DRIVING PASSION | TRANSFORMING LIVES | HITTING MARKS
Access to the platform, log in using your account on:.
Forgotten your username or password?

Industrial Automation
Trial class.

Pre-School (K1 to K2) Trial Class
Want to learn, how to Read, Write and Count? Let your child continue developing their skills using our platform.
Elementary (Grades 1 to 6) Trial Class
Learn, Explore and Grow.

Junior High School (Grade 7 to 10) Trial Class
World-class flexible learning platform for creating passionate, goal-oriented, and purpose-driven students.
SHS Grade 11 Physical Science Trial Class
SHS Grade 12 Understanding Culture, Society and Politics Trial Class
Stay in touch, nextgencollege.education.
- https://nextgencollege.education
- Mobile : 09057084413 | 09171885649
- [email protected]
Welcome to Brightspace by D2L
New Designs for School Next Generation K-12: 10 Implications for HigherEd

Tom Vander Ark CEO + Partner Getting Smart

We’ve all had the experience of truly purposeful, authentic learning and know how valuable it is. Educators are taking the best of what we know about learning, student support, effective instruction, and interpersonal skill-building to completely reimagine schools so that students experience that kind of purposeful learning all day, every day.
There are a growing number of next generation models in K-12 as a result of new thinking about learning design and deeper understandings of college and career readiness, enabled by cheap devices, better tools, and foundation support.
There are a growing number of next generation models in K-12 as a result of new thinking about learning design and deeper understandings of college and career readiness, enabled by cheap devices, better tools, and foundation support. They personalize learning in blended and competency-based environments . These models revolve around students and learning, rather than teachers and direct instruction as the primary pedagogy.
We’ve chronicled the development of next-gen schools ( here and here ) and see hundreds of districts and networks adopting next-gen strategies. We’re optimistic that broader adoption of these strategies will produce better student outcomes. Following are 10 examples of next-gen learning in K-12.
10 examples of next-gen K-12
Summit Public Schools : well articulated goals, innovative platform blends playlists and projects.
Brooklyn Lab built Cortex, their own personalized learning platform.
Kettle Moraine , a Milwaukee area district, created new small themed flex academies to expand options and manage change.
DSST is the best high poverty STEM network and a values-first organization , it will soon account for 25% of graduates in Denver–and more will be going to college.
IDEA Public Schools operates 44 schools in low-income south Texas communities. The blended elementary schools feed AP/IB high schools which send all of their graduates to college.
Quest Early College , Spring Texas, where 80% of grads leave with an AA degree from Lone Star College; great service learning program.
Metro Early College High School in Columbus features the Bridge intersession team taught by OSU and Metro faculty demonstrates readiness for college classes.
Career Path High on campus of Davis Applied Technology College is a CTE early college.
RAMTEC , Marion, Ohio, where students learn and teach robotics .
VLACS offers full and part-time online learning to New Hampshire students which are part of a statewide, policy-fueled push for proficiency-based graduation and college admissions.
These examples are not single course innovations, they are engineered solutions. The first half are districts or networks; the other half are schoolwide models. There are hundreds of examples and they have big implications for HigherEd.
We see 10 implications for HigherEd; some directly as a result of next-gen models, some resulting from next-gen policies, some from EdTech and consumer variables impacting both K-12 and HigherEd.
Preparation variables: #1-3
Better prep: Almost every state has adopted higher standards in reading, writing, and math that will, over time, result in better college preparation.
Better mindset: Following the lead of next-gen models, a growing number of K-12 schools are promoting a growth mindset and high agency learning. Stronger executive functions should result in improved persistence and self management.
More credit: The expansion of dual enrollment and other college credit options are increasing the percentage of students entering college with a significant amount of credit.
Consumer variables impacting K-12 and HigherEd: #4-7
Better employability: Led by next-gen models and scholars like David Conley , there is a stronger K-12 focus on success skills. Persistent youth unemployment following the Great Recession has made more young people aware of the need for work experiences and job skills.
Better LX: widespread use of personalized and blended learning is creating a generation of demanding consumers that expect high engagement learner experience (LX) with some ability to customize their own pathway. Many learners will be seeking more active and applied learning in more authentic settings.
More CBE: There is a slow but steady increase in the percentage of K-12 students able to learn at their own pace and progress based on demonstrated mastery. Competency-based education (CBE) is working its way in from the edges including credit for prior/outside learning, individual pacing, rolling enrollment.
More options: In addition to school choice, high school students in most states have access to online learning options and, increasingly, to authentic learning experiences outside of school (externships); the combination is creating a more demanding consumer and setting the stage for a unbundled HigherEd experience.
Infrastructure variables impacting K-12 and HigherEd: #8-10
Blended staffing: Next-gen models incorporate differentiated and distributed staffing. New models leverage the talent of great educators and support educators in teams, with most working in facilitating/coaching roles. Speech therapists, language teachers, and mentors are all available at a distance address problems and expand options.
Mobile: With nearly ubiquitous mobile penetration, learning platforms and tools must increasingly be optimized for mobile use (e.g., DreamDegree ).
Integrated IT: The old challenge of “technology integration” is being replaced by an integrated design opportunity, next-gen learner experience supported by an integrated IT stack (LX+IT, e.g., College for America ). Behind all of it is machine learning : adaptive learning, conversion optimization, and operational efficiency. Some HigherEd models will take advantage of this opportunity, but most likely will not.
In short, HigherEd institutions will need to enable a bundled multi-provider experience (or risk becoming part-time providers), focus on employability skills and experiences, and take learner experience much more seriously.
This blog was originally posted on GettingSmart .
Tom Vander Ark
Ceo + partner, getting smart.
Tom Vander Ark is an advocate for innovations in learning. As CEO of Getting Smart, he advises school districts and networks, education foundations and funders and impact organizations on the path forward. A prolific writer and speaker, Tom is author of Getting Smart ; Smart Cities That Work for Everyone ; Smart Parents ; and Better Together . Previously, Tom served as the first Executive Director of Education for the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. He also served as a public school superintendent in Washington state and has extensive private sector experience. Tom co-founded the first education venture fund, Learn Capital.
Read More About New Designs for School

