Health Sciences Informatics, PhD
School of medicine.
The Ph.D. in Health Sciences Informatics offers the opportunity to participate in ground-breaking research projects in clinical informatics and data science at one of the world’s finest biomedical research institutions. In keeping with the traditions of the Johns Hopkins University and the Johns Hopkins Hospital, the Ph.D. program seeks excellence and commitment in its students to further the prevention and management of disease through the continued exploration and development of health informatics, health IT, and data science. Resources include a highly collaborative clinical faculty committed to research at the patient, provider, and system levels. The admissions process will be highly selective and finely calibrated to complement the expertise of faculty mentors.
Areas of research:
- Clinical Decision Support
- Global Health Informatics
- Health Information Exchange (HIE)
- Human Computer Interaction
- Multi-Center Real World Data
- Patient Quality & Safety
- Population Health Analytics
- Precision Medicine Analytics
- Standard Terminologies
- Telemedicine
- Translational Bioinformatics
Individuals wishing to prepare themselves for careers as independent researchers in health sciences informatics, with applications experience in informatics across the entire health/healthcare life cycle, should apply for admission to the doctoral program.

Admission Criteria
Applicants with the following types of degrees and qualifications will be considered:
- BA or BS, with relevant technical and quantitative competencies and a record of scientific accomplishment as an undergraduate;
- BA or BS, with relevant technical and quantitative competencies and a minimum of five years professional experience in a relevant field (e.g., biomedical research, data science, public health, etc.); or
- MA, MS, MPH, MLIS, MD, PhD, or other terminal degree, with relevant technical and quantitative competencies
Relevant fields include: medicine, dentistry, veterinary science, nursing, ancillary clinical sciences, public health, librarianship, biomedical science, bioengineering and pharmaceutical sciences, and computer and information science. An undergraduate minor or major in information or computer science is highly desirable.
The application is made available online through Johns Hopkins School of Medicine's website . Please note that paper applications are no longer accepted. The supporting documents listed below must be received by the SOM admissions office by December 15 of the following year. Applications will not be reviewed until they are complete and we have all supporting letters and documentation.
- Curriculum Vitae (including list of peer-reviewed publications and scientific presentations)
- Three Letters of Recommendation
- Statement of Purpose
- Official Transcripts from undergraduate and any graduate studies
- Certification of terminal degree
- You are also encouraged to submit a portfolio of published research, writing samples, and/or samples of website or system development
Please track submission of supporting documentation through the SLATE admissions portal.
If you have questions about your qualifications for this program, please contact [email protected]
Program Requirements
The PhD curriculum will be highly customized based on the student's background and needs. Specific courses and milestones will be developed in partnership with the student's advisor and the PhD Program Director.
The proposed curriculum is founded on four high-level principles:
- Achieving a balance between theory and research, and between breadth and depth of knowledge
- Creating a curriculum around student needs, background, and goals
- Teaching and research excellence
- Modeling professional behavior locally and nationally.
Individualized curriculum plans will be developed to build proficiencies in the following areas:
- Foundations of biomedical informatics: e.g., lifecycle of information systems, decision support
- Information and computer science: e.g., software engineering, programming languages, design and analysis of algorithms, data structures.
- Research methodology: research design, epidemiology, and systems evaluation; mathematics for computer science (discrete mathematics, probability theory), mathematical statistics, applied statistics, mathematics for statistics (linear algebra, sampling theory, statistical inference theory, probability); ethnographic methods.
- Implementation sciences: methods from the social sciences (e.g., organizational behavior and management, evaluation, ethics, health policy, communication, cognitive learning sciences, psychology, and sociological knowledge and methods), health economics, evidence-based practice, safety, quality.
- Specific informatics domains: clinical informatics, public health informatics, analytics
- Practical experience: experience in informatics research, experience with health information technology.
Basic Requirements & Credit Distribution
- 15 "core" quarter credits (5 courses)
- 8 quarter credits of Student Seminar & Grand Rounds
- 60 elective quarter credits
- 6 quarter credits practicum/research rotation
- 36 mentored research quarter credits (12 in year 1, 24 in year 2)
- Research Ethics
- Mission, Facts and Figures
- Deans, Chairs and Staff
- Leadership Council
- Dean in the News
- Get Involved
- DEIB Mission
- Message from DEIB Associate Dean
- News and Media
- Reading Lists
- The Yale and Slavery Research Project
- Photo Gallery
- Winslow Medal
- Coat of Arms & Mace
- $50 Million Challenge
- For Pandemic Prevention and Global Health
- For Understanding the Health Impacts of Climate Change
- For Health Equity and Justice
- For Powering Health Solutions through Data Science
- For Future Leaders
- For Faculty Leaders
- For Transformational Efforts
- Data, Leadership, and Collaboration at the School of Public Health
- An abiding love for Yale turns into a lasting gift – in 15 minutes
- Endowed Professorship Created at Critical Time for Yale School of Public Health
- Brotherly encouragement spurs gift to support students
- Prestipino creates opportunities for YSPH students, now and later
- Alumna gives back to the school that “opened doors” in male-dominated field
- For Public Health, a Broad Mission and a Way to Amplify Impact
- Couple Endows Scholarship to Put Dreams in Reach for YSPH Students
- A Match Made at YSPH
- A HAPPY Meeting of Public Health and the Arts
- Generous Gift Bolsters Diversity & Inclusion
- Alumni Donations Aid Record Number of YSPH Students
- YSPH’s Rapid Response Fund Needs Donations – Rapidly
- Podiatric Medicine and Orthopedics as Public Health Prevention
- Investing in Future Public Health Leaders
- Support for Veterans and Midcareer Students
- Donor Eases Burden for Policy Students
- A Personal Inspiration for Support of Cancer Research
- Reducing the Burden of Student Debt
- Learning About Global Health Through Global Travel
- A Meeting in Dubai, and a Donation to the School
- Rapid Response Fund
- Planned Giving
- Testimonials
- Faculty, Postdoc Jobs
- For the Media
- Issues List
- PDF Issues for Download
- Editorial Style Guide
- Social Media
- Shared Humanity Podcast
- Health & Veritas Podcast
- Accreditation
- Faculty Directory by Name
- Career Achievement Awards
- Annual Research Awards
- Teaching Spotlights
- Biostatistics
- Chronic Disease Epidemiology
- Climate Change and Health Concentration
- Environmental Health Sciences
- Epidemiology of Microbial Diseases
- Global Health
- Health Policy and Management
- Maternal and Child Health Promotion Track
- Public Health Modeling Concentration
- Regulatory Affairs Track
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- U.S. Health Justice Concentration
- Why Public Health at Yale
- Events and Contact
- What Does it Take to be a Successful YSPH Student?
- How to Apply and FAQs
- Incoming Student Gateway
- Traveling to Yale
- Meet Students and Alumni
- Past Internship Spotlights
- Student-run Organizations
- MS and PhD Student Leaders
- Staff Spotlights
- Life in New Haven
- Libraries at Yale
- The MPH Internship Experience
- Practicum Course Offerings
- Summer Funding and Fellowships
- Downs Fellowship Committee
- Stolwijk Fellowship
- Climate Change and Health
- Career Management Center
- What You Can Do with a Yale MPH
- MPH Career Outcomes
- MS Career Outcomes
- PhD Career Outcomes
- Employer Recruiting
- Tuition and Expenses
- External Funding and Scholarships
- External Fellowships for PhD Candidates
- Alumni Spotlights
- Bulldog Perks
- Stay Involved
- Board of Directors
- Emerging Majority Affairs Committee
- Award Nomination Form
- Board Nomination Form
- Alumni Engagement Plus
- Mentorship Program
- The Mentoring Process
- For Mentors
- For Students
- Recent Graduate Program
- Transcript and Verification Requests
- Applied Practice and Student Research
- Competencies and Career Paths
- Applied Practice and Internships
- Student Research
- Seminar and Events
- Competencies and Career paths
- Why the YSPH Executive MPH
- Message from the Program Director
- Two-year Hybrid MPH Schedule
- The Faculty
- Student Profiles
- Newsletter Articles
- Approved Electives
- Physicians Associates Program
- Joint Degrees with International Partners
- MS in Biostatistics Standard Pathway
- MS Implementation and Prevention Science Methods Pathway
- MS Data Sciences Pathway
- Internships and Student Research
- Competencies
- Degree Requirements - Quantitative Specialization
- Degree Requirements - Clinical Specialization
- Degree Requirements- PhD Biostatistics Standard Pathway
- Degree Requirements- PhD Biostatistics Implementation and Prevention Science Methods Pathway
- Meet PhD Students in Biostatistics
- Meet PhD Students in CDE
- Degree Requirements and Timeline
- Meet PhD Students in EHS
- Meet PhD Students in EMD
- Meet PhD Students in HPM
- Degree Requirements - PhD in Social and Behavioral Sciences
- Degree Requirements - PhD SBS Program Maternal and Child Health Promotion
- Meet PhD Students in SBS
- Differences between MPH and MS degrees
- Academic Calendar
- Translational Alcohol Research Program
- Molecular Virology/Epidemiology Training Program (MoVE-Kaz)
- For Public Health Practitioners and Workforce Development
- Course Description
- Instructors
- Registration
- Coursera Offerings
- Non-degree Students
- International Initiatives & Partnerships
- NIH-funded Summer Research Experience in Environmental Health (SREEH)
- Summer International Program in Environmental Health Sciences (SIPEHS)
- 2022 Student Awards
- APHA Annual Meeting & Expo
- National Public Health Week (NPHW)
- Leaders in Public Health
- YSPH Dean's Lectures
- The Role of Data in Public Health Equity & Innovation Conference
- Innovating for the Public Good
- Practice- and community-based research and initiatives
- Practice and community-based research and initiatives
- Activist in Residence Program
- Publications
- Health Care Systems and Policy
- Heart Disease and Stroke
- Panels, Seminars and Workshops (Recordings)
- Rapid Response Fund Projects
- SalivaDirect™
- Emerging Infections Program - COVID-NET
- Public Health Modeling Unit Projects
- HIV-AIDS-TB
- The Lancet 2023 Series on Breastfeeding
- 'Omics
- News in Biostatistics
- Biostatistics Overview
- Seminars and Events
- Seminar Recordings
- Statistical Genetics/Genomics, Spatial Statistics and Modeling
- Causal Inference, Observational Studies and Implementation Science Methodology
Health Informatics, Data Science and Reproducibility
- Clinical Trials and Outcomes
- Machine Learning and High Dimensional Data Analysis
- News in CDE
- Nutrition, Diabetes, Obesity
- Maternal and Child Health
- Outcomes Research
- Health Disparities
- Women's Health
- News in EHS
- EHS Seminar Recordings
- Climate change and energy impacts on health
- Developmental origins of health and disease
- Environmental justice and health disparities
- Enviromental related health outcomes
- Green chemistry solutions
- Novel approaches to assess environmental exposures and early markers of effect
- 1,4 Dioxane
- Reproducibility
- Tissue Imaging Mass Spectrometry
- Alcohol and Cancer
- Olive Oil and Health
- Lightning Talks
- News in EMD
- Antimicrobial Resistance
- Applied Public Health and Implementation Science
- Emerging Infections and Climate Change
- Global Health/Tropical Diseases
- HIV and Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Marginalized Population Health & Equity
- Pathogen Genomics, Diagnostics, and Molecular Epidemiology
- Vector-borne and Zoonotic Diseases
- Disease Areas
- EMD Research Day
- News in HPM
- Health Systems Reform
- Quality, Efficiency and Equity of Healthcare
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health
- Modeling: Policy, Operations and Disease
- Pharmaceuticals, Vaccines and Medical Devices
- Health and Wellbeing
- News in SBS
- Aging Health
- Community Engagement
- Health Equity
- Mental Health
- Reproductive Health
- Sexuality and Health
- Nutrition, Exercise
- Stigma Prevention
- Community Partners
- For Public Health Practitioners
- Reports and Publications
- Fellows Stipend Application
- Agency Application
- Past Fellows
- PHFP in the News
- Frequently Asked Questions
- International Activity
- Research Publications
- Grant Listings
- Modeling Analyses
- 3 Essential Questions Series
INFORMATION FOR
- Prospective Students
- Incoming Students
- myYSPH Members
Faculty of Interest
Professor of Biomedical Informatics & Data Science; Vice Chair for Education, Biomedical Informatics & Data Science; Professor, Biostatistics
- Health Services
- Health Services Research
- Medical Informatics
- Medical Informatics Applications
- Preventive Medicine
- Public Health
- Public Health Informatics
- Informatics
Associate Professor of Biostatistics, Associate Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, Associate Professor of Management, and Associate Professor of Statistics and Data Science; Co-director, Public Health Modeling Concentration
Department Chair and Professor of Biostatistics; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health; Director, Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Shared Resource
Assistant Professor of Biostatistics (Health Informatics)
- Telemedicine
- Healthcare Disparities
- Consumer Health Informatics
Assistant Professor of Biostatistics; Co-Training Director, Health Informatics MS
- Computer Simulation
- Neurosciences
- Computational Biology
Elihu Professor of Biostatistics and Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology; Co-Leader, Genomics, Genetics, & Epigenetics Research Program
- Bacterial Infections and Mycoses
- Cell Transformation, Neoplastic
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Computing Methodologies
- Biological Evolution
- Genetic Engineering
- Microbiological Phenomena
- Models, Genetic
- Models, Theoretical
- Neoplasm Metastasis
- Models, Statistical
- Likelihood Functions
- Logistic Models
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Sequence Analysis, DNA
- Nonlinear Dynamics
- Molecular Epidemiology
- Gene Transfer Techniques
- Crops, Agricultural
- Evolution, Molecular
- Sequence Analysis, Protein
- Gene Expression Profiling
- Microarray Analysis
- Genetic Speciation
- Host-Pathogen Interactions
- Genetic Phenomena
- Mathematical Concepts
- Phenomena and Processes
Associate Professor of Biostatistics; Associate Professor, Biomedical Informatics & Data Science
Ira V. Hiscock Professor of Biostatistics, Professor of Genetics and Professor of Statistics and Data Science; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health
- Single-Cell Analysis
- Wearable Electronic Devices
Centers and other resources
- Center for Biomedical Data Science
- Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation (CERSI)
- Collaborative Center for Statistics in Science (C²S²) C²S² fosters collaborations involving statistical methods and technology in scientific research, for understanding disease etiologies and developing treatment and prevention strategies.
- Crawford Lab
- Hongyu Zhao Lab - Center for Statistical Genomics and Proteomics
- Yale Center for Analytical Sciences (YCAS) YCAS collaborative team provides expertise in the design, conduct, and analysis of health and health care studies, methodological development, and education and training.
- Academic Programs
PhD in Health Sciences Informatics Program
The PhD is a campus based program only.
Directed by Hadi Kharrazi, MD, PhD, the program offers the opportunity to participate in ground breaking research projects in clinical informatics at one of the world’s finest medical schools. In keeping with the tradition of the Johns Hopkins University and the Johns Hopkins Hospital, the program seeks excellence and commitment in its students to further the prevention and management of disease through the continued exploration and development of health IT. Division resources include a highly collaborative clinical faculty committed to research at the patient, provider and system levels. The admissions process will be highly selective and finely calibrated to complement the expertise of faculty mentors.
Areas of research:
- Clinical Decision Support
- Global Health Informatics
- Health Information Exchange (HIE)
- Human Computer Interaction
- Multi-Center Real World Data
- Patient Quality & Safety
- Population Health Analytics
- Precision Medicine Analytics
- Standard Terminologies
- Telemedicine
- Translational Bioinformatics
Vivien Thomas Scholars Initiative
As diverse PhD students at Johns Hopkins, Vivien Thomas scholars will receive the academic and financial support needed to ensure their success, including up to six years of full tuition support, a stipend, health insurance and other benefits, along with significant mentorship, research, professional development and community-building opportunities.
Click here to read more.
Application Requirements for the PhD in Health Sciences Informatics
Applicants with the following degrees and qualifications will be considered:
- BA or BS, or
- BA or BS, and a minimum of five years professional experience in a relevant field, or
- MA, MLS, MD or other PhD, with no further requirements.
"Relevant fields" include medicine, dentistry, veterinary science, nursing, ancillary clinical sciences, public health, librarianship, biomedical basic science, bioengineering and pharmaceutical sciences and computer and information science. An undergraduate minor or major in information or computer science is highly desirable.
The Application Process
Applications for the class entering in academic year 2025-2026 will be accepted starting in September 1, 2024 through December 15, 2024. (The application is made available through the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine here. )
Please note that paper applications are no longer accepted. The supporting documents listed below must be received by the SOM admissions office by December 15, 2024 . Applications will not be reviewed until they are complete and we have all supporting letters and documentation.
- Curriculum vitae
- Three letters of recommendation
- Official transcript of school record
- Certification of terminal degree
- Statement of Purpose
- You may also submit a portfolio of published research, or samples of website or system development to support your application if you wish.
This program does not require the GRE.
Important Transcript Information
It is the policy of the School of Medicine Registrar that new students have a complete set of original transcripts on file prior to matriculation showing the degree awarded and date. An official transcript is one that is addressed to the Office of Graduate Student Affairs and sent directly from the granting institution to Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Office of Graduate Student Affairs, 1830 East Monument Street, Ste. 620, Baltimore, MD 21287. The transcript envelope must be sealed and stamped on arrival at the OGSA office. Transcripts addressed to the student can not be accepted even if they are sent to the OGSA address above.
Program Description
Individuals wishing to prepare themselves for careers as independent researchers in health sciences informatics, with applications experience in informatics across the entire health/healthcare life cycle, should apply for admission to the doctoral program. The following are specific requirements:
- A student should plan and successfully complete a coherent program of study including the core curriculum, Oral Examination, and additional requirements of the Research Master’s program. In addition, doctoral candidates are expected to take at least two more advanced courses. In the first year, two or three research rotations are strongly encouraged. The Master’s requirements, as well as the Oral Examination, should be completed by the end of the second year in the program. Doctoral students routinely will not be receiving a Masters degree on their way to the PhD; particular exceptions will be decided on a case-by-case basis. Doctoral students are generally advanced to PhD candidacy after passing the Oral Examination. A student’s academic advisor has primary responsibility for the adequacy of the program, which is regularly reviewed by the Doctoral Study Committee (DSC) of the Health Sciences Informatics (HSI) program.
- The student must have a minimum of two consecutive semesters (four quarters) of full time enrollment and resident on campus as a graduate student
- To remain in the PhD program, each student must receive no less than an B in core courses, must attain a grade point average (GPA) as outlined above, and must pass a comprehensive exam covering introductory level graduate material in any curriculum category in which he or she fails to attain a GPA of 3.0. The student must fulfill these requirements and apply for admission to candidacy for the PhD by the end of six quarters of study (excluding summers). In addition, reasonable progress in the student’s research activities is expected of all doctoral candidates.
- During the third year of training, generally in the Winter Quarter, each doctoral student is required to present a pre-proposal seminar that describes evolving research plans and allows program faculty to assure that the student is making good progress toward the definition of a doctoral dissertation topic. By the end of nine quarters (excluding summers), each student must orally present a thesis proposal to a dissertation committee that generally includes at least one member of the Graduate Study Committee of the Health Sciences Informatics program. The committee determines whether the student’s general knowledge of the field, and the details of the planned thesis, are sufficient to justify proceeding with the dissertation.
- As part of the training for the PhD, each student is required to be a teaching assistant for two courses approved by the DHSI Executive Committee; one should be completed in the first two years of study.
- The most important requirement for the PhD degree is the dissertation. Prior to the oral dissertation proposal and defense, each student must secure the agreement of a member of the program faculty to act as dissertation advisor. The University Preliminary Oral Exam (UPO) committee must consist of five faculty members, two of whom to be from outside the program, with the chair of the UPO committee coming from outside the program. The Thesis Committee comprises the principal advisor, who must be an active member of the HSI program faculty, and other, approved non HSI faculty members. Thesis committees must meet formally at least annually. Upon completion of the thesis research, each student must then prepare a formal written thesis, based on guidelines provide by the Doctor of Philosophy Board of the University.
- No oral examination is required upon completion of the dissertation. The oral defense of the dissertation proposal satisfies the University oral examination requirement.
- The student is expected to demonstrate the ability to present scholarly material orally and present his or her research in a lecture at a formal seminar, lecture, or scientific conference.
- The dissertation must be accepted by a reading committee composed of the principal dissertation advisor, a member of the program faculty, and a third member chosen from anywhere within the University. All University guidelines for thesis preparation and final graduation must be met.
