Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic

RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
This topic will provide an overview of major issues related to breech presentation, including choosing the best route for delivery. Techniques for breech delivery, with a focus on the technique for vaginal breech delivery, are discussed separately. (See "Delivery of the singleton fetus in breech presentation" .)
TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION
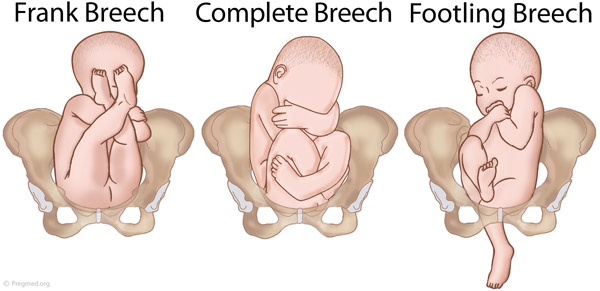
● Frank breech – Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
● Complete breech – Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
Enter search terms to find related medical topics, multimedia and more.
Advanced Search:
- Use “ “ for exact phrases.
- For example: “pediatric abdominal pain”
- Use – to remove results with certain keywords.
- For example: abdominal pain -pediatric
- Use OR to account for alternate keywords.
- For example: teenager OR adolescent
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
, MD, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
- 3D Models (0)
- Calculators (0)

Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery Operative Vaginal Delivery Operative vaginal delivery involves application of forceps or a vacuum extractor to the fetal head to assist during the second stage of labor and facilitate delivery. Indications for forceps... read more , or cesarean delivery Cesarean Delivery Cesarean delivery is surgical delivery by incision into the uterus. The rate of cesarean delivery was 32% in the United States in 2021 (see March of Dimes: Delivery Method). The rate has fluctuated... read more .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor Preterm Labor Labor (regular uterine contractions resulting in cervical change) that begins before 37 weeks gestation is considered preterm. Risk factors include prelabor rupture of membranes, uterine abnormalities... read more
Multiple gestation Multifetal Pregnancy Multifetal pregnancy is presence of > 1 fetus in the uterus. Multifetal (multiple) pregnancy occurs in up to 1 of 30 deliveries. Risk factors for multiple pregnancy include Ovarian stimulation... read more
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Perinatal death
It is best to detect abnormal fetal lie or presentation before delivery. During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks. This technique involves gently pressing on the maternal abdomen to reposition the fetus. A dose of a short-acting tocolytic ( terbutaline 0.25 mg subcutaneously) may help. The success rate is about 50 to 75%. For persistent abnormal lie or presentation, cesarean delivery is usually done at 39 weeks or when the woman presents in labor.

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery Operative Vaginal Delivery Operative vaginal delivery involves application of forceps or a vacuum extractor to the fetal head to assist during the second stage of labor and facilitate delivery. Indications for forceps... read more or cesarean delivery Cesarean Delivery Cesarean delivery is surgical delivery by incision into the uterus. The rate of cesarean delivery was 32% in the United States in 2021 (see March of Dimes: Delivery Method). The rate has fluctuated... read more is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article

Was This Page Helpful?

Test your knowledge
Brought to you by Merck & Co, Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the US and Canada) — dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
- Permissions
- Cookie Settings
- Terms of use
- Veterinary Manual
- IN THIS TOPIC
Management of Breech Presentation (Green-top Guideline No. 20b)
Summary: The aim of this guideline is to aid decision making regarding the route of delivery and choice of various techniques used during delivery. It does not include antenatal or postnatal care. Information regarding external cephalic version is the topic of the separate Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Green-top Guideline No. 20a, External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation .
Breech presentation occurs in 3–4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. Term babies presenting by the breech have worse outcomes than cephalic presenting babies, irrespective of the mode of delivery.
A large reduction in the incidence of planned vaginal breech birth followed publication of the Term Breech Trial. Nevertheless, due to various circumstances vaginal breech births will continue. Lack of experience has led to a loss of skills essential for these deliveries. Conversely, caesarean section can has serious long-term consequences.
COVID disclaimer: This guideline was developed as part of the regular updates to programme of Green-top Guidelines, as outlined in our document Developing a Green-top Guideline: Guidance for developers , and prior to the emergence of COVID-19.
Version history: This is the fourth edition of this guideline.
Please note that the RCOG Guidelines Committee regularly assesses the need to update the information provided in this publication. Further information on this review is available on request.
Developer declaration of interests:
Mr M Griffiths is a member of Doctors for a Woman's right to Choose on Abortion. He is an unpaid member of a Quality Standards Advisory Committee at NICE, for which he does receive expenses for related travel, accommodation and meals.
Mr LWM Impey is Director of Oxford Fetal Medicine Ltd. and a member of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. He also holds patents related to ultrasound processing, which are of no relevance to the Breech guidelines.
Professor DJ Murphy provides medicolegal expert opinions in Scotland and Ireland for which she is remunerated.
Dr LK Penna: None declared.
- Access the PDF version of this guideline on Wiley
- Access the web version of this guideline on Wiley
This page was last reviewed 16 March 2017.
- Open access
- Published: 03 May 2020
Revisiting the management of term breech presentation: a proposal for overcoming some of the controversies
- Lionel Carbillon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6367-4828 1 , 2 ,
- Amelie Benbara 2 ,
- Ahmed Tigaizin 2 ,
- Rouba Murtada 2 ,
- Marion Fermaut 2 ,
- Fatma Belmaghni 2 ,
- Alexandre Bricou 2 &
- Jeremy Boujenah 2
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 20 , Article number: 263 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
12k Accesses
11 Citations
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
The debate surrounding the management of term breech presentation has excessively focused on the mode of delivery. Indeed, a steady decline in the rate of vaginal breech delivery has been observed over the last three decades, and the soundness of the vaginal route was seriously challenged at the beginning of the 2000s. However, associations between adverse perinatal outcomes and antenatal risk factors have been observed in foetuses that remain in the breech presentation in late gestation, confirming older data and raising the question of the role of these antenatal risk factors in adverse perinatal outcomes. Thus, aspects beyond the mode of delivery must be considered regarding the awareness and adequate management of such situations in term breech pregnancies.
In the context of the most recent meta-analysis and with the publication of large-scale epidemiologic studies from medical birth registries in countries that have not abruptly altered their criteria for individual decision-making regarding the breech delivery mode, the currently available data provide essential clues to understanding the underlying maternal-foetal conditions beyond the delivery mode that play a role in perinatal outcomes, such as foetal growth restriction and gestational diabetes mellitus. In view of such data, an accurate evaluation of these underlying conditions is necessary in cases of persistent term breech presentation. Timely breech detection, estimated foetal weight/growth curves and foetal/maternal well-being should be considered along with these possible antenatal risk factors; a thorough analysis of foetal presentation and an evaluation of the possible benefit of external cephalic version and pelvic adequacy in each specific situation of persistent breech presentation should be performed.
The adequate management of term breech pregnancies requires screening and the efficient identification of breech presentation at 36 weeks of gestation, followed by thorough evaluations of foetal weight, growth and mobility, while obstetric history, antenatal gestational disorders and pelvis size/conformation are considered. The management plan, including external cephalic version and follow-up based on the maternal/foetal condition and potentially associated disorders, should be organized on a case-by-case basis by a skilled team after the woman is informed and helped to make a reasoned decision regarding delivery route.
Peer Review reports
The ideal management of women with term breech presentation remains a matter of intense debate. The rate of vaginal delivery has steadily declined in the last decades of the last century [ 1 ]. In 2000, the Term Breech Trial (TBT) Collaborative Group concluded that a composite variable combining perinatal and neonatal mortality or serious neonatal morbidity was significantly lower in the planned caesarean section (CS) group than in the planned vaginal birth group [ 2 ], which marked an apparent turning point in this controversy. Based on the short-term outcomes presented in the TBT study, the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) [ 3 ] and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) [ 4 ] recommended over the next few years that all women with persistent singleton breech presentation at term should undergo a planned CS delivery. An important and almost immediate impact on the practice was also observed in some countries that previously had a high proportion of vaginal breech deliveries [ 5 ]. TBT was the largest randomized trial ever published on the term breech mode of delivery. However, despite its undeniable strengths, a number of weaknesses have been identified. Specifically, there was a lack of adherence to strict criteria for vaginal birth in an important proportion of the included patients and nonoptimal methods of labour management as recognized by the TBT group itself [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. In addition, when the TBT Collaborative Group published the 2-year analysis of paediatric outcomes, despite a large (greater than 50%) post-randomization loss to follow-up [ 9 ], these researchers found no reduction in the risk of death or neurodevelopmental delay in children at 2 years of age, thus raising questions regarding the real lessons to be drawn from this trial. Using multiple logistic regression analyses, the TBT group also reported [ 10 ] that the risk of maternal morbidity was lowest following vaginal birth (odds ratio [OR] 1.0) and highest following CS after active labour (36.1% in the TBT) (OR 3.33; 95% CI 1.75–6.33, P < 0.001), particularly after a short second stage < 30 min (OR 0.25; 95% CI 0.11–0.57, P < 0.001) [ 9 ].
Later, population-based retrospective studies helped refine the consequences of applying recommendations of systematically planned CS for women with term breech presentation at the population level. Hartnack Tharin et al. [ 11 ] found that the rate of CS for term breech deliveries increased from 79.6 to 94.2% between 1997 and 2008 in Denmark, while intrapartum or early neonatal mortality decreased from 0.13 to 0.05% [relative risk (RR) 0.38 (95% CI 0.15–0.98)], which was a significant but lower reduction than the difference reported in the TBT. Using the Dutch National Perinatal Registry from 1999 to 2007, Vlemmix et al. [ 12 ] stated that after publication of the TBT, the elective CS rate increased from 24 to 60%, and overall perinatal mortality and short-term morbidity decreased. In contrast, these outcomes remained stable in the planned vaginal birth group. However, the authors estimated that 338 CS deliveries would need to be performed to prevent one perinatal death, and Schutte et al. [ 13 ] estimated the perinatal case fatality rate for elective CS for breech presentation in 2000–2002 at 0.47/1000 operations. At the same time, in the Netherlands the incidence of severe maternal morbidity (SMM) was estimated at 6.4/1000 during an elective CS compared with 3.9/1000 during an attempted vaginal delivery (OR 1.7; 95% CI 1.4–2.0), with an increased risk for SMM in the next pregnancy (OR 3.0; 95% CI 2.7–3.3) [ 14 ], despite the numerous facilities and adequate resources allocated to perinatal care in such a high-income country.
