- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]


Research Paper vs Research Proposal v Thesis: 5 differences

Some students may be confused concerning the difference between a research proposal and a research paper. This is understandable if it is the first time a student is writing either of the two types of research.
This is because some students may have been used to writing essays that take a much simpler format and approach in writing the content.
Therefore, if you are one of those students who are not sure of the difference(s) between a research proposal and a research paper, do not worry.

Research Proposal vs Research Paper
Now, what is the difference between a research proposal and a research paper? This section will elaborate on the differences between the two while exploring their comparisons with other types of academic papers.
A research proposal is a preliminary paper that is submitted to the instructor so that the researcher can be granted permission to proceed with the actual research paper. It proposes what the research project will be all about. On the other hand, a research paper is an academic piece that presents what one found out after in-depth research on a specified topic.
Let us understand each of them in deeper detail. What this means is that a research proposal “proposes” what the researcher will be going to tackle within the main paper.
As such, they should clarify or provide details as to what the main research paper will be tackling the topic, the expected hypothesis and claims, the type of studies used, the methodologies, the population in which the research will be conducted, and the expected implications of the research.
A research proposal needs to demonstrate the importance of the actual research to the discipline and society in general. Without this, then the research proposal would not pass, and no actual research will be conducted to produce the research paper.
When it comes to the actual research paper, it can be regarded as the work that will be produced after the research proposal has been approved and a research go-ahead has been granted to the researcher(s).
Therefore, the research paper will be a complete paper that reports what has been researched, the findings of the studies conducted, and the discussions concerning the findings. It will not be like a research proposal that will be proposing things that will happen in the future.
It should be noted that this is a major or simplified difference between a research proposal and a research paper. The next sections of this article will discuss in detail the main differences between them, plus their differences with other types of papers.
Need Help with your Homework or Essays?
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal can be regarded as an academic preliminary request for research that is meant to be submitted to the instructor before the writer or student is given the go-ahead to proceed with writing the research paper.

What this means is that a research proposal will ‘propose’ what the research paper will be all about and the merits of the research to the discipline and society in general.
Therefore, a research proposal is written before a research paper is written.
If a research proposal fails to be approved, then the researcher or student will not be allowed to write a research paper.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper can be regarded as a formal academic piece written by students or researchers after the instructor or academic committee has approved their research proposals to tackle a particular research topic in a specific discipline to find solutions through qualitative and/or quantitative studies.
Therefore, a research paper is a long piece of academic writing that utilizes the research proposal’s topic and claims to test a hypothesis. The research paper aims not to propose a study but to conduct an actual study that would benefit the discipline and society.
Differences between a Research Proposal and a Research Paper
As we have noted above, there is a big difference between a research proposal and a research paper. Below are some of the major differences between the two:
1. The Time of Being Written
One of the most notable differences between a research proposal and a research paper is that a research proposal is written before a research paper. This is because a research proposal is meant to ‘propose’ what the writer, student, or researcher is going to write in their main research paper. As such, a research proposal has to be approved before a research paper is written.
The second difference between a research proposal and a research paper is the purpose of the two pieces of writing. The main aim of a research proposal is to present to the instructor what will be tackled within the research paper.
On the other hand, the purpose of a research paper is to academically present research that has already been conducted by the writer or the researcher. A research paper is a final presentation concerning a particular topic.
3. Use of Grammatical Tenses
Another difference between a research proposal and a research paper is that while the proposal uses future tense (will be, shall be, and so on), a research paper uses a grammatical tense that describes things that have already been done.
This is because the research has already been conducted. When it comes to the analysis of the findings and discussions, the present tense can be used because things are unfolding.
4. Context and Audience
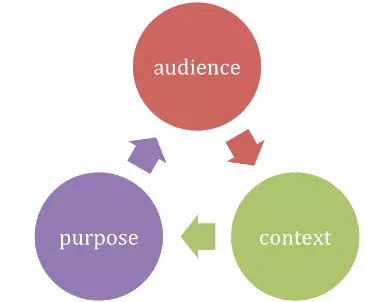
The context of a research proposal is to present “proposals” of ideas that will be used to build upon a research paper.
As such, the audience will be the instructor or a research committee that is meant to gauge the relevance of the proposal to the topic.
On the other hand, a research paper is not formulated to lead to research but to describe the research.
Therefore, a research paper will target the instructor and any reader who is interested in the topic, discipline, or study.
Finally, the difference between a research proposal and a research paper is the length. A research proposal is considerably shorter compared to a research paper because of the content. A research paper will contain a lot of detail concerning the topic, the type of research, the findings, discussions, and conclusions because research has already been conducted.
We can Write your Papers! No Plagiarism
Get that A on your next essay assignment without the hassles. Any topic or subject. 100% Plagiarism-Free Essays.
Difference Between a Thesis and a Research Proposal
The main difference between a thesis and a research proposal is their purpose. A thesis is a formal academic piece of writing done on a particular topic that has not yet been explored. This is why a thesis has a prospectus stage where the student has to consult with a committee. On the other hand, a research proposal proposes the topic and the research to be done.
Therefore, a research proposal will not require a prospectus stage or a committee, and it can be written by any student within an institution of higher learning.
However, an undergraduate student can also write a research proposal to their instructor to ‘propose’ a research paper.
Difference Between a Thesis and a Research Paper
The major difference between a thesis and a research paper is that a thesis is a longer and more detailed piece of writing that is written by post-graduate students, while a research paper will be comparatively shorter with fewer details because undergraduate students mostly write it.

As such, a thesis can take a very long time to write, for example, 20 years if it tackles socio-economic or environmental issues that may take a lot of time to unfold.
However, a research paper takes a shorter time to write. It may take even 3 months to complete a research paper because it does not explore very complex issues.
The length also matters. A thesis is longer than a research paper by far. Check out the optimal length for a thesis compared to a research paper length and notice the difference.
Check out the guide on the differences in thesis vs theory vs hypothesis to get a wider idea of the three. This will help you know how these three are applied in a dissertation of a research paper.

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Someone to format my paper in APA for me
How to Write and Cite Sources in APA and MLA for Term Papers

Background Information in an Essay
Background Information in an Essay: How to Write and Example

research paper length
How Long Should a Research Paper be: From Intro to conclusion

