What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.

Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Topic Sentence + Examples
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
- What Is a Topic Sentence?
- 5 Steps to Writing a Good Topic Sentence
Elements of a Good Topic Sentence
Common pitfalls to avoid.
- Where To Get Your Essay Edited For Free
Crafting the perfect essay takes time and dedication. There are so many elements you have to worry about, such as tone, purpose, and correct spelling and grammar. Writing a strong topic sentences is another critical part in writing a cohesive essay.
Without a strong topic sentence, you risk losing your reader and perhaps part of your grade. If it’s a college admissions essay, then you need it to be as strong as possible to back up your application. Learn about what steps you should take to write a strong topic sentence.
What Is a Topic Sentence?
People often confuse a topic sentence with a thesis statement. A thesis statement is typically at the end of your opening paragraph, that dictates the main argument you’ll be making in your essay.
Throughout your essay, you’ll have multiple topic sentences, as each paragraph should start off with one. This beginning sentence is used to direct the topic of the paragraph and outline the flow of the following sentences. It’s used to help guide your reader and to continue to keep them hooked on your overall essay. Without topic sentences, your essay will be unorganized, lack transitions, and sound very choppy. To write a good topic sentence, there are several steps to take.
Writing a Good Topic Sentence: 5 Steps
Step 1: decide what you’re going to write about..
When you see the essay prompt, you’ll have some time to think through what you want to say and why. You have to decide if it’s a persuasive essay, informative, narrative, or descriptive. Determine your purpose for writing the essay after reading through the prompt. Whether it’s an assignment for school or if it’s to get into college, you need to make sure you have that purpose clearly outlined.
Step 2: Create a thesis statement.
One of the first things you need to do is create a thesis statement. This is typically a sentence with three points that you’ll back up throughout your essay.
For example: The Office became a cultural phenomenon because it spurred the careers of many of today’s successful movie stars, it talked about situations that most American workers can relate to, and even 15 years later, offers funny, relevant content that helps to break down prejudices.
You then use that thesis statement to create an essay around the points you want to make.
Step 3: Make your essay outline.
Once you have the points you want to make within your thesis statement hammered out, make an outline for your essay. This is where you’ll start to create your topic sentence for each paragraph. You want to clearly state the main idea of that paragraph in the very first sentence. From there, you back up that main idea with facts and reputable sources. Make sure your topic sentence is clear, but does not just announce your topic.
For example, do not write something like: “In this paragraph, I will discuss why it’s bad that poachers are killing giraffes.”
Instead, write something that clearly states your idea with a reasonable opinion and that gives direction to the paragraph: “Giraffes are a key part of the African ecosystem, so it’s important to enforce regulations against the poachers who are killing them for their body parts.”
You’d then follow that up with reasons why giraffes are a key part of the African ecosystem and how poachers are destroying their population.
Step 4: Begin writing your essay.
Once you have your thesis statement and you’ve created an outline with supporting paragraphs and their topic sentences, you can begin writing your essay. It’s important to make that outline before just jumping in–a disorganized essay can spell disaster for you as you continue to write, and could result in a poor grade. Many times, teachers will even require you to turn in your outline as part of your overall essay grade.
Step 5: Proofread and check your resources.
After you’ve written the essay, go back through it with a fine tooth comb. Read through each topic sentence and the paragraphs that follow to ensure that you’ve written clear, solid topic sentences throughout and that the paragraphs with them make sense. During the proofreading phase, you also need to recheck the sources you’re using. Make sure each source is reputable. In other words, do not use sites like Wikipedia where anyone can go in and edit an article to add misinformation. Use sites that:
- Are actual reputable news sources, such as the New York Times , CNN, CBS News
- Have domain names that end in .edu or .gov
- Come from an encyclopedia, such as Encyclopedia Britannica
Using sites that are not reputable could jeopardize the validity of your argument.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Now that you know the steps to set yourself up for success when writing a topic sentence, there are certain elements that go into a quality first sentence. Always make sure that your topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph. You don’t want to make your reader hunt for the point you’re trying to make. Check out some key elements of a good topic sentence:
Make sure your topic sentence isn’t too vague.
You need a topic sentence that has some specifics to it. It also needs to hook in your reader in some way with an opinion. A vague sentence makes it harder to write a paragraph that can clearly backs up your thoughts. For example:
DON’T: “In Pride and Prejudice, Mr. Bingley seems like a nice guy.”
DO: “When Mr. Bingley is first introduced, he comes across as a kind person because he speaks to everyone and doesn’t immediately pass judgment.”
Choose a reasonable opinion.
Your topic sentence should clearly outline whatever point you’re trying to make in the paragraph, but you want to pick a reasonable opinion that you can easily reinforce with facts and statistics. Here’s an example of what you should and should not do:
DON’T: “It’s obvious that Mr. Bingley was a total loser with no backbone.”
DO: “Mr. Bingley could have shown more confidence in his choices and stood up to Mr. Darcy when he found himself in love with Jane Bennet.”
You can then back that up with facts, saying that he was a wealthy Englishman and thus one of the key players in society at the time, which should have given him more confidence. If he’d been more confident, perhaps he would not have left and devastated Jane.
Use your topic sentence as a transition.
Along with telling the reader the point of your next paragraph, your topic sentence should also serve as a transition from the previous paragraph. Without a transition, the essay can feel like it’s choppy and disjointed. For example:
DON’T: “Mr. Bingley is a good man and here’s why.”
DO: “Although Mr. Bingley did break Jane’s heart by leaving, he ended up redeeming himself by returning to Netherfield Hall.”
Keep your topic sentence short.
A long, drawn-out topic sentence can risk losing your reader. Many times, it’s hard to determine the point of a sentence when it goes on for too long. You want a clear, concise sentence that draws in the reader but also leaves some room for you to expand on it in the following paragraph.
DON’T: “Throughout the novel of Pride and Prejudice, Mr. Bingley was often quite different from Mr. Darcy as he would treat all people in a friendly manner, considering them all his friends and acquaintances, even agreeing to throw a ball after Elizabeth’s sisters rudely demanded he do so and was gracious to Mr. and Mrs. Bennet as well despite their manners.”
DO: “Overall, Mr. Bingley served as a foil to Mr. Darcy throughout the story by treating everyone around him equally with dignity and grace.”
Writing an essay can be overwhelming at times, but so long as you avoid some of these common pitfalls, it can be easier to get it done on time.
Don’t wait until the last minute.
If your teacher assigns you an essay or tells you that you have an essay test coming up, don’t wait until the day before to do anything about it. You have to plan or study and you need to give yourself time to do that. If you know it takes you a while to write something, then start planning it as soon as you get the assignment.
Don’t forget to write an outline.
Along with planning, make sure you have that outline written up and planned out well. It will serve as your guideline for writing the essay. Without it, you’ll face the risk of a disorganized essay that does not clearly illustrate your point.
Ask for help if you need it.
This may be the most important pitfall to avoid. If you get in over your head while writing, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Ask a friend to review the essay or ask your teacher for guidance.
Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Once you’ve finished your essay, you may want additional input. There are tools out there to help, but CollegeVine’s free peer essay review tool can provide you with actionable feedback from students just like you. CollegeVine’s tool has helped many students and may be able to help you, too! Asking for peer feedback can help to refine your essay and it never hurts to have an extra set of eyes read through what you’ve written. Check out the free tool today!

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. Topic sentences reveal the main point of a paragraph. They show the relationship of each paragraph to the essay's thesis, telegraph the point of a paragraph, and tell your reader what to expect in the paragraph that follows. Topic sentences also establish their relevance right away, making clear why the points they're making are important to the essay's main ideas. They argue rather than report. Signposts , as their name suggests, prepare the reader for a change in the argument's direction. They show how far the essay's argument has progressed vis-ˆ-vis the claims of the thesis.
Topic sentences and signposts occupy a middle ground in the writing process. They are neither the first thing a writer needs to address (thesis and the broad strokes of an essay's structure are); nor are they the last (that's when you attend to sentence-level editing and polishing). Topic sentences and signposts deliver an essay's structure and meaning to a reader, so they are useful diagnostic tools to the writer—they let you know if your thesis is arguable—and essential guides to the reader
Forms of Topic Sentences
Sometimes topic sentences are actually two or even three sentences long. If the first makes a claim, the second might reflect on that claim, explaining it further. Think of these sentences as asking and answering two critical questions: How does the phenomenon you're discussing operate? Why does it operate as it does?
There's no set formula for writing a topic sentence. Rather, you should work to vary the form your topic sentences take. Repeated too often, any method grows wearisome. Here are a few approaches.
Complex sentences. Topic sentences at the beginning of a paragraph frequently combine with a transition from the previous paragraph. This might be done by writing a sentence that contains both subordinate and independent clauses, as in the example below.
Although Young Woman with a Water Pitcher depicts an unknown, middle-class woman at an ordinary task, the image is more than "realistic"; the painter [Vermeer] has imposed his own order upon it to strengthen it.
This sentence employs a useful principle of transitions: always move from old to new information. The subordinate clause (from "although" to "task") recaps information from previous paragraphs; the independent clauses (starting with "the image" and "the painter") introduce the new information—a claim about how the image works ("more than Ôrealistic'") and why it works as it does (Vermeer "strengthens" the image by "imposing order").
Questions. Questions, sometimes in pairs, also make good topic sentences (and signposts). Consider the following: "Does the promise of stability justify this unchanging hierarchy?" We may fairly assume that the paragraph or section that follows will answer the question. Questions are by definition a form of inquiry, and thus demand an answer. Good essays strive for this forward momentum.
Bridge sentences. Like questions, "bridge sentences" (the term is John Trimble's) make an excellent substitute for more formal topic sentences. Bridge sentences indicate both what came before and what comes next (they "bridge" paragraphs) without the formal trappings of multiple clauses: "But there is a clue to this puzzle."
Pivots. Topic sentences don't always appear at the beginning of a paragraph. When they come in the middle, they indicate that the paragraph will change direction, or "pivot." This strategy is particularly useful for dealing with counter-evidence: a paragraph starts out conceding a point or stating a fact ("Psychologist Sharon Hymer uses the term Ônarcissistic friendship' to describe the early stage of a friendship like the one between Celie and Shug"); after following up on this initial statement with evidence, it then reverses direction and establishes a claim ("Yet ... this narcissistic stage of Celie and Shug's relationship is merely a transitory one. Hymer herself concedes . . . "). The pivot always needs a signal, a word like "but," "yet," or "however," or a longer phrase or sentence that indicates an about-face. It often needs more than one sentence to make its point.
Signposts operate as topic sentences for whole sections in an essay. (In longer essays, sections often contain more than a single paragraph.) They inform a reader that the essay is taking a turn in its argument: delving into a related topic such as a counter-argument, stepping up its claims with a complication, or pausing to give essential historical or scholarly background. Because they reveal the architecture of the essay itself, signposts remind readers of what the essay's stakes are: what it's about, and why it's being written.
Signposting can be accomplished in a sentence or two at the beginning of a paragraph or in whole paragraphs that serve as transitions between one part of the argument and the next. The following example comes from an essay examining how a painting by Monet, The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, challenges Zola's declarations about Impressionist art. The student writer wonders whether Monet's Impressionism is really as devoted to avoiding "ideas" in favor of direct sense impressions as Zola's claims would seem to suggest. This is the start of the essay's third section:
It is evident in this painting that Monet found his Gare Saint-Lazare motif fascinating at the most fundamental level of the play of light as well as the loftiest level of social relevance. Arrival of a Train explores both extremes of expression. At the fundamental extreme, Monet satisfies the Impressionist objective of capturing the full-spectrum effects of light on a scene.
The writer signposts this section in the first sentence, reminding readers of the stakes of the essay itself with the simultaneous references to sense impression ("play of light") and intellectual content ("social relevance"). The second sentence follows up on this idea, while the third serves as a topic sentence for the paragraph. The paragraph after that starts off with a topic sentence about the "cultural message" of the painting, something that the signposting sentence predicts by not only reminding readers of the essay's stakes but also, and quite clearly, indicating what the section itself will contain.
Copyright 2000, Elizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
How to Generate Strong Essay Topics, With 30 Topic Examples

