- No results found

Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile Industry: A Case Study Of Ford Motor Company
Share "Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile Industry: A Case Study Of Ford Motor Company"
Academic year: 2020
Loading.... (view fulltext now)
Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile
Industry: a case study of ford motor company.
Abstract: Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is an essential change in the processes and structure of any company. That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted to the changing regime of FORD Motor Company since 1900s. A critical evaluation of Ford was made with the help of Situation-Actor-Process and Learning-Action-Performance (SAP-LAP Analysis), Strength, Weakness, Opportunities and Threat (SWOT Analysis), Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Social (PESTEL Analysis) and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA).The results revealed that Ford is a very dynamic company which changes as per the requirement of the market. Repeated BPR activities helped the company in remaining the world leader till date.
Key words: Business Process Re-engineering, SAP-LAP, SWOT, PESTEL, DEA, Ford Motor
I. INTRODUCTION
Ford Motor Company was founded in 1903. It was ranked fourth in the fortune 500 companies for the year 2000. It has eight automotive brands (Aston- Martin, Jaguar, Volvo, Lincoln, Mercury, Ford, and Mazda) and four service divisions (Ford Credit, Hertz, Quality Care, and Quik-Fit). Ford has its presence in more than 200 countries and territories, with a workforce of 400,000 approximately and 140 manufacturing plants [1]. The Ford Motor Company, at least until World War II, was also occupied in ”human engineering”. Gradually, Ford was able to go from a creative idea to near to optimum assessment of demand, to engineering, manufacturing, and logistics, to the relationship with the customers. Ford used e-commerce internally to start with, which they called it internet inside. Then, they used internet in traditional B2B applications and B2C applications, and also to facilitate the ongoing relationship with customers. Ford also applied technology inside their vehicles, through Telematics initiatives, which created the internet on wheels. In due course of time, Ford allied with the best technology partners.
Business Process Re-engineering implementation can be characterized as the implementation of purposeful and basic change in business processes to achieve sudden improvements in performance.
Dr. Sanjeev Tandon
Army Institute of Management & Technology, Gr. Noida, India
Dr. Surabhi Goyal
Kavita Sharma
M. S. Abhilash
performance of the company. After re-engineering of vital business processes, new ways of company management are required.
This paper gives an understanding through a contextual investigation research into the relationship between strategic planning and BPR of an automobile major Ford. Organizations have experienced major change. The impetus for these changes comes as a reaction to competitive pressures and proactive action to improve corporate responsiveness [2]. Change of overall process is very complicated as it includes the manipulation of interactive relationships among organizational sub-components such as management, people, structure, technology and rewards. Drawing from a huge number of literature on implementation with innovation, socio-technical design and the management information systems, this case study is focusing on the accompanying inquiries:
1. What are the issues with Ford which are identified with execution of business procedure re-engineering?
2. What is the relative seriousness of these issues?
3. How do these issues of Ford identify with the achievement of BPR?
4. What is the impact of BPR on the overall performance of the Ford Motor?
This study discusses about the implementation of BPR concept at various stages of business life of Ford. Following sections will discuss about the objective, review of literature, research methodology, data analysis tools, implementation, recommendations and conclusion of the study.
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
companies have also benefited from reengineering; Richard L. Florida of Carnegie Mellon University found that 60 percent of 2,000 companies he surveyed showed improved returns from restructuring work [9]. Accounting and Finance departments [10][11], production and supply logistics[12], human resources departments[13], and government agencies, such as, the US Department of Commerce Patent and Trademark Office[14], and the Metropolitan Transportation Authority in Los Angeles have undergone BPR. By identifying procedures and applications software programs of the re-engineered accounts payable systems that was described in Michael Hammer’s seminal article in the Harvard Business Review [4], internal controls assures that organizations realize the benefits of re-engineering is demonstrated.
III. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
This study was conducted with special reference to the BPR in the automobile industry. In this study, the focus was restricted to the changing regime of FORD Motor Co.
The research encircles the following objectives:
1. To critically evaluate the BPR activities of FORD Motor Company.
2. To analyze the impact of BPR on the efficient performance of the company in a time span of last 25 years.
On the basis of this statement, the hypothesis framed is as follows:
H0-There is no impact of BPR activities on the overall efficient performance of the company.
The data will be tested on this assumption and results will be extracted.
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The study revolves around the historical challenges, their respective solutions and impact on the performance of Ford Motor Company in its history of more than 25 years. The study is descriptive in nature.
i. Problem definition: To develop a deep understanding of essence of the process of BPR to maximize attainment of business goals.
ii. Research Design : The research design employed to satisfy the objectives in this research is descriptive research.
iii. Data Collection Methods:
Secondary Data: The data was collected through various magazines, books, journals and websites (e-journals), Ford Motor Annual reports, financial statement from stock exchanges, research papers and Ford website. For analyzing the data, SAP-LAP analysis, SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis and DEA analysis are being used.
A. SAP-LAP ANALYSIS
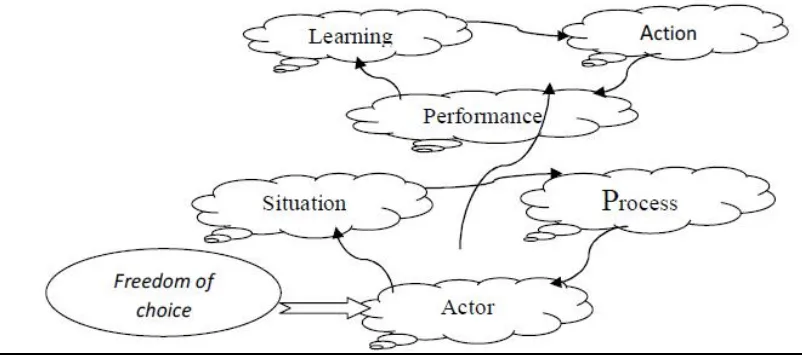
For analyzing the collected data, SAP-LAP framework has been used. This framework is developed by Prof Sushil Kumar, IIT, Delhi. According to him,“SAP-LAP paradigm is the inquiry in management which is equally applicable in non formal service sector” [15]. This framework can be used for case analysis, managerial investigation and problem solving. It comprises of three basic elements i.e. situation, actor and process. The interplay of situation actor process (SAP) leads to learning action performance (LAP) [16] (Refer Figure 1).
Figure 1: SAP-LAP Model
(Note: Retrieved from Dubey, D K Sen and A ATalankar, 2012.
http://www.vsrdjournals.com/ME/Issue/2012_12_December/Web/1_Sandeep_Kumar_Dubey_1065_Research_Article_VSRDIJ MAPE_December_2012.pdf)
process, customer interface process, performance management process, technology transfer process, innovation and investment process, distribution process and so on.[16].
The interface of "actor" and "process" defines the structure, systems and strategies that need to be transformed for organizational change. The interface of "process" and "situation" defines the incident to be taken care of and adaptation and response of the process to the changing environment.
The interaction and synthesis of SAP leads to Learning-Action-Performance (LAP). The researcher needs to learn about the SAP and bring out key learning issues of interest. Based on the learning, the action is to be taken on situation, actor or process or the relevant interfaces. On the basis of efficient and effective actions, performance is generated. Here, the “situation” examines all the time lines like the past, present and the expected future; the “actor” explores various views, roles and capabilities, freedom of choice; the “process” explains how the inputs are converted into outputs, and other alternative ways of doing the process; “learning” refers to the key issues related to the SAP; “action” refers to what can be done to improve SAP; “performance” indicates the impact of system’s performance on SAP.
B. DEA ( DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS)
Over the past few decades, data envelopment analysis (DEA) is being used for evaluating the relative efficiencies of decision making units (DMUs) within a homogenous set. DEA is an approach to estimate the manufacture function of organizations and organizational units and enables the assessment of their efficiency. The envelopment surface will differ depending on the scale assumptions that underpin the model. Two scale are generally employed: constant returns to scale (CRS), and variable returns to scale (VRS). CRS reflects the fact that output is proportionately changing with inputs are changed; VRS reflects that production technology may exhibit increasing, constant and decreasing returns to scale.
This model includes 2 inputs and 3 outputs of Ford Motor Company. The inputs and outputs are discussed below. The inputs are:
1. Number of employees from 1991-2015.
2. Selling and administrative expenses for the period 1991-2015. The outputs are:
The data related with these variables were shown in Table 1.
