11 Inspiring UX Case Studies That Every Designer Should Study

A UX case study is a sort of detailed overview of a designer's work. They are often part of a UX designer's portfolio and showcase the designer's skill in managing tasks and problems. From a recruiter's perspective, such a UX portfolio shows the skill, insights, knowledge, and talent of the designer.
Therefore, UX case studies play an important role in the recruitment and demand for designers.

What Makes a Powerful Case Study
Building a UX case study includes showing the design process through compelling stories. They will use plain language to demonstrate how they handled key design issues, offering a comprehensive view of their process. Well done case studies often include:
- A problem statement and solutions with real applications.
- Relevant numbers, data, or testimonials to demonstrate the work and efforts.
- A story that directly connects the problem to the solution.
Any competent UX professional will know that creating a stunning UX case study is about the little details.
11 Best UX Case Studies for Designers
The best way to understand what a good case study looks like is to go over other examples. Each of these UX case study examples shows a designer's insights, basic skills, and other designers' lessons learned through their experience.
1. Promo.com web editor

For this video-creation platform , UX designer Sascha was brought on to revamp v2.0, adding new features that could work alongside the existing UX design. The point was to work on interface details that would help create a user friendly platform, and that users could find simple enough to use.
User personas mapped by the UX designer revealed the most common confusion to be the process of inserting particular features into the video, such as subtitles. The designer's goal, therefore, was to create a platform with improved editor controls.
The designer then used a common text-editor layout to include top and side navigation bars that made it easy to access and implement text editing.
Key Learnings from Promo.com
This case study focuses on addressing a particular problem that customers were currently facing. Its main theme is to show a problem, and how the product designer addressed this problem. Its strength points include:
- clearly highlighting the problem (i.e. inaccessible and limited video-text editor options)
- conduction research to understand the nature of the problem and the kind of solutions customers want
- implementing research insights into the redesign to create a platform that actively served customer needs
2. Productivity tracker app
The main concept behind this UX case study is to address a pre-existing problem through the design of the app. Immediately from the start, the study highlights a common pain point among users: that of a lack of productivity due to device usage.
This UX case study example addressed some of the main problems within existing productivity apps included:a poor UI and UX that made navigation difficult
- a poorly-built information architecture
- limited functions on the mobile application
Key Learnings from the Productivity app case study
The case study highlights the simple design process that was then used to build the app. Wireframes were created, a moldboard developed, and finally, individual pages of the app were designed in line with the initial goals.
3. Postmates Unlimited

This case study clearly identifies the improvements made to the Postmates app in a simple overview before jumping into greater detail. The redesign goal, which it achieved, was to improve the experience and other interface details of the app.
The problems identified included:
- usability that led to high support ticket volume.
- technical app infrastructure issues that prevented scalability.
- lack of efficient product management, such as batching orders.
A UX research course can help understand the kind of research needed for a case study. The app redesign involved bringing couriers in and running usability testing on improvements. The final model, therefore, had input from real users on what worked and what caused issues.
Key Learnings from Postmates
The Postmates redesign works as a great UX case study for the simple way it approaches problem-solving. Following an overview of the work, it addresses the problems faced by users of the app. It then establishes research processes and highlights how changes were made to reduce these issues.
4. TV Guide

Addressing the fragmentation of content across channels, this case study sought to redesign how people consume media. The key problems identified included:
- the overabundance of content across various TV and streaming platforms
- the difficulty in discovering and managing content across all platforms
To deliver on the key goals of content personalization, smart recommendations, and offering cross-platform content search, the design process included conducting interviews, surveys, and checking customer reviews.
The design of TV Guide enables users to get custom recommendations sourced from friends' and family's watchlists.
Key Learnings from TV Guide
Like previous UX design case studies, this one tackled the issue head-on. Describing the research process, it goes into detail regarding the approach used by the UX designers to create the app. It takes readers on a journey, from identifying pain points, to testing solutions, and implementing the final version.
5. The FlexBox Inspector

Designer Victoria discusses how she developed the investigator tool for the Mozilla Firefox browser. Surveys into understanding the problems with the existing CSS Flexbox tool revealed a need for a user-friendly design. Interviews with a senior designer and other designers helped developers understand the features design-focused tools ought to have. A feature analysis revealed what most users look for in such tools.
The final result of the development process was a design that incorporated several new features, including:
- a new layout
- color-coded design
- multiple entry points to make workflow management efficient
Key Learnings from the Flexbox
This UX design case study starts with a clear goal, then addresses multiple user needs. It clearly defines the design process behind each feature developed by the time, and the reasoning for including that feature. To give a complete picture, it also discusses why certain features or processes were excluded.
6. The Current State of Checkouts

This Baymard UX design case study looks into the checkout process in over 70 e-commerce websites. Through competitive analysis, it isolates problem points in the UX design, which, if addressed, could improve the customer's checkout process.
The study found at least 31 common issues that were easily preventable. The study was designed and conducted on a large scale, over 12 years, to incorporate changing design patterns into the review.
Recommendations based on findings include:
- prominent guest checkout option
- simple password requirements
- specific delivery period
- price comparison tool for shipping vs store pickup
Key Learnings from Checkout Case Study
Each identified issue is backed up by data and research to highlight its importance. Further research backs up each recommendation made within the case study, with usability testing to support the idea. As far as UX case studies go, this one provides practical insight into an existing, widely used e-commerce feature, and offers practical solutions.
7. New York Times App

Using a creative illustration website, the designers proposed a landing page feature "Timely" that could counter the problems faced by the NYT app . Its major issues included too much irrelevant content, low usage, and undesirable coverage of content.
The goal behind Timely was to improve user incentives, build long-term loyalty, and encourage reading. Design mapping for the app covered:
- identifying the problem
- understanding audience needs
- creating wireframes
- designing and prototyping
The end result was an app that could help readers get notifications regarding news of interest at convenient moments (at breakfast, before bed). This encouraged interaction and improved readability with short-form articles.
Key Learnings from NYT App
The UX case study proposes a problem solution that works with an existing information architecture, instead adding custom graphics to the mobile app. It leads from a simple problem statement to discuss the project that could address these issues without changing was customers already loved.

UX case studies focused on redesign include the FitBit redesign, which started off by understanding personas and what users expect from a fitness tracker. Developing use cases and personas, Guerilla usability testing was employed to assess pain points.
These pain points were then ranked based on their importance to users and to app performance. They were addressed through:
- Highlighting essential parts and features of the app
- Changing easily missed icons to more recognizable icons
- relabelling tracking options to guide users better to its usage
Key Learnings from Fitbit
While the case study maps user experiences and offers solutions, it does not begin with an intensive research-based approach. The prototype is successful in testing, but problem factors are not identified with research-based statistics, meaning key factors could have been ignored.
9. Rating System UX

The designer behind the rating system UX redesign sought to solve issues with the 5-star rating system. Highlighted issues included:
- the lack of subjective accuracy of a 5-point rating system
- the issue of calculating the average of a zero-star rating
- average ratings are misleading
Better alternatives include:
- 5-star emoticon rating that relates the user experience
- Like/dislike buttons that make approval/disapproval simple
The final design incorporated both these styles to make full use of the rating system.
Key Learnings from Rating System UX
The UX case study stemmed from insight into the limitations of the existing rating system. The new design addressed old issues and incorporated better efficiencies.

The Intuit redesign was focused on making content readable, more engaging, and accessible. Looking into product personalization, the content was found to be lacking aesthetic value, as well as being hard to find. The goal was to create content that was easy to find, clear, and consistent.
The implemented solutions included:
- increased readability with increased body text and header spacing
- table of contents on the sidebar for easier navigation
- visible and prominent search bar
- illustrations and designs for pretty visuals
Key Learnings from Intuit
The Intuit case study approaches the problem from a practical point of view. It begins with isolating problems with the interface, in particular with the content. This is an example of a case study that breaks down problems into broader categories, and solves each problem with a practical solution.

This UX case study about a social platform tackles a commonly-faced problem from existing platforms. It addresses the issue of recognizing non-monetary user engagement, to help creators identify their user base.
The case study addresses the problem statement and establishes the design process (building wireframes and prototypes) as well as conducting user testing. The final result is to develop "Discover" pages, engaging layouts, and animated interactions to increase usability.
Key Learnings from Jambb
The study goes into detail regarding problem identification, then moves on to propose solutions that take into account the perspective of all stakeholders involved. It then explains why each design decision was made, and proves its efficacy through testing and prototyping.
Key Takeaways
Developing good UX case studies examples is as much about the details you include as the ones you leave out. Going over UX courses can give you a better understanding of what your case study should look like. A good case study should provide an overview of the problem, include numbers and statistics, and offer practical solutions that directly address the problem. The above-discussed UX case studies provide a good example of the dos and don'ts of a well-structured UX design case study that should be part of every UX portfolio .
Additional Resources
Check out these resources to learn more about UX case studies:
8 UX Case Studies to Read
UX Design Case Study
Frequently Asked Questions
Upskill your design team effectively.
Equip your design team with the best-in-class design training that sticks.
Do you know your design team skill level? Send them this quick test & see where their skills stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Level up your design career
Get step-by-step guide how to build or advance your UX design career.
Do you know your design skills level? Take a quick test & see where you stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Continue reading
The impact of ux design on application success: exploring costs and trends, 7 top ux careers & specialisations: skills, paths & opportunities, 15 figma plugins to boost your design workflow, cookie settings 🍪.
- Interactive UX learning for all levels
- 20+ UX courses and career paths
- Personalized learning & practice
Design-first companies are training their design teams. Are you?
- Measure & identify team skill gaps
- Tailor learning for your team’s needs
- Unlock extensive learning library
- Visualize team growth over time
- Retain your designers
Get a free custom homepage design for your new website.
Design, UI, UX , Inspiration
15 excellent ux case studies every creative should read.
- By Sandra Boicheva
- October 21st, 2021
In a previous article, we talked about UX portfolios and how they carefully craft a story of how designers work. Interestingly enough, recruiters decide if a UX freelance designer or an agency is a good match within 5 minutes into the portfolio . In order to persuade these recruiters, the portfolio needs to present an appealing story that showcases the skill, the thought process, and the choices taken for key parts of the designs. With this in mind, today we’ll talk about UX case studies and give 15 excellent examples of case studies with compelling stories.
The Storytelling Approach in UX Case Studies
An essential part of the portfolio of a UX designer is the case studies that pack a showcase of the designer’s skills, way of thinking, insights in the form of compelling stories. These case studies are often the selling point as recruiters look for freelancers and agencies who can communicate their ideas through design and explain themselves in a clear and appealing way. So how does this work?
Photography by Alvaro Reyes
Just like with every other story, UX case studies also start with an introduction, have a middle, and end with a conclusion .
- Introduction: This UX case study example starts with a design brief and presents the main challenges and requirements. In short, the UX designer presents the problem, their solution, and their role.
- Middle: The actual story of the case study example explains the design process and the techniques used. This usually starts with obstacles, design thinking, research, and unexpected challenges. All these elements lead to the best part of the story: the action part. It is where the story unveils the designer’s insights, ideas, choices, testing, and decisions.
- Conclusion: The final reveal shows the results and gives space for reflection where the designer explains what they’ve learned, and what they’ve achieved.
Now as we gave you the introduction, let’s get to the main storyline and enjoy 15 UX case studies that tell a compelling story.
1. Car Dealer Website for Mercedes-Benz Ukraine by Fulcrum
This case study is a pure pleasure to read. It’s well-structured, easy to read, and still features all the relevant information one needs to understand the project. As the previous client’s website was based on the official Mercedes Benz template, Fulcrum had to develop an appealing and functional website that would require less time to maintain, be more user-friendly, and increase user trust.
- Intro: Starts with a summary of the task.
- Problem: Lists the reasons why the website needs a redesign.
- Project Goals: Lists the 4 main goals with quick summaries.
- Project: Showcases different elements of the website with desktop and mobile comparison.
- Functionality: Explains how the website functionality helps clients to find, and order spare parts within minutes.
- Admin Panel: Lists how the new admin panel helps the client customize without external help.
- Elements: Grid, fonts, colors.
- Tech Stack: Shows the tools used for the backend, mobile, admin panel, and cloud.
- Client review: The case study ends with a 5-star review by the marketing director of Mercedes Benz Ukraine, Olga Belova.
This case study is an example of a detailed but easy to scan and read story from top to bottom, featuring all relevant information and ending on the highest note: the client’s review.
Advertisement
2. Galaxy Z Flips 5G Website by DFY
This is a big project that covers every aspect of the website, including the UX strategy. The creative studio aimed to fully illustrate and demonstrate the significant upgrades over previous models and to enable two-way communication with the customers through an interactive experience.
- Intro: Summary of the project and roles.
- Interactive Experience: The main project goal.
- Demonstration: Explains the decision to feature 360-degree views and hands-on videos instead of technical terms.
- Screens: Includes high-quality screenshots of significant pages and features.
- Ecosystem: Highlight a page with easy navigation across different products as a marketing decision that makes cross-selling seamless.
- Essentials: Showcases a slider of all products with key features that provide ample information.
- Showroom: Interactive experience that helps the user “play around” with the product.
- Credits: As a conclusion, DFY features the stakeholders involved.
A strong presentation of a very ambitious project. It keeps the case study visual while still providing enough insight into the thought process and the most important decisions.
3. Jambb Social Platform by Finna Wang
Here we have a beautiful case study for a platform that aims to help creators grow their communities by recognizing and rewarding their base of supporters. It tackles a curious problem that 99% of fans who contribute in non-monetary ways don’t get the same content, access, and recognition they deserve. This means the creators need a way to identify their fans across all social platforms to grow their business and give recognition. To get a clear picture of what the design has to accomplish, Finna Wang conducted stakeholder interviews with the majority of the client’s team.
- Intro: Listing roles, dates, team, and used tools.
- Project Overview: The main concept and the reasons behind it.
- Exploration: What problem will the platform solve, preliminary research, and conclusions from the research. The section includes the project scope and problem statement.
- Design Process: A thorough explanation of the discoveries and the exact steps.
- User Flows: 3 user flows based on common tasks that the target user/fan would do on the site.
- Design Studio: Visualization process with wireframes, sitemap, prototypes.
- Design Iterations: The designer highlights the iterations they were primary behind.
- Style Guide: Typography, colors, visual elements breakdown.
- Usability Testing: Beta site vs Figma prototype; usertesting.com, revised problem statement.
- Prototype: Features an accessible high fidelity prototype in Figma you can view.
- Takeaways: Conclusions.
An extremely detailed professionally made and well-structured UX case study. It goes a step further by listing specific conclusions from the conducted research and featuring an accessible Figma prototype.
4. Memento Media by Masha Keyhani
This case study is dedicated to a very interesting project for saving family stories. It aims to help users capture and record memories from their past. To do so, the design team performed user research and competitive analysis. The entire project took a 6-week sprint.
- Overview: Introducing the client and the purpose of the app.
- My Role: Explaining the roles of the designer and their team.
- Design Process: A brief introduction of the design process and the design toolkit
- Home: The purpose of the Homepage and the thought process behind it.
- Question Selection: The decision behind this screen.
- Recording Process: Building the recording feature and the decisions behind it.
- User research: a thorough guide with the main focuses, strategies, and competitor analysts, including interviews.
- Research Objectives: The designer gives the intent of their research, the demographics, synthesis, and usability testing insights.
- Propositions: Challenges and solutions
- User Flow: Altering the user flow based on testing and feedback.
- Wireframes: Sketches, Lo-Fi wireframing.
- Design System: Typography, colors, iconography, design elements.
- The Prototype: It shows a preview of the final screens.
This UX study case is very valuable for the insights it presents. The design features a detailed explanation of the thinking process, the research phase, analysts, and testing which could help other creatives take some good advice from it for their future research.
5. Perfect Recipes App by Tubik
Here we have a UX case study for designing a simple mobile app for cooking, recipes, and food shopping. It aims to step away from traditional recipe apps by creating something more universal for users who love cooking with extended functionality. The best idea behind it is finding recipes based on what supplies the user currently has at home.
- Intro: Introducing the concept and the team behind it.
- Project: What they wanted to make and what features would make the app different than the competitors.
- UI design: The decisions behind the design.
- Personalization: Explaining how the app gives the user room for personalization and customizing the features according to their personal preferences.
- Recipe Cards and Engaging Photos: The decisions behind the visuals.
- Cook Now feature: Explaining the feature.
- Shopping List: Explaining the feature.
- Pantry feature: The idea to sync up the app with AmazonGo services. This case study section features a video.
- Bottom Line: What the team learned.
This UX case study is a good example of how to present your concept if you have your own idea for an app. You could also check the interactive preview of the app here .
6. SAM App by Mike Wilson
The client is the Seattle Art Museum while the challenge is to provide engaging multimedia content for users as well as self-guided tours. Mile Wilson has to create an experience that will encourage repeat visits and increase events and exhibition attendance.
- Intro: Listing time for the project, team members, and roles.
- The Client: A brief introduction of Seattle Art Museum
- The Challenge: What the app needs to accomplish.
- Research and Planning: Explaining the process for gathering insights, distributing surveys, interviews, and identifying specific ways to streamline the museum experience.
- Sloane: Creating the primary persona. This includes age, bio, goals, skills, and frustrations.
- Designing the Solution: Here the case study features the results of their research, information architecture, user flows, early sketching, paper prototypes, and wireframes.
- Conclusion: Explaining the outcome, what the team would have done differently, what’s next, and the key takeaways.
What we can take as a valuable insight aside from the detailed research analysis, is the structure of the conclusion. Usually, most case studies give the outcome and preview screens. However, here we have a showcase of what the designer has learned from the project, what they would do differently, and how they can improve from the experience.
7. Elmenus Case Study
This is a case study by UX designers Marwa Kamaleldin, Mario Maged, Nehal Nehad, and Abanoub Yacoub for redesigning a platform with over 6K restaurants. It aims to help users on the territory of Egypt to find delivery and dine-out restaurants.
- Overview: What is the platform, why the platform is getting redesigned, what is the target audience. This section also includes the 6 steps of the team’s design process.
- User Journey Map: A scheme of user scenarios and expectations with all phases and actions.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Principles, issues, recommendations, and severity of the issues of the old design.
- First Usability Testing: Goals, audience, and tasks with new user scenarios and actions based on the heuristic evaluation. It features a smaller section that lists the most severe issues from usability for the old design.
- Business Strategy: A comprehensive scheme that links problems, objectives, customer segment, measurements of success, and KPIs.
- Solutions: Ideas to solve all 4 issues.
- Wireframes: 4 directions of wireframes.
- Styleguide: Colors, fonts, typeface, components, iconography, spacing method.
- Design: Screens of the different screens and interactions.
- Second Usability Testing: Updated personas, scenarios, and goals. The section also features before-and-after screenshots.
- Outcome: Did the team solve the problem or not.
A highly visual and perfectly structured plan and process for redesigning a website. The case study shows how the team discovers the issues with the old design and what decisions they made to fix these issues.
8. LinkedIn Recruiter Tool by Evelynma
A fresh weekend project exploring the recruiting space of LinkedIn to find a way to help make it easier for recruiters to connect with ideal candidates.
- Background Info: What made the designer do the project.
- Problem and Solution: A good analysis of the problem followed by the designer’s solution.
- Process: This section includes an analysis of interviewing 7 passive candidates, 1 active candidate, 3 recruiters, and 1 hiring manager. The designer also includes their journey map of the recruiting experience, a sketch of creating personas, and the final 3 personas.
- Storyboard and User Flow Diagrams: The winning scenario for Laura’s persona and user flow diagram.
- Sketches and Paper Prototypes: Sticky notes for paper prototypes for the mobile experience.
- Visual Design: Web and mobile final design following the original LinkedIn pattern.
- Outcome: Explaining the opportunity.
This is an excellent UX case study when it comes to personal UX design projects. creating a solution to a client’s problem aside, personal project concepts is definitely something future recruiters would love to see as it showcases the creativity of the designers even further.
9. Turbofan Engine Diagnostics by Havana Nguyen
The UX designer and their team had to redesign some legacy diagnostics software to modernize the software, facilitate data transfers from new hardware, and improve usability. They built the desktop and mobile app for iOS and Android.
- Problem: The case study explain the main problem and what the team had to do to solve it.
- My Role: As a lead UX designer on a complicated 18-month project, Havana Nguyen had a lot of work to do, summarized in a list of 5 main tasks.
- Unique Challenges: This section includes 4 main challenges that made the project so complex. ( Btw, there’s a photo of sketched wireframes literally written on the wall.)
- My Process: The section includes a description of the UX design process highlighted into 5 comprehensive points.
- Final Thoughts: What the designer has learned for 18 months.
The most impressive thing about this case study is that it manages to summarize and explain well an extremely complex project. There are no prototypes and app screens since it’s an exclusive app for the clients to use.
10. Databox by FireArt
A very interesting project for Firearts’s team to solve the real AL & ML challenges across a variety of different industries. The Databox project is about building scalable data pipeline infrastructure & deploy machine learning and artificial intelligence models.
- Overview: The introduction of the case study narrows down the project goal, the great challenge ahead, and the solution.
- How We Start: The necessary phases of the design process to get an understanding of a product.
- User Flow: The entire scheme from the entry point through a set of steps towards the final action of the product.
- Wireframes: A small selection of wireframe previews after testing different scenarios.
- Styleguide: Typography, colors, components.
- Visual Design: Screenshots in light and dark mode.
A short visual case study that summarizes the huge amount of work into a few sections.
11. Travel and Training by Nikitin Team
Here’s another short and sweet case study for an app with a complete and up-to-date directory of fitness organizations in detailed maps of world cities.
- Overview: Explaining the project.
- Map Screen : Outlining the search feature by categories.
- Profiles: Profile customization section.
- Fitness Clubs: Explaining the feature.
- Icons: A preview of the icons for the app.
- App in Action: A video of the user experience.
This case study has fewer sections, however, it’s very easy to read and comprehend.
12. Carna by Ozmo
Ozmo provides a highly visual case study for a mobile application and passing various complexities of courses. The main goal for the UX designer is to develop a design and recognizable visual corporate identity with elaborate illustrations.
- Intro: A visual project preview with a brief description of the goal and role.
- Identity: Colors, fonts, and logo.
- Wireframes: The thinking process.
- Interactions: Showcase of the main interactions with animated visuals.
- Conclusion: Preview of the final screens.
The case study is short and highly visual, easy to scan and comprehend. Even without enough insight and text copy, we can clearly understand the thought process behind and what the designer was working to accomplish.
13. An Approach to Digitization in Education by Moritz Oesterlau
This case study is for an online platform for challenge-based learning. The designer’s role was to create an entire product design from research to conception, visualization, and testing. It’s a very in-depth UX case study extremely valuable for creatives in terms of how to structure the works in their portfolio.
- Intro: Introducing the client, project time, sector, and the designer’s role.
- Competitive Analysis: the case study starts off with the process of creating competitive profiles. It explains the opportunities and challenges of e-learning that were taken into consideration.
- Interviews and Surveys: Listing the goals of these surveys as well as the valuable insights they found.
- Building Empathy: The process and defining the three target profiles and how will the project cater to their needs. This section includes a PDF of the user personas.
- Structure of the Course Curriculum: Again with the attached PDF files, you can see the schemes of the task model and customer experience map.
- Information Architecture: The defined and evaluated sitemap for TINIA
- Wireframing, Prototyping, and Usability Testing : An exploration of the work process with paper and clickable prototypes.
- Visual Design: Styleguide preview and detailed PDF.
- A/B and Click Tests: Reviewing the usability assumptions.
- Conclusion: A detailed reflection about the importance of the project, what the designer learned, and what the outcome was.
This is a very important case study and there’s a lot to take from it. First, the project was too ambitious and the goal was too big and vague. Although the result is rather an approximation and, above all, at the conceptual level requires further work, the case study is incredibly insightful, informative, and insightful.
14. In-class Review Game by Elizabeth Lin
This project was never realized but the case study remains and it’s worth checking out. Elizabeth Lin takes on how to create an engaging in-class review game with a lot of research, brainstorming, and a well-structured detailed process.
- Intro: What makes the project special.
- Research: Explaining how they approached the research and what they’ve learned.
- Brainstorming: the process and narrowing all How Might We questions to one final question: How might we create an engaging in-class math review game.
- Game Loop and Storyboarding: Sketch of the core game loop and the general flow of the game.
- Prototyping: Outlining basic game mechanics and rounds in detail.
- Future Explorations: The case study goes further with explorations showing how the product could look if we expanded upon the idea even further.
- What Happened?: The outcome of the project.
This case study tells the story of the project in detail and expands on it with great ideas for future development.
15. Virtual Makeup Studio by Zara Dei
And for our last example, this is a case study that tells the story of an app-free shippable makeover experience integrated with the Covergirl website. The team has to find a way to improve conversion by supporting customers in their purchase decisions as well as to increase basket size by encouraging them to buy complementary products.
- Intro: Introducing the project and the main challenges.
- Discovery and Research: Using existing product information on the website to improve the experience.
- Onboarding and Perceived Performance: Avoiding compatibility issues and the barrier of a user having to download an app. The section explains the ideas for features that will keep users engaged, such as a camera with face scan animation.
- Fallback Experience and Error States: Providing clear error messaging along with troubleshooting instructions.
- Interactions: explaining the main interactions and the decisions behind them.
- Shared Design Language: Explaining the decision to provide links on each product page so users could be directed to their preferred retailer to place their order. Including recommended products to provide users with alternatives.
- Outcome and Learning: The good ending.
- Project Information: Listing all stakeholders, the UX designer’s role in a bullet list, and design tools.
In Conclusion
These were the 15 UX case studies we wanted to share with you as they all tell their story differently. If we can take something valuable about what are the best practices for making an outstanding case study, it will be something like this.
Just like with literature, storytelling isn’t a blueprint: you can write short stories, long in-depth analyses, or create a visual novel to show your story rather than tell. The detailed in-depth UX case studies with lots of insights aren’t superior to the shorter visual ones or vice versa. What’s important is for a case study to give a comprehensive view of the process, challenges, decisions, and design thinking behind the completed project .
In conclusion, a UX case study should always include a summary; the challenges; the personas; roles and responsibilities; the process; as well as the outcomes, and lessons learned.
Video Recap
Take a look at the special video we’ve made to visualize and discuss the most interesting and creative ideas implemented in the case studies.