NGLC Invites Applications from New England High School Teams for Our Fall 2024 Learning Excursion
March 21, 2024

Bring Your Vision for Student Success to Life with NGLC and Bravely
March 13, 2024

How to Nurture Diverse and Inclusive Classrooms through Play
Rebecca Horrace, Playful Insights Consulting, and Laura Dattile, PlanToys USA
March 5, 2024
Unlock your child’s full potential. Enroll today!
866.968.7512
Schools and Programs
Why choose k12, student experience, career & college prep, career prep, career prep offerings, career fields, college prep, adult learning, k12 for business, k12 for school districts, see all products.
Parent & Student Login
English | Español
" * " indicates required fields
Online Education Done Right
Help your child reach their full potential with personalized learning from K12.

Find a school near me
Outside of the U.S.?
Need More Info?
K12 and you.
Every student deserves an education built to meet their unique needs. With K12 online school, your child can find their personalized path to success — learning at their own pace, in their own place with an engaging curriculum that supports individual learning styles.
With K12, students experience:
- A quality online education focused on skill-building and socialization
- A flexible learning system that suits their schedule and needs
- Award-winning curricula to uncover their unique interests and spark a passion for learning
- A supportive learning environment featuring expert instruction, innovative technology, and engaging, collaborative resources
SEE THE K12 DIFFERENCE
Your Questions, Answered
Learn more about the K12 learning experience. Browse our frequently asked questions.
EXPLORE FAQs
Online School For Every Type of Learner
Whether you’re looking for public school, private school, or just a few classes, we have an online education option for every student. Tailored to your child’s unique schedule, needs, and interests, K12 programs empower students to succeed and instill a lifelong love of learning.
Online Public School
Embark on an engaging learning journey. Enroll your child in a K12 online public school, where they’ll enjoy individualized learning led by state-certified teachers.

Online Private School
Through K12 online private school, students receive an engaging, hands-on education that accommodates flexible schedules and fosters independence. Explore this tuition-based option today.

Online Homeschool
Supplement your child’s homeschool education with challenging, engaging, and highly interactive K12 courses that speak to individual interests and help fill in knowledge gaps.
DISCOVER HOMESCHOOL

Individual Classes
Personalize your child’s education with supplemental coursework. All individual classes are taught by K12 teachers and come with hands-on materials that help students catch up, get ahead, and explore their interests.
DISCOVER CLASSES


Tutoring Services
Support student success with flexible, dynamic tutoring from K12 state-certified teachers.
DISCOVER TUTORING
As an award-winning, fully accredited online school, K12 combines highly qualified teachers with an engaging curriculum and a user-friendly online learning platform. The result? A supportive learning environment that helps every student thrive.

Take Advantage of the Expertise That Sets K12 Apart
As a leader in educational management, K12 has accumulated various awards and accolades from national organizations, award bodies, and independent researchers. Our consistent level of quality goes above and beyond traditional schooling norms. We’re always looking for ways to improve our practices and empower more students to achieve their best.
- Cognia-accredited
- Award-winning curricula
- Research-backed curricula
- State-certified teachers
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR CREDENTIALS

Students have chosen K12 education since 2000.

Of parents say K12 helped their child prepare for the future.

States offer tuition-free K12 programs.
A Great Educational Experience Starts Here
K12 students are empowered to achieve their best with hands-on learning, flexible scheduling, and guidance from both teachers and parents. Students learn in the comfort of their own home, free from distractions, with live online instruction, self-led assignments, and interactive activities that fuel personal growth.

