc.
Besides, you can pay attention to the language and tonality of the speaker to see how they used humor, stories, and emotional phrases to connect with audiences.
Considering these insights, you can prepare your topic and present it flawlessly.
8. Take Peer Review and Feedback
Feedback is a way to learn where you lag and how you can improve further to build your credibility, professional knowledge and image.
By receiving feedback from peers, you can identify blind spots, fragile areas, and how your content is perceived by others, enabling you to refine your work, address weaknesses, and develop new skills.
Moreover, this presentation tip can strengthen your relationships with your peers while helping you present better every time.
Also Read: Tips for Building Professional Relationships in College .
9. Stay Elegant and Attractive with Your Attire
What you wear and how you wear it matters when it comes to presenting in front of the public.
The clothes you wear can greatly impact how your audience perceives you and your message. So, ensure to present yourself properly and professionally to attract your audience.
Here is how to dress up for class presentations:
- Keep your outfits simple, comfortable, and elegant.
- Avoid flashy colors and designs.
- Choose outfits according to the environment and temperature.
- Get your outfits properly stitched with the right fit.
- Choose the right and soothing footwear.
10. Post-Presentation Reflection
Reviewing your past presentations can help drag strengths and areas for growth, which can help you make informed decisions and optimize your performance.
For example, by analyzing your performance, you can assess what works well and what doesn't. This involves identifying areas for improvement concerning the use of visuals, snippets, icons, infographics, etc.
Knowing these can help you make targeted improvements to enhance your future presentations.
Wrapping Up
A successful class presentation in college is vital for students’ academic and professional journey.
It helps students develop valuable skills that will serve them in their future careers and provides them with an opportunity to showcase their knowledge and ideas to a wider audience.
By mastering the art of presentation, students can set themselves apart from their peers and position themselves for success in their chosen careers.
So, use the above-mentioned presentation tips for students to speak more confidently, sharing your thoughts and ideas.

University Frames
Subscribe to our blog.
Enter your email address:
Latest Offers

Latest Posts
- 8 Trending Diploma Frames for Enhancing Your Space with Style
- 39 Trending Graduation Cap Ideas in 2024
- March Madness Sale: Save Big and Get 20% Off at University Frames
- Get Your Game On with University Frames this March Madness!
Category: College Life Hack
Tags: Class Presentation Tips Class Presentation Tips for College Students college tips presentation tips

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7.4 Public Speaking and Class Presentations
Learning objectives.
- Know how to overcome nervousness and anxiety associated with public speaking and giving class presentations.
- Effectively use the six-step process to prepare for and deliver a class presentation.
- Create effective visual aids for use in class presentations.
- Work with a group to successfully plan and deliver a class presentation.
Public speaking—giving an oral presentation before a class or another group of people—is a special form of interaction common in education. You will likely be asked to give a presentation in one of your classes at some point, and your future career may also involve public speaking. It’s important to develop skills for this form of communication.
Public speaking is like participating in class—sharing your thoughts, ideas, and questions with others in the group. In other ways, however, public speaking is very different. You stand in front of the class to speak, rather than from your usual seat—and for most students, that changes the psychology of the situation. You also have time outside of class to prepare your presentation, allowing you to plan it carefully—and, for many, giving more time to worry about it and experience even more anxiety!
Overcoming Anxiety
Although a few people seem to be natural public speakers, most of us feel some stage fright or anxiety about having to speak to a group, at least at first. This is completely normal. We feel like everyone is staring at us and seeing our every flaw, and we’re sure we’ll forget what we want to say or mess up. Take comfort from knowing that almost everyone else is dreading giving class presentations the same as you are! But you can learn to overcome your anxiety and prepare in a way that not only safely gets you through the experience but also leads to success in your presentation. The following are proven strategies for overcoming anxiety when speaking in public:
- Understand anxiety. Since stage fright is normal, don’t try to deny that you’re feeling anxious. A little anxiety can help motivate you to prepare and do your best. Accept this aspect of the process and work to overcome it. Anxiety is usually worst just before you begin and but eases up once you’ve begun.
- Understand that your audience actually wants you to succeed. They’re not looking for faults or hoping you’ll fail. Other students and your instructors are on your side, not your enemy. They likely won’t even see your anxiety.
- Reduce anxiety by preparing and practicing. The next section discusses the preparation process in more detail. The more fully you prepare and the more often you have practice, the more your anxiety will go away.
- Focus on what you’re saying, not how you’re saying it. Keep in mind that you have ideas to share, and this is what your classmates and instructors are interested in. Don’t obsess about speaking, but focus on the content of your presentation. Think, for example, of how easily you share your ideas with a friend or family member, as you naturally speak your mind. The same can work with public speaking if you focus on the ideas themselves.
- Develop self-confidence. As you prepare, you will make notes you can refer to during the presentation. You’re not going to forget what you want to say. The more you practice, the more confident you’ll become.
Guidelines for Presentations
Preparing and delivering a presentation in class (or in business or other settings) is a process very similar to the learning process discussed in Chapter 4 “Listening, Taking Notes, and Remembering” , Chapter 5 “Reading to Learn” , and Chapter 6 “Preparing for and Taking Tests” and the writing process discussed in Chapter 8 “Writing for Classes” . The process breaks down into these six basic steps:
- Analyze your audience and goals
- Plan, research, and organize your content
- Draft and revise the presentation
- Prepare speaking notes
- Practice the presentation
- Deliver the presentation
Step 1: Analyze Your Audience and Goals
Who will see and hear your presentation—and why? Obviously, other students and the instructor. But you still need to think about what they already know, and don’t know, about your topic. If your topic relates to subject matter in class lectures and readings, consider what background information they already have and be careful not to give a boring recap of things they already know. It may be important, however, to show how your specific topic fits in with subjects that have been discussed already in class, especially in the beginning of your presentation, but be sure to focus on your new topic.
New terms and concepts may become familiar to you while doing your research and preparation, but remember to define and explain them to other students. Consider how much explanation or examples will be needed for your audience to grasp your points. If your topic involves anything controversial or may provoke emotion, consider your audience’s attitudes and choose your words carefully. Thinking about your audience will help you find ways to get their attention and keep them interested.
Be sure you are clear about the goals for the presentation. Are you primarily presenting new information or arguing for a position? Are you giving an overview or a detailed report? Review the assignment and talk with the instructor if you’re unsure. Your goals guide everything in the presentation: what you say, how much you say, what order you say it in, what visual aids you use, whether you use humor or personal examples, and so forth.
Step 2: Plan, Research, and Organize Your Content
Starting with the assignment and your goals, brainstorm your topic. Jot notes on specific topics that seem important. Often you’ll do reading or research to gather more information. Take notes as you would with any reading. As you research the topic at this stage, don’t worry at first about how much content you are gathering. It’s better to know too much and then pick out the most important things to say than to rush ahead to drafting the presentation and then realize you don’t have enough material.
Organizing a presentation is similar to organizing topics in a class paper and uses the same principles. Introduce your topic and state your main idea (thesis), go into more detail about specific ideas, and conclude your presentation. Look for a logical order for the specifics in the middle. Some topics work best in chronological (time) order or with a compare-and-contrast organization. If your goal is to persuade the audience, build up to the strongest reason. Put similar ideas together and add transitions between different ideas.
While researching your topic and outlining your main points, think about visual aids that may help the presentation.
Also start thinking about how much time you have for the presentation, but don’t limit yourself yet in the outline stage.
Step 3: Draft and Revise the Presentation
Unless required by the assignment, you don’t need to actually write out the presentation in full sentences and paragraphs. How much you write depends on your own learning and speaking style. Some students speak well from brief phrases written in an outline, while other students find it easier to write sentences out completely. There’s nothing wrong with writing the presentation out fully like a script if that helps you be sure you will say what you intend to—just so you don’t actually get up and read from the script.
You can’t know for sure how long a presentation will last until you rehearse it later, but you can estimate the time while drafting it. On the average, it takes two to three minutes to speak what can be written on a standard double-spaced page—but with visual aids, pauses, and audience interaction, it may take longer. While this is only a rough guide, you can start out thinking of a ten-minute presentation as the equivalent of a three to four-page paper.
Never wait until the last minute to draft your presentation. Arrange your time to prepare the first draft and then come back to it a day or two later to ask these questions:
- Am I going on too long about minor points? Could the audience get bored?
- Do I have good explanations and reasons for my main points? Do I need more data or better examples? Where would visual aids be most effective?
- Am I using the best words for this topic and this audience? Should I be more or less informal in the way I talk?
- Does it all hold together and flow well from one point to the next? Do I need a better introduction or transition when I shift from one idea to another?
Visual Aids in Presentations
Except for very short informal presentations, most presentations gain from visuals—and visual aids are often expected. If encouraged or allowed to include visuals in your presentation, plan to do so. Consider all possible types:
- Charts or graphs
- Photos or other images
- Video clips
- Handouts (only when necessary—they can be distracting)
Use the available technology, whether it’s an overhead projector, PowerPoint slides, a flip chart, or posters. (Talk to your instructor about resources and software for designing your visuals.) Follow these guidelines:
Design your visuals carefully. Here are some basic rules:
- Use a simple, neutral background. A light-colored background with text in a dark color works best for words; a dark background used like matting works best for photos.
- Minimize the amount of text in visuals—more than eight words per slide is usually too much. Avoid simply presenting word outlines of what you are saying. Make sure text is large enough for the audience to read.
- Don’t use more than two pictures in a slide, and use two only to make a direct comparison. Montages are hard to focus on and distract the viewer from what you’re saying. Use images only when they support your presentation; don’t use clip art just as decoration.
- Don’t put a table of numbers in a visual aid. If you need to illustrate numerical data, use a graph. (Microsoft Excel can make them for you easily.)
- Don’t use sound effects. Use a very brief recording only if directly related to your main points.
- Don’t use visual special effects such as dissolves, spins, box-outs, or other transitions. They are distracting. Use animation sparingly and only if it helps make a point.
- Don’t use so many visuals or move through them so quickly that the audience gives all its attention to them rather than to you.
- Practice your presentation using your visual aids, because they affect your timing.
- Explain visuals when needed but not when they’re obvious.
- Keep your eyes on your audience, only briefly glancing at visuals to stay in synch with them.
- Don’t hand out a printout of your visuals. Your audience should keep their eyes on you instead of fiddling around with paper.
Step 4: Prepare Speaking Notes
As mentioned earlier, it’s not a good idea to read your presentation from a written page rather than deliver it. To keep your audience’s attention, it’s important to make eye contact with them and to use a normal speaking voice—and you can’t do this if you keep your eyes on a written script.
Speaking notes are a brief outline for your presentation. You might write them on index cards or sheets of paper. Include important facts and data as well as keywords for your main ideas, but don’t write too much. (If you forget things later when you start practicing, you can always add more to your outline then.) Be sure to number your cards or pages to prevent a last-minute mix-up.
Think especially about how to open and close your presentation, because these two moments have the most impact of the whole presentation. Use the opening to capture the audience’s attention, but be sure it is appropriate for your audience and the goals. Here are some possibilities for your opening:
- A striking fact or example (illustrating an issue or a problem)
- A brief interesting or humorous anecdote (historical, personal, or current event)
- A question to the audience
- An interesting quotation
Then relate the opening to your topic and your main point and move into the body of the presentation.
Your closing mirrors the opening. Transition from your last point to a brief summary that pulls your ideas together. You might end with a challenge to the audience, a strong statement about your topic, or a personal reflection on what you have been saying. Just make sure you have a final sentence planned so that you don’t end up uncomfortably fumbling around at the end (“Well, I guess that ends my presentation”).
Step 5: Practice the Presentation
Practice may be the most important step. It is also the best way to get over stage fright and gain confidence.
Practice first in an empty room where you imagine people sitting, so that you can move your eyes around the room to this “audience.” The first time through, focus on putting your outlined notes into full sentences in your natural speaking voice. Don’t read your notes aloud. Glance down at your notes only briefly and then look up immediately around the room. Practice two or three times just to find the right words to explain your points and feel more comfortable working with your notes. Time yourself, but don’t obsess over your presentation being the exact length required. If your presentation is much too long, however, adjust it now in your notes so that you don’t start memorizing things that you might accidentally still say later on even though you cut them from your notes.
Once you feel good speaking from your notes, practice to add some more polish to your delivery. You might want to record or videotape your presentation or ask a friend or roommate to watch your presentation. Pay attention to these aspects of how you speak:
- Try to speak in your natural voice, not in a monotone as if you were just reading aloud. If you will be presenting in a large room without a microphone, you will need to speak louder than usual, but still try to use a natural voice.
- In usual conversation, we speed up and slow down and vary the intensity of our words to show how we feel about what we’re saying. Practice changes in your delivery style to emphasize key points.
- Don’t keep looking at your notes. It’s fine if you use words that are different from those you wrote down—the more you rehearse without looking at your notes, the more natural sounding you will be.
- Be sure you can pronounce all new words and technical terms correctly. Practice saying them slowly and clearly to yourself until you can say them naturally.
- Don’t forget transitions. Listeners need a cue when you’re moving to a new idea. Practice phrases such as “ Another important reason for this is…” or “Now let’s move on to why this is so.…”
- Watch out for all those little “filler” words people use so often, such as “like,” “you know,” “well,” and “uh.” They’re very distracting to most audiences. Listen to or watch your tape to see if you are using these fillers or ask your friend to point it out.
- Pay attention to body language when practicing. Stand up straight and tall in every practice session so that you become used to it. Unless you have to stand at a podium to use a fixed microphone in your presentation, practice moving around while you speak; this helps keep the audience watching you. Use hand and arm gestures if they are natural for you, but don’t try to make up gestures for the presentation because they will look phony. Most important, keep your eyes moving over the audience. Practice smiling and pausing at key points.
- Finally, it’s a good idea to be ready in case of an accident. Most likely your presentation will go smoothly, you’ll stay on track with your notes, and your PowerPoint slides will work fine, but sometimes a mishap happens. Be ready to joke about it, rather than becoming flustered. If the computer fails and you lose your visuals, say something like, “Well, that’s a shame, I had some really great photos to show you!” If you drop your index cards or notes, or accidentally skip ahead in your presentation and then have to backtrack, make a joke: “Sorry about that, I was so excited to get to my next point that I’m afraid I lost control there for a moment!” Let your audience laugh with you—they’ll still be on your side, and you can defuse the incident and move on without becoming more nervous.
Step 6: Deliver the Presentation
Be sure to get enough sleep and eat a healthy breakfast. Don’t drink too much caffeine or else you’ll become hyper and nervous. Wear your favorite—and appropriate—clothing and comfortable shoes.
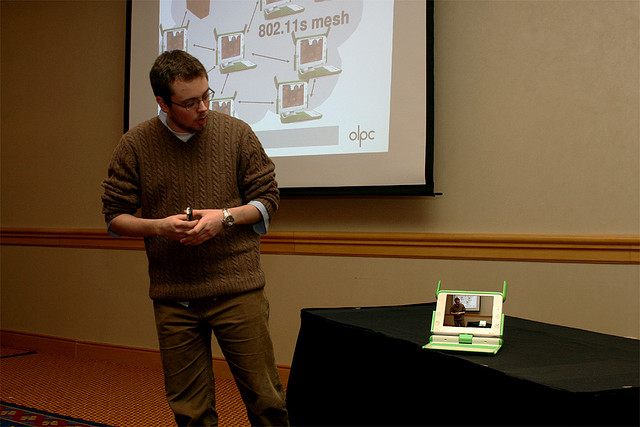

