Example 15 mark answer in style of AQA Economics
There are several misconceptions about 15 mark questions.
As students have requested this, here is an example 15 mark answer.
There are also tips and common mistakes to avoid.
For more model answers and practice questions, check out the links below:

How to structure a 15 mark answer
Example question, final point 3, most common mistakes, two or three points in a 15 mark question, how long should you spend on a 15 mark question, do you need to evaluate in 15 mark questions, related posts, latest posts.
To my students, I usually recommend three points (but you can also do two points if each point is more detailed). You can also start with a few key definitions.
For each point, complete a chain of analysis. Add some data to show real-world application.
You do not need evaluation in a 15 mark question for AQA.
Here is a practice question I have created in the style of AQA Economics A-level. I have kept the question simple, to focus on exam technique:
Explain how an increase in interest rates by the Bank of England affects the UK economy . (15 marks)
Example answer
The interest rate is the reward for saving and the cost of borrowing. Aggregate demand is the total demand in the economy.
A higher interest rate means greater incentive to save. So consumers save more and spend less.
Consumers also spend less because borrowing is more expensive, so they are less willing to buy goods by borrowing, which could include houses (through mortgages) or cars.
This means consumption falls. Consumption is the largest component, at 65%, of aggregate demand in the UK.
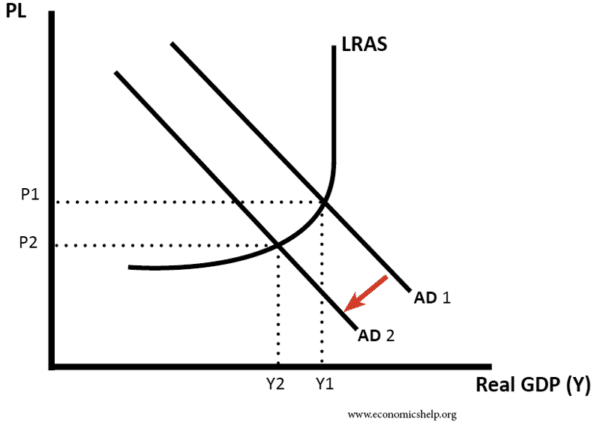
As consumption is a component of aggregate demand (AD=C+I+G+X-M), aggregate demand shifts left from AD to AD1. This means a reduction in the price level from PL to PL1 and a fall in real GDP from Y to Y1.

A higher interest increases borrowing costs for firms. This makes firms less willing to borrow. So firms borrow less, so they invest less.
As investment is a component of AD, AD shifts further to the left from AD1 to AD2. Gross investment is about 17% of aggregate demand for the UK.
This reduces real output further from Y1 to Y2. There may also be a multiplier effect, when a one-off change in a component of AD leads to an even greater change in real national income.
Reduced investment means some companies that would receive these investment flows no longer receive them. So these companies have reduced profits and may cut wages. This further reduces consumer demand, which further reduces real incomes and hence again demand, so AD falls further.
In 2022 the Bank of England’s interest rate, “Bank Rate”, increased from 0.25% to 3%. A higher interest rate relative to other economies means a relatively higher rate of return on savings in the UK. So there are hot money inflows into the UK.
This increases demand for the pound, so the pound appreciates. A stronger pound makes imports cheaper and exports dearer.
This increases demand for imports and reduces demand for exports. Assume the Marshall Lerner condition holds, that is export and import demand are sufficiently responsive to price changes (specifically the absolute values of the PED of exports plus the PED of imports sum to at least 1).
Then the appreciation will lead to a fall in the total value of net exports. As net exports are a component of AD, AD further decreases, shifting further left. So real GDP and the price level fall further.
This answer would likely score full marks or close to it.
The answer starts with two relevant definitions.
Then there are three points, each with well explained chains of analysis.
For more guidance on AQA Economics exam technique, click the link below:
Each point has a relevant fact / piece of data. This satisfies the application requirement.
There is also a graph that is explained in the text. I recommend at least one graph, if not two, per 15 mark question.
If you draw a graph, make sure to explain it in the text too.
For some statistics on the components of real GDP / aggregate demand, see the link here .
1) Not knowing where to start. Think about relevant graphs or ideas you have learnt. Graphs can provide a really good starting point in a lot of answers. For macro, you could think about how you could use AS-AD graphs to answer the question. For micro, think about cost-revenue diagrams or supply-demand diagrams.
2) Forgetting definitions . If you start with two definitions, then this won’t be a problem.
3) Forgetting application . Try to remember to get three pieces of data into your answer from the real economy. Think about what’s going on in the UK economy when you write your answer.
4) Errors in explanation . This is the hardest to fix. You just need to learn the course content well here.
For how to answer a 9 mark question, check out the link here:
Other questions
I recommend three points. But two can also work, provided they are more detailed than the points above.
15-20 minutes. Saving more time for the 25 mark questions will help score well in the 25 mark questions.
No. But may be credited as analysis in this question.
To see more A-level economics resources, check out the links below:
- 6 Practice Papers for A Level Economics 2024
- The economics of why people give gifts
- What economic theory says about immigration
- Can the free market provide public goods?
- How the UK tackles market power, mergers and big tech
The Curious Economist
Economic news for students.
- [ April 8, 2024 ] Turkey’s Inflation Soars to 68.5% Economic News
- [ April 8, 2024 ] EU Probes into Chinese Solar Firms for Possible Unfair Subsidies Consumer and Business Behaviour
- [ March 20, 2024 ] Japan Bids Farewell to Negative Interest Rates Aggregate Demand and Supply
- [ March 19, 2024 ] Uber to Pay $271.8 Million in Landmark Australian Settlement Consumer and Business Behaviour
- [ March 15, 2024 ] Europe on the Brink: Calls for Immediate Climate Action Economic News
Model 15-Markers

Unlock your potential with these IB economics model answers, designed to provide a deeper understanding of key topics and real-world examples.
