
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
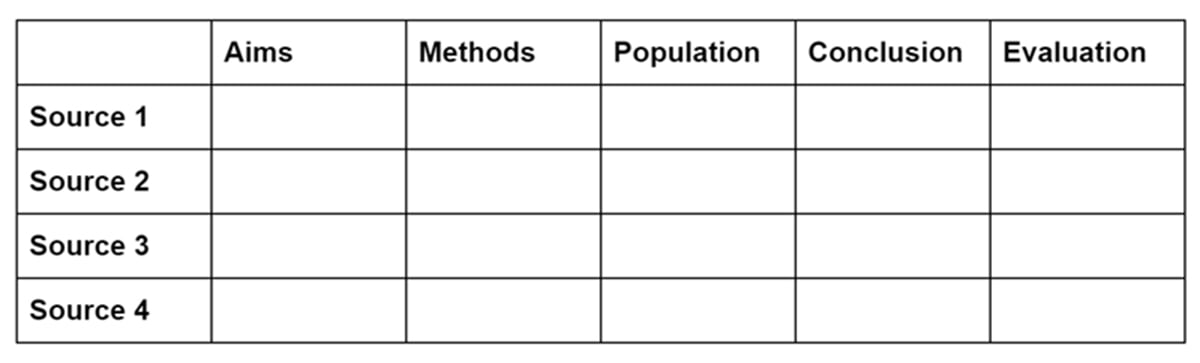
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
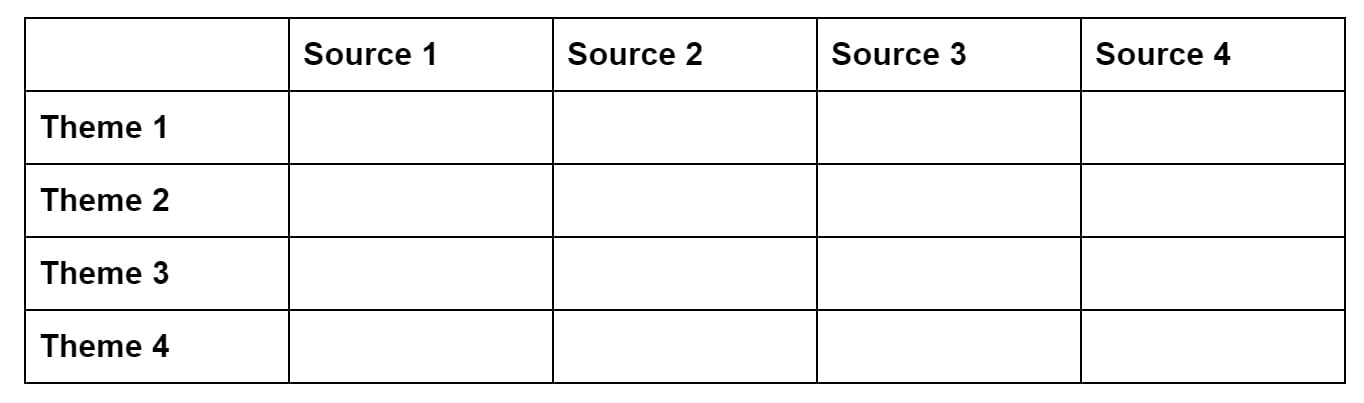
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
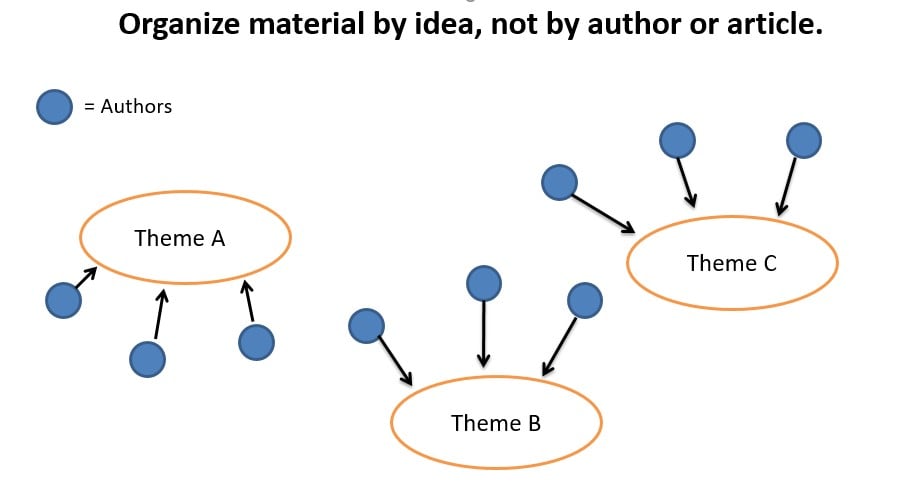
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay

How to Write a Literature Review - A Self-Guided Tutorial
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the question
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Searching article databases - video
- Finding the article full-text
- Citation trails
- When to stop searching
- Citation Managers
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write literature review
- Additional Resources
You can meet with a librarian to talk about your literature review, or other library-related topics.

You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

Synthesis Vizualization
Four examples of student writing.
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Synthesis Matrix Example

From Jennifer Lim
Synthesis Templates
Synthesis grids are organizational tools used to record the main concepts of your sources and can help you make connections about how your sources relate to one another.
- Source Template Basic Literature Review Source Template from Walden University Writing Center to help record the main findings and concepts from different articles.