You may use computerized visual aids when you give a presentation to a class.
John Haynes Photography – OLPC – CC BY-ND 2.0.
Remember, your audience is on your side! If you’re still nervous before your turn, take a few deep breaths. Rehearse your opening lines in your mind. Smile as you move to the front of the room, looking at your audience. You’ll see some friendly faces smiling back encouragingly. As you start the presentation, move your eyes among those giving you a warm reception—and if you see some student looking bored or doing something else, just ignore them. But don’t focus on any one person in the audience for too long, which could make them nervous or cause them to look away.
Don’t keep looking at your watch or a clock: If your rehearsal times were close to your assigned time, your presentation will be also. If you do notice that you’re running behind schedule, it may be that you’re saying too much out of nervousness. Use your notes to get back on track and keep the pace moving. But it’s better to deliver your presentation naturally and fluidly and be a bit long or short than to try to change your words and end up sounding unnatural.
At the closing, deliver your last line with confidence, sweeping your eyes over the audience. If appropriate, ask if there are any questions. When you’re done, pause, smile, say “Thank you,” and walk back to your seat.
Later on, ask other students and your instructor for comments. Be open minded—don’t just ask for praise. If you hear a suggestion for improvement, file that in your memory for next time.
Group Presentations
You may be assigned to give a presentation in a small group. The six-step process discussed previously works for group presentations, too, although group dynamics often call for additional planning and shared responsibilities:
- Schedule a group meeting as soon as possible to get started. Don’t let another student put things off. Explain that you’re too busy and won’t have time at the last minute.
- Begin by analyzing your audience and your goals together as a group to make sure everyone understands the assignment the same. Discuss who should do what. While everyone should talk about what content to include, from here onward, you will take on specialized roles. One or more may begin research and gathering information. Others who are good writers may volunteer to draft the presentation, while one or more others may develop the visual aids. Those who have public speaking experience may volunteer to do all or most of the speaking (unless the assignment requires everyone to have a speaking role). You also need a team leader to keep everyone on schedule, organize meetings, and so on. The best team leader is an even-tempered student with good social skills, who can motivate everyone to cooperate.
- Steps 2 and 3 can likely be carried out individually with assigned tasks, but group members should stay in touch. For example, the person developing the visuals should be talking to those doing the researching and drafting to see what visuals are needed and get started finding or creating them.
- Before preparing notes in step 4, meet again to go over the content and plan for visuals. Everyone should be comfortable with the plan so far. Make final decisions about who will do each section of the presentation. Set the time for each segment. Then speakers should prepare their own speaking notes. Let someone with strong speaking skills open or close the presentation (or both), with others doing the other parts.
- The whole group should be present for practice sessions in step 5, even if not everyone is speaking. Those not speaking should take notes and give feedback. If one student is doing most of the presenting, an alternate should be chosen in case the first choice is sick on the scheduled day. The alternate also needs to practice.
- During the delivery, especially if using technology for visual aids, one student should manage the visuals while others do the presenting. If several students present different segments, plan the transition from one to another so that the presentation keeps flowing without pauses.
Additional Resources
For Class Presentations
Using PowerPoint. A step-by-step illustrated tutorial for learning how to create effective visual presentations with PowerPoint. https://www.baruch.cuny.edu/tutorials/powerpoint/
“How to Give a Bad Talk.” A humorous look (with some very good advice) on what not to do when preparing for and giving a class presentation. http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~pattrsn/talks/BadTalk.pdf
Class presentations on YouTube. Search YouTube with the phrase “class presentation” and look for video examples of actual students giving class presentations. Observing and critiquing the presentations of other students are good ways to get started preparing your own and learning from others. Here’s a good example of a student group presentation on a topic we can all relate to (how body language works):
In this presentation, take note of
- how students make good eye contact with the audience;
- the first student’s natural speaking voice and tone, and how she did not have to use her note cards very often (obviously she practiced well);
- some differences among these students;
- the use of PowerPoint slides within the presentation (some better than others);
- the appropriate occasional use of humor;
- the division of presentation responsibilities within the student group;
- each presenter’s interaction with the audience.
Key Takeaways
- Public speaking skills are important because you will likely give presentations in class and perhaps in a future job.
- Overcome anxiety about public speaking by understanding your feelings, preparing well and practicing your delivery, and focusing on your subject.
Follow a six-step process to prepare and deliver a presentation:
- Deliver the presentation and seek feedback
- Use visual aids to support a presentation, creating visuals that are relevant, attractive, and powerful.
- The success of a group presentation depends on effective group meetings, successful division of roles, and repeated group practices.
Checkpoint Exercises
If you have given a class presentation in the past, what worked best for you? (If you have not given a presentation yet as a student, what aspect do you think will be most difficult for you?)
__________________________________________________________________
Name the two most important things you can do to reduce anxiety about a class presentation you will have to give.
For each of the following statements about class presentations, circle T for true or F for false:
Describe how best to use body language (facial expressions, eye movements, gestures, etc.) when giving a presentation.
If you were assigned along with three other students to give a group presentation in the class using this textbook, what would be your preferred role in the preparation stages? Your least preferred role? If you had to take your least preferred role, what single thing would you want to work hardest on to make the presentation successful?
College Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Give an Excellent Presentation (College Students)
Last Updated: March 3, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 86% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 128,741 times.
College seminars are conducted to test the presentation skills of a student or a group and also allow the student to convey their knowledge to the audience. When students don't come prepared, the presentation may become disorganized, unclear, and dull. It would make them confused during the presentation and lead to vague answers during the questionnaires.

- Think of your main topic and break it down into 3 specific ideas. This will help you to focus your discussion and remain clear. Keep the 3 ideas simple and have them in your mind. Write out your main points, then picture what you're talking about so you can visualize what you're going to talk about.
- To help you create the "soft humor," don't take yourself too seriously. Second, identify the fears and insecurities around the topic so you can address these in a way that shows we all have these fears, insecurities and taboos and that our feelings are normal. This helps keep you in the moment and present with the audience and allows you to recognize the reality of the effect of your topic on yourself and the audience.
- Tell the audience you're excited about what you're talking about. This can make your excited mood infectious and lead them to be willing to come on this journey with you.

- You could try doing something fun, like bringing with you a relevant object, doing a magic trick or a dance move to take things out of the ordinary and add some life to your talk.
- Another fun approach is to try a meditation and ask the audience to relax - feel your toes relax, your feet, etc.
- If you want the audience to move around, don't hesitate to ask. Ask them to stand up and stretch, to shake hands with the person next to them, or to do a twirl on the spot.
- You could try asking the audience to say a bunch of affirmations out loud with you, to get them caught up in the mood you're creating and help them to see its relevance to them too.

- You can ask the audience to imagine something along with you, asking them to close their eyes and think about something with you, then resume with eye contact following this.

What Is The Best Way To Start a Presentation?
Community Q&A
- Take 10 belly breaths if you have last minute stage fright. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Use images in your slides. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Come early to the venue where you will be presenting. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Answer the questions asked after the presentation. Do not divert or change the topic. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://education.seattlepi.com/give-good-speech-presentations-college-1147.html
- ↑ https://www.princeton.edu/~archss/webpdfs08/BaharMartonosi.pdf
About this article

Reader Success Stories
Mohammad Shamshad
Oct 8, 2016
Did this article help you?
Sandip Kulkarni
Apr 2, 2019
Robbin Singh
Sep 19, 2016
Nandini Soni
Mar 16, 2016

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
50 Creative Ideas to Nail Your College Presentation

We’d be willing to bet that most college students enjoy presentations about as much as they like their 7am class. Whether they’re designing them, or in the audience, there are likely a million and one things they’d rather be doing (like napping in their dorm room). In fact, 79% will say that most presentations today suck. And 35% of millennials say that they will only engage with content they feel has a great story or theme. With a reputation like that, it’s no wonder students avoid presentations at all costs.
As a result, many will end up procrastinating, losing sleep over choosing a topic, and piecing a deck together at the last minute. According to research, 47% of presenters put in more than eight hours into designing their presentations. You do the math. Eight hours at the eleventh hour equals an all-nighter.
Luckily, that doesn’t mean the final product has to be a poorly thought-out frankendeck.
Creative presentation ideas for college students
A lot can ride on a class presentation. It might be your last project at the end of the semester that determines the fate of your final grade, or maybe it’s a group project that counts for half of your participation in the class. Whatever the stakes are, we’re here to help you nail your next college presentation.

Pick the right topic
Before committing to your topics for presentations in college, you should consider things like what excites you, what you’re knowledgeable in and what you’d be interested in learning more about, books or movies that inspire you, world events, buzz-worthy pop culture, and what topics relate to your class course. How can you apply these things to your next class presentation?
You’re in college, so it’s very likely that your classmates will be sleeping, or staring out the window, while you’re presenting at the front of the room. To keep them engaged, make it interesting with these unique college presentation ideas.
College presentation ideas
- The evolution of a specific product— like the cell phone
- A presentation on your favorite celebrity
- A history of the most influential presidents of the United States
- How modern medicine is made
- The highest paid [BLANK] in 2021
- A how-to presentation on something you’re passionate about— like building cars
- A book that you think should be made into a movie (and why)
- Your favorite cultural recipe
- Who built the Sphinx of Egypt
- Social media now and then
- Shakespeare’s hits and misses
- Debunking a conspiracy theory
- Unexpected traditions
- Who invented the SAT, and what is it?
- The most popular travel destinations for young adults in their 20s
- What is van life anyway?
- How is education different now than it was in the ‘70s
- How to live a more sustainable life
- The evolution of humans
- The history of the Internet
- Is organic really better?
- How to get the most out of an internship
- What employers are actually looking for on your resume, and how to write one
- Everything you need to know about global warming
- The top places with the most expensive cost of living in the United States
- The rise of TikTok
- What is influencer marketing and why is it so important?
- Classic movies that should be cancelled in 2021, and why
- Is eating vegan really better for your health?
- Are aliens real?
- Everything you need to know about the Big Bang Theory
- Why streaming services are the demise of classic cable
- Marijuana then and now: the process of getting it legalized
- 15 Memorable things about [blank]
- A comprehensive timeline of feminism
- Is print— newspapers, magazines, books— dead?
- The easiest foreign language to learn on your own
- The best life hacks I learned on TikTok
- What does white privilege mean to millennials and Generation Z?
- Understanding finance for young adults 101
- Everything you need to know about life after college
- The difference between electric cars and gas cars
- What is artificial intelligence anyway?
- How thrifting can help the environment
- The evolution of presentations: from caveman to TedTalks
- Applying your degree in real life
- The origins of your favorite music genre
- Everything you need to about becoming a surgeon
- The life cycle of [blank]
- Life without technology: where would we be without modern technology?
Make it beautiful
You have your topic, now what? Did you wait until the absolute last second to get started? Here’s the good news: no need for an all-nighter. Beautiful.ai can help you nail your college presentation in a pinch. The ease of use, and intuitive controls, help you create something brilliant in minutes, not hours. Start inspired with our inspiration gallery of pre-built templates and customize them to fit your content.
It’s important to connect with your audience on an emotional level, so make sure to pick trendy colors, modern fonts, and high-quality visual assets to compliment your presentation and evoke emotion. Engage your audience (especially your professor) with dynamic animations, or videos, to help control the narrative and direct their attention to the key takeaways.
Pro tip: use the shareable link to share your deck out with classmates, teachers, or social media friends after class.

Jordan Turner
Jordan is a Bay Area writer, social media manager, and content strategist.
Recommended Articles
How to rock your next executive presentation, up-level your presentation in minutes with visual aids, the ultimate guide to sales and creating winning sales presentations, how presentations can help in the face of economic uncertainty.
How to Make a Google Slides Presentation for College
Want to make your college presentation stand out from the rest? Here are some tips for making a professional presentation in Google Slides.
Presentation assignments help you build your speaking skills. They can help you conquer your fear of public speaking, too. If you use Google Slides, it’s easy to set up a college presentation.
First, we’ll go over how to use Google Slides’ five basic features to create your presentation. After that, you’ll find three key tips to make your presentation great.
Creating a College Presentation in Google Slides
The five key features of Google Slides are the Templates, Themes, Layouts, Add-Ons, and Presenter View.
1. Choose a Template
Google Slides comes with lots of premade templates. You can use them to save time designing each slide. View Google’s included templates by clicking Template Gallery on the Slides homepage.
You can also find useful Google Slides templates around the web . Try to find a template that matches your presentation’s goal. For instance, a sales pitch template will work as an argument or business plan.
Once you find a good template, click its name at the top left to change it. Next, save it to use again in the future.
To save a copy, go to File > Make a Copy > Entire Presentation . Give the copy a generic name, like Marketing Presentation , and save it to your Drive. This gives you a clean copy to make future presentations from.
It’s a good idea to save a handful of templates this way. Look at your course outlines to see what kinds you will need.
2. Share With Teammates
If you are presenting as part of a group, go to the Share button at the top-right to get a link for your classmates. Be sure that permissions are set to Anyone with the link and Editor . This way, your team members can join with a single click.
You can also give access using an email. Click on Add people and groups , and either type in or select your groupmates’ email addresses. You can share your Slides to non-Gmail accounts , too.
3. Select a Theme
On the right-hand side, you will see several Themes available. Themes put a fresh look on an old template. Select an appropriate theme for your project. Try to find one you have not used for that class before.
Depending on the template, you might need to make some changes after changing the theme. For instance, you might have to move text that overlaps with the new border. You may also need to change the font color if it’s hard to read on the new background.
To move an element, click and drag. To change colors, select the text or graphic, then choose a new color from the context menu.
4. Choose Slide Layouts
Right-click a slide and select Apply Layout to see the options. The best ones to use are Title Only , One-column text , and Big Number . These options leave plenty of room for graphics. They help you avoid crowded slides that are hard to read.
You don’t need Main Point slides if the section is only one or two slides long. For longer sections, Main Point slides let you review the section's contents. But slides that only stay up long enough to state the title will break the flow of your presentation.
5. Use Add-Ons to Improve the Visuals
You can make good use of Google Slides Add-Ons to import special elements. They let you add flow charts, math formulas, and convert images into slides.
Take a moment to install add-ons for all the graphics design software you use. Slides should always rely more on graphics than text, so the more options you have, the better.
6. Practice in Presenter View
You can find Presenter View by clicking the dropdown arrow on the Slideshow setting. It's in the top-right corner of the screen. Presenter View allows you to see the current slide, a preview of the next one, and your notes. At the same time, it sends the slide to display elsewhere.
You can even view the notes on your phone while you present. However, in some settings, using a personal phone looks unprofessional. Talk with your professor about expectations. You may also be able to use or borrow a tablet for the presentation.
Presenter View also includes a timer at the top-left. Practicing in this mode lets you get an accurate idea of how long each slide takes. This helps you adjust the timing as you present. You can notice when you need to save time by summarizing, and when you can slow down for more detail.
Tips for a Great Presentation
Now that your slide structure is in place, it’s time to start designing the slides.
1. Use the Notes Panel
Audiences can’t listen and read at the same time. If the slides and speaking are the same, you force the audience to ignore half of your presentation. Instead, use the Notes panel at the bottom of the screen to organize what you will say.
You can click and drag on the panel’s border to give yourself more space. Use bulleted lists and bolding, so you can read at a glance.
You can't make eye contact with the audience if you are reading notes. So instead of a read-aloud script, use the notes as reminders. Use shorthand and keywords instead of full sentences.
2. Focus on the Graphics
Your speaking is the most important part of the presentation, so reduce the text by as much as possible. Instead, use graphics to help the audience understand and remember your main points.
If you’re presenting numbers, adding a chart from Google Sheets can help the audience visualize them. You can also use photos to create a visual reference. For instance, if you talk about a brand, showing the logo can help the audience remember it.
You can find lots of graphic options in the Insert menu. You can also import them from another site using an Add-On . Once you’ve added a chart, click its top-right corner to open the menu. Then select View Source to change the data in Google Sheets.
Try to choose high-resolution images that look good with your theme colors. All slides should have more graphics and blank space than text. Text size should be at least 24, to make sure people can read it from far away.
3. Practice Makes Perfect
In the end, the essential part of a presentation isn’t the slides; it’s how you present them. Therefore, practicing several times is critical. Smooth flow and speaker confidence are usually worth a lot of marks, and practice is the only way to improve them.
When you practice, act as if it's the real thing. Stand at the front of the room, and make eye contact with your practice audience. If possible, try to practice in the same room that you will present.
It can be hard to practice with no audience. If you are giving a solo presentation, offer to practice with classmates. You can give each other constructive criticism. If you can’t find any people, practice speaking to a rubber duck. Even a toy with a face is better than an empty room.
Ace Your Presentations With Google Slides
Using Google Slides, you can put an “A+” presentation together in no time. Then, you can use themes, layouts, and other features to fill them in.
It’s important to focus on your speaking skills. A good speaker should know how to engage their audience. Getting them involved with some interactive segments is a great way to do that.