By studying these model answers, you’ll gain a solid foundation in economic concepts, learn how to structure your essays effectively, and develop critical analysis skills. As you explore the real-world examples provided, you’ll also gain an appreciation for the complexities and nuances of economic policies and their impacts on various societies.
Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and confidence needed to succeed in your IB economics journey, ensuring that you’re well-equipped to tackle any question or challenge that comes your way.
Click on the questions below to see a model essay!
Microeconomics
Using real-world examples, discuss the consequences of a price ceiling on stakeholders
Using real-world examples, evaluate different approaches to managing common access resources
Using real-world examples, evaluate the policies a government might adopt to respond to a market situation in which significant asymmetric information exists
Using real-world examples, evaluate the effects for stakeholders of a government imposing an indirect tax on a particular good
Using real-world examples, evaluate the view that government regulation is the most effective way to deal with negative externalities of consumption
Using real-world examples, evaluate the view that governments should always try to prevent the creation of barriers to entry in a market.
Using real-world examples, evaluate the impact of large firms having significant market power.
Macroeconomics
Using real-world examples evaluate the claim that according to the Keynesian and monetarist models a decrease in AD will always be deflationary.
Using real-world examples evaluate the view that economic growth will always lead to an improvement in living standards
Using real-world examples, evaluate the effectiveness of monetary policy to achieve low unemployment
Global Economy
Using real-world examples, discuss the possible implications of a persistent current account deficit
Using real-world examples, discuss the consequences of a fall in a country’s exchange rate
Copyright © 2024 | MH Magazine WordPress Theme by MH Themes

Tips for writing economics essays
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation – primarily designed for A Level students.
1. Understand the question
Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
For example:
Q. Examine the macroeconomic implications of a significant fall in UK House prices, combined with a simultaneous loosening of Monetary Policy.
In plain English.
- Discuss the effect of falling house prices on the economy
- Discuss the effect of falling interest rates (loose monetary policy) on economy
In effect, there are two distinct parts to this question. It is a valid response, to deal with each separately, before considering both together.
It helps to keep reminding yourself of the question as you answer. Sometimes candidates start off well, but towards the end forget what the question was. Bear in mind, failure to answer the question can lead to a very low mark.
2. Write in simple sentences
For clarity of thought, it is usually best for students to write short sentences. The main thing is to avoid combining too many ideas into one sentence. If you write in short sentences, it may sound a little stilted; but it is worth remembering that there are no extra marks for a Shakespearian grasp of English. (at least in Economics Exams)
Look at this response to a question:
Q. What is the impact of higher interest rates?
Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing. As a result, those with mortgages will have lower disposable income. Also, consumers have less incentive to borrow and spend on credit cards. Therefore consumption will be lower. This fall in consumption will cause a fall in Aggregate Demand and therefore lead to lower economic growth. A fall in AD will also reduce inflation.
I could have combined 1 or 2 sentences together, but here I wanted to show that short sentences can aid clarity of thought. Nothing is wasted in the above example.
Simple sentences help you to focus on one thing at once, which is another important tip.
3. Answer the question
Quite frequently, when marking economic essays, you see a candidate who has a reasonable knowledge of economics, but unfortunately does not answer the question. Therefore, as a result, they can get zero for a question. It may seem harsh, but if you don’t answer the question, the examiner can’t give any marks.
At the end of each paragraph you can ask yourself; how does this paragraph answer the question? If necessary, you can write a one-sentence summary, which directly answers the question. Don’t wait until the end of the essay to realise you have answered a different question.
Discuss the impact of Euro membership on UK fiscal and monetary policy?
Most students will have revised a question on: “The benefits and costs of the Euro. Therefore, as soon as they see the Euro in the title, they put down all their notes on the benefits and costs of the Euro. However, this question is quite specific; it only wishes to know the impact on fiscal and monetary policy.
The “joke” goes, put 10 economists in a room and you will get 11 different answers. Why? you may ask. The nature of economics is that quite often there is no “right” answer. It is important that we always consider other points of view, and discuss various different, potential outcomes. This is what we mean by evaluation.
Macro-evaluation
- Depends on the state of the economy – full capacity or recession?
- Time lags – it may take 18 months for interest rates to have an effect
- Depends on other variables in the economy . Higher investment could be offset by fall in consumer spending.
- The significance of factors . A fall in exports to the US is only a small proportion of UK AD. However, a recession in Europe is more significant because 50% of UK exports go to EU.
- Consider the impact on all macroeconomic objectives . For example, higher interest rates may reduce inflation, but what about economic growth, unemployment, current account and balance of payments?
- Consider both the supply and demand side . For example, expansionary fiscal policy can help to reduce demand-deficient unemployment, however, it will be ineffective in solving demand-side unemployment (e.g. structural unemployment)
Example question :
The effect of raising interest rates will reduce consumer spending.
- However , if confidence is high, higher interest rates may not actually discourage consumer spending.
