Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples

Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.

Statistics Made Easy
What is an Alternative Hypothesis in Statistics?
Often in statistics we want to test whether or not some assumption is true about a population parameter .
For example, we might assume that the mean weight of a certain population of turtle is 300 pounds.
To determine if this assumption is true, we’ll go out and collect a sample of turtles and weigh each of them. Using this sample data, we’ll conduct a hypothesis test .
The first step in a hypothesis test is to define the null and alternative hypotheses .
These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false.
These two hypotheses are defined as follows:
Null hypothesis (H 0 ): The sample data is consistent with the prevailing belief about the population parameter.
Alternative hypothesis (H A ): The sample data suggests that the assumption made in the null hypothesis is not true. In other words, there is some non-random cause influencing the data.
Types of Alternative Hypotheses
There are two types of alternative hypotheses:
A one-tailed hypothesis involves making a “greater than” or “less than ” statement. For example, suppose we assume the mean height of a male in the U.S. is greater than or equal to 70 inches.
The null and alternative hypotheses in this case would be:
- Null hypothesis: µ ≥ 70 inches
- Alternative hypothesis: µ < 70 inches
A two-tailed hypothesis involves making an “equal to” or “not equal to” statement. For example, suppose we assume the mean height of a male in the U.S. is equal to 70 inches.
- Null hypothesis: µ = 70 inches
- Alternative hypothesis: µ ≠ 70 inches
Note: The “equal” sign is always included in the null hypothesis, whether it is =, ≥, or ≤.
Examples of Alternative Hypotheses
The following examples illustrate how to define the null and alternative hypotheses for different research problems.
Example 1: A biologist wants to test if the mean weight of a certain population of turtle is different from the widely-accepted mean weight of 300 pounds.
The null and alternative hypothesis for this research study would be:
- Null hypothesis: µ = 300 pounds
- Alternative hypothesis: µ ≠ 300 pounds
If we reject the null hypothesis, this means we have sufficient evidence from the sample data to say that the true mean weight of this population of turtles is different from 300 pounds.
Example 2: An engineer wants to test whether a new battery can produce higher mean watts than the current industry standard of 50 watts.
- Null hypothesis: µ ≤ 50 watts
- Alternative hypothesis: µ > 50 watts
If we reject the null hypothesis, this means we have sufficient evidence from the sample data to say that the true mean watts produced by the new battery is greater than the current industry standard of 50 watts.
Example 3: A botanist wants to know if a new gardening method produces less waste than the standard gardening method that produces 20 pounds of waste.
- Null hypothesis: µ ≥ 20 pounds
- Alternative hypothesis: µ < 20 pounds
If we reject the null hypothesis, this means we have sufficient evidence from the sample data to say that the true mean weight produced by this new gardening method is less than 20 pounds.
When to Reject the Null Hypothesis
Whenever we conduct a hypothesis test, we use sample data to calculate a test-statistic and a corresponding p-value.
If the p-value is less than some significance level (common choices are 0.10, 0.05, and 0.01), then we reject the null hypothesis.
This means we have sufficient evidence from the sample data to say that the assumption made by the null hypothesis is not true.
If the p-value is not less than some significance level, then we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
This means our sample data did not provide us with evidence that the assumption made by the null hypothesis was not true.
Additional Resource: An Explanation of P-Values and Statistical Significance
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Statistics
Course: ap®︎/college statistics > unit 10.
- Idea behind hypothesis testing
Examples of null and alternative hypotheses
- Writing null and alternative hypotheses
- P-values and significance tests
- Comparing P-values to different significance levels
- Estimating a P-value from a simulation
- Estimating P-values from simulations
- Using P-values to make conclusions
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
Alternative hypothesis
by Marco Taboga , PhD
In a statistical test, observed data is used to decide whether or not to reject a restriction on the data-generating probability distribution.
The assumption that the restriction is true is called null hypothesis , while the statement that the restriction is not true is called alternative hypothesis.
A correct specification of the alternative hypothesis is essential to decide between one-tailed and two-tailed tests.
Table of contents
Mathematical setting
Choice between one-tailed and two-tailed tests, the critical region, the interpretation of the rejection, the interpretation must be coherent with the alternative hypothesis.