Whether you’re writing an analytical essay, a reflective essay, or a compare-and-contrast essay, you are generally focused on one central theme. An essay topic is the subject—it’s what an essay is about. Essay topics can be broad or narrow, simple or complex—every essay has a topic. Determining your topic is generally the first step in writing an essay.
Give your writing extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
What is an essay topic?
Essay topics are the broad subjects essays discuss. The purpose of an essay topic is to shape your essay. By defining your essay topic, you determine what you’ll explore in your writing, how you will investigate the topic, the elements you’ll cover (and which you’ll leave out), and the sources you will use to support your thesis statement.
For example, you might write an argumentative essay in support of requiring all students at your university to take a media literacy course during their first year . This potential new requirement would be your essay topic.
Sometimes, your instructor will assign an essay topic. When this is the case, you can jump right to thinking up ways of exploring that topic and developing your thesis statement. Other times, you will need to determine your own essay topic—and your instructor might or might not provide guidance in choosing the topic. When you’re on your own with determining ideas for an essay topic, there are a few different strategies you can use:
- Freewriting. Start with the type of essay you’ve been assigned (analytical, compare-and-contrast, personal, etc.) and let your mind wander. Write down any questions that come to mind, insights you have, observations about these questions or insights, and points that interest you.
- Researching others’ thoughts about the subject. This strategy works when you have a general idea of the subject you’d like to write about. You can familiarize yourself with the discourse surrounding that subject and read what others have said about it. Getting familiar with others’ writing can inspire you to add your take to the existing body of knowledge surrounding the subject.
- Answering the question you want to know the answer to. Think about the type of essay you plan to write and questions you would find satisfying to have answered in essay form.
- Finding gaps in the existing knowledge about your subject. This piggybacks on the strategy of exploring what others have said about it—what hasn’t been said? This could be your opportunity to write a thought-provoking original essay about your topic.
You can use these strategies for other kinds of writing, too, like creative writing and blog posts.
How to come up with an essay topic
Before you start exploring potential essay topic ideas, think about the kind of essay you are planning to write. Strong essay topics vary between types, so make your essay’s goal a significant part of choosing a topic. Keep the following in mind for each of the following types of essays :
Argumentative
An argumentative essay needs to support an argument. It also needs to demonstrate the flaws in a counter-argument. When you’re tasked with writing an argumentative essay, generate essay topics that have clear “sides” that can be supported and defended by discussing specific pieces of evidence. Choose an issue you can support through strong evidence, such as likely repercussions for changing the legal voting age.
Compare-and-contrast
In a compare-and-contrast essay , you need to show the similarities and differences between two subjects. Kick-start your topic development (or brainstorm if it’s a collaborative project) by thinking about subjects you can compare and contrast, such as the themes in two poems. Think about the specific angles you can take on the subjects you’ll focus on, and consider the comparisons you’ll make in your writing.
A political essay is an essay that examines present social and political challenges and proposes solutions to them. For example, a political essay might propose improvements to the housing market in the United States. To generate essay topics for a political essay, think about the issues that affect you or people you know, or historical trends and current events. You might have a unique perspective on proposed legislation or present political challenges, or you might simply provide a fresh voice in this discourse. Another strategy is to read the news and find a topic that’s trending, relevant, and something you have the knowledge and/or resources to write a strong essay about.
An analytical essay drills down to the components present in a work or an issue and addresses these components to reach conclusions. For example, your analytical essay topic might be how online classes have changed our relationship to education forever. As you explore essay topics for an analytical essay, think about something that interests or confuses you. In your analytical essay, you engage with the topic by questioning it and breaking it down, so choose a topic that’s got room to dive deep.
A personal essay is a reflective piece of writing that explores and discusses a topic from your own life. Unlike other kinds of essays, which support their positions through objective references to facts, statistics, scholarly insights, and other written works, a personal essay discusses its author’s own thoughts and feelings. There is no pressure to be objective in a personal essay; think of it as a chapter from your autobiography or a diary entry. To come up with essay topic ideas for a personal essay, think about events and experiences that have left a lasting impression on you.
Similar to an argumentative essay, a persuasive essay aims to persuade the reader to support a specific action or stance. The difference is that in a persuasive essay, the author’s goal is to persuade the reader to agree with their position, while an argumentative essay aims to show the reader why its thesis statement is objectively true. Strong persuasive essay topics are topics that are trending and divisive, such as the merits of dropping SAT scores from university admissions decisions.
Essay topic vs. thesis statement
An essay topic isn’t the same as its thesis statement. However, the two are closely related. An essay’s thesis statement concisely states the author’s position on the essay’s topic. In other words, the thesis statement narrows the topic down to a specific statement that the author then explores, analyzes, and—depending on the type of essay—defends in the body paragraphs.
Here are a few examples of essay topics and accompanying thesis statements:
Topic: Changing the legal voting age
Thesis statement: When nations lower the legal voting age to 16, youth civic participation increases. To combat low voter turnout among young adults, the United States should reduce the voting age to 16.
Topic: Does exercise matter if you eat a healthy diet?
Thesis statement: Research shows that while diet plays a significant role in an individual’s overall health and fitness, regular exercise plays a crucial role in strengthening bones and muscles, maintaining weight, and reducing an individual’s risk of disease.
Similarly, an essay topic is not the same as an essay title—but there is a relationship between an essay’s topic and title. An essay title should make its essay’s topic clear to the reader.
30 essay topic examples
Persuasive essay topics.
- The harms of single-use plastic
- Planned obsolescence
- Pineapple on pizza
- How can we be better neighbors?
- Ways to make writing easier for high school students
Personal essay topics
- My grandmother’s cooking
- My favorite dinosaur
- A pivotal trip I took
- My reaction to reading my own published writing
- Why I’ll never have another pet pig
Argumentative essay topics
- Should cars be banned from downtown?
- Why do we get addicted to social media?
- Should the library be open 24/7?
- Should high schools eliminate summer vacation?
- Are we too apathetic about the amount of data we share?
Analytical essay topics
- Themes of love in Frankenstein and House of Leaves
- Grammar’s role in communication
- Information retention when writing notes by hand
- Dogs as symbolism in Wuthering Heights
- Music education in elementary schools
Political essay topics
- The Electoral College’s validity in modern elections
- Student debt forgiveness
- Strategies for increasing voter turnout
- Potential outcomes of redrawing voting districts
- What if we let AI govern us?
Compare and contrast essay topics
- For commuters, are trains or buses a more environmentally friendly option?
- Vegan versus vegetarian diets
- A comparison of the writing styles of Toni Morrison’s early and later works
- Qualitative versus quantitative data in sociology
- The Handmaid’s Tale television show versus the original novel
Essay topics FAQs
An essay topic is a subject area about which an essay is written. An essay topic can be fairly broad or quite narrow.
What’s the purpose of an essay topic?
The purpose of an essay topic is to give the author something to discuss in their writing. An essay topic is what an essay is “about,” giving the author a subject to explore, analyze, discuss, defend, or describe.
What’s the difference between an essay topic and a thesis statement?
An essay topic is much broader than a thesis statement. A thesis statement summarizes the essay author’s position on the essay’s topic or a specific aspect of the essay’s topic.
What are examples of strong essay topics?

How To Write An Essay
Topic Sentence

Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
Published on: Jan 13, 2021
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
As a student, you have probably heard the term "topic sentence" thrown around a lot in your English or writing classes. But do you really understand what it means and how important it is for effective writing?
Well, many students struggle with crafting strong topic sentences that effectively convey their ideas. They may find themselves unsure of how to make their topic sentence stand out in a sea of other ideas.
In this blog, we will explore the art of writing a great topic sentence, with examples and tips to help you enhance your skills. By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of how to craft a topic sentence that will make your writing clear, concise, and engaging.
So let’s get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Topic Sentence?
A topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph in an essay that introduces the main idea or topic of that paragraph. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, letting them know what to expect in the upcoming paragraph.
Purpose of Topic Sentence
The purpose of a topic sentence is to clearly and concisely convey the main point of the paragraph to the reader.
It helps to guide the reader through the essay, making it easier for them to follow the overall argument or narrative.
Features of a Good Topic Sentence
A good topic sentence has a few key features. Letâs take a look:
- Expresses the main idea of the paragraph or essay clearly and concisely.
- Is specific and focused , avoiding vague or overly general statements.
- Introduces the main point and is typically located at the beginning of the paragraph or essay.
- Presents a claim or position that is arguable or debatable, which the rest of the paragraph or essay will support.
- Can be a complete sentence or a concise phrase that effectively conveys the main idea.
- Is relevant to the thesis statement and overall topic of the essay.
- Engages the reader by creating interest and highlighting the significance of the topic.
- Is well-written and avoids grammar and spelling errors.
- Provides a roadmap for the rest of the paragraph or essay by indicating what will be covered.
- Encourages coherence and unity in the writing by linking the paragraph or essay to the broader topic.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Types of Topic Sentences
There are several different types of topic sentences that can be used in writing to introduce the reader through a paragraph or essay.
Simple Statement Topic Sentence This is the most common type of topic sentence, which straightforwardly states the main point or idea of the paragraph or essay.
Example: The rise of social media has revolutionized the way people communicate with each other.
Complex Topic Sentence This type of topic sentence is more nuanced and may require some explanation or elaboration to fully understand.
Example: While the rise of social media has had many positive effects on communication, it has also led to concerns about privacy and online harassment.
Pivot Topic Sentence A pivot topic sentence begins by connecting the current paragraph or idea to the previous one, before pivoting to introduce a new point or idea.
Example: Building on the idea of social media's impact on communication, it is important to consider how it has also affected business and marketing strategies.
Question Topic Sentence A question topic sentence poses a question that the rest of the paragraph or essay will answer or explore.
Example: How has social media changed the way businesses interact with customers and advertise their products?
Command Topic Sentence This type of topic sentence gives a directive or instruction, often used in persuasive or argumentative essays.
Example: Support local businesses by shopping at independently owned stores instead of large chains.
How to Write a Topic Sentence?
Here are a few instructions to help you write a good topic sentence.
Step#1 Clearly State The Main Idea
A topic sentence is the first paragraph of the paragraph. It must clearly explain the particular subject that would be discussed in the paragraph. This should be stated in very clear language so that the reader can easily understand the idea.
Also, it should include a bit of your personal opinion and also the main idea.
Step#2 Hook Your Reader
Grab your reader's attention with an intriguing topic sentence. It would excite and make the reader curious about the content and convince them to read the particular part.
Look out for some amazing hook examples and see what fits your essay type.
Use a meaningful and relevant question or a fact as a topic sentence of the paragraph. Make sure that you have identified your audience and are developing everything accordingly.
Step#3 Keep It Short and Precise
The paragraph topic sentence must be expressive enough that a reader understands your point of view effortlessly. This is only possible if you keep everything to the point, short, and meaningful.
Choose the words in such a way that they help you express your idea in an ideal way. Avoid using complex sentences and use independent clauses.
A topic sentence acts as a link between a paragraph and the main thesis statement. It should be specific and connected to the overall essay. Keeping it short and precise helps maintain the paragraph's flow and its relevance to the rest of the writing.
Step#4 Give A Reasonable Opinion
The body paragraph explains a topic sentence. This is why it is important that you should write this sentence in such a way that it can be explained in the paragraph. If you are mentioning a fact in the topic statement, make sure that you have authentic evidence to support it.
While the topic sentence is an integral part of the paragraph, it should stand out and possess a distinctiveness that sets it apart from the other sentences. This can be achieved by employing transition words and establishing connections between sentences.
Step#5 Use The Topic Sentence As A Transition
The topic sentences that serve as transition sentences can be considered a guide for the readers. This way, they can help the reader to move through the essay in a flow.
Write this sentence in such a way that it creates a gateway between the previous paragraph and the rest of the essay. Moreover, it will also help keep the essay organized, and the reader understands the point of a paragraph.
Step#6 Look For Some Good Examples
Examples can help you learn a thing in a better way. If you are new to writing topic sentences, it can help to look at some examples. Find some great examples of topic sentences relevant to your essay topic.
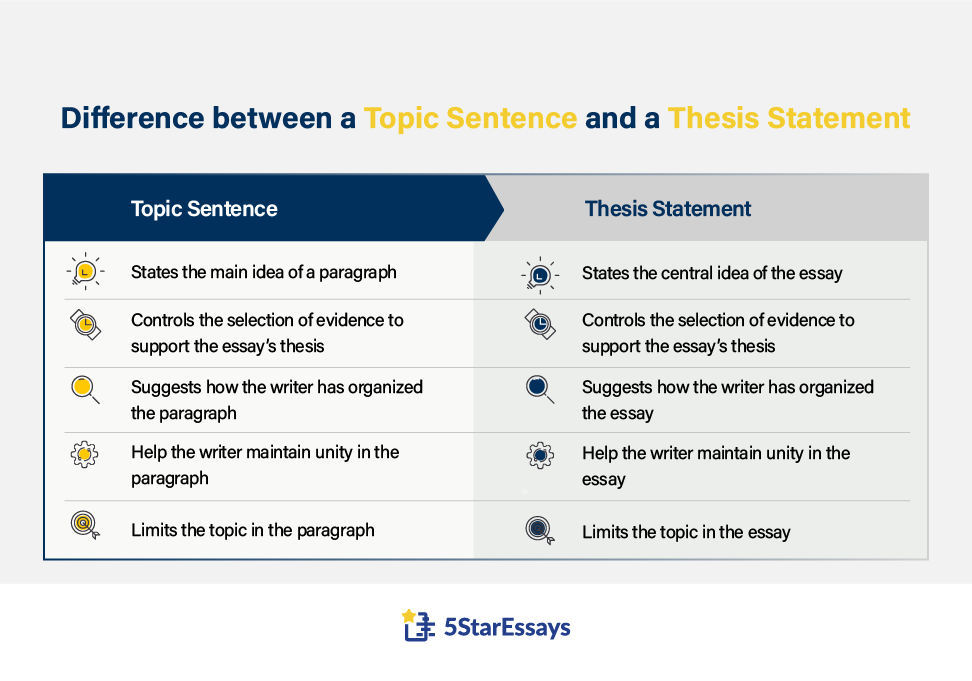
Difference Between Topic Sentence and Thesis Sentence
Here's a table outlining the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis statement:
Good Topic Sentence Examples
Here are ten examples of good topic sentences:
- "Despite the advancements in technology, traditional forms of communication are still essential in today's society."
- "The theme of power is prevalent throughout Shakespeare's play, Macbeth."
- "In recent years, there has been a growing concern over the impact of climate change on our planet."
- "The legalization of marijuana has been a topic of debate for many years." "Education is the key to success in life."
- "The rise of social media has greatly impacted the way we communicate with one another."
- "The effects of childhood trauma can have a lasting impact on mental health."
- "The concept of justice is explored in depth in Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird."
- "Eating a balanced diet is crucial for maintaining good health."
- "The Industrial Revolution had a profound effect on the world as we know it today."
The Bottom Line!
An opening sentence is crucial to grab your reader's attention and set the tone for your piece of writing. The topic sentence introduces the controlling idea and acts as an important sentence in the essay outline.
Effective topic sentences are necessary for a well-structured and organized essay. It's an integral part of the writing process that should not be overlooked.
Make sure to spend time crafting a compelling topic sentence that clearly conveys your main point and guides your readers throughout your essay. You can even take ideas from an AI essay generator to get started.
However, if you find yourself struggling to write a good opening sentence, don't worry! CollegeEssay.org is here to help you with all your writing needs. We have the best online essay writing service providing top-quality essays that are sure to impress your professors.
So, why wait? Contact our essay writing service now and take the first step toward academic success!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a topic sentence.
A topic sentence can be multiple sentences long. The first sets the context for your ideas, while the second provides more depth on what you are saying beyond just stating it outright.
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Essay Writing Guide
What Is A Topic Sentence
Last updated on: Jun 13, 2023
What is a Topic Sentence - An Easy Guide with Writing Steps & Examples
By: Nova A.
11 min read
Reviewed By: Melisa C.
Published on: Mar 12, 2019

A topic sentence is the opening sentence at the beginning of each paragraph. These sentences tell the readers about the main idea that will be discussed in that paragraph.
It is most important part of a body paragraph, and knowing how to write a good topic sentence is essential for writing an essay . However, writing an effective topic sentence could be tough.
If you find it difficult to write clear and engaging topic sentences, you are not alone. But don’t worry!
This blog will help you understand topic sentences better with examples. Also, you’ll get step-by-step guide and tips for writing more effective topic sentences.
So let’s dive in!

