Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!

Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How long does it take to write a dissertation, published by steve tippins on july 11, 2019 july 11, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:00 am
How long does it take to write a dissertation? The most accurate (and least helpful) answer is, it depends. Since that’s probably not the answer you’re looking for, I’ll use the rest of the article to address the realities of how long it takes to write a dissertation.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation?
Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months. These are average numbers based upon the scores of doctoral students that I have worked with over the years, and they generally hold true.
I have seen people take less time and more time, but I believe that with concerted effort, the 13-20 month timeframe is reasonable.
“Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months.”
University Requirements
Once you hit the dissertation stage, some schools require a minimum number of hours in the dissertation area before you can graduate. Many schools require the equivalent of one year of dissertation credits to graduate.
So, even if you can finish your dissertation in three months, you will still have to pay for nine more months of dissertation credits before you can graduate. However, unless research and writing is your superpower, I wouldn’t worry about having to pay extra tuition.
But this requirement does offer some insight into how long it takes to write a dissertation. Based on this requirement, it’s reasonable to expect that writing your dissertation will take a year of more. This is consistent with my experience.

However, this timeframe is based on several assumptions. First, I am assuming that you are continually working towards finishing your dissertation. This means that no family emergencies, funding conundrums, or work issues get in the way of completing. Second, there are no major changes in your dissertation committee. Third, you will have access to the data that you need.
Assuming these assumptions hold true, this article should give you a general idea of how long it might take to write your dissertation.
How Long Does it Take to Write A Dissertation? Stage-By-Stage
Let’s break down each stage of the dissertation writing process and how long it takes.
Prospectus
This is the hardest one to judge, as this is where you lay the groundwork for the rest of your dissertation and get buy-in from committee members. Normally this takes from 3-6 months. Not all of this is writing time, though–much of it is spent refining your topic and your approach.
Why does this stage take so long? For many people, starting to express themselves using an academic voice can take time. This can hold up the review process as your committee members ask for writing-related revisions before they even get to evaluating the content. Don’t worry, once you learn the academic language things will start to flow more easily.
One common mistake students make is lack of specificity, both in their writing in general and in their topic focus.
Proposal (Chapters 1-3)

Chapter 1 is often an expansion of your Prospectus. However, you’ll be expected to develop your ideas more and have even more specificity on things like your research question and methodology, so don’t underestimate how long this chapter will take.
Chapter 2 can take some time as you will be digging deep into the literature but I think this can be done in 3-4 months. One caution, some people, and committees, like to start with Chapter 2 so that you are immersed in the literature before completing Chapters 1 and 3. Regardless of where you start, 3-4 months is a good estimate.
Chapter 3 requires an in-depth explanation of your methodology. I suggest working closely with your Chair on this one to avoid multiple submissions and revisions. Get clear on your methodology and make sure you and your chair are on the same page before you write, and continue to check in with your chair, if possible, throughout the process.
IRB Approval
While this step can be full of details and require several iterations it seems that allowing 2 months is sufficient. Most schools have an IRB form that must be submitted. To save time you can usually start filling out the form while your committee is reviewing your Proposal.
Collecting Data
This step varies a great deal. If you are using readily available secondary data this can take a week but if you are interviewing hard to get individuals or have trouble finding a sufficient number of people for your sample this can take 4 months or more. I think 1-4 months should be appropriate
Chapters 4 and 5
These two chapters are the easiest to write as in Chapter 4 you are reporting your results and in Chapter 5 you explain what the results mean. I believe that these two chapters can be written in 2 months.

Defense and Completion
You will need to defend your dissertation and then go through all of the university requirements to finalize the completion of your dissertation. I would allow 2 months for this process.
Variables That Affect How Long It Takes to Write A Dissertation
When students say something like, “I’m going to finish my dissertation in three months,” they likely aren’t considering all of the variables besides the actual writing. Even if you’re a fast writer, you’ll have to wait on your committee’s comments,
Timing Issues
Many schools have response times for committee members. This is important when looking at how long it takes to finish a dissertation. For example, it you have two committee members and they each get up to 2 weeks for a review, it can take up to a month to get a document reviewed, each time you submit. So, plan for these periods of time when thinking about how long that it will take you.
Addressing Comments
How long it takes to write your dissertation also depends on your ability to address your committee’s comments thoroughly. It’s not uncommon for a committee member to send a draft back several times, even if their comments were addressed adequately, because they notice new issues each time they read it. Save yourself considerable time by making sure you address their comments fully, thus avoiding unnecessary time waiting to hear the same feedback.

This is the biggest variable in the dissertation model. How dedicated are you to the process? How much actual time do you have? How many outside interests/requirements do you have? Are you easily distracted? How clean does your workspace need to be? (This may seem like a strange thing to discuss, but many people need to work in a clean space and can get very interested in cleaning if they have to write). Are you in a full-time program or in a part time program? Are you holding down a job? Do you have children?
All of these things will affect how much time you have to put into writing–or rather, how disciplined you need to be about making time to write.
One of the things that can influence how long it takes to write your dissertation is your committee. Choose your committee wisely. If you work under the assumption that the only good dissertation is a done dissertation, then you want a committee that will be helpful and not trying to prove themselves on your back. When you find a Chair that you can work with ask her/him which of their colleagues they work well with (it’s also worth finding out who they don’t work well with).
Find out how they like to receive material to review. Some members like to see pieces of chapters and some like to see completed documents. Once you know their preferences, you can efficiently submit what they want when they want it.
How Long Does it Take to Write a Dissertation? Summary
Barring unforeseen events, the normal time range for finishing a dissertation seems to be 13-19 months, which can be rounded to one to one and a half years. If you are proactive and efficient, you can usually be at the shorter end of the time range.

That means using downtime to do things like changing the tense of your approved Proposal from future tense to past tense and completing things like you Abstract and Acknowledgement sections before final approval.
I hope that you can be efficient in this process and finish as quickly as possible. Remember, “the only good dissertation is a done dissertation.”
On that note, I offer coaching services to help students through the dissertation writing process, as well as editing services for those who need help with their writing.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Thesis and Dissertation: Getting Started

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The resources in this section are designed to provide guidance for the first steps of the thesis or dissertation writing process. They offer tools to support the planning and managing of your project, including writing out your weekly schedule, outlining your goals, and organzing the various working elements of your project.
Weekly Goals Sheet (a.k.a. Life Map) [Word Doc]
This editable handout provides a place for you to fill in available time blocks on a weekly chart that will help you visualize the amount of time you have available to write. By using this chart, you will be able to work your writing goals into your schedule and put these goals into perspective with your day-to-day plans and responsibilities each week. This handout also contains a formula to help you determine the minimum number of pages you would need to write per day in order to complete your writing on time.
Setting a Production Schedule (Word Doc)
This editable handout can help you make sense of the various steps involved in the production of your thesis or dissertation and determine how long each step might take. A large part of this process involves (1) seeking out the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding specific document formatting requirements, (2) understanding research protocol limitations, (3) making note of deadlines, and (4) understanding your personal writing habits.
Creating a Roadmap (PDF)
Part of organizing your writing involves having a clear sense of how the different working parts relate to one another. Creating a roadmap for your dissertation early on can help you determine what the final document will include and how all the pieces are connected. This resource offers guidance on several approaches to creating a roadmap, including creating lists, maps, nut-shells, visuals, and different methods for outlining. It is important to remember that you can create more than one roadmap (or more than one type of roadmap) depending on how the different approaches discussed here meet your needs.
How Long Does it Take to Write a Dissertation? [2024 Guide]
Reading through the requirements for a PhD program may prompt you to ask, “How long does it take to write a dissertation?”

You probably already know that this is a major project, but you may be curious about how much of your life you’ll need to commit to the process.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Dissertation writing can vary significantly from one student to the next. Even still, learning more about dissertations can help you have a better idea of what you can expect in terms of time commitment and workload.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation?