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
The Difference Between Research Papers and Proposals
Research papers and proposals are two distinct yet closely related writing projects that can be confusing to differentiate between. This article seeks to explore the similarities and differences between research papers and proposals in order to better inform readers of their respective purpose, style, scope, structure, audience, and more. By the end of this article readers will have a greater understanding of both types of written work so they may make an informed decision about which project is best suited for their needs.
I. Introduction to Research Papers and Proposals
Ii. definition of research paper, iii. components of a research paper, iv. definition of proposal, v. components of a proposal, vi. differences between a research paper and proposal, vii. conclusion.
A World of Possibilities Research papers and proposals offer a window into the unlimited world of ideas. Whether it be delving into scientific discovery, exploring philosophical concepts, or uncovering ancient literature, these two forms of writing open up doors to new possibilities. But what exactly are research papers and proposals? While they share some similarities in terms of structure and purpose, there are key differences between them that should not be overlooked.
- Research Papers: typically involve an investigation process leading towards a synthesis report on any given topic – for example analyzing trends in poverty alleviation strategies worldwide.
- Proposals: focus more on offering solutions; often outlining various steps or processes needed to address particular issues – such as proposing changes within existing health care systems.
. It’s important to keep this distinction in mind when selecting which type is most suitable for your purposes.
A research paper is a type of academic writing that involves the use of scholarly sources and an analysis to investigate specific topics. Research papers often rely on primary or secondary data, such as surveys or experiments, to analyze and explain their findings. The resulting document provides new insights into a topic by examining existing information in a fresh way.
- Offers an initial exploration , providing possible solutions for further study.
The main components of a research paper, regardless of its subject or length, is the same. As such it is essential to understand what they are and how to include them in your work.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of your topic and explain why the issue you’re discussing matters. Additionally, be sure to note any gaps in knowledge that may exist regarding this particular topic so you can address these throughout the course of your paper.
- Literature Review: After providing background information on your chosen topic or problem area, conduct a thorough review of relevant literature from reliable sources. This will enable you to discuss current practices related to this field as well as explore various theories surrounding it.
A Proposal: An Overview
- At its core, a proposal is an offer of solutions to a particular problem.
- Proposals can come in many forms and for various purposes, but the basic structure remains the same across disciplines.
Therefore, when crafting a proposal you must demonstrate why your proposed plan not only provides a remedy but also brings value by outlining potential benefits as well as risks associated with the suggested solution. Additionally, explain who will benefit from this proposition (e.g., customers/stakeholders) and what resources are needed to implement such changes in order facilitate success. In addition to convincing others that they need your services/product/idea; effective communication goes hand-in-hand with successful selling. Use clear language and succinctly convey why this initiative would be beneficial and worth investing in.
A research proposal and paper are two distinct entities, although many individuals use the terms interchangeably. A research paper is a document that contains an analysis of data gathered from multiple sources on a particular topic. It must be well written with proper citations for any outside resources used in its composition. In contrast, a research proposal , while also including elements such as data collection methods and conclusions about the results of said methods, aims to persuade others to invest their own time or money into studying the same subject.
When constructing either type of document it’s important to consider all components necessary for successful completion:
- Problem Statement – Provides evidence that there is something worth exploring further.
- Literature Review – Examines previous studies related to your topic so you can place your work within larger context of existing knowledge.
- Research Methodology – Describes how you intend gather information; typically quantitative or qualitative approaches are employed.
Comparing a Research Paper and Proposal Research papers and proposals share certain elements, yet differ in purpose and execution. While both may involve extensive research, the former is generally focused on an existing topic or area of study while the latter endeavors to introduce a new concept. Below are some key points that differentiate between these two types of documents.
- A research paper , which can be based on primary sources such as interviews or surveys, typically begins with an introduction to its topic followed by analysis that supports it.
- In contrast, a proposal , often written for academic purposes like grant funding applications or college admissions decisions, provides specific information regarding what should be done in order to solve problems related to its subject matter.
. Generally speaking, this includes detailed descriptions about possible solutions along with any pertinent background data needed for evaluation.
In this research paper, the purpose was to compare and contrast a research proposal with an actual written research paper. Through exploring both topics in detail, it has been shown that there is a stark difference between them. A research proposal is more focused on providing an outline of what the researcher intends to accomplish whereas the completed project will go into far greater detail about each aspect of their study.
- Research Proposal : The primary aim of a proposal document is for approval by supervisors or academics; they are used as a tool for clarifying ideas and setting out clear objectives before any data collection takes place.
- Research Paper: This requires extensive work after approval has been given – from collecting relevant data to analysing results, all prior knowledge must be synthesised in order to form conclusions which can then be presented through writing.
In conclusion, this article has outlined the differences between research papers and proposals. Research papers are often used to explore a subject or answer questions through experiments and analyses while proposals attempt to present an argument for approval from another individual or organization. Knowing the distinction between these two forms of writing can help individuals better understand how best to approach their own projects and properly communicate with colleagues in academic settings.
How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
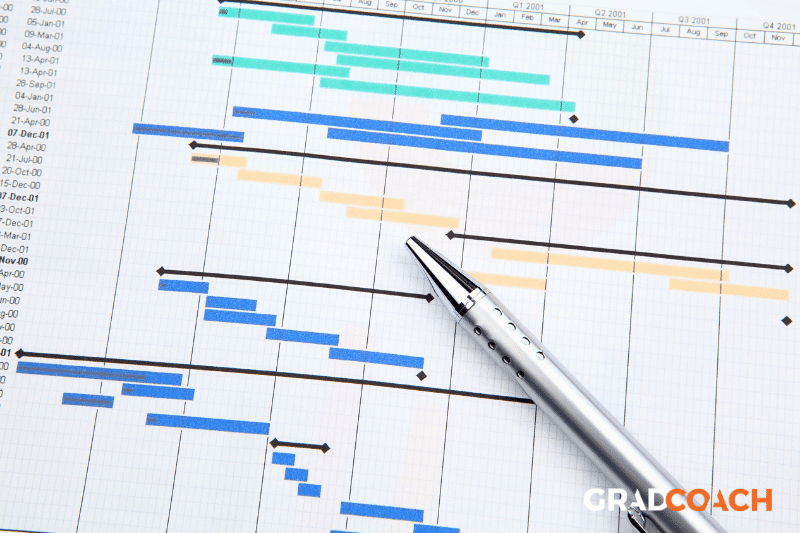
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
University Libraries
Writing a dissertation or thesis proposal, what is a proposal, what is the purpose of a proposal.
- Video Tutorials
- Select a Topic
- Research Questions
- Search the Literature
- Plan Before Reviewing
- Review the Literature
- Write the Review
- IRB Approval
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation or thesis.
In the graduate student timeline, the proposal comes after successfully passing qualifying or comprehensive exams and before starting the research for a dissertation or thesis.
Each UNT department has slightly different proposal requirements, so be sure to check with your advisor or the department's graduate advisor before you start!
- Examples of Proposals from UTexas More than 20 completed dissertation proposals are available to read at the UT Intellectual Entrepreneurship website.
- Dissertation Proposal Guidelines This document from the Department of Communication at the University of Washington is a good example of what you might be expected to include in a proposal.
The purpose of a proposal is to convince your dissertation or thesis committee that you are ready to start your research project and to create a plan for your dissertation or thesis work. You will submit your proposal to your committee for review and then you will do your proposal defense, during which you present your plan and the committee asks questions about it. The committee wants to know if your research questions have academic merit and whether you have chosen the right methods to answer the questions.
- How to Prepare a Successful Dissertation Proposal Defense Some general tips for a proposal defense from synonym.com
Need help? Then use the library's Ask Us service. Get help from real people face-to-face, by phone, or by email.
- Next: Resources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.unt.edu/Dissertation-thesis-proposal
Additional Links
UNT: Apply now UNT: Schedule a tour UNT: Get more info about the University of North Texas
UNT: Disclaimer | UNT: AA/EOE/ADA | UNT: Privacy | UNT: Electronic Accessibility | UNT: Required Links | UNT: UNT Home
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 11 November 2022.
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it’s about, how you’ll conduct it, and why it’s worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student.
A dissertation proposal should generally include:
- An introduction to your topic and aims
- A literature review of the current state of knowledge
- An outline of your proposed methodology
- A discussion of the possible implications of the research
- A bibliography of relevant sources
Dissertation proposals vary a lot in terms of length and structure, so make sure to follow any guidelines given to you by your institution, and check with your supervisor when you’re unsure.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: coming up with an idea, step 2: presenting your idea in the introduction, step 3: exploring related research in the literature review, step 4: describing your methodology, step 5: outlining the potential implications of your research, step 6: creating a reference list or bibliography.
Before writing your proposal, it’s important to come up with a strong idea for your dissertation.
Find an area of your field that interests you and do some preliminary reading in that area. What are the key concerns of other researchers? What do they suggest as areas for further research, and what strikes you personally as an interesting gap in the field?
Once you have an idea, consider how to narrow it down and the best way to frame it. Don’t be too ambitious or too vague – a dissertation topic needs to be specific enough to be feasible. Move from a broad field of interest to a specific niche:
- Russian literature 19th century Russian literature The novels of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky
- Social media Mental health effects of social media Influence of social media on young adults suffering from anxiety
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like most academic texts, a dissertation proposal begins with an introduction . This is where you introduce the topic of your research, provide some background, and most importantly, present your aim , objectives and research question(s) .
Try to dive straight into your chosen topic: What’s at stake in your research? Why is it interesting? Don’t spend too long on generalisations or grand statements:
- Social media is the most important technological trend of the 21st century. It has changed the world and influences our lives every day.
- Psychologists generally agree that the ubiquity of social media in the lives of young adults today has a profound impact on their mental health. However, the exact nature of this impact needs further investigation.
Once your area of research is clear, you can present more background and context. What does the reader need to know to understand your proposed questions? What’s the current state of research on this topic, and what will your dissertation contribute to the field?
If you’re including a literature review, you don’t need to go into too much detail at this point, but give the reader a general sense of the debates that you’re intervening in.
This leads you into the most important part of the introduction: your aim, objectives and research question(s) . These should be clearly identifiable and stand out from the text – for example, you could present them using bullet points or bold font.
Make sure that your research questions are specific and workable – something you can reasonably answer within the scope of your dissertation. Avoid being too broad or having too many different questions. Remember that your goal in a dissertation proposal is to convince the reader that your research is valuable and feasible:
- Does social media harm mental health?
- What is the impact of daily social media use on 18– to 25–year–olds suffering from general anxiety disorder?
Now that your topic is clear, it’s time to explore existing research covering similar ideas. This is important because it shows you what is missing from other research in the field and ensures that you’re not asking a question someone else has already answered.
You’ve probably already done some preliminary reading, but now that your topic is more clearly defined, you need to thoroughly analyse and evaluate the most relevant sources in your literature review .
Here you should summarise the findings of other researchers and comment on gaps and problems in their studies. There may be a lot of research to cover, so make effective use of paraphrasing to write concisely:
- Smith and Prakash state that ‘our results indicate a 25% decrease in the incidence of mechanical failure after the new formula was applied’.
- Smith and Prakash’s formula reduced mechanical failures by 25%.
The point is to identify findings and theories that will influence your own research, but also to highlight gaps and limitations in previous research which your dissertation can address:
- Subsequent research has failed to replicate this result, however, suggesting a flaw in Smith and Prakash’s methods. It is likely that the failure resulted from…
Next, you’ll describe your proposed methodology : the specific things you hope to do, the structure of your research and the methods that you will use to gather and analyse data.
You should get quite specific in this section – you need to convince your supervisor that you’ve thought through your approach to the research and can realistically carry it out. This section will look quite different, and vary in length, depending on your field of study.
You may be engaged in more empirical research, focusing on data collection and discovering new information, or more theoretical research, attempting to develop a new conceptual model or add nuance to an existing one.
Dissertation research often involves both, but the content of your methodology section will vary according to how important each approach is to your dissertation.
Empirical research
Empirical research involves collecting new data and analysing it in order to answer your research questions. It can be quantitative (focused on numbers), qualitative (focused on words and meanings), or a combination of both.
With empirical research, it’s important to describe in detail how you plan to collect your data:
- Will you use surveys ? A lab experiment ? Interviews?
- What variables will you measure?
- How will you select a representative sample ?
- If other people will participate in your research, what measures will you take to ensure they are treated ethically?
- What tools (conceptual and physical) will you use, and why?
It’s appropriate to cite other research here. When you need to justify your choice of a particular research method or tool, for example, you can cite a text describing the advantages and appropriate usage of that method.
Don’t overdo this, though; you don’t need to reiterate the whole theoretical literature, just what’s relevant to the choices you have made.
Moreover, your research will necessarily involve analysing the data after you have collected it. Though you don’t know yet what the data will look like, it’s important to know what you’re looking for and indicate what methods (e.g. statistical tests , thematic analysis ) you will use.
Theoretical research
You can also do theoretical research that doesn’t involve original data collection. In this case, your methodology section will focus more on the theory you plan to work with in your dissertation: relevant conceptual models and the approach you intend to take.
For example, a literary analysis dissertation rarely involves collecting new data, but it’s still necessary to explain the theoretical approach that will be taken to the text(s) under discussion, as well as which parts of the text(s) you will focus on:
- This dissertation will utilise Foucault’s theory of panopticism to explore the theme of surveillance in Orwell’s 1984 and Kafka’s The Trial…
Here, you may refer to the same theorists you have already discussed in the literature review. In this case, the emphasis is placed on how you plan to use their contributions in your own research.
You’ll usually conclude your dissertation proposal with a section discussing what you expect your research to achieve.
You obviously can’t be too sure: you don’t know yet what your results and conclusions will be. Instead, you should describe the projected implications and contribution to knowledge of your dissertation.
First, consider the potential implications of your research. Will you:
- Develop or test a theory?
- Provide new information to governments or businesses?
- Challenge a commonly held belief?
- Suggest an improvement to a specific process?
Describe the intended result of your research and the theoretical or practical impact it will have:
Finally, it’s sensible to conclude by briefly restating the contribution to knowledge you hope to make: the specific question(s) you hope to answer and the gap the answer(s) will fill in existing knowledge:
Like any academic text, it’s important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal.
Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing – commonly used styles include Harvard , Vancouver , APA , or MHRA . If your department does not have specific requirements, choose a style and apply it consistently.
A reference list includes only the sources that you cited in your proposal. A bibliography is slightly different: it can include every source you consulted in preparing the proposal, even if you didn’t mention it in the text. In the case of a dissertation proposal, a bibliography may also list relevant sources that you haven’t yet read, but that you intend to use during the research itself.
Check with your supervisor what type of bibliography or reference list you should include.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 11). How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/proposal/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

