

Research Methods in Psychology - 4th American Edition
(40 reviews)
Carrie Cuttler, Washington State University
Rajiv S. Jhangiani, Kwantlen Polytechnic University
Dana C. Leighton, Texas A&M University, Texarkana
Copyright Year: 2019
ISBN 13: 9781999198107
Publisher: Kwantlen Polytechnic University
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Beth Mechlin, Associate Professor of Psychology & Neuroscience, Earlham College on 3/19/24
This is an extremely comprehensive text for an undergraduate psychology course about research methods. It does an excellent job covering the basics of a variety of types of research design. It also includes important topics related to research... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
This is an extremely comprehensive text for an undergraduate psychology course about research methods. It does an excellent job covering the basics of a variety of types of research design. It also includes important topics related to research such as ethics, finding journal articles, and writing reports in APA format.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
I did not notice any errors in this text.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The content is very relevant. It will likely need to be updated over time in order to keep research examples relevant. Additionally, APA formatting guidelines may need to be updated when a new publication manual is released. However, these should be easy updates for the authors to make when the time comes.
Clarity rating: 5
This text is very clear and easy to follow. The explanations are easy for college students to understand. The authors use a lot of examples to help illustrate specific concepts. They also incorporate a variety of relevant outside sources (such as videos) to provide additional examples.
Consistency rating: 5
The text is consistent and flows well from one section to the next. At the end of each large section (similar to a chapter) the authors provide key takeaways and exercises.
Modularity rating: 5
This text is very modular. It is easy to pick and choose which sections you want to use in your course when. Each section can stand alone fairly easily.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The text is very well organized. Information flows smoothly from one topic to the next.
Interface rating: 5
The interface is great. The text is easy to navigate and the images display well (I only noticed 1 image in which the formatting was a tad off).
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
I did not notice any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The text is culturally relevant.
This is an excellent text for an undergraduate research methods course in the field of Psychology. I have been using the text for my Research Methods and Statistics course for a few years now. This text focuses on research methods, so I do use another text to cover statistical information. I do highly recommend this text for research methods. It is comprehensive, clear, and easy for students to use.
Reviewed by William Johnson, Lecturer, Old Dominion University on 1/12/24
This textbook covers every topic that I teach in my Research Methods course aside from psychology careers (which I would not really expect it to cover). read more
This textbook covers every topic that I teach in my Research Methods course aside from psychology careers (which I would not really expect it to cover).
I have not noticed any inaccurate information (other than directed students to read Malcolm Gladwell). I appreciate that the textbook includes information on research errors that have not been supported by replication efforts, such as embodied cognition.
Many of the basic concepts of research methods are rather timeless, but I appreciate that the text includes newer research as examples while also including "classic" studies that exemplify different methods.
The writing is clear and simple. The keywords are bolded and reveal a definition when clicked, which students often find very helpful. Many of the figures are very helpful in helping students understand various methods (I really like the ones in the single-subject design subchapter).
The book is very consistent in its terminology and writing style, which I see as a positive compared to other open psychology textbooks where each chapter is written by subject matter experts (such as the NOBA intro textbook).
Modularity rating: 4
I teach this textbook almost entirely in order (except for moving chapters 12 & 13 earlier in the semester to aid students in writing Results sections in their final papers). I think that the organization and consistency of the book reduces its modularity, in that earlier chapters are genuinely helpful for later chapters.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I preferred the organization of previous editions, which had "Theory in Research" as its own chapter. If I were organizing the textbook, I am not sure that I would have out descriptive or inferential statistics as the final two chapters (I would have likely put Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research as the final chapter). I also would not have put information about replicability and open science in the inferential statistics section.
The text is easy to read and the formatting is attractive. My only minor complaint is that some of the longer subchapters can be a pretty long scroll, but I understand the desire for their only to be one page per subchapter/topic.
I have not noticed any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I do not think the textbook is insensitive, but there is not much thought given to adapting research instruments across cultures. For instance, talking about how different constructs might have different underlying distributions in different cultures would be useful for students. In the survey methods section, a discussion of back translation or emic personality trait measurement/development for example might be a nice addition.
I choose to use this textbook in my methods classes, but I do miss the organization of the previous American editions. Overall, I recommend this textbook to my colleagues.
Reviewed by Brianna Ewert, Psychology Instructor, Salish Kootenai College on 12/30/22
This text includes the majority of content included in our undergraduate Research Methods in Psychology course. The glossary provides concise definitions of key terms. This text includes most of the background knowledge we expect our students to... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This text includes the majority of content included in our undergraduate Research Methods in Psychology course. The glossary provides concise definitions of key terms. This text includes most of the background knowledge we expect our students to have as well as skill-based sections that will support them in developing their own research projects.
The content I have read is accurate and error-free.
The content is relevant and up-to-date.
The text is clear and concise. I find it pleasantly readable and anticipate undergraduate students will find it readable and understandable as well.
The terminology appears to be consistent throughout the text.
The modular sections stand alone and lend themselves to alignment with the syllabus of a particular course. I anticipate readily selecting relevant modules to assign in my course.
The book is logically organized with clear and section headings and subheadings. Content on a particular topic is easy to locate.
The text is easy to navigate and the format/design are clean and clear. There are not interface issues, distortions or distracting format in the pdf or online versions.
The text is grammatically correct.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I have not found culturally insensitive and offensive language or content in the text. For my courses, I would add examples and supplemental materials that are relevant for students at a Tribal College.
This textbook includes supplemental instructor materials, included slides and worksheets. I plan to adopt this text this year in our Research Methods in Psychology course. I expect it to be a benefit to the course and students.
Reviewed by Sara Peters, Associate Professor of Psychology, Newberry College on 11/3/22
This text serves as an excellent resource for introducing survey research methods topics to undergraduate students. It begins with a background of the science of psychology, the scientific method, and research ethics, before moving into the main... read more
This text serves as an excellent resource for introducing survey research methods topics to undergraduate students. It begins with a background of the science of psychology, the scientific method, and research ethics, before moving into the main types of research. This text covers experimental, non-experimental, survey, and quasi-experimental approaches, among others. It extends to factorial and single subject research, and within each topic is a subset (such as observational research, field studies, etc.) depending on the section.
I could find no accuracy issues with the text, and appreciated the discussions of research and cited studies.
There are revised editions of this textbook (this being the 4th), and the examples are up to date and clear. The inclusion of exercises at the end of each chapter offer potential for students to continue working with material in meaningful ways as they move through the book and (and course).
The prose for this text is well aimed at the undergraduate population. This book can easily be utilized for freshman/sophomore level students. It introduces the scientific terminology surrounding research methods and experimental design in a clear way, and the authors provide extensive examples of different studies and applications.
Terminology is consistent throughout the text. Aligns well with other research methods and statistics sources, so the vocabulary is transferrable beyond the text itself.
Navigating this book is a breeze. There are 13 chapters, and each have subsections that can be assigned. Within each chapter subsection, there is a set of learning objectives, and paragraphs are mixed in with tables and figures for students to have different visuals. Different application assignments within each chapter are highlighted with boxes, so students can think more deeply given a set of constructs as they consider different information. The last subsection in each chapter has key summaries and exercises.
The sections and topics in this text are very straightforward. The authors begin with an introduction of psychology as a science, and move into the scientific method, research ethics, and psychological measurement. They then present multiple different research methodologies that are well known and heavily utilized within the social sciences, before concluding with information on how to present your research, and also analyze your data. The text even provides links throughout to other free resources for a reader.
This book can be navigated either online (using a drop-down menu), or as a pdf download, so students can have an electronic copy if needed. All pictures and text display properly on screen, with no distortions. Very easy to use.
There were no grammatical errors, and nothing distracting within the text.
This book includes inclusive material in the discussion of research ethics, as well as when giving examples of the different types of research approaches. While there is always room for improvement in terms of examples, I was satisfied with the breadth of research the authors presented.
This text provides an overview of both research methods, and a nice introduction to statistics for a social science student. It would be a good choice for a survey research methods class, and if looking to change a statistics class into an open resource class, could also serve as a great resource.
Reviewed by Sharlene Fedorowicz, Adjunct Professor, Bridgewater State University on 6/23/21
The comprehensiveness of this book was appropriate for an introductory undergraduate psychology course. Critical topics are covered that are necessary for psychology students to obtain foundational learning concepts for research. Sections within... read more
The comprehensiveness of this book was appropriate for an introductory undergraduate psychology course. Critical topics are covered that are necessary for psychology students to obtain foundational learning concepts for research. Sections within the text and each chapter provide areas for class discussion with students to dive deeper into key concepts for better learning comprehension. The text covered APA format along with examples of research studies to supplement the learning. The text segues appropriately by introducing the science of psychology, followed by scientific method and ethics before getting into the core of scientific research in the field of psychology. Details are provided in quantitative and qualitative research, correlations, surveys, and research design. Overall, the text is fully comprehensive and necessary introductory research concepts.
The text appears to be accurate with no issues related to content.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The text provided relevant research information to support the learning. The content was up-to-date with a variety of different examples related to the different fields of psychology. However, some topics such as in the pseudoscience section were not very relevant and bordered the line of beliefs. Here, more current or relevant solid examples would provide more relevancy in this part of the text. Bringing in more solid or concrete examples that are more current for students may have been more appropriate such as lack of connection between information found on social media versus real science.
The language and flow of the chapters accompanied by the terms, concepts, and examples of applied research allows for clarity of learning content. Terms were introduced at the appropriate time with the support of concepts and current or classic research. The writing style flows nicely and segues easily from concept to concept. The text is easy for students to understand and grasp the details related to psychological research and science.
The text provides consistency in the outline of each chapter. The beginning section chapter starts objectives as an overview to help students unpack the learning content. Key terms are consistently bolded followed by concept or definition and relevant examples. Research examples are pertinent and provide students with an opportunity to understand application of the contents. Practice exercises are provided with in the chapter and at the and in order for students to integrate learning concepts from within the text.
Sections and subsections are clearly organized and divided appropriately for ease-of-use. The topics are easily discernible and follow the flow of ideal learning routines for students. The sections and subsections are consistently outlined for each concept module. The modularity provides consistency allowing for students to focus on content rather than trying to discern how to pull out the information differently from each chapter or section. In addition, each section and subsection allow for flexibility in learning or expanding concepts within the content area.
The organization of the textbook was easy to follow and each major topic was outlined clearly. However, the chapter on presenting research may be more appropriately placed toward the end of the book rather than in the middle of the chapters related to research and research design. In addition, more information could have been provided upfront around APA format so that students could identify the format of citations within the text as practice for students throughout the book.
The interface of the book lends itself to a nice layout with appropriate examples and links to break up the different sections in the chapters. Examples where appropriate and provided engagement opportunities for the students for each learning module. Images and QR codes or easily viewed and used. Key terms are highlighted in relevant figures, graphs, and tables were appropriately placed. Overall, the interface of the text assisted with the organization and flow of learning material.
No grammatical errors were detected in this book.
The text appears to be culturally sensitive and not offensive. A variety of current and classic research examples are relevant. However, more examples of research from women, minorities, and ethnicities would strengthen the culture of this textbook. Instructors may need to supplement some research in this area to provide additional inclusivity.
Overall, I was impressed by the layout of the textbook and the ease of use. The layout provides a set of expectations for students related to the routine of how the book is laid out and how students will be able to unpack the information. Research examples were relevant, although I see areas where I will supplement information. The book provides opportunities for students to dive deeper into the learning and have rich conversations in the classroom. I plan to start using the psychology textbook for my students starting next year.
Reviewed by Anna Behler, Assistant Professo, North Carolina State University on 6/1/21
The text is very thorough and covers all of the necessary topics for an undergraduate psychology research methods course. There is even coverage of qualitative research, case studies, and the replication crisis which I have not seen in some other... read more
The text is very thorough and covers all of the necessary topics for an undergraduate psychology research methods course. There is even coverage of qualitative research, case studies, and the replication crisis which I have not seen in some other texts.
There were no issues with the accuracy of the text.
The content is very up to date and relevant for a research methods course. The only updates that will likely be necessary in the coming years are updates to examples and modifications to the section on APA formatting.
The clarity of the writing was good, and the chapters were written in a way that was accessible and easy to follow.
I did not note any issues with consistency.
Each chapter is divided into multiple subsections. This makes the chapters even easier to read, as they are broken down into short and easy to navigate sections. These sections make it easy to assign readings as needed depending on which topics are being covered in class.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The organization was one of the few areas of weakness, and I felt that the chapters were ordered somewhat oddly. However, this is something that is easily fixed, as chapters (and even subsections) can be assigned in whatever order is needed.
There were no issues of note with the interface, and the PDF of the text was easy to navigate.
The text was well written and there were no grammatical/writing errors of note.
Overall, the book did not contain any notable instances of bias. However, it would probably be appropriate to offer a more thorough discussion of the WEIRD problem in psychology research.
Reviewed by Seth Surgan, Professor, Worcester State University on 5/24/21
Pitched very well for a 200-level Research Methods course. This text provided students with solid basis for class discussion and the further development of their understanding of fundamental concepts. read more
Pitched very well for a 200-level Research Methods course. This text provided students with solid basis for class discussion and the further development of their understanding of fundamental concepts.
No issues with accuracy.
Coverage was on target, relevant, and applicable, with good examples from a variety of subfields within Psychology.
Clearly written -- students often struggle with the dry, technical nature of concepts in Research Methods. Part of the reason I chose this text in the first place was how favorably it compared to other options in terms of clarity.
No problems with inconsistent of shifting language. This is extremely important in Research Methods, where there are many closely related terms. Language was consistent and compatible with other textbook options that were available to my students.
Chapters are broken down into sections that are reasonably sized and conceptually appropriate.
The organization of this textbook fit perfectly with the syllabus I've been using (in one form or another) for 15+ years.
This textbook was easy to navigate and available in a variety of formats.
No problems at all.
Examples show an eye toward inclusivity. I did not detect any insensitive or offensive examples or undertones.
I have used this textbook for a 200-level Research Methods course run over a single summer session. This was my first experience using an OER textbook and I don't plan on going back.
Reviewed by Laura Getz, Assistant Professor, University of San Diego on 4/29/21
The topics covered seemed to be at an appropriate level for beginner undergraduate psychology students; the learning objectives for each subsection and the key takeaways and exercises for each chapter are also very helpful in guiding students’... read more
The topics covered seemed to be at an appropriate level for beginner undergraduate psychology students; the learning objectives for each subsection and the key takeaways and exercises for each chapter are also very helpful in guiding students’ attention to what is most relevant. The glossary is also thorough and a good resource for clear definitions. I would like to see a final chapter on a “big picture” or integrating key ideas of replication, meta-analysis, and open science.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, I like the way information is presented. I had a few specific issues with definitions for ordinal variables being quantitative (1st, 2nd, 3rd aren’t really numbers as much as ranked categories), the lack of specificity about different forms of validity (face, content, criterion, and discriminant all just labeled “validity” whereas internal and external validity appear in different sections), and the lack of clear distinction between correlational and quasi-experimental variables (e.g., in some places, country of origin is listed as making a design quasi-experimental, but in other chapters it is defined as correlational).
Some of the specific studies/experiments mentioned do not seem like the best or most relevant for students to learn about the topics, but for the most part, content is up-to-date and can definitely be updated with new studies to illustrate concepts with relative ease.
Besides the few concepts I listed above in “accuracy”, I feel the text was very accessible, provides clear definitions, and many examples to illustrate any potential technical/jargon terms.
I did not notice any issues with inconsistent terms except for terms that do have more than one way of describing the same concept (e.g., 2-sample vs. independent samples t-test)
I assigned the chapters out of order with relative ease, and students did not comment about it being burdensome to navigate.
The order of chapters sometimes did not make sense to me (e.g., Experimental before Non-experimental designs, Quasi-experimental designs separate from other non-experimental designs, waiting until Chapter 11 to talk about writing), but for the most part, the chapter subsections were logical and clear.
Interface rating: 4
I had no issues navigating the online version of the textbook other than taking a while to figure out how to move forward and back within the text itself rather than going back to the table of contents (this might just be a browser issue, but is still worth considering).
No grammatical errors of note.
There was nothing explicitly insensitive or offensive about the text, but there were many places where I felt like more focus on diversity and individual differences could be helpful. For example, ethics and history of psychological testing would definitely be a place to bring in issues of systemic racism and/or sexism and a focus on WEIRD samples (which is mentioned briefly at another point).
I was very satisfied with this free resource overall, and I recommend it for beginning level undergraduate psychology research methods courses.
Reviewed by Laura Stull, Associate Professor, Anderson University on 4/23/21
This book covers essential topics and areas related to conducting introductory psychological research. It covers all critical topics, including the scientific method, research ethics, research designs, and basic descriptive and inferential... read more
This book covers essential topics and areas related to conducting introductory psychological research. It covers all critical topics, including the scientific method, research ethics, research designs, and basic descriptive and inferential statistics. It even goes beyond other texts in terms of offering specific guidance in areas like how to conduct research literature searches and psychological measurement development. The only area that appears slightly lacking is detailed guidance in the mechanics of writing in APA style (though excellent basic information is provided in chapter 11).
All content appears accurate. For example, experimental designs discussed, descriptive and inferential statistical guidance, and critical ethical issues are all accurately addressed, See comment on relevance below regarding some outdated information.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
Chapter 11 on APA style does not appear to cover the most current version of the APA style guide (7th edition). While much of the information in Chapter 11 is still current, there are specifics that did change from 6th to 7th edition of the APA manual and so, in order to be current, this information would have to be supplemented with external sources.
The book is extremely well organized, written in language and terms that should be easily understood by undergraduate freshmen, and explains all necessary technical jargon.
The text is consistent throughout in terms of terminology and the organizational framework (which aids in the readability of the text).
The text is divided into intuitive and common units based on basic psychological research methodology. It is clear and easy to follow and is divided in a way that would allow omission of some information if necessary (such as "single subject research") or reorganization of information (such as presenting survey research before experimental research) without disruption to the course as a whole.
As stated previously, the book is organized in a clear and logical fashion. Not only are the chapters presented in a logical order (starting with basic and critical information like overviews of the scientific method and research ethics and progressing to more complex topics like statistical analyses).
No issues with interface were noted. Helpful images/charts/web resources (e.g., Youtube videos) are embedded throughout and are even easy to follow in a print version of the text.
No grammatical issues were noted.
No issues with cultural bias are noted. Examples are included that address topics that are culturally sensitive in nature.
I ordered a print version of the text so that I could also view it as students would who prefer a print version. I am extremely impressed with what is offered. It covers all of the key content that I am currently covering with a (non-open source) textbook in an introduction to research methods course. The only concern I have is that APA style is not completely current and would need to be supplemented with a style guide. However, I consider this a minimal issue given all of the many strengths of the book.
Reviewed by Anika Gearhart, Instructor (TT), Leeward Community College on 4/22/21
Includes the majority of elements you expect from a textbook covering research methods. Some topics that could have been covered in a bit more depth were factorial research designs (no coverage of 3 or more independent variables) and external... read more
Includes the majority of elements you expect from a textbook covering research methods. Some topics that could have been covered in a bit more depth were factorial research designs (no coverage of 3 or more independent variables) and external validity (or the validities in general).
Nothing found that was inaccurate.
Looks like a few updates could be made to chapter 11 to bring it up to date with APA 7. Otherwise, most examples are current.
Very clear, a great fit for those very new to the topic.
The framework is clear and logical, and the learning objectives are very helpful for orienting the reader immediately to the main goals of each section.
Subsections are well-organized and clear. Titles for sections and subsections are clear.
Though I think the flow of this textbook for the most part is excellent, I would make two changes: move chapter 5 down with the other chapters on experimental research and move chapter 11 to the very end. I feel that this would allow for a more logical presentation of content.
The webpage navigation is easy to use and intuitive, the ebook download works as designed, and the page can be embedded directly into a variety of LMS sites or used with a variety of devices.
I found no grammatical errors in this book.
While there were some examples of studies that included participants from several cultures, the book does not touch on ecological validity, an important external validity issue tied to cultural psychology, and there is no mention of the WEIRD culture issue in psychology, which seems somewhat necessary when orienting new psychology students to research methods today.
I currently use and enjoy this textbook in my research methods class. Overall, it has been a great addition to the course, and I am easily able to supplement any areas that I feel aren't covered with enough breadth.
Reviewed by Amy Foley, Instructor/Field & Clinical Placement Coordinator, University of Indianapolis on 3/11/21
This text provides a comprehensive overview of the research process from ideation to proposal. It covers research designs common to psychology and related fields. read more
This text provides a comprehensive overview of the research process from ideation to proposal. It covers research designs common to psychology and related fields.
Accurate information!
This book is current and lines up well with the music therapy research course I teach as a supplemental text for students to understand research designs.
Clear language for psychology and related fields.
The format of the text is consistent. I appreciate the examples, different colored boxes, questions, and links to external sources such as video clips.
It is easy to navigate this text by chapters and smaller units within each chapter. The only confusion that has come from using this text includes the fact that the larger units have roman numerals and the individual chapters have numbers. I have told students to "read unit six" and they only read the small chapter 6, not the entire unit for example.
Flows well!
I have not experienced any interface issues.
I have not found any grammar errors.
Book appears culturally relevant.
This is a great resource for research methods courses in psychology or related fields. I am glad to have used several chapters of this text within the music therapy research course I teach where students learn about research design and then create their own research proposal.
Reviewed by Veronica Howard, Associate Professor, University of Alaska Anchorage on 1/11/21, updated 1/11/21
VERY impressed by the coverage of single subject designs. I would recommend this content to colleagues. read more
VERY impressed by the coverage of single subject designs. I would recommend this content to colleagues.
Content appears accurate.
By expanding to include more contemporary research perspectives, the authors have created a wonderful dynamic that permits the text to be the foundation for many courses as well as revision and remixing for other authors.
Book easy to read, follow.
Consistency rating: 4
Content overall consistent. Only mild inconsistency in writing style between chapters.
Exceptionally modular. All content neatly divided into units with smaller portions. This would be a great book to use in a course that meets bi-weekly, or adapted into other formats.
Content organized in a clear and logical fashion, and would guide students through a semester-long course on research methods, starting with review content, broad overview of procedures (including limitations), then highlighting less common (though relevant) procedures.
Rich variety of formats for use.
No errors found.
I would appreciate more cultural examples.
Reviewed by Greg Mullin, Associate Professor, Bunker Hill Community College on 12/30/20, updated 1/6/21
I was VERY pleased with the comprehensiveness of the text. I believe it actually has an edge over the publisher-based text that I've been using for years. Each major topic was thoroughly covered with more than enough detail on individual concepts. read more
I was VERY pleased with the comprehensiveness of the text. I believe it actually has an edge over the publisher-based text that I've been using for years. Each major topic was thoroughly covered with more than enough detail on individual concepts.
I did not find any errors within the text. The authors provided an unbiased representation of research methods in psychology.
The content connects to classic, timeless examples in the field, but also mixes in a fair amount of more current, relatable examples. I feel like I'll be able to use this version of the text for many years without its age showing.
The authors present a clear and efficient writing style throughout that is rich with relatable examples. The only area that may be a bit much for undergraduate-level student understanding is the topic of statistics. I personally scale back my discussion of statistics in my Intro to Research Methods course, but for those that prefer a deeper dive, the higher-level elements are there.
I did not notice any shifts with the use of terminology or with the structural framework of the text. The text is very consistent and organized in an easily digestible way.
The authors do a fantastic job breaking complex topics down into manageable chunks both as a whole and within chapters. As I was reading, I could easily see how I could align my current approach of teaching Intro to Research Methods with their modulated presentation of the material.
I effortlessly moved through the text given the structural organization. All topics are presented in a logical fashion that allowed each message to be delivered to the reader with ease.
I read the text through the PDF version and found no issue with the interface. All image and text-based material was presented clearly.
I cannot recall coming across any grammatical errors. The text is very well written.
I did not find the text to be culturally insensitive in any way. The authors use inclusive language and even encourage that style of writing in the chapter on Presenting Your Research. I would have liked to see more cross-cultural research examples and more of an extended effort to include the theme of diversity throughout, but at no point did I find the text to be offensive.
This is a fantastic text and I look forward to adopting it for my Intro to Research Methods course in the Spring. :)
Reviewed by Maureen O'Connell, Adjunct Professor, Bunker Hill Community College on 12/15/20, updated 12/18/20
This text edition has covered all ideas and areas of research methods in psychology. It has provided a glossary of terms, sample APA format, and sample research papers. read more
This text edition has covered all ideas and areas of research methods in psychology. It has provided a glossary of terms, sample APA format, and sample research papers.
The content is unbiased, accurate, and I did not find any errors in the text.
The content is current and up-to-date. I found that the text can be added to should material change, the arrangement of the text/content makes it easily accessible to add material, if necessary.
The text is clear, easy to understand, simplistic writing at times, but I find this text easy for students to comprehend. All text is relevant to the content of behavioral research.
The text and terminology is consistent.
The text is organized well and sectioned appropriately. The information is presented in an easy-to-read format, with sections that can be assigned at various points during the semester and the reader can easily locate this.
The topics in the text are organized in a logical and clear manner. It flows really well.
The text is presented well, including charts, diagrams, and images. There did not appear to be any confusion with this text.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text was culturally appropriate and not offensive. Clear examples of potential biases were outlined in this text which I found quite helpful for the reader.
Overall, I found this to be a great edition. Much of the time I spend researching outside material for students has been included in this text. I enjoyed the format, easier to navigate, helpful to students by providing an updated version of discussions and practice assignments, and visually more appealing.
Reviewed by Brittany Jeye, Assistant Professor of Psychology, Worcester State University on 6/26/20
All of the main topics in a Research Methods course are covered in this textbook (e.g., scientific method, ethics, measurement, experimental design, hypothesis testing, APA style, etc.). Some of these topics are not covered as in-depth as in other... read more
All of the main topics in a Research Methods course are covered in this textbook (e.g., scientific method, ethics, measurement, experimental design, hypothesis testing, APA style, etc.). Some of these topics are not covered as in-depth as in other Research Method textbooks I have used previously, but this actually may be a positive depending on the students and course level (that is, students may only need a solid overview of certain topics without getting overwhelmed with too many details). It also gives the instructor the ability to add content as needed, which helps with flexibility in course design.
I did not note any errors or inaccurate/biasing statements in the text.
For the most part, everything was up to date. There was a good mix of classic research and newer studies presented and/or used as examples, which kept the chapters interesting, topical and relevant. I only noted the section on APA Style in the chapter “Presenting Your Research” which may need some updating to be in line with the new APA 7th edition. However, there should be only minor edits needed (the chapter itself was great overview and introduction to the main points of APA style) and it looks like they should be relatively easy to implement.