Before you sit down to write your PhD dissertation, it makes sense to figure out approximately how long the process is going to take you. That way, you can approach this project with reasonable expectations in mind.
Having an idea of the common timeframe for dissertations may also encourage you to set realistic goals. Many students write their dissertations within 1 to 2 years. In other words, once you reach All But Dissertation (ABD) status, you might be less than 2 years away from completing your PhD program.
You might be anxious to type your dissertation in less than 12 months so that you can move on with your life. While that’s understandable, you may be putting undue pressure on yourself. In fact, your school may require you to spend at least a year on your dissertation.
It’s also possible that you expect to need more than 2 years. As long as you keep moving, that’s okay. Just remember to check your university’s rules. Some schools set a time limit on doctoral enrollment.
No matter how long the process takes, you’ll go through multiple steps as you work toward your goal:
- Selecting a topic
- Reviewing relevant literature
- Developing a research project
- Conducting research and analyzing the data you gather
- Outlining your paper
- Writing the first draft
- Editing and producing a final draft
You may begin some of these steps, such as deciding on your topic, during the coursework portion of your program. Eventually, though, you’ll move into ABD status, and it will be time to focus solely on the dissertation.
Some students lose motivation at that point. If life is too busy, your wallet feels too strained, or you don’t have a good support system, you may feel like throwing in the towel. It can be especially tempting to quit if the project simply feels too overwhelming. To try and avoid these obstacles to finishing your PhD, it can help to make a plan for writing your dissertation.
You can break the project down into steps, carve out writing time, set attainable goals, and move progressively closer to a final product of which you’ll be proud.
Tips for Dissertation Writing

The answer to “How long does a dissertation take?” depends in large part on your process. Putting the following tips into practice may help you finish more quickly:
- Understand the assignment . Reading other people’s dissertations can help you get a feel for what you’ll be doing yourself.
- Dive in early . The sooner you start working on this project, the sooner you’ll be able to finish.
- Craft an outline . Organizing your thoughts into a workable dissertation structure can make all the difference.
- Schedule daily sessions . It’s strategic to make sure you write a bit each day. Some people recommend 2 hours of daily writing, but that’s not the best fit for everyone. Figure out how much time you can commit, and pencil it into your calendar.
- Stretch your legs . Even during a marathon writing session, it helps to give yourself breaks. You might take a quick walk or do some stretches.
- Get excited about your goals . It’s beneficial to break your process down into milestones and celebrate each time you achieve one.
Finally, it helps to surround yourself with a great support team—such as family, friends, and your faculty advisor—to whom you can turn when times feel tough.
How Long Is a Dissertation?

Each student’s dissertation is a slightly different length. Typically, though, most dissertations are between 100 and 300 pages long. It’s common for them to include about 80,000 words. Some are closer to 100,000 words.
Your school may set guidelines for the length of your paper. The requirements may even vary from one department to the next. For example, dissertations in the natural or physical sciences are often under 100 pages. Dissertations in fields like theology and history commonly contain several hundred pages.
The content will be broken into various chapters, such as the introduction, the methodology, and the results.
What’s the Difference Between a Doctoral Dissertation vs. Thesis?
The words “thesis” and “dissertation” are often used in similar contexts. You can think about which one you’ll be writing during your doctoral studies.
While a dissertation is the standard final project for a PhD, theses are more common at the master’s degree level. In addition, some programs don’t require a dissertation, like several online doctoral programs in education without dissertation , but require a capstone.
Writing a Dissertation

Whether you are just beginning the PhD journey or have reached ABD status , there’s a dissertation in your future.
Yes, writing a dissertation is a task that is going to take a significant amount of time and effort. But now that you have a better idea of what to expect, you are one step closer to your goal. You can make a plan, block out time, and get your dissertation written.
Remember to surround yourself with support and ask for help as needed. Cheer yourself on throughout the process, and celebrate each milestone. It may take a few years, but you can accomplish this goal!


Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
How Long Does It Take to Write an Education Dissertation? Guide to Sharing Research Findings

Writing a dissertation is the culmination of a doctoral education program . It is an exacting task, calling for dedication and perseverance, especially when you experience time constraints due to work or family obligations. Gaining a clear understanding of how long it takes to write an education dissertation and carefully planning your dissertation process—from carving out time in your busy daily schedule to setting achievement milestones to keep a steady pace—are crucial steps to earning a doctoral degree.
It takes longer than a year for most PhD students to complete a first draft of a dissertation. Students typically spend one to two years conducting research and reviewing literature while they complete doctoral courses before tackling a dissertation draft. The writing process typically takes a year or two beyond that. It can take five or more years for PhD students who get stuck in research phases, experience writer’s block, or have a high level of distractions or time constraints. The average time for students to complete all requirements for a doctorate in the US is nearly six years, according to U.S. News & World Report .
The Education Dissertation Timeline
About how long will the dissertation process take? Many factors can influence the dissertation timeline length, such as:
- Job status : Doctoral students working in full- or part-time positions will need to be diligent about dedicating time to their dissertation work.
- Academic support : PhD students with strong support from faculty members, mentors, and peers are likely to find greater success in keeping the dissertation process on track.
- Topic selection : An initial dissertation topic’s success can keep a timeline on track. When doctoral students change a dissertation’s focus midstream, it typically adds extra research time.
- Time management : Writing a dissertation takes careful planning and scheduling. When students stick to their schedules and work efficiently, they’re more likely to complete their dissertations sooner.
The Dissertation Process
Before doctoral students can submit a dissertation proposal, they must complete all of their doctorate-level coursework and pass their comprehensive exams. This designates them as doctoral candidates. However, just because a student hasn’t achieved candidate status does not mean they can’t or shouldn’t start the dissertation process. On the contrary, students are expected to identify their dissertation topic and start preparing for the proposal while they are engaged in graduate coursework.
Many of the classes offered in a Doctorate of Education (EdD) program will help students explore potential topics and research techniques. For example, American University’s online EdD program includes three weekend residency sessions during which students connect with faculty and participate in workshops to help them develop their dissertations. The program also includes two course sessions on applied research methods to familiarize students with qualitative and quantitative research methods.
The dissertation process includes the following steps:
1. Draft and Defend a Proposal
The dissertation proposal may include the first few chapters of the dissertation. Students must be prepared to defend the proposal to the dissertation committee, which will evaluate the topic itself and approve, deny, or request revisions to the proposal. Many education dissertation topics relate to leadership strategies, literacy, or future learning trends.
2. Conduct Research
This stage can include conducting surveys and interviews on the chosen education topic. Students look for evidence to support their hypotheses, take notes, and conduct interviews along the way.
3. Conduct Literature Review
Students need to gather a broad range of articles and books that are pertinent to their dissertation topic. Resources cited in the dissertation are included in a bibliography.
4. Create an Outline
Structuring research and data in an outline helps students stay focused and organized during the dissertation writing stages.
5. Write the Dissertation
The elements of a dissertation paper can include abstract, introduction, background, hypothesis, literature review, methodology, conclusion, and bibliography sections. Universities often provide templates and style guides to help students format their dissertations correctly.
Tips for Writing a Dissertation
Your dissertation strategy should take into account your unique strengths and weaknesses. If you know that you are most productive in the morning, for instance, schedule your research and writing time for early in the day. To successfully navigate the dissertation process, you should:
Get familiar with the dissertation process before you begin writing. Look at dissertation samples and guideline documents to get a firm grasp on formatting and style. Keep yourself on track by setting milestone deadlines.
Write Often
Don’t put off the writing process. It’s easy to find excuses not to write, such as having a busy schedule or feeling that your argument isn’t fully formed. But sitting down to write every day, for at least two hours (with at least one break), can help you find your voice and establish your structure through experimentation.
Don’t Get Discouraged
Writing a dissertation can be a trial-and-error process. You will have to be self-reliant in many of the independent learning stages, including finding quality research sources and conducting your own studies. Don’t give in to self-doubt when you hit a roadblock and remember not to sacrifice your health and well-being by overstressing about your progress.
Find a Good Mentor
Students should feel comfortable checking in with a supervisor or committee member when they need support, advice, or encouragement. Making sure that you have an engaged and enthusiastic mentor can make a big difference in the dissertation process. Some mentors encourage regular meetings to keep in touch. Connecting with a group of peers who are also drafting dissertations can give you feedback as well. In addition, university libraries often support dissertation work through research and writing labs.
Sharing Your Research Findings
Once you’ve determined how long it will take you to write your education dissertation, consider how actively you’ll pursue publication. Students often want to share their work with a greater audience so that others can benefit from their insights.
Typically, a university will require students to publish their dissertation in an electronic database. For instance, American University requires students to submit dissertations to the ProQuest Dissertations and Theses (PQDT) database and the American University Digital Research Archive (AUDRA).
Publication is also a plus on any academic CV. Some students reformat their dissertation into an article (or articles) for submission to a professional journal, or even as a book for publication. Others present their findings at educational conferences. Regardless of the arena, sharing a dissertation with a wider audience is a rewarding capstone achievement.
Advance Your Career as an Education Leader
Individuals who are passionate about improving the education system through cutting-edge learning strategies should consider pursuing an advanced degree program. American University’s School of Education online provides a number of high-quality degree programs, including a Doctorate of Education (EdD) in Education Policy and Leadership . The university’s EdD program provides a flexible, part-time learning environment that helps education professionals gain the skills to effect positive change across all school levels and community settings.
What’s the Difference Between Educational Equity and Equality?
The Role of Educational Leadership in Forming a School and Community Partnership
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Requirements, Career Outlook, and Salary
American University, Submitting Your Thesis and Dissertation Files Electronically
Inside Higher Ed, “Give It a Rest”
Inside Higher Ed, “How to Draft a Dissertation in a Year”
Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education , “Preparing for Dissertation Writing: Doctoral Education Students’ Perceptions”
U.S. News & World Report , “How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?”
Request Information