On the other hand, new guidelines were published in 2009 by the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada (SOGC) stating that “planned vaginal delivery is reasonable in selected women with a term singleton breech foetus”. Afterwards, a study [ 15 ] including 52,671 breech deliveries in Canada (2003–2011) reported in 2011 that vaginal deliveries increased from 2.7% in 2003 to 3.9%. In this study, a concomitant increase in composite neonatal mortality and morbidity rates was observed with an adjusted rate ratio of 3.60 (95% CI 2.50–5.15), compared with CS without labour [ 15 ]. Moreover, CS with labour also increased from 8.7 to 9.8%, highlighting the particular difficulty in returning to previous practices after the clinical skills required to conduct a vaginal breech delivery have declined [ 15 , 16 ].
Some authors recently considered that “the TBT recommendations should be withdrawn” [ 6 ], while others still consider that the “results (of the TBT) are generalizable” [ 16 , 17 ]. Nevertheless, national guideline bodies have partially reversed their recommendations based on these discussions [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. However, as rightly noted by Joseph et al. [ 16 ], the availability of clinical skills has declined in some of these countries, raising concerns from a pedagogic resident education and training standpoint [ 16 ]. In this regard, a meaningful role could be given to the possibility of training by simulation in building and maintaining specific skills and competencies for vaginal breech delivery.
A new meta-analysis [ 21 ] and several large-scale epidemiologic datasets from medical birth registries [ 22 , 23 , 24 ] recently evaluated risk factors associated with adverse perinatal outcomes in planned vaginal breech labours at term. These investigations were conducted in countries that have not abruptly modified their policies and that have continuously applied similar strict criteria over the last several decades for individual decision-making in cases of term breech presentation. We believe that the time has come to go beyond the sole question of delivery mode in the management of these situations.
Term breech presentation: are we asking the right questions?
It now appears time to expand our thinking and, considering recent important data that help elucidate the underlying significance of persistent breech presentation at term, to offer more dynamic and multidisciplinary insight into the management of these cases.
Indeed, similar to some older studies [ 25 , 26 , 27 ], several recent population-based studies [ 22 , 23 ] strongly suggest that the increased risk observed in foetuses that remain in the breech presentation at term is closely linked to antenatal or underlying disorders that may be associated with the breech presentation and is not solely due to the mode of delivery. Because adverse outcomes can be caused by underlying or gestational disorders, any discussion that is limited to delivery mode seems too restrictive and does not address the whole issue.
Most recent large-scale data
Deterministic or accidental breech presentation.
In a recent Finnish population-based case-control study including all singleton deliveries from 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2014 and excluding preterm deliveries, antepartum-diagnosed stillbirths, placenta previa and infants with congenital malformations (499,206 foetuses at term), Macharey et al. [ 22 ] evaluated the antenatal risk factors associated with adverse perinatal outcomes in planned vaginal breech labour at term. They found that the stillbirth rate was significantly higher in cases of planned vaginal breech labour than in cases of cephalic presentation (0.2 vs 0.1%, respectively), which was correlated with foetal growth restriction, oligohydramnios, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and a history of CS. Furthermore, in another recent survey based on the same cohort of mother-neonate dyads that also excluded congenital malformations, placenta previa and prelabour stillbirths [ 23 ], this same group showed that breech presentation at term was significantly associated with antenatal stillbirth and a number of individual obstetric risk factors for adverse perinatal outcomes, including oligohydramnios, foetal growth restriction, gestational diabetes, history of CS section and congenital anomalies. Among all planned singleton vaginal deliveries with the foetus in the breech presentation at term, a composite adverse perinatal outcome defined as umbilical arterial pH < 7.00, 5-min Apgar score below 7 and/or neonatal mortality during the first 6 days of life (excluding stillbirth) was associated with foetal growth restriction (aOR 2.94 [1.30–6.67]), oligohydramnios (adjusted OR 2.94 [1.15–7.81]), gestational diabetes (aOR 2.89[1.54–5.40]), and a history of CS (aOR 2.94 [1.28–6.77]).
In another recent population-based study based on perinatal data of all (650,968) children born in Norway from 1999 to 2009 [ 24 ], the authors recognized the limitations of most registry-based studies, as the selection of women with breech presentation and planned vaginal delivery was based on criteria that might have identified pregnancies with a lower risk of adverse outcomes compared with those selected for CS delivery. Moreover, in this study [ 24 ], the intrapartum conversion of some of the planned vaginal deliveries to an emergency CS delivery may have increased the risk for adverse outcome in the CS group. However, Bjellmo et al. [ 24 ] conducted an innovative analysis comparing breech deliveries to vaginal cephalic births. Thus, they showed that singleton children born at term without congenital malformations had a higher risk for stillbirth and neonatal mortality if they were born in the breech presentation “regardless of whether they were born vaginally or by CS delivery” (0.9 per 1000 in those actually delivered vaginally and 0.8 per 1000 in those actually born by CS delivery) compared with those born by vaginal cephalic delivery (0.3 per 1000). Of note, among those children born in the breech rather than in the cephalic presentation, these authors [ 24 ] found that a higher proportion of infants were born small for gestational age (SGA). However, these authors [ 23 ] did not distinguish foetal growth restriction among SGA neonates. In their interpretation, Bjellmo et al. [ 23 ] considered that “the overall higher risk for stillbirth and the higher proportion of infants born SGA among children born in the breech than in the cephalic presentation may suggest that foetuses with antenatal acquired risk factors for adverse outcomes are more likely to present in the breech than in the cephalic presentation at birth.” According to these authors, the findings were most likely explained by a combination of antenatal acquired risk factors for neonatal death with increased vulnerability to the birth process. Of note, in the TBT group, birth weights of less than 2.8 kg were also associated with adverse perinatal outcomes ( P = 0.003) [ 10 ]. In fact, a limitation in the Norwegian study [ 24 ] was that, unlike Macharey et al., the authors did not distinguish foetal growth restriction among these SGA neonates. Indeed, in a large cohort study conducted with the National Health Service region in England through a multivariable analysis of 92,218 normally formed singletons delivered during 2009–2011 from 24 weeks of gestation, including 389 stillbirths, Gardosi et al. [ 25 ] showed that foetal growth restriction had the largest population attributable risk for stillbirth which was fivefold greater if it was not detected antenatally than when it was (32.0% v 6.2%). The above data suggest that some antenatal features associated with term breech presentation, notably foetal growth restriction, and some gestational disorders (such as uncontrolled gestational diabetes mellitus) could affect the prognosis in term breech cases. Previous data also support this conclusion; Luterkort M et al. [ 26 ] had previously reported in a prospective follow-up of 228 pregnancies with the foetus in the breech presentation in the 33rd gestational week that the 96 foetuses (42%) who remained in the breech presentation at delivery weighed 4.9% less than their vertex controls after adjustments were made for gestational age and had an increased frequency of oligohydramnios. Krebs et al. [ 27 ] later confirmed this association between breech presentation and foetal growth restriction from a register-based, case-control cohort of infants with cerebral palsy born between 1979 and 1986 in East Denmark.
In fact, as reported by Fox and Chapman [ 28 ], up to 21% of all foetuses adopt a noncephalic presentation at 28–29 weeks of gestation, and this proportion progressively decreases to 5% from 37 to 38 weeks [ 28 ]. Certain conditions, such as uterine malformation, can disturb both this continuous process of spontaneous cephalic version and normal foetal growth, thereby leading to increased term breech presentation rates in these cases [ 29 ]. This point highlights the importance of estimating foetal weight and well-being in cases of persistent breech presentation at term. Furthermore, even some cases of controlled GDM may be associated with excess foetal weight during the last weeks of pregnancy, leading to possible dystocia due to this overgrowth, or with other GDM-related complications, such as preeclampsia; thus, foetal weight estimates should be monitored closely beginning in the 37th week of gestation, with regular reassessment as long as the patient has not delivered.
The impact of strict criteria on the selection of vaginal delivery
From a broad perspective, in the most recent meta-analysis investigating the risks of planned vaginal breech delivery versus planned CS for term breech birth [ 21 ], the overall heterogeneity (I 2 = 36%) was informative. The variability of neonatal mortality among 14 studies accounting for 74,094 breech vaginal deliveries was low (ranging from 0.08 to 0.37%). On the other hand, neonatal mortality was markedly higher in only 2 studies authored by Singh et al. [ 30 ] and Hannah et al. [ 2 ] (the TBT). These two studies [ 2 , 30 ] accounted for 1099 breech vaginal deliveries (1.5% of births) and had perinatal mortality rates as high as 21 and 1.3%, respectively, for planned vaginal births (25.6% of perinatal deaths). The same was true for neurological morbidity, which was 3.4 and 1%, respectively, in the studies by Singh et al. [ 30 ] and TBT [ 2 ], while it ranged from 0.07 to 0.2% in the 14 other studies encompassing 74,094 breech vaginal deliveries conducted with the implementation of more stringent exclusion criteria for vaginal breech delivery.
In these 14 studies accounting for 74,094 breech vaginal deliveries, the retrospective observational cohort study from the Finnish Medical Birth Register [ 31 ] and the prospective observational study PREMODA [ 32 ] (as well as the more recent Norwegian Medical Birth Registry study) applied similar pre-established exclusion criteria for planned vaginal birth. In the PREMODA study, an increased absolute rate of perinatal death or serious neonatal morbidity was observed in both the planned vaginal group (1.60, 95% CI 1.14–2.17) and planned CS delivery group (1.45 [1.16–1.81]) with breech presentation among the total population of 264,105 births, but the planned vaginal group and the planned CS delivery group with breech presentation did not differ significantly for the combined outcome of foetal/neonatal mortality or serious morbidity (odds ratio [OR] = 1.10, 95% CI [0.75–1.61]). The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists proposes comparable pre-established criteria for the management of term breech presentation, recommending that “women should be informed that a higher risk of planned vaginal breech birth is expected where there are independent indications for CS section and in circumstances such as a hyperextended neck on ultrasound, high estimated foetal weight (more than 3,800 g), low estimated weight (less than tenth centile), footling presentation, [and] evidence of antenatal foetal compromise” but considers that “the role of pelvimetry is unclear” [ 20 ]. Of note concerning this last point, Van Loon et al. showed in a randomized controlled trial [ 33 ] that the adequacy of pelvis size, as assessed by pelvimetry, improved the selection of delivery route. In line with them, two recent studies support this view [ 34 , 35 ]. Other authors also included criteria for the adequate management and continuous monitoring of foetal heart rate during labour (which is common in maternity wards of most high-income countries but could be monitored intermittently in the TBT). Indeed, decreased variability and late decelerations are more prevalent during breech deliveries than vertex deliveries [ 36 ], and good labour progress is a predictor of better neonatal outcomes [ 37 ]. In the Finnish Medical Birth Register [ 31 ], 1270 women (43.6%) were selected as candidates for vaginal breech delivery, and the selection quality was confirmed by the low conversion rate of vaginal to CS breech delivery (11.4%). This rate was higher (36.1%) in the TBT [ 30 ].