Elementary Day in The Life
K12 online elementary school combines live online instruction with fun, interactive activities that inspire students to explore their unique interests. Students learn in their own safe environment, with all class materials sent directly to their door. Day In The Life Micah And Sarai School Safety Sample Lesson
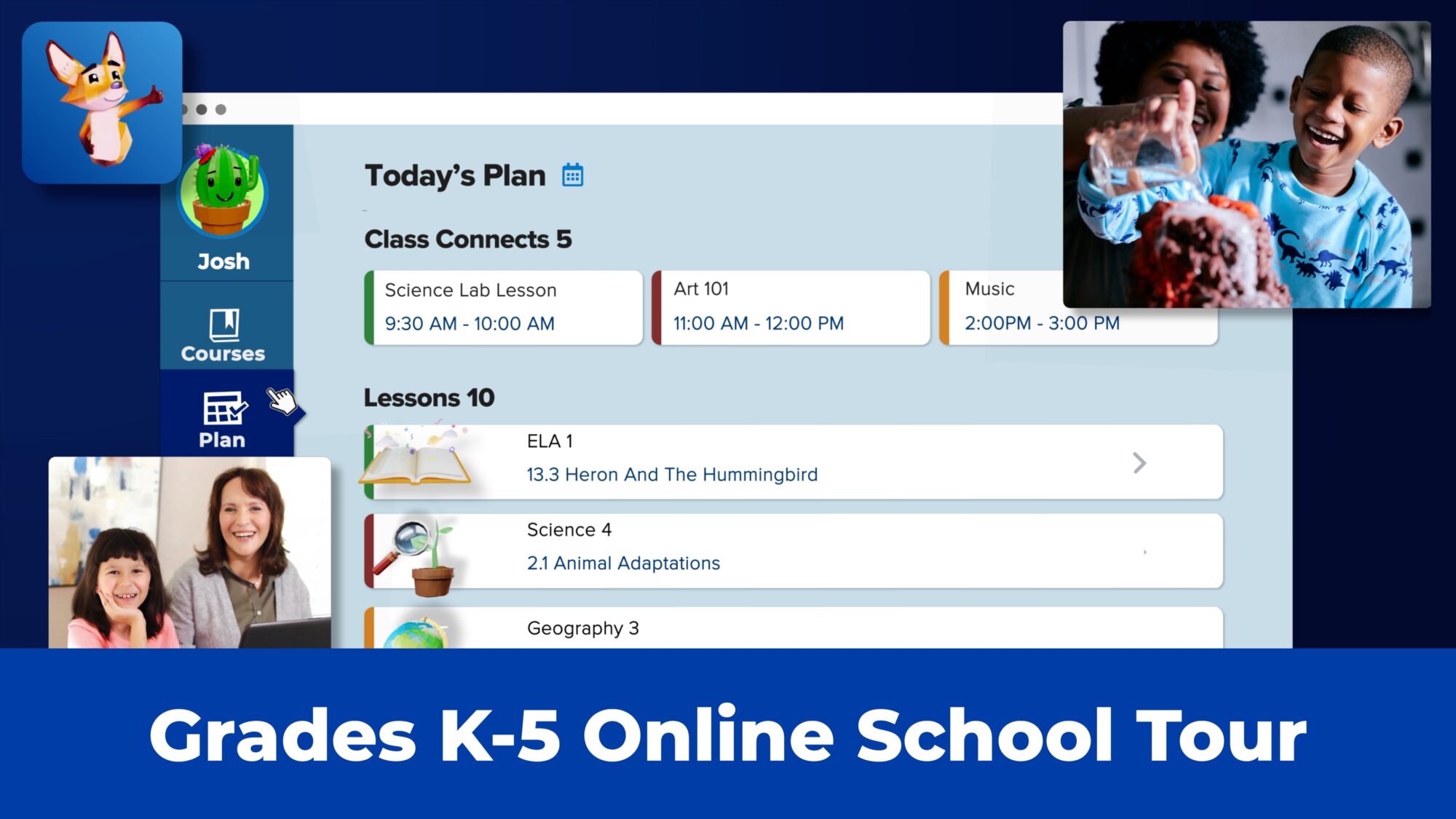
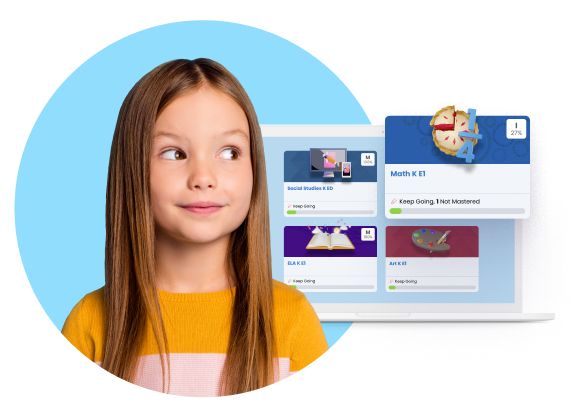
School Tour
K12 students in grades K-5 participate in online coursework with interactive lesson plans and personalized instruction from teachers, designed to make learning fun and engaging.
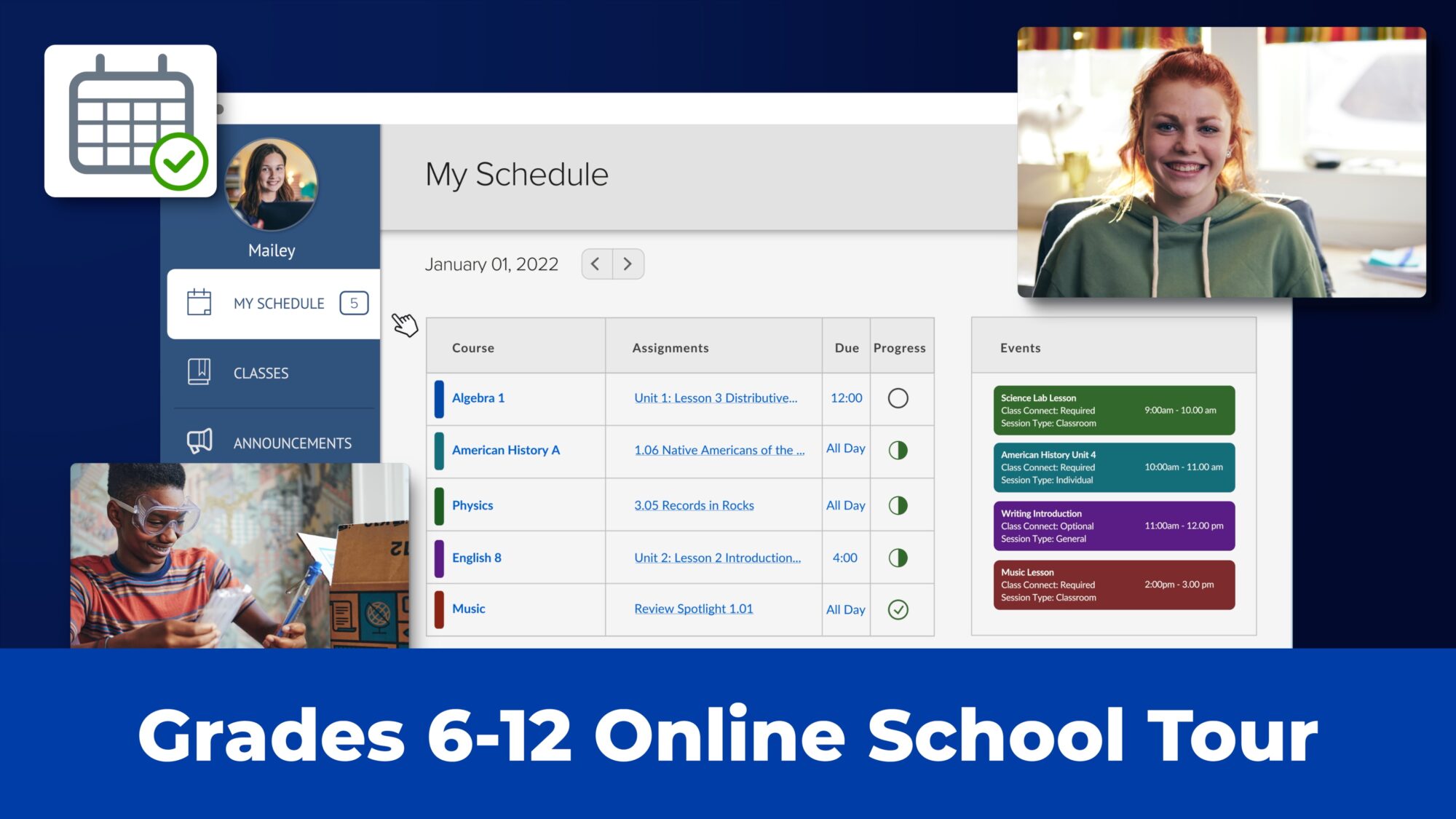
K12 students in grades 6-12 find success through online education that fosters independence and encourages them to explore their individual interests.