In the meantime, why not browse through some more related insights on web development and web design?
- The 30 Best UX Books Every Creative Should Read in 2022
- Great UI Animation Examples to Make Your Jaw Drop [+Tips and Freebies]
- 60 Superb App Design Inspiration Examples
Popular Posts
- 20 UI/UX Design Trends that will Rock 2023 [Updated]
- Best 15 UI Color Palette & Scheme Generators for the Perfect Interface Design
- 10 Golden UI Design Principles and How To Use Them
- GET A QUICK QUOTE
Subscribe for our newsletter
We hate boring. Our newsletters are relevant and on point. Excited? Let’s do this!
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design
15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
By Alice Corner , Jan 12, 2023

Have you ever bought something — within the last 10 years or so — without reading its reviews or without a recommendation or prior experience of using it?
If the answer is no — or at least, rarely — you get my point.
Positive reviews matter for selling to regular customers, and for B2B or SaaS businesses, detailed case studies are important too.
Wondering how to craft a compelling case study ? No worries—I’ve got you covered with 15 marketing case study templates , helpful tips, and examples to ensure your case study converts effectively.
Click to jump ahead:
- What is a Case Study?
Business Case Study Examples
Simple case study examples.
- Marketing Case Study Examples
Sales Case Study Examples
- Case Study FAQs
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth, detailed analysis of a specific real-world situation. For example, a case study can be about an individual, group, event, organization, or phenomenon. The purpose of a case study is to understand its complexities and gain insights into a particular instance or situation.
In the context of a business, however, case studies take customer success stories and explore how they use your product to help them achieve their business goals.

As well as being valuable marketing tools , case studies are a good way to evaluate your product as it allows you to objectively examine how others are using it.
It’s also a good way to interview your customers about why they work with you.
Related: What is a Case Study? [+6 Types of Case Studies]
Marketing Case Study Template
A marketing case study showcases how your product or services helped potential clients achieve their business goals. You can also create case studies of internal, successful marketing projects. A marketing case study typically includes:
- Company background and history
- The challenge
- How you helped
- Specific actions taken
- Visuals or Data
- Client testimonials
Here’s an example of a marketing case study template:

Whether you’re a B2B or B2C company, business case studies can be a powerful resource to help with your sales, marketing, and even internal departmental awareness.
Business and business management case studies should encompass strategic insights alongside anecdotal and qualitative findings, like in the business case study examples below.
Conduct a B2B case study by researching the company holistically
When it comes to writing a case study, make sure you approach the company holistically and analyze everything from their social media to their sales.
Think about every avenue your product or service has been of use to your case study company, and ask them about the impact this has had on their wider company goals.

In business case study examples like the one above, we can see that the company has been thought about holistically simply by the use of icons.
By combining social media icons with icons that show in-person communication we know that this is a well-researched and thorough case study.
This case study report example could also be used within an annual or end-of-year report.
Highlight the key takeaway from your marketing case study
To create a compelling case study, identify the key takeaways from your research. Use catchy language to sum up this information in a sentence, and present this sentence at the top of your page.
This is “at a glance” information and it allows people to gain a top-level understanding of the content immediately.

You can use a large, bold, contrasting font to help this information stand out from the page and provide interest.
Learn how to choose fonts effectively with our Venngage guide and once you’ve done that.
Upload your fonts and brand colors to Venngage using the My Brand Kit tool and see them automatically applied to your designs.
The heading is the ideal place to put the most impactful information, as this is the first thing that people will read.
In this example, the stat of “Increase[d] lead quality by 90%” is used as the header. It makes customers want to read more to find out how exactly lead quality was increased by such a massive amount.

If you’re conducting an in-person interview, you could highlight a direct quote or insight provided by your interview subject.
Pick out a catchy sentence or phrase, or the key piece of information your interview subject provided and use that as a way to draw a potential customer in.
Use charts to visualize data in your business case studies
Charts are an excellent way to visualize data and to bring statistics and information to life. Charts make information easier to understand and to illustrate trends or patterns.
Making charts is even easier with Venngage.
In this consulting case study example, we can see that a chart has been used to demonstrate the difference in lead value within the Lead Elves case study.
Adding a chart here helps break up the information and add visual value to the case study.

Using charts in your case study can also be useful if you’re creating a project management case study.
You could use a Gantt chart or a project timeline to show how you have managed the project successfully.

Use direct quotes to build trust in your marketing case study
To add an extra layer of authenticity you can include a direct quote from your customer within your case study.
According to research from Nielsen , 92% of people will trust a recommendation from a peer and 70% trust recommendations even if they’re from somebody they don’t know.

So if you have a customer or client who can’t stop singing your praises, make sure you get a direct quote from them and include it in your case study.
You can either lift part of the conversation or interview, or you can specifically request a quote. Make sure to ask for permission before using the quote.

This design uses a bright contrasting speech bubble to show that it includes a direct quote, and helps the quote stand out from the rest of the text.
This will help draw the customer’s attention directly to the quote, in turn influencing them to use your product or service.
Less is often more, and this is especially true when it comes to creating designs. Whilst you want to create a professional-looking, well-written and design case study – there’s no need to overcomplicate things.
These simple case study examples show that smart clean designs and informative content can be an effective way to showcase your successes.
Use colors and fonts to create a professional-looking case study
Business case studies shouldn’t be boring. In fact, they should be beautifully and professionally designed.
This means the normal rules of design apply. Use fonts, colors, and icons to create an interesting and visually appealing case study.
In this case study example, we can see how multiple fonts have been used to help differentiate between the headers and content, as well as complementary colors and eye-catching icons.

Marketing case study examples
Marketing case studies are incredibly useful for showing your marketing successes. Every successful marketing campaign relies on influencing a consumer’s behavior, and a great case study can be a great way to spotlight your biggest wins.
In the marketing case study examples below, a variety of designs and techniques to create impactful and effective case studies.
Show off impressive results with a bold marketing case study
Case studies are meant to show off your successes, so make sure you feature your positive results prominently. Using bold and bright colors as well as contrasting shapes, large bold fonts, and simple icons is a great way to highlight your wins.
In well-written case study examples like the one below, the big wins are highlighted on the second page with a bright orange color and are highlighted in circles.
Making the important data stand out is especially important when attracting a prospective customer with marketing case studies.

Use a simple but clear layout in your case study
Using a simple layout in your case study can be incredibly effective, like in the example of a case study below.
Keeping a clean white background, and using slim lines to help separate the sections is an easy way to format your case study.
Making the information clear helps draw attention to the important results, and it helps improve the accessibility of the design .
Business case study examples like this would sit nicely within a larger report, with a consistent layout throughout.

Use visuals and icons to create an engaging and branded business case study
Nobody wants to read pages and pages of text — and that’s why Venngage wants to help you communicate your ideas visually.
Using icons, graphics, photos, or patterns helps create a much more engaging design.
With this Blue Cap case study icons, colors, and impactful pattern designs have been used to create an engaging design that catches your eye.

Use a monochromatic color palette to create a professional and clean case study
Let your research shine by using a monochromatic and minimalistic color palette.
By sticking to one color, and leaving lots of blank space you can ensure your design doesn’t distract a potential customer from your case study content.

In this case study on Polygon Media, the design is simple and professional, and the layout allows the prospective customer to follow the flow of information.
The gradient effect on the left-hand column helps break up the white background and adds an interesting visual effect.

Did you know you can generate an accessible color palette with Venngage? Try our free accessible color palette generator today and create a case study that delivers and looks pleasant to the eye:
Add long term goals in your case study
When creating a case study it’s a great idea to look at both the short term and the long term goals of the company to gain the best understanding possible of the insights they provide.
Short-term goals will be what the company or person hopes to achieve in the next few months, and long-term goals are what the company hopes to achieve in the next few years.
Check out this modern pattern design example of a case study below:

In this case study example, the short and long-term goals are clearly distinguished by light blue boxes and placed side by side so that they are easy to compare.

Use a strong introductory paragraph to outline the overall strategy and goals before outlining the specific short-term and long-term goals to help with clarity.
This strategy can also be handy when creating a consulting case study.
Use data to make concrete points about your sales and successes
When conducting any sort of research stats, facts, and figures are like gold dust (aka, really valuable).
Being able to quantify your findings is important to help understand the information fully. Saying sales increased 10% is much more effective than saying sales increased.
While sales dashboards generally tend it make it all about the numbers and charts, in sales case study examples, like this one, the key data and findings can be presented with icons. This contributes to the potential customer’s better understanding of the report.
They can clearly comprehend the information and it shows that the case study has been well researched.

Use emotive, persuasive, or action based language in your marketing case study
Create a compelling case study by using emotive, persuasive and action-based language when customizing your case study template.

In this well-written case study example, we can see that phrases such as “Results that Speak Volumes” and “Drive Sales” have been used.
Using persuasive language like you would in a blog post. It helps inspire potential customers to take action now.

Keep your potential customers in mind when creating a customer case study for marketing
82% of marketers use case studies in their marketing because it’s such an effective tool to help quickly gain customers’ trust and to showcase the potential of your product.
Why are case studies such an important tool in content marketing?
By writing a case study you’re telling potential customers that they can trust you because you’re showing them that other people do.
Not only that, but if you have a SaaS product, business case studies are a great way to show how other people are effectively using your product in their company.
In this case study, Network is demonstrating how their product has been used by Vortex Co. with great success; instantly showing other potential customers that their tool works and is worth using.

Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Case studies are particularly effective as a sales technique.
A sales case study is like an extended customer testimonial, not only sharing opinions of your product – but showcasing the results you helped your customer achieve.
Make impactful statistics pop in your sales case study
Writing a case study doesn’t mean using text as the only medium for sharing results.
You should use icons to highlight areas of your research that are particularly interesting or relevant, like in this example of a case study:

Icons are a great way to help summarize information quickly and can act as visual cues to help draw the customer’s attention to certain areas of the page.
In some of the business case study examples above, icons are used to represent the impressive areas of growth and are presented in a way that grabs your attention.
Use high contrast shapes and colors to draw attention to key information in your sales case study
Help the key information stand out within your case study by using high contrast shapes and colors.
Use a complementary or contrasting color, or use a shape such as a rectangle or a circle for maximum impact.

This design has used dark blue rectangles to help separate the information and make it easier to read.
Coupled with icons and strong statistics, this information stands out on the page and is easily digestible and retainable for a potential customer.

Case Study Examples Summary
Once you have created your case study, it’s best practice to update your examples on a regular basis to include up-to-date statistics, data, and information.
You should update your business case study examples often if you are sharing them on your website .
It’s also important that your case study sits within your brand guidelines – find out how Venngage’s My Brand Kit tool can help you create consistently branded case study templates.
Case studies are important marketing tools – but they shouldn’t be the only tool in your toolbox. Content marketing is also a valuable way to earn consumer trust.
Case Study FAQ
Why should you write a case study.
Case studies are an effective marketing technique to engage potential customers and help build trust.
By producing case studies featuring your current clients or customers, you are showcasing how your tool or product can be used. You’re also showing that other people endorse your product.
In addition to being a good way to gather positive testimonials from existing customers , business case studies are good educational resources and can be shared amongst your company or team, and used as a reference for future projects.
How should you write a case study?
To create a great case study, you should think strategically. The first step, before starting your case study research, is to think about what you aim to learn or what you aim to prove.
You might be aiming to learn how a company makes sales or develops a new product. If this is the case, base your questions around this.
You can learn more about writing a case study from our extensive guide.
Related: How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Some good questions you could ask would be:
- Why do you use our tool or service?
- How often do you use our tool or service?
- What does the process of using our product look like to you?
- If our product didn’t exist, what would you be doing instead?
- What is the number one benefit you’ve found from using our tool?
You might also enjoy:
- 12 Essential Consulting Templates For Marketing, Planning and Branding
- Best Marketing Strategies for Consultants and Freelancers in 2019 [Study + Infographic]
20+ Outstanding UX/UI Design Case Studies

Discover an expertly curated collection of 20+ inspirational UX/UI design case studies that will empower you to create outstanding case studies for your own portfolio.
- Comprehensive end-to-end case studies covering research, ideation, design, testing, and conclusions.
- Perfect for designers building portfolios and looking for inspiration to create their own case studies.
- Learn new methods and techniques, improve your understanding, and apply them to your projects.
- Gain insights from the successes and challenges of accomplished designers.
Want to get access to 30+ more case studies including smart tagging system?
Download full version
All case studies included in this collection are sourced from real designers' portfolios and are used for the purpose of learning and inspiration. The original authors retain all rights to their work.

