- How to Prepare for Law School
- How to brief a case
- E-mail This Page
- Print This Page

How to write a case brief for law school: Excerpt reproduced from Introduction to the Study of Law: Cases and Materials ,
Third edition (lexisnexis 2009) by michael makdisi & john makdisi.
C. HOW TO BRIEF
The previous section described the parts of a case in order to make it easier to read and identify the pertinent information that you will use to create your briefs. This section will describe the parts of a brief in order to give you an idea about what a brief is, what is helpful to include in a brief, and what purpose it serves. Case briefs are a necessary study aid in law school that helps to encapsulate and analyze the mountainous mass of material that law students must digest. The case brief represents a final product after reading a case, rereading it, taking it apart, and putting it back together again. In addition to its function as a tool for self-instruction and referencing, the case brief also provides a valuable “cheat sheet” for class participation.
Who will read your brief? Most professors will espouse the value of briefing but will never ask to see that you have, in fact, briefed. As a practicing lawyer, your client doesn’t care if you brief, so long as you win the case. The judges certainly don’t care if you brief, so long as you competently practice the law. You are the person that the brief will serve! Keep this in mind when deciding what elements to include as part of your brief and when deciding what information to include under those elements.
What are the elements of a brief? Different people will tell you to include different things in your brief. Most likely, upon entering law school, this will happen with one or more of your instructors. While opinions may vary, four elements that are essential to any useful brief are the following:
(a) Facts (name of the case and its parties, what happened factually and procedurally, and the judgment)
(b) Issues (what is in dispute)
(c) Holding (the applied rule of law)
(d) Rationale (reasons for the holding)
If you include nothing but these four elements, you should have everything you need in order to recall effectively the information from the case during class or several months later when studying for exams.
Because briefs are made for yourself, you may want to include other elements that expand the four elements listed above. Depending on the case, the inclusion of additional elements may be useful. For example, a case that has a long and important section expounding dicta might call for a separate section in your brief labeled: Dicta. Whatever elements you decide to include, however, remember that the brief is a tool intended for personal use. To the extent that more elements will help with organization and use of the brief, include them. On the other hand, if you find that having more elements makes your brief cumbersome and hard to use, cut back on the number of elements. At a minimum, however, make sure you include the four elements listed above.
Elements that you may want to consider including in addition to the four basic elements are:
(e) Dicta (commentary about the decision that was not the basis for the decision)
(f) Dissent (if a valuable dissenting opinion exits, the dissent’s opinion)
(g) Party’s Arguments (each party’s opposing argument concerning the ultimate issue)
(h) Comments (personal commentary)
Personal comments can be useful if you have a thought that does not fit elsewhere. In the personal experience of one of the authors, this element was used to label cases as specific kinds (e.g., as a case of vicarious liability) or make mental notes about what he found peculiar or puzzling about cases. This element allowed him to release his thoughts (without losing them) so that he could move on to other cases.
In addition to these elements, it may help you to organize your thoughts, as some people do, by dividing Facts into separate elements:
(1) Facts of the case (what actually happened, the controversy)
(2) Procedural History (what events within the court system led to the present case)
(3) Judgment (what the court actually decided)
Procedural History is usually minimal and most of the time irrelevant to the ultimate importance of a case; however, this is not always true. One subject in which Procedure History is virtually always relevant is Civil Procedure.
When describing the Judgment of the case, distinguish it from the Holding. The Judgment is the factual determination by the court, in favor of one party, such as “affirmed,” “reversed,” or “remanded.” In contrast, the Holding is the applied rule of law that serves as the basis for the ultimate judgment.
Remember that the purpose of a brief is to remind you of the important details that make the case significant in terms of the law. It will be a reference tool when you are drilled by a professor and will be a study aid when you prepare for exams. A brief is also like a puzzle piece.
The elements of the brief create the unique shape and colors of the piece, and, when combined with other pieces, the picture of the common law takes form. A well-constructed brief will save you lots of time by removing the need to return to the case to remember the important details and also by making it easier to put together the pieces of the common law puzzle.
D. EXTRACTING THE RELEVANT INFORMATION: ANNOTATING AND HIGHLIGHTING
So now that you know the basic elements of a brief, what information is important to include under each element? The simple answer is: whatever is relevant. But what parts of a case are relevant? When you read your first few cases, you may think that everything that the judge said was relevant to his ultimate conclusion. Even if this were true, what is relevant for the judge to make his decision is not always relevant for you to include in your brief. Remember, the reason to make a brief is not to persuade the world that the ultimate decision in the case is a sound one, but rather to aid in refreshing your memory concerning the most important parts of the case.
What facts are relevant to include in a brief? You should include the facts that are necessary to remind you of the story. If you forget the story, you will not remember how the law in the case was applied. You should also include the facts that are dispositive to the decision in the case. For instance, if the fact that a car is white is a determining factor in the case, the brief should note that the case involves a white car and not simply a car. To the extent that the procedural history either helps you to remember the case or plays an important role in the ultimate outcome, you should include these facts as well.
What issues and conclusions are relevant to include in a brief? There is usually one main issue on which the court rests its decision. This may seem simple, but the court may talk about multiple issues, and may discuss multiple arguments from both sides of the case. Be sure to distinguish the issues from the arguments made by the parties. The relevant issue or issues, and corresponding conclusions, are the ones for which the court made a final decision and which are binding. The court may discuss intermediate conclusions or issues, but stay focused on the main issue and conclusion which binds future courts.
What rationale is important to include in a brief? This is probably the most difficult aspect of the case to determine. Remember that everything that is discussed may have been relevant to the judge, but it is not necessarily relevant to the rationale of the decision. The goal is to remind yourself of the basic reasoning that the court used to come to its decision and the key factors that made the decision favor one side or the other.
A brief should be brief! Overly long or cumbersome briefs are not very helpful because you will not be able to skim them easily when you review your notes or when the professor drills you. On the other hand, a brief that is too short will be equally unhelpful because it lacks sufficient information to refresh your memory. Try to keep your briefs to one page in length. This will make it easy for you to organize and reference them.
Do not get discouraged. Learning to brief and figuring out exactly what to include will take time and practice. The more you brief, the easier it will become to extract the relevant information.
While a brief is an extremely helpful and important study aid, annotating and highlighting are other tools for breaking down the mass of material in your casebook. The remainder of this section will discuss these different techniques and show how they complement and enhance the briefing process.
Annotating Cases
Many of you probably already read with a pencil or pen, but if you do not, now is the time to get in the habit. Cases are so dense and full of information that you will find yourself spending considerable amounts of time rereading cases to find what you need. An effective way to reduce this time is to annotate the margins of the casebook. Your pencil (or pen) will be one of your best friends while reading a case. It will allow you to mark off the different sections (such as facts, procedural history, or conclusions), thus allowing you to clear your mind of thoughts and providing an invaluable resource when briefing and reviewing.
You might be wondering why annotating is important if you make an adequate, well-constructed brief. By their very nature briefs cannot cover everything in a case. Even with a thorough, well-constructed brief you may want to reference the original case in order to reread dicta that might not have seemed important at the time, to review the complete procedural history or set of facts, or to scour the rationale for a better understanding of the case; annotating makes these tasks easier. Whether you return to a case after a few hours or a few months, annotations will swiftly guide you to the pertinent parts of the case by providing a roadmap of the important sections. Your textual markings and margin notes will refresh your memory and restore specific thoughts you might have had about either the case in general or an individual passage.
Annotations will also remind you of forgotten thoughts and random ideas by providing a medium for personal comments.
In addition to making it easier to review an original case, annotating cases during the first review of a case makes the briefing process easier. With adequate annotations, the important details needed for your brief will be much easier to retrieve. Without annotations, you will likely have difficulty locating the information you seek even in the short cases. It might seem strange that it would be hard to reference a short case, but even a short case will likely take you at least fifteen to twenty-five minutes to read, while longer cases may take as much as thirty minutes to an hour to complete. No matter how long it takes, the dense material of all cases makes it difficult to remember all your thoughts, and trying to locate specific sections of the analysis may feel like you are trying to locate a needle in a haystack. An annotation in the margin, however, will not only swiftly guide you to a pertinent section, but will also refresh the thoughts that you had while reading that section.
When you read a case for the first time, read for the story and for a basic understanding of the dispute, the issues, the rationale, and the decision. As you hit these elements (or what you think are these elements) make a mark in the margins. Your markings can be as simple as “facts” (with a bracket that indicates the relevant part of the paragraph). When you spot an issue, you may simply mark “issue” or instead provide a synopsis in your own words. When a case sparks an idea — write that idea in the margin as well — you never know when a seemingly irrelevant idea might turn into something more.
Finally, when you spot a particularly important part of the text, underline it (or highlight it as described below).
With a basic understanding of the case, and with annotations in the margin, the second read-through of the case should be much easier. You can direct your reading to the most important sections and will have an easier time identifying what is and is not important. Continue rereading the case until you have identified all the relevant information that you need to make your brief, including the issue(s), the facts, the holding, and the relevant parts of the analysis.
Pencil or pen — which is better to use when annotating? Our recommendation is a mechanical pencil. Mechanical pencils make finer markings than regular pencils, and also than ballpoint pens. Although you might think a pencil might smear more than a pen, with its sharp point a mechanical pencil uses very little excess lead and will not smear as much as you might imagine. A mechanical pencil will also give you the freedom to make mistakes without consequences. When you first start annotating, you may think that some passages are more important than they really are, and therefore you may resist the urge to make a mark in order to preserve your book and prevent false guideposts. With a pencil, however, the ability to erase and rewrite removes this problem.
Highlighting
Why highlight? Like annotating, highlighting may seem unimportant if you create thorough, well-constructed briefs, but highlighting directly helps you to brief. It makes cases, especially the more complicated ones, easy to digest, review and use to extract information.
Highlighting takes advantage of colors to provide a uniquely effective method for reviewing and referencing a case. If you prefer a visual approach to learning, you may find highlighting to be a very effective tool.
If annotating and highlighting are so effective, why brief? Because the process of summarizing a case and putting it into your own words within a brief provides an understanding of the law and of the case that you cannot gain through the process of highlighting or annotating.
The process of putting the case into your own words forces you to digest the material, while annotating and highlighting can be accomplished in a much more passive manner.
What should you highlight? Similar to annotating, the best parts of the case to highlight are those that represent the needed information for your brief such as the facts, the issue, the holding and the rationale.
Unlike annotating, highlighting provides an effective way to color code, which makes referring to the case even easier. In addition, Highlighters are particularly useful in marking off entire sections by using brackets. These brackets will allow you to color-code the case without highlighting all the text, leaving the most important phrases untouched for a more detailed highlight marking or underlining.
Highlighting is a personal tool, and therefore should be used to the extent that highlighting helps, but should be modified in a way that makes it personally time efficient and beneficial. For instance, you might combine the use of annotations in the margins with the visual benefit of highlighting the relevant text. You may prefer to underline the relevant text with a pencil, but to use a highlighter to bracket off the different sections of a case. Whatever you choose to do, make sure that it works for you, regardless of what others recommend. The techniques in the remainder of this section will describe ways to make full use of your highlighters.
First, buy yourself a set of multi-colored highlighters, with at least four, or perhaps five or six different colors. Yellow, pink, and orange are usually the brightest. Depending on the brand, purple and green can be dark, but still work well. Although blue is a beautiful color, it tends to darken and hide the text.
Therefore we recommend that you save blue for the elements that you rarely highlight.
For each different section of the case, choose a color, and use that color only when highlighting the section of the case designated for that color. Consider using yellow for the text that you tend to highlight most frequently. Because yellow is the brightest, you may be inclined to use yellow for the Conclusions in order to make them stand out the most. If you do this, however, you will exhaust your other colors much faster than yellow and this will require that you purchase an entire set of new highlighters when a single color runs out because colors such as green are not sold separately. If instead you choose to use yellow on a more frequently highlighted section such as the Analysis, when it comes time to replace your yellow marker, you will need only to replace your yellow highlighter individually. In the personal experience on one of the authors, the sections of cases that seemed to demand the most highlighter attention were the
Facts and the Analysis, while the Issues and Holdings demanded the least. Other Considerations and
Procedural History required lots of highlighting in particular cases although not in every case.
Experiment if you must, but try to choose a color scheme early on in the semester and stick with it. That way, when you come back to the first cases of the semester, you will not be confused with multiple color schemes. The basic sections of a case for which you should consider giving a different color are:
Procedural History
Issue (and questions presented)
Holding (and conclusions)
Analysis (rationale)
Other Considerations (such as dicta)
Not all of these sections demand a separate color. You may find that combining Facts and Procedural History or Issues and Holdings works best. Furthermore, as mentioned above, some sections may not warrant highlighting in every case (e.g., dicta probably do not need to be highlighted unless they are particularly important). If you decide that a single color is all that you need, then stick to one, but if you find yourself highlighting lots of text from many different sections, reconsider the use of at least a few different colors. Highlighters make text stand out, but only when used appropriately. The use of many colors enables you to highlight more text without reducing the highlighter’s effectiveness. Three to four colors provides decent color variation without the cumbersomeness of handling too many markers.
Once you are comfortable with your color scheme, determining exactly what to highlight still may be difficult. Similar to knowing what to annotate, experience will perfect your highlighting skills. Be careful not to highlight everything, thus ruining your highlighters’ effectiveness; at the same time, do not be afraid to make mistakes.
Now that we have covered the basics of reading, annotating, highlighting, and briefing a case, you are ready to start practicing. Keep the tips and techniques mentioned in this chapter in mind when you tackle the four topics in the remainder of this book. If you have difficultly, refer back to this chapter to help guide you as you master the case method of study and the art of using the common law.
Have questions about law school? Check out our Facebook page , follow us on Twitter or start networking with law students and lawyers on LexTalk .
More Helpful Links
- The American Legal System
- How to Brief a Case
- How to Read a Casebook 101
- Top 20 Things You Need to Know About Law School
- Learn to Spot Issues Like a Lawyer
- Why an Internet Search is Not Legal Research
- Why go to Law School?
- What’s the Most Challenging Part of Law School?
- What advice would you give yourself about law school?