Middle School
K12 middle school students learn through instructional videos, self-assessments, and interactive activities that provide a rewarding learning experience. A robust STEM program is also available to encourage students to explore different subjects and develop real-world skills. Explore STEM Middle School Sample Lesson
High School
K12 high school students get ready for post-graduate success through a combination of standards-based coursework and career and college preparation courses. High schoolers also meet with counselors to get actionable guidance on college applications and career pursuits. Arianna Day In The Life Graduation And Career Prep High School Sample Lesson

Passionate Teachers, Skilled in Online Learning
Specially trained in online education, K12 teachers are passionate about helping students thrive. They get to know students on an individual level, tailoring instruction to your child’s unique learning style.
MEET OUR TEACHERS

Have questions? Contact us to jumpstart your child’s future with K12.
Become an Insider
Sign up today to receive premium content.

Technology Inside Next-Gen Learning Environments Continues to Evolve

Larry is a freelance writer, author, and educator. He has taught English at both the high school and college level, and worked with struggling writers.
K–12 classrooms essentially have been set up in much the same way since the days of Horace Mann in 1830s Massachusetts.
Students sit in rows, facing forward, in order to see the blackboard and the teacher , who is ready to share knowledge that students are expected to receive.
Increasingly, schools have turned away from that model as they strive to create active-learning classroom spaces that are more conducive to modern learning methods and thought .
A new study underway at Virginia Tech seeks to understand the effects of physical space on course engagement and learning . Led by Timothy Baird, assistant professor of geography in the College of National Resources and Environment and senior fellow for the Institute for Creativity, Arts, and Technology, the study hypothesizes that greater engagement occurs in active-learning spaces and leads to better learning outcomes.
“We’re trying to figure out what engagement, critical thinking and community actually look like in the classroom, so we can better nudge space, teachers and students toward all that magic,” Baird says.
The study incorporates motion-tracking cameras that take a few pictures of the class every second. The pictures are processed via machine learning and used to build a 3D model of classroom activities. From those models, Baird and his team can examine subtle classroom behaviors and patterns linked to learning.
While it’s impossible to accurately predict the layout of the future K–12 classroom, it’s easy to imagine it incorporating active-learning technology at every possible turn.
MORE FROM EDTECH: Schools sketch out modern learning environments and then make them a reality.
What Is in Store for K–12 Modern Classrooms?
Jody Britten, a senior associate at the Metiri Group , predicts that 3D pens , 3D printers , tablets , cloud-based laptops and data visualization tools, such as Tableau and QlikView , will all have a place in the modern classroom.
3D pens in particular will encourage creativity in students, allowing users to draw a 3D structure in midair or create a raised graphic on a piece of paper or flat surface. 3D pens used in conjunction with data visualization tools add an element of dynamism to information and figures.
Increase in academic engagement resulting from improvements to classroom layouts, such as adding space for independent work
“What will students need access to in order to learn in an authentic manner?” Britten asks. “Active-learning technology allows them to move from consuming information to creating and thinking on a deeper level.”
MORE FROM EDTECH: Check out how modern classrooms and personalized learning are the perfect pair.
Human Teachers Will Always Have a Place in the Classroom
As Baird and his team learn more about the role physical space plays in learning environments, he recognizes the role of teachers .
“Space can push teachers to try different things and take chances,” he says. “New technologies may push teachers in new directions — hopefully toward more human connections with students.”
In the SCALE UP room at Virginia Tech, Baird included more small group activities and discussion, and encouraged use of whiteboards, along with new strategies to leverage the space.
But the human element has been, and will continue to be, key to tying everything together in next-gen , modern learning environments.
“A more open and collaboration-friendly atmosphere is helpful,” says Eric L. Blake, principal of Brooklyn’s Science, Technology and Research Early College School . “But we still need teachers to use a toolkit of solid and battle-tested classroom strategies to engage all learners.”