7 Best Tips to Ace Presentations in College
Are you nervous about presentations in college ? Maybe you have a huge presentation coming up and you’re worried about your presentation skills.
First, just know, you’ll be fine and you’re gonna do great! You want to know why??
Because this post gives you 7 of my best tips to ace your next college presentation , from someone who hated giving presentations in college but aced them every time!
This post may contain affiliate links, which means we may receive a commission, at no extra cost to you, if you make a purchase through a link. Please see our full disclosure for further information.

Presentations are a huge part of your college courses! No matter what major or field you’re studying, you’ll always have to deliver some sort of presentation.
And crazy enough, presentations aren’t just busy work in college. Once you enter your career, you’ll still be expected to give presentations in some way or another.
That’s why it’s so important for you to work on your presentation skills while in college! Honestly, it should be one of the first skills you work on during your freshman year .
Here’s A Gem: If you want to really up your presentation skills game, take a public speaking or debate class ! That was how I was really able to utilize each one of these tips to become a better presenter.
Related: 77 Insanely Funny Debate Topics for College Students
Ready to ace your next presentation?
Read on for seven tips to ace presentations in college!
Want to get an A on your next test?
Chegg will help you easily ace your courses!
- Rent your textbooks (for cheaper than on campus)
- Solve math problems in seconds
- Get instant help with your papers (no more trying to figure out MLA!)
- FREE DoorDash Student membership (goodbye delivery fees!)
Click here to sign up for their writing help free trial while the deal lasts!
Do You Have To Do Presentations In College?
Yes, you have to do presentations in college . I know that’s not what you want to hear, but truthfully there’s no way around it. Every major has some sort of presentation as a part of your college classes.
Even though all majors have presentations, some majors have far less than others. If you’re majoring in something like math or the sciences, you probably won’t spend too much time doing presentations.
But if you’re getting a degree in the College of Arts, or majoring in an area like communication, history, or psychology, then buckle up my friend! You will spend a lot of time creating and delivering presentations in college.
( and probably doing papers too! I love this writing tool for helping me write the best papers in my classes)
The upside is that this is great preparation for your future career! For example, if you’re majoring in something like marketing, presentations in college are a great way to practice for your future career, where you’ll probably have to do public presentations to a group of people in your office, department, or industry.
Get My Mega List of Student Discounts!
I saved hundreds of dollars in college just by using student discounts at my favorite stores. Get the FREE list so you can too!
You can unsubscribe anytime. For more details, review our Privacy Policy.
Opt in to receive news and updates.
You Got It!
The Mega List should land in your email shortly!
How Often Do You Do Presentations In College?
How often you do presentations in college depends on a few different factors like your college, major, class curriculum, professor, and more. Generally speaking, if you’re in a major that requires excellent communication skills, like communication, business, finance, etc. then you’ll probably have at least 1 presentation assignment per class.
Let’s do the math real quick.
If you are a full-time student taking 5 classes per semester and each class has 1 presentation assignment, that roughly equals 5 presentations per semester or 10 presentations per academic year.
But again this is all dependent on a ton of different factors, so you may do less or more presentations based on your specific circumstances.
Pro Tip: If you hate public speaking or are really bad at it, you’ll want to choose your major carefully! If you choose a major with lots of presentation expectations you’ll either need to use these tips to get better or go with another major that doesn’t require so many presentations.
My major was in communications, so I did more presentations than 1 per class.
(I usually had to do 1 small presentation that wasn’t a huge deal and 1 big presentation for finals with most of my major classes)
Tip 1: You’re the Expert
Delivering a good presentation is much easier if you know exactly what you’re talking about! Before you assume your position before the audience, you must become an expert on the topic.
To reach that level, follow these two steps:
Preparation is the KEY to a successful and effective presentation (and a good grade!)
You will need to research and prepare your topic and presentation structure well. The goal is for you to know exactly what to say within each section of your presentation.
Here’s some areas you’ll need to think about:
- Make sure you are comfortable with whatever platform you are using to deliver your presentation slides. (Most students use either PowerPoint, Canva , or Google Slides)
- Prepare well for the Q&A section. Write down some possible questions your audience could ask and have some answers to you won’t be caught off guard.
Remember, do not wait until the last minute to start preparing!
Confidence in your presentation skills comes from practice!
Yes, practicing might be boring, but more practice means better performance. For solo presentations, try practicing in front of a mirror. Better yet, practice in front of family or friends to foresee the reaction of your audience. That way, you can assess your intonation and body language.
(I used to practice in my car or sometimes even recorded myself and listened to it on the campus bus)
If you’re doing group presentations, schedule practice sessions a few days before the actual presentation day so you all can work out the kinks and feel ready as a team!
Tip 2: Manage Your Time
College presentations usually have a time limit (can range from anywhere to 5-45 mins) .
Give yourself plenty of time to get through the material and have time left for questions at the end. Make sure you don’t go beyond your allocated time. You might risk losing your audience or it could negatively affect your grade.
Here are some excellent guidelines to help you manage your time during a presentation:
- Wear a watch during the presentation to keep check of your time.
- Dedicate 2-3 minutes to each slide.
- Don’t use “transitions” between slides.
- Write a notes script for yourself with key points that you have to touch on for each slide.
Using these tips will help you limit rambling and keep good watch of your timing during the presentation.
Tip 3: One Image Is Worth a Thousand Words
Use graphics instead of wordy slides!
Images can express ideas and capture attention a lot faster than words. Besides, they totally make your presentation more interesting and engaging.
Let the audience see only images that you explain. That makes you seem like someone who doesn’t need help to remember the subject matter. You can even add video clips for more interaction or memes if they relate to your topic and audience.
Another important thing here is not to read the information off the slides. If you use bulky slides, you fall into trouble.
For starters, you’ll find yourself reading automatically, which makes you seem unprepared. In addition, your audience will also read the slides. You’ll end up losing their attention since they’ll be reading and not listening to you.
The big point here is to avoid putting lots of words on your slides.
If you need help remembering the content, create a cheat sheet for yourself with bullet points to remind you of the content.
Here’s A Gem: For online presentations, use a split screen! Have one screen for your notes, and another to see the slides and audience.
Tip 4: Make It Interactive
The key to giving a great presentation is to captivate your audience, so you must try to get the audience members involved!
If you keep the people busy, they’ll listen to you and learn something new, and you won’t end up with sleepy faces all around. (you know the one where people are staring at you but you know they’re not listening)
Luckily, there are several ways to captivate your audience. For instance:
- Maintain eye contact
- Ask questions
- Tell anecdotes and add specific situations to tell a story if you can
- Personalize the information you provide
- Don’t pack your presentation with big words or fancy jargon- keep it clear and simple
Tip 5: Feel Free to Improvise
You don’t have to memorize everything!
(Wooo, are you feeling better after hearing that?!)
No one knows what you’re planning to say. So if you forget something… improvise.
Skip parts, add sentences, or change the order of your lines. That’s totally okay! What you want to avoid is stuttering or having long silences within your speech. Those can make you look unprepared and unconfident.
I love to add some improvisation because it makes your presentation interesting and unexpected. That little nuances really help you capture your audience and gain their attention.
Tip 6:Use Strong Body Language
Body language is super important for your presentations especially if you’re doing in-class presentations vs. a virtual presentation.
If this is your first time doing a presentation in college, it can totally be nerve-racking being at the front of the class with all eyes on you, especially if you have stage fright. Look I get it, presentations get you out of your comfort zone.
That’s why it’s so important to practice, practice, practice!
Practicing your body language is an easy way for you to instantly feel more comfortable. It adds a lot to your work by showcasing your confidence, knowledge, and style. The most important thing you want to make sure of is that you’re comfortable and confident in your knowledge.
- Start strong with the right posture. Don’t droop your shoulders or lower your head.
- Maintain good eye contact with your audience. Find a focal point and use that when you’re speaking (like a wall clock!)
- Use your hands to give dramatic effects when you speak. Don’t keep your hands in your pockets. It can make you look nervous.
Nervous Habits
Avoid nervous habits like nail biting or rocking back and forth. These can be distracting for your audience.
To overcome nervousness , try these steps:
- Take a deep breath and scan your audience.
- Look for a friendly face with a warm smile to make it your focal point.
- Smile to your audience and show confidence.
- Joke about your nervousness.
Your voice plays a crucial role in the presentation. You want to sound natural and confident. A lot of mistakes college students make is trying to sound like someone they are not during a presentation.
Don’t put on this “fake voice” to sound confident! Use professional language and be yourself!
Tip 7: Employ the Rule of Three
In his book Rhetoric, Aristotle states that people tend to remember three things only out of every speech. Do you know how to use the rule of three for your benefit? Here’s a few key points:
Three Takeaways
Know the three most important takeaways in your presentation!
Make a short list of these three main points of information that you want your audience to remember. Repeat them in every section of your presentation naturally as it fits the flow of your content.
Three Sections
Divide your presentation into three main sections: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
Your introduction is by far the most important part of your presentation. A killer opening can captivate your audience longer than you’d expect!
Use a catchy introduction to hook your audience. For example, you can begin with:
- A joke
Before You Go
Now that you got all the secret sauce to rock your presentations in college, here’s another set of tips you need!
Did you know I have 7 secrets for how to survive your 8am classes in college?
Well now you do! Check out this post for all the GEMs I’m spilling for surviving your dreaded 8am’s!
Click here to read 7 Secrets to Survive 8am Classes in College !
This post was about presentations in college .
Check Out More College Tips:
- 77 Insanely Funny Debate Topics For College Students
- How to Poop In College: Student’s Guide to Peaceful Pooping On Campus
- How to Get Free College Shirts (5 Easy Ways)
Jordan is the creator behind The College Gems, bringing a wealth of experience from her background in student affairs throughout the higher education space. Dedicated to helping students thrive, she combines her academic expertise and personal journey to offer advice that help college students and parents thrive throughout their college journey.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
- Twin Cities
- Campus Today
- Directories
University of Minnesota Crookston
- Mission, Vision & Values
- Campus Directory
- Campus Maps/Directions
- Transportation and Lodging
- Crookston Community
- Chancellor's Office
- Quick Facts
- Tuition & Costs
- Institutional Effectiveness
- Organizational Chart
- Accreditation
- Strategic Planning
- Awards and Recognition
- Policies & Procedures
- Campus Reporting
- Public Safety
- Admissions Home
- First Year Student
- Transfer Student
- Online Student
- International Student
- Military Veteran Student
- PSEO Student
- More Student Types...
- Financial Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Request Info
- Visit Campus
- Admitted Students
- Majors, Minors & Programs
- Agriculture and Natural Resources
- Humanities, Social Sciences, and Education
- Math, Science and Technology
- Teacher Education Unit
- Class Schedules & Registration
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Organizations
- Events Calendar
- Student Activities
- Outdoor Equipment Rental
- Intramural & Club Sports
- Wellness Center
- Golden Eagle Athletics
- Health Services
- Career Services
- Counseling Services
- Success Center/Tutoring
- Computer Help Desk
- Scholarships & Aid
- Eagle's Essentials Pantry
- Transportation
- Dining Options
- Residential Life
- Safety & Security
- Crookston & NW Minnesota
- Important Dates & Deadlines
- Cross Country
- Equestrian - Jumping Seat
- Equestrian - Western
- Teambackers
- Campus News
- Student Dates & Deadlines
- Social Media
- Publications & Archives
- Summer Camps
- Alumni/Donor Awards
- Alumni and Donor Relations

Writing Center
Effective presentations checklist, create a shared meaning between the you, the speaker, and your audience.
Having the knowledge and skills to effectively design and deliver a dynamic presentation is essential in the academic and professional world, regardless of field. Most colleges and universities require students to complete a public speaking course. In addition, many large organizations send employees to training course to develop their skills in this area. Why is it so important for college students and employees to be effective in this context?
The bottom line is that presentations are used to create a shared meaning between the speaker and the audience. Whether it is to inform peers of the results of your course project, communicate changes in the organization, provide updates on projects to your boss and co-workers, persuade the organization to invest in new technology, convince the city council to reduce waste, or recognize the accomplishments of a valued employee, the goal of a presentation needs to be accomplished. By using strategic design and delivery techniques, you increase your chances of accomplishing your goal. In addition, your successful efforts will leave others with a positive impression of your communication and leadership skills.
While there are a tremendous number of resources available on the internet to assist individuals wanting to increase the effectiveness of their presentations, the following checklist provides the basic things you should consider. This checklist contains items that are included within UMN Crookston’s Public Speaking course (SPCH 1101).
1. What are the logistical considerations/constraints of the speaking event?
If you don’t know the answers to the questions below, ask the person inviting you to speak. Although the following is not an exhaustive list, it may help you determine other questions you want to ask:
- What is the occasion/event that I’ll be speaking at (purpose)?
- Where is the presentation located?
- How many people will be in the audience?
- What is the start time for my presentation?
- How much time do I have to speak? Does that include time for questions?
- What should I wear?
- What type of presentation aid would you recommend for this audience
- What technology is available for me to use (screen, projector, computer, etc.)?
- If I have handouts, how many copies should I make?
- Will there be someone available to help if I need assistance with set-up, technology, etc.?
2. Know your audience.
The more you know about your audience, the more you can tailor your presentation to them, thus making it more relevant and increasing your likelihood of accomplishing your goal. If you don’t know the answers to the questions below, ask the person inviting you to speak. Although the following is not an exhaustive list, it may help you determine other questions you want to ask:
- Who will be in the audience (position, demographics, etc.)?
- How much to the audience know about the presentation topic?
- What is the audience’s overall attitude towards the topic?
3. What is the purpose of the presentation?
The answer to this question will help you determine how to organize your presentation as well as choose the appropriate content. If you don’t know the answers to the questions below, as the person inviting you to speak. Although the following is not an exhaustive list, it may help you determine other questions you want to ask:
- Is the purpose to inform the audience?
- Is the purpose to persuade the audience?
- Is the purpose to deliver a presentation at a special occasion (toast, recognition, award, etc.)?
- Do you have suggestions on what content the presentation should contain?
4. Create a speaking outline with appropriate content.
Creating an outline will help you gather your thoughts and put structure of the content you want to deliver. If your presentation is not organized your audience may have difficulty understanding your content, and you will be less likely to accomplish your goal. Remember that audience members will not have a written manuscript to refer to if they get lost during your presentation. Based on the purpose, constraints, and audience of your presentation, consider including the following items:
Introduction:
- Attention catcher – get their attention with a statement, quote, startling statistic, story, etc.
- Speaker credibility – tell the audience why you are credible to speak on this topic (education experience, interest, etc.).
- Listener relevance statement – tell the audience why this topic is important to them.
- Thesis statement – tell the audience what your presentation is about and what you are trying to accomplish.
- Main points and sub-points – each main point should include information that supports the thesis.
- You may want to include research to support your efforts. If you do include outside research, you need to orally cite it in order to enhance your credibility and give credit to the original sources.
- Each main point should be balanced: i.e. you should spend roughly the same amount of time on each main point.
- Between your main points, you should include transitions that help the listeners understand how the ideas relate to one another.
Conclusion:
- Thesis restatement – remind the audience of your presentation topic and purpose.
- Main point review – remind the audience of your main points (in the order in which they appeared in your presentation).
- Clincher statement – leave the audience with something to think about regarding your presentation.
5. Effectively deliver your presentation.
Along with content and structure, delivery can either enhance or detract from achieving your goal. We have all attended presentations in which the presenter’s delivery style either enhanced our learning or was so distracting that we stopped listening. The following lists several basic things to consider when delivering your presentation:
- Wear appropriate and comfortable clothing.
- Maintain good eye contact with your audience during at least 90% of your presentation.
- Use the space provided – don’t just stand in one spot.
- Use hand gestures that are appropriate.
- Use your voice and facial expressions.
- Portray confidence.
- Smile when appropriate.
- Eliminate distracting behaviors (repetitive gestures, chewing gum, verbal tics, etc.).
- Don’t just read your speech off of your paper, outline, or note cards; speak in a conversational style.
- Face the audience and not the screen.
- Don’t read off the screen.
- Ensure that your slideshow is visually pleasing – easy to read with few distracting elements.
- Ensure that your slideshow is free from errors.
6. Practice, practice, practice.
An important component of effective presentation delivery is practice. Determine the practice method that works best for you (in front of a mirror, in front of a friend, in the room where you will be delivering your presentation, etc.). Consider practicing several days before delivering your presentation. The more you practice, the more confident you will be with your content, organization, and delivery methods.
7. Dealing with speech anxiety.
Almost everyone experiences some level of speech anxiety when delivering a presentation. Effective presenters are those who use that energy to help them in their efforts. Consider the following when managing your speech anxiety before and/or during your presentation:
- Practice helps lessen speech anxiety.
- Don’t let negative self-talk undermine your efforts. Instead, turn those negative messages – like “I’m going to embarrass myself” or “I’m going to fall” – into positive messages – like “I’m going to be successful” and “I am poised and self-confident.
- Visualize your success.
- Remember to breathe.
- Pretend you’re confident.
- Remember that your audience wants you to be successful.
- Drink water prior to delivering your presentation to avoid a dry mouth/throat.
- Remember that the audience will likely not notice your anxiety.
Whether you are a college student or a working professional, this checklist outlines basic strategies you should consider when designing and delivering an effective presentation. In addition to this checklist, you are encouraged to investigate the many resources and tools in the library and on the internet that can aid you in your efforts. Similar to other skills (athletics, singing, acting, canoeing, etc.), the more experience you have delivering presentations, the more effective you will be.
By Kevin D. Thompson, Ph.D. Last updated October 2016 by Allison Haas, M.A.