Get advice about law school from law students and legal professionals at the LexTalk legal community
Legal Research & Practical Guidance
Build your legal strategy and do vital work using authoritative primary law, analysis, guidance, court records and validation tools.
Search vast LexisNexis resources without selecting sources or using search commands.
Federal and state court dockets and documents for research, tracking, and profiling.
Practical Guidance
Current practical guidance from leading practitioners for managing transactional matters.
Lexis Securities Mosaic
Track and analyze SEC filings, U.S. agency information, industry news and current awareness.
News, Company Research & Media Monitoring Solutions
Quickly uncover up-to-date facts, news and insight essential to your decisions and business development.
LexisNexis Newsdesk
A fresh take on media monitoring & analysis to help you find the hidden gems that can impact your business.
Current, authoritative news, social media, company, financial and industry sources.
Media Intelligence Research & Analytics
Identify prospects and compile business profiles that help you close more deals.
Lexis Diligence
Corporate due diligence research tool.
- Intellectual Property
Stay up to speed with trends, track your competition, promote innovation and protect your intellectual assets.
TotalPatent One
The world's largest collection of full-text and bibliographic patent databases.
Patent Advisor
Predictive and revealing analytics for more efficient patent prosecution.
PatentOptimizer
Patent application drafting and analysis tools.
The CaseMap Suite of Litigation Tools
Comprised of four unique components, the CaseMap Suite can help you organize, analyze and present your entire case.
Compile relevant case facts, documents, research and issues into a centralized location for better assessment.
Manage litigation documents—share, search, review, produce, etc.—across your discovery team.
Quickly assemble your data and produce impactful timelines for pennies apiece.
See case presentations from a new angle with technology-driven Sanction software.
Practice & Legal Department Management
Address the business side of your legal activities with solutions to manage, track and analyze matters, finances, critical processes, relationships and performance.
CounselLink
A centralized repository for matter, e-billing and spend management.
Dashboards that display, track and manage your practice, clients and business tasks.
TimeMatters
Organize, associate and track case contacts, documents, events, phone calls, billing, etc.
InterAction
Comprehensive customer relationship management system for law firms.
Compliance & Due Diligence
Stay on top of regulatory and legislative changes, perform due diligence and manage compliance with ease, speed and confidence.
Customizable tools for tracking and reporting legislative and regulatory activity.
IntegraCheck | Integrity Due Diligence
In-depth due-diligence investigation reports.
Just for you Solutions & resources for your organization, department, role or individual work:
- Corporate Communications
- Information Professional
- Marketing & Competitive Intelligence
- Media Organizations
- Political Organizations
- Third-Party Due Diligence
- Sales & Business Development Professionals
- Strategy & Business Development Professionals
- Non-Profit Organizations
- Professional Services
- Technology Professionals
- Librarians & Information Professionals
- Paralegals & Legal Assistants
- Marketing Directors
- Law Department Management
- Litigation Management
- Tax Accounting
- View All »
- Faculty & Adminstration
- Public Libraries
- University & High School Students
- Law School Student Publications
- Portal Sign In
Browse by Industry
- Financial Services
- Health Care
- Life Sciences
- Manufacturing
- Retail & Sales
Browse by Department
- Corporate Compliance
- Corporate Counsel
- Procurement & Supply Chain
- Tax & Accounting
Visit the LexisNexis Store to purchase products that will assist you in your professional success Shop by :
- Jurisdiction
- Practice Area
- Banking Compliance
- Immigration
- Real Estate
- Workers' Comp
- Business Solutions
- Partner Products
- American Health Lawyers Association
- NITA: National Institute for Trial Advocacy
- The Florida Bar
Support & Training
Quick links.
- Lexis+ Support
- Lexis Support
- Nexis Support
- Practical Guidance Support
- CourtLink Support
- Lexis Securities Mosaic Support
- Digital Library Support
- LexTalk: Gain peer-to-peer, product support
- LexisNexis University
- Request Telephonic Training
- Support Center Resources
- Training on the Go
Communities & Blogs
Our Blogs and Communities feature a broad array of trending news and topics within socially interactive environments. Connect, explore and find the answers you need to further your goals.
- Blogs & Newsletters
- Blog Mosaic
- Business of Law Blog
- Corporate Law Advisory
- Legal Content Insider
- State Net Capitol Journal
- News & Trending Topics
- Legal Insights & Trends
- Practical Guidance Journal
- Professional Communities
- Business Insight Solutions – Partner Portal
- Corporate InfoPro (Corporate Information Professionals)
- InfoPro (Legal Information Professionals)
- LexisNexis for Developers
- Litigators Verdict & Settlement Exchange
Writing Effective Legal Case Briefs for Law Students
How to write a case brief, complete with examples.
tl;dr - Case briefs help your understanding of legal concepts and enable you to better prepare for exams. Here are some example case briefs .
As a new law student, one of the essential skills you need to develop is the ability to write effective legal case briefs. A case brief is a concise summary of a legal case that highlights the key issues, legal principles, and holdings of the court. Writing a good case brief can help you better understand the law, prepare for class discussions and exams, and become a more effective legal professional. In this article, we'll explore the key elements of a good legal case brief and provide some tips on how to write one effectively.
Legal case briefs are an essential tool for you as a law student, as they provide a concise and organized summary of a court case. Case brief examples serve as a means for you to understand the facts, issues, and legal principles underlying a court decision, and are crucial in helping you develop analytical and critical thinking skills.
One of the primary reasons why case briefs are important for you is that they help you understand the law in a practical and applied manner. In law school, you study legal principles and concepts in a theoretical sense. However, case briefs provide a means for you to see how these principles are applied in real-world situations. By analyzing and dissecting court decisions, you are able to gain a better understanding of how legal principles and concepts are applied in practice. For example, case brief examples of landmark cases like Marbury v. Madison or Brown v. Board of Education can help you understand the historical and legal significance of these cases.
Understand the Structure of a Legal Case Brief
Before we dive into the details of how to write a good legal case brief, it's important to understand its structure. A typical legal case brief, such as the examples of case briefs available on LSD , includes the following sections:
- Title and Citation: This section includes the name of the case, the court that decided the case, and the citation (i.e., the reference that identifies where the case is published).
- Facts: This section provides a brief summary of the key facts of the case, including who the parties are, what they did, and how the case came to court.
- Issues: This section identifies the legal issues that the court was asked to decide, and focuses on the questions that the court addressed in its decision.
- Holding: This section summarizes the court's decision on the legal issues presented in the case.
- Analysis: This section provides an explanation of the court's reasoning in arriving at its holding, including the legal principles and rules that the court relied on.
Focus on the Key Facts and Issues
When writing a case brief, it's important to focus on the key facts and legal issues presented in the case. You should avoid including unnecessary details or information that is not relevant to the legal issues. Instead, focus on the facts and issues that are essential to understanding the court's decision. This is evident in many examples of case briefs written by legal professionals.
Identify the Legal Principles and Rules
In addition to focusing on the key facts and issues, it's important to identify the legal principles and rules that the court relied on in arriving at its decision. This will help you understand the court's reasoning and the legal principles that are relevant to the case. Many examples of case briefs available online also highlight the legal principles and rules that were applied in a particular case.
Use Clear and Concise Language
A good legal case brief should be written in clear and concise language, as seen in examples of case briefs written by legal professionals. You should avoid using legal jargon or technical terms that may be difficult for a layperson to understand. Instead, use plain language that accurately conveys the meaning of the court's decision.
Be Organized and Structured
To make your case brief more effective, it's important to be organized and structured in your writing. Use headings and subheadings to separate different sections of your brief, and make sure that each section flows logically from one to the next. This is evident in many examples of case briefs available online, which are organized and structured in a clear and logical manner.
So, what’s the point?
Developing analytical and critical thinking skills.
Writing case briefs helps you develop analytical and critical thinking skills. By analyzing court decisions and identifying key facts, issues, and legal principles, you are practicing your ability to think critically and to identify relevant legal issues. Case briefs provide a practical way to develop these skills and apply them to real-world legal problems.
To further develop your analytical and critical thinking skills, you can practice writing your own case briefs. Take a recent court decision and write a brief that summarizes the key facts, issues, and legal principles involved. This will help you become more proficient at identifying relevant information and organizing it in a structured manner.
Preparing for Class and Exams
In addition to being a valuable tool for developing analytical skills, case briefs also help you prepare for class discussions and exams. As you read cases and write briefs, you are gaining a deeper understanding of the law and the reasoning behind court decisions. This knowledge will help you participate more effectively in class discussions and will also help you prepare for law school exams.
To get the most out of case briefs when preparing for exams, you can practice writing case briefs for cases that you studied throughout the year, or to hypotheticals from past exams. This will help you apply the analytical skills you've developed to new situations and ensure that you are able to communicate your understanding of legal principles effectively.
In conclusion, case briefs are an essential tool for law students as they provide a practical application of legal principles, help develop analytical and critical thinking skills, and aid in preparing for class discussions and exams. By studying case brief examples, practicing writing your own briefs, and developing a deep understanding of the law in context, you can become a more proficient and effective student and legal professional. For examples, check out LSD's case brief database .

Tech-focused creator of LSD.Law. I built LSD while applying to law school. I saw unequal access to knowledge and built LSD to level the playing field and help applicants make thoughtful, well-informed decisions in the application process.
- Data download
Help us make LSD better!

Legal Research & Writing Guide
- Legal Abbreviations
- Shepard's Citations
- Citation Examples
- How to Find State Statutes
- The U.S. Supreme Court
- Constitutional Law
How to Read a Case
How to brief a case, recommended videos.
- Case Page Numbering
- Using Nexis Uni Citation Tools
Research Help
Need further assistance email us or make an appointment., email: [email protected], helpful youtube channels.
The following online resources offer guidance for reading case law and court decisions.
- How to Read a Court Decision This guide from Roosevelt University describes the different parts of a court decision.
- LexisNexis: How to Read a Law School Casebook Features an excerpt from Guide to the Study of Law: An Introduction, 2nd ed. (LexisNexis 2001) by L.H. LaRue.
The following online resources provide useful tips for writing case briefs and outlines.
- How to Brief a Case Features an excerpt from "How to Study Law and Take Law Exams in a Nutshell" with a step-by-step guide to briefing cases
- LexisNexis: How to Write a Case Brief Features an excerpt reproduced from Introduction to the Study of Law: Cases and Materials.
- Case Briefing: The Law School Playbook
- Case Reading: The Law School Playbook
- Introduction to Cases / Anatomy of a Case
- How To Write A Case Brief or Case Outline for Law School (With An Example)
- How to Read a Case: And Understand What it Means
- << Previous: Constitutional Law
- Next: Case Page Numbering >>
- Last Updated: Sep 13, 2023 1:34 PM
- URL: https://egcc.libguides.com/legal-research
- 0 Shopping Cart $ 0.00 -->

🌟 Turn Setback into Success! Our Free 5-Day Mastery Class starts April 29! Designed specifically for those who failed the bar, learn essential strategies, reset your mindset, and craft a personalized study plan. Register now —spots are limited!
Explore Your Path to Bar Exam Success! Book a free 20-minute consultation with our experts to find the best bar prep services tailored to your needs. Schedule your call today !
🌟 Boost Your Bar Exam Prep with JD Advising! Looking for one-on-one attention in your bar prep? Our expert bar exam tutors are ready to help you pass! Sign up early before spots fill up!
After working with [my law school tutor], Jonathan, I earned grades high enough to land a summer associate position at a big law firm as a 1L. Jonathan was great because not only was he well versed in my 1L courses, but he also is a successful lawyer and a graduate of my law school. It was great being able to talk to someone who not only understood the rigor of my 1L classes, but also had proven tips for success in and beyond law school.
My [law school] tutor Melissa was very flexible to my needs and interests. She helped me achieve Honors grades in three of my four doctrinal courses of my 1L Fall semester. Very grateful for this opportunity.

What is an example of a law school case brief template?
Here, we’ll provide you with a proposed case brief template as an example of how you might organize your own. We’ll then show you how this template would work in the context of a real case that you could be assigned in your first year of law school. Below, we provide you with more information on what to include in this template. Let’s start with the template.
Update: Try our NEW law school study aids for free here ! Get access to the best law school outlines, hundreds of flashcards, short-answer problems written by top law school professors, multiple-choice questions, and more!
Note: if you haven’t yet downloaded our free guide on how to succeed in law school, do so here !
Even better, join our FREE law school prep course here !
A case brief template: a sample for law students
Template of a case brief, name of case.
Start by saying the name of the case at the top of your case brief—for example, Smith v. Jones.
Identify the parties. Who is the plaintiff? The defendant? Once you identify who’s who, you might want to abbreviate the parties as “P” and “D.”
Identify the procedural posture of the case. Are we at the trial or appellate level? State or federal court? At which stage in the litigation was the case in when the issue arose?
Identify the legal issue that the opinion is addressing. Often, the cases assigned in a casebook are shorter excerpts of a much longer opinion, so the issue will be apparent. Be mindful of where in the casebook a particular case is being presented—i.e., if the case appears in a section on negligence in tort law, even if the court also mentions causation or damages, there’s a good chance the main issue will be negligence.
Briefly summarize the relevant facts of the case. The keyword here is relevant . An opinion will often include several extraneous facts that are not directly relevant to the court’s analysis. Feel free to add some irrelevant facts if they are necessary to understand what happened, but don’t get too carried away. For example, if a Torts case involves a motor vehicle accident, don’t get hung up on the color or make and model of the car unless the court makes clear that those facts are relevant in some way. On the other hand, you’ll surely want to include, for example, any information about whether a driver was distracted or trying to avoid an obstacle in the road. In other words, focus on legally significant facts . If you find yourself struggling with this, don’t worry! You will get better as time goes on!
Identify the rule of law that the court applied. This may be straightforward when, for example, the court applies a well-established negligence rule such as the reasonable person standard. On the other hand, this may be a bit more complex when the court fashions a new rule. For example, the court might be deciding an issue of first impression and have to decide whether an individual should be considered negligent simply for violating a statute—regardless of whether that violation was reasonable. Or, for example, the court might be applying a well-established rule to a novel factual scenario, and the mere application of the rule to that novel factual scenario creates, in effect, a new rule.
Analysis/application
This is where you need to describe the court’s reasoning. If the court applied a well-established rule, explain how the court applied that rule to the facts. Which facts were most relevant? Which were insignificant? If the court fashioned a new rule, on the other hand, explain how the court developed the rule and why it chose to do so.
This is the court’s legal conclusion. For example, did the court hold that the defendant was negligent under a particular set of facts? The holding can be thought of as the product of the rule of law and the analysis. Be careful not to confuse the holding with the court’s judgment, which we’ll discuss below.
This is where you should describe the court’s ultimate disposition of the case. Did the court grant or deny a motion? Affirm or reverse a lower court? The judgment can usually be just a few words at the end of your case brief.
Policy (optional)
If the court provides any public policy reasons for its adoption of a new rule—or its application of an old rule to a novel situation—you may want to briefly note those reasons here. Put simply, policy usually consists of the court explaining the purpose of a rule and its application to a particular factual situation.
Dicta (optional)
Sometimes the court provides an extended discussion of an issue that is not necessary to reach the holding. This is known as “dicta.” And although it might provide insight into how the court will address similar situations in the future, it is not considered essential to the court’s holding and thus is not binding law. Of course, lawyers (and judges) may disagree about just what constitutes dicta and what doesn’t, but in any event, if you think the court provides useful dicta, it may be worth jotting down a brief sentence or two.
Dissent (optional)
Not every case has a dissenting opinion, but if your casebook includes one, it’s not an accident. Oftentimes, a dissent can be just as important as a majority opinion, especially if it highlights a major disagreement in the law or points out significant gaps in the majority’s reasoning. Further, there’s a good chance that your professor will want to discuss it. In short, jotting down one or two sentences about the dissent’s point of view will get you thinking about the case from a different perspective and will make you even more prepared for class discussions.
Sample of a case brief
Now that you’ve seen how a brief should be organized, let’s apply the above template to one of the most famous cases that you’ll study in your first year of law school: Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad Co. (248 NY3d 339 [1928]). This case was decided by the New York Court of Appeals in 1928, and the author of the majority opinion is Benjamin Cardozo—a prolific jurist who later went on to serve as an Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court.
Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad Co.
Helen Palsgraf is the plaintiff (P) and Long Island Railroad is the defendant (D).
The jury found for P in a negligence suit. D appealed. The appellate division affirmed, 3-2. D appealed to the court of appeals.
Is D liable for causing P’s injuries? More specifically, did D owe a duty to P rendering D liable to P for the conduct of the guards?
Two men were running on a train platform to catch a train. One of the men was carrying a package and seemed unsteady. A guard on one of the train cars reached out to help the man, and a guard on the train platform—who was also trying to help—pushed the man from behind. In the process, the man lost his grip on the package and it fell onto the rails. The package was small and appeared unremarkable, but it contained fireworks and exploded when it fell. The shock of the explosion threw down multiple scales at the other end of the platform. One of the scales struck P, causing injury.
A D owes a duty to a P when the “orbit” of danger to P is reasonably foreseeable—i.e., a danger that would be foreseen by the “eye of reasonable vigilance.”
Negligence is based on the relationship between the parties. The relationship between P and D is expressed by a duty that D owes to P. Unless D violates that duty, there is no negligence. In short, there must first be a duty relationship between P and D in order for there to be any possibility of finding D negligent. The duty that D owes to P extends as far as the eye of reasonable vigilance would reasonably foresee a danger to P. If a P can pass through this rigorous test of negligence at the front end, a D is liable for all consequences of his actions.
Here, the danger to P was not reasonably foreseeable by the eye of reasonable vigilance, so D did not owe a duty to P. D owed a duty to the man who was running to catch the train, and the conduct of the guard invaded the man’s property interest, but P cannot sue to vindicate this interest. However, P could potentially sue the man with the package containing fireworks.
Under these facts, D did not owe a duty to P and was therefore not liable to P for her injuries.
The decision of the appellate division is reversed.
If railroads could be held liable for this type of situation, they would be forced to raise ticket prices, etc. Further, it would be impractical for a railroad to check every package in order to guard against this type of danger.
The issue of whether a duty exists is a question of law for a court to decide, but if it is unclear whether a danger to a prospective P was within the orbit of reasonably foreseeable harm, then the court should send the case to the jury.
Judge Andrews argued that the question of duty should focus on the relationship between a D and society, not a D and a particular P. If a D acts unreasonably, he is liable to anyone who is injured as a result, regardless of whether the injured P is in the zone of reasonably foreseeable danger. Even if no reasonably foreseeable harm results from a D’s actions, he is still liable because negligence itself is unreasonable. Contrary to Judge Cardozo’s approach of making the negligence test rigorous at the front end by limiting the definition of duty, Judge Andrews would use proximate cause in a policy-oriented way to limit liability at the back end. In other words, courts should employ proximate cause to draw a line where the law declines to further trace a series of events due to social policy considerations.
So, there you have it. You’ll notice that in the above sample, the outline of the dissenting opinion was a bit longer. This is because Palsgraf involves such a stark difference of opinion and reasoning between the majority and dissent. Other than this, the above sample is a pretty standard case brief. You should now feel prepared to tackle a case brief of your own!
Go to the next topic, Why shouldn’t I brief cases in law school?
Seeking success in law school.
- Benefit from personalized one-on-one tutoring by our seasoned law school tutors.
- Explore our NEW and highly acclaimed law school study aids , available for a free trial.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Public Interest

