We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphs and Charts

Decision Tree Analysis Examples and How to Use Them
By Letícia Fonseca , May 05, 2022
The purpose of a decision tree analysis is to show how various alternatives can create different possible solutions to solve problems. A decision tree, in contrast to traditional problem-solving methods, gives a “visual” means of recognizing uncertain outcomes that could result from certain choices or decisions.
For those who have never worked with decision trees before, this article will explain how they function and it will also provide some examples to illustrate the ideas.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a decision tree analysis, what is the importance of using a decision tree analysis, when do you use or apply a decision tree analysis, easy 5 step process of a decision node analysis, decision tree analysis examples, decision tree symbols you need to know, how to create a decision node diagram with venngage, faqs on decision tree analysis.
A decision tree is a diagram that depicts the many options for solving an issue. Given particular criteria, decision trees usually provide the best beneficial option, or a combination of alternatives, for many cases. By employing easy-to-understand axes and graphics, a decision tree makes difficult situations more manageable. An event, action, decision, or attribute linked with the problem under investigation is represented by each box or node.
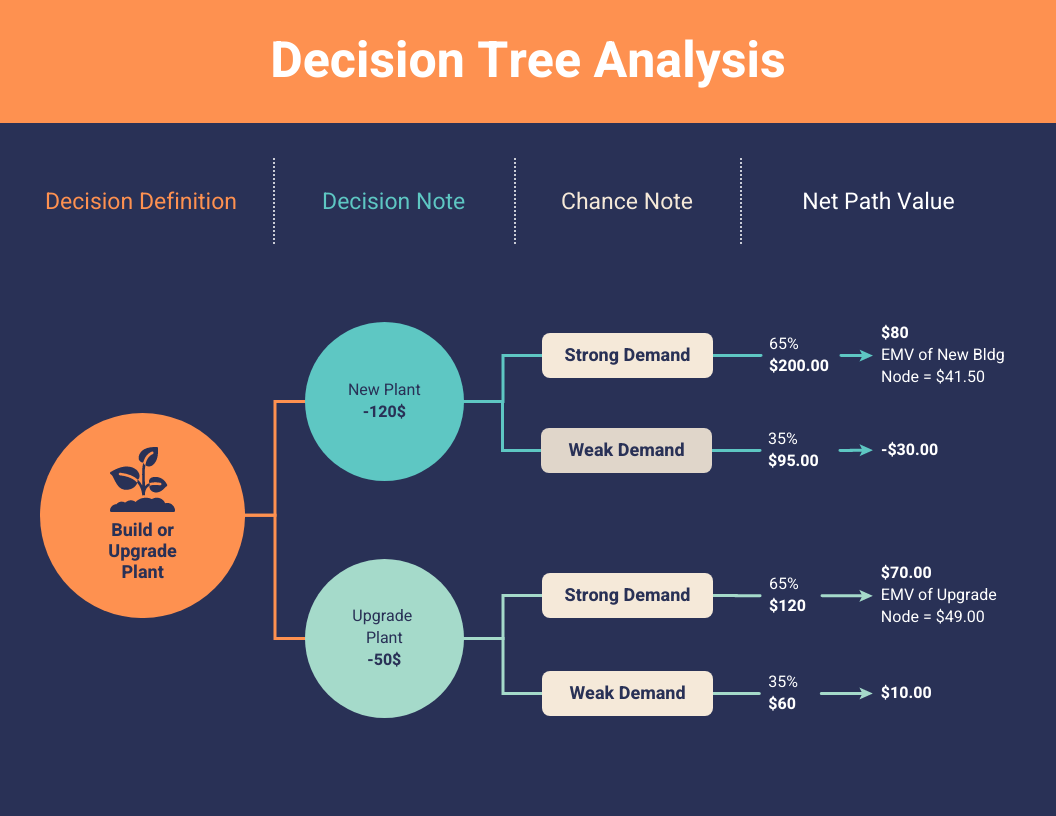
For risk assessment, asset values, manufacturing costs, marketing strategies, investment plans, failure mode effects analyses (FMEA), and scenario-building, a decision tree is used in business planning. Data from a decision tree can also build predictive models.
There are four basic forms of decision tree analysis , each with its own set of benefits and scenarios for which it is most useful. These subtypes include decision under certainty, decision under risk, decision-making, and decision under uncertainty. In terms of how they are addressed and applied to diverse situations, each type has its unique impact.
Return to Table of Contents
Business owners and other decision-makers can use a decision tree to help them consider their alternatives and the potential repercussions of each one. The examination of a decision tree can be used to:
- Determine the level of risk that each option entails. Before making a final decision, you can see how changing one component impacts others, so you can identify where more research or information is needed. Data from decision trees can also be utilized to build predictive models or to analyze an expected value.
- Demonstrate how particular acts or occurrences may unfold in the context of other events. It’s easy to see how different decisions and possible outcomes interact when you’re looking at decision trees.
- Concentrate your efforts. The most effective ways for reaching the desired and final outcome are shown in decision trees. They can be utilized in a multitude of industries, including goal setting, project management, manufacturing, marketing, and more.
Advantages of using a tree diagram as a decision-making tool
Decision tree analysis can be used to make complex decisions easier. They explain how changing one factor impacts the other and how it affects other factors by simplifying concepts. A summary of data can also be included in a decision tree as a reference or as part of a report. They show which methods are most effective in reaching the outcome, but they don’t say what those strategies should be.
Even if new information arises later that contradicts previous assumptions and hypotheses, decision-makers may find it difficult to change their minds once they have made and implemented an initial choice. Decision-makers can use decision-making tools like tree analysis to experiment with different options before reaching a final decision; this can help them gain expertise in making difficult decisions.
When presented with a well-reasoned argument based on facts rather than simply articulating their own opinion, decision-makers may find it easier to persuade others of their preferred solution. A decision tree is very useful when there is any uncertainty regarding which course of action will be most advantageous or when prior data is inadequate or partial.
Before implementing possible solutions, a decision tree analysis can assist business owners and other decision-makers in considering the potential ramifications of different solutions.
Disadvantages of using a tree diagram as a decision-making tool
Rather than displaying real outcomes, decision trees only show patterns connected with decisions. Because decision trees don’t provide information on aspects like implementation, timeliness, and prices, more research may be needed to figure out if a particular plan is viable.
This type of model does not provide insight into why certain events are likely while others are not, but it can be used to develop prediction models that illustrate the chance of an event occurring in certain situations.
A decision tree diagram employs symbols to represent the problem’s events, actions, decisions, or qualities. Given particular criteria, decision trees usually provide the best beneficial option, or a combination of alternatives, for many cases.
By employing easy-to-understand axes and drawings, as well as breaking down the critical components involved with each choice or course of action, decision trees help make difficult situations more manageable. This type of analysis seeks to help you make better decisions about your business operations by identifying potential risks and expected consequences.
In this case, the tree can be seen as a metaphor for problem-solving: it has numerous roots that descend into diverse soil types and reflect one’s varied options or courses of action, while each branch represents the possible and uncertain outcomes. The act of creating a “tree” based on specified criteria or initial possible solutions has to be implemented.
You may start with a query like, “What is the best approach for my company to grow sales?” After that, you’d make a list of feasible actions to take, as well as the probable results of each one. The goal of a decision tree analysis is to help you understand the potential repercussions of your decisions before you make them so that you have the best chance of making a good decision.
Regardless of the level of risk involved, decision tree analysis can be a beneficial tool for both people and groups who want to make educated decisions.
This style of problem-solving helps people make better decisions by allowing them to better comprehend what they’re entering into before they commit too much money or resources. The five-step decision tree analysis procedure is as follows:
- Determine your options
Which can help deal with an issue or answer a question. A problem to be addressed, a goal to be achieved, and additional criteria that will influence the outcome are all required for decision tree analysis to be successful, especially when there are multiple options for resolving a problem or a topic.
- Examine the most effective course of action