Thesis vs. Research Paper: Know the Differences
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents. This brief guide discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper.

This article discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. After all, both terms share the same domain, academic writing . Moreover, characteristics like the writing style, tone, and structure of a thesis and research paper are also homogenous to a certain degree. Hence, it is not surprising that many people mistake one for the other.
However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper
The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify.
Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final academic term. It generally consists of putting forward an argument and backing it up with individual research and existing data.
How to Write a Perfect Ph.D. Thesis
How to Choose a Thesis or Dissertation Topic: 6 Tips
5 Common Mistakes When Writing a Thesis or Dissertation
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Research Paper: A research paper is also an academic document, albeit shorter compared to a thesis. It consists of conducting independent and extensive research on a topic and compiling the data in a structured and comprehensible form. A research paper demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study along with strong analytical skills.
7 Tips to Write an Effective Research Paper
7 Steps to Publishing in a Scientific Journal
Publishing Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
How to Formulate Research Questions
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of a thesis and a research paper, it is time to dig deeper. To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart.
1. Writing objectives
The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk. Hence, it needs to exemplify the scope of your knowledge in your study field. That is why choosing an intriguing thesis topic and putting forward your arguments convincingly in favor of it is crucial.
A research paper is written as a part of a course's curriculum or written for publication in a peer-review journal. Its purpose is to contribute something new to the knowledge base of its topic.
2. Structure
Although both documents share quite a few similarities in their structures, the framework of a thesis is more rigid. Also, almost every university has its proprietary guidelines set out for thesis writing.
Comparatively, a research paper only needs to keep the IMRAD format consistent throughout its length. When planning to publish your research paper in a peer-review journal, you also must follow your target journal guidelines.
3. Time Taken
A thesis is an extensive document encompassing the entire duration of a master's or doctoral course and as such, it takes months and even years to write.
A research paper, being less lengthy, typically takes a few weeks or a few months to complete.
4. Supervision
Writing a thesis entails working with a faculty supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track. However, a research paper is more of a solo project and rarely needs a dedicated supervisor to oversee.
5. Finalization
The final stage of thesis completion is a viva voce examination and a thesis defense. It includes proffering your thesis to the examination board or a thesis committee for a questionnaire and related discussions. Whether or not you will receive a degree depends on the result of this examination and the defense.
A research paper is said to be complete when you finalize a draft, check it for plagiarism, and proofread for any language and contextual errors . Now all that's left is to submit it to the assigned authority.
What is Plagiarism | How to Avoid It
How to Choose the Right Plagiarism Checker for Your Academic Works
5 Practical Ways to Avoid Plagiarism
10 Common Grammar Mistakes in Academic Writing
Guide to Avoid Common Mistakes in Sentence Structuring
In the context of academic writing, a thesis and a research paper might appear the same. But, there are some fundamental differences that set apart the two writing formats. However, since both the documents come under the scope of academic writing, they also share some similarities. Both require formal language, formal tone, factually correct information & proper citations. Also, editing and proofreading are a must for both. Editing and Proofreading ensure that your document is properly formatted and devoid of all grammatical & contextual errors. So, the next time when you come across a thesis vs. research paper argument, keep these differences in mind.
Editing or Proofreading? Which Service Should I Choose?
Thesis Proofreading and Editing Services
8 Benefits of Using Professional Proofreading and Editing Services
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
How Much Do Proofreading and Editing Cost?
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Some students find it difficult to understand and write error-free coursework papers. So, it requires pouring multiple skills, attention, and energy to frame impressive coursework. Here we present few such tips for flawless coursework.

The American Psychological Association (APA) introduced the 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual in October 2019. This edition replaced the previous one, the 6th edition of the manual. Since then, several things have changed. The latest edition also updated the formatting of digital object identifiers (DOI) in APA Style. This article addresses when to include DOIs and uniform resource locators (URLs) in APA Style references.

The corpus research suggests that the most often used tenses in academic writing are the simple present, the simple past, and the present perfect. Then, what comes next is the future tense.


Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper: Unraveling the Distinction in 2023
Are you puzzled in the difference between Thesis and Research Paper? If yes, then have a close look at this blog post to explore everything about the difference between Thesis and Research Paper
In the realm of academia, students and researchers encounter various types of written assignments that require rigorous investigation and analysis. Among these assignments, the thesis and research paper are two common forms of scholarly writing.
While both contribute to the advancement of knowledge and demonstrate a student’s research capabilities, there are distinct differences between them in terms of purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length.
Understanding these differences is essential for students embarking on their academic journey or researchers seeking to make meaningful contributions to their respective fields.
By grasping the unique characteristics of a thesis and a research paper, individuals can navigate the academic landscape more effectively, align their research objectives, and tailor their writing to meet the specific expectations of each form of scholarly communication.
In this discussion, we will delve into the dissimilarities between a thesis and a research paper, shedding light on the distinct purposes they serve, the scope of their investigations, the level of originality they demand, the structure they adhere to, the evaluation criteria they face, and the length of time they require for completion.
By examining these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how a thesis and a research paper differ, allowing students and researchers to approach these academic assignments with greater clarity and confidence.
Whether you are a student embarking on your undergraduate or postgraduate journey, or a researcher striving to contribute to the scholarly discourse in your field, gaining a thorough understanding of the differences between a thesis and a research paper will serve as a valuable guide in effectively formulating research questions, conducting comprehensive investigations, and presenting your findings in a manner that aligns with the expectations of your academic community.
So, let us explore the unique characteristics that set a thesis and a research paper apart, empowering you to navigate the academic landscape and engage in scholarly pursuits with distinction and purpose.
Definition and Purpose of a Thesis
Table of Contents
A thesis is a significant academic document that showcases a student’s in-depth understanding of a particular subject and their ability to conduct independent research.
It is a formal written work that presents original findings, arguments, or theories, aiming to contribute new knowledge to the academic community. A thesis is typically pursued as a requirement for obtaining a higher academic degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D.
The purpose of a thesis is multifold. Firstly, it serves as a demonstration of the student’s comprehensive understanding of the chosen field of study. It requires an extensive exploration of the existing literature, theories, methodologies, or experiments related to the research topic.
By delving deeply into the subject matter, a thesis allows students to showcase their analytical and critical thinking abilities, as well as their proficiency in synthesizing and evaluating complex information.
Secondly, a thesis aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge within the specific academic discipline. It demands original research and the identification of a research gap, which the student then strives to fill through their investigations.
By conducting thorough research, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing meaningful conclusions, a thesis can offer new insights, propose novel theories, or develop innovative methodologies. Through their contribution, students endeavor to advance the understanding and knowledge within their field of study.
Lastly, a thesis serves as a requirement for obtaining a higher academic degree. It demonstrates the student’s research capabilities and scholarly competence, validating their readiness to contribute to their chosen field as a qualified professional or researcher.
Successful completion of a thesis signifies the mastery of research skills, the ability to work independently, and the capacity to engage in academic discourse.
Overall, a thesis represents a significant academic achievement, reflecting the culmination of a student’s academic journey and their dedication to expanding knowledge within their field. It serves as a testament to their intellectual capabilities, research prowess, and their potential to make meaningful contributions to their respective disciplines.
Definition and Purpose of a Research Paper
A research paper is a scholarly document that presents the results of a study or investigation conducted by a researcher or a group of researchers. It is a written work that focuses on addressing a specific research question, exploring a hypothesis, or investigating a particular topic within a given academic field. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge by presenting new insights, analyzing data, or providing a critical analysis of existing information.
Research papers are essential in various academic disciplines, including sciences, social sciences, humanities, and more. They serve as a means to communicate research findings, share knowledge, and engage in scholarly discussions.
Through research papers, researchers aim to advance understanding, challenge existing theories or assumptions, or propose new perspectives on a particular subject.
The primary purpose of a research paper is to contribute to the existing knowledge within a specific field of study. Researchers conduct a thorough review of relevant literature and studies to identify gaps or areas that require further investigation.
They formulate a research question or hypothesis and design a methodology to collect and analyze data that can answer the research question or test the hypothesis. The research paper then presents the findings, interpretations, and conclusions derived from the analysis of the collected data.
Research papers also play a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge. They provide a platform for researchers to share their findings with the broader academic community.
By publishing research papers in academic journals, presenting them at conferences, or sharing them through other scholarly channels, researchers contribute to the ongoing conversations within their field. Other researchers can build upon the findings, validate or challenge the results, and collectively advance knowledge in a collaborative manner.
Moreover, research papers help researchers develop critical thinking skills, enhance their research methodology expertise, and contribute to their academic and professional growth.
Engaging in the research process, from formulating a research question to conducting data analysis, strengthens researchers’ abilities to think analytically, critically evaluate information, and draw meaningful conclusions. Research papers also provide opportunities for researchers to develop their academic writing skills, allowing them to effectively communicate their research findings and insights.
Difference Between Thesis and Research paper (Tabular Form)
Here’s a comparison between a thesis and a research paper in tabular form:
Please note that the specific characteristics may vary depending on the institution and academic discipline. This table provides a general overview of the key differences between a thesis and a research paper.
Difference Between Thesis and Research paper
Thesis and research paper are two distinct academic documents that have several differences. Here are the key dissimilarities between a thesis and a research paper:
Purpose and Objective
Have a close look at the purpose and objective comparison.
A thesis serves the purpose of demonstrating a student’s in-depth understanding of a subject, showcasing their analytical and critical thinking abilities, and contributing new knowledge to the academic community.
It aims to obtain a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D. For example, a Ph.D. thesis in biology may involve conducting original research to discover a new species or proposing a novel scientific theory.
Research Paper
The primary purpose of a research paper is to contribute to existing knowledge on a subject and engage in scholarly discussions. It focuses on exploring a research question or hypothesis, presenting findings, and analyzing the collected data.
For example, a research paper in economics may investigate the impact of a specific policy on economic growth by analyzing data from various sources.
Scope and Depth
Have a close look at the scope and depth comparison.
A thesis requires extensive research and an exhaustive exploration of the chosen topic. It involves delving deeply into the existing literature, critically analyzing previous studies, and offering an extensive review of relevant theories, methodologies, or experiments.
The scope of a thesis is broader, aiming to cover various aspects of the chosen field. For example, a thesis in history may involve examining multiple historical events, analyzing primary sources, and comparing different historical interpretations.
While a research paper also requires research, its scope of exploration is usually narrower compared to a thesis. Research papers often focus on addressing specific research questions, providing detailed analysis, or presenting findings within a limited context.
The scope of a research paper is more focused on a specific aspect or angle of the topic. For example, a research paper in psychology may investigate the effects of a particular therapy technique on a specific group of individuals.
Originality and Contribution
Have a close look at the originality and contribution comparison.
A thesis demands original research and substantial contribution to the existing body of knowledge in the field. It requires students to identify a research gap, formulate research questions, and conduct extensive investigations to fill that gap.
A thesis should provide novel insights, theories, or methodologies that contribute to the advancement of the field. For example, a thesis in computer science may involve developing a new algorithm or software application to solve a complex problem.
While a research paper also requires originality, its scope of contribution is typically narrower compared to a thesis. Research papers often focus on addressing specific aspects or angles of a topic, providing detailed analysis, or presenting findings within a limited context.
They may offer new perspectives or interpretations but may not be as extensive in terms of contributing to the overall knowledge in the field. For example, a research paper in sociology may present a new analysis of existing survey data to support or challenge existing sociological theories.
Structure and Formatting
Have a close look at structure and formatting comparison.
A thesis follows a specific structure that includes various sections such as a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices (if applicable).