New Case Study
How to avoid (and repair) these 3 critical design blunders

Case studies

Design Blunders

Social Proof: Why people's behaviors affect our actions
Social Proof

Adobe: The growing issue with “Free” trials UX
Adobe Trial UX

Letterboxd: How to nail product market fit with clear Jobs‑To‑Be‑Done
Jobs-To-Be-Done

Spotify Wrapped: 6 psychology principles that make it go viral every year
Spotify Wrapped

The psychology of Temu’s casino‑like shopping UX
Temu Onboarding

GoDaddy: How to improve checkout flows ethically
GoDaddy Checkout UX

Framing Effect: Why context affects decisions
Framing effect

The psychology behind highly effective landing pages
Landing page conversion

Apple vs Meta Threads: The Illusion of Privacy
Apple privacy policy

Beehiiv subscription: 5 small UX mistakes that make a BIG difference
Newsletter subscription

The Search War: Bing AI Chat vs. Google

The Psychology Behind Loom's Explosive Growth
Loom onboarding

Episode 1: Can Bing's new AI search challenge Google?
Bing onboarding

Typeform: How to offboard users the right way
Typeform offboarding

How to increase signup confirmation rates with Sniper Links
Email confirmation UX

Labor Perception Bias: Why faster isn't always better
Labor perception bias

Tech ethics: If cookie consent prompts were honest…
Cookie consent

Amber Alert Redesign: 5 UX Improvements That Could Save Lives
Amber alerts UX

Google: How to increase feature adoption the right way
Google feature adoption

How Linkedin Increased Notification Opt-in Rates by 500%
Linkedin notifications

The Psychology of Advertising: Why this ad made me stop scrolling
Advertising psychology

The Ugly Truth About Net Promoter Score Surveys
Net promoter surveys

The Psychology Behind Amazon's Purchase Experience
Amazon purchase UX

One Simple Psychology Framework To Improve Your Onboarding
Blinkist onboarding

How Blinkist Increased Trial Conversions by 23% (Ethically)
Trial paywall optimization

YouTube’s Attempt To Solve The Paradox of Choice
Youtube retention

Adobe: The Psychology of User Offboarding
Adobe offboarding

Signal: How To Ethically Boost Your Revenues
Signal monetization

Chrome vs Brave: How To Use Ethical Design To Win Customers
Brave onboarding

The Psychology of Clubhouse’s User Retention (...and churn)
Clubhouse retention

The Scary Future Of Instagram
Instagram monetization

The Psychology of Misinformation on Facebook
Facebook misinformation

The Psychology Behind TikTok's Addictive Feed
Tiktok feed psychology

How To Properly Apply Jobs-To-Be-Done To User Onboarding
Headspace onboarding

How To Notify Users Without Being Spammy
Lifecycle emails

User Onboarding: Is HEY Email Worth It?
Hey onboarding

7 Product Team Pitfalls You Should Avoid
Product team pitfalls

How Tinder Converts 8% Of Singles Into Customers In Less Than 15min.
Tinder monetization

Coronavirus Dashboard UX: How Design Impacts Your Perception
COVID dashboard UX

How Morning Brew Grew To 1.5 Million Subs In 5 Years
Morning Brew retention

Uber Eats: How To Ethically Use Scarcity To Increase Sales
Uber Eats retention

Airbnb: How To Reduce Churn With Personalization
Airbnb personalization

6 Ways Mario Kart Tour Triggers You Into Gambling Your Money
Mario Kart monetization

Strava: 7 Strategies To Convert More Freemium Users
Strava monetization

Tesla: How To Grow Through Word-of-Mouth
Tesla charging UX

How Hopper Perfectly Nails Permission Requests UX
Hopper onboarding

9 Ways To Boost SaaS Revenues With A Better Upgrade UX
Zapier monetization

Superhuman's Secret 1-on-1 Onboarding Revealed
Superhuman onboarding

Trello User Onboarding: 7 Tactics To Inspire You
Trello onboarding

5 Deadly Onboarding Mistakes You Should Avoid
Sleepzy onboarding

Duolingo's User Retention: 8 Tactics Tested On 300 Million Users
Duolingo retention

Calm Referral Strategy: Drive Viral Growth With Simple Rewards
Calm referrals

Spotify vs Apple: How Spotify is betting $230M on podcasts to win over Apple users (Ep. 2)
Spotify onboarding

Spotify vs Apple: How Spotify is betting $230M on podcasts to win over Apple users (Ep. 1)
Spotify vs Apple
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
How to Write Great Case Studies for Your UX Design Portfolio
Well, the answer is really simple: write your UX case studies like stories. You see, when you present your case study as a story, you’ll find it far easier to give it a satisfying structure and captivate your reader. What’s more, you’ll make it easy for recruiters to imagine what it’s like to work with you, as they get to understand how you work. This makes your case study powerful and increases your chances of getting your first interview. Let’s take a closer look at what makes story-based case studies so impactful.
Since your case studies first and foremost serve to help you get an interview in your job application, they should answer the following questions (grouped into three categories, based on you as a person, your skill set and the way you do things):
Who are you? What drives you and what’s your background?
What UX skills do you possess?
How do you approach and solve a problem? How do you work with others?
As it turns out, when you tell a narrative through your case studies, you answer these questions effectively. Here are the 3 main reasons why you should write your UX case studies like stories and how this helps you stand out from other applicants.
Because Stories Allow Recruiters to Imagine What it’s Like to Work with You
“Narrative imagining—story—is the fundamental instrument of thought. Rational capacities depend upon it. It is our chief means of looking into the future, of predicting, of planning, and of explaining.” —Mark Turner, cognitive scientist and author
When a recruiter reads your case study, they want to find out if you’ll be a great addition to their team. They want to know not only if you have the right skills and attitude, but also whether they’d enjoy working with you.
When you tell a story, you make it intuitive for a recruiter to imagine what it’s like to work with you . That’s because we use stories to learn and imagine all the time—in fact, people have since the dawn of human history. Therefore, recruiters will find it easier to look into the future and predict if they’d like to work with you when they read a story-based case study. They’ll find it easier to understand who you are and how you solve a problem.

Since the dawn of human history, we have used stories to imagine and learn about our world. Help recruiters understand you by telling a story about your design process .
© Mike Erskine, Fair Use
This sentiment is echoed by Sarah Bellrichard, Senior Vice President of Wholesale Internet Solutions & UX at the American bank Wells Fargo. She shared her tip on case studies and interviews:
“My tip would be, tell stories. When designers present a flat portfolio it doesn’t tell me about how they approach the work they do and how they deal with the ebbs and flows of design. Tell me how you navigate from start to end of a project.” —Sarah Bellrichard, SVP of Wholesale Internet Solutions & UX, Wells Fargo
Because Stories Give Your Case Studies Structure
“Sometimes reality is too complex. Stories give it form.” —Jean Luc Godard, French-Swiss film director
If you’ve worked on a design project before, then you’re painfully aware of just how messy life can be. Deadlines change, project goals shift, and new findings can fundamentally alter design specifications.
Stories will give your past experiences form and make your case studies better organized . You can re-arrange your experience into a meaningful sequence of events—i.e., progress—towards your results. Otherwise, your case study will likely seem chaotic.
The arc of a story—introduction, middle, conclusion—is the perfect order to tell your messy progress towards a project’s final results. Let’s illustrate:
In the introduction :
You set up the context of your project, for instance through a design brief.
You introduce your team’s main goals and some of the main obstacles you faced
In a classic story, this is where we meet the heroes and learn about the venture/goal they’re reaching for and why they’re not satisfied with their current lives.
In the middle :
You illustrate your approach to solving the problem.
You bring your reader through your journey of how you used industry standard practices to tackle the problem. It’s important that you describe what you did and what your team members did, so the recruiter knows what skills and knowledge you possess.
In a classic story, this is where we follow our heroes struggling to conquer the beasts, villains and problems as they strive to reach their goals.
Finally, in the conclusion :
You showcase the final product and the results you and your team achieved.
You reflect upon what you’ve learnt and recount any follow-up tweaks you’ve made to the product.
In a classic story, this is where the heroes reach their goals―they experience personal growth , reap the rewards of their hard work and live happily ever after.
See how nicely it all fits into a story arc?

When you arrange your case study in a story arc, your journey becomes more ordered and meaningful.
© Teo Yu Siang and the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
There’s more! You’ll also find it easier to write your case study when you arrange it like a story. You see, the introduction-middle-conclusion structure of a story forms a skeleton for you to fill in the “meat” of your journey. On top of that, recruiters who read your case study will also find the familiar arc of a story satisfying. Talk about a win-win situation!
Because Stories Captivate
“Tell me the facts and I’ll learn. Tell me the truth and I’ll believe. But tell me a story and it will live in my heart forever.” —Native American proverb
Okay, your case study will most likely not live in your recruiter’s heart forever, but your story-based case study will definitely stand out from other purely fact-based case studies, as your story will engage and captivate your recruiter. You see, a narrative is more engaging and provides a better reading experience than a dry, factual account ever could. It naturally makes the reader feel involved in the story and weaves a common thread throughout the case study.
UX recruiters are incredibly busy. They’ll typically spend only 5 minutes scanning your case studies because they have so many applicants to process. Given that, you have a much better chance if you can capture your reader’s attention for the whole 5 minutes.
And there’s no better way to captivate someone than through a story.
Let’s demonstrate that in an ultra-brief case study―yours should be more detailed and in-depth. Below, you’ll find the same journey told in two ways: first in a factual manner, then in a narrative fashion. See which version you find more engaging.
Factual : User interviews were conducted with 12 people to evaluate the effectiveness of the prototype . The main finding was that the assumption that users shopped based on their weekly nutritional needs was invalid. This finding was used to create a new iteration of the product, which was tested and found to be 50% more successful than the previous version.
Narrative : We conducted interviews with 12 people to evaluate if our prototype was effective. Our finding threw a giant spanner in the works. We realized our assumption—that users shopped based on their weekly nutritional needs—was dead wrong. Undefeated, we scrambled to create a new iteration, and ran another round of tests. This time, it worked—the success rate shot up by a whopping 50%!
You probably find the narrative version way more interesting—and so will your recruiters.
Notice in the factual version how flat and lifeless the account is? Sure, the figures are there, but it looks as if you’re reporting on what someone else did. This tells a recruiter that you’re distant and non-engaged—that you didn’t take ownership in what you’re talking about.
So, embrace the liberating and captivating format of a story. Go ahead and describe how your finding proved you dead wrong and how you scrambled upon meeting a temporary setback.
Best practice:
Convey your emotions and write in an active, engaging tone of voice .
Include the team’s frustrations, problems you faced and new insights you learnt.
Include people: write “we”, “I” and “our team”.
This way, you’ll give your case studies flavor . Furthermore, you’ll reveal who you are and how you work―and your recruiters will come back for more.

Stories naturally captivate us—use that power to captivate your recruiters, too.
© Prasanna Kumar, Fair Use
Turn Your Case Studies into Stories
Of course, we’re not saying that you should write a novel to explain what happened in your project. Your case studies should still be short and sweet, but they also should be punchy and engaging.
In fact, when we sat down with Stephen Gay, Design Lead at Google’s AdWords, to ask him about the importance of a portfolio, he explained that he sees UX case studies as stories about the applicants.
- Transcript loading…
To a recruiter like Stephen Gay, case studies are stories that tell him about the applicants. Author / copyright holder: The Interaction Design Foundation. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
As Stephen astutely pointed out, we UX designers regularly use the power of stories in our work. So, use this same storytelling approach in your case studies, too!
The Take Away
The best way to write a case study is to tell it like a story. This way, your case studies become a vessel through which recruiters can imagine a future working with you, since they get to experience and understand exactly how you solve a design problem. Your recruiters will also enjoy the familiarity and structure of a story arc, and they’ll find the reading experience much more engaging. So, go ahead—inject humanity, color and passion into your case studies. Be a storyteller.
References and Where to Learn More
You can find Sarah Bellrichard’s tip on case studies in this article by Justinmind, which gathers tips and insights on how to do well in interviews.
Hero image: © Rawpixel, Fair Use.
Design for a Better World with Don Norman

Get Weekly Design Insights
What you should read next, interaction design foundation reviews: answers to frequently asked questions by members.
- 2 weeks ago
10 UI Designer Portfolio Examples

What Tech Job is Right for Me? A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Career Path

How to Succeed as a Designer on Agile Teams: Embrace Imperfection
Your Guide to Hamburger Menus
- 3 weeks ago
How to Design with AI: 5 Insights from the IxDF Course
Tree Testing: A Complete Guide
The Role of Micro-interactions in Modern UX

How to Design UI Forms in 2024: Your Best Guide
What is Eye Tracking in UX?
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
How to Design Case Studies for Your Clients

Why Case Study Design Matters
Case studies are more than just feel-good success stories for your client’s audience to read.
They’re powerful tools for showcasing your client’s products and services in the very best possible light.
That’s why every aspect of your client’s case study has to count. Not just the information and the statistics and the positive experience of the case study’s subject, but everything that goes into creating the experience of an individual who is reading this case study and thinking hard about whether they should invest in your client’s products or services.
We’re talking about the copywriting, the illustrations and icons, the infographics, everything!
And that’s where you, as a designer, come into play!
Because if your client’s reader isn’t engaged and captivated by the information they’re seeing, they’re not likely to stick around. The layout and design have got to hit their mark every time for your client’s case studies to have the impact they want them to have.
So, what makes for a great case study or report design?
If you’re scratching your head, then this blog is here to help shine some light. Consider today’s blog your handy guide for creating captivating and strategic case study design that showcases your client’s offerings in the best possible way!
How Does a Case Study Tell a Story?

A case study can be an extremely effective marketing tool, even more so than ads, websites, or product demos.
Why? Because a case study isn’t an ad, a case study involves a real-world situation or problem that a real-world business faced and the journey they went through to resolve it, which naturally makes for a great story.
A good case study first introduces the subject, whether it's a business or an individual, and sets the stage for the story by outlining their challenges. It then describes the solution that alleviated this problem (your client’s products and services), the steps it took to implement that solution, and the obstacles it overcame to get there.
The results should show, through the use of data collection, statistics, etc., how your client’s brand was able to help the subject of the case study in whatever way they needed that help. Depending on the type of case study, the results could be increased brand awareness, increased conversions on an ecommerce site , or a boost in revenue due to optimized marketing strategies.
If presented right, this can be huge for a business! It gives real-life context to the pain points their potential customers have and the data analysis to prove that their products or services can get the job done!
And, as a designer, your role in all this is to make sure that the reader of this case study is getting the full effect of this real-life success story. Sure, the copywriter will handle writing a case study, but your job to take those words and enhance them through images, illustrations, layout, and more to present the narrative in the best way possible and guide the reader from beginning to end.
Designing Case Studies: What You Need to Know
Now that you know why case studies are so important, here is what you need to know to design a top-notch case study for your next client!
1. Understand Your Client’s Needs
It’s always a good idea to make sure that you really understand the message your client is looking to display with their case study.
Look through their other content and familiarize yourself with their brand guide so you can be sure that your design aligns with their messaging and their brand. It’s also good to familiarize yourself with the industry your client is in as well as their audience so that you can be sure your design is keeping them engaged.
2. The Right Graphics for the Story
A successful case study is going to need a good number of images and photos to break up all of that text into manageable bites and better explain complex information.
Roll up your sleeves and crank up Adobe Illustrator, because custom graphics is the way to go here. The style will be up to your client and their brand, but common needs for case studies include:
- Illustrations
- Photo treatments
These graphics are extremely handy for not only breaking up big blocks of text but also highlighting important information and making the content easy to navigate and understand.
Refer to your client’s brand guide to get the style right for the custom illustrations and icons you’ll need for their case study. If they don’t have any guidelines for illustrations and icons, then be a pal and kindly refer them here .
3. The Best Way to Visualize Data
Showcasing data effectively in a case study is absolutely crucial to its success. It doesn’t matter how impressive the numbers are if the reader can’t understand them or get a good grasp on their impact.
So, the data you’re working with, whether it's in the form of charts and graphs, statistics, or whatever else your client asks for must be presented in a way that is clear and straightforward. Use colors, type hierarchy, callouts, or whatever you need to best present your information.
Compelling infographics are a great way to do this. Using your client’s brand guide, you can whip up some infographic design templates to use throughout the case study to effectively show the collected data and what it means.
4. A Compelling Color Palette
The right colors not only make a case study visually appealing as readers navigate through the information but can ensure that your client’s case study is on brand, consistent, and a step above the rest of the competition.
Consider also using your colors to strategically highlight key information, such as numbers or data, and to invoke the right emotions as your reader moves through the narrative.
With so much data and information to present, be sure to also use a color palette that works well with your graphics and font. Your headers, captions, and text should be easy to read against whatever color background you’ve chosen.
5. Strategic Layout

The way your case study is laid out is also a crucial component in how readable and user-friendly the final result will be.
Collaborate with the copywriter, if possible, and make sure that the case study has a clear structure. The copy, the data, and your infographics, photos, and images should tell a story: a beginning (before the brand’s product and service), a middle (introducing the product or service), and an end (how the product or service improved the subject’s operations).
Use the power of type hierarchy as well to call out key information, keep text organized, and make the content easier to read.
Conducting a case study involves collecting tons of information, but no matter how much info is presented, you don’t want any portions of your case study to look crowded or busy. Be sure to have enough white space on each page to keep your design looking clean.
Some ways to lay images or photos out neatly are by the use of grids, columns, icons, and by teaming up with the copywriter to insert navigation aids, like clear page numbers, a table of contents, clearly defined sections, an index, or whatever else you think the reader would need to be able to easily follow along.
6. Spotlight Key Information
In addition to using type hierarchy and color scheme to call out the juiciest bits of information, consider also using bullets, lists, quotations, callouts, and even arrows to guide the reader’s eyes to what’s most crucial.
If the specific case study you’re designing for is about complex machinery or products a potential customer might not be familiar with, things might get confusing fast.
Clear it up by adding labels and captions to photos and illustrations to help the reader better understand important technical information and not feel overwhelmed or lost by the data being presented.
Looking for an Outlet for Those Design Skills?
If all of this has you nodding along, then, great! You may already have the design know-how to create visually stunning and easy-to-navigate case studies, reports, or whitepapers.
So, if you’re looking for an outlet for those skills, why not consider joining the Designity community?
Designity is a 100% remote CaaS (creative as a service) platform that is made up of experienced Creative Directors and the top 3% of US-based creative talent, including graphic designers , illustrators, copywriters, video editors, animators, and more.
As part of the Designity community, you’d enjoy competitive pay, a remote work environment, and the freedom to work on your own schedule from wherever you have a good WiFi connection!
You’ll also get to work on a variety of different projects with an even larger variety of clients and industries. And, best of all, you’ll get to team up with that creative talent described earlier and be part of a one-stop shop dream team that creates multiple case studies, whitepapers, brochures, and whatever marketing collateral you want to work on!
Think you have what it takes?
Why not apply today and put your skills to the test?
Share this post:

Creative Directors Make the Difference

13 best product design case studies for 2024
Product, Behind the scene
Box Annotations
Very clear and easy to read case study with video explains how it works, and great visual.
Behind the scene
Tumblr Queue V2
Aileen, an intern shared the story of her internship project at Tumblr. Great visuals and ease of reading make it a great case study!
Freshalian Pasta - UX Writing Case Study
Discover how words shape User Experience and how to find them
Designing Facebook Collage
Christophe shared an inspiring process on how his team created Facebook Collage
Designing the UI of Google Translate
The design story behind making Google Translate
User research, User retention
Pathrise Resources
Very detailed case study on how to increase user engagement and retention
Product, User retention
8 tactics tested on 300M users
Learn how Duolongo gets people to come back.
The evolution of HEY
Learn how Hey.com was built, from idea to launch.
The making of Bloggi
A full story of how Hernán built Bloggi. An inspiring story for you to write about your side project.
Product, Process, Redesign
Uber - Perfecting the Pickup
Simon shared the whole process when redesigning Uber Rider. A greate example on creating a case study.
Product, Process
Building SoundCloud
An in-depth retrospective on building SoundCloud from Michael Nino.
Product, Redesign
Apple Music Case Study
Jason Yuan got rejected by Apple Music. So he spent 3 months to redesign it.
Web, UI Design
Lonely Planet
This case study from Ueno is agreat example on how to write and design a case study for a web project.
Curated design portfolio inspirations and case studies. Delivered every Monday.
- Portfolio Tips
- Career Tips
- Portfolio Examples
- Get UXfolio!
6 Excellent Product Designer Case Studies & 8 Tips for Yours

What is the recipe for perfect product design case studies? The dozens of design leads and HR managers we’ve interviewed say that they expect a blend of
- storytelling
- stunning visuals and
- personality.
This article will guide you through the steps of creating case studies that check all those marks, and more! This is your one-stop source of tips and steps based on actual research, and real-life examples.
Let’s be honest: putting together a case study can be rather difficult. However, there are some techniques and tools that can help you along the way. One of those tools is UXfolio , our portfolio builder that makes the whole process faster and easier. Obviously, these 8 tips apply regardless of the tool you are using to build your product designer case studies.
1. Inject your personality into your case studies
Showing personality in a product design portfolio , case study, or resumé can be challenging. Finding the balance between just enough and too much takes time and experimentation. Still, if you want to set yourself apart, you have to find ways to inject your personality into everything you submit with an application.
Here’s a pro tip: whenever you relate something back to yourself, to your personal experience with the project, you’ll allow a small bit of your personality to shine. If you don’t go overboard, you will show just enough of yourself for recruiters to see the type of person and designer you are.
Define what you do
There are ways to sprinkle tidbits of your personality into everything you make. Start by clearly defining what you do. Do this in your portfolio and at the beginning of every case study: In what quality were you part of the project?
Find personal connection to the product
Next, you can share your connection with the product. Your case study intro is perfect for this. Answer questions such as:
- How did it relate to you (if it did)?
- Did you have any experience in this niche before?
- Were you using similar products before?
Talk about your experience throughout the process
In the body of your case study go on and talk about your experience throughout the project. Maybe this was your first time using a specific UX method. Let your readers know! Then go on and share what you liked about it, and what you didn’t.
Juniors have it easier
Leslie’s Meal Planner case study is the perfect example of a product designer case study based on a mock project. Putting together a portfolio as a junior designer – who doesn’t have real-life projects yet – is challenging to say the least. Most design leads advise juniors to build a portfolio based on
- internship experiences ,
- mock projects, or
The secret is to treat these mock-projects exactly as you’d treat real-life projects. Put in the research, testing, and the same effort you’d put in a real-life project. The best thing about mock-projects is that they provide plenty of room for your personality to shine. Just base them on topics or apps that interest you and let your readers know.
Check out Leslie’s introduction:
“I’ve been struggling with food allergies for years, so it seemed obvious that I will try to find a solution to this common problem.”
Immediately in her intro, we learn something personal about her. It is easy to see why she’s passionate about the topic. By kicking it off on a personal note, she pulls in the readers immediately.
This approach aligns with the advice that Marc Greenberg , UX lead of Robotics at Postmates, gave to junior designers:
“Start close to you. Everyone can identify where their own frustrations, troubles, and difficulties lie. The first step is to design solutions to those things.”
2. Put everything in context
Both HR managers and design leads list ‘lack of explanation’ as a common reason for rejection. Our experience through expert reviews supports their statement.
Stop defining UX methods in your case studies
Many designers will list the methods they have used during a project. They do a good job of explaining the general purpose of said methods. The only problem is that both HR managers and design leads are aware of what ‘A/B testing’ is and what purpose it serves. What they don’t know is:
- Why did you choose that method for that specific project?
- What did you learn (or did not learn) by using that method?
- How did your findings influence the project?
By failing to answer those questions, your case study will fail to fulfill its purpose. The key is storytelling. In the context of UX portfolios, the word storytelling refers to the story of a specific design project and not the story of UX design in general. Storifying your design process is not that hard of a task. Just follow the golden rule:
Whenever you mention something in a case study, explain why it’s relevant to the project at hand and how it influenced your process.
Better Cover, a product design case study by Joanna Yoon, illustrates how to place research in context. Joanna lists the methods she used, then goes on to provide numbers and results. She presents the results in a visual way, which makes it even easier to digest all the data. And this takes us to our next tip: visuals.