Taking into account the potential rewards as well as the risks and expenses that each alternative may entail. If you’re starting a new firm, for example, you’ll need to decide what kind of business model or service to offer, how many employees to hire, where to situate your company, and so on.
- Determine how a specific course will affect your company’s long-term success.
Depending on the data being studied, several criteria are defined for decision tree analysis. For instance, by comparing the cost of a drug or therapy to the effects of other potential therapies, decision tree analysis can be used to determine how effective a drug or treatment will be. When making decisions, a decision tree analysis can also assist in prioritizing the expected values of various factors.
- Use each alternative course of action to examine multiple possible outcomes
This way you can decide which decision you believe is the best and what criteria it meets (the “branches” of your decision tree). Concentrate on determining which solutions are most likely to bring you closer to attaining your goal of resolving your problem while still meeting any of the earlier specified important requirements or additional considerations.
- To evaluate which choice will be most effective
Compare the potential outcomes of each branch. Implement and track the effects of decision tree analysis to ensure that you appropriately assess the benefits and drawbacks of several options so that you can concentrate on the ones that offer the best return on investment while minimizing the risks and drawbacks.
Many businesses employ decision tree analysis to establish an effective business, marketing, and advertising strategies. Based on the probable consequences of each given course of action, decision trees assist marketers to evaluate which of their target audiences may respond most favorably to different sorts of advertisements or campaigns.
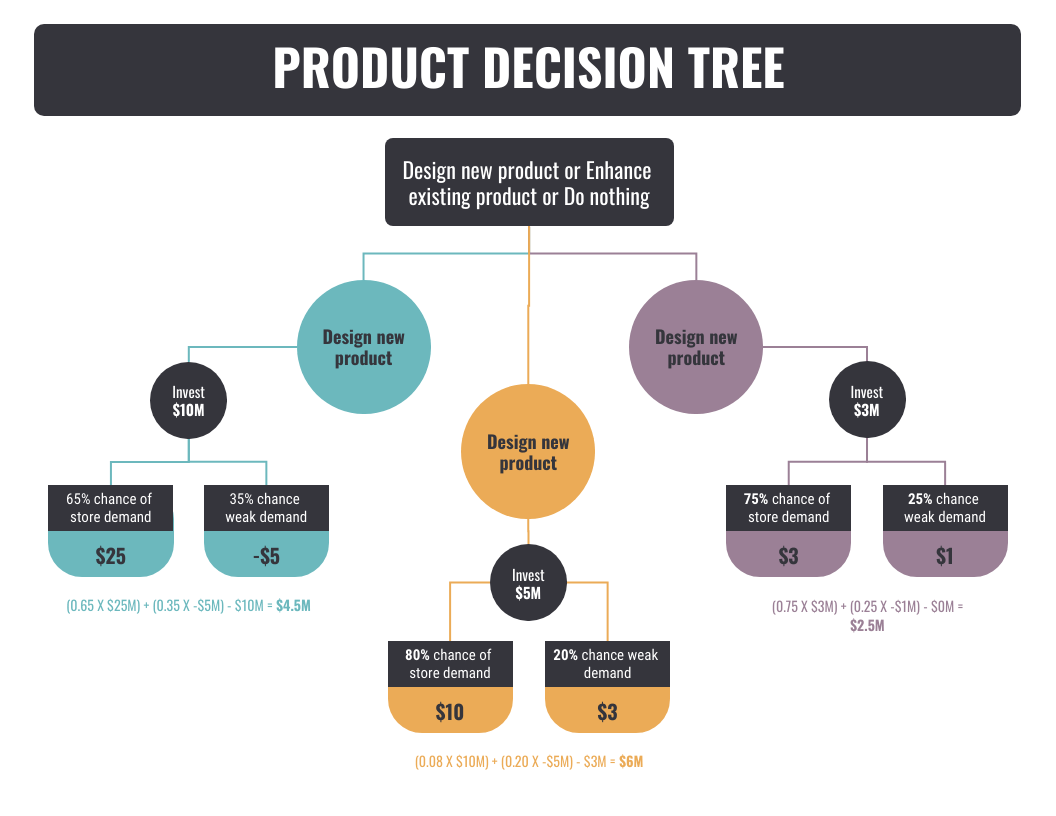
A decision tree example is that a marketer might wonder which style of advertising strategy will yield the best results. The decision tree analysis would assist them in determining the best way to create an ad campaign, whether print or online, considering how each option could affect sales in specific markets, and then deciding which option would deliver the best results while staying within their budget.
Another decision tree diagram example is when a corporation that wishes to grow sales might start by determining their course of action, which includes the many marketing methods that they can use to create leads. Before making a decision, they may use a decision tree analysis to explore each alternative and assess the probable repercussions.
If a company chooses TV ads as their proposed solution, decision tree analysis might help them figure out what aspects of their TV adverts (e.g. tone of voice and visual style) make consumers more inclined to buy, so they can better target new customers or get more out of their advertising dollars.
Related: 15+ Decision Tree Infographics to Visualize Problems and Make Better Decisions
Venngage is an online tool that allows you to quickly design attractive and informative decision trees. You’ll need two key components to make a decision node analysis:
- Decision Nodes
Decision nodes are the building blocks of decision tree analysis, and they represent the various options or courses of action open to people or groups. Typically, decision trees have 4-5 decision nodes. To ensure that you can analyze your data afterward, decision nodes should have the same kind as your data: numerical, categorical, etc.
- Decision Branches
In a decision node, decision branches contain both the results and information connected to each choice or alternative. Decision branches normally appear before and after Decision Nodes, however, they can appear in a variety of numbers and directions.
Venngage has built-in templates that are already arranged according to various data kinds, which can assist in swiftly building decision nodes and decision branches. Here’s how to create one with Venngage:
- Sign up for a free account here .
- From Home or your dashboard, click on Templates.
- There are hundreds of templates to pick from, but Venngage’s built-in Search engine makes it simple to find what you’re looking for.
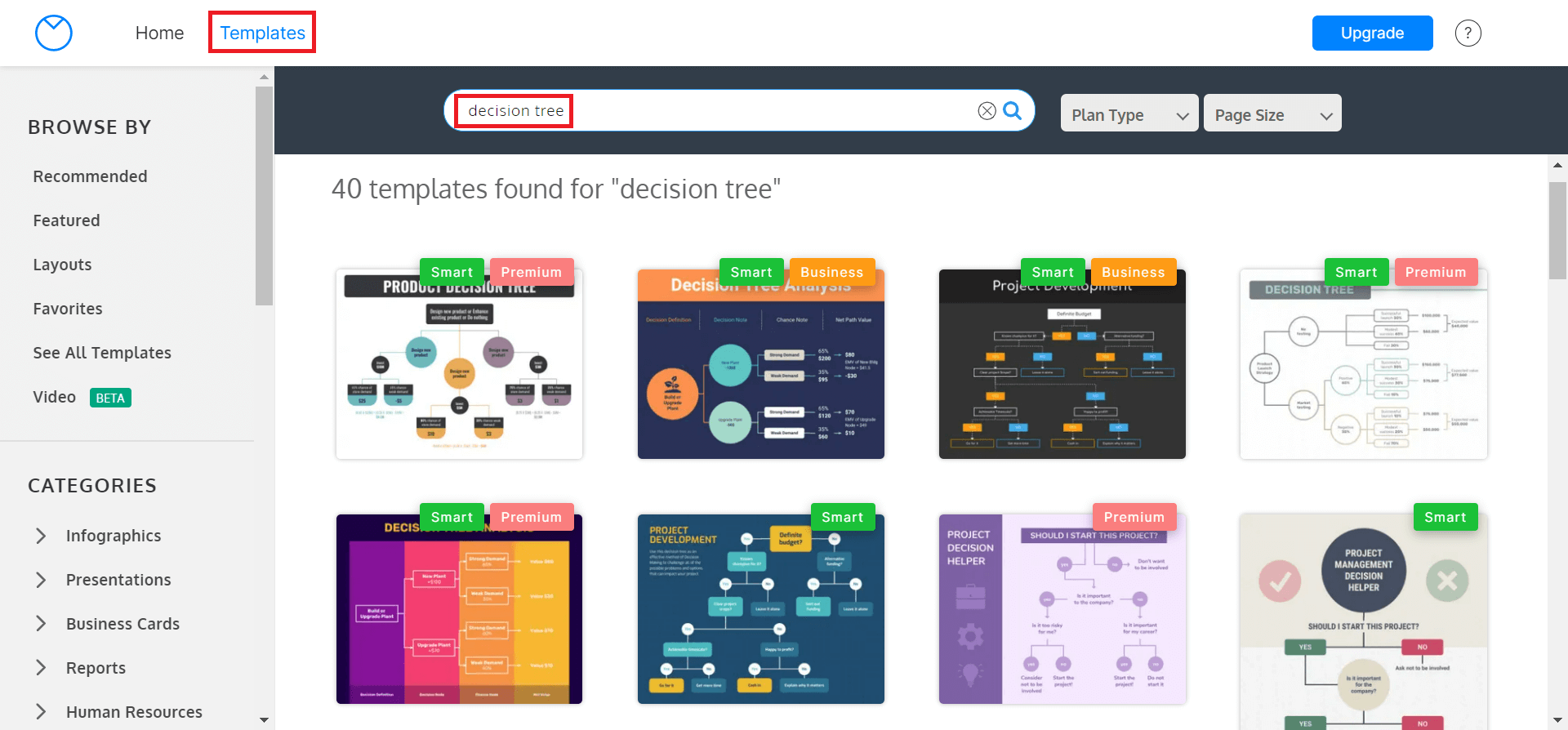
- Once you have chosen the template that’s best for you, click Create to begin editing.
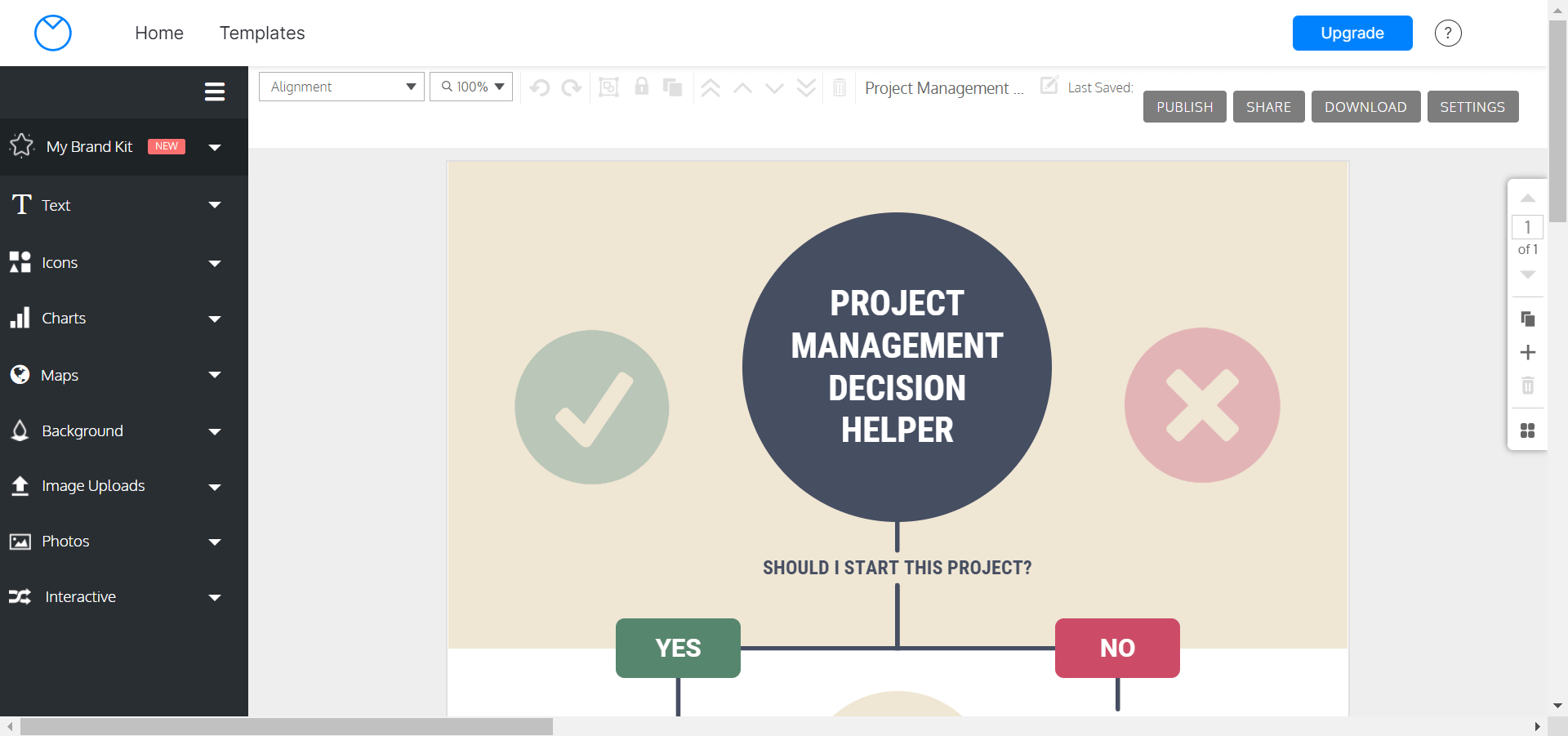
- Venngage allows you to download your project as a PNG, PNG HD, or PDF file with a Premium plan, and an Interactive PDF, PowerPoint, or HTML file with a Business plan.
Venngage also has a business feature called My Brand Kit that enables you to add your company’s logo, color palette, and fonts to all your designs with a single click.
For example, you can make the previous decision tree analysis template reflect your brand design by uploading your brand logo, fonts, and color palette using Venngage’s branding feature.
Not only are Venngage templates free to use and professionally designed, but they are also tailored for various use cases and industries to fit your exact needs and requirements.
A business account also includes the real-time collaboration feature , so you can invite members of your team to work simultaneously on a project.
Venngage allows you to share your decision tree online as well as download it as a PNG or PDF file. That way, your design will always be presentation-ready.
How important is a decision tree in management?
Project managers can utilize decision tree analysis to produce successful solutions, making it a key element of their success process. They can use a decision tree to think about how each decision will affect the company as a whole and make sure that all factors are taken into account before making a decision.
This decision tree can assist you in making smarter investments as well as identifying any dangers or negative outcomes that may arise as a result of certain choices. You will have more information on what works best if you explore all potential outcomes so that you can make better decisions in the future.
What is a decision tree in system analysis?
For studying several systems that work together, a decision tree is useful. You can use decision tree analysis to see how each portion of a system interacts with the others, which can help you solve any flaws or restrictions in the system.
Create a professional decision tree with Venngage
Simply defined, a decision tree analysis is a visual representation of the alternative solutions and expected outcomes you have while making a decision. It can help you quickly see all your potential outcomes and how each option might play out.
Venngage makes the process of creating a decision tree simple and offers a variety of templates to help you. It is the most user-friendly platform for building professional-looking decision trees and other data visualizations. Sign up for a free account and give it a shot right now. You might be amazed at how much easier it is to make judgments when you have all of your options in front of you.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- What is decision tree analysis? 5 steps ...
What is decision tree analysis? 5 steps to make better decisions