- The Executive Committee documents that all Divisional or committee requirements have been met.
Program Handbook
Details about our program's policies are provided in our handbook here .
In addition, mentoring advising and resources are provided in this appendix .
An annual discussion and planning form is provided here for your reference.
Course Offerings
The proposed curriculum is founded on four high-level principles:
- Balance between theory and research, and between breadth and depth of knowledge: By providing a mix of research and practical experiences and a mix of curricular requirements.
- Student-oriented curriculum design: By creating the curriculum around student needs, background, and goals, and aiming at long-term competence using a combination of broadly-applicable methodological knowledge, and a strong emphasis on self-learning skills.
- Teaching and research excellence: By placing emphasis on student and teaching quality rather than quantity, by concentrating on targeted areas of biomedical informatics, and by close student guidance and supervision.
- Developing leadership: By modeling professional behavior locally and nationally.
The Health Sciences Informatics Doctoral Curriculum integrates knowledge and skills from:
- Foundations of biomedical informatics: Includes the lifecycle of information systems, decision support.
- Information and computer science: E.g. computer organization, computability, complexity, operating systems, networks, compilers and formal languages, data bases, software engineering, programming languages, design and analysis of algorithms, data structures.
- Research methodology: Includes research design, epidemiology, and systems evaluation; mathematics for computer science (discrete mathematics, probability theory), mathematical statistics, applied statistics, mathematics for statistics (linear algebra, sampling theory, statistical inference theory, probability).
- Implementation sciences: Methods from the social sciences (e.g., organizational behavior and management, evaluation, ethics, health policy, communication, cognitive learning sciences, psychology, and sociological knowledge and methods.) Health economics, evidence-based practice, safety, quality.
- Specific informatics domains: Clinical informatics, public health informatics.
- Practical experience: Experience in informatics research, experience with health information technology.
To achieve in-depth learning of the above knowledge and skills we adopt a student-oriented curriculum design, whereby we identify “teaching or learning processes,” that is, structured activities geared towards learning (i.e., courses/projects/assignments, seminars, examinations, defenses, theses, teaching requirements, directed study, research, service, internships). These processes were selected, adapted, or created in order to meet a set of pre-specified learning objectives that were identified by the faculty as being important for graduates to master.
The requirements are:
- 35 quarter credits/17.5 semester credits Core Courses (9 courses + research seminar 8 quarters)
- 48 quarter credits/24 semester credits Electives (may include optional practicum/research)
- 6 quarter credits/3 semester credits ME 250.855 practicum/ research rotation
- 36 quarter credits/18 semester credits ME 250.854 Mentored Research
- 125 TOTAL quarter credits/62.5 semester credits
Students are required to be trained in HIPAA and IRB submission, and to take the Course of Research Ethics.
IRB Compliance Training:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/institutional_review_board/training_req…
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Best Doctorates in Health Informatics: Top PhD Programs, Career Paths, and Salaries
Health informatics is an exciting public health field that is rapidly growing. To advance your career, you should consider pursuing one of the best PhDs in Health Informatics. These programs will prepare you for one of the many health informatics jobs available to PhD-holders.
A health informatics PhD takes about four to six years to complete, either online or in person. Continue reading to find our picks for 10 of the best PhDs in Health Informatics, as well as some of the top-paying jobs and PhD in Health Informatics salary information.
Find your bootcamp match
What is a phd in health informatics.
A PhD in Health Informatics is a doctoral degree program that combines medical knowledge with computer and data science, engineering, and information science. This degree focuses on health information management and the collection, storage, and analysis of medical and patient data in the healthcare industry and clinical practice.
How to Get Into a Health Informatics PhD Program: Admission Requirements
The requirements to get into a health informatics PhD program include having a minimum of an undergraduate degree in a related field. Some PhD programs require a Master’s Degree in Health Informatics and at least three to five years of relevant work experience. Each program will require official transcripts from previous universities.
Additional requirements may include two to three letters of recommendation, GRE or GMAT test scores, a current resume, and a personal statement. English as a second language (ESL) students will need to provide proof of English proficiency in the form of Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) exam scores or the equivalent.
PhD in Health Information Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or Master’s Degree in Health Informatics or a related field
- Letters of recommendation
- Standardized test scores, such as GRE or GMAT
- Current resume showing relevant work experience
- Personal statement
- TOEFL exam or equivalent (for ESL students)
Health Informatics PhD Acceptance Rates: How Hard Is It to Get Into a PhD Program in Health Informatics?
It can be hard to get into a health informatics PhD program, but not harder than many other types of doctorate programs. Most schools have an acceptance rate of less than 40 percent. Doctoral students must be highly focused and qualified in their previous academic and work experience to be accepted into a PhD program.
How to Get Into the Best Universities
[query_class_embed] how-to-get-into-*school
Best PhDs in Health Informatics: In Brief
Best universities for health informatics phds: where to get a phd in health informatics.
You can find some of the best universities for health informatics across the United States in our list above. Depending on the school, you might have the option to choose between online or in-person learning. Below, we’ll take a close look at the best PhDs in Health Informatics.
Dakota State University was founded in 1881 as a teacher’s school. While educating future teachers remains an essential objective of the university, it has since shifted to focus on technology. The public university now enrolls over 3,000 undergraduate and graduate students annually.
PhD in Information Systems
This flexible PhD in Information Systems program will allow students to learn comprehensive information systems with specialization options in healthcare, analytics, or security. Students will receive a balance of both theory and practice in key informatics concepts with the choice of completing this program full-time, part-time, online, or on campus.
PhD in Information Systems Overview
- Program Length: 3 years
- Acceptance Rate: Not stated
- Tuition and Fees: $3,365/semester (in-state); $5,965/semester (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: General scholarships, graduate assistantships
Dakota State University Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s degree or higher
- 3.0 minimum GPA
- GRE exam scores
- Knowledge of business fundamentals and information systems
Indiana University was founded in 1820 as a public research university and the flagship campus of the Indiana University system. It began as State Seminary College before becoming Indiana College in 1829. Indiana University offers over 400 graduate degree and certificate programs to more than 8,500 graduate students.
PhD in Informatics
The PhD in Informatics program at Indiana University offers a specialization track in health. The program focuses on the standards, terminology, and electronic health data exchange of informatics. In addition, students will learn about mining clinical data, as well as developing and implementing health applications.
PhD in Informatics Overview
- Program Length: 4-5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 38.3%
- Tuition: $26,449/year
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Tuition remission, associate instructor and teaching assistant opportunities (full-time students only)
Indiana University Bloomington Admission Requirements
- GRE scores (optional)
- Official transcripts
- Three letters of recommendation
- Current resume
Liberty University is a private, nonprofit university that was founded in 1971. It is a private Evangelical university and one of the largest Christian universities in the world. Liberty University offers over 75 online and on-campus doctoral degree programs to more than 33,000 graduate students.
Doctor of Business Administration in Healthcare Management
The Liberty University Doctorate in Business Administration in Healthcare Management offers a practical approach to healthcare informatics and trains students in healthcare management, quality healthcare systems, and human resource development. This 60-credit program can be completed entirely online within three years.
Doctor of Business Administration in Healthcare Management Overview
- Acceptance Rate: 50%
- Tuition and Fees: $595/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Loans, federal aid, scholarships
Liberty University Admission Requirements
- Master's Degree in Business Administration or a related field
- Statement of purpose
University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) became an autonomous university in the University of Alabama System in 1969. UAB is a public research institution that is renowned for its graduate programs in health management and medicine. The university offers over 150 master’s and doctorate programs to more than 8,500 graduate students.
PhD in Administration-Health Services
The University of Alabama at Birmingham’s PhD in Administration Health Service interdisciplinary program teaches students the fundamentals of health economics, health insurance, and the development of the US healthcare system. Students will also learn administrative theory, healthcare finance, and health policy.
PhD in Administration-Health Services Overview
- Program Length: 3-6 years
- Tuition and Fees: $465/credit (in-state); $1,098/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Primary instructor or teaching assistant positions, research assistantships, doctoral fellowships for minority students, and Blazer Graduate Fellowships
University of Alabama Birmingham Admission Requirements
- Master's or bachelor's degree with relevant work experience
- Updated resume
- GRE or GMAT exam scores
- Admissions interview
University of Florida (UF) is a public, land-grant research institution founded in 1906. The university is ranked 28th on the US News & World Report’s list of national universities . UF offers more than 700 doctoral degree programs to over 16,000 graduate students enrolled at its Gainesville campus.
PhD in Medical Sciences, Biomedical Informatics
This 90-credit UF PhD program trains students in biomedical informatics, an interdisciplinary, health-centered field consisting of engineering, computing, biostatistics, medicine, and data science. Students of this program will learn cutting-edge technology, tools, and research methods to prepare them for health informatics careers in research and academia.
PhD in Medical Sciences, Biomedical Informatics Overview
- Program Length: 5-6 years
- Acceptance Rate: 26%
- Tuition and Fees: $12,740/year (in-state); $30,134/year (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Fellowships, McNair Doctoral Scholars Program, graduate research and teaching assistantships, tuition waivers, a yearly stipend of approximately $29,700
University of Florida Admission Requirements
- Master’s or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field
- 3.0 GPA (for bachelor’s degree holders)
University of Iowa (UI) is a large public research university founded in 1847. UI was the first coeducation medical school in the country and is the oldest university in Iowa. The university offers more than 100 graduate programs, 12 of which are among the top ten programs in the country.
PhD in Health Informatics
The University of Iowa’s 72-credit PhD in Health Informatics degree program focuses on the processes used to improve healthcare-related data utilization. Students will explore topics such as storing medical information and important state and federal regulations regarding health care.
PhD in Health Informatics Overview
- Acceptance Rate: 29%
- Tuition and Fees: $12,065/year (in-state); $31,012/year (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Iowa Recruitment Fellowships, Post-Comprehensive Research Awards, Center for Advancement’s Student Impact Grant, T. Anne Cleary International Dissertation Research Fellowships
University of Iowa Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or master’s degree
University of Minnesota was founded in 1851 and is the oldest university in Minnesota. University of Minnesota began as a struggling college prep school before finding its footing and becoming the flagship campus of the University of Minnesota system. It is now the largest public university in Minnesota with a total enrollment of more than 51,000 students.
PhD in Health Informatics
This PhD in Health Informatics degree program offers multiple specialization options. The 70-credit Clinical Informatics track trains students in relevant clinical application methods, teaching them about health data, biostatistical methods, coding system analysis, and human-computer interactions.
- Program Length: 4 years
- Acceptance Rate: 66%
- Tuition and Fees: $8,922/semester (in-state); $13,806/semester (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Merit-based fellowships, graduate teaching, research assistantships
University of Minnesota Admission Requirements
- 3.5 minimum GPA recommended
- GRE exam scores
University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston was created in 1972 as part of the University of Texas System. UT Health Science Center at Houston is a part of the Texas Medical Center, which is the largest in the world of its kind. The university is considered Texas' source of health education and was the first to offer an advanced degree in health informatics.
PhD in Biomedical Informatics
University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston features a 93-credit, on-campus doctoral program that trains students in fundamental informatics concepts, theories, and practices that can be applied to all areas of health care. Students work in teams to conduct cutting-edge research and aim to solve real-world biomedical problems in the field.
PhD in Biomedical Informatics Overview
- Program Length: 4-years
- Tuition and Fees: $4,944/semester (in-state); $11,808/semester (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Full-ride scholarships based on merit, graduate teaching, research assistantships
University of Texas Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or master’s degree
- Three letters of recommendation
- Personal goals statement
University of Utah opened its doors in 1850 as University of Deseret. In 1892, the college changed its name to University of Utah. It remains the oldest institute of higher education in Utah. The university offers more than 200 graduate and doctoral degree programs to over 8,000 graduate students.
PhD in Biomedical Informatics
University of Utah’s PhD in Biomedical Informatics program has a specialization track in Health Care and Clinical Informatics. This program works closely with the Nursing Informatics program to teach students how to support the implementation of evidence-based practices, as well as the foundational concepts and technology of electronic health records.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
- Program Length: 3-4 years
- Tuition and Fees: $4,139.44/credit (in-state); $7,384.96/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Fully funded tuition for all admitted students, including a yearly stipend of $29,710
University of Utah Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s degree or higher
- 3.3 minimum GPA
Founded as Milwaukee Normal School in 1885, University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee is the largest university in the Milwaukee metro area. Since changing its name to University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee (UWM) in 1956, it has become home to over 24,000 students and 4,700 graduate students.
PhD in Biomedical and Health Informatics
Students enrolled in UWM’s biomedical PhD program are trained in health care management processes and technology that support medical records, instrumentation, and information processing needs of consumers and clinics. Students of this program will have the necessary skills and expertise to become research leaders in the field.
PhD in Biomedical and Health Informatics Overview
- Program Length: 3-5 years
- Tuition and Fees: $12,219/year (in-state); $25,650/year (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: McNair Fellowship, graduate teaching and research assistantships, Advanced Opportunity Program Fellowship, Distinguished Dissertation Fellowship, Distinguished Graduate Student Fellowship
University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee Admission Requirements
- Master’s Degree in Biomedical and Health Informatics or a related field ( exceptionally qualified candidates with a bachelor’s degree in a related field may be considered)
Can You Get a PhD in Health Informatics Online?
Yes, you can get a PhD in Health Informatics online. An online program allows you to take courses that fit into your personal work schedule, as many programs are intended for students who are already working in the health informatics field.
Best Online PhD Programs in Health Informatics
How long does it take to get a phd in health informatics.
It typically takes between three to five years of full-time study to get a PhD in Health Informatics. Usually, core courses are completed within the first two years and electives are completed in the third year. In the final year of your health information technology doctoral degree program, you will work on your dissertation, capstone project, or doctoral thesis. Some programs require a comprehensive exam in addition to the culminating project requirement.
Is a PhD in Health Informatics Hard?
Yes, a PhD in Health Informatics can be hard to obtain, with many hours spent studying and conducting research in challenging areas of the field. A health informatics program requires students to have knowledge in complicated disciplines like computer science, biostatistics, and medicine.
Additionally, a PhD requires more than just technical skills. You’ll also need to focus on important soft skills such as leadership, communication, and teamwork. Nonetheless, with hard work and dedication, getting a PhD in Health Informatics is more than possible to achieve.
How Much Does It Cost to Get a PhD in Health Informatics?
It costs $19,314 to get a PhD in Health Informatics, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. However, this value is an average of the tuition costs of all graduate degree-granting institutions. The total cost will vary on different factors, such as whether the university is public or private and whether you are a resident or non-resident.
How to Pay for a PhD in Health Informatics: PhD Funding Options
Most schools offer numerous PhD funding options that students can take advantage of to pay for a PhD in Health Informatics program. These options often include loans, scholarships, and fellowships. Most of these options are based on merit and need, so you should look into what options are offered by the school and how to apply for them.
Some schools also offer fully-funded PhD programs that cover the total cost of tuition and fees, as well as provide a yearly stipend. In these programs, students work in research or teaching assistantships in exchange.
Best Online Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] online-*subject-masters-degrees
What Is the Difference Between a Health Informatics Master’s Degree and PhD?
The difference between a health informatics master’s degree and a PhD is the curriculum and the overall length and level of study. A master’s degree is a graduate program that will help you obtain the relevant technical skills needed for a job in the health informatics field. These degrees typically take two years and go beyond the general topics taught in an undergraduate program.
While a master’s degree features more advanced studies than a bachelor’s degree, the PhD takes it a step further and focuses on specific learning tracks like data science, clinical informatics, and precision medicine informatics. PhDs take four to six years to complete and are the highest educational qualification you can receive in any field of study.
Master’s vs PhD in Health Informatics Job Outlook
Health informatics is a rapidly growing field. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, medical and health services managers have an outlook of 32 percent job growth by 2030. This profession requires a master’s degree and many years of relevant experience, or a PhD, DHA, or equivalent.
On the other hand, records and health information specialists, a profession that only requires an associate or bachelor’s degree, are expected to see job growth of nine percent by 2030 , a rate that is much lower than that of health services managers.
Difference in Salary for Health Informatics Master’s vs PhD
The average salary for someone with a Master’s Degree in Health Informatics is approximately $65,000 per year, according to PayScale. In comparison, PhD holders earn an average annual salary of $119,000 per year . PhD candidates are more qualified by default and can work in high-paying senior managerial and research positions, or teach in higher education institutions.
Related Health Informatics Degrees
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-health-informatics-associate-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-health-informatics-bachelors-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/health-informatics-masters-degrees/
Why You Should Get a PhD in Health Informatics
You should get a PhD in Health Informatics because you will gain in-depth, expert-level knowledge of the healthcare industry and the skills necessary to best support patient information storage. A PhD program will allow you to learn excellent research, technical, analytical, and theoretical skills and concepts that will prepare you for the career of your choice.
Reasons for Getting a PhD in Health Informatics
- Career opportunities. Health informatics is a growing field with plenty of career opportunities. As more jobs open in this field, more managers with the appropriate education are necessary. Those with a PhD are the most qualified candidates and will find an abundance of available positions to apply for.
- Interesting work. There are many interesting and exciting facets to a career in the health informatics field. An analytically-minded candidate can create databases, analyze patient data, and create applications to maintain data and ensure patient privacy.
- Higher earning potential. Having a PhD enables you to demand a high salary and great benefits. Because it is the highest qualification possible, PhD holders are able to negotiate higher salary compensation in comparison to those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees.
- Specialized education. A PhD allows you to focus on specific areas of health informatics that interest you most. This specialization experience can make you an expert on a particular subject and help you with your career after graduation.
Getting a PhD in Health Informatics: Health Informatics PhD Coursework