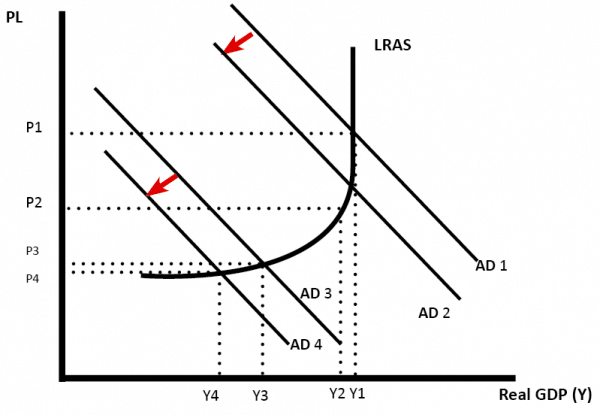
If the economy is close to full capacity a rise in interest rates may reduce inflation but not reduce growth. (AD falls from AD1 to AD2)
- However , if there is already a slowdown in the economy, rising interest rates may cause a recession. (AD3 to AD3)
Micro-evaluation
1. The impact depends on elasticity of demand
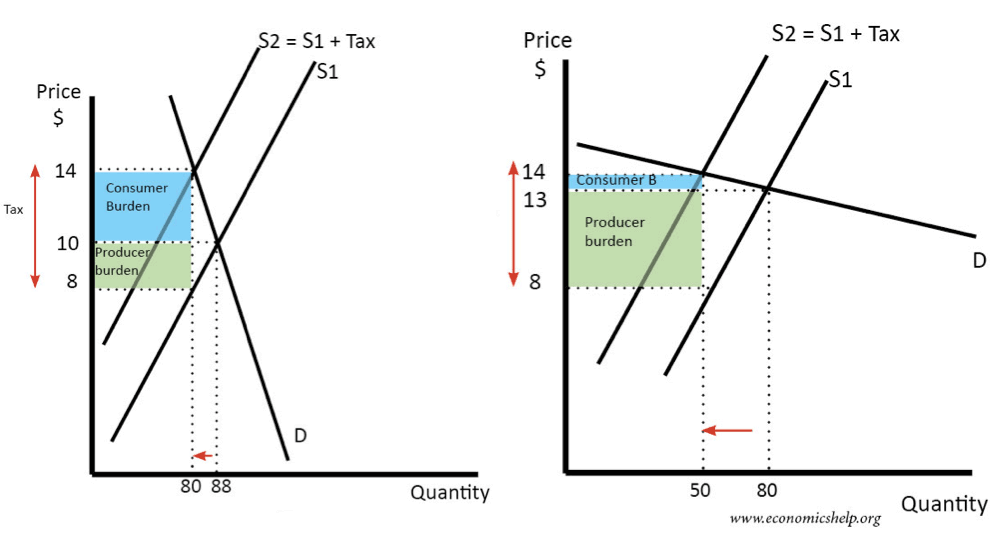
In both diagrams, we place the same tax on the good, causing supply to shift to the left.
- When demand is price inelastic, the tax causes only a small fall in demand.
- If demand is price elastic, the tax causes a bigger percentage fall in demand.
2. Time lag
In the short term, demand for petrol is likely to be price inelastic. However, over time, consumers may find alternatives, e.g. they buy electric cars. In the short-term, investment will not increase capacity, but over time, it may help to increase a firms profitability. Time lags.
3. Depends on market structure
If markets are competitive, then we can expect prices to remain low. However, if a firm has monopoly power, then we can expect higher prices.
4. Depends on business objectives
If a firm is seeking to maximise profits, we can expect prices to rise. However, if a firm is seeking to maximise market share, it may seek to cut prices – even if it means less profit.
5. Behavioural economics
In economics, we usually assume individuals are rational and seeking to maximise their utility. However, in the real world, people are subject to bias and may not meet expectations of classical economic theory. For example, the present-bias suggest consumers will give much higher weighting to present levels of happiness and ignore future costs. This may explain over-consumption of demerit goods and under-consumption of merit goods. See: behavioural economics

Exam tips for economics – Comprehensive e-book guide for just £5
8 thoughts on “Tips for writing economics essays”
I really want to know the difference between discussion questions and analysis questions and how to answer them in a correct way to get good credit in Economics
Analysis just involves one sided answers while Discussion questions involve using two points of view
This is a great lesson learnd by me
how can I actually manage my time
The evaluation points in this article are really useful! The thing I struggle with is analysis and application. I have all the knowledge and I have learnt the evaluation points like J-curve analysis and marshall learner condition, but my chains of reasoning are not good enough. I will try the shorter sentences recommended in this article.
What kind of method for costing analysis is most suitable for a craft brewery, in order to analyze the cost of production of different types of beer_
Really useful!Especially for the CIE exam papers
Does anyone know how to evaluate in those advantages/disadvantages essay questions where you would basically analyse the benefits of something and then evaluate? Struggling because wouldn’t the evaluation just be the disadvantages ?? Like how would you evaluate without just stating the disadvantage?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
How to Write a Good Economics Essay
Governor November 28, 2019 Real World Applications 3 Comments
Many students ask “How to write an economics essay?” This Guide to Writing a Good Economics Essay is applicable to both IB economics as well as the Singapore JC A-Level H2 economics examinations. Many of the pointers here are also applicable to large-mark case study questions.
6 Steps to Writing a Good Economics Essay
Step 1: dissect the question.
Make sure you analyse and fully understand the KEYWORDS and REQUIREMENTS of the question. This is a very important skill that is taught in our economics tuition classes .
For example, “Best”, “Most Effective” are closely related but mean different things.
Paraphrase the question to make it simpler if necessary.
Take note of the command word (eg: Explain, Discuss) as it determines the approach needed for the essay, for example, whether two sides are needed or one side is sufficient. Below are some common examples found in economics essay questions:
Command Words Action Required
Account for Explain why
Analyse Break it down into step-by-step explanations
Assess For & Against. Consider other factors.
Compare Identify Similarities & Differences
Distinguish Point out differences
Discuss Explore both sides
Evaluate The Good and The Bad.
Explain Show why and how
Explain whether Cover both possibilities
Examine Look closely. How so and how not so?