3. Keep it visually consistent
Your taste level will be judged based on your portfolio and case studies, and not only the products that you’ve designed. Ideally, while working on something, you think in personas, mood boards, and design systems. Do the same when putting your portfolio together! After all, it’s a product designed by you.
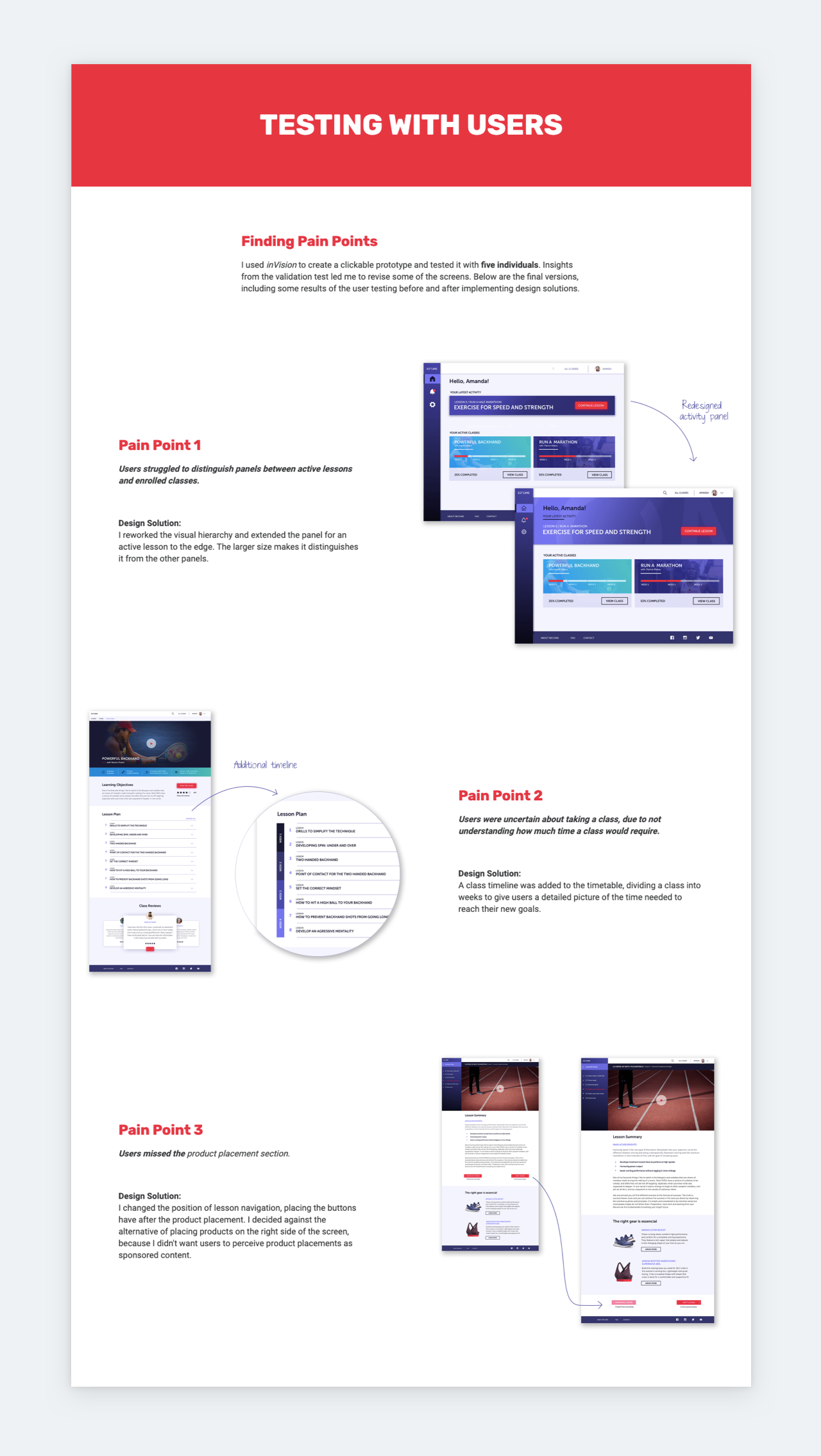
Stop over-designing
Don’t go overboard with your portfolio design. The more stuff you add, the higher your chances of not matching the tastes of others. What’s even worse, you’ll ruin the UX of your portfolio. Check out what Spotify’s Paul Farino had to say about over-designed portfolios:
“I see some portfolios that may take ten seconds to load and it’s very flashy and there’s a lot going on on the screen. But those animations and that extra flare don’t contribute to the story you’re trying to tell. It actually just makes it a poor experience.”
You might think that things floating into the screen left and right show that you are tech-savvy and on-trend, but you are actually over-designing, which ruins an experience that would be seamless otherwise.
There are many well-written product design case studies out there that fail because of presentation. Design is the easiest part of case studies, especially if you are working from a template, such as the templates that you can generate via UXfolio .


Be mindful of colors
Keep in mind: your case study will already include some colors from the product itself. The safe thing is to use matching colors. Introducing new colors on top of what you inherit from the product is a risk that you should not take. It creates a mess, especially if your viewer doesn’t have the time to take it all in. Focus on keeping your fonts and colors consistent throughout the case study, portfolio, and resume.
Make it easy to skim
UX/UI Recruitment Consultant, Joe Jackson , advises UX designers to
“Make it digestible, skimmable, and impactful.”
Your case studies’ users – recruiters and design leads – spend a maximum of 3 minutes with one portfolio. If you have 3 case studies, that’s less than a minute per one. This means that you have to prioritize visual hierarchy.
Take the text of your case study, and see how it would work without the images. Did you use enough headings? Are they applied consistently for the same type of content? Can you organize some of your data into tables or illustrations? Did you use matching colors on your visuals?
Visual consistency checklist:
- Is my content organized into logical chunks consistently?
- Are my fonts consistent throughout the case study?
- Do I have a good text-to-image ratio?
- Is the style of my illustrations and images consistent?
As you can see the keyword here is ‘consistency’
4. UIs matter
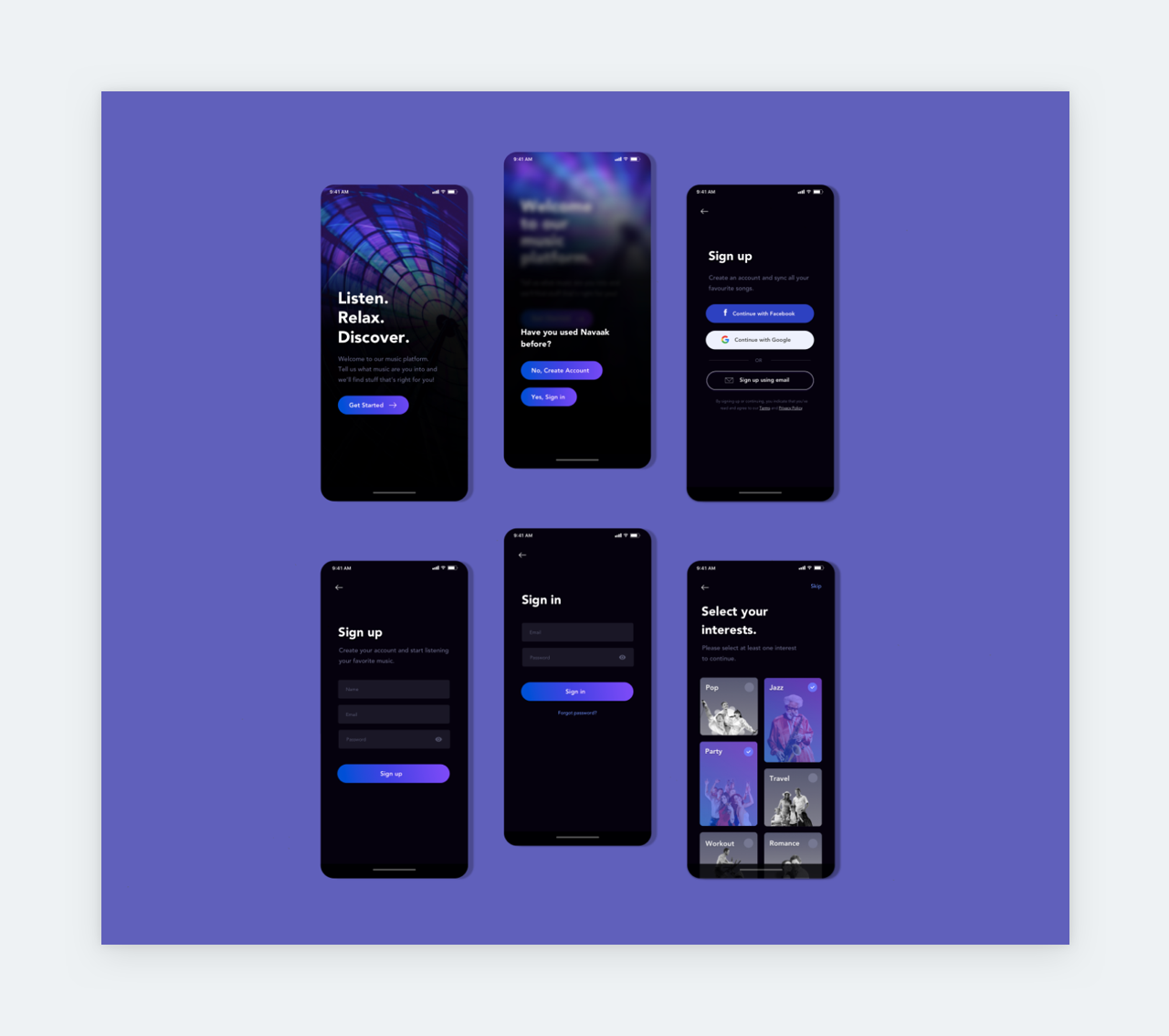
When you ask HR managers whether UIs matter in UX portfolios, the answer will be ‘yes’. They know that UI and UX design are not the same. But that doesn’t change the fact that having stunning UIs in your case studies will increase your chances of landing a job. It’s not right, but it’s true. If you want to maximize your chances of success, accept the fact that UIs matter.
Here’s what Tony Aube , Google AI’s Sr. Product Designer had to say about this:
“I believe UX portfolios have too much text and explanation about the design process, while they don’t have enough visuals. The truth is — and I have learned this the hard way — recruiters respond a lot more to visuals than to text.”
The thinking process behind this is very simple:
“If you can’t figure out something as simple as proper drop shadows, I doubt you will do a good job on a multimillion-dollar purchase flow redesign.”
Reasonable.

Just leave them out
If your UIs are not yet polished, it’s better to leave them out of your case studies. Remember: you will be judged on everything you present. It doesn’t matter if you explain right next to it that you have just dipped into visual design. The image will linger. If you don’t do UIs, stick to wireframes and protos, otherwise, you risk shooting yourself in the leg.
5. Deliver on the promises you made in your resume
Your resume, cover letter, about page, and case studies must be aligned both visually and content-wise. If you promise serious research-game in your resume, your case studies should stand proof for that. This way, by the time the HR manager finishes with your submission, they will be convinced that you are indeed big on research. But for this to happen, your entire application must reinforce the statements you make.
Make everything match
When you are eyeing one specific position at a company, align everything you submit with the job description. From your resume to your case studies, everything should support the fact that you are the best candidate. It might seem like too much effort, but in the end, it’ll be worth it. The least, you’ll end up with a brilliant portfolio.
There are plenty of UXfolio users who make great use of the multiple portfolios feature. They create different (password-protected) portfolios, tailored for different applications, and even different positions, such as product designer and UX writer. They understand the impact of a customized application.

6. Show your best work only
If you do a bad job with your own ‘product’, how could they trust you to do a good job with theirs?
Avoid showing mediocre or unfinished work. As mentioned before, you will be judged on everything you present, regardless of any explanation you provide. If your case study is still “in the works” or “coming,” do not feature it in your portfolio! If a case study doesn’t feel right to you, it won’t feel right to the HR manager either. And so on. You get the message: if it’s shaky it doesn’t have a place in your portfolio.
Apply this to everything
The same applies to the visuals you present. If they are shabby, you will be the applicant with the shabby visuals. You must treat your portfolio like you would treat a client. If you do a bad job with your own ‘product’, how could they trust you to do a good job with theirs?
Ask your teacher, your peers, or literally anyone to give feedback on your portfolio. Spam hundreds of Facebook groups with your case study, ask your teachers to review it, send it to HR managers for review. In UXfolio , you can request peer reviews as well as expert reviews. The latter will be given by our designers, who have seen thousands of portfolios.
Here’s Trevor Denton’s advice on the matter:
“Quality over quantity. Many designers oversaturate their portfolio with projects. You don’t need to show me every single thing that you’ve done. Show me the things that you’re most proud of!”
7. Reflect and plan

Close your case studies with reflections and learnings. We work in an industry that evolves at a rapid pace. We must do the same to keep relevant. And openness to learn new things is at the core of evolution.
Mention what you’ve gained professionally from each project, even if it’s a mock-project.
Even the most mundane projects can bring something that contributes to your professional growth. It’s all just a matter of perspective. So, mention what you’ve gained professionally from each project, even if it’s a mock-project.
End with ‘Next steps’
As a product designer, you are well aware that a product is rarely finished. There are always tweaks that could make it even better. There are things that you find important but you couldn’t accomplish. Collect all of these into a ‘Next steps’ section, to show your awareness. Such a section also proves that you think ahead.
So, give your reflections and lay out your plans and ideas for future improvements.

8. Give credit for good karma
Paul Farino , Spotify’s Sr. Product Designer put it best:
“A lot of times we see case studies at a large company and you know they had a ton of other designers, whether researchers or product folks involved. It usually makes for good karma to give credit.”
Not only is it good karma, but it is also extremely beneficial for you. Most positions require the candidate to be a good team player. What better way to show that you fit that criteria than giving credit to the people that have contributed to your work? However, there is a way to do this right.
Let’s say, you have been working closely with front-end developers. When you mention this, describe what type of a collaboration it was. What did it involve? How did you make it work? Maybe you had a dedicated researcher to help you collect all the data. Mention how did you align the research and design. How did the researchers’ work influence yours? It’s all about giving context.
Take the advice of Google UX Design Lead, Koji Pereira :
“No good product gets created by one person. So you don’t have to mention names, but it makes for good practice to just say, ‘In this project, I had two designers and five engineers working with me.’ (…) We at Google want to know if you’ve ever worked with a researcher. Have you ever worked with an engineer or a PM?”
Build meaningful case studies with UXfolio!
UXfolio is a powerful portfolio and case study building tool that’ll save you hours of work. Our pre-made case study sections come with image ideas and text prompts that’ll guide you through the entire process. Your only job is to focus on the content! Try UXfolio for free!