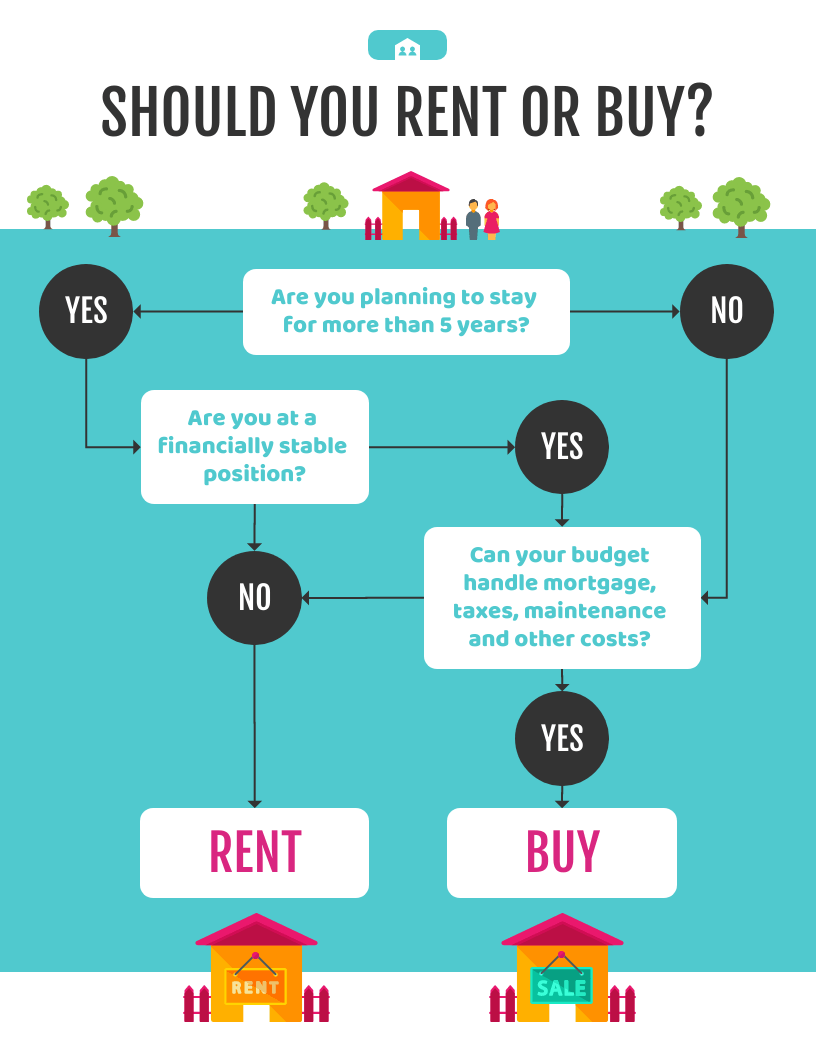
Decision tree analysis involves visually outlining the potential outcomes, costs, and consequences of a complex decision. These trees are particularly helpful for analyzing quantitative data and making a decision based on numbers. In this article, we’ll explain how to use a decision tree to calculate the expected value of each outcome and assess the best course of action. Plus, get an example of what a finished decision tree will look like.
Have you ever made a decision knowing your choice would have major consequences? If you have, you know that it’s especially difficult to determine the best course of action when you aren’t sure what the outcomes will be.
What is a decision tree?
A decision tree is a flowchart that starts with one main idea and then branches out based on the consequences of your decisions. It’s called a “decision tree” because the model typically looks like a tree with branches.
These trees are used for decision tree analysis, which involves visually outlining the potential outcomes, costs, and consequences of a complex decision. You can use a decision tree to calculate the expected value of each outcome based on the decisions and consequences that led to it. Then, by comparing the outcomes to one another, you can quickly assess the best course of action. You can also use a decision tree to solve problems, manage costs, and reveal opportunities.
Decision tree symbols
A decision tree includes the following symbols:
Alternative branches: Alternative branches are two lines that branch out from one decision on your decision tree. These branches show two outcomes or decisions that stem from the initial decision on your tree.
Decision nodes: Decision nodes are squares and represent a decision being made on your tree. Every decision tree starts with a decision node.
Chance nodes: Chance nodes are circles that show multiple possible outcomes.
End nodes: End nodes are triangles that show a final outcome.
A decision tree analysis combines these symbols with notes explaining your decisions and outcomes, and any relevant values to explain your profits or losses. You can manually draw your decision tree or use a flowchart tool to map out your tree digitally.
What is decision tree analysis used for?
You can use decision tree analysis to make decisions in many areas including operations, budget planning, and project management . Where possible, include quantitative data and numbers to create an effective tree. The more data you have, the easier it will be for you to determine expected values and analyze solutions based on numbers.
For example, if you’re trying to determine which project is most cost-effective, you can use a decision tree to analyze the potential outcomes of each project and choose the project that will most likely result in highest earnings.
How to create a decision tree
Follow these five steps to create a decision tree diagram to analyze uncertain outcomes and reach the most logical solution.
![decision tree analysis problem solving [inline illustration] decision tree analysis in five steps (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/06bd6d24-56d2-4550-b13b-f2b3fac01c6a/inline-project-planning-decision-tree-analysis-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Start with your idea
Begin your diagram with one main idea or decision. You’ll start your tree with a decision node before adding single branches to the various decisions you’re deciding between.
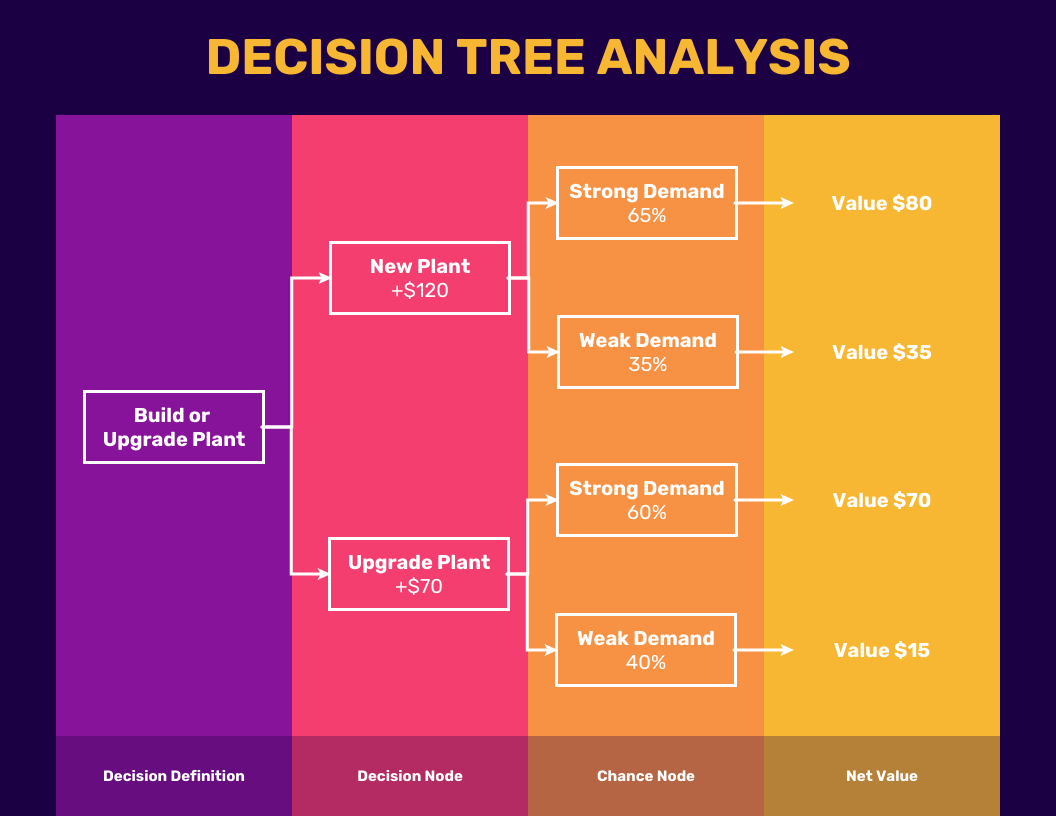
For example, if you want to create an app but can’t decide whether to build a new one or upgrade an existing one, use a decision tree to assess the possible outcomes of each.
In this case, the initial decision node is:
Create an app
The three options—or branches—you’re deciding between are:
Building a new scheduling app
Upgrading an existing scheduling app
Building a team productivity app
2. Add chance and decision nodes
After adding your main idea to the tree, continue adding chance or decision nodes after each decision to expand your tree further. A chance node may need an alternative branch after it because there could be more than one potential outcome for choosing that decision.
For example, if you decide to build a new scheduling app, there’s a chance that your revenue from the app will be large if it’s successful with customers. There’s also a chance the app will be unsuccessful, which could result in a small revenue. Mapping both potential outcomes in your decision tree is key.
3. Expand until you reach end points
Keep adding chance and decision nodes to your decision tree until you can’t expand the tree further. At this point, add end nodes to your tree to signify the completion of the tree creation process.
Once you’ve completed your tree, you can begin analyzing each of the decisions.
4. Calculate tree values
Ideally, your decision tree will have quantitative data associated with it. The most common data used in decision trees is monetary value.
For example, it’ll cost your company a specific amount of money to build or upgrade an app. It’ll also cost more or less money to create one app over another. Writing these values in your tree under each decision can help you in the decision-making process .
You can also try to estimate expected value you’ll create, whether large or small, for each decision. Once you know the cost of each outcome and the probability it will occur, you can calculate the expected value of each outcome using the following formula:
Expected value (EV) = (First possible outcome x Likelihood of outcome) + (Second possible outcome x Likelihood of outcome) - Cost
Calculate the expected value by multiplying both possible outcomes by the likelihood that each outcome will occur and then adding those values. You’ll also need to subtract any initial costs from your total.
5. Evaluate outcomes
Once you have your expected outcomes for each decision, determine which decision is best for you based on the amount of risk you’re willing to take. The highest expected value may not always be the one you want to go for. That’s because, even though it could result in a high reward, it also means taking on the highest level of project risk .
Keep in mind that the expected value in decision tree analysis comes from a probability algorithm. It’s up to you and your team to determine how to best evaluate the outcomes of the tree.
Pros and cons of decision tree analysis
Used properly, decision tree analysis can help you make better decisions, but it also has its drawbacks. As long as you understand the flaws associated with decision trees, you can reap the benefits of this decision-making tool.
![decision tree analysis problem solving [inline illustration] pros and cons of decision tree analysis (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ab6b5d75-1d26-4ec1-a00c-4d657e4dd7be/inline-project-planning-decision-tree-analysis-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
When you’re struggling with a complex decision and juggling a lot of data, decision trees can help you visualize the possible consequences or payoffs associated with each choice.
Transparent: The best part about decision trees is that they provide a focused approach to decision making for you and your team. When you parse out each decision and calculate their expected value, you’ll have a clear idea about which decision makes the most sense for you to move forward with.
Efficient: Decision trees are efficient because they require little time and few resources to create. Other decision-making tools like surveys, user testing , or prototypes can take months and a lot of money to complete. A decision tree is a simple and efficient way to decide what to do.
Flexible: If you come up with a new idea once you’ve created your tree, you can add that decision into the tree with little work. You can also add branches for possible outcomes if you gain information during your analysis.
There are drawbacks to a decision tree that make it a less-than-perfect decision-making tool. By understanding these drawbacks, you can use your tree as part of a larger forecasting process.
Complex: While decision trees often come to definite end points, they can become complex if you add too many decisions to your tree. If your tree branches off in many directions, you may have a hard time keeping the tree under wraps and calculating your expected values. The best way to use a decision tree is to keep it simple so it doesn’t cause confusion or lose its benefits. This may mean using other decision-making tools to narrow down your options, then using a decision tree once you only have a few options left.
Unstable: It’s important to keep the values within your decision tree stable so that your equations stay accurate. If you change even a small part of the data, the larger data can fall apart.
Risky: Because the decision tree uses a probability algorithm, the expected value you calculate is an estimation, not an accurate prediction of each outcome. This means you must take these estimations with a grain of salt. If you don’t sufficiently weigh the probability and payoffs of your outcomes, you could take on a lot of risk with the decision you choose.
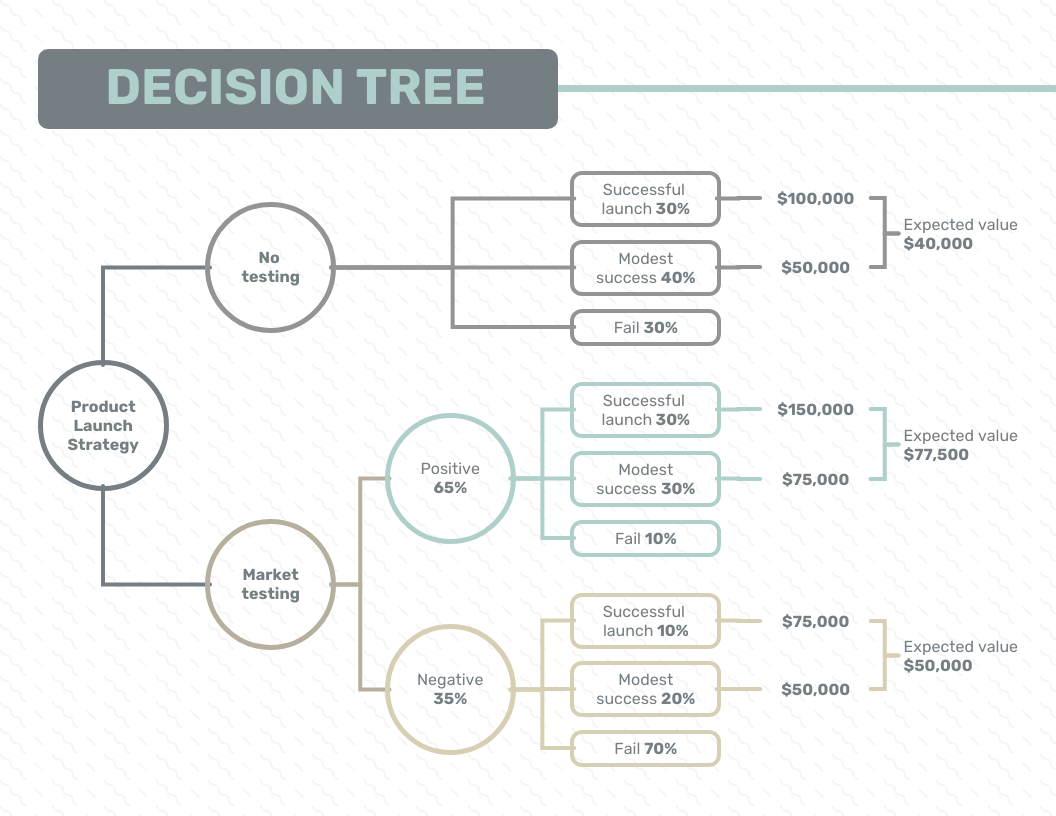
Decision tree analysis example
In the decision tree analysis example below, you can see how you would map out your tree diagram if you were choosing between building or upgrading a new software app.
As the tree branches out, your outcomes involve large and small revenues and your project costs are taken out of your expected values.
Decision nodes from this example :
Build new scheduling app: $50K
Upgrade existing scheduling app: $25K
Build team productivity app: $75K
Chance nodes from this example:
Large and small revenue for decision one: 40 and 55%
Large and small revenue for decision two: 60 and 38%
Large and small revenue for decision three: 55 and 45%
End nodes from this example:
Potential profits for decision one: $200K or $150K
Potential profits for decision two: $100K or $80K
Potential profits for decision three: $250K or $200K
![decision tree analysis problem solving [inline illustration] decision tree analysis (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d3d2161f-6968-4d42-ab08-23a005d1ee0c/inline-project-planning-decision-tree-analysis-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Although building a new team productivity app would cost the most money for the team, the decision tree analysis shows that this project would also result in the most expected value for the company.
Use a decision tree to find the best outcome
You can draw a decision tree by hand, but using decision tree software to map out possible solutions will make it easier to add various elements to your flowchart, make changes when needed, and calculate tree values. With Asana’s Lucidchart integration, you can build a detailed diagram and share it with your team in a centralized project management tool .
Decision tree software will make you feel confident in your decision-making skills so you can successfully lead your team and manage projects.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