- Power function
Accepting the alternative
More details, keep reading the glossary.
In order to fully understand the concept of alternative hypothesis, we need to remember the essential elements of a statistical inference problem:
we observe a sample drawn from an unknown probability distribution;
in principle, any valid probability distribution could have generated the sample;
however, we usually place some a priori restrictions on the set of possible data-generating distributions;
A couple of simple examples follow.
When we conduct a statistical test, we formulate a null hypothesis as a restriction on the statistical model.
The alternative hypothesis is
The alternative hypothesis is used to decide whether a test should be one-tailed or two-tailed.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic falls within a critical region that has been chosen by the statistician.
The critical region is a set of values that may comprise:
only the left tail of the distribution or only the right tail (one-tailed test);
both the left and the right tail (two-tailed test).
The choice of the critical region depends on the alternative hypothesis. Let us see why.
The interpretation is different depending on the tail of the distribution in which the test statistic falls.
![definition of alternative hypothesis maths [eq7]](https://www.statlect.com/images/alternative-hypothesis__27.png)
The choice between a one-tailed or a two-tailed test needs to be done in such a way that the interpretation of a rejection is always coherent with the alternative hypothesis.
When we deal with the power function of a test, the term "alternative hypothesis" has a special meaning.
We conclude with a caveat about the interpretation of the outcome of a test of hypothesis.
The interpretation of a rejection of the null is controversial.
According to some statisticians, rejecting the null is equivalent to accepting the alternative.
However, others deem that rejecting the null does not necessarily imply accepting the alternative. In fact, it is possible to think of situations in which both hypotheses can be rejected. Let us see why.
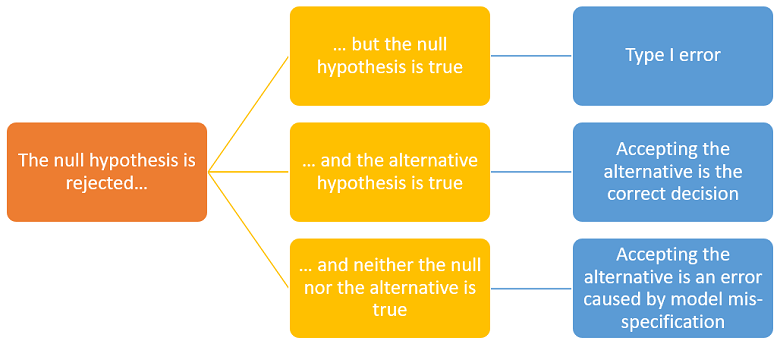
According to the conceptual framework illustrated by the images above, there are three possibilities:
the null is true;
the alternative is true;
neither the null nor the alternative is true because the true data-generating distribution has been excluded from the statistical model (we say that the model is mis-specified).
If we are in case 3, accepting the alternative after a rejection of the null is an incorrect decision. Moreover, a second test in which the alternative becomes the new null may lead us to another rejection.
You can find more details about the alternative hypothesis in the lecture on Hypothesis testing .
Previous entry: Almost sure
Next entry: Binomial coefficient
How to cite
Please cite as:
Taboga, Marco (2021). "Alternative hypothesis", Lectures on probability theory and mathematical statistics. Kindle Direct Publishing. Online appendix. https://www.statlect.com/glossary/alternative-hypothesis.
Most of the learning materials found on this website are now available in a traditional textbook format.
- Maximum likelihood
- Binomial distribution
- Beta distribution
- Convergence in probability
- Delta method
- Exponential distribution
- Chi-square distribution
- Set estimation
- Wishart distribution
- Mathematical tools
- Fundamentals of probability
- Probability distributions
- Asymptotic theory
- Fundamentals of statistics
- About Statlect
- Cookies, privacy and terms of use
- Precision matrix
- Loss function
- Integrable variable
- Critical value
- To enhance your privacy,
- we removed the social buttons,
- but don't forget to share .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.1 Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 36507
Section 9.1 Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Learning Objective:
In this section, you will:
• Understand the general concept and use the terminology of hypothesis testing
I claim that my coin is a fair coin. This means that the probability of heads and the probability of tails are both 50% or 0.50.
