Earthquake shakes Kazakhstan's biggest city
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Olzhas Auyezov; Editing by Clarence Fernandez
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab


World Chevron

Singapore to resume flying F-16 jets after crash this month
Singapore will resume flying its F-16 fleet after suspending training when one of the jets crashed earlier this month, the defence ministry on Saturday.

Content Search
Kazakhstan: interview on almaty earthquake preparedness.
ALMATY, 30 November (IRIN) - The Kazakh commercial capital Almaty, which was last destroyed by earthquakes in 1887 and 1911, is likely to suffer a major quake in the next 10 to 15 years, experts say. In an interview with IRIN, the deputy Director of Seismology at the National Academy of Sciences, Askar Ospanov, and Baurzhan Iskakov, the chief of local emergency services, outlined the dangers. But with sound preparation, loss of life and damage to buildings and infrastructure could be kept to a minimum, they say. QUESTION: Askar Ospanov, how susceptible is Almaty and southern Kazakhstan to another devastating earthquake?
ANSWER: Serious seismic activity in our region tends to occur every 80 to 100 years. The last period of seismological activity happened between 1885 and 1911. During that period there were serious eaarthquakes at Belovodskoye in 1885, Vernenskoye two years later and Keminskoye in 1889. These quakes dissipated the accumulated energy in the earth's crust. Today the crust has accumulated enough energy again and that energy is most likely to take the form of another series of earthquakes around this period - within the next 10 to 15 years. We do not know for sure that a strong earthquake will happen during this period, but the probability is high.
Q: Already last year a large earthquake happened in the Zhambyl region. Was that the start of this new seismic activity you have just spoken about?
A: According to preliminary findings, the earthquake in Zhambyl region did not release any energy from the earth's crust around Almaty, although this needs additional study. Our calculations predict that an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.5 on the Richter scale could hit the Almaty region. But this kind of shock is survivable without significant human and material losses if preparation is good.
Q: What sort of earthquake preparedeness are you advocating?
A: The Institution of Seismology has worked out a special programme for 2005-2010 at the instance of Almaty city authorities. It will be expensive, but it will save lives and will be lower than the cost of repairing the earthquake damage.
Q: Baurzhan Beysenovich, in the case of a serious earthquake, how many people in Almaty could be injured or made homeless?
A: In the case of such an earthquake, at least 5 percent of the population could be killed or injured and around 40 percent made homeless.
Q: How many buildings in the city are effectively earthquake proof?
A: That's difficult to predict and would depend greatly on the intensity of any quake. We estimate about 10 percent would be fully destroyed, 20 percent we think would be partially damaged and and about 70 percent would come through more or less unscathed. Most constructions in Almaty are enough strong and stand the earthquake not more than 9 scores. These are standards of construction. The firmness depends on [the quality of] soil any one district of the city.
Q: What should be done now to reduce the number of victims you have predicted in any quake?
A: Firstly, there are more than 1,000 houses in the city that are in very poor conditon - these should be knocked down immediately as they are death traps. More than 2,000 other structures need emergency repairs to strengthen them in the event of an earthquake. These measures would save many lives. Vast stocks of tents, blankets, food, medicine and water purification equipment need to be put in accessible places, these measures would also reduce death considerably. But city residents should have emergency rations of foodstuffs and medicine in their houses if they are to have a chance of surviving the inevitable shortages that would follow a big quake.
But another issue here is the lack of awareness among the population - people in the city are generally not so serious about safety concerns. We need more active involvement from people in earthquake exercises and trainings. Only 40 percent of companies and organisations have purchased tents and have trained employees on what to do in the event of a crisis of this nature.
Q: Will there be any warning of a serious earthquake?
A: We hope so, the equipment for research and early warning has improved and the network of the seismic monitoring around of the city of Almaty, [set up] in cooperation with Japanese seismologists, is now comprehensive. A system which allows authorities to disconnect gas and electricity supply lines at the first signs of an earthquake will be installed in 2005. But being prepared is the key to survival.
IRIN-Asia Tel: +92-51-2211451 Fax: +92-51-2292918 Email: [email protected]
[This Item is Delivered to the "Asia-English" Service of the UN's IRIN humanitarian information unit, but may not necessarily reflect the views of the United Nations. For further information, free subscriptions, or to change your keywords, contact e-mail: [email protected] or Web: http://www.irinnews.org . If you re-print, copy, archive or re-post this item, please retain this credit and disclaimer. Reposting by commercial sites requires written IRIN permission.]
Copyright (c) UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs 2004
Related Content
Kazakhstan + 3 more
Central Asia Appeal No. 01.87/2003 Programme Update No. 1
Kazakhstan: earthquake - information bulletin n° 1, kazakhstan's new domestic violence law is welcome but further reforms need to close remaining protection gaps.
Kazakhstan + 1 more
Kazakhstan 2024-2026 IFRC network country plan (7 May 2024)
Take the Quiz: Find the Best State for You »
What's the best state for you », earthquake shakes kazakhstan's biggest city.
Earthquake Shakes Kazakhstan's Biggest City