As noted by methodologists [ 38 ], real-world prenatal patient care is subject to decision-making based on the continuous evaluation of risk factors, medical history, comorbidities, behavioural aspects, and other factors that indeed cannot be strictly reproduced in randomized controlled trials. For example, in the TBT [ 2 ], an upper limit of 4000–4500 g was given for estimated foetal weight. However, as the duration between randomization and delivery inevitably lengthened in the planned vaginal delivery group, a significantly higher number of macrosomic neonates were born in the planned vaginal delivery group ( P = 0.002). In actuality, an informed woman who opts for vaginal delivery at 36 or 37 weeks of gestation usually changes her mind if she has not delivered several weeks later and if the clinician tells her that the birthweight will probably exceed 3800–4000 g, with an associated increased risk of adverse perinatal outcomes. Thus, in cases of even minor glycaemic disorder, special attention should be paid in the 37th week of gestation to foetal weight estimates and the possible occurrence of preeclampsia or associated gestational disorders; moreover, cases of SGA foetuses with possible foetal growth restriction should be closely followed, regardless of the delivery mode chosen by the patient [ 26 , 39 ].
How might we maximize patient benefit from a safe external cephalic version attempt?
With the restrictive practice of breech vaginal delivery in the last 15 years, national colleges of obstetricians (RCOG, ACOG, SOGC and RANZCOG) and FIGO updated their guidelines and recommended external cephalic version (ECV) at term to limit the increase in elective CS rate for cases of term breech presentation. However, recent data urge us to develop a broader perspective and an accurate assessment of the real impact of various ECV policies.
Indeed, the true impact of ECV may first be limited by the timely detection of breech presentation. In a retrospective cohort study of 394 consecutive cases of breech presentation at term, Hemelaar et al. [ 40 ] found that over two periods separated by 10 years (1998–1999 and 2008–2009), the proportion of breech presentations not diagnosed antenatally increased from 23.2 to 32.5% ( P = 0.04), causing 52.8% of women who were eligible for ECV to miss an attempt in 2008–2009. The authors also reported that the proportion of women who declined ECV during the same period decreased significantly from 19.1 to 9.0%.
Eligibility is a second limitation. In Australia, a large-scale survey [ 41 ] showed that 22.3% of 32,321 singleton breech pregnancies were considered ineligible (due to oligohydramnios, antepartum haemorrhage or abruption, previous CS or pelvic abnormality, placenta previa, placenta accreta, or an infant with major congenital anomalies). In this survey [ 41 ], only 10.5% of the singleton breech pregnancies had an ECV. In a systematic review, Rosman et al. [ 42 ] identified 60 studies that reported 39 different contraindications and five guidelines with 18 contraindications (varying from five to 13 contraindications per guideline), with oligohydramnios being the only contraindication that was consistently mentioned in all guidelines. Thus, there was no general consensus on the eligibility of patients for ECV, but contraindications generally include all conditions in which this procedure may be associated with a particular risk for the foetus or mother. These conditions include the following: severe intrauterine growth restriction, abnormal umbilical artery Doppler index and/or nonreassuring foetal heart rate, which may require an emergency CS birth; foetuses with a hyperextended head and significant foetal or uterine malformations, which may carry a particular foetal risk; rhesus alloimmunization, which might be reactivated by the procedure; and recent vaginal bleeding or ruptured membranes, which were associated with cord prolapse in 33% of reported cases after ECV attempt [ 43 ].
If CS or rapid delivery is indicated for another obstetric condition, ECV is also contraindicated, notably in cases of placenta previa, severe preeclampsia, and increased risk of placental abruption. Other situations, such as maternal obesity, nonsevere SGA foetuses, and nonsevere oligohydramnios, merely decrease the likelihood of ECV success. In contexts such as severe oligohydramnios or multiple gestations, ECV is simply impracticable, except for a second twin after delivery of the first. Furthermore, previous uterine surgery (CS delivery, myomectomy, or hysteroplasty) is considered a relative contraindication for ECV by some but not all authors [ 44 ]. On the other hand, in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus, incomplete or uncontrolled glucose levels are associated with an increased risk of foetal macrosomia in late pregnancy, and even if the estimated foetal weight seems compatible with a planned vaginal delivery when the mode of delivery is discussed, rapid foetal growth during the last weeks may lead to major difficulties during delivery. Therefore, in such a context, we believe there is potential for a particular benefit from successful ECV at 36 weeks.
Predictors of successful ECV
Pinard previously observed that unengaged breech presentation is an important predictor of successful ECV [ 45 ]; the same observation was made by Lau et al. [ 46 ], Aisenbrey et al. [ 47 ], and Hutton et al. [ 48 ]. In the large series of 1776 ECVs published by Hutton et al. [ 48 ], descent and impaction of the breech foetus were the most discriminating factors for predicting successful ECV, regardless of parity. Other predictors of success include parity [ 45 , 47 , 49 , 50 ], abundant amniotic fluid [ 49 , 50 , 51 ], nonfrank breech presentation [ 47 ], gestational age under 38 weeks [ 43 ], and posterior placenta [ 50 ]. In contrast, nulliparity and tense uterus are associated with a lower likelihood of success [ 44 , 48 , 52 ].
Velzel et al. [ 53 ] recently reviewed prediction models, most of which were developed without any external validation, and found that the most reliable predictors of successful ECV were nonimpacted breech presentation, parity and uterine softness (which usually go hand in hand), normal amniotic fluid index, posterior placental location, and, as noted by Pinard [ 45 ], foetal head in a palpable situation. These criteria might be used to support patient counselling and decision-making about ECV and to reduce the proportion of women declining ECV, particularly in the most favourable situations for ECV.
Obstetric outcomes after an ECV attempt
De Hundt et al. [ 54 ] conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis and showed that women who have had a successful ECV for breech presentation are at increased risk for CS delivery (OR 2.2; 95% CI 1.6–3.0) and instrumental vaginal delivery (OR 1.4; 95% CI 1.1–1.7) compared with women with spontaneous cephalic presentation. Interestingly, stratification by time delay between successful ECV and delivery revealed a trend for increased risk of CS during the first week after ECV [ 55 ]. Furthermore, in a cohort of 301 women with successful ECV, De Hundt et al. [ 56 ] found that nulliparity was the only of seven factors that predicted the risk of CS and instrumental vaginal delivery (OR 2.7; 95% CI 1.2–6.1). Based on a retrospective, population-based cohort study using the CDC’s birth data files from the US in 2006, Balayla et al. [ 57 ] also showed that relative to breech controls without an ECV attempt, cases of ECV failure with persistent breech presentation and labour attempts were associated with increased odds of CS delivery (adjusted OR 1.38; 95% CI 1.21–1.57), assisted ventilation at birth (aOR 1.50; 95% CI 1.27–1.78), 5-min Apgar score < 7 (aOR 1.35; 95% CI 1.20–1.51), and neonatal intensive care unit admission (aOR 1.48; 95% CI 1.20–1.82).
This information should also be considered in the dialog with women regarding the way in which late pregnancy and delivery should be managed based on existing data, their own situations and their wishes.
The true benefit of an active and systematic ECV policy is widely appreciated [ 58 , 59 ], and such evaluation may be subject to bias. Burgos et al. [ 58 ] found that their policy decreased the rate of breech presentation at delivery by 39.0% and decreased the CS rate for cases of breech presentation at term from 59 to 44%. On the other hand, Coppola et al. [ 59 ] reported that their CS rate was not significantly reduced in the planned ECV group, even after adjustments were made for age, parity and previous CS delivery. Thus, each perinatal centre should implement an appropriate and coherent policy in accordance with the prevalence of pathologies in the population.
Towards a consensus for a global shared vision and management of term breech presentation that could include the following
A policy of breech presentation screening at 36 weeks of gestation is efficient and cost effective [ 60 ].
Such screening should allow timely ECV and a careful evaluation of potential underlying antenatal risks, considering obstetric history, estimated foetal weight/growth and potential gestational disorders [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 ].
Foetal weight estimates based on clinical and ultrasound examinations are essential, despite the large confidence interval of all available algorithms for producing such estimates. Vaginal birth may be excluded when the estimated foetal weight approximates the upper limit used for selection in most national guidelines (3800 g) [ 18 , 19 , 20 ], particularly in the absence of previous successful vaginal delivery.
Before vaginal delivery is considered, clinical pelvic examination is universally recommended to rule out pathological pelvic contraction. Radiologic or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pelvimetry is not universally conducted [ 20 , 23 , 24 , 31 , 32 ]. However, Van Loon et al. [ 33 ] demonstrated in a randomized controlled trial that the use of MRI pelvimetry in breech presentation at term allowed better selection of delivery route, with a significantly lower emergency CS rate. More specifically, several recent studies [ 34 , 35 ] have evaluated the contribution of pelvimetry and found that MRI pelvimetry provided useful criteria for the preselection and counselling of women with breech presentation and the desire for vaginal delivery. Therefore, pelvimetry is diversely used in Europe for the preselection and counselling of women (particularly nulliparous women) with breech presentation and is specifically used in regions where vaginal delivery is still considered an option [ 35 ].
In cases of failed ECV with persistent breech presentation, this policy should allow customized care tailored to each situation in the last weeks of pregnancy.
A discussion with the informed patient is essential. One must thoroughly consider the experience of the health care team/the availability of clinical skills required for conducting a vaginal breech delivery and carefully select women who are eligible for planned vaginal delivery (considering obstetric history and the criteria described above for the choice between planned vaginal and CS deliveries) [ 20 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 28 ].
Regardless of the planned mode of delivery [ 22 ], adequate follow-up during the last weeks of pregnancy is mandatory, with particular consideration of possible associated underlying disorders (particularly foetal growth restriction or excessive foetal weight in cases of gestational diabetes mellitus) [ 24 , 25 , 26 ]. Thus, the foetal weight estimation should be carefully considered in the 37th week of gestation, even in cases of minor glycaemic disorder, with regular reassessments and a plan for CS delivery if the patient remains pregnant for many more weeks and if foetal weight estimates reach approximately 3600–3800 g.
If vaginal delivery is planned, careful labour management by a skilled team is needed, accompanied by continuous foetal heart rate monitoring [ 36 ] and a particular focus on the rate of progress in the second delivery stage [ 37 ]. When such conditions are not or cannot be fulfilled, a planned CS may be the best choice.
When a CS has been planned, adequate follow-up during the last weeks of pregnancy and careful calculation of the delivery date are needed, taking into account possible comorbidities and gestational disorders.
