Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Megan McIntyre - University of Arkansas
The main idea. The argument of an essay. The thesis. It’s a tricky thing to define “thesis” because theses come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. A thesis can be a sentence, two sentences, perhaps even an entire paragraph. Every thesis, though, regardless of where in an essay it appears, does a few important things:
- A thesis acts as a unifying idea for every piece of evidence in an essay.
- A thesis results from research in addition to the writer’s own beliefs or opinions.
- A thesis answers a specific question.
There are lots of ways to create a successful thesis because good theses come in all sorts of varieties. What all successful argumentative theses have in common, though, are the following characteristics:
- A good thesis statement is arguable. In other words, the writer’s claim might be challenged or opposed.
- A good thesis statement expresses one main idea, and that idea controls what is said, what is left out, and how the delivered evidence is organized.
- A good thesis statement is specific and insightful.
- A good thesis statement encourages discussion.
- A good thesis statement is supported by relevant evidence. Every paragraph should contribute to proving the thesis to be valid
Developing a Thesis
- Define the Rhetorical Situation: The key to developing an appropriate thesis is to begin by examining the rhetorical situation: What is the purpose of your essay (e.g., to inform, to persuade, to analyze)? To whom are you writing (e.g., classmates, members of a particular interest or age group)?
- Choose a Topic: Based on the purpose of and audience for your essay, what is an appropriate topic? Moreover, what is an appropriate topic that also interests you personally?
- Start with What You Know: What do you know about your topic? What have you heard on the news about your topic? Do you have personal experiences related to your topic? If so, what are they?
- Research What You Don’t Know: Start by searching the library databases (e.g., with Academic Search Premier or WorldCat). It’s best to begin by searching with your general topic and then refining your initial results. Gather a variety of sources and start reading. Some general reading on your topic will help you with the next step.
- Take a Position: Before you take a position, be sure you have done ample reading and you are aware of the various positions regarding your topic. Most issues have more nuances than basic understandings suggest. It is not enough to be “for” or “against” an issue. You must be able to support your position with evidence and logical reasoning, and research can help you in this regard.
Refining Your Thesis
After choosing a position, in forming reasoning for your decision, you must be clear and specific. You must be able to substantiate your claim using authoritative, credible, and relevant source material. Theses tend, in draft form, to begin as general and to become more specific as you do more research. Let’s look at how we might turn a weak thesis into a strong thesis.
Weak thesis:
On April 20, 2010, the explosion of the Deepwater Horizon oil platform caused the largest man-made disaster in U.S. history.
This thesis has a serious problem for two reasons: it doesn’t actually make an argument. It simply states an unproven fact: that the Deepwater Horizon oil spill is the largest man-made disaster in U.S. history. In order to be successful, a thesis must be arguable and supported by evidence. If we consider that a thesis must be a statement that reasonable people may disagree with and a position substantiated with credible evidence, this thesis is problematic because no one will disagree with the date the oil spill occurred and because the claim that the oil spill was the largest man-made disaster in U.S. history is unsubstantiated.
A still weak thesis:
Many people are to blame for the oil spill that resulted from the explosion of the Deepwater Horizon oil platform, which caused the largest man-made environmental disaster in U.S. history.
This thesis is better than the first because it does more than state a fact, but it is still problematic: it is not specific enough, and the claim that the Deepwater Horizon oil spill is the “largest man-made” disaster is still unsubstantiated. This thesis might, instead, attempt to answer the following questions: “Who is to blame for the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?” and “Why might it be considered the largest man-made environmental disaster in the U.S. history?” A successful thesis must be arguable and must answer a specific question.
A better thesis:
BP, President George W. Bush, President Barack Obama, Republicans in Congress, Democrats in Congress, and every citizen in the United States share the blame for the oil spill that resulted from the explosion of the Deepwater Horizon oil platform, which some consider the largest man-made environmental disaster in U.S. history, and in order to prevent another such disaster, Congress must develop better regulations, oil companies must enact better maintenance procedures, and Americans must decrease their dependence on oil.
This thesis is certainly more specific, but it’s trying to do too much. Proving that all parties mentioned are to blame for the Deepwater Horizon oil spill and that the solutions mentioned will prevent another oil disaster requires covering a lot of ground. A good thesis is arguable and specific, but also has one main idea. This thesis has too many main ideas.
An even better thesis:
Oil companies and the federal government share responsibility for the Gulf oil spill that resulted from the April 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion.
This thesis works better than the previous versions because it’s arguable, specific, and focused on one main idea, but not so specific as to greatly limit discussion of the topic. From an essay based on such a thesis, readers will expect evidence that supports the claim that oil companies and the federal government hold joint responsibility for the Gulf oil spill.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Research Essentials
- Develop a Question
- Identify Keywords
- Search Tips
- Too Few/Many Results?
- Use Sources
- Scholarly vs Popular
What Is a Thesis?
Crafting a thesis.