- Out of 200 flips of the coin, tails is tossed 102 times. What can we conclude about my claim?
- Out of 200 flips of the coin, tails is tossed 21 times. What can we conclude about my claim?
Hypothesis is a claim about the value of a population parameter.
Hypothesis Testing is a procedure for determining whether the hypothesis stated is a reasonable statement and should not be rejected, or is unreasonable and should be rejected.
Hypothesis testing begins by considering two hypotheses. They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
- The null hypothesis , typically denoted with H 0 . The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality (=, ≤ or ≥)
- The alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with H a or H 1 , using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, (≠, >, or <).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Example 1: We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
Example 2: We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
Example 3: In an issue of U.S. News and World Report, an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
For more information and examples see online textbook OpenStax Introductory Statistics pages 505-508.
“ Introduction to Statistics ” by OpenStax , used is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license
Module 9: Hypothesis Testing With One Sample
Null and alternative hypotheses, learning outcomes.
- Describe hypothesis testing in general and in practice
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 : The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
H a : The alternative hypothesis : It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make adecision. There are two options for a decision . They are “reject H 0 ” if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or “do not reject H 0 ” or “decline to reject H 0 ” if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
H 0 : No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30
H a : More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. p = 0.25
H a : The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. p ≠ 0.25
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ = 2.0
H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 66 H a : μ __ 66
- H 0 : μ = 66
- H a : μ ≠ 66
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ ≥ 5
H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 45 H a : μ __ 45
- H 0 : μ ≥ 45
- H a : μ < 45
In an issue of U.S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : p ≤ 0.066
H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p __ 0.40 H a : p __ 0.40
- H 0 : p = 0.40
- H a : p > 0.40
Concept Review
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with H 0 . The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality (=, ≤ or ≥) Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with H a or H 1 , using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., (≠, >, or <). If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis. Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
H 0 and H a are contradictory.
- OpenStax, Statistics, Null and Alternative Hypotheses. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:58/Introductory_Statistics . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Introductory Statistics . Authored by : Barbara Illowski, Susan Dean. Provided by : Open Stax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- Simple hypothesis testing | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy. Authored by : Khan Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/5D1gV37bKXY . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
Alternative Hypothesis
There are two sorts of statistical hypotheses. Null hypothesis. The null hypothesis, denoted by H0, is typically the hypothesis that sample observations result purely from chance. Alternative hypothesis. The choice hypothesis, denoted by H1 or Ha, is that the hypothesis that sample observations are influenced by some non-random cause. For example, suppose we wanted to […]
There are two sorts of statistical hypotheses.
Null hypothesis. The null hypothesis, denoted by H0, is typically the hypothesis that sample observations result purely from chance.
Alternative hypothesis. The choice hypothesis, denoted by H1 or Ha, is that the hypothesis that sample observations are influenced by some non-random cause.
For example, suppose we wanted to work out whether a coin was fair and balanced. A null hypothesis could be that half the flips would end in Heads and half, in Tails. the choice hypothesis could be that the amount of Heads and Tails would be very different. Symbolically, these hypotheses would be expressed as
H0: p = 0.5
Suppose we flipped the coin 50 times, leading to 40 Heads and 10 Tails. Given this result, we might be inclined to reject the null hypothesis. That is, we might conclude that the coin was probably not fair and balanced.
Weekly newsletter
No spam. Just the latest releases and tips, interesting articles, and exclusive interviews in your inbox every week.
You may also like
False negative.
While understanding the hypothesis, two errors can be quite confusing. These two errors are false negative and false positive. You can also refer to the false-negative error as type II error and false-positive as type I error. While you are learning, you might think these errors have no use and will only waste your time […]
Box Plot Review
A box plot or box and whisker plot help you display the database distribution on a five-number summary. The first quartile Q1 will be the minimum, the third quartile Q3 will be the median, and the fifth quartile Q5 will be the maximum. You can find the outliers and their values by using a box […]

Bayesian Networks
Creating a probabilistic model can be challenging but proves helpful in machine learning. To create such a graphical model, you need to find the probabilistic relationships between variables. Suppose you are creating a graphical representation of the variables. You need to represent the variables as nodes and conditional independence as the absence of edges. Graphical […]

Privacy Overview
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 : The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
H a : The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 . This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject H 0 " if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject H 0 " or "decline to reject H 0 " if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.

Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ .30 H a : More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introductory Statistics 2e
- Publication date: Dec 13, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics-2e/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Dec 6, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.3.1: Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 109930

The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
\(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
\(H_a\): The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to \(H_0\) and what we conclude when we reject \(H_0\). This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject \(H_0\)" or "decline to reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
\(H_{0}\) always has a symbol with an equal in it. \(H_{a}\) never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- \(H_{0}\): No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p \leq 30\)
- \(H_{a}\): More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p > 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. \(p = 0.25\)
- \(H_{a}\): The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. \(p \neq 0.25\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 2.0\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 2.0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol \((=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >)\) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 66\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 5\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 5\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 45\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.066\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.066\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (\(=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >\)) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.40\)
COLLABORATIVE EXERCISE
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we:
- Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality \((=, \leq \text{or} \geq)\)
- Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{a}\) or \(H_{1}\), using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., \((\neq, >, \text{or} <)\).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
\(H_{0}\) and \(H_{a}\) are contradictory.
- If \(\alpha \leq p\)-value, then do not reject \(H_{0}\).
- If\(\alpha > p\)-value, then reject \(H_{0}\).
\(\alpha\) is preconceived. Its value is set before the hypothesis test starts. The \(p\)-value is calculated from the data.References
Data from the National Institute of Mental Health. Available online at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/depression.cfm .
A hypothesis is a proposition that is consistent with known data, but has been neither verified nor shown to be false.
In statistics, a hypothesis (sometimes called a statistical hypothesis) refers to a statement on which hypothesis testing will be based. Particularly important statistical hypotheses include the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis .
In symbolic logic , a hypothesis is the first part of an implication (with the second part being known as the predicate ).
In general mathematical usage, "hypothesis" is roughly synonymous with " conjecture ."
Explore with Wolfram|Alpha
More things to try:
- 1275 to base 7
- focal parameter of an ellipse with semiaxes 4,3
Cite this as:
Weisstein, Eric W. "Hypothesis." From MathWorld --A Wolfram Web Resource. https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Hypothesis.html
Subject classifications
- Math Article
Null Hypothesis
In mathematics, Statistics deals with the study of research and surveys on the numerical data. For taking surveys, we have to define the hypothesis. Generally, there are two types of hypothesis. One is a null hypothesis, and another is an alternative hypothesis .
In probability and statistics, the null hypothesis is a comprehensive statement or default status that there is zero happening or nothing happening. For example, there is no connection among groups or no association between two measured events. It is generally assumed here that the hypothesis is true until any other proof has been brought into the light to deny the hypothesis. Let us learn more here with definition, symbol, principle, types and example, in this article.
Table of contents:
- Comparison with Alternative Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition
The null hypothesis is a kind of hypothesis which explains the population parameter whose purpose is to test the validity of the given experimental data. This hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on the viability of the given population or sample . In other words, the null hypothesis is a hypothesis in which the sample observations results from the chance. It is said to be a statement in which the surveyors wants to examine the data. It is denoted by H 0 .
Null Hypothesis Symbol
In statistics, the null hypothesis is usually denoted by letter H with subscript ‘0’ (zero), such that H 0 . It is pronounced as H-null or H-zero or H-nought. At the same time, the alternative hypothesis expresses the observations determined by the non-random cause. It is represented by H 1 or H a .
Null Hypothesis Principle
The principle followed for null hypothesis testing is, collecting the data and determining the chances of a given set of data during the study on some random sample, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. In case if the given data does not face the expected null hypothesis, then the outcome will be quite weaker, and they conclude by saying that the given set of data does not provide strong evidence against the null hypothesis because of insufficient evidence. Finally, the researchers tend to reject that.
Null Hypothesis Formula
Here, the hypothesis test formulas are given below for reference.
The formula for the null hypothesis is:
H 0 : p = p 0
The formula for the alternative hypothesis is:
H a = p >p 0 , < p 0 ≠ p 0
The formula for the test static is:
Remember that, p 0 is the null hypothesis and p – hat is the sample proportion.