Term breech presentation is a condition for which personalized obstetrical care is particularly needed. The best way is likely to be as follows: first, efficiently screen for breech presentation at 36–37 weeks of gestation; second, thoroughly evaluate the maternal/foetal condition, foetal weight and growth potential, and the type (frank, complete, or footling) and mobility of breech presentation; and three, consider the obstetric history and pelvic size/conformation. The management plan, including ECV and follow-up during the last weeks, should then be organized taking into account antenatal risk factors on a case-by-case basis by a skilled team after informing the woman, discussing her personal situation and criteria and helping her make a rational decision. Foetal overgrowth or growth restriction and/or oligohydramnios may necessitate timely CS, and the mode of delivery should be re-evaluated as necessary according to obstetric conditions (e.g., estimated foetal weight and Bishop score).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Caesarean section
External cephalic version
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- Severe maternal morbidity
Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada
Term breech trial
Trends in vaginal breech delivery. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2015;69:1237–9.
Hannah ME, Hannah WJ, Hewson SA, Hodnett ED, Saigal S, Willan AR. Planned caesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomized multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group Lancet. 2000;356(9239):1375–83.
CAS Google Scholar
RCOG. Setting standards to improve women’s health. 2001.
Google Scholar
ACOG committee opinion: number 265, December 2001. Mode of term single breech delivery. Committee on Obstetric Practice. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:1189–90.
Rietberg CC, Elferink-Stinkens PM, Visser GH. The effect of the term breech trial on medical intervention behaviour and neonatal outcome in the Netherlands: an analysis of 35,453 term breech infants. BJOG. 2005;112:205–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Glezerman M. Five years to the term breech trial: the rise and fall of a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1162–7.
Article Google Scholar
Kotaska A. Inappropriate use of randomised trials to evaluate complex phenomena: case study of vaginal breech delivery. BMJ. 2004;329(7473):1039–42.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Su M, McLeod L, Ross S, et al. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group Factors associated with adverse perinatal outcome in the Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:740–5.
Whyte H, Hannah ME, Saigal S, et al. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group. Outcomes of children at 2 years after planned cesarean birth versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191:864–71.
Su M, McLeod L, Ross S, et al. Factors associated with maternal morbidity in the term breech trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2007;29:324–30.
Hartnack Tharin JE, Rasmussen S. Krebs L consequences of the term breech trial in Denmark. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90:767–71.
Vlemmix F, Bergenhenegouwen L, Schaaf JM, et al. Term breech deliveries in the Netherlands: did the increased cesarean rate affect neonatal outcome? A population-based cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2014;93:888–96.
Schutte JM, Steegers EA, Santema JG, Schuitemaker NW, van Roosmalen J, Maternal Mortality Committee of the Netherlands society of obstetrics. Maternal deaths after elective cesarean section for breech presentation in the Netherlands. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2007;86:240–3.
van Dillen J, Zwart JJ, Schutte J, Bloemenkamp KW, van Roosmalen J. Severe acute maternal morbidity and mode of delivery in the Netherlands. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2010;89(11):1460–5.
Lyons J, Pressey T, Bartholomew S, Liu S, Liston R, Joseph KS. Delivery of breech presentation at term gestation, Canada, 2003 to 2011. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1153–61.
Joseph KS, Pressey T, Lyons J, Bartholomew S, Liu S, Muraca G, et al. Once more unto the breech: planned vaginal delivery compared with planned cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1162–7.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Thornton JG. The term breech trial results are generalisable. BJOG. 2016;123(1):58.
ACOG Committee Opinion No. 340. Mode of term singleton breech delivery. ACOG Committee on obstetric practice. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:235–7.
SOGC clinical practice guideline: Vaginal delivery of breech presentation: no. 226, June 2009, Kotaska A, Menticoglou S, Gagnon R, Farine D, Basso M, Bos H, Delisle MF, Grabowska K, Hudon L, Mundle W, Murphy-Kaulbeck L, Ouellet A, Pressey T, Roggensack A. Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2009;107:169–76.
RCOG. Setting standards to improve women’s health. Guideline No. 20b. December 2006, actualized in March 2017.
Berhan Y, Haileamlak A. The risks of planned vaginal breech delivery versus planned caesarean section for term breech birth: a meta-analysis including observational studies. BJOG. 2016;123:49–57.
Macharey G, Gissler M, Rahkonen L, et al. Breech presentation at term and associated obstetric risks factors-a nationwide population based cohort study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:833–8.
Macharey G, Gissler M, Ulander VM, et al. Risk factors associated with adverse perinatal outcome in planned vaginal breech labors at term: a retrospective population-based case-control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:93.
Bjellmo S, Andersen GL, Martinussen MP, et al. Is vaginal breech delivery associated with higher risk for perinatal death and cerebral palsy compared with vaginal cephalic birth? Registry-based cohort study in Norway. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e014979.
Gardosi J, Madurasinghe V, Williams M, Malik A, Francis A. Maternal and fetal risk factors for stillbirth: population based study. BMJ. 2013;346:f108.
Luterkort M, Persson PH, Weldner BM. Maternal and fetal factors in breech presentation. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:55–9.
Krebs L, Topp M, Langhoff-Roos J. The relation of breech presentation at term to cerebral palsy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:943–7.
Fox AJ, Chapman MG. Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;46:341–4.
Hiersch L, Yeoshoua E, Miremberg H, et al. The association between Mullerian anomalies and short-term pregnancy outcome. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29:2573–8.
Singh A, Mishra N, Dewangan R. Delivery in breech presentation: the decision making. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2012;62:401–5.
Ulander VM, Gissler M, Nuutila M, Ylikorkala O. Are health expectations of term breech infants unrealistically high? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2004;83:180–6.
Goffinet F, Carayol M, Foidart JM, et al. Is planned vaginal delivery for breech presentation at term still an option? Results of an observational prospective survey in France and Belgium. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:1002–11.
Van Loon AJ, Mantingh A, Serlier EK, Kroon G, Mooyaart EL, Huisjes HJ. Randomised controlled trial of magnetic-resonance pelvimetry in breech presentation at term. Lancet. 1997;350:1799–80.
Hoffmann J, Thomassen K, Stumpp P, Grothoff M, Engel C, Kahn T, Stepan H. New MRI Criteria for Successful Vaginal Breech Delivery in Primiparae. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161028.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Klemt AS, Schulze S, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. MRI-based pelvimetric measurements as predictors for a successful vaginal breech delivery in the Frankfurt breech at term cohort (FRABAT). Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2019;232:10–7.
Toivonen E, Palomäki O, Huhtala H, Uotila J. Cardiotocography in breech versus vertex delivery: an examiner-blinded, cross-sectional nested case-control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:319.
Macharey G, Ulander VM, Heinonen S, Kostev K, Nuutila M, Väisänen-Tommiska M. Risk factors and outcomes in “well-selected” vaginal breech deliveries: a retrospective observational study. J Perinat Med. 2017;45:291–7.
Goodin A, Delcher C, Valenzuela C, Wang X, Zhu Y, Roussos-Ross D, Brown JD. The power and pitfalls of big data research in obstetrics and gynecology: a Consumer's guide. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2017;72:669–82.
Vargha P, Fülöp V, Tabák ÁG. Breech presentation: its predictors and consequences. An analysis of the Hungarian Tauffer obstetric database (1996-2011). Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016;95:347–54.
Hemelaar J, Lim LN, Impey LW. The impact of an ECV service is limited by antenatal breech detection: a retrospective cohort study. Birth. 2015;42:165–72.
Bin YS, Roberts CL, Nicholl MC, Ford JB. Uptake of external cephalic version for term breech presentation: an Australian population study, 2002-2012. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:244.
Rosman AN, Guijt A, Vlemmix F, Rijnders M, Mol BW, Kok M. Contraindications for external cephalic version in breech presentation at term: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013;92:137–42.
Quist-Nelson J, Landers K, McCurdy R, Berghella V. External cephalic version in premature rupture of membranes: a systematic review. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30:2257–61.
Burgos J, Cobos P, Rodríguez L, et al. Is external cephalic version at term contraindicated in previous caesarean section? A prospective comparative cohort study. BJOG. 2014;121:230–5.
Traité du palper abdominal au point de vue obstétrical et de la version par manœuvres externes / par A. Pinard. PARIS H. LATJWEREYNS, LIBRAIRE-ÉDITEUR, 1878.
Lau TK, Lo KW, Wan D, Rogers MS. Predictors of successful external cephalic version at term: a prospective study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:798–802.
Aisenbrey GA, Catanzarite VA, Nelson C. External cephalic version: predictors of success. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;94:783–6.
Hutton EK, Simioni JC, Thabane L. Predictors of success of external cephalic version and cephalic presentation at birth among 1253 women with non-cephalic presentation using logistic regression and classification tree analyses. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017;96:1012–20.
Kew N, DuPlessis J, La Paglia D, Williams K. Predictors of cephalic vaginal delivery following external cephalic version: an eight-year single-Centre study of 447 cases. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2017;2017:3028398.
Salzer L, Nagar R, Melamed N, Wiznitzer A, Peled Y, Yogev Y. Predictors of successful external cephalic version and assessment of success for vaginal delivery. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28:49–54.
Buhimschi CS, Buhimschi IA, Wehrum MJ, et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of myometrial thickness and prediction of a successful external cephalic version. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:913–20.
De La Version Par Manoeuvres Externes by Justus Heinrich Wigand (translated in french by François-Joseph Herrgott).
Velzel J, de Hundt M, Mulder FM, et al. Prediction models for successful external cephalic version: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2015;195:160–7.
De Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, Mol BW, Kok M. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(6):1327–34.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Boujenah J, Fleury C, Bonneau C, Pharisien I, Tigaizin A, Carbillon L. Successful external cephalic version is an independent factor for caesarean section during trial of labor - a matched controlled study. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2017;46:737–42.
De Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Bais JM, de Groot CJ, Mol BW, Kok M. Risk factors for cesarean section and instrumental vaginal delivery after successful external cephalic version. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29:2005–7.
Balayla J, Dahdouh EM, Villeneuve S, Boucher M, Gauthier RJ, Audibert F. Obstetrical and neonatal outcomes following unsuccessful external cephalic version: a stratified analysis amongst failures, successes, and controls. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28:605–10.
Burgos J, Rodríguez L, Cobos P, et al. Management of breech presentation at term: a retrospective cohort study of 10 years of experience. J Perinatol. 2015;35:803–8.