To What Extent Yes…..But….Judgment
Remember to look out for the context in the question. This is usually given in the form of a country (eg: Singapore). The examples in your essay must be tailored to this particular context (for example, do not suggest interest rate policy for Singapore as that is considered infeasible in the Singapore context). If no context is given, any real-world example can be used.
Keep in mind the question throughout the essay and remember to always answer the question. Don’t go off-point!
Common Examiner’s Comment : Not Answering Question (NAQ))
Step 2: Plan Your Answer
Take some time to consider what economic framework you will use to approach the question. Scribble down your main thesis and anti-thesis points. Ensure they ANSWER THE QUESTION.
Step 3: Essay Introduction
In the introduction, include definitions of keywords in the question and spell out the economic framework you will employ for your answer as well as key definitions.

Step 4: Body of Essay
In the body , there will be several paragraphs.
The number of points/paragraphs depends on the question. It is common to require 2 main points for each 10 mark essay and similarly for 15 mark essay questions. Under each main point, there may be 1-2 sub-points.
Use one paragraph for each sub-point you are making.
However, do not be too focussed on the number of points or paragraphs. The key is to answer the question.
For each body paragraph , use TET’s PEEL(ED) structure. Include only one main idea per paragraph.
- Point – Write your point in the first sentence so that markers will know what the paragraph will be about. The topic sentence must directly answer the question!
- Explanation – Explain what you mean
- Elaboration – Provide further analysis with clear step-by-step economic reasoning. This part may be done with examples as well as diagrams.
- Link – Link your explanations back to the Point and to answer the question.
- Exemplification – Give an example to support your reasoning. It can be statistics or real-world examples (for Case Studies, evidences from the Case must be uncovered!)
- Diagram – Where possible, araw an appropriate diagram with correct labelling and refer to it in your answer. This is crucial to show economic reasoning. Diagrams are very important for economics essays!
These are of course much easier said than done! Thus, students in our economics tuition classes are regularly honed to achieve such output including with tips and tricks to spark off the correct thinking process.
Our resources including the Study Guides for A Level and IB economics also provide a very powerful and handy reference on the depth of analysis required to score the highest marks.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Mere statements and claims. No economic rigour.
Step 5: In-Body Evaluation
This applies especially to the 15 mark essays for A-Level Economics. A total of 5 marks is catered for Evaluation. Students should attempt to achieve about 2-3 in-body evaluation marks by pointing out how the thesis and anti-thesis points may not be true due to certain assumptions made that may not hold. Students may write “However,….may not necessarily happen……It would depend on whether….”. This statement can be written after the associated sub-point has been made.
Step 6: CONCLUDING SECTION
This only applies to the 15 mark essay questions.
Earn more evaluation marks by making a reasoned judgement. Deliver your verdict like a Judge!
Check back on the question before you embark on this. Ensure your judgement answers the question.
So the question now is, how does a judge arrive at and deliver a verdict? Certainly, you should not be summarising or merely paraphrasing your main points in the conclusion. Obviously, you cannot expect more marks by saying the same thing over and over again!
After a verdict and reasons have been provided, consider providing further relevant insights and/or recommendations.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Repetitive. Mere Summary.
Here are some quite common types of Concluding Sections
- Consider the relative importance of thesis and anti-thesis factors. Which factors are most important or pertinent in the given context? For example, certain policies better fit specifc types of economies.
- Consider short-term vs long-term pros and cons. Do the short-term benefits outweigh the long-term costs? Is the policy more effective in the long-term, and if so, how pressing is the problem that needs to be addressed?
- Suggest a multi-policy approach, in which each policy has strengths and weaknesses that allow them to complement each other.
There is no way to really memorise evaluation points as every question and context is different. After all, you are being tested on higher-order thinking!
There are other evaluation tips that our students will receive but the key point here is that the training of the mind to think and apply economics is essential. That is where our weekly economics lessons come into play and that is why our students are often asked questions in class and trained to think on their feet. As ex-student Xue Min from YIJC testified, Chief Tutor Mr. Kelvin Hong does not just spoon-feeds our students but mentors them in their thinking to arrive at the answers. This was different from other tutors that her classmates experienced and eventually this was the key to Xue Min’s A grade.
In your essay, write in simple and clear sentences. Everything you write should be value-adding. You do not have to spend time showing off vocabulary as no extra points are awarded for language. Focus on economic reasoning. Use succinct and effective examples which support the point you are trying to make as well as accurate diagrammatic analyses.
For samples of great economics essays, please check out our free Economics Model Essays and sample Past JC A-Level Economics Questions and Answers .
For our econs publications that are sold worldwide, please check out our A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays Publications
About The Economics Tutor
Founded by Kelvin Hong in 1998, The Economics Tutor is one of the leading economics tuition in Singapore. We provide a comprehensive program to guide students in understanding complex economic concepts and applying them through case study analyses, essay writing and discussion of real world events.
For 24 years, the way we teach JC Economics Tuition (A Level Economics Tuition) and IB Economics Tuition classes helped learners appreciate economics and everything it entails on a much larger scale. We take things step-by-step, implement effective techniques in memorising frameworks and give every student the chance to nurture their ideas.
We don’t just solely focus on helping you get stellar grades and perfect scores. We make sure that we also hone the critical thinking skills and investment / business decisions you can use outside the four walls of your classroom.
Looking for a fun, engaging and probably the best economics tutor in Singapore? Look no further—check out our extensive and high quality economics resources on the website such as our IB and A Level Economics Publication. Click here to order .
Book your lesson today and master the nuances of economics in our next class!
its good knowledgeable post regarding ib economics commentaries. i just wanted to admin can i use your blog as reference to my students .
Go ahead. We are all for helping students learn economics well.
Thank you, A lot of info!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
See You In Our Next Econs Lesson!