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

9 Easy Rules to Make a Good PowerPoint Presentation
Table of contents
- 1 How to Start an Excellent PowerPoint Presentation?
- 2 Tips On How To Make Your PowerPoint Presentation Perfect
- 3 9 Rules On How To Make A Great PowerPoint Presentation?
- 4 How to Make Your PPT Project Fast?
Today, regardless of whether you are in a school, college or university, a PowerPoint presentation is a common and widely-used method of engaging students and evaluating their knowledge and skills. This form of a multimedia project is multipurpose. With the help of a good PowerPoint presentation, a teacher or professor can not only make a lesson more interactive and engaging for the class, but also discover the knowledge and talents of his students. How to make a good PowerPoint presentation? Let's find out.
How to Start an Excellent PowerPoint Presentation?
Why do you have to do it? First, such projects are evaluated just like any other assignment, which means if you fail it, you get a low grade, and your overall academic performance drops. However, this is not the main reason. In addition, creating PowerPoint slides gives you many new useful skills and improve the ones you already have – you boost your critical thinking, research, and writing skills, not mentioning that you learn to use various techniques in your studies and gain some public speaking experience.
Thus, this task is useful in many different ways. Finally, it is fun! No one will argue that creating a PPT presentation is much more engaging and fun than writing a research paper of 10 or more pages! It is also a simple way to increase your grade. It is much easier to get an A for your presentation than to get a high grade for a thesis, which once more proves that this is a useful and important skill for all students.
How to make a great PowerPoint project? Although we have said that it is much easier than submitting a paper worthy of an A, you should not think that you will not come across certain challenges during this process. Keep in mind, that a good project delivers the necessary information to the audience, but the best PowerPoint presentations engage, impress, and stay in memory for a long time. Therefore, your main goal is to make it informative and interesting.
How to impress the class and your teacher? There are many factors that are going to influence the effectiveness and interest of your project, some of them are:
- High-quality content.
- Attractive visual files.
- Engaging files.
- Speaking confidence, etc.
There are many more PowerPoint tips to keep in mind. In this post, we will give you the top nine PowerPoint presentation tips that will definitely come in handy for every student or other people engaged in similar activities.
Tips On How To Make Your PowerPoint Presentation Perfect
How to make a good PowerPoint presentation for college? The process of making effective PowerPoint presentations is long and complicated. Luckily, we have tips and tricks that should help you with the outcome. Once you know these, you will see presentation slides as words, and you will develop your presentation skills in no time. At the same time, you can use these tips and tricks for any presentation, which is always a good idea. The design tips for effective PowerPoint presentation can make a massive difference with your grade. Hence, they are important and beneficial. Once you know these, you can start creating a PowerPoint presentation. Let’s see tips and tricks that have a huge effect on the PPT process and PPT results.
Simplify The Words In any Microsoft PowerPoint presentation, there are a few seconds time a person can see the slide. It should contain simple words and short ones, so a reader can get only the most valuable information. This is essential when working with PPT. A good PowerPoint presentation will be visible and easy to understand within seconds.
Avoid Using All Capital Letters It looks confusing and won’t be seen in a good PowerPoint presentation. This is actually one of the PowerPoint design tips that have a huge role in all of this. You can add images on each slide, but make sure they don't interfere with the text. As always, know your audience first.
Light Text and Dark Background As you can see, this is a simple tip that has a huge effect. You can use dark text and a light background. The goal is the same. It should make the text more visible, and it is more important than the background. Use this for all lines of text, mandatory bullet points, and also key phrases.
Don't Use Text Fly-Ins These will not improve your presentation skills. The effects are not very amusing when you are discussing business, and they are something most people have seen countless times. It is one of the tips and tricks that is simple but works well with all PPT presentations and has a huge effect on the outcome.
Use HD Images You should only use HD images. These will make your slides look better and more professional. They can make any presentation so much better and more appealing. Use the best images you can find. Keep in mind that you must not use low-quality images at any point.
Avoid Using Animations The situation here is the same as with text fly-ins. These animations will get old fast, and they don't contribute to the overall value of your presentation. Keep things simple and easy. This is the best thing you can do and works well with any presentation and with any purpose. Check out professional presentations, and you will see no animations.
Don't Flip Too Much Your presentation should have a decent number of slides, but not too many. If you flip too much, you will lose the focus and attention of the audience. Just add all the facts and data you need and nothing more.
9 Rules On How To Make A Great PowerPoint Presentation?
There are many nuances to consider. However, there is no reason to deny that a student has to adhere to a few important rules in order to create a winning project, so here we have gathered all these rules for you! They will help you rock your PPT presentation! Besides, these slide tips can also come in handy for those students who are wondering how to write an essay with Google Slides themes.
1. Show your creativity
This is the first thing to keep in mind! A PowerPoint project is not about making it “right” or “wrong” – it is about showing your personality, so let your creativity out and try to surprise everyone with your unique artistic vision.
2. Add high-quality media files
It is not a secret that 90% of PowerPoint presentation's success is by graphics. This is the main thing that will attract your audience's attention. Therefore, you should always use high-quality pictures and videos, not mentioning that all files have to be relevant to your topic and also engaging (consider adding some unusual and fun graphics).
3. Don’t overload it with animation
Without a doubt, nice-looking transitions and animations between your slides attract more attention, but they may also distract your audience. Try to keep it simple and classy.
4. Choose a good theme
A well-planned visual theme will help you make your slides look organic and harmonic. However, do not use templates. Using common templates removes your personal touch from the work, and it becomes too vanilla and won’t be memorable.
5. Avoid providing too much text or bullet lists
Why does it matter? The main idea of pay for PowerPoint presentation is simplicity! This type of project does not have to be overloaded with text – this will be your function as a speaker to share more information with the audience, while your slides only have to contain the main points! Therefore, minimize the amount of text.
6. Try to read less
Another thing that contributes to the success of your presentation is your confidence as a speaker, which is not shown if you are reading from the slides all the time. One of the most important tips for a PPT presentation is to stay confident and do not use a written paper to read the whole text from.
7. Use of charts and diagrams
This is something you should use! Often, charts and diagrams can highlight or explain the message you are trying to deliver much better than any text, but you have to use them carefully to avoid common mistakes as inappropriate size, lack of consistency, etc.
This is one of the most significant PowerPoint design tips! Although choosing fonts may not seem like a big problem, an inappropriate font can ruin the whole impression of your work! Choose fonts that will be easy to read and would look harmonious in your presentation.
9. Less is better
There is a rule that can help you make a perfect presentation – the 10/20/30 rule recommends you to include not more than 10 slides in your project, limit the time of presentation to a maximum of 20 minutes, and use minimum 30-point font size to make it easy to read. You won’t make a mistake if you follow this rule.

How to Make Your PPT Project Fast?
Where to get great PowerPoint presentations? If you are still not confident in your abilities after reading our PowerPoint guidelines, it’s okay, and it is also fine if you just don’t want to bother yourself with a time-consuming task like this. You can enlist the help of professional writers here at PapersOwl !
Our team is ready to do its best to prepare excellent PowerPoint slides for you on any presentation topics for college students and of any complexity, and we can also do it promptly – even within a day or less. Why should you buy PowerPoint presentations online from a professional? It gives you many benefits:
- You are avoiding common mistakes.
- You save time.
- You don’t have to work on an assignment that seems complicated or boring to you.
- You can hire a professional writer with an MA or Ph.D. degree to be assured of great results.
- You get a chance to boost your grades quickly and easily!
Another great news is that at PapersOwl, you can also use presentation writing services with college assignments on various subjects – therefore, by choosing PapersOwl once, you obtain a reliable friend for all times. We can tackle any task, and we guarantee that you will be satisfied!
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
A | Conducting and Presenting Research
Turning information into knowledge.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the difference between information and knowledge?
- What is information literacy?
- What are the steps to a good research study?
What Is the Difference between Information and Knowledge?
Life is a series of problems needing solutions. We need to find information that matters and then discover why it matters. Curiosity, then, is a response to an environment of exploration, manifesting in wanting to know “why” or “how.” How do you make sense of the world? How does information translate to knowledge? Connecting ideas, thinking critically, acting responsibly, and communicating effectively are all essential to lifelong learning and active engagement in today’s world. You need to become proficient, ethical users and producers of information in a globally connected world. It is important to be able to reason, manage resources, work productively with others, acquire and evaluate information effectively, organize information, interpret and communicate the information, and work with an ever-evolving variety of technologies. In other words, you need to become information-savvy consumers and producers. You need to be able to adapt to, understand, evaluate, and make use of technology so you can be citizens that shape our society, rather than being its pawns. What you learn is often what you will want to communicate to others.
What Is Information Literacy?
Human beings are passionate, curious, and always seeking to connect with each other and make sense of things. Learning is more effective when new information is meaningful and linked to some personal experience or prior knowledge. Learning is about both context and content. It is necessary to learn how to assess, evaluate, and connect in order to make information become knowledge. Information literacy skills are the hallmark of the ability to do research. What is important is for you to learn how to find information that “matters” and then figure out why it might matter.
Information literacy is a link between the life experiences of you as a student, the academic world of scholarship, and the postcollege real world of application of learning. An information-literate person has the ability to ask questions and knows the difference between ignorance and understanding. (When do I need information?) Information literacy builds a lifelong ability to determine where information is kept (Where is the best place to find this?) and in what forms knowledge is stored (Which knowledge products will likely have what I need?).
Information literacy relies on the use of a critical mind to discern credible from not credible, valid from not valid. It is actually the core of the first-year experience. It lasts, while the specifics of particular courses fade over time. After all, the nature of research, the core of higher education, is a learning process: “How do I learn about something?” Communication skills are essential to your ability to both learn and share what you’ve learned.
What Are the Steps to a Good Research Study?
Research is a part of life. In fact, you conduct research daily. You look things up whenever you want a hotel or a good restaurant in a new city, or a recipe for cookies you’d like to make for a party. Sometimes you use Google for answers, and other times you ask people to help you answer your question. At times you might need to visit specific websites to find good information on the kind of used car you should buy or tickets to a sporting event or concert you hope to attend. All of this is part of research at its most basic level—asking a question and then answering it. Research can be defined as an activity that produces new knowledge. However, it is not timeless. Questions change, and so do answers. New questions bring new light to bear on any topic or issue. For example, consider the way we have controlled the use of pesticides. Over time, we moved from acceptance to shock and now horror at some of the side effects. It is new information on pesticides that has influenced our change in thinking. And the reason we know this information is that someone did the research and then communicated it to our community through newscasts, newspapers, online sites, and so forth.
We often accept ideas as fact. For instance, how do we come to believe such things as “Three out of four dentists recommend . . . ” or “McDonald’s french fries are preferred three to one over . . .”? Or that heroin is addictive, or that putting infants in car seats prevents fatal injuries, or that drinking while pregnant can be harmful? It is important to know that these statements are the result of questions that led to serious research. Understanding the methods used to do research will help us understand how we come to know what we know. In cases such as these, someone was interested in knowing the answer to a particular question, planned a research study, and then published the findings. When people do this kind of research, their purpose is not only to find an answer but also to communicate what they found to the rest of us. They are communicating new knowledge.
Research is exploration and the search for possible answers to questions. Most students think research is about finding answers, but it is more about the questions we ask that lead us to the answers. Good research starts with good questions. Researchers ask themselves a question, create a possible answer in the form of a hypothesis, and then begin a process of gathering information with a methodology. If we understand how important questions are to doing research, we are then better able to determine the credibility and validity of the information sources we use. When evaluating sources, we can ask: Why should I believe this author? What does she know that makes her someone I should pay attention to? And when deciding on credibility, we can ask: What did the author do to convince me his answer is the correct one? Did the evidence really match the question the author was asking? Thus, information literacy is the ability to evaluate sources on the basis of what questions were asked, determine if those are the best questions to ask, assess whether the answers offered really answer the questions, and decide if the author is prepared to answer those questions well. Remember the literacies that Howard Rheingold suggested in the “Communicating” chapter. Using these as guides leads us to mindfully explore the vast array of information available to us. And when we do so, we won’t find ourselves taking information at face value and passing it on as though it were valid, like some of the “fake news” that is prevalent today.
So let’s start the process of doing research. The activity below will help you begin the process. After this, you will be introduced to the simple steps you need to take to do the research and then communicate your findings appropriately.
Pick a topic you might like to research or have already been assigned to research for a class. Then take a close look at the list of knowledge products below, and rank them in order of which ones you would most likely use for a research paper. After ranking them, explain why you put them in that order.
- Books: histories, pictures, topic overviews
- Journals: research studies, expert opinions, analyses, lists of other information sources
- Magazines: basic and recent information, pictures, reviews
- Newspapers: very recent information, place-specific information, reviews
- Films, videos, television, music: pictures, speeches, sound
- Internet sources: current or historical information from a variety of sources or individuals, data or commentary compiled by individuals or specific organizations or companies, graphics, sound, music, animation, video, pictures
- Conversations, interviews: opinions, direct experiences, personal viewpoints, attitudes, histories
- Government publications: reports, studies, statistics, laws, regulations
- Documents: reports, laws, statistics, facts
- Diaries: personal stories, histories, opinions, reflections
These can also categorized by types of knowledge products. For your research, you have to choose wisely among these, too. There are scholarly knowledge products, which are mostly written for scholars in a particular field. The author is identified, and credentials are available. Sources are documented, and technical language is often used. Secondly, some knowledge products might be considered professional . These are written for professionals in a field, the author is most often identified, sources are not always documented, and the language may or may not be technical. Finally, there are popular knowledge products, which communicate a broad range of information. The author is often not identified, sources are often not documented, and language is not technical. Because they are commercial products packaged for wide sales, they often use color and have numerous ads.
When you are faced with a research assignment, it is important for you to be able to create successful search strategies. You need to find sources for specific purposes and audiences and be able to critically evaluate these sources. When doing research, you also have to incorporate the information you find for specific purposes, acknowledge the sources, and provide citations. To make this easier to understand, think of scholarly writing as a simple story told with a particular set of conventions (rules). What are these conventions? They are: a research question, a hypothesis, a methodology, a review of the literature, an interpretation of your work, and an analysis of the significance of what you’ve found.
Research Question
First of all, you need a topic. This is often the most difficult part of the whole process. So begin by thinking of something that is really interesting to you. Let’s take music for an example. You need to ask some questions about music to start the process. Some examples of questions are:
- What does music mean?
- What is the function of music?
- What is the value of music?
- What is the significance of music?
- How is music made?
- What causes music to happen?
The easiest way to come up with questions regarding whatever topic you choose is to start with basic questioning words: who , what , why , when , where , how , might , could , can , should , will , must , did , and so forth. You can ask better questions, and this will help you narrow down your hypothesis. For instance, why does music change over time? Who will play this music? How did this music come about? Why should we listen to this music?
Pick a topic and try to describe it:
- Name your topic: I am studying __________
- Suggest a question: Because I want to find out who/how/why/whether/when/what _______________
- State a rationale for the question: In order to understand who/what/where/how/why/whether ___________
Going through this exercise every time you are tasked with writing a research paper will help you clarify what you want to accomplish and why.
Scholars use information to answer one or more questions inspired by a topic of interest. Usually, a scholarly question identifies a problem and a solution. Such questions are usually written in the form of a hypothesis, which is a statement about the relationship between two things that identifies both a problem and an answer or solution. An example of a hypothesis would be: Different genres of music have an effect on the mood of the people listening to them. The questions asked to get to this hypothesis might be: Does music have an effect on mood? Do people listen to music to make them feel better? What kind of music is used as a way to energize the listener? Is there one type of music that is better than others for calming someone down?
Your hypothesis must reflect what is known about a research topic in such a way that your research project will add new knowledge and insight to what is already known. In order to arrive at a hypothesis that achieves this goal, you must learn as much as possible about your topic so you can narrow down your hypotheses to what you don’t know. Then your research project will produce new knowledge. Your hypothesis is about what you don’t know . However, you might find that you can’t prove your hypothesis. You might find evidence that contradicts it, and you will have to reflect on why your hypothesis might have been wrong.
Find two newspaper articles to analyze. Read through them and answer the following:
- What questions are being answered in the articles?
- What questions do you think need to be answered?
- What was the hypothesis that the writer of these articles was working from?
It is important to be able to find the hypothesis that a writer has constructed to tell you a story. You have to make sure you understand what they are trying to “prove” and what questions they asked in order to do so.

