
120+ Exciting 5th Grade Science Project Ideas With Hypothesis In 2023

Are you ready to embark on an exciting journey into the world of 5th-grade science projects with hypotheses? Science projects are not just about fun experiments; they also involve forming hypotheses to make educated guesses about outcomes. But what makes a good hypothesis for a science project? In this blog, we’ll explore the key components of a successful hypothesis.
Selecting the right 5th-grade science project can be a challenge, and we’ll share some valuable tips to help you choose the perfect one. We’ll dive into the importance of combining hypothesis with your science project and why it’s a vital aspect of learning and discovery.
But that’s not all! We’ve also compiled an extensive list of 120+ exciting 5th-grade science project ideas with hypothesis, providing you with a wealth of inspiration for your next scientific adventure. Stay tuned with us to unleash the world of 5th-grade science project ideas with hypothesis and nurture your curiosity in the process.
What Is A Good Hypothesis For A Science Project?
Table of Contents
A good hypothesis for a science project is like a smart guess. It helps scientists figure out what they think will happen in their experiment. To make a good hypothesis, you need to use words like if and then. For example, If I water the plant every day, then it will grow taller. This shows what you’re going to do and what you expect to see.
In addition, a strong hypothesis also needs to be testable. That means you can experiment to see if it’s true or not. It’s like a detective’s clue that leads you to find the answer. Scientists use good hypotheses to guide their experiments and learn new things about the world. So, making a good hypothesis is an important part of any science project.
Things To Remember While Selecting A 5th Grade Science Project Ideas With Hypothesis
Here are some things to remember while selecting a 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis:
1. Personal Interest
Choose a 5th-grade science project that interests you. Picking a topic you’re curious about makes the project more enjoyable. Whether it’s plants, animals, or space, your passion can make learning fun.
2. Age-Appropriate
Make sure the project is right for your grade level. A 5th-grade project shouldn’t be too simple or too complex. It should match your skills and what you’ve learned in school.
3. Available Resources
Check if you have access to the materials you need. Some projects might need special tools or expensive stuff. It’s essential to choose something you can do with the materials you have.
4. Safety First
Keep safety in mind. Select a project that’s safe to do at home or in school. Make sure you won’t be using anything harmful or dangerous.
5. Clear Instructions
Look for a project with clear instructions. It’s easier when you know what to do step by step. Projects with easy-to-follow directions help you succeed and learn better.
Developing A Hypothesis For Your Science Project
Developing a hypothesis for your science project is a crucial step. It’s like making an educated guess about what you think will happen during your experiment. Here are seven key points to consider while creating a hypothesis:
- Identify the Variables: Determine the two things you’re testing in your experiment, the if and then parts. For example, if you’re testing plant growth, the variables could be amount of sunlight and plant height.
- Be Specific: Make sure your hypothesis is clear and precise. Avoid vague or broad statements. The more specific, the better.
- Predict the Outcome: Your hypothesis should state what you expect to happen. Will one variable cause a change in the other? State your prediction clearly.
- Use If-Then Statements : Craft your hypothesis using if-then statements to show the relationship between the variables. For instance, If the amount of sunlight increases, then the plant height will also increase.
- Keep It Testable: Ensure that your hypothesis is something you can test through an experiment. It should lead to concrete results that you can measure.
- Avoid Bias: Make sure your hypothesis doesn’t show your personal beliefs. It should be based on research and evidence, not what you want to happen.
- Revisit and Revise : As you conduct your experiment, be ready to adjust your hypothesis if the results don’t match your initial prediction. Science is all about learning and adapting.
Here we have a list of 120+ exciting 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis in 2023:
- Balloon Rocket
Hypothesis – If I inflate a balloon and release it, then it will move forward because of the escaping air.
- Moldy Bread
Hypothesis – I think bread left in different conditions will develop mold at varying rates.
- Growing Plants
Hypothesis – If I give plants different amounts of water, then they will grow differently.
- Magnet Magic
Hypothesis – I predict that magnets will attract some objects but not others.
- Lemon Battery
Hypothesis – I believe I can create a battery using a lemon because it is acidic.
- Volcano Eruption
Hypothesis – I expect that a mixture of vinegar and baking soda will create a volcanic eruption.
- Density of Liquids
Hypothesis – I think different liquids have different densities, and some will float on top of others.
- Solar Still
Hypothesis – I predict that a solar still can collect clean water from dirty water through evaporation.
- Bouncing Balls
Hypothesis – I believe that balls made from different materials will bounce to different heights.
- Static Electricity
Hypothesis – I think rubbing a balloon on my hair will create static electricity that attracts objects.
- Fruit Battery
Hypothesis – I expect that fruits like oranges and lemons can power a small light bulb.
- Color-Changing Milk
Hypothesis – I predict that adding soap to milk with food coloring will make colorful patterns.
- Tornado in a Bottle
Hypothesis – I think that by swirling water and dish soap in a bottle, I can create a tornado-like vortex.
- Water Filtration
Hypothesis – I believe that by using sand and gravel, I can filter impurities from water.
- Rust Formation
Hypothesis – I predict that metal objects left in water will rust over time.
- Candy Dissolving
Hypothesis – I think that different candies will dissolve at different rates in water.
- Seed Germination
Hypothesis – If I plant seeds in various conditions, then they will sprout at different rates.
Hypothesis – I expect that by using a simple rain gauge, I can measure rainfall accurately.
- Sound Vibrations
Hypothesis – I believe that different objects will produce different sounds when struck.
- Egg Drop Challenge
Hypothesis – I predict that if I design a protective container, the egg will survive a fall.
- Paper Airplanes
Hypothesis – I think that altering the shape of paper airplanes will affect their flight distance.
- Food Preservation
Hypothesis – I expect that different methods of food preservation will keep food fresh longer.
- Homemade Slime
Hypothesis – I believe that mixing glue and borax will create a slimy substance.
Hypothesis – I predict that combining oil and water with Alka-Seltzer will create a mesmerizing lava lamp effect.
- Air Pressure
Hypothesis – I think air pressure can be measured with a simple barometer.
- Crystal Growth
Hypothesis – I expect that I can grow crystals by dissolving substances in water.
- Ocean Currents
Hypothesis – I predict that hot water and cold water will create ocean currents in a container.
- Rainbow in a Jar
Hypothesis – I believe I can create a rainbow by layering different liquids with different densities.
- Static Electricity Levitation
Hypothesis – I think that static electricity can make a small object levitate.
- Melting Ice
Hypothesis – I predict that adding salt to ice will cause it to melt faster.
- Potato Battery
Hypothesis – I expect that a potato can conduct electricity and power a small device.
- Pendulum Swing
Hypothesis – I believe that the length of a pendulum will affect its swing time.
- Soda Geyser
Hypothesis – I predict that dropping Mentos candies into soda will create a geyser.
- Chromatography
Hypothesis – I think I can separate the colors in markers using chromatography.
- Heat Transfer
Hypothesis – I expect that different materials will transfer heat at varying rates.
- Rainfall and Runoff
Hypothesis – I predict that if I simulate rainfall on different surfaces, some will produce more runoff.
- Fizzy Lemonade
Hypothesis – I believe that combining lemon juice and baking soda will make lemonade fizzier.
- Rock Identification
Hypothesis – I think I can identify different rocks by their characteristics.
Hypothesis – I predict that by cutting a straw, I can make it produce musical sounds like an oboe.
- Taste Perception
Hypothesis – I expect that people’s taste perception may change when their sense of smell is altered.
- Color-Changing Flowers
Hypothesis – I believe that adding food coloring to water will change the color of white flowers.
- Solar Cooker
Hypothesis – I predict that a solar cooker can cook food using only the sun’s energy.
- Tornado Formation
Hypothesis – I think that rotating two bottles will create a tornado effect.
- Vinegar and Baking Soda Rocket
Hypothesis – I expect that mixing vinegar and baking soda in a bottle will launch it into the air.
- Popsicle Stick Bridge
Hypothesis – I predict that I can build a strong bridge using only popsicle sticks and glue.
- Rainfall Patterns
Hypothesis – I believe that rainfall patterns can be different in various parts of the world.
- Chemical Reactions
Hypothesis – I think mixing certain chemicals will result in a visible reaction.
- Fruit Decomposition
Hypothesis – I predict that different fruits will decompose at different rates.
- Balancing Act
Hypothesis – I expect that I can balance various objects on a pivot point.
- Photosynthesis Simulation
Hypothesis – I believe that using a simple setup, I can show how plants perform photosynthesis.
- Sinking and Floating
Hypothesis – I think that objects with different densities will either sink or float in water.
- Tooth Decay
Hypothesis – I predict that different liquids will affect teeth differently, simulating tooth decay.
- Rainwater Collection
Hypothesis – I expect that by using a funnel, I can collect rainwater efficiently.
- Soundproofing
Hypothesis – I think that different materials will block sound to varying degrees.
- Egg in a Bottle
Hypothesis – I predict that I can place a peeled hard-boiled egg into a bottle without breaking it.
- Water Wheel
Hypothesis – I believe that the flow of water can make a small wheel turn.
- Invisible Ink
Hypothesis – I expect that I can create invisible ink that reveals messages under certain conditions.
- Heat from the Sun
Hypothesis – I predict that a dark-colored object will get hotter in the sun than a light-colored one.
- Layered Liquids
Hypothesis – I think that liquids of different densities will form layers when mixed.
- Candle Burning
Hypothesis – I predict that different types of candles will burn at different rates.
- Buoyancy with Clay Boats
Hypothesis – I believe I can make clay boats that float and carry small loads.
Hypothesis – I expect that a mixture of cornstarch and water will behave strangely, like a liquid and a solid.
- Magnetic Slime
Hypothesis – I predict that adding iron filings to slime will make it magnetic.
- Stalactites and Stalagmites
Hypothesis – I think I can grow stalactites and stalagmites using a simple solution.
Hypothesis – I expect that different substances will have varying pH levels, which can be tested with indicator paper.
- Solar Still for Drinking Water
Hypothesis – I believe that a solar still can produce clean drinking water from saltwater.
Hypothesis – I predict that I can create a sundial that tells time using the sun’s shadow.
- Dissolving Sugar
Hypothesis – I expect that sugar will dissolve faster in hot water than in cold water.
- Balloon Inflator
Hypothesis – I think that a chemical reaction in a bottle can inflate a balloon.
- Baking Soda and Vinegar Boat
Hypothesis – I predict that a boat made from materials like baking soda and vinegar will move.
- Oil Spill Cleanup
Hypothesis – I believe that using different materials can help clean up an oil spill in water.
- Seed Dispersal
Hypothesis – I predict that seeds can be dispersed in various ways, such as by wind or animals.
- Lemonade Sweetness
Hypothesis – I expect that lemonade sweetness can be adjusted by adding sugar in different amounts.
- Density of Solids
Hypothesis – I think different solid objects will have different densities, which can be measured.
- Making Ice Cream
Hypothesis – I predict that I can make ice cream by mxing ingredients and using ice and salt.
- Conduction and Insulation
Hypothesis – I believe that different materials will either conduct or insulate heat.
- Centrifugal Force
Hypothesis – I predict that spinning an object will create a centrifugal force that affects its path.
- Balloon-Powered Car
Hypothesis – I expect that a car powered by a balloon will move because of the escaping air.
- Candle Extinguisher
Hypothesis – I think that covering a candle with a glass will extinguish it by using up the oxygen inside.
- Water Filter Comparison
Hypothesis – I predict that different water filters will remove impurities to varying degrees.
- Capillary Action
Hypothesis – I expect that water will rise differently in materials with varying capillary action.
- Static Electricity and Salt
Hypothesis – I believe that salt can be moved with static electricity.
- Food Coloring in Flowers
Hypothesis – I predict that adding food coloring to water will change the color of flowers.
- Bottle Trombone
Hypothesis – I think I can make a simple trombone-like instrument using a plastic bottle.
- Windmill Power
Hypothesis – I expect that a windmill can generate power when exposed to wind.
- Chewing Gum Flavor
Hypothesis – I predict that the flavor of chewing gum changes over time as it’s chewed.
- Yeast Balloons
Hypothesis – I believe that yeast will produce gas that can inflate a balloon.
- Water Wheel Efficiency
Hypothesis – I think that the design of a water wheel affects its efficiency in generating power.
- Simple Electric Circuit
Hypothesis – I expect that I can make a light bulb glow by completing an electric circuit.
- Sugar Crystal Lollipop
Hypothesis – I predict that sugar crystals will grow on a string dipped in a sugary solution.
- Temperature and Magnetism
Hypothesis – I believe that magnets will behave differently at various temperatures.
- Styrofoam and Acetone
Hypothesis – I expect that acetone will dissolve styrofoam.
- Starch in Foods
Hypothesis – I think I can test for the presence of starch in different foods using iodine.
- Balloon-Powered Boat
Hypothesis – I predict that a boat powered by a balloon will move on water.
- Melting Chocolate
Hypothesis – I expect that chocolate will melt at different rates when heated.
- Air Pollution and Plant Growth
Hypothesis – I believe that exposing plants to air pollution will affect their growth.
- Simple Motor
Hypothesis – I predict that I can build a simple motor that turns when an electric current flows through it.
- Lemon Battery Voltage
Hypothesis – I expect that different fruits will produce varying amounts of electricity when used as batteries.
- Fireworks in a Jar
Hypothesis – I think that mixing oil and colored water will create a fireworks-like display in a jar.
- Bending Water with Static Electricity
Hypothesis – I predict that static electricity can bend a stream of water from a faucet.
- Soda Can Fizz
Hypothesis – I expect that dropping a mentos candy into a soda can will cause fizzing.
- Tornado Tube
Hypothesis – I believe that connecting two plastic bottles with a tornado tube will create a vortex.
- Magnetic Attraction and Distance
Hypothesis – I predict that magnets will attract objects from varying distances.
- Heat Absorption by Colors
Hypothesis – I think that objects of different colors will absorb heat differently under sunlight.
- Lemon Battery Power
Hypothesis – I expect that a lemon battery can power a small LED light.
- Strawberry DNA Extraction
Hypothesis – I believe I can extract DNA from strawberries using common household items.
- Marshmallow Density
Hypothesis – I predict that marshmallows of different shapes and sizes have different densities.
- Balloon-Powered Windmill
Hypothesis – I think a windmill with balloons will turn when exposed to air.
- Spinning Colors
Hypothesis – I expect that spinning a color wheel will create the illusion of blending colors.
- Sound and Vibration
Hypothesis – I predict that different objects will create different sounds when struck and vibrate differently.
- Rock Erosion
Hypothesis – I believe that different rocks will erode at varying rates when exposed to water.
- Air Pressure and Crushed Can
Hypothesis – I expect that changing air pressure will crush an empty can.
- Straw Flute
Hypothesis – I think that cutting and blowing through a straw can produce musical notes.
- Bottle Rocket
Hypothesis – I predict that a bottle rocket filled with water and pressurized air will launch into the air.
- Fruit Electricity
Hypothesis – I believe that different fruits can produce electricity using simple circuits.
- Melting Snow and Ice
Hypothesis – I expect that different substances can help melt snow and ice at varying rates.
- Plant Growth in Different Soils
Hypothesis – I think that different soils will affect the growth of plants differently.
- Static Electricity and Salt and Pepper
Hypothesis – I predict that salt and pepper can be moved with static electricity.
- Floating Paperclip
Hypothesis – I expect that surface tension can make a paperclip float on water.
- Crayon Melt Art
Hypothesis – I believe that crayons will melt and create art when heated.
- Balloon-Powered Hovercraft
Hypothesis – I predict that a hovercraft powered by balloons will glide over a smooth surface.
- Research Topics For Commerce Students
- Maths Project Ideas For College Students
Importance Of 5th Grade Science Project Ideas With Hypothesis For Students
In this section, we will discuss the importance of 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis for students:
1. Hands-On Learning
5th-grade science projects with hypotheses offer students a chance to learn through doing. They get to experiment, make predictions, and see the real-world results. This hands-on approach helps students grasp scientific concepts better.
2. Critical Thinking
These projects encourage critical thinking. Students have to come up with educated guesses (hypotheses) and then analyze their experiments’ outcomes. It teaches them to think logically and solve problems.
3. Curiosity and Exploration
Science projects fuel curiosity. They allow students to explore topics they find interesting, making learning more engaging. This curiosity can spark a lifelong interest in science.
4. Application of Knowledge
The things that students have learned in school can be used in real life. It helps them understand that science is not just in books, but all around them. This makes their education more useful.
5. Confidence Building
Successfully completing a science project with a hypothesis can boost a student’s confidence. They see that they can tackle challenging tasks and find solutions. This confidence can extend to other areas of their education and life.
Understanding what makes a good hypothesis is the first step in any 5th-grade science project with a hypothesis. It’s all about making educated guesses and having clear if-then statements. Remember to choose a project that matches your interest, is safe, and fits your grade level. With over 120 exciting 5th-grade science project ideas with hypothesis, you have a world of possibilities to explore.
Moreover, these projects offer hands-on learning, boost critical thinking, and ignite curiosity. They let you apply what you’ve learned in school to real life. Completing these projects can build your confidence, showing that you can tackle challenges and make discoveries. So, dive into the world of 5th-grade science project ideas with hypothesis and start your exciting scientific journey!
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
5th Grade Science Project Ideas with Hypothesis

