Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


CAPPELLO CAMBRIDGE CELTA ASSIGNMENT 2 LANGUAGE RELATED TASK

2020, Cambridge CELTA
Teacher Education in Teaching English to Speakers of Second/Foreign Languages (TESOL) - Brazilian Student - Brazilian Learner. CAPPELLO CAMBRIDGE CELTA ASSIGNMENT 2 LANGUAGE RELATED TASK
Related Papers
BELT - Brazilian English Language Teaching Journal
Cristina Perna
English As An International Language: Issues From The Brazilian Classrooms Perspective
Gislaine Schineider de Melo
This essay starts from one doubt the learners, whose nations speak other languages may manifest when they take English classes for the first time: “Teacher, why do we have tostudy English in the school?” It is interesting how this question addresses not only teachers, butthe entire community of academic linguists, researches and studious to discuss the role of English language and the syllabus relating it to the communication and globalization, which feed deep reflections on teachers` understanding about the English as a foreign language (EFL),English as an International Language (EIL), TESOL, and how it becomes fundamental for diversified areas of studying, as well as its widening over the world. Some other questions emerge and remind the readers there are English language institutions of teaching which reinforce the importance of keeping the English native speaking pronunciation in classes, what may leave non-native teachers in a narrow path, because they have to perform English native speaking at the same time they have to avoid their own accent and personal identities on teaching practices; quite hard, not even ethical and it may sound funny. Teacher´s preferences may motivate the learners´ pronunciation when they are alphabetizing their students in the English language. The influence can be also supported by the cultural productions: movies, music, fashion, books or even countries and their respective lifestyle. A natural pronunciation performed in classrooms can represent the initiative of language teachers to promote free practice of teaching and learning process without domain, or interference, in order to let the learners be comfortable to express themselves naturally, thus, respecting their accents, preserving their personal identities for keeping the plurality in the educational environment. The learners´ cultural diversity may have to be taken into account when designers of programs plan their courses and materials. Teachers could enjoy the opportunity to advocate on behalf of the transcultural teaching maintenance when they do not teach predominance based on traditions. Issues can be reflected and may be reevaluated up from the mentioned starting points and extending them to the International English teaching debate promoted by Dr. Majid Safadaran Mosazadeh among the TEFL master academics.
Mário Cruz , Cristina Pinto
Laura Torres-Zuniga
The main objective of this volume is to contribute to teachers’ both pre-service and in-service professional development by providing them with the necessary theoretical knowledge base as well as practical suggestions and activities for the English as a Foreign Language (EFL) classroom at the educational stages of Compulsory Secondary Education (ESO), Upper (non-compulsory) Secondary Education (Bachillerato) and Official Schools of Languages. The topics covered in the present book are usually dealt with in the specific module of EFL Complementos de formación disciplinar of the Masters’ Degree in Teacher Training for Compulsory and Upper Secondary Education, Vocational Education and Official Schools of Language: English as an International Language, the Intercultural Communicative Competence, the application of literature to EFL teaching, and the analysis and evaluation of EFL materials from a general perspective and from the angle of activity typology and sequencing in particular.
Belt Brazilian English Language Teaching Journal
Carina S Fragozo
Kamyla Vega
English Language Teaching
Fernanda C . A . Batista
Only three percent of Brazilians are estimated to speak English despite the status of this language as a mandatory subject in grades 10 to 12 of basic education and preferred foreign language in grades 5 to 9. This paper will analyse possible reasons for this fact. The widespread concept in the Brazilian society that speaking English is beneficial to individuals because it provides access to the globalised world does not seem to be enough to promote the actual learning of the language by the majority of the population, and it is argued here that this fact has to do with a gap in the foreign language teaching policy documents: the 2015 National Education Guidelines and Framework Law (LDB 2015), the Brazilian National Curriculum Parameters for Primary Education (PCN-EF), and the Brazilian National Curriculum Parameters for Secondary Education (PCN-EM). These documents do not prescribe the necessary conditions for English Language Teaching (ELT) to take place effectively, but, instead, provide suggestions for teachers on how to adapt to the status quo, which means focusing on reading to the detriment of the other aspects of the English language due to a number of factors ranging from a lack of resources to a large number of students per class.
Entrepalavras
Alexandre Badim
Vanessa Castaño
The present research project is intended to explore the realities of teaching and learning English in three public schools of Pereira city. The project also seeks to contribute to a diagnosis of the methods that English teachers use in class and the way in which their teaching practices correspond to the principles established by the National Ministry of Education with respect to the teaching of English in Colombia; and finally, to identify factors that influence the English learning process. The study was conducted with the participation of students from sixth to eleventh grade chosen randomly and six language teachers of three public schools in Pereira, one of them belonging to a rural zone. The instruments used to gather information were observations, field notes, interviews and questionnaires. The outcomes of the research indicate that some techniques associated with the Grammar Translation Method were used by the English teachers we observed since their classes were focused on ...
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
LONTAR: Jurnal Ilmu Komunikasi
Fredy Adiwijaya
Massimo Malinverni
Revista Brasileira de Educação Especial
Cristina Broglia Feitosa de Lacerda
Engenharia Agrícola
Marco Junior
Rodrigo Brunini
Kontekstualita
taufik mulyadin
Udensi Ekea E Udensi
Enfoque (Panama)
sandra villada
Sian Williams
Biophysical Journal
Epileptic disorders : international epilepsy journal with videotape
luisa londoño
in: Anna Polo /Ester Pietrobon (Eds.), Apprendere una lingua tra uso e canone letterario. Gli esempi nella riflessione linguistica in Europa (secoli XVI-XVIII), Ledizioni, Milano
Paolo Silvestri
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology
Jurnal Farmasi Galenika (Galenika Journal of Pharmacy)
Agustinus Widodo
Camila de Vasconcelos
Osvaldo Asato
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Elixabet Diaz de Cerio
Trika Pitana
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation
Suriya Prakash T D
Soumia Hani
Miodrag Colic
Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences
zahida batool
Future Generation Computer Systems
Águas Subterrâneas
Sara Vassolo
IJASS JOURNAL
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