The text was very well-written and was presented at an accessible level for undergraduates new to Research Methods. Terms were well-defined with a helpful glossary at the end of the textbook.
The consistent structure of the textbook is huge positive. Each chapter begins with learning objectives and ends with bulleted key takeaways. There are also good exercises and learning activities for students at the end of each chapter. Instructors may need to add their own activities for chapters that do not go into a lot of depth (there are also instructor resources online, which may have more options available).
This is one of the biggest strengths of this textbook, in my opinion. I appreciate how each chapter is broken down into clearly defined subsections. The chapters and the subsections, in particular, are not lengthy, which is great for students’ learning. These subsections could be reorganized and used in a variety of ways to suit the needs of a particular course (or even as standalone subsections).
The topics were presented in a logical manner. As mentioned above, since the textbook is very modular, I feel that you could easily rearrange the chapters to fit your needs (for example, presenting survey design before experimental research or making the presenting your research section a standalone unit).
I downloaded the textbook as an ebook, which was very easy to use/navigate. There were no problems reading any of the text or figures/tables. I also appreciated that you could open the ebook using a variety of apps (Kindle, iBook, etc.) depending on your preference (and this is good for students who have a variety of technical needs).
There were no grammatical errors noted.
The examples were inclusive of races, ethnicity and background and there were not any examples that were culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. In future iterations of the replicability section, it may be beneficial to touch upon the “weird” phenomena in psychology research (that many studies use participants who are western, educated and from industrialized, rich and democratic countries) as a point to engage students in improving psychological practices.
I will definitely consider switching to this textbook in the future for Research Methods.
Reviewed by Alice Frye, Associate Teaching Professor, University of Massachusetts Lowell on 6/22/20
Hits all the necessary marks from ways of knowing to measurement, research designs, and presentation. Comparable in detail and content to other Research Methods texts I have used for teaching. read more
Hits all the necessary marks from ways of knowing to measurement, research designs, and presentation. Comparable in detail and content to other Research Methods texts I have used for teaching.
Correct and to the point. Complex ideas such as internal consistency reliability and discriminant validity are well handled--correct descriptions that are also succinct and articulated simply and with clear examples that are easy for a student reader to grasp.
Seems likely to have good staying power. One area that has changed quickly in the past is the usefulness of various research data bases. So it is possible that portion could become more quickly outdated, but there is no predicting that. The current descriptions are useful.
Very clearly written without being condescending, overly casual or clunky.
Excellent consistency throughout in terms of organization, language usage, level of detail and tone.
Imho this is one of the particular strengths of the text. Chapters are well divided into discrete parts, which seems likely to be a benefit in cohorts of students who are increasingly accustomed to digesting small amounts of information.
Well organized, straightforward structure that is maintained throughout.
No problems with the interface.
The grammar level is another notable strength. Ideas are articulated clearly, and with sophistication, but in a syntactically very straightforward manner.
The text isn't biased or offensive. I wish that to illustrate various points and research designs it had drawn more frequently on research studies that incorporate a specific focus on race and ethnicity.
This is a very good text. As good as any for profit text I have used to teach a research methods course, if not better.
Reviewed by Lauren Mathieu-Frasier, Adjunct Instructor, University of Indianapolis on 1/13/20
As other reviews have mentioned, this textbook provides a comprehensive look at multiple concepts for an introductory course in research methods in psychology. Some of the concepts (i.e., variables, external validity) are briefly described and... read more
As other reviews have mentioned, this textbook provides a comprehensive look at multiple concepts for an introductory course in research methods in psychology. Some of the concepts (i.e., variables, external validity) are briefly described and glossed over that it will take additional information, examples, and reinforcement from instructors in the classroom. Other sections and concepts, like ethics or reporting of research were well-described and thorough.
It appeared that the information was accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
The information is up-to-date. In the section on APA presentation, it looks like the minor adjustments to the APA Publication Manual 7th Edition would need to be included. However, this section gives a good foundation and the instructor can easily implement the changes.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clearly written written and provides an appropriate context when terminology is used.
There aren't any issues with consistency in the textbook.
The division of smaller sections can be beneficial when reading it and assigning it to classes. The sections are clearly organized based on learning objectives.
The textbook is organized in a logical, clear manner. There may be topics that instructors choose to present in a different manner (non-experimental and survey research prior to experimental). However, this doesn't generally impact the organization and flow of the book.
While reading and utilizing the book, there weren't any navigation issues that could impact the readability of the book. Students could find this textbook easy to use.
Grammatical errors were not noted.
There weren't any issues with cultural sensitivity in the examples of studies used in the textbook.
Reviewed by Tiffany Kindratt, Assistant Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 1/1/20
The text is comprehensive with an effective glossary of terms at the end. It would be beneficial to include additional examples and exercises for students to better understand concepts covered in Chapter II, Overview of the Scientific Method,... read more
The text is comprehensive with an effective glossary of terms at the end. It would be beneficial to include additional examples and exercises for students to better understand concepts covered in Chapter II, Overview of the Scientific Method, Chapter IV, Psychological Measurement, and Chapter XII Descriptive Statistics.
The text is accurate and there are minimal type/grammatical errors throughout. The verbiage is written in an unbiased manner consistently throughout the textbook.
The content is up-to-date, and examples can be easily updated for future versions. As a public health instructor, I would be interested in seeing examples of community-based examples in future versions. The current examples provided are relevant for undergraduate public health students as well as psychology students.
The text is written in a clear manner. The studies used can be easily understood by undergraduate students in other social science fields, such as public health. More examples and exercises using inferential statistics would be helpful for students to better grasp the concepts.
The framework for each chapter and terminology used are consistent. It is helpful that each section within each chapter begins with learning objectives and the chapter ends with key takeaways and exercises.
The text is clearly divided into sections within each chapter. When I first started reviewing this textbook, I thought each section was actually a very short chapter. I would recommend including a listing of all of the objectives covered in each chapter at the beginning to improve the modularity of the text.
Some of the topics do not follow a logical order. For example, it would be more appropriate to discuss ethics before providing the overview of the scientific method. It would be better to discuss statistics used to determine results before describing how to write manuscripts. However, the text is written in a way that that the chapters could be assigned to students in a different order without impacting the students’ comprehension of the concepts.
I did not encounter any interface issues when reviewing this text. All links worked and there were no distortions of the images or charts that may confuse the reader. There are several data tables throughout the text which are left-aligned and there is a large amount of empty white space next it. I would rearrange the text in future versions to make better use of this space.
The text contains minimal grammatical errors.
The examples are culturally relevant. I did not see any examples that may be considered culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
As an instructor for an undergraduate public health sciences and methods course, I will consider using some of the content in this text to supplement the current textbook in the future.
Reviewed by Mickey White, Assistant Professor, East Tennessee State University on 10/23/19
The table of contents is well-formatted and comprehensive. Easy to navigate and find exactly what is needed, students would be able to quickly find needed subjects. read more
The table of contents is well-formatted and comprehensive. Easy to navigate and find exactly what is needed, students would be able to quickly find needed subjects.
Content appears to be accurate and up-to-date.
This text is useful and relevant, particularly with regard to expressing and reporting descriptive statistics and results. As APA updates, the text will be easy to edit, as the sections are separated.
Easy to read and engaging.
Chapters were laid out in a consistent manner, which allows readers to know what is coming. The subsections contained a brief overview and terminology was consistent throughout. The glossary added additional information.
Sections and subsections are delineated in a usable format.
The key takeaways were useful, including the exercises at the end of each chapter.
Reading the book online is a little difficult to navigate page-by-page, but e-pub and PDF formats are easy to navigate.
No errors noted.
Would be helpful to have a clearer exploration of cultural factors impacting research, including historical bias in assessment and research outside of research ethics.
Reviewed by Robert Michael, Assistant Professor, University of Louisiana at Lafayette on 10/14/19
Successfully spans the gamut of topics expected in a Research Methods textbook. Some topics are covered in-depth, while others are addressed only at a surface level. Instructors may therefore need to carefully arrange class material for topics in... read more
Successfully spans the gamut of topics expected in a Research Methods textbook. Some topics are covered in-depth, while others are addressed only at a surface level. Instructors may therefore need to carefully arrange class material for topics in which depth of knowledge is an important learning outcome.
The factual content was error-free, according to my reading. I did spot a few grammatical and typographical errors, but they were infrequent and minor.
Great to see nuanced—although limited—discussion of issues with Null Hypothesis Significance Testing, Reproducibility in Psychological Science, and so forth. I expect that these areas are likely to grow in future editions, perhaps supplementing or even replacing more traditional material.
Extremely easy to read with multiple examples throughout to illustrate the principles being covered. Many of these examples are "classics" that students can easily relate to. Plus, who doesn't like XKCD comics?
The textbook is structured sensibly. At times, certain authors' "voices" seemed apparent in the writing, but I suspect this variability is unlikely to be noticed by or even bothersome to the vast majority of readers.
The topics are easily divisible and seem to follow routine expectations. Instructors might find it beneficial and/or necessary to incorporate some of the statistical thinking and learning into various earlier chapters to facilitate student understanding in-the-moment, rather than trying to leave all the statistics to the end.
Sensible and easy-to-follow structure. As per "Modularity", the Statistical sections may benefit from instructors folding in such learning throughout, rather than only at the end.
Beautifully presented, crisp, easy-to-read and navigate. Caveat: I read this online, in a web-browser, on only one device. I haven't tested across multiple platforms.
High quality writing throughout. Only a few minor slip-ups that could be easily fixed.
Includes limited culturally relevant material where appropriate.
Reviewed by Matthew DeCarlo, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 6/26/19
The authors do a great job of simplifying the concepts of research methods and presenting them in a way that is understandable. There is a tradeoff between brevity and depth here. Faculty who adopt this textbook may need to spend more time in... read more
The authors do a great job of simplifying the concepts of research methods and presenting them in a way that is understandable. There is a tradeoff between brevity and depth here. Faculty who adopt this textbook may need to spend more time in class going in depth into concepts, rather than relying on the textbook for all of the information related to key concepts. The text does not cover qualitative methods in detail.
The textbook provides an accurate picture of research methods. The tone is objective and without bias.
The textbook is highly relevant and up to date. Examples are drawn from modern theories and articles.
The writing is a fantastic mix of objective and authoritative while also being approachable.
The book coheres well together. Each chapter and section are uniform.
This book fits very well within a traditional 16 week semester, covering roughly a chapter per week. One could take out specific chapters and assign them individually if research methods is taught in a different way from a standard research textbook.
Content is very well organized. The table of contents is easy to navigate and each chapter is presented in a clear and consistent manner. The use of a two-tier table of contents is particularly helpful.
Standard pressbooks interface, which is great. Uses all of the standard components of Pressbooks well, though the lack of H5P and interactive content is a drawback.
I did not notice any grammar errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 2
The book does not deal with cultural competence and humility in the research process. Integration of action research and decolonization perspectives would be helpful.
Reviewed by Christopher Garris, Associate Professor, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 5/24/19
Most content areas in this textbook were covered appropriately extensively. Notably, this textbook included some content that is commonly missing in other textbooks (e.g. presenting your research). There were some areas where more elaboration... read more
Most content areas in this textbook were covered appropriately extensively. Notably, this textbook included some content that is commonly missing in other textbooks (e.g. presenting your research). There were some areas where more elaboration and more examples were needed. For example, the section covering measurement validities included all the important concepts, but needed more guidance for student comprehension. Also, the beginning chapters on 'common sense' reasoning and pseudoscience seemed a little too brief.
Overall, this textbook appeared to be free from glaring errors. There were a couple of instances of concern, but were not errors, per se. For example, the cut-off for Cronbach's alpha was stated definitively at .80, while this value likely would be debated among researchers.
This textbook was presented in such a way that seemed protect it from becoming obsolete within the next few years. This is important for continued, consistent use of the book. The authors have revised this book, and those revisions are clearly summarized in the text. Importantly, the APA section of the textbook appears to be up-to-date. Also, the use of QR codes throughout the text is a nice touch that students may appreciate.
Connected to comprehensiveness, there are some important content areas that I felt were lacking in elaboration and examples (e.g. testing the validity of measurement; introduction of experimental design), which inhibits clarity. Overall, however, the topics seemed to be presented in a straightforward, accessible manner. The textbook includes links to informative videos and walk-throughs where appropriate, which seem to be potentially beneficial for student comprehension. The textbook includes tools designed to aid learning, namely "Key Takeaways" and "Exercises" sections at the end of most modules, but not all. "Key Takeaways" seemed valuable, as they were a nice bookend to the learning objectives stated at the beginning of each module. "Exercises" did not appear to be as valuable, especially for the less-motivated student. On their face, these seemed to be more designed for instructors to use as class activities/active learning. Lastly, many modules of the textbook were text-heavy and visually unappealing. While this is superficial, the inclusion of additional graphics, example boxes, or figures in these text-heavy modules might be beneficial.
The textbook appeared to be internally consistent with its approach and use of terminology.
The textbook had a tendency to 'throw out' big concepts very briefly in earlier modules (e.g. sampling, experimental/non-experimental design), and then cover them in more detail in later modules. This would have been less problematic if the text would explicitly inform the student that these concepts would be elaborated upon later. Beyond this issue, the textbook seems to lend itself to being divided up and used on module-by-module basis.
The organization of the chapters did not make intuitive sense to me. The fact that correlation followed experimental research, and that descriptive research was the second-to-last module in the sequence was confusing. That said, textbook is written in such a way that an instructor easily assign the modules in the order that works best for their class.
Overall, the interface worked smoothly and there were few technical issues. Where there were issues (e.g. inconsistent spacing between lines and words), they were negligible.
The text seemed to be free from glaring grammatical problems.
Because this is a methodology textbook, it does not lend itself to too much cultural criticism. That said, the book did not rely on overly controversial examples, but also didn't shy away from important cultural topics (e.g. gender stereotypes, vaccines).
Reviewed by Michel Heijnen, Assistant Professor, University of North Carolina Wilmington on 3/27/18
The book covers all areas related to research methods, not only for the field of psychology, but also to other related fields like exercise science. Topics include ethics, developing a research questions, experimental designs, non-experimental... read more
The book covers all areas related to research methods, not only for the field of psychology, but also to other related fields like exercise science. Topics include ethics, developing a research questions, experimental designs, non-experimental designs, and basic statistics, making this book a great resource for undergraduate research methods classes.
Reviewed content is accurate and seems free of any personal bias.
The topic of research methods in general is not expected to change quickly. It is not expected that this text will become obsolete in the near future. Furthermore, for both the field of psychology as well as other related fields, the examples will continue to have an application to explain certain concepts and will not be outdated soon, even with new research emerging every day.
The text is written so an undergraduate student should be able to understand the concepts. The examples provided in the text greatly contribute to the understanding of the topics and the proposed exercises at the end of each chapter will further apply the knowledge.
The layout and writing style are consistent throughout the text.
Layout of the text is clear, with multiple subsection within each chapter. Each chapter can easily be split into multiple subsection to assign to students. No evidence of self-refers was observed, and individual chapters could be assigned to students without needed to read all preceding chapters. For example, Chapter 4 may not be particularly useful to students outside of psychology, but an instructor can easily reorganize the text and skip this chapter while students can still understand following chapters.
Topics are addressed in a logical manner. Overall, an introduction to research is provided first (including ethics to research), which is followed by different types of research, and concludes with types of analysis.
No images or tables are distorted, making the text easy to read.
No grammatical errors observed in text.
Text is not offensive and does not appear to be culturally insensitive.
I believe that this book is a great resource and, as mentioned previously, can be used for a wider audience than just psychology as the basics of research methods can be applied to various fields, including exercise science.
Reviewed by Chris Koch, Professor of Psychology, George Fox University on 3/27/18
All appropriate areas and topics are covered in the text. In that sense, this book is equivalent to other top texts dealing with research methods in psychology. The appeal of this book is the brevity and clarity. Therefore, some may find that,... read more
All appropriate areas and topics are covered in the text. In that sense, this book is equivalent to other top texts dealing with research methods in psychology. The appeal of this book is the brevity and clarity. Therefore, some may find that, although the topics are covered, topics may not be covered as thoroughly they might like. Overall, the coverage is solid for an introductory course in research methods.
In terms of presentation, this book could be more comprehensive. Each chapter does start with a set of learning objectives and ends with "takeaways" and a short set of exercises. However, it lacks detailed chapter outlines, summaries, and glossaries. Furthermore, an index does not accompany the text.
I found the book to be accurate with content being fairly presented. There was no underlying bias throughout the book.
This is an introductory text for research methods. The basics of research methods have been consistent for some time. The examples used in the text fit the concepts well. Therefore, it should not be quickly dated. It is organized in such a way that sections could be easily modified with more current examples as needed.
The text is easy to read. It is succinct yet engaging. Examples are clear and terminology is adequately defined.
New terms and concepts are dealt with chapter by chapter. However, those things which go across chapters are consistently presented.
The material for each chapter is presented in subsections with each subsection being tied to a particular learning objective. It is possible to use the book by subsection instead of by chapter. In fact, I did that during class by discussing the majority of one chapter, discussing another chapter, and then covering what I previously skipped,
In general, the book follows a "traditional" organization, matching the organization of many competing books. As mentioned in regard to modularity, I did not follow the organization of the book exactly as it was laid out. This may not necessarily reflect poorly on the book, however, since I have never followed the order of any research methods book. My three exams covered chapter 1 through 4, chapters 5, 6, part of 8, and chapters 7, the remainder of 8, 9, and 10. Once we collected data I covered chapters 11 through 13.
Interface rating: 3
The text and images are clear and distortion free. The text is available in several formats including epub, pdf, mobi, odt, and wxr. Unfortunately, the electronic format is not taken full advantage of. The text could be more interactive. As it is, it is just text and images. Therefore, the interface could be improved.
The book appeared to be well written and edited.
I did not find anything in the book that was culturally insensitive or offensive. However, more examples of cross-cultural research could be included.
I was, honestly, surprised by how much I liked the text. The material was presented in easy to follow format that is consistent with how I think about research methods. That made the text extremely easy to use. Students also thought the book was highly accessible Each chapter was relatively short but informative and easy to read.
Reviewed by Kevin White, Assistant Professor, East Carolina University on 2/1/18
This book covers all relevant topics for an introduction to research methods course in the social sciences, including measurement, sampling, basic research design, and ethics. The chapters were long enough to be somewhat comprehensive, but short... read more
This book covers all relevant topics for an introduction to research methods course in the social sciences, including measurement, sampling, basic research design, and ethics. The chapters were long enough to be somewhat comprehensive, but short enough to be digestible for students in an introductory-level class. Student reviews of the book have so far been very positive. The only section of the text for which more detail may be helpful is 2.3 (Reviewing the Research Literature), in which more specific instructions related to literature searches may be helpful to students.
I did not notice any issues related to accuracy. Content appeared to be accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
One advantage of this book is that it is relevant to other applied fields outside of psychology (e.g., social work, counseling, etc.). Also, the exercises at the end of chapter sections are helpful.
The clarity of the text provides students with succinct definitions for research-related concepts, without unnecessary discipline-specific jargon. One suggestion for future editions would be to make the distinctions between different types of non-experimental research a bit more clear for students in introductory classes (e.g., "Correlational Research" in Section 7.2).
Formatting and terminology was consistent throughout this text.
A nice feature of this book is that instructors can select individual sections within chapters, or even jump between sections within chapters. For example, Section 1.4 may not fit for a class that is less clinically-oriented in nature.
The flow of the text was appropriate, with ethics close to the beginning of the book (and an entire chapter devoted to it), and descriptive/inferential statistics at the end.
I did not notice any problems related to interface. I had no trouble accessing or reading the text, and the images were clear.
The text contained no discernible grammatical errors.
The book does not appear to be culturally insensitive in any discernible way, and explicitly addresses prejudice in research (e.g., Section 5.2). However, I think that continuing to add more examples that relate to specific marginalized groups would help improve the text (and especially exercises).
Overall, this book is very useful for an introductory research methods course in psychology or social work, and I highly recommend.
Reviewed by Elizabeth Do, Instructor, Virginia Commonwealth University on 2/1/18
Although this textbook does provide good information regarding introductory concepts necessary for the understanding of correlational designs, and is presented in a logical order. It does not, however, cover qualitative methodologies, or research... read more
Although this textbook does provide good information regarding introductory concepts necessary for the understanding of correlational designs, and is presented in a logical order. It does not, however, cover qualitative methodologies, or research ethics as it relates to other countries outside of the US.
There does not seem to be any errors within the text.
Since this textbook covers a topic that is unlikely to change over the years and it's content is up-to-date, it remains relevant to the field.
The textbook is written at an appropriate level for undergraduate students and is useful in that it does explain important terminology.
There does not seem to be any major inconsistencies within the text.
Overall, the text is very well organized - it is separated into chapters that are divided up into modules and within each module, there are clear learning objectives. It is also helpful that the textbook includes useful exercises for students to practice what they've read about from the text.
The topics covered by this textbook are presented in an order that is logical. The writing is clear and the examples are very useful. However, more information could be provided in some of the chapters and it would be useful to include a table of contents that links to the different chapters within the PDF copy, for reader's ease in navigation when looking for specific terms and/or topics.
Overall, the PDF copy of the textbook made it easy to read; however, there did seem to be a few links that were missing. Additionally, it would be helpful to have some of the graphs printed in color to help with ease of following explanations provided by the text. The inclusion of a table of contents would also be useful for greater ease with navigation.
There does not seem to be any grammatical errors in the textbook. Also, the textbook is written in a clear way, and the information flows nicely.
This textbook focuses primarily on examples from the United States. It does not seem to be culturally insensitive or offensive in anyway and I liked that it included content regarding the avoidance of biased language (chapter 11).
This textbook makes the material very accessible, and it is easy to read/follow examples.
Reviewed by Eric Lindsey, Professor, Penn State University Berks Campus on 2/1/18
The content of the Research Methods in Psychology textbook was very thorough and covered what I would consider to be the important concepts and issues pertaining to research methods. I would judge that the textbook has a comparable coverage of... read more
The content of the Research Methods in Psychology textbook was very thorough and covered what I would consider to be the important concepts and issues pertaining to research methods. I would judge that the textbook has a comparable coverage of information to other textbooks I have reviewed, including the current textbook I am using. The range of scholarly sources included in the textbook was good, with an appropriate balance between older and classic research examples and newer more cutting edge research information. Overall, the textbook provides substantive coverage of the science of conducting research in the field of psychology, supported by good examples, and thoughtful questions.
The textbook adopts a coherent and student-friendly format, and offers a precise introduction to psychological research methodology that includes consideration of a broad range of qualitative and quantitative methods to help students identify and evaluate the best approach for their research needs. The textbook offers a detailed review of the way that psychological researchers approach their craft. The author guides the reader through all aspects of the research process including formulating objectives, choosing research methods, securing research participants, as well as advice on how to effectively collect, analyze and interpret data and disseminate those findings to others through a variety of presentation and publication venues. The textbook offers relevant supplemental information in textboxes that is highly relevant to the material in the accompanying text and should prove helpful to learners. Likewise the graphics and figures that are included are highly relevant and clearly linked to the material presented in the text. The information covered by the textbook reflects an accurate summary of current techniques and methods used in research in the field of psychology. The presentation of information addresses the pros and cons of different research strategies in an objective and evenhanded way.
The range of scholarly sources included in the textbook was good, with an appropriate balance between older, classic research evidence and newer, cutting edge research. Overall, the textbook provides substantive coverage of the science on most topics in research methods of psychology, supported by good case studies, and thoughtful questions. The book is generally up to date, with adequate coverage of basic data collection methods and statistical techniques. Likewise the review of APA style guidelines is reflects the current manual and I like the way the author summarizes changes from the older version of the APA manual. The organization of the textbook does appear to lend itself to editing and adding new information with updates in the future.
I found the textbook chapters to be well written, in a straightforward yet conversational manner. It gives the reader an impression of being taught by a knowledgeable yet approachable expert. The writing style gives the learner a feeling of being guided through the lessons and supported in a very conversational approach. The experience of reading the textbook is less like being taught and more like a colleague sharing information. Furthermore, the style keeps the reader engaged but doesn't detract from its educational purpose. I also appreciate that the writing is appropriately concise. No explanations are so wordy as to overwhelm or lull the reader to sleep, but at the same time the information is not so vague that the reader can't understand the point at all.
The book’s main aim is to enable students to develop their own skills as researchers, so they can generate and advance common knowledge on a variety of psychological topics. The book achieves this objective by introducing its readers, step-by-step, to psychological research design, while maintaining an excellent balance between substance and attention grabbing examples that is uncommon in other research methods textbooks. Its accessible language and easy-to-follow structure and examples lend themselves to encouraging readers to move away from the mere memorization of facts, formulas and techniques towards a more critical evaluation of their own ideas and work – both inside and outside the classroom. The content of the chapters have a very good flow that help the reader to connect information in a progressive manner as they proceed through the textbook.
Each chapter goes into adequate depth in reviewing both past and current research related to the topic that it covers for an undergraduate textbook on research methods in psychology. The information within each chapter flows well from point-to-point, so that the reader comes away feeling like there is a progression in the information presented. The only limitation that I see is that I felt the author could do a little more to let the reader know how information is connected from chapter to chapter. Rather than just drawing the reader’s attention to things that were mentioned in previous chapters, it would be nice to have brief comments about how issues in one chapter relate to topics covered in previous chapters.
In my opinion the chapters are arranged in easily digestible units that are manageable in 30-40 minute reading sessions. In fact, the author designed the chapters of the textbook in a way to make it easy to chunk information, and start and stop to easily pick up where one leaves off from one reading session to another. I also found the flow of information to be appropriate, with chapters containing just the right amount of detail for use in my introductory course in research methods in psychology.
The book is organized into thirteen chapters. The order of the chapters offers a logical progression from a broad overview of information about the principles and theory behind research in psychology, to more specific issues concerning the techniques and mechanics of conducting research. Each chapter ends with a summary of key takeaways from the chapter and exercises that do more than ask for content regurgitation. I find the organization of the textbook to be effective, and matches my approach to the course very well. I would not make any changes to the overall format with the exception of moving chapter 11 on presenting research to the end of the textbook, after the chapters on statistical analysis and interpretation.
I found the quality of the appearance of the textbook to be very good. The textbook features appropriate text and section/header font sizes that allow for an adequate zooming level to read large or smalls sections of text, that will give readers flexibility to match their personal preference. There are learning objectives at the start of each chapter to help students know what to expect. Key terms are highlighted in a separate color that are easily distinguishable in the body of the page. There are very useful visuals in every chapter, including tables, figures, and graphs. Relevant supplemental information is also highlighted in well formatted text boxes that are color coded to indicate what type of information is included. My only criticism is that the photographs included in the text are of low quality, and there are so few in the textbook that I feel it would have been better to just leave them out.