Methodology
Education is about discovery. This means that you need to learn how to question, evaluate, and determine the worth, credibility, and relevance of what you, as a student, find. Thus, when doing research, you need that hypothesis to begin the rest of your research.
The next step is to come up with key words or concepts that describe your topic. Start by preparing an outline for yourself. List the key words (for instance, on the topic of music, some key words might be music , instruments , genres , musicians , and so on). Then create a list of narrower terms, which are more specific things that you want to know about your topic, such as time frames , geography , population , and age groups . Finally, you can list broader terms that are the larger subjects that include your key words. For music these could be cultural expression , jazz , hip-hop , singers , and so forth. Your methodology will be a compilation of the sources you decide to review. It is an orderly approach to problem solving and gathering useful data, using such sources and strategies as interviews, public documents, surveys, experiments, the Internet, and many more.
The kind of methodology you decide to use depends on the type of research you will be conducting. You could do exploratory research , which basically answers the question “Does something exist?” This “something” could be an event, a thing, or an idea, such as a concert or music designed for relaxation. Or perhaps you want to do descriptive research , which is the kind of study that defines something by describing its characteristics, behaviors, or actions. For instance, you could describe a genre of music, how it was created, and what instruments are usually used to compose this type of music. A third type of research you may want to do is called prediction research , which involves identifying relationships that make it possible for us to speculate about one thing by knowing about something else. Music has taken many turns over time, and you might want to suggest that the next phase of music might all be electronically produced. And finally, you could choose to do explanatory research . This type of research examines cause-and-effect relationships. For example, there is music created to tell a particular story in a specific manner. This might be true of rap music. To study this, you would use explanatory research to describe this phenomenon.
Review of the Literature
One other piece of the research puzzle is a review of the literature. The literature in a particular field is its discourse , which is actually a conversation over time about a topic. When you do your literature review, you are inserting yourself in the middle of such a conversation and getting information only from that particular time and perspective. For instance, if you want to study the effects of music on children, you will find a wide variety of sources that will give you information about the topic. You will discover that many people have been interested in the issue and have done studies trying to find out the answer. These studies have been done over many years, and the perspectives involved have changed accordingly. The discourse continues over time, and you can insert information into the conversation by conducting your own research.
Thus, a review of the literature finds, evaluates, and integrates past research. It is a critical synthesis of research literature that:
- shows how previous studies relate to one another.
- shows similarities and differences between studies.
- discriminates between relevant and irrelevant information.
- indicates weaknesses in previous work.
The purpose of the literature review is to synthesize many specific events and details into a comprehensive whole. Synthesis results from weaving together many smaller generalizations and interpretations into a coherent main theme. You will find that a literature review is always required of an assigned research paper for a course. The purpose is to enable you to critically analyze a segment of an already published body of knowledge. A comprehensive literature review encompasses the following elements:
- Start the introduction by describing the problem or issue you are addressing, then focus on your research hypotheses or questions.
- Explicitly state the significance of the topic in the introduction.
- Present the review as an essay, not an annotated list.
- Emphasize the findings of previous research you have found.
- Point out the trends and themes in the literature.
- Point out the gaps in the literature.
- Express opinions about the quality and importance of the research you have found.
- Use the review to suggest that there is a need for more study.
Avoiding Plagiarism
You certainly have heard about plagiarism and how important it is not to let yourself participate in it. It is so easy to read through many other people’s work and grab a sentence here and there to put into your own paper. As you’re struggling to come up with ideas, you may also find yourself borrowing from others. Neither of these is a good idea.
Plagiarism often starts with the note-taking stage of the research process. Thus, when taking notes, be sure to distinguish between paraphrases and direct quotations. When you are copying an exact quotation, be extremely precise. Note all the information you will need for the citation. It is a good idea to make a system for yourself, perhaps color coding, when doing your research. Make direct quotations one color and your own paraphrasing of ideas another color. Both quotations and paraphrases need to be cited with sources, both within the paper and at the end.
Learning how to use the ideas of others to add weight to your own ideas involves effort and a commitment to academic honesty. It is not always clear exactly how or when to use sources, and sometimes you might need advice or guidance. Since your professors are most familiar with the expectations of their disciplines, they are the best people to ask. Your college likely offers support in the writing lab or online. If you need more guidance, the Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) has a section on safe practices for researching and drafting , where you can find excellent advice on identifying plagiarism and preventing yourself from plagiarizing.
While the process of writing authentically and avoiding plagiarism must be focused from the start, you can avoid a world of trouble by double-checking your near-final work with a source identification site or plagiarism detector. Doing so can help you avoid any unintentional reuse of others’ work and may simply identify a source you forgot to cite. Chegg Writing allows you to upload or paste in your paper for a detailed source evaluation. Note that this is only a check step; you must follow best practices to ensure that you don’t plagiarize.
Validity and Credibility
Before you move on to interpreting your data and addressing the significance of what you found, you need to understand the concepts of validity and credibility. There are many ways you can check the validity of a piece of information. Can you find contradictory or confirmatory data? Can you find evidence that disputes what you are reading? If so, use this information. It is always useful to mention opposing ideas. Ultimately, doing so might strengthen your own ideas. Is the topic within the expertise of the person offering the information? Was the method chosen to convey this information the best method to use? The credibility of the author is another important aspect of checking your sources. In other words, evaluate the authors. Are they experts on the topic? Do they have credentials to write on this particular topic? Has this author written anything else on this topic?
Evidence is the way we show that we are using the experiences, values, research, and perspectives of others. To be information literate is to apply the concepts of subjective and objective evidence to our selection, use, and evaluation of information. When we read a website or view a television program, can we recognize that a particular set of values and perspectives is being used? Are we able to identify when evidence is being used? Can we determine that the evidence being used shows a relevant connection between values, perspectives, and conclusions? Are enough different values and perspectives being presented that the conclusions can be considered objective? It is important to learn how to determine the validity and credibility of sources.
The Internet presents its own challenges when it comes to discovering valid and credible information. When looking at a website, you should be able to answer the following questions: Who is responsible for the site (i.e., who is the author)? What can you find out about the responsible party? Where does the site’s information come from (e.g., opinions, facts, documents, quotes, excerpts)? What are the key concepts, issues, and “facts” on the site? And finally, can the key elements of the site be verified by another site or source? In other words, if you want to find some information online, you shouldn’t just Google the topic and then depend on the first website that pops up.
For certain topics and types of information, you may need to dig deeper. Take into account the funding behind a website. Look up the author, and see if they have written anything else and if there are any obvious biases present in that writing. As an example, if you find a website about vaccinations and autism, and this website was put up by a parent group that opposes vaccinations, you have found information that has biases built in from the start. The point of view presented is most likely one-sided, and thus you need to look for more balanced sources to learn if there is in fact some relationship between childhood vaccinations and the onset of autism. This is just an example; you can find sources ranging from reasonably trustworthy to totally untrustworthy on any topic.
Interpretation
Interpretation is the task of drawing inferences from the facts that you collect in your research. It is a search for the broader meaning of your research findings. This is where you try to make sense of what you discovered. In this part of your research, you should discuss the most important knowledge you gained about your topic from your sources. Here is where you go back to your hypothesis and research questions to discuss your findings and whether or not your hypothesis is correct.
Significance
Remember that earlier it was stated, “Life is a series of problems needing solutions.” Consequently, an increased amount of inquiry leads to progress as we continue to expand our knowledge base on a variety of topics. Whatever you find in your research study has significance, as it adds to our knowledge in a particular area. In this section of your writing, it is important to describe the process by which you located your information and then provide advice to other researchers on how to effectively and efficiently find information on this topic. This allows for the continuation of inquiry and the development of more data and knowledge. This is where you communicate to others the new knowledge you discover in your research.
I Did the Research—How Do I Present It?
- How do I communicate my research findings?
- What are the elements of a good oral presentation?
- How do I successfully prepare a visual presentation?
Oral Presentations
When giving an oral presentation, you should pay special attention to voice, body, and attitude. If you take the following tips into consideration, you should do a fine job of conveying your ideas to an audience.
Voice is more than the sum of the noises you make as you speak. Pay attention to inflection, which is the change in pitch or loudness of your voice. You can deliberately use inflection to make a point, to get people’s attention, or to make it very obvious that what you are saying right now is important. You can also change the volume of your voice. Speak too softly, and people will think you are shy or unwilling to share your ideas; speak too loudly, and people will think you are shouting at them. Control your volume to fit the audience.
Some people have a tendency to rush through their presentations . This means they speed up their speech, and the audience has a difficult time following along. Take care to control the speed at which you give a presentation so that everyone can listen comfortably. Also, to add to the comfort of the listeners, it is always nice to use a conversational tone in a presentation.
This includes such components as stance, gesture, and eye contact—in other words, overall body language. How do you stand when you are giving a presentation? Do you move around and fidget? Do you look down at the ground or stare at your note cards? Are you chewing gum or sticking your hands in and out of your pockets nervously? Obviously, you don’t want to do any of these things. Make eye contact as often as possible. Stand in a comfortable manner, but don’t fidget. Use gestures sparingly to make certain points.
Attitude is everything. Your enthusiasm for your presentation will prime the audience. If you are bored by your own words, the audience will be yawning. If you are jazzed by what you have to offer, they will sit up in their seats and listen intently. Also, be interested in your audience. Let them know that you are excited to share your ideas with them because they are worth your effort.
Visual Presentations
You might also think about using technology to make your presentation. Perhaps you will do a slide presentation in addition to orally communicating your ideas to your class or another group. Keep in mind that the best presentations are those with minimal words or pictures on the screen, just enough to illustrate the information conveyed in your oral presentation. Do a search on lecture slides or presentation slides to find myriad suggestions on how to create them effectively. You may also create videos to communicate what you found in your research. Today, there are many different ways to take the information you found and create something memorable with which to share your knowledge.
When you are making a presentation that includes a visual component, pay attention to three elements: design, method, and function.
The design includes such elements as size, shape, color, scale, and contrast. You have a vast array of options for designing a background or structuring the visual part of your presentation, whether online or offline.
The method is how you visually present your ideas. Will it be better to show your ideas by drawing a picture, including a photograph, using clip art, or showing a video? Or will it be more powerful to depict your ideas through a range of colors or shapes? These decisions you make will alter the impact of your presentation. Will you present your ideas literally, as with a photograph, or in the abstract, as in some artistic rendition of an idea? For instance, if you decide to introduce your ideas symbolically, a picture of a pond surrounded by tall trees may be the best way to present the concept of a calm person.
The function is the purpose of the visual part of your presentation. Are you telling a story? Communicating a message? Creating movement for the audience to follow? Summarizing an idea? Motivating people to agree with an idea? Supporting and confirming what you are telling your audience? Knowing the function of the visual element of your presentation will make your decisions about design and method more meaningful and successful.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Amy Baldwin
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Success
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/a-conducting-and-presenting-research
© Sep 20, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Module 8: Study Skills
Presentation types, learning outcomes.
- Identify common types of presentation tasks in a college class, including individual and group projects

Imagine you are walking across your campus. As you pass the student center, you see a couple of people who have set up at a table outside, and they’re passing out information about the student honor society. Open windows in the music building share the sounds of someone practicing the piano in the art studio. Upon entering your class building, you are greeted by student-made posters illustrating various phases of the process of cell division. An open class door allows you to watch a young man in a lab coat and protective gear pour liquid nitrogen over items in a tray while the rest of his classmates look on with great interest. Your own instructor is setting up the computer screen at the front of your class when you walk in, loading up the PowerPoint that he plans to use for the day.
All of these scenes are examples of presentations, and it’s very likely that you’ll be asked to participate in similar activities during your college career. Presenting, whether face-to-face or online, is a skill you will hone as a college student in preparation for your future career.
Presentations can take many forms and potentially serve many purposes. When reading the definitions below, keep in mind that many presentations often combine several elements into a hybrid form. You may have to pick and choose what will work best for you depending on the instructor and the course. Let’s start with the different genres or types of presentations.
Informative
Some presentation assignments will ask you simply to deliver information about a topic. Often these presentations involve research, which you will shape and present to your instructor and classmates. Typically, informative presentations ask that you NOT share your opinion about the subject at hand (which can be more challenging than it seems). With an informative presentation, your goal is to educate your audience by presenting a summary of your research and sticking to the facts.
Unlike informative presentations, persuasive presentations ask that you not only form an opinion about your subject but also convince your audience to come around to your point of view. These presentations often involve research, and the findings of your research will be used to bolster the persuasive case you’re making.
Lesson Delivery
You may be asked to do a lesson delivery presentation, which will require you to specialize in one topic of the course and give your fellow classmates instruction about it. In short, you become the teacher of a subject. Often your presentation will be the only time that this subject is covered in the class, so you will be responsible for making sure that you provide clear, detailed, and relevant information about it. You may also be asked to provide questions on the subject to be included in a quiz or test.
Demonstration
These action-based presentations typically model some behavior or subject matter that has been introduced previously in the class. Unlike the lesson delivery presentation, a demonstration adds a level of performance in which you show and tell the audience what you know. You might perform the demonstration yourself, as a way of illustrating the concept or procedure, or you might provide classmates with instructions and guidance as they do it themselves.
Poster presentations should convey all the information on a subject necessary for a viewer to consider on her own. They often consist of short, punchy wording accompanied by strong visuals—graphs, charts, images, and/or illustrations. Posters frequently require research to prepare, and they allow for some creativity in design. Depending on the assignment, your poster may be part of a gallery of poster presentations with your classmates. Your poster has to communicate everything that is important without you being there to explain it to your audience.
Similar to poster presentations, online presentations are generally asynchronous— meaning they don’t require you to be present at the same time as your viewer. They often serve similar purposes as poster presentations, but due to the online format, they allow for more interactive possibilities, such as sharing a pertinent video or animated graph. Your online presentation must stand alone to teach your audience everything they need to know.
Solo and Group Presentations
You may be asked to present as an individual or as part of a group.
Individual presentations put all the responsibility for preparation, research, and delivery on you. You rightfully take all the credit for the final product you produce.
Group presentations , in contrast, often involve more complicated tasks and therefore require more participants to make them. Your instructor may make suggestions about how the work should be divided, or the group may delegate tasks internally. Grades may be assigned equally to everyone in the group, though many instructors assign individual grades based on some participation-level factor to inspire each member to pull his or her own weight.
Presentation assignments are often open to creative interpretation, which gives you a lot of room to explore new techniques and add a personal touch to the task.
group presentation: one in which you will collaborate with others to divide the work and perhaps to focus individually on different aspects of the topic
individual presentation: one in which the preparation, research, and delivery are entirely your responsibility
- College Success. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of Overplanning Kills Magic. Authored by : University of the Fraser Valley. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/mSNUJj . License : CC BY: Attribution

Like what you're reading?
Need a good presentation topic? Here are hundreds of them.
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera November 04, 2022
If you’re looking for good topics for presentations, you’ve landed on the right page. In this article, you’ll find plenty of good presentation topics, tips on choosing the most suitable topic for you, and essential design elements to make your presentation a success.
Many factors go into an excellent presentation. You need to have confident body language and engage your audience to hold their attention. You also need eye-catching visual aids like images, data visualizations, GIFs, and others (all of which you can find in Prezi ), not to mention a great opening to grab attention and a strong closing line to stay memorable. However, the most essential aspect of your presentation is the topic. It’s the core of your presentation, so it has to be strong, insightful, attention-grabbing, and appealing to yourself and your audience in order to evolve into a successful presentation everyone will love.