By using this site, you allow the use of cookies, and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
Business development
- Billing management software
- Court management software
- Legal calendaring solutions
Practice management & growth
- Project & knowledge management
- Workflow automation software
Corporate & business organization
- Business practice & procedure
Legal forms
- Legal form-building software
Legal data & document management
- Data management
- Data-driven insights
- Document management
- Document storage & retrieval
Drafting software, service & guidance
- Contract services
- Drafting software
- Electronic evidence
Financial management
- Outside counsel spend
Law firm marketing
- Attracting & retaining clients
- Custom legal marketing services
Legal research & guidance
- Anywhere access to reference books
- Due diligence
- Legal research technology
Trial readiness, process & case guidance
- Case management software
- Matter management
Recommended Products
Conduct legal research efficiently and confidently using trusted content, proprietary editorial enhancements, and advanced technology.
Fast track case onboarding and practice with confidence. Tap into a team of experts who create and maintain timely, reliable, and accurate resources so you can jumpstart your work.
A business management tool for legal professionals that automates workflow. Simplify project management, increase profits, and improve client satisfaction.
- All products
Tax & Accounting
Audit & accounting.
- Accounting & financial management
- Audit workflow
- Engagement compilation & review
- Guidance & standards
- Internal audit & controls
- Quality control
Data & document management
- Certificate management
- Data management & mining
- Document storage & organization
Estate planning
- Estate planning & taxation
- Wealth management
Financial planning & analysis
- Financial reporting
Payroll, compensation, pension & benefits
- Payroll & workforce management services
- Healthcare plans
- Billing management
- Client management
- Cost management
- Practice management
- Workflow management
Professional development & education
- Product training & education
- Professional development
Tax planning & preparation
- Financial close
- Income tax compliance
- Tax automation
- Tax compliance
- Tax planning
- Tax preparation
- Sales & use tax
- Transfer pricing
- Fixed asset depreciation
Tax research & guidance
- Federal tax
- State & local tax
- International tax
- Tax laws & regulations
- Partnership taxation
- Research powered by AI
- Specialized industry taxation
- Credits & incentives
- Uncertain tax positions
A powerful tax and accounting research tool. Get more accurate and efficient results with the power of AI, cognitive computing, and machine learning.
Provides a full line of federal, state, and local programs. Save time with tax planning, preparation, and compliance.
Automate workpaper preparation and eliminate data entry
Trade & Supply
Customs & duties management.
- Customs law compliance & administration
Global trade compliance & management
- Global export compliance & management
- Global trade analysis
- Denied party screening
Product & service classification
- Harmonized Tariff System classification
Supply chain & procurement technology
- Foreign-trade zone (FTZ) management
- Supply chain compliance
Software that keeps supply chain data in one central location. Optimize operations, connect with external partners, create reports and keep inventory accurate.
Automate sales and use tax, GST, and VAT compliance. Consolidate multiple country-specific spreadsheets into a single, customizable solution and improve tax filing and return accuracy.
Risk & Fraud
Risk & compliance management.
- Regulatory compliance management
Fraud prevention, detection & investigations
- Fraud prevention technology
Risk management & investigations
- Investigation technology
- Document retrieval & due diligence services
Search volumes of data with intuitive navigation and simple filtering parameters. Prevent, detect, and investigate crime.
Identify patterns of potentially fraudulent behavior with actionable analytics and protect resources and program integrity.
Analyze data to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraud. Focus investigation resources on the highest risks and protect programs by reducing improper payments.
News & Media
Who we serve.
- Broadcasters
- Governments
- Marketers & Advertisers
- Professionals
- Sports Media
- Corporate Communications
- Health & Pharma
- Machine Learning & AI
Content Types
- All Content Types
- Human Interest
- Business & Finance
- Entertainment & Lifestyle
- Reuters Community
- Reuters Plus - Content Studio
- Advertising Solutions
- Sponsorship
- Verification Services
- Action Images
- Reuters Connect
- World News Express
- Reuters Pictures Platform
- API & Feeds
- Reuters.com Platform
Media Solutions
- User Generated Content
- Reuters Ready
- Ready-to-Publish
- Case studies
- Reuters Partners
- Standards & values
- Leadership team
- Reuters Best
- Webinars & online events
Around the globe, with unmatched speed and scale, Reuters Connect gives you the power to serve your audiences in a whole new way.
Reuters Plus, the commercial content studio at the heart of Reuters, builds campaign content that helps you to connect with your audiences in meaningful and hyper-targeted ways.
Reuters.com provides readers with a rich, immersive multimedia experience when accessing the latest fast-moving global news and in-depth reporting.
- Reuters Media Center
- Jurisdiction
- Practice area
- View all legal
- Organization
- View all tax
Featured Products
- Blacks Law Dictionary
- Thomson Reuters ProView
- Recently updated products
- New products
Shop our latest titles
ProView Quickfinder favorite libraries
- Visit legal store
- Visit tax store
APIs by industry
- Risk & Fraud APIs
- Tax & Accounting APIs
- Trade & Supply APIs
Use case library
- Legal API use cases
- Risk & Fraud API use cases
- Tax & Accounting API use cases
- Trade & Supply API use cases
Related sites
United states support.
- Account help & support
- Communities
- Product help & support
- Product training
International support
- Legal UK, Ireland & Europe support
New releases
- Westlaw Precision
- 1040 Quickfinder Handbook
Join a TR community
- ONESOURCE community login
- Checkpoint community login
- CS community login
- TR Community
Free trials & demos
- Westlaw Edge
- Practical Law
- Checkpoint Edge
- Onvio Firm Management
- Proview eReader

How to do legal research in 3 steps
Knowing where to start a difficult legal research project can be a challenge. But if you already understand the basics of legal research, the process can be significantly easier — not to mention quicker.
Solid research skills are crucial to crafting a winning argument. So, whether you are a law school student or a seasoned attorney with years of experience, knowing how to perform legal research is important — including where to start and the steps to follow.
What is legal research, and where do I start?
Black's Law Dictionary defines legal research as “[t]he finding and assembling of authorities that bear on a question of law." But what does that actually mean? It means that legal research is the process you use to identify and find the laws — including statutes, regulations, and court opinions — that apply to the facts of your case.
In most instances, the purpose of legal research is to find support for a specific legal issue or decision. For example, attorneys must conduct legal research if they need court opinions — that is, case law — to back up a legal argument they are making in a motion or brief filed with the court.
Alternatively, lawyers may need legal research to provide clients with accurate legal guidance . In the case of law students, they often use legal research to complete memos and briefs for class. But these are just a few situations in which legal research is necessary.
Why is legal research hard?
Each step — from defining research questions to synthesizing findings — demands critical thinking and rigorous analysis.
1. Identifying the legal issue is not so straightforward. Legal research involves interpreting many legal precedents and theories to justify your questions. Finding the right issue takes time and patience.
2. There's too much to research. Attorneys now face a great deal of case law and statutory material. The sheer volume forces the researcher to be efficient by following a methodology based on a solid foundation of legal knowledge and principles.
3. The law is a fluid doctrine. It changes with time, and staying updated with the latest legal codes, precedents, and statutes means the most resourceful lawyer needs to assess the relevance and importance of new decisions.
Legal research can pose quite a challenge, but professionals can improve it at every stage of the process .
Step 1: Key questions to ask yourself when starting legal research
Before you begin looking for laws and court opinions, you first need to define the scope of your legal research project. There are several key questions you can use to help do this.

What are the facts?
Always gather the essential facts so you know the “who, what, why, when, where, and how” of your case. Take the time to write everything down, especially since you will likely need to include a statement of facts in an eventual filing or brief anyway. Even if you don't think a fact may be relevant now, write it down because it may be relevant later. These facts will also be helpful when identifying your legal issue.
What is the actual legal issue?
You will never know what to research if you don't know what your legal issue is. Does your client need help collecting money from an insurance company following a car accident involving a negligent driver? How about a criminal case involving excluding evidence found during an alleged illegal stop?
No matter the legal research project, you must identify the relevant legal problem and the outcome or relief sought. This information will guide your research so you can stay focused and on topic.
What is the relevant jurisdiction?
Don't cast your net too wide regarding legal research; you should focus on the relevant jurisdiction. For example, does your case deal with federal or state law? If it is state law, which state? You may find a case in California state court that is precisely on point, but it won't be beneficial if your legal project involves New York law.
Where to start legal research: The library, online, or even AI?
In years past, future attorneys were trained in law school to perform research in the library. But now, you can find almost everything from the library — and more — online. While you can certainly still use the library if you want, you will probably be costing yourself valuable time if you do.
When it comes to online research, some people start with free legal research options , including search engines like Google or Bing. But to ensure your legal research is comprehensive, you will want to use an online research service designed specifically for the law, such as Westlaw . Not only do online solutions like Westlaw have all the legal sources you need, but they also include artificial intelligence research features that help make quick work of your research
Step 2: How to find relevant case law and other primary sources of law
Now that you have gathered the facts and know your legal issue, the next step is knowing what to look for. After all, you will need the law to support your legal argument, whether providing guidance to a client or writing an internal memo, brief, or some other legal document.
But what type of law do you need? The answer: primary sources of law. Some of the more important types of primary law include:
- Case law, which are court opinions or decisions issued by federal or state courts
- Statutes, including legislation passed by both the U.S. Congress and state lawmakers
- Regulations, including those issued by either federal or state agencies
- Constitutions, both federal and state
Searching for primary sources of law
So, if it's primary law you want, it makes sense to begin searching there first, right? Not so fast. While you will need primary sources of law to support your case, in many instances, it is much easier — and a more efficient use of your time — to begin your search with secondary sources such as practice guides, treatises, and legal articles.
Why? Because secondary sources provide a thorough overview of legal topics, meaning you don't have to start your research from scratch. After secondary sources, you can move on to primary sources of law.
For example, while no two legal research projects are the same, the order in which you will want to search different types of sources may look something like this:
- Secondary sources . If you are researching a new legal principle or an unfamiliar area of the law, the best place to start is secondary sources, including law journals, practice guides , legal encyclopedias, and treatises. They are a good jumping-off point for legal research since they've already done the work for you. As an added bonus, they can save you additional time since they often identify and cite important statutes and seminal cases.
- Case law . If you have already found some case law in secondary sources, great, you have something to work with. But if not, don't fret. You can still search for relevant case law in a variety of ways, including running a search in a case law research tool.
Once you find a helpful case, you can use it to find others. For example, in Westlaw, most cases contain headnotes that summarize each of the case's important legal issues. These headnotes are also assigned a Key Number based on the topic associated with that legal issue. So, once you find a good case, you can use the headnotes and Key Numbers within it to quickly find more relevant case law.
- Statutes and regulations . In many instances, secondary sources and case law list the statutes and regulations relevant to your legal issue. But if you haven't found anything yet, you can still search for statutes and regs online like you do with cases.
Once you know which statute or reg is pertinent to your case, pull up the annotated version on Westlaw. Why the annotated version? Because the annotations will include vital information, such as a list of important cases that cite your statute or reg. Sometimes, these cases are even organized by topic — just one more way to find the case law you need to support your legal argument.
Keep in mind, though, that legal research isn't always a linear process. You may start out going from source to source as outlined above and then find yourself needing to go back to secondary sources once you have a better grasp of the legal issue. In other instances, you may even find the answer you are looking for in a source not listed above, like a sample brief filed with the court by another attorney. Ultimately, you need to go where the information takes you.
Step 3: Make sure you are using ‘good’ law
One of the most important steps with every legal research project is to verify that you are using “good" law — meaning a court hasn't invalidated it or struck it down in some way. After all, it probably won't look good to a judge if you cite a case that has been overruled or use a statute deemed unconstitutional. It doesn't necessarily mean you can never cite these sources; you just need to take a closer look before you do.
The simplest way to find out if something is still good law is to use a legal tool known as a citator, which will show you subsequent cases that have cited your source as well as any negative history, including if it has been overruled, reversed, questioned, or merely differentiated.
For instance, if a case, statute, or regulation has any negative history — and therefore may no longer be good law — KeyCite, the citator on Westlaw, will warn you. Specifically, KeyCite will show a flag or icon at the top of the document, along with a little blurb about the negative history. This alert system allows you to quickly know if there may be anything you need to worry about.
Some examples of these flags and icons include:
- A red flag on a case warns you it is no longer good for at least one point of law, meaning it may have been overruled or reversed on appeal.
- A yellow flag on a case warns that it has some negative history but is not expressly overruled or reversed, meaning another court may have criticized it or pointed out the holding was limited to a specific fact pattern.
- A blue-striped flag on a case warns you that it has been appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court or the U.S. Court of Appeals.
- The KeyCite Overruling Risk icon on a case warns you that the case may be implicitly undermined because it relies on another case that has been overruled.
Another bonus of using a citator like KeyCite is that it also provides a list of other cases that merely cite your source — it can lead to additional sources you previously didn't know about.
Perseverance is vital when it comes to legal research
Given that legal research is a complex process, it will likely come as no surprise that this guide cannot provide everything you need to know.
There is a reason why there are entire law school courses and countless books focused solely on legal research methodology. In fact, many attorneys will spend their entire careers honing their research skills — and even then, they may not have perfected the process.
So, if you are just beginning, don't get discouraged if you find legal research difficult — almost everyone does at first. With enough time, patience, and dedication, you can master the art of legal research.
Thomson Reuters originally published this article on November 10, 2020.
Related insights

