clock This article was published more than 4 years ago

What Finland is really doing to improve its acclaimed schools

Finland has been paid outsized attention in the education world since its students scored the highest among dozens of countries around the globe on an international test some 20 years ago.
And while it is no longer No. 1 — as the education sector was hurt in the 2008 recession, and budget cuts led to larger class sizes and fewer staff in schools — it is still regarded as one of the more successful systems in the world.
In an effort to improve, the Finnish government began taking some steps in recent years, and some of that reform has made for worldwide headlines. But as it turns out, some of that coverage just isn’t true.
A few years ago, for example, a change in curriculum sparked stories that Finland was giving up teaching traditional subjects. Nope .
You can find stories on the Internet saying Finnish kids don’t get any homework. Nope.
Even amid its difficulties, American author William Doyle, who lived there and sent his then-7-year-old son to a Finnish school, wrote in 2016 that they do a lot of things right:
What is Finland’s secret? A whole-child-centered, research-and-evidence based school system, run by highly professionalized teachers. These are global education best practices, not cultural quirks applicable only to Finland.
‘I have seen the school of tomorrow. It is here today, in Finland.’
Here is a piece looking at changes underway in Finnish schools by two people who know what is really going on. They are Pasi Sahlberg and Peter Johnson. Johnson is director of education of the Finnish city of Kokkola. Sahlberg is professor of education policy at the University of New South Wales in Sydney. He is one of the world’s leading experts on school reform and is the author of the best-selling “ Finnish Lessons: What Can the World Learn About Educational Change in Finland ?”
No, Finland isn’t ditching traditional school subjects. Here’s what’s really happening.
By Pasi Sahlberg and Peter Johnson
Finland has been in the spotlight of the education world since it appeared, against all odds, on the top of the rankings of an international test known as PISA , the Program for International Student Assessment, in the early 2000s. Tens of thousands visitors have traveled to the country to see how to improve their own schools. Hundreds of articles have been written to explain why Finnish education is so marvelous — or sometimes that it isn’t. Millions of tweets have been shared and read, often leading to debates about the real nature of Finland’s schools and about teaching and learning there.
We have learned a lot about why some education systems — such as Alberta, Ontario, Japan and Finland — perform better year after year than others in terms of quality and equity of student outcomes. We also understand now better why some other education systems — for example, England, Australia, the United States and Sweden — have not been able to improve their school systems regardless of politicians’ promises, large-scale reforms and truckloads of money spent on haphazard efforts to change schools during the past two decades.
Among these important lessons are:
- Education systems and schools shouldn’t be managed like business corporations where tough competition, measurement-based accountability and performance-determined pay are common principles. Instead, successful education systems rely on collaboration, trust, and collegial responsibility in and between schools.
- The teaching profession shouldn’t be perceived as a technical, temporary craft that anyone with a little guidance can do. Successful education systems rely on continuous professionalization of teaching and school leadership that requires advanced academic education, solid scientific and practical knowledge, and continuous on-the-job training.
- The quality of education shouldn’t be judged by the level of literacy and numeracy test scores alone. Successful education systems are designed to emphasize whole-child development, equity of education outcomes, well being, and arts, music, drama and physical education as important elements of curriculum.
Besides these useful lessons about how and why education systems work as they do, there are misunderstandings, incorrect interpretations, myths and even deliberate lies about how to best improve education systems. Because Finland has been such a popular target of searching for the key to the betterment of education, there are also many stories about Finnish schools that are not true.
Part of the reason reporting and research often fail to paint bigger and more accurate picture of the actual situation is that most of the documents and resources that describe and define the Finnish education system are only available in Finnish and Swedish. Most foreign education observers and commentators are therefore unable to follow the conversations and debates taking place in the country.
For example, only very few of those who actively comment on education in Finland have ever read Finnish education law , the national core curriculum or any of thousands of curricula designed by municipalities and schools that explain and describe what schools ought to do and why.
The other reason many efforts to report about Finnish education remain incomplete — and sometimes incorrect — is that education is seen as an isolated island disconnected from other sectors and public policies. It is wrong to believe that what children learn or don’t learn in school could be explained by looking at only schools and what they do alone.