Are you a 5th grader on a quest to discover the wonders of science? Well, you’re in luck! We’ve compiled a list of the top 100 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis to help you embark on your scientific journey. These projects are not only fun but also educational, giving you the opportunity to learn while having a blast.
Science projects are a great way to explore your curiosity, test hypotheses, and better understand the world around you. So, let’s dive right into our list of exciting science project ideas and start making hypotheses!
Top 100 5th Grade Science Project Ideas with Hypothesis
1. The Color-Changing Milk Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing milk, dish soap, and food coloring will create a mesmerizing display of color.
2. The Vinegar and Baking Soda Volcano Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: When vinegar reacts with baking soda, it will create a volcanic eruption.
3. The Seed Germination Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different types of seeds will germinate at different rates.
4. The Balloon Rocket Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Launching a balloon rocket will demonstrate Newton’s third law of motion.
5. The Lemon Battery Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A lemon can be used to generate electricity and power a small LED light.
6. The Egg Drop Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Creating a protective structure for an egg will prevent it from breaking when dropped from a height.
7. The Water Cycle in a Bag Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: By creating a closed system in a bag, you can observe the water cycle in action.
8. The Solar System Model Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Building a model of the solar system will help understand the arrangement of planets and their sizes.
9. The Density Tower Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Liquids with different densities can be layered in a container, forming a colorful tower.
10. The Magnetic Slime Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing magnetic particles with slime will result in a magnetic slime that can be controlled with a magnet.
11. The Paper Airplane Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different designs of paper airplanes will have different flight patterns.
12. The Rainbow in a Jar Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Layering liquids of different densities in a jar will create a colorful rainbow effect.
13. The Homemade Compass Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A homemade compass can accurately determine the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field.
14. The Germs on Surfaces Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different surfaces may harbor varying amounts of germs, and some may be cleaner than others.
15. The Pendulum Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: The length of a pendulum affects the time it takes to swing back and forth.
16. The Water Filtration Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Various materials can be used to filter dirty water and make it clean.
17. The Lava Lamp Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing oil and water with food coloring will create a mesmerizing “lava lamp” effect.
18. The Static Electricity Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Rubbing balloons against different materials will generate static electricity and make objects cling to them.
19. The Rainbow Paper Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Water and sunlight can combine to create a stunning rainbow on white paper.
20. The Music and Plant Growth Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Playing different types of music to plants will affect their growth patterns.
21. The Vinegar and Eggshell Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Soaking an eggshell in vinegar will demonstrate the effects of acid on calcium.
22. The Moldy Bread Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Bread exposed to different conditions will develop mold at varying rates.
23. The Potato Battery Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Potatoes can be used to generate electricity and power a small digital clock.
24. The Dissolving Candy Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different types of candy will dissolve at varying speeds in water.
25. The Osmosis in Gummy Bears Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Gummy bears placed in different solutions will absorb or release water, changing their size.
26. The Melting Ice Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Various substances, such as salt or sugar, can be used to melt ice at different rates.
27. The Color-Changing Carnations Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Carnations can absorb colored water, changing the color of their petals.
28. The Rock Candy Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Crystals can be grown on a string by dissolving sugar in water.
29. The Invisible Ink Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Writing with invisible ink will reveal a hidden message when exposed to heat.
30. The Magic Milk Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Swirling dish soap on the surface of milk will create beautiful, colorful patterns.
31. The Egg in a Bottle Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: An egg can be placed inside a bottle without breaking it using heat and air pressure.
32. The Popcorn Popping Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Popcorn kernels will pop when heated due to the buildup of pressure inside.
33. The Density of Liquids Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different liquids have different densities, which can be determined by their ability to float or sink in each other.
34. The Lemonade Stand Profit Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Running a lemonade stand on different days will yield varying levels of profit.
35. The Homemade Stethoscope Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A homemade stethoscope can be used to listen to different sounds within the body.
36. The Salt and Ice Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Salt can be used to lower the freezing point of ice, allowing you to create ice sculptures.
37. The pH of Household Substances Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different household substances will have varying pH levels, and they can be tested using pH strips.
38. The Rainbow Fire Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Burning different metal salts will produce colorful flames.
39. The Raisins and Soda Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Raisins placed in a glass of soda will exhibit a dancing effect as they move up and down.
40. The Paper Chromatography Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different colors in markers can be separated by capillary action on paper.
41. The Slime Time Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing glue and Borax solution will create a stretchy, gooey slime.
42. The Skittles Rainbow Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Placing different colored Skittles in water will create a colorful rainbow pattern.
43. The Magic Sand Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Magic sand repels water and can be used to create underwater structures.
44. The Baking Soda and Vinegar Balloons Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Inflating balloons with the gas produced by the reaction between baking soda and vinegar.
45. The Water and Oil Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Water and oil do not mix, and their separation can be observed in a homemade lava lamp.
46. The Solar Oven Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A homemade solar oven can be used to cook food using sunlight.
47. The Fizzing Lemonade Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing lemonade with baking soda will create a fizzing, carbonated drink.
48. The Magnet Maze Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Creating a maze with hidden magnets and using a magnetic wand will lead to exciting discoveries.
49. The Glow-in-the-Dark Slime Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Glow-in-the-dark paint can be added to slime to make it illuminate in the dark.
50. The Crystal Snowflakes Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Borax crystals can be grown on pipe cleaners in the shape of snowflakes.
51. The Wind Speed Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different shapes and sizes of windmills will affect the speed at which they spin.
52. The Paper Towel Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Paper towels from different brands will have varying absorption capabilities.
53. The Fruit Battery Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Various fruits can be used to generate electricity and power a small LED light.
54. The Growing Beans Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Growing beans under different conditions, like sunlight and water, will affect their growth.
55. The Mentos and Soda Explosion Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Dropping Mentos candy into soda will create a spectacular eruption.
56. The Tooth Decay Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different drinks will lead to varying levels of tooth decay when teeth are soaked in them.
57. The Rainbow Sugar Water Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Sugar water can be used to create colorful rainbow layers.
58. The Fingerprint Analysis Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Each person’s fingerprint is unique, and it can be analyzed and compared.
59. The Oil Spill Cleanup Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different materials can be used to clean up an oil spill, and their effectiveness can be tested.
60. The pH of Soil Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different types of soil will have varying pH levels, which can affect plant growth.
61. The Lemon Juice Clock Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Lemon juice can be used to power a clock with the help of electrodes.
62. The Separation of Mixtures Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Various mixtures can be separated into their individual components using different methods.
63. The Soundproofing Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different materials can be used to soundproof a room, and their effectiveness can be tested.
64. The Potato Clock Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Potatoes can be used to power a clock with the help of electrodes.
65. The Growing Crystals Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing water and sugar or salt will result in the formation of crystals.
66. The Toothpick Bridge Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Building bridges with toothpicks and glue will demonstrate the principles of engineering and physics.
67. The Egg Floatation Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: The density of water can be changed by adding salt, causing an egg to float.
68. The Homemade Lava Lamp Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A homemade lava lamp can be created using oil, water, and an effervescent tablet.
69. The Cornstarch and Water Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing cornstarch and water will create a substance that behaves like both a solid and a liquid.
70. The Magnetic Field Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different objects will be attracted or repelled by a magnet’s magnetic field.
71. The Coin Cleaning Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Various methods can be used to clean old, tarnished coins.
72. The Paper Bridge Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Building bridges with sheets of paper will test their strength and weight-bearing capacity.
73. The Homemade Volcano Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A homemade volcano model can erupt with the help of baking soda and vinegar.
74. The Earthquake Simulation Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Simulating an earthquake by shaking a container of sand will demonstrate the principles of seismic activity.
75. The Water Surface Tension Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different liquids will affect the surface tension of water, causing objects to float or sink.
76. The Vinegar and Egg Experiment Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Soaking an egg in vinegar will cause it to swell and change in texture.
77. The Fireproof Balloon Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A balloon can be made fireproof by filling it with water.
78. The Rainbow Fireworks Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Burning different metal salts will create a beautiful and colorful fireworks display.
79. The Mystery Substance Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A mystery substance can be identified by testing its properties, such as solubility and conductivity.
80. The Geyser Eruption Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing Mentos candy with soda will create a geyser-like eruption.
81. The Floating Orange Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: An orange can be made to float in water by changing the amount of salt in the water.
82. The Paper Cup Telephone Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A simple telephone can be made using two paper cups and string, allowing for communication over a distance.
83. The Ice Cube Race Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different shapes of ice cubes will melt at varying rates.
84. The Lemon Volcano Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: A lemon can be turned into a volcano by adding baking soda and creating a fizzy eruption.
85. The Light and Plant Growth Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Plants require different amounts of light for growth, and this can be tested using different light sources.
86. The Raisin Dance Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Raisins will “dance” in a glass of soda due to the carbonation.
87. The Rainbow Density Tower Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Liquids with different densities can be layered in a container, forming a colorful density tower.
88. The Rainbow Slime Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing various colors of slime will create a mesmerizing rainbow effect.
89. The Static Electricity Balloons Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Rubbing balloons against different materials will generate static electricity, making them cling to each other.
90. The Solar Eclipse Model Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Building a model of a solar eclipse will help understand the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
91. The Chemical Reaction Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Mixing two or more chemicals will result in a visible chemical reaction.
92. The Heat Conduction Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Different materials will conduct heat at varying rates, which can be tested using a hot plate.
93. The Acid Rain Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Simulating acid rain by spraying vinegar on plant leaves will show its harmful effects.
94. The Growing Gummy Bears Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Gummy bears placed in water will absorb it, growing in size.
95. The Weather Forecast Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Creating a homemade weather station will allow you to predict the weather based on observations.
96. The Colorful Ice Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Adding food coloring to water before freezing it will result in colorful ice cubes.
97. The Crystal Garden Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Growing crystals in a container filled with a super-saturated solution will create a crystal garden.
98. The Colorful Eggshells Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Coloring eggshells with different substances will create vibrant, colorful shells.
99. The Balancing Act Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Creating a balance scale with household items will help understand the concept of weight and balance.
100. The Invisible Force Hypothesis:
Hypothesis: Demonstrating the force of magnetism by testing objects for their magnetic properties.
Final Words
These are just a few of the exciting 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis. Remember that the key to a successful science project is to start with a clear hypothesis, conduct experiments carefully, and document your findings. Whether you’re exploring the mysteries of chemistry, physics, biology, or environmental science, these projects are a fantastic way to learn and have fun at the same time.
So, gather your materials, make your hypotheses, and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of science. Who knows, you might even discover something new and groundbreaking along the way!
Related Posts