- Data Analytics
- 3D printing
Related Articles

Unlock white papers, personalized recommendations and other premium content for an in-depth look at evolving IT
Copyright © 2024 CDW LLC 200 N. Milwaukee Avenue , Vernon Hills, IL 60061 Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Your favorite state, in photos
- Get our new newsletter to follow the story of California in pictures.
- Get our new newsletter to see extraordinary moments of Californians in pictures.
- Newsletters
- Environment
- 2024 Voter Guide
- Digital Democracy
- Daily Newsletter
- Data & Trackers
- California Divide
- CalMatters for Learning
- College Journalism Network
- What’s Working
- Youth Journalism
- Manage donation
- News and Awards
- Sponsorship
- Inside the Newsroom
- CalMatters en Español
K-12 Education
California could require kids to learn how to manage money. Should voters decide curriculum?

Share this:
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

A ballot initiative that would require a personal finance class in high school circumvents the usual process for curriculum changes.
School curriculum is usually the purview of education experts, but this fall it could be decided by California voters, who will vote on adding a new requirement for high school students: a one-semester class in managing personal finances.
California’s Secretary of State is poised to certify that the California Personal Finance Act is eligible for the November ballot, which would add financial literacy to the list of high school graduation requirements beginning with the class of 2030.
Students would learn about paying for college, online banking, taxes, budgeting, credit, retirement accounts, loans, how the stock market works and other topics. The issue is critical, organizers said, as students face a shifting economy and difficult decisions about college, careers and their futures.
“No one comes out of the womb knowing how to manage their credit score. It has to be taught,” said Tim Ranzetta, co-founder of a personal finance education nonprofit and a chief backer of the initiative. “And right now there’s a dramatic gap between what students know and what they need to know. We have to change that.”
Voters seem to agree with him. A 2022 survey of adults nationwide showed that nearly 90% support a financial literacy requirement in high school, and nearly as many wished they had taken such a course when they were students.
That’s not surprising, considering the financial woes many people incur. The average credit card debt in California is $8,366, the sixth-highest rate in the country, and 1 in 6 borrowers nationwide are in default on their student loans .
Financial literacy already in classrooms
But some education experts have pushed back, not because they’re opposed to financial literacy for students but because they question whether voters are best equipped to dictate what’s taught in classrooms.
Currently, the state’s History-Social Studies framework includes a one-semester course in economics , required for graduation, that covers much of the same material proposed by the financial literacy ballot initiative proponents. Financial literacy is also included in first, second and ninth grade curriculum. First graders, for example, learn that money can be exchanged for goods and services, and people make decisions about how to spend their money.
But Ranzetta said the curriculum, which was last updated in 2017, doesn’t focus enough on financial literacy. Personal finance is covered for only a few weeks in the economics course; the rest covers more abstract economic concepts like international trade, resource allocation and the benefits and drawbacks of capitalism. Individual teachers can choose how much they want to focus on certain topics.
State Superintendent Tony Thurmond wouldn’t answer questions about the ballot initiative, although he endorsed it. Linda Darling-Hammond, president of the State Board of Education, also wouldn’t answer questions.
Leaving curriculum decisions to voters is ‘a bad idea’
The proposed ballot initiative so far has almost zero opposition, but some are questioning the idea of letting voters — and not education experts — decide what students learn in the classroom. Ordinarily, curriculum in California is developed by a group of teachers and subject-matter professionals who serve on the Instructional Quality Commission , which meets publicly six times a year. New curriculum is subject to multiple reviews, edits and public vetting, ultimately going before the State Board of Education for adoption. Local school boards can adjust curriculum according to the needs of their students.
“Most voters don’t know much about education policy, and having them decide what can be taught in schools is a bad idea,” said Morgan Polikoff, an education professor at the University of Southern California. “We already have a process in place for adopting curriculum, and if people are unhappy with it there are plenty of avenues to have their voices heard — they can go to meetings, they can vote people out of office, they can talk to their representatives.”
“No one comes out of the womb knowing how to manage their credit score. It has to be taught.” Tim Ranzetta, co-founder of next gen personal finance
Polikoff worries that adopting curriculum through ballot initiatives could set a dangerous precedent. Religious or anti-LGBTQ curriculum, for example, could be approved by voters, setting up costly and lengthy legal showdowns with the state Department of Education.
Curriculum can be complicated, as well. When writing new curricula, the Instructional Quality Commission looks at the broader context, making sure students get new material every year that builds on what they learned previously, subjects don’t overlap and topics are flexible enough for teachers to adapt lessons to the individual needs of their students. Textbooks and tests are also taken into consideration.
Legislature weighs in
Most curriculum updates and changes originate with the commission, but sometimes the Legislature weighs in. The state’s new ethnic studies and media literacy requirements, for example, stemmed from Assembly bills. Another bill, AB 2097 , would add computer science as a graduation requirement.
AB 2927 , a financial literacy bill proposed by Democrat Kevin McCarty of Sacramento, would actually do almost the same thing as the ballot initiative. The bill would require financial literacy as a graduation requirement, although it would go into effect until 2031, a year later than the ballot measure.
Bruce Fuller, education professor at UC Berkeley, said he worries about the increasing politicization of curriculum — either from the Legislature or those pushing for ballot initiatives.
“We have these political interests unabashedly trying to control what’s taught in the classroom, instead of leaving it up to teachers and locally elected school boards,” Fuller said. “We should trust those folks to devise thoughtful curriculum that’s appropriate for their students.”
He also questioned the ever-growing list of graduation requirements. High schools only offer six or seven class periods a day, and with more required classes there’s less room for art and other electives. Some districts have started adding an extra period so students can fit in all the classes they need to take to graduate, finish a career pathway and qualify for California’s public universities.
“We have these political interests unabashedly trying to control what’s taught in the classroom, instead of leaving it up to teachers and locally elected school boards.” Bruce Fuller, education professor at UC Berkeley
“I’m not sure how adding more required classes is going to motivate restless teenagers,” Fuller said. “With more requirements, we’re giving them almost no chance to study things they’re actually interested in.”
McCarty’s bill is not the Legislature’s first attempt to wade into financial literacy. A dozen bills requiring financial literacy have died or been vetoed in recent years, in most cases because financial literacy curriculum already exists and the state already has a system for adopting curriculum.
As Gov. Jerry Brown wrote in 2018 when he vetoed a bill that would have made financial literacy materials available to teachers: “This bill is unnecessary. The History-Social Science Framework already contains financial literacy content for pupils in kindergarten through grade 12, as well as a financial literacy elective.”
“I recognize the value of the process, but it’s slow and so far it hasn’t worked in California. The issue is too urgent and too popular to wait any longer.” Tim Ranzetta, co-founder of next gen personal finance
Ranzetta said the Legislature’s inability to pass a financial literacy curriculum is what spurred him to take the matter directly to voters.
“I recognize the value of the process, but it’s slow and so far it hasn’t worked in California,” he said. “The issue is too urgent and too popular to wait any longer.”
Ranzetta grew up in New Jersey, where his father was a banker and his mother was a community volunteer who raised six children. He learned financial literacy from his parents, and assumed other young people did, too. It wasn’t until he started volunteering at an East Palo Alto high school that he realized many students are clueless about money, and that ignorance can hamper them throughout their lives. But they were eager to learn, he said, and share the information with their parents.
That experience inspired him to start NextGen Personal Finance, which offers free financial literacy curriculum and training for teachers. At least 7,000 teachers in California and more than 100,000 nationwide have participated, he said.
A class that demystifies money