How to choose a good presentation topic
There are millions of topics you could create a presentation on, but what defines a good topic? If you’re struggling to either come up with a good topic for a presentation or you can’t decide between multiple ones, here are a few questions you should ask yourself before choosing a topic.
What’s the goal of your presentation?
When you’re choosing a topic, consider the meaning behind it. Ask yourself what the purpose of talking about this topic is, and what you want to say about it. Whatever topic you choose to present, the conclusion needs to provide a takeaway or lesson you want to communicate to your audience. A meaningful goal will make your presentation more memorable.
Are you interested in the topic?
If you’re not interested in the topic, others won’t be curious either. Interest, enthusiasm, and passion enrich your presentation and are noticeable when presenting. Interest shines through and inspires others to find the topic as fascinating as you do. Think about the last time you saw someone sharing something they were passionate about – their excitement drew people in to pay closer attention to what they were saying.
When choosing a topic, you need to find it or a particular angle of it interesting for yourself. For example, perhaps you’re not a pop music enthusiast, but you’re passionate about studying cultural phenomena. In this case, you can talk about pop music’s influence on early 2000s youth culture.
Will your audience find this topic relatable?
While you have to find the topic you’re presenting interesting, you also have to think about your audience. When choosing a subject, consider your audience’s background in terms of demographics, interests, culture, and knowledge level about the topic. Think about what others will find fascinating and relevant, so they’re not bored or confused during your presentation.
Do you have prior experience or knowledge about this topic?
Personal experiences are always great to share in a presentation, providing your unique perspective for anyone listening. While you can easily prepare your presentation based on a quick Google search, it won’t make the same lasting impact on your audience. Choose a topic you have some prior knowledge about, or have an interesting opinion you can share with others. It’ll make your presentation more engaging and memorable.

Ideas for good presentation topics
It’s not easy to come up with a good presentation topic from scratch. It’s much easier to get inspired from other good presentation topics to build your topic on. Whether you’re looking for presentation ideas for work, about me presentation ideas, unique or easy presentation topics, you’ll find them all here.
Without further ado, here are some good presentation topics to choose from or get inspired by.
Presentation topics about social media
- The role of social media in portraying gender stereotypes
- How social media impacts our body image
- How social media shaped Gen Z
- The most significant differences between the Facebook and TikTok generations
- The negative effects of social media
- The positive impacts of social media
- The effects of social media on behavior
- How social media impacts our physical (or mental) health
- How social media has shaped our understanding of mass media
- Should we teach about social media in schools?
- The rise of social media influencers
- How AR Instagram filters impact our self-image
- How to go viral on social media?
- The origins of social media echo chambers
- Social media as a news outlet
Author: Ish Verduzco
Presentation topics about movies
- How movies influence our understanding of good and evil
- Beauty standards represented in movies
- How female characters are depicted in Hollywood movies
- How horror movies and global fears have developed through time
- The adverse effects of romance movies
- How movies have changed our understanding of the Western culture
- Charlie Chaplin and the silent movie era
- The globalization of culture: Hollywood vs. Bollywood
- The psychology behind the music in films
- The ethics of using animals in movies
- Social media’s influence on the film industry
- The history of filmmaking
- The role of color in movies
- The cultural impact of romance movies
- How are gender stereotypes depicted in Hollywood movies?
Author: Cinto Marti
Presentation topics about music
- The impact of pop music on beauty standards
- Should digital music be free for everyone?
- The psychology behind the music in advertisements
- The effectiveness of sound therapy
- Can music inspire criminal behavior?
- The psychological effects of metal music
- The origins of K-pop
- How does music influence our understanding of the world?
- Can music help in the learning process?
- The positive effects of classical music
- The history of hip hop
- Why is music education essential in schools?
- The psychological benefits of playing piano
- Can anyone become a famous musician?
- The role of music in fashion
Author: Prezi Editorial
Presentation topics about health
- The link between food and mental health
- Inequality in the healthcare system
- Myths about healthy practices
- Simple practices that help you stay healthy
- Health education in schools: Should it change?
- Toxic positivity and mental health
- The impact of superfoods on our health
- The psychology behind unhealthy eating habits
- Sex education in schools: Why should we have it?
- How to trick yourself into getting better: The placebo effect
- How to strengthen your immune system
- How to tell if someone is depressed
- The health benefits of regular exercise
- The impact of junk food on mental health
- Stress-caused diseases
Author: Prezi Education Team
Presentation topics about human psychology
- What is social depression?
- What triggers panic attacks?
- The impact of testosterone on aggressive behavior
- How to overcome social anxiety
- Differences in the functioning of the brain of a child and adult
- The impact of violent video games on children’s brain development
- How does the use of social media influence our attention span?
- How to overcome childhood trauma
- The influence of marijuana on the human brain
- How does behavioral therapy work
- The psychology behind fame
- The causes of personality disorders
- The differences in brain functioning between men and women
- What happens in therapy sessions?
- The psychology of substance abuse
Presentation topics about self-development
- The impact of exercise on productivity
- How to deal with stress
- How to deal with procrastination
- The positive effects of meditation
- Why new–year’s resolutions don’t work
- How to overcome bad habits
- The impact of negative thoughts
- The negative effects of self-criticism
- The role of creativity in self-development
- Benefits of journaling
- How to learn something fast
- How to be mindful
- The importance of curiosity
- How to become more self-aware
- Why it’s essential to spend time with yourself
Author: Nir Eyal
Presentation topics about education
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of online education?
- The positive effects of a gap year
- Should university education be free?
- Inequality in education access
- How language learning benefits brain development
- Emerging gender issues in education
- The importance of socialization in school
- School bullying and student development
- The benefits of reading
- Is the education system broken?
- What you don’t learn in college
- The link between education and brain development
- The history of schools
- The gender gap in STEM
- The connection between equality in education and economic growth
Presentation topics about culture
- Is graffiti a form of art or street vandalism?
- Cultural diversity in the workplace
- The impact of culture on gender roles
- The issue with orientalism
- Are humans the only species that has culture?
- How do different cultures view death?
- The ethical issues of pop culture
- The impact of culture on personal development
- Sexism in different cultures
- The impact of globalization on local cultures
- The viral spread of the #metoo movement
- The history of subcultures
- The problem with romanticizing toxic relationships in movies
- 90s pop-culture influence on fashion trends
- The evolution of cultural psychology
Author: Devin Banerjee
Presentation ideas for work
- What it’s like to be a digital nomad?
- How to deal with workplace conflicts
- The secret to a productive day
- How to set achievable goals
- The importance of diversity in a workplace
- The positive effects of creative thinking at work
- How to give constructive feedback
- The characteristics of a valuable team member
- Inequality and the glass ceiling
- Racial discrimination in the workplace
- Work habits of different cultures
- How is work perceived in various countries?
- Technological development and the future of work
- The importance of a healthy work/life balance
- The rise of health problems in office work
Author: Charles Huang
Presentation topics about hybrid work
- The positive effects of hybrid work on work/life balance
- Is hybrid work the future work model?
- How to stay connected in a hybrid work model
- The challenges of hybrid work nobody talks about
- How to stay productive when working from home
- The social effects of hybrid work
- The economic impacts of hybrid work
- Case study: Hybrid work model in [company]
- What causes Zoom fatigue?
- The problem with online meetings
- Is hybrid work better than remote work?
- How to develop a close relationship with colleagues in a hybrid work model
- What kind of company culture is best for a hybrid work model?
- Is hybrid work sustainable?
- Cybersecurity consideration for hybrid working
Author: Barbie Brewer
Presentation topics about public speaking
- The importance of body language in public speeches
- How to appear confident when you’re not
- How to become a better orator
- The use of eye contact in public speaking
- Breathing exercises that will calm you down before public speaking
- The benefits of public speaking
- Ways to improve public speaking skills
- How to leave a great first impression on stage
- How to engage your audience during a public speech
- How to best structure your public speech
- How to end your presentation speech
- Can anyone learn to be good at public speaking?
- How to prepare for a public speech
- What not to do right before a public speech
- How to address a controversial topic in a public speech
Author: Prezi Team
Presentation topics about entrepreneurship and leadership
- The main principles of a good leader
- The impact of leadership skills on professional performance
- The mistake every entrepreneur makes
- How to successfully lead a cross-cultural team
- How to celebrate inclusivity in a diverse team
- What are the common personality traits of a successful entrepreneur?
- The impact of entrepreneurship on the global economy
- The characteristics of a leader
- The most common challenges of entrepreneurship
- Can anyone learn to become a successful leader?
- What affects new venture growth?
- The psychology of leadership
- What is crowdsourcing?
- The benefits of being an entrepreneur
- Common mistakes leaders make
Author: Jill Sinclair
Presentation topics about technology
- The rise of technological development
- Is technology addictive?
- Should we use drones for military and non-military purposes?
- The sustainability of electric cars
- What are deepfakes?
- Limitations of AI machines
- The future of programming
- Ethical issues of AI
- The future of AR in business
- How VR can be used in the medical field
Author: David Vandegrift
Sales presentation topics
- How to make a cold email intro
- What is sales enablement?
- How to build better relationships with customers
- The best way to improve pipeline management
- Coaching via verbal and written role-play
- How to plan cold calls
- What’s a deal-breaker for most customers?
- All about personalized coaching
- How to manage objections
- How to close more deals
- How to keep your prospects engaged
- Effective sales communication strategies
- How to conduct a competitor analysis
- The most valuable sales skills
- What soft skills do you need to become a successful sales rep?
Author: Cindy McGovern
Easy presentation topics
- Benefits of daily exercise and how to incorporate it into your routine
- Simple and nutritious meal recipes
- Tips for improving time management and productivity
- The importance of recycling
- The history of a local landmark or festival
- Ways to reduce stress
- Exploring different types of renewable energy sources and their impact on the environment
- The basics of budgeting and saving money for future goals
- The benefits of social media for professional use
- Tips for overcoming stage fright
- How to start a meditation practice
- The impact of technology on modern society
- The basics of personal finance
- The health benefits of a plant-based diet
- The history of Earth Day
Good how to presentation topics
- How to create a successful social media marketing strategy
- How to give a persuasive presentation
- How to create effective and engaging content for your blog
- How to discover your strengths and weaknesses
- How to use project management tools to increase productivity
- How to make the most out of boring meetings
- How to build a personal brand
- How to conduct effective market research
- How to use data analytics to improve decision-making
- How to improve your decision-making process
- How to write a winning proposal
- How to create a visually stunning presentation
- How to manage stressful situations at work
- How to make friends as an adult
- How to network at work events
About me presentation ideas
- My journey to becoming who I am today
- My passion for [insert topic or activity]
- My career aspirations and goals
- My travels and adventures around the world
- My hobbies and interests outside of work/school
- My role models and influences
- My strengths and weaknesses
- My favorite books, movies, and TV shows
- My proudest achievements and accomplishments
- My favorite childhood memories
- My family and friends
- My education and academic background
- My volunteer and community service experience
- My personality traits and values
- My vision for the future and how I plan to achieve it
Author: Adam Grant
Student presentation ideas
- The history and evolution of video games
- The history and cultural impact of tattoos
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The effects of globalization on local cultures and economies
- The role of education in promoting social justice and equity
- The ethical implications of autonomous weapons in warfare
- The impact of mass media on society and culture
- The causes and effects of deforestation on biodiversity and climate change
- The history and cultural significance of dance in different parts of the world
- The psychology of addiction and recovery
- The impact of the gig economy on labor rights and job security
- The history and impact of feminism on gender equality
- The benefits and drawbacks of renewable energy sources
- The impact of colonialism on indigenous cultures and identities
- The role of technology in promoting global connectivity and intercultural understanding
Author: Edward Quinn
How to create a good presentation
If you know what you want to present on, it’s time to create an impactful presentation that grabs everyone’s attention. Presentation design plays a crucial role in how your presentation is received and remembered. To stand out and leave a memorable impact on your audience, create a Prezi presentation. Instead of a linear, slide-based presentation, offer an engaging and dynamic storytelling experience to your audience. Breathe life into your presentation with motion, zoom, and spatial relationships. When creating your presentation, consider the following three essential elements:
Visuals play a significant part in presentation design. They evoke emotions, make a memorable impact, and give more context to the story. Not to mention, 65% of people are visual learners , so visual aids are helpful when explaining a complex topic.
In your presentation, include different types of visuals, such as images, videos, GIFs, and stickers, all of which you can find in Prezi’s content library. When selecting your visuals, consider what’s relevant and brings additional value to the story. Only add what’s meaningful and necessary. A video or image at the right place and time will enrich the viewing experience and make your presentation more memorable.
The layout of your presentation is the structure of your story. It’ll help you introduce the topic, intrigue your audience, and unfold the layers of your topic one by one until you disclose your main arguments and summarize the presentation. A good presentation layout has a hierarchical, chronological, or logical flow that leads the viewer from start to finish.
If you’re creating a Prezi presentation, you can create a dynamic storytelling experience by experimenting with your layout. Instead of going from slide to slide, you can zoom in and out of topics and experiment with different shapes, animations, and effects that draw the viewer into your story world. Here’s an example of a Prezi presentation with a great storytelling layout:
Author: Lydia Antonatos
Data visualizations can elevate your presentation from being a good one to a great one. By providing data behind your arguments, you’ll appear more trustworthy and confident in your audience’s eyes.
Add charts, graphs, interactive maps, and more to your presentations with Prezi Design. You can choose from a wide selection of charts and maps to illustrate your data. With interactive elements, you’ll be able to engage your audience and make a memorable impact.
Engaging visuals, a well-structured layout, and relevant data visualizations will provide a great starting base to create a memorable presentation. Discover other tips and tricks that make your presentation effective and capture people’s attention.
Choosing a topic for a presentation isn’t easy. When selecting a topic, think about the goal of your presentation, your interest and knowledge about the topic, and whether or not your audience will find it relevant and interesting for them. Also, get inspired by other topics that’ll help you figure out what you want to talk about. Lastly, when creating your presentation, consider the impact of visuals, layout, and data visualizations. To simplify the creation process, follow the step-by-step process of making a presentation with helpful tips and resources.

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

15 templates

26 templates
49 templates

american history
76 templates

great barrier reef
17 templates

39 templates
University Presentation templates
Download and edit now our university-related templates are you looking for a fresh design for a lesson or maybe you need an elegant template for your thesis defense in slidesgo we offer a lot of presentations for students and teachers alike, related collections.

174 templates

153 templates

99 templates

71 templates

Foreign Language
67 templates

66 templates

53 templates

Language Arts
20 templates

Social Studies
18 templates

14 templates

10 templates

9 templates

Emotional Intelligence
8 templates

6 templates

Physical Education
5 templates

4 templates

3 templates

Calendar & Weather
2 templates

Social Skills

It seems that you like this template!
College medieval studies: the 9th century.
Download the College Medieval Studies: The 9th Century presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work. Edit...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
University Agenda and Organizer
Organize your subjects, lessons and activities with this University Agenda presentation. Many slides look like different types of notebooks and diaries, and we include isometric illustrations. The main colors of the slides are cream and red, which looks like the binding of a day book. The heavy serif titles, with...