Top 10 Easy ways to improve programming skills for beginners
Programming skillsProgramming is a mixture of several skills which means it is not probable to study it in a speedy Period, relatively it will come…

How to Hire someone to do my Statistics Homework for Me?
Students ask to do my statistics homework for me. Although there are many online tutors or statistics homework service providing websites available to help you…
Science Fair Wizard
- Pick a topic
- Determine a problem
- Investigate your problem
- Formulate a hypothesis
Experimenting
- Define the problem
- Select your variables
- Draft your hypothesis
- Write your procedure
- Get permissions
- Test your hypothesis
- Compile your data
- Write your research paper
- Construct your exhibit
- Prepare your presentation
- Show Time! Pre-science fair checklist
- Submit your paperwork

Step 5C: Draft your hypothesis
Your draft hypothesis statement should include the following:
- the question or problem you are trying to answer;
- how the independent variable will be changed;
- the measurable or testable effect it will have on the dependent variable ;
- and your best guess as to what you think the outcome will be.
Use the space on the Experiment Design Worksheet to draft your hypothesis statement.
Tip: A hypothesis problem can be stated in different ways. Here are some examples:
As a question: Does temperature affect the rate of plant growth? As a statement: Temperature may affect the rate of plant growth. As an if/then statement: If temperature is related to the rate of plant growth, then changing the temperature will change the rate of plant growth.
A hypothesis is a statement that predicts the outcome of your experiment, and is informed by the research you have done on your topic.
The digital library project
- Most Recent
- Free Silly Handwriting
- Easy Sub Plans Template
- Sprinkle Topped Shop
- My TpT Shop
- Amazon Favorites
- Free Video Series
The Sprinkle Topped Teacher

7 Easy Scientific Method Experiments
Kids’ natural curiosity never fails to amaze me. Their imaginations and observation skills run wild, especially at the elementary level. And the classroom is the perfect place to explore and exercise their curious minds!
When it comes to introducing younger students to scientific concepts like drawing observations and conclusions, the scientific method is a great place to start. It doesn’t have to be anything crazy. I’ve seen some pretty intense resources that teach the scientific method for kids, and they’ve been anything but kid friendly!
My preferred way to teach science is to boil the scientific method down to these 5 steps:
- Asking a research question
- Making a hypothesis
- Doing the experiment
- Taking observations
- Writing a conclusion
Keeping the scientific method for kids simple lets them explore their world without confusing them too much. When it comes to science concepts, we want to ease younger students in — not overwhelm them. This helps kids build a love of science that will last their whole lives!
With all that being said, I’ve gathered my favorite easy scientific method experiments for younger students into one bundle for you! These 7 Easy Science Experiments to Teach the Scientific Method are amazing because they all follow the same framework. This helps students know what to expect when it’s time to experiment and keeps your curriculum cohesive. Once we do one or two, my class gets into a nice groove and doesn’t need much direction on my part.
Plus, each of these experiments are available in a digital format, so they’re perfect for in-person or distance learning! And since they are so easy for students to follow, students will have no problem completing them at home.
What are the 7 easy scientific method experiments?
I’m glad you asked! Here is everything that is included in the scientific method for kids bundle:
1. Rainbow Milk Experiment
In the Rainbow Milk Magic Experiment, students will combine milk, dish soap, and food coloring to learn all about why the colors begin to swirl and look as if they are exploding into a rainbow. This is such a simple science experiment that works great with students of any age!

2. Tornado in a Bottle Experiment
This Tornado in a Bottle Experiment is the perfect way to teach the scientific method to kids. Students will practice measuring to fill a water bottle, then add dish soap and of course some glitter! They will then create a vortex to simulate a tornado and learn all about tornadoes.

3. Fingerprint Science Experiment
In the Fingerprint Science Experiment, students will become detectives and investigate their fingerprints while learning about the scientific method! This STEM fingerprint science experiment will cover the three types of fingerprints and super fun facts about fingerprints in humans and animals.

4. Marshmallow Toothpick Tower Science Experiment
The Marshmallow Toothpick Tower Science Experiment teaches students about building structures. They get to build their own masterpieces with marshmallows and toothpicks. As a bonus, this one ends in a tasty snack that students can enjoy!

5. Coffee Filter Digital Science Experiment
Students will learn about pigment and chromatography through this engaging experiment. They will get to draw a picture on a coffee filter using markers and observe what happens when it is sprayed with water. This is a fantastic way to introduce students to the concept of chemistry!

6. Slime Experiment
What kid doesn’t love slime?! This fun experiment lets them make their own with just a few household supplies. I love using this one during Halloween — it’s got the perfect spooky vibe!

7. Clean a Dirty Penny Science Experiment
Students love to collect and bring in a dirty penny for this science experiment. Students discover which cleaning solution works best to clean it and why using the scientific method! All you need are pennies, water, dish soap, salt, and vinegar. It’s a great option for Presidents’ Day, too!

What’s included in each scientific method for kids experiment?
I recently edited this bundle of experiments to include a table of contents, digital versions on Google Slides, and some great teacher tips to help your experiments run smoothly and make life easier for you. Each experiment includes…
● Explanation of the experiment, great for parents to follow at home!
● Guiding Question and Hypothesis
● Experiment (Picture and written)
● Observations (Picture and written)
● Conclusion
● The science behind the experiment explained (includes fill in the blank option as well)
There you have it: everything you need to teach the scientific method to your students or a child at home!
Teaching the scientific method to kids doesn’t have to be complicated. It’s best to stick to 5 steps and use the same experimental format to keep science lessons cohesive. My 7 Easy Science Experiments to Teach the Scientific Method are an amazing option for anyone looking to introduce students to key STEM concepts!
How often do you experiment in your classroom? What’s your favorite experiment to do? I’d love to hear your thoughts!
Share this:
You may also like, the 20 minute sub plan checklist, low-prep, easy st. patrick’s day activity, amazon favorites for the classroom part 2, 2nd grade fractions activity, number search puzzle for fun multiplication and division practice.
What is a hypothesis?
No. A hypothesis is sometimes described as an educated guess. That's not the same thing as a guess and not really a good description of a hypothesis either. Let's try working through an example.
If you put an ice cube on a plate and place it on the table, what will happen? A very young child might guess that it will still be there in a couple of hours. Most people would agree with the hypothesis that:
An ice cube will melt in less than 30 minutes.
You could put sit and watch the ice cube melt and think you've proved a hypothesis. But you will have missed some important steps.
For a good science fair project you need to do quite a bit of research before any experimenting. Start by finding some information about how and why water melts. You could read a book, do a bit of Google searching, or even ask an expert. For our example, you could learn about how temperature and air pressure can change the state of water. Don't forget that elevation above sea level changes air pressure too.
Now, using all your research, try to restate that hypothesis.
An ice cube will melt in less than 30 minutes in a room at sea level with a temperature of 20C or 68F.
But wait a minute. What is the ice made from? What if the ice cube was made from salt water, or you sprinkled salt on a regular ice cube? Time for some more research. Would adding salt make a difference? Turns out it does. Would other chemicals change the melting time?
Using this new information, let's try that hypothesis again.
An ice cube made with tap water will melt in less than 30 minutes in a room at sea level with a temperature of 20C or 68F.
Does that seem like an educated guess? No, it sounds like you are stating the obvious.
At this point, it is obvious only because of your research. You haven't actually done the experiment. Now it's time to run the experiment to support the hypothesis.
A hypothesis isn't an educated guess. It is a tentative explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation.
Once you do the experiment and find out if it supports the hypothesis, it becomes part of scientific theory.
Notes to Parents:
- Every parent must use their own judgment in choosing which activities are safe for their own children. While Science Kids at Home makes every effort to provide activity ideas that are safe and fun for children it is your responsibility to choose the activities that are safe in your own home.
- Science Kids at Home has checked the external web links on this page that we created. We believe these links provide interesting information that is appropriate for kids. However, the internet is a constantly changing place and these links may not work or the external web site may have changed. We also have no control over the "Ads by Google" links, but these should be related to kids science and crafts. You are responsible for supervising your own children. If you ever find a link that you feel is inappropriate, please let us know.
Kids Science Gifts Science Experiments Science Fair Projects Science Topics Creative Kids Blog
Kids Crafts Privacy Policy Copyright © 2016 Science Kids at Home, all rights reserved.
Hypothesis For Kids
Crafting a hypothesis isn’t just for scientists in white lab coats; even young budding researchers can join in the fun! When kids learn to frame their curious wonders as hypothesis statements, they pave the way for exciting discoveries. Our guide breaks down the world of hypothesis writing into kid-friendly chunks, complete with relatable thesis statement examples and easy-to-follow tips. Dive in to spark a love for inquiry and nurture young scientific minds!
What is an example of a Hypothesis for Kids?
Question: Do plants grow taller when they are watered with coffee instead of water?
Hypothesis: If I water a plant with coffee instead of water, then the plant will not grow as tall because coffee might have substances that aren’t good for plants.
This hypothesis is based on a simple observation or question a child might have, and it predicts a specific outcome (the plant not growing as tall) due to a specific condition (being watered with coffee). It’s presented in simple language suitable for kids.
100 Kids Hypothesis Statement Examples