C. Adopted Model
This model will adopt theOutput orientated DEAconsidering both CRS (Constant Returns to Scale) and VRS (Variable returns to Scale). This method is majorly used to get more flexible and reliable results. The CRS assumption is used when all DMUS are operating at an optimal level. The use of the CRS specification when all firms are not operating at the optimal scale results in measures of TE (Technical Efficiency) which are mystified by scale efficiencies (SE). SE is calculated by estimating both the CRS and VRS models and looking at the difference [17]. VRS model is basically the CRS with an additional constraint added to the Linear programming (LP) problem [18]. The analysis was done on 25 years data of Ford between 1991 and 2015. The highest efficiency degree that can be achieved is 100 per cent.
According to Farell, if a given firm uses quantities of inputs, defined by the point P, to produce a unit of output, the TE of that firm could be represented by the distance QP. This is usually expressed in percentage terms by the ratio QP/0P, which represents the percentage by which all inputs could be reduced. The TE of a firm is most commonly measured by the ratio TE = 0Q/0P, which is equal to one minus QP/0P. It values between zero and one, and hence provides an indicator of the degree of TE of the firm. A value of one indicates the firm is fully efficient. Another type of efficiency is allocative efficiency (AE). The AE of the firm operating at P s defined to be the ratio AE = 0R/0Q , RQ represents the reduction in production costs that would occur if production occur at the allocatively (and technically) efficient point Q’, instead of at the TE, point Q.
The total economic efficiency is defined to be the ratio, EE = 0R/0P, where RP can also be interpreted in terms of cost reduction. The DEA mathematical model is as follows:
Max h = Σruryrj0/ Σi ν ixi jsubject to
Σruryrj/Σi ν ixi j< 1, j = 1,Λ, n (for all j) In simpler words:
Efficiency = Σweighted outputs/Σweighted inputs
D. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a contraction for strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. It is a structured planning method that evaluates Abovementioned four elements of a project or business venture [20]. SWOT analysis can be done for companies well as for product, place, industry, or person. It involves specifying the business objective or project and identifying all the factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieve that objective.
E. PESTEL Analysis
A PESTEL analysis is a tool used for external environment players. It can be used to analyze and monitor the external environment of the company. The strategic management tool gauges the macro environmental factors. The results make decision taking much easier.
The different macro-environmental factors can affect business strategies. The aim is to assess how exactly the factors influence business performance. PESTEL judges 6 types of environmental influences. They are political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal. These are not independent factors but are interdependent.
V. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
With the help of data collected and various statistical tools mentioned above, a detailed data analysis of internal and external environment was done. All inferences were tested on the basis of hypothesis framed and results were combined and concluded. To recall, the first objective of the study was
“To critically evaluate the BPR activities of FORD Motor Company”
This objective was analysed with the help of results obtained from SAP-LAP analysis, SWOT analysis and PESTEL analysis.
A. SAP-LAP Analysis
SAP-LAP framework of BPR in Ford Motor is discussed in annexure 1. The table discusses the working, people, process, issues, actions and performance of the company. It will help in drawing conclusions about the hypotheses framed in the beginning of the study.
INFERENCES DRAWN FROM THE FINDINGS OF SAP-LAP ANALYSIS
Basis Ford Motor Performance
Industry Profile Ford Motor is a fifth largest distinctive car manufacturing company in the world. Product Focus Ford motor is a renowned manufacturer of cars, SUVs, Trucks, Vans and
IPR Profile Ford legal profile includes 3591 trademarks, 5780 patent grants and 412 patent applications
Relationship between Sales and Growth of the Company
They are not mutually correlated due to dependence of revenue more on segmented automobiles than the newer technologies.
Financial Position The last fiscal year revenue counts to $12.37 billion.
Several Issues The ability to manage growth, intense competition among Indian and overseas motor companies and much of too dependency on America's best-selling F-Series truck and SUV sales for profits. The performance of average worker with difference to the management of international operations and reduced demand for technology used in existing products are also the issues of Ford.
Prospective Solutions for the Issues
Product-wise, Ford has achieved its goal of delivering 25 new products from 2012 to the close of 2015. It also transformed its Valencia plant into one of the most advanced and productive automotive plants, where each worker got specialized in one task with one tool. Also, Ford launched a key restructuring effort including the closing of five plants, the abolition of 35,000 jobs, over $9 billion in cost cutting, and the shuttering of several car lines including the Mercury Cougar and the Lincoln Continental.
Future Plans Ford initiated many steps to provide better services like a new environmental initiative called the Partnership for a Cleaner Environment (PACE) with limited suppliers. They planned and implemented best practices for energy, greenhouse gas emissions and water use reduction. They introduced various motivational sprees for employees and simultaneously continued safety measures for them. Ford raised awareness of supply chain sustainability through training of new purchasing personnel and global supplier technical assistance staff.
B. Interpretation of SAP-LAP Analysis
This analysis was done to make a detailed discussion of the changing phases of Ford. On the basis of above mentioned criteria (Refer table 1), few inferences have been drawn:
2. Although quite an old company, Ford believed in dynamism and that too at global level. Thousands of IPRs and changing organizational structures are examples of it.
3. One of the major backbone of Ford is its products and brand loyalty. Customers trust Ford technologies and products by the name. It is because of this reason the sale is not dependent on the IPRs.
4. Although Ford had been through tough times like, plant shut down, retrenchments, shutting down the production of major segments of cars, supply chain issues, but the top management of the company had always kept a futuristic endeavor and they kept on experimenting new strategies. 5. They also have shown interest in CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) by providing aids to the
employees and the society at large. They are also working for producing more eco-friendly automobiles for future consumption.
This shows that Ford Motor is surely a long run successful player of automobile industry. Various BPR inclusions whether related to Supply Chain or Information Technology or Human Resource have been made but they never refrained themselves from changes.
On the basis of the findings and interpretation done, it can be said that the null hypothesis of the study is rejected and there is a positive relationship between Ford Motor performance and BPR. Ford has in fact used this strategic option more rigorously.
SWOT ANALYSIS OF FORD Strengths
Experienced organizations
Global reach (more than 200 countries & territories)
Human engineering
Use of e commerce internally
Proven expertise in manufacturing, research and development and automobile marketing
Strong position in the American auto market. Implemented best practices for
environmental issues
Dependence of revenue
Dependency on other best selling cars sale & profit
incapability to match the production targets or sales volume of the top five automakers: Toyota, Volkswagen, General Motors, Renault-Nissan and Hyundai Kia
Reduction in demand for technology
Adversely affected by the global recession & Euro crisis
High cost structure
Opportunities
Green technology formula
Demonstration of sustainability model.
Increase their number of research and development centres.
A proper employee retention strategy shall be framed .
Growing auto markets, particularly in expanding economies such as China, Mexico and India.
Increased levels of e-commerce, which
might increase the demand for light commercial vehicles used for delivery.
Growth through product development
Expanding automobile sector
Improving business scenario due to expansion of consumer base
Lower fuel prices could reduce the demand for costlier fuel vehicles such as hybrids and electrics.
Aggressive competitive rivalry
New entry of high-tech firms
Fluctuating oil prices
Increasing usage of public transport and increased fuel costs
Production problems in local plants due to labor and similar issues
C. Interpretation of SWOT Analysis
The data collected for SWOT analysis was extracted from secondary sources like company website, annual reports and various research papers published. On the basis of observations mentioned in SWOT analysis (Refer table 2), it was seen that Ford Motor is a global company having its reach in almost all countries. The company is enjoying brand loyalty as well as an arena of new potential customers. They are also following the best practices for human engineering. On the contrary, the revenues of Ford are highly dependent on the performance of its close competitors. They are also not much apt of handling environmental issues which they need to work upon as soon as possible. As far as opportunities are concerned, they are entering into green technology supported by increased R & D activities and increasing global reach. Still company needs to prepare themselves for some unseen threats like fuel price fluctuations, aggressive cut-throat competition and increased use of public transport.
D. PESTEL Analysis
Figure 2: PESTEL Analysis of Ford Motor Company
E. Interpretation of PESTEL Analysis
growth. Also, it among the top most fortune 500 companies increasing its goodwill as well as investor support. Socially, the company is taking aggressive steps in doing CSR activities and maintaining the ecological level around the globe. Technically, Ford is now adapting newer researches and also gearede up in having more R & D centres to pace up the sales of the company. Environmentally, although emitting pollution is one of the issues of the company but then they are putting efforts by going for R & D in more fuel efficient vehicles and their economic pricing. Last, on legal aspect, Ford is very vigilant about the varied rules, regulations and laws of various countries in which they are dealing. They also look after their IPRs very well. So, on overall basis, FORD is doing well in their external business environment.