I found no grammatical errors in my review of the textbook. The textbook is generally well written, and the style of writing is at a level that is appropriate for an undergraduate class.
Although the textbook contains no instances of presenting information that is cultural insensitive or offensive, it does not offer an culturally inclusive review of information pertaining to research methods in psychology. I found no inclusion of examples of research conducting with non European American samples included in the summary of studies. Likewise the authors do place much attention on the issue of cultural sensitivity when conducing research. If there is one major weakness of the textbook I would say it is in this area, but based on my experience it is not an uncommon characteristic of textbooks on research methods in psychology.
Reviewed by zehra peynircioglu, Professor, American University on 2/1/18
Short and sweet in most areas. Covers the basic concepts, not very comprehensively but definitely adequately so for a general beginning-level research methods course. For instance, I would liked to have seen a "separate" chapter on correlational... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
Short and sweet in most areas. Covers the basic concepts, not very comprehensively but definitely adequately so for a general beginning-level research methods course. For instance, I would liked to have seen a "separate" chapter on correlational research (there is one on single subject research and one on survey research), a discussion of the importance of providing a theoretical rationale for "getting an idea" (most students are fine with finding interesting and feasible project ideas but cannot give a theoretical rationale) before or after Chapter 4 on Theory, or a chapter on neuroscientific methods, which are becoming more and more popular. Nevertheless, it touches on most traditional areas that are in other books.
I did not find any errors or biases
This is one area where there is not much danger of going obsolete any time soon. The examples might need to be updated periodically (my students tend to not like dated materials, however relevant), but that should be easy.
Very clear and accessible prose. Despite the brevity, the concepts are put forth quite clearly. I like the "not much fluff" mentality. There is also adequate explanations of jargon and technical terminology.
I could not find any inconsistencies. The style and exposition frameworks are also quite consistent.
Yes, the modularity is fine. The chapters follow a logical pattern, so there should not be too much of a need for jumping around. And even if jumping around is needed depending on teaching style, the sections are solid in terms of being able to stand alone (or as an accompaniment to lectures).
Yes, the contents is ordered logically and the high modularity helps with any reorganization that an instructor may favor. In my case, for instance, Ch. 1 is fine, but I would skip it because it's mostly a repetition of what most introductory psychology books also say. I would also discuss non-experimental methods before going into experimental design. But such changes are easy to do, and if someone followed the book's own organization, there would also be a logical flow.
As far as I could see, the text is free of significant interface issues, at least in the pdf version
I could not find any errors.
As far as I could see, the book was culturally relevant.
I loved the short and sweet learning objectives, key takeaway sections, and the exercises. They are not overwhelming and can be used in class discussions, too.
Reviewed by George Woodbury, Graduate Student, Miami University, Ohio on 6/20/17
This text covers the typical areas for an undergraduate psychology course in research design. There is no table of contents included with the downloadable version, although there is a table of contents on the website (which excludes sub-sections... read more
This text covers the typical areas for an undergraduate psychology course in research design. There is no table of contents included with the downloadable version, although there is a table of contents on the website (which excludes sub-sections of chapters). The sections on statistics are not extensive enough to be useful in and of themselves, but they are useful for transitions to a follow-up statistics course. There does not seem to be a glossary of terms, which made it difficult at times for my read through and I assume later for students who decide to print the text. The text is comprehensive without being wordy or tedious.
Relatively minor errors; There does not seem to be explicit cultural or methodological bias in the text.
The content is up-to-date, and examples from the psychology literature are generally within the last 25 years. Barring extensive restructuring in the fundamentals of methodology and design in psychology, any updates will be very easy to implement.
Text will be very clear and easy to read for students fluent in English. There is little jargon/technical terminology used, and the vocabulary that is provided in the text is contemporary
There do not seem to be obvious shifts in the terminology or the framework. The text is internally consistent in that regard.
The text is well divided into chapter and subsections. Each chapter is relatively self-contained, so there are little issues with referring to past material that may have been skipped. The learning objectives at the beginning of the chapter are very useful. Blocks of text are well divided with headings.
As mentioned above, the topics of the text follow the well-established trajectory of undergraduate psychology courses. This makes it very logical and clear.
The lack of a good table of contents made it difficult to navigate the text for my read through. There were links to an outside photo-hosting website (flickr) for some of the stock photos, which contained the photos of the original creators of the photos. This may be distracting or confusing to readers. However, the hyperlinks in general helped with navigation with the PDF.
No more grammatical errors than a standard, edited textbook.
Very few examples explicitly include other races, ethnicities, or backgrounds, however the examples seem to intentionally avoid cultural bias. Overall, the writing seems to be appropriately focused on avoiding culturally insensitive or offensive content.
After having examined several textbooks on research design and methodology related to psychology, this book stands out as superior.
Reviewed by Angela Curl, Assistant Professor, Miami University (Ohio) on 6/20/17
"Research Methods in Psychology" covers most research method topics comprehensively. The author does an excellent job explaining main concepts. The chapter on causation is very detailed and well-written as well as the chapter on research ethics.... read more
"Research Methods in Psychology" covers most research method topics comprehensively. The author does an excellent job explaining main concepts. The chapter on causation is very detailed and well-written as well as the chapter on research ethics. However, the explanations of data analysis seem to address upper level students rather than beginners. For example, in the “Describing Statistical Relationships” chapter, the author does not give detailed enough explanations for key terms. A reader who is not versed in research terminology, in my opinion, would struggle to understand the process. While most topics are covered, there are some large gaps. For example, this textbook has very little content related to qualitative research methods (five pages).
The content appears to be accurate and unbias.
The majority of the content will not become obsolete within a short time period-- many of the information can be used for the coming years, as the information provided is, overall, general in nature. The notably exceptions are the content on APA Code of Ethics and the APA Publication Manual, which both rely heavily on outdated versions, which limits the usefulness of these sections. In addition, it would be helpful to incorporate research studies that have been published after 2011.
The majority of the text is clear, with content that is easy for undergraduate students to read and understand. The key points included in the chapters are helpful, but some chapters seem to be missing key points (i.e., the key points do not accurately represent the overall chapter).
The text seems to be internally consistent in its terminology and organization.
Each chapter is broken into subsections that can be used alone. For example, section 5.2 covers reliability and validity of measurement. This could be extremely helpful for educators to select specific content for assigned readings.
The topics are presented in a logical matter for the most part. However, the PDF version of the book does not include a table of contents, and none of the formats has a glossary or index. This can make it difficult to quickly navigate to specific topics or terms, especially when explanations do not appear where expected. For example, the definitions of independent and dependent variables is provided under the heading “Correlation Does Not Imply Causation” (p. 22).
The text is consistent but needs more visual representations throughout the book, rather than heavily in some chapters and none at all in other chapters. Similarly, the text within the chapters is not easily readable due to the large sections of text with little to no graphics or breaks.
The interface of the text is adequate. However, the formatting of the PDF is sometimes weak. For example, the textbook has a number of pages with large blank spaces and other pages are taken up with large photos or graphics. The number of pages (and cost of printing) could have been reduced, or more graphics added to maximize utility.
I found no grammatical errors.
Text appears to be culturally sensitive. I appreciated the inclusion of the content about avoiding biased language (chapter 11).
Instructors who adopt this book would likely benefit from either selecting certain chapters/modules and/or integrating multiple texts together to address the shortcomings of this text. Further, the sole focus on psychology limits the use of this textbook for introductory research methods for other disciplines (e.g., social work, sociology).
Reviewed by Pramit Nadpara, Assistant Professor, Virginia Commonwealth University on 4/11/17
The text book provides good information in certain areas, while not comprehensive information in other areas. The text provides practical information, especially the section on survey development was good. Additional information on sampling... read more
The text book provides good information in certain areas, while not comprehensive information in other areas. The text provides practical information, especially the section on survey development was good. Additional information on sampling strategies would have been beneficial for the readers.
There are no errors.
Research method is a common topic and the fundamentals of it will not change over the years. Therefore, the book is relevant and will not become obsolete.
Clarity rating: 3
The text in the book is clear. Certain aspects of the text could have been presented more clearly. For example, the section on main effects and interactions are some concepts that students may have difficulty understanding. Those areas could be explained more clearly with an example.
Consistency rating: 3
Graphs in the book lacks titles and variable names. Also, the format of chapter title page needs to be consistent.
At times there were related topics spread across several chapters. This could be corrected for a better read by the audience..
The book text is very clear, and the flow from one topic to the next was adequate. However, having a outline would help the reader.
The PDF copy of the book was a easy read. There were few links that were missing though.
There were no grammatical errors.
The text is not offensive and examples in it are mostly based on historical US based experiments.
I would start of by saying that I am a supporter of the Open Textbook concept. In this day and age, there are a variety of Research Methods book/text available on the market. While this book covers research methods basics, it cannot be recommended in its current form as an acceptable alternative to the standard text. Modifications to the text as recommended by myself and other reviewers might improve the quality of this book in the future.
Reviewed by Meghan Babcock, Instructor, University of Texas at Arlington on 4/11/17
This text includes all important areas that are featured in other Research Methods textbooks and are presented in a logical order. The text includes great examples and provides the references which can be assigned as supplemental readings. In... read more
This text includes all important areas that are featured in other Research Methods textbooks and are presented in a logical order. The text includes great examples and provides the references which can be assigned as supplemental readings. In addition, the chapters end with exercises that can be completed in class or as part of a laboratory assignment. This text would be a great addition to a Research Methods course or an Introductory Statistics course for Psychology majors.
The content is accurate. I did not find any errors and the material is unbiased.
Yes - the content is up to date and would be easy to update if/when necessary.
The text is written at an appropriate level for undergraduate students and explains important terminology. The research studies that the author references are ones that undergraduate psychology majors should be familiar with. The only section that was questionable to me was that on multiple regression in section 8.3 (Complex Correlational Designs). I am unaware of other introductory Research Methods textbooks that cover this analysis, especially without describing simple regression first.
The text is consistent in terms of terminology. The framework is also consistent - the chapters begin with Learning Objectives and ends with Key Takeaways and Exercises.
The text is divisible into smaller reading sections - possibly too many. The sections are brief, and in some instances too brief (e.g., the section on qualitative research). I think that the section headers are helpful for instructors who plan on using this text in conjunction with another text in their course.
The topics were presented in a logical fashion and are similar to other published Research Methods texts. The writing is very clear and great examples are provided. I think that some of the sections are rather brief and more information and examples could be provided.
I did not see any interface issues. All of the links worked properly and the tables and figures were accurate and free of errors. I particularly liked the figures in section 5.2 on reliability of measurement.
There are three comments that I have about the interface, however. First, I was expecting the keywords in blue font to be linked to a glossary, but they were not. I would have appreciated this feature. Second, I read this text as a PDF on an iPad and this version lacking was the Table of Contents (TOC) feature. Although I was able to view the TOC in different versions, I would have appreciated it in the PDF version. Also, it would be nice if the TOC was clickable (i.e., you could click on a section and it automatically directed you to that section). Third, I think the reader of this text would benefit from a glossary at the end of each chapter and/or an index at the end of the text. The "Key Takeaways" sections at the end of each chapter were helpful, but I think that a glossary would be a nice addition as well.
I did not notice any grammatical errors of any kind. The text was easy to read and I think that undergraduate students would agree.
The text was not insensitive or offensive to any races, ethnicities, or backgrounds. I appreciated the section on avoiding biased language when writing manuscripts (e.g., using 'children with learning disabilities' instead of 'special children' or using 'African American' instead of 'minority').
I think that this text would be a nice addition to a Research Methods & Statistics course in psychology. There are some sections that I found particularly helpful: (1) 2.2 and 2.3 - the author gives detailed information about generating research questions and reviewing the literature; (2) 9.2 - this section focuses on constructing survey questionnaires; (3) 11.2 and 11.3 - the author talks about writing a research report and about presenting at conferences. These sections will be great additions to an undergraduate Research Methods course. The brief introduction to APA style was also helpful, but should be supplemented with the most recent APA style manual.
Reviewed by Shannon Layman, Lecturer, University of Texas at Arlington on 4/11/17
The sections in this textbook are overall more brief than in previous Methods texts that I have used. Sometimes this brevity is helpful in terms of getting to the point of the text and moving on. In other cases, some topics could use a bit more... read more
The sections in this textbook are overall more brief than in previous Methods texts that I have used. Sometimes this brevity is helpful in terms of getting to the point of the text and moving on. In other cases, some topics could use a bit more detail to establish a better foundation of the content before moving on to examples and/or the next topic.
I did not find any incorrect information or gross language issues.
Basic statistical and/or methodological texts tend to stay current and up-to-date because the topics in this field have not changed over the decades. Any updated methodologies would be found in a more advanced methods text.
The text is very clear and the ideas are easy to follow/ presented in a logical manner. The most helpful thing about this textbook is that the author arrives at the point of the topic very quickly. Another helpful point about this textbook is the relevancy of the examples used. The examples appear to be accessible to a wide audience and do not require specialization or previous knowledge of other fields of psychology.
I feel this text is very consistent throughout. The ideas build on each other and no terms are discussed in later chapters without being established in previous chapters.
Each chapter had multiple subsections which would allow for smaller reading sections throughout the course. The amount of content in each section and chapter appeared to be less than what I have encountered in other Methods texts.
The organization of the topics in this textbook follows the same or similar organization that I see in other textbooks. As I mentioned previously, the ideas build very well throughout the text.
I did not find any issues with navigation or distortion of the figures in the text.
There were not any obvious and/or egregious grammatical errors that I encountered in this text.
This topic is not really an issue with a Methods textbook as the topics are more so conceptual as opposed to topical. That being said, I did not see an issue with any examples used.
I have no other comments than what I addressed previously.
Reviewed by Sarah Allred, Associate Professor, Rutgers University, Camden on 2/8/17
Mixed. For some topics, there is more (and more practical) information than in most textbooks. I appreciated the very practical advice to students about how to plot data (in statistics chapters). Similarly, there is practical advice about how... read more
Mixed. For some topics, there is more (and more practical) information than in most textbooks. I appreciated the very practical advice to students about how to plot data (in statistics chapters). Similarly, there is practical advice about how to comply with ethical guidelines. The section on item development in surveys was very good.
On the other hand, there is far too little information about some subjects. For example, independent and dependent variables are introduced in passing in an early chapter and then referred to only much later in the text. In my experience, students have a surprisingly difficult time grasping this concept. Another important example is sampling; I would have preferred much more information on types of samples and sampling techniques, and the problems that arise from poor sampling. A third example is the introduction to basic experimental design. Variables, measurement, validity, and reliability are all introduced in one chapter.
I did not see an index or glossary.
I found no errors.
The fundamentals of research methods do not change much. Given the current replication crisis in psychology, it might be helpful to have something about replicability.
Mixed. The text itself is spare and clear. The style of the book is to explain a concept in very few words. There are some excellent aspects of this, but on the other hand, there are some concepts that students have a very difficult time undersatnding if they are not embedded in concrete examples. For example, the section on main effects and interactions shows bar graphs of interactions, but this is presented without variable names or axis titles, and separate from any specific experiment.
Sometimes the chapter stucture is laid out on the title page, and other times it is not. Some graphs lack titles and variable names.
The chapters can be stand alone, but sometimes I found conceptually similar pieces spread across several chapters, and conceptually different pieces in the same chapters.
The individual sentences and paragraphs are always very clear. However, I felt that more tables/outlines of major concepts would have been helpful. For example, perhaps a flow chart of different kinds of experimental designs would be useful. (See section on comprehensiveness for more about organization).
The flow from one topic to the next was adequate.
I read the pdf. Perhaps the interface is more pleasant on other devices, but I found the different formats and fonts in image/captions/main text/figure labels distracting. Many if the instances of apparently hyperlinked (blue) text to do not link to anything.
I found no grammatical errors, and prose is standard academic English.
Like most psychology textbooks available in the US, examples are focused on important experiments in US history.
I really wanted to be happy with this text. I am a supporter of the Open Textbook concept, and I wanted to find this book an acceptable alternative to the variety of Research Methods texts I’ve used. Unfortunately, I cannot recommend this book as superior in quality.
Reviewed by Joel Malin, Assistant Professor, Miami University on 8/21/16
This textbook covers all or nearly all of what I believe are important topics to provide an introduction to research methods in psychology. One minor issue is that the pdf version, which I reviewed, does not include an index or a glossary. As... read more
This textbook covers all or nearly all of what I believe are important topics to provide an introduction to research methods in psychology. One minor issue is that the pdf version, which I reviewed, does not include an index or a glossary. As such, it may be difficult for readers to zero in on material that they need, and/or to get a full sense of what will be covered and in what order.
I did not notice errors.
The book provides a solid overview of key issues related to introductory research methods, many of which are nearly timeless.
The writing is clear and accessible. It was easy and pleasing to read.
Terms are clearly defined and build upon each other as the book progresses.
I believe the text is organized in such a way that it could be easily divided into smaller sections.
The order in which material is presented seems to be well thought out and sensible.
I did not notice any issues with the interface. I reviewed the pdf version and thought the images were very helpful.
The book is written in a culturally relevant manner.
Reviewed by Abbey Dvorak, Assistant Professor, University of Kansas on 8/21/16
The text includes basic, essential information needed for students in an introductory research methods course. In addition, the text includes three chapters (i.e., research ethics, theory, and APA style) that are typically absent from or... read more
The text includes basic, essential information needed for students in an introductory research methods course. In addition, the text includes three chapters (i.e., research ethics, theory, and APA style) that are typically absent from or inadequately covered in similar texts. However, I did have some areas of concern regarding the coverage of qualitative and mixed methods approaches, and nonparametric tests. Although the author advocates for the research question to guide the choice of approach and design, minimal attention is given to the various qualitative designs (e.g., phenomenology, narrative, participatory action, etc.) beyond grounded theory and case studies, with no mention of the different types of mixed methods designs (e.g., concurrent, explanatory, exploratory) that are prevalent today. In addition, common nonparametric tests (e.g., Wilcoxon, Mann-Whitney, etc.) and parametric tests for categorical data (e.g., chi-square, Fisher’s exact, etc.) are not mentioned.
The text overall is accurate and free of errors. I noticed in the qualitative research sub-section, the author describes qualitative research in general, but does not mention common practices associated with qualitative research, such as transcribing interviews, coding data (e.g., different approaches to coding, different types of codes), and data analysis procedures. The information that is included appears accurate.
The text appears up-to-date and includes basic research information and classic examples that rarely change, which may allow the text to be used for many years. However, the author may want to add information about mixed methods research, a growing research approach, in order for the text to stay relevant across time.
The text includes clear, accessible, straightforward language with minimal jargon. When the author introduces a new term, the term is immediately defined and described. The author also provides interesting examples to clarify and expand understanding of terms and concepts throughout the text.
The text is internally consistent and uses similar language and vocabulary throughout. The author uses real-life examples across chapters in order to provide depth and insight into the information. In addition, the vocabulary, concepts, and organization are consistent with other research methods textbooks.
The modules are short, concise, and manageable for students; the material within each module is logically focused and related to each other. I may move the modules and the sub-topics within them into a slightly different order for my class, and add the information mentioned above, but overall, this is very good.
The author presents topics and structures chapters in a logical and organized manner. The epub and online version do not include page numbers in the text, but the pdf does; this may be confusing when referencing the text or answering student questions. The book ends somewhat abruptly after the chapter on inferential statistics; the text may benefit from a concluding chapter to bring everything together, perhaps with a culminating example that walks the reader through creating the research question, choosing a research approach/design, etc., all the way to writing the research report.
I used and compared the pdf, epub, and online versions of the text. The epub and online versions include a clickable table of contents, but the pdf does not. The table format is inconsistent across the three versions; in the epub version (viewed through ibooks), the table data does not always line up correctly, making it difficult to interpret quickly. In the pdf and online versions, the table format looks different, but the data are lined up. No index made it difficult to quickly find areas of interest in the text; however, I could use the Find/Search functions in all three versions to search and find needed items.
As I read through this text, I did not detect any glaring grammatical errors. Overall, I think the text is written quite well in a style that is accessible to students.
The author uses inclusive, person-first language, and the text does not seem to be offensive or insensitive. As I read, I did notice that topics such as diversity and cultural competency are absent.
I enjoyed reading this text and am very excited to have a free research methods text for my students that I may supplement as needed. I wish there was a test question bank and/or flashcards for my students to help them study, but perhaps that could be added in the future. Overall, this is a great resource!
Reviewed by Karen Pikula, Psychology Instructor PhD, Central Lakes College on 1/7/16
The text covers all the areas and ideas of the subject of research methods in psychology for the learner that is just entering the field. The authors cover all of the content of an introductory research methods textbook and use exemplary examples... read more
The text covers all the areas and ideas of the subject of research methods in psychology for the learner that is just entering the field. The authors cover all of the content of an introductory research methods textbook and use exemplary examples that make those concepts relevent to a beginning researcher. As the authors state, the material is presented in such a manner as to encourage learners to not only be effective consumers of current research but also engage as critical thinkers in the many diverse situations one encounters in everyday life.
The content is accurate, error free, and unbiased. It explains both quantiative and qualitative methods in an unbiased manner. It is a bit slim on qualitative. It would be nice to have a bit more information on, for example, creating interview questions, coding, and qualitative data anaylisis.
The text is up to date, having just been revised. This revision was authored by Rajiv Jhangiani (Capilano University, North Vancouver) and includes the addition of a table of contents and cover page that the original text did not have, changes to Chapter 3 (Research Ethics) to include a contemporary example of an ethical breach and to reflect Canadian ethical guidelines and privacy laws, additional information regarding online data collection in Chapter 9 (Survey Research). Jhangiani has correcte of errors in the text and formulae, as well as changing spelling from US to Canadian conventions. The text is also now available in a inexpensive hard copy which students can purchase online or college bookstores can stock. This makes the text current and updates should be minimal.
The text is very easy to read and also very interesting as the authors supplement content with amazing real life examples.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
This text is easily and readily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned at different points within a course. I am going to use this text in conjunction with the OER OpenStax Psychology text for my Honors Psychology course. I currently use the OER Openstax Psychology textbook for my Positive Psychology course as well as my General Psychology course,
The topics in the text are presented in logical and clear fashion. The way they are presented allows the text to be used in conjuction with other textbooks as a secondary resource.
The text is free of significant interface issues. It is written in a manner that follows the natural process of doing research.
The text contained no noted grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive and actually has been revised to accomodate Canadian ethical guidelines as well as those of the APA.
I have to say that I am excited to have found this revised edition. My students will be so happy that there is also a reasonable priced hard coopy for them to purchase. They love the OpenStax Psychology text with the hard copy available from our bookstore. I do wish there were PowerPoints available for the text as well as a test bank. That is always a bonus!
Reviewed by Alyssa Gibbons, Instructor, Colorado State University on 1/7/16
This text covers everything I would consider essential for a first course in research methods, including some areas that are not consistently found in introductory texts (e.g., qualitative research, criticisms of null hypothesis significance... read more
This text covers everything I would consider essential for a first course in research methods, including some areas that are not consistently found in introductory texts (e.g., qualitative research, criticisms of null hypothesis significance testing). The chapters on ethics (Ch. 3) and theory (Ch. 4) are more comprehensive than most I have seen at this level, but not to the extent of information overload; rather, they anticipate and address many questions that undergraduates often have about these issues.
There is no index or table of contents provided in the PDF, and the table of contents on the website is very broad, but the material is well organized and it would not be hard for an instructor to create such a table. Chapter 2.1 is intended to be an introduction to several key terms and ideas (e.g., variable, correlation) that could serve as a sort of glossary.
I found the text to be highly accurate throughout; terms are defined precisely and correctly.
Where there are controversies or differences of opinion in the field, the author presents both sides of the argument in a respectful and unbiased manner. He explicitly discourages students from dismissing any one approach as inherently flawed, discussing not only the advantages and disadvantages of all methods (including nonexperimental ones) but also ways researchers address the disadvantages.
In several places, the textbook explicitly addresses the history and development of various methods (e.g., qualitative research, null hypothesis significance testing) and the ways in which researchers' views have changed. This allows the author to present current thinking and debate in these areas yet still expose students to older ideas they are likely to encounter as they read the research literature. I think this approach sets students up well to encounter future methodological advances; as a field, we refine our methods over time. I think the author could easily integrate new developments in future editions, or instructors could introduce such developments as supplementary material without creating confusion by contradicting the test.
The examples are generally drawn from classic psychological studies that have held up well over time; I think they will appeal to students for some time to come and not appear dated.
The only area in which I did not feel the content was entirely up to date was in the area of psychological measurement; Chapter 5.2 is based on the traditional view and not the more comprehensive modern or holistic view as presented in the 1999 AERA/APA Standards for Educational and Psychological Measurement. However, a comprehensive treatment of measurement validity is probably not necessary for most undergraduates at this stage, and they will certainly encounter the older framework in the research literature.
The textbook does an excellent job of presenting concepts in simple, accessible language without introducing error by oversimplification. The author consistently anticipates common points of confusion, clarifies terms, and even suggests ways for students to remember key distinctions. Terms are clearly and concretely defined when they are introduced. In contrast to many texts I have used, the terms that are highlighted in the text are actually the terms I would want my students to remember and study; the author refrains from using psychological jargon that is not central to the concepts he is discussing.
I noticed no major inconsistencies or gaps.
The division of sections within each chapter is useful; although I liked the overall organization of the text, there were points at which I would likely assign sections in a slightly different order and I felt I could do this easily without loss of continuity. The one place I would have liked more modularity was in the discussion of inferential statistics: t-tests, ANOVA, and Pearson's r are all covered within Chapter 13.2. On the one hand, this enables students to see the relationships and similarities among these tests, but on the other, this is a lot for students to take in at once.
I found the overall organization of the book to be quite logical, mirroring the sequence of steps a researcher would use to develop a research question, design a study, etc. As discussed above, the modularity of the book makes it easy to reorder sections to suit the structure of a particular class (for example, I might have students read the section on APA writing earlier in the semester as they begin drafting their own research proposals). I like the inclusion of ethics very early on in the text, establishing the importance of this topic for all research design choices.
One organizational feature I particularly appreciated was the consistent integration of conceptual and practical ideas; for example, in the discussion of psychological measurement, reliability and validity are discussed alongside the importance of giving clear instructions and making sure participants cannot be identified by their writing implements. This gives students an accurate and honest picture of the research process - some of the choices we make are driven by scientific ideals and some are driven by practical lessons learned. Students often have questions related to these mundane aspects of conducting research and it is helpful to have them so clearly addressed.
