- Assignment Statement
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program .
Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted by a variable name.

The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator . The symbol is ‘=’ .
Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign ‘==’.
The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is :
variable = expression ;
variable = variable name
expression = it could be either a direct value or a math expression/formula or a function call
Few programming languages such as Java, C, C++ require data type to be specified for the variable, so that it is easy to allocate memory space and store those values during program execution.
data_type variable_name = value ;
In the above-given examples, Variable ‘a’ is assigned a value in the same statement as per its defined data type. A data type is only declared for Variable ‘b’. In the 3 rd line of code, Variable ‘a’ is reassigned the value 25. The 4 th line of code assigns the value for Variable ‘b’.

Assignment Statement Forms
This is one of the most common forms of Assignment Statements. Here the Variable name is defined, initialized, and assigned a value in the same statement. This form is generally used when we want to use the Variable quite a few times and we do not want to change its value very frequently.
Tuple Assignment
Generally, we use this form when we want to define and assign values for more than 1 variable at the same time. This saves time and is an easy method. Note that here every individual variable has a different value assigned to it.
(Code In Python)
Sequence Assignment
(Code in Python)
Multiple-target Assignment or Chain Assignment
In this format, a single value is assigned to two or more variables.
Augmented Assignment
In this format, we use the combination of mathematical expressions and values for the Variable. Other augmented Assignment forms are: &=, -=, **=, etc.
Browse more Topics Under Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Concept of Data types
- Built-in Data Types
- Constants in Programing Language
- Access Modifier
- Variables of Built-in-Datatypes
- Declaration/Initialization of Variables
- Type Modifier
Few Rules for Assignment Statement
Few Rules to be followed while writing the Assignment Statements are:
- Variable names must begin with a letter, underscore, non-number character. Each language has its own conventions.
- The Data type defined and the variable value must match.
- A variable name once defined can only be used once in the program. You cannot define it again to store other types of value.
- If you assign a new value to an existing variable, it will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value.
FAQs on Assignment Statement
Q1. Which of the following shows the syntax of an assignment statement ?
- variablename = expression ;
- expression = variable ;
- datatype = variablename ;
- expression = datatype variable ;
Answer – Option A.
Q2. What is an expression ?
- Same as statement
- List of statements that make up a program
- Combination of literals, operators, variables, math formulas used to calculate a value
- Numbers expressed in digits
Answer – Option C.
Q3. What are the two steps that take place when an assignment statement is executed?
- Evaluate the expression, store the value in the variable
- Reserve memory, fill it with value
- Evaluate variable, store the result
- Store the value in the variable, evaluate the expression.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Variables in Programming Language
- Concept of Data Types
- Declaration of Variables
- Type Modifiers
- Access Modifiers
- Constants in Programming Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Kenneth Leroy Busbee
An assignment statement sets and/or re-sets the value stored in the storage location(s) denoted by a variable name; in other words, it copies a value into the variable. [1]
The assignment operator allows us to change the value of a modifiable data object (for beginning programmers this typically means a variable). It is associated with the concept of moving a value into the storage location (again usually a variable). Within most programming languages the symbol used for assignment is the equal symbol. But bite your tongue, when you see the = symbol you need to start thinking: assignment. The assignment operator has two operands. The one to the left of the operator is usually an identifier name for a variable. The one to the right of the operator is a value.
Simple Assignment
The value 21 is moved to the memory location for the variable named: age. Another way to say it: age is assigned the value 21.
Assignment with an Expression
The item to the right of the assignment operator is an expression. The expression will be evaluated and the answer is 14. The value 14 would be assigned to the variable named: total_cousins.
Assignment with Identifier Names in the Expression
The expression to the right of the assignment operator contains some identifier names. The program would fetch the values stored in those variables; add them together and get a value of 44; then assign the 44 to the total_students variable.
- cnx.org: Programming Fundamentals – A Modular Structured Approach using C++
- Wikipedia: Assignment (computer science) ↵
Programming Fundamentals Copyright © 2018 by Kenneth Leroy Busbee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
CS105: Introduction to Python
Variables and assignment statements.
Computers must be able to remember and store data. This can be accomplished by creating a variable to house a given value. The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command:
in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a . Next, type the command:
in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. This variable will remember the value 3.45 until it is assigned a different value. To see this, type these two commands:
You should see the new value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. The new value has "overwritten" the old value. We must be careful since once an old value has been overwritten, it is no longer remembered. The new value is now what is being remembered.
Although we will not discuss arithmetic operations in detail until the next unit, you can at least be equipped with the syntax for basic operations: + (addition), - (subtraction), * (multiplication), / (division)
For example, entering these command sequentially into the command line window:
would result in 12.32 being echoed to the screen (just as you would expect from a calculator). The syntax for multiplication works similarly. For example:
would result in 35 being echoed to the screen because the variable b has been assigned the value a * 5 where, at the time of execution, the variable a contains a value of 7.
After you read, you should be able to execute simple assignment commands using integer and float values in the command window of the Repl.it IDE. Try typing some more of the examples from this web page to convince yourself that a variable has been assigned a specific value.
In programming, we associate names with values so that we can remember and use them later. Recall Example 1. The repeated computation in that algorithm relied on remembering the intermediate sum and the integer to be added to that sum to get the new sum. In expressing the algorithm, we used th e names current and sum .
In programming, a name that refers to a value in this fashion is called a variable . When we think of values as data stored somewhere i n the computer, we can have a mental image such as the one below for the value 10 stored in the computer and the variable x , which is the name we give to 10. What is most important is to see that there is a binding between x and 10.
The term variable comes from the fact that values that are bound to variables can change throughout computation. Bindings as shown above are created, and changed by assignment statements . An assignment statement associates the name to the left of the symbol = with the value denoted by the expression on the right of =. The binding in the picture is created using an assignment statemen t of the form x = 10 . We usually read such an assignment statement as "10 is assigned to x" or "x is set to 10".
If we want to change the value that x refers to, we can use another assignment statement to do that. Suppose we execute x = 25 in the state where x is bound to 10.Then our image becomes as follows:
Choosing variable names
Suppose that we u sed the variables x and y in place of the variables side and area in the examples above. Now, if we were to compute some other value for the square that depends on the length of the side , such as the perimeter or length of the diagonal, we would have to remember which of x and y , referred to the length of the side because x and y are not as descriptive as side and area . In choosing variable names, we have to keep in mind that programs are read and maintained by human beings, not only executed by machines.
Note about syntax
In Python, variable identifiers can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits (provided they don't start with a digit) and the special character _ (underscore). Although it is legal to use uppercase letters in variable identifiers, we typically do not use them by convention. Variable identifiers are also case-sensitive. For example, side and Side are two different variable identifiers.
There is a collection of words, called reserved words (also known as keywords), in Python that have built-in meanings and therefore cannot be used as variable names. For the list of Python's keywords See 2.3.1 of the Python Language Reference.
Syntax and Sema ntic Errors
Now that we know how to write arithmetic expressions and assignment statements in Python, we can pause and think about what Python does if we write something that the Python interpreter cannot interpret. Python informs us about such problems by giving an error message. Broadly speaking there are two categories for Python errors:
- Syntax errors: These occur when we write Python expressions or statements that are not well-formed according to Python's syntax. For example, if we attempt to write an assignment statement such as 13 = age , Python gives a syntax error. This is because Python syntax says that for an assignment statement to be well-formed it must contain a variable on the left hand side (LHS) of the assignment operator "=" and a well-formed expression on the right hand side (RHS), and 13 is not a variable.
- Semantic errors: These occur when the Python interpreter cannot evaluate expressions or execute statements because they cannot be associated with a "meaning" that the interpreter can use. For example, the expression age + 1 is well-formed but it has a meaning only when age is already bound to a value. If we attempt to evaluate this expression before age is bound to some value by a prior assignment then Python gives a semantic error.
Even though we have used numerical expressions in all of our examples so far, assignments are not confined to numerical types. They could involve expressions built from any defined type. Recall the table that summarizes the basic types in Python.
The following video shows execution of assignment statements involving strings. It also introduces some commonly used operators on strings. For more information see the online documentation. In the video below, you see the Python shell displaying "=> None" after the assignment statements. This is unique to the Python shell presented in the video. In most Python programming environments, nothing is displayed after an assignment statement. The difference in behavior stems from version differences between the programming environment used in the video and in the activities, and can be safely ignored.
Distinguishing Expressions and Assignments
So far in the module, we have been careful to keep the distinction between the terms expression and statement because there is a conceptual difference between them, which is sometimes overlooked. Expressions denote values; they are evaluated to yield a value. On the other hand, statements are commands (instructions) that change the state of the computer. You can think of state here as some representation of computer memory and the binding of variables and values in the memory. In a state where the variable side is bound to the integer 3, and the variable area is yet unbound, the value of the expression side + 2 is 5. The assignment statement side = side + 2 , changes the state so that value 5 is bound to side in the new state. Note that when you type an expression in the Python shell, Python evaluates the expression and you get a value in return. On the other hand, if you type an assignment statement nothing is returned. Assignment statements do not return a value. Try, for example, typing x = 100 + 50 . Python adds 100 to 50, gets the value 150, and binds x to 150. However, we only see the prompt >>> after Python does the assignment. We don't see the change in the state until we inspect the value of x , by invoking x .
What we have learned so far can be summarized as using the Python interpreter to manipulate values of some primitive data types such as integers, real numbers, and character strings by evaluating expressions that involve built-in operators on these types. Assignments statements let us name the values that appear in expressions. While what we have learned so far allows us to do some computations conveniently, they are limited in their generality and reusability. Next, we introduce functions as a means to make computations more general and reusable.