On this Page
What is a Topic Sentence in a Paragraph?
A topic sentence is the opening sentence of the body paragraphs of your essay. It introduces the main idea of that paragraph.
So what is the purpose of a topic sentence?
It serves as a guidepost, indicating the main purpose and point of the paragraph. Essentially, it is a concise and direct statement that captures the essence of what you want to convey.
A topic sentence is defined by the following characteristics:
- It is the first sentence of a paragraph
- It indicates the main idea of the paragraph
- Acts as a signpost and transition sentence, ensuring clarity and cohesiveness of an essay.
Why are Topic Sentences Important?
Topic sentences are an essential component of body paragraphs , especially in academic writing which is more formal. Here’s why good these sentences are necessary for an essay:
- They help maintain the organization and coherence of the essay.
Topic sentences act as a roadmap for your essay, providing a clear path for your readers to follow. They establish the main ideas or arguments of each paragraph, allowing your essay to flow logically and coherently.
By presenting a central focus in each paragraph, they help you maintain a strong sense of organization. Also, they prevent your essay from becoming a jumbled collection of random thoughts.
- They enhance clarity and readability.
Well-crafted topic sentences promote clarity and conciseness in your writing by summarizing the main idea in a concise manner.
Moreover, they serve as signposts that signal the beginning of a particular discussion. This creates a smooth reading experience and reduces the chances of confusion.
- They help the reader skim through the essay.
These sentences provide readers with a preview of what each paragraph will discuss. This helps them grasp the main point before delving into the rest of the paragraph.
They also enable the readers to quickly grasp the content of a paragraph. This makes it easier for them to skim through the main ideas of the essay without reading it word-by-word.
Topic Sentence vs Thesis Statement: Main Differences
Topic sentences are similar to thesis statements as they fulfill a similar purpose: they show the reader what the paragraph or essay is about.
However, a thesis statement is written at the end of the essay introduction, and it presents the main idea of the entire paper or essay. Whereas, a topic sentence presents the main idea of a specific paragraph, and is the first sentence of that paragraph.
Here are the major differences between topic sentences and thesis statements:
How to Write a Topic Sentence? Here are 4 Simple Steps
If you think about it, writing such a sentence seems like a simple task. All you have to do is write one line about the idea you’ll discuss, and you’re done.
Well, it’s not as easy as it sounds. You need to follow some conditions to write good opening lines for your body paragraphs.
Here are the steps to write engaging topic sentences:
1. Develop your Thesis Statement
Writing a specific and self-defining thesis statement is the first step in writing an essay. A thesis statement is necessary as it lays out the main points or structure of your entire essay.
Having a thesis statement helps you figure out what your body paragraphs will be about. This, in turn, helps you identify each paragraphs controlling idea and craft a topic sentence.
2. Identify the Controlling Ideas of Your Body Paragraphs
Once you have a thesis statement for your essay, identify the main idea or central theme of the paragraphs.
Ask yourself, "What is the key point I want to convey in this paragraph?" This will serve as the focus and topic of your paragraph. Moreover, identifying your main points will also help you make an essay outline.
Here’s an example of how you can identify the main ideas of your body paragraphs:
3. Write your Topic Sentence
Now that you know the main idea of each paragraph, you should attempt to write your topic sentences. It is not necessary that you get the sentences right the first time. Try different variations and see which of the sentences explains the paragraph idea in a better way.
Ensure that your topic sentence relates directly to your thesis statement or the main argument of your essay. The topic sentence should support and reinforce the overall message you want to convey in your writing.
The example below shows topic sentences based on the main ideas identified in step 2:
4. Revise and Make your Topic Sentences Better
A strong topic sentence should be clear, concise, and directly related to your thesis statement. They should also be logically connected to the previous paragraph. It is important that you revise, make them better, and rewrite the sentences as you progress with the paper.
Make sure that they reflect the main theme of the paragraph and are according to the paragraph’s content. Use appropriate transition words for essays when transitioning from one paragraph to another.
Read on to learn about different types of topic sentences. They will help you to write, rewrite, and revise your opening sentences in the best ways.
What are the Different Types of Topic Sentences?
Here are some common types of topic sentences you can incorporate in your essay.
[Infographic]
- Statement of Fact or Information
This type of topic sentence presents a straightforward statement of fact or information that sets the stage for the paragraph. It provides essential background knowledge or introduces a key concept.
- Hook or Shocker
This kind of sentence presents a shocking statement of fact about the paragraph’s key idea. This type of topic sentence aims to grab the reader’s attention and make them want to read more.
- Illustration or Example
An illustration or example topic sentence provides a specific instance or anecdote to support the main idea of the paragraph. It helps to clarify and reinforce your argument by providing concrete evidence or a real-life scenario.
- Question or Thought-Provoking Statement
A topic sentence in the form of a question or thought-provoking statement engages readers by encouraging them to seek an answer. It stimulates curiosity and anticipation for what follows in the paragraph.
You can also watch this video that explains topic sentences in a simple way:
Topic Sentence Examples
‘What is a topic sentence example?’
Check out some helpful and effective topic sentence examples to help you get started.
- Professional baking is a lot more than mixing some flour, eggs, and sugar into a bowl and putting it into the oven; it requires precision, attention to detail, and dedication to the craft.
- Writing is a thorough and time-consuming process, but with some dedicated practice, you can become a better writer.
- Learning a foreign language opens doors to several new opportunities that are not only available when a person is familiar with his mother tongue.
- Home remodeling is an exciting project, but without proper designer skills and taste, it could turn into a disaster.
- Several human activities are the main reasons behind global environmental pollution, and excess usage of plastic is one such cause.
Helpful Tips for Writing Better Topic Sentences
You’ve read some great examples, but how can you write similarly effective topic sentences yourself? Here are some amazing tips to help you out.
- Be Clear and Concise: Focus on expressing the main idea of the paragraph in a concise and direct manner. Avoid unnecessary details or convoluted language that may confuse your readers.
- Consider the Paragraph's Focus: Avoid including multiple ideas or concepts within a single topic sentence. Instead, focus on one central point for each paragraph.
- Vary Your Sentence Structure: To maintain reader interest and engagement, vary the structure of your topic sentences. Experiment with different types, such as simple sentences, rhetorical questions, or even shocking facts.
- Use Strong and Descriptive Language: Choose powerful and descriptive words that accurately capture the essence of your main idea. Avoid vague or generic language that lacks impact. Instead, opt for words that evoke emotions or create vivid imagery.
- Seek Feedback: Consider sharing your writing with others and seeking feedback on your paragraphs. Ask for input on clarity, coherence, transitions, and overall effectiveness.
A great topic sentence directs the reader about the main content of the paragraph. It is brief and engages the reader.
Remember, mastering the art of writing effective topic sentences takes practice and refinement. As you develop your writing skills, focus on crafting clear and engaging topic sentences that align with your thesis statement.
However, we understand that writing essays can still be challenging, especially when faced with tight deadlines or complex assignments.
That's where 5staressays.com comes in!
If you’re short on time or lack good writing skills, you can team up with a professional essay writer. Our ‘ write my essay ’ service works with professional and subject-expert writers that help you write engaging and A-worthy essays.
So contact us and get quality papers at the most pocket-friendly rates!
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is the topic sentence located in your essay.
Topic sentences come at the beginning of body paragraphs. They are the first sentence of a paragraph and introduces the main idea of that paragraph.
Can a topic sentence be a question?
Yes, a topic sentence could be a question. You can use a rhetorical question or an interrogative sentence to engage your reader and encourage them to read on.
How long is a topic sentence?
It depends on the depth of the idea. Usually, it is just one sentence, but in some cases, it could be composed of two sentences. However, the first few lines of the paragraph should be able to present its main idea effectively.

Law, Marketing
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write an Essay - A Complete Guide with Examples

- The Art of Effective Writing: Thesis Statements Examples and Tips

- Writing a 500 Word Essay - Easy Guide

- A Complete Essay Outline - Guidelines and Format

- 220 Best Transition Words for Essays

- Essay Format: Detailed Writing Tips & Examples

- How to Write a Conclusion - Examples & Tips

- Essay Topics: 100+ Best Essay Topics for your Guidance

- How to Title an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Titles

- How to Write a Perfect 1000 Word Essay

- How To Make An Essay Longer - Easy Guide For Beginners

- Learn How to Start an Essay Effectively with Easy Guidelines

- Types of Sentences With Examples

- Hook Examples: How to Start Your Essay Effectively

- Essay Writing Tips - Essential Do’s and Don’ts to Craft Better Essays

- How To Write A Thesis Statement - A Step by Step Guide

- Art Topics - 200+ Brilliant Ideas to Begin With

- Writing Conventions and Tips for College Students

People Also Read
- autobiography vs memoir
- how to write an editorial
- quantitative research
- process analysis essay
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- College essay
- Choosing Your College Essay Topic | Ideas & Examples
Choosing Your College Essay Topic | Ideas & Examples
Published on October 25, 2021 by Kirsten Courault . Revised on July 3, 2023.
A strong essay topic sets you up to write a unique, memorable college application essay . Your topic should be personal, original, and specific. Take time to brainstorm the right topic for you.
Table of contents
What makes a good topic, brainstorming questions to get started, discover the best topic for you, how to make a common topic compelling, frequently asked questions about college application essays, other interesting articles.
Here are some guidelines for a good essay topic:
- It’s focused on you and your experience
- It shares something different from the rest of your application
- It’s specific and original (not many students could write a similar essay)
- It affords the opportunity to share your positive stories and qualities
In most cases, avoid topics that
- Reflect poorly on your character and behavior
- Deal with a challenge or traumatic experience without a lesson learned or positive outlook
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Spend time reflecting on and writing out answers to the following questions. After doing this exercise, you should be able to identify a few strong topics for your college essay.
Writing about yourself can be difficult. If you’re struggling to identify your topic, try these two strategies.
Start with your qualities
After identifying your positive qualities or values, brainstorm stories that demonstrate these qualities.
Start with a story
If you already have some memorable stories in mind that you’d like to write about, think about which qualities and values you can demonstrate with those stories.
Talk it through
To make sure you choose the right topic, ask for advice from trusted friends or family members who know you well. They can help you brainstorm ideas and remember stories, and they can give you feedback on your potential essay topics.
You can also work with a guidance counselor, teacher, or other mentor to discuss which ideas are most promising. If you plan ahead , you can even workshop multiple draft essays to see which topic works best.
If you do choose a common topic, ensure you have the following to craft a unique essay:
- Surprising or unexpected story arcs
- Interesting insight or connections
- An advanced writing style
Here are a few examples of how to craft strong essays from cliché topics.
Here’s a checklist you can use to confirm that your college essay topic is right for you.
College essay topic checklist
My topic is focused on me, not on someone else.
My topic shares something different from the rest of my application.
My topic is specific and original (not many students could write a similar essay).
My topic reflects positively on my character and behavior.
If I chose to write about a traumatic or challenging experience, my essay will focus on how I overcame it or gained insight.
If I chose a common topic, my essay will have a surprising story arc, interesting insight, and/or an advanced writing style.
Good topic!
It looks like your topic is a good choice. It's specific, it avoids clichés, and it reflects positively on you.
There are no foolproof college essay topics —whatever your topic, the key is to write about it effectively. However, a good topic
- Is meaningful, specific, and personal to you
- Focuses on you and your experiences
- Reveals something beyond your test scores, grades, and extracurriculars
- Is creative and original
Yes—admissions officers don’t expect everyone to have a totally unique college essay topic . But you must differentiate your essay from others by having a surprising story arc, an interesting insight, and/or an advanced writing style .
To decide on a good college essay topic , spend time thoughtfully answering brainstorming questions. If you still have trouble identifying topics, try the following two strategies:
- Identify your qualities → Brainstorm stories that demonstrate these qualities
- Identify memorable stories → Connect your qualities to these stories
You can also ask family, friends, or mentors to help you brainstorm topics, give feedback on your potential essay topics, or recall key stories that showcase your qualities.
Most topics are acceptable for college essays if you can use them to demonstrate personal growth or a lesson learned. However, there are a few difficult topics for college essays that should be avoided. Avoid topics that are:
- Overly personal (e.g. graphic details of illness or injury, romantic or sexual relationships)
- Not personal enough (e.g. broad solutions to world problems, inspiring people or things)
- Too negative (e.g. an in-depth look at your flaws, put-downs of others, criticizing the need for a college essay)
- Too boring (e.g. a resume of your academic achievements and extracurriculars)
- Inappropriate for a college essay (e.g. illegal activities, offensive humor, false accounts of yourself, bragging about privilege)
Here’s a brief list of college essay topics that may be considered cliché:
- Extracurriculars, especially sports
- Role models
- Dealing with a personal tragedy or death in the family
- Struggling with new life situations (immigrant stories, moving homes, parents’ divorce)
- Becoming a better person after community service, traveling, or summer camp
- Overcoming a difficult class
- Using a common object as an extended metaphor
It’s easier to write a standout essay with a unique topic. However, it’s possible to make a common topic compelling with interesting story arcs, uncommon connections, and an advanced writing style.
If you want to know more about academic writing , effective communication , or parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Transition words
- Passive voice
- Paraphrasing
Communication
- How to end an email
- Ms, mrs, miss
- How to start an email
- I hope this email finds you well
- Hope you are doing well
Parts of speech
- Personal pronouns
- Conjunctions

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Courault, K. (2023, July 03). Choosing Your College Essay Topic | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/college-essay/essay-topic/
Is this article helpful?