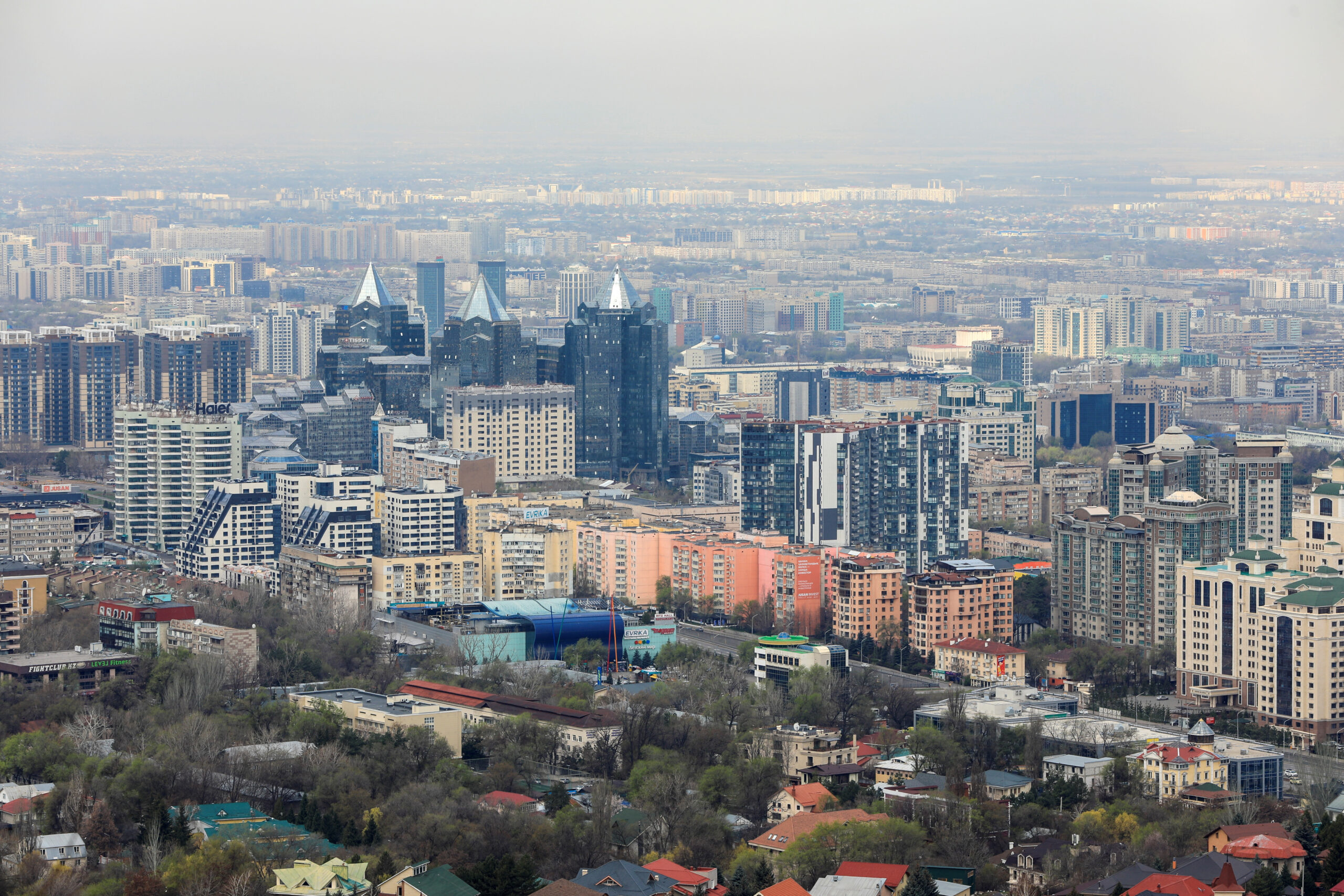
FILE PHOTO: A general view shows the city of Almaty, Kazakhstan, April 8, 2023. REUTERS/Pavel Mikheyev/File Photo
ALMATY (Reuters) - An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off.
The quake of magnitude estimated at about 5 in Almaty by Kazakhstan's emergencies ministry, was also felt in Bishkek, the capital of neighbouring Kyrgyzstan.
(Reporting by Olzhas Auyezov; Editing by Clarence Fernandez)
Copyright 2024 Thomson Reuters .
Join the Conversation
Tags: earthquakes , Kazakhstan , Kyrgyzstan
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Flag Display Rattles SCOTUS Experts
Lauren Camera May 17, 2024

Will Trump Testify in His Own Trial?
Laura Mannweiler May 17, 2024

Viral House Spat Shows Chaotic Congress
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 17, 2024

QUOTES: Trump on Gun Control Policy
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 17, 2024

Leading Indicators: Economy Is Softening
Tim Smart May 17, 2024

Key Moments From Cohen Cross-Examination
Laura Mannweiler May 16, 2024

- COP Climate Change
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Cancer Research
- Diseases & Conditions
- Mental Health
- Women’s Health
- Circular Economy
- Sustainable Development
- Agriculture
- Research & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Publications
- Academic Articles
- Health & Social Care
- Environment
- HR & Training
- Health Research
- North America Analysis
- Asia Analysis
- Our Audience
- Marketing Information Pack
- Prestige Contributors
- Testimonials

- North America
- Open Access News
- Environment News
The importance of earthquake preparedness, mitigation and resiliency

Several experts from the Nazarbayev University , Kazakhstan share their views here on the importance of earthquake preparedness, mitigation and resiliency
Throughout history, earthquakes have caused extensive damage in users areas with complex infrastructures and a high population density. Over the past century, millions of people have lost their lives due to earthquakes with many of those deaths occurring in the continental interiors.
Although regions and cities on continental interiors experience earthquakes less often than those along plate boundaries, this leads to a lack of effective action and preparation for earthquakes as the memory of such events fades over long periods of time. Earthquakes are particularly devastating in more built-up areas, such as large cities, as the destruction caused to buildings leads to higher injuries and fatalities as well as immense financial damage.
This is particularly true of Central Asia and the Tien Shan region; over the past century, the Central Asian cities of Ashgabat, Tashkent, Almaty and Dushanbe have experienced particularly devastating earthquakes. Despite relatively few destructive earthquakes in recent times, numerous faults in this region mean that hazard awareness remains high.
Due to the damage and fatalities earthquakes can cause in these highly-populated and built-up areas, the estimation of seismic activity in urban areas is important in all earthquake-prone regions, including Central Asia. Increased earthquake-induced damages in cities are often a result of local geological conditions and soil properties, as well as surface topography and the presence of lakes or other soft deposits. These geological properties combined with the high vulnerability of buildings can result in extreme disasters and high death tolls during earthquakes.
Seismic microzonation
Densely-populated cities can prepare for and mitigate the effects of earthquakes through seismic microzonation. This would involve seismologists dividing cities into specific microzones depending on-site effects and soil properties of each area. The objective of seismic microzonation is to provide estimates of the hazard for each microzone due to earthquakes shaking; for example, determining zones in large cities where buildings will suffer the most and least damage. This is necessary as an earthquake is felt differently throughout a city based on factors, such as distance from the epicentre and type of buildings and type of soil; damage will be more severe for buildings constructed on soft soil as it is less stable than those built on hard rock.
The idea behind microzonation is to develop building codes specific to different areas within a city so that new buildings can be constructed accordingly. The identification of the complex underground structures of the cities can be challenging, but it is necessary for assessing the risk of the effects of earthquakes. By analysing the characteristics of the ground conditions, we can better assess the specific effects earthquakes will have on a region and establish microzones.
In order to be able to predict the essential consequences of earthquakes, we need to develop a physically-based ground-motion prediction methodology incorporated with probabilistic seismic hazard analyses (PSHA). Compared to empirical ground-motion predictions, the simulation methodology is derived from physics and source, path and site effects through statistical approaches. This provides much more flexible and better-suited solutions, especially in complex city environments. Thus, it allows for rapid solutions that would be valid for many earthquake-affected areas, including Central Asia.
The Central Asian network of strong-motion services has continued to develop and grow with a number of programmes, including the Central Asian Seismic Network of CAIAG and the ACROSS Strong Motion Network, emerging over the past decade. Different countries, such as the U.S., Japan, China and some other countries located in seismic active zones, have cooperated on the registration of ground motion fluctuations, buildings and constructions during strong earthquakes.
However, a database of engineering- seismological records on strong ground-motions and new methods for processing and analysing data should be developed through international cooperation. This database would (1) support engineers and seismologists in evaluating the seismic risk of an area; (2) determine the parameters of strong earthquakes and; (3) develop methods for calculating seismic effects. This will increase the reliability of future buildings and structures and influence how buildings are adapted to mitigate the effects of earthquakes, ultimately reducing structural damage.
Finally, the seismic microzonation of densely-populated cities and physically-based ground-motion simulation incorporated with PSHA based on the extensive database compiled through international cooperation will be significantly useful for predicting and mitigating the effects of earthquakes in the future.
Contributor Details