- Sample Literature Review Grids This spreadsheet contains multiple tabs with different grid templates. Download or create your own copy to begin recording notes.
- << Previous: 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- Next: 7. Write literature review >>
- Last Updated: Mar 7, 2024 2:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/literature-review


- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Using Evidence: Synthesis
Synthesis video playlist.
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.

Basics of Synthesis
As you incorporate published writing into your own writing, you should aim for synthesis of the material.
Synthesizing requires critical reading and thinking in order to compare different material, highlighting similarities, differences, and connections. When writers synthesize successfully, they present new ideas based on interpretations of other evidence or arguments. You can also think of synthesis as an extension of—or a more complicated form of—analysis. One main difference is that synthesis involves multiple sources, while analysis often focuses on one source.
Conceptually, it can be helpful to think about synthesis existing at both the local (or paragraph) level and the global (or paper) level.
Local Synthesis
Local synthesis occurs at the paragraph level when writers connect individual pieces of evidence from multiple sources to support a paragraph’s main idea and advance a paper’s thesis statement. A common example in academic writing is a scholarly paragraph that includes a main idea, evidence from multiple sources, and analysis of those multiple sources together.
Global Synthesis
Global synthesis occurs at the paper (or, sometimes, section) level when writers connect ideas across paragraphs or sections to create a new narrative whole. A literature review , which can either stand alone or be a section/chapter within a capstone, is a common example of a place where global synthesis is necessary. However, in almost all academic writing, global synthesis is created by and sometimes referred to as good cohesion and flow.
Synthesis in Literature Reviews
While any types of scholarly writing can include synthesis, it is most often discussed in the context of literature reviews. Visit our literature review pages for more information about synthesis in literature reviews.
Related Webinars
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Analysis
- Next Page: Citing Sources Properly
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills

Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Literature Reviews
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
How to synthesize
Approaches to synthesis.
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic.
Here are some examples of how to approach synthesizing the literature:
💡 By themes or concepts
🕘 Historically or chronologically
📊 By methodology
These organizational approaches can also be used when writing your review. It can be beneficial to begin organizing your references by these approaches in your citation manager by using folders, groups, or collections.
Create a synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix allows you to visually organize your literature.
Topic: ______________________________________________
Topic: Chemical exposure to workers in nail salons
- << Previous: 4. Organize your results
- Next: 6. Write the review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 12:40 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/lit-reviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries


Library Guides
Literature reviews: synthesis.
- Criticality
Synthesise Information
So, how can you create paragraphs within your literature review that demonstrates your knowledge of the scholarship that has been done in your field of study?
You will need to present a synthesis of the texts you read.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains synthesis for us in the following video:
Synthesising Texts
What is synthesis?
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation.
With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source(s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
The sources will provide different perspectives and evidence on a topic. They will be put together when agreeing, contrasted when disagreeing. The sources must be referenced.
Perfect your synthesis by showing the flow of your reasoning, expressing critical evaluation of the sources and drawing conclusions.
When you synthesise think of "using strategic thinking to resolve a problem requiring the integration of diverse pieces of information around a structuring theme" (Mateos and Sole 2009, p448).
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise.
How to synthesise in a literature review:
Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an outline.
Read the literature and identify these themes/issues.
Critically analyse the texts asking: how does the text I'm reading relate to the other texts I've read on the same topic? Is it in agreement? Does it differ in its perspective? Is it stronger or weaker? How does it differ (could be scope, methods, year of publication etc.). Draw your conclusions on the state of the literature on the topic.
Start writing your literature review, structuring it according to the outline you planned.
Put together sources stating the same point; contrast sources presenting counter-arguments or different points.
Present your critical analysis.
Always provide the references.
The best synthesis requires a "recursive process" whereby you read the source texts, identify relevant parts, take notes, produce drafts, re-read the source texts, revise your text, re-write... (Mateos and Sole, 2009).
What is good synthesis?
The quality of your synthesis can be assessed considering the following (Mateos and Sole, 2009, p439):
Integration and connection of the information from the source texts around a structuring theme.
Selection of ideas necessary for producing the synthesis.
Appropriateness of the interpretation.
Elaboration of the content.
Example of Synthesis
Original texts (fictitious):
Synthesis:
Animal experimentation is a subject of heated debate. Some argue that painful experiments should be banned. Indeed it has been demonstrated that such experiments make animals suffer physically and psychologically (Chowdhury 2012; Panatta and Hudson 2016). On the other hand, it has been argued that animal experimentation can save human lives and reduce harm on humans (Smith 2008). This argument is only valid for toxicological testing, not for tests that, for example, merely improve the efficacy of a cosmetic (Turner 2015). It can be suggested that animal experimentation should be regulated to only allow toxicological risk assessment, and the suffering to the animals should be minimised.
Bibliography
Mateos, M. and Sole, I. (2009). Synthesising Information from various texts: A Study of Procedures and Products at Different Educational Levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 24 (4), 435-451. Available from https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178760 [Accessed 29 June 2021].
- << Previous: Structure
- Next: Criticality >>
- Last Updated: Nov 18, 2023 10:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/literature-reviews
CONNECT WITH US
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

Synthesis: What is it?