Kirsten Courault
Other students also liked, college essay format & structure | example outlines, what do colleges look for in an essay | examples & tips, how to make your college essay stand out | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Writing Topic Sentences — Purpose, Structure, and Examples

What is a topic sentence?
A topic sentence in academic writing identifies how a body paragraph relates to the overall purpose of an essay stated in the thesis statement . Topic sentences are usually at the beginning of a paragraph and identify the paragraph’s controlling idea.
While an essay’s thesis statement identifies the point of the essay in its entirety, the topic sentence has a much narrower focus, as it relates only to the paragraph in which it is located.

What is the purpose of a topic sentence?
The purpose of a topic sentence is to inform the reader of the main idea of the paragraph and how it connects to the overall objective of the essay. An effective topic sentence accomplishes one or more of the following:
Makes a claim
Supports other claims made in the paper
Identifies the purpose of the rest of the paragraph
Relates the paragraph to the purpose of the paper
Precedes information that defends a claim

How to write a topic sentence
To write a topic sentence, incorporate the following guidelines:
Determine the thesis of the essay.
Identify the main supports that help prove the thesis.
Use each main support to structure a topic sentence for each paragraph.
Compose a sentence that answers the following questions:
What will the paragraph prove?
How does the paragraph connect to the thesis?

Where is the topic sentence in a paragraph?
Topic sentences can be placed at the beginning or end of a paragraph.
Although it does not need to be the first sentence, the topic sentence should be placed at the beginning of the paragraph so the reader can quickly identify the purpose of the paragraph.
While not a common placement for a topic sentence, some writers use topic sentences at the end of a paragraph. Writers who choose this method want the reader to deduce the main point of the paragraph by presenting the evidence first.
Topic sentence examples
The following list identifies topic sentences based on the provided thesis statements for five-paragraph essays:
Thesis Statement: Capital punishment should be banned because it is inhumane, unconstitutional, and ineffective at deterring crime.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: The inhumane nature of the death penalty proves it should be abolished.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Capital punishment should be outlawed because it violates the Constitution.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Because the death penalty does not effectively deter criminal behavior, states should not continue to use it.
Thesis Statement: College athletes should be financially compensated because they sacrifice their minds and bodies, cannot hold an outside job, and increase the school’s revenue.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: Student athletes should be paid for their performance because of sports’ impact on their minds and bodies.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Because most college athletes cannot play their sport and hold a job, colleges should give them a living wage.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Student-athletes’ ability to increase their college’s revenue proves they should be awarded financial compensation.