This structured format provides a comprehensive framework for presenting the research and analysis conducted. Each section has its purpose and contributes to the overall coherence of the thesis.
A research paper usually has a more flexible structure, depending on the field of study and the specific requirements of the assignment or publication. However, it commonly includes sections like a title, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, and references.
The structure may vary based on the specific guidelines or preferences of the intended publication. The flexibility allows researchers to adapt the structure to the needs of their study while maintaining the logical flow of information.
Evaluation and Audience
Have a close look at evolution and audience comparison.
A thesis is primarily evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. The evaluation process involves comprehensive scrutiny of the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and the overall contribution to the field.
The audience for a thesis is typically limited to the academic community, including the student’s advisors, faculty members, and fellow researchers. The evaluation focuses on the originality, quality, and depth of the research conducted.
Research papers cater to a broader audience, including scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field. They are often evaluated through peer review processes before being published in academic journals or presented at conferences.
The evaluation criteria for research papers may vary depending on the publication or assignment guidelines, but they generally emphasize the clarity of research objectives, methodology, data analysis, and the significance of the findings. The evaluation focuses on the validity and contribution of the research to the existing knowledge.
Length and Time Frame
Have a close look at length and time frame comparison.
A thesis is typically longer in length compared to a research paper. It requires a more extensive investigation and analysis, resulting in a higher word count. The time frame to complete a thesis is also longer, often spanning several semesters or years.
The extended length and timeframe allow students to engage in thorough research, conduct experiments, gather data, and provide a comprehensive analysis of the chosen topic.
Research papers are generally shorter in length compared to a thesis. They focus on specific aspects or angles of a topic, resulting in a relatively shorter word count. The time frame to complete a research paper is shorter, often within a semester or a few weeks.
The shorter length and timeframe require researchers to narrow down their focus and present a concise analysis of the chosen research question.
Have a close look at purpose and objective comparison.
A thesis serves as a culmination of a student’s academic journey, demonstrating their mastery of a subject area and their ability to conduct independent research. It aims to contribute new knowledge, theories, or methodologies to the academic community, advancing the understanding of the chosen field.
The primary objective is to obtain a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., and showcase expertise in a specialized area of study.
The primary purpose of a research paper is to communicate the results of a specific study or investigation to the academic community. It aims to contribute to existing knowledge by presenting new findings, interpretations, or analyses on a specific research question or topic.
Research papers can be standalone publications or part of a broader research project, providing insights and contributing to ongoing scholarly discussions.
Have a close look at scope and depth comparison.
A thesis requires a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of a subject, often involving extensive literature review, data collection, and analysis. It typically covers a broader scope within the chosen field, aiming to provide a holistic understanding of the topic and its various aspects.
A thesis often requires a more extensive examination of theoretical frameworks, methodologies, and relevant literature, presenting a well-rounded analysis.
Research papers often focus on a specific aspect or angle of a topic, narrowing down the scope of the study. The depth of exploration in a research paper is more limited compared to a thesis, as it emphasizes detailed analysis and findings related to the specific research question.
While research papers may include literature review and references, the analysis is usually more targeted and specific to the research question being addressed.
Have a close look at originality and contribution comparison.
A thesis requires a higher level of originality and contribution to the field. It should offer new insights, theories, methodologies, or empirical evidence that expand existing knowledge and advance the field of study.
A thesis often addresses a research gap or poses new research questions, aiming to fill a void in the existing body of knowledge.
While research papers also require originality, their contribution is typically more limited in scope. Research papers often build upon existing theories, methodologies, or data, offering new interpretations or perspectives within a specific context.
They may present incremental findings, replication studies, or comparative analyses that deepen understanding in a focused area of study.
A thesis follows a structured format that varies across institutions and disciplines. It typically includes sections such as a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices (if applicable).
The structure ensures logical flow, provides context, and allows for comprehensive presentation of research and analysis.
Research papers also have a flexible structure, but they commonly include sections like a title, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results and analysis, discussion, conclusion, and references. The specific structure may vary based on publication guidelines or the nature of the study.
The structure aims to present the research question, methodology, findings, and analysis in a coherent and understandable manner.
Have a close look at evaluation and audience comparison.
Theses are primarily evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. The evaluation process involves rigorous scrutiny of the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and overall contribution to the field.
The audience for a thesis is typically limited to the academic community, including the student’s advisors, faculty members, and fellow researchers.
Research papers are evaluated through peer review processes before publication or presentation. The evaluation criteria may vary depending on the specific guidelines or intended publication, but they generally assess the clarity of research objectives, methodology, data analysis, and the significance of the findings.
The audience for research papers includes scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field, aiming to contribute to ongoing scholarly discussions and inform future research.
Theses are typically longer in length compared to research papers. The word count for a thesis can vary significantly, ranging from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand words, depending on the level of study and institution’s requirements.
The time frame to complete a thesis is longer, often spanning several semesters or years, allowing for thorough research, data collection, analysis, and the writing process.
Research papers are generally shorter in length compared to theses. The word count for research papers varies depending on the specific requirements of the publication or assignment, but it is typically more concise compared to a thesis.
The time frame to complete a research paper is shorter, often within a semester or a few weeks, necessitating focused research, analysis, and writing within a more limited timeframe.
In conclusion, the difference between a thesis and a research paper lies in their purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length. A thesis represents the culmination of a student’s academic journey, aiming to obtain a higher degree and contribute new knowledge to the academic community.
It requires extensive research, in-depth exploration of the chosen topic, and a broader scope that covers various aspects of the field. A thesis demands originality and substantial contribution, often addressing research gaps and presenting novel insights or methodologies.
On the other hand, a research paper focuses on presenting specific findings, interpretations, or analyses within a narrower scope. While it also requires originality, its contribution is usually more limited, building upon existing theories or data to offer new perspectives or interpretations.
Research papers have a flexible structure, adapting to the requirements of the publication or assignment, while the thesis follows a specific and comprehensive format.
Theses are primarily evaluated by a committee of experts in the field, targeting the academic community, while research papers undergo peer review processes for publication and cater to a broader audience of scholars, researchers, and professionals.
Furthermore, the length and time frame differ between the two. Theses are generally longer, spanning several semesters or years, allowing for thorough research and analysis, while research papers are shorter and completed within a semester or a few weeks, requiring focused research and concise presentation of findings.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for students and researchers to navigate their academic endeavors effectively. Whether one aims to pursue advanced degrees or contribute to scholarly discussions, recognizing the unique characteristics of the thesis and research paper helps in formulating research objectives, selecting appropriate methodologies, and presenting research outcomes in a manner suitable to their intended audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main objective of a thesis.
The main objective of a thesis is to demonstrate a student’s in-depth understanding of a subject, showcase their analytical and critical thinking abilities, and contribute new knowledge to the academic community.
Can a research paper be considered a thesis?
No, a research paper and a thesis are distinct academic documents. While both involve research and analysis, a thesis is more comprehensive, requires a higher level of originality, and aims for a higher academic degree.
How long does it take to complete a thesis?
The duration to complete a thesis can vary depending on the program and the nature of the research. It often takes several semesters or years to conduct the necessary research, collect data, analyze findings, and write the thesis.
Who evaluates a thesis?
A thesis is typically evaluated by a committee of professors or experts in the field. They assess the research methodology, data analysis, theoretical frameworks, and the overall contribution to the field.
What is the audience for a research paper?
The audience for a research paper includes scholars, researchers, and professionals in the respective field. Research papers are often published in academic journals or presented at conferences to engage in scholarly discussions.
Similar Articles