Coppola C, Mottet N, Mariet AS, et al. Impact of the external cephalic version on the obstetrical prognosis in a team with a high success rate of vaginal delivery in breech presentation. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016;45:859–65.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Wastlund, et al. Screening for breech presentation using universal late-pregnancy ultrasonography: A prospective cohort study and cost effectiveness analysis. PLoS Med. 2019;16(4):e1002778.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Author information, authors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, Assistance Publique – Hopitaux de Paris, Avenue du 14 juillet, Hôpital Jean Verdier, 93140, Bondy Cedex, France
Lionel Carbillon
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris, Hôpital Jean Verdier, Bondy, France
Lionel Carbillon, Amelie Benbara, Ahmed Tigaizin, Rouba Murtada, Marion Fermaut, Fatma Belmaghni, Alexandre Bricou & Jeremy Boujenah
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Study conception and design: LC, AB, JB, AT, FB, AB. Analysis and interpretation of data: LC, JB. Drafting of manuscript: LC. Critical revision: LC, JB, RM, MF. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lionel Carbillon .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Carbillon, L., Benbara, A., Tigaizin, A. et al. Revisiting the management of term breech presentation: a proposal for overcoming some of the controversies. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 20 , 263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-2831-4
Download citation
Received : 08 August 2019
Accepted : 20 February 2020
Published : 03 May 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-2831-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Term breech delivery
- Small-for-gestational-age
- Foetal growth restriction
- Oligohydramnios
- Delivery route
- Perinatal mortality
- Perinatal morbidity
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Breech presentation: diagnosis and management
Key messages.
- All women with a breech presentation should be offered an external cephalic version (ECV) from 37 weeks, if there are no contraindications.
- Elective caesarean section (ELCS) for a singleton breech at term has been shown to reduce perinatal and neonatal mortality rates.
- Planning for vaginal breech birth requires careful assessment of suitability criteria, contraindications and the ability of the service to provide experienced personnel.
In June 2023, we commenced a project to review and update the Maternity and Neonatal eHandbook guidelines, with a view to targeting completion in 2024. Please be aware that pending this review, some of the current guidelines may be out of date. In the meantime, we recommend that you also refer to more contemporaneous evidence.
Breech and external cephalic version
Breech presentation is when the fetus is lying longitudinally and its buttocks, foot or feet are presenting instead of its head.
Figure 1. Breech presentations
- Breech presentation occurs in three to four per cent of term deliveries and is more common in nulliparous women.
- External cephalic version (ECV) from 37 weeks has been shown to decrease the incidence of breech presentation at term and the subsequent elective caesarean section (ELCS) rate.
- Vaginal breech birth increases the risk of low Apgar scores and more serious short-term complications, but evidence has not shown an increase in long-term morbidity.
- Emergency caesarean section (EMCS) is needed in approximately 40 per cent of women planning a vaginal breech birth.
- 0.5/1000 with ELCS for breech >39 weeks gestation
- 2.0/1000 planned vaginal breech birth >39/40
- 1.0/1000 with planned cephalic birth.
- A reduction in planned vaginal breech birth followed publication of the Term Breech Trial (TBT) in 2001.
- Acquisition of skills necessary to manage breech presentation (for example, ECV) is important to optimise outcomes.
Clinical suspicion of breech presentation
- Abdominal palpation: if the presenting part is irregular and not ballotable or if the fetal head is ballotable at the fundus
- Pelvic examination: head not felt in the pelvis
- Cord prolapse
- Very thick meconium after rupture of membranes
- Fetal heart heard higher in the abdomen
In cases of extended breech, the breech may not be ballotable and the fetal heart may be heard in the same location as expected for a cephalic presentation.
If breech presentation is suspected, an ultrasound examination will confirm diagnosis.
Cord prolapse is an obstetric emergency. Urgent delivery is indicated after confirming gestation and fetal viability.
Diagnosis: preterm ≤36+6 weeks
- Breech presentation is a normal finding in preterm pregnancy.
- If diagnosed at the 35-36 week antenatal visit, refer the woman for ultrasound scan to enable assessment prior to ECV.
- Mode of birth in a breech preterm delivery depends on the clinical circumstances.
Diagnosis: ≥37+0 weeks
- determine type of breech presentation
- determine extension/flexion of fetal head
- locate position of placenta and exclude placenta praevia
- exclude fetal congenital abnormality
- calculate amniotic fluid index
- estimate fetal weight.
Practice points
- Offer ECV if there are no contraindications.
- If ECV is declined or unsuccessful, provide counselling on risks and benefits of a planned vaginal birth versus an ELCS.
- Inform the woman that there are fewer maternal complications with a successful vaginal birth, however the risk to the woman increases significantly if there is a need for an EMCS.
- Inform the woman that caesarean section increases the risk of complication in future pregnancies, including the risk of a repeat caesarean section and the risk of invasive placentation.
- If the woman chooses an ELCS, document consent and organise booking for 39 weeks gestation.
Information and decision making
Women with a breech presentation should have the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and treatment, in partnership with the clinicians providing care.
Planning for birth requires careful assessment for risk of poor outcomes relating to planned vaginal breech birth. If any risk factors are identified, inform the woman that an ELCS is recommended due to increased perinatal risk.
Good communication between clinicians and women is essential. Treatment, care and information provided should:
- take into account women's individual needs and preferences
- be supported by evidence-based, written information tailored to the needs of the individual woman
- be culturally appropriate
- be accessible to women, their partners, support people and families
- take into account any specific needs, such as physical or cognitive disabilities or limitations to their ability to understand spoken or written English.
Documentation
The following should be documented in the woman's hospital medical record and (where applicable) in her hand-held medical record:
- discussion of risks and benefits of vaginal breech birth and ELCS
- discussion of the woman's questions about planned vaginal breech birth and ELCS
- discussion of ECV, if applicable
- consultation, referral and escalation
External cephalic version (ECV)
- ECV can be offered from 37 weeks gestation
- The woman must provide written consent prior to the procedure
- The success rate of ECV is 40-60 per cent
- Approximately one in 200 ECV attempts will lead to EMCS
- ECV should only be performed by a suitably trained, experienced clinician
- continuous electronic fetal monitoring (EFM)
- capability to perform an EMCS.
Contraindications
Table 1. Contraindications to ECV
Precautions
- Hypertension
- Oligohydramnios
- Nuchal cord
Escalate care to a consultant obstetrician if considering ECV in these circumstances.
- Perform a CTG prior to the procedure - continue until RANZCOG criteria for a normal antenatal CTG are met.
- 250 microg s/c, 30 minutes prior to the procedure.
- Administer Anti-D immunoglobulin if the woman is rhesus negative.
- Do not make more than four attempts at ECV, for a suggested maximum time of ten minutes in total.
- Undertake CTG monitoring post-procedure until RANZCOG criteria for a normal antenatal CTG are met.

Emergency management
Urgent delivery is indicated in the event of the following complications:
- abnormal CTG
- vaginal bleeding
- unexplained pain.
Initiate emergency response as per local guidelines.
Alternatives to ECV
There is a lack of evidence to support the use of moxibustion, acupuncture or postural techniques to achieve a vertex presentation after 35 weeks gestation.
Criteria for a planned vaginal breech birth
- Documented evidence of counselling regarding mode of birth
- Documentation of informed consent, including written consent from the woman
- Estimated fetal weight of 2500-4000g
- Flexed fetal head
- Emergency theatre facilities available on site
- Availability of suitably skilled healthcare professional
- Frank or complete breech presentation
- No previous caesarean section.
- Cord presentation
- Fetal growth restriction or macrosomia
- Any presentation other than a frank or complete breech
- Extension of the fetal head
- Fetal anomaly incompatible with vaginal delivery
- Clinically inadequate maternal pelvis
- Previous caesarean section
- Inability of the service to provide experienced personnel.
If an ELCS is booked
- Confirm presentation by ultrasound scan when a woman presents for ELCS.
- If fetal presentation is cephalic on admission for ELCS, plan ongoing management with the woman.
Intrapartum management
Fetal monitoring.
- Advise the woman that continuous EFM may lead to improved neonatal outcomes.
- Where continuous EFM is declined, perform intermittent EFM or intermittent auscultation, with conversion to EFM if an abnormality is detected.
- A fetal scalp electrode can be applied to the breech.
Position of the woman
- The optimal maternal position for birth is upright.
- Lithotomy may be appropriate, depending on the accoucheur's training and experience.
Pain relief
- Epidural analgesia may increase the risk of intervention with a vaginal breech birth.
- Epidural analgesia may impact on the woman's ability to push spontaneously in the second stage of labour.
Induction of labour (IOL)
See the IOL eHandbook page for more detail.
- IOL may be offered if clinical circumstances are favourable and the woman wishes to have a vaginal birth.
- Augmentation (in the absence of an epidural) should be avoided as adequate progress in the absence of augmentation may be the best indicator of feto-pelvic proportions.
The capacity to offer IOL will depend on clinician experience and availability and service capability.
First stage
- Manage with the same principles as a cephalic presentation.
- Labour should be expected to progress as for a cephalic presentation.
- If progress in the first stage is slow, consider a caesarean section.
- If an epidural is in situ and contractions are less than 4:10, consult with a senior obstetrician.
- Avoid routine amniotomy to avoid the risk of cord prolapse or cord compression.
Second stage
- Allow passive descent of the breech to the perineum prior to active pushing.
- If breech is not visible within one hour of passive descent, a caesarean section is normally recommended.
- Active second stage should be ½ hour for a multigravida and one hour for a primipara.
- All midwives and obstetricians should be familiar with the techniques and manoeuvres required to assist a vaginal breech birth.
- Ensure a consultant obstetrician is present for birth.
- Ensure a senior paediatric clinician is present for birth.
VIDEO: Maternity Training International - Vaginal Breech Birth
- Encouragement of maternal pushing (if at all) should not begin until the presenting part is visible.
- A hands-off approach is recommended.
- Significant cord compression is common once buttocks have passed the perineum.
- Timely intervention is recommended if there is slow progress once the umbilicus has delivered.
- Allow spontaneous birth of the trunk and limbs by maternal effort as breech extraction can cause extension of the arms and head.
- Grasp the fetus around the bony pelvic girdle, not soft tissue, to avoid trauma.
- Assist birth if there is a delay of more than five minutes from delivery of the buttocks to the head, or of more than three minutes from the umbilicus to the head.
- Signs that delivery should be expedited also include lack of tone or colour or sign of poor fetal condition.
- Ensure fetal back remains in the anterior position.
- Routine episiotomy not recommended.
- Lovset's manoeuvre for extended arms.
- Reverse Lovset's manoeuvre may be used to reduce nuchal arms.
- Supra-pubic pressure may aide flexion of the fetal head.
- Maricueau-Smellie-Veit manoeuvre or forceps may be used to deliver the after coming head.
Undiagnosed breech in labour
- This occurs in approximately 25 per cent of breech presentations.
- Management depends on the stage of labour when presenting.
- Assessment is required around increased complications, informed consent and suitability of skilled expertise.
- Do not routinely offer caesarean section to women in active second stage.
- If there is no senior obstetrician skilled in breech delivery, an EMCS is the preferred option.
- If time permits, a detailed ultrasound scan to estimate position of fetal neck and legs and estimated fetal weight should be made and the woman counselled.
Entrapment of the fetal head
This is an extreme emergency
This complication is often due to poor selection for vaginal breech birth.
- A vaginal examination (VE) should be performed to ensure that the cervix is fully dilated.