At Berkeley High, Crystal Rigley Janis teaches two economics classes and three personal finance classes, covering topics she wishes she knew as a young person: how to negotiate a salary, not relying on gut instinct when investing, and avoiding individual stocks in favor of index funds.
“It took me 15 years to understand those things, and it probably cost me millions of dollars,” said Rigley, who worked for several years at a wealth management firm before going into teaching. “I don’t want other people to make the mistakes I did.”
Eliza Maier, a senior, was so inspired by Rigley’s class that she opened a Roth IRA when she turned 18 and transferred money from her low-interest savings account. The class, she said, helped demystify money and the role it can play in major life choices.
“We learned that money isn’t good or bad – it’s a tool,” Maier said. “It can help you realize your goals. It can help you be prepared for whatever happens in your life. I didn’t know anything about money when I started taking this class, but I think it’s so important, especially for high school students.”
more on financial literacy

California keeps expanding school curricula. What about improving key subjects?

Why California should make personal finance a high school graduation requirement
We want to hear from you
Want to submit a guest commentary or reaction to an article we wrote? You can find our submission guidelines here . Please contact CalMatters with any commentary questions: [email protected]
Carolyn Jones K-12 Education Reporter
Carolyn Jones covers K-12 education for CalMatters. Previously, she worked at EdSource, the San Francisco Chronicle and the Oakland Tribune. She recently served as a Fulbright Specialist in Albania focusing... More by Carolyn Jones
We've recently sent you an authentication link. Please, check your inbox!
Sign in with a password below, or sign in using your email .
Get a code sent to your email to sign in, or sign in using a password .
Enter the code you received via email to sign in, or sign in using a password .
Subscribe to our newsletters:
- WeeklyMatters Catch up on the top stories in California with a summary of our reporting and commentary from the past week.
- Weekly Walters Get a digest of new insights from veteran journalist Dan Walters, who holds powerful people in California accountable.
- WhatMatters Start your day with a comprehensive rundown of the most important stories in California politics and policy.
- Inequality Insights Your weekly must-read to stay on top of inequality, one of California’s most pressing issues.
Sign in with your email
Lost your password?
Try a different email
Send another code
Sign in with a password
The New Ivies: As Employers Sour On The Super-Elite, These 20 Colleges Shine
The Ivy League is losing its standing as America’s producer of great talent. Here are the schools producing the hard-working high achievers that employers crave.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Critics cite university responses to campus protests as just one of many grievances they have with the Ivy League.
F or the entirety of America’s existence, the Ivy League has provided an essential service. In sorting the best and the brightest upon admission and then rigorously educating them, these “Ancient Eight” universities have provided employers, investors and even voters a meritocratic seal of approval. Some one-third of U.S. presidents and the current Forbes 400 list of richest Americans are Ivy alums, as well as eight sitting members of the Supreme Court.
But as evident just by reading or watching the news, something feels distinctly off on Ivy League campuses. The eight colleges have faced a barrage of complaints in recent years over admissions policies that put together a class of amalgamated specialists instead well-rounded, bright students; grade inflation at top schools Harvard and Yale; and most recently, university officials’ responses to on-campus protests against the war in Gaza.
So if the Ivies aren’t the Ivies anymore, which schools exactly are? Using an exclusive survey of hiring managers, Forbes introduces the New Ivies—the 10 public universities and 10 ascendant private ones turning out the smart, driven graduates craved by employers of all types.
Our methodology was as follows. After disqualifying the Ivies (and we used the Ivy-plus yardstick, which includes Stanford, MIT, Duke and the University of Chicago, as well as the eight classics Harvard, Yale, Princeton, Brown, Penn, Columbia, Dartmouth and Cornell), we started with 1,743 colleges of at least 4,000 students (understanding that small liberal arts schools have always offered a more boutique experience and are hard to compare with research universities). Using 2022 admissions data, the most recent available, we then screened for schools with high standardized test scores (our New Ivies average a robust 1482 SAT and 33 ACT) and where at least half the applicants supplied the scores, regardless of whether they were required to do so for admission—in other words, places that still rely heavily on objective measures of success.
We also screened with a selectivity yardstick (below a 20% admission rate at private schools, 50% at publics). And then from there, we took the 32 remaining schools and surveyed our hiring manager respondents about each one.
Many of the schools on our list are well known; Johns Hopkins and University of Michigan have long been considered Ivy caliber institutions, while Vanderbilt, Rice and Emory are often referred to as Southern Ivies. Others like New York’s Binghamton University are already respected in their geographic areas, but now are attracting wider notice.
Data Research: Rina Torchinsky
THE PUBLIC IVIES
These 10 state universities, spread across the U.S., attract high-achievers and turn out hard-working, highly-regarded employees. (Military academies were not included in our analysis. California universities were excluded because they don’t consider test scores.)
THE NEW PRIVATE IVIES
These 10 private schools, located in nine states and Washington D.C., are attracting the smartest students and plaudits from employers. Our analysis excluded schools with fewer than 4,000 students, the eight old Ivies and four Ivy-plus schools—Stanford, MIT, Duke and Chicago.
MORE FROM FORBES