Size: 170 KB
Children’s innate curiosity lays the foundation for numerous questions about the world around them. Framing these questions as good hypothesis statements can transform them into exciting learning experiments. Presented below are relatable and straightforward examples crafted especially for young minds, offering them a structured way to articulate their wonders and predictions.
- Sunlight & Plant Growth : If a plant gets more sunlight, then it will grow taller.
- Sugary Drinks & Tooth Decay : Drinking sugary drinks daily will lead to faster tooth decay.
- Chocolates & Energy : Eating chocolate will make me feel more energetic.
- Moon Phases & Sleep : I’ll sleep more during a full moon night.
- Homework & Weekend Moods : If I finish my homework on Friday, I’ll be happier over the weekend.
- Pets & Happiness : Owning a pet will make a child happier.
- Rain & Worms : Worms come out more after it rains.
- Shadows & Time of Day : Shadows are longer in the evening than at noon.
- Snow & School Holidays : More snow means there’s a better chance of school being canceled.
- Ice Cream & Brain Freeze : Eating ice cream too fast will give me a brain freeze.
- Video Games & Dreams : Playing video games before bed might make my dreams more vivid.
- Green Vegetables & Strength : Eating more green vegetables will make me stronger.
- Bicycles & Balance : The more I practice, the better I’ll get at riding my bike without training wheels.
- Stars & Wishes : If I wish on the first star I see at night, my wish might come true.
- Cartoons & Laughing : Watching my favorite cartoon will always make me laugh.
- Soda & Bone Health : Drinking soda every day will make my bones weaker.
- Beach Visits & Sunburn : If I don’t wear sunscreen at the beach, I’ll get sunburned.
- Loud Noises & Pet Behavior : My cat hides when she hears loud noises.
- Bedtime & Morning Energy : Going to bed early will make me feel more energetic in the morning.
- Healthy Snacks & Hunger : Eating a healthy snack will keep me full for longer. …
- Toys & Sharing : The more toys I have, the more I want to share with my friends.
- Homemade Cookies & Taste : Homemade cookies always taste better than store-bought ones.
- Books & Imagination : The more books I read, the more adventures I can imagine.
- Jumping & Height : The more I practice, the higher I can jump.
- Singing & Mood : Singing my favorite song always makes me happy.
- Snowmen & Temperature : If the temperature rises, my snowman will melt faster.
- Costumes & Play : Wearing a costume will make playtime more fun.
- Gardening & Patience : Waiting for my plants to grow teaches me patience.
- Night Lights & Sleep : Having a night light makes it easier for me to sleep.
- Handwriting & Practice : The more I practice, the better my handwriting will become.
- Painting & Creativity : Using more colors in my painting lets me express my creativity better.
- Puzzles & Problem Solving : The more puzzles I solve, the better I become at problem-solving.
- Dancing & Coordination : The more I dance, the more coordinated I will become.
- Stargazing & Constellations : If I stargaze every night, I’ll recognize more constellations.
- Bird Watching & Species Knowledge : The more I watch birds, the more species I can identify.
- Cooking & Skill : If I help in the kitchen often, I’ll become a better cook.
- Swimming & Confidence : The more I swim, the more confident I become in the water.
- Trees & Birds’ Nests : The taller the tree, the more likely it is to have birds’ nests.
- Roller Skating & Balance : If I roller skate every weekend, I’ll improve my balance.
- Drawing & Observation : The more I draw, the better I become at observing details.
- Sandcastles & Water : If I use wet sand, I can build a stronger sandcastle.
- Hiking & Endurance : The more I hike, the farther I can walk without getting tired.
- Camping & Outdoor Skills : If I go camping often, I’ll learn more about surviving outdoors.
- Magic Tricks & Practice : The more I practice a magic trick, the better I’ll get at performing it.
- Stickers & Collection : If I collect stickers, my album will become more colorful.
- Board Games & Strategy : The more board games I play, the better strategist I’ll become.
- Pets & Responsibility : The more I take care of my pet, the more responsible I become.
- Music & Concentration : Listening to calm music while studying will help me concentrate better.
- Photographs & Memories : The more photos I take, the more memories I can preserve.
- Rainbows & Rain : If it rains while the sun is out, I might see a rainbow.
- Museums & Knowledge : Every time I visit a museum, I learn something new.
- Fruits & Health : Eating more fruits will keep me healthier.
- Stories & Vocabulary : The more stories I listen to, the more new words I learn.
- Trees & Fresh Air : The more trees there are in a park, the fresher the air will be.
- Diary & Feelings : Writing in my diary helps me understand my feelings better.
- Planets & Telescopes : If I look through a telescope, I’ll see more planets clearly.
- Crafting & Creativity : The more crafts I make, the more creative I become.
- Snowflakes & Patterns : Every snowflake has a unique pattern.
- Jokes & Laughter : The funnier the joke, the louder I’ll laugh.
- Riddles & Thinking : Solving riddles makes me think harder.
- Nature Walks & Observations : The quieter I am on a nature walk, the more animals I’ll spot.
- Building Blocks & Structures : The more blocks I use, the taller my tower will be.
- Kites & Wind : If there’s more wind, my kite will fly higher.
- Popcorn & Movie Nights : Watching a movie with popcorn makes it more enjoyable.
- Stars & Wishes : If I see a shooting star, I should make a wish.
- Diets & Energy : Eating a balanced diet gives me more energy for playtime.
- Clay & Sculptures : The more I play with clay, the better my sculptures will be.
- Insects & Magnifying Glass : Using a magnifying glass will let me see more details of tiny insects.
- Aquarium Visits & Marine Knowledge : Every time I visit the aquarium, I discover a new marine creature.
- Yoga & Flexibility : If I practice yoga daily, I’ll become more flexible.
- Toothpaste & Bubbles : The more toothpaste I use, the more bubbles I’ll get while brushing.
- Journals & Memories : Writing in my journal every day helps me remember special moments.
- Piggy Banks & Savings : The more coins I save, the heavier my piggy bank will get.
- Baking & Measurements : If I measure ingredients accurately, my cake will turn out better.
- Coloring Books & Art Skills : The more I color, the better I get at staying inside the lines.
- Picnics & Outdoor Fun : Having a picnic makes a sunny day even more enjoyable.
- Recycling & Environment : The more I recycle, the cleaner my environment will be.
- Treasure Hunts & Discoveries : Every treasure hunt has a new discovery waiting.
- Milk & Bone Health : Drinking milk daily will make my bones stronger.
- Puppet Shows & Stories : The more puppet shows I watch, the more stories I learn.
- Field Trips & Learning : Every field trip to a new place teaches me something different.
- Chores & Responsibility : The more chores I do, the more responsible I feel.
- Fishing & Patience : Fishing teaches me to be patient while waiting for a catch.
- Fairy Tales & Imagination : Listening to fairy tales expands my imagination.
- Homemade Pizza & Toppings : The more toppings I add, the tastier my homemade pizza will be.
- Gardens & Butterflies : If I plant more flowers, I’ll see more butterflies in my garden.
- Raincoats & Puddles : Wearing a raincoat lets me jump in puddles without getting wet.
- Gymnastics & Balance : The more I practice gymnastics, the better my balance will be.
- Origami & Craft Skills : The more origami I fold, the better my craft skills become.
- Basketball & Shooting Skills : The more I practice, the better I get at shooting baskets.
- Fireflies & Night Beauty : Catching fireflies makes summer nights magical.
- Books & Knowledge : The more books I read, the smarter I become.
- Pillows & Forts : With more pillows, I can build a bigger fort.
- Lemonade & Summers : Drinking lemonade makes hot summer days refreshing.
- Bicycles & Balance : The more I practice, the better I get at riding my bike without training wheels.
- Pencils & Drawings : If I have colored pencils, my drawings will be more colorful.
- Ice Cream & Happiness : Eating ice cream always makes me happy.
- Beach Visits & Shell Collections : Every time I visit the beach, I find new shells for my collection.
- Jump Ropes & Fitness : The more I jump rope, the fitter I become.
- Tea Parties & Imagination : Hosting tea parties lets my imagination run wild.
Simple Hypothesis Statement Examples for Kids
Simple hypothesis are straightforward predictions that can be tested easily. They help children understand the relationship between two variables. Here are some examples tailored just for kids.
- Plants & Sunlight : Plants placed near the window will grow taller than those in the dark.
- Chocolates & Happiness : Eating chocolates can make kids feel happier.
- Rain & Puddles : The more it rains, the bigger the puddles become.
- Homework & Learning : Doing homework helps kids understand lessons better.
- Toys & Sharing : Sharing toys with friends makes playtime more fun.
- Pets & Care : Taking care of a pet fish helps it live longer.
- Storytime & Sleep : Listening to a bedtime story helps kids sleep faster.
- Brushing & Cavity : Brushing teeth daily prevents cavities.
- Games & Skill : Playing a new game every day improves problem-solving skills.
- Baking & Patience : Waiting for cookies to bake teaches patience.
Hypothesis Statement Examples for Kids Psychology
Child psychology hypothesis delves into how kids think, behave, and process emotions. These hypotheses help understand the psychological aspects of children’s behaviors.
- Emotions & Colors : Kids might feel calm when surrounded by blue and energetic with red.
- Friendship & Self-esteem : Making friends can boost a child’s self-confidence.
- Learning Styles & Memory : Some kids remember better by seeing, while others by doing.
- Play & Development : Pretend play is crucial for cognitive development.
- Rewards & Motivation : Giving small rewards can motivate kids to finish tasks.
- Music & Mood : Listening to soft music can calm a child’s anxiety.
- Sibling Bonds & Sharing : Having siblings can influence a child’s willingness to share.
- Feedback & Performance : Positive feedback can improve a kid’s academic performance.
- Outdoor Play & Attention Span : Playing outside can help kids concentrate better in class.
- Dreams & Reality : Kids sometimes can’t differentiate between dreams and reality.
Hypothesis Examples in Kid Friendly Words
Phrasing hypothesis in simple words makes it relatable and easier for kids to grasp. Here are examples with kid-friendly language.
- Socks & Warmth : Wearing socks will keep my toes toasty.
- Jumping & Energy : The more I jump, the more energy I feel.
- Sandcastles & Water : A little water makes my sandcastle stand tall.
- Stickers & Smiles : Getting a sticker makes my day shine brighter.
- Rainbows & Rain : After the rain, I might see a rainbow.
- Slides & Speed : The taller the slide, the faster I go.
- Hugs & Love : Giving hugs makes me and my friends feel loved.
- Stars & Counting : The darker it is, the more stars I can count.
- Paint & Mess : The more paint I use, the messier it gets.
- Bubbles & Wind : If I blow my bubble wand, the wind will carry them high.
Hypothesis Statement Examples for Kids in Research
Even in a research setting, research hypothesis should be age-appropriate for kids. These examples focus on concepts children might encounter in structured studies.
- Reading & Vocabulary : Kids who read daily might have a richer vocabulary.
- Games & Math Skills : Playing number games can improve math skills.
- Experiments & Curiosity : Conducting science experiments can make kids more curious.
- Doodles & Creativity : Drawing daily might enhance a child’s creativity.
- Learning Methods & Retention : Kids who learn with visuals might remember lessons better.
- Discussions & Understanding : Talking about a topic can deepen understanding.
- Observation & Knowledge : Observing nature can increase a kid’s knowledge about the environment.
- Puzzles & Cognitive Skills : Solving puzzles regularly might enhance logical thinking.
- Music & Rhythmic Abilities : Kids who practice music might develop better rhythm skills.
- Teamwork & Social Skills : Group projects can boost a child’s social skills.
Hypothesis Statement Examples for Kids Science Fair
Science fairs are a chance for kids to delve into the world of experiments and observations. Here are hypotheses suitable for these events.
- Magnet & Metals : Certain metals will be attracted to a magnet.
- Plants & Colored Light : Plants might grow differently under blue and red lights.
- Eggs & Vinegar : An egg in vinegar might become bouncy.
- Solar Panels & Sunlight : Solar panels will generate more power on sunny days.
- Volcanoes & Eruptions : Mixing baking soda and vinegar will make a mini eruption.
- Mirrors & Reflection : Shiny surfaces can reflect light better than dull ones.
- Battery & Energy : Fresh batteries will make a toy run faster.
- Density & Floating : Objects with lower density will float in water.
- Shadows & Light Source : Moving the light source will change the shadow’s direction.
- Freezing & States : Water turns solid when kept in the freezer.
Hypothesis Statement Examples for Science Experiments
Experiments let kids test out their predictions in real-time. Here are hypotheses crafted for various scientific tests.
- Salt & Boiling Point : Adding salt will make water boil at a higher temperature.
- Plants & Music : Playing music might affect a plant’s growth rate.
- Rust & Moisture : Metals kept in a moist environment will rust faster.
- Candles & Oxygen : A candle will burn out faster in an enclosed jar.
- Fruits & Browning : Lemon juice can prevent cut fruits from browning.
- Yeast & Sugar : Adding sugar will make yeast activate more vigorously.
- Density & Layers : Different liquids will form layers based on their density.
- Acids & Bases : Red cabbage juice will change color in acids and bases.
- Soil Types & Water : Sandy soil will drain water faster than clay.
- Thermometers & Temperatures : Thermometers will show higher readings in the sun.
Hypothesis Statement Examples for Kids At Home
These hypotheses are crafted for experiments and observations kids can easily make at home, using everyday items.
- Chores & Time : Setting a timer will make me finish my chores faster.
- Pets & Behavior : My cat sleeps more during the day than at night.
- Recycling & Environment : Recycling more can reduce the trash in my home.
- Cooking & Tastes : Adding spices will change the taste of my food.
- Family Time & Bonding : Playing board games strengthens our family bond.
- Cleaning & Organization : Organizing my toys daily will keep my room tidier.
- Watering & Plant Health : Watering my plant regularly will keep its leaves green.
- Decor & Mood : Changing the room decor can influence my mood.
- Journals & Memories : Writing in my journal daily will help me remember fun events.
- Photos & Growth : Taking monthly photos will show how much I’ve grown.
How do you write a hypothesis for kids? – A Step by Step Guide
Step 1: Start with Curiosity Begin with a question that your child is curious about. This could be something simple, like “Why is the sky blue?” or “Do plants need sunlight to grow?”
Step 2: Observe and Research Before formulating the hypothesis, encourage your child to observe the world around them. If possible, read or watch videos about the topic to gather information. The idea is to get a general understanding of the subject.
Step 3: Keep it Simple For kids, it’s essential to keep the hypothesis straightforward and concise. Use language that is easy to understand and relatable to their age.
Step 4: Make a Predictable Statement Help your child frame their hypothesis as an “If… then…” statement. For example, “If I water a plant every day, then it will grow taller.”
Step 5: Ensure Testability Ensure that the hypothesis can be tested using simple experiments or observations. It should be something they can prove or disprove through hands-on activities.
Step 6: Avoid Certainty Teach kids that a hypothesis is not a definitive statement of fact but rather a best guess based on what they know. It’s okay if the hypothesis turns out to be wrong; the learning process is more important.
Step 7: Review and Refine After forming the initial hypothesis, review it with your child. Discuss if it can be made simpler or clearer. Refinement aids in better understanding and testing.
Step 8: Test the Hypothesis This is the fun part! Plan an experiment or set of observations to test the hypothesis. Whether the hypothesis is proven correct or not, the experience provides a learning opportunity.
Tips for Writing Hypothesis for Kids
- Encourage Curiosity : Always encourage your child to ask questions about the world around them. It’s the first step to formulating a hypothesis.
- Use Familiar Language : Use words that the child understands and can relate to. Avoid jargon or technical terms.
- Make it Fun : Turn the process of forming a hypothesis into a game or a storytelling session. This will keep kids engaged.
- Use Visual Aids : Kids often respond well to visuals. Drawing or using props can help in understanding and formulating the hypothesis.
- Stay Open-minded : It’s essential to teach kids that it’s okay if their hypothesis is wrong. The process of discovery and learning is what’s crucial.
- Practice Regularly : The more often kids practice forming hypotheses, the better they get at it. Use everyday situations as opportunities.
- Link to Real-life Scenarios : Relate the hypothesis to real-life situations or personal experiences. For instance, if discussing plants, you can relate it to a plant you have at home.
- Collaborate : Sometimes, two heads are better than one. Encourage group activities where kids can discuss and come up with hypotheses together.
- Encourage Documentation : Keeping a journal or notebook where they document their hypotheses and results can be a great learning tool.
- Celebrate Efforts : Regardless of whether the hypothesis was correct, celebrate the effort and the learning journey. This reinforces the idea that the process is more important than the outcome.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Science Fair Project Ideas for Kids, Middle & High School Students ⋅
How to Write a Hypothesis of Magic Milk for 5th Grade