The second objective of the study was
“To analyze the impact of BPR on the efficient performance of the company in a time span of last 25 years”
On the basis of this objective, a hypothesis is framed saying
H0 - There is no impact of BPR on the overall performance of the company.
This hypothesis will be tested through DEA analysis. In this analysis, an output oriented DEA model is taken and TE of both CRS and VRS are recorded and compared. The results are compared and inefficiencies were taken out to extract out the reasons behind it.
F. DEA Analysis
The results of DEA analysis of Ford motor Company is mentioned in Table 3.
DEA ANALYSIS OF FORD MOTOR COMPANY Output orientated Malmquist DEA
DISTANCES SUMMARY
Year CRS VRS
4 0.675 0.737
5 0.888 0.889
11 0.908 0.944
18 0.794 0.899
20 0.913 0.929
22 0.945 0.968
24 0.919 0.99
25 0.88 0.995
Mean 0.929 0.974
Maximum 1 1
Minimum 0.675 0.737
G. Interpretation of DEA Analysis
On the basis of the results extracted through DEA (refer table 3), it can be seen that in most of the years, FORD had given efficient performance as per the inputs added and out derived. Still, as per CRS, there were 13 times that Ford Motor was unable to match its benchmark and as per VRS, there were 5 years where Ford did not performed well. The minimum being Year 4. On an average, the performance of Ford is almost near to efficiency.
to counteract declining demand.This results into upgradation in the overall working of the organization. This was done in the name of Business Process Re-engineering.
V. CONCLUSION
This study revolves around the BPR changes experienced by Ford. Since 1903 till 2015, many changes happened in Ford. Whether it is expansion or diversification or contraction, Ford did everything to stay in competition. Like any other company, there were issues with Ford, but strong and well organized BPR strategies helped them to emerge as winners of all time. Thus, driving the company to become one of the top leaders of automobile industry globally. To end this, on the basis of literature reviews done, some recommendations are as follows:
To sum up, Ford Motor Company is a growth oriented company which excels into varied departments of its own outshining competition. With the help of BPR initiatives, Ford has demonstrated sustainability model consistently. But, in the era of competition, Ford has to innovate Green Technology formula to emerge as a winner. Ford has miles to go yet.
[1] Naseer and Greenhalgh (2000). Ford Motor Company’s CEO Jack Naseer on transformational change, e-business and environmental responsibility. Interview by Leonard Greenhalgh. Academy of Management executive. 14(3), pp- 46-51. [2] Grover V, Jeong, S. Ryul, Kettinger and others (1995). The implementation of business process re-engineering. Journal of Management Information System. 12(1), pp- 109-144.
[3] Davenport, T. H. (1993). Process innovation; reengineering work through information technology . Boston, Harvard Business School Press.
[4] Hammer and Champy, “ Reengineering the Corporation : A Manifesto of Business Revolution ,” Harper Business Publications (1991).
[6] Committee of sponsoring Organizations of Treadway Commission (COSO) (1992). Internal controls- Integrated Frameworks. American Institute of certified public Accountants. New Jersey. Ed. 2.
[7] Currid, Cheryl and company (1991). Computing strategies for re-engineering in your organization. Prima Publishing, Rocklin, California.
[8] Klimas, Anthony J. (1997). Re-engineering in the real world. Management Acounting . 78(11), pp. 30-36.
[9] Gleckman, H. (1993). A Technology payoff, a sweeping reorganization of work itself is boosting productivity. Business Week . 3323, pp. 57-68.
[10] Hildebrand, C. (1994). Financial affairs. CIO . 7(11), pp. 62-68.
[11] Schmidt, D. (1994). The Credit manager’s Re-engineering Primer. Business Credit.. 96(1), pp. 29-32.
[12] Kallock, Roger W. (1994). Moments of truth are a call for action. Transportation and Distribution. 35(2), pp. 57. [13] Shahooth K, Battall A.H. (2006). Using Data envelopment analysis to measure cost efficiency with an application on Islamic banks. Sci. J. Adm. Dev . 4, pp. 134-156.
[14] Sushil (2012). Flowing stream strategy: Leveraging strategic change with continuity. Springer .
[15] Sanders, Robert L. (1997). If marx has been a Business Process re-engineer. ARMA Records Management Quaterly. 31(2), pp. 58-64.
[16] Smith B. (1994). Business Process re-engineering: More than a buzzword. HR focus . 71(1). Pp. 17-19.
[17] Ramaj T. (2015). Data Envelopment Analysis: An application to measure Technical Efficiency of Hotel units in Elbasan, Albania. Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology. 2 (8), pp. 2141-2146.
[18] Sushil (1997). Flexibility System management: an evolving paradigm. System Research and behavioural science . 14(4), pp. 259-279.
[19] Banaeian, N. (2004). Application of Data Envelopment Analysis to Evaluate Efficiency of Commercial Greenhouse Strawberry. Research Journal of Applied Sciences Eng. Technology . 3(3), pp. 185–193.
[20] Negi and Zseni (2016). SWOT analysis of dry Toilets. 3 International Conference rd on Environmental and Economic
Impact on Sustainable Development. 203. Extracted from
http://www.witpress.com/Secure/elibrary/papers/EID16/EID16023FU1.pdf
ANNEXURE: 1
SAP-LAP ANALYSIS OF FORD MOTOR COMPANY
Situation Issues
1. How company entered into automobile industry?
1. Henry Ford builds a quadric-cycle. In June 1903, he established Ford Motor Company. Five years later, Ford introduced the model T and sold over 15 million units in next 2 decades.
2. How is the present performance of the
company? 2. In 2014, Ford sold approximately 6,323,000 vehiclesthroughout the world.
3. What is expected from the company? 3. The annual revenues are at $ 140.6 M. with operatingmargin of 6.8% in 2015. 4. A variety of new technologies have joined stereo lithography.
5. With the 3D printing machines running nearly 24*7, the facility has become a kind of virtual sandbox for
6. With about 199,000 employees and 67 plants worldwide, the company’s core business includes designing, manufacturing, marketing, financing and servicing a full line of Ford cars, trucks, SUVs and electrified vehicles, as well as Lincoln luxury vehicles. Actor
1. What are the world views? 1. Ford is fifth biggest automobile manufacturer in world.
2. What roles and capabilities are exhibit? 2. Firm’s intensive growth strategies aligned to its genericstrategy for competitive advantage.
3. In what domains is freedom of choice available?
3. Ford is aggressively pursuing opportunities through Ford Smart Mobility, the company’s plan to be a leader in various domains like connectivity, mobility, autonomous vehicles, the customer experience, and data and analytics.
4. Vision of Ford? 4. Ford is present in Motorsports like Formula One, Rally,Sports cars, Touring cars & sponsorship of events 5. Capitalizing on the models exclusively designed for the type of markets e.g. ford Ikon for India
6. People working together as a team. Process
1.What is being done? 1. In the 2014 Euro NCAP assessments, earned a five-starsafety rating for the Ford Mondeo.
2. What are the variables and parameters 2. On April 30, 2015, Ford entered into an Amended andRestated Relationship Agreement with Ford Credit.
3. What can be changed?
3. In 2015, Ford also entered into collective bargaining agreements with Argentina, Brazil, France, Germany, India, Mexico, New Zealand, Romania, Taiwan, Thailand and the United Kingdom.
5. How is it being done?
5. Substantial pension and post-retirement health care and life insurance liabilities impairing liquidity or financial condition.
6. What, why and how else?
6. Ford was honored by the Ethisphere Institute – for the sixth year in a row – as one of the World’s Most Ethical Companies.
Synthesis Learning
1. What are the key issues related to situation? 1. The ability to manage growth, intense competitionamong varied motor companies.
2. What are the key issues related to actors? 2. Ford is too dependent on America's best-selling F-Series truck and SUV sales for profits
3. What are the key issues related to process?
3.The average worker performed several tasks in the production of each component, and used a variety of tools in the process.
4. The ability to manage the international operations and reduction in the demand for technology.
1. What can be done to improve situation?
1. Product-wise, delivering 25 new products from the end of 2012 through the end of 2015, and it's recently focused on performance vehicles such as the Focus RS, Focus ST, Fiesta ST, and the newly available 2015 Mustang helped Ford in achieving the goal.
2. What can be done to improve actors? 2. Ford transformed its Valencia plant into one of the mostadvanced and productive automotive plants on the planet. 3. What can be done to improve process? 3. Each worker specialize in one task with one tool..