- How Long Is a PhD Thesis?
- Doing a PhD
It’s no secret that one of the most challenging aspects of a PhD degree is the volume of work that goes into writing your thesis . So this raises the question, exactly how long is a thesis?
Unfortunately, there’s no one size fits all answer to this question. However, from the analysis of over 100 PhD theses, the average thesis length is between 80,000 and 100,000 words. A further analysis of 1000 PhD thesis shows the average number of pages to be 204 . In reality, the actual word count for each PhD thesis will depend on the specific subject and the university it is being hosted by. This is because universities set their own word length requirements, with most found to be opting for around 100,000.
To find out more about how these word limits differ between universities, how the average word count from STEM thesis differ from non-STEM thesis and a more detailed breakdown from the analysis of over 1000 PhDs, carry on reading the below.
Word Count Differences Between Universities
For any PhD student writing a thesis, they will find that their document will be subject to a word limit set by their university. In nearly all cases, the limit only concerns the maximum number of words and doesn’t place any restrictions on the minimum word limit. The reason for this is that the student will be expected to write their thesis with the aim of clearly explaining their research, and so it is up to the student to determine what he deems appropriate.
Saying this, it is well accepted amongst PhD students and supervisors that the absence of a lower limit doesn’t suggest that a thesis can be ‘light’. Your thesis will focus on several years worth of original research and explore new ideas, theories or concepts. Besides this, your thesis will need to cover a wide range of topics such as your literature review, research methodology, results and conclusion. Therefore, your examiners will expect the length of your thesis to be proportional to convey all this information to a sufficient level.
Selecting a handful of universities at random, they state the following thesis word limits on their website:
- University of Edinburgh: 100,000
- University of Exeter: 100,000
- University of Leister: 80,000
- University of Bath: 80,000
- University of Warwick: 70,000
The above universities set upper word limits that apply across the board, however, some universities, such as the University of Birmingham and the University of Sheffield, set different word limits for different departments. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts these limits:
- Arts & Humanities: 75,000
- Medicine, Dentistry & Health: 75,000
- Science: 80,000
- Social Sciences: 75,000-100,000
Although there’s a range of limit, it’s safe to say that the majority fall within the 80,000 to 100,000 bracket.

Word Count Based on Data from past Theses
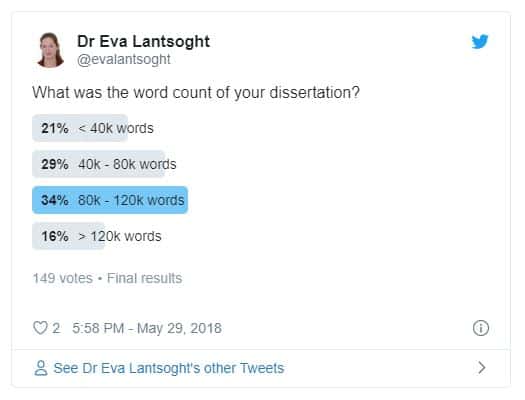
A poll of 149 postdocs.
In mid-2019, Dr Eva Lantsoght, a published author, academic blogger and Structural Engineering Professor, conducted a poll which asked postgraduate doctoral students to share the length of their final thesis. 149 PostDoc students responded to the survey, with the majority reporting a length falling within the ‘80,000 – 120,000 words’ bracket as seen below.
Analysis of 1000 PhD Theses
Over a three-year time period, Dr Ian Brailsford, a then Postgraduate Learning Adviser at the University of Auckland, analysed 1000 doctoral thesis submitted to his university’s library. The PhD theses which formed the basis of his analysis were produced between 2008 to 2017 and showed:
- Average number of pages = 204
- Median number of pages = 198
- Average number of chapters = 7.6
We should note that the above metrics only cover the content falling within the main body of the thesis. This includes the introduction, literature review, methods section, results chapter, discussions and conclusions. All other sections, such as the title page, abstract, table of contents, acknowledgements, bibliography and appendices were omitted from the count.
Although it’s impossible to draw the exact word count from the number of pages alone, by using the universities recommended format of 12pt Times New Roman and 1.5 lines spacing, and assuming 10% of the main body are figures and footnotes, this equates to an average main body of 52,000 words.
STEM vs Non-STEM
As part of Dr Ian Brailsford’s analysis, he also compared the length of STEM doctorate theses to non-STEM theses. He found that STEM theses tended to be shorter. In fact, he found STEM theses to have a medium page length of 159 whilst non-STEM theses had a medium of around 223 pages. This is a 40% increase in average length!
Can You Exceed the Word Count?
Whilst most universities will allow you to go over the word count if you need to, it comes with the caveat that you must have a very strong reason for needing to do so. Besides this, your supervisor will also need to support your request. This is to acknowledge that they have reviewed your situation and agree that exceeding the word limit will be absolutely necessary to avoid detriment unnecessary detriment to your work.
This means that whilst it is possible to submit a thesis over 100,000 words or more, it’s unlikely that your research project will need to.
How Does This Compare to a Masters Dissertation?
The average Masters dissertation length is approximately 20,000 words whilst a thesis is 4 to 5 times this length at approximately 80,000 – 100,000.
The key reason for this difference is because of the level of knowledge they convey. A Master’s dissertation focuses on concluding from existing knowledge whilst a PhD thesis focuses on drawing a conclusion from new knowledge. As a result, the thesis is significantly longer as the new knowledge needs to be well documented so it can be verified, disseminated and used to shape future research.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Related Reading
Unfortunately, the completion of your thesis doesn’t mark the end of your degree just yet. Once you submit your thesis, it’s time to start preparing for your viva – the all-to-fun thesis defence interview! To help you prepare for this, we’ve produced a helpful guide which you can read here: The Complete Guide to PhD Vivas.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

- Recommendations
- Notifications
- My Favorites
Favorites, recommendations, and notifications are only available for UCLA Graduate Students at this time.
Access features exclusively for UCLA students and staff.
As a student, you can:
- Add funding awards to your favorites list
- Get notified of upcoming deadlines and events
- Receive personalized recommendations for funding awards
We're Sorry
You've signed in with a UCLA undergraduate student account.
UCLA Graduate Programs