First, let's be perfectly clear about what synthesizing your research isn't :
- - It isn't just summarizing the material you read
- - It isn't generating a collection of annotations or comments (like an annotated bibliography)
- - It isn't compiling a report on every single thing ever written in relation to your topic
When you synthesize your research, your job is to help your reader understand the current state of the conversation on your topic, relative to your research question. That may include doing the following:
- - Selecting and using representative work on the topic
- - Identifying and discussing trends in published data or results
- - Identifying and explaining the impact of common features (study populations, interventions, etc.) that appear frequently in the literature
- - Explaining controversies, disputes, or central issues in the literature that are relevant to your research question
- - Identifying gaps in the literature, where more research is needed
- - Establishing the discussion to which your own research contributes and demonstrating the value of your contribution
Essentially, you're telling your reader where they are (and where you are) in the scholarly conversation about your project.
Synthesis: How do I do it?
Synthesis, step by step.
This is what you need to do before you write your review.
- Identify and clearly describe your research question (you may find the Formulating PICOT Questions table at the Additional Resources tab helpful).
- Collect sources relevant to your research question.
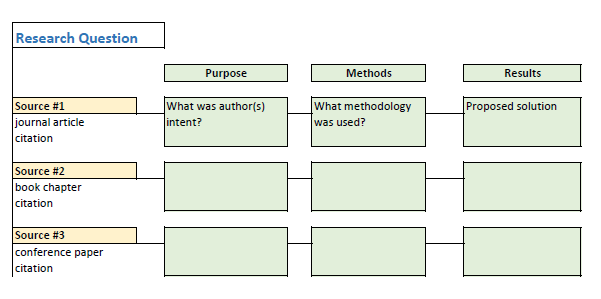
- Organize and describe the sources you've found -- your job is to identify what types of sources you've collected (reviews, clinical trials, etc.), identify their purpose (what are they measuring, testing, or trying to discover?), determine the level of evidence they represent (see the Levels of Evidence table at the Additional Resources tab ), and briefly explain their major findings . Use a Research Table to document this step.
- Study the information you've put in your Research Table and examine your collected sources, looking for similarities and differences . Pay particular attention to populations , methods (especially relative to levels of evidence), and findings .
- Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question.
Analysis tips
- - Sometimes, what you don't find in the literature is as important as what you do find -- look for questions that the existing research hasn't answered yet.
- - If any of the sources you've collected refer to or respond to each other, keep an eye on how they're related -- it may provide a clue as to whether or not study results have been successfully replicated.
- - Sorting your collected sources by level of evidence can provide valuable insight into how a particular topic has been covered, and it may help you to identify gaps worth addressing in your own work.
- << Previous: What is a Literature Review?
- Next: Using Research & Synthesis Tables >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Synthesizing Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you look for areas where your sources agree or disagree and try to draw broader conclusions about your topic based on what your sources say, you are engaging in synthesis. Writing a research paper usually requires synthesizing the available sources in order to provide new insight or a different perspective into your particular topic (as opposed to simply restating what each individual source says about your research topic).
Note that synthesizing is not the same as summarizing.
- A summary restates the information in one or more sources without providing new insight or reaching new conclusions.
- A synthesis draws on multiple sources to reach a broader conclusion.
There are two types of syntheses: explanatory syntheses and argumentative syntheses . Explanatory syntheses seek to bring sources together to explain a perspective and the reasoning behind it. Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions.
In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the pros and cons of encouraging healthy eating in children, you would want to separate your sources to find which ones agree with each other and which ones disagree.
After you have a good idea of what your sources are saying, you want to construct your body paragraphs in a way that acknowledges different sources and highlights where you can draw new conclusions.
As you continue synthesizing, here are a few points to remember:
- Don’t force a relationship between sources if there isn’t one. Not all of your sources have to complement one another.
- Do your best to highlight the relationships between sources in very clear ways.
- Don’t ignore any outliers in your research. It’s important to take note of every perspective (even those that disagree with your broader conclusions).
Example Syntheses
Below are two examples of synthesis: one where synthesis is NOT utilized well, and one where it is.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for KidsHealth , encourages parents to be role models for their children by not dieting or vocalizing concerns about their body image. The first popular diet began in 1863. William Banting named it the “Banting” diet after himself, and it consisted of eating fruits, vegetables, meat, and dry wine. Despite the fact that dieting has been around for over a hundred and fifty years, parents should not diet because it hinders children’s understanding of healthy eating.
In this sample paragraph, the paragraph begins with one idea then drastically shifts to another. Rather than comparing the sources, the author simply describes their content. This leads the paragraph to veer in an different direction at the end, and it prevents the paragraph from expressing any strong arguments or conclusions.
An example of a stronger synthesis can be found below.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Different scientists and educators have different strategies for promoting a well-rounded diet while still encouraging body positivity in children. David R. Just and Joseph Price suggest in their article “Using Incentives to Encourage Healthy Eating in Children” that children are more likely to eat fruits and vegetables if they are given a reward (855-856). Similarly, Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for Kids Health , encourages parents to be role models for their children. She states that “parents who are always dieting or complaining about their bodies may foster these same negative feelings in their kids. Try to keep a positive approach about food” (Ben-Joseph). Martha J. Nepper and Weiwen Chai support Ben-Joseph’s suggestions in their article “Parents’ Barriers and Strategies to Promote Healthy Eating among School-age Children.” Nepper and Chai note, “Parents felt that patience, consistency, educating themselves on proper nutrition, and having more healthy foods available in the home were important strategies when developing healthy eating habits for their children.” By following some of these ideas, parents can help their children develop healthy eating habits while still maintaining body positivity.