4. The company takes a $2.1 billion charge to cover the cost of replacing Firestone tires on its vehicles
5. Ford launched a major restructuring effort that included the closure of five plants, the elimination of 35,000 jobs, over $9 billion in cost cutting measures, and the shuttering of several car lines including the Mercury Cougar and the Lincoln Continental.
Performance
1. What will be its impact on situation? 1. Began pilot of a new environmental initiative called thePartnership for a Cleaner Environment (PACE).
2. How will the actors be affected?
2. Raised awareness of supply chain sustainability internally through training of new purchasing personnel and global supplier technical assistance staff.
3. How will the performance of the process be
affected? 3. Earned the highest possible Overall Vehicle Score offive stars in the New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) of the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHSTA) for 15 Ford Motor Company vehicles.
4. Safety measures improved substantially
5. Kicked off a series of mobility experiments as part of Ford Smart Mobility.
ANNEXURE: 2
DEA VARIABLES FOR THE STUDY
Inputs Outputs
Number of Employees (in'000)
Selling, administrative
expenses Automativerevenues EPS expensesTotal
1991 332 3993 72051 0.93 75820
1992 325 4434 84407 -2.4 86182
1993 322 4968 91568 -7.81 90136
1994 338 11280 107137 2.27 101311
1995 347 7860 110496 4.97 11420
1996 372 6625 118023 3.58 115507
1997 364 7082 122935 3.73 115989
1998 345 7616 119083 5.75 112398
1999 375 11010 135022 18.17 128594
2000 352 9838 140765 3.69 135489
2001 359 9778 130736 -3.02 138222
2002 350 9758 134273 -0.55 162077
2003 328 10152 138442 0.27 163970
2004 325 11455 147134 1.21 168042
2005 300 24588 153413 0.88 178408
2006 200 19148 141727 -6.73 177038
2007 245 21169 152691 -1.4 177751
2008 205 21065 127635 -6.5 159296
2009 117 13029 103868 0.91 119,715
2010 164 11909 119280 1.9 122,296
2011 164 10884 128168 5.33 129,321
2012 171 11494 126567 1.47 127,961
2013 181 13176 139369 1.83 134,108
2014 187 14117 135782 0.81 143,745
Related documents
Following the Start condition, the 24XX32A monitors the SDA bus checking the device type identifier being transmitted and, upon receiving a ‘ 1010 ’ code and appropriate device
Sport therapist Education Motivation Communication Sports Science Patient Psychology Sports Medicine. A cardio-vascular therapist needs an
As underlined previously, the presence of the status-seeking behavior will lead to an excessive capital accumulation and ignoring the influence of social sta- tus may therefore yield
The interferometric and holographic NDE systems provide a capability for measur- ing this local displacement increase, and generate a displacement-field image where the crack
If you visit an out-of-network provider, you must get an itemized receipt from the provider and submit that receipt to Heritage Vision Plans for reimbursement.. The receipt will
Through the guidance and leadership of the Ford STEAM Council, Ford Motor Company provides Ford NGL students with scholarships, learning challenges, and other growth
Lyman-break galaxies are used as a well-understood, high- redshift background sample allowing mass measurements of lenses at unprecedented high redshifts using weak
The sales revenue recognized at the commencement of the lease term by a manufacturer or dealer lessor is equal to the fair value of the asset, or, if higher, the present
Business Process Reengineering: A Crucial Approach for Enhanced Organizational Sustainability
- First Online: 04 February 2024
Cite this chapter

- Jean Dagher 20 &
- Laura Fayad 20
Part of the book series: Contributions to Environmental Sciences & Innovative Business Technology ((CESIBT))
99 Accesses
This study investigates Business Process Reengineering (BPR) in contemporary management as a visionary strategy for managers wishing to reengineer their distressed firms for enhanced organizational sustainability through advancing organizational performance. It presents a unique setting for businesses withdrawn from the case of Lebanon and introduces novel dynamics on the implementation and outcomes of BPR initiatives. This article follows a qualitative exploratory method through interviews with 42 managers in distressed Lebanese micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs), to identify noteworthy common themes about BPR activities, organizational performance indicators, and their relationships. The results pinpoint the key role of BPR activities namely cultural change and technology implementation in MSMEs. Furthermore, the most significant improvements of BPR can be achieved in financial success and employee retention indicators. Organizations can leverage these organizational performance indicators to drive sustainable practices. The lessons learned highlight the contextual relevance of the Lebanese MSMEs; the crisis dynamics’ impact on BPR implementation and outcomes; the importance of proper management of BPR to face potential challenges and risks; the significance of psychological and emotional effects; and the potential impacts of cultural change and technology implementation. This study further provides future research opportunities in organizational, cultural, management, digital transformation, or other contexts.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abdolvand N, Albadvi A, Ferdowsi Z (2008) Assessing readiness for business process reengineering. Bus Process Manag J 14(4):497–511
Article Google Scholar
Afsar B, Al-Ghazali B, Umrani W (2020) Retracted: Corporate social responsibility, work meaningfulness, and employee engagement: The joint moderating effects of incremental moral belief and moral identity centrality. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 27(3):1264–1278
Ahmad T, Van Looy A (2020) Business process management and digital innovations: a systematic literature review. Sustainability 12(17):6827
Air Force Magazine (2012) Air Force cancels expeditionary combat support system program. https://www.airforcemag.com/article/1112ecss/
Al-Dahash R, Alsarayreh F (2020) The impact of business process reengineering on organizational performance: a case study of Johnson and Johnson’s supply chain processes. Int J Bus Manag 5(1):1–14
Google Scholar
Al-Fawaeer M, Ridha MB, Yousif ASH (2019) An investigation into the relationship between business processes re-engineering (BPR) and employees’ performance: an empirical study at the Jordanian public shareholding companies. Rev Appl Socio-Econ Res 17(1):5–17
Aljazeera (2023) Lebanon’s currency value plunges to 100,000 against US dollar. https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2023/3/14/lebanons-currency-value-plunges-to-100000-against-the-dollar
Al-Mashari M, Zairi M (1999) Business process reengineering: a survey of international experience. Bus Process Manag J 5(1):13–29
Al-Mashari M, Al-Mudimigh A, Zairi M (2003) Enterprise resource planning: a taxonomy of critical factors. Eur J Oper Res 146(2):352–364
Al-Muhrami MAS, Alawi NAM (2023) The impact of business process re-engineering on institutional performance of the Yemeni General Electricity Corporation, Aden, Malaysia. Int J Bus Manag 11(1):7–18
Anderson EW, Fornell C, Lehmann DR (1994) Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: findings from Sweden. J Mark 58(3):53–66
Atallah NM (2023) Is there life after the Lebanese lira? The National News. https://www.thenationalnews.com/mena/lebanon/2023/03/14/is-there-life-after-the-lebanese-lira/
Awolusi OD, Atiku OS (2019) Business process re-engineering and profitability in the Nigerian Oil and Gas Industry: the mediating influence of operational performance. Inf Manag Bus Rev 11(3(I)):13–26
Bako YA, Banmeke MB (2019) The impact of business process re-engineering on organizational performance: a study of commercial banks and micro-finance banks in Ilaro. J Manag Technol 5(1):1–14
Barney JB, Ketchen DJ Jr, Wright M (2011) The future of resource-based theory: revitalization or decline? J Manag 37(5):1299–1315
Bassen A, Kovács AM (2020) Environmental, social and governance key performance indicators from a capital market perspective. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, pp 809–820
Baxter R, MacLeod M (2019) Financial management: principles and applications, 9th edn. Pearson Australia
Braun V, Clarke V (2012) Thematic analysis. In: Cooper H, Camic PM, Long DL, Panter AT, Rindskopf D, Sher KJ (eds) APA Handbook of research methods in psychology, vol 2: Research designs: quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 57–71
Bryman A (2012) Social research methods. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Budiono A, Loice R (2012) Business process reengineering in motorcycle workshop X for business sustainability. Procedia Econ Finance 4:33–43
Bulchand-Gidumal J, Melián-González S, Lopez-Valcarcel BG (2013) A social media analysis of the contribution of destinations to client satisfaction with hotels. Int J Hosp Manag 35:44–47
Business Insider (2013) Nike's biggest failure: the story of how the shoe giant flubbed its ‘Biggest Project Ever. https://www.businessinsider.com/nikes-biggest-failure-2013-5
Cagliano AC, Grimaldi S, Rafele C (2011) A systemic methodology for risk management in healthcare sector. Saf Sci 49(5):695–708
Cascio WF (2018) Managing human resources: productivity, quality of work life, profits. McGraw-Hill Education
Cebeci U, Tekdal M (2019) The impact of business process reengineering on financial performance: a meta-analysis. J Bus Res 100:192–201
Chakraborty G, Srivastava P, Marshall F (2007) Are drivers of customer satisfaction different for buyers/users from different functional areas? J Bus Indus Mark 22(1):20–28
Champy J (1995) Reengineering management: the mandates for leadership. Harper Collins Publisher, New York
Combs-Harris JA (2021) An inclusive leadership model to integrate organizational dynamics, change management, change leadership, and diversity and inclusion needs for the successful implementation of business transformations. Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
ComputerWorld (2014) Waste management sues SAP over ERP implementation. https://www.computerworld.com/article/2488802/waste-management-sues-sap-over-erp-implementation.html
Credit Libanais (2023) Annual inflation in Lebanon at 263.84% in March 2023. https://economics.creditlibanais.com/Article/211590#en
Creswell JW (2014) Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches, 4th edn. SAGE Publications, New York, NY
Daft RL (2000) Organization theory and design, 7th edn. South-Western College Publishing, Thomson
Dagher J (2017) The Lebanese armed forces engaging Nahr Al-Bared Palestinian refugee camp using the instruments of national power. US Army Command and General Staff College: Fort Leavenworth, United States.