5.0 stars out of 130 G o o g l e reviews
#1 Economics Tuition Singapore – Kelvin Hong - The Economics Tutor
- +65 9336 7511
- [email protected]
- About JC A Level Economics
- About IB Economics
- Testimonials
- A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays
- Blog Resources
- Economics Videos
- Economics Notes, Infographics & Mindmaps
- Real-World Examples
- Economics Definitions
- Past A Level Economics Questions & Answers
- Fees & Schedule
- Register / Schedule a Class
- Bishan Economics Tuition
Copyright © 2024 The Economics Tutor

How to Tackle 15 Mark Questions in IB Economics (Paper 1 and 2)

International Baccalaureate (IB) economics is a challenging subject that requires a deep understanding of economic concepts, theories, and models. In paper 1 and 2, there are a variety of question types, but the 15 mark questions are considered to be the most challenging. These questions usually require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world situations, to explain, analyze, or evaluate a specific economic issue.
Here are some tips and strategies to help you tackle 15 mark questions in IB economics:
1. Read the question carefully: Before you start writing, make sure you understand the question and what is being asked. Break down the question into smaller parts and identify the key words, concepts, and theories that you need to use in your answer.
2. Plan your answer: Once you understand the question, take a few minutes to plan your answer. Identify the main points you want to make, the economic concepts and theories you need to use, and the evidence you need to support your argument.
3. Use a structured approach: When writing your answer, use a structured approach to ensure that your answer is clear, organized, and well-supported. Start with an introduction that sets the context and provides a brief overview of your answer. Follow this with several body paragraphs, each addressing a different aspect of the question. Finally, conclude your answer by summarizing your main points and providing a clear conclusion.
4. Use examples: Use real-world examples to illustrate and support your points. This will not only help you to better understand the concepts, but also help you to engage the reader and make your answer more interesting and relevant.
5. Apply economic concepts and theories: Use the economic concepts and theories you have learned to analyze and evaluate the issue being discussed in the question. Make sure you apply the concepts and theories correctly and explain how they relate to the issue at hand.
6. Evaluate: 15 mark questions often require you to evaluate a specific issue or policy. When evaluating, consider both the positive and negative effects, and provide evidence to support your argument.
7. Write legibly and neatly: Finally, make sure your answer is legible and well-organized. Write in clear, concise sentences and use headings and subheadings to make your answer easy to follow.
In conclusion, 15 mark questions in IB economics can be challenging, but with careful preparation and the right approach, they can also be some of the most rewarding questions in the exam. By following the tips and strategies outlined above, you can improve your chances of success and achieve the grades you deserve.
Recent Posts
Breaking Down the IB Economics SL Syllabus
Current IB Math vs Old IB Math
IB Math AI: A Guide to the Syllabus
Comentários
IA, EE & TOK
Trial lesson
Work with us
For You Education 慧理教育
Tel: +852 2480 1000
Email: [email protected]
Administration and Teaching Centre: 7/F, Catic Plaza, 8 Causeway Road, Causeway Bay, Hong Kong
School Registration Number: 605492
Teaching Centre:
Room 2, 21/F, Wealth Commercial Centre, 48 Kwong Wa Street, Kowloon
© Copyright. For You Education Limited . All Rights Reserved.
Up: Home : Study Guidance > Effective Writing and Referencing > Structuring an Essay
- Structuring an Essay
The standard way to think about structuring an essay is in three parts.
Introduction
This should explain why the question is important. It should also signpost how you are going to tackle the question in the main body of the essay and it can include the conclusion of your argument.
The introduction should be short and concise – you rarely get any marks for it directly. Most students spend too long on their introductions, at the expense of their analysis and conclusion (especially in exam questions).
This should be a series of paragraphs. Each might be a self-contained argument (which follows the Thesis – Justification – Support rhetoric) or the argument might be spread over several paragraphs (if your justification is long, for example).
It is important to make sure your paragraphs flow logically. Typically they will be ordered in terms of importance, although other orderings are possible (e.g. chronological).
This should restate your main argument (although not in exactly the same words as the introduction). You can remind readers why the issue is important, and make some tentative policy implications from your analysis.
It might also be possible to mention other considerations which are possible areas of future investigation but which you haven’t had time/space to address.
See Bray et al . for more about structure.
Previous: What makes good support?
Next: Referencing
Share this page: Email , Facebook , LinkedIn , Twitter
- Note Taking in Economics
- Effective Economics Reading
- Data Collection for Economics Assignments
- Writing the Economics Essay
- What makes good justification?
- What makes good support?
- Referencing
- Presentation and Group Work
- Revision for an Economics Exam
- Maths Help for Economics Students
Published by The Economics Network at the University of Bristol . All rights reserved. Feedback: [email protected] Supported by the Royal Economic Society and the Scottish Economic Society
Writing for Economics
Up: Economics Network > Writing for Economics
Essay writing
The idea of setting essays is to offer you the chance to make a longer, more complex argument. Nonetheless, in the model we recommend, the fundamentals remain the same. In each paragraph, a flow of main idea (thesis) — explanation / reasoning (justification) — evidence / example (support) is an excellent structure to use. If you read through academic writing, you will find this structure over and over. The same is true for professional writing. There are of course other structures, however this one always works and makes you sound concise and clear.
An essay has conventional sections that it is wise to follow. These are an introduction, main body and a conclusion. The 'LSE' essay structure can be described as 'say what you're going to say (intro), say it in detail (main body), say what you've said (conclusion)'. Although this may appear repetitive, it offers the reader great clarity. Also, if you think about the executive summary, background, analysis and conclusions / recommendations sections of a business report, you can see that a similar structure holds.
In your essay, try to follow this structure for your essay sections.