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…

How to Write an Assignment Introduction – 6 Best Tips
In essence, the writing tasks in academic tenure students are an integral part of any curriculum. Whether in high school,…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Dissertation Proposal | Examples, Steps & Structure

Introduction
What is the dissertation proposal process, what is the difference between a dissertation and a dissertation proposal, what are the elements of a dissertation proposal, what does a good dissertation proposal look like, how do you present a dissertation proposal.
With the dissertation as the culminating work that leads to successful completion of a doctoral degree, the dissertation proposal or thesis proposal serves as the backbone of the research that will ultimately inform your research agenda in the dissertation stage and beyond. A well-crafted proposed study details the research problem , your research question , and your methodology for studying the dissertation topic.
In this article, we will provide a brief introduction of the components of a good dissertation proposal, why they are important, and what needs to be incorporated into a proposal to allow your committee to conduct further study on your topic.

A typical doctoral program requires a dissertation or thesis through which a doctoral student demonstrates their knowledge and expertise in the prevailing theories and methodologies in their chosen research area. By the time a student is ready for the dissertation proposal stage, they will have taken the necessary coursework on theory and research methods or have demonstrated their expertise in lab work or written publications.
Most doctoral programs also require students to complete comprehensive examinations (these may go by other names such as qualifying exams or preliminary exams). These assess the ability to understand and synthesize scientific knowledge in a given research field. What separates the dissertation proposal from these examinations is that the dissertation proposal asks students to create an entirely new study that builds on that existing knowledge, separating fully-fledged researchers and scientists from merely scholars familiar with expert knowledge.
Needless to say, the dissertation proposal is the precursor to the eventual dissertation. Think of the proposal as a request for permission to conduct the study that you need to conduct to write and defend your dissertation.
Because a rigorous research process is also extensive and drawn out, the proposal is also a reflection of the expertise you have about the dissertation topic. Committee members want to know if you have the necessary knowledge about the existing research to be able to generate empirical knowledge through a full dissertation study.
Once you have conducted your research, the dissertation itself will often take components from your written proposal in providing a comprehensive report on the scholarly knowledge you have generated and how you generated it. That said, the overall scholarly work will likely evolve between the proposal stage and the final dissertation, making the proposal a useful foundation on which your entire research agenda is built.
Turn data into insights with ATLAS.ti
Powerful data analysis built into an intuitive interface. Try ATLAS.ti with a free trial today.
By this point in a doctoral program, a student is already familiar with components in a research paper such as a thesis statement, a research question , https://atlasti.com/guides/qualitative-research-guide-part-1/qualitative-research-methods methodology , and findings and discussion sections. These aspects are commonly found in journal articles and conference presentations. However, a dissertation proposal is most likely a lengthy document as your dissertation committee will expect certain things that may not always belong in a journal article with the level of detail found in a proposal.
Problem statement
A clear dissertation proposal outlines the problem that the proposed research aims to address. An effective problem statement can identify the potential value of the research if it is approved and conducted. It also elevates the research from an inquiry generated from pure intellectual curiosity to a directed study that the greater academic community will find relevant and compelling.
Identifying a problem that research can solve is less about a personal interest and more about justifying why the research deserves to go forward. A good dissertation proposal should make the case that the research can expand theoretical knowledge or identify applications to address practical concerns.
Research questions are the product of a good problem statement. Whereas a useful problem statement will establish the relevance of the study, a research question will focus on aspects of the problem that, when addressed through research, will yield useful theoretical developments or practical insights.
Research background
Once the proposed project is justified in terms of its potential value, the next question is whether existing research has something to say about the problem. A thorough literature review is necessary to be able to identify the necessary gaps in the theory or methodology.
A thorough survey of the research background can also provide a useful theoretical framework that researchers can use to conduct data collection and analysis . Basing your analytical approach on published research will establish useful connections between your research and existing scientific knowledge, a quality that your committee will look for in determining the importance of your proposed study.
Proposed methodology
With a useful theoretical background in mind, the methodology section lays out what the study will look like if it is approved. In a nutshell, a comprehensive treatment of the methodology should include descriptions of the research context (e.g., the participants and the broader environment they occupy), data collection procedures, data analysis strategies, and any expected outcomes.
A thorough explanation of the methodological approach you will apply to your study is critical to a successful proposal. Compared to an explanation of methods in a peer-reviewed journal article, the methodology is expected to take up an entire chapter in your dissertation, so the methods section in your proposal should be just as long. Be prepared to explain not only what strategies for data collection and analysis you choose but why they are appropriate for your research topic and research questions.
The expected outcomes represent the student's best guess as to what might happen and what insights might be collected during the course of the study. This is similar to a research hypothesis in that an expected outcome provides a sort of baseline that the researcher should use to determine the extent of the novelty in the findings.
At this point, dissertation committee members are looking at the extent to which a doctoral student can design a transparent and rigorous study that can contribute new knowledge to the existing body of relevant literature on a given research topic. Especially in the social sciences, the approach a researcher takes in generating new knowledge is often more important than the new knowledge itself, making the methods section arguably the most critical component in your proposal.
Successful dissertation proposals serve both as compelling arguments justifying future research as well as written knowledge that can be incorporated into the eventual dissertation. Oftentimes, students are advised that the dissertation proposal has a similar structure to that of the first few chapters of a dissertation, as they describe the research problem , background, and methodology .
In that sense, a good proposal will help the student save time in writing what will be an even lengthier dissertation. To your advisor and your committee, a successful proposal is less an examination than it is a tool or formal process to help you through the doctoral journey.
Throughout the process of writing your proposal, it's important to communicate with the members of your dissertation committee so they can clarify their expectations regarding what belongs in the proposal. Ultimately, beyond the accepted norms regarding what goes into a typical dissertation proposal, it is up to your committee to determine if you have the expertise and appropriate methodological approach to conduct novel research.
The proposal will most likely be the longest report you will write in your doctoral program, with the exception of the dissertation itself. That's because you will need to describe your research design in the kind of painstaking detail that often isn't included in a typical peer-reviewed research article or academic presentation.
In general terms, the more detail that you can provide in your proposal, the clearer your research agenda as you collect and analyze data , and the easier your dissertation will be to write. However, a dissertation proposal is more than simply a word or page count. It is a document that is intended to "sell" the value of your research to your committee.
Your committee will be made up of your advisor and other faculty members in your university (with some exceptions depending on your doctoral program). These members need to be convinced that your research can contribute to the larger body of scholarly knowledge within the university and in the greater academic community as a whole. As a result, a good proposal is not an encyclopedic presentation of knowledge, but an informed synthesis of theory and methodology that points out where research in a particular topic should be conducted next.
In addition to the substance of your proposal, also pay attention to the packaging of your proposal. Little details such as the title page and reference list also provide indicators that you have carefully thought about the research you want to conduct, and show your level of commitment as a future career scholar. As with submitting a research paper for publication in a peer-reviewed journal, developing the dissertation proposal should also be done with the necessary care that demonstrates a professional attitude toward literacy practices and best practices in academic research.
Typically, the dissertation proposal will need to be presented in person to your committee. This is a chance for your committee to confirm they have read the proposal, offer feedback to strengthen the research design, and offer their approval for you to go ahead and conduct your research if it is a strong enough proposal. In many respects, the proposal meeting is a dry run for the kind of questions you will likely face from your committee when it comes time to defend your dissertation.
Even if you successfully defend your proposal, your advisor may ask for revisions to the written proposal based on the feedback your committee provides. These revisions are not only crucial to the eventual data collection and analysis but to strengthening the argument you will make about the validity and novelty of your research later on.