ELT Planning
Tefl tips and ideas from a developing teacher.

Home › CELTA tips › CELTA tip: language analysis assignment
CELTA tip: language analysis assignment
By Pete on May 12, 2015 • ( 23 )
The language analysis assignment is quite straightforward. It’s in two parts, grammar and vocabulary. You’re given a particular grammar structure or lexical items, and you have to analyse it and explain how you would go about teaching it. That’s about it really. It might sound simple, but that doesn’t make it easy!
During the course you’ll learn how to introduce target language, more than likely in this order:
Meaning, Form, Pronunciation, Appropriacy
For both grammar and vocabulary items, we were told to lay the analysis out like this:
a) Analysis of meaning (say what it means!)
b) Describe how you would convey the meaning
c) Check students understanding
d) Highlight the form
e) mention any phonological features of the target language
Here are some general tips:
- For conveying the meaning of a grammar point, you should think about putting the target language in a context . For a word or phrase, think about how ‘concrete’ the word is – you might be able to just show a picture of it, draw it, mime it, etc. It might not be as complicated as you think.
- To check understanding of a grammar point, timelines might be useful. Also, use concept checking questions (CCQs) . It’s worth getting in the habit of using these as you need them often when you’re teaching. Don’t worry, I’m still bad at thinking of them on the spot, and I’ve been teaching 5 years!
- ‘highlighting the form’ might include giving collocations – words that commonly go alongside the target language. E.g. if you were teaching the word ‘promise’, it might be relevant to teach ‘break a promise’ and ‘keep a promise’
- Features of pronunciation which might be worth teaching include contractions (I am = I’m) and weak forms , among other things.
- Whichever target language you are asked to analyse for this assignment, the level of the students should be considered very carefully. Make sure you’re not complicating things by using difficult vocabulary, grade your language appropriately .
- You might have to mention ‘ appropriacy ’ when you teach a language item. This means whether it is ok to use the item in certain contexts (e.g. formal/informal situations)
I’m sure you’ll get plenty of advice from your tutors on how to do this task. Still, here’s an example of how I did one grammar point and one vocabulary item. You can download my full assignment if you want to see how it looked. The word limit for this assignment was 1000 words which I’d say is plenty for a thorough analysis of each item.
(note: V1 = present simple, V2 = past simple, V3 = past participle)
Example grammar answer:
Target structure: she’s just gone out
a) Analyse the meaning
‘ she’s just gone out’
She was at home (i.e. somewhere). Now, she’s not at home. She only left home a short time ago.
b) Convey the meaning
At ten past six, I arrived at Lady Gaga’s house. I knocked on the door [action]. Her mum opened the door.
I said to her mum, “is Lady Gaga at home?”
Her mum said, “sorry, Lady Gaga is not here”.
I said, “Oh, er… me and Lady Gaga have a date at six o’clock. ”
Her mum said, “You are late. Lady Gaga was here at 6pm, but she’s just gone out”
c) Checking meaning
Is Lady Gaga at home now? No
Was she at home at six o’clock? Yes
So, she left home a long time ago? No
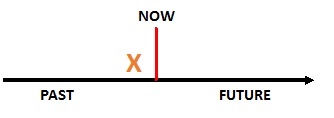
(use the above to aid explanation, showing the event happened in the recent past)
Present Perfect
She has just gone out
S + has / have + Adv V3
e) Phonology
(bold shows stress)
She’s just gone out
with ‘out’, this makes a phrasal verb – ‘gone out’. With phrasal verbs, the stress is on the preposition
Example vocabulary answer:
Target word: Library (elementary)
a) Meaning analysis
A room or building where you can borrow books (DVDs, etc), read, study, etc.
b) Convey meaning
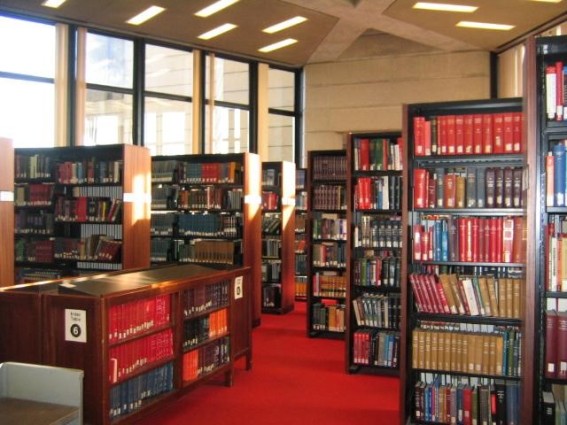