File Your Electronic Thesis or Dissertation (ETD)
Ready to file.
Review the formatting requirements for filing theses and dissertations and University policy regarding graduate thesis and dissertation public dissemination in UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination .
To begin the ETD filing process OR to check the approval status of your ETD:
During the filing process, you may choose your publishing agreement, register your copyright, and order copies of your manuscript.
FILING DEADLINES
See also: Filing Deadlines Chart
Deadline for Registered Students and Students on Filing Fee to Submit their Manuscript via ProQuest & Receive Committee Member Approval
*Complete Degree Requirements includes: completion of the online ETD Filing Application (button above), all committee members have reported approval of your manuscript and the passing of the final oral examination (if applicable) to the Division of Graduate Education; submission of a final PDF via ProQuest including requested changes from the Division of Graduate Education, and receipt of the Division of Graduate Education confirmation email of the formal completion of degree requirements.
See the UCLA term calendar for the degree – award date , which is the final day of the term, also the deadline to submit manuscripts and to complete graduate degree requirements.
Deadlines for previous academic terms are available in the Registrar’s Office online calendar archive .
PREPARING TO FILE YOUR ETD
- Review UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination
- Register and Enroll for the term, or apply for Filing Fee
- Review Graduation Requirements
- Changing your Name on your Thesis or Dissertation
THESIS & DISSERTATION COMMITTEES
- Thesis Committee Regulations
- Minimum Standards for Doctoral Committee Constitution
- Change Committee Members
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
- ETD Workshops & Drop-In Hours
- ETD Workshop Presentation Slides
- Video: Formatting Tutorial
- UCLA Library Scholarly Communication Services (Copyright Assistance)
ETD & FILING FAQS
1. What happens to the thesis or dissertation a graduate student files?
In the past, the physical manuscript was placed on the shelves of the UCLA library where it could be accessed by visitors and through the international interlibrary loan network. Today, digital access to the document is provided through the University of California Digital Library , our institutional repository. Additionally, the abstracts of theses and dissertations worldwide are indexed by ProQuest , SciFinder and other abstracting services. In the past, interested scholars who wanted to obtain copies of theses and dissertations would either write to the author or purchase paper, microfilm or microfiche copies from ProQuest, but now they can purchase electronic copies instead. Technology changes aside, graduate students retain the copyright on your dissertation, and will receive royalties when copies are purchased. See University of California Copyright for more information.
2. Can graduate students file their thesis or dissertation from outside the US?
Yes. Graduate students do not need to be physically present on campus to submit their thesis or dissertations. Graduate students only need access to the internet.
3. Do graduate students have to be registered when they file?
Graduate students must either register and enroll or, if eligible, use the Filing Fee .
4. Can a graduate student file during the Summer?
Yes. In order for a graduate student to file and receive a Summer degree, students must either register and enroll in a minimum of 4 units in a Summer Session or be on Filing Fee status.
5. Can a graduate student still file on paper?
No. Since March 13, 2012, only electronic filing is available for graduate students.
6. How can graduate students order hard copies of my thesis or dissertation?
Graduate students may order hard copies through ProQuest. Copies take about 5 weeks to ship after the manuscript is published by ProQuest. Graduate students can also order copies through the UC Bindery .
7. I’ve included co-authored works in my thesis or dissertation. How do I cite them?
You must include in your Acknowledgments section any material based on co-authored work that is published, in-press, submitted, or in preparation for publication. For each segment of the work that involved co-authors, you must identify (briefly describe) and acknowledge the specific contributions of each co-author. For details, see page 15 of UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination .
8. Will my thesis or dissertation manuscript be sold to third-party retailers?
No. A graduate student’s thesis or dissertation is not shared with Amazon. ProQuest’s reseller program with Amazon has been discontinued, with all existing agreements ending in 2014.
1. What are the filing deadlines for graduate students?
See the Deadlines above. Deadlines of past academic terms are available in the Registrar’s Office online calendar archive .
2. What counts as submitting my thesis or dissertation by the deadline?
All of the following must occur by 5pm PT on the day of official deadline:
- All committee members have approved electronically
- Committee has certified you have passed the final oral exam (if applicable)
- A graduate student has submitted a final PDF via ProQuest
- A graduate student has completed the online Division of Graduate Education process using the link at the top of this page
- If the Division of Graduate Education requests any changes, the graduate student will have submitted the specific changes within the designated time period
3. How will the Division of Graduate Education determine my thesis or dissertation filing date and whether I’ve met the deadline?
The last date that all of the items listed above is complete will be your filing date for your thesis or dissertation. For example, if you submit your final dissertation PDF and complete the online process on May 31, three committee members sign on June 1, and the final committee member signs on June 2, your filing date will be June 2 assuming you have met all other degree requirements.
1. What is a certifying member?
Certifying members are responsible for approving your dissertation. Effective Fall 2016, all doctoral committee members must read, approve, and certify the dissertation. All committee members must enter a decision for the final oral exam, if required.
2. Do my thesis or dissertation committee members need to sign the committee page?
Certifying committee members approve the thesis or dissertation electronically. There is no signature page, but rather a committee page listing your certifying committee members in the manuscript.
3. Can a committee member approve a thesis or dissertation from outside of Los Angeles?
Yes. Professors can approve a thesis or dissertation from anywhere with access to the internet.
4. A graduate student’s UCLA faculty committee member prefers to use a non-UCLA email address. Can an email request be sent to that email address?
No. UCLA faculty will be notified via their official UCLA business email addresses. Graduate students are welcome to send a reminder email to their non-UCLA email address with the link (https://go.grad.ucla.edu) to the approval page.
5. How do committee members who are not from UCLA approve theses or dissertations?
Committee members from outside UCLA will still receive the email notification and go to a similar approval page as UCLA faculty.
6. Can graduate students check the status of when their committee members approve their manuscripts electronically?
Yes, after graduate students complete the online process they can log back into the ETD Filing Application to check the status.
Formatting Guide
1. What special characters can graduate students use in their titles?
Only the ones approved by UCLA. The list can be found on the Formatting and Filing Information page.
FYI: ProQuest will NOT publish any special characters included in your title although the special characters will display when you submit your thesis or dissertation.
2. Does the Division of Graduate Education have a LaTeX template?
No. Please consult with your graduate department or program.
3. Can the Division of Graduate Education check my thesis or dissertation formatting before submitting it to ProQuest ?
The Division of Graduate Education will only check your thesis or dissertation formatting once you have submitted it to ProQuest, or during designated ETD Drop-In Hours.
Release of Manuscript
1. Why will my thesis or dissertation be available for public access after it has been filed by the university?
The UCLA Graduate Thesis and Public Dissemination Policy affirms the university’s commitment to open access of scholarly work.
It is the University of California’s expectation that the research and scholarly work conducted by graduate students that is incorporated into theses and dissertations will be made available to the public. UCLA requires that research and scholarly work conducted by graduate students and incorporated into theses and dissertations be made publicly available through the University of California’s institutional repository, eScholarship .
All theses and dissertations are available as open access via UC eScholarship unless a delayed release is selected.
2. When will I be able to view my thesis or dissertation on ProQuest?
6-8 weeks after you receive final confirmation from the Division of Graduate Education.
3. When will I be able to view my thesis or dissertation on UC eScholarship?
2-3 months after you receive final confirmation from the Division of Graduate Education.
4. What is the UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Submission Agreement?
The UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Submission Agreement allows graduate students to affirm their understanding of the rights and responsibilities associated with the submission of their manuscripts to the campus institutional repository, eScholarship .
All thesis and dissertation filers will complete the institutional repository agreement as part of the submission process via ProQuest.
In the process of filing a thesis or dissertation via ProQuest, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a degree at UCLA, graduate students agree to grant a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free, perpetual license to The Regents of the University of California (University). Graduate students retain copyright.
1. What does it mean for graduate students to register the copyright of their thesis or dissertation?
The copyright of your work is inherent upon creation. Graduate Students do not need to register their copyright to enjoy copyright protection, but registration does provide some benefits. For full detail, read the U.S. Copyright Office circular “ Copyright Basics “. The benefits of registration are outlined on Page 7 of the circular.
2. I found images on the internet that I want to use in my thesis or dissertation. Is this OK?
Graduate Students should assume that anything produced by someone other than themselves is protected by copyright unless they determine otherwise. This includes items found on the internet. Items in copyright will need either permission or a fair use justification.
If you have flexibility in the final selection of your images, search for images that are 1) in the public domain, or 2) made available for reuse via a Creative Commons license . Such images can be incorporated into your dissertation without permission or concern for fair use.
3. I’ve provided attribution and a citation for the source material I used in my thesis or dissertation. That’s all I need, right ?
Proper attribution is absolutely required; that’s a part of academic integrity and good scholarship. But copyright permission, if necessary, is an entirely separate matter and covered by U.S. Code Title 17 .
4. Do I need permission for every image, chart and graph that I use in my thesis or dissertation from other sources?
It depends. Some materials may qualify under fair use, and others are best used with permission. Graduate students should consult the filing procedures for more detail, or for consultation on a specific situation, get assistance from a UCLA librarian at [email protected] .