Take advantage of ATLAS.ti's capabilities with a free trial
Start using ATLAS.ti today to make the most of your qualitative data.


- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Difference between A Proposal and Thesis

2022, The Difference between A Proposal and Thesis
It is worth to note that every school/faculty or department of a given institution of higher learning has its unique format or guideline for proposal or thesis writing. An overwhelming majority of scholars and students of research find it difficult when it comes to giving a difference between A Proposal and Thesis.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
On the other hand, a research report is the culmination of the research endeavour. It is a great way to explain the research work and its outcome to a group of people. It is the outcome of the study conducted at the time of the research process.
This article will help you understand the difference between research proposal and research report.
Content: Research Proposal Vs Research Report
Comparison chart, definition of research proposal.
Research Proposal can be defined as the document prepared by the researcher so as to give a description of the research program in detail. It is typically a request for research funding, for the subject under study. In other words, a research proposal is a summary of the research process, with which the reader can get quick information regarding the research project.
The research proposal seeks final approval, for which it is submitted to the relevant authority. After the research proposal is submitted, it is being evaluated, considering a number of factors like the cost involved, potential impact, soundness of the plan to undertake the project.
It aims at presenting and justifying the need and importance to carry out the study, as well as to present the practical ways, of conducting the research. And for this, persuasive evidence should be provided in the research proposal, to highlight the necessity of the research.
Further, it must discuss the main issues and questions, which the researcher will address in the study. Along with that, it must highlight the fundamental area of the research study.
A research proposal can be prepared in a number of formats, which differs on the basis of their length. It contains an introduction, problem hypothesis, objectives, assumptions, methodology, justification and implication of the research project.
Definition of Research Report
Research Report can be defined as the document in which the researched and analysed data is organized and presented by the researcher in a systematic manner. It is a publication, comprising of the purpose, scope, hypothesis, methodology, findings, limitations, recommendations and conclusion of the research project.
Simply put, a research report is the record of the research process. It is one of the most important segments of the research, as the research work is said to be incomplete if the report is not prepared.
A research report is a document containing collected and considered facts, taken to provide succinct and comprehensible information to people.
Once the research process is over, the entire work is produced in a written material, which is called a research report . It covers the description of the research activities, in an elaborated manner. It contains Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Data Collection, Data Analysis, Discussion of Results and Findings, Bibliography and Appendices.
A research report acts as a method to record the research work and its outcome, for future reference.
Key Differences Between Research Proposal and Research Report
The difference between research proposal and research report is discussed as under:
- A research proposal signifies a theoretical framework within which the research is carried out. In finer terms, a research proposal is a sketch for the collection, measurement and analysis of data. A research report implies a scientific write-up on the research findings, which is prepared in a specific format.
- While the preparation of a research proposal is considered as the first step to research work, preparation of a research report is the final step to the research work.
- A research proposal is prepared at the beginning of the project. In contrast, the research report is prepared after the completion of the project
- A research proposal is written in the future tense, whereas the tense used in the research report is past tense, as well as it is written in the third person
- The length of a research proposal is about 4-10 pages. On the contrary, the length of the research report is about 100 to 300 pages.
- The research proposal is concerned with the problem or topic to be investigated. Conversely, the research report focuses on the results of the completed research work.
- The research proposal determines what will be researched, the relevance of the research and the ways to conduct the researched. As against, the research report determines what is researched, sources of data collection, ways of data collection (i.e. survey, interview, or questionnaire), result and findings, recommendations for future research, etc.
- Research Proposal includes three chapters i.e. Introduction, Literature Review, Research Methodology. Contrastingly, Research Report covers the following chapters – Introduction, Literature Review, Research Methodology, Results, Interpretation and Analysis, Conclusion and Recommendation.
Basically, a research proposal defines the planning stage of the research work, which is prepared in written format, to know its worth. On the other hand, the research report signifies the concluding stage of the research work.
You Might Also Like:

getachew says
December 24, 2020 at 6:48 pm
tha’s good
Agyei Yaw says
July 27, 2021 at 3:25 am
Good.it help students nurses in Ghana
Ijaz hussain says
December 27, 2021 at 12:08 am
March 15, 2022 at 10:19 pm
well explained in a summarized way.
Yacob yahaya says
June 24, 2023 at 4:05 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Aimlay Foundation
- Pharma Courses
- Become a Partner
- Medical Courses
- Life@Aimlay
- Web Stories

- Thesis Writing
- Law Admission
- Dissertation
- Honorary doctorate
- Educational Academy
- Management Courses
- Research Paper Writing
- YouTube Journal
PhD | Thesis Writing | Law Admission | Dissertation | Biography | Pharma | Honorary doctorate | Educational Academy | Management Courses | Research Paper Writing | YouTube Journal
Difference between a Research Proposal and a Synopsis
- September 5, 2022
- Research Paper Writing , Thesis Writing , YouTube Journal
- No Comments