University Introduction
Going from high school to college is a big step in the academic life of any person. Make these new students feel at home studying in your college by using our new free template, whose friendly design can turn your presentation into the best introduction for them.

Sociology Major for College: Émile Durkheim Theories
Download the Sociology Major for College: Émile Durkheim Theories presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work....

Computer Science College Major
If you are a guru of computers, most likely you've studied computer science in college. Would you like to show others what a major in this field has to offer and what it could contribute to their professional development? Customize this template and let them feel the future, at least...

University Marketing Campaign
Launch a marketing campaign for your university! If you are looking for new students, use this funny template and explain a little bit more about your institution, degrees, your competitors… Let’s study!

College Center
Promoting a college usually means being excessively formal and focusing on expensive activities that... Nah! Our approach in this new template is quite different. We wanted this presentation to feel more approachable, to project a more friendly message to future students. Explain the enrollment process, the curriculum or the academic...

University Graduation Yearbook
The end of an era is near, and what an era it is! Your time at college will be one of the moments you'll want to remember forever, so how about creating a yearbook for your graduation? Your wishes are about to come true with this template for you to...

Biology Major for College: Inmunology
Download the Biology Major for College: Inmunology presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work. Edit this...

College Newsletter
Keep your college students up to date with what’s been happening recently on the campus with an effective newsletter. This template is what you need to make them look at things from another perspective!

College Achievement Certificates
This collection of diplomas and certificates is the perfect template for you to create something that you would feel proud to give to your students. Each slide is different, but every single design is elegant, geometric and contains some little details in gold color. It's great for college-level courses!

College Final Year Project
Download the College Final Year Project presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work. Edit this Google...

Cost Reduction in Manufacturing Industry Thesis Defense
Download the Cost Reduction in Manufacturing Industry Thesis Defense presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase your research in...

College Pastel Notes
Between classes, project works and studying, keeping up with everything seems difficult, especially at college level, right? Fear not, because Slidesgo has just created this template for you! To cheer you up, the first thing we came up with is bright pastel colors and many doodle-like illustrations—a fun touch is...

Elegant Style University Lesson
If elegance is one of your qualities, convey it also in your university classes with this Slidesgo template for professors. It has a predominant cream tone that contrasts perfectly with the blue and red of its elements. It is ideal especially for history classes, because of its stately style. Edit...

Master's Degree in International Migration
Download the Master's Degree in International Migration presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work. Edit this...

College Interview Tips
In some countries, universities carry out some interviews with potential students in order to assess whether they're suitable for studying there. Customize our new template and provide some tips on how to make the most of these situations and impress the interviewers. Attention-grabbing illustrations and a modern, colorful style is...
- Page 1 of 56
Apply to College
Get answers to commonly asked questions about the college application process.

Getty Images
The college application process can be daunting, especially for students and families going through it for the first time.
Choose your topic of interest below – including college essays, extracurricular activities, standardized tests, admissions deadlines, waitlists and transferring – and you'll see a list of articles with advice on how to effectively navigate that part of the application process.
How Do I Apply to College?
To apply to college, keep in mind that you need to start early in high school and do your research to find the right fit. The following articles offer advice on how to get in to college.
- What should I know about the college application process?
- What are the biggest college application mistakes to avoid?
- How can I complete my college applications on time?
- What are ways to make my college applications stand out?
- How do I get into college with a low GPA?
- Which colleges have the highest application fees?
- What questions should I ask my high school counselor when applying to college?
- What does the Supreme Court's ban on race-conscious admissions mean for me?
- What should I know about the Common App?
- How can I apply through the Common Black College Application?
What Are the Different Types of Colleges and Where Should I Apply?
From smaller liberal arts colleges to bigger public universities, you have a lot of school types to consider. Here's what to keep in mind about applying to different schools.
- What's the difference between a college and a university?
- What is a liberal arts college?
- What are the cost differences between a private and public college?
- What are reasons to consider a community college?
- How do larger public colleges compare to smaller private schools?
- How many colleges should I apply to?
- How do I narrow down my list of colleges?
- What are tips for picking the right school?
- How do I get into an Ivy League school?
- Should I go to an urban, suburban or rural college?
How Do I Write a College Essay?
Use the college essay to give admissions officers insight into who you are. The tips in these articles will help you tackle the application essay with confidence.
- What are tips for writing the college application essay?
- What are grammar and style mistakes to avoid in a college essay?
- How do I finish my college essays on time?
- What are some examples of good college essays?
What Kind of Extracurricular Activities Can Help Me Get Into College?
Whether you're involved in a club or have a job, colleges want to know how you spend time outside of the classroom. Read on to learn about the role of extracurricular activities in college applications.
- How do colleges weigh extracurricular activities in an application?
- What are ways to discuss work experience on a college application?
- How do I turn extracurriculars into scholarships?
How Important Are Standardized Test Scores?
Schools have varying policies when it comes to admissions tests like the SAT and ACT. Here's what you need to know about college entrance exams.
- Are schools changing their testing requirements?
- What is a good score on the SAT?
- What is a good score on the ACT?
- How has the SAT changed?
- How can I perform well on ACT or SAT test day?
What Do I Need to Know About Recommendation Letters?
Applications typically require recommendation letters written by people who know you well. Read the following articles to find out who, when and how to ask for letters.
- How do I ask for a letter of recommendation for college?
- What are some examples of college recommendation letters?
- What myths about college recommendation letters should I be aware of?
When Are College Application Deadlines?
Some colleges offer early decision or early action admissions, in which you apply early and receive a response before other applicants. In general, though, most colleges have a January deadline for regular applications. These articles compare the different application deadlines: early action, early decision, regular decision and rolling admissions.
- When should I apply to college?
- What are the differences between early action and early decision?
- What should I know about restrictive early action?
- What happens if I back out of an early decision offer?
- Which colleges have later application deadlines?
- What is rolling admissions?
- What colleges offer rolling admissions?
What Are Tips for Applying as an International Student?
Applying to U.S. universities as an international student can be challenging. The articles below can help you understand the admissions process if you're applying from abroad.
- Which U.S. colleges have the most international students?
- Which colleges offer the most financial aid to international students?
- Which colleges accept the most international students?
- What should I know about scholarships as an international student?
- How do I prepare to apply to college as an international student?
- What mistakes should I avoid when applying to a U.S. university?
- What's the difference between TOEFL and IELTS?
- What should I know about playing sports as an international student?
What If I Apply and Am Put on a Waitlist?
A college may put you on a waitlist and not offer you a spot until after the typical May 1 decision deadline. Here's what you need to know if you're wait-listed.
- What do I do if I've been put on a waitlist?
- What colleges admit the lowest percentage of students off the waitlist?
- What should I do while I wait for admissions decisions?
What Do I Need to Know When Transferring Schools?
Transferring may make sense if your college isn't a good fit or you want to finish a degree at a four-year school after community college. Read tips below on transferring schools.
- How can I prepare for a successful college transfer?
- How do I transfer from a community college?
- What's the process of transferring as an international student?
- How does transferring colleges impact student loans?
- Which schools have the most transfer students?
Best Colleges Rankings
For students who need help narrowing down the list of colleges and universities to apply to, the U.S. News Best Colleges rankings can serve as a good starting point.
- National Universities
- National Liberal Arts Colleges
- Regional Universities
- Regional Colleges
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Undergraduate Engineering Programs
- Historically Black Colleges and Universities
- More College Lists
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Nonacademic factors in college searches.
Sarah Wood May 28, 2024

Takeaways From the NCAA’s Settlement
Laura Mannweiler May 24, 2024

New Best Engineering Rankings June 18
Robert Morse and Eric Brooks May 24, 2024

Premedical Programs: What to Know
Sarah Wood May 21, 2024

How Geography Affects College Admissions
Cole Claybourn May 21, 2024

Q&A: College Alumni Engagement
LaMont Jones, Jr. May 20, 2024

10 Destination West Coast College Towns
Cole Claybourn May 16, 2024

Scholarships for Lesser-Known Sports
Sarah Wood May 15, 2024

Should Students Submit Test Scores?
Sarah Wood May 13, 2024

Poll: Antisemitism a Problem on Campus
Lauren Camera May 13, 2024

May 29, 2024
NSF-Funded Program Advances Geosciences Opportunities for Community College Students
- Campus Life
- Earth Sciences
For the second year, a group of community college students has been immersed into cutting-edge research at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego.
The students are a part of the Scripps Geosciences Educational Opportunities (Scripps-GEO) program, a semester-long experience where community college students are exposed to research opportunities at Scripps Oceanography. The program aims to provide experience and knowledge in geosciences, as well as ocean and atmospheric sciences.
The Scripps-GEO program was funded by the National Science Foundation’s GEOPaths program in 2020, but the COVID-19 pandemic postponed the start of the program until January 2022 . The late Scripps Teaching Professor Jane Teranes created the program in hopes of introducing community college students to research and encouraging transfers to undergraduate programs at Scripps.
Following the passing of Teranes in the summer of 2022, the program has carried on thanks to the efforts of Scripps Oceanography faculty members Cathy Constable, Emily Chin and several other Scripps colleagues.
“Jane made a wonderful start with this program and it's a privilege to be able to continue her efforts,” said Constable, professor of geophysics at Scripps. “The research internship experience goes beyond the traditional classroom experience and highlights a path to opportunities available after transfer to four-year universities. It's great getting to work with and encourage a group of highly motivated students so early in their careers, and we hope to see several of them continue their engagement with Scripps' education and research in the future.”
There are 13 students, known as GEO-Scholars, taking part in this year’s program. GEO-Scholars conduct research through paid internships with Scripps scientists including Colleen Petrik, Wenyuan Fan, Melissa Carter, Ross Parnell-Turner, Lynn Russell and others. Students work approximately 10 hours a week, engaging in hands-on activities including researching in labs, learning lab techniques, instruction in how to code and more.
In addition to research training, the program provides mentoring and workshops to prepare students for careers at four-year universities and careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). At the end of the program in May, students showcase and present their semester-long research findings to academics, professionals and other students at the Mesa College Research Conference.
The Scripps-GEO program is for undergraduate students currently enrolled in the following San Diego-area community colleges: Mesa College, San Diego City College, Mira Costa College, Southwestern College, and Miramar College. Geoscience and STEM colleagues at the community colleges assist Scripps in encouraging students to apply for the program.
“As a community college instructor, I'm deeply grateful that our students have the opportunity to work with the world-class researchers at Scripps,” said Donald Barrie, a geology professor and student mentor at Mesa College. “Opportunities like the Scripps-GEO program are transformative because students get to experience the thrill of scientific discovery for themselves. Now, more than ever, we need to cultivate the next generation of geoscientists, and this is what Scripps excels at.”
Application information for the spring 2025 program will be available this fall. Please contact Cathy Constable ( [email protected] ) or Emily Chin ( [email protected] ) for more information about the Scripps-GEO program.
We asked several GEO-Scholars about their experience in the 2024 Scripps-GEO program. Learn more about the students below.

Holly Ross is currently attending San Diego Mesa College and majoring in biology. Ross served as a boatswain’s mate in the United States Coast Guard for six years, and now interns at Scripps with geophysics professor Wenyuan Fan.
Why were you interested in coming to Scripps for this opportunity?
I was interested in interning at Scripps Institution of Oceanography because UC San Diego has always been my dream school. After six years in the U.S. Coast Guard, this position represents my first opportunity in the civilian sector. The Scripps-GEO program offers me the chance to work alongside professors and engage in meaningful research. Given my background of working at sea, Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the perfect setting for me to combine my passion for the ocean and scientific research.
What are you currently studying? What research are you working on at Scripps?
I am pursuing a degree in biology at San Diego Mesa College and transferring to UC San Diego as a junior this fall. Participating in the STEM-focused Scripps-GEO program allowed me to explore areas beyond my major. My research project concentrates on analyzing the frequency and size distribution of submarine landslides in the Gulf of Mexico. Under the guidance of Scripps geophysics professor Wenyuan Fan we are developing a detailed map of submarine landslides in the western Gulf of Mexico and evaluating the associated risks, including tsunamis and damage to offshore infrastructure.
How has your experience been so far? What is your favorite part about the program?
My experience has been incredible. I've enjoyed collaborating with other STEM students and professors. In particular, I've enjoyed hearing professors discuss their data and share stories from their research trips abroad. My favorite part of the program has been working on my project at the Pinpoint Cafe, sipping coffee while overlooking Scripps Pier and watching the waves!
What do you hope to gain from this experience?
This experience has taught me how to conduct scientific research, think creatively, and develop new skills, such as designing a scientific poster to highlight our methods and findings. My main goal with this opportunity is to better understand my academic and career aspirations. The Scripps-GEO program has provided valuable insights and guided my future direction by exposing me to potential career paths.

Jose Segura Figueroa is currently attending San Diego City College majoring in geology. Last year, he was accepted to programs that took him to places like the eastern Sierra Nevada, Berlin-Ichthyosaur State Park, Grand Canyon, and Rainbow Basin. During these experiences, he fell in love with doing field work.
I was drawn to the Scripps-GEO program primarily because of my deep-rooted passion for geosciences and my aspiration to pursue a career as a geoscientist. From an early age, I've been captivated by the intricate workings of our planet, especially in areas like geology, volcanology and earth sciences. The program offered an exceptional chance to immerse myself in research, providing invaluable exposure to real-world scientific inquiry. Moreover, it presented a unique opportunity to gain hands-on experience and insight into the path I envision for my future career in geosciences.
I'm currently collaborating with mentor Professor Emily Chin and Professor Jeffrey Gee on a research project examining the textures and microstructures of rock samples from the Poe Mountain Intrusion in Wyoming's Laramie Anorthosite Complex. Our goals include gaining insights into the region's geological history and the processes shaping the North American continent. We aim to use rock texture to understand deformation processes, delve into mineralogy and petrology and utilize Matlab and MTEX software. This work sheds light on a significant period in Earth's history marked by large-scale magmatic processes shaping the crust.
From diving into lab work to connecting with the community, every moment has been welcoming and enriching. The highlight of my experience has been the Friday seminars, where we delve into the fascinating realms of Earth, atmosphere, and ocean sciences. These sessions not only broaden our understanding but also fuel our passion for exploration. Through hands-on research projects, we're actively honing our skills in data interpretation and scientific inquiry. Looking ahead, I'm excited about the opportunities to visit research facilities, engage with experts from academia and industry, and refine our job-seeking skills. Each day brings new discoveries and challenges, shaping us into well-rounded professionals ready to make a difference in the world of science. Scripps has become more than just a place of study; it's a community where curiosity thrives and dreams take flight.
From this experience, I hope to gain a multifaceted set of skills, knowledge, and insights that will serve as a solid foundation for my future endeavors in the field of geosciences. Specifically, I aim to deepen my understanding of geologic processes, scientific research methodologies, and develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for addressing complex research. I also aspire to cultivate a network of mentors, peers, and professionals within the scientific community, fostering collaborative relationships and opportunities for continued growth and learning. Ultimately, I hope this experience will not only enrich my academic and professional journey but also empower me to make meaningful contributions to the understanding of our planet.

Daniel Self is currently attending Southwestern College and will transfer to San Diego State University (SDSU) in the fall to study electrical and computer engineering. He was a participant in the NASA Community College Aerospace Scholars program at Ames Research Center. He is passionate about research and technology and how the two can be combined to improve society.
I have wanted to contribute to scientific research since I started at community college. I imagined the discovery of a new idea or phenomenon would be a fulfilling achievement. As I learned more about the research community, I became aware of the reputation Scripps Institution of Oceanography holds within the world of groundbreaking research. When this opportunity became available, I knew immediately that I wanted to be involved.
I am currently studying computer and electrical engineering and will transfer to SDSU in the fall. My research at Scripps is focused on heat waves and weather patterns in Southern California. I analyzed weather station data to see how heat waves are related to various weather patterns that can occur in this region. This research provides insight as to how heat waves might ultimately affect public health, notably in the form of excessive heat and wildfires. The results from my analysis should improve the predictability of these adverse situations.
My experience so far has been amazing, I feel fortunate to work at this beautiful campus. My favorite part of the program is the people I work with. At Scripps’ SoCal Heat Hub , I have two mentors, Rachel Clemesha and Kristen Guirguis, who have inspired me so much. I have learned so much from them and now hope to continue my involvement with geosciences, even though I am an engineering major. Another inspiration is my poster co-author, Alexander Weyant, whose background in physics/math has shown me it’s possible to have a diverse education before working in geoscience.
This experience has already opened my eyes to so many possibilities for my future. I am more confident than ever in myself and the path I am on. The weekly talks from Scripps scientists, lab tours, poster projects, and hands-on experiences have all been incredible. I am deeply inspired by the subject matter I have been exposed to. I only hope that Scripps will continue to be a part of my education or career, because it is such a rewarding environment to be in.