In this example, the author puts different sources in conversation with one another. Rather than simply describing the content of the sources in order, the author uses transitions (like "similarly") and makes the relationship between the sources evident.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- synthesize key sources connecting them with the research question and topic area.
7.1 Overview of synthesizing
7.1.1 putting the pieces together.
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question.

Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the results of your analysis into your own literature review. Each paper collected should be critically evaluated and weighed for “adequacy, appropriateness, and thoroughness” ( Garrard, 2017 ) before inclusion in your own review. Papers that do not meet this criteria likely should not be included in your literature review.
Begin the synthesis process by creating a grid, table, or an outline where you will summarize, using common themes you have identified and the sources you have found. The summary grid or outline will help you compare and contrast the themes so you can see the relationships among them as well as areas where you may need to do more searching. Whichever method you choose, this type of organization will help you to both understand the information you find and structure the writing of your review. Remember, although “the means of summarizing can vary, the key at this point is to make sure you understand what you’ve found and how it relates to your topic and research question” ( Bennard et al., 2014 ).
As you read through the material you gather, look for common themes as they may provide the structure for your literature review. And, remember, research is an iterative process: it is not unusual to go back and search information sources for more material.
At one extreme, if you are claiming, ‘There are no prior publications on this topic,’ it is more likely that you have not found them yet and may need to broaden your search. At another extreme, writing a complete literature review can be difficult with a well-trod topic. Do not cite it all; instead cite what is most relevant. If that still leaves too much to include, be sure to reference influential sources…as well as high-quality work that clearly connects to the points you make. ( Klingner, Scanlon, & Pressley, 2005 ).
7.2 Creating a summary table
Literature reviews can be organized sequentially or by topic, theme, method, results, theory, or argument. It’s important to develop categories that are meaningful and relevant to your research question. Take detailed notes on each article and use a consistent format for capturing all the information each article provides. These notes and the summary table can be done manually, using note cards. However, given the amount of information you will be recording, an electronic file created in a word processing or spreadsheet is more manageable. Examples of fields you may want to capture in your notes include:
- Authors’ names
- Article title
- Publication year
- Main purpose of the article
- Methodology or research design
- Participants
- Measurement
- Conclusions
Other fields that will be useful when you begin to synthesize the sum total of your research:
- Specific details of the article or research that are especially relevant to your study
- Key terms and definitions
- Strengths or weaknesses in research design
- Relationships to other studies
- Possible gaps in the research or literature (for example, many research articles conclude with the statement “more research is needed in this area”)
- Finally, note how closely each article relates to your topic. You may want to rank these as high, medium, or low relevance. For papers that you decide not to include, you may want to note your reasoning for exclusion, such as ‘small sample size’, ‘local case study,’ or ‘lacks evidence to support assertion.’
This short video demonstrates how a nursing researcher might create a summary table.
7.2.1 Creating a Summary Table

Summary tables can be organized by author or by theme, for example:
For a summary table template, see http://blogs.monm.edu/writingatmc/files/2013/04/Synthesis-Matrix-Template.pdf
7.3 Creating a summary outline
An alternate way to organize your articles for synthesis it to create an outline. After you have collected the articles you intend to use (and have put aside the ones you won’t be using), it’s time to identify the conclusions that can be drawn from the articles as a group.
Based on your review of the collected articles, group them by categories. You may wish to further organize them by topic and then chronologically or alphabetically by author. For each topic or subtopic you identified during your critical analysis of the paper, determine what those papers have in common. Likewise, determine which ones in the group differ. If there are contradictory findings, you may be able to identify methodological or theoretical differences that could account for the contradiction (for example, differences in population demographics). Determine what general conclusions you can report about the topic or subtopic as the entire group of studies relate to it. For example, you may have several studies that agree on outcome, such as ‘hands on learning is best for science in elementary school’ or that ‘continuing education is the best method for updating nursing certification.’ In that case, you may want to organize by methodology used in the studies rather than by outcome.
Organize your outline in a logical order and prepare to write the first draft of your literature review. That order might be from broad to more specific, or it may be sequential or chronological, going from foundational literature to more current. Remember, “an effective literature review need not denote the entire historical record, but rather establish the raison d’etre for the current study and in doing so cite that literature distinctly pertinent for theoretical, methodological, or empirical reasons.” ( Milardo, 2015, p. 22 ).
As you organize the summarized documents into a logical structure, you are also appraising and synthesizing complex information from multiple sources. Your literature review is the result of your research that synthesizes new and old information and creates new knowledge.
7.4 Additional resources:
Literature Reviews: Using a Matrix to Organize Research / Saint Mary’s University of Minnesota
Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources / Indiana University
Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix / Florida International University
Sample Literature Reviews Grid / Complied by Lindsay Roberts
Select three or four articles on a single topic of interest to you. Then enter them into an outline or table in the categories you feel are important to a research question. Try both the grid and the outline if you can to see which suits you better. The attached grid contains the fields suggested in the video .
Literature Review Table
Test yourself.
- Select two articles from your own summary table or outline and write a paragraph explaining how and why the sources relate to each other and your review of the literature.
- In your literature review, under what topic or subtopic will you place the paragraph you just wrote?
Image attribution
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3.2 Synthesizing literature
Learning objectives.
- Connect the sources you read with key concepts in your research question and proposal
- Systematize the information and facts from each source you read
Putting the pieces together
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic and argument to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question.

Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected, as well as your ability to integrate the results of your analysis into your own literature review. Each source you collect should be critically evaluated and weighed based on the criteria from Chapter 2 before you include it in your review.
Begin the synthesis process by creating a grid, table, or an outline where you will summarize your literature review findings, using common themes you have identified and the sources you have found. The summary, grid, or outline will help you compare and contrast the themes, so you can see the relationships among them as well as areas where you may need to do more searching. A basic summary table is provided in Figure 3.2. Whichever method you choose, this type of organization will help you to both understand the information you find and structure the writing of your review. Remember, although “the means of summarizing can vary, the key at this point is to make sure you understand what you’ve found and how it relates to your topic and research question” (Bennard et al., 2014, para. 10).
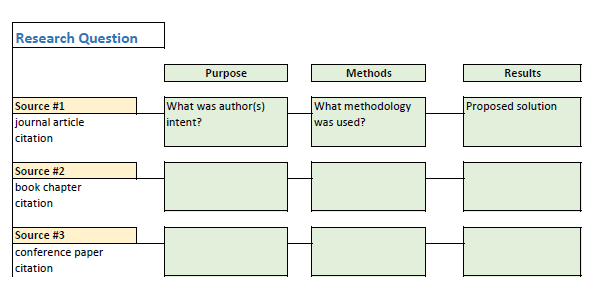
As you read through the material you gather, look for common themes as they may provide the structure for your literature review. And, remember, writing a literature review is an iterative process. It is not unusual to go back and search academic databases for more sources of information as you read the articles you’ve collected.
Literature reviews can be organized sequentially or by topic, theme, method, results, theory, or argument. It’s important to develop categories that are meaningful and relevant to your research question. Take detailed notes on each article and use a consistent format for capturing all the information each article provides. These notes and the summary table can be done manually using note cards. However, given the amount of information you will be recording, an electronic file created in a word processing or spreadsheet (like this example Literature Search Template ) is more manageable. Examples of fields you may want to capture in your notes include:
- Authors’ names
- Article title
- Publication year
- Main purpose of the article
- Methodology or research design
- Participants
- Measurement
- Conclusions
Other fields that will be useful when you begin to synthesize the sum total of your research:
- Specific details of the article or research that are especially relevant to your study
- Key terms and definitions
- Strengths or weaknesses in research design
- Relationships to other studies
- Possible gaps in the research or literature (for example, many research articles conclude with the statement “more research is needed in this area”)
- Finally, note how closely each article relates to your topic. You may want to rank these as high, medium, or low relevance. For papers that you decide not to include, you may want to note your reasoning for exclusion, such as small sample size, local case study, or lacks evidence to support conclusions.
An example of how to organize summary tables by author or theme is shown in Table 3.1.
Here is an example summary table template .
Creating a topical outline
An alternative way to organize your articles for synthesis it to create an outline. After you have collected the articles you intend to use (and have put aside the ones you won’t be using), it’s time to extract as much as possible from the facts provided in those articles. You are starting your research project without a lot of hard facts on the topics you want to study, and by using the literature reviews provided in academic journal articles, you can gain a lot of knowledge about a topic in a short period of time.

As you read an article in detail, try copying the information you find relevant to your research topic in a separate word processing document. Copying and pasting from PDF to Word can be a pain because PDFs are image files not documents. To make that easier, use the HTML version of the article, convert the PDF to Word in Adobe Acrobat or another PDF reader, or use “paste special” command to paste the content into Word without formatting. If it’s an old PDF, you may have to simply type out the information you need. It can be a messy job, but having all of your facts in one place is very helpful for drafting your literature review. Of course, you will not be using other authors’ words in your own literature review, but this is a good way to start compiling your notes.
You should copy and paste any fact or argument you consider important. Some good examples include definitions of concepts, statistics about the size of the social problem, and empirical evidence about the key variables in the research question, among countless others. It’s a good idea to consult with your professor and the syllabus for the course about what they are looking for when they read your literature review. Facts for your literature review are principally found in the introduction, results, and discussion section of an empirical article or at any point in a non-empirical article. Copy and paste into your notes anything you may want to use in your literature review.
Importantly, you must make sure you note the original source of that information. Nothing is worse than searching your articles for hours only to realize you forgot to note where your facts came from. If you found a statistic that the author used in the introduction, it almost certainly came from another source that the author cited in a footnote or internal citation. You will want to check the original source to make sure the author represented the information correctly. Moreover, you may want to read the original study to learn more about your topic and discover other sources relevant to your inquiry.
Assuming you have pulled all of the facts out of multiple articles, it’s time to start thinking about how these pieces of information relate to each other. Start grouping each fact into categories and subcategories as shown in Figure 3.3. For example, a statistic stating that homeless single adults are more likely to be male may fit into a category of gender and homelessness. For each topic or subtopic you identified during your critical analysis of each paper, determine what those papers have in common. Likewise, determine which ones in the group differ. If there are contradictory findings, you may be able to identify methodological or theoretical differences that could account for the contradiction. For example, one study may sample only high-income earners or those in a rural area. Determine what general conclusions you can report about the topic or subtopic, based on all of the information you’ve found.
Create a separate document containing a topical outline that combines your facts from each source and organizes them by topic or category. As you include more facts and more sources into your topical outline, you will begin to see how each fact fits into a category and how categories are related to each other. Your category names may change over time, as may their definitions. This is a natural reflection of the learning you are doing.