Editor's Recommended Articles

RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Canada’s wildfires: British Columbia faces threat as a wildfire approaches Fort Nelson

Could weather events like snow be the real cause of Earthquakes?

Investigating the hidden risks of abandoned metal mines in Wales

Current CO2 removal plans will not meet Paris Agreement goals

Using sugar as a catalyst to convert carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide
New revised age for ancient human fossils in Southern China
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Academic Articles

Pioneering solutions for sustainable protein production in future

Global centre for climate change impacts on transboundary waters

An organizing protocol for society’s approach at responding to climate change
Follow open access government, latest publication.

Open Access Government April 2024
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- GDPR Privacy Policy
- Marketing Info Pack
- Fee Schedule

- High contrast
- Children of Kazakhstan
- UNICEF Representative in Kazakhstan
- Deputy Representative of UNICEF in Kazakhstan
- UNICEF Goodwill Ambassadors in Kazakhstan
- Our partners
- Press centre
Seasonality in Site Response: An Example from Two Historical Earthquakes in Kazakhstan

During the past 150 yr, the city of Almaty (formerly Verny) in Kazakhstan has suffered significant damage due to several large earthquakes. The 9 June 1887 Mw 7.3 Verny earthquake occurred at a time when the city mainly consisted of adobe buildings with a population of 30,000, with it being nearly totally destroyed with 300 deaths. The 3 January 1911 Mw 7.8 Kemin earthquake caused 390 deaths, with 44 in Verny itself. Remarkably, this earthquake, which occurred around 40 km from Verny, caused significant soil deformation and ground failure in the city. A crucial step toward preparing for future events, mitigating against earthquake risk, and defining opti- mal engineering designs, involves undertaking site response studies. With regard to this, we investigate the possibility that the extreme ground failure observed after the 1911 Kemin earthquake could have been enhanced by the presence of a shal- low frozen ground layer that may have inhibited the drainage of pore pressure excess through the surface, therefore inducing liquefaction at depth. We make use of information collected regarding the soil conditions around the city at the time of the earthquakes, the results from seismic noise analysis, borehole data, and surface temperature data. From these datasets, we estimated the necessary parameters for evaluating the dynamic properties of the soil in this area. We successively characterize the corresponding sediment layers at the sites of the observed liquefaction. Although the estimated soil parameters are not optimally constrained, the dynamic analysis, carried out using selected strong-motion recordings that are expected to be com- patible with the two considered events, indicated that the extensive ground failure that occurred during the Kemin event could be due to the presence of a superficial frozen soil layer. Our results indicate that for this region, possible seasonal effects should, therefore, be considered when undertaking site effect studies.
Related Papers
Robert Kayen
The preceding companion paper presented the updating of the seismic soil liquefaction triggering relationship of Cetin et al. [1], and compared the resulting updated relationship with the earlier version. In this second paper, a detailed cross-comparison is made between three triggering relationships: (1) Seed et al. [2], as slightly updated by the NCEER Working Group (Youd et al. [3]), (2) Boulanger and Idriss [4], and (3) Cetin et al. [5]. Differences between these three triggering relationships, and the apparent causes of them are examined. Also studied are the impacts of these differences on levels of conservatism with regard to evaluation of liquefaction triggering hazard, and the resulting risks for engineering projects.
Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
kemal beyen
A. Bidokhti
Abstract. In this investigation, relations between the ground’s thermal properties and 70 earthquakes with a magnitude>4 Richter in the Alborz region during a pe-riod of 12 years (1992 to 2004) were studied. Typical changes of ground temperature, 0.4 ◦C; thermal diffusivity, 0.028 m2 s−1×10−6 and ground heat flux take place a few hours prior to the earthquakes. The values of thermal dif-fusivity depend on the ground moisture content, which may change during seismic activities. The analysis of ground heat flux from the epicentre and it’s surrounding regions show some anomalous behavior before the earthquakes but with different signs in the areas close to the sea and far away from the sea. The changes of the ground’s thermal properties prior to the earthquakes in the Alborz region are attributed to the in-crease in seismic activities in the epicentre and it’s surround-ing regions. The anomalous behavior in the ground thermal properties shows great potential in providing early warni...
Bulletin of Engineering Geology and The Environment
Halil Sönmez