A rapid desktop prototyping tool

Mockplus - Design Faster. Collaborate Better.
Prototype, design, collaborate, and design systems all in Mockplus

Top 22 Stunning UX Case Studies You Should Know in 2022
An immersive yet well-structured UX case study helps UX professionals show off their design talents in portfolio websites, and let them communicate better with employers, designers and others easily.
However, as a UX designer , how can you write a perfect UX case study to easily get hired or communicate with others better?
Mockplus has handpicked 22 of the best UX design case study examples in 2022 to help you get inspiration, improve your portfolios and make your own things with ease. A step-by-step guideline about how to create a UX case study is also followed.
What is a UX case study?
A UX case study tells the story of how you create a great website or app and, in particular, what you do to improve the UX of the site. UX designers—newbies and experts alike—will often share a case study on a portfolio website as a great way to get hired. Just like sending a resumé.
So, it is a lot more than just a copy of everything you've done while designing the project. To really showcase your design talent and the breadth of your abilities, you need to make sure the following are all included:
- A full description of your role in the project;
- The biggest challenges you've faced;
- The solutions you've chosen, how you chose them and why;
- How you communicate and collaborate with others; and
- The outcomes and the lessons you’ve learned.
To this, you should feel free to add any further information that you think would help you stand out from the crowd.
It is also worth remembering that UX case studies are a good resource for UX design beginners to learn more practical design skills and to gain from the real experience of others in dealing deal with difficult or urgent problems.
22 Best UX case study examp le s you should learn
Whatever stage you’re at and whatever you are writing your case study for, these 22 top examples are bound to inspire you.
1. Perfect Recipe -UX design for cooking and shopping
Designer s : Marina Yalanska and Vlad Taran
Case Study : Perfect Recipe
This is a mobile application that enables users to search for food recipes and to buy what they need to cook different dishes.
Why d id we choose this one?
This case study illustrates the entire UX design process is very simple, plain language. Many aspects of the process are included, along with some really inspirational ideas, such as product personalization, challenges and solutions, animated interactions, and other interface details.
Extra tips :
This example is from the Tubikstudio blog, which is very popular among designers. It regularly shares different branding, UI, and UX case studies. We would strongly recommend that you follow this blog to keep yourself up to date with the latest and most creative case studies.
View details
2. GnO Well Being - Branding, Web Desing & UX
Designer : Marina Yalanska and Olga Zakharyan
Case Study : GnO Well Being
This is a creative illustration website that presents and sells a weighted designer blanket that helps you get a good night’s sleep, the first step to good health and a better life.
Why d id we choose this ?
This example is so much more than a great UX case study. In addition to the UX design , it gives you insight into many more key design issues, such as the logo, custom graphics, website pages, interactions and so on. There are many ideas here that you could copy for your own projects.
3. Splitwiser - UI/UX case redesign

Designer : Chethan KVS (a Product designer at Unacademy)
Case Study : Splitwise
This is a concept mobile app that enables users to track and split expenses with friends. The designer has also given it another name, "Splitwise."
Why do we choose this ?
This case study shares the designer's insights into key design decisions, such as why he chose this product, why he decided to redesign the logo, how to improve the onboarding and other pages, how to optimize the user flow, how to balance all pages and functions, how to enhance UX through bottom bars, interactions, gestures, view modes, and more.
Everything is explained using intuitive images, earning it thousands of “likes”. This is a great example that is bound to help you write a stunning case study on redesigning UX.
This comes from a popular media channel called "UX Planet" that regularly posts examples of the best and latest UX case studies from around the world. Another great place to keep you up to speed with the latest UX designs.
4. Deeplyapp.com - UX & visual improvements

Designer : Sladana Kozar
Case Study : Deeplyapp
This is a health and self-care website app that helps users maintain mental well-being with meditations and exercises. This case study talks you through the design process of creating a user-friendly mobile app.
This case study focuses on improvements to the UX and visual features of this mobile app. Many aspects are included to help you understand it better, such as the design background, what to build, UI flow diagram, discoverability design, visual balance, and much more. A full set of app interfaces are presented for you to study as well.
You can also check out its Part 1 post for more details.
5. Talent Envoy - improving the recruitment process
Designer : Enes Aktaş (Experienced UX designer)
Case Study : Talent Envoy
Talent Envoy is an intelligent job assistant that helps users find their ideal job and get to all the way to signing a contract faster and more easily.
This case study firstly points out the biggest challenges and problems faced by job-seekers—the shortage of US recruitment markets. It then talks to you through the detail of how the designers optimized the recruitment process. You will also find information on the user research process, the UI flowchart design, the related wireframe and Sketch designs, the main page design, and more.
All the details have clear explanations and they offer a great example of how to use user research to solve problems and improve UI interfaces.
This one comes from another hot media channel called "Muzli" which shares the latest ideas, designs, and interactions about websites or website apps from all over the world. Don’t miss out on this site if you want to stay ahead of the curve.
6. My Car Parking - UI/UX case study

Designer : Johny Vino (Experienced UX and interaction designer)
Case Study : My Car Parking
This is a mobile app that can help people get parking slots easily even when they travel beyond their normal routes.
This is a masterclass in how to write a case study that is simple, well-structured, and easy to understand. Many intuitive lists and images are used to explain the design ideas and processes.
It has received “claps” from over seven and a half thousand people and is a perfect example of how to write a well-structured and easy-to-understand case study.
7. Parking Finder App - UI/UX case study
Designer : Soumitro Sobuj
Case Study : Parking Finder App
This is another concept mobile app that makes it easy for users to find parking slots even in big or overcrowded cities.
This case study is beautifully presented and gives a good presentation of the whole design process. It covers nearly all the issues that a textbook UX case study should have, such as problems and solutions, user-centered design, design strategy, user flow, information architecture , interface wireframes and visual designs, and much more besides.
It is one of the best examples we have found of a case study that really teaches you how to write the perfect UX case study.
8. Pasion Del Cielo - coffee ordering experience

Designer : Jonathan Montalvo (Senior Designer, Branding, UXUI )
Case Study : Pasión del Cielo
This is a concept project about a real local coffee shop in Miami.
This case study demonstrates effective ways to engage users with the Pasión brand and how a site can make it as easy as possible to turn page views into coffee sales.
There is a lot of analysis included to explain the entire design process, such as analyzing the competition, feature analysis, brand and interface improvements, and much more. Most important of all, many user personas have been created to evaluate and enhance the UX.
This is a good example to check for anyone looking to improve their own UX case study. Above all, it shows what can be done with rich images, bright colors, clear layouts, and well-crafted personas.
9. Workaway App - UX redesign
Designer : Rocket Pix (UXUI, web designer )
Case Study : Workaway App
This is a mobile app that provides international hospitality services; it helps users to contact each other to organize homestays and cultural exchanges.
This UX design case study explains how the designer redesigned the Workaway App to make it easier for users. Many intuitive charts (pie charts, flow charts, line charts), cards, and images are used to illustrate the ideas.
It is simple and easy to follow, and also a good example of how to create an intuitive case study with charts and cards.
10. Receipe App - UI/UX design process
Designer : Dorothea Niederee (UX, UI designer )
Case Study : Recipe App
This is a food app design offering inspirational recipes for anyone who wants to eat healthier.
This case study gives a clear demonstration of the entire UI/UX design process. Three user personas are defined to present different users' needs. Some colors, typography, and UI elements are also shared.
This is a good example of how to define a detailed user persona in your UX case study.
11. Hobbfyy - a social and discovery app UX design
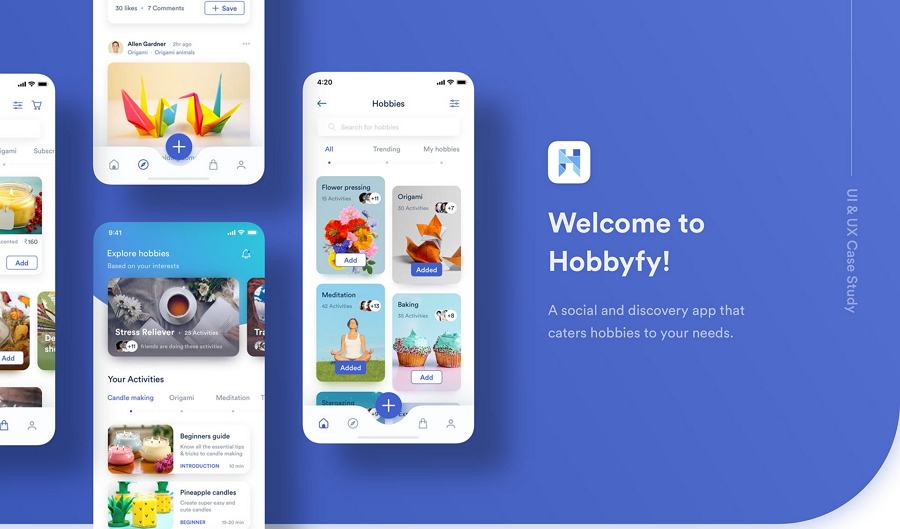
Designer : Mustafa Aljaburi (UX, UI designer )
Case Study : Hobbfyy
This is a social and discovery app that makes it quick and easy to get everything you need for your hobbies.
This case study aims to show how to develop a site that will provide its users with solutions, in this case to get what they need for their hobbies. Beautiful images, a storytelling style, and special layouts are used to explain everything.
12. Bee Better - habit tracker app UX case study

Designer : Anastasiia Mysliuk (UX, UI designer )
Case Study : Bee Better
This is a habit tracker app that makes it easy for you to develop new useful habits.
This case study aims to solve problems associated with how we form and develop habits. It helps users find solutions and make habit formation more interesting; it motivates them to maintain their useful new habits. Many aspects of design, such as problems, solutions, the design process, discovery and research, user journey map, prototypes, and much more are illustrated and explained in simple language.
This would be a good example to follow if you are looking to create an easy-to-understand UX case study.
13.Sit My Pet - pet sitting app UX case study
Designer : Aiman Fakia (UX, UI, visual designer )
Case Study : Sit My Pet
This is a pet-setting app that provides pet owners with a digital service that helps them connect with pet sitters.
This UX case study describes a site that aims to make pet sitting more easily accessible for pet owners. It analyzes both its users and its competitors very well. The way solutions are evaluated, the user stories, and other related aspects are followed in detail to give you a better understanding of the project as a whole.
This is a good example of how to develop a UX design based on user needs.
14. Groad - food ordering system UX case study
Designer : Phap (UI designer )
Case Study : Groad
This is a food ordering app offering food delivery services from stores, restaurants, cafés, fast food bars, and others.
This UX case study uses beautiful illustrations and colors to explain the entire design process. As well as the usual parts of the design process—UI flow chart, UI showcasing—the related logo and icon designs, typography, and other aspects are included. This is a good example if you are looking to learn how to create an immersive case study with beautiful illustrations and colors.
15. iOS VS Android UI/UX Case Study

Designer : Johanna Rüthers
Case Study : Econsy
Here is another concept app that helps people live more sustainably by using a scanning process to give them information about the ecological and social impact of products they are thinking of buying.
This case study explains the differences in the mobile app’s appearance when it is applied on the Human Interface Guidelines (IOS) and Material Design Guidelines (Android). This will help you to create an app that works well on both Mac and Android devices.
More UI/UX case studies & designs:
16.Timo Bank - UI/UX Case Study

Timo Bank is a mobile banking app project produced by Leo Nguyen, a freelance designer and creative director. This case study aims to provide more intuitive transfer, payment, and money management solutions for mobile users.
This is a great example to consider if you are hoping to create a better banking app.
17. Endoberry Health App Design
Endoberry Health App Design provides useful solutions for women suffering from endometriosis. In turn, this gives doctors a better understanding of individual cases. The design challenges, solutions, and UI details are displayed and explained to illustrate the design project.
18. Job Portal App
Job Portal App has been specially made for designers and freelancers. This case study uses cute illustrations, simple words, and clear storytelling to explain how the designer worked out the ideal job hunting solutions for users.
19. Cafe Website - UI/UX Case Study
Café Website gives its users a great experience by making it quick and easy to order a coffee online. Many elegant page details are displayed.
20. Ping - the matchmaker app case study

Ping is a dating app that offers users a unique and effective way to find their perfect match. As you can see, its mascot is really cute and this case study will show you how a cute mascot can enhance the UX.
21. Hubba Mobile App - UI/UX Case Study
Hubba Mobile App is a B2B online marketplace where retailers can find and purchase unique products for their stores or shops. This case study aims to explain the process of creating a special mobile app for this online marketplace. It offers a beautiful and clear presentation of the entire UI/UX design process.
22. Music App - music for children
Music App shares the fancy UI and colors from a music app made for children. It is a good example that is sure to inspire you to create a distinctive children's app.
How do you create a UX case study?
If you are still not entirely sure how to go about creating a distinctive UX case study, here are a few simple steps to walk you through the entire process from start to finish:
Step 1. Figure out your purpose
The final outcome will depend on what it is you are trying to achieve. So, before you start writing a UX design case, you should first figure out in detail what its purpose is. Ask yourself some basic questions:
- Is it for a job interview?
- Is it for improving your personal portfolio?
- Is it designed to show off your design talents on social media?
- Is it just created to practice your design skills?
- Is it made to share design experiences with other designers?
In short, figuring out your purpose and setting a goal can make the entire design process so much easier.
Step 2. Plan or outline your case study
Whatever you want to do, it is always a good idea to start with a plan. When it comes to writing a UX case study, you should also outline your entire UX case study and decide on what sections you want to include.
For example, nowadays, a good UX design case study often covers:
- Overview : Start with a short paragraph that introduces your project.
- Challenges and goals : Explain the project background and point out the biggest challenges or problems you've encountered. Explain the goals you want to achieve and how you will overcome the challenges you have identified.
- Roles and responsibilities : Tell readers what role you play in the project and the specific features of your role that will help create a better product.
- Design process : Introduce the entire design process in detail so that readers can see clearly what you have done to make life easier for users. Many employers check this part very carefully to see whether you have the basic skills and abilities they are looking for. So, never underestimate the importance of this section.
- Solutions and outcomes : No matter what problems you have faced, the solutions and the final outcomes achieved are what really matters. So, always use this section to showcase your skills and achievements.
You might also want to add further sections:
- User research : Some full-stack designers also include this to give a more comprehensive view of their design skills.
- UI designs : Some experienced designers also display their relevant UIs, and UI flow, along with low- and high-fidelity prototypes to enrich the content.
Of course, if you are a newbie, and you still have questions, why not go online and search for UX case study templates that you can study and follow.
Step 3. Explain the design process clearly
As we've explained above, the design process is always one of the most important parts of a good UX case study. You should always introduce clearly as many of the relevant parts of the process as possible. For example: show how you and your team communicate and collaborate effectively; demonstrate how you have developed ideas to address user problems; explain how you and your team have dealt with emergencies or mishaps.
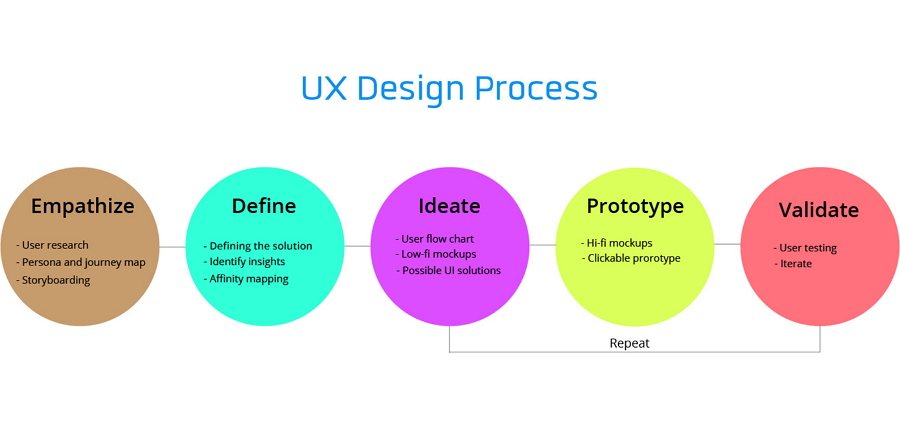
You can also introduce the UX design tools that you have chosen to simplify the entire design process. Mockplus, is an online product design platform, enabled us to adapt quickly and effectively to working from home during the recent Coronavirus lockdown. Prototyping our designs, sharing ideas, working together in an effective team, taking the process from design to handoff, it all works smoothly with this single tool.
Step 4. Improve readability and visual appeal
The content should be the main focus of your case study—but not the only focus. To make the case study as good as possible, you also need to think about its readability and visual appeal. Here are some suggestions to follow:
- Explain everything as clearly as possible.
- Add images, illustrations, charts, cards, icons, and other visuals.
- Create a clear storytelling structure or layout.
- Choose an immersive color scheme.
- Add eye-catching animations and interactions.
- Use vivid video, audio, and other multimedia resources.
The final visual effect can be make-or-break for whether your UX case study is going to stand out from the crowd. You should always take it seriously.
Step 5. Summarize
Every UX case study can be a good chance to practice and improve your design skills. So, in your conclusion, don’t forget to analyze the entire process and summarize the outcomes. Always take a minute to figure out what lessons you should take away from the process, what tips should be remembered, what should be improved, and—most important—what your next steps are going to be.
UX case studies are one of the most essential parts of a UX designer's portfolio. The ability to write a well-structured UX case study is also one of the basic skills that a competent UX professional should have. So, UX case studies play a very important role in UX designer's life.
We hope our picks of the best UX design case studies along with our step-by-step guide will help you create a stunning UX case study.
In- house content editor, specialize in SEO content writing. She is a fruit lover and visionary person.

Uploads design files from Sketch, Figma, Axure, Photoshop, and Adobe XD into our design handoff tool.

A free online prototyping tool that can create wireframes or highly interactive prototypes in just minutes.

A vector-based UI design tool enables you design in the way you want to.

Your single source of truth to build, maintain and evolve design assets in one place.

Related Content
Design Faster. Collaborate Better.
Designing the best user experience. Mockplus does it all!

Interactive prototyping
Unified collaboration

Scalable design systems
© 2014-2023 Mockplus Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
How to write the perfect web design case study to win more clients
An immersive digital portfolio is the key to landing new clients. Learn how to show off your skills with a winning web design case study.

Design and build a custom portfolio website, visually, within 21 days.

A design portfolio without case studies is like a movie with no dialogue — visually present but lacking the substance needed to convey its full meaning.
Dialogue and case studies both communicate meaning. Without dialogue, audiences struggle to understand a film’s plot, characters, and themes, similar to how clients will struggle to understand the problem you solved, your design process, and the impact of your work without a thorough case study.
When you’re competing against other designers for a project or role, a well-written web design case study sets your portfolio apart , showing potential clients what you’ve done and what you’re capable of.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth investigation into a person or group of people, a situation, event, or a product. A web design case study is a visual and textual analysis of a successful web platform, landing page , website design, or other web-based product. These types of case studies can be physical documents, but they’re often digital: PDFs, infographics, blog posts, or videos. Screenshots are an essential component, as are wireframes and mockups. But a robust web design case study also features detailed written explanations.
These visual and written elements work together to create a comprehensive assessment of the design process from start to finish, including the challenges faced, the solutions implemented, and the results achieved.
5 benefits of web design case studies
Now that we’ve touched on how case studies sell prospective clients on your work, here are a few other benefits of adding web design case studies to your portfolio website:
1. Demonstrate expertise
Case studies are a powerful marketing tool for designers to demonstrate their capabilities to potential clients or employers. A good web design case study showcases your skills and expertise in solving complex design problems.
2. Build credibility
In case studies, designers often include the name of the business, client, or project they’ve worked on, building credibility by providing real-world examples of their past work. You can even add testimonials and reviews to highlight positive feedback directly from those you’ve worked with.
3. Inspire future projects
Examining and analyzing your own work can inspire your next website build — maybe you’ll try one of the layouts that was nixed for this project or center the next design around an element you ended up loving. It also provides guidance and best practices for design projects, setting the bar for innovative design.
4. Encourage personal growth
Writing an investigation of your own design portfolio pieces after completing a project provides an excellent avenue for self-reflection. Reflecting on past projects, the struggles you’ve faced working on them, and what you’ve learned from the process will help you identify your strengths as a designer and areas of improvement to work on.
5. Improve communication
Presentations of your own work don’t just communicate the design process, decisions, and outcomes to clients. They also speak to stakeholders, including clients, team members, and management. A well-written case study illustrates a designer’s ability to effectively communicate complex design ideas and concepts, and writing it will improve your communication skills and offer insight into how effectively you work and collaborate with others.
What makes an effective web design case study?
A web design case study describes the process you took to solve a challenge with a particular web design project. A successful case study features a notable client project, a well-written narrative structure, and an engaging visual design.
Think of it as a story with an identifiable beginning, middle, and end. Throughout the story, show clients your approach to successful web design — the problem, the research you did to prepare for the project, the steps and iterations you completed throughout the process, and the final results you delivered. This narrative structure helps clients understand the project’s evolution and details your design process, making it key to an effective case study.
Case study curation and criteria
We’ve covered the basics of what a good case study looks like. But how do you determine which projects to include? If a project meets all the following criteria, it’s a good candidate for a detailed case study.
Is it relevant to the future projects you hope to explore?
If there’s a type of project you’ve completed in the past that you’d like to avoid in the future, that particular portfolio piece might not be a great option for a case study. You’re not just trying to sell yourself to clients — you’re trying to land jobs you actually want to do.
Does it have a defined initial problem?
Web design projects often arise as a result of a problem. These projects are perfect for case studies because the product design goes beyond appearance and functionality. Here are some of the issues your designs might solve:
- Poor user experience: To create a smooth, enjoyable experience for users, user experience (UX) design focuses on identifying and solving issues that cause frustration, confusion, or difficulty while using an app or a website, such as confusing navigation, misleading icons, or slow load times. Addressing these challenges lets you showcase your understanding of your target audience’s needs and demonstrates your ability to apply your creative and technical skills to solve them.
- Low search engine ranking: Redesigning a website with search engine optimization (SEO) in mind will improve its ranking in the search engine results pages, and you’ll have metrics to include in your case study to quantify the claims you’re making.
- Inconsistent branding: Brand design is a massive part of a company’s identity. A lack of alignment between the logo, colors , and other visual elements of a brand’s identity and its digital assets reflects negatively on the company, leaving customers with more questions than answers about who’s behind the brand. Good web design can bring a sense of cohesion to the company’s digital products, an achievement you can speak to in your case studies.
Does the outcome deliver measurable success?
Good design is subjective, but the best projects for case studies have data to show how successful they are. Search engine ranking is one example. You might also highlight impressive metrics for user engagement (bounce rate, time spent on the site), conversion rate (the percentage of visitors who make a purchase or fill out a form), or web traffic (the number of visitors to the website).
Is the project visually suitable for presentation?
When preparing a web design case study, consider the various formats it can be presented in, such as a video, static webpages, or interactive web content.
Selecting projects that fit your chosen presentation format is essential to showcasing your web design skills. As a web designer, it’s a given that whatever you’re presenting to potential clients needs to use thoughtful, aesthetically pleasing designs.
Design for display
There’s no single right way to present a case study. What’s most important is that your case study tells the story of the journey from an initial problem or idea to a finished product that meets the client’s needs.
A minimalist design will help you achieve this goal. But don’t confuse minimalist with boring. You can (and should) get clever with the presentation. Instead of using basic screenshots, for example, consider exhibiting your work in modern frames with immersive features. Or display screenshots of the product in its natural habitat. Webflow designer Karen Huang uses a digital screen in this user experience case study to feature a screenshot of the user interface (UI) on a smartphone screen just as users would experience it:

Build completely custom, production-ready websites — or ultra-high-fidelity prototypes — without writing a line of code. Only with Webflow.
How do you structure a case study?
The contents of every web design case study will vary, but they should all follow this basic structure:
1. A challenge

Start your case study with an introduction to your client and the problem your design solved. Include details about the project’s context, goals, and constraints. This section sets the stage for the rest of the case study and ensures the readers clearly understand what the project — and your solution — is all about.
2. A solution

Detail your approach to solving the challenge introduced in the previous section. Include information about your research, its methodology, and the data you gathered to develop your solution. Focus on your skills, not diagnostics — this is the place to showcase your intelligent approach, reasoning, and innovative ideas that ultimately resolve the challenge.
For this section, it’s helpful to break each key resolution into separate paragraphs and introduce images in chronological order to detail your design process. Screenshots of wireframes and strategy phases will paint a vivid picture of the project’s journey.
If you face any challenges or roadblocks while designing your solution, discussing them provides insight into your problem-solving skills and shows potential clients how you overcome difficulties. End this section with multiple pictures of the final product, and be sure to include a direct link to the project for potential clients and employers to peruse.
3. The impact

This section is where you’ll highlight metrics and data that back up the project’s success. Leverage metrics, user feedback, or whatever data is available to illustrate how your solution solved your client’s challenges and achieved the project’s goals. You can also include information about the potential longitudinal impact of your work and future opportunities for the project.
4. Key quotes

A case study is a perfect place to share client testimonials and add quotes from team members to help readers learn what the experts behind the project think about the build. Get creative but use quotes sparingly, sprinkling them throughout the case study to support the image or project stage the quote relates to.
Let your work do the talking
At Webflow , we offer the tools to make websites and the tutorials you need to perfect them. Learn how to start a web design business , make an online portfolio , or enhance your skills with a web design certificate with guidance from our blog and educational platform, Webflow University . Draw inspiration from our collection of templates and websites and start building your best site yet with Webflow.
Subscribe to Webflow Inspo
Get the best, coolest, and latest in design and no-code delivered to your inbox each week.
Related articles

Presenting your web design portfolio: The complete guide for winning new clients
When presenting your portfolio to a potential web design client, focus on sharing your goals, ideas, and thought processes as you worked through the projects.

4 steps to creating an impressive UX design portfolio
Your UX design portfolio helps you impress future employers and attract clients. Here are four crucial steps to creating an outstanding portfolio.

13 tips to make you a better web designer
Helpful advice to help you level up your web design skills

5 SaaS web design trends in 2017
Check out 5 of the most fascinating web design trends from ChartMogul's 2017 study of SaaS landing pages.

Show, don’t tell — create sites that do the talking for you
Advice from a seasoned web designer on how to design and build a portfolio site that will dazzle clients.

Webflow product update: August 2022
From our Memberships beta to Made in Webflow, to everything in between — here’s our half-year recap on our latest and greatest product launches since March.
Get started for free
Try Webflow for as long as you like with our free Starter plan. Purchase a paid Site plan to publish, host, and unlock additional features.
Transforming the design process at
- Interactions
- Localization
- Figma to Webflow Labs
- DevLink Labs
- Feature index
- Accessibility
- Webflow vs WordPress
- Webflow vs Squarespace
- Webflow vs Shopify
- Webflow vs Contentful
- Webflow vs Sitecore
- Careers We're Hiring
- Webflow Shop
- Accessibility statement
- Terms of Service
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Cookie preferences
- Freelancers
- Global alliances
- Marketplace
- Libraries Beta
- Hire an Expert
- Made in Webflow
- Become an Expert
- Become a Template Designer
- Become an Affiliate
5 Key Parts of a Great Design Case Study

Here are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward.
When done right, case studies are seriously complex and represent hundreds of hours of design work. At their start, they can feel like a disorganized, overwhelming mess.
Step by step, they transform into a piece of work a designer can truly be proud of because it tells the story of their growth over the project. Being able to effectively communicate and illustrate that unique story is key to a designer’s success in the interview process, and a way for them to stand out from competitors.
I’ve lost track of how many case studies I’ve reviewed in my time at Designation — it’s probably somewhere close to 1,000 by now — and in all that time, I’ve seen many important parts of case study writing come into focus.
Below are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward. Together, they can turn good designers into great design storytellers—and set them up for greater success later on as professionals.
Show your process assets purposefully.
Assets are your opportunity to show rather than tell—explain a big chunk of the process in a visual form. Assets can take many forms, and the more diversity in them, the more engaging for readers.
They include photographs, which can backup descriptions of on-site research, interviews, and teamwork; screenshots of in-progress work and art boards; sketches showing rough ideas that were fleshed out later; Post-it notes and affinity diagrams; wireframes, sometimes with color added for extra clarity for the reader; animated gifs showing microinteractions and user flows through the product; charts and tables; and so many others.
When focusing on a design or visual case study image like this shows a surprising amount of information and process—how creatively messy it can be to sketch, sorting to find ideas worthy of development, fleshing the strong ones out, and applying design elements and patterns to them.
A case study without showing assets is incomplete, but one that shows assets without explaining them is almost worse, because a designer always needs to explain their importance to the process.
The best way to do that is to use captions for each asset. But captions must always be a part of the overall story; they shouldn’t only repeat information that the asset already shows. They must provide a unique insight, and further the story for the reader. By doing this, it activates the caption and justifies its existence and the work it takes to write them by the designer.
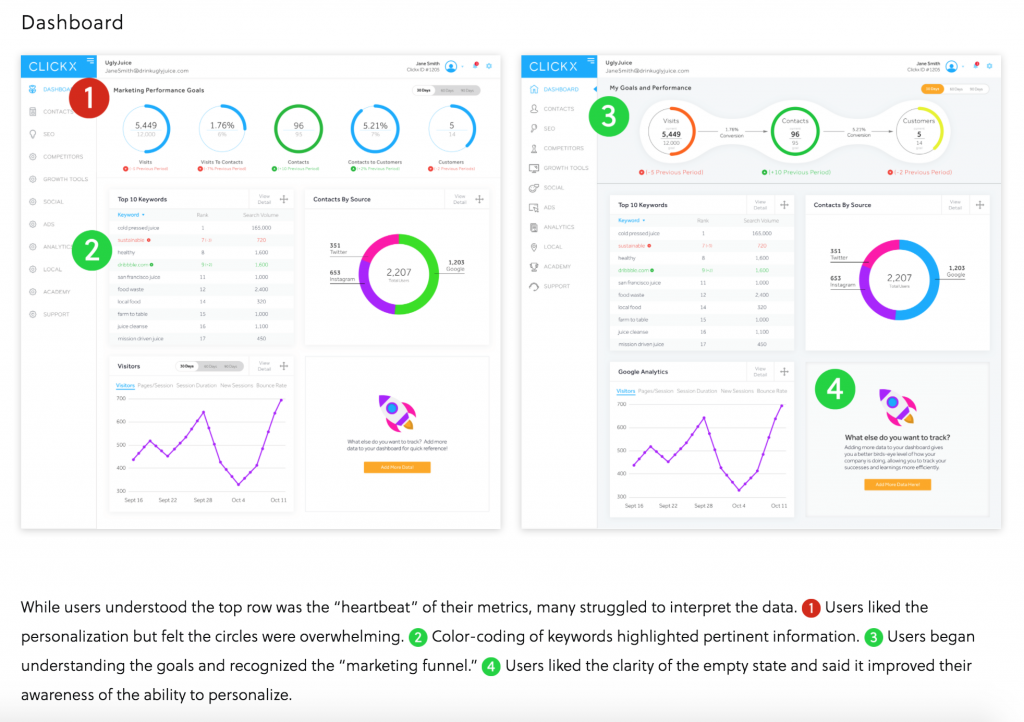
This designer used two forms of captions to illustrate their screens: Annotations that point out specific areas of concern from testers who looked at them, and a caption below that collected and synthesized them for easier comprehension.
Provide a competitive benchmark for the study.
Designers often like to downplay the research and analysis of competitors that happens near the beginning of a project because it doesn’t directly focus on the work they created. This is an unfortunate mistake because it’s a huge part of the story and it often leads directly to designers making research or design decisions later in the process.
Furthermore, designers should show off that they have a deep understanding of the competition whenever they work on a product; that they know what’s happening in the landscape and how their product fits in. Showing logos or only mentioning names of competitors isn’t anywhere near enough; designers need to discuss in detail what competitors do well, and analyze the areas in which they need improvement. Designers can provide screenshots of competitors’ products, but they need to go further and annotate or comment on them, to show a more detailed analysis.
They can’t ignore out-of-category competitors too, because that research often leads to innovative ideas that can catapult their product over in-category competitors’.
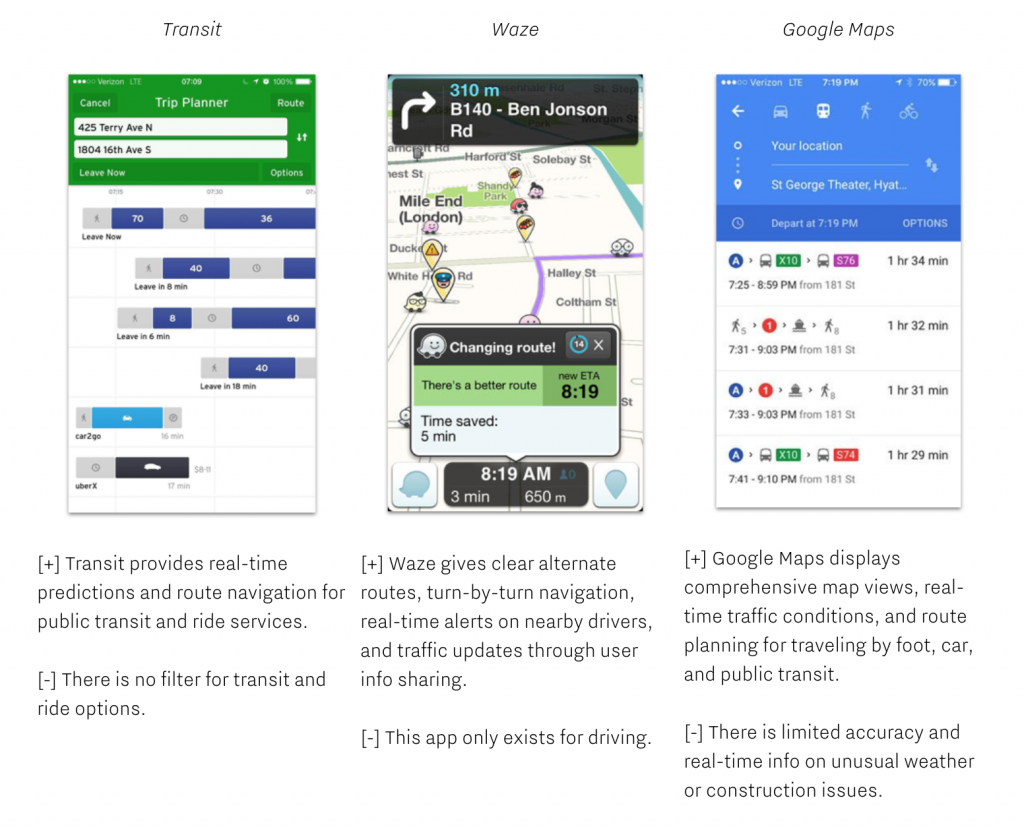
This designer looked at three competitors and called out unique areas of strength and weakness from each one, especially as they led the designer to make design decisions later in the process.
Finally, all that analysis requires synthesis, which means explaining the opportunities the designer saw for their own product after looking at the competition. This helps the designer more formally describe the end of the competitive research phase of a project and how that helped them refocus on their own product.
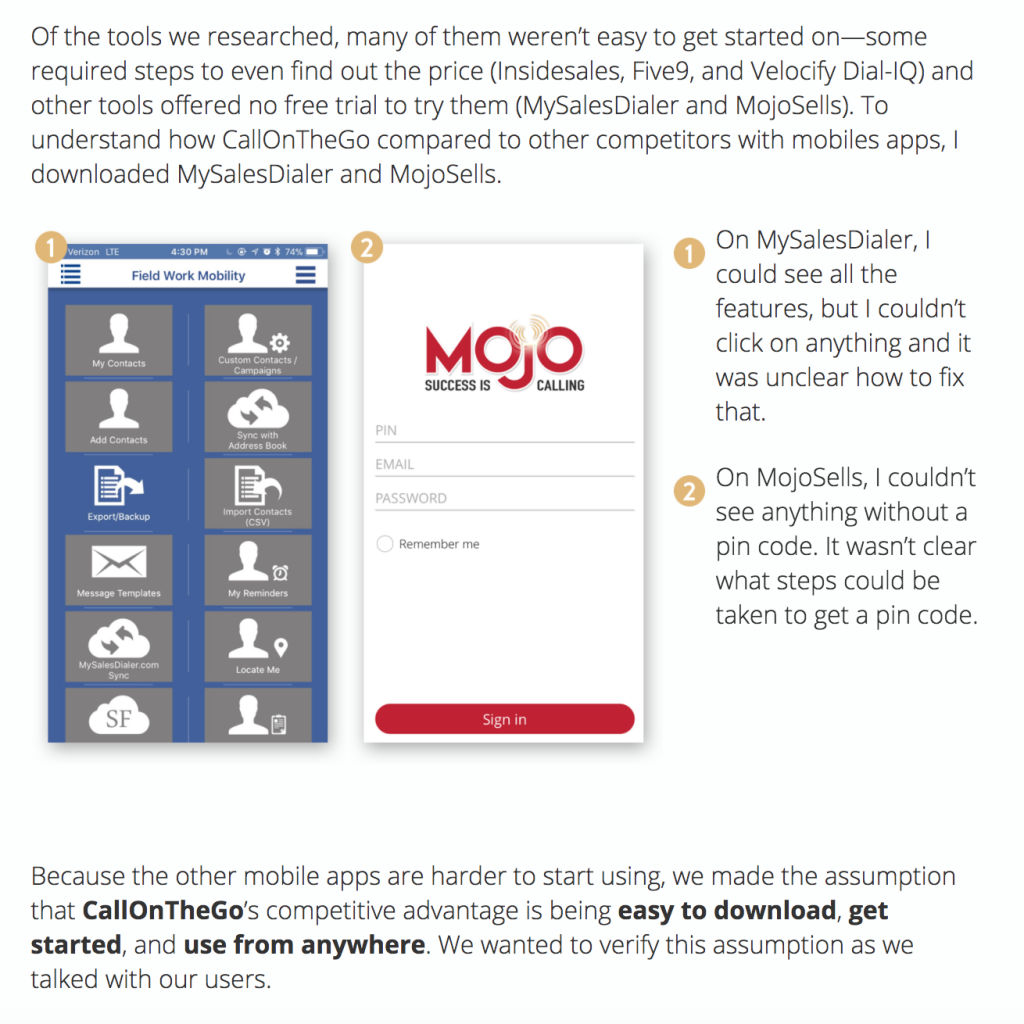
The designer analyzed competitors’ images in the center of this screen, but the text at the bottom presents what they did with that analysis: They derived an important design principle from it, which heavily impacted the next phase of their work.
Be team-centered in user experience design.
Almost every project done at Designation is done as part of a team because almost every project done as a professional designer is done as part of a team. It’s crucial for designers to reflect that in their case studies. Designers must write “we” when talking about group actions, and “I” when talking about personal design decisions or insights. In other words, we encourage designers to use “I” when they talk about where they led their team, and “we” when they supported another team member leading their team.
This is a great example of team-centered writing, where the designer discusses how the team worked together to generate concepts. She then switches to individual writing to indicate which concept she took charge of. Both extremes of this spectrum are bad in a case study—ones that only say “we” look like the designer didn’t think for themselves, and ones that only say “I” look like the designer isn’t a team player. So that balance has to always be found. Employers look for teamwork skills as much as they look for hard design skills, and a case study can be an excellent place to find records of them.
Don’t designsplain.
This is a big one. A lot of designers fall into the trap of explaining a basic element of the design process or design deliverables to the reader. You might be asking yourself: Why is this problematic? It’s because the intended readership of a designer’s case study is a hiring manager, design director, or someone else looking for evidence the designer will make a good fit for their team.
That means the designer needs to make an educated assumption that the reader is already familiar with design—and write their case study with that in mind. Unless it’s a part of their design process that was extremely unusual or the designer came up with it themselves, a designer has to assume the reader’s already familiar with it. If they don’t, they risk looking like the case study condescends to the reader, and that’s not purposeful writing.
One easy way to avoid this is for a designer to always avoid second-person writing —using “you” and “your”—which is a little too conversational for a case study anyway. They keep the focus on themselves and their work, and tell a stronger story in doing so.
Get the details right.
It might be cheating a little to clump a bunch of little steps together like this, but it’s important at the end of the case study writing process to micro-edit and make sure every detail is taken care of.
That’s why designers utilize tools like Figma to to tell their story in a professional way.
That’s making sure every word is spelled right, every publication title is italicized, and every piece of software is properly capitalized. But it’s also doing tasks like using contractions as often as possible throughout the text, removing extra spaces from between words or in front of paragraphs, knowing when to use a semicolon or an em dash, and making sure all dumb quotes are taken care of. And using writing tools like Hemingway, Grammarly, and GradeProof are a huge gift to anyone who needs a little help to take care of tricky grammar and get rid of run-on sentences.
Though tedious and time-consuming, the best way to take care of these details is to go through the complete draft and look to make one editing change at a time. Trying to edit for multiple needs causes the designer’s attention to be split in many directions—and makes them much less effective as self-editors.
Digital Designer Case Studies Conclusion
Writing effective, powerful case studies is a craft, and like all crafts, it rarely comes naturally to people. It takes skill and work, and staying in practice. The tools, resources, feedback, and processes we give every designer at Designation are able to be used for years and decades to come, so a designer can turn any work they produce into a case study anytime during their long career.
Remember: Hiring managers don’t look for designers with superpowers; they look for designers who are committed to designing better and better for as long as they practice design. And case studies are the absolute best metric for a designer to see how far they’ve come and how much they’ve learned, from tool to tool, project to project, and job to job.
Disclaimer: The information in this blog is current as of February 26, 2020. Current policies, offerings, procedures, and programs may differ.

About Flatiron School
Related posts.

Learn to Code Python: Free Lesson for Beginners

Courtney Pimentel: Sales Associate to IT

A Guide to Cloud Identity and Access Management (Cloud IAM)
Related resources.

Behind JavaScript, HTML/CSS, and SQL, Python is the fourth most popular language with 44.1% of developers. Check out this article on how you can learn this popular programming language for free.

"The most surprising thing about my time at Flatiron was discovering how much I could learn and grow in such a short amount of time."