Dagher J (2018a) America's strength: Teaching international military students. Natl Interes. https://www.nationalinterest.org/feature/americas-strength-teaching-international-military-students-26299
Dagher J (2018b) Civil-military cooperation: a relevant component of the Lebanese armed forces in today's operational environment. US Army Command and General Staff College: Fort Leavenworth, United States.
Dagher J (2018c) Intelligence and risk: Vicksburg, Guadalcanal, Iraq. War Room. https://warroom.armywarcollege.edu/articles/intel-risk-3cases/
Dagher J (2018d) Lebanese Armed Forces implementing instruments of national power as lines of effort to engage Palestinian refugee camp. MilY Rev. https://www.armyupress.army.mil/Journals/Military-Review/English-Edition-Archives/July-August-2018/Dagher-Lebanese/
Dagher J (2018e) Why institutionalize Homeland Civil-Military Cooperation. Peace Stab J. https://pksoi.armywarcollege.edu/index.php/category/pksoi-publications/peacekeepingstabilityjournal/
Dagher J (2018f) Why non-U.S. militaries Should Adopt the U.S. Army Design Methodology. The Strategy Bridge. https://thestrategybridge.org/the-bridge/2018/4/3/why-non-us-militaries-should-adopt-the-us-army-design-methodology#:~:text=When%20Army%20Design%20Methodology%20is,changes%20in%20their%20operational%20environment
Davenport TH (1993) Process innovation: reengineering work through information technology. Harvard Business Press
Davenport TH, Short JE (1990) The new industrial engineering: information technology and business process redesign. Sloan Manag Rev 31(4):11–27
DeReu D, Timmerman J (2019) Agility and business process management. Handbook on business process management 1. Springer, Cham, pp 37–62
Desiana PM, Ma’arif MS, Puspitawati H, Rachmawati R, Prijadi R, Najib M (2022) Strategy for sustainability of social enterprise in Indonesia: a structural equation modeling approach. Sustainability 14(3):1383
Dragišić N, Joković J (2018) Business processes in times of crisis. Recent Adv Inf Technol, Tour, Econ, Manag Agric 694
Economist (2009) Siemens AG: A case study in value destruction. https://www.economist.com/business/2009/04/23/a-case-study-in-value-destruction
Ehnert I (2009) Sustainable HRM: a conceptual and exploratory analysis from a paradox perspective. Springer, Heidelberg
El-Chaarani H (2016) Exploring the impact of emotional intelligence on portfolio performance. Humanomics 32(4):1–23
El-Chaarani H, El-Abiad Z (2020) Knowledge management and job performance: the case of Lebanese banking sector. Int Rev Manag Mark 10(1):91–98
Fasna MFF, Gunatilake S (2019) A process for successfully implementing BPR projects. Int J Prod Perform Manag
Fetais A, Abdella GM, Al-Khalifa KN, Hamouda AM (2022) Business process re-engineering: a literature review-based analysis of implementation measures. Information 13(4):185
Fiedler F (2015) Contingency theory of leadership. In: Organizational behavior 1: essential theories of motivation and leadership. Routledge, New York, NY, pp 232–255
Fielding N (1993) Ethnography. In: Nigel G (ed) Researching social life. Sage, London, UK, pp 155–171
Financial Times (2015) Target’s failure in Canada: Lessons learned. https://www.ft.com/content/c6091742-4618-11e5-af2f-4d6e0e5eda22
FinTech Futures (2019) Banco Santander builds ‘global platform’ to streamline operations. https://www.fintechfutures.com/2019/09/banco-santander-builds-global-platform-to-streamline-operations/
Forcadell FJ, Sanchez-Riofrio A, Guerras-Martín LÁ, Romero-Jordán D (2020) Is the restructuring-performance relationship moderated by the economic cycle and the institutional environment for corporate governance? J Bus Res 110:397–407
Freiser T (1992) The right start for BPR. Information strategy. Executive’s J (9):26–30
Gautam V, Singh S (2018) Business process reengineering for financial success in Indian public sector banks. Int J Bank Mark 36(1):96–112
Gilbert N, Stoneman P (eds) (2015) Researching social life. Sage
Given L (2008) The SAGE encyclopedia of qualitative research methods, vol 1. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Goksoy A, Ozsoy B, Vayvay O (2012) Business process reengineering: a strategic tool for managing organizational change an application in a multinational company. Int J Bus Manag 7(2):89
Griffeth RW, Hom PW, Gaertner S (2000) A meta-analysis of antecedents and correlates of employee turnover: update, moderator tests, and research implications for the next millennium. J Manag 26(3):463–488
Guest G, MacQueen KM, Namey EE (2011) Applied thematic analysis. Sage, Newbury Park, CA
Gupta AK, Govindarajan V (1994) Organizing for knowledge flows within MNCs. Int Bus Rev 3(4):443–457
Hadidi L, Abzakh A (2022) Toward an understanding of BPR perception in the construction industry: the employee attitude toward job enlargement and enrichment in Saudi Arabia. Eng Constr Archit Manag 29(1):204–221
Hammer M, Champy J (1993) Reengineering the corporation: a manifesto for business revolution. Harper and Collins Publisher, New York, NY
Hammer M (1995) Beating the risks of reengineering. Fortune 131(9):105–110
Hammer M, Stanton SA (1995) The reengineering revolution; a handbook. HarperBusiness, New York
Harika A, Sunil Kumar M, Anantha Natarajan V, Kallam S (2021) Business process reengineering: issues and challenges. In: Proceedings of second international conference on smart energy and communication: ICSEC 2020. Springer Singapore, pp 363–382
Hashem G (2020) Organizational enablers of business process reengineering implementation: an empirical study on the service sector. Int J Product Perform Manag 69(2):321–343
Hitt MA, Ireland RD, Hoskisson RE (2017) Strategic management: concepts and cases: competitiveness and globalization. Cengage Learning
Hizam-Hanafiah M, Abdul Ghani MF, Mat Isa R, Abd Hamid H (2022) Critical success factors of franchising firms: a study on franchisors and franchisees. Adm Sci 13(1):8
Hsin Chang H (2007) Critical factors and benefits in the implementation of customer relationship management. Total Qual Manag 18(5):483–508
Human Rights Watch (2023) Lebanon: Events of 2022. https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2023/chapters/lebanon#:~:text=Lebanon%20entered%20the%20fourth%20year,of%20the%20population%20into%20poverty
Ilmudeen A, Bao Y, Alharbi IM (2019) How does business-IT strategic alignment dimension impact on organizational performance measures: conjecture and empirical analysis. J Enterp Inf Manag 32(3):457–476
InformationWeek (2019) How P&G is streamlining operations with intelligent automation. https://www.informationweek.com/big-data/how-pandg-is-streamlining-operations-with-intelligent-automation/d/d-id/1335035
International Rescue Committee (2016) Market overview: Small and medium enterprises in Beirut and Mount Lebanon. A report by building markets for the International Rescue Committee (IRC). https://buildingmarkets.org/sites/default/files/irc_and_building_markets_sme_market_overview_february_2016.pdf
James EA, Slater T (2014) Do you understand how to fine-tune your methodological choices? Moving from basics to getting ready to write. In: James EA, Slater T (eds) Writing your Doctoral Dissertation or thesis faster: a proven map to success. Los Angeles, CA, Sage, pp 55–74
Jensen MC, Meckling WH (1976) Theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J Financ Econ 3(4):305–360
Jeston J, Nelis J (2008) Business process management: Practical guidelines to successful implementations. Routledge