Statement about the context of the question — explain why the question in important (either in the 'real' world or for the discipline of economics)
Give your answer to the question
Summarise your argument in support of this answer — this summary should match the order of your paragraphs
Decide on the most logical order of your paragraphs — this might be importance, chronology or causation, but the basic flow should be simple and clear
Start each paragraph with a sentence that clearly addresses the question itself — this will be your thesis for the paragraph and if a reader only read these opening sentences, they should make sense one after the other and provide a summary of your argument Follow the opening 'topic' sentence with your reasoning and evidence for why this opening statement is valid. Be specific, not general. The more detail you can bring in, the more expert you will sound and the more persuasive your argument will be
Conclusion Summarise your argument again — as you did in the intro (different words though!)
Restate your answer to the essay question
So what? — say what the significance of your answer is either in the 'real' world or to the discipline of economics
Bibliography
List the books / articles you read while researching your answer
Below you'll find two essays written by students last year. Bearing the above in mind, decide which one makes the clearer argument and which, therefore, got the higher mark.
In the year 2000, there were auctions of spectrum rights for third generation mobile telephones in several European countries. These auctions generated very different amount of revenue in different countries. How can this be explained?
Auction theory as a very useful brunch of game theory is of the great interest of modern economists. Among other reasons of its popularity stands direct importance of its ideas to modern businesses and governments. Nowadays any business sector is more or less competitive, which requires all it's participants to be dynamic and creative. Modernization and expansion is a vital part of modern business world. Governments, as owners of resources that allow businesses to expand and modernize, are always ready to sell those resources as it will eventually help businesses and certainly bring revenues.
The best way for government to sell available resources is to declare an auction. That's where auction theory comes into play. Modern auction theory is a very powerful tool for designing auctions of very profitable kind. Proper auction design will rise maximum amount of money for the government and provide companies with resources they need. However actions that maximize profits for the government have a direct influence also on the life of the citizens, as Dixit puts it: "...because of significant contributions the budget, auctions affect important macroeconomic magnitudes, such as interest rates".
So, auctions held by government, and to be more specific properly designed actions directly influence the life of modern country. In this essay I would like to make a kind of short review of auctions of spectrum rights for third generation mobile phones held in Europe in year 2000. The peculiarity of these auctions lies in the fact that revenues that were generated by European governments are different as a result of differently designed actions they held. This fact allows as to trace features of the auctions that were successful and resulted in relatively high revenues for the government.
There were 6 European countries to held spectrum right auctions in 2000. They were: United Kingdom, Austria, Germany, Italy, Netherlands and Switzerland. Let's start with United Kingdom as it was the first country to hold such kind of auctions.
Strategy that United Kingdom had chosen was selling 5 licenses during classical ascending auction. Auction resulted in huge revenues: 650 euros per capita. Firstly it should be said that auctions as any normal business activity should be competitive in order to be effective. UK spectrum auction was relatively competitive attracting 13 participants. There are several reasons why this action attracted so many participants. Firstly, UK was the first country in the world to hold spectrum rights auction. Participants were not completely aware of the usefulness of 3G cell phones, but were eager to get competitive advantage in the new generation mobile communication technology. Secondly, UK sold 5 licenses to the market with 4 major phone operators. This fact attracted new entrants, since at least one of the licenses can be potentially won by new entrants to the market. Both this facts generated highly competitive auction environment and limited possible collusions. Result of the auction was a huge success for UK government.
The next country to run spectrum rights auction in 2000 was Netherlands. This auction raised 170 euros per capita. Reason of such flop, comparing to the British result was lack of competition. When auction were run there were 5 major phone operators for 5 licenses to be sold. Few entrants decided to participate in the auction, since everybody was sure that 5 licenses will be distributed among market leaders. Another factor that made things even worse was the fact that that was an ascending auction. In this case with few participants there is a risk of collusion among market leaders. Netherlands would have generated much more money if they would some how encourage competition and change the action design in such a way that it would be possible for participants other than market leaders to place bids independently of each other to reduce collusion (sealed bid).
Italy generated 240 euros per capita and attracted 6 participants. Italy intentionally reduced amount of participants by imposing a requirements that participant of the auction must satisfy. Such situation combined with the fact that Italian auction was ascending could result in possible collusions among competitors. As a result wrong auction design resulted in low revenues.
Swiss auction was a real flop. They generated only 20 euros per capita. Here amount of participants was also artificially limited by allowing participants to join into the groups. And the price that government accepts was also reduced for some reason. Number of participants was sufficient to run profitable auction, but combination of officially permitted collusions and low reserve price resulted in absolutely insufficient revenues.
German and Austrian auctions were similar. Number of participants in both countries' auctions was low, which means that there were risks of collusion. Both countries sold licenses in blocks, allowing "number of winners be determined by bidders". Additionally Austrian government set a very low reserve price. Germany and Austria generated 615 and 100 euros per capita in revenue respectively. Germany designed auction in such a way that bids of two main market players were rationalized in a way that it resulted in high revenues.
Generally, the main difference in revenues generated from spectrum rights auctions can be explained by the difference in chosen auction design. Different auction design results in different amounts of money in revenues. Countries that tried to facilitate competitive bidding and limited the possibilities of collusion enjoyed high revenues.
Klemperer say that what really matters in auction design is "robustness against collusion and attractiveness to entry". Exactly the combination or lack of one of this factors resulted in the difference in the revenues generated by European countries. Any country that wants to increase revenues from auction must try to facilitate the competition among bidders by trying to make participation in auction as attractive as possible and eliminating any barriers for participation. There should be no cooperation between participants, as it will result in lower bids and as a consequence in low revenues. Countries should not choose auction design that facilitates collusion, as ascending auction in our case.