Discover how Cloud IAM addresses the security challenges of cloud environments, ensuring granular access control for enhanced protection and efficiency.
Privacy Overview
5 inspiring web design case studies
A good case study makes for a top calling card; check out these examples.
The reality of web design is that once you've finished a project, you hopefully move straight onto the next one. However, every site you deliver is an essential portfolio piece that demonstrates your skills and abilities, and while you'll usually want to link to your recent work on your site, it pays to do the job properly.
Rather than simply grabbing a screenshot of a landing page and a link and adding it to your online portfolio, writing up an engaging case study on your work can be a lot more worthwhile. Case studies don't need to be lengthy essays; they just need to give readers a taste of your process and provide some insight into the challenges you've faced over the course of a web build and how you solved them.
They're a great way to let potential clients know how you work, and they can also provide inspiration for other designers and developers; here are five of our favourite recent examples. Make sure you also check out our top web design tips .
- How to write engaging case studies for your portfolio
01. Museum of Science and Industry of Chicago
For a really inspiring case study, it's hard to beat DogStudio's extensive piece chronicling its work for the Museum of Science and Industry of Chicago. The museum is a vast and highly respected American institution, and you can't help but get the impression that DogStudio was punching well above its weight when it won the commission to rethink and revamp its web platform, but as this case study reveals, it carried the job off with aplomb.
Packed with revealing wireframes, imagery and animations, it's a fascinating insight into a massive and challenging build that had to cater for more than five million online visitors wanting to do everything from buy tickets through to figuring out where to park and finding information about individual exhibits.
02. National Geographic: A Bear's-Eye View of Yellowstone

Sometimes it's better to show rather than tell. For this captivating look at Yellowstone National Park as seen by four bears fitted with camera collars and GPS, Hello Monday had a wealth of footage, data and expert analysis to work with. And rather than go into dry details of how it fitted everything together, it keeps things brief in its case study , providing a short outline of the project and deliverables before moving on to an entirely visual essay that demonstrates just how much work went into creating this digital feature.
As well as a good helping of footage and screenshots showcasing what the site's all about, what we really love about this study is a section dedicated to how Hello Monday stamped its own personality on the project, breathing extra life into the feature with animation, watercolour illustrations and pencil-drawn portraits of each bear.
Get the Creative Bloq Newsletter
Daily design news, reviews, how-tos and more, as picked by the editors.
03. Once Upon a Time in… Hollywood

Currently doing big business at the box office, Quentin Tarantino's Once Upon a Time in… Hollywood is a love letter to 1960's cinema that recreates its era with Tarantino's typical attention to detail. And to create an online presence that captured the feel of 1969 Hollywood as well as the film, LA agency Watson went the extra mile to create a digital magazine that feels like it could have come off a newsstand 50 years ago.
In this case study the Watson team explain not only the thinking behind the magazine and its pitch-perfect adverts, but also how they create a physical print run of the mag that got handed out at the premiere and first-night screenings, creating a whole other social buzz as movie fans posted shots of their magazine to prove that they were there. If you're looking for ideas on how to run a strong social campaign, there's some great material here.
04. British Red Cross

Kota's case study on its recent work with the British Red Cross is a clear and concise piece that provides valuable insight on the challenges – and opportunities – of working on a campaign with an institution with clear-cut brand guidelines that need to be adhered to. In the case of the British Red Cross's OneKindThing campaign, Kota had to create a platform that stood out from previous campaigns while staying within the society's pretty epic brand guidelines.
With a handful of images and a couple of paragraphs, Kota outlines how it managed just that, and also covers some of the technical hurdles that had to be overcome to deliver the finished site. The end result was well worth the effort, as the British Red Cross testimonial at the end of the case study reveals.
05. Stonewall Forever

To mark the 50th anniversary of the Stonewall Riots, an event that helped bring about the Pride movement, Stink Digital partnered with The LGBT Community Center to create Stonewall Forever, an immersive digital experience that features key narratives and previously unheard stories from LGBTQ+ history.
Stink Digital's case study explains how it built a living monument to 50 years of Pride, based in Christopher Park, New York, but accessible anywhere through a website or AR app, and goes into some detail of the challenges of creating a WebGL monument that consists of over 10,000 individual shards with post-processing effects, but still runs at 60fps, even on low-end devices.
Beyond the technical challenges, though, this is an absorbing and insightful piece on a project that explores life before, during and after the Stonewall Riots.
Related articles:
- The hottest web design trends of 2019
- How to refine your design portfolio
- Get the perfect website layout in 27 steps
Thank you for reading 5 articles this month* Join now for unlimited access
Enjoy your first month for just £1 / $1 / €1
*Read 5 free articles per month without a subscription
Join now for unlimited access
Try first month for just £1 / $1 / €1

Jim McCauley is a writer, performer and cat-wrangler who started writing professionally way back in 1995 on PC Format magazine, and has been covering technology-related subjects ever since, whether it's hardware, software or videogames. A chance call in 2005 led to Jim taking charge of Computer Arts' website and developing an interest in the world of graphic design, and eventually led to a move over to the freshly-launched Creative Bloq in 2012. Jim now works as a freelance writer for sites including Creative Bloq, T3 and PetsRadar, specialising in design, technology, wellness and cats, while doing the occasional pantomime and street performance in Bath and designing posters for a local drama group on the side.
Related articles

- mindful design
- student success
- product design
- ui/ux design
- watch me work
- design careers
- design inspiration
7 Best UX Case Study Generators (and how to use them)
If you're looking for UX case study ideas, topics or challenges, these UX case study generators can help you create portfolio pieces and improve your UX/UI skills. Here are some of the best ones and the pros and cons of using them.
What is a case study generator?
A UX Case Study Generator is a tool that serves up hypothetical UX design project ideas, problems, challenges or exercises that you can complete on your own to practice your UX skills or use to create UX Case studies and projects for UX/UI portfolio.

UX Case Study Generators
1. UX Challenge
UX challenge provides prompts and exercises that allows you to practice your problem-solving skills and create one-off projects for your portfolio. The Challenges presented here have been created by UX Designer Yachin and are based on real-world problems.
You can browse through a few different industries or categories on the homepage and then view the details of the project brief.
With more than 15 millions prompts available, there are lots of UX/Product Design prompts to choose from. To start, click on 'Product/UX' and then Click ‘New Challenge’. If you like certain elements of the brief you can lock those in place and then click New Challenge again to regenerate the unlocked parts until you find something you like.
3. Designercize
This fun arcade game-like interface lets you choose the level of difficulty and gives you a timer so that you can test your speed. While this tool doesn’t allow you to select a specific category, you can regenerate exercises until you find one that appeals to you.
4. UX Tools Challenges
If you need practice creating specific UX deliverables or applying certain user research methods this is a great option. You can browse through a number of UX prompt cards and click on a UX challenge to view a hypothetical scenario, instructions and tutorials on how to approach the challenges.
5. Uplabs Challenges
Uplabs hosts open design challenges that you can enter for prizes. They have deadlines in place and submissions are reviewed via voting. Check out their active listings to see on-going challenges and see the submission details and requirements. You can also view past challenges and try using them as practice on your for use as UX case study ideas.
6. 100Daysofproductdesign
100 Days of Product is a series of design challenges that help you learn to tackle specific problems that arise in UX and product design roles (such as running a design sprint) and prompts you to create deliverables around them. There is also a separate set of whiteboarding challenges that you can take in preparation for interviews.

7. DesignerUp
Our Product Design course is home to one the best UX and Product Design case study creators you can find...yourself! You get to ideate on original concepts yourself from scratch, is completely unique, perfectly suited to who you are as a designer, shows your process and ensures you stand out from the crowd. You also get free access to our portfolio builder for Notion that has helped our students easily create product design case studies and land their dream roles!
UX Case Study Usage
There are 4 main ways we recommend applying these generator prompts and challenges based on your goals:
Option 1: Self-Practice - Use these as practice for yourself to develop your problem-solving skills, thinking on your toes, learning to manage your time and refining your workflow. You don’t need to show it in your portfolio but you can share it on social media and other places to get some feedback and get into the hang of doing projects and getting to know your own timing and process.
Option 2: UX Case Study Creation - Use these for your UX portfolio to create UX case studies . Give yourself a deadline, deliberately choose a project and document the process as you go. Be mindful of the projects you choose and make sure that they align with your own unique positioning as a designer and with the opportunities you want to attract.
Option 3: Whiteboard Challenge - Work on the prompts in 45 min sessions using a whiteboard like Figjam to show and tell your process. Record your screen so that you can replay it and share it with others for critique. This video could even be an incredible addition to your portfolio to showcase how you think and solve problems on the fly.
Option 4: Take-home Exercise - To simulate an interview take-home challenge or test, you can tackle a prompt or brief over the course of 8-10 hours.
Pros and Cons of Using UX Case Study Generators
There a few pros and cons about using case study generators that you should know about:
If you can do them, so can everyone else
Firstly, remember that if you have access to these design challenges and briefs so do all the other designers. That means that there is a good chance your work might end up looking similar to their work if you’re not careful. If you want to stand out, try customizing the prompts and challenges and adding your own unique spin.
Treat them as real UX projects
If you plan to feature these UX case studies in your portfolio, make sure to treat them as real UX projects; not just hypothetical exercises. Conduct actual research, analyze your findings and document your process. This will go a long way in helping you differentiate yourself from those that simply complete the challenge at face value.
Not consider real-world experience
Keep in mind that these generated UX case study projects and prompts are not considered 'real-world or ‘real- work experience’ by employers, but rather self-directed projects. They are a good first step for new UX designers to start practicing their problem solving skills on their own and refining their UX design process, but you'll have to go the extra mile if you want to use them in your portfolio to impress during interviews.
Choose the right one
If you are looking to use these ideas as UX Case studies in your portfolio, I reccomend reading this article on how to choose which case studies you should do and how to Create a Magnetic UX Case Study that will actually get you noticed and hired.
Move into doing real projects
These projects are also no substitute for doing real-world projects such as things you design and build yourself, freelance jobs, client work or open-source projects. Generated prompts and challenges cannot introduce the ambiguity of business requirements, changing stakeholder needs and team dynamics that are most sought after in a hirable UX designer. So think of these as a stepping to help you jump into the real thing as soon as possible. Here are some examples of stellar UX/UI and Product Design portfolios that we love!
The best design resources, in your inbox
Tips, tricks, articles and freebies. It's all happening in the DesignerUp Newsletter. View the archives →
We'll only send the occasional email and promise not to spam.
© Copyright 2022 DesignerUp. All Rights Reserved.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
Unveiling the best design systems: Principles, examples, and key takeaways

Systems are all around us, even if we don’t notice them. They are the hidden engines behind banking, healthcare, and even the economy. A system is like a team of different parts that work together to achieve a specific purpose. They bring order to potential chaos and make things work better and faster.
Design systems play a significant role in helping teams create consistent and scalable solutions. A robust design system helps designers and engineers work more efficiently and implement design consistency across one or more products. By leveraging common components and patterns, they can get from problem to solution much faster. This article will talk about the principles that guide successful design systems and key takeaways from a few examples to help you develop your own.
What is a design system?
Guiding principles of effective design systems, essential components of design systems.
- Case study: Example 1 — Carbon design system
- Case study: Example 2 — Audi design system
- Case study: Example 3 — Polaris
Lessons learned from the best design systems
Implementing a design system: guidelines and considerations, design system tools and resources, measuring the impact of a design system.
A design system is a centralized repository of design principles, guidelines, and reusable components that aid in design decision making. Its purpose is threefold: to promote consistency, efficiency, and brand cohesion.
Serving as a single source of truth for a team or organization, a design system establishes standards and guidelines, giving designers and developers the building blocks necessary for efficient and scalable design creation. By providing a library of shared components, a robust design system can reduce redundant workflows and boost a team’s efficiency, making it relatively quicker to go from a problem to a high-fidelity solution.
Using a design system promotes consistent user experiences across a product or platform of products. It provides the visual elements necessary to ensure cohesive branding, which is important for making digital products and websites recognizable and memorable by users.
Design principles create the foundation of a successful design system. They are shared guidelines that set the standard for design excellence and support the team’s mission to create solutions that resonate with their users. Although design systems can each have unique principles tailored toward their context, here are a few overarching ones that can contribute to their effectiveness.
Design components and patterns should be able to work well together to create unified user experiences. Cohesive design systems integrate closely related elements that can maintain visual harmony, and consistent interactions, and address a range of user needs.
By focusing on closely related elements within the design system, designers will have the necessary tools to create consistent and intuitive user journeys.
Effective design systems are composed of reusable modular components, which gives designers the building blocks to create a variety of interfaces. Modularity provides versatility in how components are arranged and configured within a layout.
This approach saves time and effort, allowing designers to easily mix and match the modules to create different page layouts while ensuring a coherent design language throughout the product.
Scalability
A design system is a living entity that continues to evolve alongside the products. Adapting to changes in the scope and scale of products ensures that visual and functional experiences are maintained across screen sizes, devices, and platforms.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Using modular design principles, focus on frequently used components that can cover a range of scenarios by creating variants. This ensures that designers have the tools available to meet the requirements of any challenge.
Accessibility
Inclusive products allow fair and equal access to all users, regardless of their ability. Design systems should have inbuilt accessibility best practices that meet WCAG accessibility standards. This considers users who experience challenges while using products in a traditional way and might require assistive tools, such as a screen reader. Even though a design system contains accessible components and elements, designers must still consider how they work together in order to design a holistic, accessible experience.
Every design system has its own unique features or characteristics; however, there are several essential components that all design systems share. Let’s explore the purpose and application of design tokens, typography, color palettes, grid systems, UI components, and documentation within a design system.
Design tokens
Design tokens are variables used by designers and engineers to communicate the values of how things should be styled when building interfaces. These tokens point to important information such as colors, font styles, spacing, or animation.
Instead of providing fixed values to hard-code into a product, which can be hard to change, design tokens ensure that everything stays consistent and works well together, even if the values themselves change.
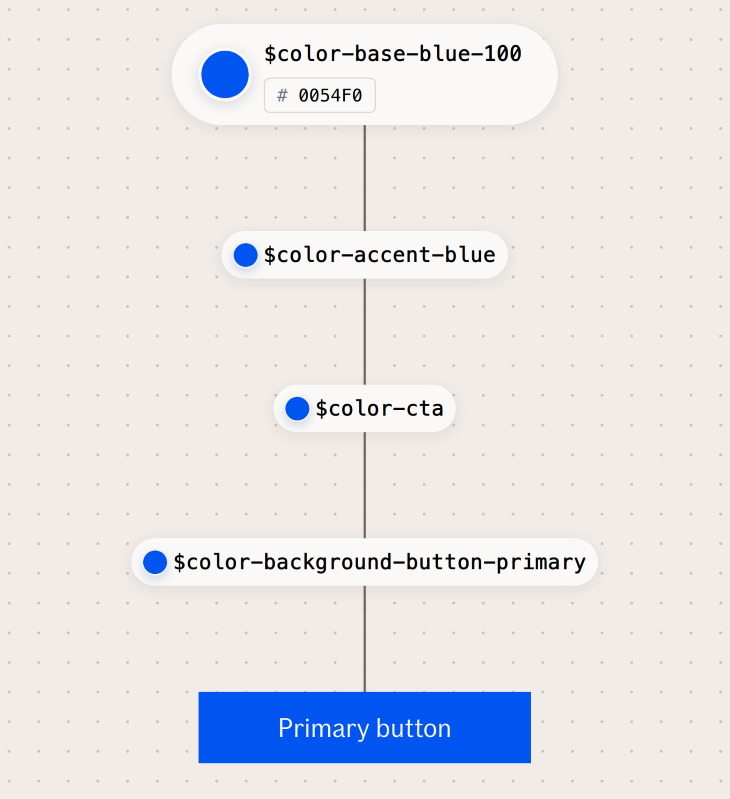
For example, a design token intentPrimary might point to a primary color value that is blue. But if the team decides to rebrand and change its primary color value to green, every element associated with the token intentPrimary will be updated to green, while the token remains unchanged. This example shows how design tokens keep design systems organized and easy to maintain.
A major component of brand and style guidelines, typography consists of selecting fonts that can be used for specific scenarios. Some key aspects of typography include choosing the brand’s typefaces, as well as defining font sizes, weights, and styles for various use cases, such as headings, subheadings, body text, or labels. Typography guidelines keep content visually organized by establishing a hierarchy and ensuring legibility across various platforms.
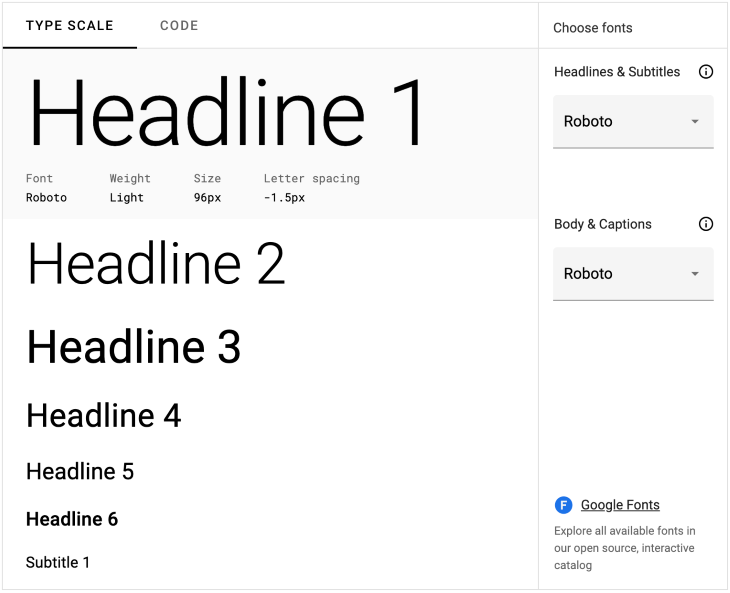
Color palette
A well-defined color palette within a design system has a number of benefits, including establishing brand identity, guiding user interactions, and maintaining visual consistency. A color palette generally consists of primary colors, secondary or tertiary colors, and background and text colors.

Before defining your colors, identify the different use cases and contexts in which color might be needed. Thoroughly test your color palette to ensure that there is sufficient contrast between background and text colors, and provide guidance on how colors should be used across different UI elements.
Grid systems
Grid systems help organize and align design elements to create cohesive layouts. A grid is a series of evenly spaced columns and rows that provide structure to designs. They can help position individual components in a way that makes information and content flow smoothly throughout a page.
A design system might have several grids to account for responsive layouts on different screen sizes, such as desktop, mobile, or tablet. The most common types of grid systems include column grids and modular grids.
A column grid system consists of a set number of columns that span the width of the page, providing vertical guidelines for visual alignment. A fluid column grid can adjust to the screen size, either by expanding the column widths or changing the number of columns used.
A modular grid system consists of columns and rows that break layouts into modules, providing more flexibility in how elements are arranged in the layout.
UI components
A design system would be incomplete without UI components, the fundamental building blocks of an interface. UI components are the elements users interact with on a page, ranging from common input controls like buttons, checkboxes, dropdowns, and radio buttons, to navigational components like search bars, breadcrumbs, pagination, and tags.
In addition, there are informational components like progress bars, tooltips, toast notifications, and modals, along with containers like accordions or panels. The components listed represent just a subset of the wide variety of UI components that contribute to a cohesive design system.
When selecting UI components for a design, it’s helpful to consider users’ mental models. Users have become accustomed to interacting with certain UI components in specific ways, so choosing the right component can help with familiarity, task completion, and ease of use.
Documentation
Finally, each design element and component should have detailed documentation to provide guidance on how to properly use them. Well-documented design systems communicate rules and best practices to aid designers and developers during the design and implementation process. It’s helpful to explain common use cases for each element, as well as how not to use them, to avoid inconsistencies in the final design.
Documentation can be communicated in the form of an overview, visual examples or use cases, and scenario explanations to give enough detail on how to use each element and avoid any confusion. It also includes working code for developers to implement and customize the element for their application.
Case study: Example 1 — Carbon design system
IBM’s Carbon is an open-source design system that provides a collection of reusable assets such as components, patterns, guidance, and code. Its primary goal is to build efficiency and consistency in the design process, giving designers a comprehensive toolkit they can leverage in their workflow. This saves designers time from building basic elements and instead allows them to focus on creating digital experiences that meet user needs.