Joseph J (2020) SMEs in Lebanon: An untapped force for recovery. American University of Beirut. https://www.aub.edu.lb/osb/news/Pages/SMEs-in-Lebanon.aspx
Kaur V (2019) Review of literature. knowledge-based dynamic capabilities: the road ahead in gaining organizational competitiveness, pp 21–76
Kettinger WJ, Teng JT, Guha S (1997) Business process change: a study of methodologies, techniques, and tools. MIS Q 55–80
Khalil OEM (2013) The impact of business process reengineering on organizational performance. Int J Econ, Commer Manag 1(6):1–15
Krishnan R, Agarwal R, Bajada C, Arshinder K (2020) Redesigning a food supply chain for environmental sustainability–an analysis of resource use and recovery. J Clean Prod 242:118374
Kumar K, Van Dissel HG (1996) Sustainable collaboration: managing conflict and cooperation in interorganizational systems. MIS Q 279–300
Kusumawati A, Rahayu KS (2020) The effect of experience quality on customer perceived value and customer satisfaction and its impact on customer loyalty. TQM J 32(6):1525–1540
Kwak YH, Anbari FT (2019) Project management for sustainable development. Routledge
Lambert EG, Barton SM, Hogan NL (2001) The missing link in employee retention. Public Pers Manag 30(2):149–157
LaPlaca PJ, Trites GJ (2019) Business process reengineering in the financial industry: an analysis of successful and unsuccessful projects. J Bus Manag 25(1):54–66
Lee RG, Dale BG (1998) Business process management: a review and evaluation. Bus Process Manag J 4(3):214–225
L'Orient Today (2023) Lebanon's inflation rate continued to climb in January. https://today.lorientlejour.com/article/1329068/lebanons-inflation-rate-continued-to-climb-in-january.html#:~:text=BEIRUT%20%E2%80%94%20The%20monthly%20consumer%20price,6.73%20percent%20in%20December%202022
Mallela R (2021) Business process reengineering and organizational performance: evidence from the Indian healthcare industry. J Health Manag 23(1):68–81
MarketLine (2020) Siemens AG—restructuring to drive sustainable growth and profitability. https://www.marketline.com/blog/siemens-ag-restructuring-to-drive-sustainable-growth-and-profitability/
Markus ML (2000) Paradigm shifts-E-business and business/systems integration. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 4(1):10
Marr B (2012) Key Performance Indicators (KPI): The 75 measures every manager needs to know. Pearson UK
Marshall MN (1996) Sampling for qualitative research. Fam Pract 13(6):522–526
Article CAS Google Scholar
McGrath RG (2013) The end of competitive advantage: How to keep your strategy moving as fast as your business. Harvard Business Review Press
Medmsmes (2020) MSME development policies and programs in Lebanon. https://www.medmsmes.eu/lebanon#:~:text=MSMEs%20are%20the%20economic%20drivers,finance%20and%20access%20to%20markets
Melao N, Pereira R (2017) The evolution of business process reengineering: a literature review. Bus Process Manag J 23(2):300–320
Mello JA (2015) Strategic human resource management. Cengage Learning
Meyer JW, Rowan B (1977) Institutionalized organizations: formal structure as myth and ceremony. Am J Sociol 83(2):340–363
Morse JM (2000) Determining sample size. Qual Health Res 10(1):3–5
Mutinda MM (2009) Assessment of human resource factors in implementation of business process reengineering at Kenya commercial bank (Doctoral dissertation)
National Audit Office (2013) National Audit Office report on the NHS's business process review. https://www.nao.org.uk/report/nhs-business-process-review/
New York Times (2007) Ford's way forward plan is showing progress. https://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/23/business/23ford.html
Nick TG (2007) Descriptive statistics. In: Ambrosius WT (ed) Topics in biostatics. Humana Press, Winston-Salem, NC, pp 33–52
Chapter Google Scholar
Nikolaevich AA (2023) Integrating employee motivation and resource optimization for sustained company growth. Sci J Actual Res 15(145):44–47
Nkomo A, Marnewick C (2021) Improving the success rate of business process re-engineering projects: a business process re-engineering framework. South African J Inf Manag 23(1):1–11
Ohno K, Higuchi T (2012) The success and failure of business process reengineering: a case study of US companies. Int J Bus Manag 7(4):62–75
Oliver RL (1999) Whence consumer loyalty? J Mark 63:33–44
Olken F, Rotem D (1986) Simple random sampling from relational databases. University of California
O’Neill P, Sohal AS (1999) Business process reengineering: a review of recent literature. Technovation 19(9):571–581
Ongeri RN, Magutu PO, Litondo K (2020) The business process re-engineering strategy: its impact on the performance of companies manufacturing food in Kenya. Eur J Bus Manag Res 5(5)
Onich TM (2006) Strategic decisions in a distressed organization: the window of opportunity. Secur Lender 62(2):52
Orazalin N, Mahmood M, Narbaev T (2019) The impact of sustainability performance indicators on financial stability: evidence from the Russian oil and gas industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8157–8168
Palumbo R, Douglas A (2023. The secret ingredient? Uncovering the effect of organizational culture on quality management: a literature review. Int J Qual Reliab Manag
Papageorgiou A, Henrysson M, Nuur C, Sinha R, Sundberg C, Vanhuyse F (2021) Mapping and assessing indicator-based frameworks for monitoring circular economy development at the city-level. Sustain Cities Soc 75:103378
Paulose D, Shakeel A (2022) Perceived experience, perceived value and customer satisfaction as antecedents to loyalty among hotel guests. J Qual Assur Hosp Tour 23(2):447–481
Petryk I (2021) Restructuring of business processes for sustainability: revealing the potential of reengineering and Kaizen. Law, Bus Sustain Her 1(1):33–42
Popova V, Sharpanskykh A (2010) Modeling organizational performance indicators. Inf Syst 35(4):505–527
Porter ME (2021) The competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance. Simon and Schuster
Probst G, Raisch S (2005) Organizational crisis: the logic of failure. Acad Manag Perspect 19(1):90–105
QSR Magazine (2020) McDonald's launches ‘Better M’ campaign. https://www.qsrmagazine.com/marketing-promotions/mcdonalds-launches-better-m-campaign
Ramsey CA, Hewitt AD (2005) A methodology for assessing sample representativeness. Environ Forensics 6(1):71–75
Reichheld FF (1996) The loyalty effect: the hidden force behind growth, profits, and lasting value. Harvard Business Press
Rust RT, Zahorik AJ (1993) Customer satisfaction, customer retention, and market share. J Retail 69(2):193–215
Scherrer PS (2003) Management turnarounds: diagnosing business ailments. Corp GovAnce: Int J Bus Soc
Schumpeter JA (2017) Essays: on entrepreneurs, innovations, business cycles and the evolution of capitalism. Routledge
Book Google Scholar
Shahul Hameed NS, Salamzadeh Y, Abdul Rahim NF, Salamzadeh A (2022) The impact of business process reengineering on organizational performance during the coronavirus pandemic: moderating role of strategic thinking. Foresight 24(5):637–655
Simpson M, Taylor N, Barker K (2004) Environmental responsibility in SMEs: does it deliver competitive advantage? Bus Strateg Environ 13(3):156–171
Singh S, Darwish TK, Potočnik K (2016) Measuring organizational performance: a case for subjective measures. Br J Manag 27(1):214–224
Slatter SS P, Lovett D (1999) Corporate recovery: managing companies in distress. Beard Books.