Decision Tree Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
Find out how decision tree analysis works, and learn how to draw and analyze a decision tree step-by-step.

In business, effective decision-making is key to success.
Easy decisions, such as “Should we buy a new espresso machine for the cafeteria?” usually require just a quick “yes” or “no” from the boss or manager.
But many decisions need serious discussion — and some are so complex that the variables should be mapped out in detail to arrive at the right conclusion.
Hiring more people or maintaining the status quo? Launching a new product line or giving the existing assortment a facelift? Purchasing HR technology or outsourcing HR to a third party?
It’s these complex, impactful decisions that benefit most from something called a decision tree — a diagramming and analytics tool that captures all the potential ramifications of a decision.
This article explains what decision tree analysis is and walks you through the process so that you can start using this tool right away.
What is decision tree analysis?
A decision tree is a visual guide for decision-making.
Imagine a tree where each branch represents a different choice or path you can take. Considering the potential outcomes and risks for these options — in other words, analyzing the possibilities shown in the decision tree — helps you determine the best decision to make.
The decision tree method stems from the field of decision theory and operations research that began in the mid-20th century. By visually mapping out the possible consequences of different actions, including uncertain outcomes from chance events, you can easily select the most reasonable path forward in a complex problem-solving situation.
Decision tree analysis is often used by project managers and other decision-makers in business planning. Complex versions are used in medical diagnoses and machine learning algorithms. Here, we’ll look at how to apply the decision tree to business-related decisions.
What does a decision tree look like?
The classic decision tree looks like a tree on its side, with the roots (the decision to be made) on the left and the branches (the options and trajectories to make the decision) stretched out to the right.
Decision tree symbols
A decision tree uses specific symbols that show the types of actions at each point in the decision-making process. Let’s review these before diving into how to use this tool.
Decision node: Usually represented by a square or rectangle, this symbol indicates a point where a decision must be made.
Chance node: Often depicted by a circle or oval, this symbol represents a point where various outcomes may occur, usually with associated probabilities.
Terminal (or end) node: Typically shown as a triangle or oval, this symbol marks the end of a particular path within the tree and often indicates the final outcome or payoff of a decision path.
Branches: These are the lines that connect the nodes. They represent the different choices or paths that can be taken from a decision node or the possible outcomes from a chance node.
Arrows: Sometimes used to indicate the direction of the flow within the tree, these symbols show the progression from the decision nodes through the chance nodes to the terminal nodes.
Annotations: While not symbols, annotations such as text, numbers, or labels are used to provide additional information on the nodes and branches. These can include details like the specific courses of action, probability, cost, or payoff associated with a particular element of the tree.
What is the difference between a decision tree and a flowchart?
A decision tree has some similarities with a flow chart. Though they may look similar, they have different purposes:
Decision tree
A decision tree is used to help make decisions. It shows different choices, outcomes, and risks , and it usually involves probabilities and calculations to determine the best path to take. It helps you analyze and weigh different options to arrive at a decision.
A flowchart is a diagram that shows a process or workflow. It outlines the step-by-step sequence of actions needed to complete a task, including the decisions that must be made along the way. However, it doesn’t usually involve weighing risks or calculating probabilities.
So, simply put, a decision tree is a guide for making a choice among various options, while a flowchart is a map for following a process or completing a task.
How to perform a decision tree analysis
Let’s walk through the decision tree analysis process step-by-step so that you can get a good feel for how this tool works.
We’ll use the example of the owner of a specialty clothing store who needs to decide whether to hire extra store help for the coming business year.
The hiring options and costs the business owner is pondering are as follows:
- Hiring a full-time person ($50K)
- Hiring a part-time person ($25K)
- Hiring temp help during anticipated peak times ($10K)
- Not hiring anyone ($0K)
Each of these choices will impact the bottom line differently. The question is, which one will offer the best revenue potential — and at the lowest risk?
Step 1: Map out the main options
Begin your decision tree analysis by clearly defining the decision to be made and the options you are considering.
To visually map this out, take a piece of paper and draw the decision node on the left-hand side in the form of a small square or rectangle.
From the decision node, draw the decision branches for the options, and write a brief description of each option along them.
Here’s what this would look like for the clothing store owner:
Step 2: Add the chance nodes
Now, do an inventory of the uncertainties you may face as you try to make this decision.
For instance, a major uncertainty in business is how steady or volatile the market for your product will be.
Examples of other uncertainties include the following:
- The potential effects of your competition launching a new or better product
- New trends or fads that redirect consumer spending
- A breakthrough in scientific research that’s beneficial for your product or service
- The possibility of a natural disaster, such as a hurricane or wildfire, occurring near your physical location
- Supply line disruptions due, for instance, to national or international conflicts
- Difficulty attracting the skilled workers you need
- A pandemic, with the potential of lockdowns and store closings
Once you are clear on what the main “chance” triggers or filters for the decision could be, capture these in some brief statements.
For instance, let’s say our specialty clothing store is located in a tourist town, and a significant portion of its annual revenue depends on seasonal sales.
The tourist revenue tends to fluctuate due to external factors, such as weather, inflation, and foreign tourists’ ability to enter the country. Based on these factors, there are historically three main possibilities for this store. It could have:
- A great year
- An average year
- A poor year
We’ll insert these possibilities as the chance nodes in our decision tree diagram.
Step 3: Calculate the monetary value of each choice
Next, determine the monetary value or outcome of each choice. This is the end node or end point of each branch, marked with a triangle.
In the clothing store example, let’s say that, in an average year, the store brings in $250K in revenue. In a great year, this amount increases to $300K, and in a poor year, it drops to $200K.
This is the baseline value — the status quo if the owner doesn’t hire any new employees that year.
The owner is familiar with employee return-on-investment (ROI) figures for the store:
- Full-time employees generate 250% of their salary cost.
- Part-time employees generate 200% of their salary cost.
- Temp employees generate 180% of their salary cost.
This produces the following results:
- Hiring a full-time person at $50K potentially brings in $125K in extra revenue.
- Hiring a part-time person at $25K brings in $50K in extra revenue.
- Hiring temp help at $10K brings in $18K in extra revenue.
We now have enough information to calculate the end node values, shown in the next image. The extra revenue amounts per new employee type are added to the baseline figures shown in the “no new hire” section.
Step 4: Analyze the results shown in your decision tree
Now, we’ve come to the analysis component of the decision tree method.
First, we’ll calculate the actual costs of the choices we can make. Let’s do this by subtracting the additional salary cost from the potential revenue as follows:
We now have a clear picture of the net monetary results of each choice. This allows for detailed analysis and lets us weigh the risks and benefits of one choice against the others.
The owner could draw several helpful conclusions from this step, ranging from obvious to not-so-obvious:
- Regardless of whether the store will experience a poor, average, or great year, hiring a new full-time employee can potentially generate a $75K increase in revenue.
- This potential increased revenue drops to $25K if a part-time worker is hired.
- Hiring one temp helper at peak times does little to increase the net revenue. So, it might be better to consider two temp hires for longer periods. (The owner could redo this part of the decision tree to work out the results of different temp hiring configurations.)
- Maintaining the status quo (with no new hirings) in a great year will probably still bring in $25K less revenue than the revenue generated in an average year after hiring a new full-time employee.
- In that same vein, even in a poor year, having that extra employee could potentially still generate an extra $75K in revenue.
Once the picture of options and possible outcomes becomes clear, the store owner can make an informed hiring decision against the backdrop of a sense of the economic climate for the coming year (the likelihood of the year becoming great, average, or poor) and the level of risk acceptable to the business.
A decision tree diagram can be made much more detailed by, for instance, adding probability calculations to each branch and more depth to the financial or other numerical values the company is using when making major business choices.
But if you apply the steps laid out in this section, you’ll be well on your way to effective decision analysis.
How an online calendar can help with decision tree analysis
One helpful tool for collecting the right raw data for your decision tree branches and options is the online calendar you’re using for your company.
Intelligent tracking software, such as Motion’s AI-driven calendar , is not just a scheduling tool — it can also be a strategic asset in decision-making. For instance, the calendar data can inform and enrich the decision tree analysis process by extracting historical data related to resource allocation and the levels of collaboration in your company.
This can result in decisions that are more aligned with your company’s actual timelines and resource availability — improving the accuracy and reliability of your decision tree analysis and the strategic planning for which you use it.
Making your own decision tree
The quickest way to draw a decision tree is to simply use a piece of paper. This will provide you with a document in hand that you can keep on file and easily modify as needed.
Tip: Draw your diagram with a pencil since you’ll likely be making quite a few changes to it.
A whiteboard is also a good option since colored markers can help distinguish the different steps and options in the tree. The one drawback here would be the decision tree’s impermanence in this scenario — even if you took pictures, you’d have to start over after erasing the board.
Some people use a spreadsheet program, such as Excel, in their decision tree-making process. This is a bit more laborious than drawing by hand, but the symbols and illustrations in the “insert” function are more than enough to draw a decision tree — and you’ll have a permanent record that you can easily update.
In addition to drawing tools on tablets and computers, you have the option of going online and using drawing software. Some of these programs have decision tree templates built in, whereas others let you create your own tree from scratch.
Here are some companies that offer free drawing tools:
Whatever method you choose, make sure to keep a copy of your decision tree — and a record of the reasoning you poured into the analysis — in your files. These documents will come in handy for future decision-making.
Give decision tree analysis a try for your complex decisions
Decision tree analysis is a powerful asset in making complex business decisions. It’s especially helpful if you prefer having a visual representation of a problem to figure out your options.
Remember to tap into the online calendar tool you’re using for your business, as this can help you extract valuable company data that will inform options in your decision tree.
Motion’s AI-driven Intelligent Calendar is one of the best resources for data analysis. Try Motion for free for 7 days to see how it can help you professionalize your decision tree analyses.

Related articles
13 Time Management Techniques to Boost Your Productivity

The Poetry of Purpose: Inspirational Purpose Statement Examples

The Secrets to Effective Sprint Planning
Put motion to the test., tech and media companies are talking about motion.