- Cite Sources
- Find Articles
- Primary Sources
More Resources
- How to Write a Thesis Statement IU Writing Tutorial Services
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements Purdue OWL
A thesis is the main point or argument of an information source. (Many, but not all, writing assignments, require a thesis.) Thesis are often answer your research question. Note that it does not have to be the only answer to your research question, a strong thesis question gives a reasonable answer. Below are some characteristics of a strong thesis.
A strong thesis is:
- Arguable: Can be supported by evidence and analysis, and can be disagreed with.
- Unique: Says something new and interesting.
- Concise and clear: Explained as simply as possible, but not at the expense of clarity.
- Unified: All parts are clearly connected.
- Focused and specific: Can be adequately and convincingly argued within the the paper, scope is not overly broad.
- Significant: Has importance to readers, answers the question "so what?"
Reading previous research is vital to developing a strong thesis. By reading what others have to say about, you'll learn what interests you, and develop interesting questions with interesting answers. Exploring broadly can help you refine your central point.
Conduct Background Research
A strong thesis is specific and unique, so you first need knowledge of the general research topic. Background research will help you narrow your research focus by answering the obvious questions with established answers; it will also help contextualize your argument in relation to other research.
Narrow the Research Topic
Ask questions as you review sources:
- What aspect(s) of the topic interest you most?
- Are there disagreements between different papers and authors?
- What questions or concerns does the topic raise for you? Example of a general research topic: Climate change and carbon emissions Example of more narrow topic: U.S. government policies on carbon emissions
Formulate and explore a relevant research question
Before committing yourself to a single viewpoint, formulate a specific question to explore. Consider different perspectives on the issue, and find sources that represent these varying views. Reflect on strengths and weaknesses in the sources' arguments. Consider sources that challenge these viewpoints.
Example: What role does and should the U.S. government play in regulating carbon emissions?
Develop a working thesis
- A working thesis has a clear focus but is not yet be fully formed. It is a good foundation for further developing a more refined argument. Example: The U.S. government has the responsibility to help reduce carbon emissions through public policy and regulation. This thesis has a clear focus but leaves some major questions unanswered. For example, why is regulation of carbon emissions important? Why should the government be held accountable for such regulation?
Continue research on the more focused topic
Is the topic:
- broad enough to yield sufficient sources and supporting evidence?
- narrow enough for in-depth and focused research?
- original enough to offer a new and meaningful perspective that will interest readers?
Fine-tune the thesis
Your thesis will probably evolve as you gather sources and ideas. If your research focus changes, you may need to re-evaluate your search strategy and to conduct additional research. This is usually a good sign of the careful thought you are putting into your work!
Example: Because climate change, which is exacerbated by high carbon emissions, adversely affects almost all citizens, the U.S. government has the responsibility to help reduce carbon emissions through public policy and regulation.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs Popular
- Next: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 10:40 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/essentials
Social media
- Instagram for Herman B Wells Library
- Facebook for IU Libraries
Additional resources
Featured databases.
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) OneSearch@IU
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Academic Search (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) ERIC (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Nexis Uni
- Resource available without restriction HathiTrust Digital Library
- Databases A-Z
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Google Scholar
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) JSTOR
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Web of Science
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Scopus
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) WorldCat
IU Libraries
- Diversity Resources
- About IU Libraries
- Alumni & Friends
- Departments & Staff
- Jobs & Libraries HR
- Intranet (Staff)
- IUL site admin
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Table of Contents


Thesis Statement
Definition:
Thesis statement is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of an essay, research paper, or any other written work.
It is usually located at the end of the introductory paragraph and provides a roadmap for the reader, indicating what the paper will be about and what the author’s position or argument is. The thesis statement should be clear, specific, and debatable, so that the reader knows what to expect and can evaluate the validity of the argument.
Structure of Thesis Statement
The structure of a thesis statement typically consists of two main parts: the topic and the argument or claim.
- Topic : The topic is the subject or issue that the paper will be addressing. It should be clear and specific, and should provide a context for the argument or claim that follows.
- Argument or claim: The argument or claim is the main point or position that the writer is taking on the topic. It should be clear and concise, and should be debatable or arguable, meaning that it can be supported with evidence and analysis.
For example, a thesis statement for an essay on the impact of social media on mental health could be:
“The excessive use of social media has a negative impact on individuals’ mental health as it leads to increased feelings of anxiety and depression, a distorted self-image, and a decline in face-to-face communication skills.”
In this example, the topic is the impact of social media on mental health, and the argument is that excessive social media use has negative effects on mental health, which will be supported by evidence throughout the essay.
How to Write Thesis Statement
Here are the steps to follow when writing a thesis statement:
- Identify your topic: Your thesis statement should be based on a clear understanding of your topic. Identify the key concepts, issues, and questions related to your topic.
- Research : Conduct research to gather information and evidence that supports your argument. Use reputable sources, such as academic journals, books, and websites.
- Brainstorm : Use brainstorming techniques to generate ideas and develop your argument. Consider different perspectives and opinions on your topic.
- Create a working thesis : Write a working thesis statement that expresses your argument or position on the topic. This statement should be concise and clear, and it should provide a roadmap for your paper.