Although I didn't encounter any problems per se with the interface, I do think it could be made more user-friendly. For example, references to figures and tables are highlighted in blue, appearing to be hyperlinks, but they were not. Having such links, as well as a linked, easily-navigable and detailed table of contents, would also be helpful (and useful to students who use assistive technology).
I noticed no grammatical errors.
Where necessary, the author uses inclusive language and there is nothing that seems clearly offensive. The examples generally reflect American psychology research, but the focus is on the methods used and not the participants or cultural context. The text could be more intentionally or proactively inclusive, but it is not insensitive or exclusive.
I am generally hard to please when it comes to textbooks, but I found very little to quibble with in this one. It is a very well-written and accessible introduction to research methods that meets students where they are, addressing their common questions, misconceptions, and concerns. Although it's not flashy, the figures, graphics, and extra resources provided are clear, helpful, and relevant.
Reviewed by Moin Syed, Assistant Professor, University of Minnesota on 6/10/15
The text is thorough in terms of covering introductory concepts that are central to experimental and correlational/association designs. I find the general exclusion of qualitative and mixed methods designs hard to defend (despite some researchers’... read more
The text is thorough in terms of covering introductory concepts that are central to experimental and correlational/association designs. I find the general exclusion of qualitative and mixed methods designs hard to defend (despite some researchers’ distaste for the methods). While these approaches were less commonly used in the recent past, they are prevalent in the early years of psychology and are ascending once again. It strikes me as odd to just ignore two whole families of methods that are used within the practice of psychology—definitely not a sustainable approach.
I do very much appreciate the emphasis on those who will both practice and consume psychology, given the wide variety of undergraduate career paths.
One glaring omission is a Table of Contents within the PDF. It would be nice to make this a linked PDF, so that clicking on the entry in a TOC (or cross-references) would jump the reader to the relevant section.
I did not see an errors. The chapter on theory is not as clear as it could be. The section “what is theory” is not very clear, and these are difficulte concepts (difference between theory, hypothesis, etc.). A bit more time spent here could have been good. Also, the discussion of functional, mechanistic, and typological theories leaves out the fourth of Pepper’s metaphors: contextualism. I’m not sure that was intentional and accidental, but it is noticeable!
This is a research methods text focused on experimental and association designs. The basics of these designs do not change a whole lot over time, so there is little likelihood that the main content will become obsolete anytime soon. Some of the examples used are a bit dated, but then again most of them are considered “classics” in the field, which I think are important to retain (and there is at least one “new classic” included in the ethics section, namely the fraudulent research linking autism to the MMR vaccine).
The text is extremely clear and accessible. In fact, it may even be *too* simple for undergraduate use. Then again, students often struggle with methods, so simplicity is good, and the simplicity can also make the book marketable to high school courses (although I doubt many high schools have methods courses).
Yes, quite consistent throughout. Carrying through the same examples into different chapters is a major strength of the text.
I don’ anticipate any problems here.
The book flows well, with brief sections. I do wonder if maybe the sections are too brief? Perhaps too many check-ins? The “key take-aways” usually come after only a few pages. As mentioned above, the book is written at a very basic level, so this brevity is consistent with that approach. It is not a problem, per se, but those considering adopting the text should be aware of this aspect.
No problems here.
I did not detect any grammatical errors. The text flows very well.
The book is fairly typical of American research methods books in that it only focuses on the U.S. context and draws its examples from “mainstream” psychology (e.g., little inclusion of ethnic minority or cross-cultural psychology). However, the text is certainly not insensitive or offensive in any way.
Nice book, thanks for writing it!
Reviewed by Rajiv Jhangiani, Instructor, Capilano University on 10/9/13
The text is well organized and written, integrates excellent pedagogical features, and covers all of the traditional areas of the topic admirably. The final two chapters provide a good bridge between the research methods course and the follow-up... read more
The text is well organized and written, integrates excellent pedagogical features, and covers all of the traditional areas of the topic admirably. The final two chapters provide a good bridge between the research methods course and the follow-up course on behavioural statistics. The text integrates real psychological measures, harnesses students' existing knowledge from introductory psychology, includes well-chosen examples from real life and research, and even includes a very practical chapter on the use of APA style for writing and referencing. On the other hand, it does not include a table of contents or an index, both of which are highly desirable. The one chapter that requires significant revision is Chapter 3 (Research Ethics), which is based on the US codes of ethics (e.g., Federal policy & APA code) and does not include any mention of the Canadian Tri-Council Policy Statement.
The very few errors I found include the following: 1. The text should read "The fact that his F score…" instead of "The fact that his t score…" on page 364 2. Some formulae are missing the line that separates the numerator from the denominator. See pages 306, 311, 315, and 361 3. Table 12.3 on page 310 lists the variance as 288 when it is 28.8
The text is up-to-date and will not soon lose relevance. The only things I would add are a brief discussion of the contemporary case of Diederik Stapel's research fraud in the chapter on Research Ethics, as well as some research concerning the external validity of web-based studies (e.g., Gosling et al.'s 2004 article in American Psychologist).
Overall, the style of writing makes this text highly accessible. The writing flows well, is well organized, and includes excellent, detailed, and clear examples and explanations for concepts. The examples often build on concepts or theories students would have covered in their introductory psychology course. Some constructive criticism: 1. When discussing z scores on page 311 it might have been helpful to point out that the mean and SD for a set of calculated z scores are 0 and 1 respectively. Good students will come to this realization themselves, but it is not a bad thing to point it out nonetheless. 2. The introduction of the concept of multiple regression might be difficult for some students to grasp. 3. The only place where I felt short of an explanation was in the use of a research example to demonstrate the use of a line graph on page 318. In this case the explanation in question does not pertain to the line graph itself but the result of the study used, which is so fascinating that students will wish for the researchers' explanation for it.
The text is internally consistent.
The text is organized very well into chapters, modules within each chapter, and learning objectives within each module. Each module also includes useful exercises that help consolidate learning.
As mentioned earlier, the style of writing makes this text highly accessible. The writing flows well, is well organized, and includes excellent, detailed, and clear examples and explanations for concepts. The examples often build on concepts or theories students would have covered in their introductory psychology course. Only rarely did I feel that the author could have assisted the student by demonstrating the set-by-step calculation of a statistic (e.g., on page 322 for the calculation of Pearson's r)
The images, graphs, and charts are clear. The only serious issues that hamper navigation are the lack of a table of contents and an index. Many of the graphs will need to be printed in colour (or otherwise modified) for the students to follow the explanations provided in the text.
The text is written rather well and is free from grammatical errors. Of course, spellings are in the US convention.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive. Of course, it is not a Canadian edition and so many of the examples (all of which are easy to comprehend) come from a US context.
I have covered most of these issues in my earlier comments. The only things left to mention are that the author should have clearly distinguished between mundane and psychological realism, and that, in my opinion, the threats to internal validity could have been grouped together and might have been closer to an exhaustive list. This review originated in the BC Open Textbook Collection and is licensed under CC BY-ND.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology
- Chapter 2: Overview of the Scientific Method
- Chapter 3: Research Ethics
- Chapter 4: Psychological Measurement
- Chapter 5: Experimental Research
- Chapter 6: Non-experimental Research
- Chapter 7: Survey Research
- Chapter 8: Quasi-Experimental Research
- Chapter 9: Factorial Designs
- Chapter 10: Single-Subject Research
- Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
- Chapter 12: Descriptive Statistics
- Chapter 13: Inferential Statistics
Ancillary Material
- Kwantlen Polytechnic University
About the Book
This fourth edition (published in 2019) was co-authored by Rajiv S. Jhangiani (Kwantlen Polytechnic University), Carrie Cuttler (Washington State University), and Dana C. Leighton (Texas A&M University—Texarkana) and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Revisions throughout the current edition include changing the chapter and section numbering system to better accommodate adaptions that remove or reorder chapters; continued reversion from the Canadian edition; general grammatical edits; replacement of “he/she” to “they” and “his/her” to “their”; removal or update of dead links; embedded videos that were not embedded; moved key takeaways and exercises from the end of each chapter section to the end of each chapter; a new cover design.
About the Contributors
Dr. Carrie Cuttler received her Ph.D. in Psychology from the University of British Columbia. She has been teaching research methods and statistics for over a decade. She is currently an Assistant Professor in the Department of Psychology at Washington State University, where she primarily studies the acute and chronic effects of cannabis on cognition, mental health, and physical health. Dr. Cuttler was also an OER Research Fellow with the Center for Open Education and she conducts research on open educational resources. She has over 50 publications including the following two published books: A Student Guide for SPSS (1st and 2nd edition) and Research Methods in Psychology: Student Lab Guide. Finally, she edited another OER entitled Essentials of Abnormal Psychology. In her spare time, she likes to travel, hike, bike, run, and watch movies with her husband and son. You can find her online at @carriecuttler or carriecuttler.com.
Dr. Rajiv Jhangiani is the Associate Vice Provost, Open Education at Kwantlen Polytechnic University in British Columbia. He is an internationally known advocate for open education whose research and practice focuses on open educational resources, student-centered pedagogies, and the scholarship of teaching and learning. Rajiv is a co-founder of the Open Pedagogy Notebook, an Ambassador for the Center for Open Science, and serves on the BC Open Education Advisory Committee. He formerly served as an Open Education Advisor and Senior Open Education Research & Advocacy Fellow with BCcampus, an OER Research Fellow with the Open Education Group, a Faculty Workshop Facilitator with the Open Textbook Network, and a Faculty Fellow with the BC Open Textbook Project. A co-author of three open textbooks in Psychology, his most recent book is Open: The Philosophy and Practices that are Revolutionizing Education and Science (2017). You can find him online at @thatpsychprof or thatpsychprof.com.
Dr. Dana C. Leighton is Assistant Professor of Psychology in the College of Arts, Science, and Education at Texas A&M University—Texarkana. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Arkansas, and has 15 years experience teaching across the psychology curriculum at community colleges, liberal arts colleges, and research universities. Dr. Leighton’s social psychology research lab studies intergroup relations, and routinely includes undergraduate students as researchers. He is also Chair of the university’s Institutional Review Board. Recently he has been researching and writing about the use of open science research practices by undergraduate researchers to increase diversity, justice, and sustainability in psychological science. He has published on his teaching methods in eBooks from the Society for the Teaching of Psychology, presented his methods at regional and national conferences, and received grants to develop new teaching methods. His teaching interests are in undergraduate research, writing skills, and online student engagement. For more about Dr. Leighton see http://www.danaleighton.net and http://danaleighton.edublogs.org
Contribute to this Page
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
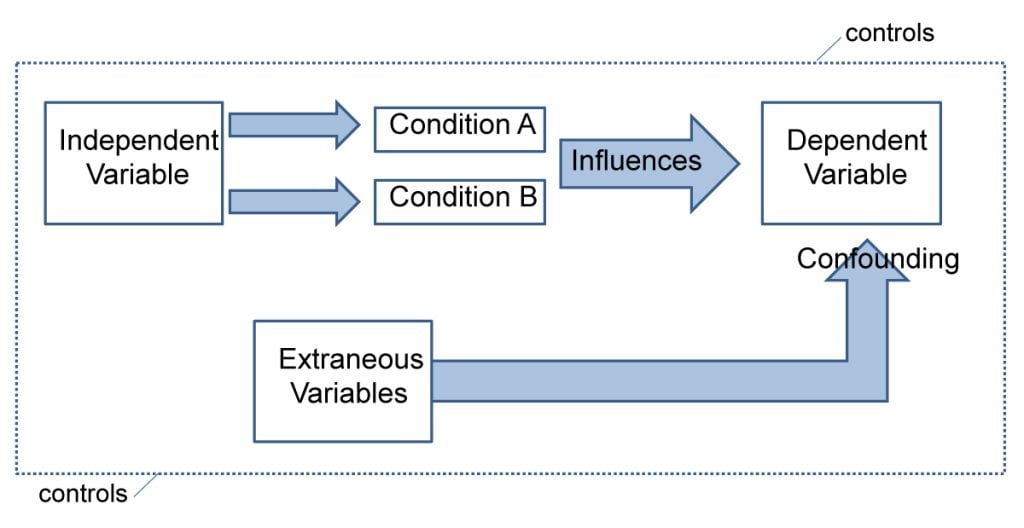
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
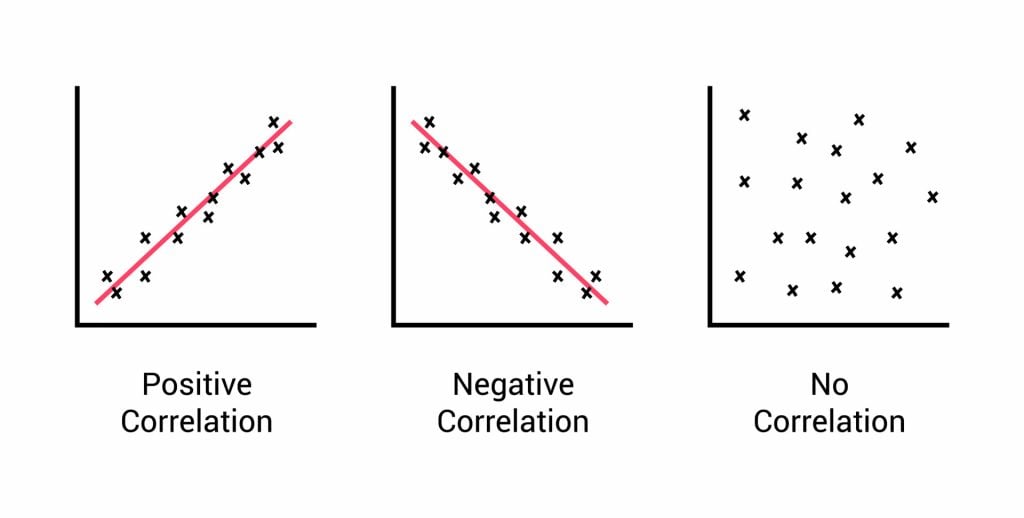
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
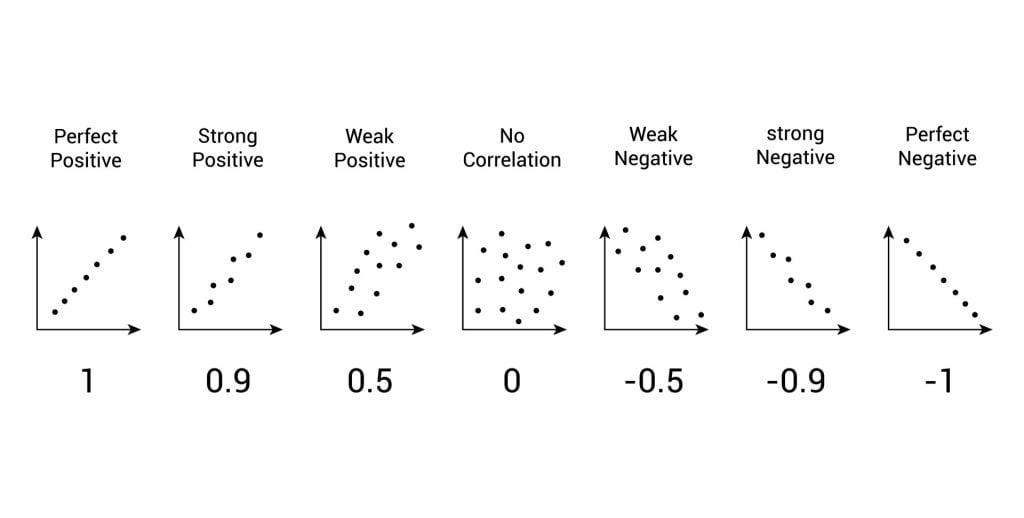
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
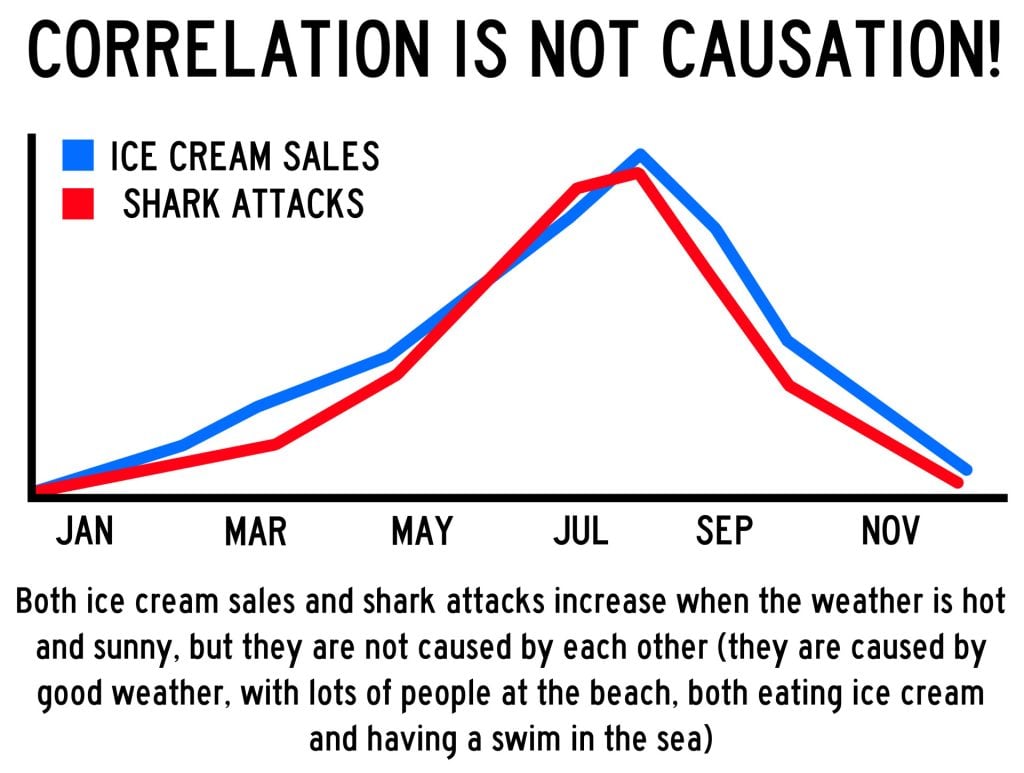
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

A-Level Psychology
A-level Psychology AQA Revision Notes

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Understanding Methods for Research in Psychology
A Psychology Research Methods Study Guide
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Types of Research in Psychology
- Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research
- Reliability and Validity
Glossary of Terms
Research in psychology focuses on a variety of topics , ranging from the development of infants to the behavior of social groups. Psychologists use the scientific method to investigate questions both systematically and empirically.
Research in psychology is important because it provides us with valuable information that helps to improve human lives. By learning more about the brain, cognition, behavior, and mental health conditions, researchers are able to solve real-world problems that affect our day-to-day lives.
At a Glance
Knowing more about how research in psychology is conducted can give you a better understanding of what those findings might mean to you. Psychology experiments can range from simple to complex, but there are some basic terms and concepts that all psychology students should understand.
Start your studies by learning more about the different types of research, the basics of experimental design, and the relationships between variables.
Research in Psychology: The Basics
The first step in your review should include a basic introduction to psychology research methods . Psychology research can have a variety of goals. What researchers learn can be used to describe, explain, predict, or change human behavior.
Psychologists use the scientific method to conduct studies and research in psychology. The basic process of conducting psychology research involves asking a question, designing a study, collecting data, analyzing results, reaching conclusions, and sharing the findings.
The Scientific Method in Psychology Research
The steps of the scientific method in psychology research are:
- Make an observation
- Ask a research question and make predictions about what you expect to find
- Test your hypothesis and gather data
- Examine the results and form conclusions
- Report your findings
Research in psychology can take several different forms. It can describe a phenomenon, explore the causes of a phenomenon, or look at relationships between one or more variables. Three of the main types of psychological research focus on:
Descriptive Studies
This type of research can tell us more about what is happening in a specific population. It relies on techniques such as observation, surveys, and case studies.
Correlational Studies
Correlational research is frequently used in psychology to look for relationships between variables. While research look at how variables are related, they do not manipulate any of the variables.
While correlational studies can suggest a relationship between two variables, finding a correlation does not prove that one variable causes a change in another. In other words, correlation does not equal causation.
Experimental Research Methods
Experiments are a research method that can look at whether changes in one variable cause changes in another. The simple experiment is one of the most basic methods of determining if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables.
A simple experiment utilizes a control group of participants who receive no treatment and an experimental group of participants who receive the treatment.
Experimenters then compare the results of the two groups to determine if the treatment had an effect.
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research in Psychology
Research in psychology can also involve collecting data at a single point in time, or gathering information at several points over a period of time.
Cross-Sectional Research
In a cross-sectional study , researchers collect data from participants at a single point in time. These are descriptive type of research and cannot be used to determine cause and effect because researchers do not manipulate the independent variables.
However, cross-sectional research does allow researchers to look at the characteristics of the population and explore relationships between different variables at a single point in time.
Longitudinal Research
A longitudinal study is a type of research in psychology that involves looking at the same group of participants over a period of time. Researchers start by collecting initial data that serves as a baseline, and then collect follow-up data at certain intervals. These studies can last days, months, or years.
The longest longitudinal study in psychology was started in 1921 and the study is planned to continue until the last participant dies or withdraws. As of 2003, more than 200 of the partipants were still alive.
The Reliability and Validity of Research in Psychology
Reliability and validity are two concepts that are also critical in psychology research. In order to trust the results, we need to know if the findings are consistent (reliability) and that we are actually measuring what we think we are measuring (validity).
Reliability
Reliability is a vital component of a valid psychological test. What is reliability? How do we measure it? Simply put, reliability refers to the consistency of a measure. A test is considered reliable if we get the same result repeatedly.
When determining the merits of a psychological test, validity is one of the most important factors to consider. What exactly is validity? One of the greatest concerns when creating a psychological test is whether or not it actually measures what we think it is measuring.
For example, a test might be designed to measure a stable personality trait but instead measures transitory emotions generated by situational or environmental conditions. A valid test ensures that the results accurately reflect the dimension undergoing assessment.
Review some of the key terms that you should know and understand about psychology research methods. Spend some time studying these terms and definitions before your exam. Some key terms that you should know include:
- Correlation
- Demand characteristic
- Dependent variable
- Hawthorne effect
- Independent variable
- Naturalistic observation
- Placebo effect
- Random assignment
- Replication
- Selective attrition
Erol A. How to conduct scientific research ? Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2017;54(2):97-98. doi:10.5152/npa.2017.0120102
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Curtis EA, Comiskey C, Dempsey O. Importance and use of correlational research . Nurse Res . 2016;23(6):20-25. doi:10.7748/nr.2016.e1382
Wang X, Cheng Z. Cross-sectional studies: Strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations . Chest . 2020;158(1S):S65-S71. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.012
Caruana EJ, Roman M, Hernández-Sánchez J, Solli P. Longitudinal studies . J Thorac Dis . 2015;7(11):E537-E540. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.10.63
Stanford Magazine. The vexing legacy of Lewis Terman .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

6 Research Methods
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different research methods used by psychologists
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, and archival research
- Compare longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches to research
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging from a series of simple questions to extensive, in-depth interviews—to well-controlled experiments.
Each of these research methods has unique strengths and weaknesses, and each method may only be appropriate for certain types of research questions. For example, studies that rely primarily on observation produce incredible amounts of information, but the ability to apply this information to the larger population is somewhat limited because of small sample sizes. Survey research, on the other hand, allows researchers to easily collect data from relatively large samples. While this allows for results to be generalized to the larger population more easily, the information that can be collected on any given survey is somewhat limited and subject to problems associated with any type of self-reported data. Some researchers conduct archival research by using existing records. While this can be a fairly inexpensive way to collect data that can provide insight into a number of research questions, researchers using this approach have no control over how or what kind of data was collected. All of the methods described thus far are correlational in nature. This means that researchers can speak to important relationships that might exist between two or more variables of interest. However, correlational data cannot be used to make claims about cause-and-effect relationships.
Correlational research can find a relationship between two variables, but the only way a researcher can claim that the relationship between the variables is cause and effect is to perform an experiment. In experimental research, there is a tremendous amount of control over variables of interest. While this is a powerful approach, experiments are often conducted in very artificial settings. This calls into question the validity of experimental findings with regard to how they would apply in real-world settings. In addition, many of the questions that psychologists would like to answer cannot be pursued through experimental research because of ethical concerns.
Clinical or Case Studies
In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center. Most incoming sensory information is sent through the thalamus before reaching higher regions of the cerebral cortex for processing.
The implications of this potential connection mean that it might be possible for one twin to experience the sensations of the other twin. For instance, if Krista is watching a particularly funny television program, Tatiana might smile or laugh even if she is not watching the program. This particular possibility has piqued the interest of many neuroscientists who seek to understand how the brain uses sensory information.
These twins represent an enormous resource in the study of the brain, and since their condition is very rare, it is likely that as long as their family agrees, scientists will follow these girls very closely throughout their lives to gain as much information as possible (Dominus, 2011).
In observational research, scientists are conducting a clinical or case study when they focus on one person or just a few individuals. Indeed, some scientists spend their entire careers studying just 10–20 individuals. Why would they do this? Obviously, when they focus their attention on a very small number of people, they can gain a tremendous amount of insight into those cases. The richness of information that is collected in clinical or case studies is unmatched by any other single research method. This allows the researcher to have a very deep understanding of the individuals and the particular phenomenon being studied.
If clinical or case studies provide so much information, why are they not more frequent among researchers? As it turns out, the major benefit of this particular approach is also a weakness. As mentioned earlier, this approach is often used when studying individuals who are interesting to researchers because they have a rare characteristic. Therefore, the individuals who serve as the focus of case studies are not like most other people. If scientists ultimately want to explain all behavior, focusing attention on such a special group of people can make it difficult to generalize any observations to the larger population as a whole. Generalizing refers to the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society. Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what’s learned to the average person may be very limited.
Naturalistic Observation
If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways if they know they are being observed. How do researchers obtain accurate information when people tend to hide their natural behavior? As an example, imagine that your professor asks everyone in your class to raise their hand if they always wash their hands after using the restroom. Chances are that almost everyone in the classroom will raise their hand, but do you think hand washing after every trip to the restroom is really that universal?
This is very similar to the phenomenon mentioned earlier in this chapter: many individuals do not feel comfortable answering a question honestly. But if we are committed to finding out the facts about hand washing, we have other options available to us.