- If a lip of cervix is still evident try to push the cervix over the fetal head.
- If the fetal head has entered the pelvis, perform the Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit manoeuvre combined with suprapubic pressure from a second attendant in a direction that maintains flexion and descent of the fetal head.
- Rotate fetal body to a lateral position and apply suprapubic pressure to flex the fetal head; if unsuccessful consider alternative manoeuvres.
- Reassess cervical dilatation; if not fully dilated consider Duhrssen incision at 2, 10 and 6 o'clock.
- A caesarean section may be performed if the baby is still alive.
Neonatal management
- Paediatric review.
- Routine observations as per your local guidelines, recorded on a track and trigger chart.
- Observe for signs of jaundice.
- Observe for signs of tissue or nerve damage.
- Hip ultrasound scan to be performed at 6-12 weeks post birth to monitor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). See Neonatal eHandbook - Developmental dysplasia of the hip .
More information
Audit and performance improvement.
All maternity services should have processes in place for:
- auditing clinical practice and outcomes
- providing feedback to clinicians on audit results
- addressing risks, if identified
- implementing change, if indicated.
Potential auditable standards are:
- number of women with a breech presentation offered ECV
- success rate of ECV
- ECV complications
- rate of planned vaginal breech birth
- breech birth outcomes for vaginal and caesarean birth.
For more information or assistance with auditing, please contact us via [email protected]
- Bue and Lauszus 2016, Moxibustion did not have an effect in a randomised clinical trial for version of breech position. Danish Medical Journal 63(2), A599
- Coulon et.al. 2014, Version of breech fetuses by moxibustion with acupuncture. Obstetrics and Gynecology 124(1), 32-39. DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000303
- Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B 2012, Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD003928. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003928.pub3
- Evans J 2012, Essentially MIDIRS Understanding Physiological Breech Birth Volume 3. Number 2. February 2012
- Hoffmann J, Thomassen K, Stumpp P, Grothoff M, Engel C, Kahn T, et al. 2016, New MRI Criteria for Successful Vaginal Breech Delivery in Primiparae. PLoS ONE 11(8): e0161028. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161028
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R 2012, Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD000051. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000051.pub2
- New South Wales Department of Health 2013, Maternity: Management of Breech Presentation HNELHD CG 13_01, NSW Government; 2013
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists 2017, External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation. Green-top Guideline No. 20a . London: RCOG; 2017
- The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RANZCOG) 2016, Management of breech presentation at term , July 2016 C-Obs-11:
- The Royal Women's Hospital 2015, Management of Breech - Clinical Guideline
- Women's and Newborn Health Service, King Edward Memorial Hospital 2015, Complications of Pregnancy Breech Presentation
Abbreviations
Get in touch, version history.
First published: November 2018 Due for review: November 2021
Uncontrolled when downloaded
Related links.
Breech presentation: Clinical practice guidelines from the French College of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians (CNGOF)
Affiliations.
- 1 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, CHU Bordeaux, Université de Bordeaux, Place Amélie Raba-Léon, 33000, Bordeaux, France. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, Hôpital Robert-Debré, APHP, 48, bd Serrurier, 75019, Paris, France; Université de Paris, Epidemiology and Statistics Research Center/CRESS, INSERM, INRA, F-75004, Paris, France.
- 3 Université de Paris, Epidemiology and Statistics Research Center/CRESS, INSERM, INRA, F-75004, Paris, France; Maternité Notre Dame de Bon Secours, Groupe Hospitalier Paris Saint-Joseph, DHU Risques et Grossesse, 185, rue Raymond Losserand, 75014, Paris, France.
- 4 Pôle Femme Et Enfant, CHU Estaing, 1 place Lucie et Raymond Aubrac, 63003, Clermont-Ferrand cedex 1, France; R2D2-EA7281, Université d'Auvergne, Faculté de Médecine, Place Henri Dunant, 63000, Clermont-Ferrand, France.
- 5 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, Centre Hospitalier Départemental, 85000, La Roche sur Yon, France.
- 6 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, CHU Bordeaux, Université de Bordeaux, Place Amélie Raba-Léon, 33000, Bordeaux, France.
- 7 Inserm, UMR1027, Equipe SPHERE, Toulouse, F-31073, France; Université de Toulouse III, UMR1027, Toulouse, F-31073, France; CHU Toulouse, Pôle de gynécologie obstétrique, Hôpital Paule de Viguier, Toulouse, F-31059, France.
- 8 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Strasbourg, Avenue Molière, BP 426, 67091, Strasbourg cedex, France; Unité INSERM UMR-S 1121 << Biomatériaux et Bioingénierie >>, 11, rue Humann, 67000, Strasbourg, France.
- 9 Collège National des Sages-Femmes de France, 136, avenue Emile Zola, 75015, Paris, France.
- 10 Département de gynécologie-obstétrique, Hôpital Poissy Saint-Germain, 10, rue du Champ-Gaillard, 78300, Poissy, France; Université Versailles-St Quentin, France.
- 11 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, Hôpital Bicêtre, APHP, 78, avenue du Général-Leclerc, 94270, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France.
- 12 Service de gynécologie-obstétrique, CHU de Rouen, Université de Rouen, France.
- PMID: 32249011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.03.033
Objective: To determine the optimal management of singleton fetuses in breech presentation.
Materials and methods: Consultation of the PubMed database, the Cochrane Library and guidelines issued by the French and foreign obstetrical societies or colleges.
Results: In France, 5% of women have breech deliveries (level of evidence [LE] 3). One third of them have a planned vaginal delivery (LE3), and 70% of these give birth vaginally (LE3). External cephalic version (ECV) is associated with lower rates of both breech presentation at birth (LE2) and of cesarean deliveries (LE3) without any increase in severe maternal (LE3) or perinatal morbidity (LE3). Women with a fetus in breech presentation at term should be informed that ECV can be attempted starting at 36 weeks of gestation (professional consensus). Planned vaginal delivery of breech presentation may be associated with a higher risk of composite perinatal mortality or serious neonatal morbidity than planned cesarean birth (LE2). These two modes do not differ for neurodevelopmental outcomes at two years (LE2), cognitive and psychomotor outcomes between 5 and 8 years (LE3), or adult intellectual performance (LE4). Short- and long-term maternal complications appear similar in the two groups, unless subsequent pregnancies are under consideration. Pregnancies after a cesarean delivery are at higher risk of uterine rupture, placenta accreta spectrum disorders, and hysterectomy (LE2). Women who want a planned vaginal delivery should be offered a pelvimetry at term (Grade C) and should have ultrasonography to verify that the fetal head is not hyperextended (professional consensus) to plan their mode of delivery. Complete breech presentation, a previous cesarean, nulliparity, and term prelabor rupture of membranes are not, each one by itself, per se contraindications to planned vaginal delivery (professional consensus). Term breech presentation is not a contraindication to labor induction when the criteria for planned vaginal delivery are met (Grade C).
Conclusion: In cases of breech presentation at term, the child and the mother are at low risk of severe morbidity after either planned vaginal or planned cesarean delivery. The French College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (CNGOF) considers that planned vaginal delivery is a reasonable option in most cases (professional consensus). The decision about the planned route of delivery should be shared by the woman and her healthcare provider, who must respect her right to autonomy.
Keywords: Breech presentation; External cephalic version; Maternal and neonatal morbidity; Planned cesarean delivery; Planned vaginal delivery; Trial of labor.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Publication types
- Breech Presentation*
- Delivery, Obstetric
- France / epidemiology
- Gynecology*
- Infant, Newborn
- Version, Fetal*
- Open access
- Published: 01 April 2024
Clinical features of intussusception in children secondary to small bowel tumours: a retrospective study of 31 cases
- Li Wang 1 na1 ,
- Hanwen Zhang 1 na1 ,
- Dayong Wang 1 ,
- Qiulong Shen 1 ,
- Liuming Huang 1 nAff2 &
- Tingting Liu 1 nAff2
BMC Pediatrics volume 24 , Article number: 227 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Summarizing the clinical features of children with intussusception secondary to small bowel tumours and enhancing awareness of the disease.
Retrospective summary of children with intussusception admitted to our emergency department from January 2016 to January 2022, who underwent surgery and were diagnosed with small bowel tumours. Summarize the types of tumours, clinical presentation, treatment, and prognosis.
Thirty-one patients were included in our study, 24 males and 7 females, with an age of onset ranging from 1 m to 11y 5 m. Post-operative pathology revealed 4 types of small intestinal tumour, 17 lymphomas, 10 adenomas, 4 inflammatory myofibroblastomas and 1 lipoma. The majority of tumours in the small bowel occur in the ileum (83.9%, 26/31). Abdominal pain, vomiting and bloody stools were the most common clinical signs. Operative findings indicated that the small bowel (54.8%, 17/31) and ileocolic gut were the main sites of intussusception. Two types of procedure were applied: segmental bowel resection (28 cases) and wedge resection of mass in bowel wall (3 cases). All patients recovered well postoperatively, with no surgical complications observed. However, the primary diseases leading to intussusception showed slight differences in long-term prognosis due to variations in tumor types.
Conclusions
Lymphoma is the most common cause of intussusception in pediatric patients with small bowel tumours, followed by adenoma. Small bowel tumours in children tend to occur in the ileum. Therefore, the treatment of SBT patients not only requires surgeons to address symptoms through surgery and obtain tissue samples but also relies heavily on the expertise of pathologists for accurate diagnosis. This has a significant impact on the overall prognosis of these patients.
Peer Review reports
Intussusception in children is a common clinical condition that can be classified into two main types: primary and secondary. Gas enema treatment is usually effective in curing primary intussusception and recurrence is rare [ 1 ]. Nevertheless, secondary intussusception may recur and is typically associated with underlying organic pathology. These organic lesions, primarily Meckel’s diverticulum, polyps, tumors, etc., are frequently found at the head of the bowel where secondary intussusception occurs [ 2 , 3 ].
Small bowel tumors (SBT) are uncommon, especially in children with an incidence of approximately 1 per 100,000. Intussusception caused by SBT is an even rarer condition, and there are fewer instances where pediatric patients specifically seek medical attention for intussusception that is secondary to SBT [ 4 ]. As a result, the majority of cases involving intussusception that is secondary to SBT in pediatric patients are typically published as case reports [ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Currently, there is no comprehensive summary available on the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and clinical outcomes of intussusception that is secondary to SBT in children. In pursuit of this objective, we retrospectively gathered a cohort of pediatric patients with intussusception that was secondary to SBT and treated at our hospital. We meticulously examined their case characteristics and compiled our clinical observations for comprehensive analysis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Patients aged < 18 years with intussusception were enrolled in the current study from January 2016 to January 2022. All patients were diagnosed with intussusception attributable to SBT based on preoperative imaging or surgical findings. Patients were excluded if their clinical data were lost, pathological examination was unclear, or if the intussusception was associated with other types of intestinal polyps. Informed consent was obtained from the parents/guardians of all patients. This study complied with the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the local ethics committee (approval number: 2022-E-173-R).