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.1: Assignment statements
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40850

- Allen B. Downey
- Olin College via Green Tea Press
An assignment statement creates a new variable and gives it a value:
This example makes three assignments. The first assigns a string to a new variable named message ; the second gives the integer 17 to n ; the third assigns the (approximate) value of \(\pi\) to pi .
A common way to represent variables on paper is to write the name with an arrow pointing to its value. This kind of figure is called a state diagram because it shows what state each of the variables is in (think of it as the variable’s state of mind). Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the result of the previous example.

- Free Python 3 Tutorial
- Control Flow
- Exception Handling
- Python Programs
- Python Projects
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Database
- Data Science With Python
- Machine Learning with Python
- Memory Management in Python
- Ways to increment Iterator from inside the For loop in Python
- How to Break out of multiple loops in Python ?
- Scope Resolution in Python | LEGB Rule
- How to add Python to Windows PATH?
- Benefits of Double Division Operator over Single Division Operator in Python
- Specifying the increment in for-loops in Python
- How to use Variables in Python3?
- Check multiple conditions in if statement - Python
- Difference between dir() and vars() in Python
- Variables under the hood in Python
- Understanding the Execution of Python Program
- Viewing all defined variables in Python
- Convert Python String to Float datatype
- Python Main Function
- What is the difference between Python's Module, Package and Library?
- How to convert Float to Int in Python?
- Context Variables in Python
- Why does Python automatically exit a script when it’s done?
Different Forms of Assignment Statements in Python
We use Python assignment statements to assign objects to names. The target of an assignment statement is written on the left side of the equal sign (=), and the object on the right can be an arbitrary expression that computes an object.
There are some important properties of assignment in Python :-
- Assignment creates object references instead of copying the objects.
- Python creates a variable name the first time when they are assigned a value.
- Names must be assigned before being referenced.
- There are some operations that perform assignments implicitly.
Assignment statement forms :-
1. Basic form:
This form is the most common form.
2. Tuple assignment:
When we code a tuple on the left side of the =, Python pairs objects on the right side with targets on the left by position and assigns them from left to right. Therefore, the values of x and y are 50 and 100 respectively.
3. List assignment:
This works in the same way as the tuple assignment.
4. Sequence assignment:
In recent version of Python, tuple and list assignment have been generalized into instances of what we now call sequence assignment – any sequence of names can be assigned to any sequence of values, and Python assigns the items one at a time by position.
5. Extended Sequence unpacking:
It allows us to be more flexible in how we select portions of a sequence to assign.
Here, p is matched with the first character in the string on the right and q with the rest. The starred name (*q) is assigned a list, which collects all items in the sequence not assigned to other names.
This is especially handy for a common coding pattern such as splitting a sequence and accessing its front and rest part.
6. Multiple- target assignment:
In this form, Python assigns a reference to the same object (the object which is rightmost) to all the target on the left.
7. Augmented assignment :
The augmented assignment is a shorthand assignment that combines an expression and an assignment.
There are several other augmented assignment forms:
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- python-basics
- Google Releases ‘Prompting Guide’ With Tips For Gemini In Workspace
- Google Cloud Next 24 | Gmail Voice Input, Gemini for Google Chat, Meet ‘Translate for me,’ & More
- 10 Best Viber Alternatives for Better Communication
- 12 Best Database Management Software in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Next: Execution Control Expressions , Previous: Arithmetic , Up: Top [ Contents ][ Index ]
7 Assignment Expressions
As a general concept in programming, an assignment is a construct that stores a new value into a place where values can be stored—for instance, in a variable. Such places are called lvalues (see Lvalues ) because they are locations that hold a value.
An assignment in C is an expression because it has a value; we call it an assignment expression . A simple assignment looks like
We say it assigns the value of the expression value-to-store to the location lvalue , or that it stores value-to-store there. You can think of the “l” in “lvalue” as standing for “left,” since that’s what you put on the left side of the assignment operator.
However, that’s not the only way to use an lvalue, and not all lvalues can be assigned to. To use the lvalue in the left side of an assignment, it has to be modifiable . In C, that means it was not declared with the type qualifier const (see const ).
The value of the assignment expression is that of lvalue after the new value is stored in it. This means you can use an assignment inside other expressions. Assignment operators are right-associative so that
is equivalent to
This is the only useful way for them to associate; the other way,
would be invalid since an assignment expression such as x = y is not valid as an lvalue.
Warning: Write parentheses around an assignment if you nest it inside another expression, unless that is a conditional expression, or comma-separated series, or another assignment.
- Contributors
Basic Statements in Python
Table of contents, what is a statement in python, statement set, multi-line statements, simple statements, expression statements, the assert statement, the try statement.