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
THE MANY SINS OF MOSCOW�S NEW ST. ANDREWS COLLEGE
by Nick Gier
For a full accreditation report on NSA see this link . For articles on the Wilson Saga click this link .
In April 2000, I gave a talk to the students and faculty of New St. Andrews College (NSA), a small Calvinist college established in Moscow in 1994. At that time I congratulated Douglas Wilson, founder of the college, on the success of both NSA and his K-12 Logos School. Wilson appeared to enjoy a story I told about him as a student in the philosophy department, and it got a good laugh from the audience. I also announced that I was prepared to help NSA students with their senior theses. In the previous year I had spent about 60 hours helping a bright NSA student with a thesis on Buddhism.
In December 2002, I invited NSA faculty and students to the regional meeting of the American Academy of Religion. It was held in Moscow in May 2003, and 40 percent of the papers were presented by faculty from conservative Christian colleges. NSA president Roy Atwood defended their absence by saying that they �had better things to do.�
Wilson wrote an article �Why Evangelical Colleges Are Not� in Chronicles (September, 1998), the journal of the far right Rockford Institute. The hostility displayed against reputable evangelical colleges in this article not only shows blatant disrespect for these fine schools, but it manifests shameful disregard for the entire academic enterprise.
In a letter to the Moscow-Pullman Daily News on May 23, 2003, Atwood wrote that his college was an accredited institution. At a legal hearing before the Latah County Commissioners in April 2003, the NSA attorney also testified that NSA was accredited. The problem, however, is that NSA did not receive its accreditation until November 29, 2005.
In October, 2003, the community learned of the existence of Wilson�s booklet on slavery in the Antebellum South in which he stated that �there has never been a multi-racial society which has existed with such mutual intimacy and harmony in the history of the world" (p. 24). It was later discovered that 20 percent of this text was lifted from another book. When two UI history professors wrote a paper criticizing Wilson, his reaction was to write Governor Kempthorne and request that the professors be disciplined.
Only recently did I learn that NSA faculty celebrated April Fools of 1999 by stealing letterhead from the UI provost�s office to distribute an announcement of visiting feminist scholars who would give their presentations topless. There is nothing wrong with a good joke, but one usually tries to avoid criminal activity in pulling stunts such as this. Recently Wilson defended this action in his blog: �By the time you receive this, our local police will probably have forgotten all about it, so a little bragging is now safe. . . . [My son-in-law], . . . encouraged by some winks and nudges from me, . . . made up a flyer which announced a topless and proud lecture series by topless feminist scholars.�
An important academic virtue is �collegiality,� which consists of respect for, and cooperation with, all members of the academic community. I believe that we can conclude from NSA�s actions that it has not been a very good academic citizen. The supreme irony is that 9 of the15 NSA faculty have, or are expecting, 13 UI degrees.
The following are some more disturbing NSA facts:
Only 27 percent of the college�s faculty have PhDs. NSA has the resources to hire PhDs, but evidently chooses not to do so. Their less than prestigious accrediting agency requires that only one third of the faculty have the doctorate.
Two of the college�s senior fellows, presumably equivalent to full professors, do not have PhDs. Generally, a PhD is required at the lowest rank of assistant professor.
Although full resumes are not available on NSA�s website, it appears that a majority of the faculty�s published books are from Canon Press, Wilson�s own creation and the publisher of the infamous slavery booklet.
Of special concern is the fact that Wilson�s brother, his son, and his son-in-law are on the college�s faculty.
Steve Wilkins and George Grant are regular speakers at Wilson�s annual conferences in Moscow. Grant has a mail order doctorate and Wilkins is a conservative Calvinist minister from Louisiana. Wilkins is a founding director of the League of the South, which has been declared a hate group by the Southern Poverty Law Center. The Confederate flag used to hang in Wilson�s office and Logos School displayed it at its social functions.
When a Moscow journalist interviewed Wilson, Grant, and Wilkins in February, 2004, they each proudly affirmed their belief that only propertied males should vote. Always the jokester, Wilson said that democracy was just like two coyotes and a lamb voting on what to have for lunch.
There are well qualified students at NSA and some competent faculty, just as there are good, decent people who attend Wilson�s 800-member Christ Church. One can usually spot these people because they frequently speak of Wilson�s goal of achieving �truth, goodness, and beauty.� These fine folks need to be reminded that their leaders have not always told the truth, that condoning slavery is not good, and that calling for the execution of homosexuals is just plain ugly.
Grade 11 or Grade 12
1st semester, 2nd semester.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Grade 12. Grade 11 or Grade 12. Flexi Orientation & Platform Overview (SHS) Upskill. Industrial Automation & Control Systems. TESDA Courses. NextGen Summit. Trial Class. Mastering NextGen Flexi. Contact us. Follow us. Contact site support. You are not logged in. Get the mobile app. Powered by Moodle.