The Adana-Ceyhan earthquake (Ms=6.2) occurred in the southern part of Turkey on 27 June 1998 and resulted in the loss of 145 lives and extensive damage to buildings in Ceyhan town and the settlement areas in its vicinity. Soil liquefaction, ground failure due to lateral spreading and rock falls occurred. The area of Adana is characterised by a large alluvial basin with a delta shape. Most of the basin is filled with Quaternary recent Holocene deposits. The recent rapid deposition of sediments and the very shallow groundwater table throughout the basin create conditions conducive to liquefaction. The results of a preliminary investigation of soil liquefaction caused by the earthquake and liquefaction assessments based on field performance data are presented together with evaluations concerning the likely contribution of the soils to the damage sustained by buildings. The results of the liquefaction susceptibility analysis indicated that the data from the liquefied sites were within the empirical bounds suggested by the field-performance evaluation method. It was also shown that shallow sand layers should have liquefied and the surface disruption observed on the site could be predicted by the bounds used for the relationships between the thickness of liquefiable sediments and the overlying non-liquefiable soil. Site-response analyses based on acceleration response spectra from the actual earthquake's strong motion records revealed that soil behaviour was one of the most significant factors in the damage to buildings caused by the earthquake. Le tremblement de terre de Adana-Ceyhan survenu au sud de la Turquie le 27 juin 1998 á cause la perte de 145 vies humaines, des dommages étendus aux édifices dans la district de Ceyhan et la subsidence des alentours. La liquéfaction du sol, des mouvements latéraux de terrain et des choutes rocheuse sont aussi survenus dans la district. Dans cet article, les resultats d'une étude préliminaire de la liquéfaction du sol causée par le tremblement de terre, l'évaluation des liquéfaction basées sur les données terrain expérimentale ainsi que la contribution possible du sol sur les dommages causées aux édifices sont présentés. La region de Çukurova est un delta caracterisé par une grande plaine alluviale. Le pluspart de la region áété remblayée par des depots récent d'Holocène de l'aire Quaternaire. L'accumulation rapide des sédiments récents ainsi que la faible profoundeur de la nappe superfacielle dans le bassin a conduit à des conditions favorables à l'apparition de liquéfaction du sol. Les resultats des analyses de susceptibilité de liquéfaction ont montré que les données provenant des sites du sol liquéfiés sont dans les limites empiriques de la methode d'évaluation des performances de terrain. Il a aussi été montré que des couches de sable peu profondes ont pu étre liquéfiées et que les données provenant des sites avec ruptures de surface ont été predités dans les limités utilisées par les relations entre épaisseur des sediments liquéfiables et l'épaisseur du sol non-liquéfiable des couches supéreures. Les analyses de la response des sites basées ou les spectres de response des accelérations provenant des enregirstements des actuels tremblement de terre, ont revelé que le comportement du sol a été un au des facteurs majeurs sur les dommages des édifices causés par le tremblement de terre.
civil.iisc.ernet.in
Anbazhagan Panjamani
Leslie Youd , Turan Durgunoğlu
Valuable cases were presented regarding seismic performance of the shallow mat foundations of building structures in Adapazari, Turkey, during the 17 August 1999 Kocaeli ͑İzmit͒ earthquake. The authors attributed the occurrence of displacements of various forms and levels of the mats essentially to the liquefaction or cyclic softening of the saturated fine surface soils of ML/CL type, which dominated those sites. Subsequently, through contrasting the presumed field liquefaction to the analysis results, they evalu-ated the predictive capability of field-penetration-testing-based liquefaction triggering procedures. It was concluded that in Adapazari, the soils, though they contained significant amounts of clay-size particles and had grain-size distributions within ranges that were believed not to be susceptible to liquefaction, yet liquefied. Among others, the major drawback of the paper under discus-sion appears to be a priori reasoning of soil liquefaction to explain the observed di...
Ethem Balık
mehmet celebi
Dr. Amartya Kumar Bhattacharya
RELATED PAPERS
Social Development Issues
marius zaharia
Libro fisica para ciencias e ingenieria
David Eidman Calsin Malpartida
Journal of Religion & Society
Nicolae Roddy
El simbolismo de la forja en las puertas románicas
Fernando Ezquerra Lapetra
JUAN CARLOS LOPEZ VALDEZ
Southern African Business Review
Suné Donoghue
IEEE Transactions on …
Sarangarajan Parthasarathy
Sciencia Scripts
Aamir Al-Mosawi
Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology
Marco Dettori
Giselle Wolchuk
Acta Amazonica
Maria Elias
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery
Fumio Chikamori
Alexey N . Averkin
Conhecimento & Diversidade
lenilda austrilino
TENCON 2003. Conference on Convergent Technologies for Asia-Pacific Region
vivek kumar
Frontiers in physiology
Dott/Prof. Raffaele Ivan Cincione
Idris Alamin
Acta Neuropathologica
Ricardo Lloyd
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
Osama Fouad
怎么办理迈阿密大学毕业证 um毕业证文凭证书英文注册证明原版一模一样
Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira
Michele Ricieri Bastos
Computer Networks
Anura Jayasumana
Annals of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Frontiers in Immunology
Frederick Goldman
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Kazakhstan Earthquake Report
- Earthquake List
Map of Latest Earthquakes near Kazakhstan
Recent kazakhstan earthquake news.
These are the latest articles published related to earthquakes occurring near Kazakhstan. Check our Earthquake News section for a complete overview of articles written on earthquakes near Kazakhstan and elsewhere.

Kazakhstan Earthquake Statistics
A total of 824 earthquakes with a magnitude of four or above have struck within 300 km (186 mi) of Kazakhstan in the past 10 years. This comes down to a yearly average of 82 earthquakes per year, or 6 per month. On average an earthquake will hit near Kazakhstan roughly every 4 days.
A relatively large number of earthquakes occurred near Kazakhstan in 2024. A total of 225 earthquakes (mag 4+) were detected within 300 km of Kazakhstan that year. The strongest had a 7 magnitude.