A PhD in Health Informatics program requires several core courses to earn your degree. Health informatics PhD coursework explores the fundamentals of informatics, as well as specialization or elective courses based on your interests. Below are a few of the most common courses you may see in a program’s health informatics curriculum.
Introduction to Health Informatics
In an introductory informatics course, students will learn fundamental informatics concepts with a more refined look at the relevant health information technology used in the field. The course explores the data types, use of data, and relevant modeling processes to store and process patient data.
Introduction to Biostatistics
An introduction to biostatistics class focuses on biological data and the statistical techniques used to sample and analyze data. Students work with hypothesis tests, simple linear regression, and categorical data analysis.
Database Systems
Database systems classes explain how to create and query databases. Students will learn how to use SQL, ER diagrams, and develop relational databases. They will also learn to program web applications using JDBC or PHP.
Human-Computer Interactions
Human-computer interactions courses teach students about UX design programs and how consumer behavior applies to user experience design. This course also covers the concepts and practices of informatics architecture.
Health Information Technology Policy
Health information technology policy focuses on key policy issues in the United States. Some courses may also cover a few international policies. They focus on the three major areas of consumer, clinical, and biomedical informatics.
Best Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] *subject-masters-degrees
How to Get a PhD in Health Informatics: Doctoral Program Requirements
Knowing exactly how to get a PhD in Health Informatics is essential before applying for a doctoral program. Many programs require a certain amount of credit hours, publication requirements, and a dissertation or capstone project. While each program varies slightly, you should be prepared to complete each of the following steps before you graduate.
All universities will require a certain amount of credit hours to be completed before graduation. These requirements can range from 60 to more than 100 credit hours for a PhD program.
Some universities require a capstone project in place of a doctoral thesis. Students typically spend their final year of studies working on a capstone project. You will have to announce your project to the department and have it approved before you start working on it.
Many universities require PhD candidates to spend their final semesters working on a research dissertation or thesis. Your thesis will need to consist of original research with a full explanation of the conclusions you've reached during your project.
Once you have completed your thesis, you will have to attend a meeting with your advisor and other PhD department faculty. During this meeting, you will orally present your research and findings, and you will be asked questions about your thesis. You must answer the questions in a way that convinces the faculty that you have successfully completed doctorate-level work.
During your first and second years of the PhD program, you will have to take and pass comprehensive exams. These exams are often quite challenging and prove that you have successfully retained and mastered the information learned in your first few years of study.
Potential Careers With a Health Informatics Degree
[query_class_embed] how-to-become-a-*profession
PhD in Health Informatics Salary and Job Outlook
Professionals with a PhD in Health Informatics can earn six-figure salaries per year. Health informatics is a growing field, with most jobs featuring an above-average job growth outlook within the next decade.
What Can You Do With a PhD in Health Informatics?
With a PhD in Health Informatics, you can work in the public or private health care system, keeping clinics and hospitals in line with federal regulations. Many career options requiring a PhD in Health Informatics include leadership or educator roles.
Best Jobs with a PhD in Health Informatics
- Health IT Project Manager
- Nursing Informatics Director
- Health Services Director
- Postsecondary Education Administrator
- Clinical Analyst
What Is the Average Salary for a PhD in Health Informatics?
The average salary for someone with a PhD in Health Informatics is $119,000 per year . Health informatics can extend to nursing informatics director roles, which require a Doctor of Nursing Practice degree. However, these professionals perform many of the same tasks as those with a PhD.
Highest-Paying Health Informatics Jobs for PhD Grads
Best health informatics jobs with a doctorate.
The best health informatics jobs for doctoral degree holders include management and director positions. Most of these positions require a postgraduate degree and several years of relevant work experience in the informatics field.
Health IT project managers are in charge of installing and maintaining hardware, software, and all computer-related activities and goals for a health organization. In addition, they analyze an organization’s technological needs and work to ensure project objectives and goals are completed by required deadlines.
- Salary with a Health InformaticsPhD: $159,010
- Job Outlook: 11% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 482,000
- Highest-Paying States: New York, California, and New Jersey
A nurse informatics director is a nurse practitioner responsible for being a bridge between the clinical side and IT department of a health organization. These professionals facilitate communication between vendors, faculty, and IT department staff. They also evaluate new IT applications and train staff on new technology.
- Salary with a Doctorate Nurse Practitioner- Nurse Executive: $123,780
- Job Outlook: 45% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 271,900
- Highest-Paying States: California, New Jersey, New York
A postsecondary teacher develops a teaching plan for the relevant informatics courses they teach. They may teach multiple lessons in their department each semester. They instruct university students on course topics, stay informed about subject changes, and assess student progress.
- Salary with a Health Informatics PhD: $102,720
- Job Outlook: 12% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 242,700
- Highest-Paying States: Washington, Mississippi, and Connecticut
A health services manager is directly responsible for developing and overseeing important clinical department tasks. These tasks include hiring, training, evaluating, and supervising all clinical employees. They must also work with financial department staff to develop relevant program budgets.
- Salary with a Health Informatics PhD: $101,340
- Job Outlook: 32% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 429,800
- Highest-Paying States: New York, Washington DC, and Massachusetts
A clinical analyst is responsible for evaluating data and maintaining a healthcare facility’s clinical information system. It is a clinical analyst’s responsibility to create and maintain all database systems used by the facility, interpret and analyze data, and come up with solutions to technical problems.
- Salary with a Health Informatics PhD: $70,601
- Number of Jobs: 100,500
- Highest-Paying States: Washington DC, Massachusetts, and California
Is a PhD in Health Informatics Worth It?
Yes, a PhD in Health Informatics is worth it. With a rapid growth rate, there is a need for well-educated employees in the field. Doctoral degree holders have the option of choosing between working on the analytical or technical sides to meet their interests.
A doctoral student in health informatics should focus on finding a program that matches their desired learning track. Several graduate schools offer focused informatics tracks that will allow you to use the informatics practices that interest you most.
Additional Reading About Health Informatics
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/health-informatics/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/health-informatics-careers/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/masters-in-health-informatics-scholarships/
PhD in Health Informatics FAQ
Yes, you can work from home with a degree in health informatics. However, many of the positions that are exclusively available to PhD-holders require you to work in person.
Yes, health informatics is considered a STEM major. With an educational focus on the health care field and data analysis, health informatics falls into both categories of science and technology.
No, you don’t need to know how to code for a health informatics degree. However, it may be beneficial to have some coding knowledge if you are tasked with building a new database.
No, you typically cannot work as a health informatics professional without a degree. It is a technical field that requires a foundational understanding of the relevant systems and protocols. Therefore, you must have at least a bachelor’s degree to begin your professional journey and gain experience in the field.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Center for Health Data Science
The Center for Health Data Science leverages data in combination with knowledge across disciplines and places, with the ultimate goal of addressing quality of life and other public health priorities. CHDS enhances interdisciplinary public health research, teaching and practice through leveraging and developing data science methods in conjunction with public health knowledge, frameworks and action as well as with other disciplines such as computer science, urban planning and sociology. CHDS values and promotes pluralistic knowledge discovery and action, such as through cross-border student and faculty exchanges based on long-term relationships, and by working directly with practitioners on the ground to help address community needs.
Visit Website
- Current Students
- Faculty + Staff
- Alumni + Friends
- Parents + Family
- Community + Visitors
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificates
- Arts & Design
- Business & Industry
- Communications & Media
- Data Analytics & Information
- Health & Wellness
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Music & Performing Arts
- Public Service
- Multidisciplinary
- Still Exploring & Undetermined
- International
- Bienvenidos
- Featured Videos
- College Tour
- Tuition & Aid
- Student Life
- Search Type Search Search
- Quicklinks:
- STUDENT EMAIL
- UNT DIRECTORY
- INFO FOR CURRENT STUDENTS
- INFO FOR FACULTY + STAFF
- INFO FOR ALUMNI + FRIENDS
- INFO FOR PARENTS + FAMILY
- INFO FOR COMMUNITY + VISITORS
- UNT LIBRARIES
- UNT CALENDAR
- JOBS AT UNT

Information Science Ph.D. With a Concentration in Health Informatics
Want more info.
We're so glad you're interested in UNT! Let us know if you'd like more information and we'll get you everything you need.
Why Earn an Information Science Ph.D. With a Concentration in Health Informatics?
The UNT Information Science Ph.D. program with a concentration in Health Informatics responds to the varied and changing needs of an information age, increasing recognition of the central role of information and information technologies in individual, social, economic and cultural affairs.
The mission of UNT's Information Science Ph.D. program is to provide a center of excellence in graduate education and research. Its primary goals are to:
- Nurture critical and reflective thinking on the fundamental issues and elements of problems of utilization of information
- Foster an environment of substantive and productive mentoring and apprenticeship
- Prepare scholars passionate about the role of information in human affairs
- Foster cross-disciplinary thinking and research.
Students are recruited to the program from a wide range of disciplines and encouraged to expand and refocus their expertise and skills in cutting-edge areas of information science that cross disciplinary boundaries. The multifaceted nature of information science warrants the focusing of resources, courses and faculties from a broad range of academic units.
- Research and publication
- Pedagogical practices
- Critical thinking
- Leadership ability
- Data analysis
Information Science Ph.D. With a Concentration in Health Informatics Highlights
What can you do with an information science ph.d. with a concentration in health informatics.
There is a great need for a health care workforce that possesses the skills and competencies that this concentration provides. Graduates will be able to work in health care as well as health information management settings.
Information Science Ph.D. With a Concentration in Health Informatics Courses You Could Take
Learn More About UNT
Explore more options.
Information Data Science Ph.D.
Consumer Behavior and Experience Management Information Science Ph.D.
It’s easy to apply online. Join us and discover why we’re the choice of nearly 47,000 students.
Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.
Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
Public Health Data Science
The MS in Biostatistics Public Health Data Science Track (MS/PHDS) is designed for students interested in careers as biostatisticians applying statistical methods in health-related research settings. The MS/PHDS Track provides core training in biostatistical theory, methods, and applications, but adds a distinct emphasis on modern approaches to statistical learning, reproducible and transparent code, and data management. It is an appropriate program for students who intend to conclude their studies with the MS degree as well as those who want to pursue a PhD in biostatistics
All MS/PHDS candidates begin their studies in the fall semester. The length of the MS/PHDS program varies with the background, training, and experience of the candidate, but the usual period needed to complete the 36 credit MS/PHDS degree is two years (four semesters). In addition to fulfilling their course work, all MS/PHDS students also complete a one-term practicum and capstone experience.
Competencies
Through a curriculum of 36 credit hours of course work, a practicum, and the capstone experience, the MS/PHDS track provides students with the skills necessary for a career as a public health data scientist and a rigorous grounding in traditional biostatistics.
In addition to achieving the MS in Biostatistics core competencies, students in the PHDS Track gain the following specific competencies in the areas of public health and collaborative research, the foundations of applied data science, teaching biostatistics and biostatistical research. Upon satisfactory completion of the MS/PHDS, graduates will be able to:
Public Health and Collaborative Research
- Formulate and prepare a written statistical plan for analysis of public health research data that clearly reflects the research hypotheses of the proposal in a manner that resonates with both co-investigators and peer reviewers;
- Prepare written summaries of quantitative analyses for journal publication, presentations at scientific meetings, grant applications, and review by regulatory agencies;
Foundations of Applied Data Science
- Develop expertise in one or more statistical software and database management packages (often R and SQL, among others) routinely used by data science professionals;
- Implement a reproducible workflow for data analysis projects, including robust project organization, transparent data management, and reproducible analysis results;
- Develop and execute analysis strategies that use traditional statistical tools or modern approaches to statistical learning, depending on the nature of the scientific questions of interest;
- Identify the uses to which data management can be put in practical statistical analysis, including the establishment of standards for documentation, archiving, auditing, and confidentiality; guidelines for accessibility; security; structural issues; and data cleaning;
Teaching Biostatistics
- Review and illustrate selected principles of study design, probability theory, estimation, hypothesis testing, statistical learning, and data analytic techniques to public health students enrolled in introductory level graduate public health courses; and
Biostatistical Research
- Apply probabilistic, statistical, and data scientific reasoning to structure thinking and solve a wide range of problems in public health.
Course Requirements
MS/PHDS graduates are expected to master the mathematical and biostatistical concepts and techniques presented in the curriculum’s required courses. Each student's program is designed on an individual basis in consultation with a faculty advisor taking into consideration the student's prior educational experience.
Students who have mastered an academic area through previous training may have the corresponding course requirement waived. Some students, such as those with undergraduate majors in statistics or mathematics, may apply to have several courses waived. Students wishing to waive one or more courses must request approval in writing from their advisors and the Director of Academic Programs. These students must still complete a minimum of 36 points to earn the MS/PHDS degree.
Required Courses
Below is the required course work. Students consult their faculty advisors before registering for classes to plan their programs based on their individual background, goals, and the appropriate sequencing of courses. Waiver of any required courses (with prior written approval of their faculty advisor and the Director of Academic Programs) enables students to take other, higher level classes.
*Students who have strong math background and/or have taken basic machine learning methods, can substitute the P8106 Data Science II with P9120 Topics in Statistical Learning and Data Mining I.
Students choose four or more courses from the list below or from alternatives approved by their academic advisors.
Sample Timeline
Below is a sample timeline for MS/PHDS candidates. Note that course schedules change from year to year, so that class days/times in future years will differ from the sample schedule below; you must check the current course schedule for each year on the course directory page .
Practicum Requirement
One term of practical experience is required of all students, providing educational opportunities that are different from and supplementary to the more academic aspects of the program. The practicum may be fulfilled during the school year or over the summer. Arrangements are made on an individual basis in consultation with faculty advisors who must approve both the proposed practicum project prior to its initiation, and the report submitted at the conclusion of the practicum experience. Students will be required to make a poster presentation at the department’s Annual Practicum Poster Symposium which is held in early May.
Capstone Experience
A formal, culminating experience for the MS degree is required for graduation. The capstone consulting seminar is designed to enable students to demonstrate their ability to integrate their academic studies with the role of biostatistical consultant/collaborator, which will comprise the major portion of their future professional practice.
As part of the seminar, students are required to attend several sessions of the Biostatistics Consulting Service (BCS). The Consultation Service offers advice on data analysis and appropriate methods of data presentation for publications, and provides design recommendations for public health and clinical research, including preparation of grant proposals. Biostatistics faculty and research staff members conduct all consultation sessions with students observing, modeling, and participating in the consultations.
In the capstone seminar, students present their experience and the statistical issues that emerged in their consultations, developing statistical report writing and presentation skills essential to their professional practice in biomedical and public health research projects.
Paul McCullough Director of Academic Programs Department of Biostatistics Columbia University [email protected]
- Visit the Gateway
- Visit the Alliance
- Visit HDR UK Futures
HDR UK-Turing Wellcome PhD Programme in Health Data Science
This truly outstanding and generously funded four-year programme at top UK universities provides you a pathway to join the UK’s leaders in health data research.
What this unique PhD programme offers you
Four-year programme: An initial foundation year allows students to gain real experience and insight into health data research.

Hosted by leading universities: Our host universities are among the very best in health data research.
Nurturing each student: Our programme aims to identify the particular abilities and interests of each student, and gear their PhD experience to effectively develop them.
Leadership Programme: Students benefit from a bespoke expert-led programme to develop the skills they need to understand, collaborate and influence others.
Generous funding: Students have their tuition fees (UK Home rate), college fees (where applicable), research expenses and travel costs paid and receive an enhanced, tax-free stipend with increases every year. (Y1 outside London: £23,955, Y1 in London: £25,954)
Building networks and experience: We actively support students in building networks and contacts in academia, the NHS and industry as well as taking internships and other opportunities to gain real-world experience. This includes a post-PhD bursary to support your next career step.
Team spirit: Strong relationships are built between our entire cohort of students through joint activities that build a genuine team spirit.
Personal support: Each student has their own Director of Studies who is an additional point of contact during their time with us. All students are also further supported by the PhD team.

“The PhD programme has enabled me to gain first-hand experience in modern health data science approaches. It’s a truly unrivalled opportunity.” Steven Wambua
Who is the PhD programme for?
We recruit enthusiastic, talented students who want to use data-driven research to develop and shape the UK’s response to the most complex health challenges of our times.
Applicants must have (or be on track to obtain):
- A first class or 2:1 undergraduate degree in statistics, mathematics, computer / data science, physics or an allied subject or
- Another undergraduate degree subject and outcome but can demonstrate their suitability for this programme through additional qualifications or research experience.
Active or currently registered health care professionals are not eligible and should consider the Wellcome PhD Fellowships for Health Professionals .
Applicants also need to meet the following criteria:
- Successful admission to the specified degree programme at one of our partner universities. Students will be expected to meet the admissions requirements of that department and university but do not need to hold the offer at the point of application.
- Two satisfactory academic or relevant references.
- Proof of a legal right to study in the UK or ability to satisfy the current requirements of UK Visa and Immigration.
Training is in-person, hybrid and virtual throughout the first year.
We are committed to a diverse and inclusive research culture . We welcome those who are returning from the workplace, international candidates and everyone underrepresented in STEM and academia. For further details see our FAQs .
We cannot accept applicants who are looking for a part-time PhD or those who are aiming to study whilst continuing to be employed elsewhere.
We aim to accommodate specific needs and personal circumstances. Please make us aware of individual circumstances when applying or contact us directly at [email protected] . Please note our applicant privacy notice .
If you have questions or require adjustments to the application process, please contact us below via email or telephone (+44 (0)770 847 8846).
There are no nationality restrictions and international students are able to apply. However, applicants are advised the award only covers fees at the UK/Home level. International students will be required to secure an additional scholarship from Queen’s University Belfast (after receiving a offer from us at interview) to cover the difference between Home and Overseas fees. This will limit the university choices available:
(Please be aware that these are usually highly competitive and will need to be applied for separately in your application to Queen’s University Belfast post-offer. A successful application to the PhD programme does not guarantee a fee waiver or scholarship. We do not accept applications from candidates who are self-funding.)
We are currently only recruiting for Queen’s University Belfast.
These are only initial programmes of study for Year 1. Students may transfer to a new university programme from Year 2 after research projects have been confirmed.
Is this the PhD future for you?
Watch our Applicant Open Day hosted by our current students to find out more about the programme and whether it’s for you.

Applications are currently: Closed
The application process.
Details required:
- Contact details
- Details and transcripts of university qualification(s)
- Any relevant job history
- Answers to personal-statement type questions (250-words maximum for each answer)
- Contact details for two referees
- There is no need to apply to the university, submit a research proposal, provide IELTS scores or contact supervisors at this stage
Submitted applications will first be checked for eligibility and then will undergo a first stage review. This will involve triage by the PhD Team in April 2024 . Successful applicants will be invited to an interview in May 2024 .
After receiving an offer, applications will be invited to apply to Queen’s University Belfast.

Selection criteria
Applicants should demonstrate that they meet the following criteria:
* These criteria will be assessed at interview via a pre-interview exercise.
HDR UK reserves the right to reject applicants who do not meet the criteria at any stage. Regretfully, we can only provide feedback for candidates who reach interview.
Programme Structure
The four-year programme is divided in two. There is an initial Foundation Year followed by a three-year research project. The first year combines the best in university-based training with HDR UK-led national activities. And we support students to produce game-changing research plans and their projects are backed by substantial research funding.