Display the picture above. Elicit if possible, or model the word.
c) Checking understanding
Is this a book shop? No
Can I take the books? Yes
Forever? No
Can I read here? Yes
In here can I TALK LIKE THIS!!!!!!! (loudly…) No
d) Form: Library is a noun. It is countable (‘library’ becomes ‘libraries’). ‘Library book’ is a common collocation.
e) Phonology: The stress is on the first syllable. The word is sometimes spoken as only two syllables (i.e. ‘lai-bri’, not ‘lai-brer-ri’). Although not incorrect, it might be best if the teacher chooses one spoken form and is consistent.
A final tip on this assignment. You might find that it takes a while to analyse each item thoroughly. Don’t worry. It does get easier with practice. Make the most of the time you spend on this assignment and really think about the process you are undertaking – it will become commonplace in your lesson planning. Good luck with the assignment!
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
Categories: CELTA tips
Tags: analysing language , CELTA , CELTA assignment 2 , efl , elt , IH , IH Budapest , meaning before form , pass the CELTA , teacher training , tefl
Your blog is so useful. I really loved it. Thank you so much for sharing things like this.
Like Liked by 1 person
This is incredibly helpful for CELTA trainees. Well done Pete on writing such a supportive and invaluable post.
Thanks it’s very helpful
This is useful for CELTA candidates in teaching English abroad.
It’s really simple and straightforward tip for newly born teacher like me…I do appreciate and thank for your sharing…..
great tips,thank you so much for your help
I have a quick question. do you write this assignments at the school or prepare them at home?
Hi Natalia. Write the assignment wherever you feel comfortable. You might benefit from doing it at school as you could run your ideas past an experienced teacher and they might give you some tips. Plus, there may be a library at school with grammar reference books which might help.
Please help. I have the celta in 4 weeks and I can understand grammar and teaching methods but I cannot for the life of me get the word stress write. NONE OF IT!!! help tips please??
I can do it when I know someone is wrong but I cannot write it on paper or underline words when people ask me to.
you mean “right” not “write” don’t you ?
Thank you for this very useful post. It’s broken down the task to our understanding.
Pleasure! Glad it was useful 🙂
Hello Peter,
Thanks for the post its really helpful. I have a question though, I’m having pre-CELTA assignments which i presume are the same as CELTA although there is one extra thing there: Apart from Grammar and Vocabulary analysis, I have to list all potential problems the students might have. Now in you post I can’t find that. Could you kindly give some help in that as well?
Hi Saboor. It’s been a long while since I did this assignment but it sounds like you need to list anticipated problems and solutions. This is a common thing to include in an observer lesson plan. Think about the language you are introducing: what problems might the learners have with this? E.g. Are there features of the pronunciation of the word that learners from your context might find difficult? Problems don’t have to relate to language only, they might relate to task set up, classroom management, just about any part of your practice. However, for the purpose of your assignment it sounds like the focus is on the language
Hello Peter, Thanks for the fast response. Your tips are really helpful and now I’ve a clear idea of what I have to do. If you like, I can share the assignment with you after I’m done with it via Email and I’d more than appreciate your comments on it. That’s of course if you have time and agree with it.
Sorry Saboor, but I’m not actually a CELTA trainer so I don’t know if my feedback is reliable! Good luck with the assignment though, and I hope the course goes well 🙂
Please don’t say sorry. And thanks for the help. I’ll surely try my best.
Hi Peter, I really want to thanks you for these tips. I am a non native speaker who have just started the CLTA course. I am feeling quite disadvantaged because of this fac. I was looking for some resources to improve my understanding when I came across this blog. really useful. do you have any other platform that I can follow for more tips?
- Useful links for CELTA | Sandy Millin
- English Teaching last hip! – BlogLang!
- 12 tiny tips for writing lesson plans | ELT planning
- How to get a CELTA Pass A | ELT planning
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Full name: ____CAPPELLO, Cyro Jr _____ To be completed by CELTA tutor Overall grade: General comments: International House London Teacher Training A MEMBER OF THE INTERNATIONAL HOUSE WORLD ORGANISATION Page 2 of 9 CAPPELLO Assignment 2: LANGUAGE RELATED TASKS 1st Grammar structure : …everything that has happened to us during the day.
Pt1420 Unit 1 Assignment 2. Hi Class, the assignment 2 will be a group assignment by due 3/12, 11:59pm. You write your own reflection (450 words) as your writing sample and combine it with the html tag that we have learned in the class. 211 Words.
CELTA tip: language analysis assignment. By Pete on May 12, 2015 • ( 23 ) The language analysis assignment is quite straightforward. It’s in two parts, grammar and vocabulary. You’re given a particular grammar structure or lexical items, and you have to analyse it and explain how you would go about teaching it. That’s about it really.