Magnitude Distribution
The table below visualizes the distribution of all earthquakes that occurred within 300km of Kazakhstan in the past 10 years. No earthquakes with a magnitude of 7 or above have occurred near Kazakhstan during this time. Usually, higher magnitudes are less common than lower magnitudes. Small earthquakes with a magnitude below 4 on the Richter scale have been omitted from this overview.
Strongest earthquakes near Kazakhstan
The strongest recent earthquake of the past 10 years near Kazakhstan occurred on Jan 23, 2024 00:09 local time (Asia/Almaty timezone). It had a magnitude of 7 and struck 263 kilometers (163 mi) south-southeast of Almaty , at a depth of 13 km. Discover more strong earthquakes near Kazakhstan in the list below.
A longer time ago, a MAG-8 earthquake struck on Jan 4, 1911 04:33, 38 kilometers (24 mi) south-southeast of Almaty. It is the strongest earthquake near Kazakhstan in the past 124 years (Our data goes back to January 1st, 1900).
In the table below you will find the strongest earthquakes that occurred near Kazakhstan in the past 10 years. You can use the tabs to find the heaviest historic earthquakes since the year 1900 or within a specific year or distance from Kazakhstan.
Frequently Asked Questions
These questions are commonly asked in relation to earthquakes occurring near Kazakhstan.
When was the last earthquake in Kazakhstan?
A 4 magnitude earthquake hit near Kazakhstan on the afternoon of May 13, 2024 at 12:44 local time (Asia/Almaty). The center of this earthquake was located 142km south of Taraz at a depth of 25km under land. Check the list on our website for any earthquakes occurring near Kazakhstan in the past hours.
What was the strongest earthquake near Kazakhstan?
A 8 magnitude earthquake hit near Kazakhstan on the night of January 4, 1911 at 04:33 local time (Asia/Almaty). The center of this earthquake was located 38km south-southwest of Almaty at a depth of 20km under land. This is the strongest earthquake that occurred near Kazakhstan since the year 1900.
How often do earthquakes occur near Kazakhstan?
In the past 10 years, 824 earthquakes with a magnitude of four or higher occurred within a 300 kilometer range from Kazakhstan. This averages to 82 earthquakes yearly, or one earthquake every 4 days.
Reliable earthquake data sourced from multiple organizations, including:

- Earthquake News
Countries by Continent
- North-America
- South-America
- Top Countries
- Afghanistan
- El Salvador
- Papua New Guinea
- The Philippines
- The United States
- Timor-Leste
Global Reports
- Latest Earthquakes
- Strongest Earthquakes
- About Earthquakelist.org
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 - Earthquakelist.org.
Loading Earthquake Details...
By providing an email address. I agree to the Terms of Use and acknowledge that I have read the Privacy Policy .
Earthquake shakes Kazakhstan’s biggest city

A general view shows the city of Almaty, Kazakhstan, April 8, 2023. REUTERS FILE PHOTO
ALMATY — An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan’s biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off.
The quake of magnitude estimated at about 5 in Almaty by Kazakhstan’s emergencies ministry, was also felt in Bishkek, the capital of neighboring Kyrgyzstan.
READ: 7.1 quake strikes Kyrgyzstan-Xinjiang border, injuries reported
Subscribe to our daily newsletter
Disclaimer: Comments do not represent the views of INQUIRER.net. We reserve the right to exclude comments which are inconsistent with our editorial standards. FULL DISCLAIMER
© copyright 1997-2024 inquirer.net | all rights reserved.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By continuing, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. To find out more, please click this link.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters

New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Earthquake shakes Kazakhstan's biggest city
ALMATY (Reuters) - An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off.
The quake of magnitude estimated at about 5 in Almaty by Kazakhstan's emergencies ministry, was also felt in Bishkek, the capital of neighbouring Kyrgyzstan.
(Reporting by Olzhas Auyezov; Editing by Clarence Fernandez)
Recommended Stories
Dolphins owner stephen ross reportedly declined $10 billion for team, stadium and f1 race.
The value of the Dolphins and Formula One racing is enormous.
PGA Championship: Will Zalatoris says group of players considered asking for postponement after death, Scottie Scheffler arrest
It was a surreal day at the PGA Championship.
Welcome to the WNBA: Caitlin Clark's regular-season debut is anything but easy
Clark set the Indiana Fever’s franchise record for turnovers (10), shot 5-of-15 from the floor and struggled with the Connecticut Sun’s physical defense.
Caitlin Clark, Fever facing plenty of growing pains early after another blowout loss in home debut
The atmosphere was electric for Clark's home debut and there were brief flashes from the Fever, but it's clear they've got plenty to work on before they can compete with the WNBA's elite teams.
NBA Draft Combine reactions: Edey oh my, Bronny James is ready & whose stock is rising? | On the Clock with Krysten Peek
Yahoo Sports NBA draft expert Krysten Peek is back for another season of On the Clock with Krysten Peek. Krysten just spent the week in Chicago at the NBA Draft Combine and kicks off draft season joined by CBS Sports' Kyle Boone.
2024 NBA Mock Draft 7.0: Who will the Hawks take at No. 1? Our projections for every pick with lottery order now set
With the lottery order set, here's a look at Yahoo Sports' projections for both rounds of the 2024 NBA Draft.
World No. 1 Scottie Scheffler tees off at PGA Championship after being arrested, charged with felony for incident outside Valhalla
Scottie Scheffler was arrested by police en route to Valhalla Golf Club during a traffic incident.
2024 Wide Receiver rankings for fantasy football
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first wide receiver rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
Fox Sports host Doug Gottlieb hired as Green Bay's coach, will reportedly still host radio show
Gottlieb's repeatedly courted controversy in his media role and will reportedly continue to host his nationally syndicated radio show while coaching Green Bay.
What scouts think of Bronny James' NBA prospects
The biggest question looming over the NBA draft combine this week: How will Bronny James do?
2024 NFL schedule: Everything you need to know about this season's slate of games
Here's what you need to know about the 2024 NFL schedule after Wednesday night's announcement.
NFL schedule release: The top 10 must watch games of the regular season
What are the most anticipated games for this NFL season?
The Spin: Making a call on 5 slumping fantasy baseball stars
All five of these hitters were drafted highly in fantasy baseball leagues. So far, they have not lived up to their ADPs — and that's an understatement. Scott Pianowski analyzes.
Scottie Scheffler releases statement following arrest: 'There was a big misunderstanding of what I thought I was being asked to do'
Scheffler was arrested following an incident with an officer outside the entrance to Valhalla Golf Club.
Rory McIlroy files for divorce from wife Erica after seven years of marriage
On the eve of the PGA Championship, Rory McIlroy has filed for divorce from his wife, Erica.
2024 Tight end rankings for fantasy football
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first tight end rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
Memorial Day sales 2024: Everything we know, including early deals you can shop now
Mark your calendar: The holiday weekend runs May 24-27, but you don't have to wait to save.
Attorneys say Scottie Scheffler likely won't face felony conviction: 'Probably about a zero percent chance'
Scottie Scheffler will likely avoid the most serious charges filed against him stemming from Friday morning's altercation with police.
Fantasy Baseball Numbers Do Lie: Luck evening out will change fortunes for these 5 players
Dalton Del Don puts some fraudulent stats under the magnifying glass as we move through Week 7 of the fantasy baseball season.
Lionel Messi's salary, Inter Miami's payroll are MLS record highs
Even without his Apple deal and his equity in Inter Miami, Lionel Messi is making more money than all but a few MLS teams.
- USD 12345.12
- EUR 13501.86
- Google play
- Tashkent +18°C
- Tashkent reg
- About Daryo
- Editorial office
- Terms of use
- Privacy policy
- News archive
- Advertisement
- Instagram | Main
- Instagram | Lifestyle
- Instagram | Sport
- Facebook | Main
- YouTube | Daryo
- YouTube | Daryo in Russian
- YouTube | Daryo Global
7 magnitude earthquake strikes Kazakhstan, ripple effects felt across Central Asia
In a seismic event recorded on January 23, 2024, at 00:09:02 Almaty time (January 22, 2024, at 18:09:02 GMT), a significant earthquake occurred with its epicenter situated 264 km southeast of Almaty on the border of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. The seismic activity was registered by the network of seismic stations operated by "NNTSSN and I" under the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Kazlenta.kz reported.
Key Details of the Earthquake:
- Epicenter: Located on the Kazakhstan-Kyrgyzstan border
- Energy Class: 15.1
- Magnitude MPV: 6.7
- Coordinates: 41.22° N, 1.78° W
- Depth: 65 km
The earthquake's impact prompted a swift response from relevant government agencies, as outlined by the city Emergency Situations Department. Following the interaction algorithm, notifications were sent to the appropriate authorities, and monitoring efforts were initiated to assess potential destruction. The operational duty officer of the police department received information to conduct visual inspections of buildings and structures in the city for signs of damage, telegram news channel Centralasianow reported.
The earthquake's effects were not limited to the Kazakhstan-Kyrgyzstan border, as a magnitude 7 earthquake was observed on the border of Kyrgyzstan and the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China. The strength of the seismic activity reverberated across various regions of Uzbekistan.
Perceived Power in the Republic of Uzbekistan:
- Tashkent: 3 points, located 862 km from the epicenter
- Andijan region: 3-4 points, situated 602 km away
- Fergana region: 3-4 points, approximately 656 km from the epicenter
- Namangan region: 3-4 points, with a distance of 657 km from the epicenter
Residents are reported to be taking to the streets, Ulysmedia.kz reported .
Earlier, the head of the emergency response department of Almaty, Bekbolat Bugabaev, noted that in case of danger, it is necessary not to panic and go to a safe place. And he clarified that rescuers are ready for magnitude 7 earthquakes.
Follow Daryo's official Instagram and Twitter pages to keep current on world news.