Also, read:
Types of Null Hypothesis
There are different types of hypothesis. They are:
Simple Hypothesis
It completely specifies the population distribution. In this method, the sampling distribution is the function of the sample size.
Composite Hypothesis
The composite hypothesis is one that does not completely specify the population distribution.
Exact Hypothesis
Exact hypothesis defines the exact value of the parameter. For example μ= 50
Inexact Hypothesis
This type of hypothesis does not define the exact value of the parameter. But it denotes a specific range or interval. For example 45< μ <60
Null Hypothesis Rejection
Sometimes the null hypothesis is rejected too. If this hypothesis is rejected means, that research could be invalid. Many researchers will neglect this hypothesis as it is merely opposite to the alternate hypothesis. It is a better practice to create a hypothesis and test it. The goal of researchers is not to reject the hypothesis. But it is evident that a perfect statistical model is always associated with the failure to reject the null hypothesis.
How do you Find the Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis says there is no correlation between the measured event (the dependent variable) and the independent variable. We don’t have to believe that the null hypothesis is true to test it. On the contrast, you will possibly assume that there is a connection between a set of variables ( dependent and independent).
When is Null Hypothesis Rejected?
The null hypothesis is rejected using the P-value approach. If the P-value is less than or equal to the α, there should be a rejection of the null hypothesis in favour of the alternate hypothesis. In case, if P-value is greater than α, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Now, let us discuss the difference between the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis Examples
Here, some of the examples of the null hypothesis are given below. Go through the below ones to understand the concept of the null hypothesis in a better way.
If a medicine reduces the risk of cardiac stroke, then the null hypothesis should be “the medicine does not reduce the chance of cardiac stroke”. This testing can be performed by the administration of a drug to a certain group of people in a controlled way. If the survey shows that there is a significant change in the people, then the hypothesis is rejected.
Few more examples are:
1). Are there is 100% chance of getting affected by dengue?
Ans: There could be chances of getting affected by dengue but not 100%.
2). Do teenagers are using mobile phones more than grown-ups to access the internet?
Ans: Age has no limit on using mobile phones to access the internet.
3). Does having apple daily will not cause fever?
Ans: Having apple daily does not assure of not having fever, but increases the immunity to fight against such diseases.
4). Do the children more good in doing mathematical calculations than grown-ups?
Ans: Age has no effect on Mathematical skills.
In many common applications, the choice of the null hypothesis is not automated, but the testing and calculations may be automated. Also, the choice of the null hypothesis is completely based on previous experiences and inconsistent advice. The choice can be more complicated and based on the variety of applications and the diversity of the objectives.
The main limitation for the choice of the null hypothesis is that the hypothesis suggested by the data is based on the reasoning which proves nothing. It means that if some hypothesis provides a summary of the data set, then there would be no value in the testing of the hypothesis on the particular set of data.
Frequently Asked Questions on Null Hypothesis
What is meant by the null hypothesis.
In Statistics, a null hypothesis is a type of hypothesis which explains the population parameter whose purpose is to test the validity of the given experimental data.
What are the benefits of hypothesis testing?
Hypothesis testing is defined as a form of inferential statistics, which allows making conclusions from the entire population based on the sample representative.
When a null hypothesis is accepted and rejected?
The null hypothesis is either accepted or rejected in terms of the given data. If P-value is less than α, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, and if the P-value is greater than α, then the null hypothesis is accepted in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Why is the null hypothesis important?
The importance of the null hypothesis is that it provides an approximate description of the phenomena of the given data. It allows the investigators to directly test the relational statement in a research study.
How to accept or reject the null hypothesis in the chi-square test?
If the result of the chi-square test is bigger than the critical value in the table, then the data does not fit the model, which represents the rejection of the null hypothesis.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question. When the research question asks "Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?": The null hypothesis ( H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis ( Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the ...
Definition. The alternative hypothesis is a statement used in statistical inference experiment. It is contradictory to the null hypothesis and denoted by H a or H 1. We can also say that it is simply an alternative to the null. In hypothesis testing, an alternative theory is a statement which a researcher is testing.