In Python, statements are instructions or commands that you write to perform specific actions or tasks. They are the building blocks of a Python program.
A statement is a line of code that performs a specific action. It is the smallest unit of code that can be executed by the Python interpreter.
Assignment Statement
In this example, the value 10 is assigned to the variable x using the assignment statement.
Conditional Statement
In this example, the if-else statement is used to check the value of x and print a corresponding message.
By using statements, programmers can instruct the computer to perform a variety of tasks, from simple arithmetic operations to complex decision-making processes. Proper use of statements is crucial to writing efficient and effective Python code.
Here's a table summarizing various types of statements in Python:
Please note that this table provides a brief overview of each statement type, and there may be additional details and variations for each statement.
Multi-line statements are a convenient way to write long code in Python without making it cluttered. They allow you to write several lines of code as a single statement, making it easier for developers to read and understand the code. Here are two examples of multi-line statements in Python:
- Using backslash:
- Using parentheses:
Simple statements are the smallest unit of execution in Python programming language and they do not contain any logical or conditional expressions. They are usually composed of a single line of code and can perform basic operations such as assigning values to variables , printing out values, or calling functions .
Examples of simple statements in Python:
Simple statements are essential to programming in Python and are often used in combination with more complex statements to create robust programs and applications.
Expression statements in Python are lines of code that evaluate and produce a value. They are used to assign values to variables, call functions, and perform other operations that produce a result.
In this example, we assign the value 5 to the variable x , then add 3 to x and assign the result ( 8 ) to the variable y . Finally, we print the value of y .
In this example, we define a function square that takes one argument ( x ) and returns its square. We then call the function with the argument 5 and assign the result ( 25 ) to the variable result . Finally, we print the value of result .
Overall, expression statements are an essential part of Python programming and allow for the execution of mathematical and computational operations.
The assert statement in Python is used to test conditions and trigger an error if the condition is not met. It is often used for debugging and testing purposes.
Where condition is the expression that is tested, and message is the optional error message that is displayed when the condition is not met.
In this example, the assert statement tests whether x is equal to 5 . If the condition is met, the statement has no effect. If the condition is not met, an error will be raised with the message x should be 5 .
In this example, the assert statement tests whether y is not equal to 0 before performing the division. If the condition is met, the division proceeds as normal. If the condition is not met, an error will be raised with the message Cannot divide by zero .
Overall, assert statements are a useful tool in Python for debugging and testing, as they can help catch errors early on. They are also easily disabled in production code to avoid any unnecessary overhead.
The try statement in Python is used to catch exceptions that may occur during the execution of a block of code. It ensures that even when an error occurs, the code does not stop running.
Examples of Error Processing
Dive deep into the topic.
- Match Statements
- Operators in Python Statements
- The IF Statement

Contribute with us!
Do not hesitate to contribute to Python tutorials on GitHub: create a fork, update content and issue a pull request.


- Table of Contents
- Course Home
- Assignments
- Peer Instruction (Instructor)
- Peer Instruction (Student)
- Change Course
- Instructor's Page
- Progress Page
- Edit Profile
- Change Password
- Scratch ActiveCode
- Scratch Activecode
- Instructors Guide
- About Runestone
- Report A Problem
- 1.1 Getting Started
- 1.1.1 Preface
- 1.1.2 About the AP CSA Exam
- 1.1.3 Transitioning from AP CSP to AP CSA
- 1.1.4 Java Development Environments
- 1.1.5 Growth Mindset and Pair Programming
- 1.1.6 Pretest for the AP CSA Exam
- 1.1.7 Survey
- 1.2 Why Programming? Why Java?
- 1.3 Variables and Data Types
- 1.4 Expressions and Assignment Statements
- 1.5 Compound Assignment Operators
- 1.6 Casting and Ranges of Values
- 1.7 Unit 1 Summary
- 1.8 Mixed Up Code Practice
- 1.9 Toggle Mixed Up or Write Code Practice
- 1.10 Coding Practice
- 1.11 Multiple Choice Exercises
- 1.3. Variables and Data Types" data-toggle="tooltip">
- 1.5. Compound Assignment Operators' data-toggle="tooltip" >
Time estimate: 90 min.
1.4. Expressions and Assignment Statements ¶
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables.
1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶
Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator = . An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side. The value of the expression (which can contain math operators and other variables) on the right of the = sign is stored in the variable on the left.
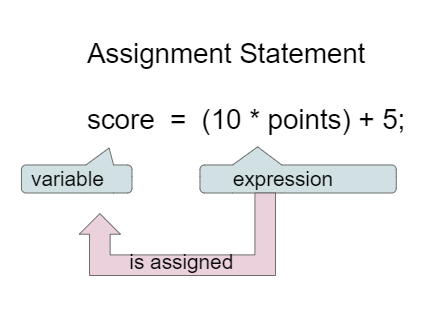
Figure 1: Assignment Statement (variable = expression;) ¶
Instead of saying equals for the = in an assignment statement, say “gets” or “is assigned” to remember that the variable gets or is assigned the value on the right. In the figure above score is assigned the value of the expression 10 times points (which is another variable) plus 5.
The following video by Dr. Colleen Lewis shows how variables can change values in memory using assignment statements.
As we saw in the video, we can set one variable’s value to a copy of the value of another variable like y = x; . This won’t change the value of the variable that you are copying from.
Let’s step through the following code in the Java visualizer to see the values in memory. Click on the Next button at the bottom of the code to see how the values of the variables change. You can run the visualizer on any Active Code in this e-book by just clicking on the Code Lens button at the top of each Active Code.
Activity: CodeLens 1.4.1.2 (asgn_viz1)