5. I’ve obtained verbal permission to use copyrighted material in my thesis or dissertation. Is this sufficient?
Written permission is best. It can be as simple as an email granting permission. Graduate students should retain copies of all permissions in their files.
6. How do graduate students determine what they can use without permission under Fair Use?
If graduate students do not know the four-factor balancing test of Fair Use , they need to become familiar with it. For more information on Fair Use, we recommend you explore the UC Copyright website .
7. Can I use an article, which I previously authored and published, as a chapter in my thesis or dissertation without permission?
It depends on the agreement you signed with your publisher. Most agreements require you to transfer your copyright to the publisher. If this is the case, you must request permission from the publisher to “reprint” the article as a chapter in your thesis or dissertation. However, some agreements specify that you retain the right to reprint the article in your dissertation. Read your author agreement to see if you retained such rights; if you are unsure, consult with a UCLA librarian at [email protected] .
8. After my thesis or dissertation is published, can I reuse one of the chapters as the basis of a future journal article?
If portions of your thesis or dissertation have been previously published as journal articles, you are bound by the agreement you signed when that content was published. But in regards to the remaining, unique content of your thesis or dissertation: Yes, you own the copyright of your thesis or dissertation, and are free to adapt and republish it as you see fit.
9. For those items that require permission, do graduate students need that permission before they file?
Though it is highly recommended that graduate students secure permissions as early as possible, they DO NOT need those permissions in order before they file their theses or dissertations. Permissions are only necessary from ProQuest’s perspective, and theses or dissertations will be published on ProQuest only after the filing process is complete. So, there is a window of several weeks for graduate students to finish gathering permissions.
10. What happens if a graduate student cannot produce the necessary permissions if/when a copyright owner objects and ProQuest asks for them ?
If the inclusion of copyrighted material is challenged by the copyright owner of the material and/or ProQuest, then the publication will be removed from ProQuest until the issue is resolved. A full citation and abstract of the graduate student’s thesis or dissertation will remain.
This rare issue (less than 1% of dissertations are challenged in this manner) is most commonly resolved by redacting or removing the copyrighted content from your thesis or dissertation and resubmitting the modified document to ProQuest. This will require the graduate student to pay a processing fee to ProQuest. Keep in mind that the copyright owner must be amenable to this as a resolution.
11. Won’t having my thesis or dissertation freely available online reduce my chances of securing a book deal and/or publishing portions as journal articles?
If you are concerned that such availability would impact your ability to later publish the thesis or dissertation as a monograph, or derive a journal article from a chapter, several studies of publisher practices have shown that this is not the case. In a 2011 Publisher’s Survey , only 6% of monograph publishers and 3% of journal editors would “never” consider a work derived from a publicly available ETD. If you have concerns, you can embargo your dissertation for up to two years.
Delayed Public Dissemination (Embargo)
1. What does delayed public dissemination (embargo) mean?
Delayed public dissemination, commonly known as embargo, postpones public distribution of the thesis or dissertation that has been approved and filed with the university.
2. I chose to delay the release of my thesis or dissertation? When will the embargo begin?
The delayed release period in ProQuest will begin on the date that ProQuest receives your submission.
The delayed release period in eScholarship will begin on the date that your submission is approved by the Division of Graduate Education.
3. Can I request to delay the release of my thesis or dissertation for more than two years?
Under rare circumstances and prior to the filing of the thesis or dissertation, the Dean of Graduate Education may approve requests for time-delimited embargoes beyond the two-year limit. Please see UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination for more information on the exception request process.
4. I did not delay the public dissemination of my thesis or dissertation at the time of submission. Can I request an embargo in eScholarship post-submission?
Graduate students who wish to delay public dissemination in eScholarship must select this option at the time they submit their theses or dissertations to the Division of Graduate Education via ProQuest. Requests to embargo a thesis or dissertation after the manuscript has been filed in UC eScholarship are permissible only in exceptional circumstances, and require Division of Graduate Education approval.
Please see UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination for more information on the exception request process.
5. I think (or my research adviser thinks) that my thesis or dissertation work contains classified, secret or confidential information that cannot be disclosed to the public. Can I restrict access?
The University of California and UCLA do not have security clearances that permit the conduct of classified research on the UCLA campus (see page 2 of Responsibility for Executing Research Memo ). Further, the UCLA Graduate Council does not endorse the conduct of confidential research by graduate students; in instances where it is approved, the end results must be in an academically acceptable thesis or dissertation that can be deposited at the University without restricting access to it. In some cases, for example when a patent is being filed, it may be reasonable and appropriate to put in place an embargo that delays public release of the thesis or dissertation. Such an embargo should not be permanent, however. See UCLA Thesis and Dissertation Filing Requirements & Public Dissemination for guidelines and instructions on this option.
6. I have heard that publishers won’t publish articles based on results that have been presented in preliminary form in my dissertation. Is that true?
In general, no. Publishers recognize that work described in theses and dissertations is often preliminary and may require additional research and writing before it can be submitted to the journal. Theses and dissertations also have not undergone peer review. Consequently, the vast majority of scientific and scholarly publications do not view theses and dissertations as constituting prior publication that would render articles based on the work ineligible for consideration.
7. Depending on the academic field, books/monographs are considered the primary form of publication and the basis for getting an academic position. Do graduate students jeopardize their chance of getting future books published if their theses or dissertations are “out there”?
What publishers say is, “A dissertation is not a book.” The process of turning the dissertation into a book involves considerable transformation, which may include additional research, shifts in scope or emphasis, broadening or narrowing, refining of the arguments, and/or changes in style to appeal to the target audience. Because of these significant differences, and the fact that dissertations are not marketed, most publishers do not consider making a dissertation available in a public repository such as eScholarship (the UC Digital Library) as cause for rejecting a book proposal.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Ten things I wish I'd known before starting my dissertation
The sun is shining but many students won't see the daylight. Because it's that time of year again – dissertation time.
Luckily for me, my D-Day (dissertation hand-in day) has already been and gone. But I remember it well.
The 10,000-word spiral-bound paper squatted on my desk in various forms of completion was my Allied forces; the history department in-tray was my Normandy. And when Eisenhower talked about a "great crusade toward which we have striven these many months", he was bang on.
I remember first encountering the Undergraduate Dissertation Handbook, feeling my heart sink at how long the massive file took to download, and began to think about possible (but in hindsight, wildly over-ambitious) topics. Here's what I've learned since, and wish I'd known back then…
1 ) If your dissertation supervisor isn't right, change. Mine was brilliant. If you don't feel like they're giving you the right advice, request to swap to someone else – providing it's early on and your reason is valid, your department shouldn't have a problem with it. In my experience, it doesn't matter too much whether they're an expert on your topic. What counts is whether they're approachable, reliable, reassuring, give detailed feedback and don't mind the odd panicked email. They are your lifeline and your best chance of success.
2 ) If you mention working on your dissertation to family, friends or near-strangers, they will ask you what it's about, and they will be expecting a more impressive answer than you can give. So prepare for looks of confusion and disappointment. People anticipate grandeur in history dissertation topics – war, genocide, the formation of modern society. They don't think much of researching an obscure piece of 1970s disability legislation. But they're not the ones marking it.
3 ) If they ask follow-up questions, they're probably just being polite.
4 ) Do not ask friends how much work they've done. You'll end up paranoid – or they will. Either way, you don't have time for it.
5 ) There will be one day during the process when you will freak out, doubt your entire thesis and decide to start again from scratch. You might even come up with a new question and start working on it, depending on how long the breakdown lasts. You will at some point run out of steam and collapse in an exhausted, tear-stained heap. But unless there are serious flaws in your work (unlikely) and your supervisor recommends starting again (highly unlikely), don't do it. It's just panic, it'll pass.
6 ) A lot of the work you do will not make it into your dissertation. The first few days in archives, I felt like everything I was unearthing was a gem, and when I sat down to write, it seemed as if it was all gold. But a brutal editing down to the word count has left much of that early material at the wayside.
7 ) You will print like you have never printed before. If you're using a university or library printer, it will start to affect your weekly budget in a big way. If you're printing from your room, "paper jam" will come to be the most dreaded two words in the English language.
8 ) Your dissertation will interfere with whatever else you have going on – a social life, sporting commitments, societies, other essay demands. Don't even try and give up biscuits for Lent, they'll basically become their own food group when you're too busy to cook and desperate for sugar.
9 ) Your time is not your own. Even if you're super-organised, plan your time down to the last hour and don't have a single moment of deadline panic, you'll still find that thoughts of your dissertation will creep up on you when you least expect it. You'll fall asleep thinking about it, dream about it and wake up thinking about. You'll feel guilty when you're not working on it, and mired in self-doubt when you are.
10 ) Finishing it will be one of the best things you've ever done. It's worth the hard work to know you've completed what's likely to be your biggest, most important, single piece of work. Be proud of it.