Food Coloring & Science Projects
The “magic milk” experiment is a great way to introduce children to scientific experimentation, and also writing hypotheses. According to Steve Spangler’s “Color Changing Milk,” milk is a mixture of protein, fat and nutrients suspended in a mostly water solution. Food coloring, which dissipates in water, is held in place by the fat and protein in the milk. The fat and protein react to disruptions in the milk. The dish soap disrupts the chemical bonds that hold them in solution because it forms a bond with the fat. “The molecules of fat bend, roll, twist, and contort in all directions as the soap molecules race around to join up with the fat molecules.” This activity pushes the colors around. Students should write a hypothesis about what the soap will do to the food coloring in the milk before they perform the experiment.

Instruct students that a hypothesis is a statement that can be tested. According to Access Excellence, it should guess at “how two variables might be related,” in a testable way.

Define the variables in the experiment. Hypotheses are often formed from observations. It is helpful for students to observe how food coloring acts in water, milk and oil before they attempt to write a hypothesis. Teach them that soap bonds with oil and fat. This is how it cleans dirty dishes. The variables in this experiment are the soap and the food coloring.

Identify which variable is the independent variable and which is the dependent variable. Access Excellence defines these as, “the independent variable is the one you, the ‘scientist’ control and the dependent variable is the one that you observe and/or measure the results.” In this case, the soap is the independent variable and the food coloring is the dependent variable.

Using the two variables, form an “if, then” statement. If I add soap to the milk, then the food coloring will mix with the milk. Students should make their best guess; hypotheses don’t have to be correct, just testable.
Perform the experiment as indicated in Steve Spangler’s “Color Changing Milk,” but only dip the cotton swab in the milk once or twice.
Revise the hypothesis if you wish to give the experiment more depth. A more formal hypothesis thinks in terms of how the variables are related to each other. If soap can make food coloring mix with milk, then adding more soap to the milk in different places will cause the food coloring to mix with the milk faster.
Repeat the experiment using a fresh batch of milk and food coloring. Use multiple cotton swabs and stick them in different places.
Things You'll Need
This experiment can be furthered by expanding the medium being used. Try it with buttermilk or nonfat milk. Try using pepper instead of food coloring. Try it using a clean cotton swab or toothpick. Talk about surface tension.
Students should be warned that although food coloring is not toxic, dish soap can be. Do not drink milk that has soap in it.
Related Articles
The difference between research questions & hypothesis, science fair projects on milk & food coloring, a science fair project on smell affecting taste, how to neutralize food coloring in water, last-minute science fair project ideas, how to make homemade glue out of milk for a science..., how to explain math answers, what are the independent variables for a moldy bread..., how to measure carbonation in soft drinks for a science..., how to extract dna from oranges, easy kids' science fair experiments about germs, how to write a testable hypothesis, how to do cool science experiments with rubbing alcohol..., how to make a 1% sucrose solution, how to grow a plant from a bean as a science project, does ice melt faster in water or soda, science fair project on clouds, how does urea denature proteins, how to do a science project step-by-step.
- “Color Changing Milk” Steve Spangler
About the Author
A resident of New Mexico, Deborah Brenna has been writing since 2003. She is an expert in gardening, home improvement, cooking, science, medicine and the outdoors. Brenna has a Bachelor of Arts and Sciences in English from the University of New Mexico.
Photo Credits
BananaStock/BananaStock/Getty Images
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
We Have More Great Sciencing Articles!
Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an educated guess about what you think will happen in a scientific experiment, based on your observations. Before conducting the experiment, you propose a hypothesis so that you can determine if your prediction is supported.
There are several ways you can state a hypothesis, but the best hypotheses are ones you can test and easily refute. Why would you want to disprove or discard your own hypothesis? Well, it is the easiest way to demonstrate that two factors are related. Here are some good scientific hypothesis examples:
- Hypothesis: All forks have three tines. This would be disproven if you find any fork with a different number of tines.
- Hypothesis: There is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer. While it is difficult to establish cause and effect in health issues, you can apply statistics to data to discredit or support this hypothesis.
- Hypothesis: Plants require liquid water to survive. This would be disproven if you find a plant that doesn't need it.
- Hypothesis: Cats do not show a paw preference (equivalent to being right- or left-handed). You could gather data around the number of times cats bat at a toy with either paw and analyze the data to determine whether cats, on the whole, favor one paw over the other. Be careful here, because individual cats, like people, might (or might not) express a preference. A large sample size would be helpful.
- Hypothesis: If plants are watered with a 10% detergent solution, their growth will be negatively affected. Some people prefer to state a hypothesis in an "If, then" format. An alternate hypothesis might be: Plant growth will be unaffected by water with a 10% detergent solution.
- Scientific Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- Middle School Science Fair Project Ideas
- Effect of Acids and Bases on the Browning of Apples
- High School Science Fair Projects
- How to Write a Science Fair Project Report

- Kindergarten
- Middle School
- High School
- Math Worksheets
- Language Arts
- Social Studies
Hypothesis Examples
A hypothesis has classical been referred to as an educated guess. In the context of the scientific method, this description is somewhat correct. After a problem is identified, the scientist would typically conduct some research about the problem and then make a hypothesis about what will happen during his or her experiment. A better explanation of the purpose of a hypothesis is that a hypothesis is a proposed solution to a problem. Hypotheses have not yet been supported by any measurable data. In fact, we often confuse this term with the word theory in our everyday language. People say that they have theories about different situations and problems that occur in their lives but a theory implies that there has been much data to support the explanation. When we use this term we are actually referring to a hypothesis. For example, someone might say, "I have a theory about why Jane won't go out on a date with Billy." Since there is no data to support this explanation, this is actually a hypothesis. In the world of statistics and science, most hypotheses are written as "if...then" statements. For example someone performing experiments on plant growth might report this hypothesis: "If I give a plant an unlimited amount of sunlight, then the plant will grow to its largest possible size." Hypotheses cannot be proven correct from the data obtained in the experiment, instead hypotheses are either supported by the data collected or refuted by the data collected.
1. If I replace the battery in my car, then my car will get better gas mileage.
2. If I eat more vegetables, then I will lose weight faster.
3. If I add fertilizer to my garden, then my plants will grow faster.
4. If I brush my teeth every day, then I will not develop cavities.
5. If I take my vitamins every day, then I will not feel tired.
6. If 50 mL of water are added to my plants each day and they grow, then adding 100 mL of water each day will make them grow even more.
More Topics
- Handwriting
- Difference Between
- 2020 Calendar
- Online Calculators
- Multiplication
50 Fantastic 5th Grade Science Projects, Experiments, and Activities
For the classroom or science fair.