Null hypothesis: µ ≥ 70 inches. Alternative hypothesis: µ < 70 inches. A two-tailed hypothesis involves making an "equal to" or "not equal to" statement. For example, suppose we assume the mean height of a male in the U.S. is equal to 70 inches. The null and alternative hypotheses in this case would be: Null hypothesis: µ = 70 inches.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. The null hypothesis (\ (H_ {0}\)) is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
Two Types of Errors. The format of the testing procedure in general terms is to take a sample and use the information it contains to come to a decision about the two hypotheses. As stated before our decision will always be either. reject the null hypothesis \ (H_0\) in favor of the alternative \ (H_a\) presented, or.
It is the opposite of your research hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis--that is, the research hypothesis--is the idea, phenomenon, observation that you want to prove. If you suspect that girls take longer to get ready for school than boys, then: Alternative: girls time > boys time. Null: girls time <= boys time.
Notation. Usually, the null hypothesis is denoted by , while the alternative hypothesis is denoted by . Mathematical setting. In order to fully understand the concept of alternative hypothesis, we need to remember the essential elements of a statistical inference problem: we observe a sample drawn from an unknown probability distribution;
The alternative hypothesis is simply the reverse of the null hypothesis, and there are three options, depending on where we expect the difference to lie. Thus, our alternative hypothesis is the mathematical way of stating our research question. If we expect our obtained sample mean to be above or below the null hypothesis value, which we call a ...
Section 9.1 Null and Alternative Hypothesis. Learning Objective: In this section, you will: • Understand the general concept and use the terminology of hypothesis testing. I claim that my coin is a fair coin. This means that the probability of heads and the probability of tails are both 50% or 0.50. Out of 200 flips of the coin, tails is ...
The alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis are types of conjectures used in statistical tests, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions or making judgments on the basis of data. In statistical hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis are two mutually exclusive statements.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
2. The research (alternative) hypothesis. For example, = .75 versus ≠ .75. p .10 versus p < .10. The objective of hypothesis testing is to decide, based on sample information, if the alternative hypotheses is actually supported by the data. We usually do new research to challenge the existing (accepted) beliefs.
There are two sorts of statistical hypotheses. Null hypothesis. The null hypothesis, denoted by H0, is typically the hypothesis that sample observations result purely from chance. Alternative hypothesis. The choice hypothesis, denoted by H1 or Ha, is that the hypothesis that sample observations are influenced by some non-random cause. For example, suppose we wanted to […]
The Hypothesis will be: The accepted fact, i.e., ethanol boils at 173.1∘F 173.1 ∘ F is the null hypothesis, and our proposed theory that ethanol boils at 174∘F 174 ∘ F is the alternative hypothesis. 2.It is assumed that the bearing capacity of a bridge is over 12 tons. Develop a hypothesis to support this study.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
A true hypothesis can be a fact or a historical event. A null hypothesis denotes a 'no change' event or fact. It is denoted by H0. An alternative hypothesis is an alternative of null. It is denoted by Ha or H1. For example, a null hypothesis is that your friend is going to win a lottery.
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
There are two options for a decision. They are "reject H0 H 0 " if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject H0 H 0 " or "decline to reject H0 H 0 " if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis. Table 12.3.1.1 12.3.1. 1: Mathematical Symbols Used in H0 H 0 and Ha H a: H0 H 0.
A hypothesis is a proposition that is consistent with known data, but has been neither verified nor shown to be false. In statistics, a hypothesis (sometimes called a statistical hypothesis) refers to a statement on which hypothesis testing will be based. Particularly important statistical hypotheses include the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. In symbolic logic, a hypothesis is the ...
The null hypothesis is denoted by H 0. Alternative Hypothesis. In an alternative hypothesis, the simple observations are easily influenced by some random cause. It is denoted by the H a or H 1. Empirical Hypothesis. An empirical hypothesis is formed by the experiments and based on the evidence. Statistical Hypothesis
Here, the hypothesis test formulas are given below for reference. The formula for the null hypothesis is: H 0 : p = p 0. The formula for the alternative hypothesis is: H a = p >p 0, < p 0 ≠ p 0. The formula for the test static is: Remember that, p 0 is the null hypothesis and p - hat is the sample proportion.