Westlaw tip of the week: Checking cases with KeyCite

Why legislative history matters when crafting a winning argument

Case law research tools: The most useful free and paid offerings

Request a trial and experience the fastest way to find what you need

Case Studies
The program’s portfolio of situational case studies presents narratives of real-life events and asks students to identify and analyze the relevant legal, social, business, ethical, and scientific issues involved. Playing the role of protagonist in each case study—such as a private attorney counseling a biotechnology company facing hazardous waste issues, or a federal official seeking to develop an effective fishery management plan—students formulate appropriate strategies for achieving workable solutions to conflicts, then discuss and debate their recommendations in class. This interactive approach to learning bolsters students’ acquisition of skills in critical areas: factual investigation, legal research, counseling, persuasive oral communication, and recognition and resolution of ethical dilemmas, to name a few.
The Stanford Law School Case Studies Collection is an exciting innovation in law school teaching designed to hone students’ problem-solving skills and stimulate creativity. The Collection includes situational case studies and interactive simulations (collectively referred to as “Case Materials”) that place students in the roles of lawyers and policy makers and teach fundamental lawyering skills such as investigating facts, counseling, and resolving ethical dilemmas.
In June of 1997 the Environmental and Natural Resources Law Policy Program hired an experienced environmental lawyer to develop “situational” case studies for use in classroom instruction to better prepare students for the practice of law in the real world. Most of the case studies have been field tested in the classroom and evaluated for effectiveness in increasing student mastery of fundamental lawyering skills and increasing student participation in classroom discussion. Feedback from students has been excellent. Stanford Law School plans to unveil case studies collections in the areas of Law and Business in the coming years.
You can use this site to download Case Materials for examination. With prior permission from Stanford Law School, instructors can also obtain copies of Case Materials they want to use in the classroom for free. This Case Studies Collection will be updated regularly as we add new Case Materials and revise existing Materials, so visit the site from time to time for new developments!
As used in our website, the phrase “case materials” refers to case studies and simulations, as well as accompanying exhibits and teaching notes. While both case studies and simulations can be used as tools in the “case study teaching method,” they are different in form and manner of use. A case study is a narrative that recounts the factual history of an event or series of events. It is typically used as the basis for in-class analysis and discussion. A simulation is a set of facts, roles and rules that establishes the framework for an in-class participatory exercise.
Research has shown that existing law school teaching methods and curricula do not adequately teach students the full complement of “lawyering” skills they need to competently practice law. The traditional appellate case method assumes that a problem has reached a point where litigation is the only alternative, and presents students with a scenario in which all relevant issues have been identified, the questions of law narrowly focused, and the questions of fact resolved. Skills-oriented courses and clinical programs (such as law clinics and externships) have made significant contributions to law schools’9 ability to teach lawyering skills. Their reach, however, has been limited by a combination of factors, including their high cost and the relatively few law students who actually take advantage of these programs.
While we do not envision the case study method displacing the appellate case method or clinical programs, we do believe that the case method can be used in conjunction with existing teaching methods to add considerable educational value. Case studies and simulations immerse students in real-world problems and situations, requiring them to grapple with the vagaries and complexities of these problems in a relatively risk-free environment – the classroom.
Incorporation of case studies and simulations into environmental law school curriculums can bolster student skill acquisition in the critical areas listed below. Based on a 1990-1991 American Bar Association questionnaire, the MacCrate Task Force concluded that traditional law school curricula and teaching methods fall short in teaching these fundamental lawyering skills:
- problem solving
- legal research
- factual investigation
- persuasive oral communications
- negotiation
- recognizing and resolving ethical dilemmas
- organization and management of legal work
The case study teaching method is adapted from the case method developed and used successfully for many years by the nation’s leading business schools. The method uses a narrative of actual events to teach and hone the skills students need to competently practice law. Students identify for themselves the relevant legal, social, business, and scientific issues presented, and identify appropriate responses regarding those issues. Suggested questions for class discussion are prepared in connection with each case study, itself the product of long, probing interviews of the people involved in the actual events. These narratives, or case studies, may be long or short, and portray emotion, character, setting and dialogue. Students present their thoughts on key issues during class discussion, usually from the viewpoint of the key protagonist in the case study.
Simulations are typically used to reinforce and synthesize concepts, skills and substantive law already covered in a course. The simulations are designed for limited instructor and maximum student involvement during the exercise itself. However, once the exercise has drawn to a close, ample time should be allotted for a debriefing session. During the debriefing, instructors and students can engage in a candid discussion of the relative effectiveness of different approaches used during the simulation, clear up any lingering questions about substantive issues, and probe ethical and/or policy issues raised by the simulation.
Requesting Permission to Copy or to Use Materials
Send your request for permission to use or copy Case Materials to [email protected] . To assist us in reviewing such requests and tracking the actual use of our Case Materials, please provide a description of the course (of up to 500 words) for which the Case Materials will be used. In addition, please include a brief description of the kind of course for which the Case Materials are intended, including:
- Whether the course is an elective or required course, undergraduate, graduate, or continuing education.
- The nature of the academic program and institution in which the course will be taught, such as law school, business school, Earth Sciences department, public interest law firm, etc.
- The number of times the course has been offered.
- Expected enrollment for the course.
- The history of the course’s development.
Case Studies
Explore case studies of previous cases which Allan Rouben has represented. Find examples of case studies in all focus areas of law.
Legroulx v. Pitre: Striking Jury Notice, Charter of Rights and Freedoms and Rules of Civil Procedure
Background: A complicated action was proceeding in Ottawa before Justice Denis Power and a jury. The plaintiff’s injuries, arising out of a car accident, raised difficult issues of causation and required that complex medical evidence be heard. The plaintiff’s lawyers considered the medical issues were too complex for the jury and brought a motion to …
Legroulx v. Pitre: Striking Jury Notice, Charter of Rights and Freedoms and Rules of Civil Procedure Read More »
Lucia’s Case: Appeal, Civil Litigation, Jurisdiction and Forum non Conveniens
Background: Lucia resides in Ontario with her family, and was involved in a car accident in Michigan. She brought suit in the Ontario Superior Court of Justice against the driver and owner of the vehicle, as well as her own insurer given that the Michigan defendants claimed the accident was caused by an unknown vehicle. …
Lucia’s Case: Appeal, Civil Litigation, Jurisdiction and Forum non Conveniens Read More »
Patrizia’s Case: Appeals, Civil Litigation, Negligence and Minimum Maintenance Standards
Background: Patrizia was driving to work early on a snowy morning in April. The roads in Milton were snow covered and slippery. Weather forecasts from the day before predicted an 80% chance of snow, yet the Town of Milton had not scheduled an evening patrol to monitor the roads and clear the snow. Tragically, as …
Patrizia’s Case: Appeals, Civil Litigation, Negligence and Minimum Maintenance Standards Read More »
F.A.’s Case: Criminal Law, Appeals, Sexual Assault and Ineffective Assistance of Counsel
Background: F.A. worked in a medical facility with a much younger female co-worker. There was flirting between them. They went out together one evening, meeting up in a park and later driving around in F.A.’s car. He said he had a surprise for her at the office so they parked close by. Instead of going …
F.A.’s Case: Criminal Law, Appeals, Sexual Assault and Ineffective Assistance of Counsel Read More »
Clare’s Case: Labour Law, Duty of Fair Representation and Ontario Labour Relations Board
Background: Clare had been working for General Motors for 23 years before his termination. The company claimed that he had threated a supervisor after being told that a urine sample he had given was diluted. Clare denied the allegation and asked the Union, Canadian Auto Workers Local 222, to grieve the termination. He communicated frequently …
Clare’s Case: Labour Law, Duty of Fair Representation and Ontario Labour Relations Board Read More »
- Find a Lawyer
- Ask a Lawyer
- Research the Law
- Law Schools
- Laws & Regs
- Newsletters
- Justia Connect
- Pro Membership
- Basic Membership
- Justia Lawyer Directory
- Platinum Placements
- Gold Placements
- Justia Elevate
- Justia Amplify
- PPC Management
- Google Business Profile
- Social Media
- Justia Onward Blog
US Case Law
The United States Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. Lower courts on the federal level include the US Courts of Appeals, US District Courts, the US Court of Claims, and the US Court of International Trade and US Bankruptcy Courts. Federal courts hear cases involving matters related to the United States Constitution, other federal laws and regulations, and certain matters that involve parties from different states or countries and large sums of money in dispute.
Each state has its own judicial system that includes trial and appellate courts. The highest court in each state is often referred to as the “supreme” court, although there are some exceptions to this rule, for example, the New York Court of Appeals or the Maryland Court of Appeals. State courts generally hear cases involving state constitutional matters, state law and regulations, although state courts may also generally hear cases involving federal laws. States also usually have courts that handle only a specific subset of legal matters, such as family law and probate.
Case law, also known as precedent or common law, is the body of prior judicial decisions that guide judges deciding issues before them. Depending on the relationship between the deciding court and the precedent, case law may be binding or merely persuasive. For example, a decision by the US Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit is binding on all federal district courts within the Fifth Circuit, but a court sitting in California (whether a federal or state court) is not strictly bound to follow the Fifth Circuit’s prior decision. Similarly, a decision by one district court in New York is not binding on another district court, but the original court’s reasoning might help guide the second court in reaching its decision.
Decisions by the US Supreme Court are binding on all federal and state courts.
US Federal Courts
Reported opinions from the us federal courts of appeals.
- Federal Reporter, 2nd Series (F.2d) (1924-1993)
- Federal Reporter, 3rd Series (F.3d) (1993-present)
Opinions From the US Federal Courts of Appeals
- US Court of Appeals for the First Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Eleventh Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit
- US Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces
- US Court of International Trade
- US Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court of Review
- Bankruptcy Reporter (B.R.) (1980-present)
- Federal Reporter, 2nd Series (F.2d) (1924-1932)
- Federal Supplement (F. Supp.) (1933-1998)
- Federal Supplement, 2nd Series (F. Supp. 2d) (1998-present)
- Connecticut
- District of Columbia
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia
- US District Court for the District of Guam
- US District Court for the District of Puerto Rico
- US District Court for the District of the Northern Mariana Islands
- US District Court for the District of the US Virgin Islands
- Emergency Court of Appeals (1942-1974)
- US Court of Appeals for Veterans Claims
- US Court of Claims (1855-1982)
- US Court of Customs and Patent Appeals (1909-1982)
- US Court of Federal Claims
- US Tax Court
State Courts
Foreign and international courts.
- Australia Courts
- Canada Courts
- Israel Courts
- United Kingdom Courts
- International Courts
- Bankruptcy Lawyers
- Business Lawyers
- Criminal Lawyers
- Employment Lawyers
- Estate Planning Lawyers
- Family Lawyers
- Personal Injury Lawyers
- Estate Planning
- Personal Injury
- Business Formation
- Business Operations
- Intellectual Property
- International Trade
- Real Estate
- Financial Aid
- Course Outlines
- Law Journals
- US Constitution
- Regulations
- Supreme Court
- Circuit Courts
- District Courts
- Dockets & Filings
- State Constitutions
- State Codes
- State Case Law
- Legal Blogs
- Business Forms
- Product Recalls
- Justia Connect Membership
- Justia Premium Placements
- Justia Elevate (SEO, Websites)
- Justia Amplify (PPC, GBP)
- Testimonials
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
- --> Login or Sign Up