Most efforts to explain why Finland’s schools are better than others or why they do worse today than before fail to see these interdependencies in Finnish society that are essential in understanding education as an ecosystem.
Here are some of those common myths about Finnish schools.
First, in recent years there have been claims that the Finnish secret to educational greatness is that children don’t have homework.
Another commonly held belief is that Finnish authorities have decided to scrap subjects from school curriculum and replace them by interdisciplinary projects or themes.
And a more recent notion is that all schools in Finland are required to follow a national curriculum and implement the same teaching method called “phenomenon-based learning” (that is elsewhere known as “project-based learning”).
All of these are false.
In 2014, Finnish state authorities revised the national core curriculum (NCC) for basic education. The core curriculum provides a common direction and basis for renewing school education and instruction. Only a very few international commentators of Finnish school reform have read this central document. Unfortunately, not many parents in Finland are familiar with it, either. Still, many people seem to have strong opinions about the direction Finnish schools are moving — the wrong way, they say, without really understanding the roles and responsibilities of schools and teachers in their communities.
Before making any judgments about what is great or wrong in Finland, it is important to understand the fundamentals of Finnish school system. Here are some basics.
First, education providers, most districts in 311 municipalities, draw up local curricula and annual work plans on the basis of the NCC. Schools though actually take the lead in curriculum planning under the supervision of municipal authorities.
Second, the NCC is a fairly loose regulatory document in terms of what schools should teach, how they arrange their work and the desired outcomes. Schools have, therefore, a lot of flexibility and autonomy in curriculum design, and there may be significant variation in school curricula from one place to another.
Finally, because of this decentralized nature of authority in Finnish education system, schools in Finland can have different profiles and practical arrangements making the curriculum model unique in the world. It is incorrect to make any general conclusions based on what one or two schools do.
Current school reform in Finland aims at those same overall goals that the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development — which gives the PISA exams every three years to 15-year-olds in multiple countries — as well as governments and many students say are essential for them: to develop safe and collaborative school culture and to promote holistic approaches in teaching and learning. The NCC states that the specific aim at the school level is that children would:
- understand the relationship and interdependencies between different learning contents;
- be able to combine the knowledge and skills learned in different disciplines to form meaningful wholes; and
- be able to apply knowledge and use it in collaborative learning settings.
All schools in Finland are required to revise their curricula according to this new framework. Some schools have taken only small steps from where they were before, while some others went on with much bolder plans. One of those is the Pontus School in Lappeenranta, a city in the eastern part of Finland.
The Pontus School is a new primary school and kindergarten for some 550 children from ages 1 to 12. It was built three years ago to support the pedagogy and spirit of the 2014 NCC. The Pontus School was in international news recently when the Finnish Broadcasting Company reported that parents have filed complaints over the “failure” of the new school.
But according to Lappeenranta education authorities, there have been only two complaints by parents, both being handled by Regional Authorities. That’s all. It is not enough to call that a failure.
What we can learn from Finland, again, is that it is important to make sure parents, children and media better understand the nature of school reforms underway.
“Some parents are not familiar with what schools are doing,” said Anu Liljestrom, superintendent of the education department in Lappeenranta. “We still have a lot of work to do to explain what, how and why teaching methods are different nowadays,” she said to a local newspaper. The Pontus School is a new school, and it decided to use the opportunity provided by new design to change pedagogy and learning.
Ultimately, it is wrong to think that reading, writing and arithmetic will disappear in Finnish classrooms.
For most of the school year, teaching in Finnish schools will continue to be based on subject-based curricula, including at the Pontus School.
What is new is that now all schools are required to design at least one week-long project for all students that is interdisciplinary and based on students’ interests. Some schools do that better more often than others, and some succeed sooner than others.
Yes, there are challenges in implementing the new ideas. We have seen many schools succeed at creating new opportunities for students to learn knowledge and skills they need in their lives.
It is too early to tell whether Finland’s current direction in education meets all expectations. What we know is that schools in Finland should take even bolder steps to meet the needs of the future as described in national goals and international strategies. Collaboration among schools, trust in teachers and visionary leadership are those building blocks that will make all that possible.