Thesis Statement: Using alternative energy sources can help lessen the impact of global climate change.
Support Paragraph 1 Topic Sentence: Through the widespread use of solar power, countries can limit the environmental impact of other energy sources.
Support Paragraph 2 Topic Sentence: Utilizing more wind turbines as a power source can help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Support Paragraph 3 Topic Sentence: Using geothermal power will effectively decrease the world's reliance on fossil fuels.
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Using Topic Sentences
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
What is a topic sentence?
A topic sentence states the main point of a paragraph: it serves as a mini-thesis for the paragraph. You might think of it as a signpost for your readers—or a headline—something that alerts them to the most important, interpretive points in your essay. When read in sequence, your essay’s topic sentences will provide a sketch of the essay’s argument. Thus topics sentences help protect your readers from confusion by guiding them through the argument. But topic sentences can also help you to improve your essay by making it easier for you to recognize gaps or weaknesses in your argument.
Where do topic sentences go?
Topic sentences usually appear at the very beginning of paragraphs. In the following example from Anatomy of Criticism , Northrop Frye establishes the figure of the tragic hero as someone more than human, but less than divine. He backs up his claim with examples of characters from literature, religion and mythology whose tragic stature is a function of their ability to mediate between their fellow human beings and a power that transcends the merely human:
The tragic hero is typically on top of the wheel of fortune, half-way between human society on the ground and the something greater in the sky. Prometheus, Adam, and Christ hang between heaven and earth, between a world of paradisal freedom and a world of bondage. Tragic heroes are so much the highest points in their human landscape that they seem the inevitable conductors of the power about them, great trees more likely to be struck by lightning than a clump of grass. Conductors may of course be instruments as well as victims of the divine lightning: Milton’s Samson destroys the Philistine temple with himself, and Hamlet nearly exterminates the Danish court in his own fall.
The structure of Frye’s paragraph is simple yet powerful: the topic sentence makes an abstract point, and the rest of the paragraph elaborates on that point using concrete examples as evidence.
Does a topic sentence have to be at the beginning of a paragraph?
No, though this is usually the most logical place for it. Sometimes a transitional sentence or two will come before a topic sentence:
We found in comedy that the term bomolochos or buffoon need not be restricted to farce, but could be extended to cover comic characters who are primarily entertainers, with the function of increasing or focusing the comic mood. The corresponding contrasting type is the suppliant, the character, often female, who presents a picture of unmitigated helplessness and destitution. Such a figure is pathetic, and pathos, though it seems a gentler and more relaxed mood than tragedy, is even more terrifying. Its basis is the exclusion of an individual from the group; hence it attacks the deepest fear in ourselves that we possess—a fear much deeper than the relatively cosy and sociable bogey of hell. In the suppliant pity and terror are brought to the highest possible pitch of intensity, and the awful consequences of rejecting the suppliant for all concerned is a central theme of Greek tragedy.
The context for this passage is an extended discussion of the characteristics of tragedy. In this paragraph, Frye begins by drawing a parallel between the figure of the buffoon in comedy and that of the suppliant in tragedy. His discussion of the buffoon occurred in a earlier section of the chapter, a section devoted to comedy. The first sentence of the current paragraph is transitional: it prepares the way for the topic sentence. The delayed topic sentence contributes to the coherence of Frye’s discussion by drawing an explicit connection between key ideas in the book. In essays, the connection is usually between the last paragraph and the current one.
Sometimes writers save a topic sentence for the end of a paragraph. You may, for example, occasionally find that giving away your point at the beginning of a paragraph does not allow you to build your argument toward an effective climax.
How do I come up with a topic sentence? And what makes a good one?
Ask yourself what’s going on in your paragraph. Why have you chosen to include the information you have? Why is the paragraph important in the context of your argument? What point are you trying to make?
Relating your topic sentences to your thesis can help strengthen the coherence of your essay. If you include a thesis statement in your introduction, then think of incorporating a keyword from that statement into the topic sentence. But you need not be overly explicit when you echo the thesis statement. Better to be subtle rather than heavy-handed. Do not forget that your topic sentence should do more than just establish a connection between your paragraph and your thesis. Use a topic sentence to show how your paragraph contributes to the development of your argument by moving it that one extra step forward. If your topic sentence merely restates your thesis, then either your paragraph is redundant or your topic sentence needs to be reformulated. If several of your topic sentences restate your thesis, even if they do so in different words, then your essay is probably repetitive.
Does every paragraph need one?
No, but most do. Sometimes a paragraph helps to develop the same point as in the previous paragraph, and so a new topic sentence would be redundant. And sometimes the evidence in your paragraph makes your point so effectively that your topic sentence can remain implicit. But if you are in doubt, it’s best to use one.
What Is a Topic Sentence?
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A topic sentence is a sentence , sometimes at the beginning of a paragraph , that states or suggests the main idea (or topic ) of a paragraph.
Not all paragraphs begin with topic sentences. In some, the topic sentence appears in the middle or at the end. In others, the topic sentence is implied or absent altogether.
Examples and Observations
- " Salva and the other boys made cows out of clay. The more cows you made, the richer you were. But they had to be fine, healthy animals. It took time to make a lump of clay look like a good cow. The boys would challenge each other to see who could make the most and best cows." (Linda Sue Park, A Long Walk to Water . Clarion, 2010)
- " Momma bought two bolts of cloth each year for winter and summer clothes. She made my school dresses, underslips, bloomers, handkerchiefs, Bailey's shirts, shorts, her aprons, house dresses and waists from the rolls shipped to Stamps by Sears and Roebuck. . . ." (Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings . Random House, 1969)
- " You discover what it is like to be hungry. With bread and margarine in your belly, you go out and look into the shop windows. Everywhere there is food insulting you in huge, wasteful piles; whole dead pigs, baskets of hot loaves, great yellow blocks of butter, strings of sausages, mountains of potatoes, vast Gruyère cheeses like grindstones. A snivelling self-pity comes over you at the sight of so much food. You plan to grab a loaf and run, swallowing it before they catch you; and you refrain, from pure funk." (George Orwell, Down and Out in Paris and London . Victor Gollancz, 1933)
- " The flavor that salt imparts to food is just one of the attributes that manufacturers rely on. For them, salt is nothing less than a miracle worker in processed foods. It makes sugar taste sweeter. It adds crunch to crackers and frozen waffles. It delays spoilage so that the products can sit longer on the shelf. And, just as importantly, it masks the otherwise bitter or dull taste that hounds so many processed foods before salt is added." (Michael Moss, Salt, Sugar, Fat: How the Food Giants Hooked Us . Random House, 2013)
- " The very idea of retirement is a relatively new invention. For most of human history, people worked until they died or were too infirm to lift a finger (at which point they died pretty fast anyway). It was the German statesman Otto von Bismarck who first floated the concept, in 1883, when he proposed that his unemployed countrymen over the age of 65 be given a pension. This move was designed to fend off Marxist agitation—and to do so on the cheap, since few Germans survived to that ripe old age." (Jessica Bruder, "The End of Retirement." Harper's , August 2014)
- " Grandma's room I regarded as a dark den of primitive rites and practices. On Friday evenings whoever was home gathered at her door while she lit her Sabbath candles. . . ." (E.L. Doctorow, World's Fair . Random House, 1985)
- " Genealogy is an ancient human preoccupation. The God of Hebrew Scripture promised Abraham descendants beyond number, like the stars in the sky and the sand on the seashore. The apostles Matthew and Luke claim that Abraham's lineage went on to include King David and eventually Jesus, though the specifics of their accounts are contradictory. Muslims trace Mohammed's line back through Abraham, to Adam and Eve." (Maud Newton, "America's Ancestry Craze." Harper's , June 2014)
- " O nce, in a restaurant in Italy with my family, I occasioned enormous merriment, as a nineteenth-century humorist would have put it, by confusing two Italian words. I thought I had, very suavely, ordered for dessert fragoline —those lovely little wild strawberries. Instead, I seem to have asked for fagiolini —green beans. The waiter ceremoniously brought me a plate of green beans with my coffee, along with the flan and the gelato for the kids. The significant insight the mistake provided—arriving mere microseconds after the laughter of those kids, who for some reason still bring up the occasion, often—was about the arbitrary nature of language: the single 'r' rolled right makes one a master of the trattoria, an 'r' unrolled the family fool. . . ." (Adam Gopnik, "Word Magic." The New Yorker , May 26, 2014)
- " In seventeenth-century Europe, the transformation of man into soldier took on a new form, more concerted and disciplined, and far less pleasant, than wine. New recruits and even seasoned veterans were endlessly drilled, hour after hour, until each man began to feel himself part of a single, giant fighting machine. . . ." (Barbara Ehrenreich, Blood Rites: Origins and History of the Passions of War . Henry Holt and Company, 1997)
- " What is the appeal of train travel? Ask almost any foamer, and he or she will invariably answer, 'The romance of it!' But just what this means, they cannot really say. It's tempting to think that we are simply equating romance with pleasure, with the superior comfort of a train, especially seated up high in the observation cars. . . ." (Kevin Baker, "21st Century Limited: The Lost Glory of America's Railroads." Harper's , July 2014)
- " Because science fiction spans the spectrum from the plausible to the fanciful, its relationship with science has been both nurturing and contentious. For every author who meticulously examines the latest developments in physics or computing, there are other authors who invent 'impossible' technology to serve as a plot device (like Le Guin’s faster-than-light communicator, the ansible) or to enable social commentary, the way H. G. Wells uses his time machine to take the reader to the far future to witness the calamitous destiny of the human race." (Eileen Gunn, "Brave New Words." Smithsonian , May 2014)
- " I passed all the other courses that I took at my university, but I could never pass botany. . . ." (James Thurber, My Life and Hard Times . Harper & Row, 1933)
- " What is there about this wonderful woman? From next door, she comes striding, down the lawn, beneath the clothesline, laden with cookies she has just baked, or with baby togs she no longer needs, and one's heart goes out. Pops out. The clothesline, the rusted swing set, the limbs of the dying elm, the lilacs past bloom are lit up like rods of neon by her casual washday energy and cheer, a cheer one has done nothing to infuse." (John Updike, "One's Neighbor's Wife." Hugging the Shore: Essays and Criticism . Knopf, 1983)
- " Television. Why do I watch it? The parade of politicians every evening: I have only to see the heavy, blank faces so familiar since childhood to feel gloom and nausea. . . ." (J.M. Coetzee, Age of Iron . Random House, 1990)
- " Anyone who has made the coast-to-coast journey across America, whether by train or by car, has probably passed through Garden City, but it is reasonable to assume that few travelers remember the event. It seems just another fair-sized town in the middle--almost the exact middle--of the continental United States. . . ." (Truman Capote, In Cold Blood . Random House, 1966)
- " Rodeo, like baseball, is an American sport and has been around almost as long. . . ." (Gretel Ehrlich, The Solace of Open Spaces . Viking Penguin, 1985)
- " What a piece of work is a book! I am not talking about writing or printing. I am talking about the codex we may leaf through, that may be put away on a shelf for whole centuries and will remain there, unchanged and handy. . . ." (William Golding, A Moving Target . Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 1982)
Characteristics of an Effective Topic Sentence
- "A good topic sentence is concise and emphatic . It is no longer than the idea requires, and it stresses the important word or phrase. Here, for instance, is the topic sentence which opens a paragraph about the collapse of the stock market in 1929: "The Bull Market was dead."(Frederick Lewis Allen) Notice several things. (1) Allen's sentence is brief . Not all topics can be explained in six words, but whether they take six or sixty, they should be phrased in no more words than are absolutely necessary. (2) The sentence is clear and strong: you understand exactly what Allen means. (3) It places the keyword—'dead'—at the end, where it gets heavy stress and leads naturally into what will follow. . . . (4) The sentence stands first in the paragraph. This is where topic sentences generally belong: at or near the beginning." (Thomas S. Kane, The New Oxford Guide to Writing . Oxford Univ. Press, 1988)
Positioning a Topic Sentence
"If you want readers to see your point immediately, open with the topic sentence . This strategy can be particularly useful in letters of application or in argumentative writing. . . . "When specific details lead up to a generalization, putting the topic sentence at the end of the paragraph makes sense. . . . "Occasionally a paragraph's main idea is so obvious that it does not need to be stated explicitly in a topic sentence." (Andrea Lunsford, The St. Martin's Handbook . Bedford/St. Martin's, 2008)
Guidelines for Composing Topic Sentences
"The topic sentence is the most important sentence in your paragraph. Carefully worded and restricted, it helps you generate and control your information. An effective topic sentence also helps readers grasp your main idea quickly. As you draft your paragraphs, pay close attention to the following three guidelines:
- Make sure you provide a topic sentence. . . .
- Put your topic sentence first.
- Be sure your topic sentence is focused. If restricted, a topic sentence discusses only one central idea. A broad or unrestricted topic sentence leads to a shaky, incomplete paragraph for two reasons:
- The paragraph will not contain enough information to support the topic sentence .
- A broad topic sentence will not summarize or forecast specific information in the paragraph."
(Philip C. Kolin, Successful Writing at Work , 9th ed. Wadsworth, 2010)
Testing for Topic Sentences
"When testing your article for topic sentences , you should be able to look at each paragraph and say what the topic sentence is. Having said it, look at all the other sentences in the paragraph and test them to make sure they support it. . . .
"If you find that you have come up with the same topic sentence more than once, you have two paragraphs doing the same work. Cut one of them out.
"If you find a paragraph that has several sentences that don't support the topic sentence, see if all the outlaw sentences support some other topic sentence and turn the one paragraph into two." (Gary Provost, "How to Test Your Articles for the 8 Essentials of Nonfiction." Handbook of Magazine Article Writing , ed. by Jean M. Fredette. Writer's Digest Books, 1988)
Frequency of Topic Sentences
"Teachers and textbook writers should exercise caution in making statements about the frequency with which contemporary professional writers use simple or even explicit topic sentences in expository paragraphs. It is abundantly clear that students should not be told that professional writers usually begin their paragraphs with topic sentences." (Richard Braddock, "The Frequency and Placement of Topic Sentences in Expository Prose." Research in the Teaching of English . Winter 1974)
- How to Teach Topic Sentences Using Models
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Practice in Supporting a Topic Sentence with Specific Details
- Practice Composing Effective Topic Sentences
- Paragraph Writing
- Unity in Composition
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Best Practices for the Most Effective Use of Paragraphs
- How to Write a Descriptive Paragraph
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Supporting Detail in Composition and Speech
- Writers on Writing: The Art of Paragraphing
- How To Write an Essay
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- Essay Guides
- Basics of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Topic Sentence for an Essay: Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Topic Sentence for an Essay: Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A topic sentence is the first sentence in a body paragraph that summarizes its main idea. It's like a mini-thesis statement for each body paragraph. A well-crafted topic sentence should be focused and specific, so that your audience has a clue of what the paragraph will be about.
While it's usually 1 sentence long, students often find it tricky to highlight the key idea of a passage. That's why our essay writing service is here to help you. In this blog, we will shed more light on how to write a topic sentence for a body paragraph of an essay and provide decent examples to help you engage your readers. But before we get down to suggestion, let's begin with a definition.
What Is a Topic Sentence: Definition
A topic sentence is the first sentence of a body paragraph that captures its central point. By providing a succinct preview of the whole section, it serves as a roadmap and keeps writing organized.
A good topic sentence should be clear, concise and connected to a thesis statement. Your task is to grab the reader's attention, encouraging them to continue reading. Additionally, you will need to back up your key point by evidence and in-depth analysis.
Topic sentences also act as transitions that link paragraphs to one another. It's like building a bridge between sections allowing readers to move fluently throughout your essay.
Topic Sentence vs Thesis: What's the Difference?
Quite often, students confuse a topic sentence with a thesis statement. Let's clarify the difference between these 2 components.
A thesis statement is the main argument of the whole paper. It usually appears at the end of an essay introduction and presents your central position or claim. A topic sentence introduces the main idea of a single paragraph and should relate back to your thesis.
Take a glance at this example to understand the distinction.
Thesis: The widespread use of social media has had a significant impact on society, affecting communication, relationships, and self-image. Topic sentence 1: Social media has transformed the way we communicate, providing new opportunities for connection and interaction. Topic sentence 2: The rise of social media has also had an impact on relationships, both positive and negative, with increased access to information and social pressure affecting how people relate to one another. Topic sentence 3: Social media has been linked to negative effects on self-image, with the constant pressure to present a perfect online persona leading to increased anxiety and decreased self-esteem.
What Is the Purpose of a Topic Sentence?
The primary purpose of a topic sentence boils down to emphasizing on the point you want to make in any specific section. It also serves other goals:
- Guides the writer in developing content of each paragraph
- Ties your paragraph back to the larger argument of your paper
- Allows readers to follow your line of thought
- Creates coherence of your writing piece
- Makes ideas easier to follow.
Now that you know what a topic sentence in an essay body is and its purpose, let's discuss its main types.
Types of Topic Sentences and Examples
There are multiple approaches to previewing your paragraph's main point. Depending on the essay type, you may opt for different types of topic sentences – cause and effect, problem-solution, comparison and contrast. They can also appear in the form of a suggestion, question or a simple transition. Below we will define each type and provide topic sentence examples.
General to Specific
This type of topic sentence begins with a broad statement and then narrows down to a specific point.
Many factors contribute to climate change, but one of the most significant is the burning of fossil fuels.
Specific to General
In this case, you will start with a particular detail and then broaden out to a larger point.
The amount of trash in our oceans is staggering, highlighting the urgent need for more effective waste management policies.
Cause and Effect
Such sentences present a causal relationship between 2 ideas, events or phenomena. This type of topic sentence is usually used in cause and effect essays .
Poor nutrition can lead to obesity.
Comparison and Contrast
Sometimes, you may be assigned to compare 2 different concepts. If you are writing a compare and contrast essay , you will need to build topic sentences for each paragraph that reflect the comparison.
While traditional classroom learning has many benefits, online learning offers greater flexibility and convenience for students with busy schedules.
Problem-Solution
As the name suggests, this type of sentence primarily focuses on how to solve a specific issue. You will use this approach when working on a problem-solution essay .
It is becoming increasingly difficult for families to afford housing in major cities, suggesting that governments should pursue policies aimed at making rental costs more affordable.
Advice/Suggestion
Suggestions are an integral part of most kinds of essays. Whether you are writing a persuasive essay or a how-to guide, you need to express an opinion and provide a call for action. That's when you will turn your topic sentence into a piece of advice or guideline.
It is important for young people to develop an understanding of financial literacy, including budgeting and saving.
Sometimes, you may open a paragraph with a question in order to entice the reader and make them more interested in your opinion. Such questions should be used sparingly and confined to the introduction.
What can individuals do to reduce their impact on climate change?
When you are navigating from one paragraph to another, it is important that you make a seamless connection between ideas. The goal is to make the reader feel like they are continuously progressing through your essay. That's when essay transition words come into play. Here's how to create a topic sentence that can be used for linking.
On the other hand, this approach has its shortcomings that cannot be ignored.
How to Write a Good Topic Sentence for an Essay: 5 Easy Steps
When writing a topic sentence, there are 2 important aspects to keep in mind:
- You should be specific and focus only on a single idea or point.
- Stay on the point and don’t cover too many specifics in one sentence.
Now let’s take a look at the steps involved in the process. Follow these detailed guidelines on how to write a topic sentence and arrange your essay properly.
1. Determine the Main Idea of Your Writing
Before you write a topic sentence for body paragraphs, identify your essay’s main idea, or the point you’re trying to prove. The key argument is usually hidden in your thesis statement. Read through your thesis and think about the overall point that you are trying to make. Powered by the main idea, you can start thinking how to structure your body paragraphs and what specific points to discuss in each section.
The modern educational system should be redesigned to ensure that all students receive a well-rounded education.
2. Break Down the Main Idea into Smaller Pieces
The next step is to split your idea into smaller points. Try to recognize major supporting points or subtopics that reinforce your thesis statement. It can be helpful to create an outline or diagram to map out the essay structure and organize your arguments. By doing so, you will see how your central idea can be separated into more manageable subpoints.
- Subpoint 1 : Prioritizing teaching arts, music, and physical education along with core subjects
- Subpoint 2: Engaging students in experiential learning (internships, service learning)
- Subpoint 3: Enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
>> Read more: How to Write an Essay Outline
3. Make Sure Each Body Paragraph Serves a Specific Purpose
The purpose of each body paragraph is to take one of the subpoints and explain it in detail. In order to do that, make a topic sentence focused and to the point.
One common mistake is integrating too many details in one sentence.
Remember, the goal of your topic sentence is to introduce a single idea. For that, you need to establish the evidence and examples you want to use in your paragraph. Once you are clear on the goal of each paragraph, you can start creating your topic sentence.
❌ Example of a weak topic sentence
Fostering a well-rounded education should involve offering more classes in music, art and physical education, but also providing more opportunities for students to be involved in experiential learning.
In the above topic sentence example, a student combines 2 different ideas in 1 sentence. Eventually, this may lead to unnecessary confusion. Here's how this sentence may be improved.
✓ Example of a strong topic sentence
In order to nurture a well-rounded education, schools should prioritize teaching music, art, and physical education along with core subjects.
4. Grab Reader's Attention
The best topic sentence is the one that sounds compelling and captivates the reader's attention. Just like in the essay introduction, here you also need to integrate a hook. There are several hook techniques that you can use to involve your audience in your body paragraph:
- Using surprising facts or statistics that challenge the reader's assumptions or expectations
- Opening your paragraph with a rhetorical question that encourages to consider a new angle
- Starting a topic sentence with an anecdote or personal story illustrating your point.
Have you ever wondered why many schools are not providing enough classes in music, art and physical education?
>> Learn more: How to Write a Hook for an Essay
Trigger words can also be used to persuade your audience read further. These are the words and phrases that evoke emotions or psychological reactions. Below you can find some of the most efficient trigger words for your topic sentences.
Popular trigger words
When you write a topic sentence that elicits a strong emotional response, you will be able to interest more readers.
5. Write a Topic Sentence
Before you get down to actually writing a topic sentence for an essay body paragraph, remember that it should contain condensed information on your point. Still, you don't want to give away all supporting details or evidence from the get-go. Try to find balance between introducing your ideas and leaving some space for developing your argument further in the body.
Keep in mind the overall structure and flow of your essay. Your topic sentence should match a larger claim stated in your thesis. Otherwise, it will appear out of context and may potentially ruin the entire argument.
Examine good topic sentences examples for essays presented below to get more ideas on how to create your own.
Essay Topic Sentence Examples
Whether you're writing an argumentative , descriptive , or narrative essay , a strong topic sentence plays a crucial role in setting the stage for your main ideas. In this section, we will offer multiple examples of topic sentences. Inspect each topic sentence example for an essay to see how theory can be implemented in practice.
Topic sentence example for an argumentative essay
Social media has a negative impact on mental health , as it creates unrealistic expectations and promotes constant comparison to others.
Descriptive essay topic sentence example
The salty ocean air and the sound of seagulls created a calming and peaceful atmosphere on the beach.
Example of a topic sentence for cause-and-effect writing
Due to the increase in air pollution, many cities are experiencing a rise in respiratory illnesses among their populations.
Topic Sentence Writing Tips
Here are some valuable tips for writing a powerful topic sentence in a paragraph.
- Keep it brief but informative. Your topic sentence should contain only relevant information that directly supports the main point.
- Associate it to your primary claim. Make sure that your subpoints are intertwined and contribute to your fundamental assertion.
- Be precise. Make sure that you use specific language and avoid generalizations.
- Make it flow. Each body paragraph should build on the previous one and lead the reader towards your essay conclusion .
- Apply active voice. Using an active voice in your topic sentence can help to create a sense of urgency and engagement.
Bottom Line on How to Write a Topic Sentence
Crafting a powerful topic sentence is not easy, but with practice, you will be able to start your paragraphs in a convincing manner. Make sure that each opening is clear and reflects your main idea in a brief, yet, meaningful way. Keep these tips and examples in mind when writing topic sentences for your next essay.
Reach out to StudyCrumb, and have your essay written by an expert. Each academician is experienced in such tasks and can deliver a perfect paper quickly upon ‘ do my homework ’ request.
FAQ About Writing Topic Sentences
1. how to start off a topic sentence.
A good way to start a topic sentence is by introducing the specific idea or concept that you are going to discuss. It should be concise and directly related to the point of your essay. For example: " The increase in air pollution has led to an alarming rise in respiratory illnesses in cities ." This sentence states the main point of your topic and sets the tone for what follows.
2. Can a topic sentence be a question?
Yes, a topic sentence can be a question. In fact, beginning a paragraph with a question can create a sense of curiosity and encourage readers to think critically about your topic. Be sure to follow up the question with a clear and concise statement that provides a direct answer.
3. How long should a topic sentence be?
A topic sentence should be concise and to the point, ideally no longer than 1 or 2 sentences long. It should make a preview to the main idea of the paragraph, while also leaving enough room for developing your arguments and evidence.
4. How to write a strong topic sentence?
To compose a strong topic sentence, clearly state the main idea of your body paragraph. Avoid vague or general statements. Instead, your topic sentence should grab the reader's attention and make them want to keep reading. It's suggested to link it to your thesis statement of your paper to ensure that you stay on track.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like