1-4-3: What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes? You can step through this code by clicking on this Java visualizer link.
- x = 0, y = 1, z = 2
- These are the initial values in the variable, but the values are changed.
- x = 1, y = 2, z = 3
- x changes to y's initial value, y's value is doubled, and z is set to 3
- x = 2, y = 2, z = 3
- Remember that the equal sign doesn't mean that the two sides are equal. It sets the value for the variable on the left to the value from evaluating the right side.
- x = 0, y = 0, z = 3
The following has the correct code to ‘swap’ the values in x and y (so that x ends up with y’s initial value and y ends up with x’s initial value), but the code is mixed up and contains one extra block which is not needed in a correct solution. Drag the needed blocks from the left into the correct order on the right. Check your solution by clicking on the Check button. You will be told if any of the blocks are in the wrong order or if you need to remove one or more blocks. After three incorrect attempts you will be able to use the Help Me button to make the problem easier.
1.4.2. Adding 1 to a Variable ¶
If you use a variable to keep score, you would probably increment it (add one to the current value) whenever score should go up. You can do this by setting the variable to the current value of the variable plus one ( score = score + 1 ) as shown below. The formula would look strange in math class, but it makes sense in coding because it is assigning a new value to the variable on the left that comes from evaluating the arithmetic expression on the right. So, the score variable is set to the previous value of score plus 1.
Try the code below to see how score is incremented by 1. Try substituting 2 instead of 1 to see what happens.
1.4.3. Input with Variables ¶
Variables are a powerful abstraction in programming because the same algorithm can be used with different input values saved in variables. The code below ( Java Scanner Input Repl using the Scanner class or Java Console Input Repl using the Console class) will say hello to anyone who types in their name for different name values. Click on run and then type in your name. Then, try run again and type in a friend’s name. The code works for any name: behold, the power of variables!
Although you will not be tested in the AP CSA exam on using the Java input or the Scanner or Console classes, learning how to do input in Java is very useful and fun. For more information on using the Scanner class, go to https://www.w3schools.com/java/java_user_input.asp , and for the newer Console class, https://howtodoinjava.com/java-examples/console-input-output/ .
1.4.4. Operators ¶
Java uses the standard mathematical operators for addition ( + ), subtraction ( - ), and division ( / ). The multiplication operator is written as * , as it is in most programming languages, since the character sets used until relatively recently didn’t have a character for a real multiplication sign, × , and keyboards still don’t have a key for it. Likewise no ÷ .
You may be used to using ^ for exponentiation, either from a graphing calculator or tools like Desmos. Confusingly ^ is an operator in Java, but it has a completely different meaning than exponentiation and isn’t even exactly an arithmetic operator. You will learn how to use the Math.pow method to do exponents in Unit 2.
Arithmetic expressions can be of type int or double . An arithmetic expression consisting only of int values will evaluate to an int value. An arithmetic expression that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value. (You may have noticed that + was also used to combine String and other values into new String s. More on this when we talk about String s more fully in Unit 2.)
Java uses the operator == to test if the value on the left is equal to the value on the right and != to test if two items are not equal. Don’t get one equal sign = confused with two equal signs == . They mean very different things in Java. One equal sign is used to assign a value to a variable. Two equal signs are used to test a variable to see if it is a certain value and that returns true or false as you’ll see below. Also note that using == and != with double values can produce surprising results. Because double values are only an approximation of the real numbers even things that should be mathematically equivalent might not be represented by the exactly same double value and thus will not be == . To see this for yourself, write a line of code below to print the value of the expression 0.3 == 0.1 + 0.2 ; it will be false !

Run the code below to see all the operators in action. Do all of those operators do what you expected? What about 2 / 3? Isn’t it surprising that it prints 0? See the note below.
When Java sees you doing integer division (or any operation with integers) it assumes you want an integer result so it throws away anything after the decimal point in the answer. This is called truncating division . If you need a double answer, you should make at least one of the values in the expression a double like 2.0.
With division, another thing to watch out for is dividing by 0. An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException error message. Try it in one of the active code windows above.
Operators can be used to create compound expressions with more than one operator. You can either use a literal value which is a fixed value like 2, or variables in them. When compound expressions are evaluated, operator precedence rules are used, just like when we do math (remember PEMDAS?), so that * , / , and % are done before + and - . However, anything in parentheses is done first. It doesn’t hurt to put in extra parentheses if you are unsure as to what will be done first or just to make it more clear.
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right. Remember to consider operator precedence . How do the parentheses change the precedence?
1.4.5. The Remainder Operator ¶
The operator % in Java is the remainder operator. Like the other arithmetic operators is takes two operands. Mathematically it returns the remainder after dividing the first number by the second, using truncating integer division. For instance, 5 % 2 evaluates to 1 since 2 goes into 5 two times with a remainder of 1.
While you may not have heard of remainder as an operator, think back to elementary school math. Remember when you first learned long division, before they taught you about decimals, how when you did a long division that didn’t divide evenly, you gave the answer as the number of even divisions and the remainder. That remainder is what is returned by this operator. In the figures below, the remainders are the same values that would be returned by 2 % 3 and 5 % 2 .