- Blogging students
- Higher education
- Advice for students
Most viewed
- How it works
How to Write a Dissertation in Ten Days or Less
Published by Owen Ingram at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On April 19, 2024
Can you Complete your Dissertation in Ten Days?
Most students struggle at some point with deadlines, and we regularly get asked questions such as ‘Can you write a dissertation in a month?’ and ‘Can you write a dissertation in three days?’ We do not judge why you are in this situation, we’re here to help you get your dissertation done. The answer to the questions is yes. But of course, the less time you have, the more pressure you are under.
How Long Does it Take to Write a 10,000-word Dissertation?
This is a common question, as is “How long does it take to write a 7,000-word dissertation?” There is no figure in hours or days that answers this; it differs for everyone. “Is it possible to write a 10,000-word dissertation in two days?” Well, yes. But you will only find out if you can do it when the two days are up. You need to get started immediately, follow our advice and use our dissertation guides . But we are not claiming it’s easy.
Can I Complete my Dissertation in 3 Days? How Fast do I Need to Write?
If you have to produce 10,000 words in ten days, you have to average 1,000 a day. If you have two days, then 5,000 per day and if you work on it for 12 hours each of those days, you need to turn out 417 words per hour. A tall order, but it can be done. Do not let panic or pressure overwhelm you; and remember, it is perfectly acceptable to ask for help . You can stop asking your friends ‘How quickly can you write a dissertation?’ You are going to show them how quickly.
Can I Really Produce 10,000 Words in a Week?
How long d oes it take to write a 10k word dissertation? To give you some perspective, most people speak this many words in a day with no effort. You probably have more than enough words in your notes. It will make a big difference if you have your research project results analysis done already. If this is the case, you ‘only’ need to write them up. If you already made a good start but you are having trouble progressing, maybe you just need to focus on writing up your findings or certain chapters or areas.
You might think your notes are messy and disorganised or that they lack the right academic sound. Regardless, do not think of this task as producing all 10,000 words, rather, it is laying out your notes, organising them, and giving them a more formal, academic tone.
Can you Write a Dissertation in a Day?
Can you write a dissertation in a day? This is surely the most demanding academic writing challenge. It means 100% focus and work: Type up your notes, ensuring they have an academic/formal tone to them. Keep going, section by section and as it grows, you will start to see your dissertation appear.
Preparing to Write your Dissertation Fast
Prepare to start work.
You know your subject well, and you have probably written many essays on it by now. The main difference is that this assignment is longer. So, let’s get started. You need to prepare well; normal life can be suspended for the time you will spend working. The first preparations to make concern you and where you are going to work.
Distractions and Interruptions
Turn off your phone and avoid TV. If you are really serious, you will really do it. When you procrastinate or allow yourself to be distracted, what do you do? Gaming? Staring out of the window? Baking? Make these things difficult or impossible to do. Be aware of something called productive procrastination. This is when you do something productive but it’s not what you are meant to be doing. Do not mistake activity for productivity. When you find yourself vacuuming around your desk, snap out of it.
I’m Writing my Dissertation all Week. Quiet, Please
Some people can work with music playing, and some need silence. Listening to words, whether sung or spoken, can distract you when producing text. If there is something that will help you, such as instrumental music, use it. Make sure everyone knows what you are doing and ask them to leave you alone (except for bringing you food and drinks). Can someone else handle your duties and obligations for a while?
Create a Work Area
Set up a workplace and de-clutter it. Remove irrelevant books and anything you can fiddle with. Gather all your materials: this means textbooks, notes on paper and in digital form. Your research is likely over, but you will need everything to hand.
Give all materials specific places and keep them there. As you use them, you will remember where they are. Putting them down in different places will mean time lost looking for them, which will add frustration to the work.
Do All of your Legwork Before Starting
Getting up and walking away from the desk unnecessarily uses time you do not have. Do not let shopping trips interrupt your work. If you do not have enough food and supplies in before starting, get them first. Certain foods/snacks can help get you through, maybe you can suspend your usual health regime for a while. You need to feel comfortable in this. But do not overdo the caffeine or sugar .
Make a Work Schedule
Look ahead at your available time and make a schedule. If you work 21 hours on the first day, you might find yourself burnt out the next day. Sleep when you have to, work when you feel good. How long can you realistically work each day? Be careful not to create an unrealistic schedule, you will not keep up to it and will become demoralised. Remember that writing the dissertation is only 1% of your entire course; it is acceptable to get help at this late stage.
Where to Start
Start here – write an outline.
As well as a work schedule, you need a dissertation structure . You may be tempted to think that making an outline for your dissertation is extra work, that it would be quicker to just start writing. That would be like going on a driving tour to every European country with no plan. Without regular destinations, you will drift about aimlessly.
You can save time by focussing only on the main parts of the dissertation. If you run out of time, it will be better if the parts not completed are the less significant ones, although ideally nothing should be left unfinished. This is an exercise in prioritisation: Write the most valuable, points-scoring parts first.
Sacrifices May be Necessary
With a tight time limit, you might have to make sacrifices. People with the luxury of time will spend a day or more on just the table of contents or references section . You might not have this option. The focus has to be on the rapid production of text and its quality; things like detailed formatting and page layout will be secondary.
Prioritising your Order of Work
In the detailed plan below, skip the greyed-out parts to start with. You can use this to create an outline by adding a note under each part of the different sections stating what you are going to include there. This is where the job starts to appear less daunting; 10,000 now becomes 2,000 for this section, 1,000 for that section… The mountain becomes a set of smaller hills. And the introduction section can be written after the body, it is easier and quicker that way.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Writing the Dissertation Body
When you have an outline, you need to put some meat on those bones and build a body. Working from start to finish may be best (skipping the introduction), but the order you work in is your choice. If your notes are not in order, a quick way to identify notes that apply to the different sections is to mark them with different coloured highlighters as in the table above. This will draw your eyes to the relevant notes quickly. You can do this on your computer screen by highlighting similarly.
After the main body, the introduction is next. This will be easier to write because all the information will be fresh in your mind. What next? The appendices or the parts at the front? This should be your decision based on remaining time.
Good Practices for Writing your Dissertation
Ignore spelling and grammar.
Do not pay attention to spelling, grammar, and language rules at this stage. Attending to spelling and grammatical details as you work will distract you and spoil your flow. Spelling and grammatical mistakes do not matter in a work in progress. You can turn checking functions off until you reach the editing and proofreading stage. Concentrate only on writing up your notes, do not switch between tasks.
Attend to One Part of the Dissertation at a Time
Constantly switching between research, writing, and tidying up the reference section is inefficient. Each time you switch, your mind needs time to catch up then settle into that activity. By focussing, we mean you should do all the analysis in one session until it is finished, all the writing of major sections in another, and sorting out the reference section can be done in one sitting. Less switching saves time and usually turns out a better job.
Take Regular Short Breaks
Save and Back up Routinely
When you leave the desk, click to save your work. Also do this after any burst of writing, and at regular intervals. Back up your work on another drive too. This is one of the most important things you will write. Treat it as the valuable document that it is.
For when you resume work, make sure you know where you left off, highlight it if that helps. When you come back to your work the next day, sometimes you can’t remember where you were; it can be difficult to resume the same line of thought. A habit of Ernest Hemingway was to leave an unfinished sentence to come back to so that he could…
Have a Strict but Simple Method of Noting Sources
Every time you quote or paraphrase something, note the source. Use a simple referencing technique while writing that does not demand much time. One such method is for the first in-text reference, just put (1) after the quote, use (2) for the second and so on. Start a list of sources that correspond to each number. You could highlight the numbers in a specific colour so you can attend to them later and not miss any. Missing just one reference, even accidentally, will still count as plagiarism . Before you start, be absolutely clear whether you are including a reference list or bibliography . Completing your list according to the required style ( Harvard , Chicago, etc.) can be done in one session.
Get a Qualified Appraisal of your Work
You will need someone to read your finished work. Having it read by someone unfamiliar with the subject and the structure of dissertations will be unproductive. Ideally it should be someone who understands the topic. And these days that person need not be physically present; you can email your draft to someone to get an opinion on changes & improvements .
Writing your Dissertation in Days
We are not going to sugar-coat the task of producing a dissertation in days rather than months and weeks. It is not easy, and regardless of what caused you to have such a short time remaining, it puts all your work in jeopardy. When someone asks us “Can I complete my dissertation in three days?” we have to answer yes, you can, but… It depends on the individual, how much work you have done so far, your personal circumstances, your other obligations, how much of those three days can you dedicate to the task.
How to Write a Dissertation Fast Checklist
Frequently asked questions, can i write my dissertation in under a week.
The short answer is yes but there are several factors to consider that may help or hinder you. Few people have the support around them to allow them to drop all commitments and focus on just one task. Also, few people will have taken on such a large a task in such a short time before, and might become overwhelmed.
The dissertation is where your study course culminates; all the time, effort, and expense you have invested should come to fruition here. This might not be a good time for maybe I can do it . Maybe you can make it to the bank before it closes. No? Oh, well, you can go tomorrow. Maybe I can write 10,000 words in a week. If the answer is no, the consequences are more serious.
This guide and all the other dissertation guides on this site are here to help you with every aspect of dissertation writing. You can also contact us directly through the chat box or Whatsapp.
I have to write my dissertation in three days. Where do I start?
Start by getting organised. Gather all the materials you need, create a work area, get rid of distractions, and if possible, delegate any obligations or chores to someone else for the duration. Then read this guide from the start. If you need further help when you are deep into the writing, just ask us. We exist just for this purpose. Our team and expert writers have handled almost every kind of dissertation emergency.
Can I do my research, analysis, and write my dissertation in ten days?
The more time you have, the better. But carrying out the research and analysis in such a short time will be very demanding. It can be done though; our team can do this in under a week. You would need a great level of support around you and an impressive level of determination and focus. If you supply the determination, we can provide the support .
What helped you finish your dissertation quickly?
To finish your dissertation quickly, prioritise tasks, set realistic goals, maintain a consistent work schedule, minimise distractions, seek feedback from advisors regularly, and break down the writing process into manageable chunks. Use effective time management techniques, such as the Pomodoro Technique, and stay organised with thorough planning and research strategies.
You May Also Like
Find out if you need permission to publish your UK dissertation. Understand copyright, university rules, and third-party content.
Find out all you need to know about paraphrasing and how paraphrasing is essential in essay and assignment writing here.
Not familiar with how to proofread and edit your dissertation? Find out the best tips and do’s and don’ts of proofreading and editing a dissertation here.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Master’s Thesis Length: How Long Should A Master’s Thesis Be?