On this topic
7.6 magnitude earthquake strikes japan, tsunami warning follows , tokayev expresses condolences to japan’s prime minister in wake of earthquake , turkey initiates criminal cases against over 600 people for building collapse during 2023 earthquake , kazakhstan bans russian tv presenter tina kandelaki from entering over controversial remarks, kazakhstan and bonifiche ferraresi partner for agro-alliance with pasta production and export expansion, president tokayev discusses food security with un wfp director cindy mccain .
Found an error in the text?
Thank you. We have received your message and will fix the error as soon as possible.
Earthquake Essay for Students and Children

500+ Words Essay on Earthquake
Simply speaking, Earthquake means the shaking of the Earth’s surface. It is a sudden trembling of the surface of the Earth. Earthquakes certainly are a terrible natural disaster. Furthermore, Earthquakes can cause huge damage to life and property. Some Earthquakes are weak in nature and probably go unnoticed. In contrast, some Earthquakes are major and violent. The major Earthquakes are almost always devastating in nature. Most noteworthy, the occurrence of an Earthquake is quite unpredictable. This is what makes them so dangerous.

Types of Earthquake
Tectonic Earthquake: The Earth’s crust comprises of the slab of rocks of uneven shapes. These slab of rocks are tectonic plates. Furthermore, there is energy stored here. This energy causes tectonic plates to push away from each other or towards each other. As time passes, the energy and movement build up pressure between two plates.
Therefore, this enormous pressure causes the fault line to form. Also, the center point of this disturbance is the focus of the Earthquake. Consequently, waves of energy travel from focus to the surface. This results in shaking of the surface.
Volcanic Earthquake: This Earthquake is related to volcanic activity. Above all, the magnitude of such Earthquakes is weak. These Earthquakes are of two types. The first type is Volcano-tectonic earthquake. Here tremors occur due to injection or withdrawal of Magma. In contrast, the second type is Long-period earthquake. Here Earthquake occurs due to the pressure changes among the Earth’s layers.
Collapse Earthquake: These Earthquakes occur in the caverns and mines. Furthermore, these Earthquakes are of weak magnitude. Undergrounds blasts are probably the cause of collapsing of mines. Above all, this collapsing of mines causes seismic waves. Consequently, these seismic waves cause an Earthquake.
Explosive Earthquake: These Earthquakes almost always occur due to the testing of nuclear weapons. When a nuclear weapon detonates, a big blast occurs. This results in the release of a huge amount of energy. This probably results in Earthquakes.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Effects of Earthquakes
First of all, the shaking of the ground is the most notable effect of the Earthquake. Furthermore, ground rupture also occurs along with shaking. This results in severe damage to infrastructure facilities. The severity of the Earthquake depends upon the magnitude and distance from the epicenter. Also, the local geographical conditions play a role in determining the severity. Ground rupture refers to the visible breaking of the Earth’s surface.
Another significant effect of Earthquake is landslides. Landslides occur due to slope instability. This slope instability happens because of Earthquake.
Earthquakes can cause soil liquefaction. This happens when water-saturated granular material loses its strength. Therefore, it transforms from solid to a liquid. Consequently, rigid structures sink into the liquefied deposits.
Earthquakes can result in fires. This happens because Earthquake damages the electric power and gas lines. Above all, it becomes extremely difficult to stop a fire once it begins.
Earthquakes can also create the infamous Tsunamis. Tsunamis are long-wavelength sea waves. These sea waves are caused by the sudden or abrupt movement of large volumes of water. This is because of an Earthquake in the ocean. Above all, Tsunamis can travel at a speed of 600-800 kilometers per hour. These tsunamis can cause massive destruction when they hit the sea coast.
In conclusion, an Earthquake is a great and terrifying phenomenon of Earth. It shows the frailty of humans against nature. It is a tremendous occurrence that certainly shocks everyone. Above all, Earthquake lasts only for a few seconds but can cause unimaginable damage.
FAQs on Earthquake
Q1 Why does an explosive Earthquake occurs?
A1 An explosive Earthquake occurs due to the testing of nuclear weapons.
Q2 Why do landslides occur because of Earthquake?
A2 Landslides happen due to slope instability. Most noteworthy, this slope instability is caused by an Earthquake.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- For subscribers