Suppose we send a classmate into the restroom to actually watch whether everyone washes their hands after using the restroom. Will our observer blend into the restroom environment by wearing a white lab coat, sitting with a clipboard, and staring at the sinks? We want our researcher to be inconspicuous—perhaps standing at one of the sinks pretending to put in contact lenses while secretly recording the relevant information. This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation : observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand peer exclusion, Suzanne Fanger collaborated with colleagues at the University of Texas to observe the behavior of preschool children on a playground. How did the observers remain inconspicuous over the duration of the study? They equipped a few of the children with wireless microphones (which the children quickly forgot about) and observed while taking notes from a distance. Also, the children in that particular preschool (a “laboratory preschool”) were accustomed to having observers on the playground (Fanger, Frankel, & Hazen, 2012).
It is critical that the observer be as unobtrusive and as inconspicuous as possible: when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to behave naturally. If you have any doubt about this, ask yourself how your driving behavior might differ in two situations: In the first situation, you are driving down a deserted highway during the middle of the day; in the second situation, you are being followed by a police car down the same deserted highway.

It should be pointed out that naturalistic observation is not limited to research involving humans. Indeed, some of the best-known examples of naturalistic observation involve researchers going into the field to observe various kinds of animals in their own environments. As with human studies, the researchers maintain their distance and avoid interfering with the animal subjects so as not to influence their natural behaviors. Scientists have used this technique to study social hierarchies and interactions among animals ranging from ground squirrels to gorillas. The information provided by these studies is invaluable in understanding how those animals organize socially and communicate with one another. The anthropologist Jane Goodall , for example, spent nearly five decades observing the behavior of chimpanzees in Africa. As an illustration of the types of concerns that a researcher might encounter in naturalistic observation, some scientists criticized Goodall for giving the chimps names instead of referring to them by numbers—using names was thought to undermine the emotional detachment required for the objectivity of the study (McKie, 2010).

The greatest benefit of naturalistic observation is the validity , or accuracy, of information collected unobtrusively in a natural setting. Having individuals behave as they normally would in a given situation means that we have a higher degree of ecological validity, or realism, than we might achieve with other research approaches. Therefore, our ability to generalize the findings of the research to real-world situations is enhanced. If done correctly, we need not worry about people or animals modifying their behavior simply because they are being observed. Sometimes, people may assume that reality programs give us a glimpse into authentic human behavior. However, the principle of inconspicuous observation is violated as reality stars are followed by camera crews and are interviewed on camera for personal confessionals. Given that environment, we must doubt how natural and realistic their behaviors are.
The major downside of naturalistic observation is that they are often difficult to set up and control. In our restroom study, what if you stood in the restroom all day prepared to record people’s hand-washing behavior and no one came in? Or, what if you have been closely observing a troop of gorillas for weeks only to find that they migrated to a new place while you were sleeping in your tent? The benefit of realistic data comes at a cost. As a researcher, you have no control over when (or if) you have behavior to observe. In addition, this type of observational research often requires significant investments of time, money, and a good dose of luck.
Sometimes studies involve structured observation. In these cases, people are observed while engaging in set, specific tasks. An excellent example of structured observation comes from Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth (you will read more about this in the chapter on lifespan development). The Strange Situation is a procedure used to evaluate attachment styles that exist between an infant and caregiver. In this scenario, caregivers bring their infants into a room filled with toys. The Strange Situation involves a number of phases, including a stranger coming into the room, the caregiver leaving the room, and the caregiver’s return to the room. The infant’s behavior is closely monitored at each phase, but it is the behavior of the infant upon being reunited with the caregiver that is most telling in terms of characterizing the infant’s attachment style with the caregiver.
Another potential problem in observational research is observer bias . Generally, people who act as observers are closely involved in the research project and may unconsciously skew their observations to fit their research goals or expectations. To protect against this type of bias, researchers should have clear criteria established for the types of behaviors recorded and how those behaviors should be classified. In addition, researchers often compare observations of the same event by multiple observers, in order to test inter-rater reliability : a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of observations by different observers.
Often, psychologists develop surveys as a means of gathering data. Surveys are lists of questions to be answered by research participants and can be delivered as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally. Generally, the survey itself can be completed in a short time, and the ease of administering a survey makes it easy to collect data from a large number of people.
Surveys allow researchers to gather data from larger samples than may be afforded by other research methods . A sample is a subset of individuals selected from a population , which is the overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in. Researchers study the sample and seek to generalize their findings to the population.

There are both strengths and weaknesses to using surveys in comparison to case studies. By using surveys, we can collect information from a larger sample of people. A larger sample is better able to reflect the actual diversity of the population, thus allowing better generalizability. Therefore, if our sample is sufficiently large and diverse, we can assume that the data we collect from the survey can be generalized to the larger population with more certainty than the information collected through a case study. However, given the greater number of people involved, we are not able to collect the same depth of information on each person that would be collected in a case study.
Another potential weakness of surveys is something we touched on earlier in this chapter: People don’t always give accurate responses. They may lie, misremember, or answer questions in a way that they think makes them look good. For example, people may report drinking less alcohol than is actually the case.
Any number of research questions can be answered through the use of surveys. One real-world example is the research conducted by Jenkins, Ruppel, Kizer, Yehl, and Griffin (2012) about the backlash against the US Arab-American community following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Jenkins and colleagues wanted to determine to what extent these negative attitudes toward Arab Americans still existed nearly a decade after the attacks occurred. In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions asking directly about the participant’s overt prejudicial attitudes toward people of various ethnicities. The survey also asked indirect questions about how likely the participant would be to interact with a person of a given ethnicity in a variety of settings (such as, “How likely do you think it is that you would introduce yourself to a person of Arab-American descent?”). The results of the research suggested that participants were unwilling to report prejudicial attitudes toward any ethnic group. However, there were significant differences between their pattern of responses to questions about social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to other ethnic groups: they indicated less willingness for social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to the other ethnic groups. This suggested that the participants harbored subtle forms of prejudice against Arab-Americans, despite their assertions that this was not the case (Jenkins et al., 2012).
Archival Research
Some researchers gain access to large amounts of data without interacting with a single research participant. Instead, they use existing records to answer various research questions. This type of research approach is known as [ pb_glossary id=”132 “]archival research [/pb_glossary] . Archival research relies on looking at past records or data sets to look for interesting patterns or relationships.
For example, a researcher might access the academic records of all individuals who enrolled in college within the past ten years and calculate how long it took them to complete their degrees, as well as course loads, grades, and extracurricular involvement. Archival research could provide important information about who is most likely to complete their education, and it could help identify important risk factors for struggling students.

In comparing archival research to other research methods, there are several important distinctions. For one, the researcher employing archival research never directly interacts with research participants. Therefore, the investment of time and money to collect data is considerably less with archival research. Additionally, researchers have no control over what information was originally collected. Therefore, research questions have to be tailored so they can be answered within the structure of the existing data sets. There is also no guarantee of consistency between the records from one source to another, which might make comparing and contrasting different data sets problematic.
Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Research
Sometimes we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. When we test the same group of individuals repeatedly over an extended period of time, we are conducting longitudinal research. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time. For example, we may survey a group of individuals about their dietary habits at age 20, retest them a decade later at age 30, and then again at age 40.
Another approach is cross-sectional research. In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time. Using the dietary habits example above, the researcher might directly compare different groups of people by age. Instead of following a group of people for 20 years to see how their dietary habits changed from decade to decade, the researcher would study a group of 20-year-old individuals and compare them to a group of 30-year-old individuals and a group of 40-year-old individuals. While cross-sectional research requires a shorter-term investment, it is also limited by differences that exist between the different generations (or cohorts) that have nothing to do with age, per se, but rather reflect the social and cultural experiences of different generations of individuals that make them different from one another.
To illustrate this concept, consider the following survey findings. In recent years there has been significant growth in the popular support of same-sex marriage. Many studies on this topic break down survey participants into different age groups. In general, younger people are more supportive of same-sex marriage than those who are older (Jones, 2013). Does this mean that as we age we become less open to the idea of same-sex marriage, or does this mean that older individuals have different perspectives because of the social climates in which they grew up? Longitudinal research is a powerful approach because the same individuals are involved in the research project over time, which means that the researchers need to be less concerned with differences among cohorts affecting the results of their study.
Often longitudinal studies are employed when researching various diseases in an effort to understand particular risk factors. Such studies often involve tens of thousands of individuals who are followed for several decades. Given the enormous number of people involved in these studies, researchers can feel confident that their findings can be generalized to the larger population. The Cancer Prevention Study-3 (CPS-3) is one of a series of longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society aimed at determining predictive risk factors associated with cancer. When participants enter the study, they complete a survey about their lives and family histories, providing information on factors that might cause or prevent the development of cancer. Then every few years the participants receive additional surveys to complete. In the end, hundreds of thousands of participants will be tracked over 20 years to determine which of them develop cancer and which do not.
Clearly, this type of research is important and potentially very informative. For instance, earlier longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society provided some of the first scientific demonstrations of the now well-established links between increased rates of cancer and smoking (American Cancer Society, n.d.).

As with any research strategy, longitudinal research is not without limitations. For one, these studies require an incredible time investment by the researcher and research participants. Given that some longitudinal studies take years, if not decades, to complete, the results will not be known for a considerable period of time. In addition to the time demands, these studies also require a substantial financial investment. Many researchers are unable to commit the resources necessary to see a longitudinal project through to the end.
Research participants must also be willing to continue their participation for an extended period of time, and this can be problematic. People move, get married and take new names, get ill, and eventually die. Even without significant life changes, some people may simply choose to discontinue their participation in the project. As a result, the attrition rates, or reduction in the number of research participants due to dropouts, in longitudinal studies are quite high and increase over the course of a project. For this reason, researchers using this approach typically recruit many participants fully expecting that a substantial number will drop out before the end. As the study progresses, they continually check whether the sample still represents the larger population and make adjustments as necessary.
Test Your Understanding
The clinical or case study involves studying just a few individuals for an extended period of time. While this approach provides an incredible depth of information, the ability to generalize these observations to the larger population is problematic. Naturalistic observation involves observing behavior in a natural setting and allows for the collection of valid, true-to-life information from realistic situations. However, naturalistic observation does not allow for much control and often requires quite a bit of time and money to perform. Researchers strive to ensure that their tools for collecting data are both reliable (consistent and replicable) and valid (accurate).
Surveys can be administered in a number of ways and make it possible to collect large amounts of data quickly. However, the depth of information that can be collected through surveys is somewhat limited compared to a clinical or case study.
Archival research involves studying existing data sets to answer research questions.
Longitudinal research has been incredibly helpful to researchers who need to collect data on how people change over time. Cross-sectional research compares multiple segments of a population at a single time.
Review Questions
Critical thinking questions.
Case studies might prove especially helpful using individuals who have rare conditions. For instance, if one wanted to study multiple personality disorder then the case study approach with individuals diagnosed with multiple personality disorder would be helpful.
The behavior displayed on these programs would be more realistic if the cameras were mounted in hidden locations, or if the people who appear on these programs did not know when they were being recorded.
Longitudinal research would be an excellent approach in studying the effectiveness of this program because it would follow students as they aged to determine if their choices regarding alcohol and drugs were affected by their participation in the program.
Answers will vary. Possibilities include research on hiring practices based on human resource records, and research that follows former prisoners to determine if the time that they were incarcerated provided any sort of positive influence on their likelihood of engaging in criminal behavior in the future.
Personal Application Questions
A friend of yours is working part-time in a local pet store. Your friend has become increasingly interested in how dogs normally communicate and interact with each other, and is thinking of visiting a local veterinary clinic to see how dogs interact in the waiting room. After reading this section, do you think this is the best way to better understand such interactions? Do you have any suggestions that might result in more valid data?
As a college student, you are no doubt concerned about the grades that you earn while completing your coursework. If you wanted to know how overall GPA is related to success in life after college, how would you choose to approach this question and what kind of resources would you need to conduct this research?
Research Methods Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Introduction to Psychology/Research Methods in Psychology
RESEARCH METHOD IN PSYCHOLOGY.
Research psychology encompasses the study of behavior for use in academic settings, and contains numerous areas. It contains the areas of abnormal psychology, biological psychology, cognitive psychology, comparative psychology, developmental psychology, personality psychology, social psychology and others. All branches of psychology can have a research component to them. Research psychology is contrasted with applied psychology.
Research in psychology is conducted in broad accord with the standards of the scientific method, encompassing both qualitative ethological and quantitative statistical modalities to generate and evaluate explanatory hypotheses with regard to psychological phenomena. Where research ethics and the state of development in a given research domain permits, investigation may be pursued by experimental protocols. Psychology tends to be eclectic, drawing on scientific knowledge from other fields to help explain and understand psychological phenomena. Qualitative psychological research utilizes a broad spectrum of observational methods, including action research, ethography, exploratory statistics, structured interviews, and participant observation, to enable the gathering of rich information unattainable by classical experimentation. Research in humanistic psychology is more typically pursued by ethnographic, historical, and historiographic methods.
The testing of different aspects of psychological function is a significant area of contemporary psychology. Psychometric and statistical methods predominate, including various well-known standardized tests as well as those created ad hoc as the situation or experiment requires.
Academic psychologists may focus purely on research and psychological theory, aiming to further psychological understanding in a particular area, while other psychologists may work in applied psychology to deploy such knowledge for immediate and practical benefit. However, these approaches are not mutually exclusive and most psychologists will be involved in both researching and applying psychology at some point during their career. Clinical psychology, among many of the various disciplines of psychology, aims at developing in practicing psychologists knowledge of and experience with research and experimental methods which they will continue to build up as well as employ as they treat individuals with psychological issues or use psychology to help others.
When an area of interest requires specific training and specialist knowledge, especially in applied areas, psychological associations normally establish a governing body to manage training requirements. Similarly, requirements may be laid down for university degrees in psychology, so that students acquire an adequate knowledge in a number of areas. Additionally, areas of practical psychology, where psychologists offer treatment to others, may require that psychologists be licensed by government regulatory bodies as well.
Quantitative psychology involves the application of statistical analysis to psychological research, and the development of novel statistical approaches for measuring and explaining human behavior. It is a young field (only recently have Ph.D. programs in quantitative psychology been formed), and it is loosely comprised of the subfields psychometrics and mathematical psychology.
Psychometrics is the field of psychology concerned with the theory and technique of psychological measurement, which includes the measurement of knowledge, abilities, attitudes, interests, achievement in particular degree or course, and personality traits (Carl Dellomos, 2009). Measurement of these unobservable phenomena is difficult, and much of the research and accumulated knowledge in this discipline has been developed in an attempt to properly define and quantify such phenomena. Psychometric research typically involves two major research tasks, namely: (i) the construction of instruments and procedures for measurement; and (ii) the development and refinement of theoretical approaches to measurement.
Psychology is a science, to be approached as such. Experiments should be designed using the scientific method.
There are several research methods that psychologists employ:
- 1.1 Nomothetic (Quantitative Approach)
- 1.2 Idiographic (Qualitative Approach)
- 2.1 Descriptive Studies
- 2.2 Factorial Design
- 2.3 Correlational Study
- 2.4 Experiments
- 2.5 Naturalistic Observation
- 2.6 Self Report
- 3.1.1 Statistical Symbols
- 3.1.2 Frequency Distribution
- 3.1.3 Measures of Central Tendency
- 3.1.4 Measures of Variability
- 3.2 Case Studies
- 4 Basic Concepts
Approaches in Psychology Research [ edit | edit source ]
Nomothetic (quantitative approach) [ edit | edit source ].
This approach is basically used in inferential and descriptive statistics as both mediums of scientific method of investigation in analyzing, presenting, and interpretation of data gathered by the researcher through standardized or objective instruments (e.g. psychological Tests). Nomothetic can also be defined as data that is collected from a specifically defined number of individuals (sample) to measure certain tendencies while making hypothetical predictions about human behaviors (population). The term “nomothetic” comes from the Greek word “nomos” meaning “law”. Psychologists who adopt this approach are mainly concerned with studying what we share with others. That is to say in establishing laws or generalizations. (Carl Dellomos, 2009)
Idiographic (Qualitative Approach) [ edit | edit source ]
This approach tends not to use inferential or descriptive statistics, but rather uses qualitative methods of data gathering such as interviews, diaries, and other written materials, obtained from or provided by the expected or anticipated respondents of a particular research. The term “idiographic” comes from the Greek word “idios” meaning “own” or “private”. Psychologists interested in this aspect of experience seek to discover what makes each of us unique. Despite the importance of our genetic individuality, proceeding from biology, the distinction between the nomothetic and the idiographic is often equated with two types of science — the natural sciences concerned with discovering laws of nature, and the social sciences concerned with individual meanings. We can examine these differences further by seeing how they relate to personality theory.(Carl Dellomos, 2009)
Both approaches were introduced by Gordon Allport. (Carl Dellomos, 2009)
Research Designs [ edit | edit source ]
Research design is the way in which the overall study is ran, this goes for the way the data is collected, measured, and interpreted. Considered as the backbone of an experiment as it sets the overall presence for how things will flow throughout duration of the study. There are four main types of research designs that are used within the psychology field: descriptive or qualitative, correlational, casual comparative/ quasi-experimental, and experimental. The method of data collection also varies, with self-report on one end of the spectrum, and naturalistic observation on the other.
Descriptive Studies [ edit | edit source ]
The Studies that do not test specific relationships between variables are called descriptive studies. In this research method, general or specific behaviors or attributes are observed and measured, without respect to each other. These studies are generally the design of choice for breaking into new areas, as the vast but often inconclusive amount of information collected can be drawn upon for future hypotheses.
An example of such a study would be a researcher inquiring into the quality of mental health institutions. This would be done by observation or measurements of various criteria, as opposed to relationships between variables. Alternatively, the study could be conducted without any specific criteria in mind.

Factorial Design [ edit | edit source ]
Every level of one independent variable is joined with every level of the others in a factorial design to create every possible combination. Because this particular design contains two variables, each of which has two levels, it is known as a 2 × 2 (or "two-by-two") factorial design. There would be six different conditions in a 3 × 2 factorial design if one of the independent variables had a third level. Observe that the product of the levels' numbers is the total number of possible circumstances. There are four conditions in a 2 × 2 factorial design, six in a 3 × 2 factorial design, twenty in a 4 × 5 factorial design, and so on. It's also important to note that every number in the notation indicates a single independent variable or component. Because this particular design contains two variables, each of which has two levels, it is known as a 2 × 2 (or "two-by-two") factorial design. There would be six different conditions in a 3 × 2 factorial design if one of the independent variables had a third level. Observe that the product of the levels' numbers is the total number of possible circumstances. There are four conditions in a 2 × 2 factorial design, six in a 3 × 2 factorial design, twenty in a 4 × 5 factorial design, and so on. It's also important to note that every number in the notation indicates a single independent variable or component.
Correlational Study [ edit | edit source ]
This method of statistical analysis shows the relationship between two variables. For example, research has shown that alcohol dependence correlates with depression. That is to say, the more alcohol people consume, the more depressed they become. On the other hand, it could be the other way around as well: the more depressed people become, the more likely they are to consume alcohol.
The attributes of correlations include strength and direction. The direction may be positive (both variables both increase or decrease together), negative (one variable increases while the other decreases) or unrelated (a random relationship between variables). The strength of a correlation ranges from -1 to +1 with a 0 reflecting no relationship between variables. A correlational study serves only to describe/predict behavior and not to explain it. This is so because a third variable could be shown to cause the occurrence of one of the variables. Furthermore, only experiments can prove causation.
Experiments [ edit | edit source ]
Experiments are generally the studies that are the most precise and have the most weight to them due to their conclusive power. They are particularly effective in proving hypotheses about cause and effect relationships between variables. A hypothesis is a prediction of how one variable relates to another. There are two types of hypotheses, null and directional . The null is a prediction that there will not be any change in the dependent variable when the researcher changes the independent variable. The directional hypothesis states that the change in the independent variable will induce a change in the dependent variable. In a true experiment, all variables are held constant except for the independent variable, which is manipulated. Thus, any changes in the experimental groups can be solely attributed to the action of the independent variable. This is called being objective .
For instance, in an experiment to test whether music improves people's memories, we would have a sheet of paper with ten unrelated words on it for people to memorize. The control group would have no music playing in the background while the experimental group would have some music in the background. Because as researchers we have adhered to the scientific method and held all variables as constant as possible, if the experimental group does report better recollection of words, then we could assume that the music had an effect on memory. However, we must be certain to do our best to ensure that any controllable differences between the two groups are eliminated in order to ensure that no confounding variable interferes with the experiment.
There are two main ways to pick, or sample the subjects in an experiment, random and stratified . In a random sampling each person has an equal chance at being picked. This means that if 80% of the population being sampled from are Christian, then 80% of the sample will be Christian. If the researcher wanted all religions represented equally, he would employ stratified sampling. For instance, the experiment could be performed only on women, or on mixed groups with equal numbers of each sex in them, to eliminate the possibility of biased results from one gender having better average memory than the other.
Steps must be taken to make sure that there is no experimenter bias . Two common forms of bias are demand characteristics and expectancy effects. If a researcher expects certain results from an experiment and influences the subjects response this is called demand characteristics. If the experimenter inadvertently interprets the information to be as expected in their hypothesis it is called expectancy effect. To counteract experimenter bias the subjects can be kept uninformed on the intentions of the experiment, which is called single blind. If the people collecting the information and the subjects giving it are kept uninformed then it is called a double blind experiment.
The experiment should also be reported so that other researchers can repeat it. If an experiment isn't repeatable it will not hold much weight in the scientific community. To help an experiment be repeatable the researcher should have the variables be measureable, this is called being empirical .
Whether researching humans or animals the experiment should be ethical. When humans are the subjects they should be informed of what the study is, consent to being in it, be debriefed afterwards, and their information should also be kept confidential .
Naturalistic Observation [ edit | edit source ]
Researchers study organisms in their natural environments or habitats without trying to manipulate or control anything. In this method, the researcher observes the behavior under study in its natural setting while attempting to avoid influencing or controlling it. The observations are done in a naturalistic setting without any preparation or participation of the researcher. Therefore, the behavior is observed in public places, streets, homes, and schools. Observing people from other cultures response in the same setting is a way to provide information for cross-cultural research .
Self Report [ edit | edit source ]
This method includes tests , questionnaires , and interviews . All of which do the same thing, give the subject a stimuli, i.e. the question, and get a response. The advantage of using these is the ability to inexpensively and rapidly collect vast amounts of data. This allows a psychologist to compare one person, or a group of peoples results to thousands of others. The disadvantage is that they are not always telling what the subject's response is but what the subject says is the response.
Information Display [ edit | edit source ]
Statistics [ edit | edit source ].
Once the information is gathered it has to be put into some kind of form, usually numerical. Statistics deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of numerical data. The goal of statistics is to summarize the data and let descriptions or inferences be made . Inferences are used when making predictions of the relationships of variables. Descriptions are concise displays, using statistical symbols ,of the information in frequency distributions, measures of central tendency , or measures of variability .
Statistical Symbols [ edit | edit source ]
There are agreed upon standard symbols used in statistical displays. These symbols can be used by themselves or in equations.
N = number of scores
X = score (or scores)
d = difference of a score from the mean
D = difference in rank
r or ρ = correlation
SD = standard deviation
Frequency Distribution [ edit | edit source ]
A frequency distribution is obtained by taking the score and splitting them into subgroups. The subgroups are then put on either a histogram (bar graph) or a frequency polygram (line graph). When a frequency distribution has most of the scores on one side of the graph it is considered skewed. If it has most of the scores in the middle with equal amounts on both sides it is considered symmetrical.
Measures of Central Tendency [ edit | edit source ]
In measures of central tendency there is one number that is used to represent a group of numbers. This number is either the mean , median , or the mode .
Measures of Variability [ edit | edit source ]
Variability is concerned with the dispersal of the scores, called variability i.e. are the scores clustered together or spread out. Range and standard deviation are the measures most commonly used. To find the range just subtract the number of the lowest score from the number of the highest score. This can be deceiving if most of the scores are bunched together and one of the scores is very far away from it. In this case standard deviation must be used. A formula commonly used for standard deviation is SD = the square root of Σd²/N.
Case Studies [ edit | edit source ]
In the course of treating a patient a psychologist will take records of problems, insights, and techniques that were important in the patients treatment. A clinical case history may be drawn upon by researchers to expose a factor that is important for understanding a behavior. Case studies repeat and are used as guides for psychologists.
Basic Concepts [ edit | edit source ]
- a. independent variable = variable that one manipulates in order to see if it has any effect on the dependent variable (eg. in the example above, the independent variable would be music and its effect on memory)
- b. dependent variable = variable that depends on the effect of the independent variable (e.g. in the example above, the dependent variable would be memory and better recollection of words)
- c. double-blind procedure = procedure in which neither the researcher nor the subjects know which group (experimental or control) the subjects are in in order to minimize experimenter cues.
- d. single-blind procedure = procedure in which only the researcher knows which group which kind of subject is in.
- e. experimenter cues - subtle and often unintentional cues that the experimenter makes which implies which group which kind of subject is in. for example, if an experimenter believes that music does indeed improve memory, some cues would be the experimenter's smiling/winking at the experimental group. This smile/wink would imply to the subjects in the experimental group that the researcher is secretly implying that they're in the experimental group.
- f. placebo effect - a treatment works because of the patient's belief that it works and not because it actually does.
- g. experimenter - the person who is researching through the participant.
- Book:Introduction to Psychology
Navigation menu

Research Methods in Psychology
Introduction ¶.
Welcome to Research Methods in Psychology , the Stony Brook edition!
Goals of Science Education ¶
In 2009, Bruce Alberts, the editor of Science (a leading scientific publication) published an editorial [Alb09] in which he described the strange mismatch between science education as it is practiced in classrooms around the world and the way one would educate future scientists. Citing a report by the U.S. National Academies [C+07] , he highlights four learning objectives of any science education:
know, use, and interpret scientific explanations of the natural world
prepare students to generate and evaluate scientific evidence and explanations
understand the nature and development of scientific knowledge
participate productively in scientific practices and discourse
In practice, actual science education strongly emphasizes the first of these (and almost exclusively the “know” part). As Dr. Alberts put it, instead of, “learning how to think scientifically, students are generally being told about science and asked to remember facts”.
This is may be true in many scientific programs, but seems particularly true in programs such as psychology. Within undergraduate psychology programs, there tend to only two required courses that actually teach students how to do more than know : statistics and research methods. These courses are often students’ least favorite courses in the entire curriculum, which means that they are tolerated rather than emphasized. This is a shame, but perhaps not entirely surprising. Not every academic program should resemble a trade school program. On the other hand, a lack of critical thinking hurts everyone. Simple, intuitive answers are appealing even when dealing with complex problems. Confidence is often as persuasive, if not more persuasive, than evidence. In short, it is not hyperbolic to say that a fully realized science education constitutes part of “basic education of everyone in the modern world” [Alb09] .