Foundation year
3-5 day immersion events allow students to gain insight into the work of HDR UK, and our academic, clinical and industry partners. Courses may be residential (expenses provided) with up to a week away from their home university or online. Students undertake an intensive deep dive into an important area of health data science. Immersion topics include risk prediction, oncology, clinical trials, epidemiology and bioinformatics. Past immersion weeks have been hosted by the Universities of Birmingham, Manchester, Oxford and University College London and the European Bioinformatics Institute.
The immersion events encourage students to work together and stimulate new interactions:
- Axes of Prognosis
- The Different Facets of Data
Research areas
PhD research projects can be linked to The Institute’s:
- Research priorities
- Research hubs
- Partnerships
Team working
Students operate as a national cohort and work collaboratively with others, overcoming traditional institutional silos. Students are registered with a partner university but can draw on academic expertise from across the HDR UK network and are supported to formulate research activities that bring together experts from across the UK.
- You can contact us at [email protected] or phone (+44 (0)770 847 8846).
- For details of how we process applicants’ data see PhD Applicant Privacy Notice .
Students have access to graduate-level courses and research project rotation in their university to introduce them to different areas of health data science and enable them to develop a bespoke research project under the guidance of our expert university leads.
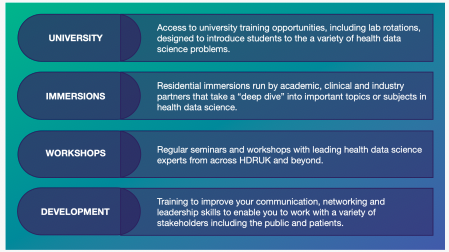
Regular workshops and short courses introduce students to the work of HDR UK experts across our hubs, themes and priority areas and to external organisations. Past contributors have included NHSX, IQVIA and AstraZeneca.
Immersion and workshop events allow students to better understand the wider health and social care landscape and accelerate their potential to become sector leaders. They also enable students to develop more ambitious PhD research projects by stimulating collaboration with external academics, industry-based organisations, or by using national data infrastructure.
Training is provided by academic, industry and NHS experts to promote personal and professional development in leadership capability, cross-sector collaborative skills and inter-disciplinary working. In particular, HDR UK is committed to working with public and patients to build increased trust in health data research as well as designing solutions focused on improving patient outcomes and experience. Students will develop communication and collaborative skills to help put them at the forefront of this mission.
At the end of the Foundation Year students design a bespoke three-year research project and a multi-disciplinary supervision team based on their training experiences.
Research proposals will be rigorously reviewed by expert academics and public-patient representatives to ensure they are of the highest standards in terms of ambition, scientific methodology and impact on patient outcomes.
The research will be carried out at their home university and could be linked to HDR UK research priorities , research hubs or partnerships .

This includes short immersions plus longer practical real-world projects with businesses and other organisations at the cutting edge of everything from medical devices, to life sciences, to vaccines. Students also learn about leadership theory and attend specially-convened seminars from senior figures in relevant areas of healthcare.
Networks and experience: Students will be actively supported in building networks and contacts in academia, the NHS and industry as well as taking internships and other opportunities to gain real-world experience.
Team working: Students operate as a national cohort, building strong relationships through joint activities and overcoming traditional institutional silos.
Workshops: Regular workshops and short courses introduce the work of HDR UK experts and to external organisations.
Immersion events: These allow students to better understand the wider health and social care landscape and accelerate students’ potential to become a sector leader. They also enable them to develop an ambitious PhD research project.
Researcher development: Training is provided by academic, industry and NHS experts to promote personal and professional development in cross-sector collaborative skills, communication and inter-disciplinary working.
“Our Leadership Programme will give PhD students the chance to develop the practical skills they need to bring people together to use health data science to deliver much-needed innovations and advances in health and care,” Professor Peter Bannister
Our partners
Programme partners include NHS Digital, AstraZeneca, Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and University Hospitals Birmingham.
More broadly it will work with winners of the NHSX AI Innovation Award , which funds and supports promising artificial intelligence technologies in health and care. There will also be opportunities with businesses on the DTI listed top 100 digital health innovators which are using big data for healthcare innovation.

Master’s Degree Scholarships
We offer 10 annual Master’s degree scholarships worth £10,000 for students with an interest in dementia or diabetes research.

Undergraduate Summer Internship in Health Data Research
Apply for a summer work placement in health data research at a UK research organisation, with an HDR UK-Wellcome Biomedical Vacation Scholarship

Join the HDR UK Alumni Network
HDR UK’s online Alumni Network brings together the amazing people who have been part of our training and education programmes.
Our host universities

- - - - Meet our PhD students
Our PhD students come from a wide range of backgrounds - discover who they are and what their experiences have been as part of the PhD programme
Meet the PhD Programme team

Our wider team consists of leading experts in disciplines including theoretical physics, computer science, mathematics and statistics, applied mathematics and biochemistry.
- Miguel Bernabeu – University of Edinburgh
- Ioanna Manolopoulou – University College London
- Niels Peek – University of Manchester
- Iain Styles – Queen’s University Belfast
- Paul Taylor – University College London
- Catalina Vallejos – University of Edinburgh
- Angela Wood – University of Cambridge
- David Wong – University of Manchester
- Tom Nichols – University of Oxford
- Magnus Rattray – University of Manchester
Still accepting applications for online and hybrid programs!
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Accessibility Policy
- Report an Accessibility Issue

Health Data Science Concentration
Course information.
In addition to the existing core and elective courses in the Master of Science or PhD programs, the Health Data Science concentration features four core courses and five elective courses. Some of these courses are part of the current Master of Science program courses and some are new courses designed specifically for the Health Data Science concentration. One of the four core courses replace required courses for the traditional MS degree (BIOS 653: Applied Statistics III – Longitudinal Data Analysis).
Core and Elective Courses
Featured core courses in the Health Data Science concentration
Additional core courses can be found here.
Featured elective courses in the Health Data Science concentration
Course Selection Roadmap
Students' computing skills will be assessed for election of courses from the Health Data Science concentration and other degree core/elective courses. First-year MS students in Biostatistics can access information and advice from the department and faculty to plan their sequence of course selections. Ongoing PhD students are able to complete this concentration. If they choose this route, some additional coursework is needed in order to meet the requirements of both the PhD and the HDS concentration.
HDS students must complete for their capstone courses (i) all four credits of BIOSTAT 699 and (ii) BIOSTAT 629 (1-2 credits). Biostat 629 will correspond to one or two comprehensive projects on mobile health, electronic health records, imaging data, omics data, etc.
Tables I and II below present two examples of course selections for a student with modest computing skills (e.g. having little knowledge of R programming) and for a student with strong computing skills (e.g. having extensive knowledge and experience in R, C++ and Python programming), respectively.
BIOS 607 is designed to prepare students with computing skills. In this way the Health Data Science concentration is more flexible and inclusive as a professional training program for workforce in health data analytics.
Table I. A possible sequence of course selections by an incoming MS student with modest computing skills, who begins with the three modules of BIOS 607.
Table II. A possible sequence of course selections by a first-year MS student with strong computing skills, who does not take BIOSTAT 607 but begins with BIOSTAT 625.
Note that there is one course (BIOS 653) not included in the curriculum of the Health Data Science concentration that is required by the PhD qualifying exams. Students interested in pursuing a PhD should take 653 in place of an elective the 2nd fall semester. Students already in the PhD program should take BIOS 653 for their qualifying exams.
Admissions Information
Students must be admitted to the Master of Science or PhD program in the University of Michigan School of Public Health's Department of Biostatistics. Once admitted, students will declare their intention to pursue the Health Data Science concentration at the end of their first year, by the end of May.
Have Questions?
For more information about the Health Data Science concentration, contact one of our graduate program coordinators.
Fatma Nedjari
Phone: 734-615-9812 Email: [email protected]
Nicole Fenech
Phone: 734-615-9817 Email: [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
How/when do i apply for this program.
The Health Data Science concentration is not an option in the MS application, and thus there is no application procedure. Interested students should simply declare their intention to complete the Health Data Science concentration by May before their first (Fall) semester at Michigan Public Health by notifying a graduate program coordinator (Fatma Nedjari or Nicole Fenech). Students are encouraged to consult with their academic adviser about Health Data Science course selection.
Will I get in? Is there a cap? Am I automatically in? Are there more prerequisites?
There is no screening or selection procedure. This concentration program is open to all incoming Biostatistics MS students and operated as an automatic enrollment option. Interested students are encouraged to make a decision as soon as they arrive in their first Fall semester since the concentration courses are spread out over two years. As a specific track within the MS program, all Health Data Science courses require the same prerequisites as those in the core courses in the MS program.
When will I know if I get in the concentration program?
You may either notify a graduate program coordinator about your desire to pursue the Health Data Science subplan immediately after you decide to accept your admission offer to the Biostatistics MS program or in the beginning of your first Fall semester. At the stage of enrollment, simply follow the courses required by the Health Data Science concentration.
I have been admitted directly from a bachelor's degree program to the PhD program (or I definitely want to do the PhD program). Am I eligible for this Health Data Science concentration?
Yes, although masters' students interested in applying for the PhD program must be sure to include BIOS 653 (Theory and Application of Longitudinal Data Analysis) in their coursework.
Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Alumni and Donors
- Community Partners and Employers
- About Public Health
- How Do I Apply?
- Departments
- Findings magazine
Student Resources
- Career Development
- Certificates
- Internships
- The Heights Intranet
- Update Contact Info
- Report Website Feedback
DiscoverDataScience.org
PhD in Data Science – Your Guide to Choosing a Doctorate Degree Program

Created by aasif.faizal
Professional opportunities in data science are growing incredibly fast. That’s great news for students looking to pursue a career as a data scientist. But it also means that there are a lot more options out there to investigate and understand before developing the best educational path for you.
A PhD is the most advanced data science degree you can get, reflecting a depth of knowledge and technical expertise that will put you at the top of your field.

This means that PhD programs are the most time-intensive degree option out there, typically requiring that students complete dissertations involving rigorous research. This means that PhDs are not for everyone. Indeed, many who work in the world of big data hold master’s degrees rather than PhDs, which tend to involve the same coursework as PhD programs without a dissertation component. However, for the right candidate, a PhD program is the perfect choice to become a true expert on your area of focus.
If you’ve concluded that a data science PhD is the right path for you, this guide is intended to help you choose the best program to suit your needs. It will walk through some of the key considerations while picking graduate data science programs and some of the nuts and bolts (like course load and tuition costs) that are part of the data science PhD decision-making process.
Data Science PhD vs. Masters: Choosing the right option for you
If you’re considering pursuing a data science PhD, it’s worth knowing that such an advanced degree isn’t strictly necessary in order to get good work opportunities. Many who work in the field of big data only hold master’s degrees, which is the level of education expected to be a competitive candidate for data science positions.
So why pursue a data science PhD?
Simply put, a PhD in data science will leave you qualified to enter the big data industry at a high level from the outset.
You’ll be eligible for advanced positions within companies, holding greater responsibilities, keeping more direct communication with leadership, and having more influence on important data-driven decisions. You’re also likely to receive greater compensation to match your rank.
However, PhDs are not for everyone. Dissertations require a great deal of time and an interest in intensive research. If you are eager to jumpstart a career quickly, a master’s program will give you the preparation you need to hit the ground running. PhDs are appropriate for those who want to commit their time and effort to schooling as a long-term investment in their professional trajectory.
For more information on the difference between data science PhD’s and master’s programs, take a look at our guide here.
Topics include:
- Can I get an Online Ph.D in Data Science?
- Overview of Ph.d Coursework
Preparing for a Doctorate Program
Building a solid track record of professional experience, things to consider when choosing a school.
- What Does it Cost to Get a Ph.D in Data Science?
- School Listings
Data Science PhD Programs, Historically
Historically, data science PhD programs were one of the main avenues to get a good data-related position in academia or industry. But, PhD programs are heavily research oriented and require a somewhat long term investment of time, money, and energy to obtain. The issue that some data science PhD holders are reporting, especially in industry settings, is that that the state of the art is moving so quickly, and that the data science industry is evolving so rapidly, that an abundance of research oriented expertise is not always what’s heavily sought after.
Instead, many companies are looking for candidates who are up to date with the latest data science techniques and technologies, and are willing to pivot to match emerging trends and practices.
One recent development that is making the data science graduate school decisions more complex is the introduction of specialty master’s degrees, that focus on rigorous but compact, professional training. Both students and companies are realizing the value of an intensive, more industry-focused degree that can provide sufficient enough training to manage complex projects and that are more client oriented, opposed to research oriented.
However, not all prospective data science PhD students are looking for jobs in industry. There are some pretty amazing research opportunities opening up across a variety of academic fields that are making use of new data collection and analysis tools. Experts that understand how to leverage data systems including statistics and computer science to analyze trends and build models will be in high demand.
Can You Get a PhD in Data Science Online?
While it is not common to get a data science Ph.D. online, there are currently two options for those looking to take advantage of the flexibility of an online program.
Indiana University Bloomington and Northcentral University both offer online Ph.D. programs with either a minor or specialization in data science.
Given the trend for schools to continue increasing online offerings, expect to see additional schools adding this option in the near future.

Overview of PhD Coursework
A PhD requires a lot of academic work, which generally requires between four and five years (sometimes longer) to complete.
Here are some of the high level factors to consider and evaluate when comparing data science graduate programs.
How many credits are required for a PhD in data science?
On average, it takes 71 credits to graduate with a PhD in data science — far longer (almost double) than traditional master’s degree programs. In addition to coursework, most PhD students also have research and teaching responsibilities that can be simultaneously demanding and really great career preparation.
What’s the core curriculum like?
In a data science doctoral program, you’ll be expected to learn many skills and also how to apply them across domains and disciplines. Core curriculums will vary from program to program, but almost all will have a core foundation of statistics.
All PhD candidates will have to take a qualifying exam. This can vary from university to university, but to give you some insight, it is broken up into three phases at Yale. They have a practical exam, a theory exam and an oral exam. The goal is to make sure doctoral students are developing the appropriate level of expertise.
Dissertation
One of the final steps of a PhD program involves presenting original research findings in a formal document called a dissertation. These will provide background and context, as well as findings and analysis, and can contribute to the understanding and evolution of data science. A dissertation idea most often provides the framework for how a PhD candidate’s graduate school experience will unfold, so it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate while considering research opportunities.
Since data science is such a rapidly evolving field and because choosing the right PhD program is such an important factor in developing a successful career path, there are some steps that prospective doctoral students can take in advance to find the best-fitting opportunity.
Join professional associations
Even before being fully credentials, joining professional associations and organizations such as the Data Science Association and the American Association of Big Data Professionals is a good way to get exposure to the field. Many professional societies are welcoming to new members and even encourage student participation with things like discounted membership fees and awards and contest categories for student researchers. One of the biggest advantages to joining is that these professional associations bring together other data scientists for conference events, research-sharing opportunities, networking and continuing education opportunities.
Leverage your social network
Be on the lookout to make professional connections with professors, peers, and members of industry. There are a number of LinkedIn groups dedicated to data science. A well-maintained professional network is always useful to have when looking for advice or letters of recommendation while applying to graduate school and then later while applying for jobs and other career-related opportunities.
Kaggle competitions
Kaggle competitions provide the opportunity to solve real-world data science problems and win prizes. A list of data science problems can be found at Kaggle.com . Winning one of these competitions is a good way to demonstrate professional interest and experience.
Internships
Internships are a great way to get real-world experience in data science while also getting to work for top names in the world of business. For example, IBM offers a data science internship which would also help to stand out when applying for PhD programs, as well as in seeking employment in the future.
Demonstrating professional experience is not only important when looking for jobs, but it can also help while applying for graduate school. There are a number of ways for prospective students to gain exposure to the field and explore different facets of data science careers.
Get certified
There are a number of data-related certificate programs that are open to people with a variety of academic and professional experience. DeZyre has an excellent guide to different certifications, some of which might help provide good background for graduate school applications.
Conferences
Conferences are a great place to meet people presenting new and exciting research in the data science field and bounce ideas off of newfound connections. Like professional societies and organizations, discounted student rates are available to encourage student participation. In addition, some conferences will waive fees if you are presenting a poster or research at the conference, which is an extra incentive to present.