ADB EXPERTS ARE READY TO SUPPORT THE GOVERNMENT IN TAX REFORMS

THE UNITED KINGDOM MAY PROVIDE £4 BILLION TO FINANCE KAZAKHSTAN-BASED PROJECTS THAT SHOULD INCLUDE UK CONTENT

IT IS MORE COST-EFFICIENT FOR COMPANIES TO RENT DATA PROCESSING CENTERS FROM PROFESSIONALS

I BELIEVE THAT KAZAKH PEACEKEEPERS HAVE MADE AN EFFECTIVE CONTRIBUTION TO THE UN PEACEKEEPING COMMITMENTS IN AFRICA AND AROUND THE WORLD
- Subscription
- Media Monitoring

- LATEST NEWS
Press center

- Enter username and password
Username Error message here!
Password Show Error message here!
Recent Earthquakes Near Kazakhstan
- Recent Quakes
- Biggest Quakes
- The Middle East
- Almaty, Almaty Qalasy, Kazakhstan
- Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan
- Ürümqi, Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu, China
- Tashkent, Toshkent Shahri, Uzbekistan
- Andorra la Vella
- Sant Julià de Loria
- Eastern Kazakhstan
- Kazakhstan Xinjiang Border
- Central Kazakhstan
- Southern Xinjiang, China
- Eastern Uzbekistan
- Northwestern Kashmir
- Northern Xinjiang, China
- Russia Kazakhstan Border
- Southwestern Siberia, Russia
- Russia Xinjiang Border
- Western Uzbekistan
- Hindu Kush, Afghanistan
Kazakhstan has had: (M1.5 or greater)
- 0 earthquakes in the past 24 hours
- 0 earthquakes in the past 7 days
- 3 earthquakes in the past 30 days
- 73 earthquakes in the past 365 days
The largest earthquake in Kazakhstan:
- this month: 4.4 in Kegen , Almaty Oblysy , Kazakhstan
- this year: 7.0 in Aykol , Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu , China
4.4 magnitude earthquake
2024-05-06 04:12:56 UTC at 04:12 May 06, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 42.715, 79.266 34.2 km from Kegen (21.2 miles)
Depth: 9 km
4.3 magnitude earthquake
2024-04-28 11:31:09 UTC at 11:31 April 28, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.395, 79.006 106.2 km from Aykol (66.2 miles)
Depth: 6 km
4.0 magnitude earthquake
2024-04-22 19:09:43 UTC at 19:09 April 22, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 46.232, 53.331 25.2 km from Qaraton (15.2 miles)
Western Kazakhstan
2024-04-18 00:23:36 UTC at 00:23 April 18, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.304, 78.807 118.2 km from Aykol (73.2 miles)
Depth: 10 km
4.6 magnitude earthquake
2024-04-14 13:51:01 UTC at 13:51 April 14, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.384, 78.591 116.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (72.2 miles)
2024-03-15 02:47:16 UTC at 02:47 March 15, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.38, 78.298 109.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (68.2 miles)
5.1 magnitude earthquake
2024-03-06 00:09:59 UTC at 00:09 March 06, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.313, 78.692 127.2 km from Aykol (79.2 miles)
5.3 magnitude earthquake
2024-03-04 06:22:04 UTC at 06:22 March 04, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 42.903, 76.971 29.2 km from Cholpon-Ata (18.2 miles)
2024-02-26 17:46:04 UTC at 17:46 February 26, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.29, 78.723 124.2 km from Aykol (77.2 miles)
2024-02-21 18:26:45 UTC at 18:26 February 21, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.395, 78.682 119.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (74.2 miles)
2024-02-18 08:59:15 UTC at 08:59 February 18, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.424, 78.913 114.2 km from Aykol (71.2 miles)
5.0 magnitude earthquake
2024-02-15 03:52:40 UTC at 03:52 February 15, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.275, 78.826 115.2 km from Aykol (71.2 miles)
4.1 magnitude earthquake
2024-02-12 15:52:52 UTC at 15:52 February 12, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.337, 78.712 126.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (78.2 miles)
4.9 magnitude earthquake
2024-02-11 04:57:13 UTC at 04:57 February 11, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.288, 78.733 123.2 km from Aykol (76.2 miles)
2024-02-11 03:03:37 UTC at 03:03 February 11, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.273, 78.764 120.2 km from Aykol (74.2 miles)
4.8 magnitude earthquake
2024-02-10 08:25:01 UTC at 08:25 February 10, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 50.888, 84.378 27.2 km from Ust’-Kan (16.2 miles)
Depth: 44 km
2024-02-03 08:36:30 UTC at 08:36 February 03, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.342, 78.698 125.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (77.2 miles)
2024-01-31 19:21:27 UTC at 19:21 January 31, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.344, 78.742 124.2 km from Aykol (77.2 miles)
2024-01-30 01:44:58 UTC at 01:44 January 30, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.259, 78.75 121.2 km from Aykol (75.2 miles)
2024-01-29 23:30:55 UTC at 23:30 January 29, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.3, 78.602 125.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (78.2 miles)
5.7 magnitude earthquake
2024-01-29 22:27:41 UTC at 22:27 January 29, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.187, 78.716 122.2 km from Aykol (75.2 miles)
2024-01-28 09:52:20 UTC at 09:52 January 28, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.489, 78.312 114.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (71.2 miles)
2024-01-27 09:03:05 UTC at 09:03 January 27, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.291, 78.633 127.2 km from Kyzyl-Suu (79.2 miles)
Depth: 11 km
2024-01-26 12:05:37 UTC at 12:05 January 26, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.283, 78.87 112.2 km from Aykol (69.2 miles)
2024-01-26 11:40:45 UTC at 11:40 January 26, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.258, 78.805 116.2 km from Aykol (72.2 miles)
4.5 magnitude earthquake
2024-01-26 10:16:48 UTC at 10:16 January 26, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.313, 78.827 116.2 km from Aykol (72.2 miles)