- Refine your thesis : Revise your working thesis as you continue to research and develop your argument. Make sure your thesis is specific, debatable, and well-supported by evidence.
- Check for coherence : Ensure that your thesis statement is coherent with the rest of your paper. Make sure that your supporting arguments and evidence align with your thesis.
- Revisit your thesis statement : After completing your paper, revisit your thesis statement to ensure that it accurately reflects the content and scope of your work.
How to Start a Thesis Statement
Here are some steps you can follow to start a thesis statement:
- Choose your topic: Start by selecting a topic that you are interested in and that is relevant to your assignment or research question.
- Narrow your focus : Once you have your topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect or angle that you will be exploring in your paper.
- Conduct research : Conduct some research on your topic to gather information and form an understanding of the existing knowledge on the subject.
- I dentify your main argument : Based on your research, identify the main argument or point you want to make in your paper.
- Write a draft thesis statement : Using the main argument you identified, draft a preliminary thesis statement that clearly expresses your point of view.
- Refine your thesis statement : Revise and refine your thesis statement to make sure it is clear, specific, and strong. Make sure that your thesis statement is supported by evidence and relevant to your topic.
Where is the Thesis Statement Located
In academic writing, the thesis statement is usually located in the introduction paragraph of an essay or research paper. It serves as a concise summary of the main point or argument that the writer will be making in the rest of the paper. The thesis statement is typically located towards the end of the introduction and may consist of one or two sentences.
How Long Should A Thesis Statement Be
Thesis Statement Should be between 1-2 sentences and no more than 25-30 words. It should be clear, concise, and focused on the main point or argument of the paper. A good thesis statement should not be too broad or too narrow but should strike a balance between these two extremes. It should also be supported by evidence and analysis throughout the paper.
For example, if you are writing a five-paragraph essay, your thesis statement should be one sentence that summarizes the main point of the essay. If you are writing a research paper, your thesis statement may be two or three sentences long, as it may require more explanation and support.
Thesis Statement Examples
Here are a few examples of thesis statements:
- For an argumentative essay: “The use of smartphones in classrooms should be banned, as it distracts students from learning and hinders their academic performance.”
- For a literary analysis essay: “In George Orwell’s 1984, the use of propaganda and censorship is a powerful tool used by the government to maintain control over the citizens.”
- For a research paper: “The impact of social media on mental health is a growing concern, and this study aims to explore the relationship between social media use and depression in young adults.”
- For a compare and contrast essay : “Although both American and British English are forms of the English language, they differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and spelling.”
- For an expository essay: “The importance of regular exercise for overall health and well-being cannot be overstated, as it reduces the risk of chronic diseases, improves mood and cognitive function, and enhances physical fitness.”
- For a persuasive essay: “The government should invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as they are more sustainable and environmentally friendly than fossil fuels.”
- For a history research paper: “The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s was a pivotal moment in American history that paved the way for greater racial equality and social justice.”
- For a literary comparison essay: “In The Great Gatsby and Death of a Salesman, the theme of the American Dream is portrayed differently, with one exposing its emptiness and the other showing its destructive power.”
- For a science experiment report: “The hypothesis that increasing the amount of sunlight a plant receives will result in greater growth is supported by the results of this experiment.”
- For an analysis of a social issue : “The gender pay gap in the United States is a pervasive problem that is perpetuated by systemic discrimination and unequal access to education and opportunities.”
Good Thesis Statements Examples
Some Good Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “The legalization of marijuana for medical use has proven to be a beneficial alternative to traditional pain management techniques, with numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and provides specific information about the benefits of medical marijuana and the evidence supporting its use.
- “The rise of social media has fundamentally changed the way we communicate and interact with each other, with both positive and negative effects on our relationships and mental health.”
This thesis statement provides a clear argument and focus for the essay, exploring the impact of social media on communication and mental health.
- “The portrayal of women in advertising perpetuates harmful stereotypes and reinforces gender inequality, contributing to a larger societal issue of sexism and misogyny.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, analyzing the negative effects of advertising on women and the larger societal issue of gender inequality.
- “The implementation of renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and transitioning to a more sustainable future.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, emphasizing the importance of renewable energy sources in addressing climate change and promoting sustainability.
- “The American Dream is an illusion that perpetuates social and economic inequality, as it is based on the false notion of equal opportunity for all.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, critiquing the concept of the American Dream and its perpetuation of inequality.
Bad Thesis Statements Examples
Some Bad Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “In this essay, I will talk about my favorite hobby.”
This thesis statement is too vague and does not give any specific information about the writer’s favorite hobby or what the essay will be about.
- “This paper will explore the benefits and drawbacks of social media.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a clear argument or focus for the essay.
- “The world is a beautiful place.”
This thesis statement is an opinion and does not provide any specific information or argument that can be discussed or analyzed in an essay.
- “The impact of climate change is bad.”
This thesis statement is too broad and does not provide any specific information about the impacts of climate change or the focus of the essay.
- “I am going to write about the history of the United States.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a specific focus or argument for the essay.