- Education System
- Fins and Fun

Homework in Finland School

How many parents are bracing themselves for nightly battles to get their kids to finish their homework every year with the beginning of a school year? Thousands and thousands of them. Though not in Finland. The truth is that there is nearly no homework in the country with one of the top education systems in the world. Finnish people believe that besides homework, there are many more things that can improve child’s performance in school, such as having dinner with their families, exercising or getting a good night’s sleep.
Do We Need Homework?
There are different homework policies around the world. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) keeps track of such policies and compares the amount of homework of students from different countries. For example, an average high school student in the US has to spend about 6 hours a day doing homework, while in Finland, the amount of time spent on after school learning is about 3 hours a day. Nevertheless, these are exactly Finnish students who lead the world in global scores for math and science. It means that despite the belief that homework increases student performance, OECD graph shows the opposite. Though there are some exceptions such as education system in Japan, South Korea, and some other Asian countries. In fact, according to OECD, the more time students spend on homework, the worse they perform in school.
Finnish education approach shows the world that when it comes to homework, less is more. It is worth to mention that the world has caught onto this idea and, according to the latest OECD report, the average number of hours spent by students doing their homework decreased in nearly all countries around the world.
So what Finland knows about homework that the rest of the world does not? There is no simple answer, as the success of education system in Finland is provided by many factors, starting from poverty rates in the country to parental leave policies to the availability of preschools. Nevertheless, one of the greatest secrets of the success of education system in Finland is the way Finns teach their children.
How to Teach Like The Finns?
There are three main points that have to be mentioned when it comes to the success of education system in Finland.
First of all, Finns teach their children in a “playful” manner and allow them to enjoy their childhood. For example, did you know that in average, students in Finland only have three to four classes a day? Furthermore, there are several breaks and recesses (15-20 minutes) during a school day when children can play outside whatever the weather. According to statistics, children need physical activity in order to learn better. Also, less time in the classroom allows Finnish teachers to think, plan and create more effective lessons.
Secondly, Finns pay high respect to teachers. That is why one of the most sought after positions in Finland is the position of a primary school teacher. Only 10% of applicants to the teaching programs are accepted. In addition to a high competition, each primary school teacher in Finland must earn a Master’s degree that provides Finnish teachers with the same status as doctors or lawyers.
High standards applied to applicants for the university teaching programs assure parents of a high quality of teaching and allow teachers to innovate without bureaucracy or excessive regulation.
Thirdly, there is a lot of individual attention for each student. Classes in Finland are smaller than in the most of other countries and for the first six years of study, teachers get to know their students, their individual needs, and learning styles. If there are some weaker students, they are provided by extra assistance. Overall, Finnish education system promotes warmth, collaboration, encouragement, and assessment which means that teachers in this country are ready to do their best to help students but not to gain more control over them.
The combination of these three fundamentals is the key to success of any education system in the world and Finns are exactly those people who proved by way of example that less is more, especially when it comes to the amount of homework.

System of education in Finland

School System in Finland

Finland Education Reform

Fins and Fun: Distinctive Features of Education in Finland

10 Facts About Education in Finland
- Privacy policy

Don’t Let Faulty Plumbing Ruin your Child’s Lesson

Flagship of Distance Education
- Sustainability
- Responsible Business
- Small Medium Business
- Pitch A Story

Image Credit- Wikipedia , Pixabay (Representational)
No Tests, No Homework! Here's How Finland Has Emerged As A Global Example Of Quality, Inclusive Education

Writer: Mrinalini Kaushik (Remote Intern)
Mrinalini kaushik.
She is a student of journalism, keen on learning new ways to unlearn, deconstructing news and life. Interested in exploring new media as medium is the message. Avid follower of sports and politics
Others/World, 15 May 2022 3:40 AM GMT
Editor : shiva chaudhary | .