Clinical outcome evaluation indicators
Primary outcome.
Clinical presentation and pathological findings.
Secondary outcomes
Baseline, imaging, surgical and follow-up data.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using standardized statistical software (Statistical Package for Social Science; version 19.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). Non-normally distributed data were expressed as median (25th, 75th interquartile range). Enumeration data were expressed as frequency, rate, or composition ratio, and tested with the chi-squared test. P values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Baseline characteristics & clinical presentation
This study collected clinical data from 31 children with SBT-associated intussusception, based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria above, with a gender distribution of 24 males and 7 females. The age range of the patients was between 1 month and 11 years and 5 months, with a mean age of 47.4 ± 36.5 months. Among all patients, 26 individuals are over 2 years old, and the distribution of disease onset ages was relatively uniform, with 7 cases in the infant stage, 7 in the toddler stage, 8 in the preschool stage, and 9 in the school-age stage. The duration of illness ranged from 1 to 90 days with a median duration of 5.0 (2.8, 20.3) days.
The major symptoms reported by the patients were abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stools. The most commonly reported complaint was recurrent abdominal pain. Other symptoms included recurrent cases of intussusception and wasting. Among all patients, 23 cases (74.2%) presented with abdominal pain as a symptom, mainly characterized by dull pain and inflammatory stimulus-like pain. Thirteen cases (41.9%) exhibited vomiting, while nine cases (29.0%) had bloody stools. Two cases (6.5%) showed signs of wasting (mainly manifested as emaciation and anemia), and postoperative pathology confirmed Burkitt lymphoma and lipoma, respectively. Additionally, two cases (6.5%) of pediatric patients experienced recurrent intussusception, both attributed to Burkitt lymphoma.
Ancillary examinations
All patients had preoperative ultrasounds that showed suggestive signs of intussusception, with the typical “concentric circles” pattern observed (Fig. 1 ). 17 patients had intussusception in the small bowel, while 14 patients had it in the ileocecal region. Out of the 31 patients, 28 suggested that the sleeve’s secondary factor was due to occupation of the intestinal wall. In 8 cases, the tumour and its type were accurately identified, with 5 cases being lymphoma and 3 cases being adenomyoma. Among patients with ileocecal intussusception, only 3 cases showed no evidence of a primary intestinal tumor during preoperative examination.
Ultrasound images of SBTs. (1) Lymphoma; (2) Adenomyoma; (3) Inflammatory myofibroblastoma; (4) Lipoma
Surgical characteristics
All surgical procedures went smoothly, and the SBT lesions were visible to the naked eye intraoperatively. The procedures performed included segmental bowel resection with anastomosis in 28 cases and wedge resection of intestinal wall masses (consisted of 2 cases of adenomyoma and 1 case of lipoma). Lymphomas and adenomyomas are more frequently found in the ileum, while myofibroblastomas exclusively occur in the ileum. Only one case of lipoma was detected in the jejunum. Four patients with adenomyoma and one patient with inflammatory myofibroblastoma were found to have experienced intraoperative intestinal necrosis during the course of their surgery. According to our patient information, SBT are more commonly found in the ileum, but there is no significant difference in the prevalence of different types of SBT (Table 1 ; Fig. 2 ).
Surgical specimens for SBTs. (1) Lymphoma; (2) Adenomyoma; (3) Inflammatory myofibroblastoma; (4) Lipoma
Pathological characteristics
The pathology results suggested that all 17 cases of lymphoma were indicative of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Among the cases reviewed, there were 9 instances of Burkitt’s lymphoma (average length 19.8 ± 27.0 cm), 5 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (average length 10.4 ± 5.5 cm), 2 cases of high-grade mature B-lymphocytoma, and 1 case of lymphoblastoma.
Follow-up & prognosis
All patients were followed up for a period of 3 months to 6 years. Only one patient with adenomyoma experienced a recurrence of primary intussusception one week after surgery. The remaining patients did not have any surgery-related complications in the short or long term. Patients with lymphoma were monitored for a period ranging from 6 m to 6y. Among the 11 children who were monitored for 6 m to 5y, none had a recurrence of the condition. Four patients were lost to follow-up, and four died. Patients with inflammatory myofibroblastoma, adenomyoma, and lipoma were monitored for a period ranging from 6 months to 5.5 years. In patients with adenomyoma and lipoma who underwent wedge resection of the intestinal wall mass, the prognosis was not bad as there were no reported cases of recurrence or metastases in the digestive tract or elsewhere during the follow-up period.
The small intestine comprises roughly 75% of the total length and 90% of the total surface area of the gastrointestinal tract (GI) [ 4 ]. Tumors of the small intestine are considered rare, with an incidence rate of 0.01 per 1,000 population [ 4 ]. The occurrence of SBT in children is even more infrequent. Moreover, the clinical manifestation of SBT in children is nonspecific, and recurrent intussusception is the most common initial presentation. Intussusception is more common in children, with 80% of cases occurring in patients aged ≤ 2 years, and primary intussusception is the most common form [ 9 , 10 , 11 ]. However, as in our study, where 26 patients were above the age of 2 years, it is consistent with the fact that secondary intussusception is more prevalent in older children. In many cases, emergency surgery is necessary for these patients, and a definitive diagnosis typically requires pathological examination of the specimen.
There are often distinguishing features between the two types of intussusceptions, which can aid the doctor in making a differential diagnosis. These features include clinical symptoms, disease history and supplementary tests. The classic clinical symptoms of primary intussusception are characterized by the triad of intermittent abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stools [ 12 ]. In contrast, secondary intestinal obstruction usually lacks the simultaneous presence of all three typical symptoms [ 13 ]. Out of our patients, only three exhibited the classic triad of abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stools, while the majority presented with recurrent abdominal pain. The disease duration of primary intussusception is usually less than 1d. But if the disease persists for longer than 3 days, physicians should be vigilant in detecting potential triggers [ 14 ]. The extended duration of illness in the majority of our patients, with 28 cases (82.4%) persisting for more than 3 days, corroborated their view. However, the above evidence is insufficient to support a diagnosis of intussusception and SBT. Intussusception is typically diagnosed with ultrasound alone, but only 61.4% of positive cases clearly indicate the presence of an inciting factor [ 15 ]. Based on the ultrasound findings, all patients show evidence of intussusception and are able to differentiate the type. Out of the patients included in our study, 28 cases indicated the presence of secondary factors, while only 8 suggested the presence of SBT. Among the 31 patients with intussusception, 3 cases (10.0%) of ileocolic intussusception showed no indications of secondary factors on ultrasound examination. Upon reviewing their medical records, it was discovered that the tumors measured 0.5cm1.0 cm (adenomyoma with concurrent intestinal necrosis), 1.8 cm*1.1 cm (adenomyoma with concurrent intestinal necrosis), and 0.5 cm*0.7 cm (lymphoblastic lymphoma without any signs of intestinal necrosis). Considering these factors, we believe that the small size of the tumor and the potential presence of intestinal necrosis may increase the difficulty of preoperative ultrasound diagnosis. While a definitive preoperative diagnosis in children with intestinal intussusception caused by SBT may present challenges, we recommend, drawing from our clinical expertise, that SBT should be considered in cases where children have a history of intestinal intussusception lasting over 3 days and are aged above 2 years. In addition, if ultrasound indicates the presence of secondary factors, caution should be raised regarding the possibility of SBT.
Currently, more than 40 distinct histological types of benign and malignant neoplasms are recognized as solid pseudopapillary tumors (SBTs). Among benign lesions in adults, common types include leiomyoma, adenoma, lipoma, and hamartoma. Malignant lesions often comprise adenocarcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors, sarcoma, and lymphoma, as highlighted in references [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. However, the pathological spectrum of SBTs in children differs significantly from that observed in adults. In our study, lymphoma constituted 55.9% of all tumors, while adenomyoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, and lipoma accounted for 29.4%, 11.8%, and 2.9%, respectively.
While intussusception in children traditionally occurs in the ileocolic region, our findings suggest that secondary intussusception resulting from small intestinal tumors in children is more likely to manifest as small bowel intussusception. This observation aligns with previous research by Lin et al. [ 20 ], who identified small bowel intussusception as the predominant type in secondary intussusception cases.
The primary treatment approach for intussusception in children secondary to SBT involves surgical intervention, with segmental resection and wedge resection being the principal surgical modalities [ 21 ]. Although postoperative pathology is crucial for a definitive diagnosis of SBT, our experience indicates that intraoperative assessment of tumor morphology can aid in identifying its pathological type. Lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastoma typically present with distinctive surface characteristics, such as surface indentations on the plasma membrane and rounded, granular, or lobulated protrusions on the mucosal surface, with a firm texture. However, distinguishing between these two types can be challenging. Therefore, in cases involving either type of tumor, consideration should be given to performing a segmental bowel resection. Gross visualization during surgery is usually sufficient to ensure complete removal of the tumor [ 4 ]. Although intraoperative frozen section pathology was not performed in our cases, post-operative pathology confirmed complete tumor removal.
Lymphoma can manifest in various locations, necessitating a thorough examination of the entire small bowel. The serosal surface of adenomyoma exhibits bubble-like protrusions, while the mucosal surface appears as smooth protrusions. Lipomas, on the other hand, present as polypoid lesions protruding from the mucosal surface, occasionally with ulceration at the base, making them challenging to distinguish from polyps. Nevertheless, based on their gross morphology, adenomyomas and lipomas can be identified as benign tumors. Depending on their size, segmental intestinal resection or wedge resection may be performed [ 22 ].
Subsequently, the prognosis of SBT in children is contingent upon its pathological type. Chemotherapy emerges as the primary treatment option for gastrointestinal lymphoma, while surgery is generally reserved for patients facing challenging diagnoses, gastrointestinal perforations, and intestinal obstruction [ 23 , 24 ]. Complete resection remains the principal treatment modality for other tumor types, with incomplete resection standing as a significant contributor to recurrence [ 25 ].
Intussusception secondary to SBT in pediatric patients represents a rare and challenging condition for preoperative diagnosis. Surgical intervention is essential for children with recurrent episodes of intussusception and for those in whom ultrasound indicates the presence of a “primary cause,” with the definitive diagnosis often dependent on intraoperative observations and postoperative pathology. This study compiles the clinical characteristics of pediatric patients diagnosed with SBT in our hospital over recent years, thereby furnishing valuable clinical insights for both pediatric emergency surgery and general surgical practitioners.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Jiang J, Jiang B, Parashar U, Nguyen T, Bines J, Patel MM. Childhood intussusception: a literature review. PLoS ONE. 2013;7:e68482.