Applications of Thesis Statement
A thesis statement has several important applications in academic writing, including:
- Guides the reader: A thesis statement serves as a roadmap for the reader, telling them what to expect from the rest of the paper and helping them to understand the main argument or focus of the essay or research paper.
- Focuses the writer: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Organizes the paper: A thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Evaluates sources: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not.
- Helps with revision: A strong thesis statement can help the writer to revise their paper, as they can use it as a reference point to ensure that every paragraph and piece of evidence supports their main argument or claim.
Purpose of Thesis Statement
The purpose of a thesis statement is to:
- Identify the main focus or argument of the essay or research paper: A thesis statement is typically a one or two-sentence statement that identifies the main argument or claim of the paper. It should be clear, specific, and debatable, and should guide the reader on what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- Provide direction and guidance to the reader: A thesis statement helps the reader to understand the main focus of the paper and what the writer is trying to convey. It also provides a roadmap for the reader to follow, making it easier for them to understand the structure and organization of the paper.
- Focus the writer and help with organization: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information. Additionally, a clear thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Provide a basis for evaluation and analysis: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not. It also provides a basis for analyzing and evaluating the evidence presented in the paper, helping the writer to determine whether or not it supports their main argument or claim.
When to Write Thesis Statement
A thesis statement should be written early in the writing process, ideally before any significant research or drafting has taken place. This is because the thesis statement serves as the foundation for the rest of the paper, providing a clear and concise summary of the paper’s main argument or claim. By identifying the main argument or claim early in the writing process, the writer can stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
However, it is important to note that the thesis statement is not necessarily set in stone and may need to be revised as the paper is developed. As the writer conducts research and develops their argument, they may find that their original thesis statement needs to be modified or refined. Therefore, it is important to revisit and revise the thesis statement throughout the writing process to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
Characteristics of Thesis Statement
Some of the key characteristics of a strong thesis statement include:
- Clarity : A thesis statement should be clear and easy to understand, clearly conveying the main argument or claim of the paper.
- Specificity : A thesis statement should be specific and focused, addressing a single idea or topic rather than being overly broad or general.
- Debatable : A thesis statement should be debatable, meaning that there should be room for disagreement or debate. It should not be a statement of fact or a summary of the paper, but rather a statement that can be supported with evidence and analysis.
- Coherent : A thesis statement should be coherent, meaning that it should be logical and consistent with the rest of the paper. It should not contradict other parts of the paper or be confusing or ambiguous.
- Relevant : A thesis statement should be relevant to the topic of the paper and should address the main question or problem being investigated.
- Arguable : A thesis statement should present an argument that can be supported with evidence and analysis, rather than simply stating an opinion or belief.
Advantages of Thesis Statement
There are several advantages of having a strong thesis statement in academic writing, including:
- Focuses the writer : Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Establishes credibility: A strong thesis statement establishes the writer’s credibility and expertise on the topic, as it demonstrates their understanding of the issue and their ability to make a persuasive argument.
- Engages the reader: A well-crafted thesis statement can engage the reader and encourage them to continue reading the paper, as it presents a clear and interesting argument that is worth exploring.
Limitations of Thesis Statement
While a strong thesis statement is an essential component of academic writing, there are also some limitations to consider, including:
- Can be restrictive: A thesis statement can be restrictive if it is too narrow or specific, limiting the writer’s ability to explore related topics or ideas. It is important to strike a balance between a focused thesis statement and one that allows for some flexibility and exploration.
- Can oversimplify complex topics: A thesis statement can oversimplify complex topics, presenting them as black and white issues rather than acknowledging their complexity and nuance. It is important to be aware of the limitations of a thesis statement and to acknowledge the complexities of the topic being addressed.
- Can limit creativity: A thesis statement can limit creativity and experimentation in writing, as the writer may feel constrained by the need to support their main argument or claim. It is important to balance the need for a clear and focused thesis statement with the desire for creativity and exploration in the writing process.
- May require revision: A thesis statement may require revision as the writer conducts research and develops their argument, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. It is important to be flexible and open to revising the thesis statement as needed to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statement to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling idea —the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe . These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement , an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
1. Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people , everything , society , or life , with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
2. Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke . The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
3. Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
4. Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
In the first section of Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
- Effective Thesis Statements
What is a Thesis Statement?
- A thesis statement tells a reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. Such a statement is also called an “argument,” a “main idea,” or a “controlling idea.”
- A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should “telegraph” how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay
- A standard place for your thesis is at the end of the introductory paragraph.
- A thesis is an interpretation of a subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel that others might dispute.
- A strong thesis not only grabs the interest of your reader, who now wants to see you support your unique interpretation, it also provides a focus for your argument, one to which every part of your paper refers in the development of your position.
- A thesis keeps the writer centered on the matter at hand and reduces the risk of intellectual wandering. Likewise, a thesis provides the reader with a “road map,” clearly laying out the intellectual route ahead.
- A thesis statement avoids the first person (“I believe,” “In my opinion”).