It can be hard to quantify what makes a good-fit when it comes to data science graduate school programs. There are easy to evaluate factors, such as cost and location, and then there are harder to evaluate criteria such as networking opportunities, accessibility to professors, and the up-to-dateness of the program’s curriculum.
Nevertheless, there are some key relevant considerations when applying to almost any data science graduate program.
What most schools will require when applying:
- All undergraduate and graduate transcripts
- A statement of intent for the program (reason for applying and future plans)
- Letters of reference
- Application fee
- Online application
- A curriculum vitae (outlining all of your academic and professional accomplishments)
What Does it Cost to Get a PhD in Data Science?
The great news is that many PhD data science programs are supported by fellowships and stipends. Some are completely funded, meaning the school will pay tuition and basic living expenses. Here are several examples of fully funded programs:
- University of Southern California
- University of Nevada, Reno
- Kennesaw State University
- Worcester Polytechnic Institute
- University of Maryland
For all other programs, the average range of tuition, depending on the school can range anywhere from $1,300 per credit hour to $2,000 amount per credit hour. Remember, typical PhD programs in data science are between 60 and 75 credit hours, meaning you could spend up to $150,000 over several years.
That’s why the financial aspects are so important to evaluate when assessing PhD programs, because some schools offer full stipends so that you are able to attend without having to find supplemental scholarships or tuition assistance.
Can I become a professor of data science with a PhD.? Yes! If you are interested in teaching at the college or graduate level, a PhD is the degree needed to establish the full expertise expected to be a professor. Some data scientists who hold PhDs start by entering the field of big data and pivot over to teaching after gaining a significant amount of work experience. If you’re driven to teach others or to pursue advanced research in data science, a PhD is the right degree for you.
Do I need a master’s in order to pursue a PhD.? No. Many who pursue PhDs in Data Science do not already hold advanced degrees, and many PhD programs include all the coursework of a master’s program in the first two years of school. For many students, this is the most time-effective option, allowing you to complete your education in a single pass rather than interrupting your studies after your master’s program.
Can I choose to pursue a PhD after already receiving my master’s? Yes. A master’s program can be an opportunity to get the lay of the land and determine the specific career path you’d like to forge in the world of big data. Some schools may allow you to simply extend your academic timeline after receiving your master’s degree, and it is also possible to return to school to receive a PhD if you have been working in the field for some time.
If a PhD. isn’t necessary, is it a waste of time? While not all students are candidates for PhDs, for the right students – who are keen on doing in-depth research, have the time to devote to many years of school, and potentially have an interest in continuing to work in academia – a PhD is a great choice. For more information on this question, take a look at our article Is a Data Science PhD. Worth It?
Complete List of Data Science PhD Programs
Below you will find the most comprehensive list of schools offering a doctorate in data science. Each school listing contains a link to the program specific page, GRE or a master’s degree requirements, and a link to a page with detailed course information.
Note that the listing only contains true data science programs. Other similar programs are often lumped together on other sites, but we have chosen to list programs such as data analytics and business intelligence on a separate section of the website.
Boise State University – Boise, Idaho PhD in Computing – Data Science Concentration
The Data Science emphasis focuses on the development of mathematical and statistical algorithms, software, and computing systems to extract knowledge or insights from data.
In 60 credits, students complete an Introduction to Graduate Studies, 12 credits of core courses, 6 credits of data science elective courses, 10 credits of other elective courses, a Doctoral Comprehensive Examination worth 1 credit, and a 30-credit dissertation.
Electives can be taken in focus areas such as Anthropology, Biometry, Ecology/Evolution and Behavior, Econometrics, Electrical Engineering, Earth Dynamics and Informatics, Geoscience, Geostatistics, Hydrology and Hydrogeology, Materials Science, and Transportation Science.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $7,236 total (Resident), $24,573 total (Non-resident)
View Course Offerings
Bowling Green State University – Bowling Green, Ohio Ph.D. in Data Science
Data Science students at Bowling Green intertwine knowledge of computer science with statistics.
Students learn techniques in analyzing structured, unstructured, and dynamic datasets.
Courses train students to understand the principles of analytic methods and articulating the strengths and limitations of analytical methods.
The program requires 60 credit hours in the studies of Computer Science (6 credit hours), Statistics (6 credit hours), Data Science Exploration and Communication, Ethical Issues, Advanced Data Mining, and Applied Data Science Experience.
Students must also complete 21 credit hours of elective courses, a qualifying exam, a preliminary exam, and a dissertation.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $8,418 (Resident), $14,410 (Non-resident)
Brown University – Providence, Rhode Island PhD in Computer Science – Concentration in Data Science
Brown University’s database group is a world leader in systems-oriented database research; they seek PhD candidates with strong system-building skills who are interested in researching TupleWare, MLbase, MDCC, Crowd DB, or PIQL.
In order to gain entrance, applicants should consider first doing a research internship at Brown with this group. Other ways to boost an application are to take and do well at massive open online courses, do an internship at a large company, and get involved in a large open-source software project.
Coding well in C++ is preferred.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $62,680 total
Chapman University – Irvine, California Doctorate in Computational and Data Sciences
Candidates for the doctorate in computational and data science at Chapman University begin by completing 13 core credits in basic methodologies and techniques of computational science.
Students complete 45 credits of electives, which are personalized to match the specific interests and research topics of the student.
Finally, students complete up to 12 credits in dissertation research.
Applicants must have completed courses in differential equations, data structures, and probability and statistics, or take specific foundation courses, before beginning coursework toward the PhD.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $37,538 per year
Clemson University / Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) – Joint Program – Clemson, South Carolina & Charleston, South Carolina Doctor of Philosophy in Biomedical Data Science and Informatics – Clemson
The PhD in biomedical data science and informatics is a joint program co-authored by Clemson University and the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC).
Students choose one of three tracks to pursue: precision medicine, population health, and clinical and translational informatics. Students complete 65-68 credit hours, and take courses in each of 5 areas: biomedical informatics foundations and applications; computing/math/statistics/engineering; population health, health systems, and policy; biomedical/medical domain; and lab rotations, seminars, and doctoral research.
Applicants must have a bachelor’s in health science, computing, mathematics, statistics, engineering, or a related field, and it is recommended to also have competency in a second of these areas.
Program requirements include a year of calculus and college biology, as well as experience in computer programming.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $10,858 total (South Carolina Resident), $22,566 total (Non-resident)
View Course Offerings – Clemson
George Mason University – Fairfax, Virginia Doctor of Philosophy in Computational Sciences and Informatics – Emphasis in Data Science
George Mason’s PhD in computational sciences and informatics requires a minimum of 72 credit hours, though this can be reduced if a student has already completed a master’s. 48 credits are toward graduate coursework, and an additional 24 are for dissertation research.
Students choose an area of emphasis—either computer modeling and simulation or data science—and completed 18 credits of the coursework in this area. Students are expected to completed the coursework in 4-5 years.
Applicants to this program must have a bachelor’s degree in a natural science, mathematics, engineering, or computer science, and must have knowledge and experience with differential equations and computer programming.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $13,426 total (Virginia Resident), $35,377 total (Non-resident)
Harrisburg University of Science and Technology – Harrisburg, Pennsylvania Doctor of Philosophy in Data Sciences
Harrisburg University’s PhD in data science is a 4-5 year program, the first 2 of which make up the Harrisburg master’s in analytics.
Beyond this, PhD candidates complete six milestones to obtain the degree, including 18 semester hours in doctoral-level courses, such as multivariate data analysis, graph theory, machine learning.
Following the completion of ANLY 760 Doctoral Research Seminar, students in the program complete their 12 hours of dissertation research bringing the total program hours to 36.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $14,940 total
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai – New York, New York Genetics and Data Science, PhD
As part of the Biomedical Science PhD program, the Genetics and Data Science multidisciplinary training offers research opportunities that expand on genetic research and modern genomics. The training also integrates several disciplines of biomedical sciences with machine learning, network modeling, and big data analysis.
Students in the Genetics and Data Science program complete a predetermined course schedule with a total of 64 credits and 3 years of study.
Additional course requirements and electives include laboratory rotations, a thesis proposal exam and thesis defense, Computer Systems, Intro to Algorithms, Machine Learning for Biomedical Data Science, Translational Genomics, and Practical Analysis of a Personal Genome.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Not Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $31,303 total
Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis – Indianapolis, Indiana PhD in Data Science PhD Minor in Applied Data Science
Doctoral candidates pursuing the PhD in data science at Indiana University-Purdue must display competency in research, data analytics, and at management and infrastructure to earn the degree.
The PhD is comprised of 24 credits of a data science core, 18 credits of methods courses, 18 credits of a specialization, written and oral qualifying exams, and 30 credits of dissertation research. All requirements must be completed within 7 years.
Applicants are generally expected to have a master’s in social science, health, data science, or computer science.
Currently a majority of the PhD students at IUPUI are funded by faculty grants and two are funded by the federal government. None of the students are self funded.
IUPUI also offers a PhD Minor in Applied Data Science that is 12-18 credits. The minor is open to students enrolled at IUPUI or IU Bloomington in a doctoral program other than Data Science.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $9,228 per year (Indiana Resident), $25,368 per year (Non-resident)
Jackson State University – Jackson, Mississippi PhD Computational and Data-Enabled Science and Engineering
Jackson State University offers a PhD in computational and data-enabled science and engineering with 5 concentration areas: computational biology and bioinformatics, computational science and engineering, computational physical science, computation public health, and computational mathematics and social science.
Students complete 12 credits of common core courses, 12 credits in the specialization, 24 credits of electives, and 24 credits in dissertation research.
Students may complete the doctoral program in as little as 5 years and no more than 8 years.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $8,270 total
Kennesaw State University – Kennesaw, Georgia PhD in Analytics and Data Science
Students pursuing a PhD in analytics and data science at Kennesaw State University must complete 78 credit hours: 48 course hours and 6 electives (spread over 4 years of study), a minimum 12 credit hours for dissertation research, and a minimum 12 credit-hour internship.
Prior to dissertation research, the comprehensive examination will cover material from the three areas of study: computer science, mathematics, and statistics.
Successful applicants will have a master’s degree in a computational field, calculus I and II, programming experience, modeling experience, and are encouraged to have a base SAS certification.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $5,328 total (Georgia Resident), $19,188 total (Non-resident)
New Jersey Institute of Technology – Newark, New Jersey PhD in Business Data Science
Students may enter the PhD program in business data science at the New Jersey Institute of Technology with either a relevant bachelor’s or master’s degree. Students with bachelor’s degrees begin with 36 credits of advanced courses, and those with master’s take 18 credits before moving on to credits in dissertation research.
Core courses include business research methods, data mining and analysis, data management system design, statistical computing with SAS and R, and regression analysis.
Students take qualifying examinations at the end of years 1 and 2, and must defend their dissertations successfully by the end of year 6.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $21,932 total (New Jersey Resident), $32,426 total (Non-resident)
New York University – New York, New York PhD in Data Science
Doctoral candidates in data science at New York University must complete 72 credit hours, pass a comprehensive and qualifying exam, and defend a dissertation with 10 years of entering the program.
Required courses include an introduction to data science, probability and statistics for data science, machine learning and computational statistics, big data, and inference and representation.
Applicants must have an undergraduate or master’s degree in fields such as mathematics, statistics, computer science, engineering, or other scientific disciplines. Experience with calculus, probability, statistics, and computer programming is also required.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $37,332 per year
View Course Offering
Northcentral University – San Diego, California PhD in Data Science-TIM
Northcentral University offers a PhD in technology and innovation management with a specialization in data science.
The program requires 60 credit hours, including 6-7 core courses, 3 in research, a PhD portfolio, and 4 dissertation courses.
The data science specialization requires 6 courses: data mining, knowledge management, quantitative methods for data analytics and business intelligence, data visualization, predicting the future, and big data integration.
Applicants must have a master’s already.
Delivery Method: Online GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $16,794 total
Stevens Institute of Technology – Hoboken, New Jersey Ph.D. in Data Science
Stevens Institute of Technology has developed a data science Ph.D. program geared to help graduates become innovators in the space.
The rigorous curriculum emphasizes mathematical and statistical modeling, machine learning, computational systems and data management.
The program is directed by Dr. Ted Stohr, a recognized thought leader in the information systems, operations and business process management arenas.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $39,408 per year
University at Buffalo – Buffalo, New York PhD Computational and Data-Enabled Science and Engineering
The curriculum for the University of Buffalo’s PhD in computational and data-enabled science and engineering centers around three areas: data science, applied mathematics and numerical methods, and high performance and data intensive computing. 9 credit course of courses must be completed in each of these three areas. Altogether, the program consists of 72 credit hours, and should be completed in 4-5 years. A master’s degree is required for admission; courses taken during the master’s may be able to count toward some of the core coursework requirements.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $11,310 per year (New York Resident), $23,100 per year (Non-resident)
University of Colorado Denver – Denver, Colorado PhD in Big Data Science and Engineering
The University of Colorado – Denver offers a unique program for those students who have already received admission to the computer science and information systems PhD program.
The Big Data Science and Engineering (BDSE) program is a PhD fellowship program that allows selected students to pursue research in the area of big data science and engineering. This new fellowship program was created to train more computer scientists in data science application fields such as health informatics, geosciences, precision and personalized medicine, business analytics, and smart cities and cybersecurity.
Students in the doctoral program must complete 30 credit hours of computer science classes beyond a master’s level, and 30 credit hours of dissertation research.
The BDSE fellowship requires students to have an advisor both in the core disciplines (either computer science or mathematics and statistics) as well as an advisor in the application discipline (medicine and public health, business, or geosciences).
In addition, the fellowship covers full stipend, tuition, and fees up to ~50k for BDSE fellows annually. Important eligibility requirements can be found here.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $55,260 total
University of Marylan d – College Park, Maryland PhD in Information Studies
Data science is a potential research area for doctoral candidates in information studies at the University of Maryland – College Park. This includes big data, data analytics, and data mining.
Applicants for the PhD must have taken the following courses in undergraduate studies: programming languages, data structures, design and analysis of computer algorithms, calculus I and II, and linear algebra.
Students must complete 6 qualifying courses, 2 elective graduate courses, and at least 12 credit hours of dissertation research.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $16,238 total (Maryland Resident), $35,388 total (Non-resident)
University of Massachusetts Boston – Boston, Massachusetts PhD in Business Administration – Information Systems for Data Science Track
The University of Massachusetts – Boston offers a PhD in information systems for data science. As this is a business degree, students must complete coursework in their first two years with a focus on data for business; for example, taking courses such as business in context: markets, technologies, and societies.
Students must take and pass qualifying exams at the end of year 1, comprehensive exams at the end of year 2, and defend their theses at the end of year 4.
Those with a degree in statistics, economics, math, computer science, management sciences, information systems, and other related fields are especially encouraged, though a quantitative degree is not necessary.
Students accepted by the program are ordinarily offered full tuition credits and a stipend ($25,000 per year) to cover educational expenses and help defray living costs for up to three years of study.
During the first two years of coursework, they are assigned to a faculty member as a research assistant; for the third year students will be engaged in instructional activities. Funding for the fourth year is merit-based from a limited pool of program funds
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $18,894 total (in-state), $36,879 (out-of-state)
University of Nevada Reno – Reno, Nevada PhD in Statistics and Data Science
The University of Nevada – Reno’s doctoral program in statistics and data science is comprised of 72 credit hours to be completed over the course of 4-5 years. Coursework is all within the scope of statistics, with titles such as statistical theory, probability theory, linear models, multivariate analysis, statistical learning, statistical computing, time series analysis.
The completion of a Master’s degree in mathematics or statistics prior to enrollment in the doctoral program is strongly recommended, but not required.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $5,814 total (in-state), $22,356 (out-of-state)
University of Southern California – Los Angles, California PhD in Data Sciences & Operations
USC Marshall School of Business offers a PhD in data sciences and operations to be completed in 5 years.
Students can choose either a track in operations management or in statistics. Both tracks require 4 courses in fall and spring of the first 2 years, as well as a research paper and courses during the summers. Year 3 is devoted to dissertation preparation and year 4 and/or 5 to dissertation defense.
A bachelor’s degree is necessary for application, but no field or further experience is required.
Students should complete 60 units of coursework. If the students are admitted with Advanced Standing (e.g., Master’s Degree in appropriate field), this requirement may be reduced to 40 credits.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $63,468 total
University of Tennessee-Knoxville – Knoxville, Tennessee The Data Science and Engineering PhD
The data science and engineering PhD at the University of Tennessee – Knoxville requires 36 hours of coursework and 36 hours of dissertation research. For those entering with an MS degree, only 24 hours of course work is required.
The core curriculum includes work in statistics, machine learning, and scripting languages and is enhanced by 6 hours in courses that focus either on policy issues related to data, or technology entrepreneurship.
Students must also choose a knowledge specialization in one of these fields: health and biological sciences, advanced manufacturing, materials science, environmental and climate science, transportation science, national security, urban systems science, and advanced data science.
Applicants must have a bachelor’s or master’s degree in engineering or a scientific field.
All students that are admitted will be supported by a research fellowship and tuition will be included.
Many students will perform research with scientists from Oak Ridge national lab, which is located about 30 minutes drive from campus.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $11,468 total (Tennessee Resident), $29,656 total (Non-resident)
University of Vermont – Burlington, Vermont Complex Systems and Data Science (CSDS), PhD
Through the College of Engineering and Mathematical Sciences, the Complex Systems and Data Science (CSDS) PhD program is pan-disciplinary and provides computational and theoretical training. Students may customize the program depending on their chosen area of focus.
Students in this program work in research groups across campus.
Core courses include Data Science, Principles of Complex Systems and Modeling Complex Systems. Elective courses include Machine Learning, Complex Networks, Evolutionary Computation, Human/Computer Interaction, and Data Mining.
The program requires at least 75 credits to graduate with approval by the student graduate studies committee.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Not Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $12,204 total (Vermont Resident), $30,960 total (Non-resident)
University of Washington Seattle Campus – Seattle, Washington PhD in Big Data and Data Science
The University of Washington’s PhD program in data science has 2 key goals: training of new data scientists and cyberinfrastructure development, i.e., development of open-source tools and services that scientists around the world can use for big data analysis.
Students must take core courses in data management, machine learning, data visualization, and statistics.
Students are also required to complete at least one internship that covers practical work in big data.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $17,004 per year (Washington resident), $30,477 (non-resident)
University of Wisconsin-Madison – Madison, Wisconsin PhD in Biomedical Data Science
The PhD program in Biomedical Data Science offered by the Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics at UW-Madison is unique, in blending the best of statistics and computer science, biostatistics and biomedical informatics.
Students complete three year-long course sequences in biostatistics theory and methods, computer science/informatics, and a specialized sequence to fit their interests.
Students also complete three research rotations within their first two years in the program, to both expand their breadth of knowledge and assist in identifying a research advisor.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $10,728 total (in-state), $24,054 total (out-of-state)
Vanderbilt University – Nashville, Tennessee Data Science Track of the BMI PhD Program
The PhD in biomedical informatics at Vanderbilt has the option of a data science track.
Students complete courses in the areas of biomedical informatics (3 courses), computer science (4 courses), statistical methods (4 courses), and biomedical science (2 courses). Students are expected to complete core courses and defend their dissertations within 5 years of beginning the program.
Applicants must have a bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering, biology, biochemistry, nursing, mathematics, statistics, physics, information management, or some other health-related field.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $53,160 per year
Washington University in St. Louis – St. Louis, Missouri Doctorate in Computational & Data Sciences
Washington University now offers an interdisciplinary Ph.D. in Computational & Data Sciences where students can choose from one of four tracks (Computational Methodologies, Political Science, Psychological & Brain Sciences, or Social Work & Public Health).
Students are fully funded and will receive a stipend for at least five years contingent on making sufficient progress in the program.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $59,420 total
Worcester Polytechnic Institute – Worcester, Massachusetts PhD in Data Science
The PhD in data science at Worcester Polytechnic Institute focuses on 5 areas: integrative data science, business intelligence and case studies, data access and management, data analytics and mining, and mathematical analysis.
Students first complete a master’s in data science, and then complete 60 credit hours beyond the master’s, including 30 credit hours of research.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $28,980 per year
Yale University – New Haven, Connecticut PhD Program – Department of Stats and Data Science
The PhD in statistics and data science at Yale University offers broad training in the areas of statistical theory, probability theory, stochastic processes, asymptotics, information theory, machine learning, data analysis, statistical computing, and graphical methods. Students complete 12 courses in the first year in these topics.
Students are required to teach one course each semester of their third and fourth years.
Most students complete and defend their dissertations in their fifth year.
Applicants should have an educational background in statistics, with an undergraduate major in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or similar field.
Delivery Method: Campus GRE: Required 2022-2023 Tuition: $46,900 total

- Related Programs
Health Data
This course provides an introduction to data sources commonly used for health care research and analysis. Topics will include publicly available data sources, identifying strengths and weaknesses of data sources, and data management. By the end of the course students will be able to identify a large number of available data sources for research and analysis, understand their strengths and weaknesses, assess whether a particular data source is appropriate for a given project, and manage and work with health data.
Weill Cornell Medicine Graduate School of Medical Sciences 1300 York Ave. Box 65 New York, NY 10065 Phone: (212) 746-6565 Fax: (212) 746-8906
Global main menu
Health data in practice mres.
Part of: Global Health and Development

This MRes is the entry point to the 4 year PhD Programme in Health Data in Practice, funded by the Wellcome Trust. Acceptance onto the MRes in Health Data in Practice constitutes entry onto the 4 year PhD programme in Health Data in Practice; progression to PhD requires successful (i.e. pass or above) completion of the MRes. This course is not currently available as a standalone MRes in Health Data in Practice.
Applications for September 2024 entry will close on 5 January 2024
• Be part of a prestigious Wellcome Trust-funded interdisciplinary programme with access to leading researchers at the forefront of health data research
• Gain an ‘in-practice’ context to health data science research with access to real-world data and health settings
• Benefit from generous resources and support
• Access innovative career development support during your PhD and a unique ‘Transition fund’ to support successful transition to the next stage of your career
Study options
- Full-time September 2024 | 1 year
What you'll study
Our Wellcome-funded doctoral training programme applies human-centred data research to health and care data, and will introduce you to a wider context for your research, enabling you to draw on concepts, disciplines and methods underpinning algorithmic designs, sensing and data capture, human-data interactions, qualitative and quantitative evaluation and decision-making, in real-world settings. You will develop as a future scientific leader able to apply interdisciplinary perspectives to your research and realise the potential of innovations in health data research for the benefit of patients, the public, health care systems, and society.
The Wellcome Trust Health Data in Practice programme combines scientific excellence with a commitment to improving the working environment and transition support for trainees.
Please visit our website for more information and application guidance.
Additional costs
Studentships are fully funded including a stipend, tuition fees, research and training costs for the 4 year period of study. Additionally students will be able to apply to the Transition Fund in their final year of study to assist students in successfully navigating to the next stage of their career. Further details on the support provided can be found here .
Students will undertake six taught modules (120 credits in total) and a 60 credit independent project module. In total 180 credits are required to achieve the MRes.
- Four compulsory modules (75 credits in total)
- Three elective modules (45 credits in total)
- A 15,000 word dissertation (60 credits)
The course structure and modules are for 2022-23 entry. Availability of elective modules depends on staffing and timetabling and may be varied.
Compulsory:
Health Data in Practice
Effective and efficient evaluation, qualitative methods for health research.
- Introduction to Social Science Research 2: quantitative methods and data
- Design for Human Interaction
- Natural Language Processing
- Applied Statistics
- Interactive System Design
- Neural Networks and NLP
- Risk and Decision-making for Data Science and AI
- Machine Learning
- Data Mining