Figure 1: Long division showing the integer result and the remainder ¶
Sometimes people—including Professor Lewis in the next video—will call % the modulo , or mod , operator. That is not actually correct though the difference between remainder and modulo, which uses Euclidean division instead of truncating integer division, only matters when negative operands are involved and the signs of the operands differ. With positive operands, remainder and mod give the same results. Java does have a method Math.floorMod in the Math class if you need to use modulo instead of remainder, but % is all you need in the AP exam.
Here’s the video .
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right.
The result of x % y when x is smaller than y is always x. The value y can’t go into x at all (goes in 0 times), since x is smaller than y, so the result is just x. So if you see 2 % 3 the result is 2.
1-4-10: What is the result of 158 % 10?
- This would be the result of 158 divided by 10. % gives you the remainder.
- % gives you the remainder after the division.
- When you divide 158 by 10 you get a remainder of 8.
1-4-11: What is the result of 3 % 8?
- 8 goes into 3 no times so the remainder is 3. The remainder of a smaller number divided by a larger number is always the smaller number!
- This would be the remainder if the question was 8 % 3 but here we are asking for the reminder after we divide 3 by 8.
- What is the remainder after you divide 3 by 8?
1.4.6. Programming Challenge : Dog Years ¶

In this programming challenge, you will calculate your age, and your pet’s age from your birthdates, and your pet’s age in dog years. In the code below, type in the current year, the year you were born, the year your dog or cat was born (if you don’t have one, make one up!) in the variables below. Then write formulas in assignment statements to calculate how old you are, how old your dog or cat is, and how old they are in dog years which is 7 times a human year. Finally, print it all out. If you are pair programming, switch drivers (who has control of the keyboard in pair programming) after every line of code.
Calculate your age and your pet’s age from the birthdates, and then your pet’s age in dog years.
Your teacher may suggest that you use a Java IDE like repl.it for this challenge so that you can use input to get these values using the Scanner class . Here is a repl template that you can use to get started if you want to try the challenge with input.
1.4.7. Summary ¶
Arithmetic expressions include expressions of type int and double .
The arithmetic operators consist of + , - , * , / , and % also known as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and remainder.
An arithmetic operation that uses two int values will evaluate to an int value. With integer division, any decimal part in the result will be thrown away.
An arithmetic operation that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value.
Operators can be used to construct compound expressions.
During evaluation, operands are associated with operators according to operator precedence to determine how they are grouped. ( * , / , % have precedence over + and - , unless parentheses are used to group those.)
An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException .
The assignment operator ( = ) allows a program to initialize or change the value stored in a variable. The value of the expression on the right is stored in the variable on the left.
During execution, expressions are evaluated to produce a single value.
The value of an expression has a type based on the types of the values and operators used in the expression.
1.4.8. AP Practice ¶
The following is a 2019 AP CSA sample question.
1-4-13: Consider the following code segment.
What is printed when the code segment is executed?
- 0.666666666666667
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence.
- Yes, this is equivalent to (5 + ((a/b)*c) - 1).
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence, and that an int/int gives an int truncated result where everything to the right of the decimal point is dropped.

Assignment Statements
Simple assignment.
- variable = expression;
- The expression is evaluated and the result is assigned to the variable
The simple assignment operator "=", assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left.
Compound Assignment
- variable = variable op expression;
- Statements with the same variable on each side of the equals sign
- May use the shortcut assignment operators (compound assignment)
When writing any kind of program, there will be many instances where you will need to use a variable as part of an expression and you will want to assign the result of that expression into the same variable. An example of this kind of operation is when you want to increment a variable by some value (variable or constant). For example, if we wanted to add 5 to a variable called x, we could write it as x = x + 5 since we want to add 5 to the value of x and store the result back in x.
Because it is extremely common to have the same variable on both sides of the expression, C provides a shortcut notation. This is implemented with one of a series of compound assignment operators. Using the same example, if we wanted to add 5 to the variable x, we could write it as x += 5. Similar operations may be carried out using one of the many compound operators shown in Table 2.
- Test Yourself #4
- $S$ is the start nonterminal of $G$
- $w$ is a sequence of terminals or $\varepsilon$
- A grammar is right recursive in $X$ if: $$X \stackrel{+}\longrightarrow {\dots}X$$ (in one or more steps, $X$ derives a sequence of symbols that ends with an $X$).
The grammar given above for arithmetic expressions is both left and right recursive in nonterminals exp and term (can you write the derivation steps that show this?).
First, we'll modify the grammar so that parse trees correctly reflect the fact that addition and subtraction have the same, lowest precedence; multiplication and division have the same, middle precedence; and exponentiation has the highest precedence:
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | xList xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | xList PLUS
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | PLUS xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | xList COMMA xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | xList COMMA PLUS
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS | PLUS COMMA xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS SEMICOLON | xList xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS SEMICOLON | xList PLUS SEMICOLON
- xList $\longrightarrow$ PLUS SEMICOLON | PLUS SEMICOLON xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS | xList xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS | xList PLUS
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS | PLUS xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS SEMICOLON | xList xList
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS SEMICOLON | xList PLUS SEMICOLON
- xList $\longrightarrow$ $\varepsilon$ | PLUS SEMICOLON | PLUS SEMICOLON xList
A class is the word "class", optionally preceded by the word "public", followed by an identifier, followed by an open curly brace, followed by the class body, followed by a closing curly brace:
A class body is a list of zero or more field and/or method definitions:
Statement vs Expression – What's the Difference in Programming?

Learning the syntax of a programming language is key if you want to use that language effectively. This is true for both new and experienced developers.
And one of the most important things to pay attention to while learning a programming language is whether the code you're dealing with is a statement or an expression.
It can sometimes be confusing to differentiate between statements and expressions in programming. So this article is meant to simplify the differences so that you can improve your programming skills and become a better developer.
What is an Expression in Programming?