Writing a thesis is one of the requirements for obtaining a master’s degree. If you are currently running a postgraduate program, you may be wondering what the actual length of a master’s thesis is.
A thesis is a comprehensive exploration of a topic or area of interest. The idea is to chart your learning journey and conclude by discussing what you have learned and what others might learn from it, including opportunities for further research.
It can be as long as it takes to discuss your topic in detail. This is anything around 50 to 300 pages, including a bibliography. However, different institutions have standards for content, format, and length expectations.
This article discusses the length and structure of a master’s thesis in detail.
What is a master’s thesis?

A master’s thesis is a research project written by students in a master’s degree program to demonstrate their interest and expertise in a specific topic within their field of study. It is the final requirement for a master’s degree.
The thesis is a culmination of existing research and data that master’s students marshal and combine to make up a hypothesis that challenges an existing argument in the field or develops new arguments for academic debate.
Students are usually assigned an advisor who provides guidance and supervises their work. Once the thesis is complete, students must defend their work to a panel of two or more departmental faculty members.
How long is a master’s thesis?
A master’s thesis has no mandatory length. It can be anywhere from 50 to 300 pages depending on factors such as departmental requirements, university guidelines, topic, and research methodology.
However, what is most important is that your thesis contains all the necessary information about the topic clearly and concisely. Your argument must also be well structured with relevant references, figures, and tables to support your claim.
In fact, the quality of your work should be prioritized above the length of your work.
Ultimately, the aim is to demonstrate your mastery in the field by demonstrating the academic expertise and research skills you have developed throughout the master’s program.
Master thesis structure
Given the differences in the degree requirements between universities, Master’s theses do not follow the same structure. However, a typical master’s thesis follows these format:
- Title page
- Acknowledgment
- Table of contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Data collection
- Chapter 4: Analysis
- Chapter 5: Conclusion
- Reference list
- Statement of independent work
- Appendix (optional)
1. Title page
This is basically a page to tell your name, university, essay topic, and supervisor’s name.
2. Acknowledgment
This is the part where you appreciate those who contributed to the preparation of your thesis. If you probably received a fellowship or obtained data from an institution, then you should recognize and thank them here.
You should also thank your advisor, friends, and family who supported you during the course of your work.
3. Abstract
The abstract is a crucial part of your thesis. It is a one-page summary covering the questions you intend to answer, the data used, the methodology employed, and your findings.
The aim of an abstract is to give the thesis committee a brief but concise insight into what your research work entails.
4. Table of contents
It is a list of all the chapters and subsections contained in your work alongside the page number where each chapter begins.
Additionally, you need to provide a list of figures and tables with the page number to find them in the thesis.
5. Introduction
The introduction is the first chapter of a thesis. It provides context for the rest of the paper, telling readers what the scope of your work is and what you aim to achieve.
It doesn’t have to be technical rather it should communicate why your topic is relevant. The introduction should also highlight other chapters of your work and touch down on at least one research question.
6. Literature review
The literature review is the part of your thesis where you establish your arguments using various pre-existing scholarly publications and demonstrating your knowledge about your topic.
It is aimed to give a scientific overview of how your work contributes to existing knowledge on the subject matter. In other words, it shows readers the literature gap you hope to fill. For instance, your thesis may be based on new sets of data, methods, or applications.
7. Research methods
This chapter details the data used in your research and the method of gathering or collecting them. This could be qualitative data such as open-ended surveys, case studies, and more.
However, not all theses require a section covering research methods. Arts and humanities students for instance do not undertake research that involves fixed methodologies.
Instead, they outline their theoretical perspectives and methods in their introductions without explaining their data collection and analysis methods in detail.
8. Data analysis and findings
Data analysis and finding involve experimenting with the gathered data and presenting your result in a graphical, tabular, or chart form. The result could also be a written description of the research and findings.
9. Discussion
This is the largest part of a thesis containing a series of chapters. The chapters should flow logically and build your arguments from one chapter to the next.
The length of the discussion is based on the total length of the thesis. So, for a thesis of about 20,000 words, the discussion section may be 15,000 words.
10. Conclusion
A thesis conclusion is where you tie up your arguments and evidence and summarize your discussions stating key points.
It should also include explaining whether your research questions are confirmed or rejected based on your research and comparing your findings with existing publications.
Not only that, the conclusion should state parts of your topic that you couldn’t touch. This helps buttress what your research has achieved and parts others can explore for future studies.
11. List of reference
This is simply a list of all the sources you cited in your work.
12. Statement of Independent work
It is a declaration to confirm that your thesis was done independently by you. The declaration takes the format:
“I hereby confirm that this paper was written independently by me and did not use any sources other than citations and that all passages and ideas taken from other sources are cited accordingly”.
13. Appendix (or appendices)
The appendix is usually optional in a thesis. It is material that complements your argument. This could be a questionnaire or a case study.
If the content is too large to go into the body of your paper or could distract readers, then your research could use an appendix.
How to write a master’s thesis
There is a lot that goes into writing a master’s thesis. Aside from the fact that this is a large project that cannot be rushed, there are some requirements that you must adhere to.
That said, the first thing you should consider is approaching your advisor for guidance on your work. Second, look at past publications to see their structure and study their content.
Additionally, when choosing a topic, it’s best to find a subject that interests you, then create an outline to direct your flow, and make sure to keep a list of references used in your work.
A master’s thesis is longer than an undergraduate thesis, so, it would help if you start working on time to avoid rushing or late submission.
How fast can you write a master’s thesis?
Generally, students have two semesters to write their master’s thesis (usually the last two semesters of their degree program).
Can you finish your thesis in 3 weeks?
Let’s say you write at least 1000 words daily in three weeks that would be around 20,000 words. But it will be really difficult to achieve. Plus, it would be hard to do quality work in 3 weeks.
Can a master’s thesis be written in 20 pages?
20 pages may be too little to capture your arguments comprehensively in a master’s thesis. A typical master’s thesis has a length of about 50 pages and above.
A master’s thesis can be any length depending on how long it takes to thoroughly discuss your topic. Basically, you should follow the guideline given by your institution and advisor.
Your work must also demonstrate great quality, so you want to give it your best shot. Perhaps you have a short time to complete your thesis, don’t fret. Simply think about how many words you need to write every day to meet up and develop plans to achieve your goal.
In all of this, you want to avoid plagiarism in your work, as this can have serious consequences. Read this article to know if paraphrasing is plagiarism.
I hope this article helped. Thanks for reading.
You may also like:
- Best Webinar Platforms [+ 10 Alternatives]
- Best Cameras For Quality Photographs And Videos: Top-Rated For Every Budget
- 15 Best Laptops For Video Editing: Top Picks For Amateurs & Pros
- Best Camera Bags And Cases For Your Camera
- Best Camera Stabilizers For Video: Top Picks For Online Course Creators
People Also Read:

Why Do Waiters Get Paid So Little [+ How To Make More Money]

Navigating Workplace Norms: Can You Email A Resignation Letter?

Difference Between Roles And Responsibilities

Does Suspension Mean Termination?

Moral Claim: Definition, Significance, Contemporary Issues, & Challenges

Why Can’t You Flush The Toilet After A Drug Test?
How Long Does It Take To Include My Dissertation Or Thesis In ProQuest?
- Article Number: 000032609
The process generally takes 8 to 12 weeks from the time we receive your materials. Be advised that universities sometimes hold materials before sending them on to ProQuest.
If you have submitted electronically you will receive a confirmation email which includes your manuscript ID number. This email is automatically generated from a third party uploading site and does not indicate that ProQuest has received your materials.
Our time fluctuates depending on the current volume coming in. We make every effort to have your work available in ProQuest within our time frame of eight to 12 weeks. Please help us streamline this process by making sure that everything submitted is in order. Pay special attention to providing a signature, abstract, and contact address.
Please contact ProQuest customer service if you have further questions.
https://support.proquest.com/s/article/How-long-does-it-take-to-include-my-dissertation-or-thesis-in-ProQuest?language=en_US
Privacy regulations require that we get your consent to continue to collect, store and use the personal information submitted for account creation or collected while using our services.
I consent to the collection and use of my personal information consistent with the Privacy Policy . I acknowledge that use of the service is subject to the Terms & Conditions .
Report a Problem with this Article
Submit a case.
Having an issue? Submit a Support Case and we'll get right on it.
Chat with Us
Chat is now available. If you are looking for quick feedback, chat with us now.
We're here to help. Give us a call if you aren't finding answers to your questions.
ProQuest ExLibris is committed to empowering researchers and librarians around the world.
Copyright © 2024 ProQuest LLC

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How long is a dissertation? Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education: An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000-15,000 words. A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words. A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words.
How long does it take to write a dissertation? At the bachelor's and master's levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. ... A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words;
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
Barring unforeseen events, the normal time range for finishing a dissertation seems to be 13-19 months, which can be rounded to one to one and a half years. If you are proactive and efficient, you can usually be at the shorter end of the time range.
A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words; A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words ... How long does it take to write a dissertation? At the bachelor's and master's levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety ...
This editable handout can help you make sense of the various steps involved in the production of your thesis or dissertation and determine how long each step might take. A large part of this process involves (1) seeking out the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding specific document formatting requirements, (2) understanding ...
Each student's dissertation is a slightly different length. Typically, though, most dissertations are between 100 and 300 pages long. It's common for them to include about 80,000 words.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DISSERTATION HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE TO DO A MASTERS DISSERTATION? ... 4 What kinds of skills and capabilities will you need to do your dissertation? What is a Masters? Chapter-01.qxd 11/12/2004 12:41 PM Page 3. 4 / ESSENTIAL PREPARATION FOR YOUR DISSERTATION
How long should a PhD thesis be? A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words (100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The Education Dissertation Timeline. About how long will the dissertation process take? Many factors can influence the dissertation timeline length, such as: Job status: Doctoral students working in full- or part-time positions will need to be diligent about dedicating time to their dissertation work.
The average Masters dissertation length is approximately 20,000 words whilst a thesis is 4 to 5 times this length at approximately 80,000 - 100,000. The key reason for this difference is because of the level of knowledge they convey. A Master's dissertation focuses on concluding from existing knowledge whilst a PhD thesis focuses on drawing ...
The last date that all of the items listed above is complete will be your filing date for your thesis or dissertation. For example, if you submit your final dissertation PDF and complete the online process on May 31, three committee members sign on June 1, and the final committee member signs on June 2, your filing date will be June 2 assuming ...
4) Do not ask friends how much work they've done. You'll end up paranoid - or they will. Either way, you don't have time for it. 5) There will be one day during the process when you will freak ...
How Long Should it Be? How Long Does it Take? A master's thesis is generally 40-80 pages, not including the bibliography. However, the length will vary according to the topic and the method of analysis, so the appropriate length will be determined by you and your committee. Students who write a master's thesis generally do so over two ...
Most master's degree programs require you to take 30 to 60 credit hours of coursework. Some programs involve as many as 72 credit hours. It's possible to complete a 34-credit Master of Applied Data Science degree in as little as twelve months. A 72-credit Master of Business Administration (MBA), on the other hand, will likely take two to ...
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
If you have to produce 10,000 words in ten days, you have to average 1,000 a day. If you have two days, then 5,000 per day and if you work on it for 12 hours each of those days, you need to turn out 417 words per hour. A tall order, but it can be done.
I suggest setting targets that allow you to finish writing in eight days, not 10. This gives you some padding in case life gets in the way. To be clear, there are 192 hours in eight days. Allowing for a 12-hour work day, then you need to write 15,000 words in 96 hours or about 156 words an hour. Set a target of 400 words an hour.
Master's programs often require 30 to 60 credit hours, but that number can vary. Every course awards between 1 and 5 credits each, with most courses being between 3 and 5 credits. Check your institution's program for further information. At Stanford, the number of units required to earn a master's degree is usually 45, but may vary ...
In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5-7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3-5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation. In the rest of the world, students normally have a master's degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3-5 years.
This is the largest part of a thesis containing a series of chapters. The chapters should flow logically and build your arguments from one chapter to the next. The length of the discussion is based on the total length of the thesis. So, for a thesis of about 20,000 words, the discussion section may be 15,000 words. 10.
TreeofLife 2853 posts. This is pretty standard though for a taught masters - the research project is generally only 3-4 months long. Students are expected to complete everything from literature review, to research, to analysis to writing up in that time. It's only 13,000 to 20,000 words generally as well. Zutterfly 279 posts.
Just writing a 200 page document isn't that hard. Most people probably can do that in about 3 months or less. But if you can't treat writing the thesis as a full time job and only get to write 5-10 pages a week, it obviously takes a little longer. Add to that multiple rounds of feedback from colleagues and advisors.
How Long Does It Take To Include My Dissertation Or Thesis In ProQuest? Article Number: 000032609. The process generally takes 8 to 12 weeks from the time we receive your materials. Be advised that universities sometimes hold materials before sending them on to ProQuest. If you have submitted electronically you will receive a confirmation email ...
Writing the proposal took about two weeks. Research took about three months. Writing the dissertation took about two months. All together, it took me 6 months to put together the dissertation. Reply 2. 5 years ago. A. Anonymous #2. Around 2 months.