Short courses
Discover our medicine and dentistry short courses that you can study on campus or online.
Compulsory/Core modules
Epidemiology and statistics for health data scientists.
This module will provide an introduction to epidemiology and statistics with a focus on quantitative analytic approaches. Develop the knowledge and understanding necessary to design, analyse and interpret epidemiological studies with an application to public health and clinical practice. Gain practical skills in using statistical software to clean data, perform statistical analyses and display data. Learn to interpret findings crucial for evidence-based healthcare research, critically evaluate research and contribute to advancements in public health. This module equips students with the expertise to tackle complex health challenges through advanced epidemiological approaches and statistical modelling.
Dissertation
In this module, students will work on a piece of independently produced research relevant to one of the programmes four scientific themes (Human-Data Interaction, Health Data in Practice, Effective and Efficient Evaluation, and Actionable Information). Students will be assisted in topic choice and guided through the process by one of the scientific theme leads but will be expected to collect data themselves, or organise access to it, and write the thesis independently. Potential topics will be identified in consultation with scientific theme leads and other academic staff involved with the programme, and a list will be made available early in Semester 2. The scientific theme leads will endeavour to facilitate student preferences. Some topics may be broad enough to accommodate more than one student at a time.
The module provides an introduction to health data in practice with a focus on health care delivery challenges and patient and population health outcomes from an interdisciplinary perspective. It will provide students with a grounding in legal and ethical frameworks governing health data access and use, and the role of patient, health professional and public engagement for delivering the full potential of health data sciences for public benefit.
The module will introduce learners to principles of effective and efficient evaluation, exploring different uses of health data in evaluation, for example in recruitment, or to measure outcomes. It will cover research designs that use health data or can be conducted within health data, including cluster-randomised trials, stepped-wedge designs, trials-within-cohorts/registries, interrupted-time-series. The role of devices such as wearables or mobile phone apps in evaluation, cost-effective analyses, use of qualitative methods, and ethics of evaluation will also be covered.
This module will introduce learners to the principles of interpretive research and to a broad range of qualitative research practice including: interviews; focus groups; ethnographic approaches; participatory research methods; qualitative synthesis; mixed- methods designs. The importance of integrating theory and ensuring ethical practice in the design, conduct and analysis of research will be emphasised throughout. The module will lead learners through the research cycle from formulation of research idea to ensuring research impact with a focus on learning-by-doing and improving reflective practice.
Elective modules
Your assessments will take a number of different forms, including:
• coursework essays • assignments • presentations • examinations
You will need to achieve at least an overall pass in the MRes in order to progress to PhD.
You will experience a range of teaching methods, including small group seminars, lectures and problem-based learning tutorials. You will develop critical analysis, written and verbal communication skills, and have plenty of contact with academics and your dissertation will be supervised by one or more of the PhD Programme Co-Directors.
The current supervisor pool for your PhD project can be viewed here .

Professor Pat Healey
Professor Healey is the Head of the Cognitive Science Research Group. He recently served as Senior Researcher in Residence at the Digital Catapult and as 2016 International Visiting Chair in Empirical Foundations of Linguistics at Sorbonne Cite / Paris 7.

Professor Borislava (Boby) Mihaylova
Prof. Mihaylova leads the Health Economics and Policy Research Unit. Her research is the area of health economic evaluation, prognostic disease modelling and evidence synthesis to inform targeting of policies and treatments.
Where you'll learn
At Queen Mary you will have access to a number of advanced facilities but will be based at the Whitechapel campus. As a postgraduate student you will also have access to facilities such as the Graduate Centre and a Learning Resources Centre, open around the clock, with 200 networked PCs solely for the use of postgraduate students.
About the Institute
Wolfson institute of population health.
This course is based at the Wolfson Institute of Population Health, which delivers internationally recognised research and teaching in population health. The Wolfson Institute is a part of Queen Mary University of London’s faculty of medicine and dentistry.
The work of our researchers and educators has had a significant impact on lives across the world. We provide integrated teaching and training opportunities delivered by leaders in the field. By sharing knowledge and pushing the boundaries of research, we will continue to advance population health and preventive medicine on a global scale.
Queen Mary is a member of the Russell Group of leading research universities in the UK and the Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry proudly holds an Athena Swan Gold Award in recognition of our commitment to gender equality.
Wolfson Institute
- Tel: +44 (0)20 7882 2013
- Wolfson Institute Facebook
- Wolfson Institute Twitter
Career paths
You will be supported in your career transition through individualised, coherent career management support with access to mobility opportunities, mentoring, enterprise support and internships, as well as embedding integrated placements and internships within the training pathways.
At the end of the third year of your PhD, you will meet with the Programme Director and your supervisor to discuss career transitions and develop a plan for placements, training and skills development. You will also have the opportunity to apply to the Programme Transition Fund.
The Faculty provides support for work and industry placements for doctoral students reaching the end of their PhD and transitioning into new roles. As well as working closely with the NHS, we have access to industry partners through MedCity’s Collaborate to Innovate programme. Students can access an eight-week QIncubator programme and other careers support offered by the Careers and Enterprise team.
- 92% of Institute postgraduate taught graduates are in employment or further study 15 months after graduation (2020/21)
- 84% of Institute postgraduate taught graduates are in highly skilled work or graduate study (2020/21)
Fees and funding
Full-time study.
September 2024 | 1 year
- Home: £4,700
- Overseas: £4,700 EU/EEA/Swiss students
Unconditional deposit
Overseas: £2000 Information about deposits
Queen Mary alumni can get a £1000, 10% or 20% discount on their fees depending on the programme of study. Find out more about the Alumni Loyalty Award
There are a number of ways you can fund your postgraduate degree.
- Scholarships and bursaries
- Postgraduate loans (UK students)
- Country-specific scholarships for international students
Our Advice and Counselling service offers specialist support on financial issues, which you can access as soon as you apply for a place at Queen Mary. Before you apply, you can access our funding guides and advice on managing your money:
- Advice for UK and EU students
- Advice for international students
Entry requirements
Degree requirements.
Relevant subjects include quantitative disciplines such as Statistics, Computer Sciences, Mathematics, Bioinformatics and Biomedical Sciences, and qualitative disciplines such as Anthropology, Ethnography and Social Sciences.
Other routes
Candidates with other relevant qualifications or research experience may also be eligible. Please contact us if you would like to discuss your eligibility.
Find out more about how to apply for our postgraduate taught courses.
International
Afghanistan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Master Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90%; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80%; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70%; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Albania We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Algeria We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licence; Diplome de [subject area]; Diplome d'Etudes Superieures; Diplome de Docteur end Pharmacie; or Diplome de Docteur en Medecine from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Angola We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Grau de Licenciado/a (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 17 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 15 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 13 out of 20
Argentina We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo/ Grado de Licenciado/ Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6.5 out of 10
Armenia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 87 out of 100 UK 2:1 degree: 75 out of 100 UK 2:2 degree: 61 out of 100
Australia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) or Bachelor Honours degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: High Distinction; or First Class with Honours UK 2:1 degree: Distinction; or Upper Second Class with Honours UK 2:2 degree: Credit; or Lower Second Class with Honours
Austria We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 1.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: 2.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5.0
The above relates to grading scale where 1 is the highest and 5 is the lowest.
Azerbaijan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90%; or GPA 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 80%; or GPA 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 70%; or GPA 3.5 out of 5
Bahamas We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from the University of West Indies. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours
Bahrain We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or 90 out of 100 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0; or 80 out of 100 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.3 out of 4.0; or 74 out of 100
Bangladesh We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.2 to 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 to 3.3 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.3 to 2.7 out of 4.0
Offer conditions will vary depending on the institution you are applying from. For some institutions/degrees we will ask for different grades to above, so this is only a guide.
Barbados We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from the University of West Indies, Cave Hill or Barbados Community College. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours*; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0** UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours*; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0** UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours*; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0**
*relates to: the University of West Indies, Cave Hill.
**relates to: Barbados Community College.
Belarus We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9 out of 10; or 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 7 out of 10; or 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 5 out of 10; or 3.5 out of 5
Belgium We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80% or 16/20*; or 78%** UK 2:1 degree: 70% or 14/20*; or 72%** UK 2:2 degree: 60% or 12/20*; or 65%**
*Flanders (Dutch-speaking)/ Wallonia (French-speaking) **German-speaking
Belize We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from the University of West Indies. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours
Benin We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Maitrise or Masters from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Bolivia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Bachiller Universitario or Licenciado / Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85%* or 80%** UK 2:1 degree: 75%* or 70%** UK 2:2 degree: 65%* or 60%**
*relates to: Titulo de Bachiller Universitario
**relates to: Licenciado / Titulo de [subject area]
Bosnia and Herzegovina We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7.5 out of 10
Botswana We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 5 years) or Master Degree from the University of Botswana. UK 1st class degree: 80% UK 2:1 degree: 70% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
Brazil We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Título de Bacharel / Título de [subject area] or Título de Licenciado/a (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8.25 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6.5 out of 10
The above grades assumes that the grading scale has a pass mark of 5.
Brunei We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours
Bulgaria We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 5.75 out of 6.0 UK 2:1 degree: 4.75 out of 6.0 UK 2:2 degree: 4.0 out of 6.0
Burundi We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diplome d'Etudes Approfondies from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85%; or 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 75%; or 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 60%; or 12 out of 20
Cambodia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80%; or GPA 3.5 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 70%; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 60%; or GPA 2.35 out of 4.0
Cameroon We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree; Licence; Diplome d'Etudes Superieures de Commerce; Diplome d'Ingenieur de Conception/ Travaux; Doctorat en Medecine/ Pharmacie; or Maitrise or Master 1 from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20; or GPA 3.6 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Canada We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Bachelor Honours Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.6 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.2 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Chile We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Grado de Licenciado en [subject area] or Titulo (Professional) de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 6.5 out of 7 UK 2:1 degree: 5.5 out of 7 UK 2:2 degree: 5 out of 7
China We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 85 to 95% UK 2:1 degree: 75 to 85% UK 2:2 degree: 70 to 80%
Offer conditions will vary depending on the institution you are applying from.
Colombia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado en [subject area] or Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.60 out of 5.00 UK 2:1 degree: 4.00 out of 5.00 UK 2:2 degree: 3.50 out of 5.00
Congo, Dem. Rep. of We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diplome d'Etudes Approfondies or Diplome d'Etudes Speciales from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20; or 90% UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20; or 80% UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20; or 70%
Congo, Rep. of We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diplome d'Etudes Superieures or Maitrise from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Costa Rica We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachiller or Licenciado from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7.5 out of 10
Croatia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Advanced Diploma of Higher Education Level VII/1 (Diploma - Visoko obrazovanje) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.5 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3 out of 5
Cuba We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado/ Arquitecto/ Doctor/ Ingeniero from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5
Cyprus We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8 out of 10; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 7.0 out of 10; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 6.0 out of 10; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Czech Republic We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 1.2 out of 4 UK 2:1 degree: 1.5 out of 4 UK 2:2 degree: 2.5 out of 4
The above relates to grading scale where 1 is the highest and 4 is the lowest.
Denmark We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 12 out of 12 (2007 onwards); or 11 out of 13 (before 2007) UK 2:1 degree: 7 out of 12 (2007 onwards); or 8 out of 13 (before 2007) UK 2:2 degree: 4 out of 12 (2007 onwards); or 7 out of 13 (before 2007)
Dominican Republic We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado/ Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 95/100 UK 2:1 degree: 85/100 UK 2:2 degree: 78/100
Ecuador We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado / Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90%; or 9/10; or 19/20; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80%; or 8/10; or 18/20; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70%; or 7/10; or 14/20; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Egypt We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 85%; or GPA 3.7 out of 4 UK 2:1 degree: 75%; or GPA 3.0 out of 4 UK 2:2 degree: 65%; or GPA 2.5 out of 4
El Salvador We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado/ Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 5 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6.5 out of 10
Eritrea We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Estonia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree; University Specialist's Diploma; or Professional Higher Education Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.5 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 3.5 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 2 out of 5
The above grades assumes that 1 is the pass mark.
Eswatini We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80% UK 2:1 degree: 70% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
Ethiopia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Fiji We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from one of the following institutions: Fiji National University, the University of Fiji, or the University of South Pacific, Fiji. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.0 out of 5.0*; or overall grade A with High Distinction pass**; or GPA 4.0 out of 4.5*** UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.33 out of 5.0*; or overall grade B with Credit pass**; or GPA 3.5 out of 4.5*** UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.33 out of 5.0*; or overall grade S (Satisfactory)**; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.5***
*relates to Fiji National University
**relate to the University of Fiji
***relates to the University of South Pacific, Fiji
Finland We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree/ Kandidaatti/ Kandidat (minimum 180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution; or Bachelor degree (Ammattikorkeakoulututkinto/ Yrkeshögskoleexamen) from a recognised University of Applied Sciences. UK 1st class degree: 4.5 out of 5; or 2.8 out of 3 UK 2:1 degree: 3.5 out of 5; or 2 out of 3 UK 2:2 degree: 2.5 out of 5; or 1.4 out of 3
France We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licence; Grade de Licence; Diplome d'Ingenieur; or Maitrise from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 12 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 11 out of 20
Gambia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80%; or GPA 4.0 out of 4.3 UK 2:1 degree: 67%; or GPA 3.3 out of 4.3 UK 2:2 degree: 60%; or GPA 2.7 out of 4.3
Georgia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 91 out of 100; or 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 81 out of 100; or 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 71 out of 100; or 3.5 out of 5
Germany We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 1.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: 2.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5.0
Ghana We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class UK 2:1 degree: Second Class (Upper Division) UK 2:2 degree: Second Class (Lower Division)
Greece We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Degrees from recognised selected institutions in the University sector or Degrees (awarded after 2003) from recognised Technological Educational Institutes. UK 1st class degree: 8 out of 10*; or 9 out of 10** UK 2:1 degree: 7 out of 10*; or 7.5 out of 10** UK 2:2 degree: 6 out of 10*; or 6.8 out of 10**
*Relates to degrees from the University Sector. **Relates to degrees from Technological Educational Institutes.
Grenada We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from the University of West Indies. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours
Guatemala We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado / Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% UK 2:1 degree: 80% UK 2:2 degree: 70%
The above grades assumes that the pass mark is 61% or less.
Guinea We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Master; Maitrise; Diplome d'Etudes Superieures; or Diplome d'Etudes Approfondies from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Guyana We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Graduate Diploma (Postgraduate) or Masters degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Honduras We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado/a / Grado Academico de Licenciatura (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90%; or 4.7 out of 5; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80%; or 4.0 out of 5; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70%; or 3.5 out of 5; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Hong Kong We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours
Hungary We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor degree (Alapfokozat) or University Diploma (Egyetemi Oklevel) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.75 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5
Iceland We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor degree (Baccalaureus or Bakkalarprof) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8.25 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7.25 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6.5 out of 10
India We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 75% to 80% UK 2:1 degree: 60% to 70% UK 2:2 degree: 50% to 60%
Offer conditions will vary depending on the institution you are applying from. For some institutions/degrees we will ask for different grades to above, so this is only a guide.
For India, offers may be made on the GPA scale.
We do not consider the Bachelor of Vocation (B. Voc.) for Masters entry.
Indonesia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Sarjna I (S1) Bachelor Degree or Diploma IV (D4) (minimum 4 years) from selected degree programmes and institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.6 to 3.8 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 to 3.2 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.67 to 2.8 out of 4.0
Offer conditions will vary depending on the institution you are applying from and the degree that you study.
Iran We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 17.5 to 18.5 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 15 to 16 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 13.5 to 14 out of 20
Iraq We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85 out of 100 UK 2:1 degree: 75 out of 100 UK 2:2 degree: 60 out of 100
Ireland We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Honours Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours UK 2:1 degree: Second Class Honours Grade I UK 2:2 degree: Second Class Honours Grade II
Israel We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% UK 2:1 degree: 80% UK 2:2 degree: 65%
Italy We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Laurea (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 110 out of 110 UK 2:1 degree: 105 out of 110 UK 2:2 degree: 94 out of 110
Cote D’ivoire (Ivory Coast) We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diplome d'Ingenieur; Doctorat en Medicine; Maitrise; Master; Diplome d'Etudes Approfondies; or Diplome d'Etudes Superieures Specialisees from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Jamaica We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from the University of West Indies (UWI) or a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or First Class Honours from the UWI UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0; or Upper Second Class Honours from the UWI UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0; or Lower Second Class Honours from the UWI
Japan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: S overall* or A overall**; or 90%; or GPA 3.70 out of 4.00 UK 2:1 degree: A overall* or B overall**; or 80%; or GPA 3.00 out of 4.00 UK 2:2 degree: B overall* or C overall**; or 70%; or GPA 2.3 out of 4.00
*Overall mark is from the grading scale: S, A, B, C (S is highest mark) **Overall mark is from the grading scale: A, B, C, D (A is highest mark)
Jordan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85%; or GPA of 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 75%; or GPA of 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70%; or GPA of 2.5 out of 4.0
Kazakhstan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 3.8 out of 4.0/4.33; or 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 3.33 out of 4.0/4.33; or 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 2.67 out of 4.0/4.33; or 3.5 out of 5
Kenya We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours; or GPA 3.6 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: Second Class Honours Upper Division; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: Second Class Honours Lower Division; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Kosovo We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7.5 out of 10
Kuwait We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.67 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.67 out of 4.0
Kyrgyzstan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5; or GPA 3.7 out of 4 UK 2:1 degree: 4.0 out of 5; or GPA 3.0 out of 4 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5; or GPA 2.4 out of 4
Laos We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Latvia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (awarded after 2002) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6 out of 10
Lebanon We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree; Licence; or Maitrise from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% or Grade A; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or 16 out of 20 (French system) UK 2:1 degree: 80% or Grade B; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0; or 13 out of 20 (French system) UK 2:2 degree: 70% or Grade C; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.0; or 12 out of 20 (French system)
Lesotho We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours Degree (minimum 5 years total HE study); Masters Degree or Postgraduate Diploma from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 80% UK 2:1 degree: 70% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
Liberia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80% or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70% or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Libya We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 85%; or 3.7 out of 4.0 GPA UK 2:1 degree: 75%; or 3.0 out of 4.0 GPA UK 2:2 degree: 65%; or 2.6 out of 4.0 GPA
Liechtenstein We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 5.6 out of 6.0 UK 2:1 degree: 5.0 out of 6.0 UK 2:2 degree: 4.4 out of 6.0
Lithuania We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Luxembourg We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Macau We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (Licenciatura) (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Macedonia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diploma of Completed Higher Education - Level VII/1 or Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Madagascar We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Maîtrise; Diplome d'Ingenieur; Diplôme d'Etat de Docteur en Médecine; Diplôme d’Etat de Docteur en Chirurgie Dentaire; Diplôme d'Études Approfondies; Diplôme de Magistère (Première Partie) – also known as Master 1; or Diplôme de Master – also known as Master 2 from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Malawi We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 80% or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 70% or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 60% or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Malaysia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: Class 1; or 3.7 out of 4.0 CGPA UK 2:1 degree: Class 2 division 1; or 3.0 out of 4.0 CGPA UK 2:2 degree: Class 2 division 2; or 2.6 out of 4.0 CGPA
Maldives We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (awarded from 2000) from the Maldives National University. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Malta We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Bachelor Honours Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class Honours; or Category I UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class Honours; or Category IIA UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours; or Category IIB
Mauritius We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: Class I; or 70% UK 2:1 degree: Class II division I; or 60% UK 2:2 degree: Class II division II; or 50%
Offer conditions will vary depending on the grading scale used by your institution.
Mexico We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado/ Titulo (Profesional) de [subject area] from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.0 to 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.0 to 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7.0 to 7.5 out of 10
Offer conditions will vary depending on the grading scale your institution uses.
Moldova We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (Diploma de Licenta) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6.5 out of 10
Monaco We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Mongolia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.6 out of 4.0; or 90%; or grade A UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.2 out of 4.0; or 80%; or grade B UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.8 out of 4.0; or 70%; or grade C
Montenegro We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diploma of Completed Academic Undergraduate Studies; Diploma of Professional Undergraduate Studies; or Advanced Diploma of Higher Education from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.5 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Morocco We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Diplome d'Ecoles Nationales de Commerce et de Gestion; Diplome de Docteur Veterinaire; Doctorat en Medecine; Docteur en Medecine Dentaire; Licence; Diplome d'Inegeniuer d'Etat; Diplome de Doctorat en Pharmacie; or Maitrise from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 13 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 11 out of 20
Mozambique We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Grau de Licenciado (minimum 4 years) or Grau de Mestre from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Myanmar We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80% or GPA of 4.7 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: 70% or GPA of 4.0 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: 60% or GPA of 3.5 out of 5.0
Namibia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours Degree or Professional Bachelor Degree (NQF level 8 qualifications) - these to be awarded after 2008 from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80% UK 2:1 degree: 70% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
Nepal We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 80%; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 65%; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 55%; or GPA of 2.4 out of 4.0
Bachelor in Nursing Science are not considered equivalent to UK Bachelor degrees.
Netherlands We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 7 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 6 out of 10
New Zealand We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) or Bachelor Honours Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: A-*; or First Class Honours** UK 2:1 degree: B*; or Second Class (Division 1) Honours** UK 2:2 degree: C+*; or Second Class (Division 2) Honours**
*from a Bachelor degree **from a Bachelor Honours degree
Nigeria We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.50 out of 5.00; or GPA 6.0 out of 7.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.50 out of 5.00; or GPA 4.6 out of 7.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.80 out of 5.00; or GPA 3.0 out of 7.0
Norway We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: Overall B grade with at least 75 ECTS (of 180 ECTS min overall) at grade A or above. UK 2:1 degree: Overall B grade UK 2:2 degree: Overall C grade
Oman We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Pakistan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.0 to 3.8 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 2.6 to 3.6 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.0 to 3.0 out of 4.0
Palestine, State of We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80% or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70% or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Panama We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado / Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 91% UK 2:1 degree: 81% UK 2:2 degree: 71%
Papua New Guinea We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: Class I UK 2:1 degree: Class II, division A UK 2:2 degree: Class II, division B
Paraguay We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado / Titulo de [professional title] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out fo 5
Peru We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Grado Academico de Bachiller or Titulo de Licenciado/ Titulo (Professional) de [subject area] from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 17 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Philippines We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions or Juris Doctor; Bachelor of Laws; Doctor of Medicine; Doctor of Dentistry/ Optometry/ Veterinary Medicine; or Masters Degree from recognised institutions. UK 1st class degree: 3.6 out of 4.0; or 94%; or 1.25 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 3.0 out of 4.0; or 86%; or 1.75 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 2.5 out of 4.0; or 80%; or 2.5 out of 5
The above 'out of 5' scale assumes 1 is highest mark and 3 is the pass mark.
Poland We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licencjat or Inzynier (minimum 3 years) - these must be awarded after 2001 from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.8 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: 4.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: 3.8 out of 5.0
The above grades are based on the 2 to 5 scale, where 3 is the pass mark and 5 is the highest mark.
Portugal We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licenciado (minimum 180 ECTS credits) or Diploma de Estudos Superiores Especializados (DESE) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 14 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 12 out of 20
Puerto Rico We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90/100 or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 80/100 or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 70/100 or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Qatar We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or GPA 4.4 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0; or GPA 3.6 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0; or GPA 2.8 out of 5.0
Romania We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.75 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8.0 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7.0 out of 10
Russia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5
Rwanda We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours Degree (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85%; or 17 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 70%; or 15 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 60%; or 13 out of 20
Saudi Arabia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.75 out of 5.0; or GPA 3.75 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.75 out of 5.0; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 5.0; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Senegal We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Maîtrise; Master II; Diplôme d'Études Approfondies (DEA); Diplôme d'Études Supérieures Specialisées (DESS); Diplôme d'État de Docteur en Médecine; Diplôme d'Ingénieur; Diplôme de Docteur en Chirurgie Dentaire; or Diplôme de Pharmacien from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16/20 UK 2:1 degree: 14/20 UK 2:2 degree: 12/20
Serbia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Advanced Diploma of Higher Education from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Sierra Leone We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (Honours) or a Masters degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: First Class honours; or GPA 4.7 out of 5; or GPA 3.75 out of 4 UK 2:1 degree: Upper Second Class honours; or GPA 4 out of 5; or GPA 3.25 out of 4 UK 2:2 degree: Lower Second Class Honours; or GPA 3.4 out of 5; or GPA 2.75 out of 4
Singapore We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) or Bachelor Honours degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.3 out of 5.0; or GPA 3.6 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.8 out of 5.0; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 3.3 out of 5.0; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Slovakia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (180 ECTS credits) (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 93%; or 1 overall (on 1 to 4 scale, where 1 is highest mark) UK 2:1 degree: 86%; or 1.5 overall (on 1 to 4 scale, where 1 is highest mark) UK 2:2 degree: 72%; or 2.5 overall (on 1 to 4 scale, where 1 is highest mark)
Slovenia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Univerzitetni Diplomant (180 ECTS credits) (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 9.5 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 7 out of 10
Somalia Bachelor degrees from Somalia are not considered for direct entry to our postgraduate taught programmes. Holders of Bachelor degrees from Somali National University can be considered for our Pre-Masters programmes on a case by case basis.
South Africa We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: NQF Level 8 qualifications such as Bachelor Honours degrees or Professional Bachelor degrees from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 75% UK 2:1 degree: 70% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
South Korea We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.2 out of 4.5; or GPA 4.0 out of 4.3; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.5 out of 4.5; or GPA 3.3 out of 4.3; or GPA 3.2 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.5; or GPA 2.8 out of 4.3; or GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Spain We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo Universitario Oficial de Graduado en [subject area] (Grado) or Titulo Universitario Oficial de Licenciado en [subject area] (Licenciatura) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8.0 out of 10; or 2.5 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 7.0 out of 10; or 2.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 6.0 out of 10; or 1.5 out of 4.0
Sri Lanka We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (Special or Honours) or Bachelor Degree (Professional) (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.5 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Sudan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Honours degree from a recognised institution or Bachelor degree in one of the following Professional subjects: Architecture; Dentistry; Engineering; Medicine/Surgery from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 80% UK 2:1 degree: 65% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
Sweden We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (Kandidatexamen) or Professional Bachelor Degree (Yrkesexamenfrom) (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: Overall B grade with at least 75 ECTS at grade A or above (180 ECTS minimum overall); or at least 65% of credits graded at VG overall UK 2:1 degree: Overall B grade (180 ECTS minimum overall); or at least 50% of credits graded at VG overall UK 2:2 degree: Overall C grade (180 ECTS minimum overall); or at least 20% of credits graded at VG overall.
Switzerland We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor degree (180 ECTS credits) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 5.5 out of 6; or 9 out of 10 UK 2:1 degree: 5 out of 6; or 8 out of 10 UK 2:2 degree: 4.25 out of 6; or 7 out of 10
Syria We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 85% UK 2:1 degree: 75% UK 2:2 degree: 65%
Taiwan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from selected institutions. UK 1st class degree: 85 to 90% UK 2:1 degree: 70 to 75% UK 2:2 degree: 65 to 70%
Tajikistan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Specialist Diploma or Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5
Tanzania We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.4 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.5 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.7 out of 5.0
Thailand We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.40 to 3.60 out of 4.00 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.00 to 3.20 out of 4.00 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.40 to 2.60 out of 4.00
Offer conditions will vary depending on the institution you are applying from.
Trinidad and Tobago We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or First Class Honours from the University of West Indies UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0; or Upper Second Class Honours from the University of West Indies UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.4 out of 4.0; or Lower Second Class Honours from the University of West Indies
Tunisia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Licence; Diplome National d'Architecture; Maitrise; Diplome National d'Ingeniuer; or Doctorat en Medecine / Veterinaire from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 16 out of 20 UK 2:1 degree: 13 out of 20 UK 2:2 degree: 11 out of 20
Turkey We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.40 to 3.60 out of 4.00 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 2.80 to 3.00 out of 4.00 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.30 to 2.50 out of 4.00
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.60 out of 4.00 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.00 out of 4.00 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.50 out of 4.00
Turkmenistan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Diploma of Higher Education (awarded after 2007) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 3.5 out of 5
Turks and Caicos Islands We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (accredited by the Council of Community Colleges of Jamaica) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0; or 80% UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.3 out of 4.0; or 75% UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.7 out of 4.0; or 65%
Uganda We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 3 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 4.4 out of 5.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 4.0 out of 5.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 5.0
Ukraine We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 10 out of 12; or 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 8 out of 12; or 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 6 out of 12; or 3.5 out of 5
United Arab Emirates We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
United States of America We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: GPA 3.2 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: GPA 2.5 out of 4.0
Uruguay We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado/ Titulo de [subject area] (minimum 4 years) from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 10 to 11 out of 12 UK 2:1 degree: 7 to 9 out of 12 UK 2:2 degree: 6 to 7 out of 12
Uzbekistan We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) or Specialist Diploma from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90%; or 4.7 out of 5 UK 2:1 degree: 80%; or 4.0 out of 5 UK 2:2 degree: 71%; or 3.5 out of 5
Venezuela We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Titulo de Licenciado/ Titulo de [subject area] from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 81% UK 2:1 degree: 71% UK 2:2 degree: 61%
Non-percentage grading scales, for example scales out of 20, 10, 9 or 5, will have different requirements.
Vietnam We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 8.0 out of 10; or GPA 3.7 out of 4 UK 2:1 degree: 7.0 out of 10; or GPA 3.0 out of 4 UK 2:2 degree: 5.7 out of 10; or GPA 2.4 out of 4
Yemen We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters (Majister) degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 90% UK 2:1 degree: 80% UK 2:2 degree: 65%
Bachelor Degrees from Lebanese International University (in Yemen) can be considered for entry to postgraduate taught programmes - please see Lebanon for guidance on grade requirements for this.
Zambia We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Masters Degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 75%; or GPA 3.7 out of 4.0 UK 2:1 degree: 65%; or GPA 3.0 out of 4.0 UK 2:2 degree: 55%; or GPA 2.4 out of 4.0
Zimbabwe We normally consider the following qualifications for entry to our postgraduate taught programmes: Bachelor Degree (minimum 4 years) or Bachelor Honours degree from a recognised institution. UK 1st class degree: 75% UK 2:1 degree: 65% UK 2:2 degree: 60%
English language requirements
If you got your degree in an English speaking country or if it was taught in English, and you studied within the last five years, you might not need an English language qualification - find out more .
English language entry requirements for programmes within the Wolfson Institute
You may be able to meet the English language requirement for your programme by joining a summer pre-sessional programme before starting your degree.
Visas and immigration
Find out how to apply for a student visa .
Institute of Population Health Sciences
- Tel: +44 (0)20 7882 7325
Postgraduate Admissions
Related courses, global public health and policy mres, mental health: psychological therapies mres, social science enquiry in creative arts and mental health mres, mental health: cultural psychology and psychiatry mres.