In the beginning, we can say that a summary is a brief, compact overview of the main points in a longer document. The purpose is to give readers an idea of what’s in the full-length document without reading it all & how to write synopsis. A synopsis for thesis can be a shorter version of your document that’s designed to give readers an overview of your ideas and conclusions. A research proposal is a formal document that outlines the scope and direction of an academic study or research project. It includes a plan for how you will collect data and analyze it, as well as how you will present your results with un understanding the difference between research proposal and synopsis
An Overview of both Documents:
Synopsis vs Research Proposal
A synopsis is a short form of your full research proposal and is just the introduction to the report. It convinces readers that you understand their problem and can provide a solution.
A research proposal is a detailed plan of how you will conduct your study. The research proposal includes a study design, which includes the specific questions that need to be answered, sampling strategy, data collection methods, analysis plan and reporting format.
How to write a Synopsis?
A synopsis for thesis is a brief, concise description of your paper. With learning how to write synopsis, communicate the main ideas and arguments in your paper and to tell someone else what you’re going to say. A good synopsis is a way for you to organize your ideas before you write the whole thing, and it helps others determine if they want to read further.
A synopsis for thesis is a summary of your article. It should be written in the following format:
- Title of your book or article (in bold)
- Author’s name and contact details (in italics)
- The main idea of your article or book (in bold)
- Introduction (optional)
- Body (in bold)
- Conclusion (optional)
How to write a Research Proposal?
Research Proposal – It is a document in which you state your thesis and goals, along with the method and rationale for your research. A thesis statement is the single most important part of a research proposal. It should be clear, concise, and specific.
The main purpose of this proposal is to get funding for your research. The proposal should also demonstrate how well-equipped you are to do the research.
This proposal aims to develop a new way of understanding the world through a systematic and comprehensive analysis of how society learns about the world.
This paper will focus on how people make sense of the w around them by using tools such as languages, maps, technology and science, thereby contributing to our ability to understand our surroundings.
Difference between a Research Proposal and a Synopsis for thesis:
The basic difference between a research proposal and a synopsis is that the former is more in-depth, whereas the latter is more condensed. However, this does not mean that researchers should not write synopses for their publications. To do so is to miss out on useful information that can be added later.
The advantage of writing a synopsis is that it provides a reader with an overview of your research project without having to read through large amounts of text. It also helps to explain your research topic and why it is relevant. A synopsis will help you decide whether or not your topic is worth pursuing further by ensuring that there are enough sources available for you to continue your research.
What is the purpose of our research proposal?
The purpose of the research proposal is to convince your advisor or committee that there is enough merit in your proposal to justify their funding of the project and their time reviewing it. A good proposal will include:
- An overview of the problem or question you are addressing
- A detailed description of how you plan to address this question or solve this problem
- A clear statement of what evidence supports your claim and how you will use this evidence to support your claim
- A discussion about how well-known and accepted methods can be used as part of this work (this is called quantitative analysis).

Why do people confuse the two?
In the first place, a research proposal is not a synopsis. A summary should be brief and to the point, while a research proposal would have all of your data and evidence lined up on one page.
A synopsis for thesis is written in the first-person voice and focuses on the story’s main points without delving too far into details. A synopsis can help readers get an idea of what you’re writing about or help them find information on a particular topic. It’s often used in book sales to determine if they have enough information on their hands to sell your book or not.
An academic or professional author writes a research proposal as part of their job. It is meant to provide evidence that supports their argument through data and statistical analysis.
Tips for writing a Research Proposal flawlessly:
- Writing a research proposal is not as easy as it seems. You must choose the right topic and then write the proposal in a way that will convince your reader of your ability to carry out the research.
- The first step in writing a research proposal is to select an area of study or research in which you are interested. If you have any previous experience with this topic, consider using it as part of your proposal. If not, find someone with previous experience in the field and ask them for their advice.
- Once you have decided on a topic, begin by writing down what you know about this area of interest. This can include anything from books or articles to news stories or television shows that have aired about the topic. Ensure all relevant information about this topic, including key terms or definitions.
- Once you have written down everything you know about your topic, it’s time to develop an outline for your dissertation proposal. An outline is an organised list of topics that will make up each chapter of your dissertation proposal and should include subtopics within each topic area (for example, introduction, background information; objectives; methods; data collection).
The more important your paper, the more likely you’ll need to write a research proposal and a synopsis. A research proposal is usually the first step in the writing process, an overview of the topic you plan to tackle later. A synopsis, on the other hand, is a concise summary of the content of your paper. We hope this blog has given you a proper explanation for understanding the differences.
Share this Article
Send your query, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main difference between a thesis and a research proposal is their purpose. A thesis is a formal academic piece of writing done on a particular topic that has not yet been explored. This is why a thesis has a prospectus stage where the student has to consult with a committee. On the other hand, a research proposal proposes the topic and the ...
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that's needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the ...
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. ... The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have ...
VI. Differences between a Research Paper and Proposal. Research papers and proposals share certain elements, yet differ in purpose and execution. While both may involve extensive research, the former is generally focused on an existing topic or area of study while the latter endeavors to introduce a new concept.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
The proposal, sometimes called the prospectus, is composed mainly of the Introduction, Research Questions, Literature Review, Research Significance and Methodology. It may also include a dissertation/thesis outline and a timeline for your proposed research. You will be able to reuse the proposal when you actually write the entire dissertation ...
Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
Gather all the necessary information before you start writing, and stick to formats that highlight the value of your proposal. The usual flow of writing a thesis proposal is as follows. 1. Outline. Start by coming up with a detailed description of the major points you'll be making in your thesis. 2.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper. The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify. Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final ...
Conclusion. In brief, the main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long research paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while a research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic. Moreover, in an academic context, students may be required to write research papers ...
It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals. The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
In conclusion, the difference between a thesis and a research paper lies in their purpose, scope, originality, structure, evaluation, and length. A thesis represents the culmination of a student's academic journey, aiming to obtain a higher degree and contribute new knowledge to the academic community. It requires extensive research, in-depth ...
A good dissertation proposal should make the case that the research can expand theoretical knowledge or identify applications to address practical concerns. Research questions are the product of a good problem statement. Whereas a useful problem statement will establish the relevance of the study, a research question will focus on aspects of ...
How to Write a Research Proposal and a Thesis - 2 nd ed. M.E. Hamid (2013) ( 12 ) RE F E R E N C E S ( B IB L I O G R A P H Y )
Difference Between Aims and Objectives. Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify: The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved. Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
Download PDF. The Difference Between a Proposal and a Thesis It is worth to note that every school/faculty or department of a given institution of higher learning has its unique format or guideline for proposal or thesis writing. An overwhelming majority of scholars and students of research find it difficult when it comes to giving a difference ...
The difference between research proposal and research report is discussed as under: A research proposal signifies a theoretical framework within which the research is carried out. In finer terms, a research proposal is a sketch for the collection, measurement and analysis of data.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a ...
In some countries, whenever someone applies for a Ph.D. admission, the universities ask for a research proposal. A research proposal includes a literature review and bibliography. If the research is paper-based research, i.e. no popular survey or experiment is involved, I see no further need for research work.
A research report describes the whole research study and is submitted after the competition of the whole research project. Thus, the main difference between research proposal and research report is that a research proposal describes the proposed research and research design whereas a research report describes the completed research, including ...
The basic difference between a research proposal and a synopsis is that the former is more in-depth, whereas the latter is more condensed. However, this does not mean that researchers should not write synopses for their publications. To do so is to miss out on useful information that can be added later. The advantage of writing a synopsis is ...