Chapter 4: Structuring, Paragraphing, and Styling
4.3 Topic Sentences
Amanda Lloyd
Function and Elements of a Topic Sentence
A topic sentence is usually the first sentence of a body paragraph. The purpose of a topic sentence is to identify the topic of your paragraph and indicate the function of that paragraph in some way.
In order to create an effective topic sentence, you should do the following:
- Use a transitional device to effortlessly segue from the idea discussed in the previous paragraph.
When choosing a transitional device, you should consider whether your new paragraph will build onto the topic of your previous paragraph, begin to develop a new key idea or sub-claim, or present a counterargument or concession.
See section 4.6 for information regarding when to begin a new paragraph and section 4.7 for help with transitional words and phrases.
- Clearly identify the key idea or sub-claim that you intend to expand upon in your new paragraph.
Even if you are building onto the idea of the previous paragraph, you will still need to identify the sub-claim in your topic sentence. When constructing a topic sentence, you may feel as though you are stating the obvious or being repetitive, but your readers will need this information to guide them to a thorough understanding of your ideas.
- Make a connection to the claim you make in your thesis statement.
It might help to think of your topic sentence as a mini thesis statement. In your body paragraph, you should be expanding upon the claim you make in your thesis. For this reason, you should link your topic sentence to your thesis statement. Doing so tells your readers, “This is the point I mentioned in my thesis that I now intend to support and either prove or explain further.”
To connect to your thesis, you should consider the function of the body paragraph, which will usually depend upon the type of essay you are writing; for example, your topic sentence should suggest whether your goal is to inform or persuade your readers (your topic sentence should indicate whether or not you have an opinion or perspective on the topic).
4.3 Topic Sentences by Amanda Lloyd is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.

Essay Topic Sentence
Crafting an impeccable essay often hinges on the strength of its topic sentence. This pivotal sentence sets the tone, offers a glimpse into the content, and captivates the reader’s curiosity. Delve into the nuanced world of essay topic sentences, explore sterling Sentence examples , and arm yourself with tried-and-true tips to perfect this vital writing element.
What is the Essay Topic Sentence? – Definition
An essay topic sentence is the opening sentence of a paragraph that provides a concise summary of what the paragraph will address. It serves as a roadmap, guiding readers through the main idea or argument of that particular section, ensuring clarity and coherence.
What is the best Example of an Essay Topic Sentence?
Imagine writing an essay about the benefits of a balanced diet. An exemplary topic sentence might be: “A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, plays an indispensable role in maintaining optimal health and preventing various ailments.” This sentence not only introduces the topic of a balanced diet but also hints at the benefits that the subsequent sentences in the paragraph will explore in detail.
100 Essay Topic Sentence Examples

Size: 152 KB
Essay topic sentences are the guiding lights of your paragraphs, illuminating the main ideas and ensuring readers navigate smoothly through your piece. Crafting a compelling topic sentence is paramount for grasping attention and setting the tone for the ensuing discussion. Here are 100 sterling examples that encapsulate various subjects and themes, each with its distinct allure to captivate readers instantly.
- The Renaissance era ushered in a wave of unparalleled artistic and intellectual achievements.
- Urbanization poses both challenges and opportunities for modern societies.
- Climate change impacts global ecosystems, from polar ice caps to tropical rainforests.
- Social media platforms influence contemporary communication and human interactions.
- Mental well-being plays an equally significant role as physical health in overall wellness.
- Education systems require ongoing reforms to cater to the evolving needs of society.
- Space exploration holds the promise of discoveries beyond our planetary confines.
- Wildlife conservation ensures the preservation of Earth’s rich biodiversity.
- Digital advancements reshape business models and consumer behaviors.
- Historical monuments stand as testament to a civilization’s legacy and prowess.
- Reading habits enrich the mind, offering both knowledge and escapism.
- Global economies interact in intricate networks of trade and diplomacy.
- Alternative energy sources promise a sustainable solution to environmental concerns.
- Emotional intelligence plays a pivotal role in interpersonal success and leadership.
- Modern transportation bridges geographical divides, bringing cultures closer.
- Culinary arts reflect the rich tapestry of world cultures and histories.
- Migration patterns reveal socio-economic factors and global trends.
- Sustainable farming practices benefit both the environment and consumers.
- Oceanic ecosystems harbor mysteries yet to be fully unraveled by science.
- Artificial intelligence challenges the boundaries of technological capabilities.
- Childhood memories shape our adult personalities and choices.
- Green technology offers innovative solutions to pressing environmental issues.
- Philanthropic endeavors aim to bridge societal disparities and uplift communities.
- Literary classics transcend time, remaining relevant across generations.
- Photography captures fleeting moments, turning them into timeless memories.
- Global tourism boosts economies while fostering cross-cultural understanding.
- Musical genres evoke emotions, from nostalgia to exhilaration.
- Ancient civilizations laid the foundations for contemporary societies and norms.
- Virtual reality immerses users in simulated environments, from gaming to training.
- Language evolution tracks societal shifts and historical influences.
- Modern architecture melds functionality with aesthetic appeal.
- Astronomical studies probe the mysteries of the cosmos.
- Entrepreneurial ventures drive innovation and economic growth.
- Fitness regimes promote holistic health and longevity.
- The fashion industry sets global trends while reflecting societal shifts.
- Psychological theories delve into the intricate workings of the human mind.
- Parenting styles influence a child’s development and worldview.
- Technological disruptions challenge traditional business models.
- Documentary films highlight societal issues and human stories.
- Gardening offers therapeutic benefits and a connection with nature.
- Modern medicine offers revolutionary treatments and hopes for chronic ailments.
- Cultural festivals celebrate a community’s heritage and traditions.
- Robotics is transforming sectors from healthcare to manufacturing.
- Urban planning addresses the challenges of rapidly expanding cities.
- Environmental policies aim to mitigate the effects of industrialization.
- Video games merge entertainment with interactive storytelling techniques.
- Graphic novels combine visual art with narrative depth.
- Theatre arts encompass a spectrum of genres, from tragedy to farce.
- Digital marketing targets consumers using online platforms and data analytics.
- Ancient mythologies provide insights into early human beliefs and values.
- Quantum physics challenges our understanding of the universe’s fundamental nature.
- Human rights movements fight for equality, justice, and freedom globally.
- Online education facilitates learning beyond geographical boundaries.
- Microfinance initiatives empower marginalized communities through financial inclusivity.
- Space telescopes capture awe-inspiring images of distant galaxies and stars.
- Holistic therapies combine traditional and modern practices for overall wellness.
- Archaeological digs reveal secrets of bygone eras and lost civilizations.
- Modern sculptures reflect contemporary societal values and artistic experimentation.
- Nano-technology holds potential for advancements from medicine to electronics.
- Digital art allows limitless creativity with the help of technology.
- Global collaborations foster advancements in research and innovations.
- Local cuisines represent the heart of a culture, infused with history and flavors.
- Renewable energy initiatives combat the global energy crisis and climate change.
- Ethical consumerism encourages responsible production and purchasing behaviors.
- Wildlife documentaries raise awareness about endangered species and habitats.
- Start-up ecosystems boost economic growth and technological innovations.
- Classic literature resonates with themes that remain relevant across ages.
- Mental health awareness breaks stigmas and fosters supportive communities.
- Biographical works provide a window into influential personalities’ lives.
- Adventure sports push human limits and offer adrenaline-filled experiences.
- Underwater exploration uncovers marine biodiversity and submerged secrets.
- E-commerce platforms reshape the shopping experience in the digital age.
- Sustainable fashion champions eco-friendly materials and ethical production.
- Forensic science plays a crucial role in solving criminal cases.
- Digital privacy measures protect user data from breaches and misuse.
- Animated films enthrall audiences with imaginative stories and visuals.
- Hydroponic farming offers soil-less agricultural solutions.
- Artificial neural networks simulate human brain processes for machine learning.
- Classical dance forms preserve age-old traditions and storytelling techniques.
- 3D printing technology revolutionizes manufacturing and prototyping processes.
- Ancient cartography charts historical perceptions of the world and explorations.
- Digital currencies are reshaping the landscape of financial transactions globally.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy offers tools to reshape negative thought patterns.
- Space tourism heralds a new era of extraterrestrial travel for civilians.
- Marine conservation efforts strive to protect our oceans’ fragile ecosystems.
- Molecular gastronomy melds culinary arts with scientific principles.
- Traditional craftsmanship preserves skills passed down through generations.
- Augmented reality applications blur the boundaries between the digital and real worlds.
- Public transportation systems facilitate urban mobility and reduce carbon footprints.
- Jazz music captures improvisational brilliance and rhythmic complexities.
- Antique collecting cherishes artifacts from bygone eras, each with its unique story.
- Gene editing techniques hold the promise of eradicating genetic disorders.
- Organic agriculture prioritizes natural growth processes and shuns chemical interventions.
- Adventure travel invigorates the spirit with challenges and uncharted experiences.
- Photojournalism chronicles real-life events, capturing moments that resonate deeply.
- Neuroscience research explores the intricate workings of the human brain.
- Contemporary dance expresses emotions and stories through fluid movements.
- Ecosystem restoration projects aim to revive habitats and promote biodiversity.
- Pet adoption campaigns advocate for giving shelter animals a second chance.
- Solar-powered solutions present sustainable alternatives to conventional energy sources.
Each of these topic sentences encapsulates a distinct theme or idea, forming a foundation upon which a robust, engaging essay can be constructed. By crafting clear and compelling topic sentences, writers can navigate their readers through diverse landscapes of thought, ensuring a coherent and memorable journey.
Is a topic sentence 1 sentence?
Absolutely, a topic sentence is typically one sentence that succinctly captures the main idea or central theme of a paragraph. Its primary role is to provide clarity and direction, giving readers a concise overview of what to expect in the subsequent lines. The topic sentence functions much like a thesis statement for a paragraph, presenting the focal point around which other sentences revolve. By offering a clear snapshot of the paragraph’s intent, it helps readers grasp the essence of the content and understand the progression of ideas.
Are topic sentences always the first sentence?
Traditionally, topic sentences often appear at the beginning of a paragraph, setting the tone and direction for the following sentences. However, they don’t always have to be the first sentence. The placement can vary based on the writing style, structure, and the purpose of the text.
- Beginning: In academic and many forms of informative writing, topic sentences usually start the paragraph. This placement offers immediate clarity and direction to readers.
- Middle: Sometimes, writers might begin with a few introductory sentences before delving into the main idea, which is then presented in the form of a topic sentence in the middle of the paragraph. This can be especially effective in narrative or creative writing where setting a scene or building anticipation is crucial.
- End: In certain cases, the topic sentence might conclude a paragraph, serving as a summarization or a transitional point leading to the next section.
- Implied: Occasionally, especially in more narrative or descriptive paragraphs, the main idea might be implied rather than explicitly stated in a single topic sentence.
Regardless of its position, the role of the topic sentence remains the same: to anchor the reader and provide a clear focus for the paragraph. The key is to ensure that wherever the topic sentence is placed, it should effectively guide the reader through the content and highlight the central theme.
How do you write Essay Topic Sentences? – Step by Step Guide
The quality of an essay often hinges on its topic sentences. These crucial components anchor each paragraph, guiding the reader and establishing a clear focus. Here’s a step-by-step guide to crafting compelling essay topic sentences:
- Understand the Paragraph’s Purpose: Before penning a topic sentence, grasp the main idea or argument your paragraph intends to convey.
- Be Clear and Concise: The topic sentence should succinctly summarize the paragraph’s central theme. Avoid ambiguity or overly complex language.
- Stay Relevant: Ensure your topic sentence aligns with the thesis or main argument of your essay.
- Use Specific Language: Instead of broad generalities, be precise. For instance, instead of “Books are beneficial,” say “Reading classic literature enriches one’s vocabulary and cognitive skills.”
- Avoid Mere Statements of Fact: A topic sentence should provide insight or a perspective rather than just stating an obvious fact.
- Incorporate Transitional Words: Especially in longer essays, use transitional phrases like “Furthermore,” “However,” or “In contrast” to guide the reader and indicate the flow of ideas.
- Test its Strength: Once written, check if your topic sentence provides a clear roadmap for the paragraph. It should set expectations for what’s to come.
- Iterate and Refine: Don’t be afraid to revise your topic sentence multiple times until it feels just right. It’s an integral part of the writing process.
Tips for Using Essay Topic Sentences
Topic sentences can elevate the quality of your essay when used effectively. Here are some tips to make the most of them:
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure that your topic sentences are consistent in style and tone throughout the essay.
- Vary Sentence Structures: While maintaining clarity, try different structures to keep your writing dynamic and engaging.
- Link to Previous Ideas: Especially in longer essays, make sure your topic sentences build upon the ideas from previous paragraphs. This creates a cohesive flow.
- Stay On Topic: A common pitfall is to deviate from the main idea. Ensure your topic sentence and the subsequent content remain aligned.
- Avoid Overly General Statements: Aim for specificity in your topic sentences to give readers a clear idea of what to expect.
- Seek Feedback: Have someone review your essay, paying particular attention to topic sentences. Fresh eyes can often spot inconsistencies or areas of improvement.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, crafting excellent topic sentences improves with practice. The more you write and revise, the more intuitive the process becomes.
By mastering the art of essay topic sentences, you can guide your readers smoothly through your content, ensuring clarity, engagement, and a strong narrative flow.
Essay Topic Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an essay topic about your dream job and why you want it
Choose an essay topic discussing the best day of your life and what made it so special