Shiva Chaudhary
Digital Editor
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
Creatives : Shiva Chaudhary
Student-oriented approach to education in finland has been recognised as the most well-developed educational system in the world and ranks third in education worldwide..
"A quality education grants us the ability to fight the war on ignorance and poverty," - Charles Rangel
The uniqueness of the Finnish education model is encapsulated in its values of neither giving homework to students every day nor conducting regular tests and exams. Instead, it is listening to what the kids want and treating them as independent thinkers of society.
In Finland, the aim is to let students be happy and respect themselves and others.
Goodbye Standardised Exams
There is absolutely no program of nationwide standard testing, such as in India or the U.S, where those exams are the decisive points of one's admission to higher education like Board Examinations or Common Entrance Tests.
In an event organised by Shiksha Sanskriti Utthan Nyas, RSS Chief Mohan Bhagwat remarked, "It is because they teach their children to face life struggles and not score in an examination," reported The Print .
Students in Finland are graded based on individual performance and evaluation criteria decided by their teachers themselves. Overall progress is tracked by their government's Ministry of Education, where they sample groups of students across schools in Finland.
Value-Based Education
They are primarily focused on making school a safe and equal space as children learn from the environment.
All Finland schools have offered since the 1980s free school meals, access to healthcare, a focus on mental health through psychological counselling for everyone and guidance sessions for each student to understand their wants and needs.
Education in Finland is not about marks or ranks but about creating an atmosphere of social equality, harmony and happiness for the students to ease learning experiences.
Most of the students spend half an hour at home after school to work on their studies. They mostly get everything done in the duration of the school timings as they only have a few classes every day. They are given several 15 -20 minutes breaks to eat, do recreational activities, relax, and do other work. There is no regiment in school or a rigid timetable, thus, causing less stress as given in the World Economic Forum .
Everyone Is Equal - Cooperate, Not Compete
The schools do not put pressure on ranking students, schools, or competitions, and they believe that a real winner doesn't compete; they help others come up to their level to make everyone on par.
Even though individualism is promoted during evaluation based on every student's needs, collectivity and fostering cooperation among students and teachers are deemed crucial.
While most schools worldwide believe in Charles Darwin's survival of the fittest, Finland follows the opposite but still comes out at the top.
Student-Oriented Model
The school teachers believe in a simple thumb rule; students are children who need to be happy when they attend school to learn and give their best. Focus is put upon teaching students to be critical thinkers of what they know, engage in society, and decide for themselves what they want.
In various schools, playgrounds are created by children's input as the architect talks to the children about what they want or what they feel like playing before setting up the playground.
Compared To The Indian Education Model
Firstly, Finnish children enrol in schools at the age of six rather than in India, where the school age is usually three or four years old. Their childhood is free from constricting education or forced work, and they are given free rein over how they socialise and participate in society.
Secondly, all schools in Finland are free of tuition fees as there are no private schools. Thus, education is not treated as a business. Even tuition outside schools is not allowed or needed, leaving no scope for commodifying education, unlike in India, where multiple coaching centres and private schools require exorbitant fees.
Thirdly, the school hours in Finland do not start early morning at 6 am, or 7 am as done in India. Finland schools begin from 9.30 am as research in World Economic Forum has indicated that schools starting at an early age is detrimental to their health and maturation. The school ends by mostly 2 pm.
Lastly, there is no homework or surprise test given to students in Finland. Teachers believe that the time wasted on assignments can be used to perform hobbies, art, sports, or cooking. This can teach life lessons and have a therapeutic stress-relieving effect on children. Indian schools tend to give a lot of homework to prove their commitment to studying and constantly revise what they learn in school.
Delhi Govt's Focus On Education
The Delhi model of education transformed under the Aam Aadmi Party's (AAP) tenure in the capital. In line with the Finnish model, Delhi government schools have adopted 'Happiness Classes' to ensure students' mental wellness through courses on mindfulness, problem-solving, social and emotional relationships, etc., from 1st to 8th classes.
Delhi government also introduced 'Entrepreneurial Mindset Classes' in 2019 to instil business and critical thinking skills among students of 9th to 12th classes. The practical approach in this class is indicated in the 'Business Blasters', a competition started by the Delhi government to encourage students to come up with start-up ideas and students were provided with ₹1000. Approximately 51,000 students participated in the first edition of the competition, according to Citizen Matters .
Through these endeavours, India is steadily investing in creating human resources that can get employment and generate employment for themselves.
India is at its demographic dividend stage; more than half of its population is within the working-age group of 14 to 60 years. Education is an essential factor in utilising this considerable advantage to grow economically and socially. Finland's education model is how India can strive closer to its goal and progress as a nation.
Also Read: Connaissance! Delhi Board of School Education Pens MoU To Add French In Government Schools

We are an independent and public-spirited digital media platform for Indian millennials. We report news and issues that matter as well as give you the opportunity to take action.