A complete topical outline is a long list of facts, arranged by category about your topic. As you step back from the outline, you should understand the topic areas where you have enough information to make strong conclusions about what the literature says. You should also assess in what areas you need to do more research before you can write a robust literature review. The topical outline should serve as a transitional document between the notes you write on each source and the literature review you submit to your professor. It is important to note that they contain plagiarized information that is copied and pasted directly from the primary sources. That’s okay because these are just notes and are not meant to be turned in as your own ideas. For your final literature review, you must paraphrase these sources to avoid plagiarism. More importantly, you should keep your voice and ideas front-and-center in what you write as this is your analysis of the literature. Make strong claims and support them thoroughly using facts you found in the literature. We will pick up the task of writing your literature review in section 3.3.
Additional resources for synthesizing literature
There are many ways to approach synthesizing literature. We’ve reviewed two examples here: summary tables and topical outlines. Other examples you may encounter include annotated bibliographies and synthesis matrices. As you are learning research, find a method that works for you. Reviewing the literature is a core component of evidence-based practice in social work at any level. See the resources below if you need some additional help:
Literature Reviews: Using a Matrix to Organize Research / Saint Mary’s University of Minnesota
Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources / Indiana University
Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix / Florida International University
Sample Literature Reviews Grid / Complied by Lindsay Roberts
Killam, Laura (2013) . Literature review preparation: Creating a summary table . Includes transcript.
Key Takeaways
- It is necessary to take notes on research articles as you read. Try to develop a system that works for you to keep your notes organized, such as a summary table.
- Summary tables and topical outlines help researchers synthesize sources for the purpose of writing a literature review.
Image attributions
Pieces of the puzzle by congerdesign cc-0, adult diary by pexels cc-0.
- Figure 3.2 copied from Frederiksen, L. & Phelps, S. F. (2018). Literature reviews for education and nursing graduate students. Shared under a CC-BY 4.0 license. ↵
- This table was adapted from the work of Amanda Parsons ↵
Guidebook for Social Work Literature Reviews and Research Questions Copyright © 2020 by Rebecca Mauldin and Matthew DeCarlo is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Chapter 5: Writing a Summary and Synthesizing
5.5 Synthesis and Literature Reviews
Literature reviews : synthesis and research.
Why do we seek to understand the ways that authors or sources “converse” with one another? So that we can synthesize various perspectives on a topic to more deeply understand it.
In academic writing, this understanding of the “conversation” may become the content of an explanatory synthesis paper – a paper in which you, the writer, point out various various themes or key points from a conversation on a particular topic. Notice that the example of synthesis in “What Synthesis Is” acknowledges that guns and gun control inspire passionate responses in Americans, that more than one kind of weapon is involved in gun violence, that guns in America are both legally and illegally owned, and that there are many constituencies whose experience with guns needs to considered if sound gun-control policy is to be achieved. The writer of this synthesis isn’t “pretending” to be objective (“Although gun violence is a problem in American today, people who want to increase gun control clearly don’t understand the Second Amendment”); nor is the writer arguing a point or attempting to persuade the audience to accept one perspective. The writer is making a claim about gun control that demonstrates his or her deepest understanding of the issue.
Another assignment that you may complete that also applies your synthesis skills is a l iterature review . Literature reviews are often found in the beginning of scholarly journal articles to contextualize the author’s own research. Sometimes, literature reviews are done for their own sake; some scholarly articles are just Literature reviews.
Literature reviews (sometimes shortened to “lit reviews”) synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic. The literature review provides context for the author’s own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author’s research grows. Context = credibility in academic writing. When writers are able to produce a literature review, they demonstrate the breadth of their knowledge about how others have already studied and discussed their topic.
- Literature reviews are most often arranged by topic or theme , much like a traditional explanatory synthesis paper.
- If one is looking at a topic that has a long history of research and scholarship, one may conduct a chronological literature review, one that looks at how the research topic has been studied and discussed in various time periods (i.e., what was published ten years ago, five years ago, and within the last year, for example).
- Finally, in some instances, one might seek to craft a literature review that is organized by discipline or field. This type of literature review could offer information about how different academic fields have examined a particular topic (i.e., what is the current research being done by biologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by psychologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by [ insert academic discipline] on this topic?).
A Literature Review offers only a report on what others have already written about. The Literature Review does not reflect the author’s own argument or contributions to the field of research. Instead, it indicates that the author has read others’ important contributions and understands what has come before him or her. Sometimes, literature reviews are stand alone assignments or publications. Sometimes, they fit into a larger essay or article (especially in many of the scholarly articles that you will read throughout college. For more information on how literature reviews are a part of scholarly articles, see chapter 10.5 )
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.
Should I do a synthesis (i.e. literature review)?
- Questions & Quandaries
- Published: 18 April 2024
Cite this article
- H. Carrie Chen 1 ,
- Ayelet Kuper 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Jennifer Cleland 5 &
- Patricia O’Sullivan 6
This column is intended to address the kinds of knotty problems and dilemmas with which many scholars grapple in studying health professions education. In this article, the authors address the question of whether one should conduct a literature review or knowledge synthesis, considering the why, when, and how, as well as its potential pitfalls. The goal is to guide supervisors and students who are considering whether to embark on a literature review in education research.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Two junior colleagues come to you to ask your advice about carrying out a literature review on a particular topic. “Should they?” immediately pops into your mind, followed closely by, if yes, then what kind of literature review is appropriate? Our experience is that colleagues often come to suggest a literature review to “kick start” their research (in fact, some academic programs require them as part of degree requirements), without a full understanding of the work involved, the different types of literature review, and what type of literature review might be most suitable for their research question. In this Questions and Quandaries, we address the question of literature reviews in education research, considering the why, when, and how, as well as potential pitfalls.