There’s something so fascinating about hands-on science experiments and projects. They make learning so meaningful and so much fun! These 5th grade science projects help kids explore biology, physics, chemistry, and a whole lot more. Try one at the 5th grade science fair, or use a few to liven up your lesson plans.
To make things even easier, we’ve rated every one of these 5th grade science projects based on difficulty and materials:
Difficulty:
- Easy: Low or no-prep experiments you can do pretty much anytime
- Medium: These take a little more setup or a longer time to complete
- Advanced: Experiments like these take a fairly big commitment of time or effort
- Basic: Simple items you probably already have around the house
- Medium: Items that you might not already have but are easy to get your hands on
- Advanced: These require specialized or more expensive supplies to complete
5th Grade Science Fair Projects
Stem challenge 5th grade science projects, 5th grade matter and energy science activities, more 5th grade science projects and activities.
Choosing a science fair project means finding a subject that really interests you and coming up with a unique question to answer. Use some of these 5th grade science fair project ideas to create a cool experiment all your own.
Stop soil erosion with plants
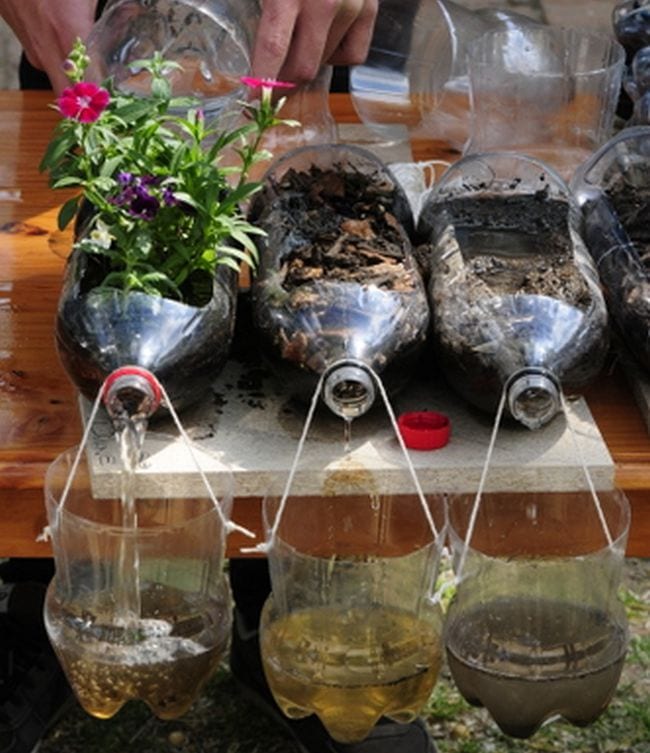

Difficulty: Medium / Materials: Medium
Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to natural disasters like landslides as well as causing problems for farmers, who lose valuable topsoil. Try this experiment to learn how plants help keep soil in place naturally, and change up the variables like soil composition or types of plants.
Learn more: Soil Erosion Experiment at Life Is a Garden
Blow square bubbles
Bubble science experiments are always a hit! In this one, kids construct a device to see if they can blow a square bubble instead of a round one.

Discover the delights of decomposition
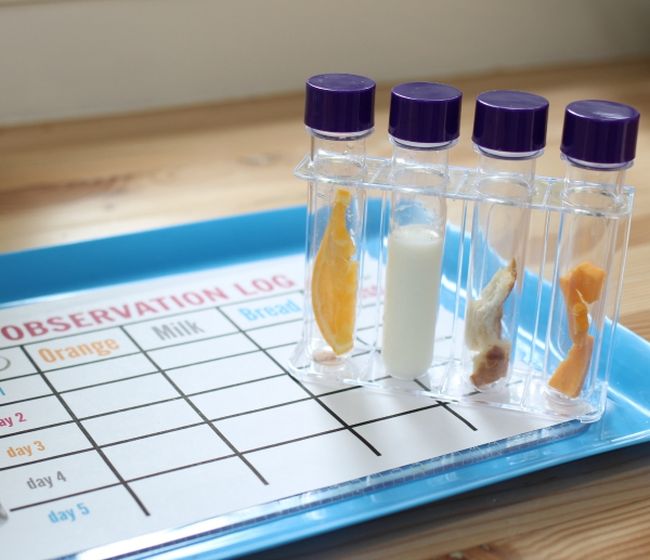
Difficulty: Easy / Materials: Medium
This is a good chance to apply the scientific method and practice your observation skills, using only basic kitchen supplies. Ask the question: “Which food will rot (decompose) the fastest?” Have students hypothesize, observe, and then report their findings. Get a printable observation sheet at the link below.
Learn more: Food Decomposition at No Time for Flash Cards
Mix up some magic sand

What if you could make sand that was “afraid” of water? This 5th grade science experiment uses waterproofing spray to create you-gotta-see-it-to-believe-it hydrophobic sand.
Learn more: Hydrophobic Sand at Teaching Mama
Make your own bouncy balls

Students learn about polymers as they mix borax with cornstarch, glue, and water in this playful experiment. Experiment with size, shape, and ingredients to see which work best.
Learn more: DIY Bouncy Balls at Babble Dabble Do
Study water filtration
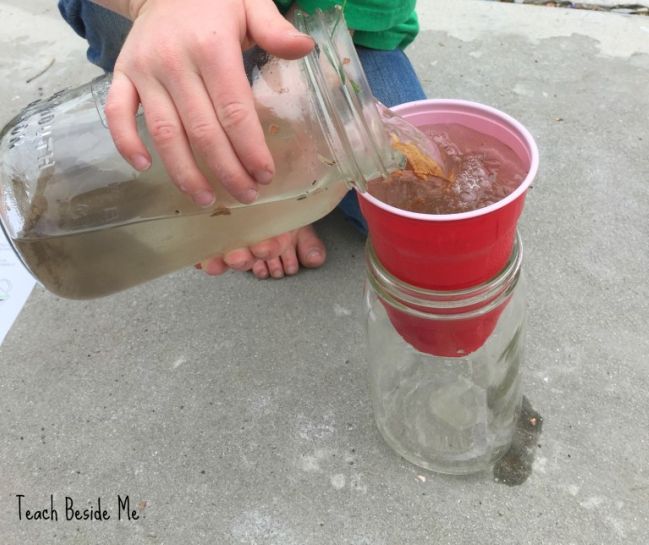

Difficulty: Easy / Materials: Basic
See the process of water purification firsthand. Layer coffee filters, sand, and gravel in the bottom of an empty cup punched with holes. Place the cup in an empty jar, pour in dirty water, and watch what happens. Mix up the variables, and you’ve got a cool 5th grade science fair project.
Learn more: Water Purification at Teach Beside Me
Find out if a dog’s mouth is cleaner than a human’s

Settle an age-old debate with this 5th grade science fair project. Collect saliva from both humans and canines with cotton swabs and place each sample in labeled petri dishes. Check the bacterial colonies in each and compare the results.
Learn more: Dog’s Mouth Project at Sciencing
Explore basic genetics

Send your students on a quest to find out more about their genes and inherited traits. The link below includes a printable chart they can use to learn about recessive and dominant genes.
Learn more: Inherited Traits at Education.com
Design a biosphere

This project really brings out kids’ creativity and helps them understand that everything in a biosphere is really part of one big whole. You’ll be overwhelmed by what they come up with!
Learn more: Biosphere Project at Laney Lee
Measure heat capacity of different liquids

Your students will venture into the world of chemistry with this experiment that tests the heat capacity of different liquids, such as salt water, olive oil, and liquid soap, using a hot plate . They’ll incorporate math into their experiment when they plot their results!
Learn more: Heat Capacity at Education.com
A good STEM challenge can spark a terrific science fair project too. These also make terrific classroom activities for 5th grade science students.
Assemble an automatic water fountain
Water fountains were around long before humans harnessed the power of electricity to make pumps. Learn how they worked with this STEM challenge science project for 5th grade.
Race down a LEGO zip line

Every kid loves LEGO bricks, so incorporate them into your 5th grade science activities! Challenge kids to design and build their own zip line. You can set the parameters, like distance and slope, then let students get to work.
Learn more: Zipline at 123 Homeschool 4 Me
Slow your roll
Ball-run challenges are always fun, but this one has a twist. Your goal is to build a run that gets the ball to the bottom taking the longest time possible! This requires kids to think about friction, slopes, and other creative features.
Fly clothespin airplanes

Put your 5th grade science students’ engineering skills to the test. Provide them with clothespins and wood craft sticks , and challenge them to build a realistic airplane. Bonus points if it can actually fly!
Learn more: Clothespin Airplane at STEAMsational
Spin a candle-powered pinwheel
Prove that hot air rises by using candles to spin a homemade pinwheel. Then experiment to see how the number of candles affects the spinning speed. (As always, make sure kids use fire under safe conditions.)
Set off a chain reaction
Learn about potential and kinetic energy when you try this cool 5th grade science experiment. All you need are wood craft sticks and a bit of patience.
Bounce on a trampoline

Kids love bouncing on trampolines, but can they build one themselves? Find out with this totally fun STEM challenge. Plus, check out more 5th grade STEM challenges here.
Learn more: Trampoline STEM Challenge at Student Savvy
Build a solar oven
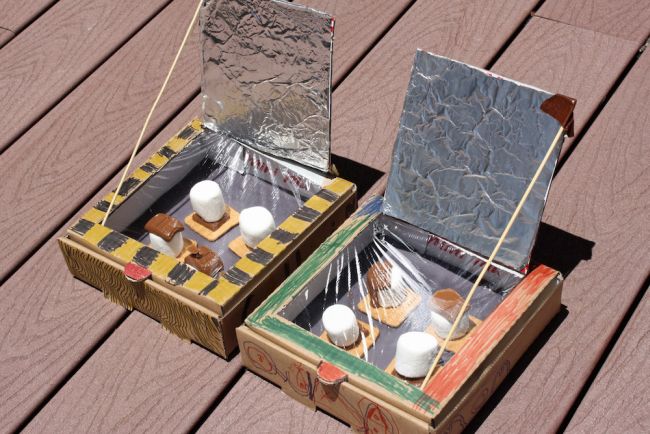

Learn about the value of solar energy by building an oven that cooks food without electricity. Enjoy your tasty treats while discussing ways we can harness the energy of the sun and why alternative energy sources are important. ( Love edible science projects? Get more ideas here. )
Learn more: DIY Solar Oven S’mores at Desert Chica
Launch your own bottle rocket
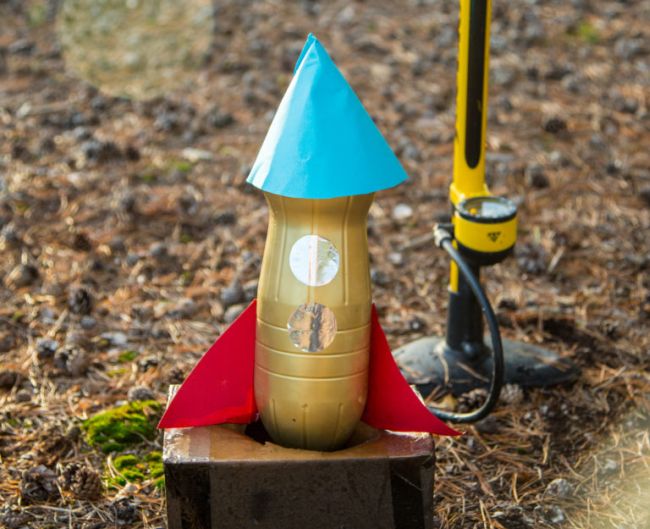