An expression is any word or group of words or symbols that is a value. In programming, an expression is a value, or anything that executes and ends up being a value.
It is necessary to understand that a value is unique. For example, const , let , 2 , 4 , s , a , true , false , and world are values because each of them is unique in meaning or character.
Let's look at some code as an example:
Judging from the code above, const , price , = , and 500 are expressions because each of them has a definite and unique meaning or value. But if we take all of them together const price = 500 - then we have a statement.
Let's look at another example:
Looking at the code above, you can see an anonymous function is assigned to a variable. Oh, wait! You might know that any function is a statement. Can it also be an expression?
Yes! A "function" and a "class" are both statements and expressions because they can perform actions (do or not do tasks) and still execute to a value.
This brings us to statements – so what are they?
What is a Statement in Programming?
A statement is a group of expressions and/or statements that you design to carry out a task or an action.
Statements are two-sided – that is, they either do tasks or don't do them. Any statement that can return a value is automatically qualified to be used as an expression. That is why a function or class is a statement and also an expression in JavaScript.
If you look at the example of the function under the section on expressions, you can see it is assigned and execute to a value passed to a variable. That is why it is an expression in that case.
Examples of Statements in Programming
Inline statements.
The whole of the code above is a statement because it carries out the task of assigning $2000 to amount . It is safe to say a line of code is a statement because most compilers or interpreters don't execute any standalone expression.