Of course there are several other reasons for difference in revenues, among them there is a fact that UK as a country that run the first spectrum rights auction in the world, might have enjoyed high revenues simply because participants were new to the licenses and had no idea of their true value. Overall economic situations in the counties as well as political might also result in differences in revenues. But the main reason for difference in profitability of the spectrum licenses auctions is difference in auction designs which were effective in some countries and not in the others.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
A.K. Dixit and S. Skeath, Games of Strategy , 2nd edition, Norton, 2004
Paul Klemperer, Auctions: Theory and Practice Electronic version of book on http://www.paulklemperer.org/index.htm
In the year 2000, European auctions of 3G mobile telecommunication licenses raised over 100 billion euros in government revenues. The countries that participated were United Kingdom, Netherlands, Italy, Switzerland, Germany and Austria. There was a big differential between revenues raised in each country with United Kingdom leading at 650 euros per capita and Switzerland coming in last at 20 euros per capita. The reasons for this big discrepancy in revenues is likely due to poor auction designs and the sequence in which the auctions took place.
When it comes to auction design, the two crucial components are attracting entry and preventing collusion. Ascending auctions encourage bidders to act collusively and deter weaker potential bidders as they know that the stronger bidder will always out bid him. On the other hand, (first-price) sealed-bid auctions act in the opposite direction from ascending auctions. It does not give bidders a chance to collude and encourages weaker bidders to participate. However, the disadvantage of using a sealed-bid auction is that it is more likely to lead to inefficient results than an ascending auction. The reason for this is that sometimes bidders with a lower value may beat opponents with a higher value. Hence, there is no perfect auction design and they must be customized to suit different environments and targets.
United Kingdom was the first to hold the auctions and they are a good example of how a well-planned auction design and good marketing strategies can lead to a favourable outcome. As there were five licenses and 4 incumbents, they had an ascending auction. To prevent collusion, each license could not be shared and each bidder was allowed no more than one license. Also, the fact that at least one license was available to new entrants lead to fierce competition from nine new entrants. To top it all off, UK had a solid marketing strategy which was planned over three years (1997 - 2000). All this helped contribute to UK raising 39 billion euros and being the most successful out of all the countries that took part in the 3G auctions.
Netherlands, Italy and Switzerland made the mistake of following UK and carrying out an ascending auction when a sealed-bid auction would have served them better. This resulted in revenues less than that achieved by UK.
In the case of Netherlands, they had five licenses and five incumbents. This deterred new entrants as well as facilitated collusion. For example, Deutsche Telekom colluded with local incumbents to bid for a 3G license. A sealed-bid would have worked better as this would have discouraged joint bidding, raise higher revenues as well as give new entrants a glimmer of hope.
Italy had their auction next but failed to learn from Netherlands and UK. Their auction design was not robust and failed to adapt to the environment in Italy. They adopted the UK design but had the additional rule that if bidders did not exceed licenses, the number of licenses would be reduced. They did not realize that having one more bidder than license does not assure that the outcome will be competitive. Also, Italy had failed to anticipate that firms would react differently to those in Netherlands and UK as they now had more information. Hence, weaker bidders were discouraged by previous auctions and did not bother to participate and since the participation rate was low, it made it easier for the strong bidders to collude. A bad auction design that was not tailored to the Italian environment and a low reserve price resulted in Italy only earning less than 25 billion euros.
Switzerland was the most unsuccessful amongst all the countries that held the auctions. It raised only 20 euros per capita in its ascending auction and this can be attributed to an unfeasible auction design, badly formulated rules and an absurdly low reserve price. Since the beginning, weaker bidders were deterred by the auction form. They felt that they did not stand a chance against the strong bidders and hence did not bother participating. This resulted in little competition. Furthermore, The Swiss government committed auction suicide when they permitted last-minute joint-bidding! This resulted in nine bidders colluding to become just four. The last mistake that the Swiss government made was to set a reserve price that was way too low. Since there were four licenses and four bidders, bidders ended up paying only the reserve price.
Germany and Austria chose a more complicated auction design.
Germany's auction design was an ascending auction of twelve blocks of spectrum from which bidders could create four three-block licenses or six two-block licenses. Germany's auction design was very susceptible to collusion and deterring new entrants but they were lucky and managed to earn high revenues.
Austria, on the other hand, adopted Germany's auction design but was not so lucky and only earned 100 euros per capita. The reason for this was that there were 6 bidders competing for 12 blocks of spectrum and a very low reserve price (one-eight of the reserve price in Germany). So instead of trying to get three blocks of spectrum, the bidders divided the 12 blocks of spectrum equally and paid the reserve price. This reason lead to Austria earning less per capita revenue than UK and Germany.
The other factor that affected the amount of revenue earned by each country was the sequence in which the auctions took place. Looking at the results of the 3G auctions held in 2000, it can be seen that the most successful auctions were the first of their type (United Kingdom and Germany). The reason for this is that between auctions, bidders learnt from previous auctions, came up with new strategies and learnt more about their rivals. However, the auction designs remained almost the same and were unable to keep up with the new ideas the bidders had come up with. This resulted in the later auctions not being as successful as the first.
In conclusion, the reason for the different revenues earned amongst the countries that took part in the 3G auctions is due to the auction designs and the sequence in which they took place. Revenues depend on how well the auction design is able to attract entry and prevent collusion. Also, it has to be able to adapt to new environments. For example, a good auction design takes into account the information bidders have and the knowledge they have gained from previous auctions. A sensible reserve price is of high importance as well and should not be overlooked like in the case of Switzerland and Germany. Lastly, auction design is not "one size fits all" and the failure of the government to design an auction that suited the country's environment lead to different revenues being earned.