A simple equation for what a thesis might look like this:
What you plan to argue + How you plan to argue it = Thesis Specific Topic+ Attitude/Angle/Argument=Thesis
Steps To Write Effective Thesis Statement
- Choose a prompt or, if appropriate, select a topic: television violence and children
- What are the effects of television violence on children?
- Violence on television increases aggressive behavior in children.
- Avoid general phrasing and/or sweeping words such as “all” or “none” or “every”.
- Lead the reader toward the topic sentences (the subtopics needed to prove the thesis).
- While poor parenting and easy access to weapons may act as contributory factors, in fact when children are exposed to television violence they become less sensitive to the pain and suffering of others, are more fearful of the world around them, and are more likely to behave in aggressive or harmful ways toward others.
The Components of an Effective Thesis Statement
- You can’t just pluck a thesis out of thin air. Even if you have a terrific insight concerning a topic, it won’t be worth much unless you can logically and persuasively support it in the body of your essay. A thesis is the evolutionary result of a thinking process, not a miraculous creation. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment .
- Substantial – Your thesis should be a claim for which it is easy to answer every reader’s question: “So what?”
- Supportable – A thesis must be a claim that you can prove with the evidence at hand (e.g., evidence from your texts or from your research). Your claim should not be outlandish, nor should it be mere personal opinion or preference (e.g., “Frederick Douglass is my favorite historical figure.”) It tackles a subject that could be adequately covered in the format of the project assigned.
- Precise – It is focused and specific. A strong thesis proves a point without discussing everything. It clearly asserts your own conclusion based on evidence. Note: Be flexible. It is perfectly okay to change your thesis!
- Arguable – It should be contestable, proposing an arguable point with which people could reasonably disagree.
- Relevant – If you are responding to an assignment, the thesis should answer the question your teacher has posed. In order to stay focused, pay attention to the task words in the assignment: summarize, argue, compare/contrast, etc.
- Aware of Counters – It anticipates and refutes the counter-arguments.
The best thesis statement is a balance of specific details and concise language. Your goal is to articulate an argument in detail without burdening the reader with too much information.
Questions To Review Your Thesis
- “Do I answer the question?” This might seem obvious, but it’s worth asking. No matter how intriguing or dazzling, a thesis that doesn’t answer the question is not a good thesis!
- “Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose?” If not, then you probably do not have a strong argument. Theses that are too vague often have this problem. If your thesis contains vague words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what makes something “successful”?
- Would anyone possible care about this thesis? So What? Does your thesis present a position or an interpretation worth pursuing? If a reader’s first response is, “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- “Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering?” Just as a thesis that doesn’t answer the question ultimately fails, so does a thesis that isn’t properly supported with evidence and reasoning.
- Does my thesis statement adequately address the direction words of the prompt: summarize, argue, compare/contrast, analyze, discuss, etc.?
Myths about Thesis Statements
- Every paper requires one . Assignments that ask you to write personal responses or to explore a subject don’t want you to seem to pre-judge the issues. Essays of literary interpretation often want you to be aware of many effects rather than seeming to box yourself into one view of the text.
- A thesis statement must come at the end of the first paragraph . This is a natural position for a statement of focus, but it’s not the only one. Some theses can be stated in the opening sentences of an essay; others need a paragraph or two of introduction; others can’t be fully formulated until the end.
- A thesis statement must be one sentence in length , no matter how many clauses it contains. Clear writing is more important than rules like these. Use two or three sentences if you need them. A complex argument may require a whole tightly-knit paragraph to make its initial statement of position.
- You can’t start writing an essay until you have a perfect thesis statement . It may be advisable to draft a hypothesis or tentative thesis statement near the start of a big project, but changing and refining a thesis is a main task of thinking your way through your ideas as you write a paper. And some essay projects need to explore the question in depth without being locked in before they can provide even a tentative answer.
- A thesis statement must give three points of support . It should indicate that the essay will explain and give evidence for its assertion, but points don’t need to come in any specific number.
Progressively Complex Thesis Statements
- Effective Thesis Statements. Provided by : Writing Guide Wikispaces. Located at : https://writingguide.wikispaces.com/Effective+Thesis+Statements . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Peer Review Checklist
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- How to Write a Summary
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice
Module: Academic Argument
Argumentative thesis statements, learning objective.
- Recognize an arguable thesis
Below are some of the key features of an argumentative thesis statement.
An argumentative thesis is . . .
An argumentative thesis must make a claim about which reasonable people can disagree. Statements of fact or areas of general agreement cannot be argumentative theses because few people disagree about them.
Junk food is bad for your health is not a debatable thesis. Most people would agree that junk food is bad for your health.
Because junk food is bad for your health, the size of sodas offered at fast-food restaurants should be regulated by the federal government is a debatable thesis. Reasonable people could agree or disagree with the statement.
An argumentative thesis takes a position, asserting the writer’s stance. Questions, vague statements, or quotations from others are not an argumentative thesis because they do not assert the writer’s viewpoint.
Federal immigration law is a tough issue about which many people disagree is not an arguable thesis because it does not assert a position.