About Harvard Law Case Studies
Case studies at harvard law school.
"[In 2004], Harvard Law School embarked on a major curricular review aimed at determining what changes might help us to prepare our students even more effectively for the complex global challenges of this new millennium."
--Supreme Court Justice and former HLS Dean Elena Kagan, 2007
One of the major initiatives that came out of this review was the Problem Solving Workshop, a required first-year program aimed at practical lawyering skills. View this short video about the Problem-Solving Workshop:
Harvard’s curricular review in 2004 challenged the accepted way of teaching law. In 2007, HLS Dean Martha Minow and Professor Todd Rakoff published these findings, "A Case for Another Case Method," in the Vanderbilt Law Review.
The Langdellian case method , which focused on "a retrospective view of facts," was falling short in teaching critical problem solving skills. What law school needed, according to Minow and Rakoff, was a new way to simulate “legal imagination.”
Minow and Rakoff wrote: "What [students] most crucially lack ... is the ability to generate the multiple characterizations, multiple versions, multiple pathways, and multiple solutions, to which they could apply their very well-honed analytic skills."
To that end, Harvard Law School instituted the Problem Solving Workshop, a required first-year course that teaches problem solving skills through the case study method . The Problem Solving Workshop encourages the use of case studies throughout the HLS curriculum.
Now, several faculty initiatives produce case studies at Harvard Law School.
The Case Development Initiative
The Case Development Initiative creates case studies for J.D. and Executive Education classes. HLS faculty use case studies to teach a variety of legal topics, including career dilemmas that lawyers face and management issues that law firms and professional service firms experience. These case studies expose participants to real-world problems that lawyers and firm leaders confront, and help them work through possible approaches and solutions. CDI was founded by Professor Ashish Nanda and is now directed by Dr. Lisa Rohrer.
Great for: discussion-based case studies, law and business, management , professional development
Sample Teaching Units: Professional Development for In-House Counsel , Professional Development for Law Firms , Leadership
Additional Information: The Case Development Initiative at Harvard Law School
Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program
The Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program , directed by Professor Robert Bordone , developed several role plays for an advanced negotiation workshop at HLS. The course, Multiparty Negotiation, Group Decision Making, and Teams , enables students to participate in and conduct complex, multiparty negotiations. "Lawyers and other professionals, irrespective of their specialty, find themselves party to negotiations with multiple (more than two) principals all the time," explains Bordone. "This course combines theory and practice to give students an opportunity to hone their skills in multiparty settings." Students work in teams to address complex, global, and professional issues. The advanced workshop integrates intellectual and experiential learning by combining readings, lectures, and discussions with frequent exercises, extensive review, live and filmed examples, individual and small group reviews, and analysis of the negotiation process and the process of learning from experience.
Great for: role plays, multiparty negotiation, DVDs , mediation
Sample Teaching Units: Critical Decisions in Negotiation
Program on Negotiation
Program on Negotiation materials use real events or fictionalized versions of events to teach negotiation and mediation theory, issues, and practice. These materials can take the form of a discussion exercise, a role playing game, a dilemma-based case study, or a factual account of a negotiation event. Events and historical contexts, such as the rise of organized labor in the United States, the conflict between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland, and the history of Zionists and Arabs in the Middle East, catalyze discussion and debate on negotiation and dispute resolution.
Great for: role plays, historical case studies, negotiation, value-based conflict resolution, water rights and environmental management, examples of Great Negotiators
Sample Teaching Units: Mediating Value-Based Conflict
Problem Solving Workshop
Problem Solving Workshop materials immerse students in the type of real-world problems faced every day by practicing lawyers. The case studies present the problem at hand and provide readings on related theory, excerpts of relevant law, and other illustrative documents, such as contracts and leases. Students complete team assignments and exercises that include tasks such as drafting a press release as general counsel of a toy company in trouble; determining, as an associate at a law firm, the possible actions open to a client facing a harassment change from a tenant; or deciding, as a new Assistant U.S. Attorney in New York, whether—and how—to charge someone with Section 8 housing fraud. Professors Todd Rakoff and Joseph Singer lead the PSW teaching group, which develops new materials yearly.
Great for: workshop-based case studies , 1Ls, J.D. programs, lawyering, problem solving , free materials
Sample Teaching Units: Problem Solving Workshop , Advanced Problem Solving Workshop: Cyberlaw, Intellectual Property, and Internet & Society
Additional Information: Information Law and Policy: Advanced Problem Solving Workshop
Case Studies Program
The Case Studies Program supports additional HLS faculty in developing case studies.
Great for: discussion-based case studies
Sample Teaching Units: Decision Making and Leadership in the Public Sector
Next: The Case Study Teaching Method >>

Legal Case Study Interviews
Many commercial law firms require candidates to undertake a case study at the final interview stage.
There is not one single format, so it is advisable to ask the recruitment team what you can expect. Below are some general points and tips which have been put together from feedback from students who have gone through the process and what we have learned from law firms.
Legal Case Study and Commercial Awareness Exercises
Bear in mind that recruiters are always trying to improve their processes so it is likely that they will find new ways to assess candidates each year. It is therefore unlikely that you will find comprehensive resources to practise legal case studies in the same type of ways that you might for management consultancy case studies (in the consulting industry, case studies are extremely well established and follow a broadly similar format during the interview).
Generally speaking legal case studies are not intended to test out technical legal skills – this is partly because they need to be fair to both law and non law students. Instead they are more likely to test the skills required to be an effective lawyer within the world of (private practice) work. So focus your efforts on your specific law firm research, ways to demonstrate your motivation, and the practice of skills they are seeking rather than on preparing for specific types of exercises.
What Is Being Tested?
The following skills and attributes are likely to be tested throughout the interview process:
- commercial awareness – for example, are you thinking about the client and the issues they may be facing? Are you thinking of the law firm as a business?
- logical thinking - are you able to think in a structured way and use your common sense to arrive at a practical solution?
- analytical skills - can you identify the key issues from a lot of information, perhaps under time pressure?
- judgement - can you summarise the main points of the arguments and come to a conclusion given a certain set of facts?
- time management - can you manage your time effectively? Can you prioritise information and activity? Will you get flustered if presented with a large volume of unfamiliar information to read?
- dealing with pressure - can you work under time pressure and stay focused and effective? Can you deal with unfamiliar facts or people and stay calm?
- resilience - how do you respond to being challenged? How do you respond when something does not go your way or in the face of a difficult problem? Can you defend your point of view?
- interpersonal skills. Are you confident in what you are saying, are you collaborative, can you develop a good rapport and productive working relationships, do you listen well, are you open to feedback, do you have a positive attitude?
- communication. Can you communicate equally effectively on paper (e.g. in writing a letter/email to a client) and face to face ( e.g. in making a presentation to a group)? Are you clear? Do you think about the tone and the reader/ audience? Do you have a high standard of general literacy? Is your answer well structured, communicated in plain English and to the point?
- negotiation skills - are you clear about what you are trying to achieve and what, if anything you are prepared to negotiate on? If you are acting on behalf of someone, are they clear about what you are doing?
- motivation – are you enjoying this even if you feel slightly nervous?
Types of Exercise and Tips for Managing Them
These exercises vary from firm to firm and can be part of an individual interview or a group exercise. The material could be given to you in any of the following formats:
- a paragraph which may be about a current affairs issue or something specifically legal: read and then discuss
- an article from, for example, the Financial Times : read and discuss/answer questions
- a one or two page client scenario with a question posed at the end. For example, 'should this new client be taken on?'
- Summary of the situation – could be in the form of an email or letter
- Client or competitor strategy
- Financial statements
- Information about employees/equipment/other assets (property)
- Contracts, leases, licences
- Litigation, possible actions, non disclosure
- Regulatory information
Tips for the paragraph and article exercises
- Read carefully
- Think about how you would summarise what the article is about in two or three sentences
- Think about the argument/point of view that is being voiced throughout the article. What would be the counter argument if you had to make it?
- Identify two or three key issues – think about political and economic aspects
- There may not be an obvious connection to the law firm. The interviewer may be wanting to stretch you intellectually and see how you think, and find out whether you have an opinion that you are able to defend
- If the article has been reproduced by the firm and is set out in numbered paragraphs, this is so that you can refer to the paragraphs by number in the discussion.
Tips for the client scenarios
Possible scenarios may include a client (or a potential client) who is considering merging or acquiring another company, or a client who is being acquired by a competitor or who is looking for some legal services. The amount of material and time you are given will determine the level of detail you are expected to cover. In general it is advisable to cover as many aspects as you can broadly, rather than cover only one or two in great detail.
You may be asked a general question such as ‘what advice would you give to the client?’ or three or four specific questions. For the latter it is most important to address all the questions rather than focusing on the detail of one and ignoring others.
It is also very useful to have researched the firm carefully. By doing do you will know facts such as where the firm has offices located (useful when there are several jurisdictions involved in the scenario) and which practice areas it has (allowing you to suggest bringing in expertise from elsewhere in the firm if appropriate).
Tips for “bundle of document” exercises
Some firms will give you anything between 5 and 20 documents to read and answer one or more questions. You may be asked to give a short presentation followed by a discussion with the interviewer(s).
- Read the question(s) carefully and follow instructions
- Flick through quickly to establish the contents and make sure you look at the back page. You may even find an index to help you
- Take a minute to plan your time and leave enough to produce a presentation or at least review your thoughts before the interview
- Use a highlighter
- Identify key elements relevant to the question(s)
- Don’t forget to consider whether the deal should even be done. Is there a deal breaker? Is there another option?
- Consider risks to the client and/or to the firm. For example are there any reputational issues associated for either party? Is there any “conflict of interest” for the firm?
- Structure the presentation: beginning, middle and end which should be short summary with recommendations. Be close to the maximum time allowed
- Be confident in your recommendations, even if you feel that your chosen line of argument is marginal. You can assess the pros and cons of a given situation, but conclude with “on balance, I recommend xyz”. Remember that solicitors are paid to make decisions and that clients need to trust their legal advisers to make them!
- Consider your audience
- Imagine this was actually a real situation at work where you were involved in working with this client – what would you really say to them?
- Check your grammar, spelling and punctuation.
Preparation
Here are some suggestions to help make you feel ready and confident to tackle these exercises:
- Make sure that you research the role of a solicitor carefully such that you have a realistic view of their daily work (in the relevant setting), their responsilbilites and activities and even an awareness of the SRA's Code of Conduct for legal service firms and individuals.
- Have a clear idea of the firm’s practice areas, what type of work they specialise in, where their offices are located, how they differentiate themselves from their key competitors and the challenges that law firms face.
- Read the firm’s annual report or review (and compare it to a competitor), follow their news on Twitter in the weeks ahead of the interview.
- Be aware of what is happening in the legal world.
- Keep up to date with current affairs including areas of business that interest you.
- Learn some basic business language, have a broad understanding of mergers and acquisitions and how they are structured. Know how to read a balance sheet.
- Be clear on the importance of technology for all businesses.
- Practise reading business articles in a set time and then summarise the key points.
- You may find it useful to become familiar with some basic analysis tools used in business such as SWOT and PESTLE as they may help you think of areas to consider in some responses. Don't go overboard with these though as they might hinder your ability to write a clear and appropriate response if they are used incorrectly.
- Complete some of the exercises that firms offer in their online work experience/online internship schemes. Many are listed on Forage.
Resources for Building Commercial Awareness
Good resources for City and global firms are:
All You Need To Know About The City by Chris Stoakes, and Commercial Law Handbook by Jake Schogger are useful preparation for understanding business terms, how deals work and general commercial awareness as it applies to the legal industry.
Useful websites include:
- My experience on case study interview: How should you prepare for a case-study interview? - a Legal Case Study on LawCareers.Net
- Chambers Student: Commercial Awareness Resources - Legal Blogs
- Chambers Student: Legal industry trends
- LawCareers.Net commercial awareness weekly round ups
- UK Government guidance on how to set up a business
- BBC News: Business
- How to Read a Balance Sheet (The Non-Boring Version)
- Linklaters “Commercial Awareness” advice
- Virtual work experience programmes for several law firms including Linklaters, White & Case and Pinsent Masons are available on the Forage platform.
- Warwick Place: news articles about challenges faced by law firms
- legalfutures.co.uk – has a free newsletter rounding up key changes and news in the legal sector.
- Our self directed learning information pages contain resources for free online courses
- Investopedia has a good dictionary for business terms.
Building Your Commercial Awareness Skills at Oxford
- Attend skills sessions run by law firms online as well as those run by The Careers Service , the Oxford Law Society , the Oxford Bar Society and the Law Faculty
- The Oxford Strategy Challenge – ideal for building up team work, commercial awareness and skills in working with business clients. Run regularly throughout the year (online).
- Insight into Strategy and Management – a short course, run each term, to improve your business knowledge.
- Develop your employability skills – includes many ideas for building these at Oxford including practical suggestions for developing your “business awareness”.
- Presentation and other assessment centre skills advice
- CareerConnect VACANCIES
- CareerConnect EVENTS
- RELATED NEWS
Looking for more?
Check the CareerConnect platform for all our upcoming events and opportunities, book appointments, find jobs and internships, and more.
Login to CareerConnect
Recommended links
Oxford Guide to Careers 202 4