Official websites use .mass.gov
Secure websites use HTTPS certificate
A lock icon ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the official website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- search across the entire site
- search in Office of Population Health
- search in Department of Public Health
- search in Executive Office of Health and Human Services
- This page, Public Health Data Warehouse (PHD), is offered by
- Office of Population Health
- Department of Public Health
Public Health Data Warehouse (PHD)
The Public Health Data Warehouse is a truly unique public health data analysis tool that links multiple data sets across state and local government to help address public health priorities.
The PHD was created in 2017, originally to provide unprecedented access to data across government to identify trends and target resources to confront the opioid epidemic. Since then, the PHD has provided timely, multi-year data to spur analysis of other pressing population health issues, including maternal and child health disparities, substance use, COVID-19, and the effects of climate change on health.
What you need to know
Contact information, public health data warehouse, help us improve mass.gov with your feedback.
The feedback will only be used for improving the website. If you need assistance, please contact the Office of Population Health . Please limit your input to 500 characters.
Thank you for your website feedback! We will use this information to improve this page.
If you would like to continue helping us improve Mass.gov, join our user panel to test new features for the site.
Seeing the human behind the data
Back to News List

Deborah Plana. Image: Gretchen Ertl
Graduating physician-scientist Deborah Plana, HST MD '24, combines passion for analysis, improving patient care.
Lisa McEvoy | Harvard Medical School
As a high school student in Miami, Deborah Plana loved the quantitative sciences. Then her biology teacher talked about new drugs being tested to treat genetic diseases and the many questions that still weren’t answered in the life sciences, and Plana’s interests expanded.
“I love physics and statistics. I love working on research that has an important technical piece. But just as much, I love to do research that could meaningfully improve patients’ lives,” said Plana, who is graduating this year from the Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology (HST) program as a physician-scientist with an MD to join her PhD.
Personal experience with cancer in her family cemented Plana’s determination to pursue a career that combines medicine and research.
“Human health problems impact people and their families so intimately,” she said.
A physician-scientist is born
While her scientific interests were born in Miami, Plana herself was born in Caracas, Venezuela. As the country moved from a democracy to a dictatorship, her parents decided to immigrate to the U.S.
Plana attended the Academy for Advanced Academics program through the Miami school system. The program allowed her to take college courses in addition to advanced placement classes, giving her the chance to be on a college campus and interact with people doing research.
As an undergraduate at MIT she majored in biological engineering with a minor in statistics and data science. She worked in the lab of bioengineer Douglas Lauffenburger , combining experiments with computation and learning how to translate preclinical work to clinical success.
“I became specifically interested in the question of how we do a better job of understanding how drugs work, how we make better drugs, and how we better assign drugs to individual patients,” she said.
Figuring out how to improve success rates for new therapies piqued Plana’s interest in taking care of patients directly. It also led her to the field of systems biology with the idea of using patient data to model how drugs behave in the body.
From bench to bedside to bench
Plana pursued her vision when she came to Harvard Medical School as an MD/PhD student. In 2022, she earned her PhD in systems, synthetic, and quantitative biology from the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (now the Griffin GSAS).
When the COVID-19 pandemic began, Plana joined her PhD adviser, Peter Sorger , the Otto Krayer Professor of Systems Pharmacology in the Blavatnik Institute at HMS, and Nicole LeBoeuf , HMS assistant professor of dermatology at Brigham and Women's Hospital, in responding to the shortages of personal protective equipment through the Greater Boston Pandemic Fabrication Team (PanFab) .
As a coordinating lead, she helped recruit students to what became a 150-person volunteer effort and managed the group’s projects. Those included the production and distribution of face shields for frontline health care workers, incorporation of sterilization of PPE into the workflow for reuse at a medical center, and creation of an open-source powered air-purifying respirator prototype.
At the same time, she was completing her thesis, Clinical Trial Data Science to Advance Precision Oncology , which looked at ways to enhance analysis of clinical trial results. In collaboration with researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, she digitized the information presented in graphs published in scientific studies and back-calculated the patient events that likely led to those results.
She showed that researchers can reanalyze existing trial data to assess drug synergy in animal models and human data, predict the likelihood of trial success from small sample sizes, and model long-term benefits of new therapies using short-term trial results. She hopes the work provides a new tool scientists can use to deal with data challenges presented by relatively small patient populations, patient stratification, pediatric populations, and patients with rare diseases.
Part of Plana’s focus on oncology stemmed from her and Sorger’s work with her other PhD adviser, Adam Palmer , at the time a postdoctoral fellow in systems pharmacology at HMS. The team worked closely with oncologists on data coming from clinical and preclinical trials to see whether they could improve how treatments are assigned to patients and understand variation in treatment response.
Plana hopes her work convinces others that it is worthwhile to share the raw data generated in clinical studies and that there are interesting insights to be gained from additional analysis — something she says many trial participants support.
“To me it seems almost a moral responsibility to make the most we can out of the data being generated,” she said. “Surveys of clinical trial participants overwhelmingly report that they want their data to be reused.”
Personalizing data
Plana shares with those patients the desire for knowledge to flow in both directions between the lab and the clinic. She looks forward to facilitating such “bench to bedside” and “bedside to bench” exchanges as she begins her residency in a combined anesthesia research track at Massachusetts General Hospital later this year.
When she finished her PhD and went back to her clinical rotations, Plana saw how much information anesthesiologists collect during surgery — blood pressure, amount of oxygen in the blood, how well patients are responding to the operation — and compared it to the data oncologists use.
“Oncologists think about how to better assign drugs to individual patients and how to manage toxicities,” she said. “I feel like anesthesiologists and critical care doctors do something similar in a very, very short time frame.”
“I want to use systems biology to identify personalized interventions for patients that are based on the same tools and principles cancer doctors use but that anesthesiologists and critical care doctors can apply in the short time frames they work within,” she said.
Head and heart
For Plana, the quantitative and the human aspects of being a physician-researcher drive each other.
“To me, they are not all that different,” she said. “So many of the things I have enjoyed researching have come from being in a clinical setting and having emotional reactions.”
“It is so important to make big choices with our heart,” she said.
For Plana, the importance of the human element also extends to the people who have influenced her, who include Lauffenburger, Sorger, and Palmer.
She also credits her parents, María Alba and Alberto, and dedicated her PhD to them. “Their bravery and vision in leaving Venezuela to come to the U.S. made this and all other opportunities possible,” she wrote.
*Originally published in Harvard Medical School.
- Partnerships
Northeastern Health Informatics Graduate Program designated as HIMSS Approved Education Partner
- Bouvé Communications
Key Takeaways
The designation puts Northeastern’s MSHI program in an exclusive group recognized by HIMSS for the program’s accomplishments in preparing students for a future in the industry.
Related topics
- Health Informatics
- Jay Spitulnik

The Master of Science in Health Informatics (MSHI) at Northeastern’s Bouvé College of Health Sciences and Khoury College of Computer Sciences has been designated as a HIMSS Approved Education Partner (AEP).
Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, Inc. (HIMSS) is a mission-driven nonprofit that supports the transformation of the health ecosystem through information and technology.
Receiving a HIMSS AEP designation means our Health Informatics graduate program “has met HIMSS’ rigorous standards for quality health information and technology education aligned to the competencies that are most critical in today’s workforce.” Our program, according to HIMSS, boasts a comprehensive curriculum that focuses on the interdisciplinary study of the design, development, adoption, and application of information, data, and technology-driven innovations in healthcare.
HIMSS says the Introduction to Health Informatics and Health Information Systems course, one of many courses in the MSHI program, “is a great example how the coursework offered by this program is preparing students for the current needs of the industry.”
This designation puts Northeastern’s MSHI program in an exclusive group of those recognized by HIMSS for accomplishments and programs that prepare learners to sit for a HIMSS professional certification exam.
Related Articles

Northeastern to host inaugural summit: Catalyzing Interdisciplinary Innovation in Public Health Technology

Physical Therapy faculty, alumni participate in 9th annual Ruck4HIT Cape Cod

Connect with us
Have more questions about Bouvé? We’re here to help.
Want to take the next step and start your journey at Bouvé?
Request more information
Interested in learning more about what Bouvé has to offer?