Federal immigration enforcement law needs to be overhauled because it puts undue constraints on state and local police is an argumentative thesis because it asserts a position that immigration enforcement law needs to be changed.
An argumentative thesis must make a claim that is logical and possible. Claims that are outrageous or impossible are not argumentative thesis.
City council members stink and should be thrown in jail is not an argumentative thesis. City council members’ ineffectiveness is not a reason to send them to jail.
City council members should be term limited to prevent one group or party from maintaining control indefinitely is an arguable thesis because term limits are possible, and shared political control is a reasonable goal.
Evidence Based
An argumentative thesis must be able to be supported by evidence. Claims that presuppose value systems, morals, or religious beliefs cannot be supported with evidence and therefore are not argumentative theses.
Individuals convicted of murder will go to hell when they die is not an argumentative thesis because its support rests on religious beliefs or values rather than evidence.
Rehabilitation programs for individuals serving life sentences should be funded because these programs reduce violence within prisons is an argumentative thesis because evidence such as case studies and statistics can be used to support it.
An argumentative thesis must be focused and narrow. A focused, narrow claim is clearer, more able to be supported with evidence, and more persuasive than a broad, general claim.
The federal government should overhaul the U.S. tax code is not an effective argumentative thesis because it is too general (What part of the government? Which tax codes? What sections of those tax codes?) and would require an overwhelming amount of evidence to be fully supported.
The U.S. House of Representative should vote to repeal the federal estate tax because the revenue generated by that tax is negligible is an effective argumentative thesis because it identifies a specific actor and action and can be fully supported with evidence about the amount of revenue the estate tax generates.
- Argumentative Thesis Statements. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY: Attribution


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.6: Paragraph Development- Supporting Claims
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58263
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Analyze the types and uses of evidence and supporting details in paragraphs
Main Ideas in Paragraphs

A paragraph is composed of multiple sentences focused on a single, clearly-defined topic. There should be one main idea per paragraph, so whenever an author moves on to a new idea, he or she will start a new paragraph. For example, this paragraph defines what a paragraph is, and now we will start a new paragraph to deal with a new idea: how a paragraph is structured.
Paragraphs are actually organized much like persuasive papers are. Just like a paper has a thesis statement followed by a body of supportive evidence, paragraphs have a topic or key sentence followed by several sentences of support or explanation.
After the topic or key sentence introduces the main idea, the remainder of the sentences in a paragraph should support or explain this topic. These additional sentences might detail the author’s position on the topic. They might also provide examples, statistics, or other evidence to support that position. At the end of the paragraph, the author may include some sort of conclusion or a transition that sets up the next idea he or she will be discussing.
Using the Thesis to Organize Paragraphs
While your main claim should guide the entire argument, key ideas included in the thesis statement can be used in topic sentences to guide your paragraphs.
Using the sample thesis statement, “Social media sites like Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube have been indispensable tools to young activists from Tahrir Square to Wall Street,” the argument might be outlined as follows:
- Introduction: Social media sites like Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube have been indispensable tools to young activists from Tahrir Square to Wall Street.
- Arab Spring
- Occupy Wall Street
- Conclusion: The Arab Spring and Occupy Wall Street movements may not have happened without the use of social media.
In the above outline, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube are used to divide the body of the essay into three main sections, and then those sections are subdivided into Egypt and the United States. Alternately, you could divide the body of the essay into two main sections—one for Egypt and the other for the United States—and then subdivide by Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. The resulting outline would look like this:
Either of these outlines would be a clear progression from the thesis statement and would help the reader to see how each key idea furthers the main claim.
Supporting Ideas and Details
A text’s thesis statement helps guide its overall organization and the development of the topic sentences that will constitute the body paragraphs. Now let’s examine the rest of the “stuff” that makes a paragraph work.
First, watch this video that details the relationship between a topic or key sentence and supporting details, using the metaphor of a house. The video establishes the difference between major and minor details, which will be useful to apply in future discussions.
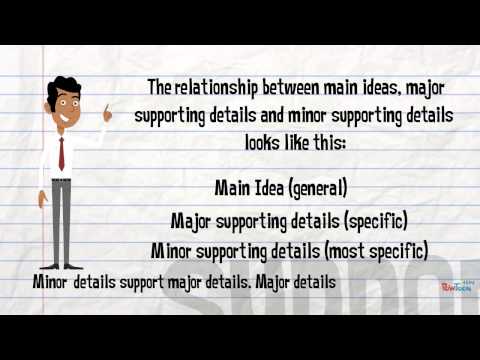
A YouTube element has been excluded from this version of the text. You can view it online here: pb.libretexts.org/ec1/?p=186
(The video has instrumental guitar for audio, but no spoken words, so can be watched without sound if desired.)
The following image shows the visual relationship between the overall thesis, topic sentences, and supporting ideas:
Remember, readers often expect the topic or key sentences to be at the beginning of the paragraph but they don’t have to be. Sometimes the paragraph’s purpose in a larger piece of writing necessitates that its topic sentence occurs elsewhere.