Topic Sentence and Paragraph Organization
Paragraph organization refers to the way sentences are structured and ordered to create a unified and cohesive body of text.
The principal features to consider in paragraph organization are the topic sentence and controlling idea, supporting details, organizational patterns, and signal words. Together, these features develop a topic and connect ideas from one point to the next, logically and fluidly. This resource explains these features and provides numerous examples of paragraph organization.
The Topic Sentence and Controlling Idea
Similar to a thesis statement, which establishes the central focus or point of a whole piece of writing, a topic sentence works at the paragraph level to express the focus and general point of an individual paragraph. A topic sentence has two parts: 1) the topic that is being discussed throughout the paragraph and 2) a controlling idea that limits the focus on the topic to one point or idea. Each additional sentence in the paragraph then develops or expounds on that point with supporting details. The example topic sentence below is from a body paragraph in an informative essay.
Example Topic Sentence and Controlling Idea
The economy also plays a role in an increase in prescription pain reliever addiction.
The example topic sentence suggests the paragraph topic is “the economy,” and the controlling idea about the economy is how it “plays a role in an increase” in opioid addition. The signal word “also” connects this topic as an additional example or contributing factor to the opioid epidemic, the focus of the paper. The example below shows the topic sentence in the context of the complete paragraph.
The economy also plays a role in an increase in prescription pain reliever addiction. According to Jungeun Olivia Lee, a social work professor at University of Southern California, “The relationship between joblessness and substance abuse is strongest among people from low socioeconomic brackets, who might not be able to afford healthier ways to relieve their stress” (2017, as cited in Khazan, 2017, para. 8). Additionally, every point the unemployment rate rises, opioid-related death rates rise by almost 4 percent (Khazan, 2017). Unemployment makes it not only difficult for those suffering from pain to afford medication or healthy alternatives, but it can also contribute to depression and varying degrees of self-medication and addiction.
Supporting Details
In a paragraph, the topic and controlling idea are developed with supporting details. Listed here are some types of supporting details found in paragraphs along with an example of each in a sentence.
Facts: statistics or evidence from research that can be verified
- The office sold seven million dollars of real estate during the boom years.
Opinions: statements, quotes, or paraphrases from subject matter experts
- According to expert tea maker, Millie Stoff, there are three easy steps to making tea.
Definitions: explanations of what a term or concept means
- A crossover is a family vehicle with the features of a sedan, a mini-van, and an SUV.
Examples: parts, pieces, instances, traits, or specimens that illustrate the essence or character of a greater whole.
- Mario is a shy, introverted young man. For example, he has few friends and mostly keeps to himself.
Anecdotes: narrative accounts of one time or recurring events
- When I visited the Washington Monument, I enjoyed the 180-degree view the most.
Descriptions: a visual or sensory depiction of a person, place, event, activity, or idea
- Frostbit leaves crunched beneath our winter boots on the path through the snow-frosted trees.
Example Paragraph and Analysis of the Supporting Details
Hiking can be exhilarating during snowy winter months. When my friend and I visited North Carolina last January, we hiked in the Blue Ridge Mountains near the highest peak, Mount Mitchell, which is6,684 feet above sea level. We first crossed a foot bridge over a rapidly moving, ice-cold river and then followed a wooded trail up to a waterfall. Frostbit leaves crunched beneath our winter boots on the path through the snow-frosted trees. We saw deer and rabbits as we trekked up the path. I assure you that nothing feels better than inhaling crisp mountain air, but the neatest part of hiking in winter, besides the beauty of the mountain, is exhaling and seeing my breath turn to frost when it hits the cold air!
The topic sentence in the example paragraph indicates that the paragraph is on “hiking,” and the focus is that hiking is “exhilarating” during winter. The sentences in the paragraph support and develop this idea with an anecdote of the writer’s experience hiking up a mountain during winter. An anecdote is a narrative account that helps a reader understand an event or situation. Had the writer said hiking was “dangerous” instead of “exhilarating,” the anecdote in addition to the visual and sensory details, facts, and opinions about the experience would have been different. Additionally, while the sample paragraph is a personal account, writers in many professions use anecdotal evidence to report events from an objective point-of-view, where the writer is not a participant but rather a witness or observer.
Paragraph Organization
Along with having topic sentences and supporting details, paragraphs are also organized to achieve a certain purpose. However, just as a paragraph can contain different types of supporting details, a paragraph may also include more than one organizational pattern. Listed here are some common patterns for organizing a paragraph:
- Cause and Effect for showing how one thing leads to another
- Chronological Order for narrating events that occurred over time
- Classification for grouping things together according to their features
- Comparison and Contrast for showing how things are similar or different
- Definition and Example for defining a term or idea and then expanding it with examples
- Description for listing details
- Episode for presenting details or information about a specific event or anecdote
- General/Specific Order for presenting a general idea followed by specific examples
- Generalization/Principle for making a general statement or applying a broad principle to explain the supporting details
- Listing for presenting ideas from least to most important
- Order of Importance for building up to or leading away from the most important point.
- Problem and Solution for presenting an issue and a way to address it
- Process/Cause for explaining what or how something happens and then why
- Spatial Order for ordering details directionally
Signal Words
Signal words are signposts or clues to a paragraph’s organization. If the word “type” is used in a sentence, for example, it signals that the ideas involve types or classification, which is an organizational pattern. Signal words are context clues that hint at what the paragraph is about and how it is organized.
Listed here are signal words associated with different types of paragraph organization.
- Cause and Effect : because, consequently, for this reason, hence, and on account of
- Chronological Order : after, at last, at (time), as long as, at the same time, as soon as, before, during, eventually, finally, in (month or year), later, meanwhile, next, on (day or date), since, second, subsequently, then, until, and whenever
- Classification : categories, classes, classifications, elements, features, groups, kinds, methods, types, varieties, and ways
- Comparison and Contrast : another, both, however, likewise, one difference, on the other hand, on the contrary, similarity, similarly, unlike, and while
- Definition and Example : concept, defined as, described as, e.g., for example, for instance, i.e., illustrates, is, is called, is stated, known as, means, refers to, specifically, such as, term, and that is to say
- Description : above, across, along, appears to be, as in, behind, below, beside, between, down, in back of, in front of, looks like, near, onto, on top of, outside, over, such as, to the right/left, and under
- Episode : a few days/weeks later, around the same time, as a result of, as it is often called, because of, began when, consequently, for this reason, just, lasted for, led to, shortly thereafter, since then, subsequently, this led to, and when
- General/Specific Order : for example, for instance, indeed, in fact, in other words, like, namely, such as, and that is
- Generalization/Principle : additionally, always, because of, clearly, conclusively, first, for instance, for example, furthermore, generally, however, if…then, in fact, it could be argued that, moreover, most convincing, never, not only…but also, often, second, therefore, third, truly, and typically
- Listing : additionally, also, and, as well as, besides, furthermore, in addition, in fact, moreover, or, plus, and too
- Order of Importance : central, chief, ending with, finishing with, key, lastly, least, main, major, finally, primary, principal, and significant
- Problem and Solution : answer, challenge, difficulty, dilemma, enigma, indicate, improve, issue, need, plan, problem, propose, resolve, respond, solve, and suggest
- Process/Cause : accordingly, as a result of, because, begins with, consequently, effects of, finally, first, for this reason, how to, how, if…then, in order to, is caused by, leads/led to, may be due to, next, so that, steps involved, therefore, thus, and when…then
- Spatial Order : above, below, behind, beside, down, east, feels, highest, looks, lowest, next to, north, smells, sounds, south, tastes, under, and west
Sample Paragraphs and Analyses of the Organization
The sample paragraphs in this section illustrate topic sentences, supporting details, organizational patterns, and signal words in context. Read each paragraph to identify the type of paragraph organization on your own, and then proceed to the analysis to check your comprehension.
Sample Paragraph 1
- In 1995, Lawrence started his real estate business, and it has since become a huge success. When Lawrence Real Estate opened its door in Oviedo, Florida, it sold seven million dollars of real estate during the first few boom years. By 2000, Lawrence decided to open two branch offices: one in Tampa in 2003 and one in Miami in 2004. By 2007, the home office and both the branch offices had survived the economic slowdown, so Lawrence and his associates expanded their business to the Carolinas and opened a branch office in Charlotte in 2020. It can be safely said that Lawrence Real Estate has become a model for success despite economic struggles and real estate devaluation.
Analysis of Paragraph 1: According to the topic sentence, which contains two coordinating clauses and therefore two subjects and two topics, this paragraph is about Lawrence and his real estate business, and the controlling idea is that they have been successful.
To understand how the supporting details are organized to present information about this topic and idea, the reader can consider the supporting details. To do this, they look at the way the sentences begin and at any signal phrases that lead readers along a certain line of thinking. Here are some key signal words: “in 1995,” “By 2000,” “By 2007,” and “in 2020.” These dates make a pattern. They go back to 1995 and then in a chronological order, they move forward to when the success of the business happened.
This paragraph uses chronological order . The reader will notice too that the last sentence returns to the beginning idea of 15 years ago. In this sentence, a final comment about the time period overall is given with respect to the new information
Sample Paragraph 2
- Making a great cup of tea is easy if you follow these three steps. First, heat a cup of water to the boiling point. Then put the tea bag in the hot water, and let it steep for at least three minutes. Finally, add creamer and sugar to taste. There is nothing tastier than a strong cup of tea early in the morning.
According to the topic sentence, which is the first sentence of the paragraph, making a cup of tea is the topic, and the controlling idea is that it’s easy to do if you follow three steps. Signal words open the following sentences: “first,” “then,” and “finally.” These indicate a sequence of steps, not times or dates as in a narrative story, but steps that happen in a specific order as in the process of doing something or informing others how to do something.
This paragraph uses process order (or process/cause). In the last sentence of this paragraph, the process is completed with a return to the original topic—a cup of tea—and a new comment about it—that a strong cup is tasty in the morning, making those three steps not only easy but also worthwhile.
Sample Paragraph 3
- The Washington Monument is divided into three main areas. The lowest section of the building houses the entrance, a gift shop, and a restaurant. The middle section consists of elevators and stairways to the top. The top section of the monument includes an observation deck with a spectacular view of the Washington D.C. area. When I visited the Washington Monument, I toured every section but enjoyed the spectacular 180-degree view the most.
Based on the topic sentence at the beginning of the paragraph, the topic is the Washington Monument, and the controlling idea is that it is divided into three main areas. The paragraph presents information about the lowest section first, the middle section second, and the top section third. The last sentence makes a remark about the most enjoyable of all the sections. This is an example of spatial organization . The information is given in the order you might see it if you were there.
Sample Paragraph 4
- There are three types of family vehicles made in the United States. The first type is the minivan. All American car manufacturers make a version of the minivan. Some say that the comfort and amenities of the minivan compare to none. The second type of family vehicle is the SUV. Some SUVs offer four-wheel-drive to navigate tough terrains, and they also offer seating for a large crowd. A third type of family vehicles is called the crossover. These vehicles supposedly have the best features of the sedan, minivan, and SUV. They are easy to maneuver, look much like a regular sedan, and sit up to six people. All of these vehicles are family friendly; they offer safety, roomy comfort, and many extra features to accommodate the special needs of families.
This paragraph shows another way to organize the details of a topic. The topic sentence of this paragraph is structured differently than the previous ones. Typically, the topic of a sentence is also the grammatical subject, but the subject in this sentence is “there,” a pronoun, and the topic that tells what the paragraph is about, “family vehicles,” is in the predicate of the sentence. The controlling idea is that there are three types made in the U.S.
The paragraph is organized according to those three types: the first type, the second type, and the third type. To conclude, there is a comment about “all of these vehicles” or all of these types of vehicles. When information is organized by types or features, the information is classified. This type of organization is classification .
Sample Paragraph 5
- Although the twin brothers share many physical characteristics, they handle themselves differently in social situations. Mario is a shy introverted young man. He has few friends and mostly keeps to himself. On the other hand, Gino is outgoing and the life of the party. Unlike Mario, Gino has many friends and feels totally at ease among big crowds. The best way to tell these identical twins apart is to invite both to a party and observe how differently they interact with the other guests.
When the topic sentence is complex (having more than one clause) as in this paragraph, there may be two subjects and therefore two topics; however, here, the subject of the first clause is “the twin brothers” and the subject for the second clause is “they,” so both subjects refer to the same topic—the twin brothers. The controlling idea is that the twin brothers share many physical characteristics but handle themselves differently socially.
The paragraph then progresses with descriptions of these similarities and differences. Contrast is created by signal phrases and words such as “although, “on the other hand,” and “unlike.” Words such as “apart” and “differently” also indicate that the organizational pattern of this paragraph is comparison and contrast .
Sample Paragraph 6
- There are many reasons why I enjoy walking tours when visiting new cities. For starters, walking through a city allows the visitor to see the details of an area without having to hurry. This often results in meeting locals and experiencing their lives and traditions first hand. Furthermore, walking tours are flexible and inexpensive because there are no strict schedules or transportation expenses. Travelers taking walking tours are rewarded with firsthand experiences in the places they visit and the opportunity to personally interact with the people who live there.
Because the first sentence begins with “there are,” the reader must move beyond the subject and verb to find the topic. Additionally, this is a complex sentence with an independent and dependent clause connected by “why,” so there may be two topics. Looking at the objects of both clauses, the reader finds “many reasons” and “walking tours.” These two topics are linked together by the controlling idea: the writer enjoys walking tours while visiting new cities for many different reasons.
The signal words build on this idea of “why” with terms such as “results” and “because.” The last sentence then sums up the ultimate effect of walking tours: Travelers are rewarded. This is an example of cause and effect organization.
Sample Paragraph 7
- Hiking can be especially exhilarating during snowy winter months. When my friend and I visited North Carolina last January, we hiked in the Blue Ridge Mountains near the highest peak, Mount Mitchell, which is 6,684 feet above sea level. We first crossed a footbridge over a rapidly moving, ice-cold river and then followed a wooded trail up to a waterfall. Frostbit leaves crunched beneath our winter boots on the path through the snow-frosted trees. We saw deer and rabbits as we trekked up the path. I assure you that nothing feels better than inhaling crisp mountain air, but the neatest part of hiking in winter, besides the beauty of the mountain, is exhaling and seeing my breath turn to frost when it hits the cold air!
In the first sentence, the topic of the paragraph is “hiking,” and the comment or main idea is that it “can be especially exhilarating during snowy winter months.” Based on this, the reader can expect supporting details to illustrate this exhilaration, but they do not know how it is organized until they look at the signal words that help progress the topic from one idea to the next.
Taking inventory of the signal words, the reader will find several time markers: “When” and “last January” set the narrative in the past while “first” and “then” develop a chronological order of events. The final summarizing sentence about hiking “in winter” reminds the reader of the season.
Within this chronology , signal words are associated with spatial organization: “over,” “up,” “beneath,” “through,” “crunched” (sounded), “saw,” “feels,” and “seeing.” Narratives typically include descriptive elements about the setting. Additionally, the concluding thought contrasts “inhaling” to “exhaling.” The reader can thus conclude that this paragraph has multiple patterns of organization that are intricately connected.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
- Skip to main content
IELTS Podcast
Pass IELTS with expert help.
10 Examples Topic Sentences for your Essays