How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 6 min read
Decision Tree Analysis
Choosing by projecting "expected outcomes".
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Decision trees are excellent tools for helping you to choose between several courses of action.
They provide a highly effective structure within which you can lay out options and investigate the possible outcomes of choosing those options. They also help you to form a balanced picture of the risks and rewards associated with each possible course of action.
Drawing a Decision Tree
You start a decision tree with a decision that you need to make. Draw a small square to represent this towards the left of a large piece of paper.
From this box draw out lines towards the right for each possible solution, and write that solution along the line. Keep the lines apart as far as possible so that you can expand your thoughts.
At the end of each line, consider the results. If the result of taking that decision is uncertain, draw a small circle. If the result is another decision that you need to make, draw another square. Squares represent decisions, and circles represent uncertain outcomes. Write the decision or factor above the square or circle. If you have completed the solution at the end of the line, just leave it blank.
Starting from the new decision squares on your diagram, draw out lines representing the options that you could select. From the circles draw lines representing possible outcomes. Again make a brief note on the line saying what it means. Keep on doing this until you have drawn out as many of the possible outcomes and decisions as you can see leading on from the original decisions.
An example of the sort of thing you will end up with is shown in figure 1:
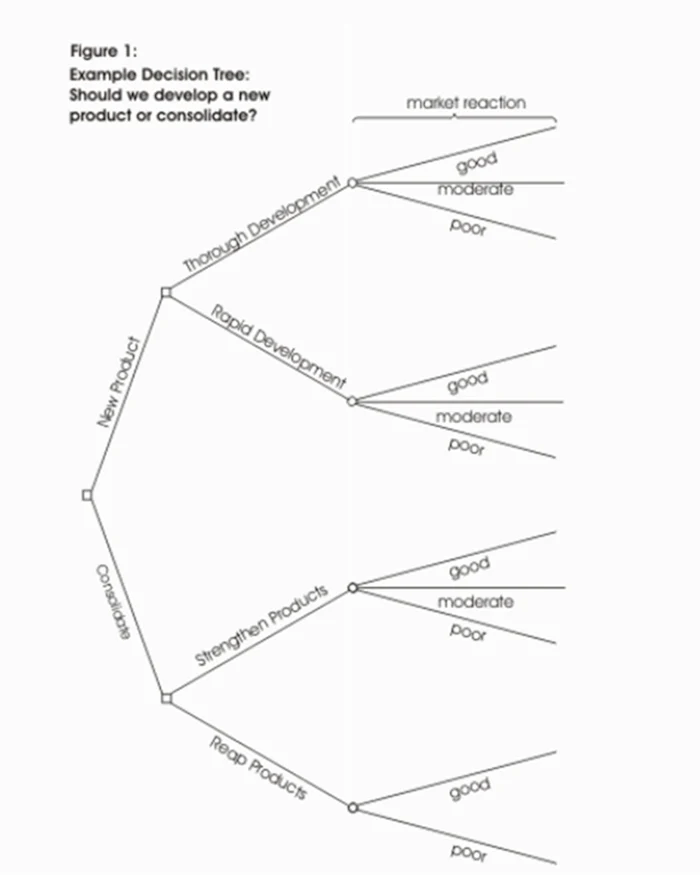
Once you have done this, review your tree diagram. Challenge each square and circle to see if there are any solutions or outcomes you have not considered. If there are, draw them in. If necessary, redraft your tree if parts of it are too congested or untidy. You should now have a good understanding of the range of possible outcomes of your decisions.
Evaluating Your Decision Tree
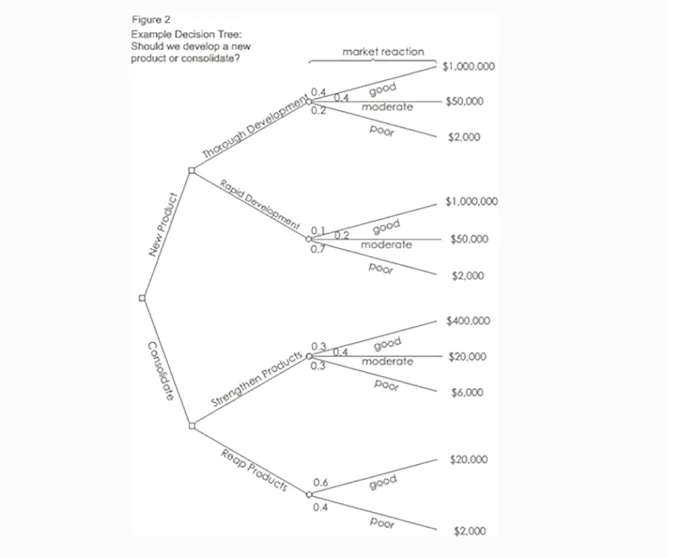
Now you are ready to evaluate the decision tree. This is where you can work out which option has the greatest worth to you. Start by assigning a cash value or score to each possible outcome. Estimate how much you think it would be worth to you if that outcome came about.
Next look at each circle (representing an uncertainty point) and estimate the probability of each outcome. If you use percentages, the total must come to 100 percent at each circle. If you use fractions, these must add up to 1. If you have data on past events you may be able to make rigorous estimates of the probabilities. Otherwise write down your best guess.
This will give you a tree like the one shown in figure 2:
Calculating Tree Values
Once you have worked out the value of the outcomes, and have assessed the probability of the outcomes of uncertainty, it is time to start calculating the values that will help you make your decision.
Start on the right-hand side of the decision tree, and work back towards the left. As you complete a set of calculations on a node (decision square or uncertainty circle), all you need to do is to record the result. You can ignore all the calculations that lead to that result from then on.
Calculating The Value of Uncertain Outcome Nodes
Where you're calculating the value of uncertain outcomes (circles on the diagram), do this by multiplying the value of the outcomes by their probability. The total for that node of the tree is the total of these values.
In the example in figure 2, the value for "new product, thorough development" is:
Figure 3 shows the calculation of uncertain outcome nodes:
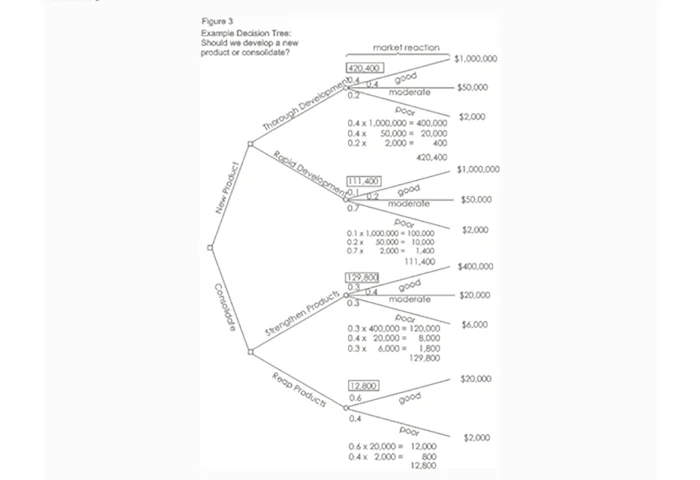
Note that the values calculated for each node are shown in the boxes.
Calculating the Value of Decision Nodes
When you are evaluating a decision node, write down the cost of each option along each decision line. Then subtract the cost from the outcome value that you have already calculated. This will give you a value that represents the benefit of that decision.
Note that amounts already spent do not count for this analysis – these are "sunk costs" and (despite emotional counter-arguments) should not be factored into the decision.
When you have calculated these decision benefits, choose the option that has the largest benefit, and take that as the decision made. This is the value of that decision node.
Figure 4 shows this calculation of decision nodes in our example:
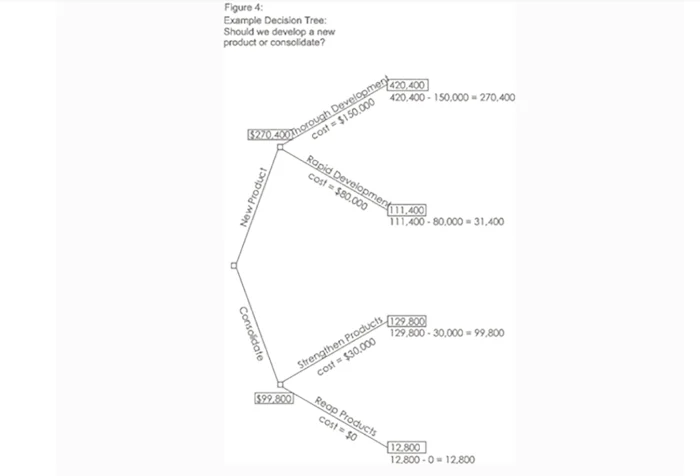
In this example, the benefit we previously calculated for "new product, thorough development" was $420,400. We estimate the future cost of this approach as $150,000. This gives a net benefit of $270,400.
The net benefit of "new product, rapid development" was $31,400. On this branch, we, therefore, choose the most valuable option, "new product, thorough development," and allocate this value to the decision node.
By applying this technique we can see that the best option is to develop a new product. It's worth much more to us to take our time and get the product right than to rush the product to market. It is better just to improve our existing products than to botch a new product, even though it costs us less.
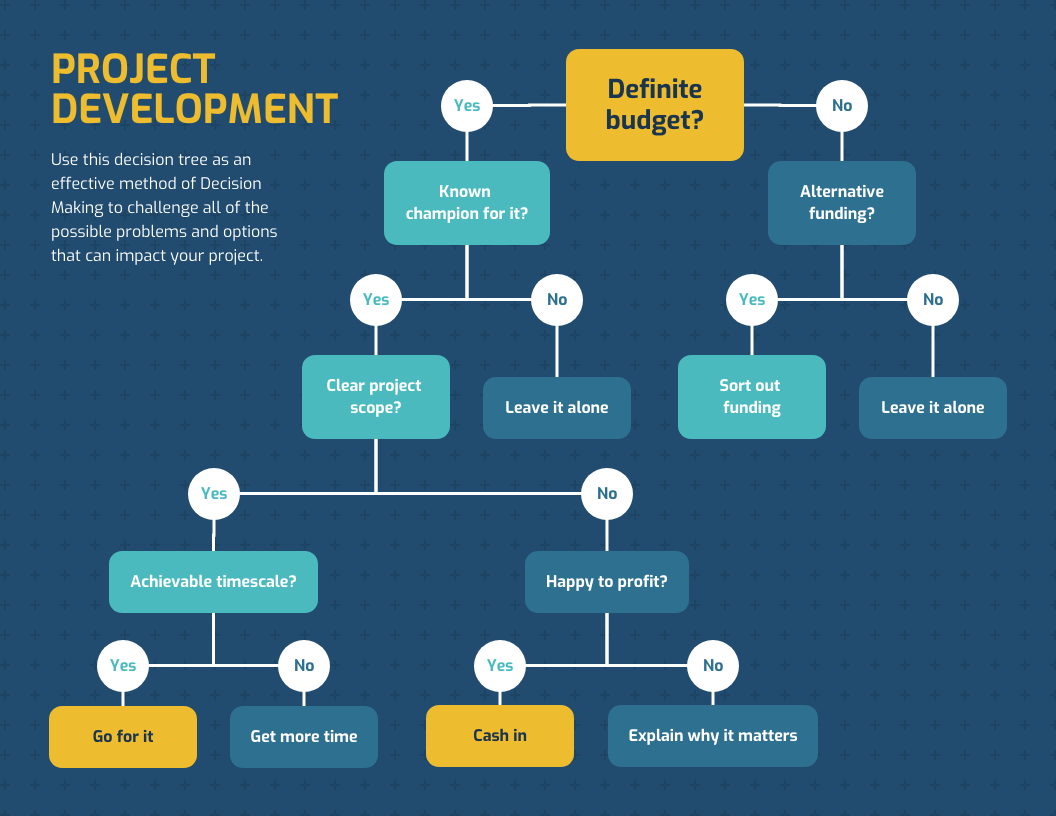
Decision trees provide an effective method of decision making because they:
- Clearly lay out the problem so that all options can be challenged.
- Allow us to analyze fully the possible consequences of a decision.
- Provide a framework to quantify the values of outcomes and the probabilities of achieving them.
- Help us to make the best decisions on the basis of existing information and best guesses.
As with all decision-making methods, decision tree analysis should be used in conjunction with common sense – decision trees are just one important part of your decision-making toolkit.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Decision matrix analysis.
Making a Decision by Weighing Up Different Factors
Quantitative Pros and Cons
Weigh up Decisions With a Simple Approach
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Pain Points Podcast - Balancing Work And Kids

Pain Points Podcast - Improving Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - what is ai.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Pain Points Podcast - How Do I Get Organized?
It's Time to Get Yourself Sorted!
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Costs for management control.
An Important Method for Short Term Cost Control is Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Memberships
Decision Tree Analysis
Decision Tree Analysis: this article describes the Decision Tree Analysis in a practical way. Next to what it is, this article also higlights the process, the “What if” thought, Visualization and Representation, a practical Decision Tree Analysis example. This article also contains a downloadable and editable template. After reading you will understand the basics of this powerful decision making and process analysis approach. Enjoy reading!
What is a Decision Tree Analysis?
The decision tree diagram is a decision making tool for decision makers. It is a graphic representation of various alternative solutions that are available to solve a problem. The manner of illustrating often proves to be decisive when making a choice.
A Decision Tree Analysis is created by answering a number of questions that are continued after each affirmative or negative answer until a final choice for a complex decision can be made.

Decision making process
The Decision Tree Analysis tool is a scientific model and is often used in the decision making process of organizations. When making a decision, the management already envisages alternative ideas and solutions.
By using a decision tree, the alternative solutions and possible choices are illustrated graphically as a result of which it becomes easier to make a well-informed choice.
This graphic representation is characterized by a tree-like structure in which the problems in decision making can be seen in the form of a flowchart, each with branches for alternative choices.
The Decision Tree Analysis makes good use of the ‘what if’ thought. There are several alternatives that consider both the possible risks and benefits that are brought about by certain choices.
The possible alternatives are also made clearly visible and therefore the decision tree provides clarity with respect to the consequences of any decisions that will be made.
Visualization and Representation
There are several ways in which a decision tree can be represented. This Analysis is commonly represented by lines, squares and circles. The squares represent decisions, the lines represent consequences and the circles represent uncertain outcomes. By keeping the lines as far apart as possible, there will be plenty of space to add new considerations and ideas and to create a new course of action.
The representation of the decision tree can be created in four steps:
- Describe the decision that needs to be made in the square.
- Draw various lines from the square and write possible solutions on each of the lines.
- Put the outcome of the solution at the end of the line. Uncertain or unclear decisions are put in a circle. When a solution leads to a new decision, the latter can be put in a new square.
- Each of the squares and circles are reviewed critically so that a final choice can be made.
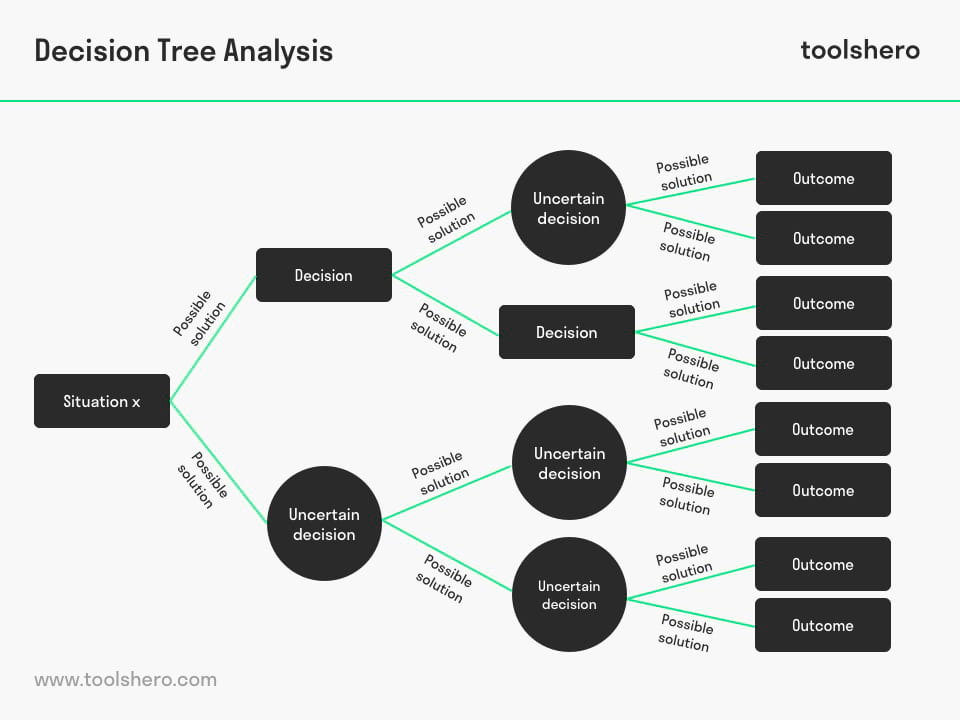
Figure 1 – the Decision Tree Analaysis model
A practical Decision Tree Analysis example
Suppose a commercial company wishes to increase its sales and the associated profits in the next year.
The different alternatives can then be mapped out by using a decision tree. There are two choice for both increase of sales and profits: 1- expansion of advertising expenditure and 2- expansion of sales activities. This creates two branches. Two new choices arise from choice 1, namely 1-1 a new advertising agency and 1-2 using the services of the existing advertising agency. Choice 2 presents two follow-up choices in turn; 2-1-working with agents or 2-2- using its own sales force.
The branching continues.
The following alternatives from 1-1 are: 1-1-1 The budget will increase by 10% -> end result: sales up 6%, profits up 2% 1-1-2 The budget will increase by 5% -> end result: sales up 4%, profits up 1.5 %
The alternatives that arise from 1.2: 1-2-1 The budget increases by 10% -> end result: sales up 5%, profits up 2.5% 1-2-2 The budget increases by 5 % -> end result: a sales up 4%, profits up 12%
From 2.1 possibly follows: 2-1-1 Set up with own dealers -> end result: sales up 20%, profits up 5% 2-1-2 Working with existing dealers -> end result: sales up 12.5%, profit up 8%
From 2.2 possibly follows: 2-2-1 Hiring of new sales staff -> end result: sales up 15%, profits up 5% 2-2-2 Motivating of existing sales staff -> end result: sales up 4%, profits up 2%.

Figure 2: an example of a Decision tree
This Analysis is particularly useful in situations in which it is considered desirable to develop various alternatives and potential outcomes of decisions in a structured manner as this will present a clear substantiation.
This method is increasingly used by medical practitioners and technicians as it enables them to make a diagnosis or determine car problems.
Decision Tree Analysis template
Start describing the different aspects of the Decision Tree Analysis with this ready to use Decision Tree Analysis template.
Download the Decision Tree Analysis template

It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is the Decision Tree Analysis applicable in today’s modern business process environment? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more additions? What are your success factors regarding the Decision Tree Analysis? Do you use this tool to calcuate the unexpected? What are advantages and disadvantages of this tool compared to other tools for decision making? Do you find it difficult to draw a decision tree?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Duncan, R. (1980). What is the right organization structure? Decision tree analysis provides the answer . Organizational Dynamics, 7(3), 59-80.
- Kim, J. K., Song, H. S., Kim, T. S., & Kim, H. K. (2005). Detecting the change of customer behavior based on decision tree analysis . Expert Systems, 22(4), 193-205.
- Prager, M. (2011). Decisions Decisions Decisions: How To Prune Your Decision Tree And Get What You Really Want . Ebook.
- Skinner, D. C. (2009). Introduction to Decision Analysis . Probabilistic Publishing.
How to cite this article: Mulder, P. (2017). Decision Tree Analysis . Retrieved [insert date] from toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/decision-making/decision-tree-analysis/
Original publication date: 02/27/2017 | Last update: 12/10/2023
Add a link to this page on your website: <a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/decision-making/decision-tree-analysis/”>Toolshero: Decision Tree Analysis</a>
Did you find this article interesting?
Your rating is more than welcome or share this article via Social media!
Average rating 4.3 / 5. Vote count: 7
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Patty Mulder
Patty Mulder is an Dutch expert on Management Skills, Personal Effectiveness and Business Communication. She is also a Content writer, Business Coach and Company Trainer and lives in the Netherlands (Europe). Note: all her articles are written in Dutch and we translated her articles to English!
Related ARTICLES

Ladder of Inference Model by Chris Argyris and Peter Senge

OODA Loop by John Boyd explained

Force Field Analysis by Kurt Lewin explained

Decision Matrix Analysis


Ladder of Participation (Arnstein)

Request for Information (RFI)
Also interesting.