Why Are Finland’s Schools Successful?
The country’s achievements in education have other nations, especially the United States, doing their homework
LynNell Hancock
Photographs by Stuart Conway
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/cd/ee/cdee1c82-f8e3-4de4-983e-8599d4485745/finland-smiles-wr.jpg)
It was the end of term at Kirkkojarvi Comprehensive School in Espoo, a sprawling suburb west of Helsinki, when Kari Louhivuori, a veteran teacher and the school’s principal, decided to try something extreme—by Finnish standards. One of his sixth-grade students, a Kosovo-Albanian boy, had drifted far off the learning grid, resisting his teacher’s best efforts. The school’s team of special educators—including a social worker, a nurse and a psychologist—convinced Louhivuori that laziness was not to blame. So he decided to hold the boy back a year, a measure so rare in Finland it’s practically obsolete.
Finland has vastly improved in reading, math and science literacy over the past decade in large part because its teachers are trusted to do whatever it takes to turn young lives around. This 13-year-old, Besart Kabashi, received something akin to royal tutoring.
“I took Besart on that year as my private student,” Louhivuori told me in his office, which boasted a Beatles “Yellow Submarine” poster on the wall and an electric guitar in the closet. When Besart was not studying science, geography and math, he was parked next to Louhivuori’s desk at the front of his class of 9- and 10-year- olds, cracking open books from a tall stack, slowly reading one, then another, then devouring them by the dozens. By the end of the year, the son of Kosovo war refugees had conquered his adopted country’s vowel-rich language and arrived at the realization that he could, in fact, learn .
Years later, a 20-year-old Besart showed up at Kirkkojarvi’s Christmas party with a bottle of Cognac and a big grin. “You helped me,” he told his former teacher. Besart had opened his own car repair firm and a cleaning company. “No big fuss,” Louhivuori told me. “This is what we do every day, prepare kids for life.”
This tale of a single rescued child hints at some of the reasons for the tiny Nordic nation’s staggering record of education success, a phenomenon that has inspired, baffled and even irked many of America’s parents and educators. Finnish schooling became an unlikely hot topic after the 2010 documentary film Waiting for “Superman” contrasted it with America’s troubled public schools.
“Whatever it takes” is an attitude that drives not just Kirkkojarvi’s 30 teachers, but most of Finland’s 62,000 educators in 3,500 schools from Lapland to Turku—professionals selected from the top 10 percent of the nation’s graduates to earn a required master’s degree in education. Many schools are small enough so that teachers know every student. If one method fails, teachers consult with colleagues to try something else. They seem to relish the challenges. Nearly 30 percent of Finland’s children receive some kind of special help during their first nine years of school. The school where Louhivuori teaches served 240 first through ninth graders last year; and in contrast with Finland’s reputation for ethnic homogeneity, more than half of its 150 elementary-level students are immigrants—from Somalia, Iraq, Russia, Bangladesh, Estonia and Ethiopia, among other nations. “Children from wealthy families with lots of education can be taught by stupid teachers,” Louhivuori said, smiling. “We try to catch the weak students. It’s deep in our thinking.”
The transformation of the Finns’ education system began some 40 years ago as the key propellent of the country’s economic recovery plan. Educators had little idea it was so successful until 2000, when the first results from the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), a standardized test given to 15-year-olds in more than 40 global venues, revealed Finnish youth to be the best young readers in the world. Three years later, they led in math. By 2006, Finland was first out of 57 countries (and a few cities) in science. In the 2009 PISA scores released last year, the nation came in second in science, third in reading and sixth in math among nearly half a million students worldwide. “I’m still surprised,” said Arjariita Heikkinen, principal of a Helsinki comprehensive school. “I didn’t realize we were that good.”
In the United States, which has muddled along in the middle for the past decade, government officials have attempted to introduce marketplace competition into public schools. In recent years, a group of Wall Street financiers and philanthropists such as Bill Gates have put money behind private-sector ideas, such as vouchers, data-driven curriculum and charter schools, which have doubled in number in the past decade. President Obama, too, has apparently bet on competition. His Race to the Top initiative invites states to compete for federal dollars using tests and other methods to measure teachers, a philosophy that would not fly in Finland. “I think, in fact, teachers would tear off their shirts,” said Timo Heikkinen, a Helsinki principal with 24 years of teaching experience. “If you only measure the statistics, you miss the human aspect.”