In this tutorial we look at 10 typical IELTS task 2 question s and suggest possible topic sentences . In the audio tutorial these sentences are further improved to avoid repetition, and rewritten to improve their effectiveness.
Topic sentences form the backbone of your IELTS Task 2 essay .
What is a Topic Sentence?
A topic sentence is a sentence that captures the essence of your paragraph. It introduces the reader to the topic or main point that you set out to make in that paragraph and sets the tone for the rest of the paragraph.
The examiner should be able to read the topic sentence, and immediately know what the rest of the paragraph will be about. So this part is very important.
Important points to consider :
- It is important to read the question extremely carefully so that you can order your arguments in a coherent manner.
- You should outline your position and write a coherent argument. It helps to plan your answer or argument before you begin.
- Each paragraph should contain one main idea/point . This is where your topic sentences come in. This sentence IS the main idea or point that you wish to make in the paragraph.
- Your essay is made of paragraphs that have supporting points. Each paragraph should come together to form a coherent whole essay. The topic sentence is just one way to make your writing shine!
Here are 10 examples of topic sentences that you can practice with for your IELTS essay. I have included the questions and examples on how you could write a paragraph.
1. Some people argue that it is the responsibility of the police to educate children about good behaviour in society, whereas others believe that parents should be responsible for teaching their children how to behave in an acceptable way. Discuss both views and give your own opinion.
It is the responsibility of the police to educate children about good behaviour …
The police and parents have a mutual responsibility to teach children about good behaviour
2. Some people believe that more women should be encouraged to pursue careers in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), while others believe that women are naturally suited for careers in the Humanities/ Social Sciences, such as teaching and psychology. Discuss your views and opinion.
There are not enough women pursuing careers in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics( STEM)
Women are better suited for careers in the Humanities/Social Sciences
3. Scientists argue that the use of modern gadgets, such as cellphones and tablets, by young people has the potential to boost creativity. Do you agree or disagree?
There has been evidence that the use of modern gadgets by young people does in fact increase their creativity
The use of modern gadgets decreases the creativity of young people
4. Social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter, have become a more important source of news and information for young people, than newspapers. Do you agree or disagree?
Example: Social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter, have become a major source of news and information for young people
Example: Newspapers are still a more important source of news and information for young people than social media networks
6. School children should be instructed in their home language for the first 6 years of school.
Example: Young learners need to be taught in their home language in the first 6 years of their education
It is not important for school children to be taught in their home language in the first few years of school
OR more advanced:
Pupils need not be taught in their home language in the first 6 years of their education
7. Nowadays women are having children at a much later age than previous generations. Do you think this a positive or negative thing? Discuss both sides.
Example: Nowadays females have children much later in life than they did in the past
Currently women start families much later in life than previously (vague?)
8. In many countries women are opting not to have children. Some people believe that having children stifles a woman’s career growth. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Example: Having children can take a toll on a woman’s career
Female careers been hindered by starting families is (unfortunately) a very common concern for both females and employers.
9. Nowadays children are exposed to more sex and violence in the media than before. What are the reasons for this? Is this a good thing or a bad thing?
Example: There are several reasons why young people see more sexual and violent media than before
1 0. Parents need to do more to protect children from cyberbullying. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Example: Parents can do a lot to protect their children from cyberbullying
Parenting nowadays has become increasingly more complex largely thanks due to the internet and cyber bullying.
Regarding protecting their children online, parents need to find a balance between their child’s online freedom and becoming online helicopter parents.
especially because most parents are not digital natives.
11. Some people think that children should not have a cell phone until they have reached their teens, whereas others believe that children should have cell phones at an early age. Discuss both views and give your own opinion
Example: Children should not be allowed to have a cell phone until they are 13
Parents should encourage cell phone use at an early age
As you have seen, there are many different ways you can write your topic sentence. The topic sentence forms the backbone of your paragraph- it is where you state your main point, so it is important to get this right.
I hope you find the above examples and tips helpful in your preparation for the IELTS writing task !
For feedback to improve your writing, check out our IELTS essay correction service .
You can download or listen to the audio version here:
| Direct Download Here | Stitcher | iTunes | Spotify | Soundcloud | Transcript |
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
For more help with your IELTS preparation , take a look at some tutorials here:
- How to get Band 9 for Task 1
- How to plan for Academic Task 1

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Make an essay outline and draft topic sentences. Next, you should make an outline of your essay's structure, planning what you want to say in each paragraph and what evidence you'll use. At this stage, you can draft a topic sentence that sums up the main point you want to make in each paragraph. The topic sentences should be more ...
First, topic sentences string together paragraphs in a way that progresses nicely and facilitates reading. Moving from one paragraph to another can feel jarring and abrupt, so topic sentences help maintain the flow of the overall piece of writing—and readers' focus as a result. Moreover, topic sentences also "preview" what the reader ...
Step 3: Make your essay outline. Once you have the points you want to make within your thesis statement hammered out, make an outline for your essay. This is where you'll start to create your topic sentence for each paragraph. You want to clearly state the main idea of that paragraph in the very first sentence.
Topic sentences and signposts make an essay's claims clear to a reader. Good essays contain both. ... The following example comes from an essay examining how a painting by Monet, The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, challenges Zola's declarations about Impressionist art. The student writer wonders whether Monet's Impressionism is really ...
When you're on your own with determining ideas for an essay topic, there are a few different strategies you can use: Freewriting. Start with the type of essay you've been assigned (analytical, compare-and-contrast, personal, etc.) and let your mind wander. Write down any questions that come to mind, insights you have, observations about ...
Examples can help you learn a thing in a better way. If you are new to writing topic sentences, it can help to look at some examples. Find some great examples of topic sentences relevant to your essay topic. Difference Between Topic Sentence and Thesis Sentence. Here's a table outlining the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis ...
For example, if you are writing an essay about domestic violence, your topic sentence could be: 1 in 4 men have experienced domestic violence from a partner. That is an interesting fact that most people do not know since most domestic violence information focuses on violence against women. However, it is just a fact.
Essentially, it is a concise and direct statement that captures the essence of what you want to convey. A topic sentence is defined by the following characteristics: It is the first sentence of a paragraph. It indicates the main idea of the paragraph. Acts as a signpost and transition sentence, ensuring clarity and cohesiveness of an essay.
If you do choose a common topic, ensure you have the following to craft a unique essay: Surprising or unexpected story arcs. Interesting insight or connections. An advanced writing style. Here are a few examples of how to craft strong essays from cliché topics. Common topic.
Make yours one to remember with these topic sentence examples. A great topic sentence gives you insight into what you can expect in a paragraph. Make yours one to remember with these topic sentence examples. ... Essays; Examples of Topic Sentences That Make the Purpose Clear By Jennifer Gunner, M.Ed. Education , Senior Writer . Updated July 6 ...
While an essay's thesis statement identifies the point of the essay in its entirety, the topic sentence has a much narrower focus, as it relates only to the paragraph in which it is located. ... Topic sentence examples. The following list identifies topic sentences based on the provided thesis statements for five-paragraph essays:
When read in sequence, your essay's topic sentences will provide a sketch of the essay's argument. Thus topics sentences help protect your readers from confusion by guiding them through the argument. But topic sentences can also help you to improve your essay by making it easier for you to recognize gaps or weaknesses in your argument.
Updated on February 12, 2020. A topic sentence is a sentence, sometimes at the beginning of a paragraph, that states or suggests the main idea (or topic) of a paragraph. Not all paragraphs begin with topic sentences. In some, the topic sentence appears in the middle or at the end. In others, the topic sentence is implied or absent altogether.
1. Identify the main point in your piece of writing. Think about the overall topic for your writing. Decide how you can introduce this idea to your readers with an interesting opening sentence. 2. Write a sentence that connects to your main idea with a what and a why. Write a clear topic sentence by describing the what and the why of an idea ...
1. Determine the Main Idea of Your Writing. Before you write a topic sentence for body paragraphs, identify your essay's main idea, or the point you're trying to prove. The key argument is usually hidden in your thesis statement. Read through your thesis and think about the overall point that you are trying to make.
The purpose of a topic sentence is to identify the topic of your paragraph and indicate the function of that paragraph in some way. In order to create an effective topic sentence, you should do the following: Use a transitional device to effortlessly segue from the idea discussed in the previous paragraph. When choosing a transitional device ...
An essay topic sentence is the opening sentence of a paragraph that provides a concise summary of what the paragraph will address. It serves as a roadmap, guiding readers through the main idea or argument of that particular section, ensuring clarity and coherence. What is the best Example of an Essay Topic Sentence? Imagine writing an essay ...
The example topic sentence below is from a body paragraph in an informative essay. Example Topic Sentence and Controlling Idea. The economy also plays a role in an increase in prescription pain reliever addiction. Analysis. The example topic sentence suggests the paragraph topic is "the economy," and the controlling idea
Topic sentence examples. To give you an idea of how to transform a topic sentence from okay to great, here are some examples: Okay: Abraham Lincoln was born in 1809. Better: Abraham Lincoln, born in 1809, was one of the most influential politicians in history.
Elementary students often write simple topic sentences that focus solely on the main idea of the paragraph. Some examples of topic sentences for this age group include: When we had a snow day, I made snow angels, drank hot cocoa, and went sledding. Students should not have to do homework because it takes a lot of time.
Summarise. Anticipate. Emphasise or expand. Conclusion. A topic sentence is one which appears, usually (but not always) at the beginning of each paragraph of an essay. The topic sentence is used to layout the ideas and arguments that will be covered within the paragraph and should be carefully planned out to ensure that they are clear enough to ...
10 Examples Topic Sentences for your Essays. In this tutorial we look at 10 typical IELTS task 2 question s and suggest possible topic sentences. In the audio tutorial these sentences are further improved to avoid repetition, and rewritten to improve their effectiveness. Topic sentences form the backbone of your IELTS Task 2 essay .