Stake RE (1995) The art of case study research. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Steel RP, Rentsch JR (1997) The dispositional approach to job satisfaction: more than a mirage, but not yet an oasis. J Organ Behav 18(3):251–273
Sturdy G (2010) Business process reengineering: strategies for occupational health and safety. Cambridge Scholars Publishing
Teece DJ (2018) Business models and dynamic capabilities. Long Range Plan 51(1):40–49
Teece DJ (2020) Business models, business strategy and innovation. Long Range Plan 53(1):1–13
Thomas RJ, Davies P (2017) Business process reengineering in the public sector: a case study of the UK’s driver and vehicle licensing agency. J Public Adm Res Theory 27(2):242–257
Venkatesh R, Mathews BP (2005) Business process reengineering: an overview. J Comput Sci 1(4):376–384
Venkatraman N, Henderson JC (1998) Real strategies for virtual organizing. Sloan Manag Rev 40(1):33–48
Virzi K (2019) Examining the success and failure factors of business process reengineering in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and North America: a literature review. Open Access Libr J 6(9):1–9
Vrontis D, El-Chaarani H, El Nemar S, Khalaf D (2019) Determinants of job satisfaction in the Lebanese construction sector. J Global Bus Adv 12(2):189–211
Vrontis D, El Chaarani H, El Nemar S, EL-Abiad, Z., Ali, R. and Trichina, E. (2022) The motivation behind an international entrepreneurial career after first employment experience”. Int J Entrep Behav Res 28(3):654–675
Wang Y, Chen L, Chen J (2020) The impact of business process reengineering on financial performance: evidence from Chinese listed firms. Sustainability 12(5):2075
Zarzycka E, Krasodomska J (2022) Non-financial key performance indicators: what determines the differences in the quality and quantity of the disclosures? J Appl Acc Res 23(1):139–162
Zia A, Rehman AU, Shah SZ (2020) Impact of business process reengineering on the performance of the banking sector: a case of Pakistan. J Bus Res 114:284–296
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all those who have contributed to the successful completion of this study. We would like to thank the managers of Lebanese micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) who generously shared their valuable time and insights with us during the interviews. Moreover, we would like to express our gratitude to our families and friends for their support, encouragement, and patience during the writing of this article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Balamand, Balamand, Lebanon
Jean Dagher & Laura Fayad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jean Dagher .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Beirut Arab University, Tripoli, Lebanon
Hani El-Chaarani
University of Nicosia, Doha, Qatar
Ibtihaj El Dandachi
Azm University, Tripoli, Lebanon
Sam El Nemar
ESA-École Supérieure des Affaires, Beirut, Lebanon
Zouhour EL Abiad
2.1.1 Interview Questions
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.

About this chapter
Dagher, J., Fayad, L. (2023). Business Process Reengineering: A Crucial Approach for Enhanced Organizational Sustainability. In: El-Chaarani, H., El Dandachi, I., El Nemar, S., EL Abiad, Z. (eds) Navigating the Intersection of Business, Sustainability and Technology. Contributions to Environmental Sciences & Innovative Business Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8572-2_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8572-2_2
Published : 04 February 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-8571-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-8572-2
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile Industry : A Case Study Of Ford Motor Company

Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is an essential change in the processes and structure of any company. That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted to the changing regime of FORD Motor Company since 1900s. A critical evaluation of Ford was made with the help of Situation-Actor-Process and Learning-Action-Performance (SAPLAP Analysis), Strength, Weakness, Opportunities and Threat (SWOT Analysis), Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Social (PESTEL Analysis) and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA).The results revealed that Ford is a very dynamic company which changes as per the requirement of the market. Repeated BPR activities helped the company in remaining the world leader till date.
Related Papers
Sujata Pujari
Faced with the growth of business enterprises as well as consideration of the increasing competition in freight business to Indonesia, MS Company realizes that the company's business process needs changes to effectively and efficiently support the decision making process as well as to increase the competitiveness of the business and the company. Business process re-engineering (BPR) is not just the program of business process improvement, but more than that, it can improve the operations of the business process as a whole. Improvement priorities of the company are on the improvement in the operation division which includes the administration, customer service and operations. Improvement of the system is done by changing the system from being manually run into a computerized system that runs with an emphasis on the achievement of improvements in the effectiveness of the speed of processing time, cost efficiency and human resources as well as an increase in level of customer service. Change of the system and program on MS Company were conducted by implementing four main phases: 1) Building vision and objective, 2) Identification of existing process, 3) Identifying process improvements, and 4) Building of a prototype. This paper explains the phases in more detail and presents the conceptual model for MS Company's BPR model.
Nasir Ameen , Oluwatosin Sorunke
This research seeks to determine how capabilities can be reengineered in an organisation by fitting the right skills to the right job so as to achieve dramatic improvement in business performance. Taking IBM as a case study, the Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) concept was examined and the critical success factors (CSFs) to its successful implementation were highlighted. An inductive approach and research philosophy of 'functional paradigm' was applied by analysing the findings of the pre and post BPR issues in IBM and creating a link between the theory of BPR and it's with a practical recommendation for future implementations. A model was created outlining the wider perspectives of BPR concept and the principles underpinning it and narrowing it down to the objective of this research using the funnelling approach of literature review and a new model was developed after the literature review incorporating the new findings from the literature review. Finally it was concluded that, BPR does not only reengineer processes but functions or core competencies and CSFs of implementing the initiative are egalitarian leadership, collaborative working environment, top management commitment, change in management technology appropriate BPR planning and methodology and use of information technology system. However for successful implementation, BPR must influence the content of the business strategy while the business strategy must support the BPR initiative. This is in addition to the fact that a BPR initiative should be driven by customer perception for optimal results.
Oluwatosin Sorunke
Olena Kasian
Reengineering is an important anti-crisis management tool because it is aimed at restructuring (redesigning, updating) business processes in order to achieve a radical, leaps and bounds improvement of the enterprise's activities. In light of the current unstable economic situation in the world, management cannot have any other basis than the search for and active use of new forms, methods, techniques, business areas, since the previous approaches no longer justify themselves. Therefore, reengineering has become one of the most effective innovations in management consulting in recent years. The statement of the problem is carried out, the main purpose and tasks of the research are determined. This study analyzes the scientific work of various economists and scientific schools on the approach to radical redesign of business processes (business reengineering). The concept of business process and features of its identification are formed. The stages of reengineering business processes of companies are studied. Focus zones have been formed in the work of enterprises that can be positively affected by business process reengineering. The main conditions for reengineering the company's business processes are determined. The main procedural aspects of business process reengineering and the main work within each procedure with its subsequent visualization are noted. The main structural elements of changes in business processes during their reengineering of the company are determined. The main conclusions of the research are formed. The main scientific approaches to the process of change in the work of companies are noted, focusing on customer-oriented management of business processes in their reengineering in the work of enterprises. The analysis of the implemented solutions of business process reengineering and possibilities of its further realization in the companies at the international level is carried out. Theoretical provisions of business process reengineering through the basic principles of its implementation are studied. The main focus areas of changes in the work of companies, which introduced the reengineering of business processes with a description of the peculiarities of the process of change in these focus areas of companies. The general conclusion on the given scientific research is formed.
South Asian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities
wameedh Khdair
The aim of the research is to know the effect that the business process re-engineering had on the performance of employees of the south refineries company – Iraq. With the addition of some observations that contribute to leaving a good impact for the purpose of seeking to develop the concept of engineering for workers. As the results were relied upon to conduct analyzes through SPSS statistical analysis program on the 350 employees in the company. The results indicated a set of concepts and indications, the most important of which are the application of the engineering concept was present in the company at a rate of 60% and the existence of a direct relationship between the dimensions of business process re-engineering and the level of job performance. The purpose of the research See the relationship between HR aspects, such as teamwork, management competency, organizational structure, IT and efficient communication for achieve beneficial outcomes by reducing costs, time and increas...
Dr. Sri Lalitha
ABSTRACT In today‘s ever changing world, the only thing that doesn‘t change is ―change‖ itself. In a world of competition driven by the three C‘s: Customer, Competition and Change, companies are looking out for new solutions for their business problems. Recently, some of more successful business corporations in the world seem to have hit upon incredible solution: Business Process Reengineering (BPR). The reason behind so many success stories of Organizations like WalMart and Taco Bell‘s sales is the same concept of BPR. Reengineering is the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of process of business for remarkable improvements in critical, contemporary measures of performance such as Cost, Quality, Service and Speed to meet Customer‘s requirement. The purpose of this paper is to clear out the confusion on BPR by reviewing various literatures of different authors. It also discusses co-existence of BPR with TQM, Organizational Process Understanding, Reengineering challenge and redesign of Organization. KEY WORDS: Business Process Reengineering, TQM, Redesign
International Journal of Scientific Management and Development
The purpose of this study was to assess the impact of re-engineering based on four measures of financial performance, ability to build production and innovation, customer satisfaction and employee communications, supply chain and related indicators in each dimension before and after the implementation of the Regional Electricity Company is a province. For the purposes of this study, the type of applied research, the descriptive nature of the survey. Population survey of managers, supervisors and experts are. Data analysis using a paired test to compare the situation before and after the re-engineering and implementation of the Friedman test was conducted to rank the variables. Results show the success of the performance impact of after the engineering re than before its implementation on the regional electric company crosses the province harder to arrange their impact: financial performance, customer satisfaction and employee communications, supply chain, capable of making, and innovation.