Borda Count Method: Basics and an Example

Project budget explained: theory and a template

SOAR Analysis: the theory plus example and template
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
BOOST YOUR SKILLS
Toolshero supports people worldwide ( 10+ million visitors from 100+ countries ) to empower themselves through an easily accessible and high-quality learning platform for personal and professional development.
By making access to scientific knowledge simple and affordable, self-development becomes attainable for everyone, including you! Join our learning platform and boost your skills with Toolshero.

POPULAR TOPICS
- Change Management
- Marketing Theories
- Problem Solving Theories
- Psychology Theories
ABOUT TOOLSHERO
- Free Toolshero e-book
- Memberships & Pricing
- Join Mind Tools

Decision Trees
Choosing by projecting "expected outcomes".

© iStockphoto Nikada
Decision trees help you to evaluate your options.
Decision Trees are excellent tools for helping you to choose between several courses of action.
They provide a highly effective structure within which you can lay out options and investigate the possible outcomes of choosing those options. They also help you to form a balanced picture of the risks and rewards associated with each possible course of action.
Drawing a Decision Tree
You start a Decision Tree with a decision that you need to make. Draw a small square to represent this towards the left of a large piece of paper.
From this box draw out lines towards the right for each possible solution, and write that solution along the line. Keep the lines apart as far as possible so that you can expand your thoughts.
At the end of each line, consider the results. If the result of taking that decision is uncertain, draw a small circle. If the result is another decision that you need to make, draw another square. Squares represent decisions, and circles represent uncertain outcomes. Write the decision or factor above the square or circle. If you have completed the solution at the end of the line, just leave it blank.
Starting from the new decision squares on your diagram, draw out lines representing the options that you could select. From the circles draw lines representing possible outcomes. Again make a brief note on the line saying what it means. Keep on doing this until you have drawn out as many of the possible outcomes and decisions as you can see leading on from the original decisions.
An example of the sort of thing you will end up with is shown in figure 1:
Once you have done this, review your tree diagram. Challenge each square and circle to see if there are any solutions or outcomes you have not considered. If there are, draw them in. If necessary, redraft your tree if parts of it are too congested or untidy. You should now have a good understanding of the range of possible outcomes of your decisions.
Evaluating Your Decision Tree
Now you are ready to evaluate the decision tree. This is where you can work out which option has the greatest worth to you. Start by assigning a cash value or score to each possible outcome. Estimate how much you think it would be worth to you if that outcome came about.
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 55 decision-making skills, like this, by joining the Mind Tools Club.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Receive new career skills every week, plus get our latest offers and a free downloadable Personal Development Plan workbook.
Next look at each circle (representing an uncertainty point) and estimate the probability of each outcome. If you use percentages, the total must come to 100 percent at each circle. If you use fractions, these must add up to 1. If you have data on past events you may be able to make rigorous estimates of the probabilities. Otherwise write down your best guess.
This will give you a tree like the one shown in figure 2:
Calculating Tree Values
Once you have worked out the value of the outcomes, and have assessed the probability of the outcomes of uncertainty, it is time to start calculating the values that will help you make your decision.
Start on the right hand side of the decision tree, and work back towards the left. As you complete a set of calculations on a node (decision square or uncertainty circle), all you need to do is to record the result. You can ignore all the calculations that lead to that result from then on.
Calculating The Value of Uncertain Outcome Nodes
Where you are calculating the value of uncertain outcomes (circles on the diagram), do this by multiplying the value of the outcomes by their probability. The total for that node of the tree is the total of these values.
In the example in figure 2, the value for "new product, thorough development" is:
Figure 3 shows the calculation of uncertain outcome nodes:
Note that the values calculated for each node are shown in the boxes.
Calculating the Value of Decision Nodes
When you are evaluating a decision node, write down the cost of each option along each decision line. Then subtract the cost from the outcome value that you have already calculated. This will give you a value that represents the benefit of that decision.
Note that amounts already spent do not count for this analysis – these are "sunk costs" and (despite emotional counter-arguments) should not be factored into the decision.
When you have calculated these decision benefits, choose the option that has the largest benefit, and take that as the decision made. This is the value of that decision node.
Figure 4 shows this calculation of decision nodes in our example:
In this example, the benefit we previously calculated for "new product, thorough development" was $420,400. We estimate the future cost of this approach as $150,000. This gives a net benefit of $270,400.
The net benefit of "new product, rapid development" was $31,400. On this branch, we, therefore, choose the most valuable option, "new product, thorough development", and allocate this value to the decision node.
By applying this technique we can see that the best option is to develop a new product. It is worth much more to us to take our time and get the product right, than to rush the product to market. It is better just to improve our existing products than to botch a new product, even though it costs us less.
Decision trees provide an effective method of Decision Making because they:
- Clearly lay out the problem so that all options can be challenged.
- Allow us to analyze fully the possible consequences of a decision.
- Provide a framework to quantify the values of outcomes and the probabilities of achieving them.
- Help us to make the best decisions on the basis of existing information and best guesses.
As with all Decision Making methods, decision tree analysis should be used in conjunction with common sense – decision trees are just one important part of your Decision Making toolkit.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter , or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!
Rate this resource
The Mind Tools Club gives you exclusive tips and tools to boost your career - plus a friendly community and support from our career coaches!

Comments (31)
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi Melissa, As the resource suggests, the value of probability outcomes is an estimate of the likelihood of that outcome occurring. If in your experience sales can increase on average by 10% over 2 years, then the outcome probability of that outcome is the percentage divided by the number of years - 5%. Thanks for your question. BillT Mind Tools Team
- Over a month ago Melissa wrote Great content! As I am very new to the finance topic, I am wondering how is the probability of outcomes calculated/estimated? Melissa
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi Sozinho1, Great to hear that. Thank you. BillT Mind Tools Team
Please wait...

Decision Tree Analysis
Decision tree analysis definition.
Decision tree analysis is the process of drawing a decision tree, which is a graphic representation of various alternative solutions that are available to solve a given problem, in order to determine the most effective courses of action. Decision trees are comprised of nodes and branches - nodes represent a test on an attribute and branches represent potential alternative outcomes.
What is Decision Tree Analysis?
A decision tree is a tree-like model that acts as a decision support tool, visually displaying decisions and their potential outcomes, consequences, and costs. From there, the “branches” can easily be evaluated and compared in order to select the best courses of action.
Decision tree analysis is helpful for solving problems, revealing potential opportunities, and making complex decisions regarding cost management, operations management, organization strategies, project selection, and production methods.
Drawing a decision tree diagram starts from left to right and consists of “burst” nodes that split into different paths. Nodes are categorized as Root nodes, which compiles the whole sample and is then split into multiple sets; Decision nodes, typically represented by squares, are sub-nodes that diverge into further possibilities; and the Terminal node, typically represented by triangles, is the final node that shows the final outcome that cannot be further categorized.
Branches, or lines, represent the various available alternatives, and sub-nodes can be eliminated via Pruning. Decision trees can be hand-drawn or created with the use of decision tree software. Analysis can be performed manually, via decision tree analysis in R, or via automated software.
Five Steps of Decision Tree Analysis
The steps in decision tree analysis consist of:
- Define the problem area for which decision making is necessary.
- Draw a decision tree with all possible solutions and their consequences.
- Input relevant variables with their respective probability values.
- Determine and allocate payoffs for each possible outcome.
- Calculate the Expected Monetary Value for every chance node in order to determine which solution is expected to provide the most value. Circles represent chance nodes in a tree diagram.
Popular applications include: decision tree analysis in risk management, decision tree analysis in healthcare, decision tree analysis in capital budgeting, decision tree business analysis, and decision tree analysis in finance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Decision Tree Analysis
There are risks and rewards associated with the process of decision tree analysis. The advantages of decision tree analysis include: simple and easy to interpret decision trees; valuable without requiring large amounts of hard data; helps decision makers ascertain best, worst, and expected results for various scenarios; and can be combined with various decision techniques.
When using decision tree analysis, there may also be some disadvantages. Disadvantages include: uncertain values can lead to complex calculations and uncertain outcomes; decision trees are unstable, and minor data changes can lead to major structure changes; information gain in decision trees can be biased; and decision trees can often be relatively inaccurate. A popular alternative to decision trees is the influence diagram, which is a more compact, mathematical graphical representation of a decision situation.
Does HEAVY.AI Offer a Decision Tree Analysis Solution?
The HEAVY.AI platform natively integrates GPU-accelerated machine learning capabilities as part of its HeavyML module. Decision tree-models such as random forest, decision tree, and gradient boosted tree models, as well as other regression and clustering algorithms can be interactively trained, evaluated, and leveraged for predictive workflows, all directly from SQL and easily embeddable in Heavy Immerse .
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Data Analysis Tutorial
- Python - Data visualization tutorial
- Machine Learning Projects
- Machine Learning Interview Questions
- Machine Learning Mathematics
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Project
- Deep Learning Interview Questions
- Computer Vision Tutorial
- Computer Vision Projects
- NLP Project
- NLP Interview Questions
- Statistics with Python
- 100 Days of Machine Learning
- What is No Free Lunch Theorem
- Difference between Best-First Search and A* Search?
- Python OpenCV - Super resolution with deep learning
- How to Perform a Brown – Forsythe Test in Python
- How to Perform Welch’s ANOVA in Python
- How to Perform an ANCOVA in Python
- Non-Linear Regression in R
- How to Develop a Random Forest Ensemble in Python
- Difference Between Agglomerative clustering and Divisive clustering
- Clustering in R Programming
- Ensemble Methods in Python
- How to Handle Imbalanced Classes in Machine Learning
- Rule Based Approach in NLP
- Train a Deep Learning Model With Pytorch
- How to Conduct a Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test in Python?
- Differences between Random Forest and AdaBoost
- Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE) in NLP
- Data Pre-Processing with Sklearn using Standard and Minmax scaler
- Difference Between Business Intelligence and Machine Learning
Solving the Multicollinearity Problem with Decision Tree
Multicollinearity is a common issue in data science, affecting various types of models, including decision trees. This article explores what multicollinearity is, why it’s problematic for decision trees, and how to address it.
Table of Content
Multicollinearity in Decision Trees
Detecting multicollinearity, stepwise guide of how decision trees handle multicollinearity, what is multicollinearity.
Multicollinearity is a problems in statistical analysis in which two or more independent variables in a regression model are significantly connected. This correlation can cause issues in model estimation and interpretation.
What are Decision Trees?
A decision tree is a type of tree structure that resembles a flowchart, with core nodes representing features, branches representing rules, and leaf nodes representing the algorithm’s outcome. It is a flexible supervised machine-learning approach that may be applied to regression and classification issues alike. It is among the most potent algorithms.
Multicollinearity in Decision Trees:
While multicollinearity in linear regression models is a well-known issue, decision trees’ implications have not been as thoroughly studied. This is primarily because decision trees do not require or assume a particular relationship between the independent variables, in contrast to linear regression models. As a result, decision trees can generate accurate predictions even in situations where there is a high level of correlation between some variables.
In decision trees, multicollinearity is handled implicitly through the feature selection process.
- Feature Importance : Decision trees evaluate the importance of features based on how well they split the data. If two features are highly correlated (multicollinear), they will essentially provide redundant information for splitting the data. In such cases, the decision tree will select one of the correlated features for splitting and may not consider the other one, as including both would not provide additional benefit in reducing impurity.
- Splitting Criteria : Decision trees use splitting criteria such as information gain or Gini impurity to determine the best feature to split at each node. If two features are highly correlated, they are likely to have similar information gain or impurity reduction. In such cases, the decision tree may choose either feature for splitting, but not both.
- Tree Structure : As the decision tree grows, it naturally filters out redundant or correlated features. If one feature has already been used for splitting at an earlier node and has effectively reduced impurity, the decision tree is less likely to select a correlated feature for splitting at subsequent nodes, as it would not provide additional information gain.
However, it’s important to note that decision trees are sensitive to small changes in the dataset, and multicollinearity can still impact their performance. Ensemble methods like random forests are often used to mitigate this sensitivity by building multiple trees on different subsets of the data and averaging the results.
Detecting multicollinearity is an important step in ensuring the reliability of your regression model. Here are two common methods for detecting multicollinearity:
- Calculate the correlation coefficient between each pair of predictor variables.
- Values close to 1 or -1 indicate a high degree of correlation.
- Identify pairs of variables with high correlation coefficients (e.g., greater than 0.7 or less than -0.7).
- VIF measures how much the variance of an estimated regression coefficient is increased due to multicollinearity.
- Calculate the VIF for each predictor variable.
- VIF values greater than 5 or 10 are often used as thresholds to indicate multicollinearity.
Python Implementation to Detect Multicollinearity
Detecting multicollinearity can be done using the correlation matrix and VIF (Variance Inflation Factor) in Python.
The correlation matrix and VIF values you provided suggest that all three variables (X1, X2, X3) are perfectly correlated with each other, resulting in infinite VIF values.
- We use np.random.rand(100, 1) * 10 to generate 100 random numbers between 0 and 10, which serves as our feature X .
- We use np.sin(X) to create the target variable y as a sine wave of the feature X .
- We add some random noise using np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=(100, 1)) to make the relationship more realistic.
- We split the dataset into training and test sets using train_test_split , with 80% of the data used for training and 20% for testing.
- We fit a Linear Regression model ( lr.fit(X_train, y_train) ) to the training data and make predictions on the test data ( lr.predict(X_test) ).
- We calculate the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the predicted and actual values using mean_squared_error .
- We fit a Decision Tree Regression model ( dtr.fit(X_train, y_train) ) to the training data and make predictions on the test data ( dtr.predict(X_test) ).
- We print the MSE for both the Linear Regression and Decision Tree Regression models to compare their performance.
Fitting Linear Regression And Decision Tree to Compare
A lower MSE indicates a better fit of the model to the data. In this example, the Decision Tree Regression model has a significantly lower MSE compared to the Linear Regression model, which shows Decision tree performs better.
Please Login to comment...