References:
A.K. Dixit and S.Skeath, Games of Strategy, 2 nd edition, Norton, 2004
Professor Kenneth Binmore, "Economic Theory Sometimes Works"
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

AQA Economics 9 and 15 mark student structure sheet
Subject: Economics
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Assessment and revision
Last updated
1 April 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A step by step, tried and tested structure for students to follow to complete 9 mark and 15 mark exam questions. This has been designed for AQA A-level Economics paper 1 and paper 2. As a regular examiner of Paper 1, I have refined this resource to ensure it allows students to achieve maximum marks on these questions.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema. Learn more →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Economics news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Economics Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
- Practice Exam Questions
External Debt Relief - 15 Mark Revision Essay (EdExcel)
Last updated 14 Mar 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Here is a suggested answer to a 15 mark question on external debt relief designed for those taking assessments for the EdExcel specification.
- Debt Relief
You might also like

Defaults today mean less jam tomorrow
25th July 2013
Overseas Aid and Economic Development
Study Notes
External Debt Relief
Aid & development - revision presentation.
Teaching PowerPoints
Debt Relief for Poorer Countries - Revision Presentation

GDP Bonds and Greek Debt
12th March 2015
Does debt relief help economies grow?
29th June 2015
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to structure a 15 mark answer. To my students, I usually recommend three points (but you can also do two points if each point is more detailed). You can also start with a few key definitions. For each point, complete a chain of analysis. Add some data to show real-world application. You do not need evaluation in a 15 mark question for AQA.
The IB Economics Paper 1 Essay Structure. In the new syllabus (May 2022 exams onward) and get to choose 1 out of 3 questions, chosen from any of the 4 units. Paper 1 is worth 20% of your final for HL students and 30% for SL students. You'll get get 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes).
Model 15-Markers. Unlock your potential with these IB economics model answers, designed to provide a deeper understanding of key topics and real-world examples. By studying these model answers, you'll gain a solid foundation in economic concepts, learn how to structure your essays effectively, and develop critical analysis skills.
15 Marker - Paper 1 & 2 - Edexcel A Level EconomicsInstagram: @econplusdalTwitter: https://twitter.com/econplusdalFacebook: https://www.facebook.com/Econplus...
Some tips for writing economics essays Includes how to answer the question, including right diagrams and evaluation - primarily designed for A Level students. 1. Understand the question. Make sure you understand the essential point of the question. If appropriate, you could try and rephrase the question into a simpler version.
IB Economics Paper 1 & 2 - 15 Marker Question - Exam Technique. IB Economics Paper 1 & 2 - 15 Marker Question - Exam Techniquehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v...
No economic rigour. Step 5: In-Body Evaluation. This applies especially to the 15 mark essays for A-Level Economics. A total of 5 marks is catered for Evaluation. Students should attempt to achieve about 2-3 in-body evaluation marks by pointing out how the thesis and anti-thesis points may not be true due to certain assumptions made that may ...
9 & 15 Marker - Paper 1 & 2 - AQA A Level EconomicsInstagram: @econplusdalTwitter: https://twitter.com/econplusdalFacebook: https://www.facebook.com/Econplus...
Economics Revision Essay Plans. This series of resources provides revision essay plans for a wide variety of essay topics, including synoptic questions. For the 2019 papers check out our collection of videos on building A* evaluation into your answers. Have you tried our series of more than 50 Quizlet revision activities?
6. Evaluate: 15 mark questions often require you to evaluate a specific issue or policy. When evaluating, consider both the positive and negative effects, and provide evidence to support your argument. 7. Write legibly and neatly: Finally, make sure your answer is legible and well-organized. Write in clear, concise sentences and use headings ...
Part b) - 25min. Essay 2 : 45 min (essentially the same as above) 1. Planning - 5min. 2. Part a) - 15min. 3. Part b) - 25min. During the stage of planning, that's where you need to highlight the keywords of the essay, try and frame out the entire essay within your head.
Introduction. This should explain why the question is important. It should also signpost how you are going to tackle the question in the main body of the essay and it can include the conclusion of your argument. The introduction should be short and concise - you rarely get any marks for it directly. Most students spend too long on their ...
Essay writing. The idea of setting essays is to offer you the chance to make a longer, more complex argument. Nonetheless, in the model we recommend, the fundamentals remain the same. In each paragraph, a flow of main idea (thesis) — explanation / reasoning (justification) — evidence / example (support) is an excellent structure to use.
Digital Monopolies - 15 Mark Revision Essay (EdExcel) Level: A-Level. Board: Edexcel. Last updated 14 Mar 2021. Share : Here is a suggested answer to this 15-mark question: Using the extracts and your own knowledge, assess the view that the dominance of digital businesses such as Google, Facebook and others is harmful to economic welfare.
15 Mark GCSE Economics Exam Question Structure. I have attached a structure for a 15 mark answer for the new AQA (9-1) GCSE Economics Specification that I am using with my students. I found there was little support online from AQA in regards of how to write a 15 mark question on the new specification so I hope it will prove somewhat useful.
A step by step, tried and tested structure for students to follow to complete 9 mark and 15 mark exam questions. This has been designed for AQA A-level Economics paper 1 and paper 2. As a regular examiner of Paper 1, I have refined this resource to ensure it allows students to achieve maximum marks on these questions.
External Debt Relief - 15 Mark Revision Essay (EdExcel) Level: A-Level. Board: Edexcel. Last updated 14 Mar 2021. Share : Here is a suggested answer to a 15 mark question on external debt relief designed for those taking assessments for the EdExcel specification.
A-Level Economics 15/25 marker structure. A. username4241818. I got a C in my Economics year 13 mock, bearing in mind there were a few reasons why this may have happened, this result has made me determined to improve as it is well off my aim of an A. I wanted to know what structure you would advise for use in the 15 and 25 mark essay questions ...