Consumers of Science ¶
But I don’t want to be a scientist! This is a common refrain when students learn that they will be required to take a course in research methods. This is totally reasonable. However, the discussion above should foreshadow the natural response. Students have enrolled in a scientific program and the majority of the objectives of a science education are, strangely, the responsibility of one or two courses. If learning how to do science is so undesirable, it’s not clear why students enrolled in an scientific program like psychology.
However, the other response, also previewed above, is that science education is not just for future scientists . If you plan on being a “consumer of science”, and it is difficult to see how you will not , then knowing how science is done is of critical importance. Here’s an example. You see a fresh headline: “Scientists: No Safe Level of Chocolate Consumption!” But you love chocolate. What to do? In a panic, you read the article thoroughly, but there is little detail about the study itself. Now what? You could, conceivably, go grab the original scientific report. But how do you do that? Even if you could get your hands on it, what would do with it? It’s written for a scientific audience and the writing is technical. Even if you could sift through the writing, how would you evaluate the study? Was design of the study appropriate for the research question? Did the authors use appropriate statistical procedures? Did they interpret the results of those procedures correctly? Without the ability to answer these questions, you will be forced to choose blindly: death by chocolate or a sad, chocolate-less life.
Epistemology ¶
John Moore [Moo99] writes that science is a special way of learning about the world (including chocolate). People, both the general public and those who have completed formal educational programs, are often confused by this. It is common to hear people talk about “science” as if it is body of knowledge; a set of “facts” and “laws” that must be accepted if one is to be a sensible, scientifically-minded individual. But science is not knowledge in the same way that cooking is not food. This is why the conventional approach to scientific education is so deficient. It given the impression that studying “all the facts” is all one needs. But evidence accumulates and shifts and knowledge of answers to old questions do not apply to new questions. Bodies of knowledge cannot keep up with a changing world, but the tools to tackle questions can.
Epistemology is a branch of philosophy concerned with the question “What do we know?” There are all sorts of routes to knowledge. None of them (or almost none) can guarantee the sort of knowledge we ultimately desire: true knowledge . But the scientific method gives us our best shot. Ready?
References ¶
Bruce Alberts. Redefining science education. 2009.
National Research Council and others. Taking science to school: Learning and teaching science in grades K-8 . National Academies Press, 2007.
John Alexander Moore. Science as a way of knowing: The foundations of modern biology . Harvard University Press, 1999.
Full license details can be found here . This textbook is an adaptation of one originally written by Paul C. Price (California State University, Fresno) and adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work’s original creator or licensee. The original text is available here .
This adaptation constitutes the Stony Brook Edition by Christian C. Luhmann (Stony Brook University). This edition incorporates the Brooklyn College edition by Matthew J. C. Crump (Brooklyn College and Graduate Center of the City University of New York) which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. The Brooklyn College edition incorporates the second Canadian edition by Rajiv S. Jhangiani (Kwantlen Polytechnic University) and I-Chant A. Chiang (Quest University Canada) which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License and incorporates the second U.S. edition authored by Dana C. Leighton (Southern Arkansas University) and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Research Methods in Psychology - Stony Brook Edition by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Dana C. Leighton, Matthew J. C. Crump, & Christian C. Luhmann is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

Research Methods
This unit includes the following chapters.
“Thinking like a Scientist” explores important considerations for evaluating the trustworthiness of conclusions and theories.
“Research Designs” explains how psychologists test research questions using a variety of methods.
“Conducting Psychology Research in the Real World” highlights the importance of conducting research outside the psychology laboratory and reviews methods for conducting psychological research in the real world.
“Statistical Thinking” uses four recent research studies to teach how to draw valid inferences from data.
“The Replication Crisis in Psychology” explains why many research findings do not replicate and suggests solutions to the problem.
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © by Utah Tech University Psychology Department is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction
Welcome to Psychology Research Methods!
Created by The Research Methods Teaching and Learning Group
This open education resource has been created for the use of PSY 321: Research Methods in Psychology at Portland State University. This will serve as your reading for PSY 321 this quarter.
The primary purpose of PSY 321: Research Methods in Psychology is to help you develop a foundation in research methods for psychology. During this course we will learn about how research scientists in the field of psychology identify questions, design studies, collect data, and present findings in a way that is clear and impactful. Upon completion of this course you will be able to:
- Locate, understand and interpret empirical research.
- Understand ethical concerns in conducting and reporting research.
- Understand the various forms of measurement.
- Understand the differences between experimental and observational research.
- Differentiate between validity and reliability.
- Design a research study to systematically investigate a hypothesis.
Building a strong foundation in research methods is an essential and important part of earning your psychology degree. This open education resource will provide you with weekly readings that support your success in this course and provide you with the breadth of knowledge you need to understand the science of psychology.
These OER materials were converted to a Pressbook under the direction of Dr. Scott Robison and with the help of Shalene Allen and Jeslin Hancock.
Psychology Research Methods Copyright © by The Research Methods Teaching and Learning Group is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Relational aggression in romantic relationship: empirical evidence among young female adults in Malaysia
- Mohammad Rahim Kamaluddin 2 ,
- Shalini Munusamy 1 ,
- Chong Sheau Tsuey 2 &
- Hilwa Abdullah & Mohd Nor 2
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 305 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
56 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Aggressive behaviour in romantic relationship is a social problem of great concern. Studies related to the influence of psychosocial factors on relational aggression are still limited. Furthermore, these factors have not been widely studied in the local context, resulting in the issue of relational aggression among young female adults still not being addressed. This study aims to explore whether psychosocial factors such as big five personality traits, adult attachment style and loneliness could predict relational aggression in romantic relationships among young female adults in Malaysia. In addition, this study aims to identify the moderating effect of social support in the relationship between psychosocial factors and relational aggression in romantic relationship.
A quantitative research approach was used with 424 young female adults in Malaysia aged between 18 and 30 years old (mean age = 24.18) were recruited through multistage sampling design by completing a questionnaire consisting of the Big Five Inventory (BFI), Experiences in Close Relationships Scale II (ECRS-II), Revised UCLA Loneliness Scale, Measure of Relational Aggression and Victimization (MRAV) and Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS).
Multiple regression analysis predicted significant relationship between agreeableness personality, loneliness, avoidant attachment style and anxious attachment style with relational aggression in romantic relationships. Hierarchical regression analysis found a significant effect of social support as a moderator between loneliness with relational aggression in romantic relationships.
Conclusions
Thus, the results show that young female adults with low level of agreeableness, high level of loneliness, avoidant attachment style and anxious attachment style are at a higher risk of engaging in relational aggression in romantic relationships. The implication of this study can help in understanding the psychosocial factors that form the basis of relational aggression in romantic relationships. Hence, the gap in knowledge warrants further research.
Peer Review reports
The development of romantic relationships among early adulthood is crucial in forming views about intimate relationships and exhibiting intimacy, power, and control [ 1 ]. Emerging adulthood is a key developmental stage for creating a healthy romantic relationship. Some romantic relationships involve aggressive behaviour between partners, which can manifest in various forms such as physical, non-physical, direct, or indirect aggression, overt or covert aggression [ 2 ]. Aggressive behaviour is a criminogenic trait linked to various violent crimes including dating violence [ 3 ]. Physical aggression involves intentionally using physical force to hurt the partner, ranging from mild actions like pushing to severe violence like choking, slapping or weapon use [ 4 ]. Emotional abuse is also a common form of abuse in romantic relationships [ 5 ]. The online dating scam is another alarming form of dating violence that can result in financial loss and severe emotional and psychological suffering ( 6 – 7 ). Relational aggression is a form of non-physical and covert aggression, involves threatening others by manipulating and acting to jeopardize romantic relationships [ 8 ]. Unlike physical aggression, relational aggression occurs without any physical force or physically threatening the individual and can be considered a type of psychological aggression, targeting perceptions, feelings, or behaviour in romantic relationship [ 9 ]. Relational aggression can be indirect, such as through negative facial expressions or spreading rumors about a partner. While there has been extensive research on physical aggression and violence in romantic relationships [ 10 , 11 , 12 ], there is relatively less research on relational aggression in romantic relationships.
Relational aggression in romantic relationships might appear as threats to end the relationship if the other person doesn’t cooperate, flirting with other people to make the other person envious, or treating the other person silently while upset [ 9 ]. In terms of relational aggression, females who utilized high levels of relational aggression had a strong tendency to see other people’s acts as hostile and malevolent, whereas males did not [ 13 ]. Examining relational aggression and its relationship with adaptive functioning in females may shed light on the critical mechanisms involved in females’ dating violence. In this study, we hope to study the psychosocial factors most related with relational aggression in females by looking at components known to relate to aggression in females, such as individual characteristics and environmental factors. There is little evidence from research on female gender to differentiate the experience of relational aggression in romantic relationships, female perpetrators will be the greatest risk of this aggressive behaviour and young female adults may experience greater psychological stress than men ( 13 – 14 ). Therefore, this study focuses only on female samples and will be done using Malaysian samples. Despite research, little is known about how relational aggression originate, persist, and have an impact on romantic relationships, including whether men and women experience these issues differently ( 13 – 14 ). Romantic relational aggression has also been linked to relationship quality, violence, psychosocial maladjustment, impulsivity, hostile attribution biases, loneliness, emotional sensitivity to relational incitements, and abuse history [ 13 ].
In addition, this study emphasizes the psychosocial aspect of a person that can cause the tendency to behave aggressively in romantic relationships. It is important to identify the psychosocial aspects of a person who tends to engage in relational aggression in romantic relationships. The link between relational aggression and psychosocial factors such as loneliness, attachment styles, and personality type has been established ( 15 – 16 ). Personality traits of aggressors have been known to be associated with dating violence ( 15 – 16 ). This study used the “Big Five” personality model (extraversion, agreeableness, openness, conscientiousness, and neuroticism) as one of the psychosocial factors. Each main trait from this model can be divided into several aspects to provide a more detailed analysis of a person’s personality. Several theorists argue that personality variable is an important predictor of aggressive behaviour in romantic relationship [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Agreeableness dimensions are often associated with aggressive behaviour [ 18 , 20 , 21 ]. Besides that, a study conducted by Ulloa et al. (2016) found individuals with a high neuroticism personality tend to be victims in relational aggression during intimate relationships [ 22 ]. The findings of this study are also supported by other research that neuroticism trait as the main personality trait that gives a strong influence on relational aggression ( 23 – 24 ).
In addition to personality traits, other factors such as the level of loneliness are also considered to be a strong predictive factor of relational aggression especially the tendency to be a victim [ 25 ]. Generally, loneliness can be associated with individuals having a lack of social support as well as showing no interest in social networks [ 25 ]. Many studies have linked aggressive behaviour with loneliness [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Loneliness is defined as a negative emotional response to the discrepancy between the desired and achieved quality of one’s social network [ 27 ]. In addition, relational aggression is caused by the loneliness faced by an individual [ 28 ]. Individuals who are lonely describe themselves negatively and have negative ideas about others. As a result, loneliness leads to a bad perception of oneself, such as being unwanted and unaccepted by others, and it leads to aggression, which is a means of using force to influence other people in interpersonal relationships [ 29 ]. Individuals with high level of loneliness are at high risk of engaging in relational aggression in romantic relationship ( 30 – 31 ). Another psychosocial aspect often associated with relational aggression is attachment style. Attachment style is said to be able to shape the probability of an individual being involved in incidents of relational aggression in romantic relationship.
An expanding corpus of research has highlighted attachment theory as a crucial paradigm for comprehending emotional and interpersonal processes that take place across the lifespan [ 32 , 33 , 34 ]. The foundation of attachment theory is the idea of an attachment behavioural system, in which attachment actions are grouped together to strengthen a particular attachment figure. A sense of personal security within the relationship can be established or maintained by intimate partner violence, according to the attachment theory. People feel startled when they sense a threat to their attachment connection, and the ensuing anxiety causes them to act in ways that protect their attachment system [ 35 ]. Individuals with different attachment style also have an influence strongly to the involvement of individuals in the occurrence of aggression ( 36 – 37 ). Besides that, individuals with avoidant attachment shows high relational aggression in romantic relationship ( 38 – 39 ). Besides that, individuals who often exhibit anxious attachment to their partners such as fear of rejection and dependency on their partner are more likely to experience relational aggression in romantic relationships ( 40 – 41 ).
The potentially moderating role of Social Support
In relation to that, social support is used as a moderator based on previous literature studies [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. Social support is also defined as interpersonal relationships and support provided by social groups that aim to provide well-being to individuals [ 42 ]. Social support from family and friends is important in contributing to positive psychological health among early adulthood and influences the act of aggressive behaviour [ 45 ]. Previous studies have shown that social support has a significant relationship with big personality traits, especially with extraversion and agreeableness [ 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. In addition, a few studies also found that family members with agreeableness trait also provide more social support [ 46 , 47 , 48 ]. Besides that, people who experience loneliness interact less with friends and family than people who do not feel lonely. In other words, the less social support a person has, the higher the level of loneliness [ 50 ]. According to earlier research, there have been negative association between relational aggression and social support as well positive association between relational aggression and psychosocial maladjustment during major developmental stages including childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood [ 51 , 52 , 53 ].
According to research, individuals with little social support from their parents were more likely to engage in verbal, physical, and relational aggression [ 54 ] whereas individuals who reported high perceived social support from peers were less likely to engage in overt and relational aggression [ 55 ]. Besides that, individuals who have supporting friends and family have lower relational aggression. Family and peer support can help to mitigate the harmful effects from using relational aggression behaviour in their romantic relationship. Adults with high levels of social support outperformed those with low levels of family and peer support in exhibiting relational aggression behaviour in romantic relationships [ 56 ]. Although both relational aggression and social support are empirically connected to maladjustment, research on the interaction effect of psychosocial factors and social support on relational aggression is still limited ( 57 – 58 ).
Besides that, a study done in US had found that there is no evidence of social support act as a moderator between psychosocial factors and dating violence [ 59 ]. Only a small amount is allocated in the extent literature to research the triad of the relationship. In accordance with that, this study will further explore to develop an understanding of the role of social support in the association between psychosocial factors and relational aggression. Among several theories of social behaviour, for this study we have used Albert Bandura (1986) social cognitive theory to help provide researchers with a comprehensive framework to understand the factors that may influence aggressive human behaviour. Although Bowlby (1969) prioritized and focused on understanding the nature of caregiver’s relationship with his infant, at the same time he also believed that bonding features are present in human life experience from “cradle to grave” [ 30 ]. Besides that, attachment style and social support combine the theory-based prediction that people with an insecure attachment style are more likely to evaluate others’ reactions negatively [ 60 ].
This study can give awareness to young female adults about the issue of relational aggression that can happen in a romantic relationship. This is because relational aggression is an issue that is not given attention in romantic relationships by women and only aggressive behaviour such as physical and sexual is considered more harmful in romantic relationships. This study can give awareness to young female adults about the characteristics of an individual who practices relational aggression in a romantic relationship and can help in finding a solution from practicing relational aggression in romantic relationship. This study can also help young adults to identify this issue so that it does not continue and affect romantic relationships in adulthood. Relational aggression is known to be a relevant social problem factor which can be a precursor to abusive romantic relationships in later adulthood [ 61 ].
A conceptual framework in this study was built based on the social cognitive theory introduced by Albert Bandura in 1986, attachment theory developed by John Bowlby (1907–1990) and the big five personality theory developed in 1949 by D. W. Fiske (1949) as well as from the findings of research on previous studies in the field of psychosocial factors and relational aggression in romantic relationship. In general, this study aims to explore whether psychosocial factors could predict relational aggression in romantic relationships. There is not much direct research that examines covert set of manipulative behaviors in romantic relationships such as relational aggression. Besides that, there are only a few studies conducted in Malaysia about relational aggression in romantic relationships compared to studies conducted in Western countries [ 53 , 54 , 55 , 60 , 61 , 62 ]. Therefore, it is important to conduct this study using respondents from Malaysia so that it can help psychologists and other parties involved to identify individuals using relational aggression in romantic relationships and from being involved in psychological problems.
The present study
This study was designed to explore whether psychosocial factors such as big five personality traits, attachment style and loneliness could predict relational aggression in romantic relationship among young female adults in Malaysian context and aims to extend findings from previous studies in this field. The researchers hypothesize that psychosocial factors, such as personality trait, attachment styles, and loneliness, will play a significant role in determining the presence and severity of relational aggression in romantic relationships. In addition, it is believed that social support will act as a moderating factor in the relationship between psychosocial factors and relational aggression. As a result, this study aims to shed light on the drivers behind relational aggression in romantic relationships and to better understand the relationship between psychosocial factors and relational aggression. This study is regarded novel because there are no known studies on relational aggression in romantic relationship in the Malaysian context as this will be the first Malaysian study to define the relational aggression in romantic relationship among the sample of young female adults in Malaysia.
Participants
An online survey was conducted with a total of 424 females from early adulthood stage, aged between 18 and 30 years old in Malaysia. According to DOSM (2021), the total population of women in early adulthood in Malaysia is 15,758.2(‘000). From the entire population in each state, the respondents aged between 18 and 30 were selected in this study using Raosoft formula. Proportionate stratified random sampling was used to recruit respondents from 13 states in Malaysia to get sufficient sample size from each state through Raosoft formula calculation in July 2022. Then, convenience sampling was used to select a study sample from the population to get a sufficient sample from each state where an advertisement was posted in social media. Inclusion criteria: [ 1 ] participants must be Malaysian; [ 2 ] female participants aged between 18 to 30 years old only; [ 3 ] currently in a romantic relationship for more than 3 months; [ 4 ] must answer all questions in relation to the most recent partner or romantic relationship; [ 5 ] informed and voluntary participation in the study. The study sample for this research consists of different races, occupation, and education background so that they will have equal opportunity to be selected as a respondent.
Instruments
Big five inventory (bfi).
The Malay version of Big Five Inventory (BFI; 63) which was developed by Muhammad et al., [ 63 ] was used to measure the five basic personality dimensions, namely extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, openness, and neuroticism. The 44-item BFI is rated on a 5-point Likert Scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). After reverse scoring, the mean score of each subscale is obtained. The Malay version of the BFI shows good internal consistency, convergent and discriminant validity [ 63 ]. The internal reliability of this scale in the current study was high, with a Cronbach’s alpha calculation of 0.78 to 0.88 with a mean of 0.81.
UCLA loneliness scale-3
The Malay version of the Rusell’s [ 64 ] UCLA Loneliness Scale [ 65 ] was used to measure loneliness. This tool consists of 20 items and is rated on a 4-point Likert scale from 1 (Never) to 4 (Always). Loneliness was assessed by averaging the scores of all items with higher scores indicating higher levels of loneliness. The internal reliability of this scale in the current study reported with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.83.
Experiences in close relationships– II (ECR-II)
The Experiences in Close Relationships Scale II (ECRS-II; 67) assessed individual differences in anxious attachment style (i.e., the extent to which individuals feel secure versus insecure about romantic partner relationships and reactions) and avoidant attachment style (i.e., the extent to which individuals feel uncomfortable with having close relationships with others versus feel safe to rely on others). The Malay version of the ECR-II [ 66 ] was used in this study. The internal reliability of this scale in the current study was high, with a Cronbach’s alpha calculation of 0.82 to 0.83 with a mean of 0.83.
Measure of relational aggression and victimization (MRAV)
This instrument was developed by Linder et al. [ 67 ]. This 56-item instrument consists of six subscales that measure six dimensions of aggression, namely relational aggression, physical aggression, relational victimization, physical sacrifice, exclusivity, and prosocial behaviour. For this study, only the subscales of relational aggression (5 items) were used. Items in this tool are rated on a 7-point Likert-type scale from 1 (Not at all True) to 7 (Very True). This questionnaire was translated into Malay language using Forward-Backward translation method and followed by content validation. CVR technique was used to measure the content validity of this questionnaire. The CVR was in the range 0.7-1 for all items and the overall mean CVR values were 0.83. According to Rahim et al. [ 68 ], in the context of measuring psychological test, tools which are available in their own native language will be more appropriate and measurement will be more accurate compared to other languages. The internal reliability of this scale in the current study was high with a Cronbach’s alpha calculation of 0.88 with a mean of 0.89.
Multidimensional scale of perceived social support (MSPSS)
This questionnaire was developed by Zimet et al. [ 69 ] and was used to measure social support of an individual. The MSPSS consists of 12 items assessing three specific sources of social support namely family, friends, and others. This test tool uses a 7-point Likert scale where (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree). In this study, the Malay version of the MSPSS tool was used which was translated and validated by Ng et al., [ 70 ]. The internal reliability of this scale in the current study was high, with a Cronbach’s alpha calculation of 0.93.
The survey was conducted from July 1 to July 26, 2022. According to Connelly [ 71 ], previous studies suggest that the sample size of the pilot study should be 10% of the sample size used for the actual study. Therefore, a pilot study was carried out before the real study with 44 respondents in the state of Selangor. The researcher chose Selangor because it is the state where the researcher is currently living, and this will make it easier to carry out the study. In the actual study, 424 participants were recruited based on Table 2 . This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of The National University of Malaysia (No: 2022 − 549). All participants were informed of the research objectives and their rights on the first screen (voluntary participation, the right to withdraw at any time and anonymity). This study was not conducted with any minors. At the start of the test, informed permission was acquired, this study only moved forward if the subject ticked the box that said, “Yes, I offer my consent to participate.” The participants’ privacy was guaranteed by the test’s anonymity and the numerical coding of their replies.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics and inferential statistics were calculated using SPSS 26.0. For inferential statistics multiple regression and hierarchical regression has been used in this study. Multiple regression was used to explore whether psychosocial factors such as big five personality traits, attachment style and loneliness could predict relational aggression in romantic relationship. A single dependent variable and numerous independent variables can be analysed using the statistical method known as multiple regression. The value of R, the multiple correlation coefficient, is shown in the “R” column. The “R Square” column displays the R 2 value, also known as the coefficient of determination, which is the percentage of the dependent variable’s variance that can be explained by the independent variables. R can be thought of as one indicator of the accuracy of the dependent variable’s prediction [ 72 ]. It is the proportion of variation accounted for by the regression model above and beyond the mean model. Hierarchical regression was used to study the effect of social support as a moderator in the relationship between psychosocial factors (personality trait, attachment style and loneliness) with relational aggression in romantic relationship. The moderation effect analysis was carried out using SPSS hierarchical regression. The hierarchical regression is a more appropriate method for determining whether a quantitative variable has a moderating effect on the relationship between two other quantitative variables [ 72 ]. If the moderation test result fell within the 95% confidence interval and contained 0, it meant that the moderation impact of social support was not significant; if it did not, it meant that the moderation effect of social support was substantial. In this study, p <.05 was regarded as statistically significant. In this study, SPSS 26.0 software were used to analyse the data.
Descriptive statistics
A total of 500 participants have completed the online survey but only 424 (M ± SD = 24.18 ± 3.21 years) participants’ responses were included after 76 questionnaires were rejected from this study as it did not meet the inclusion criteria. The highest level of education obtained by the participants is degree education. 18.2% of participants had engaged in aggression towards their romantic partner.
Inferential statistics
Table 2 shows the results of a multiple regression analysis in predicting relational aggression based on big five personality traits, attachment styles, and loneliness among young female adults in Malaysia. Among the five subscales of personality trait, agreeableness showed a significant predictor. In addition, loneliness, avoidant attachment style, and anxious-attachment style also showed significant prediction with relational aggression. Overall, the results of the regression analysis showed that agreeableness, loneliness, avoidant attachment style, and anxious attachment style together can predict 30.3% of the variance in relational aggression (R²=0.303), where [F (3,269) = 22.561, p < 0 0.05]. The subscale of agreeableness showed negative prediction (β=-0.305, p <.05) with relational aggression whereas loneliness (β = 0.364, p <.05), avoidant attachment style (β = 0.420, p <.05), and anxious attachment style (β = 0.321, p <.05) showed positive prediction with relational aggression. These findings showed that higher level of agreeableness trait contributes to lower level of relational aggression in romantic relationships. Besides that, high levels of loneliness, avoidant attachment style, and anxious attachment style contribute to higher level of relational aggression in romantic relationship.
For hierarchical regression analysis, only those variables that were significant in the multiple regression analyses were entered into hierarchical regression models which are agreeableness trait, loneliness, avoidant attachment style, and anxious attachment style. Table 3 shows the hierarchical regression analysis where R² value for Model 1 is 0.097, F (25.735) = 22.545, p <.05. This means that the agreeableness dimension accounts for 9.7% of the variance in relational aggression. While the R² value obtained for Model 2 is 0.098, F (17.410) = 15.240, p <.05. This means that social support and agreeableness dimensions contribute as much as 9.8% of the variance to relational aggression in romantic relationships. These results showed that the percentage of variance only increases by 0.1% (9.8%– 9.7%) with the presence of a moderator in this model. The results in Table 3 showed that the dimension of agreeableness as a predictor is significant with a value of β =-0.296, t = -6.333, p <.05. While social support as a predictor is not significant with β value = -0.062, t = -1.331, p >.05. After entering the moderator, the interaction term of social support and agreeableness is not significant with a value of β = -0.406, t = − 0.816 and p >.05. The agreeableness subscale was a significant predictor in the first block ( p <.05) but did not reach significance in the second block ( p =.415).
Table 4 shows the hierarchical regression analysis where R² value for Model 1 is 0.135, F (35.826) = 32.761, p <.05. This means that the loneliness level dimension accounts for 13.5% of the variance in relational aggression. While the R² value obtained for Model 2 is 0.146, F (25.874) = 23.915, p <.05. This means that social support and loneliness level dimensions contribute as much as 14.6% of the variance to relational aggression in romantic relationships. These results show that the percentage of variance only increases by 1.1% (14.6%– 13.5%) with the presence of a moderator in this model. The results in Table 4 show that the dimension of loneliness as a predictor is significant with a value of β = 0.383, t = 7.767, p <.05. While social support as a predictor is not significant with a value of β = 0.048, t = 0.964, p >.05. After entering the moderator, the interaction term of social support and loneliness is significant with a value of β = 0.550, t = 2.349 and p <.05. The loneliness subscale was a significant predictor in all blocks ( p <.05), with p =.019 in the second block.