Carbon offers a well-defined design language that includes typography, content, color palette, iconography, grid systems, motion, and accessibility guidelines. This enhances the brand identity across multiple products by defining specific visual guidelines.
Carbon also hosts a library of UI components, patterns, and data visualizations for various use cases. This ensures that design decisions are unified, leading to consistent user experiences across multiple products. Each of the base elements leaves room for customization, which allows projects to scale well as the scope evolves. This modular approach gives designers the flexibility to design for any scenario.
As an open-source design system, Carbon facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing, encouraging contributions back to the design system. This leads to continuous improvement and has a direct impact on IBM’s projects, ensuring consistent and cohesive user experiences. Also, Carbon’s focus on accessibility shows its commitment to inclusive design, which empowers designers and developers to create accessible experiences for all users, regardless of their abilities.
Case study: Example 2 — Audi design system
The Audi design system highlights its focus on speed, consistency, and quality for development across all Audi products. The design system was created to support designers and developers to build products efficiently that meet the evolving needs of their customers.
The design system acts as a single source of truth for Audi’s global product teams. Its products range from websites to in-vehicle applications, each with unique user interface requirements. Their design system offers a library of brand identity guidelines and components to ensure consistent branding and user experience regardless of the platform.
Efficiency is a common theme across design systems, and Audi’s design system aims to enhance the speed of asset creation by giving designers access to reusable components. By removing the need to recreate basic elements, designers are able to focus on innovation and quickly design pages by leveraging and customizing Audi’s purpose-built components and patterns.
Each of the UI components provides usage guidelines, as well as variations that cover different states and use cases. The documentation includes available properties for developers to understand how to customize each component.
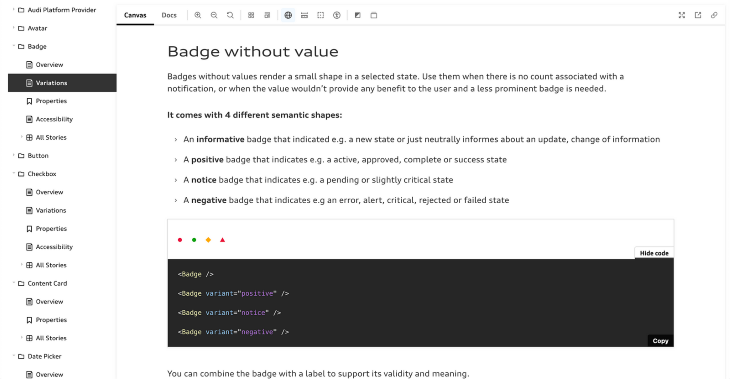
Audi emphasizes accessibility by providing WCAG and WAI-ARIA guidelines, as well as additional web accessibility resources for designers and developers to follow, ensuring that its final products allow equal and fair access to all users.
Case study: Example 3 — Polaris
Polaris is Shopify’s design system, built to guide app developers and designers in creating outstanding merchant experiences for the Shopify admin. Its focus is on enabling designers and developers to create apps that add functionality to the Shopify admin experience.

Shopify emphasizes that “Polaris is the floor, not the ceiling,” meaning that designers should use the design system as a foundation without limiting their creativity. They recommend focusing on solving problems first rather than worrying about consistency, which will come later. Polaris is meant to provide the building blocks with the added option to contribute back to the design system if a gap exists.
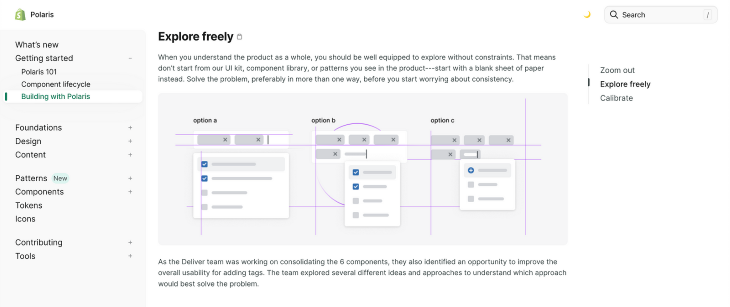
One of Polaris’ standout features is its robust content guidelines. It provides rules and best practices around actionable language, alternative text, error messages, and even grammar to ensure that the way copy is worded maintains the brand’s tone of voice and way of communicating with its users. The Do’s and Don’t’s are a great method for providing examples while explaining usage guidelines.
Polaris conveniently lays out the different variants of each UI component across the top of the page to allow users to easily view and compare to decide on the best one for their application. This convenience enhances the efficiency within a designer’s workflow, allowing them to quickly make informative design decisions.
Its icon library is easily searchable with each icon associated with multiple tags, allowing users to quickly find visual elements without knowing the specific name. It provides guidance for both designers and developers on how to access and use the icons, further enhancing their workflow efficiency.
From exploring these design systems, there are common themes and best practices that can be applied when developing your own. Some of the core principles include efficiency, consistency, open collaboration, accessibility, and clear documentation. These principles can be applied to small and midsize businesses (SMBs) to improve design and development processes.
Enhancing workflow efficiency
All three design systems emphasize the importance of efficiency in design and development. The main goal of any successful design system is to help product teams design and develop solutions faster without the need to recreate common assets. Providing reusable components saves time and effort by avoiding redundant work.
SMBs often have little resources allocated to development as they try to maintain a lean approach. By leveraging a design system, they can build efficiency into their workflow by speeding up product development and ultimately saving time and money that can be invested in other areas of the business.
Keeping experiences consistent
Consistency is another common theme of successful design systems. The purpose of a design system is to ensure that teams develop consistent experiences across all their products so that customers can quickly familiarize themselves with their tools.
Consistency is key in preventing user confusion, especially for SMBs that are in the early stages of customer adoption. This can help users quickly understand and see the value of a product without being concerned about its usability.
Contributing back to the design system
Carbon and Polaris are open source design systems that encourage contributions from the community. Design systems are considered a foundation to start building from but may have gaps that don’t address specific use cases or customer needs.
SMBs often have to adapt to changing customer requirements as they learn more about their users. Thus, their design system might not contain the necessary elements for building robust solutions.
A design system shouldn’t limit a team’s creativity by being too prescriptive, but rather spark ideas and allow for innovation. It should leave room for flexibility and scalability, especially for a small team that is growing quickly. By fostering a culture of open collaboration, design and development teams can continuously improve the design system.
Prioritizing accessibility and inclusive design
All three design systems prioritize accessibility by providing guidelines for designers and developers to build accessibility into their solutions. This ensures that product teams are considering users with disabilities creating products that are usable by all individuals.
Accessibility should be incorporated early into the development process instead of treated as an afterthought. SMBs can benefit from designing accessible products to help them reach a broader audience. It’s important to note that investing in accessibility early on can prevent teams from accumulating design debt and having to address accessibility issues later.
Implementing your own design system can seem like a daunting task. Here are practical guidelines and considerations for design system adoption, collaboration, documentation, and maintenance.
Before you jump ahead, first understand why your team needs a design system. This includes identifying any business goals and user needs that the design system would align with, such as improved designer efficiency and consistent user experiences across products. Communicating these benefits to stakeholders, such as product and development teams, can help with team adoption so that stakeholders are on board and aware of the design system’s existence.
Then, define the scope of your design system by outlining the essential elements and components that your team needs. Collaborate with your cross-functional partners, including design, development, product, and content, throughout this process to ensure alignment across teams and cover various requirements.
A guideline to consider is that proper documentation will lead to consistent experiences. It also takes the guesswork out of the team’s workflow, further enhancing their efficiency to get to results quicker. Even with limited resources, SMBs should focus on providing concise and clear documentation that outlines how to use design system elements. Investing the time and effort to document a design system clearly can lead to smoother implementation and avoid any confusion or misuse down the road.
Once your design system is up and running, provide thorough training to help your team use it effectively. Advocate for its adoption, but implement it gradually to avoid disrupting existing workflows and committing drastic product changes that might overwhelm users.
Maintaining a design system ensures that it evolves with changing customer needs and business objectives. It can be helpful to establish a regular cadence of feedback to gain input from team members in order to continuously refine the design system. Encourage team members to contribute back to the design system in order to fill gaps in the experience. Design system office hours are also a great way to broadcast any new changes or fixes to the design system components.
Many companies use Figma as their main design tool, so it’s a no-brainer to also use it to host design system assets. Teams can create a centralized library of reusable assets, including component variants and design tokens for designers to easily leverage in their Figma files.
Figma is a collaboration tool, which is perfect for enabling multiple team members to work in real time on the design system, speeding up development and ensuring everyone is aligned. Figma recently introduced Dev Mode, which allows developers to quickly inspect and translate designs to code, further accelerating design system adoption.
A popular open source tool for developing UI components within a design system is Storybook. Its main feature is the ability to build UI components in an isolated sandbox environment, which enables developers to render different variations of a component by using props and mock data. This reduces the need to spin up the entire app to test the component, saving substantial development time.
Storybook can be used to maintain documentation for how UI components behave and interact. The platform is interactive, allowing users to test out various use cases for each UI component. It also supports collaboration by allowing teams to discuss feedback during the design system development process.
Zeroheight is a centralized platform for design system hosting and documentation. It allows teams to create organized and interactive style guides, component libraries, and guidelines. Zeroheight ensures that design documentation remains up-to-date as components and guidelines evolve, making it easier to communicate changes across teams.
It also has inbuilt integrations with other design system tools, including Figma and Storybook, which help automate the workflow from design to code. Teams can import their assets from Figma and display developer resources for each component all in the same place as their design system documentation.
After your design system is implemented and teams have adopted its usage, it’s important to evaluate the impact and effectiveness that it has on your business to understand which areas are working or need improvement. The impact of a design system can be assessed by evaluating a combination of quantitative metrics and qualitative insights. This will result in a broader understanding of its performance.
In terms of quantitative metrics, it can be useful to track:
- The number of projects that use design system tokens and components
- The number of components used in each project
- The frequency of each component used across projects
These metrics will give you an idea of adoption rates across the organization, as well as which components are the most valuable to your teams. This can help in measuring which areas of the design system are most successful and which ones might need improvement.
On the other hand, qualitative insights offer a more human perspective. By gathering feedback through surveys and testing, you can begin to uncover the challenges that your team faces when using the design system and what can be done to alleviate these pain points. Continue to iterate and gather feedback in an iterative loop to improve your design system, which will lead to further adoption and success.
Setting measurable goals can help craft a clear understanding of how to improve your design system. These goals can cover things such as reduced design time, improved consistency, and increased user satisfaction. Achieving a successful design system requires an ongoing commitment to collaborate with your team: listen to their feedback and adapt to changes. The resulting value will benefit both your team and users in a significant way.
Conclusion and key takeaways
Design systems are essential for achieving design consistency and scalability in products. They also play a big role in enhancing efficiency in product development workflows. Design systems offer centralized repositories of guidelines and components, driven by principles like cohesion, modularity, scalability, and accessibility. These principles can apply to businesses of all sizes, including SMBs looking to streamline design processes and enhance user experiences.
For designers and teams interested in developing their own design systems, start by collaborating with cross-functional partners to understand its purpose and scope. Then, communicate its benefits to stakeholders so that everyone is on board.
As your team gradually adopts the design system, remember to maintain clear documentation and gather feedback from them. Using tools like Figma, Storybook, or Zeroheight can help you manage and broadcast changes to the design system as it evolves. By continuously tracking the success metrics of your design system, you can identify areas that are lacking and make the necessary improvements that your team and users will benefit from.
LogRocket : Analytics that give you UX insights without the need for interviews
LogRocket lets you replay users' product experiences to visualize struggle, see issues affecting adoption, and combine qualitative and quantitative data so you can create amazing digital experiences.
See how design choices, interactions, and issues affect your users — get a demo of LogRocket today .
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #design systems

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
What is DesignOps? The essentials of DesignOps
DesignOps is a set of best practices and principles that aims to streamline the effectiveness of design teams.

Using Zeplin for design handoff: How does it compare to Figma Dev Mode?
Let’s compare Zeplin with Figma Dev Mode to find out which suits design handoff better for your software product team!

Tips for creating a top-tier UX design portfolio in 2024
Here are some tips to help you create an effective UX design portfolio to get past the recruiter’s line and land the interview.

Using AI in accessibility: What can we do with AI?
AI can help make your designs more accessible to people with disabilities by automating tasks, such as captions, image descriptions, and more.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
HYPOTHESIS AND THEORY article
This article is part of the research topic.
Using Case Study and Narrative Pedagogy to Guide Students Through the Process of Science
Molecular Storytelling: A Conceptual Framework for Teaching and Learning with Molecular Case Studies Provisionally Accepted

- 1 School of Interdisciplinary Arts and Sciences, University of Washington Bothell, United States
- 2 Institute for Quantitative Biomedicine, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, United States
- 3 Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey,, United States
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Molecular case studies (MCSs) provide educational opportunities to explore biomolecular structure and function using data from public bioinformatics resources. The conceptual basis for the design of MCSs has yet to be fully discussed in the literature, so we present molecular storytelling as a conceptual framework for teaching with case studies. Whether the case study aims to understand the biology of a specific disease and design its treatments or track the evolution of a biosynthetic pathway, vast amounts of structural and functional data, freely available in public bioinformatics resources, can facilitate rich explorations in atomic detail. To help biology and chemistry educators use these resources for instruction, a community of scholars collaborated to create the Molecular CaseNet. This community uses storytelling to explore biomolecular structure and function while teaching biology and chemistry. In this article, we define the structure of an MCS and present an example. Then, we articulate the evolution of a conceptual framework for developing and using MCSs. Finally, we related our framework to the development of technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge (TPCK) for educators in the Molecular CaseNet. The report conceptualizes an interdisciplinary framework for teaching about the molecular world and informs lesson design and education research.
Keywords: Molecular education, Case studies, Technological pedagogical and content knowledge (TPCK), Molecular structure and function, molecular visualization, Bioinformatics education, conceptual modeling
Received: 31 Jan 2024; Accepted: 23 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Trujillo and Dutta. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Prof. Caleb M. Trujillo, University of Washington Bothell, School of Interdisciplinary Arts and Sciences, Bothell, United States
People also looked at

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
After working with many designers throughout my own career and helping many more build their job-ready portfolios, there are a few designers that I keep coming back to for inspiration and some that are inspiring a new generation of UI/UX and Product Designers to enter the field.. I've chosen 10 of our favorite UI/UX and Product Designers—a colorful tapestry of digital product architects that ...
11 Best UX Case Studies for Designers. The best way to understand what a good case study looks like is to go over other examples. Each of these UX case study examples shows a designer's insights, basic skills, and other designers' lessons learned through their experience. 1. Promo.com web editor.
5. Perfect Recipes App by Tubik. Here we have a UX case study for designing a simple mobile app for cooking, recipes, and food shopping. It aims to step away from traditional recipe apps by creating something more universal for users who love cooking with extended functionality.
All good case study designs will include a combination of photo, video, and illustrations or charts to tell a story of their clients' success. Rather than just relying on text, these visual aids back-up any claims being made as well as visually capturing the attention of readers. They are laser focused.
This means the normal rules of design apply. Use fonts, colors, and icons to create an interesting and visually appealing case study. In this case study example, we can see how multiple fonts have been used to help differentiate between the headers and content, as well as complementary colors and eye-catching icons.
Really juicy UX case studies. Pendar goes into great detail about his UX design process on every one of his projects, presenting the problem and the challenges each presented. Looking through his UX design case studies and the hypotheses the team came up with around the product problem, make for a fascinating and educational read.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
About. Discover an expertly curated collection of 20+ inspirational UX/UI design case studies that will empower you to create outstanding case studies for your own portfolio. Comprehensive end-to-end case studies covering research, ideation, design, testing, and conclusions. Perfect for designers building portfolios and looking for inspiration ...
Superhuman onboarding. Trello onboarding. Sleepzy onboarding. Duolingo retention. Calm referrals. Spotify onboarding. Spotify vs Apple. See exactly how companies like Tinder, Airbnb, Trello, Uber and Tesla design products that people love. One new user experience case study every month.
Discover why it's important to tell a story in your case studies. How to Approach UX Case Studies. Recruiters want candidates who can communicate through designs and explain themselves clearly and appealingly. While skimming UX portfolios, they'll typically decide within 5 minutes if you're a fit.So, you should boost your portfolio with 2-3 case studies of your work process containing ...
The best way to write a case study is to tell it like a story. This way, your case studies become a vessel through which recruiters can imagine a future working with you, since they get to experience and understand exactly how you solve a design problem. Your recruiters will also enjoy the familiarity and structure of a story arc, and they'll ...
Now that you know why case studies are so important, here is what you need to know to design a top-notch case study for your next client! . 1. Understand Your Client's Needs. . It's always a good idea to make sure that you really understand the message your client is looking to display with their case study. .
This case study from Ueno is agreat example on how to write and design a case study for a web project. Read case study. Curated design portfolio inspirations and case studies. Delivered every Monday. Just do it! Learn and improve your product skills with real-world portfolio examples.
One of those tools is UXfolio, our portfolio builder that makes the whole process faster and easier. Obviously, these 8 tips apply regardless of the tool you are using to build your product designer case studies. 1. Inject your personality into your case studies. Showing personality in a product design portfolio, case study, or resumé can be ...
2. GnO Well Being - Branding, Web Desing & UX. Designer: Marina Yalanska and Olga Zakharyan. Case Study: GnO Well Being. This is a creative illustration website that presents and sells a weighted designer blanket that helps you get a good night's sleep, the first step to good health and a better life.
2. Build credibility. In case studies, designers often include the name of the business, client, or project they've worked on, building credibility by providing real-world examples of their past work. You can even add testimonials and reviews to highlight positive feedback directly from those you've worked with. 3.
Here are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward. Reading Time 7 mins. When done right, case studies are seriously complex and represent hundreds of hours of design work. At their start, they can feel like a disorganized ...
1. By bestfolios.com — collecting the best designer portfolio websites, resumes and design resources. 1. Uber Scooters Platform. By Bre Huang, Product Designer at Uber. Click to see full study ...
75 Instructive Design Case Studies. Unlike other industries, the web design and development community are all about sharing knowledge and experience. We are very lucky to be part of such a great and useful learning environment, and it is up to us to embrace it — to embrace our learning experiences, and also to embrace our ability to share.
As Adam explains, an enterprise design system is a system of best practices, reusable design elements, processes, usage guidelines, and patterns that help reinforce the brand, improve the UX design process, and optimize the user experience. ... Design System Case Studies.
Make sure you also check out our top web design tips. How to write engaging case studies for your portfolio. 01. Museum of Science and Industry of Chicago. DogStudio took on a massive job with this site, and delivered (Image credit: DogStudio) For a really inspiring case study, it's hard to beat DogStudio's extensive piece chronicling its work ...
UX Case Study Usage. There are 4 main ways we recommend applying these generator prompts and challenges based on your goals: Option 1: Self-Practice - Use these as practice for yourself to develop your problem-solving skills, thinking on your toes, learning to manage your time and refining your workflow.
Source: Carbon design system Case study: Example 2 — Audi design system. The Audi design system highlights its focus on speed, consistency, and quality for development across all Audi products. The design system was created to support designers and developers to build products efficiently that meet the evolving needs of their customers.
UX/UI Design and Artificial Intelligence — Case study. A collaboration with the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), put its mark on my final project for the Ironhack bootcamp. My team's task was to re-design the interface of a platform that uses AI to cluster audio recordings from the Amazon rainforest.
The concept of Bento UI, emerging in the design world, is directly inspired by the famous Japanese lunch boxes, bentos. These are known for their ability to compactly and aesthetically organize a variety of foods within a confined space. This culinary inspiration is transposed into user interface design, where Bento UI aims to structure ...
Our 10 engaging newsletter ideas for your small business. 1. Post a job alert. Use your email list to find ideal candidates for a job position you're looking to fill. Job openings are great ...
Molecular case studies (MCSs) provide educational opportunities to explore biomolecular structure and function using data from public bioinformatics resources. The conceptual basis for the design of MCSs has yet to be fully discussed in the literature, so we present molecular storytelling as a conceptual framework for teaching with case studies. Whether the case study aims to understand the ...
5. LocaliQ's Website Grader for free SEO audits. If you need a quick, easy-to-understand website audit, LocaliQ's Free Website Grader will do the trick. Even though it's a free tool, you get a lot of information. For example, in your report you'll see: Technical SEO: Site security, site speed, mobile optimization.