Blast off with a few supplies and a little help from the laws of motion. Encourage kids to design and decorate their rockets first and see which one can fly the highest!
Learn more: Bottle Rocket at Science Sparks
Peer through a cardboard microscope
Microscopes can be pricey, so make your own at home! This is the kind of 5th grade science fair project that will really wow the judges.
Build a snack machine

Incorporate everything students learn about simple machines into one project when you challenge them to build a snack machine! Using basic supplies, they’ll need to design and construct a machine that delivers snacks from one location to another. ( Get more candy experiments here. )
Learn more: Snack Machine Challenge at Left Brain Craft Brain
Use rubber bands to sound out acoustics

Explore the ways that sound waves are affected by what’s around them using a simple rubber band “guitar.” (Your students will absolutely love playing with these!)
Learn more: Rubber Band Guitar at Science Sparks
Assemble Archimedes’ screw
Difficulty: Medium / Materials: Basic
It’s amazing how often science looks like magic—until you understand the principles behind it. Such is the case with the simple pump known as Archimedes’ screw. It’s easy to build your own and makes for a cool 5th grade science fair project.
Recycle newspaper into an engineering challenge

It’s amazing how a stack of newspapers can spark such creative engineering. Challenge students to build a tower, support a book, or even build a chair using only newspaper and tape.
Learn more: Newspaper Tower at STEM Activities for Kids
Construct a sturdy bridge
To design a safe bridge that meets the needs of the community, engineers must understand the capabilities and limitations of the bridge. This project is great for budding 5th grade engineers as they simulate constructing a bridge that serves its purpose and keeps community members safe.
Every 5th grade science curriculum is different, but many include some common concepts. Learn about the states of matter, matter and its interactions, and energy science with these neat 5th grade activities.
Model the states of matter
Create simple models to show the arrangement of molecules in solids, liquids, and gasses. Ping-Pong balls are perfect for this. ( Find more states of matter activities here. )
Drink root beer floats
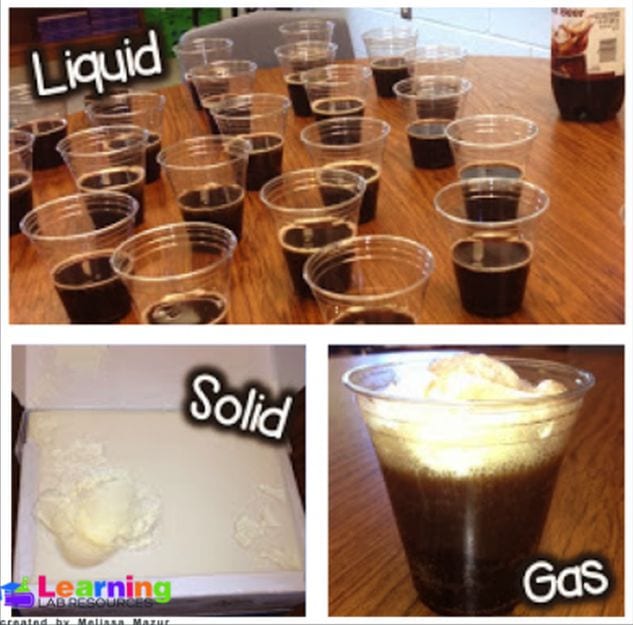

This is our favorite way to learn about the various states of matter! Treat time becomes a learning lesson with this 5th grade science matter activity.
Learn more: Teaching Matter With Root Beer Floats at Learning Lab Resources
Fill a bubble with dry ice vapor
Discover the science of sublimation by turning dry ice from a solid directly into a gas. Then play around with surface tension as the resulting vapor fills a giant bubble. This one is so cool to see in action!
Discover density with hot and cold water

There are a lot of cool science experiments you can do with density. This one is extremely simple, involving only hot and cold water and food coloring.
Learn more: Hot and Cold Water Density at STEAMsational
Learn to layer liquids

This density demo is a little more complicated than other science projects, but the effects are spectacular. Slowly layer liquids like honey, dish soap, water, and rubbing alcohol in a glass. Your 5th grade science students will be amazed when the liquids float one on top of the other like magic (except it is really science).
Learn more: Liquid Density at Wonder How To
Light(ning) it up indoors

On a cool, low-humidity day, use a foil-covered fork and a balloon to create a “lightning storm” in your classroom. Turn down the lights to give students a better view of the static electricity you’re creating.
Learn more: Indoor Lightning at Education.com
Create convection currents
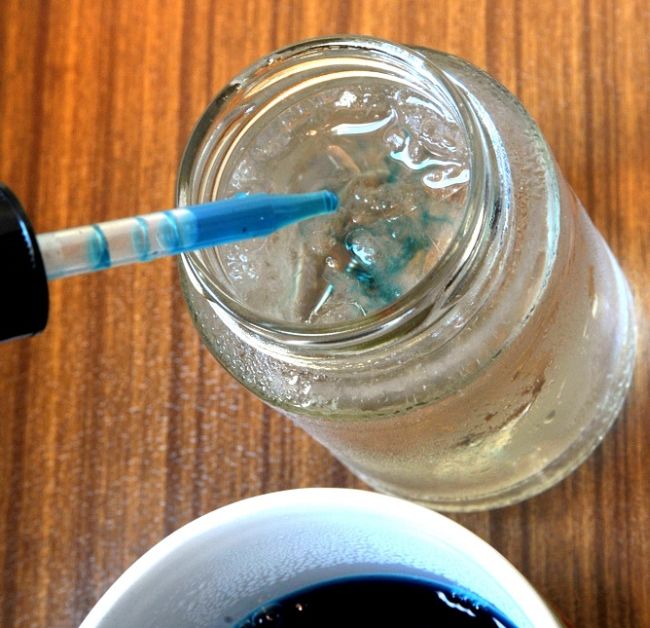

This easy experiment uses hot and cold liquids and some food coloring to explore the thermal and kinetic energy that creates convection currents. Take things a step further and research how convection currents work in large bodies of water, like oceans.
Learn more: Heat Convection at Education.com
Sink or swim with soda cans
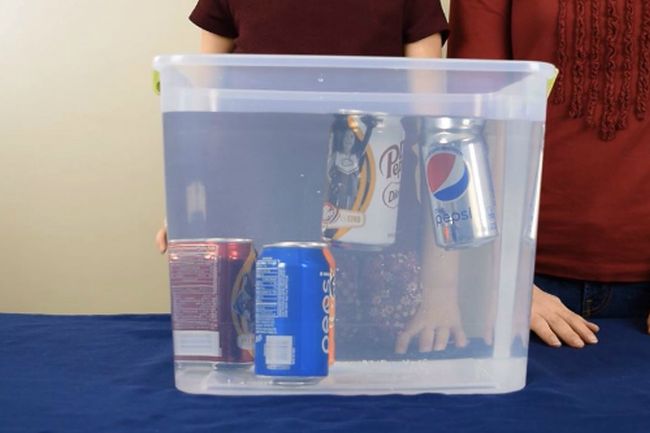

Here’s another easy density experiment. Place unopened cans of regular and diet soda into a bin of water to see which float and which sink. The differences are due to the use of sugar and artificial sweeteners.
Learn more: Sink or Swim at Cool Science Experiments HQ
Find out if water conducts electricity
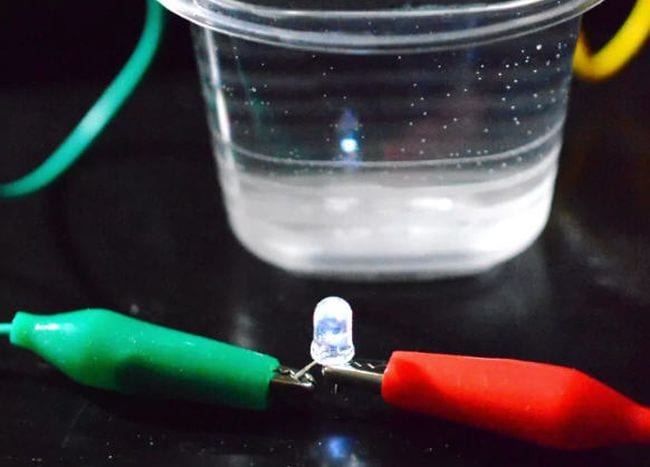
We always tell kids to get out of the water as a storm approaches. This 5th grade science project helps explain why. (Conductivity vs. non-conductivity is one of the properties of matter too.)
Learn more: Electricity and Water at Rookie Parenting
Blow up a balloon—without blowing
This is the classic science experiment that helps you teach the reactions between acids and bases, plus what happens when you mix different substances together. Fill a bottle with vinegar and a balloon with baking soda. Fit the balloon over the top, shake the baking soda down into the vinegar, and watch the balloon inflate.
Learn more: Balloon Experiments
Use these hands-on science activities to spice up your lesson plans or as enrichment projects for science-loving kids to try at home.
Erupt a baking soda volcano
Need a 5th grade science fair project? Go with a classic: the volcano ! This one’s made from salt dough, which is easy to work with and inexpensive to make.
Learn more: Baking Soda Volcano Experiment (With Free Printable Student Recording Sheet)
Peel an orange to understand plate tectonics
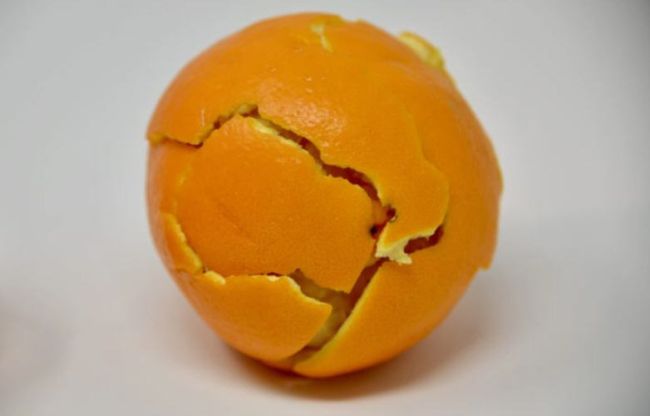

If students are learning earth science, use an orange to make plate tectonics easier to understand. Peel it, then reassemble it and look at the pieces as plates floating on the Earth’s mantle.
Learn more: Orange Tectonics at Science Sparks
Discover the strength of eggshells
We think of eggshells as very fragile, but their shape makes them surprisingly strong. Try this experiment to learn why arches are such a useful shape in architecture.
Demonstrate the “magic” leakproof bag

So simple and so amazing! All you need is a zip-top plastic bag, sharp pencils, and some water to blow your students’ minds. Once they’re suitably impressed, teach them how the “trick” works by explaining the chemistry of polymers.
Learn more: Magic Leakproof Bag at Paging Fun Mums
Explore the science of glow sticks

Glow sticks are always a big hit with kids, so they’ll have a terrific time learning about the chemical reactions that make glow sticks work.
Learn more: Glow Stick Science Experiment at A Dab of Glue Will Do
Grow crystal snowflakes
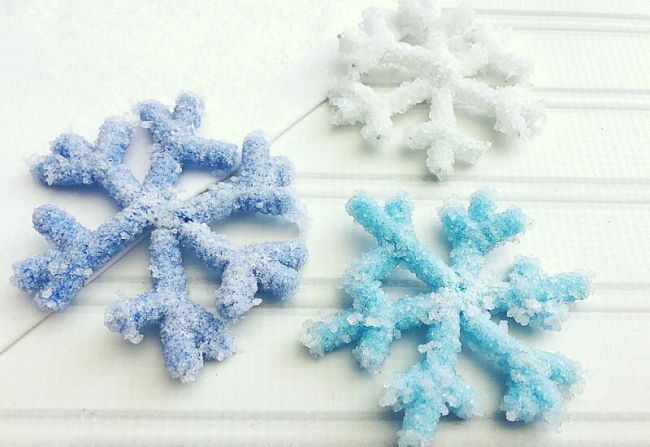