Table 5 shows the hierarchical regression analysis where R² value for Model 1 is 0.231, F (40.936) = 42.014, p <.05. This means that the attachment style dimension accounts for 23.1% of the variance in relational aggression. While the R² value obtained for Model 2 is 0.237, F (25.225) = 25.976, p <.05. This means that social support and attachment style dimensions account for 23.7% of the variance in relational aggression in romantic relationships. These results show that the percentage of variance only increases by 0.6% (23.7%– 23.1%) with the presence of a moderator in this model. The results in Table 5 show that the dimension of avoidant attachment style as a predictor is significant with a value of β = 0.368, t = 8.345, p <.05 and the dimension of anxious attachment style as a predictor is significant with a value of β = 0.244, t = 5.364, p <.05. While social support as a predictor is.
not significant with a value of β = 0.20, t = 0.447, p >.05. After entering the moderator, the interaction term of social support and attachment style was not significant on the relational aggression with values of β = 0.155, t = 0.676, p >.05 and β = 0.520, t = 2.925, p >.05. The ECR’s anxious and avoidant subscale were significant predictor in the first block ( p <.05) but did not reach significance in the second block ( p =.328;0.105).
The participants that have been selected for this study are young female adults between the age of 18 to 30 (M ± SD = 22.08 ± 3.21 years) who are currently in a romantic relationship for more than three months. Regression analysis was done, and it was found that only agreeableness trait showed significant predictor on relational aggression in romantic relationship and the other four dimensions of the big five personality in the psychosocial factor variable, which are extraversion, openness, neuroticism, and conscientiousness are not predictors or contributors to relational aggression in romantic relationships. Therefore, the findings prove that the importance of the relative contribution of personality traits of agreeableness. Generally, in an interpersonal context, personality is known to play an important role in determining the likelihood of engaging in an aggressive act. Negative emotions are generally harmful to romantic relationships. The result from our study is contradictory with the research findings by Burton et al. [ 73 ] where they have found that higher relational aggression was associated with higher levels of neuroticism and lower level of conscientiousness.
In addition, in some studies it has been found that individuals who tend to engage in relational aggression are more likely to show lower traits of agreeableness, openness and conscientiousness [ 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 ]. In our study, none of the big five personality traits except for agreeableness show significant prediction towards relational aggression in romantic relationships. This may be due to in general agreeableness traits may have stronger predictive utility than other personality traits ( 78 – 79 ). It has also been shown that agreeableness trait is negatively associated with relational aggression [ 80 , 81 , 82 ]. Agreeableness characterized as cooperation and understanding is an aspect related to motivation to maintain positive interpersonal relationships [ 83 ]. Likewise, the relationship between agreeableness and mind suggests that the former is responsible for processing social information.
Furthermore, agreeableness supports altruism while relational aggression is a type of destructive and hostile behaviour that has anti-social tendencies [ 84 ]. Therefore, this can further explain the evidence we found that agreeableness trait is associated with a negative influence on relational aggression. The trait of agreeableness has also been referred to as adaptability or reliability. There are differences in the interpretation of the dimension of agreeableness. The trait of agreeableness is considered reliable whereas Asian people generally support a collectivist culture, emphasizing social harmony and avoiding conflict [ 84 ]. Agreeableness represents the obligation to act as a group member and to make sacrifices. This cultural difference can lead to the irrelevance of agreeableness traits against relational aggression among young female adults in Malaysia. Besides that, those with higher levels of neuroticism are thought to be more likely to be aggressive. This individual is considered to have fewer stable emotions. Therefore, people who exhibit many neurotic personality traits are more prone to emotional instability and more prone to conflict with others. Conversely, agreeableness and aggressiveness are consistently negatively correlated [ 84 ].
Loneliness shows positively significant prediction towards relational aggression in romantic relationships. This is consistent with the study done by Prinstein et al., [ 55 ] which revealed that both relationally aggressive children and youth are more likely to be depressed, lonely, anxious, and socially isolated. However, according to the study done by Povedano et al., [ 85 ] found that the relationship between loneliness and relational aggression is significant and positive for boys, but not for girls. The involvement in violent behaviour would not act as a buffer for victimized girls experiencing strong feelings of loneliness, whereas it would be for boys. Lonely people usually have a negative perception of others’ intentions and behaviours in their interpersonal relationships. Along with these findings, lonely people tend to assume that their interpersonal failures stem from unchangeable and undesirable traits in their own personality, and they have a negative interpretation of other people’s intentions and interactions. Individuals who have developed a negative perception of themselves because of loneliness, feeling undesirable and unaccepted by others may resort to relational aggression, a powerful tool in which one uses force in interpersonal relationships to control other people [ 27 ].
The results of this study found a positive and significant prediction between avoidant and anxious attachment styles with relational aggression in romantic relationships. It has been established that the quality of communication between parents and children plays a crucial role in the development of a secure attachment. Our findings are in line with previous research that suggests that adolescents who have a positive relationship with their parents and communicate well with them are less likely to engage in aggressive behaviours and engage in risky activities [ 86 ]. Moreover, early attachments shape not only an individual’s sense of self and view of the world, but also their social skills, overall well-being, and future relationships. This is supported by the findings of Dervishi et al., [ 87 ] who found that adolescents with anxious attachments had higher levels of physical and verbal aggression. Studies have also shown that communication between parents and teens is strongly linked to the emergence of aggressive behaviours, with better communication resulting in a higher sense of security and an active exchange with others throughout life [ 88 , 89 , 90 ]. Essentially, individuals who are highly insecure may have difficulties controlling their anger and are more likely to engage in aggressive behaviour.
Previous research has demonstrated that individuals with insecure attachment patterns, particularly the anxious type, are at risk of experiencing negative consequences [ 91 , 92 , 93 ]. This can be attributed to a negative self-concept and high levels of rejection anxiety, leading to an over-reaction of excessive anger, and hurt in conflict situations. Research suggests that individuals with anxious attachment style have a history of persistent rejection from their partners and perceive themselves as unworthy of affection [ 94 ]. This can result in a perception of partners as untrustworthy and even threatening. It has been found that young adults with anxious attachment style are more prone to experiencing anger, compared to those with a secure or preoccupied attachment style who tend to have more positive expectations of their partners. In other words, those who have a strong sense of insecurity are likely to struggle with controlling their anger, while those with these insecurities are more likely to engage in aggressive behaviour.
Hierarchical regression analysis was carried out and it was found that social support as a moderator showed no significant effect between big five personality, avoidant and anxious attachment style with relational aggression in a romantic relationship except for loneliness subscale. The behaviour’s of loved ones that are in tune with the needs of the individual who is dealing with a stressful situation are referred to as social support [ 95 ]. The availability of support in the environment, the emotional response to stressful events, and the assessment of the consequences of these events can all be positively influenced by support from loved ones. Support from loved ones help to decrease the impact of stress by solving the victim’s problems, diminishing the perceived importance of the incident, facilitating the adoption of rational thoughts, and preventing or reducing inappropriate behaviour responses. According to previous research, social support may act as a moderator and buffer the effects of aggression and family functioning [ 96 ]. Due to the positive correlation between social support and a person’s family adjustment, social support helps to balance the negative effects of relational aggression on families [ 97 ].
This study’s finding is also consistent with the finding by Fortin et al. [ 98 ], where the moderating effect of social support is not present in female victims of physical violence. Thompson et al. [ 99 ] found that less women who have experienced relational aggression perceive the availability of social support, the more severe the violence they have experienced. The victim may also begin to blame herself more and ask for less support from her loved ones as the violence intensifies due to the bidirectional pattern of violence. Additionally, it seems that continuing in a relationship while having experienced physical abuse may have an impact on how satisfied they are with the assistance they have received [ 100 ]. These victims may also require additional forms of support, such as emotional, educational, and material support, even though they are generally happy with the assistance they have received.
Therefore, fewer confidants may have led to less robust social support. As a result, having fewer confidants may have led to social support that was insufficient and did not entirely satisfy the needs of the physical abuse victims. Besides that, social support is thought to be the most important factor that could significantly reduce loneliness [ 100 ], and it may be able to predict the trajectory of loneliness [ 101 ]. Indeed, numerous studies on the roles played by various forms of social support have found that perceived social support is more useful for predicting people’s mental health and may have a bigger impact on mental health than other forms of social support [ 102 , 103 , 104 ].
Both relational aggression and social support are empirically related to levels of loneliness, empirical literature is lacking on the interactive effects of relational aggression and social support on levels of loneliness [ 53 , 105 , 106 ]. Little is devoted in the existing literature to investigating the relationship triad. Ladd and Burgess [ 52 ] suggested that social support moderates the association between aggression and adjustment because it balances the dysfunction created by aggression. Family and peer support can act as a buffer in minimizing the negative effects of relational aggression in romantic relationships [ 107 ]. Adolescents who receive social support perform better in academic tasks and social interactions than individuals who do not have family and peer support [ 108 ]. Consistent with this research, social support, in general, and family support may act as moderating factors for the relationship between levels of loneliness and relational aggression.
Next in this study, it was found that there is no relationship between the role of social support as a moderator in the relationship between attachment style and relational aggression in romantic relationships among young female adults in Malaysia. This is contrary to the results of previous studies that suggest social support act as a moderator and minimizes or increases the effect of relational aggression on parental attachment style because social support is positively related to one’s family adjustment [ 99 ] and it has been hypothesized that social support moderates the relationship between relational aggression and parenting style. However, the findings of this current study highlight that social support as a moderator, relational aggression and parenting style are one of the factors that are very influential which affects the functioning of young people based on past studies [ 104 ]. The current findings show how social support moderates as an enhancer and buffer in attachment styles and relational aggression.
Results from previous studies differ from the current study due to several factors. Based on attachment style theory by Bowlby (1969), attachment style consists of secure attachment style, anxious attachment style, and avoidance attachment style but in this study only anxious attachment style, and avoidance attachment style alone were used to assess the attachment style of young adults. Avoidant attachment style involves fear of dependence and intimacy interpersonal, excessive need for independence and reluctance to self-disclosure. Anxious attachment styles involve fear of interpersonal rejection or neglect and distress when one’s partner is absent or unresponsive. People with an anxious attachment style always feel insecure about their romantic relationships and fear of abandonment by partner. Those with an avoidant attachment style have a common need to feel loved but not prepared emotionally to be in romantic relationships. Things like this can cause someone to use relational aggression in their romantic relationships such as manipulating partners, threatening partner to end the relationship. In addition, even if that individual has high social support but it does not affect if one is oriented in an avoidant attachment style and anxious attachment style.
Besides that, the findings of this study are consistent with a recent study by Egan and Bull [ 107 ] who found that there is no effect of social support as a moderator in the relationship between personality traits and relational aggression in romantic relationships. This is different from the perception based on personality theory developed by Goldberg [ 109 ] stating that social support is significantly associated with personality characteristics, especially extraversion, agreeableness, or emotional stability [ 107 ]. In general, from childhood to late adulthood, the relationships maintained by individuals with other people are related to individual differences in personality characteristics [ 110 ]. Personality traits that define interaction style can predict social interaction, available social support, and its perception. However, a supportive social context may also predict personality traits by providing individuals with opportunities to develop social skills, maintain social relationships, and foster prosocial behaviour. If personal experiences, roles, and social relationships can influence a person’s personality traits, social support is not only a proxy for the quality of social relationships but also a resource that can help to face the social challenges faced in middle adulthood and can predict personality traits by adapting to social roles expectations and developing social skills. Therefore, the relationship between the big five personalities and perceived social support is not only unidirectional but also reciprocal.
Limitations
As for limitations, all data used in this study were self-reported. The sensitive nature of some questions may have caused some participants to succumb to the social desirability bias and report. For instance, lower rates of relational aggression than their actual behaviour. Despite this, participants provided anonymous answers, making it less likely that they were prompted to provide biased answers. Furthermore, due to recall issues and inaccurate reporting it’s possible that both estimates of psychosocial factors and relational aggression contain measurement error. Another limitation for this study is the cross-sectional nature of these data, which precludes inferences about causal relationships is another drawback of this study.
Additionally, caution should be used when extrapolating the findings to all female samples since the participants in this study were a homogeneous sample of young female adults. Due to the study’s cross-sectional design, it is also impossible to draw conclusions about the cause-and-effect relationship between social support as a moderator in between psychosocial factors and relational aggression. To address the temporal ordering of people’s levels of social support from family and friends and their participation in relational aggression, longitudinal studies are required. Besides that, young female adults were not questioned regarding the opinions or involvement of friends in relational aggression. According to earlier studies, teenagers who have friends who engage in dating violence run a higher risk of doing so themselves [ 111 ]. Moreover, data was collected at one time point, so cause-and-effect conclusions could not be made. Besides that, the difference between the psychosocial factor’s groups couldn’t be identified clearly in relation to relational aggression in romantic relationship as only multiple regression has been conducted. A post hoc test can help in identifying the differences between specific groups and give a more meaningful finding.
Future studies
Future studies are needed on the impact of multiple placements, including their effects on unstable living situations, sibling attachment, adoption, frequent school changes, and difficulties. For instance, if an individual grew up in a family that shamed or condemned emotional expression or in a home with an abusive parent, this may associate anger with fear, danger, or damaged relationships, which will cause to develop more negative perception of their relationship with their parents and siblings. This study only focuses on female samples. Even though there are differences between the genders, both genders naturally experience anger. Men are thought to be more prone to rage despite evidence that women are more emotionally expressive. In addition, more research on gender disparities is necessary.
The current study suggests that preventive measures need to be taken to stop the symptoms of anger from getting worse. Uncontrollable anger can cause several problems, such as erratic behaviour, assault, abuse, addictions, and legal troubles. In these circumstances, anger impairs decision-making, harms relationships, and has other negative effects. Besides that, to manage anger and deal with triggers without repressing and storing it, as well as to deal without causing emotional harm, it’s crucial to recognize the warning signs of anger. Anger management techniques include breathing exercises under supervision, cognitive behavioural therapy, imagery, problem-solving, and the development of interpersonal and communication skills. Besides that, the findings of this study indicate that aimed at reducing and/or preventing relational aggression among young female adults should consider agreeableness traits ( 112 – 113 ). Young female adults who were less agreeable were likely to experience relational aggression. The findings highlight the need for additional research to pinpoint specific characteristics of the lower level of agreeableness female population that put them at risk for relational aggression in a romantic relationship.
The current study was novel in its examination of social support as a moderator of the association between psychosocial factor and relational aggression in romantic relationships. Future studies will need to test these associations further. Based on the findings from this study, there’s no evidence to support the prediction that social support would moderate this association, but future research with a better measure of social support or using different moderator variable may provide different results. Future research should investigate variables that are not included in this study that are possible predictors of relational aggression in romantic relationships. A post hoc test can be conducted further in identifying the differences between specific groups and give a more meaningful finding.
Relational forms of aggression tend to rise during adolescence (115), in part because more complex cognitive abilities are developed during this period that are necessary for successfully manipulating the relationships of others. We discovered a significant correlation between aggression and social support, which is crucial during adolescence. This research suggests that for some people, attachment style and relational aggression are highly overlapping, and possibly reciprocal. However, for some people, personality traits appear to be differentially linked to relational aggression. These results point to the need for additional research examining the moderating effects of significant correlates as well as a more nuanced strategy for relational forms of aggression during early adulthood’s prevention and intervention. Therefore, efforts to prevent young female adults from engaging in relational aggression should concentrate on all females and not just those who have been identified as perpetrators or victims. All females will be better equipped to spot relational aggression signs and help their friends if they are informed about the warning signs of relational aggression. Early adulthood could be taught about the warning signs of relational aggression through community-wide campaigns and in high school. This study will help to create awareness on the existence of relational aggression, public will be able to tackle this issue at an earlier stage rather than later and individuals will be able to identify the difference between a toxic and a non-toxic relationship.
In conclusion, many participants in this study reported having violent-free romantic relationships even though there are individuals who reported being the perpetrators of relational aggression. The current study was a first step in determining how psychosocial factors and relational aggression in romantic relationships are related to one another. Findings indicate that social support is also an important factor in understanding females’ relational aggression in romantic relationship. At the same time, results demonstrated that social support from friends and/or family has no significant effect with personality traits and attachment styles with relational aggression. This finding raises questions as to what may provide support to young female adults in relational aggression in romantic relationships. The current study’s greatest strength is the dialogue it has sparked about the importance of social support in romantic relationships between young female adults who is experiencing loneliness. This raised awareness could serve as a starting point for further study as well as the creation of programs and regulations that cater to the requirements of this population. It is necessary to create and carry out programs that encourage healthy dating interactions and inform young adults about dating violence which focuses on relational aggression. The findings also provide evidence for the significance of parental modelling in the development of romantic relationships in young adults. The findings are supported by social learning theory (Bandura, 1971), the concepts of which might be employed in investigating other areas of psychosocial factors on young adults’ relationships in the future.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Big Five Inventory
Experiences in Close Relationships– II
Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support
Measure of Relational Aggression and Victimization
UCLA Loneliness Scale
Shulman S, Connolly J. The challenge of romantic relationships in emerging adulthood. Emerg Adulthood. 2013;1:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167696812467330 .
Article Google Scholar
DeWall CN, Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. (2012). Aggression. Chapter in I. Weiner, editor, Handbook of Psychology, 2nd Edition, Volume 5, 449–466. H. Tennen & J. Suls, editors, Personality and Social Psychology. New York: Wiley.
Munusamy S, Jeyagobi S, Mohamed IN, Murthy JK, Chong ST, Abdullah H, Mohamamad Rahim Kamaluddin. Underlying familial factors for aggressive Behaviour in romantic relationships: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(8):4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084485 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Voyer P, Verreault R, Azizah GM, et al. Prevalence of physical and verbal aggressive behaviours and associated factors among older adults in long-term care facilities. BMC Geriatr. 2005;5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2318-5-13 .
Wen Huey C, Abdul Aziz AA, Mohd Hoesni S, Abd Razak MA, Kamaluddin MR. Effects of psychosocial factors towards emotional abuse among University Students who have been in romantic relationships. EDUCATUM J Soc Sci. 2021;7:107–20. https://doi.org/10.37134/ejoss.vol7.2.10.2021 .
Shaari AH, Kamaluddin MR, Paizi WF, Mohd M. Online-dating romance scam in Malaysia: an analysis of online conversations between scammers and victims. Gema Online J Lang Stud. 2019;19:97–115. https://doi.org/10.17576/gema-2019-1901-06 .
Jeyagobi S, Munusamy S, Kamaluddin MR, Ahmad Badayai AR, Kumar J. Factors influencing negative cyber-bystander behaviour: a systematic literature review. Front Public Health. 2022;10:965017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.965017 .
Crick NR. Relational aggression: the role of intent attributions, feelings of distress, and provocation type. Dev Psychopathol. 1995;7:313–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579400006520 .
Linder JR, Crick NC, Collins WA. Relational aggression and victimization in young adults’ romantic relationships: Association with perceptions of parent, peer and romantic relationship quality. Soc Dev. 2002;11(5):69–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9507.00187 .
Connolly J, Friedlander L, Pepler D, Craig W, Laporte L. The ecology of adolescent dating aggression: attitudes, relationships, media use, and socio-demographic risk factors. J Aggress Maltreatment Trauma. 2010;19:469–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2010.495028 .
Herrera VM, Wiersma JD, Cleveland HH. The influence of individual and partner characteristics on the perpetration of intimate partner violence in young adult relationships. J Youth Adolesc. 2008;37:284–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-007-9249-4 .
O’Leary KD, Slep AM. A dyadic longitudinal model of adolescent dating aggression. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2003;32:314–27. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3203_01 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Murray-Close D, Ostrov JM, Nelson DA, Crick NR, Coccaro EF. Proactive, reactive, and romantic relational aggression in adulthood: measurement, predictive validity, gender differences, and association with intermittent explosive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.09.005 .
Goldstein SE. Relational aggression in young adults’ friendships and romantic relationships. Personal Relationships. 2011;18:645–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6811.2010.01329.x .
Boladale M, Yetunde O, Adesanmi A, Olutayo A, Olanrewaju I. Personality profiles and psychopathology among students exposed to dating violence at the Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife. J Interpers Violence. 2015;30(1):168–90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260514532718 .
Dowgwillo EA, Ménard KS, Krueger RF, Pincus AL. DSM-5 pathological personality traits and intimate partner violence among male and female college students. Violence Vict. 2016;31(3):416–37. https://doi.org/10.1891/0886-6708.VV-D-14-00109 .
Carvalho J, Nobre OJ. Five-factor model of personality and sexual aggression. Int J Offender Therapy Comp. 2013;Criminology20(10):1–18.
Google Scholar
Jones SE, Miller JD, Lynam DR. Personality, antisocial behaviour, and aggression: a meta-analytic review. J Criminal Justice. 2011;39(4):329–37.
Lau KSL. (2013). Big five personality traits, pathological personality traits, and psychological dysregulation: Predicting aggression and antisocial behaviours in detained adolescents (Master’s thesis unpublished). University of New Orlean, Louisiana.
Lee V, Egan V. Predictors of aggression in southeast Asian female prisoners. Pers Indiv Differ. 2013;54(1):113–7.
Miller JD, Zeichner A, Wilson LF. Personality correlates of aggression: evidence from measures of the five-factor model, UPPS model of impulsivity, and BIS/BAS. J Interpers Violence. 2012;27:2903–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260512438279 .
Ulloa EC, Hammett JF, O’Neal DN, Lydston EE, Leon Aramburo LF. The big five. Personality trets and intimate Partner violence: findings from a large. Nationally Representative Sample Violence Victims. 2016;31(6):1100–15. https://doi.org/10.1891/0886-6708.VV-D-15-00055 .
Hovens JGFM, Giltay EJ, van Hemert AM, Penninx BWJH. Childhood maltreatment and the course of depressive and anxiety disorders: the contribution of personality characteristics. Depress Anxiety. 2016;33(1):27–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22429 .
Motevaliyan SM, Yaacob N, Juhari S, Mansor R, M., Baratvand M. Personality traits and severity of wife abuse among Iranian women. Asian Social Sci. 2014;10(7):234–41. https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v10n7p234 .
Holt M, Espelage D. Perceived social support among bullies, victims, and Bully-victims. J Youth Adolesc. 2007;36:984–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-006-9153-3 .
Sun L, Fu Z, Zheng Y. Shyness and loneliness in Chinese young adults: roles of aggression and gender. J Aggress Maltreatment Trauma. 2021;30(1):43–53.
Pavri S. Loneliness: the cause or consequence of peer victimization in children and youth. Open Psychol J. 2015;8(1):78–84.
Amapola Povedano M-J, Cava. María Carmen Monreal. Rosa Varela, Gonzalo Musitu. (2015). Victimization, loneliness, overt and relational violence at the school from a gender perspective. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2015;15:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijchp.2014.09.001 .
Kurtyılmaz Y. (2011). Relationships among relational aggression and self-esteem, social connectedness and social anxiety levels of university students (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Anadolu, Eskis¸ehir, Turkey.
Acquah EO, Topalli PZ, Wilson ML, Junttila N, Niemi PM. Adolescent loneliness and social anxiety as predictors of bullying victimisation. Int J Adolescence Youth. 2016;21(3):320–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2015.1083449 .
Brown S, Fite PJ, Stone K, Bortolato M. Accounting for the associations between child maltreatment and internalizing problems: the role of alexithymia. Child Abuse Negl. 2016;52:20–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2015.12.008 .
Bowlby J. Attachment and loss: attachment. New York, NY: Basic Books; 1969.
Jude Cassidy JD, Jones, Shaver PR. (2013). Contributions of Attachment Theory and Research: A Framework for Future Research, Translation, and Policy. Dev Psychopathol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 Nov 1. Published in final edited form as: Dev Psychopathol. 2013; 25(4 0 2): 1415–1434. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579413000692 .
Johnstone L, Boyle M. The power threat meaning Framework: overview. Leicester: British Psychological Society; 2018.
Brodski SK, Hutz CS. The repercussions of emotional abuse and parenting styles on Self-Esteem, Subjective Well-Being: a retrospective study with University students in Brazil. J Aggress Maltreatment Trauma. 2012;21(3):256–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2012.666335 .
Muñiz-Rivas M, Vera M, Povedano A. Parental style, dating violence and gender. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(15):2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152722 .
Sara E, Goldstein. Daniel Chesir-Teran & Adrienne McFaul (2008). Profiles and correlates of relational aggression in young adults’ romantic relationships. March 2007. J Youth Adolesc 37(3):251–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-007-9255-6 .
Follingstad DR, Bradley RG, Helff CM, Laughlin JE. A model for predicting dating violence: anxious attachment, angry temperament and need for relationship control. Violence Vict. 2002;17:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1891/vivi.17.1.35.33639 .
Megan Oka, Cameron C, Brown, Richard B, Miller. Attachment and relational aggression: power as a Mediating Variable. Am J Family Therapy. 2016;44(1):24–35.
Henderson AJZ, Bartholomew K, Trinke SJ, Kwong MJ. When loving means hurting: an exploration of attachment and intimate abuse in a community sample. J Family Violence. 2005;20:219–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-005-5985-y .
Ellis WE, Crooks VC, Wolfe DA. Relational aggression in peer and dating relationships: links to psychological and behavioural adjustment. Soc Dev. 2009;18:253–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2008.00468.x .
Costello J, Pickens LM, Fenton J. Social Support: a matter of connections. Chicago, IL: Chapin Hall Center for Children at the University of Chicago; 2001.
Son H, Cho HJ, Cho S, Ryu J, Kim ST. Moderating effect of Social Support between Loneliness and Depression: differences between the Young-Old and the Old-Old. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042322 .
Lence M, Kneginja TV, Vladimir R M., and, Günter N. 2017. Perceived social support as a moderator between negative life events and depression in adolescence: implications for prediction and targeted prevention. EPMA J. 2017; 8(3): 237–245. Published online 2017 Jun 23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13167-017-0095-5 .
Swickert R. Personality and social support. In: Corr P, Matthews G, editors. Cambridge handbook of personality. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press; 2009. pp. 524–40.
Chapter Google Scholar
Tong E, Bishop G, Diong S, Enkelmann H, Why Y, Ang J, Khader M. Social support and personality among male police officers in Singapore. Pers Indiv Differ. 2004;36:109–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00072-2 .
Branje S, van Lieshout C, van Aken M. Relations between agreeableness and perceived support in family relationships: why nice people are not always supportive. Int J Behav Dev. 2005;29:120–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650250444000441 .
Allemand M, Schaffhuser K, Martin M. Long-term correlated change between personality traits and perceived social support in middle adulthood. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2015;41:420–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167215569492 .
Swickert R, Hittner JB, Foster A. Big five traits interact to predict perceived social support. Pers Indiv Differ. 2010;48:736–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.01.018 .
Russell D. The causal dimension scale: a measure of how individuals perceive causes. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1982;42(6):1137–45. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.42.6.1137 .
Mikulincer M, Shaver PR. Measurement of attachment-related constructs in adulthood. Attachment in adulthood: structure, dynamics, and change. New York: Guilford Press; 2007.