Cover Letters
Sectors & Occupations
See a Careers Adviser
Connect with us
- Follow us on LinkedIn
- Follow us on 𝕏 X (Twitter)
- Follow us on Instagram
- Follow us on YouTube
- Follow us on Facebook
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about crime in the U.S.
A growing share of Americans say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress to address this year. Around six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) hold that view today, up from 47% at the beginning of Joe Biden’s presidency in 2021.
We conducted this analysis to learn more about U.S. crime patterns and how those patterns have changed over time.
The analysis relies on statistics published by the FBI, which we accessed through the Crime Data Explorer , and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS), which we accessed through the National Crime Victimization Survey data analysis tool .
To measure public attitudes about crime in the U.S., we relied on survey data from Pew Research Center and Gallup.
Additional details about each data source, including survey methodologies, are available by following the links in the text of this analysis.
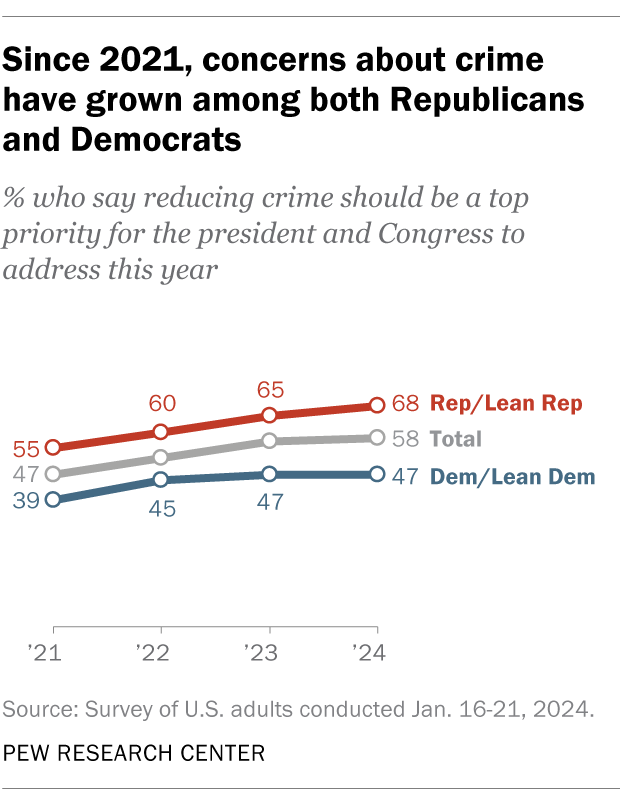
With the issue likely to come up in this year’s presidential election, here’s what we know about crime in the United States, based on the latest available data from the federal government and other sources.
How much crime is there in the U.S.?
It’s difficult to say for certain. The two primary sources of government crime statistics – the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) – paint an incomplete picture.
The FBI publishes annual data on crimes that have been reported to law enforcement, but not crimes that haven’t been reported. Historically, the FBI has also only published statistics about a handful of specific violent and property crimes, but not many other types of crime, such as drug crime. And while the FBI’s data is based on information from thousands of federal, state, county, city and other police departments, not all law enforcement agencies participate every year. In 2022, the most recent full year with available statistics, the FBI received data from 83% of participating agencies .
BJS, for its part, tracks crime by fielding a large annual survey of Americans ages 12 and older and asking them whether they were the victim of certain types of crime in the past six months. One advantage of this approach is that it captures both reported and unreported crimes. But the BJS survey has limitations of its own. Like the FBI, it focuses mainly on a handful of violent and property crimes. And since the BJS data is based on after-the-fact interviews with crime victims, it cannot provide information about one especially high-profile type of offense: murder.
All those caveats aside, looking at the FBI and BJS statistics side-by-side does give researchers a good picture of U.S. violent and property crime rates and how they have changed over time. In addition, the FBI is transitioning to a new data collection system – known as the National Incident-Based Reporting System – that eventually will provide national information on a much larger set of crimes , as well as details such as the time and place they occur and the types of weapons involved, if applicable.
Which kinds of crime are most and least common?
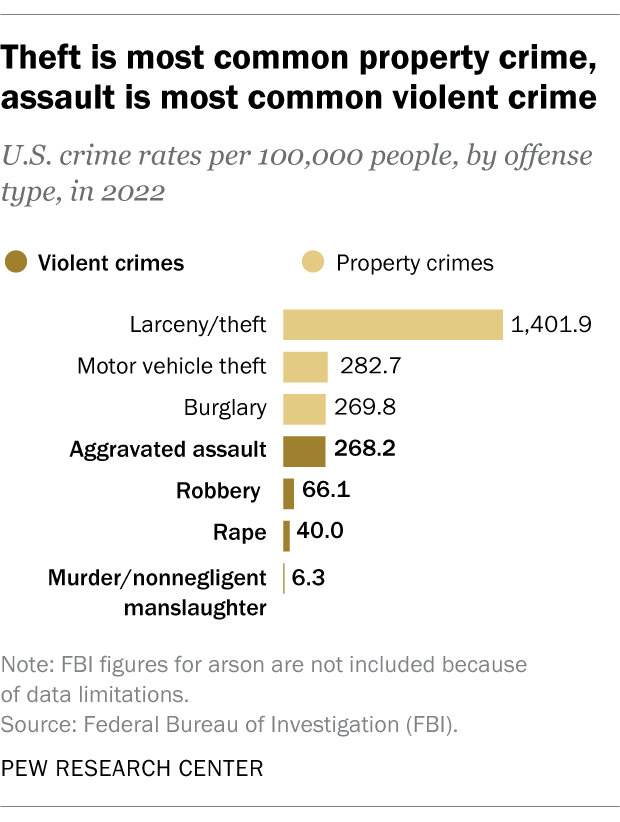
Property crime in the U.S. is much more common than violent crime. In 2022, the FBI reported a total of 1,954.4 property crimes per 100,000 people, compared with 380.7 violent crimes per 100,000 people.
By far the most common form of property crime in 2022 was larceny/theft, followed by motor vehicle theft and burglary. Among violent crimes, aggravated assault was the most common offense, followed by robbery, rape, and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter.
BJS tracks a slightly different set of offenses from the FBI, but it finds the same overall patterns, with theft the most common form of property crime in 2022 and assault the most common form of violent crime.
How have crime rates in the U.S. changed over time?
Both the FBI and BJS data show dramatic declines in U.S. violent and property crime rates since the early 1990s, when crime spiked across much of the nation.
Using the FBI data, the violent crime rate fell 49% between 1993 and 2022, with large decreases in the rates of robbery (-74%), aggravated assault (-39%) and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter (-34%). It’s not possible to calculate the change in the rape rate during this period because the FBI revised its definition of the offense in 2013 .
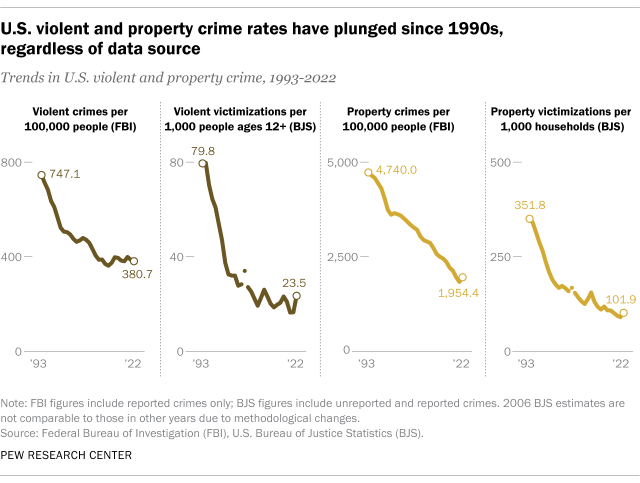
The FBI data also shows a 59% reduction in the U.S. property crime rate between 1993 and 2022, with big declines in the rates of burglary (-75%), larceny/theft (-54%) and motor vehicle theft (-53%).
Using the BJS statistics, the declines in the violent and property crime rates are even steeper than those captured in the FBI data. Per BJS, the U.S. violent and property crime rates each fell 71% between 1993 and 2022.
While crime rates have fallen sharply over the long term, the decline hasn’t always been steady. There have been notable increases in certain kinds of crime in some years, including recently.
In 2020, for example, the U.S. murder rate saw its largest single-year increase on record – and by 2022, it remained considerably higher than before the coronavirus pandemic. Preliminary data for 2023, however, suggests that the murder rate fell substantially last year .
How do Americans perceive crime in their country?
Americans tend to believe crime is up, even when official data shows it is down.
In 23 of 27 Gallup surveys conducted since 1993 , at least 60% of U.S. adults have said there is more crime nationally than there was the year before, despite the downward trend in crime rates during most of that period.
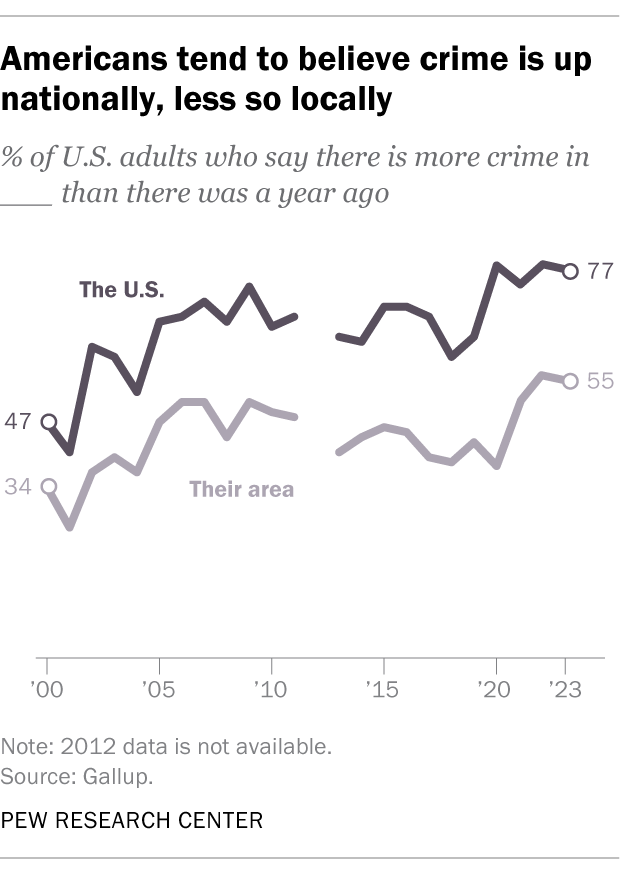
While perceptions of rising crime at the national level are common, fewer Americans believe crime is up in their own communities. In every Gallup crime survey since the 1990s, Americans have been much less likely to say crime is up in their area than to say the same about crime nationally.
Public attitudes about crime differ widely by Americans’ party affiliation, race and ethnicity, and other factors . For example, Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are much more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress this year (68% vs. 47%), according to a recent Pew Research Center survey.
How does crime in the U.S. differ by demographic characteristics?
Some groups of Americans are more likely than others to be victims of crime. In the 2022 BJS survey , for example, younger people and those with lower incomes were far more likely to report being the victim of a violent crime than older and higher-income people.
There were no major differences in violent crime victimization rates between male and female respondents or between those who identified as White, Black or Hispanic. But the victimization rate among Asian Americans (a category that includes Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders) was substantially lower than among other racial and ethnic groups.
The same BJS survey asks victims about the demographic characteristics of the offenders in the incidents they experienced.
In 2022, those who are male, younger people and those who are Black accounted for considerably larger shares of perceived offenders in violent incidents than their respective shares of the U.S. population. Men, for instance, accounted for 79% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, compared with 49% of the nation’s 12-and-older population that year. Black Americans accounted for 25% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, about twice their share of the 12-and-older population (12%).
As with all surveys, however, there are several potential sources of error, including the possibility that crime victims’ perceptions about offenders are incorrect.
How does crime in the U.S. differ geographically?
There are big geographic differences in violent and property crime rates.
For example, in 2022, there were more than 700 violent crimes per 100,000 residents in New Mexico and Alaska. That compares with fewer than 200 per 100,000 people in Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire and Maine, according to the FBI.
The FBI notes that various factors might influence an area’s crime rate, including its population density and economic conditions.
What percentage of crimes are reported to police? What percentage are solved?
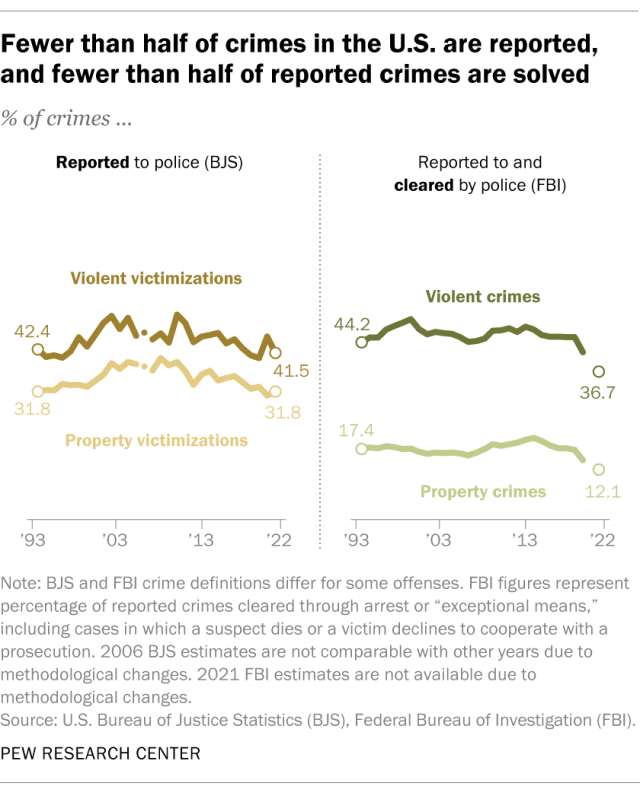
Most violent and property crimes in the U.S. are not reported to police, and most of the crimes that are reported are not solved.
In its annual survey, BJS asks crime victims whether they reported their crime to police. It found that in 2022, only 41.5% of violent crimes and 31.8% of household property crimes were reported to authorities. BJS notes that there are many reasons why crime might not be reported, including fear of reprisal or of “getting the offender in trouble,” a feeling that police “would not or could not do anything to help,” or a belief that the crime is “a personal issue or too trivial to report.”
Most of the crimes that are reported to police, meanwhile, are not solved , at least based on an FBI measure known as the clearance rate . That’s the share of cases each year that are closed, or “cleared,” through the arrest, charging and referral of a suspect for prosecution, or due to “exceptional” circumstances such as the death of a suspect or a victim’s refusal to cooperate with a prosecution. In 2022, police nationwide cleared 36.7% of violent crimes that were reported to them and 12.1% of the property crimes that came to their attention.
Which crimes are most likely to be reported to police? Which are most likely to be solved?
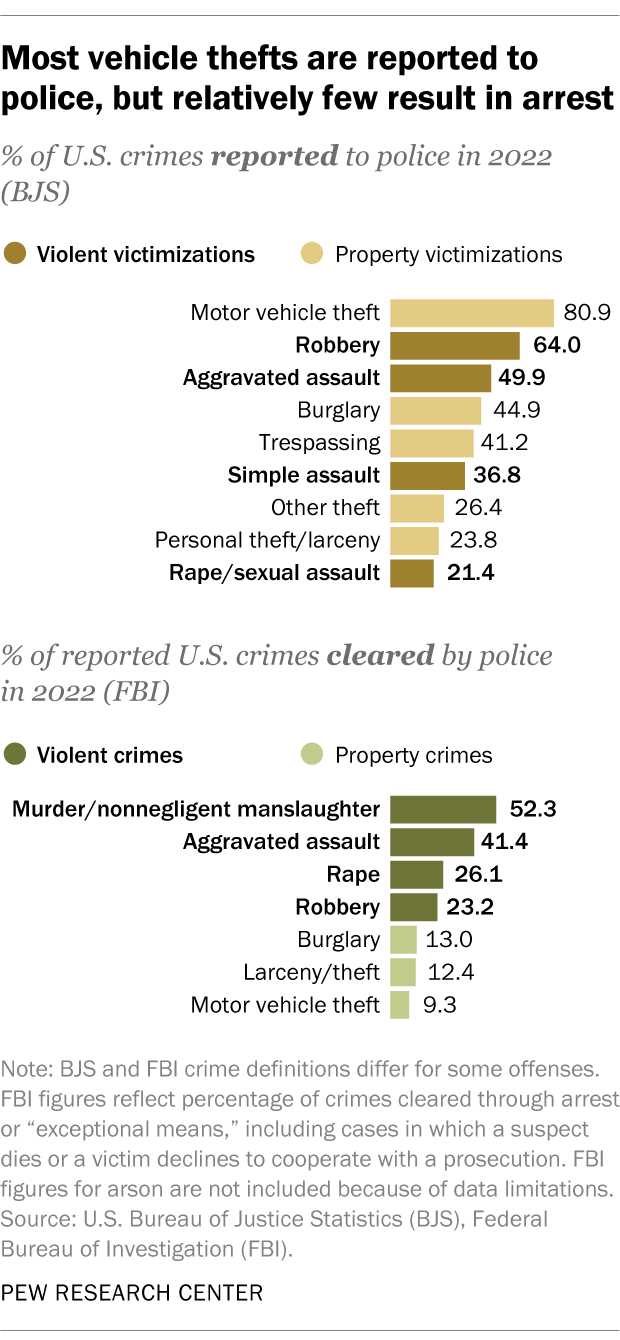
Around eight-in-ten motor vehicle thefts (80.9%) were reported to police in 2022, making them by far the most commonly reported property crime tracked by BJS. Household burglaries and trespassing offenses were reported to police at much lower rates (44.9% and 41.2%, respectively), while personal theft/larceny and other types of theft were only reported around a quarter of the time.
Among violent crimes – excluding homicide, which BJS doesn’t track – robbery was the most likely to be reported to law enforcement in 2022 (64.0%). It was followed by aggravated assault (49.9%), simple assault (36.8%) and rape/sexual assault (21.4%).
The list of crimes cleared by police in 2022 looks different from the list of crimes reported. Law enforcement officers were generally much more likely to solve violent crimes than property crimes, according to the FBI.
The most frequently solved violent crime tends to be homicide. Police cleared around half of murders and nonnegligent manslaughters (52.3%) in 2022. The clearance rates were lower for aggravated assault (41.4%), rape (26.1%) and robbery (23.2%).
When it comes to property crime, law enforcement agencies cleared 13.0% of burglaries, 12.4% of larcenies/thefts and 9.3% of motor vehicle thefts in 2022.
Are police solving more or fewer crimes than they used to?
Nationwide clearance rates for both violent and property crime are at their lowest levels since at least 1993, the FBI data shows.
Police cleared a little over a third (36.7%) of the violent crimes that came to their attention in 2022, down from nearly half (48.1%) as recently as 2013. During the same period, there were decreases for each of the four types of violent crime the FBI tracks:
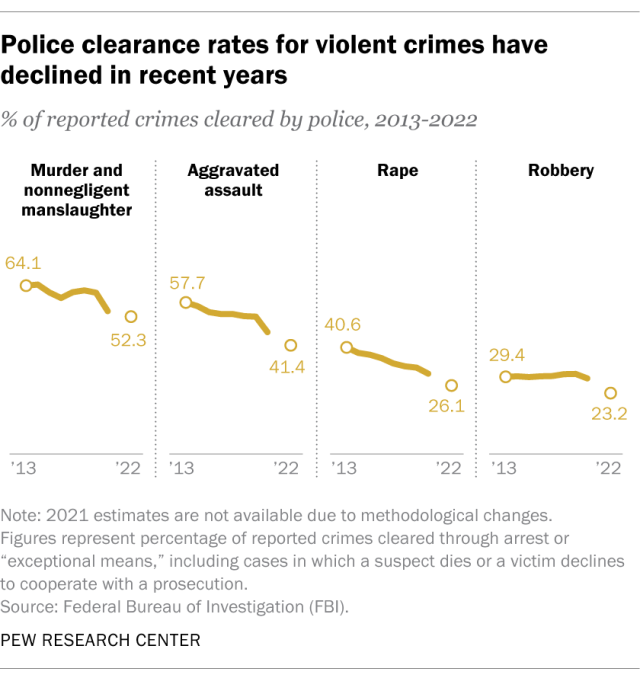
- Police cleared 52.3% of reported murders and nonnegligent homicides in 2022, down from 64.1% in 2013.
- They cleared 41.4% of aggravated assaults, down from 57.7%.
- They cleared 26.1% of rapes, down from 40.6%.
- They cleared 23.2% of robberies, down from 29.4%.
The pattern is less pronounced for property crime. Overall, law enforcement agencies cleared 12.1% of reported property crimes in 2022, down from 19.7% in 2013. The clearance rate for burglary didn’t change much, but it fell for larceny/theft (to 12.4% in 2022 from 22.4% in 2013) and motor vehicle theft (to 9.3% from 14.2%).
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Nov. 20, 2020.
- Criminal Justice