This image shows where a topic sentence might reside in the paragraph, in relation to the rest of the supporting details:
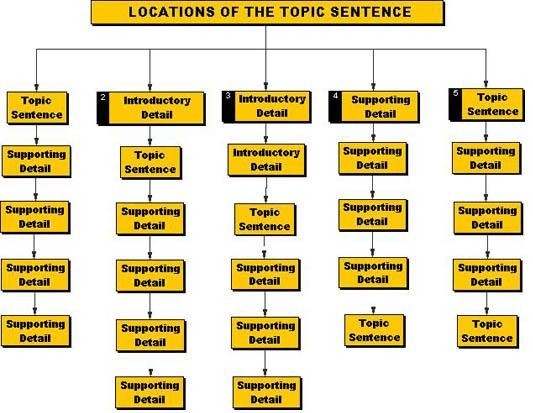
How does the structure of a body paragraph support a thesis?

Many authors use the PIE format to structure their essays. PIE = point, illustration, explanation. The point furthers a thesis or claim, the illustration provides support for the point, and the explanation tells the audience why the evidence provided furthers the point and/or the thesis.
For example, let’s consider an essay written by a college student, Tareq Hajj. He argues that his university should not use a plus/minus grading scale because the proposed scale does not include a higher weight for A+ scores/. In his argument he makes the Point that “Without the A+, students with high grades in the class would be less motivated to work even harder in order to increase their grades.”
He Illustrates with a quote from a professor who argues, “‘(students) have less incentive to try’” (Fesheraki, 2013).
Hajj then Explains that “not providing [the most motivated students] with additional motivation of a higher grade … is inequitable.”
Through his explanation, Hajj links back to his claim that, “A plus-minus grading scale … should not be used…” because, as he explains, it is “inequitable.” The PIE structure of his paragraph has served to support his thesis.
Using Evidence
Ever heard the phrase “everyone is entitled to his opinion”? It is indeed true that people are free to believe whatever they wish. However, the mere fact that a person believes something is not an argument in support of a position. If a text’s goal is to communicate effectively, it must provide valid explanations and sufficient and relevant evidence to convince its audience to accept that position.
What are the types of evidence?
Any text should provide illustrations for each of its points, but it is especially important to provide reliable evidence in an academic argument. This evidence can be based on primary source material or data (the author’s own experience and/or interviews, surveys, polls, experiments, that she may have created and administered). Evidence can also stem from secondary source material or data (books, journals, newspapers, magazines, websites or surveys, experiments, statistics, polls, and other data collected by others).
Let’s say, for example, that you are reading an argument that college instructors should let students use cell phones in class. Primary source material might include a survey the author administered that asks students if policies forbidding cell phone usage actually stops them from using their phones in class. Secondary sources might include articles about the issue of cell phone usage in class from scholarly or academic journals.
How do authors decide what kinds of evidence to use?
You’ve likely learned in the past about different types of rhetorical techniques that writers use when making claims in their writing. These appeals are referred to by their Greek names: logos (the appeal to logic), pathos (the appeal to emotion), and ethos (the appeal to authority).
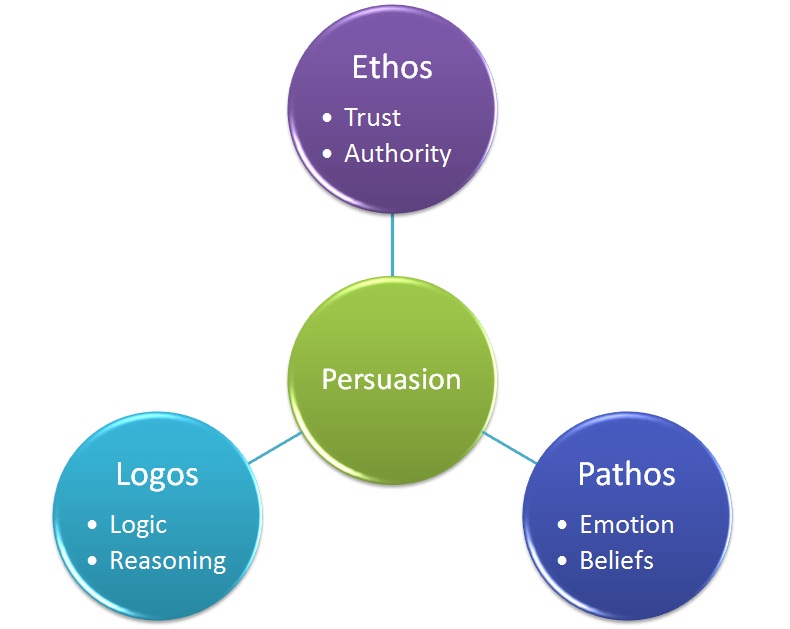
Logical Appeals (Logos)
Authors using logic to support their claims will include a combination of different types of evidence. These include the following:
- established facts
- case studies
- experiments
- analogies and logical reasoning
- citation of recognized experts on the issue
Authoritative Appeals (Ethos)
Authors using authority to support their claims may draw from different sources as evidence for their claims. These include the following:
- personal anecdotes based on substantial personal experience
- illustration of deep knowledge on the issue
- testimony of those involved first-hand on the issue
Emotional Appeals (Pathos)
Authors using emotion might support their claims with some of the same kinds of evidence but employed to achieve different ends. These include the following:
- touching personal anecdotes
- compelling narratives
- emotional or stirring testimony of those involved first-hand on the issue
As you can see, there is some overlap on these lists. One technique might work simultaneously on multiple levels.