Master of Science in Health Data Science
Leverage your skills in statistics, computer science & software engineering and begin your career in the booming field of health data science
The Master of Science (SM) in Health Data Science provides students with the rigorous quantitative training and essential computing skills needed to manage and analyze health science data in order to address important questions in public health, medicine, and basic biology.
Offered by the Department of Biostatistics, this new 60-credit program is designed to provide participants with the knowledge base and targeted skills required for rigorous work in health related data science. Students will learn to:
- Critically explore, analyze and interpret data
- Appropriately apply statistical inference to make scientific conclusions from data
- Understand and employ linear models, regression and matrix algebra
- Apply methods for high-dimensional data
- Implement machine learning algorithms
- Develop and write software
- Communicate and disseminate results via reproducible reports
- Be proficient with high performance scientific computing
- Effectively wrangle data
- Perform data visualization
- Design experiments
The SM in Health Data Science is designed to be a terminal professional degree, giving students essential skills for the job market. At the same time, it provides a strong foundation for students interested in continuing in a PhD in Biostatistics or other quantitative or computational science with an emphasis in data science.
- Career Center
- Member Login
The Impact of 2020 Events on Public Health Data Use: Insights from Recent Research
A new study in our partner journal the Milbank Quarterly finds support for using identifiable data for public health and research purposes among the public generally, but also highlights a unique decline in comfort among African Americans.
2020 was a watershed moment for public health and societal dynamics in the United States. The COVID-19 pandemic, combined with widespread protests against systemic racism, significantly influenced public attitudes on a host of issues. A new study by Schmit et al., published in one of AcademyHealth's partner journals the Milbank Quarterly , delves into how these events shaped privacy preferences and the comfort level of various demographic groups with data use in public health.
Key Findings and Context
Researchers conducted separate online surveys in February and November 2020 to gauge the public's comfort with using identifiable data for public health. These surveys involved 1,373 participants who evaluated different data-use scenarios. Questions focused on three main attributes: the type of data, who used it, and the purpose of its use.
One potentially surprising finding is that the public supported using identifiable data for public health and research purposes, even amid the upheavals of 2020. Notably, bipartisan support did not significantly change between February and November, highlighting a stable consensus on the importance of public health data activities. However, the study also uncovered a unique decline in support among African Americans, a trend not observed in other demographic groups.
The Unique Decline Among African Americans
The decrease in comfort with public health data use among African Americans is particularly concerning. This group exhibited a significant shift in preferences, showing decreased support for using identifiable data for both public health and research. The researchers suggest this may be linked to the heightened awareness of systemic racism and its persistent impacts brought to the forefront by the events of 2020.
African Americans' historical and ongoing experiences with systemic racism and exploitation in research and medical contexts likely contributed to this mistrust as well. The Tuskegee Syphilis Study is a stark example of why such concerns persist. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated these issues, as African American communities faced higher infection and mortality rates, potentially intensifying their skepticism toward data use in public health initiatives.
Broader Implications and Legislative Context
Despite the observed decline in comfort among African Americans, the general public's support for public health data use underscores a critical disconnect between public preferences and legislative action. Current legislative efforts often require more specific provisions for public health data use despite consistent public support for such applications. The study by Schmit et al. reinforces the need for policymakers to align privacy laws with public health necessities.
For instance, the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) protects educational data without exceptions for public health research. Given that education is a significant social determinant of health, excluding such data from public health research hampers our ability to effectively address and understand health disparities. This misalignment between legislative frameworks and public support for health data use highlights the urgent need for legal reforms that facilitate public health research while safeguarding privacy.
Moving Forward: Building Trust and Inclusive Policies
The findings of this study highlight the fragility of public trust, particularly among marginalized communities. Building trust requires transparent, inclusive policies that acknowledge historical injustices and strive to rectify them. Public health officials and researchers must engage with communities to understand their concerns and work collaboratively to ensure that data use benefits all societal groups equitably.
As the United States continues to navigate the complexities of public health in a post-2020 world, this study offers critical insights into how public attitudes have evolved and what steps must be taken to foster a supportive environment for public health data use. By aligning legislative efforts with public preferences and addressing the unique concerns of African Americans, we can create a more inclusive and effective public health landscape. Committing to transparent policies and addressing systemic inequities can build a future where public health initiatives are trusted, inclusive, and, ultimately, more successful.
Welcome to Harvard Online
Harvard Online presents curated online courses that combine faculty and disciplines from across the University, connecting learners around the globe with the world’s most urgent issues.
Outsmarting Implicit Bias
Designed for individuals and teams, this Harvard Online course taught by preeminent Harvard Professor Mahzarin Banaji teaches the science of implicit bias and strategies to counter the impact of bias in the workplace.
What are you interested in?
Health care leadership.
Deepen perspectives and advance insights into the strategic issues facing health care organizations today.
Harvard on Digital
Approach new digital and data strategies with an eye toward people, mindsets, and systems.
Leadership, Communication, Transformation
What kind of leader will you be?
Law in Practice
Keep up on moral, ethical, and legal arguments and continue your education beyond the classroom.
Explore Learning Paths
Benefit and Discount Programs for Organizations and Individuals
Experience Harvard Online by utilizing our wide variety of discount programs for individuals and groups.
Past participant discounts.
Learners who have enrolled in at least one qualifying Harvard Online program hosted on the HBS Online platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course, regardless of completion or certificate status in the first purchased program. Past-Participant Discounts are automatically applied to the Program Fee upon time of payment. Learn more here .
Learners who have earned a verified certificate for a HarvardX course hosted on the edX platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course using a discount code. Discounts are not available after you've submitted payment, so if you think you are eligible for a discount on a registration, please check your email for a code or contact us .
Non-profit, Government, Military, and Education Discounts
For this course we offer a 30% discount for learners who work in the nonprofit, government, military, or education fields.
Eligibility is determined by a prospective learner’s email address, ending in .org, .gov, .mil, or .edu. Interested learners can apply below for the discount and, if eligible, will receive a promo code to enter when completing payment information to enroll in a Harvard Online program. Click here to apply for these discounts.
Gather your team to experience Harvard Online courses and to enjoy the benefits of learning together:
- Single invoicing for groups of 10 or more
- Tiered discounts and pricing available with up to 50% off
- Growth reports on your team's progress
- Flexible course and partnership plans
Learn more and enroll your team !
Trending Courses
Health care strategy.
Learn from HBS Professor Leemore Dafny how to align the principles of business strategy with the unique challenges and structures of health care organizations to capture value, define your mission, and lead your organization to success.
Big Data for Social Good
Using real-world data and policy interventions as applications, this course will teach core concepts in economics and statistics and equip you to tackle some of the most pressing social challenges of our time.
Innovations in Teamwork for Health Care
In this course, experts from Harvard Business School and the T.H. Chan School of Public Health teach learners to implement a strategy for organizational teamwork in health care.
Explore All Courses
Learner Testimonials
On Data Privacy and Technology
"The course was informative on both current and future data privacy and technological innovation trends—the need for data privacy without inhibiting innovation. The team and instructors prompt critical thinking while broadening the understanding of data privacy beyond the frontiers. At the end of the course, I concluded that there was a need for a mass cultural shift towards ethical use of technology."
Joanita Nagaba Co-founder, ANJ Data Management Solutions Africa Ltd.
On Health Care Economics
“This is an amazing course. The professor did a fantastic job dissecting the complexities of healthcare into chewable chunks."
Howard H. Dinh, MD, FACC Medical Director, Cardiac Services, Greater Sacramento The Permanente Medical Group and Chief, Cardiology Kaiser Permanente, South Sacramento
"I love the way the course is structured with real-world examples and the critical thinking sessions. It forces us to reflect upon what is happening around us. People who have an interest in cybersecurity, as well as those that would like to gain more general knowledge, would greatly benefit from this course."
Anand Narayan Account Executive, Lenovo Canada
On Data Science Principles
"This is a topic that people in any industry should have at least basic knowledge of in order to create more efficient and competitive businesses, tools, and resources."
Carlos E. Sapene Chief Executive Officer
On Data Science For Business
"This course had an amazing instructor, amazing examples, and an amazing user interface that made it easy for me to grasp the material and learn simultaneously with others around the world."
Shawn Carrington, Jr. Senior Executive Officer Perspecta, Inc.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- Braunwald's Corner
- ESC Guidelines
- EHJ Dialogues
- Issue @ a Glance Podcasts
- CardioPulse
- Weekly Journal Scan
- European Heart Journal Supplements
- Year in Cardiovascular Medicine
- Asia in EHJ
- Most Cited Articles
- ESC Content Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why publish with EHJ?
- Open Access Options
- Submit from medRxiv or bioRxiv
- Author Resources
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Read & Publish
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Advertising
- Reprints and ePrints
- Sponsored Supplements
- Journals Career Network
- About European Heart Journal
- Editorial Board
- About the European Society of Cardiology
- ESC Publications
- War in Ukraine
- ESC Membership
- ESC Journals App
- Developing Countries Initiative
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Risk of heart failure in inflammatory bowel disease: a swedish population-based study.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Jiangwei Sun, Jialu Yao, Ola Olén, Jonas Halfvarson, David Bergman, Fahim Ebrahimi, Annika Rosengren, Johan Sundström, Jonas F Ludvigsson, Risk of heart failure in inflammatory bowel disease: a Swedish population-based study, European Heart Journal , 2024;, ehae338, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehae338
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Dysregulation of inflammatory and immune responses has been implicated in the pathogenesis of heart failure (HF). But even if inflammation is a prerequisite for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), little is known about HF risk in IBD.
In this Swedish nationwide cohort, patients with biopsy-confirmed IBD were identified between 1969 and 2017 [n = 81,749, Crohn’s disease (CD, n = 24,303), ulcerative colitis (UC, n = 45,709), and IBD-unclassified (IBD-U, n = 11,737)]. Each patient was matched with up to five general population reference individuals (n = 382,190) and IBD-free full siblings (n = 95,239) and followed until 31 December 2019. Flexible parametric survival models estimated the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) and standardized cumulative incidence for HF, with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
There were 5,582 incident HF identified in IBD patients (incidence rate [IR]: 50.3/10,000 person-years) and 20,343 in reference individuals (IR: 37.9) during a median follow-up of 12.4 years. IBD patients had a higher risk of HF than reference individuals (aHR 1.19, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.23). This increased risk remained significant ≥20 years after IBD diagnosis, leading to one extra HF case per 130 IBD patients until then. The increased risk was also observed across IBD subtypes: CD (IR: 46.9 vs. 34.4; aHR 1.28 [1.20 to 1.36]), UC (IR: 50.1 vs. 39.7; aHR 1.14 [1.09 to 1.19]), and IBD-U (IR: 60.9 vs. 39.0; aHR 1.28 [1.16 to 1.42]). Sibling-controlled analyses showed slightly attenuated association (IBD: aHR 1.10 [1.03 to 1.19]).
Patients with IBD had a moderately higher risk of developing HF for ≥20 years after IBD diagnosis than the general population.

- heart failure
- inflammatory bowel disease
Supplementary data
Email alerts, companion article.
- Human Immunology of Heart Failure: Deconstructing Inflammatory Risk
Related articles in PubMed
Citing articles via, looking for your next opportunity, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 1522-9645
- Print ISSN 0195-668X
- Copyright © 2024 European Society of Cardiology
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The PhD Program in Health Data Science trains the next generation of data science leaders for applications in public health and medicine. The program advances future leaders in health and biomedical data science by: (i) providing rigorous training in the fundamentals of health and biomedical data science, (ii) fostering innovative thinking for the design, conduct, analysis, and reporting of ...
The SM in Health Data Science is designed to be a terminal professional degree, giving students essential skills for the job market. At the same time, it provides a strong foundation for students interested in obtaining a PhD in biostatistics or other quantitative or computational science with an emphasis in data science and its applications in ...
The Health Data Science (HDS) area of study provides students with a blend of strong statistical and computational skills needed to manage and analyze health science data in order to address important questions in public health and biomedical sciences. This training will enable students to manage and analyze massive, noisy data sets and learn ...
The Public Health Data Science (PHDS) track retains the core training in biostatistical theory, methods, and applications, but adds a distinct emphasis on modern approaches to statistical learning, reproducible and transparent code, and data management. The length of the 36-credit program varies with the background, training, and experience of ...
Department Home APPLY NOW To learn more, email Shankar Srinivasan, Ph.D., program director. Doctor of Health Informatics Current and future leaders in health care need a good understanding of the concepts and techniques of all aspects of Health Informatics - data analytics, information
Health Sciences Informatics, PhD. The Ph.D. in Health Sciences Informatics offers the opportunity to participate in ground-breaking research projects in clinical informatics and data science at one of the world's finest biomedical research institutions. In keeping with the traditions of the Johns Hopkins University and the Johns Hopkins ...
The science of informatics drives innovation-defining approaches to information and knowledge management in biomedical research, clinical care and public health. YSPH researchers introduce, develop and evaluate new biomedically motivated methods in areas as diverse as data mining, natural language or text processing, cognitive science, human ...
The PhD program is designed for students seeking the highest level of advanced training in the area of health informatics. Students take a sequence of core courses in health informatics, computing, and biostatistics, and electives in technical and health science areas, and pursue one of four tracks: Data Science and Informatics for Learning Health Systems; Clinical Informatics; Translational ...
The Doctor of Philosophy in Health Informatics is a full-time degree program. Students have seven years to complete the program. With in-person and hybrid courses, learners will have access to faculty mentors, hands-on labs, technology infrastructure and translational real-world projects. Coursework for the program includes the following classes.
The PhD is a campus based program only. Directed by Hadi Kharrazi, MD, PhD, the program offers the opportunity to participate in ground breaking research projects in clinical informatics at one of the world's finest medical schools. In keeping with the tradition of the Johns Hopkins University and the Johns Hopkins Hospital, the program seeks ...
A PhD in Health Informatics is a doctoral degree program that combines medical knowledge with computer and data science, engineering, and information science. This degree focuses on health information management and the collection, storage, and analysis of medical and patient data in the healthcare industry and clinical practice.
CHDS enhances interdisciplinary public health research, teaching and practice through leveraging and developing data science methods in conjunction with public health knowledge, frameworks and action as well as with other disciplines such as computer science, urban planning and sociology. CHDS values and promotes pluralistic knowledge discovery ...
Hybrid. Est. time to complete: 3-4 years. Credit Hours: 60 (with master's) or 72 (with bachelor's) Empower health care providers and transform patient care. The UNT Information Science Ph.D. program (or IIS Ph.D. program) responds to the varied and changing needs of the information age, therefore offering a concentration in Health Informatics.
The MS in Biostatistics Public Health Data Science Track (MS/PHDS) is designed for students interested in careers as biostatisticians applying statistical methods in health-related research settings. The MS/PHDS Track provides core training in biostatistical theory, methods, and applications, but adds a distinct emphasis on modern approaches to ...
What this unique PhD programme offers you. Four-year programme: An initial foundation year allows students to gain real experience and insight into health data research. Research that makes a difference: The three-year doctoral research projects undertaken by our students are designed to make a genuine contribution to advancing health and care.
For more information about the Health Data Science concentration, contact one of our graduate program coordinators. Fatma Nedjari. Phone: 734-615-9812 Email: [email protected]. Nicole Fenech. Phone: 734-615-9817 Email: [email protected]
PhD in Analytics and Data Science. Students pursuing a PhD in analytics and data science at Kennesaw State University must complete 78 credit hours: 48 course hours and 6 electives (spread over 4 years of study), a minimum 12 credit hours for dissertation research, and a minimum 12 credit-hour internship.
This course provides an introduction to data sources commonly used for health care research and analysis. Topics will include publicly available data sources, identifying strengths and weaknesses of data sources, and data management. ... Weill Cornell Medicine Graduate School of Medical Sciences 1300 York Ave. Box 65 New York, NY 10065 Phone ...
The PhD is the highest degree awarded by the University of Michigan. It signifies that you have successfully mastered a body of skills and knowledge in preparation for a career as an independent scholar. Our doctoral training involves working closely with faculty on projects of mutual interest, since mastery of research methods requires hands ...
Acceptance onto the MRes in Health Data in Practice constitutes entry onto the 4 year PhD programme in Health Data in Practice; progression to PhD requires successful (i.e. pass or above) completion of the MRes. This course is not currently available as a standalone MRes in Health Data in Practice. Applications for September 2024 entry will ...
The Public Health Data Warehouse is a truly unique public health data analysis tool that links multiple data sets across state and local government to help address public health priorities. The PHD was created in 2017, originally to provide unprecedented access to data across government to identify trends and target resources to confront the ...
Plana pursued her vision when she came to Harvard Medical School as an MD/PhD student. In 2022, she earned her PhD in systems, synthetic, and quantitative biology from the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (now the Griffin GSAS). When the COVID-19 pandemic began, Plana joined her PhD adviser, Peter Sorger, the Otto Krayer Professor ...
The Master of Science in Health Informatics (MSHI) at Northeastern's Bouvé College of Health Sciences and Khoury College of Computer Sciences has been designated as a HIMSS Approved Education Partner (AEP).. Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, Inc. (HIMSS) is a mission-driven nonprofit that supports the transformation of the health ecosystem through information and ...
The SM in Health Data Science is designed to be a terminal professional degree, giving students essential skills for the job market. At the same time, it provides a strong foundation for students interested in continuing in a PhD in Biostatistics or other quantitative or computational science with an emphasis in data science.
A new study in our partner journal the Milbank Quarterly finds support for using identifiable data for public health and research purposes among the public generally, but also highlights a unique decline in comfort among African Americans. 2020 was a watershed moment for public health and societal dynamics in the United States.
A data scientist earns an average salary of $108,659 in the United States, according to Lightcast™ [1]. Demand is high for data professionals—data scientists occupations are expected to grow by 36 percent in the next 10 years (much faster than average), according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) [ 2 ].
On Health Care Economics "This is an amazing course. The professor did a fantastic job dissecting the complexities of healthcare into chewable chunks." Howard H. Dinh, MD, FACC Medical Director, Cardiac Services, Greater Sacramento The Permanente Medical Group and Chief, Cardiology Kaiser Permanente, South Sacramento
Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Program Division of Pre-medical and Pre-health Programs Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences and Professional Studies 60 N. 36th Street Health Sciences Building Philadelphia, PA 19104 267.359.2761 [email protected]
Correspondence: Jiangwei Sun, PhD, Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Nobels väg 12A, 171 65 Solna, Sweden.Email: jiangwei ...