Firtian Judiswandarta , ULE, P ALAMINA
Matthias E Elom
This study, Business Process Reengineering and Organizational Performance, spawns from the need to explore the relationship between business process reengineering and organizational performance of Innoson Technical and Industrial Company, Emene, Enugu. The main objectives are: to ascertain the degree to which each of the three decomposed variables of business process reengineering of creative rethinking, radical change and fundamental thinking relate to profitability, market share and business sustainability dimensions of performance of Innoson Technical and Industrial Company, Emene, Enugu. The study was a survey type of research of which correlational research design was employed to ascertain the degree of the magnitude of the relationship between the studied variables. Structured questionnaire was administered on the sample of two hundred and sixty one (261), out of which, two hundred and fifty (250) copies of questionnaire were successfully returned, hence used for the analysis. Data collected from the respondents were analyzed with Pearson Correlation Coefficient. The study found a significant relationship between creative rethinking and profitability of Innoson Company (r=0.60), a significant relationship between radical change and market share of Innoson Company (r= 0.91), and significant relationship between fundamental thinking and business sustainability of Innoson Company of Innoson Company (r=0.62). The implication of the findings is that effective implementation of business process reengineering thrive high performing organizations in meeting the demands of changing business environment. From the findings, the study concludes that organizations could enhance their performance, if business process reengineering is conducted effectively and recommended that the management of Innoson Technical and Industrial Company should pay adequate attention to issues relating to business process reengineering, taking into cognizance its pertinent role in radical improvement on cutting down operational costs, cycle time reduction, quality enhancement and service improvement that predict organizational performance.
Jan Bennett
RELATED PAPERS
Antonio Benedicto
Rafael Martins
Delito y Sociedad
Revista de fontes
Maria Rita Toledo
European Journal of Public Health
Irina Kazaryan
La Bouche de L'enfant et de L'adolescent
leticia vasquez
Medijska istraživanja : znanstveno-stručni časopis za novinarstvo i medije, Vol. 26 No. 2, 2020.
Tamara Kunić
International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics
JEHANGIR RASHID DAR
Mohammed Saeed
Radiotherapy and Oncology
Belinda Campbell
Danil Alfajri
International Journal Of Trendy Research In Engineering And Technology
IJTRET-International Journal of Trendy Research in Engineering and Technology
Luciana Azambuja
Jurnal Media Wahana Ekonomika
Suhada Suhada
Journal of Chromatography A
Shao-ping Li
Global Heart
Azimar Farhani
Journal of Coastal Conservation
João Santos
2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS)
Touradj Ebrahimi
Angewandte Chemie
GSTF Journal on Computing (JoC)
Narin Damnuy
IOP conference series
Muslim Abdurrahman
International Journal of Child Development and Mental Health
ponthip thammawong
Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
Oana Balint
Ioannis Polemis
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, business process reengineering in a british company: a case study.
Logistics Information Management
ISSN : 0957-6053
Article publication date: 1 October 2000
A case study conducted in a British company (Company A) on reengineering business processes is presented. It gives an example on how a case study ought to be written in order to go beyond the standard for writing an industrial report to one that is acceptable by academic peers. A good case study ought to contain information that readers can use in replicating the experiences gained and lessons learnt in future endeavours under similar settings. When a collection of good case studies is available to a practitioner or researcher he could formulate his plan for the future and avoid “re‐inventing the wheel”. This is most important to research in operations management because it lends a hand in the building up of a theory in POM to make an impact in its natural settings.
- Case studies
Gunasekaran, A. , Chung, W.W.C. and Kan, K. (2000), "Business process reengineering in a British company: a case study", Logistics Information Management , Vol. 13 No. 5, pp. 271-285. https://doi.org/10.1108/09576050010378496
Copyright © 2000, MCB UP Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download Free PDF. Download Free PDF. BPR CASE FORD. BPR CASE FORD. Jose Antonio Boggiano Bazan. ... BPR CASE STUDIES FROM LITERATURE 5.1. FORD-MOTOR COMPANY In the early 1980's, Ford, like many other American corporations was exploring for ways to reduce overhead and administrative costs. One of the places Ford believed it could lower costs ...
3 likes • 10,410 views. I. ivy buncaras. The radical change in ford motor company corporation after the Reengineering processes. Education. 1 of 29. Download Now. Download to read offline. Ford Motors Company - Business Process Reengineering - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
To recall, the first objective of the study was "To critically evaluate the BPR activities of FORD Motor Company" This objective was analysed with the help of results obtained from SAP-LAP analysis, SWOT analysis and PESTEL analysis. A. SAP-LAP Analysis SAP-LAP framework of BPR in Ford Motor is discussed in annexure 1.
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is an essential change in the processes and structure of any company. That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted to the changing regime of FORD Motor Company since 1900s. A critical evaluation of Ford was made with the help of Situation-Actor-Process and ...
Abstract: Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is an essential change in the processes and structure of any company. That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted to the changing regime of FORD Motor Company since 1900s.
In this first case study, we refer to a classic example of effective BPR that is demonstrated by Peppard and Rowland in their book "The Essence of Busines s Process Re- Engineering" [ 6, 12 ...
Business. Process. Re-Engineering (BPR) Dr. A. Albadvi. Asst. professor of IT. Tarbiat Modarres University School of Engineering, Information Technology e-mail: [email protected]. Sharif University of Technology School of Management and Economics Dept.
The results of case studies for the BPR method application in the. company are as follows: (i) restructuring strategy at Garuda Indonesia. Aircraft; (ii) worker reengineerin g in Ford Motor ...
It's the BPR case study talked about a 1,000 times online, and the story made famous in "Reengineering the Organization", a book written by American business consultants, Michael Hammer and ...
BPR-AT-FORD-MOTORS-CASE-STUDY - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Case study: Business Process Reengineering General Motors Corporation "General Motors is one of three leading automotive manufacturing companies in the United States. Based in Michigan in 1903 by Henry ford and grew to reach revenue of $150 billion and more than 370. 000 employees by 1996. CHALLENGE: need for business process reengineering in ...
76 The Business Process Reengineering Project can be acquired at a set price. However, there is something very special which cannot be bought and that is know-how, i.e. knowledge, skills and experience gained by the people working in the company. The safeguard-ing, development and improvement of this asset becomes one of the key-
This document discusses business process reengineering (BPR) as a change management approach for multinational corporations. It provides background on BPR and defines it as a management tool that examines and redesigns business processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness. The document then analyzes case studies of four multinational corporations that successfully implemented BPR - Ford ...
In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. (PDF) Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile Industry : A Case Study Of Ford Motor Company | Surabhi Goyal - Academia.edu
BPR can be due to the fact that; senior management does not always have a clear vision of what the BPR effort intends to achieve, or how to gauge or monitor the success of the programme objectives. The case study within the book demonstrates the successful application of BPR through the implementation of the "Integration Definition for
Case Study - BPR - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Ford used business process reengineering to radically change its accounts payable process. Before, Ford's purchasing department would send purchase orders to the accounts payable department and vendors. After receiving materials, vendors would invoice accounts payable.
Business process reengineering (BPR) is a powerful tool for improving organizational performance, customer satisfaction and cost efficiency. This paper provides a recent review of the BPR ...
This study investigates Business Process Reengineering (BPR) in contemporary management as a visionary strategy for managers wishing to reengineer their distressed firms for enhanced organizational sustainability through advancing organizational performance. It presents a unique setting for businesses withdrawn from the case of Lebanon and introduces novel dynamics on the implementation and ...
Case Study Ford-BPR - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. It is a classic case of business transformation applying IT as a solution
In this case study, the focus towards BPR was restricted That change can be related to work force, business processes, IT infrastructure, etc. (PDF) Business Process Re-Engineering In Automobile Industry : A Case Study Of Ford Motor Company | Dr. Surabhi Goyal - Academia.edu
A case study conducted in a British company (Company A) on reengineering business processes is presented. It gives an example on how a case study ought to be written in order to go beyond the standard for writing an industrial report to one that is acceptable by academic peers. A good case study ought to contain information that readers can use ...
Ford BPR Case - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.