Block statements
Look at the below if statement:
The if statement is a statement because it helps us check whether I love you or not. As I have said before, it is two-sided: this code finds out whether "I love you" or not, and that is why it is a statement. Also, it doesn't return any value but it can create side effects.
Here's a loop statement:
In short, any loop is a statement because if it can only do the tasks it is meant to do or not – does loop and doesn't loop. But a loop can't execute to a value in the end. They can only have side effects in JavaScript. Once they can execute to a value in a programming language, then they can also be used as an expression.
For example, you can use forloop and if statement as expressions in Python.
There is also an "IF" expression in Python. That means that something that is a statement in one language can be an expression (or both statement and expression) in another.
Look at the below function statement:
We declare the function add(firstNumber, secondNumber) and it returns a value. The function is called with two arguments as in add(2, 3) by declaration and so it is a statement. If you pay close attention, you will realize that calling the function as a statement is useless since it has no side effect.
Hey, stop! How can we turn it into an expression? Oh yeah, we can do it like this:
Though the function is now an expression the way it is called above, the whole of the code is still a statement.
Check out this class statement:
You can see that we declare the class "Person" and instantiate and assign it to "User" immediately. So, it is used as an expression.
Now, let's use it as a statement:
A class is similar to a function in the sense that it can be declared, assigned, or used as an operand just like a class. So, a class is a statement and/or an expression.
The Main Differences Between an Expression and a Statement in Programming
Expressions can be assigned or used as operands, while statements can only be declared.
Statements create side effects to be useful, while expressions are values or execute to values.
Expressions are unique in meaning, while statements are two-sided in execution. For example, 1 has a certain value while go( ) may be executed or not.
Statements are the whole structure, while expressions are the building blocks. For example, a line or a block of code is a statement.
Why You Should Know the Difference
First of all, understanding the difference between statements and expressions should make learning new programming languages less surprising. If you're used to JavaScript, you may be surprised by Python's ability to assign an if statement as a variable which is not possible in JavaScript.
Second, it makes it easy to use programming paradigms across different programming languages.
For example, a JavaScript "if statement" cannot be used as an expression because it can't execute to a value – it can only create side effects. Yet, you can use the ternary operator if you want to avoid the side effects of using an if statement in JavaScript.
For this reason, you can understand why some programmers avoid if statements by using the ternary operator in JavaScript. It is because they want to avoid side effects .
It also makes your realize why you have to be always careful about the scope of your variables whenever you use a statement. This is true because statements mostly have side effects to be useful, and it is reasonable to understand the scope of your variables and operations. For example,
Hey wait! What would be logged in the console if you ran the code above?
Tell yourself the answer first and then paste the code in the console to confirm. If you you're wrong, you need to learn more about scope and side effects. But if you're right, try to make those functions a bit better to avoid the confusion they may generate.
Knowing the difference also helps you to easily identify non-composable and composable syntaxes (functions, classes, modules, and so on) of a programming language. This makes porting your experience from one programming language to another more interesting and direct.
Wrapping Up
Now that you understand the difference between expressions and statements in programming, and you know why understanding the differences is important, you can identify pieces of code as expressions or statements while coding.
Next time, we'll go even further and help make learning a second programming language easier.
Go and get things done now! See you soon.
I am planning to share a lot about programming tips and tutorials in 2023. If you're struggling to build projects or you want to stay connected with my write-ups and videos, please join my list at YouTooCanCode or subscribe to my YouTube channel at You Too Can Code on YouTube .
Ayobami loves writing history with JavaScript(React) and PHP(Laravel). He has been making programming fun to learn for learners. Check him out on YouTube: https://bit.ly/3usOu3s
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
5.2 Assignment Statements
This Reference Manual output has not been verified, and may contain omissions or errors. Report any problems on the tracking issue
[An assignment_statement replaces the current value of a variable with the result of evaluating an expression .]
assignment _ statement ::= variable _ name := expression ;
The execution of an assignment_statement includes the evaluation of the expression and the assignment of the value of the expression into the target . [An assignment operation (as opposed to an assignment _ statement ) is performed in other contexts as well, including object initialization and by-copy parameter passing.] The target of an assignment operation is the view of the object to which a value is being assigned; the target of an assignment _ statement is the variable denoted by the variable _ name .
Don't confuse this notion of the “target” of an assignment with the notion of the “target object” of an entry call or requeue.
Don't confuse the term “assignment operation” with the assignment_statement . The assignment operation is just one part of the execution of an assignment_statement . The assignment operation is also a part of the execution of various other constructs; see 7.6.1 , “ Completion and Finalization ” for a complete list. Note that when we say, “such-and-such is assigned to so-and-so”, we mean that the assignment operation is being applied, and that so-and-so is the target of the assignment operation.
Name Resolution Rules
The variable _ name of an assignment_statement is expected to be of any type. The expected type for the expression is the type of the target.
An assignment_statement as a whole is a “complete context”, so if the variable _ name of an assignment_statement is overloaded, the expression can be used to help disambiguate it. For example:
type P1 is access R1; type P2 is access R2; 4.c function F return P1; function F return P2; 4.d X : R1; begin F.all := X; -- Right hand side helps resolve left hand side
Legality Rules
The target [denoted by the variable _ name ] shall be a variable of a nonlimited type.
If the target is of a tagged class-wide type T 'Class, then the expression shall either be dynamically tagged, or of type T and tag-indeterminate (see 3.9.2 ).
This is consistent with the general rule that a single dispatching operation shall not have both dynamically tagged and statically tagged operands. Note that for an object initialization (as opposed to the assignment_statement ), a statically tagged initialization expression is permitted, since there is no chance for confusion (or Tag _ Check failure). Also, in an object initialization, tag-indeterminate expressions of any type covered by T 'Class would be allowed, but with an assignment_statement , that might not work if the tag of the target was for a type that didn't have one of the dispatching operations in the tag-indeterminate expression.
Dynamic Semantics
For the execution of an assignment_statement , the variable _ name and the expression are first evaluated in an arbitrary order.
Other rules of the language may require that the bounds of the variable be determined prior to evaluating the expression , but that does not necessarily require evaluation of the variable _ name , as pointed out by the ACID.
When the type of the target is class-wide:
- If the expression is tag-indeterminate (see 3.9.2 ), then the controlling tag value for the expression is the tag of the target;
See 3.9.2 , “ Dispatching Operations of Tagged Types ”.
- Otherwise [(the expression is dynamically tagged)], a check is made that the tag of the value of the expression is the same as that of the target; if this check fails, Constraint _ Error is raised.
The value of the expression is converted to the subtype of the target. [The conversion can raise an exception (see 4.6 ).]
4.6 , “ Type Conversions ” defines what actions and checks are associated with subtype conversion. For non-array subtypes, it is just a constraint check presuming the types match. For array subtypes, it checks the lengths and slides if the target is constrained. “Sliding” means the array doesn't have to have the same bounds, so long as it is the same length.
In cases involving controlled types, the target is finalized, and an anonymous object can be used as an intermediate in the assignment, as described in 7.6.1 , “ Completion and Finalization ”. In any case, the converted value of the expression is then assigned to the target, which consists of the following two steps:
To be honest: 7.6.1 actually says that finalization happens always, but unless controlled types are involved, this finalization during an assignment_statement does nothing.
- The value of the target becomes the converted value.
- If any part of the target is controlled, its value is adjusted as explained in 7.6 .
If any parts of the object are controlled, abort is deferred during the assignment operation itself, but not during the rest of the execution of an assignment_statement .
NOTE The tag of an object never changes; in particular, an assignment_statement does not change the tag of the target.
The implicit subtype conversion described above for assignment_statement s is performed only for the value of the right-hand side expression as a whole; it is not performed for subcomponents of the value.
The determination of the type of the variable of an assignment_statement may require consideration of the expression if the variable name can be interpreted as the name of a variable designated by the access value returned by a function call, and similarly, as a component or slice of such a variable (see 8.6 , “ The Context of Overload Resolution ”).
Examples of assignment statements:
Value := Max _ Value - 1; Shade := Blue; 19 Next _ Frame(F)(M, N) := 2.5; -- see 4.1.1 U := Dot _ Product(V, W); -- see 6.3 20/4
Writer := (Status = > Open, Unit = > Printer, Line _ Count = > 60); -- see 3.8.1 Next.all := (72074, null, Head); -- see 3.10.1
Examples involving scalar subtype conversions:
I, J : Integer range 1 .. 10 := 5; K : Integer range 1 .. 20 := 15; ... 23 I := J; -- identical ranges K := J; -- compatible ranges J := K; -- will raise Constraint _ Error if K > 10
Examples involving array subtype conversions:
A : String(1 .. 31); B : String(3 .. 33); ... 26 A := B; -- same number of components 27 A(1 .. 9) := "tar sauce"; A(4 .. 12) := A(1 .. 9); -- A(1 .. 12) = "tartar sauce"
Assignment_statement s are well-defined even in the case of overlapping slices of the same array, because the variable _ name and expression are both evaluated before copying the value into the variable. In the above example, an implementation yielding A(1 .. 12) = "tartartartar" would be incorrect.
Extensions to Ada 83
We now allow user-defined finalization and value adjustment actions as part of assignment_statement s (see 7.6 , “ Assignment and Finalization ”).
Wording Changes from Ada 83
The special case of array assignment is subsumed by the concept of a subtype conversion, which is applied for all kinds of types, not just arrays. For arrays it provides “sliding”. For numeric types it provides conversion of a value of a universal type to the specific type of the target. For other types, it generally has no run-time effect, other than a constraint check.
We now cover in a general way in 3.7.2 the erroneous execution possible due to changing the value of a discriminant when the variable in an assignment_statement is a subcomponent that depends on discriminants.
Incompatibilities With Ada 95
The change of the limited check from a resolution rule to a legality rule is not quite upward compatible. For example
type AccNonLim is access NonLim; function Foo (Arg : in Integer) return AccNonLim; type AccLim is access Lim; function Foo (Arg : in Integer) return AccLim; Foo(2).all := Foo(1).all;
where NonLim is a nonlimited type and Lim is a limited type. The assignment is legal in Ada 95 (only the first Foo would be considered), and is ambiguous in Ada 2005. We made the change because we want limited types to be as similar to nonlimited types as possible. Limited expressions are now allowed in all other contexts (with a similar incompatibility), and it would be odd if assignments had different resolution rules (which would eliminate ambiguities in some cases). Moreover, examples like this one are rare, as they depend on assigning into overloaded function calls.
5.2.1 Target Name Symbols
@, known as the target name of an assignment statement, provides an abbreviation to avoid repetition of potentially long names in assignment statements.
target _ name ::= @
[If a target_name occurs in an assignment_statement A , the variable _ name V of A is a complete context. The target name is a constant view of V , having the nominal subtype of V .]
The complete context rule is formally given in 8.6 . The constant view rule is formally given in 3.3 ; the nominal subtype is a property taken from the target object as described below in Dynamic Semantics.
A target_name shall appear only in the expression of an assignment_statement .
For the execution of an assignment_statement with one or more target_name s appearing in its expression , the variable _ name V of the assignment_statement is evaluated first to determine the object denoted by V , and then the expression of the assignment_statement is evaluated with the evaluation of each target_name yielding a constant view of the target whose properties are otherwise identical to those of the view provided by V . The remainder of the execution of the assignment_statement is as given in 5.2 .
To be honest: The properties here include static properties like whether the target_name is aliased and the nominal subtype of the target_name . It was too weird to give separate rules for static and dynamic properties that said almost the same thing.
Use of a target_name can be erroneous if the variable _ name V is a discriminant-dependent component, and some other constituent of the expression modifies the discriminant governing the component V . The assignment probably would be erroneous anyway, but the use of a target_name eliminates the possibility that a later evaluation of V raises an exception before any erroneous execution occurs. See 3.7.2 .
Examples of the use of target name symbols:
Board(1, 1) := @ + 1.0; -- An abbreviation for Board(1, 1) := Board(1, 1) + 1.0; -- (Board is declared in 3.6.1 ). 8/5
My _ Complex _ Array : array (1 .. Max) of Complex; -- See 3.3.2 , 3.8 . ... -- Square the element in the Count (see 3.3.1 ) position: My _ Complex _ Array (Count) := (Re = > @.Re * * 2 - @.Im * * 2, Im = > 2.0 * @.Re * @.Im); -- A target _ name can be used multiple times and -- as a prefix if desired.
Extensions to Ada 2012
The target name symbol @ is new.
- 5.2.1 Target Name Symbols