John Gramlich is an associate director at Pew Research Center
8 facts about Black Lives Matter
#blacklivesmatter turns 10, support for the black lives matter movement has dropped considerably from its peak in 2020, fewer than 1% of federal criminal defendants were acquitted in 2022, before release of video showing tyre nichols’ beating, public views of police conduct had improved modestly, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
At this time, we recommend all Penn-affiliated travel to Israel, West Bank, Gaza, and Lebanon be deferred. If you are planning travel to any of these locations, please reach out to [email protected] for the most up to date risk assessment and insurance exclusions. As a reminder, it is required that all Penn-affiliated trips are registered in MyTrips . If you have questions, please contact [email protected] .
Utility Navigation
Utility links.
- University of Pennsylvania
- Office of the Provost
- Penn Global
Secondary Nav Penn Global
- For Penn Students
- For Penn Faculty
- For Alumni & Friends
Primary Nav Penn Global
Drawer menu penn global.
- Back to main menu
- Our Strategic Framework
- Perry World House
- Penn Biden Center
- Penn Abroad
- International Student & Scholar Services
- Global Support Services
- Penn in Africa
- Penn in China
- 2022 PLAC Symposium
- Pulitzer International Reporting Student Fellowship
- Connect with PLAC
- Penn in Oceania
- Penn in the Middle East
- Penn in Northern America
- Global at Penn's Schools
- Global Centers & Programs
- Global Engagement Fund
- China Research and Engagement Fund
- India Research and Engagement Fund
- Holman Africa Research and Engagement Fund
- Apply for a Convening Grant
- Apply for a Research Grant
- Manage My Grant
- Grants Database
PENN GLOBAL RESEARCH & ENGAGEMENT GRANT PROGRAM 2024 Grant Program Awardees
Basic page sidebar menu penn global.
In 2024, Penn Global will support 24 new faculty-led research and engagement projects at a total funding level of $1.5 million.
The Penn Global Research and Engagement Grant Program prioritizes projects that bring together leading scholars and practitioners across the University community and beyond to develop new insight on significant global issues in key countries and regions around the world, a core pillar of Penn’s global strategic framework.
PROJECTS SUPPORTED BY THE HOLMAN AFRICA RESEARCH AND ENGAGEMENT FUND
- Global Medical Physics Training & Development Program Stephen Avery, Perelman School of Medicine
- Developing a Dakar Greenbelt with Blue-Green Wedges Proposal Eugenie Birch, Weitzman School of Design
- Emergent Judaism in Sub-Saharan Africa Peter Decherney, School of Arts and Sciences / Sara Byala, School of Arts and Sciences
- Determinants of Cognitive Aging among Older Individuals in Ghana Irma Elo, School of Arts and Sciences
- Disrupted Aid, Displaced Lives Guy Grossman, School of Arts and Sciences
- A History of Regenerative Agriculture Practices from the Global South: Case Studies from Ethiopia, Kenya, and Zimbabwe Thabo Lenneiye, Kleinman Energy Center / Weitzman School of Design
- Penn Computerized Neurocognitive Battery Use in Botswana Public Schools Elizabeth Lowenthal, Perelman School of Medicine
- Podcasting South African Jazz Past and Present Carol Muller, School of Arts and Sciences
- Lake Victoria Megaregion Study: Joint Lakefront Initiative Frederick Steiner, Weitzman School of Design
- Leveraging an Open Source Software to Prevent and Contain AMR Jonathan Strysko, Perelman School of Medicine
- Poverty reduction and children's neurocognitive growth in Cote d'Ivoire Sharon Wolf, Graduate School of Education
- The Impacts of School Connectivity Efforts on Education Outcomes in Rwanda Christopher Yoo, Carey Law School
PROJECTS SUPPORTED BY THE INDIA RESEARCH AND ENGAGEMENT FUND
- Routes Beyond Conflict: A New Approach to Cultural Encounters in South Asia Daud Ali, School of Arts and Sciences
- Prioritizing Air Pollution in India’s Cities Tariq Thachil, Center for the Advanced Study of India / School of Arts and Sciences
- Intelligent Voicebots to Help Indian Students Learn English Lyle Ungar, School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
PROJECTS SUPPORTED BT THE CHINA RESEARCH AND ENGAGEMENT FUND
- Planning Driverless Cities in China Zhongjie Lin, Weitzman School of Design
PROJECTS SUPPORTED BY THE GLOBAL ENGAGEMENT FUND
- Education and Economic Development in Nepal Amrit Thapa, Graduate School of Education
- Explaining Climate Change Regulation in Cities: Evidence from Urban Brazil Alice Xu, School of Arts and Sciences
- Nurse Staffing Legislation for Scotland: Lessons for the U.S. and the U.K. Eileen Lake, School of Nursing
- Pathways to Education Development & Their Consequences: Finland, Korea, US Hyunjoon Park, School of Arts and Sciences
- Engaged Scholarship in Latin America: Bridging Knowledge and Action Tulia Falleti, School of Arts and Sciences
- Organizing Migrant Communities to Realize Rights in Palermo, Sicily Domenic Vitiello, Weitzman School of Design
- Exploiting Cultural Heritage in 21st Century Conflict Fiona Cunningham, School of Arts and Sciences
- Center for Integrative Global Oral Health Alonso Carrasco-Labra, School of Dental Medicine
This first-of-its-kind Global Medical Physics Training and Development Program (GMPTDP) seeks to serve as an opportunity for PSOM and SEAS graduate students to enhance their clinical requirement with a global experience, introduce them to global career opportunities and working effectively in different contexts, and strengthens partnerships for education and research between US and Africa. This would also be an exceptional opportunity for pre-med/pre-health students and students interested in health tech to have a hands-on global experience with some of the leading professionals in the field. The project will include instruction in automated radiation planning through artificial intelligence (AI); this will increase access to quality cancer care by standardizing radiation planning to reduce inter-user variability and error, decreasing workload on the limited radiation workforce, and shortening time to treatment for patients. GMPTDP will offer a summer clinical practicum to Penn students during which time they will also collaborate with UGhana to implement and evaluate AI tools in the clinical workflow.
The proposal will address today’s pressing crises of climate change, land degradation, biodiversity loss, and growing economic disparities with a holistic approach that combines regional and small-scale actions necessary to achieve sustainability. It will also tackle a key issue found across sub-Saharan Africa, many emerging economies, and economically developed countries that struggle to control rapid unplanned urbanization that vastly outpaces the carrying capacity of the surrounding environment.
The regional portion of the project will create a framework for a greenbelt that halts the expansion of the metropolitan footprint. It will also protect the Niayes, an arable strip of land that produces over 80% of the country’s vegetables, from degradation. This partnership will also form a south-south collaboration to provide insights into best practices from a city experiencing similar pressures.
The small-scale portion of the project will bolster and create synergy with ongoing governmental and grassroots initiatives aimed at restoring green spaces currently being infilled or degraded in the capital. This will help to identify overlapping goals between endeavors, leading to collaboration and mobilizing greater funding possibilities instead of competing over the same limited resources. With these partners, we will identify and design Nature-based Solutions for future implementation.
Conduct research through fieldwork to examine questions surrounding Jewish identity in Africa. Research will be presented in e.g. articles, photographic images, and films, as well as in a capstone book. In repeat site-visits to Uganda, South Africa, Ghana, and Zimbabwe, we will conduct interviews with and take photographs of stakeholders from key communities in order to document their everyday lives and religious practices.
The overall aim of this project is the development of a nationally representative study on aging in Ghana. This goal requires expanding our network of Ghanian collaborators and actively engage them in research on aging. The PIs will build on existing institutional contacts in Ghana that include:
1). Current collaboration with the Navrongo Health Research Center (NCHR) on a pilot data collection on cognitive aging in Ghana (funded by a NIA supplement and which provides the matching funds for this Global Engagement fund grant application);
2) Active collaboration with the Regional Institute for Population Studies (RIPS), University of Ghana. Elo has had a long-term collaboration with Dr. Ayaga Bawah who is the current director of RIPS.
In collaboration with UNHCR, we propose studying the effects of a dramatic drop in the level of support for refugees, using a regression discontinuity design to survey 2,500 refugee households just above and 2,500 households just below the vulnerability score cutoff that determines eligibility for full rations. This study will identify the effects of aid cuts on the welfare of an important marginalized population, and on their livelihood adaptation strategies. As UNHCR faces budgetary cuts in multiple refugee-hosting contexts, our study will inform policymakers on the effects of funding withdrawal as well as contribute to the literature on cash transfers.
The proposed project, titled "A History of Regenerative Agriculture Practices from the Global South: Case Studies from Ethiopia, Kenya, and Zimbabwe," aims to delve into the historical and contemporary practices of regenerative agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa. Anticipated Outputs and Outcomes:
1. Research Paper: The primary output of this project will be a comprehensive research paper. This paper will draw from a rich pool of historical and contemporary data to explore the history of regenerative agriculture practices in Ethiopia, Kenya, and Zimbabwe. It will document the indigenous knowledge and practices that have sustained these regions for generations.
2. Policy Digest: In addition to academic research, the project will produce a policy digest. This digest will distill the research findings into actionable insights for policymakers, both at the national and international levels. It will highlight the benefits of regenerative agriculture and provide recommendations for policy frameworks that encourage its adoption.
3. Long-term Partnerships: The project intends to establish long-term partnerships with local and regional universities, such as Great Lakes University Kisumu, Kenya. These partnerships will facilitate knowledge exchange, collaborative research, and capacity building in regenerative agriculture practices. Such collaborations align with Penn Global's goal of strengthening institutional relationships with African partners.
The Penn Computerized Neurocognitive Battery (PCNB) was developed at the University of Pennsylvania by Dr. Ruben C. Gur and colleagues to be administered as part of a comprehensive neuropsychiatric assessment. Consisting of a series of cognitive tasks that help identify individuals’ cognitive strengths and weaknesses, it has recently been culturally adapted and validated by our team for assessment of school-aged children in Botswana . The project involves partnership with the Botswana Ministry of Education and Skills Development (MoESD) to support the rollout of the PCNB for assessment of public primary and secondary school students in Botswana. The multidisciplinary Penn-based team will work with partners in Botswana to guide the PCNB rollout, evaluate fidelity to the testing standards, and track student progress after assessment and intervention. The proposed project will strengthen a well-established partnership between Drs. Elizabeth Lowenthal and J. Cobb Scott from the PSOM and in-country partners. Dr. Sharon Wolf, from Penn’s Graduate School of Education, is an expert in child development who has done extensive work with the Ministry of Education in Ghana to support improvements in early childhood education programs. She is joining the team to provide the necessary interdisciplinary perspective to help guide interventions and evaluations accompanying this new use of the PCNB to support this key program in Africa.
This project will build on exploratory research completed by December 24, 2023 in which the PI interviewed about 35 South Africans involved in jazz/improvised music mostly in Cape Town: venue owners, curators, creators, improvisers.
- Podcast series with 75-100 South African musicians interviewed with their music interspersed in the program.
- 59 minute radio program with extended excerpts of music inserted into the interview itself.
- Create a center of knowledge about South African jazz—its sound and its stories—building knowledge globally about this significant diasporic jazz community
- Expand understanding of “jazz” into a more diffuse area of improvised music making that includes a wide range of contemporary indigenous music and art making
- Partner w Lincoln Center Jazz (and South African Tourism) to host South Africans at Penn
This study focuses on the potential of a Megaregional approach for fostering sustainable development, economic growth, and social inclusion within the East African Community (EAC), with a specific focus on supporting the development of A Vision for An Inclusive Joint Lakefront across the 5 riparian counties in Kenya.
By leveraging the principles of Megaregion development, this project aims to create a unified socio-economic, planning, urbanism, cultural, and preservation strategy that transcends county boundaries and promotes collaboration further afield, among the EAC member countries surrounding the Lake Victoria Basin.
Anticipated Outputs and Outcomes:
1. Megaregion Conceptual Framework: The project will develop a comprehensive Megaregion Conceptual Framework for the Joint Lakefront region in East Africa. This framework, which different regions around the world have applied as a way of bridging local boundaries toward a unified regional vision will give the Kisumu Lake region a path toward cooperative, multi-jurisdictional planning. The Conceptual Framework will be both broad and specific, including actionable strategies, projects, and initiatives aimed at sustainable development, economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental stewardship.
2. Urbanism Projects: Specific urbanism projects will be proposed for key urban centers within the Kenyan riparian counties. These projects will serve as tangible examples of potential improvements and catalysts for broader development efforts.
3. Research Publication: The findings of the study will be captured in a research publication, contributing to academic discourse and increasing Penn's visibility in the field of African urbanism and sustainable development
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has emerged as a global crisis, causing more deaths than HIV/AIDS and malaria worldwide. By engaging in a collaborative effort with the Botswana Ministry of Health’s data scientists and experts in microbiology, human and veterinary medicine, and bioinformatics, we will aim to design new electronic medical record system modules that will:
Aim 1: Support the capturing, reporting, and submission of microbiology data from sentinel surveillance laboratories as well as pharmacies across the country
Aim 2: Develop data analytic dashboards for visualizing and characterizing regional AMR and AMC patterns
Aim 3: Submit AMR and AMC data to regional and global surveillance programs
Aim 4: Establish thresholds for alert notifications when disease activity exceeds expected incidence to serve as an early warning system for outbreak detection.
Using a novel interdisciplinary approach that bridges development economics, psychology, and neuroscience, the overall goal of this project is to improve children's development using a poverty-reduction intervention in Cote d'Ivoire (CIV). The project will directly measure the impacts of cash transfers (CTs) on neurocognitive development, providing a greater understanding of how economic interventions can support the eradication of poverty and ensure that all children flourish and realize their full potential. The project will examine causal mechanisms by which CTs support children’s healthy neurocognitive development and learning outcomes through the novel use of an advanced neuroimaging tool, functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS), direct child assessments, and parent interviews.
The proposed research, the GIGA initiative for Improving Education in Rwanda (GIER), will produce empirical evidence on the impact of connecting schools on education outcomes to enable Rwanda to better understand how to accelerate the efforts to bring connectivity to schools, how to improve instruction and learning among both teachers and students, and whether schools can become internet hubs capable of providing access e-commerce and e-government services to surrounding communities. In addition to evaluating the impact of connecting schools on educational outcomes, the research would also help determine which aspects of the program are critical to success before it is rolled out nationwide.