- Machine Learning
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
404 Not found

Solving complicated problems with decision tree
A decision tree is a graphical representation of possible solutions to a problem based on given conditions. It is called a tree because diagrammatically it starts with a single box (target variable) and ends up in numerous branches and roots (numerous solutions). It is a type of supervised learning algorithm that has target variables and in order to select solutions, it creates classifications. Based on classifications, however, it is applied to both categorical and continuous variables.
Using a decision tree, the population or samples can be split into two or more homogeneous sets. These homogeneous sets are constructed based on the most significant differentiator on input variables.
For example: suppose one has to buy a new mobile phone and is confused which brand to buy. So, the decision of that person depends on the amount of money he can spend. Therefore, the target variable here is ‘budget’. Further the possible solutions for buying a phone will be taken from ‘budget’.

Suppose if the buyer has less than Rs. 20,000 to spend on a mobile phone. The buyer can buy a variety of different mobiles from Companies 1 and 2, but cannot afford any mobile phone from other companies. So, representing this situation diagrammatically, a decision tree is made to classify the solutions in homogeneous groups of ‘budget’. This example is to provide a basic idea about how a decision tree works. In analytics, decision trees are applied in complex problems and the algorithm generates thousands of possible solutions for a problem.
Example of decision tree analysis
In this example, basic information of 70 patients is taken into consideration to see which of them are more prone to lung cancer. However, not more than two attributes, ‘Age’ and the habit of ‘Smoking’ has been tested against the possibility of having lung cancer.

Figure 2: Decision tree for lung cancer using R programming
The figure above shows the decision tree and explains the importance of each attribute along with the rules distinguishing between both the groups in the target variable. The rules defined by the decision tree are:
This explains that there are 78% chances of the patients getting lung cancer if they smoke and are over the age of 25, according to this model.
This rule node explains that out of all the patients there is 71% probability of patients not having lung cancer if they smoke but also are less than the age of 26.
This rule tells that if the patients don’t smoke, no matter what their age is, there is just a 17% probability of them having lung cancer. This means 83% of the total patients who don’t smoke are safe from lung cancer.
This decision tree model helped to understand the probability of patients having lung cancer based on two of the main attributes. Also, it helped to predict and identify which of the new patients are most likely to have lung cancer.
The probability of having lung cancer
Now computing the probability of having lung cancer using this decision tree. For a better understanding of it, a new simplified decision tree has been derived using the output decision tree from R.
Using the decision tree in the figure above:
This is the mathematical representation of the above decision tree in Figure 3. It shows the total percentage of patients having lung cancer out of all the patients who come in. It is not very difficult to calculate the probability of an outcome using the decision tree after values are presented numerically.
Applications of decision tree analysis
- Decision trees are useful in biomedical engineering for identifying features to be used in implantable devices.
- Decision trees have been recently used to non-destructively test welding quality for semiconductor manufacturing. This helps in increasing productivity for material procurement method selection to accelerate rotogravure printing for process optimization in electrochemical machining, schedule printed circuit board assembly lines to uncover flaws in a Boeing manufacturing process and quality control.
Software supporting decision tree applications with multiple independent variables are R, SAS, MATLAB, PYTHON and SPSS.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
proofreading
Decision Tree Analysis: An Efficient Approach to Strategic Decision Making

In an increasingly complex business environment, strategic decision making has become paramount for success. Among the many techniques employed by businesses, Decision Tree Analysis stands out for its clarity, ease of use, and efficiency in breaking down intricate decision processes into manageable parts.
In this article, we take a deep dive into the essence of Decision Tree Analysis, exploring its foundations, variations, and applications in the realm of business.
We'll also discuss how its implementation can be a game-changer for organizations looking to streamline their decision-making processes, providing an expert approach that is deeply user-oriented and enriched with practical examples.
Related articles:
Directive Decision-Making: Who Influences Outcomes?
Group Decision-Making: Systemic Conversation Management
Developing Problem-Solving Skills: What Employers Want
Basics of Decision Tree Analysis
Definition of Decision Tree Analysis
Decision Tree Analysis is a graphical representation of decisions and their possible consequences, which are organized in a tree-like structure. It's a tool used to support the decision-making process by visualizing various alternatives and their potential outcomes in a clear and concise manner.
This method assists decision-makers in choosing the most favorable option by mapping out the different paths a decision could lead to, taking into account the risks, costs, and benefits associated with each branch.
Components of Decision Trees: Nodes, Branches, and Final Outcomes
Central to decision trees are nodes, branches, and final outcomes. Nodes represent points of decision, chance, or termination in a tree. Decisions nodes are depicted as squares, chance nodes as circles, and end nodes signify the conclusion of a path.
Branches extend from nodes and symbolize the choices available or the uncertain outcomes that could follow. At the end of these branches lie the final outcomes , which reflect the results of following a particular path, expressed in terms of payoff or another measure of success.
Brief history of Decision Tree Analysis
Decision Tree Analysis has its roots in operations research and management science. It was developed in the mid-20th century as a tool for organizational and business strategy, and has since been refined with computational advances.
Its application has grown broadly, not just in business but also in fields like medicine, engineering, and law, making it a versatile tool for any decision-making scenario that involves uncertain outcomes.
Types of Decision Trees
Classification Trees
Classification trees are a type of Decision Tree used primarily in machine learning and statistics to categorize instances into discrete groups based on input variables. They are particularly useful in assignments that require clear differentiation – such as when a finance company must decide whether to approve or deny a loan application based on applicant's attributes.
Regression Trees
Conversely, regression trees are applied when the target variable is numerical or continuous. These trees predict the value of a target based on the input variables. For example, a real estate company might use a regression tree to predict house prices based on features like size, location, and number of bedrooms.
Explanation and examples of each
Both types of trees divide the dataset into distinct strata by making sequential, hierarchical decisions regarding the input data. In a classification tree, an insurance company may classify customers into high and low risk categories while a regression tree could help a marketing firm predict how much a customer is willing to spend based on demographic data. Interpreting these trees involves understanding the series of conditions that lead to a particular classification or prediction.
Utilizing Decision Trees in Business
Decision Tree Analysis serves as a robust tool in business, providing a framework for clear and systematic consideration of complex decision-making situations.
The importance of Decision Trees stems from their ability to simplify the decision-making process by visualizing the options and potential outcomes, thus helping businesses to evaluate the probable impacts of various choices before committing to a course of action.
Real-world examples of Decision Tree Analysis employed in various business scenarios
One real-world example of Decision Tree Analysis is in prioritizing investment opportunities. A company might use a decision tree to decide between investing in a new product line, entering a new market, or upgrading its existing infrastructure. By mapping out the potential returns and risks associated with each option, the company can make a well-informed decision. In customer service, decision trees empower agents with a script or flowchart that dictates how to respond to various customer inquiries or problems, ensuring efficiency and consistency in service delivery.
Process of Creating a Decision Tree
Steps for constructing a Decision Tree
Developing a Decision Tree begins with identifying the primary decision to be made. Afterward, the subsequent choices, uncertainties, and outcomes are added sequentially. Each branch of the tree represents a possible decision or event, and each node on the branch represents the outcome of the previous step. This iterative process continues until all significant variables are included, and all final outcomes are represented.
Tips and considerations during the tree design phase
When designing a Decision Tree, one must be thorough yet economical with the level of detail. Over-complication can make the tree unwieldy and difficult to interpret, while oversimplifying may overlook key variables. Additionally, it is important to base the branches and outcomes on accurate, reliable data and consider the tree structure's feasibility for the specific context of the business scenario.
Highlight on post-pruning and pre-pruning during decision tree construction
Trees could grow very large with many branches, potentially leading to overfitting, where the tree models the training data too closely and performs poorly on unseen data. This is where post-pruning , a tactic to trim some of the tree's branches after full development, becomes pivotal. In contrast, pre-pruning involves setting conditions that prevent the tree from becoming overly complex as it's built. Both techniques aim to enhance the model's generalization to new, unseen data.
Practical example on building a decision tree
Consider a company that needs to determine whether to launch a new product. The decision tree's root node would be the decision to launch or not, with branches considering market conditions, competitors' actions, cost of production, and potential sales revenue. As the tree expands, the outcomes become more explicit, helping leaders evaluate the risks and benefits on granule levels. This enables the company to navigate through complex market data and forecast the launch's viability.
Interpreting a Decision Tree
Explanation of how to read and interpret a Decision Tree
To interpret a Decision Tree, one must start from the root node and follow the branches based on the specific conditions they entail. At each decision node, the choice that leads to the most favorable outcome is selected. Chance nodes account for the probability of certain events happening, affecting the pathway to be taken. The eventual goal is to reach a decision that optimizes desired outcomes, such as profit or cost savings.
Common misconceptions and difficulties in interpreting Decision Trees
Some misconceptions about Decision Trees include the belief that they can impeccably predict future events or that higher complexity in a tree implies better decision-making prowess. However, in practice, simpler trees are often more robust and easier to interpret. Interpreting a Decision Tree also requires consideration of the statistical significance of branches and nodes.
Real-life example to illustrate the interpretation process
Take, for example, a retail company deciding where to expand its physical stores. The decision tree may show that urban expansion maximizes potential foot traffic, but when factoring in higher real estate costs (a chance node), suburban areas might offer a better return on investment. In this scenario, interpreting the tree involves weighing these qualitative and quantitative factors to arrive at a strategic conclusion.
Limitations of Decision Tree Analysis
Overview of potential pitfalls or limitations of utilizing Decision Trees
Despite their usefulness, Decision Trees come with potential pitfalls; they can become overly complex, making the final decision harder to interpret, or they may not efficiently handle certain types of structured data. Additionally, Decision Trees can be biased towards branches with more levels and may not be the best tool for predicting events with high uncertainty.
Strategies to overcome these limitations and improve decision tree accuracy
To improve accuracy and mitigate the limitations, tree complexity can be managed through pruning techniques. Ensemble methods like Random Forests and Gradient Boosting can be used to better handle data variance and improve predictive accuracy. Furthermore, cross-validation techniques can help ensure the tree's reliability on unseen data.
Decision Tree Analysis is a powerful and versatile tool for strategic decision making, particularly in the context of business where data-driven choices can yield significant competitive advantages. From understanding the basics to interpreting complex models and recognizing limitations, mastery of this tool requires both the big picture and attention to detail.
Nonetheless, the benefits that can be reaped from effectively applying Decision Tree Analysis are considerable, making it an essential skill in the modern, data-rich business landscape.
By providing comprehensive knowledge of the process, coupled with hands-on experiences and an expert approach, this article seeks to embolden practitioners to further explore and apply Decision Tree Analysis. For those looking to delve deeper into this topic, engaging in a problem solving course free of charge or an online certificate course can be a valuable step towards achieving proficiency in this domain. As the need for strategic decision-making processes only grows, the ability to navigate and employ Decision Tree Analysis becomes ever more crucial.
What are the fundamental principles underlying decision tree analysis in strategic decision making?
Decision tree analysis in strategic decision making, unpacking decision trees.
Decision trees allow a visual mapping of options. They reflect a sequence of choices and outcomes. Each branch represents a potential decision or event. Trees grow complex with more branches. Strategists favor decision trees for this clarity.
Core Principles of Decision Trees
Sequential Decisions Drive the Process. Trees showcase options step by step. They unfold like a story. Each decision leads to distinct consequences. Choices at one node inform the next.
Probability Factors into Analysis. Nodes assign probabilities to outcomes. Higher probability indicates a likelier result. This quantification aids in comparing options.
Outcomes Have Attached Values. Each result carries a projected value. Values may represent profits, costs, or other metrics. This helps strategists assess potential benefits.
Branches Account for Uncertainty. Decision trees accept that not all is predictable. They map uncertainty through branches. Each branch is a different scenario.
The Time Value of Money is Integral. Future returns often mean less today. Trees account for this discounting. This ensures current decisions reflect future values accurately.
Utilizing Decision Trees Effectively
Identify All Relevant Choices and Outcomes. Full mapping requires thorough brainstorming. Overlooked options may skew the analysis. Comprehensive trees present a clear strategic picture.
Estimate Probabilities and Outcomes with Care. Robust analysis hinges on accurate data. Guesswork diminishes the tree’s utility. Solid data provides a trustworthy foundation.
Review and Challenge the Tree. Trees are not set in stone. Test the logic of each branch. Peer review improves the tree’s robustness.
Incorporate Trees within a Broader Analysis Framework. Decision trees are one tool. They join forces with other analytic methods. Combine tools for a more complete strategy.
Decision trees guide through strategic fog with clarity. They demand sequential thought and value accuracy. Their visual nature simplifies the complex. Yet, they are but one tool in the decision-maker's kit. Adaptation and broad perspective enrich their use.
How can decision tree analysis contribute to risk management in strategic decision-making processes?
Decision tree analysis in risk management, understanding decision trees.
Decision trees represent a core tool. They structure choices. They display outcomes. Trees capture decision logic. They focus on measurable results. They clarify complex scenarios. Decision trees aid risk assessment. They align with strategic decision-making.
The Role of Decision Trees in Strategic Planning
In strategic planning, risks abound. Decisions must address unknowns. Trees facilitate systematic evaluation. They present visual depictions. Options break down into branches. Consequences follow logically.
Choice identification becomes streamlined . Trees list potential strategies. Each node represents a decision. Each branch symbolizes an option. Decisions lead to different paths.
Assessing Probable Outcomes and Related Risks
Trees quantify probable outcomes. They integrate probabilities. Each outcome links to a likelihood. Risk factors become quantifiable. Each path carries risk levels. Tree analysis weighs these risks.
Multi-faceted scenarios complicate strategies. Trees simplify these situations. They compare varied paths. Each shows unique risk profiles. Decision makers grasp implications.
Facilitating Clear Communication
Communication clarity is crucial. Decision trees provide clear visuals. Stakeholders see options and risks. They understand strategic decisions better. Trees ensure common understanding. Misinterpretations reduce.
Encouraging Thorough Analysis
Trees require thorough groundwork. Assumptions must be clear. Data needs accuracy. Probabilities demand rigorous estimation. Each step in a tree invites scrutiny. Reality checks become mandatory.
Each branch prompts questions. What are the costs? What gains can follow? Risks must be identified. Considerations include financial, operational, and reputational risks. Trees ensure each receives attention.
Supporting Consistent Decision-Making
Consistency in decisions is key. Trees offer systematic frameworks. They provide repeatable processes. Decisions across similar scenarios align. Variance in outcomes diminishes. Trees encourage methodical approaches.
Decision tree analysis stands out. It offers clarity and methodology. It enables nuanced risk valuation. Strategic choices become informed. Risks no longer feel insurmountable. Decision trees turn risks manageable. They support strategic decision excellence.
How does the complexity of the business environment impact the applicability of decision tree analysis in strategic decision making?
The role of decision trees in complex business environments.
Decision trees represent a tool for strategic decision-making. They outline choices, possible outcomes, and linked probabilities. They assume a tree-like structure. From each decision node, branches emerge. These branches denote potential paths. They reflect different courses of action. Each path has probabilities and outcomes.
Complexity in Business
The business environment today bears complexity. It poses challenges for decision-making tools. Uncertainty runs high. Variables interconnect intricately. Stakeholders bring diverse interests. Globalization adds layers of considerations. Technology accelerates change.
Applicability Hurdles
Complex environments strain decision trees' applicability. Simplicity is a core strength of decision trees. They lack sophistication for multilayered issues. Multiple variables can overwhelm the model. This may lead to oversimplification. Nuanced scenarios escape clear-cut categorization. Decision trees may ignore deeper, systemic factors. Intangibles like brand value or employee morale are hard to quantify.
Benefits Despite Complexity
Nevertheless, decision trees offer clear benefits. They provide a visual representation of decisions. This aids in understanding the link between actions and outcomes. They quantify probabilities and outcomes. That allows for some measure of objective comparison. They can clarify choices with clear financial implications.
Decision Trees Enhance Strategic Decision-Making
In strategic decision-making, context dictates tools. Decision trees align with decision types, goals, and available data. They function best with clear, discrete options. They serve well when probabilities are available. They thrive when outcomes are quantifiable.
Decision Trees as a Guide, Not a Panacea
Decision trees can guide but not dictate in complex environments. They work as part of a broader decision-making arsenal. They require complementation by other analytical methods. Qualitative assessments must balance the quantitative simplicity.
Adaptation and Limitations
Recognize and address decision trees' limitations. Adapt them for complexity. Include the most relevant variables only. Accept that decision trees are a starting point. They prompt more in-depth analysis where needed. They refine thinking but don't replace it.
Complex business environments present a test for decision trees. They limit but do not eliminate their usefulness. Decision-makers must deploy decision trees judiciously. They should integrate them into a diverse set of tools. Decision trees can simplify the beginnings of analysis. They cannot encapsulate the entirety of complex strategic decisions. Use them wisely. Recognize their value and boundaries.