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment (computer science) In computer programming, an assignment statement sets and/or re-sets the value stored in the storage location (s) denoted by a variable name; in other words, it copies a value into the variable. In most imperative programming languages, the assignment statement (or expression) is a fundamental construct.
The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator. The symbol is '='. Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign '=='. The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is : variable = expression ; where, variable = variable name
The assignment statement. The assignment statement is used to store a value in a variable. As in most programming languages these days, the assignment statement has the form: <variable>= <expression>; For example, once we have an int variable j, we can assign it the value of expression 4 + 6: int j; j= 4+6; As a convention, we always place a ...
•Assignment Statements •Mixed-Mode Assignment . 1-3 Introduction •Expressions are the fundamental means of specifying computations in a programming language •To understand expression evaluation, need to be familiar with the orders of operator and operand evaluation •Essence of imperative languages is dominant
Read on to see the assignment statements in action! Assignment Statements in Action. You'll find and use assignment statements everywhere in your Python code. They're a fundamental part of the language, providing an explicit way to create, initialize, and mutate variables. You can use assignment statements with plain names, like number or ...
Three interrelated programming concepts are variables, declarations and assignment statements. Variables The concept of a variable is a powerful programming idea. It's called a variable because - now pay attention - it varies. When you see it used in a program, the variable is often written like this r = 255; (r is the variable and the ...
An assignment statement sets and/or re-sets the value stored in the storage location(s) denoted by a variable name; in other words, ... Within most programming languages the symbol used for assignment is the equal symbol. But bite your tongue, when you see the = symbol you need to start thinking: assignment. The assignment operator has two ...
The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command: a=3.45. in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a. Next, type the command: a. in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to ...
The meaning of the first assignment is computing the sum of the value in Counter and 1, and saves it back to Counter. Since Counter 's current value is zero, Counter + 1 is 1+0 = 1 and hence 1 is saved into Counter. Therefore, the new value of Counter becomes 1 and its original value 0 disappears. The second assignment statement computes the ...
This page titled 2.1: Assignment statements is shared under a CC BY-NC 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Allen B. Downey (Green Tea Press) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
Assignment creates object references instead of copying the objects. Python creates a variable name the first time when they are assigned a value. Names must be assigned before being referenced. There are some operations that perform assignments implicitly. Assignment statement forms :-. 1. Basic form: Unmute.
7 Assignment Expressions. As a general concept in programming, an assignment is a construct that stores a new value into a place where values can be stored—for instance, in a variable. Such places are called lvalues (see Lvalues) because they are locations that hold a value. An assignment in C is an expression because it has a value; we call it an assignment expression.
Expression statements in Python are lines of code that evaluate and produce a value. They are used to assign values to variables, call functions, and perform other operations that produce a result. x = 5. y = x + 3. print(y) In this example, we assign the value 5 to the variable x, then add 3 to x and assign the result ( 8) to the variable y.
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables. 1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶. Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator =. An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side.
Assignment. x >>= y. x = x >> y. Table 2. When writing any kind of program, there will be many instances where you will need to use a variable as part of an expression and you will want to assign the result of that expression into the same variable. An example of this kind of operation is when you want to increment a variable by some value ...
Programming Languages Lecture 7 - Expressions and Assignment Statements Why Expressions? • Expressions are the fundamental means of specifying computations in a programming language • To understand expression evaluation, need to be familiar with the orders of operator and operand evaluation • Essence of imperative languages is dominant
Assignment: An assignment is a statement in computer programming that is used to set a value to a variable name. The operator used to do assignment is denoted with an equal sign (=). This operand works by assigning the value on the right-hand side of the operand to the operand on the left-hand side. It is possible for the same variable to hold ...
Programming Languages • It was believed in the early days of programming language development that it was sufficient to be able specify the syntax of a programming language. We now know ... Grammar For Simple Assignment Statements <assignment statement > ::= <variable> = <arithmetic expression >
In computer programming, a statement is a syntactic unit of an imperative programming language that expresses some action to be carried out. A program written in such a language is formed by a sequence of one or more statements. A statement may have internal components (e.g. expressions). Many programming languages (e.g. Ada, Algol 60, C, Java, Pascal) make a distinction between statements and ...
Here is a CFG for a language of very simple assignment statements (only statements that assign a boolean value to an identifier): ... Since every programming language includes expressions, it is useful to know how to write a grammar for an expression language so that the grammar correctly reflects the precedences and associativities of the ...
chapter 7 - Expressions and Assignment Statements. What role do expressions play in a programming language? Click the card to flip 👆. they are the fundamental means of specifying computations. Click the card to flip 👆.
Expressions are unique in meaning, while statements are two-sided in execution. For example, 1 has a certain value while go( ) may be executed or not. Statements are the whole structure, while expressions are the building blocks. For example, a line or a block of code is a statement.
Syntax. 2. assignment_statement ::=. variable_ name := expression; 3. The execution of an assignment_statement includes the evaluation of the expression and the assignment of the value of the expression into the target. [An assignment operation (as opposed to an assignment _ statement) is performed in other contexts as well, including object ...