Junior High School (Grade 7 to 10) Trial Class. World-class flexible learning platform for creating passionate, goal-oriented, and purpose-driven students.
NextGen is about driving passion, transforming lives, and hitting marks. To see individuals who are globally competitive, purpose-driven leaders, and champio...
Help strengthen next gen learning by sharing best practices, practitioner tools, and stories from the NGLC community with your colleagues. Next Generation Learning Challenges (NGLC) empowers K-12 educators to reimagine public education, offering a supportive community and many resources.
Innovative Ideas are Great, but Actionable Plans are Better. Although we challenged the field to put forth exceptional ideas, K-12 education needs practical solutions. These next gen school developers are teaching us how to completely recreate school on the same budget, with the same human resources, and for the same students as we would find ...
Login - K12 Inc. Welcome to Brightspace by D2L. Username. Password. Log In. Forgot your password? Warning.
Consumer variables impacting K-12 and HigherEd: #4-7. Better employability: Led by next-gen models and scholars like David Conley, there is a stronger K-12 focus on success skills. Persistent youth unemployment following the Great Recession has made more young people aware of the need for work experiences and job skills.
Senior High School. NGTC's FlexiLearning program trains each student to be multi-skilled and character-driven in their chosen field of expertise, that readies them for both college and employment. Expand all.
Next Generation Technological College | Plaridel. Next Generation Technological College, Plaridel, Bulacan. 10,058 likes · 231 talking about this · 1,746 were here.
1st-Sem: Practical Research 2 (Academic Track) This course develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills through quantitative research. 1st Semester. 1st-Sem: Entrepreneurship (TVL) This course deals with the concepts, underlying principles, processes and implementation of a business plan. The preliminaries of this course include the ...
K12 students in grades K-5 participate in online coursework with interactive lesson plans and personalized instruction from teachers, designed to make learning fun and engaging. Watch the Video. Play Video. School Tour. K12 students in grades 6-12 find success through online education that fosters independence and encourages them to explore ...
Better mindset: Following the lead of next-gen models, a growing number of K-12 schools are promoting a growth mindset and high agency learning. Stronger executive functions should result in improved persistence and self management. More credit: The expansion of dual enrollment and other college credit options are increasing the percentage of ...
K-12 classrooms essentially have been set up in much the same way since the days of Horace Mann in 1830s Massachusetts. Students sit in rows, facing forward, in order to see the blackboard and the teacher, who is ready to share knowledge that students are expected to receive.. Increasingly, schools have turned away from that model as they strive to create active-learning classroom spaces ...
Please enable JavaScript to continue using this application.
Early history (1147-1283) The first reference to Moscow dates from 1147 as a meeting place of Sviatoslav Olgovich and Yuri Dolgorukiy. At the time it was a minor town on the western border of Vladimir-Suzdal Principality. In 1156, Kniaz Yury Dolgoruky fortified the town with a timber fence and a moat.
In summary. A ballot initiative that would require a personal finance class in high school circumvents the usual process for curriculum changes. School curriculum is usually the purview of education experts, but this fall it could be decided by California voters, who will vote on adding a new requirement for high school students: a one-semester ...
Information and Communication Technologies includes topics such as ICT terminologies, hardware and software components, the internet and world wide web, and ICT based applications. This also covers introductory concepts of programming, database, network security, computer ethics and current trends in ICT. Grade 10. Araling Panlipunan.
Walking tour around Moscow-City.Thanks for watching!MY GEAR THAT I USEMinimalist Handheld SetupiPhone 11 128GB https://amzn.to/3zfqbboMic for Street https://...
After disqualifying the Ivies (and we used the Ivy-plus yardstick, which includes Stanford, MIT, Duke and the University of Chicago, as well as the eight classics Harvard, Yale, Princeton, Brown ...
In April 2000, I gave a talk to the students and faculty of New St. Andrews College (NSA), a small Calvinist college established in Moscow in 1994. At that time I congratulated Douglas Wilson, founder of the college, on the success of both NSA and his K-12 Logos School.
Crocus City Hall attack. / 55.82583°N 37.39028°E / 55.82583; 37.39028. On 22 March 2024, a terrorist attack which was carried out by the Islamic State (IS) occurred at the Crocus City Hall music venue in Krasnogorsk, Moscow Oblast, Russia. The attack began at around 20:00 MSK ( UTC+3 ), shortly before the Russian band Picnic was ...
The course deals with the principles and practices in marketing goods and services. It also focuses on the development of integrated marketing programs that will help grow businesses. 2nd Semester. 2nd-Sem: Practical Research 1. This course develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills through qualitative.
UVALDE, Texas - A Uvalde teacher has been honored with a national education award.. Mercedes Salas of Uvalde Elementary School is one of three winners of the annual Crystal Apple Awards ...
Grade 11 or Grade 12. Courses. Senior High School. Grade 11 or Grade 12.