He is a content producer who specializes in blog content. He has a master's degree in business administration and he lives in the Netherlands.

Developing Problem Solving Skills Since 1960s WSEIAC Report

Unlocking Problem Solving Skills: Where Do Problems Come From?

Problem Solving in 9 Steps

The First Step in Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Decision Trees for Decision-Making
- John F. Magee

Here is a [recently developed] tool for analyzing the choices, risks, objectives, monetary gains, and information needs involved in complex management decisions, like plant investment.
The management of a company that I shall call Stygian Chemical Industries, Ltd., must decide whether to build a small plant or a large one to manufacture a new product with an expected market life of 10 years. The decision hinges on what size the market for the product will be.
- JM John F. Magee was chairman of the board of directors of Arthur D. Little, Inc.
Partner Center
- Go to US Navigation
- Go to Post-it® Navigation
- Go to Page Content
- Go to Search
- Go to Contact Information
- Go to Site Map
- United States
- Collaborate your way to solutions with a decision tree
A decision tree can help you branch out to solve problems
What is a decision tree? It’s a great way to help you and your teams solve problems by looking at them in a fresh way, and Post-it® Products are the best tools for creating one.
A logic or decision tree can help you tackle a problem by breaking possible solutions down into parts and following those parts down new paths. The process of decision tree analysis is simple — get your team’s thoughts out about the problem or question, offer solutions or answers, and generate ideas about how to achieve them.

1. Start by asking a question
First, you need to define the problem or question, and that requires brainstorming with your team. A Post-it® Tabletop Easel Pad is excellent for small group brainstorming — it can be propped on a table or moved around as needed, and is perfect for on-the-fly thinking and editing. A logic tree can answer two kinds of questions — “Why?” or “How? The clearer and more specific your question, the better it will work in your logic tree. Once your team settles on a question, write it at the top of the easel pad.
2. Brainstorm the answers
Now it’s time to think of potential answers to your big question. Using one color of Post-it® Super Sticky Notes 3 in. x 3 in. , have everyone jot down possible answers and stick them beneath the question. While you brainstorm and discuss, the notes can easily be moved around, re-stuck, or rearranged. Chat about those answers, and then choose at least two or three that seem the most relevant. Remove the other notes and set them aside.
3. Collaborate toward solutions
Next, with a different color of Post-it® Super Sticky Notes 3 in. x 3 in., elaborate on some solutions with your team and stick them underneath the answers. As your decision tree template starts taking shape, the varying colors will help your team visualize the relationships between answers and solutions — and because the notes are super sticky, rearranging on the fly is no problem. Connect the related answers and solutions by drawing simple branches between the notes so it begins to look like a family tree. Some of your logic paths might end here, and that’s okay — but dig deeper if you need to!
4. Take action!
At this point, you can get down to brass tacks. How do you make your solutions reality? As you discuss specific action steps that relate to the solutions, write them down on Post-it® Super Sticky Lined Notes 4 in. x 4 in. and distribute the lists among team members. The lined notes are perfect for making orderly lists, and they can easily be stuck inside a planner or on a calendar to help keep things front and center.
The decision tree can be a powerful exercise to help you and your teams with problem solving. Post-it® Products are the right tools to turn thoughts into action, and to help you make your mark on the world by following these easy steps:
- Ask a question
- Brainstorm possible answers
- Collaborate toward a solution
- Take action!

Post-it® Easel Pads

Post-it® Super Sticky Notes

Post-it® Super Sticky Lined Notes
- Email Address
We’d like to learn about some of your shopping attitudes and behaviors and your values in life. Please indicate the statements below that you agree with.
- Generic brands are as effective as brand name products
- Money is the best measure of success
- I tend to focus on the big picture rather than specific details
- I am typically willing to pay more for high-quality items
- I live a settled life and am happy with that
- I value many tools to meet my organization needs
- Describe Your Organizational Habits Describe Your Organizational Habits It is important to plan and organize in detail – both at work and at home I plan and organize sometimes, but I am not very consistent None of the above
- Describe Your Occupation Select Your Occupation Advertising / PR / Media / Creative / Design Business Services Construction/General Labor Education Facility Manager Finance / Banking / Accounting Government / Non Profit Healthcare / Pharmaceuticals Hospitality / Travel / Events IT / Developer Legal Manufacturing Professional Organizer Real Estate Restaurant Retail Small Business Owner Stay at home parent Student Other
3M takes your privacy seriously. 3M and its authorized third parties will use the information you provided in accordance with our 3M Privacy Policy to send you communications which may include promotions, product information and service offers.
Please be aware that this information may be stored on a server located in the U.S. If you do not consent to this use of your personal information, please do not use this system.
Thank You for Subscribing
Thank you for signing up! You should receive a welcome email with additional details shortly.
Our Apologies...
An error has occurred while submitting. Please try again later...
- All Post-it Products
- Digital Apps Products
- Connections
- Productivity
- Where to Buy
- Custom Printed
- About Post-it® Brand
- Ratings & Reviews


VIDEO
COMMENTS
By Letícia Fonseca, May 05, 2022. The purpose of a decision tree analysis is to show how various alternatives can create different possible solutions to solve problems. A decision tree, in contrast to traditional problem-solving methods, gives a "visual" means of recognizing uncertain outcomes that could result from certain choices or ...
3. Expand until you reach end points. Keep adding chance and decision nodes to your decision tree until you can't expand the tree further. At this point, add end nodes to your tree to signify the completion of the tree creation process. Once you've completed your tree, you can begin analyzing each of the decisions. 4.
Example 1: The Structure of Decision Tree. Let's explain the decision tree structure with a simple example. Each decision tree has 3 key parts: a root node. leaf nodes, and. branches. No matter what type is the decision tree, it starts with a specific decision. This decision is depicted with a box - the root node.
EXTRA PROBLEM 6: SOLVING DECISION TREES. Read the following decision problem and answer the questions below. A manufacturer produces items that have a probability p of being defective . These items are formed into batches of 150 . Past experience indicates that some (batches) are of good quality (i.e. p=0.05) and others are of bad quality (i.e ...
By visually mapping out the possible consequences of different actions, including uncertain outcomes from chance events, you can easily select the most reasonable path forward in a complex problem-solving situation. Decision tree analysis is often used by project managers and other decision-makers in business planning.
Where you're calculating the value of uncertain outcomes (circles on the diagram), do this by multiplying the value of the outcomes by their probability. The total for that node of the tree is the total of these values. In the example in figure 2, the value for "new product, thorough development" is: 0.4 (probability good outcome) x $1,000,000 ...
Decision trees are used for classification and regression tasks, providing easy-to-understand models. A decision tree is a hierarchical model used in decision support that depicts decisions and their potential outcomes, incorporating chance events, resource expenses, and utility. This algorithmic model utilizes conditional control statements ...
The Decision Tree Analysis tool is a scientific model and is often used in the decision making process of organizations. When making a decision, the management already envisages alternative ideas and solutions. By using a decision tree, the alternative solutions and possible choices are illustrated graphically as a result of which it becomes ...
Key Points. Decision trees provide an effective method of Decision Making because they: Clearly lay out the problem so that all options can be challenged. Allow us to analyze fully the possible consequences of a decision. Provide a framework to quantify the values of outcomes and the probabilities of achieving them.
A decision tree is a tree-like model that acts as a decision support tool, visually displaying decisions and their potential outcomes, consequences, and costs. From there, the "branches" can easily be evaluated and compared in order to select the best courses of action. Decision tree analysis is helpful for solving problems, revealing ...
This brief video explains *the components of the decision tree*how to construct a decision tree*how to solve (fold back) a decision tree.~~~~~ Other v...
Decision tree analysis is the process of graphically charting out business decisions. In a nutshell, you list out every decision and every possible consequence while assigning probabilities and utility values (usually expressed in dollars) to each outcome. When done right, decision tree analysis compartmentalizes (and, ultimately, simplifies ...
A decision tree is a graphical representation of a problem and its possible solutions. It consists of nodes and branches that show the choices, consequences, and probabilities of each scenario. A ...
Here are two common methods for detecting multicollinearity: Correlation Matrix: Calculate the correlation coefficient between each pair of predictor variables. Values close to 1 or -1 indicate a high degree of correlation. Identify pairs of variables with high correlation coefficients (e.g., greater than 0.7 or less than -0.7).
Decision tree analysis involves visually outlining the potential outcomes, costs, and implications are a sophisticated decisions. These trees are particularly advantageous for analyzed quantitative intelligence and making a decision based on numerical. ... Decision tree example problem. Expected value (EV) = (First possible outcome x Likelihood ...
Decision tree analysis can help solve both classification & regression problems. The decision tree algorithm breaks down a dataset into smaller subsets; while during the same time, an associated decision tree is incrementally developed. ... age, etc. Let's dig right into solving this problem using a decision tree algorithm for classification ...
an example of how the decision tree can be used for detecting subscription fraud. Age Level s 14-18 . Objectives . Students will be able to: recognize a decision tree; recognize a problem where a decision tree can be useful in solving it; relate algorithms and decision trees, and be able to list some algorithms that
Solving complicated problems with decision tree. A decision tree is a graphical representation of possible solutions to a problem based on given conditions. It is called a tree because diagrammatically it starts with a single box (target variable) and ends up in numerous branches and roots (numerous solutions).
Problem Tree Analysis does not operate in isolation; rather, it is part of a suite of Analytical Methods and Decision-making Tools that facilitate comprehensive problem-solving. Its integration with other methodologies, such as SWOT analysis or Cost-Benefit Analysis, enhances the robustness of the conclusions drawn.
Definition of Decision Tree Analysis. Decision Tree Analysis is a graphical representation of decisions and their possible consequences, which are organized in a tree-like structure. It's a tool used to support the decision-making process by visualizing various alternatives and their potential outcomes in a clear and concise manner.
Decision making and problem solving Here is a [recently developed] tool for analyzing the choices, risks, objectives, monetary gains, and information needs involved in complex management decisions ...
Decision analysis is a tool that attempts to provide an analytic basis for management decisions under uncertainty. At the core of the technique is a structure called a decision tree. A decision tree contains two types of nodes, decision nodes and chance nodes. A decision node is a node at which a decision is to be made and a chance node is a ...
The process of decision tree analysis is simple — get your team's thoughts out about the problem or question, offer solutions or answers, and generate ideas about how to achieve them. 1. Start by asking a question. First, you need to define the problem or question, and that requires brainstorming with your team.