First, what is meant by literature review? The term literature review has been used to refer to both a review of the literature and a knowledge synthesis (Maggio et al., 2018 ; Siddaway et al., 2019 ). For our purposes, we employ the term as commonly used to refer to a knowledge synthesis , which is a formal comprehensive review of the existing body of literature on a topic. It is a research approach that critically integrates and synthesizes available evidence from multiple studies to provide insight and allow the drawing of conclusions. It is an example of Boyer’s scholarship of integration (Boyer, 1990 ). In contrast, a review of the literature is a relatively casual and expedient method for attaining a general overview of the state of knowledge on a given topic to make the argument that a new study is needed. In this interpretation, a literature review serves as a key starting point for anyone conducting research by identifying gaps in the literature, informing the study question, and situating one’s study in the field.
Whether a formal knowledge synthesis should be done depends on if a review is needed and what the rationale is for the review. The first question to consider is whether a literature review already exists. If no, is there enough literature published on the topic to warrant a review? If yes, does the previous review need updating? How long has it been since the last review and has the literature expanded so much or are there important new studies that need integrating to justify an updated review? Or were there flaws in the previous review that one intends to address with a new review? Or does one intend to address a different question than the focus of the previous review?
If the knowledge synthesis is to be done, it should be driven by a research question. What is the research question? Can it be answered by a review? What is the purpose of the synthesis? There are two main purposes for knowledge synthesis– knowledge support and decision support. Knowledge support summarizes the evidence while decision support takes additional analytical steps to allow for decision-making in particular contexts (Mays et al., 2005 ).
If the purpose is to provide knowledge support, then the question is how or what will the knowledge synthesis add to the literature? Will it establish the state of knowledge in an area, identify gaps in the literature/knowledge base, and/or map opportunities for future research? Cornett et al., performed a scoping review of the literature on professional identity, focusing on how professional identity is described, why the studies where done, and what constructs of identity were used. Their findings advanced understanding of the state of knowledge by indicating that professional identity studies were driven primarily by the desire to examine the impact of political, social and healthcare reforms and advances, and that the various constructs of professional identity across the literature could be categorized into five themes (Cornett et al., 2023 ).
If, on the other hand, the purpose of the knowledge synthesis is to provide decision support, for whom will the synthesis be relevant and how will it improve practice? Will the synthesis result in tools such as guidelines or recommendations for practitioners and policymakers? An example of a knowledge synthesis for decision support is a systematic review conducted by Spencer and colleagues to examine the validity evidence for use of the Ottawa Surgical Competency Operating Room Evaluation (OSCORE) assessment tool. The authors summarized their findings with recommendations for educational practice– namely supporting the use of the OSCORE for in-the-moment entrustment decisions by frontline supervisors in surgical fields but cautioning about the limited evidence for support of its use in summative promotions decisions or non-surgical contexts (Spencer et al., 2022 ).
If a knowledge synthesis is indeed appropriate, its methodology should be informed by its research question and purpose. We do not have the space to discuss the various types of knowledge synthesis except to say that several types have been described in the literature. The five most common types in health professions education are narrative reviews, systematic reviews, umbrella reviews (meta-syntheses), scoping reviews, and realist reviews (Maggio et al., 2018 ). These represent different epistemologies, serve different review purposes, use different methods, and result in different review outcomes (Gordon, 2016 ).
Each type of review lends itself best to answering a certain type of research question. For instance, narrative reviews generally describe what is known about a topic without necessarily answering a specific empirical question (Maggio et al., 2018 ). A recent example of a narrative review focused on schoolwide wellbeing programs, describing what is known about the key characteristics and mediating factors that influence student support and identifying critical tensions around confidentiality that could make or break programs (Tan et al., 2023 ). Umbrella reviews, on the other hand, synthesize evidence from multiple reviews or meta-analyses and can illuminate agreement, inconsistencies, or evolution of evidence on a topic. For example, an umbrella review on problem-based learning highlighted the shift in research focus over time from does it work, to how does it work, to how does it work in different contexts, and pointed to directions for new research (Hung et al., 2019 ).
Practical questions for those considering a literature review include whether one has the time required and an appropriate team to conduct a high-quality knowledge synthesis. Regardless of the type of knowledge synthesis and use of quantitative or qualitative methods, all require rigorous and clear methods that allow for reproducibility. This can take time, up to 12–18 months. A high-quality knowledge synthesis also requires a team whose members have expertise not only in the content matter, but also in knowledge synthesis methodology and in literature searches (i.e. a librarian). A team with multiple reviewers with a variety of perspectives can also help manage the volume of large reviews, minimize potential biases, and strengthen the critical analysis.
Finally, a pitfall one should be careful to avoid is merely summarizing everything in the literature without critical evaluation and integration of the information. A knowledge synthesis that merely bean counts or presents a collection of unconnected information that has not been reflected upon or critically analyzed does not truly advance knowledge or decision-making. Rather, it leads us back to our original question of whether it should have been done in the first place.
Boyer, E. L. (1990). Scholarship reconsidered: Priorities of the professoriate (pp. 18–21). Princeton University Press.
Cornett, M., Palermo, C., & Ash, S. (2023). Professional identity research in the health professions—a scoping review. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 28 (2), 589–642.