There are no mandated standardized tests in Finland, apart from one exam at the end of students’ senior year in high school. There are no rankings, no comparisons or competition between students, schools or regions. Finland’s schools are publicly funded. The people in the government agencies running them, from national officials to local authorities, are educators, not business people, military leaders or career politicians. Every school has the same national goals and draws from the same pool of university-trained educators. The result is that a Finnish child has a good shot at getting the same quality education no matter whether he or she lives in a rural village or a university town. The differences between weakest and strongest students are the smallest in the world, according to the most recent survey by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). “Equality is the most important word in Finnish education. All political parties on the right and left agree on this,” said Olli Luukkainen, president of Finland’s powerful teachers union.
Ninety-three percent of Finns graduate from academic or vocational high schools, 17.5 percentage points higher than the United States, and 66 percent go on to higher education, the highest rate in the European Union. Yet Finland spends about 30 percent less per student than the United States.
Still, there is a distinct absence of chest-thumping among the famously reticent Finns. They are eager to celebrate their recent world hockey championship, but PISA scores, not so much. “We prepare children to learn how to learn, not how to take a test,” said Pasi Sahlberg, a former math and physics teacher who is now in Finland’s Ministry of Education and Culture. “We are not much interested in PISA. It’s not what we are about.”
Maija Rintola stood before her chattering class of twenty-three 7- and 8-year-olds one late April day in Kirkkojarven Koulu. A tangle of multicolored threads topped her copper hair like a painted wig. The 20-year teacher was trying out her look for Vappu, the day teachers and children come to school in riotous costumes to celebrate May Day. The morning sun poured through the slate and lemon linen shades onto containers of Easter grass growing on the wooden sills. Rintola smiled and held up her open hand at a slant—her time-tested “silent giraffe,” which signaled the kids to be quiet. Little hats, coats, shoes stowed in their cubbies, the children wiggled next to their desks in their stocking feet, waiting for a turn to tell their tale from the playground. They had just returned from their regular 15 minutes of playtime outdoors between lessons. “Play is important at this age,” Rintola would later say. “We value play.”
With their wiggles unwound, the students took from their desks little bags of buttons, beans and laminated cards numbered 1 through 20. A teacher’s aide passed around yellow strips representing units of ten. At a smart board at the front of the room, Rintola ushered the class through the principles of base ten. One girl wore cat ears on her head, for no apparent reason. Another kept a stuffed mouse on her desk to remind her of home. Rintola roamed the room helping each child grasp the concepts. Those who finished early played an advanced “nut puzzle” game. After 40 minutes it was time for a hot lunch in the cathedral-like cafeteria.
Teachers in Finland spend fewer hours at school each day and spend less time in classrooms than American teachers. Teachers use the extra time to build curriculums and assess their students. Children spend far more time playing outside, even in the depths of winter. Homework is minimal. Compulsory schooling does not begin until age 7. “We have no hurry,” said Louhivuori. “Children learn better when they are ready. Why stress them out?”
It’s almost unheard of for a child to show up hungry or homeless. Finland provides three years of maternity leave and subsidized day care to parents, and preschool for all 5-year-olds, where the emphasis is on play and socializing. In addition, the state subsidizes parents, paying them around 150 euros per month for every child until he or she turns 17. Ninety-seven percent of 6-year-olds attend public preschool, where children begin some academics. Schools provide food, medical care, counseling and taxi service if needed. Student health care is free.
Even so, Rintola said her children arrived last August miles apart in reading and language levels. By April, nearly every child in the class was reading, and most were writing. Boys had been coaxed into literature with books like Kapteeni Kalsarin (“Captain Underpants”). The school’s special education teacher teamed up with Rintola to teach five children with a variety of behavioral and learning problems. The national goal for the past five years has been to mainstream all children. The only time Rintola’s children are pulled out is for Finnish as a Second Language classes, taught by a teacher with 30 years’ experience and graduate school training.
There are exceptions, though, however rare. One first-grade girl was not in Rintola’s class. The wispy 7-year-old had recently arrived from Thailand speaking not a word of Finnish. She was studying math down the hall in a special “preparing class” taught by an expert in multicultural learning. It is designed to help children keep up with their subjects while they conquer the language. Kirkkojarvi’s teachers have learned to deal with their unusually large number of immigrant students. The city of Espoo helps them out with an extra 82,000 euros a year in “positive discrimination” funds to pay for things like special resource teachers, counselors and six special needs classes.
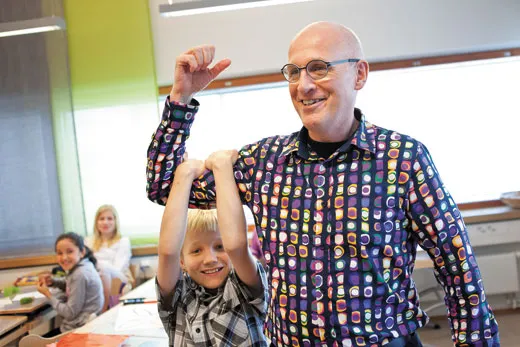