2024-01-26 02:26:07 UTC at 02:26 January 26, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.342, 78.904 111.2 km from Aykol (69.2 miles)
2024-01-25 20:01:27 UTC at 20:01 January 25, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.278, 78.89 110.2 km from Aykol (68.2 miles)
4.2 magnitude earthquake
2024-01-25 08:59:59 UTC at 08:59 January 25, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.239, 78.888 109.2 km from Aykol (67.2 miles)
2024-01-25 04:59:23 UTC at 04:59 January 25, 2024 UTC
Location: Epicenter at 41.342, 78.781 121.2 km from Aykol (75.2 miles)
Places Near Kazakhstan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ALMATY, March 4 (Reuters) - An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off. The quake of magnitude ...
News and Press Release in English on Kazakhstan about Earthquake; published on 30 Nov 2004 by TNH
In 1979, a magnitude 5.4 earthquake occurred in the Kazakh platform at 76.96° E, 45.09° N and 40 km depth (Sloan et al., 2011). This particular earthquake caused negligible damage to Almaty, but we use it as a basis to explore the effects of a larger earthquake; similar in style to the 7.7 Bhuj/Gujarat earthquake in 2001 (Copley et al., 2011).
ALMATY (Reuters) - An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off. The quake of magnitude estimated at ...
Powerful and long-lasting tremors in the early hours of January 23 in southern Kazakhstan sparked widespread alarm and prompted thousands to take to their cars and flee the country's largest city, Almaty, for safety. The epicenter of the magnitude 7.1 earthquake was registered in a sparsely inhabited area of Xinjiang, a region in northwestern ...
Several experts from the Nazarbayev University, Kazakhstan share their views here on the importance of earthquake preparedness, mitigation and resiliency. Throughout history, earthquakes have caused extensive damage in users areas with complex infrastructures and a high population density. Over the past century, millions of people have lost ...
Here, we explore the seismic hazard and risk for Almaty from specific earthquake scenarios. We run three historical-based earthquake scenarios (1887 Verny 7.3, 1889 Chilik 8.0 and 1911 Chon-Kemin 8.0) on the current population and four hypothetical scenarios for near-field faulting. By making high-resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) from ...
Disaster resilience. 75% of the Kazakhstan territory is subject to a high risk of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, landslides, mudflows, floods, epidemics, extreme temperatures, earthquakes, forest and steppe fires. UNICEF/2011/Gonzalo Bell. Available in:
Search for more papers by this author. Greg Bankoff, Corresponding Author. Greg Bankoff ... This article examines how the postsocialist state in Kazakhstan deals with potential crises such as earthquakes and the extent to which the Soviet legacy still shapes intellectual debates, state structures, and civil society organisations in in that ...
During the past 150 yr, the city of Almaty (formerly Verny) in Kazakhstan has suffered significant damage due to several large earthquakes. The 9 June 1887 Mw 7.3 Verny earthquake occurred at a time when the city mainly consisted of adobe buildings with a population of 30,000, with it being nearly totally destroyed with 300 deaths.
The strongest recent earthquake of the past 10 years near Kazakhstan occurred on Jan 23, 2024 00:09 local time (Asia/Almaty timezone). It had a magnitude of 7 and struck 263 kilometers (163 mi) south-southeast of Almaty, at a depth of 13 km. Discover more strong earthquakes near Kazakhstan in the list below.. A longer time ago, a MAG-8 earthquake struck on Jan 4, 1911 04:33, 38 kilometers (24 ...
ALMATY -- An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off. The quake of magnitude estimated at
The Minister for Emergency Situations in Kazakhstan faces a possible layoff after the departments under his ministry performed poorly in response to an earthquake that rattled the population in ...
An earthquake jolted Kazakhstan's biggest city of Almaty on Monday, sending dozens of people scurrying to safety outdoors as sirens went off. The quake of magnitude estimated at about 5 in Almaty ...
The earthquake's effects were not limited to the Kazakhstan-Kyrgyzstan border, as a magnitude 7 earthquake was observed on the border of Kyrgyzstan and the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China. The strength of the seismic activity reverberated across various regions of Uzbekistan. Perceived Power in the Republic of Uzbekistan: Tashkent: 3 ...
Most recently, the M w 7.6 2001 Bhuj earthquake in India involved slip of ∼10 m on a rupture with a length of only 20-30 km by 20 km [Schmidt and Bürgmann, 2006; Copley et al., 2011]. The 1897 M w 8.1 Assam earthquake, India, is also thought to have involved slip of 11-25 m of slip on a fault 110 km in length [Bilham and England, 2001].
The most strongest earthquake ever in Kazakhstan 11.03.1946: Jalal-Abad Region, Kyrgyzstan 7.5-7.6 X 06.05.1970 Almaty Region, Kazakhstan 6.6 05.10.1971: Jambyl Region, Kazakhstan 5.5 06.24.1978 Almaty Region, Kazakhstan 6.2-7.1 VIII 06.14.1990 East Kazakhstan Region, Kazakhstan 6.8 V 1 08.03.1990
500+ Words Essay on Earthquake. Simply speaking, Earthquake means the shaking of the Earth's surface. It is a sudden trembling of the surface of the Earth. Earthquakes certainly are a terrible natural disaster. Furthermore, Earthquakes can cause huge damage to life and property.
May 13, 2024, 03:12PM. Heads of Kazakhstan's nature reserves where 14 people died in forest fires sentenced to seven years in jail. Archive. ALMATY. Jan 23 (Interfax-Kazakhstan) - A 6.7 magnitude earthquake occurred near the Kazakh-Kyrgyz border on Tuesday at 00.09 am Almaty time, the Seismic Research Center of the Kazakh Emergency Ministry said.
Kazakhstan has had: (M1.5 or greater) 0 earthquakes in the past 24 hours. 1 earthquake in the past 7 days. 5 earthquakes in the past 30 days. 74 earthquakes in the past 365 days.