Louise Tibia is currently attending Southwestern College and will be transferring to a four-year university in fall 2024. After transferring, she plans on completing a bachelor’s degree in environmental sciences. She is passionate about biology, chemistry and teaching.
Having grown up in San Diego, I've long admired UC San Diego's renowned research endeavors, particularly the groundbreaking work conducted at Scripps Institution of Oceanography in areas such as climate change, conservation, and biodiversity. It was a no-brainer for me to take the opportunity to contribute to this legacy and immerse myself in an environment full of scientific advancements.
Under the Scripps-GEO program, I am working with Dr. Lynn Russell's lab to study atmospheric chemistry. My research focuses on investigating the dependence of liquid water content on cloud droplet distribution. While my background initially leaned towards biology and conservation, my time here has sparked an interest in atmospheric chemistry, and I hope to explore other subtopics under geoscience.
This has been an invaluable experience to me, and I am so grateful for the opportunity to be a Scripps-GEO Scholar. This is my first ever research experience, and my favorite part is how supportive the community is. I’d like to give a special shoutout to the graduate students under Dr. Lynn Russell’s lab for their continuous guidance in my research process, as well as my program coordinators for making all of this a reality. Overall, my peers have inspired the type of researcher and student I hope to be.
In the future, I intend on attending graduate school and eventually working as a professor in community colleges. This internship serves as a foundational step towards understanding the intricacies of the research process, which will undoubtedly help me with my future plans. I aspire to introduce more geoscience programs at the community college and high school levels, encouraging the next generation of passionate students.
About Scripps Oceanography
Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California San Diego is one of the world’s most important centers for global earth science research and education. In its second century of discovery, Scripps scientists work to understand and protect the planet, and investigate our oceans, Earth, and atmosphere to find solutions to our greatest environmental challenges. Scripps offers unparalleled education and training for the next generation of scientific and environmental leaders through its undergraduate, master’s and doctoral programs. The institution also operates a fleet of four oceanographic research vessels, and is home to Birch Aquarium at Scripps, the public exploration center that welcomes 500,000 visitors each year.
About UC San Diego
At the University of California San Diego, we embrace a culture of exploration and experimentation. Established in 1960, UC San Diego has been shaped by exceptional scholars who aren’t afraid to look deeper, challenge expectations and redefine conventional wisdom. As one of the top 15 research universities in the world, we are driving innovation and change to advance society, propel economic growth and make our world a better place. Learn more at ucsd.edu.
Related News
Spreading the love for planet earth, scripps student spotlight: lena stasiak, uc san diego-led science teams selected as finalists for nasa science missions to understand our changing climate, sign up for explorations now.
explorations now is the free award-winning digital science magazine from Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Join subscribers from around the world and keep up on our cutting-edge research.

- Colleges & Degrees
- Academic Calendar
- International Education
- Graduate Studies
- Accreditation
- Tuition and Fees
- Parking & Maps
- Careers with CSULB
- Alumni Home
- Alumni Volunteering
- Alumni Giving
Campus Life
- Centers & Organizations
- Commencement
- Student Life
- Office of the President
- Office of the Provost
- Administration & Finance
- Student Affairs
- University Relations & Development
- Information Technology
- Beach Shops
- Campus Directory
- Enrollment Services
- Financial Aid
- Schedule of Classes
- Student Records
- 49er Foundation
- Research Foundation

1250 BELLFLOWER BOULEVARD LONG BEACH, CALIFORNIA 90840 562.985.4111
Congrats to our 2024 Social Work Grads!
The mission of the School of Social Work is to provide professional social work education that inspires critical thinking and lifelong learning to students who will serve in diverse social work practice areas and roles, engage in collaborative research to contribute to the well-being of populations that are vulnerable and oppressed and advance social work knowledge, and strengthen our communities through meaningful partnerships.
While we commend and celebrate all CHHS graduates, the following highlights our graduates and awardees at the BASW and MSW level. To view the full graduate list, please see the 2024 CHHS Commencement Program.
School of Social Work Student Spotlight

Angela Dominguez is a person of many hobbies, interests and completely immersed herself in campus life during her time here at CSULB. She studied abroad through the School of Social Work program. She has been to Germany, London and Paris, and has many other travel sights set on her list. She is an avid concert goer, FUNKO Pop collector and loves the shows Friends, Grey’s Anatomy, Once Upon a Time, and Schitt’s Creek, to name a few. She has been a part of the Upward Bound program as an academic advisor and Project OCEAN as a Graduate Peer Educator. Angela has interned at the Orange County Department of Education, Los Angeles Department of Mental Health and Long Beach Child & Adolescent Program, to name a few.
“I chose a career in human services before I even knew what human services was,” Angela says. “As a child, I enjoyed helping others, including my teachers and my classmates; however, I was a teenager when I decided I wanted to pursue ‘helping professions,’ especially wanting to work with women and children.”
Angela’s decision to help others was a direct result of experiencing childhood and early-adult trauma herself.
“I quickly learned there were resources all around me to help me succeed. Without the help of teachers, advisors, school counselors, social workers, victim advocates and many others, I would not be where I am today. My community is responsible for the strength and resilience I have developed over the years. I cannot think of a better way to honor the work of those who came before me than to give back to the communities that raised me.”
One of the most impactful experiences during Angela’s time at CSULB was studying abroad in Germany. While in Germany, her passions were reinforced of wanting to help the underprivileged and underserved populations of society.
“I hope to serve my community by continuing to break down the stigma associated with mental health, advocating for women’s rights, and finding creative ways to meet the needs of underserved populations.”
Angela’s story of resilience and pushing herself through the Master in Social Work program, at a time when she was going through personal trials herself, is nothing short of inspiring. Angela says she found solitude in her CSULB community.
“I was convinced I did not belong in this program. How was I supposed to help others when I could barely help myself?”
Angela remembers one particular Wednesday evening, when she arrived to class with the intention of telling her professor that she was quitting the program. Usually, Angela would arrive to Professor Colunga’s class with eagerness and engagement in class.
“On this evening though, my professor could sense I was distraught and took an interest in my wellbeing. I could tell Prof. Colunga genuinely cared, so I told her all that I was going through. This woman was compassionate, empathetic and validating. She reminded me of my ‘why’ – my reason for deciding to pursue a master’s in social work in the first place.”
Adds Angela, “Looking back, I am really glad I chose to continue with the MSW program. I have met so many wonderful people in this program and found lifelong friends!”
Outstanding Applied Social Work Projects
- Project Title -- Empowerment Pathways: Navigating Success for Formerly Incarcerated Students at CSULB
( Instructor : Dr. Joanna Barreras)
- Rocio Becerra
- Jessica Clinard-Allman
- Jessica Keys
- Brent Mayhew
- Wynn Nguyen
- Project Title -- Increasing Positive Youth Engagement in George Washington Middle School
( Instructor : Dr. Jose Hurtado Reyes)
- Adriana Avalos
- Yessica Campos
- Janet Ceja-Garcia
- Jessica Chamorro
- Angela Dominguez
- Project Title -- The Student Link: Fostering Campus Connection
- Skarlet Castro
- Phoebe Hanna
- Channell Holloway-Martin
- Judith Ibarra
- Kala James
- Dominique Jefferson
- Brittany Williams
School of Social Work
Outstanding Thesis
Outstanding Thesis – Project
- Aarti Patel
- Thesis Title : Mental Health Awareness, Support, and Linkage Assistance (MASALA): A Grant Project
- Advisor – Dr. Molly Ranney
Outstanding Thesis
- Elizabeth Esquivel
- Thesis Title: Bereavement Needs of Incarcerated Adults: A Qualitative Study
Graduate Student Honors
- Stephanie Amaya
- Liliana Barroso
- Ricardo De La Torre
- Elizabeth Esquivel
- Fatima Garcia
- Carolina Hernandez Lopez
- Stephanie Lezama
- Ricardo Lopez
- Maerie Grayce Morales
- Koritza Moreno
- David Moreno Guardado
- Grace Navarrete
- Dien Nguyen
- Wynn M. Nguyen
- Rachel Margaret Reyes
- Bryan Sanchez
- Hannah Sjogren
- Adriana White
Graduate Dean’s List Awards
- Parisa Esfahani
- Aracely Guerrero Estrada
School of Social Work ( BASW )
Outstanding Student Citation Award
Cristina Lopez
Kianna Reynante
Samantha Truax
Cristy Toscano
Ruby Garcia
Jessica Metlak
Savanna Hernandez
Van Kim Ngoc Pham
Angelica Mae Tan Sano

Calendar of Events

2024 WWII Emerging Scholars Symposium - O'Connell presentation
Eisenhower, roosevelt, and truman presidential libraries online.
Presenting Scholar: Kaete O’Connell, Ph.D. “Hunger and the Hard Peace: Food Policy in U.S. Occupied Germany”
YouTube Livestream
This virtual symposium focuses on specialized topics related to the Allied effort during World War II. Each program wraps up with a Scholar Spotlight where we get to know a little bit more about each of these up and coming scholars.

All events listed in the calendar are free unless noted.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip 4: Make use of charts and graphs. We all love a good stat. Charts and graphs are a great way to present quantitative evidence and confirm the legitimacy of your claims. They make your presentation more visually appealing and make your data more memorable too. But don't delve too deep into the details.
Try not to hurt others while using humor. You can make fun of everyday situations or activities, so people can relate with them. 6. Time Management in Class Presentation. Time management is one of the best tips for presenting in class. Starting and finishing your presentation in a predefined time frame is important.
Public speaking—giving an oral presentation before a class or another group of people—is a special form of interaction common in education. You will likely be asked to give a presentation in one of your classes at some point, and your future career may also involve public speaking. It's important to develop skills for this form of ...
Steps. 1. Connect with your audience. "Preparation" is the most important task one has to do when it comes to "presentation." Being prepared and having good knowledge about the topic that is to be presented will create interest among the audience and will not let them sleep all throughout your presentation.
Here's the good news: no need for an all-nighter. Beautiful.ai can help you nail your college presentation in a pinch. The ease of use, and intuitive controls, help you create something brilliant in minutes, not hours. Start inspired with our inspiration gallery of pre-built templates and customize them to fit your content.
Making a PowerPoint. Follow these step-by-step guides on how to add certain elements to your PowerPoint presentation: Select a Design Theme. Add or Delete a Slide. Add an Image to a Slide. Add Notes to Your Slides. Add Animations.
While writing out a script can help you prepare, you shouldn't follow it word for word. Use images and text in your slides to remind you of key points you want to mention. You can also use note cards to prompt you along the way. Check. Make Eye Contact. Try to connect with your audience, not just your slides or notes.
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
In this video, learn how to make modern PowerPoint Presentations for college seminars and receive tips to deliver them with confidence. As a student, we want...
Next, save it to use again in the future. To save a copy, go to File > Make a Copy > Entire Presentation. Give the copy a generic name, like Marketing Presentation, and save it to your Drive. This gives you a clean copy to make future presentations from. It's a good idea to save a handful of templates this way.
The presentation's style, substance, and organization will be influenced by its goals and external factors. However, to be successful, each presentation calls for some skills. As a result, in this article, you will be introduced to 15 presentation tips for students which can help you strengthen this skill. Best 15 Presentation Tips for Students
Tip 2: Manage Your Time. College presentations usually have a time limit (can range from anywhere to 5-45 mins). Give yourself plenty of time to get through the material and have time left for questions at the end. Make sure you don't go beyond your allocated time.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Having the knowledge and skills to effectively design and deliver a dynamic presentation is essential in the academic and professional world, regardless of field. ... Whether you are a college student or a working professional, this checklist outlines basic strategies you should consider when designing and delivering an effective presentation. ...
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
9. Less is better. There is a rule that can help you make a perfect presentation - the 10/20/30 rule recommends you to include not more than 10 slides in your project, limit the time of presentation to a maximum of 20 minutes, and use minimum 30-point font size to make it easy to read. You won't make a mistake if you follow this rule.
Your college likely offers support in the writing lab or online. If you need more guidance, the Purdue ... there are many different ways to take the information you found and create something memorable with which to share your knowledge. When you are making a presentation that includes a visual component, pay attention to three elements: design ...
Poster. Poster presentations should convey all the information on a subject necessary for a viewer to consider on her own. They often consist of short, punchy wording accompanied by strong visuals—graphs, charts, images, and/or illustrations. Posters frequently require research to prepare, and they allow for some creativity in design.
1 Make a provocative statement. "I want to discuss with you this afternoonwhy you're going to fail to have a great career." One surefire way to get your audience's attention is to make a provocative statement that creates interest and a keen desire to know more about what you have to say. The presentation above, for example, does just that by ...
Data. Data visualizations can elevate your presentation from being a good one to a great one. By providing data behind your arguments, you'll appear more trustworthy and confident in your audience's eyes. Add charts, graphs, interactive maps, and more to your presentations with Prezi Design. You can choose from a wide selection of charts ...
These templates can also be used in Google Slides and Canva, giving you the flexibility to work in the platform you prefer. Designed for educators, trainers, students, and anyone looking to share knowledge, these templates are perfect for creating impactful presentations, conducting workshops, or delivering engaging lectures.
Some of the best presentation topic ideas for students center around topics such as current events, education, general culture, health, life skills, literature, media and science. When picking presentation topics, consider these things: your hobbies, the books you read, the kind of TV shows you watch, what topics you're good at and what you ...
Download the College Medieval Studies: The 9th Century presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency ...
Virtual College Knowledge 101 Family Presentation in English: Tues. Dec. 14th from 5:30-7:00pm: Join on MS Teams Live. Add to calendar Google Calendar iCalendar Outlook 365 Outlook Live Details Date: December 7, 2021 Time: 5:30 pm - 7:00 pm « PTSA ...
Aug. 10, 2023, at 11:15 a.m. Apply to College. More. Getty Images. The college application process can be daunting, especially for students and families going through it for the first time. Choose ...
For the second year, a group of community college students has been immersed into cutting-edge research at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego. The students are a part of the Scripps Geosciences Educational Opportunities (Scripps-GEO) program, a semester-long experience where community college students are exposed to research opportunities at Scripps Oceanography. The program ...
The mission of the School of Social Work is to provide professional social work education that inspires critical thinking and lifelong learning to students who will serve in diverse social work practice areas and roles, engage in collaborative research to contribute to the well-being of populations that are vulnerable and oppressed and advance social work knowledge, and strengthen our ...
With 4-6 weeks notice of your proposals, think about using the following as a starting point for your timeline: Week 4-6: Complete Proposal Initiation Form. Week 4-5: Provide Pre-Award Grant Specialist with preliminary IAF materials (budget justification, abstract, IRB/IACUC, major goals) Week 3: Final approval of budget and Grant Specialist ...
Custom copilot is pre-populated with information from the file/folder selection. The copilot has a default folder name, branding, description, sources you've selected, and other fields already. You can keep these fields and parameters as-is, or easily update them. Customize the identity with a name change. Customize the grounding knowledge.
Wednesday, June 5, 2024 - 1:00 p.m. to 2:00 p.m. CDT. Presenting Scholar: Kaete O'Connell, Ph.D. "Hunger and the Hard Peace: Food Policy in U.S. Occupied Germany". YouTube Livestream. This virtual symposium focuses on specialized topics related to the Allied effort during World War II. Each program wraps up with a Scholar Spotlight where ...