Article Google Scholar
Kelley-Quon LI, Arthur LG, Williams RF, Goldin AB, St PS, Beres AL, et al. Management of intussusception in children: a systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;3:587–96.
Marsicovetere P, Ivatury SJ, White B, Holubar SD. Intestinal intussusception: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017;1:30–9.
Google Scholar
Coco C, Rizzo G, Manno A, Mattana C, Verbo A. Surgical treatment of small bowel neoplasms. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;4:327–33.
Rispo A, De Sire R, D’Armiento M, De Bonis L, Tropeano FP, Ricciolino S, et al. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of ileo-ileal intussusception secondary to Vanek’s tumor. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;2:350–3.
Ivanis N, Tomas V, Vranic L, Lovasic F, Ivanis V, Zulj M, et al. Inflammatory fibroid polyp of the small intestine: a Case Report and systematic literature review. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020;3:455–60.
Takeuchi N, Semba S, Naba K, Aoki R, Nishida Y, Nomura Y, et al. Jejunal tubulovillous adenocarcinoma in adenoma presenting with entero-enteric intussusception. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2013;1:46–9.
Mouravas V, Koutsoumis G, Patoulias J, Kostopoulos I, Kottakidou R, Kallergis K, et al. Adenomyoma of the small intestine in children: a rare cause of intussusception: a case report. Turk J Pediatr. 2003;4:345–7.
Ugwu BT, Legbo JN, Dakum NK, Yiltok SJ, Mbah N, Uba FA. Childhood intussusception: a 9-year review. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2000;2:131–5.
Zonca P, Peteja M, Richter V, Vavra P, Ihnat P. [Primary malignant small bowel tumors]. Rozhl Chir. 2016;9:344–9.
Nagi B, Verma V, Vaiphei K, Kochhar R, Bhasin D, Singh K. Primary small bowel tumors: a radiologic-pathologic correlation. Abdom Imaging. 2001;5:474–80.
Plut D, Phillips GS, Johnston PR, Lee EY. Practical imaging strategies for Intussusception in Children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;6:1449–63.
Gluckman S, Karpelowsky J, Webster AC, Mcgee RG. Management for intussusception in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6:D6476.
Guo WL, Hu ZC, Tan YL, Sheng M, Wang J. Risk factors for recurrent intussusception in children: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2017;11:e18604.
Applegate KE. Intussusception in children: imaging choices. Semin Roentgenol. 2008;1:15–21.
Clift AK, Kidd M, Bodei L, Toumpanakis C, Baum RP, Oberg K, et al. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the small bowel and pancreas. Neuroendocrinology. 2020;6:444–76.
Jun SY, Park ES, Lee JJ, Chang HK, Jung ES, Oh YH, et al. Prognostic significance of stromal and intraepithelial tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020;1:105–18.
Masselli G, Guida M, Laghi F, Polettini E, Gualdi G. Magnetic resonance of small bowel tumors. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2020;1:75–88.
Jasti R, Carucci LR. Small Bowel neoplasms: a Pictorial Review. Radiographics. 2020;4:1020–38.
Lin XK, Xia QZ, Huang XZ, Han YJ, He GR, Zheng N. Clinical characteristics of intussusception secondary to pathologic lead points in children: a single-center experience with 65 cases. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;7:793–7.
Rondonotti E, Koulaouzidis A, Georgiou J, Pennazio M. Small bowel tumours: update in diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018;3:159–64.
Wilson JM, Melvin DB, Gray G, Thorbjarnarson B. Benign small bowel tumor. Ann Surg. 1975;2:247–50.
Oka P, Sidhu R. Small bowel lymphoma: clinical update and challenges for the gastroenterologist. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2022;3:270–8.
Lu PW, Fields AC, Yoo J, Irani J, Goldberg JE, Bleday R, et al. Surgical Management of Small Bowel Lymphoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021;3:757–65.
Zhang L, Chen YJ, Shang CZ, Zhong F, Zhang HW, Chen JS. [Diagnosis and treatment of primary tumor of small intestine: a report of 58 cases]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;4:356–8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Liuming Huang & Tingting Liu
Present address: Beijing Children’s Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Center for Children’s Health, No.56, Nanlishi Road, Beijing, 100045, PR China
Li Wang and Hanwen Zhang contributed equally to this study.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Emergency Surgery, Beijing Children’s Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Center for Children’s Health, Beijing, 100045, China
Li Wang, Hanwen Zhang, Dayong Wang, Qiulong Shen, Liuming Huang & Tingting Liu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.W., H.Z. and L.H. designed the study and analyzed the data. L.H., H.Z. and T.L. revised the paper and supervised the study. L.W., D.W., Q.S. and L.H. managed and treated the patients. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Liuming Huang or Tingting Liu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This retrospective study was approved by the ethics committee of Beijing Children’s Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Center for Children’s Health (2022-E-173-R). All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. And informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardians.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wang, L., Zhang, H., Wang, D. et al. Clinical features of intussusception in children secondary to small bowel tumours: a retrospective study of 31 cases. BMC Pediatr 24 , 227 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-024-04717-y
Download citation
Received : 22 May 2023
Accepted : 21 March 2024
Published : 01 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-024-04717-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Small bowel tumours
- Intussusception
BMC Pediatrics
ISSN: 1471-2431
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Breech presentation
Term hierarchy.
- C R O G V Breech presentation
- Complete breech presentation
- Frank breech presentation
- Incomplete breech presentation
Conditions with this feature
Professional guidelines, uk nice guideline ng192, caesarean birth, 2024, recent clinical studies, clinical prediction guides, recent systematic reviews.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main types of breech presentation are: Frank breech - Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term. Complete breech - Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
Clinical features. Before 36 weeks, breech presentation is not significant, as the fetus is likely to revert to a cephalic presentation. The mother will often be asymptomatic with the diagnosis being incidental. The incidence of breech presentation is approximately 20% at 28 weeks gestation, 16% at 32 weeks gestation and 3-4% at term.
During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Introduction. Breech presentation of the fetus in late pregnancy may result in prolonged or obstructed labour with resulting risks to both woman and fetus. Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman's and the baby's health. The aim of this review is to determine the most ...
Clinical practice guidelines, which focus on the risks of a Vaginal Breech Birth without also discussing the risks of a Caesarean Section when a breech presentation is diagnosed, has the potential to sway clinician attitudes and impact birth mode decision-making in maternity consumers.
Management of Breech Presentation. This is the fourth edition of this guideline originally published in 1999 and revised in 2001 and 2006 under the same title. Executive summary of recommendations ... availability of appropriate clinical expertise and informed consent.
Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. Term babies presenting by the breech have worse outcomes than cephalic presenting babies, irrespective of the ...
1. Background. The management of breech presentation continues to cause academic and clinical contention globally [[1], [2], [3]].In recent years, research has shown that if certain criteria are met, and appropriately experienced and skilled clinicians are available, Vaginal Breech Birth (VBB) is a safe option [[4], [5], [6]].However, with Caesarean Section (C/S) rates for breech presentation ...
Term breech presentation is a condition for which personalized obstetrical care is particularly needed. The best way is likely to be as follows: first, efficiently screen for breech presentation at 36-37 weeks of gestation; second, thoroughly evaluate the maternal/foetal condition, foetal weight and growth potential, and the type (frank, complete, or footling) and mobility of breech ...
Clinical management options reported in the study based on the ultrasound scan or the abdomen palpation include referral for full biophysical assessment which included umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound, early antenatal review, admission to antenatal ward, and induction of labour. ... The expected cost per person with breech presentation of ...
Diagnosis: preterm ≤36+6 weeks. Breech presentation is a normal finding in preterm pregnancy. If diagnosed at the 35-36 week antenatal visit, refer the woman for ultrasound scan to enable assessment prior to ECV. Mode of birth in a breech preterm delivery depends on the clinical circumstances.
presence of a breech presentation because they may disguise fetopelvic disproportion. Oxytocin, however, may be used for the delivery of the aftercoming head. 9. If the presentation is breech and delivery is imminent preterm, consideration may be given to a vaginal delivery in the absence of intrapartum complications. 10.
The most widely quoted study regarding the management of breech presentation at term is the 'Term Breech Trial'. Published in 2000, this large, international multicenter randomised clinical trial compared a policy of planned vaginal delivery with planned caesarean section for selected breech presentations.
Breech presentation at term is not a contraindication to the induction of labor when the criteria for vaginal delivery are met (Grade C), given the absence of evidence that induction of labor of a fetus in breech presentation at term is associated with higher perinatal morbidity than either spontaneous labor or planned cesarean delivery ...
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE No. 384, August 2019 (Replaces No. 226, June 2009) This guideline is the fourth in a 4-part series on labour and delivery. No. 384-Management of Breech Presentation at Term It is SOGC policy to review the content 5 years after publication, at which time the document may be re-affirmed or revised to reflect
Breech presentation occurs when the fetus presents to the birth canal with buttocks or feet first. This presentation creates a mechanical problem in delivery of the fetus. ... Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 3rd ed. 1997. chap75, 1000-1003. Scorza WE. Intrapartum management of breech presentation. Clin Perinatol. 1996 Mar. 23(1):31-49.
CONCLUSION: Clinical practice guidelines, which focus on the risks of a Vaginal Breech Birth without also discussing the risks of a Caesarean Section when a breech presentation is diagnosed, has the potential to sway clinician attitudes and impact birth mode decision-making in maternity consumers. To respect pregnant women's autonomy and fulfil ...
Term breech presentation is not a contraindication to labor induction when the criteria for planned vaginal delivery are met (Grade C). Conclusion: In cases of breech presentation at term, the child and the mother are at low risk of severe morbidity after either planned vaginal or planned cesarean delivery. The French College of Obstetricians ...
The above data suggest that some antenatal features associated with term breech presentation, notably foetal growth restriction, and some gestational disorders (such as uncontrolled gestational diabetes mellitus) could affect the prognosis in term breech cases. ... clinical pelvic examination is universally recommended to rule out pathological ...
What Are the Clinical Features of Breech Presentation? The diagnosis of breech presentation is not significant until 32 weeks to 35 weeks, as the fetus is likely to revert to a cephalic presentation before delivery. In 20 % of cases, breech presentation is not diagnosed until labor. This presentation is usually identified on clinical ...
Summarizing the clinical features of children with intussusception secondary to small bowel tumours and enhancing awareness of the disease. Retrospective summary of children with intussusception admitted to our emergency department from January 2016 to January 2022, who underwent surgery and were diagnosed with small bowel tumours. Summarize the types of tumours, clinical presentation ...
Clinical features of achondrogenesis type 1B (ACG1B) include extremely short limbs with short fingers and toes, hypoplasia of the thorax, protuberant abdomen, and hydropic fetal appearance caused by the abundance of soft tissue relative to the short skeleton. ... Early features may include fetal hypokinesia, breech presentation, and ...