Through historical epigraphic research, the project will test the hypothesis that historical processes and outcomes in the 14th century were precipitated by a series of related global and local factors and that, moreover, an interdisciplinary and synergistic analysis of these factors embracing climatology, hydrology, epidemiology linguistics and migration will explain the transformation of the cultural, religious and social landscapes of the time more effectively than the ‘clash of civilizations’ paradigm dominant in the field. Outputs include a public online interface for the epigraphic archive; a major international conference at Penn with colleagues from partner universities (Ghent, Pisa, Edinburgh and Penn) as well as the wider South Asia community; development of a graduate course around the research project, on multi-disciplinary approaches to the problem of Hindu-Muslim interaction in medieval India; and a public facing presentation of our findings and methods to demonstrate the path forward for Indian history. Several Penn students, including a postdoc, will be actively engaged.
India’s competitive electoral arena has failed to generate democratic accountability pressures to reduce toxic air. This project seeks to broadly understand barriers to such pressures from developing, and how to overcome them. In doing so, the project will provide the first systematic study of attitudes and behaviors of citizens and elected officials regarding air pollution in India. The project will 1) conduct in-depth interviews with elected local officials in Delhi, and a large-scale survey of elected officials in seven Indian states affected by air pollution, and 2) partner with relevant civil society organizations, international bodies like the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), domain experts at research centers like the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI), and local civic organizations (Janagraaha) to evaluate a range of potential strategies to address pollution apathy, including public information campaigns with highly affected citizens (PHFI), and local pollution reports for policymakers (Janagraaha).
The biggest benefit from generative AI such as GPT, will be the widespread availability of tutoring systems to support education. The project will use this technology to build a conversational voicebot to support Indian students in learning English. The project will engage end users (Indian tutors and their students) in the project from the beginning. The initial prototype voice-driven conversational system will be field-tested in Indian schools and adapted. The project includes 3 stages of development:
1) Develop our conversational agent. Specify the exact initial use case and Conduct preliminary user testing.
2) Fully localize to India, addressing issues identified in Phase 1 user testing.
3) Do comprehensive user testing with detailed observation of 8-12 students using the agent for multiple months; conduct additional assessments of other stakeholders.
The project partners with Ashoka University and Pratham over all three stages, including writing scholarly papers.
Through empirical policy analysis and data-based scenario planning, this project actively contributes to this global effort by investigating planning and policy responses to autonomous transportation in the US and China. In addition to publishing several research papers on this subject, the PI plans to develop a new course and organize a forum at PWCC in 2025. These initiatives are aligned with an overarching endeavor that the PI leads at the Weitzman School of Design, which aims to establish a Future Cities Lab dedicated to research and collaboration in the pursuit of sustainable cities.
This study aims to fill this gap through a more humanistic approach to measuring the impact of education on national development. Leveraging a mixed methods research design consisting of analysis of quantitative data for trends over time, observations of schools and classrooms, and qualitative inquiry via talking to people and hearing their stories, we hope to build a comprehensive picture of educational trends in Nepal and their association with intra-country development. Through this project we strive to better inform the efforts of state authorities and international organizations working to enhance sustainable development within Nepal, while concurrently creating space and guidance for further impact analyses. Among various methods of dissemination of the study’s findings, one key goal is to feed this information into writing a book on this topic.
Developing cities across the world have taken the lead in adopting local environmental regulation. Yet standard models of environmental governance begin with the assumption that local actors should have no incentives for protecting “the commons.” Given the benefits of climate change regulation are diffuse, individual local actors face a collective action problem. This project explores why some local governments bear the costs of environmental regulation while most choose to free-ride. The anticipated outputs of the project include qualitative data that illuminate case studies and the coding of quantitative spatial data sets for studying urban land-use. These different forms of data collection will allow me to develop and test a theoretical framework for understanding when and why city governments adopt environmental policy.
The proposed project will develop new insights on the issue of legislative solutions to the nurse staffing crisis, which will pertain to many U.S. states and U.K. countries. The PI will supervise the nurse survey data collection and to meet with government and nursing association stakeholders to plan the optimal preparation of reports and dissemination of results. The anticipated outputs of the project are a description of variation throughout Scotland in hospital nursing features, including nurse staffing, nurse work environments, extent of adherence to the Law’s required principles, duties, and method, and nurse intent to leave. The outcomes will be the development of capacity for sophisticated quantitative research by Scottish investigators, where such skills are greatly needed but lacking.
The proposed project will engage multi-cohort, cross-national comparisons of educational-attainment and labor-market experiences of young adults in three countries that dramatically diverge in how they have developed college education over the last three decades: Finland, South Korea and the US. It will produce comparative knowledge regarding consequences of different pathways to higher education, which has significant policy implications for educational and economic inequality in Finland, Korea, the US, and beyond. The project also will lay the foundation for ongoing collaboration among the three country teams to seek external funding for sustained collaboration on educational analyses.
With matching funds from PLAC and CLALS, we will jointly fund four scholars from diverse LAC countries to participate in workshops to engage our community regarding successful practices of community-academic partnerships.
These four scholars and practitioners from Latin America, who are experts on community-engaged scholarship, will visit the Penn campus during the early fall of 2024. As part of their various engagements on campus, these scholars will participate after the workshops as key guest speakers in the 7th edition of the Penn in Latin America and the Caribbean (PLAC) Conference, held on October 11, 2024, at the Perry World House. The conference will focus on "Public and Community Engaged Scholarship in Latin America, the Caribbean, and their Diasporas."
Palermo, Sicily, has been a leading center of migrant rights advocacy and migrant civic participation in the twenty-first century. This project will engage an existing network of diverse migrant community associations and anti-mafia organizations in Palermo to take stock of migrant rights and support systems in the city. Our partner organizations, research assistants, and cultural mediators from different communities will design and conduct a survey and interviews documenting experiences, issues and opportunities related to various rights – to asylum, housing, work, health care, food, education, and more. Our web-based report will include recommendations for city and regional authorities and other actors in civil society. The last phase of our project will involve community outreach and organizing to advance these objectives. The web site we create will be designed as the network’s information center, with a directory of civil society and services, updating an inventory not current since 2014, which our partner Diaspore per la Pace will continue to update.
This interdisciplinary project has four objectives: 1) to investigate why some governments and non-state actors elevated cultural heritage exploitation (CHX) to the strategic level of warfare alongside nuclear weapons, cyberattacks, political influence operations and other “game changers”; 2) which state or non-state actors (e.g. weak actors) use heritage for leverage in conflict and why; and 3) to identify the mechanisms through which CHX coerces an adversary (e.g. catalyzing international involvement); and 4) to identify the best policy responses for non-state actors and states to address the challenge of CHX posed by their adversaries, based on the findings produced by the first three objectives.
Identify the capacity of dental schools, organizations training oral health professionals and conducting oral health research to contribute to oral health policies in the WHO Eastern Mediterranean region, identify the barriers and facilitators to engage in OHPs, and subsequently define research priority areas for the region in collaboration with the WHO, oral health academia, researchers, and other regional stakeholders.
3539 Locust Walk University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA 19104
©2024 University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104
Footer Menu
- Report Accessibility Issues and Get Help
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
First, buy yourself a set of multi-colored highlighters, with at least four, or perhaps five or six different colors. Yellow, pink, and orange are usually the brightest. Depending on the brand, purple and green can be dark, but still work well. Although blue is a beautiful color, it tends to darken and hide the text.
Legal case briefs are an essential tool for you as a law student, as they provide a concise and organized summary of a court case. Case brief examples serve as a means for you to understand the facts, issues, and legal principles underlying a court decision, and are crucial in helping you develop analytical and critical thinking skills. One of the primary reasons why case briefs are important ...
FREE. All content is free for all to use, as we are supported by our strategic partners who utilize Casebriefs ™ to connect to the Higher Education and Professional Markets. Access the world's largest database of Free Case Briefs for Law Students. Curated from law school case books, includes links for optimal case understanding.
Cases, in turn, interpret those statutes and regulations. Cases may be the sole source of the law when the doctrine is strictly a common law doctrine. Even when law is based on a statute, cases interpreting the terms and intent of the statute are invaluable tools for legal writers. Some methods for using cases, discussed in detail below ...
Features an excerpt reproduced from Introduction to the Study of Law: Cases and Materials. Recommended Videos. Case Briefing: The Law School Playbook; Case Reading: The Law School Playbook ... How To Write A Case Brief or Case Outline for Law School (With An Example) This video from the Business Law Institute reviews how to write a case brief ...
A thorough publication on case studies, the ABCs of Case Teaching answers the question of why professors should use case studies, and offers strategies of engagement, of preparing to teach cases, debriefing, and more. It also provides a sample course packet and additional resources. Teaching with Case Studies (Stanford University, 1994)
Case Studies and Other Experiential Learning Tools from Harvard Law School. Toggle menu. 617-496-1316 Login or Sign Up; 0. ... Harvard Law School. The Case Studies. Sign In. The Case Study. a valuable tool for experiential, participant-centered learning. Learn More. Public Company Analysis.
The Case Study Teaching Method; Harvard Law Case Studies A-Z; Free Materials; Blog; Shop By Category; Harvard Law Case Studies A-Z; Free Materials; Program; Role Play; Workshop-Based Case Study; Discussion-Based Case Study; DVD; Subject; Sabrineh Ardalan; Sharon Block; Robert Bordone; Emily M. Broad Leib; Chad Carr; Robert Clark; John Coates ...
Sample of a case brief. Now that you've seen how a brief should be organized, let's apply the above template to one of the most famous cases that you'll study in your first year of law school: Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad Co. (248 NY3d 339 [1928]). This case was decided by the New York Court of Appeals in 1928, and the author of the ...
1. Identifying the legal issue is not so straightforward. Legal research involves interpreting many legal precedents and theories to justify your questions. Finding the right issue takes time and patience. 2. There's too much to research. Attorneys now face a great deal of case law and statutory material.
If you're new to creating legal case studies, learn below how writing a case study builds client trust, as well as tips for writing a compelling case study, including: Getting permission from your client. Choosing the right case. Making your case study easy to read. Providing easy access to your case study. Telling a compelling story.
an opinion as to the guilt or innocence of the defendant (if the case at hand is a criminal one). But these opinions must be subordinate to the logical conclusions that follow from the careful. application of rules to facts. The selections that follow demonstrate this process of application of rule to fact. We.
People (Colorado) v. Nathan Hall. Colorado Supreme Court 2004. Procedural History: At a preliminary hearing, the trial court dismissed case for lack of probable cause (defendant won) District court affirmed lack of probable cause (defendant won again) Appellate court reversed (People won)
The Stanford Law School Case Studies Collection is an exciting innovation in law school teaching designed to hone students' problem-solving skills and stimulate creativity. The Collection includes situational case studies and interactive simulations (collectively referred to as "Case Materials") that place students in the roles of lawyers ...
Normile did not have a contract to purchase the property from Defendant because Normile failed to accept the counteroffer before it was revoked. Citation22 Ill.313 N.C. 98, 326 S.E.2d 11 (1985) Brief Fact Summary. Plaintiffs Normile and Segal both attempted to purchase a piece of real estate from Defendant Miller.
Malone v Laskey - 1907. Example case summary. Last modified: 28th Oct 2021. The claimant lived in a house belonging to her husband's employer. The claimant's husband was a tenant, and she had a license to live at the property. Whilst using the lavatory, the cistern was dislodged by vibrations caused by the next-door neighbour's ...
The Case Study Teaching Method. It is easy to get confused between the case study method and the case method, particularly as it applies to legal education. The case method in legal education was invented by Christopher Columbus Langdell, Dean of Harvard Law School from 1870 to 1895. Langdell conceived of a way to systematize and simplify legal ...
Explore case studies of previous cases which Allan Rouben has represented. Find examples of case studies in all focus areas of law. Legroulx v. Pitre: Striking Jury Notice, Charter of Rights and Freedoms and Rules of Civil Procedure. By Allan Rouben. Background: A complicated action was proceeding in Ottawa before Justice Denis Power and a jury.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case law, also known as precedent or common law, is the body of prior judicial decisions that guide judges deciding issues before them. Depending on the relationship between the deciding court and the precedent, case law may be binding or merely persuasive. For example, a decision by the US Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit is binding on ...
Here are some examples of case study research: ... Law and Ethics. Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions. ...
These case studies expose participants to real-world problems that lawyers and firm leaders confront, and help them work through possible approaches and solutions. CDI was founded by Professor Ashish Nanda and is now directed by Dr. Lisa Rohrer. Great for: discussion-based case studies, law and business, management, professional development.
Many commercial law firms require candidates to undertake a case study at the final interview stage. There is not one single format, so it is advisable to ask the recruitment team what you can expect. Below are some general points and tips which have been put together from feedback from students who have gone through the process and what we ...
2.1. Interpretation and legal translation competence. The definition of legal competence by Šarčević (Citation 1997, 113) makes an explicit reference to 'full understanding of legal reasoning and the ability to solve legal problems, to analyse legal texts, and to foresee how a text will be interpreted and applied by courts'.Of the legal translation competence models, the model developed ...
In 2020, for example, ... That's the share of cases each year that are closed, or "cleared," through the arrest, charging and referral of a suspect for prosecution, or due to "exceptional" circumstances such as the death of a suspect or a victim's refusal to cooperate with a prosecution. ... Overall, law enforcement agencies cleared ...
The anticipated outputs of the project include qualitative data that illuminate case studies and the coding of quantitative spatial data sets for studying urban land-use. These different forms of data collection will allow me to develop and test a theoretical framework for understanding when and why city governments adopt environmental policy.