Regardless of what kind of evidence you use, an effective paragraph will guide the reader with a clear topic sentence that articulates the claim and then use evidence, illustration, support, and discussion to convince the reader.
Contributors and Attributions
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of point. Authored by : Joshua Rappeneker. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/mWga . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of How to Differentiate. Authored by : NUR SYAFIQAH ABDUL KADAR, NUR ATIKAH MANAN, NUR SHAFIQAH SHUKRI, ZHARIF ISKANDAR RAJALIE. Provided by : Verbal Warfare. Located at : verbalwarfare.wikispaces.com/Vocabulary+Building+In+English+I. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Locations of the Topic Sentence. Authored by : NUR SYAFIQAH ABDUL KADAR, NUR ATIKAH MANAN, NUR SHAFIQAH SHUKRI, ZHARIF ISKANDAR RAJALIE. Provided by : Verbal Warfare. Located at : verbalwarfare.wikispaces.com/Vocabulary+Building+In+English+I. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Persuasion. Authored by : Mrs. Adcock. Located at : agi241classes.wikispaces.com/Fifth+Grade. Project : Computer Class AGI241. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Supporting Details. Authored by : Mastering the Fundamentals of College Reading and Writing. Located at : https://youtu.be/uE74-8YAV9E . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Academic Argument Essay. Provided by : Radford University. Located at : http://lcubbison.pressbooks.com/chapter/core-101-academic-argument-essay/ . Project : Core Handbook. License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
An argumentative thesis must be able to be supported by evidence. Claims that presuppose value systems, morals, or religious beliefs cannot be supported with evidence and therefore are not argumentative theses. Let's take a look at an example: BAD: Individuals convicted of murder will go to hell when they die.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A good thesis statement is supported by relevant evidence. Every paragraph should contribute to proving the thesis to be valid; Developing a Thesis. Define the Rhetorical Situation: The key to developing an appropriate thesis is to begin by examining the rhetorical situation: What is the purpose of your essay (e.g., to inform, to persuade, to ...
A strong thesis is: Arguable: Can be supported by evidence and analysis, and can be disagreed with. Unique: Says something new and interesting. Concise and clear: Explained as simply as possible, but not at the expense of clarity. Unified: All parts are clearly connected. Focused and specific: Can be adequately and convincingly argued within ...
Make sure that your thesis statement is supported by evidence and relevant to your topic. Where is the Thesis Statement Located. In academic writing, the thesis statement is usually located in the introduction paragraph of an essay or research paper. It serves as a concise summary of the main point or argument that the writer will be making in ...
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
A thesis statement is often one sentence long, and it states your point of view. The thesis statement is not the topic of the piece of writing but rather what you have to say about that topic and what is important to tell readers. Table 5.1 "Topics and Thesis Statements" compares topics and thesis statements.
A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated. A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence. A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
The thesis needs to be narrow. Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Just as a thesis that doesn't answer the question ultimately fails, so does a thesis that isn't properly supported with evidence and reasoning. Does my thesis statement adequately address the direction words of the prompt: summarize, argue, compare/contrast, analyze, discuss, etc.? Myths about Thesis Statements. Every paper requires one ...
The U.S. House of Representative should vote to repeal the federal estate tax because the revenue generated by that tax is negligible is an effective argumentative thesis because it identifies a specific actor and action and can be fully supported with evidence about the amount of revenue the estate tax generates.
Just like a paper has a thesis statement followed by a body of supportive evidence, paragraphs have a topic or key sentence followed by several sentences of support or explanation. After the topic or key sentence introduces the main idea, the remainder of the sentences in a paragraph should support or explain this topic.
a sentence that makes a statement that will be supported in the essay. A THESIS SHOULD BE... a statement that can be argued. A STRONG THESIS MUST. be something a smart person could disagree with. WHAT IS TRUE ABOUT A THESIS? It's usually in the introduction paragraph of an essay.
True. The purpose of the research paper can never be stated in the thesis. False. The process of seeking facts that will lead to the truth is called. Research. If many areas for exploration exist within a subject, that subject is too. Broad. A general statement that summarizes the main idea and the purpose of the research paper is the.
There are a number of similarities between the two forms a main point or thesis supported by examples, illustrations, proof, or details, clear organizational structure, introduction, body, conclusion. However, since a speech is written for the purpose of being heard. You need to make adjustments in style and structure taking into account the ...
Subscription Support: 1-347-509-6837. With a solid dividend yield mitigating downside risks, Enbridge is poised to rally. Find out if ENB stock is a buy.