Kids love crystal projects, and this one results in winter decorations for your classroom. Your students will learn about supersaturated solutions and crystallization. ( See more winter science activities here. )
Learn more: Crystal Snowflakes at Little Bins for Little Hands
Escape from quicksand
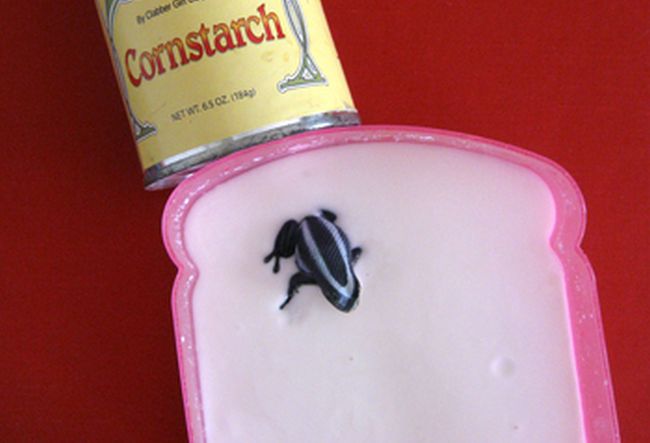

Dive deep into the science of quicksand and learn about saturation and friction along the way. You’ll create a small “quicksand” pool from cornstarch and water, then experiment to find out the best ways to escape.
Learn more: Quicksand Experiment at Education.com
Watch the heart beat with marshmallows
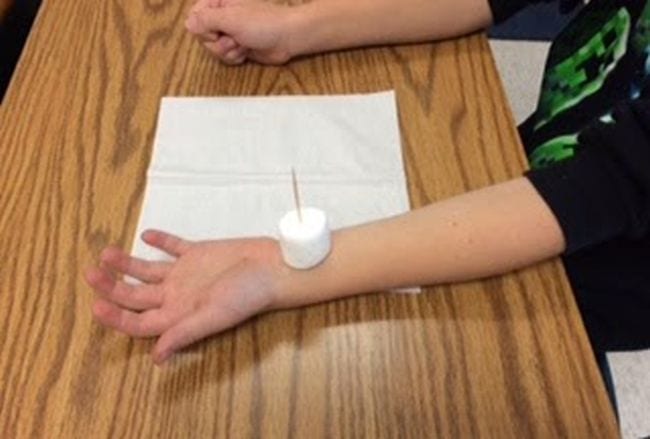
If you can get your 5th grade science class to quiet down enough for this one, they might be able to see a marshmallow jump with each beat of their hearts!
Learn more: Heartbeat Marshmallows at Growing Grade by Grade
Make a foil bug walk on water

Surface tension allows water striders to dance across the surface of the water. Re-create this scientific phenomenon with little “bugs” made of aluminum foil.
Learn more: Foil Water Strider at The Homeschool Scientist
Find out how bile breaks down fat
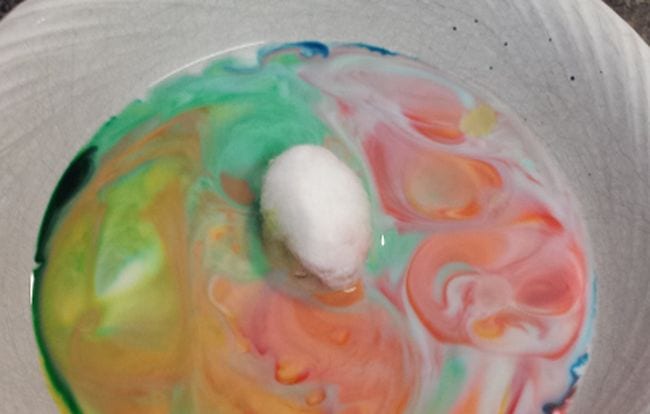

Learning about the digestive system? This 5th grade science demo explores the purpose of the bile produced by the liver, which breaks down fat.
Learn more: Bile Experiment at Simple Southern
Construct a homemade lava lamp
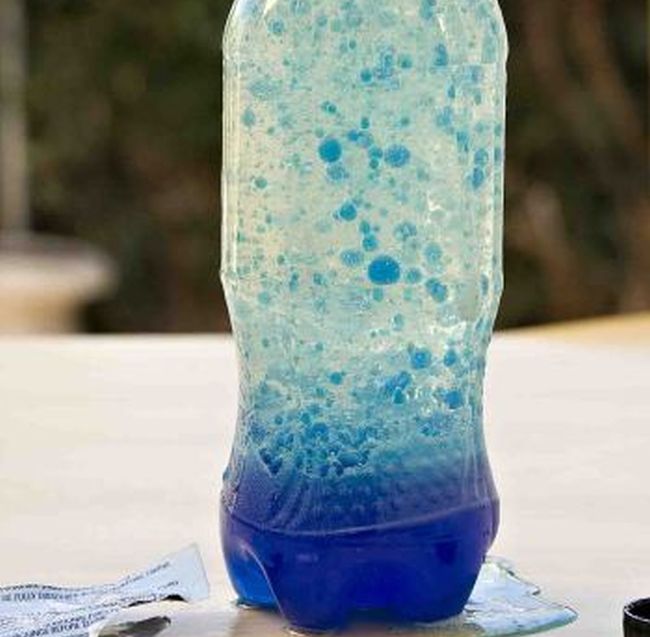

This 1970s trend is back—as a 5th grade science project! Learn about acids and bases while putting together a totally groovy lava lamp.
Learn more: Homemade Lava Lamp at Education.com
Investigate osmosis with gummy bears
Gummy bears are not only tasty, but they can also help teach your 5th graders about the concepts of osmosis and equilibrium as well as solvents and solute.
Replicate a sunset
With just water, milk powder, a flashlight, and a glass dish, your 5th graders will investigate why the sky appears to change colors as the sun sets.
Learn more: Sunset Sky at Rookie Parenting
Defy gravity with floating water
This one might cause a bit of a mess, but it’s only water, and it’s all in the name of your students discovering air pressure. All you’ll need is a cup, index card, water, and crossed fingers that your classroom doesn’t become a puddle!
Model constellations

Space delights students of all ages. The mystery and mystique is intriguing, and creating a constellation out of pipe cleaners is a fun STEM activity to explore the night sky.
Learn more: Constellations Model at STEAM Powered Family
Continue the STEM learning with these 5th Grade Math Games for Teaching Fractions, Decimals, and More .
Plus, sign up for our newsletters to get all the latest teaching tips and ideas straight to your inbox..

You Might Also Like

The Big List of Science Fair Project Ideas, Resources, and More
Options for every age, interest, and skill level! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Step 1. ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A hypothesis is a tentative, testable answer to a scientific question. Once a scientist has a scientific question she is interested in, the scientist reads up to find out what is already known on the topic. Then she uses that information to form a tentative answer to her scientific question. Sometimes people refer to the tentative answer as "an ...
In this section, we will discuss the importance of 5th grade science project ideas with hypothesis for students: 1. Hands-On Learning. 5th-grade science projects with hypotheses offer students a chance to learn through doing. They get to experiment, make predictions, and see the real-world results.
A hypothesis is the best answer to a question based on what is known. Scientists take that best answer and do experiments to see if it still makes sense or if a better answer can be made. When a scientist has a question they want to answer, they research what is already known about the topic. Then, they come up with their best answer to the ...
Follow this easy formula to write a strong hypothesis: If (I do this), then (this will happen). We call this an if - then statement. Here are some examples of an if - then statement: If I use ...
Problem 1. a) There is a positive relationship between the length of a pendulum and the period of the pendulum. This is a prediction that can be tested by various experiments. Problem 2. c) Diets ...
29. The Invisible Ink Hypothesis: Hypothesis: Writing with invisible ink will reveal a hidden message when exposed to heat. 30. The Magic Milk Hypothesis: Hypothesis: Swirling dish soap on the surface of milk will create beautiful, colorful patterns. 31. The Egg in a Bottle Hypothesis:
These books contain three developmentally appropriate reading levels for each grade span. Each level of the book conveys similar concepts, images, and vocabulary. Hypotheses. Hypotheses are statements that predict an outcome and provide a potential explanation for an experiment, based on prior knowledge. By using the resources below, students ...
Problem-Solving Ninjas in Action: Science projects are like ninja training grounds for problem-solving. Your kid faces challenges, twists, and turns, and by the end, they've got ninja-level problem-solving skills. Hypotheses, the Cool Guess Game: Forget boring theories; hypotheses become the rockstars.
Step 5C: Draft your hypothesis. Your draft hypothesis statement should include the following: and your best guess as to what you think the outcome will be. Use the space on the Experiment Design Worksheet to draft your hypothesis statement. Tip: A hypothesis problem can be stated in different ways. Here are some examples:
2. Tornado in a Bottle Experiment. This Tornado in a Bottle Experiment is the perfect way to teach the scientific method to kids. Students will practice measuring to fill a water bottle, then add dish soap and of course some glitter! They will then create a vortex to simulate a tornado and learn all about tornadoes. 3.
For a good science fair project you need to do quite a bit of research before any experimenting. Start by finding some information about how and why water melts. You could read a book, do a bit of Google searching, or even ask an expert. For our example, you could learn about how temperature and air pressure can change the state of water.
Step 5: Project Display Board 1. Title: be creative! 2. Purpose: your question, what you want to find out 3. Hypothesis: your prediction 4. Materials: a list of supplies 5. Procedure: the steps or directions that you used to conduct the experiment 6. Variables: Independent, Dependent and Controlled 7. Data: graphs or charts showing what
Phrasing hypothesis in simple words makes it relatable and easier for kids to grasp. Here are examples with kid-friendly language. Socks & Warmth: Wearing socks will keep my toes toasty. Jumping & Energy: The more I jump, the more energy I feel. Sandcastles & Water: A little water makes my sandcastle stand tall.
The fat and protein react to disruptions in the milk. The dish soap disrupts the chemical bonds that hold them in solution because it forms a bond with the fat. "The molecules of fat bend, roll, twist, and contort in all directions as the soap molecules race around to join up with the fat molecules.". This activity pushes the colors around.
Scientific Hypothesis Examples . Hypothesis: All forks have three tines. This would be disproven if you find any fork with a different number of tines. Hypothesis: There is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer.While it is difficult to establish cause and effect in health issues, you can apply statistics to data to discredit or support this hypothesis.
The best science fair projects for 5th grade begin with a hypothesis -- a supposition or proposed explanation made with limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation. ... Below, we've included examples of hypotheses for each project idea. To make a truly awesome science fair project, make these your own and consider how you can ...
Examples of Hypothesis: 1. If I replace the battery in my car, then my car will get better gas mileage. 2. If I eat more vegetables, then I will lose weight faster. 3. If I add fertilizer to my garden, then my plants will grow faster. 4. If I brush my teeth every day, then I will not develop cavities.
Fifth Grade Science Projects. (554 results) Science Buddies' fifth grade science projects are the perfect way for fifth grade students to have fun exploring science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Our fifth grade projects are written and tested by scientists and are specifically created for use by students in the fifth grade.
50 Fantastic 5th Grade Science Projects, Experiments, and Activities. For the classroom or science fair. There's something so fascinating about hands-on science experiments and projects. They make learning so meaningful and so much fun! These 5th grade science projects help kids explore biology, physics, chemistry, and a whole lot more. Try ...
Open the package of Skittles. Put the Skittles in a circle in the order of colors in a rainbow (red, orange, yellow, green, purple) on a white plate. Pour a small amount of hot water in the middle of the plate—just enough so that the water touches the candies. (Get an adult to help to make sure you don't hurt yourself).
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.