Ladd GW, Burgess KB. Do relational risks and protective factors moderate the linkages between childhood aggression and early psychological and school adjustment. J Child Dev. 2001;72(5):1579–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00366 .
Rubinlicht MA. (2011). Peer support for coping as a moderator of the relation between victimization by relational aggression and adjustment (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Bowling Green State University, Ohio, United States.
Neelam Bibi, Malik JA. 2016. Effect of Social Support on the Relationship between Relational Aggression and Family-Maladjustment: Adolescents’ Perspective Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research, 2016, Vol. 31, No. 1, 63–76.
Prinstein MJ, Boergers J, Vernberg EM. Overt and relational aggression in athletes: Social-psychological adjustmentof aggressors and victims. J Clin Child Psychol. 2001;30:479–91. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP300405 .
Smith PH, Jacquelyn W, White, Lindsay J, Holland. A longitudinal perspective on dating violence among adolescent and College-Age women. Am J Public Health 2003 July. 2003;93(7):1104–9. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.93.7.1104 .
Card NA, Stucky BD, Sawalani GM, Little TD. Direct and indirect aggression during childhood and adolescence: a meta-analytic review of gender differences, intercorrelations, and relations to maladjustment. Child Dev. 2008;79(5):1185–229.
Keenan K, Coyne C, Lahey BB. Should relational aggression be included in DSM-V? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(1):86–93.
Hammack PL, Richards MH, Luo Z, Edlynn ES, Roy K. Social support factors as moderators of community violence exposure among inner-city African American young adolescents. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2004;33:450–62. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp3303_3 .
Tackett JL, Kushner SC, Herzhoff K, Smack AJ, Reardon KW. Viewing relational aggression through multiple lenses: temperament, personality, and personality pathology. Dev Psychopathol. 2014;26(3):863–77.
Voulgaridou I, Kokkinos CM. Relational aggression in adolescents: a review of theoretical and empirical research. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;23:87–97.
Yoon JS, Barton E, Taiariol J. Relational aggression in middle school educational implications of developmental research. J Early Adolesc. 2004;24(3):303–18.
Haslina Muhamad J, Roodenburg, Dennis W, Moore. (2018). The adaptation of the Big Five Inventory in measuring Malaysian youths’ personality traits. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, Volume 5, Issue 7 (July 2018), Pages: 8–14. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2018.07.002 .
Russell DW. UCLA Loneliness Scale (Version 3): reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 1996;66(1):20–40. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa6601_2 .
Nordin NM, Mansor Abu Talib. (2009). Loneliness And Psychological Well-Being Among University Students In Malaysia. Jurnal Psikologi Malay.sia 23 (2009): 27–37. doi: spaj.ukm.my/ppppm/jpm/article/viewFile/70/53 .
Anis Nurshafiqah & Nor Mazlina Ghazali. Reliability analysis of an instrument: a preliminary study of experience in close relationship scale (ECR) among Counsellor trainees in a University March 2020. J Cogn Sci Hum Dev. 2020;6(1):81–7. https://doi.org/10.33736/jcshd.1651.2020 .
Linder JR, Crick NR, Collins WA. Relational aggression and victimization in young adults’ romantic relationships: associations with perceptions of parent, peer, and romantic relationship quality. Soc Dev. 2002;11(1):69–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9507.00187 .
Kamaluddin MR, Tharumalay RD, Sulaiman WSW, Mariamdaran SD, Norruzeyati Che Mohd Nasir. (2020). Penerokaan ciri-ciri psikometrik alat ujian agresif dalam bahasa tamil: terjemahan, kesahan dan kebolehpercayaan (exploring psychometric properties of aggression questionnaire in tamil language: translation, validity and reliability). Jurnal Psikologi Malaysia. Vol.34 No.3 (2020). doi: https://spaj.ukm.my/ppppm/jpm/article/view/603 .
Gregory D, Zimet NW, Dahlem, Sara G, Zimet, Gordon K. Farley. The Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (1988). Journal of Personality Assessment Volume 52, 1988 - Issue 1. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa5201_2 .
Ng CG, Amer Siddiq AN, Aida SA, Zainal NZ, Koh OH. (2010). Validation of the Malay version of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support (MSPSS-M) among a group of medical students in Faculty of Medicine, University Malaya. Asian J Psychiatry 2010;3(1):3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2009.12.001 .
Connelly LM. Pilot studies. Medsurg Nurs. 2008;17(6):411–2.
PubMed Google Scholar
Norman R, Draper HS. 1998. Applied Regression Analysis. 3rd Edition. John Wiley and Sons INC.
Burton L, Henninger D, Hafetz J, Cofer J. Aggression, gender-typical childhood play, and a prenatal hormonal index. Social Behav Personality. 2009;37:105–16. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2009.37.1.105 .
Fraley RC, Waller NG, Brennan KA. An item response theory analysis of self-report measures of adult attachment. J Personal Soc Psychol. 2000;78:350–65. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.78.2.350 .
Jennifer L, Tackett BB, Lahey C, van Hulle I, Waldman RF, Krueger, Paul J, Rathouz. (2013). Common genetic influences on negative emotionality and a general psychopathology factor in childhood and adolescence. J Abnorm Psychology. 2013;122(4):1142-53. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034151 .
Katie A, Gleason, Lauri A, Jensen-Campbell DS. Richardson (2004). Agreeableness as a predictor of aggression in adolescence. Journal of Aggressive Behaviour. Volume30, Issue1, February 2004, Pages 43–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20002 .
Joshua D, Miller A, Zeichner, Lauren F, Wilson. (2012). Personality Correlates of Aggression: Evidence From Measures of the Five-Factor Model, UPPS Model of Impulsivity, and BIS/BAS. Journal of Interpersonal Violence Volume 27, Issue 14, September 2012, Pages 2903–2919. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260512438279 .
Koolen S, Poorthuis A, van Aken MAG. Cognitive distortions and self-regulatory personality traits associated with proactive and reactive aggression in early adolescence. Cogn Therapy Res. 2012;36(6):776–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-011-9407-6 .
Alana Seibert L, Miller JD, Pryor LR, Reidy DE, Amos Zeichner. Personality and laboratory-based aggression: comparing the predictive power of the five-factor model, BIS/BAS, and impulsivity across context. February 2010. J Res Pers. 2010;44(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2009.09.003 .
Dinić BM, Wertag A. Effects of Dark Triad and HEXACO traits on reactive/proactive aggression: exploring the gender differences. Pers Indiv Differ. 2018;123:44–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.11.003 .
Aidt T, Rauh C. The big five personality traits and partisanship in England. Elect Stud. 2018;54:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electstud.2018.04.017 .
Anderson CA, Bushman BJ. Human aggression. Annu Rev Psychol. 2002;53:27–51. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135231 .
Quan F, Yang R, Xia LX. The longitudinal relationships among agreeableness, anger rumination, and aggression. Curr Psychol. 2021;40:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-01030-6 .
Barrick MR, Mount MK. The big five personality dimensions and job performance: a meta-analysis. Pers Psychol. 2010;44:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.1991.tb00688.x .
Povedano A, Estévez E, Martínez B, Monreal MC. A psychosocial profile of adolescent aggressors and victims at school: analysis of gender differences. J Soc Psychol. 2012;27(2012):169–82. https://doi.org/10.1174/021347412800337906 .
Lu Liu N, Wang, Tian L. (2019). The Parent-Adolescent Relationship and Risk-Taking Behaviors Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Self-Control. Front Psychol. 2019; 10: 542. Published online 2019 Mar 20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00542 .
Dervishi E, Ibrahimi S. Agressivity in adolescence and its connection to attachment. Int J Sch Cogn Psychol. 2018;5(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2469-9837.1000203 .
Sampedro R, Calvete E, Gámez-Guadix M, Orue I. Child-to-Parent Aggression in adolescents: Prevalence and reasons; Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Developmental Psychology, International Proceedings Division; Lausanne, Switzerland. 3–7 September 2013; pp. 201–204.
Maalouf E, Salameh P, Haddad C, et al. Attachment styles and their association with aggression, hostility, and anger in Lebanese adolescents: a national study. BMC Psychol. 2022;10:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-022-00813-9 .
Muris P, Meesters C, Morren M, Moorman L. Anger and hostility in adolescents: relationships with self-reported attachment style and perceived parental rearing styles. J Psychosom Res. 2004;57(3):257–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00616-0 .
Feeney JA. Implications of attachment style for patterns of health and illness. Child Care Health Dev. 2000;26(4):277–88. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2214.2000.00146.x .
Marganska A, Gallagher M, Miranda R. Adult attachment, emotion dysregulation, and symptoms of depression and generalized anxiety disorder. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2013;83(1):131–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajop.12001 .
Van Buren A, Cooley EL. Attachment styles, view of self and negative affect. North Am J Psychol. 2002;4(3):417–30.
Simpson JA, Rholes WS. Adult attachment, stress, and romantic relationships. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;13:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.04.006 .
Burnette JL, Davis DE, Green JD, Worthington EL Jr, Bradfield E. Insecure attachment and depressive symptoms: the mediating role of rumination, empathy, and forgiveness. Personality Individ Differ. 2009;46(3):276–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PAID.2008.10.016 .
Wills TA, Fegan MF. (2001). Social networks andsocial support. In A. Baum, T. A. Revenson, & J. E. Singer(Eds.), Handbook of health psychology (pp. 209–234).
Elhawi RL, Itzhaky H. Social support, mastery, self-esteem, and individual adjustment among at risk youth. Child Youth Care Forum. 2005;4:230–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-005-5906-5 .
Isabel Fortin Stéphane, Guay V, Lavoie J-M, Madeleine Beaudry. Boisvert & (2012). Intimate Partner Violence and Psychological Distress among Young Couples: Analysis of the Moderating Effect of Social Support. J Fam Viol (2012) 27:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-011-9402-4 .
Thompson MP, Kaslow NJ, Short LM, Wyckoff S. The mediating roles of perceived social support and resources inthe self-efficacy-suicide attempts relation among African americanabused women. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2002;70(4):942–9. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.70.4.942 .
Theran SA, Sullivan CM, Bogat GA, Stewart CS. Abusive partners and ex-partners: understanding the effects ofrelationship to the abuser on women’s well-being. Violence against Women. 2006;12(10):950–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077801206292871 .
Xin S, Xin Z. Birth cohort changes in Chinese college students’ loneliness and social support: one up, as another down. Int J Behav Dev. 2016;40(5):398–407. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025415597 .
Solomon Z, Bensimon M, Greene T, Horesh D, Ein-Dor T. Loneliness trajectories: the role of posttraumatic symptoms and social support. J Loss Trauma. 2015;20(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2013.815055 .
Brissette I, Scheier MF, Carver CS. The role of optimism in social network development, coping, and psychological adjustment during a life transition. J Personal Soc Psychol. 2002;82(1):102. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.82.1.102 .
Levendosky AA, Huth-Bocks A, Semel MA. Adolescent peer relationships and mental health functioning in families with domestic violence. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2002;31(2):206–18. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3102_06 .
Neelam Bibi, Jamil A, Malik. (2016). Effect of Social Support on the Relationship between Relational Aggression and Family-Maladjustment: Adolescents’ Perspective. Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research, 2016, Vol. 31, No. 1, 63–76.
Swickert Rhonda J, Hittner B, James FA. Big five traits interact to Predict Perceived Social Support. Pers Indiv Differ. 2010;48(6):736–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.01.018 .
Vincent E, Sophie Bull. Social support does not moderate the relationship between personality and risk-taking/antisocial behaviour. September 2020Personality Individual Differences. 2020;163(1):110053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.110053 .
Avshalom Caspi 1, Roberts BW, Rebecca L, Shiner. (2005). Personality development: stability and change. Annu Rev Psychology. 2005;56:453– 84. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141913 .
Goldberg LR. The structure of phenotypic personality traits. Am Psychol. 1993;48(1):26–34. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.48.1.26 .
Foshee VA, Reyes HL, Ennett ST, Suchindran C, Mathias JP, Karriker-Jaffe KJ, Bauman KE, Benefield TS. (2011). Risk and protective factors distinguishing profiles of adolescent peer and dating violence perpetration. Journal of Adolescence Health. 2011;48(4):344– 50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.07.030 .
Falb KL, Diaz-Olavarrieta C, Campos PA, Valades J, Cardenas R, Carino G, Gupta J. Evaluating a health care provider delivered intervention to reduce intimate partner violence and mitigate associated health risks: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial in Mexico City. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-772 .
Debra Pepler D, Jiang W, Craig JC. (2008). Developmental trajectories of bullying and associated factors. Child Development, 2008;79(2):325– 38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01128.x .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate all the researchers whose articles were used in the present research.
The study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, School of Medicine, International Medical University, Bandar Bukit Jalil, 57000, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Shalini Munusamy
Centre for Research in Psychology and Human Well Being, Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, National University of Malaysia, 43600, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
Mohammad Rahim Kamaluddin, Chong Sheau Tsuey & Hilwa Abdullah & Mohd Nor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
This study was developed by SM and MRK. Literature search, data organization and analysis, in addition to the writing of the first draft was carried out by SM, under the supervision of MRK, CST, and HA. Lastly, the collective effort and agreement of all authors were involved in the process of proofreading, editing, as well as the approval of the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Mohammad Rahim Kamaluddin or Shalini Munusamy .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of The National University of Malaysia (No: 2022 − 549). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kamaluddin, M.R., Munusamy, S., Sheau Tsuey, C. et al. Relational aggression in romantic relationship: empirical evidence among young female adults in Malaysia. BMC Psychol 12 , 305 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01670-4
Download citation
Received : 26 May 2023
Accepted : 17 March 2024
Published : 28 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01670-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Relational aggression
- Romantic relationship
- Social support
- Personality trait
- Attachment style
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Why Join Our Team
- How to apply
- Academic Positions
- Staff and Management Positions
- View All Positions
- Join Talent Community
OL/CC/HS233 BR2 - Introduction to Social Science Research Methods (Fall 2024)
Date: May 29, 2024
Location: Brantford, CA
Company: Wilfrid Laurier University
Faculty/Academic Area: Faculty of Human & Social Sciences
Department : FHSS Administration
Campus: Brantford
Employee Group: WLUFA
Requisition ID: 8141
Position Title: Course Instructor: OL/CC/HS233 BR2 – Introduction to Social Science Research Methods (Fall 2024)
Term: Fall 2024 (September 1 – December 31, 2024)
Days/Times: Tuesday/Thursday 1:00pm – 2:20pm
Campus: Brantford
Hours per week/Hours Total: 3 per week/36 total
Anticipated Class Size: 90
Additional Course Requirements: None
Posted on: May 30, 2024
Posting ends: June 14, 2024
Position Summary:
An introduction to social science research methods, designed to enable students to critically evaluate social science research as well as to prepare them for more specialized courses in qualitative and quantitative research. In exploring social science methods, the course will look at qualitative and quantitative approaches and a variety of methodological techniques. Students will learn about the research design process, including selecting the most appropriate techniques, framing research questions, applying ethical principles, and the collection, analysis, and interpretation of empirical data. For quantitative research, students will become familiar with multiple forms of data collection such as surveys, experiments, and secondary data analysis. For qualitative research, students will learn about techniques such as field observations, interviews, and textual analysis. Throughout the course, students will examine the advantages and limitations of different research approaches and techniques.
(Cross-listed as OL233 , CC233 and HS233).
**This course has multiple sections and a common course outline. This course will be coordinated. All instructors will be required to follow a proposed course outline.
Qualifications – Required: Master’s Degree
Qualifications – Discipline: A background in interdisciplinary study and/or research is an asset, as is prior teaching experience. Prior experience teaching online courses is preferred.
Qualifications - Other:
Please note:
- Teaching experience limited to serving as a Teaching Assistant or to delivering guest lectures will not be considered.
- In addition, applicants whose academic Leadership qualifications are limited to the context of elementary and/or secondary schools will not be considered.
Salary: $9,206.40
Application Deadline: June 14, 2024
Submit with Application:
Required for All Applicants
- CV (Maximum of 10 pages, with 12-point font and 2.54 cm margins. Pages which exceed this limit will not be considered in the committee’s evaluation of the application)
- On the CAF, applicants must clearly outline only those qualifications which are relevant for each course for which they have applied and articulate how their work and academic experience enhances their ability to teach each course.
Required for External Applicants
- Verification of highest degree
- Name and contact information for referees.
- Teaching Dossier and/or relevant supplementary documentation (Maximum of 25 pages in total, with 12-point font and 2.54 cm margins. Pages which exceed this limit will not be considered in the committee’s evaluation of the application).
Applications may be addressed to:
Dr. Rosemary A. McGowan
Leadership Program Coordinator
Leadership Program
Faculty of Human and Social Sciences
c/o Angela Jadric
To Apply:
Please click the gold “Apply Now” button located on the top right hand side of the page.
You will be asked to sign in if you have already created an account. If you are not a registered user you may create an account to apply to career opportunities. Once an account is created you will be able to sign in to apply for the position.
This appointment is in accordance with the Contract Teaching Faculty and Part-time Librarians Collective Agreement , for which the Wilfrid Laurier Faculty Association (WLUFA) is the exclusive bargaining agent. Applicants are assessed using both the “Appendix H: Assessment of CTF Candidates under 13.6.1” in the collective agreement and the program specific rubric , where applicable . Candidates should review these documents and ensure the information required is easily accessible in the application.
Please Note:
Candidate Application form (CAF) is used to apply to an individual posting and must be submitted with each application. The completed form is to be uploaded with all other application materials by the deadline listed in the course posting. Refer to Appendix I of the Contract Teaching Faculty Collective Agreement for further guidance about completing the CAF and Appendix H for details on how this form will be scored.
CTF Members (those who have taught a Laurier in the last 36 months) may wish to submit a single application to multiple course postings via the Posted Course Application Form (PCAF) Appendix G, which includes the CAF. The link to the Faculty specific PCAF is included in the email notification of posted courses you would have received from the hiring department/program/area at Laurier. The PCAF is a separate form due within 5 days of the email notification of posted courses and is submitted via Qualtrics. Refer to this notification for the link to the PCAF. Members who do not submit a PCAF may apply for posted course through a separate application for each course. Refer to the collective agreement for additional information on the PCAF.
For Supplementary Remuneration for large classes or multi-section courses, see Article 28.3
Pursuant to Article 13.5 of the Collective Agreement for Contract Teaching Faculty (CTF) and Part-time Librarians, all applicants shall apply electronically. Applications must be received by 23:59 local time of the date on the posting.
Wilfrid Laurier University endeavors to fill positions with qualified candidates who have a combination of education, experience, skills, and abilities to successfully perform the duties of the position while demonstrating Laurier's Employee Success Factors.
Diversity and creating a culture of inclusion is a key pillar of Wilfrid Laurier University's Strategic Academic Plan and is one of Laurier's core values. Laurier is committed to increasing the diversity of faculty and staff and welcomes applications from candidates from equity deserving groups. Indigenous candidates who would like to learn more about equity and inclusive programing at Laurier are welcomed to contact the Office of Indigenous Initiatives at [email protected]. Candidates from other equity deserving groups who would like to learn more about equity and inclusive programing at Laurier are welcomed to contact Equity and Accessibility at [email protected]. We have strived to make our application process accessible, however if you require any assistance applying for a position or would like this job posting in an alternative format, please contact Human Resources at [email protected].
All qualified candidates are encouraged to apply; however, Canadians and permanent residents will be given priority. In accordance with the requirements of Citizenship and Immigration Canada, the successful applicants will be required to prove they are legally able to work in Canada.
Members of the designated groups must self-identify to the appropriate Dean(s) to be considered for employment equity.
All course offerings will be contingent on adequate student registration and subject to budgetary funding.
Members of the Contract Teaching Faculty bargaining unit:
Should you be interested in learning more about this opportunity, please visit www.wlu.ca/careers for additional information and the online application system. All applications must be submitted online.
All applications shall be reviewed and considered under a set of criteria established by the part-time hiring committee. Only those applicants recommended for a position will be contacted.
Job Segment: Data Analyst, Developer, Web Design, Data, Research, Technology, Part Time, Creative
- Careers Home
- Frequently Searched Jobs
- View All Jobs
© Copyright 2020 All Rights Reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
"Research Methods in Psychology" covers most research method topics comprehensively. The author does an excellent job explaining main concepts. ... It is a very well-written and accessible introduction to research methods that meets students where they are, addressing their common questions, misconceptions, and concerns. Although it's not ...
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
Chapter 12. Mixed Methods Research in Psychology ..... 235 Timothy C. Guetterman and Analay Perez Chapter 13. The Cases W ithin Trials (CWT) Method: An Example of a Mixed Methods Research Design ..... 257 Daniel B. Fishman Chapter 14. Resear ching With American Indian and Alaska Native Communities:
Introduction: Objectives of Psychological Research and Their Relations to Research Methods. Part I. Philosophical, Ethical, and Societal Underpinnings of Psychological Research ... Mixed Methods Research in Psychology Timothy C. Guetterman and Analay Perez; Chapter 13. The "Cases Within Trials" (CWT) Method: An Example of a Mixed-Methods ...
Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types. 1. Causal or Experimental Research. When most people think of scientific experimentation, research on cause and effect is most often brought to mind. Experiments on causal relationships investigate the effect of one or more variables on one or more outcome variables.
Research in psychology focuses on a variety of topics, ranging from the development of infants to the behavior of social groups. Psychologists use the scientific method to investigate questions both systematically and empirically. Research in psychology is important because it provides us with valuable information that helps to improve human lives.
Comprehensive, clear, and practical, Introduction to Research Methods in Psychology is the essential student guide to understanding and undertaking quantitative and qualitative research in psychology. Revised throughout, this new edition includes a new chapter on 'Managing your research project'. This is the ideal guide for students just beginning and those moving on to more advanced ...
Introduction to Research Methods in Psychology Third Edition provides all the skills required to approach research methods in a logical way, showing students how to design and report experiments, collect and analyse data. The book also provides excellent coverage of questionnaire design, observation techniques, experimental designs, sampling, variables, ethics and qualitative research.
Comprehensive, straightforward and clear, Introduction to Research Methods in Psychology, 3rd edition is the essential student guide to understanding and undertaking quantitative and qualitative research in psychology. Updated throughout to include new topics such as the latest developments in online support for conducting research and data management, this new edition continues to provide a ...
978-1-107-46111-6 — Psychology Research Methods Wendy Heath Frontmatter ... and punctuated with humor, this undergradu-ate textbook provides an interesting introduction to research methodology. Psychology Research Methods allows students to become familiar with the material through examples of research relevant to their lives. The textbook
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging ...
5 Collecting data 2: questionnaires and psychometric tests. Introduction. 5.1 Questionnaires. 5.2 The first rule of questionnaire design: don't reinvent the wheel. 5.3 General principles, types and structure of questionnaires. 5.4 Writing questions and measuring attitudes. 5.5 Psychometrics.
There are four main types of research designs that are used within the psychology field: descriptive or qualitative, correlational, casual comparative/ quasi-experimental, and experimental. The method of data collection also varies, with self-report on one end of the spectrum, and naturalistic observation on the other.
This is may be true in many scientific programs, but seems particularly true in programs such as psychology. Within undergraduate psychology programs, there tend to only two required courses that actually teach students how to do more than know: statistics and research methods. These courses are often students' least favorite courses in the ...
Scienti˜ c research involves using an appropriate research method to collect data (information) relating to a question, topic or issue of interest, then summarising the data and drawing justi˜ able conclusions about it. Importantly, the research is based on scienti˜ c assumptions, attitudes and procedures, and is planned,
including plenty of examples from clinical and counseling psychology, which tend to be underrepresented in research methods textbooks. • Traditional Structure—By and large I have maintained the overall structure of the typical introductory research methods textbook, which should make it relatively easy for experienced instructors to use.
Research Methods. This unit includes the following chapters. "Thinking like a Scientist" explores important considerations for evaluating the trustworthiness of conclusions and theories. "Research Designs" explains how psychologists test research questions using a variety of methods. "Conducting Psychology Research in the Real World ...
Learn how to plan, conduct and analyze psychological research and effectively communicate the results.
The primary purpose of PSY 321: Research Methods in Psychology is to help you develop a foundation in research methods for psychology. During this course we will learn about how research scientists in the field of psychology identify questions, design studies, collect data, and present findings in a way that is clear and impactful. Upon ...
"Introduction to Research Methods and Statistics in Psychology is a new type of textbook. It is almost entirely student-centred, eminently practical and brings together a wealth of experience in the teaching of undergraduate research." "This book is not just a guide to the conduct of psychological research, it is also an effective support system for the particular problems, concerns and fears ...
PSYC2300 | Cognitive Psychology T01 | Introduction + Writing a Lab Report Learning Objectives RESEARCH METHODS Why is it important? Need to know the ins and outs of research Prepares you for honours Everything we get taught is based on research What is an IV? An independent variable is the variable that is controlled or manipulated in an experiment. They are a variable of interest that we can ...
Dementia is found to be a leading cause of disability. 1 With the global aging population, the prevalence of dementia is expected to increase to 82 million by 2030. 2,3 And in 2019, Medicare and Medicaid are estimated to spend $195 billion on Alzheimer's disease (AD), a form of dementia. 2,3 Consequently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has prioritized the prevention of cognitive decline ...
This research proposes a new promotional selection method, showing in seven laboratory studies, one field experiment, and five supplemental studies that consumers prefer promoted hedonic products when a company selects which products to promote using chance rather than more traditional intentional methods.
Introduction to Research Methods in Psychology, 3rd edition, is the ideal text for those A level students who need more than just a single chapter (as found in most A level texts) but less detail than a higher-level advanced research methods text. It provides all the skills required to approach research methods in a logical way, showing students how to design and report experiments, collect ...
Background Aggressive behaviour in romantic relationship is a social problem of great concern. Studies related to the influence of psychosocial factors on relational aggression are still limited. Furthermore, these factors have not been widely studied in the local context, resulting in the issue of relational aggression among young female adults still not being addressed. This study aims to ...
An introduction to social science research methods, designed to enable students to critically evaluate social science research as well as to prepare them for more specialized courses in qualitative and quantitative research. In exploring social science methods, the course will look at qualitative and quantitative approaches and a variety of ...
Based on: Salter Mark B., Mutlu Can E., and Frowd Philippe M., eds. Research Methods in Critical Security Studies: An Introduction, Second Edition. Abingdon and New York: Routledge, 2023. 332 pp. $160 USD (hardcover) ISBN: 978--367-62119-3
The research method used in this study was a therapeutic dialogue . Concerning the DSN-3 tool design, it must be stressed that it was created on the basis of the use of the method of "Competent Judges" (10 psychologists, including 4 doctors of psychology).