Article Google Scholar
Gordon, M. (2016). Are we talking the same paradigm? Considering methodological choices in health education systematic review. Medical Teacher , 38 (7), 746–750.
Hung, W., Dolmans, D. H. J. M., & van Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2019). A review to identify key perspectives in PBL meta-analyses and reviews: Trends, gaps and future research directions. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 24 , 943–957.
Maggio, L. A., Thomas, A., & Durning, S. J. (2018). Knowledge synthesis. In T. Swanwick, K. Forrest, & B. C. O’Brien (Eds.), Understanding Medical Education: Evidence, theory, and practice (pp. 457–469). Wiley.
Mays, N., Pope, C., & Popay, J. (2005). Systematically reviewing qualitative and quantitative evidence to inform management and policy-making in the health field. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy , 10 (1_suppl), 6–20.
Siddaway, A. P., Wood, A. M., & Hedges, L. V. (2019). How to do a systematic review: A best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annual Review of Psychology , 70 , 747–770.
Spencer, M., Sherbino, J., & Hatala, R. (2022). Examining the validity argument for the Ottawa Surgical Competency operating room evaluation (OSCORE): A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Advances in Health Sciences Education , 27 , 659–689.
Tan, E., Frambach, J., Driessen, E., & Cleland, J. (2023). Opening the black box of school-wide student wellbeing programmes: A critical narrative review informed by activity theory. Advances in Health Sciences Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-023-10261-8 . Epub ahead of print 02 July 2023.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Georgetown University School of Medicine, Washington, DC, USA
H. Carrie Chen
Wilson Centre for Research in Education, University Health Network, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Ayelet Kuper
Division of General Internal Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, Canada
Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Jennifer Cleland
University of California San Francisco School of Medicine, San Francisco, CA, USA
Patricia O’Sullivan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to H. Carrie Chen .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Chen, H.C., Kuper, A., Cleland, J. et al. Should I do a synthesis (i.e. literature review)?. Adv in Health Sci Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-024-10335-1
Download citation
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-024-10335-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this post, we'll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples. This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp. In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step.
Example of synthesizing sources. Let's take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it. Example: Poor synthesis. Lenneberg (1967) theorized that language acquisition could occur only within a critical period of development between infancy and puberty.
The Four Examples of Student Writing come from a synthesis exercise created by Candice Benjes-Small. Thanks also to Colleen Warwick for some of the original materials for this page that were adapted by J. Cleavenger 9/2011. Thanks also to Kristin Buxton and Annie Zeidman-Karpinski for introducing them to UO Libraries.
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
Structuring your synthesis essay by topic works best for more complicated ideas with different aspects that should be explored individually. Example outline: I. Introduction A. Thesis statement. II. Topic 1 A. Source A discussing Topic 1 1. A point or piece of evidence/data from Source A about Topic 1 2.
Four Examples of Student Writing. In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image. Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
Global synthesis occurs at the paper (or, sometimes, section) level when writers connect ideas across paragraphs or sections to create a new narrative whole. A literature review, which can either stand alone or be a section/chapter within a capstone, is a common example of a place where global synthesis is necessary. However, in almost all ...
How to synthesize. In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic. Synthesis.
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation. With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source (s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question. Analysis tips
When asked to synthesize sources and research, many writers start to summarize individual sources. However, this is not the same as synthesis. In a summary, you share the key points from an individual source and then move on and summarize another source. In synthesis, you need to combine the information from those multiple sources and add your ...
Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions. In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the ...
A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question. Figure 7.1. Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the ...
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic and argument to create a whole view ...
One way that seems particularly helpful in organizing literature reviews is the synthesis matrix. The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record ...
A common type of synthesis in academic writing, for example, is a literature review in which the researcher-writer collects, compares, and shows connections or differences among different scholarly sources as well as gaps in the research. With academic writing foremost in mind, Lumen Learning defines synthesis as "analysis across sources ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
As seen in Chap. 3, a common step in Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is the Literature Synthesis (Lau et al. 1997).It combines the effects of multiple primary studies to provide new knowledge on a subject, which is not possible to obtain by evaluating the studies independently (Morandi and Camargo 2015).In other words, the Synthesis is not a simple summary of results, on the opposite, it ...
Literature reviews (sometimes shortened to "lit reviews") synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic. The literature review provides context for the author's own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author's research ...
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
The first example is an early draft of the literature review. The second example is a revised version. Notice how the student's revision makes better use of synthesis at both the paragraph and sentence level. The revised example is also more accurate in its portrayal of the literature. Unrevised Paragraph: Much of the literature agrees that ...
Get multiple synthesis essay examples covering a range of topics. Learn how to craft an introduction, thesis, outlines, or write your entire synthesis essay. ... Essay writing is a craft many students have yet to master. Doing great research and having the right tools in place, such as synthesis essay examples and outlines, can make your ...
The term literature review has been used to refer to both a review of the literature and a knowledge synthesis (Maggio et al., 2018; Siddaway et al., 2019 ). For our purposes, we employ the term as commonly used to refer to a knowledge synthesis, which is a formal comprehensive review of the existing body of literature on a topic.
Evidence on global development programs often remains fragmented by thematic areas of study or regions and populations. Evidence gap maps (EGMs) are the tools that visually highlight where evidence concentrations and gaps exist in a sector or topic area and, in doing so, consolidate knowledge of these programs to inform future investments in research and programming.In the field of health ...