Rintola will teach the same children next year and possibly the next five years, depending on the needs of the school. “It’s a good system. I can make strong connections with the children,” said Rintola, who was handpicked by Louhivuori 20 years ago. “I understand who they are.” Besides Finnish, math and science, the first graders take music, art, sports, religion and textile handcrafts. English begins in third grade, Swedish in fourth. By fifth grade the children have added biology, geography, history, physics and chemistry.
Not until sixth grade will kids have the option to sit for a district-wide exam, and then only if the classroom teacher agrees to participate. Most do, out of curiosity. Results are not publicized. Finnish educators have a hard time understanding the United States’ fascination with standardized tests. “Americans like all these bars and graphs and colored charts,” Louhivuori teased, as he rummaged through his closet looking for past years’ results. “Looks like we did better than average two years ago,” he said after he found the reports. “It’s nonsense. We know much more about the children than these tests can tell us.”
I had come to Kirkkojarvi to see how the Finnish approach works with students who are not stereotypically blond, blue-eyed and Lutheran. But I wondered if Kirkkojarvi’s success against the odds might be a fluke. Some of the more vocal conservative reformers in America have grown weary of the “We-Love-Finland crowd” or so-called Finnish Envy. They argue that the United States has little to learn from a country of only 5.4 million people—4 percent of them foreign born. Yet the Finns seem to be onto something. Neighboring Norway, a country of similar size, embraces education policies similar to those in the United States. It employs standardized exams and teachers without master’s degrees. And like America, Norway’s PISA scores have been stalled in the middle ranges for the better part of a decade.
To get a second sampling, I headed east from Espoo to Helsinki and a rough neighborhood called Siilitie, Finnish for “Hedgehog Road” and known for having the oldest low-income housing project in Finland. The 50-year-old boxy school building sat in a wooded area, around the corner from a subway stop flanked by gas stations and convenience stores. Half of its 200 first- through ninth-grade students have learning disabilities. All but the most severely impaired are mixed with the general education children, in keeping with Finnish policies.
A class of first graders scampered among nearby pine and birch trees, each holding a stack of the teacher’s homemade laminated “outdoor math” cards. “Find a stick as big as your foot,” one read. “Gather 50 rocks and acorns and lay them out in groups of ten,” read another. Working in teams, the 7- and 8-year-olds raced to see how quickly they could carry out their tasks. Aleksi Gustafsson, whose master’s degree is from Helsinki University, developed the exercise after attending one of the many workshops available free to teachers. “I did research on how useful this is for kids,” he said. “It’s fun for the children to work outside. They really learn with it.”
Gustafsson’s sister, Nana Germeroth, teaches a class of mostly learning-impaired children; Gustafsson’s students have no learning or behavioral issues. The two combined most of their classes this year to mix their ideas and abilities along with the children’s varying levels. “We know each other really well,” said Germeroth, who is ten years older. “I know what Aleksi is thinking.”
The school receives 47,000 euros a year in positive discrimination money to hire aides and special education teachers, who are paid slightly higher salaries than classroom teachers because of their required sixth year of university training and the demands of their jobs. There is one teacher (or assistant) in Siilitie for every seven students.
In another classroom, two special education teachers had come up with a different kind of team teaching. Last year, Kaisa Summa, a teacher with five years’ experience, was having trouble keeping a gaggle of first-grade boys under control. She had looked longingly into Paivi Kangasvieri’s quiet second-grade room next door, wondering what secrets the 25-year-veteran colleague could share. Each had students of wide-ranging abilities and special needs. Summa asked Kangasvieri if they might combine gymnastics classes in hopes good behavior might be contagious. It worked. This year, the two decided to merge for 16 hours a week. “We complement each other,” said Kangasvieri, who describes herself as a calm and firm “father” to Summa’s warm mothering. “It is cooperative teaching at its best,” she says.
Every so often, principal Arjariita Heikkinen told me, the Helsinki district tries to close the school because the surrounding area has fewer and fewer children, only to have people in the community rise up to save it. After all, nearly 100 percent of the school’s ninth graders go on to high schools. Even many of the most severely disabled will find a place in Finland’s expanded system of vocational high schools, which are attended by 43 percent of Finnish high-school students, who prepare to work in restaurants, hospitals, construction sites and offices. “We help situate them in the right high school,” said then deputy principal Anne Roselius. “We are interested in what will become of them in life.”
Finland’s schools were not always a wonder. Until the late 1960s, Finns were still emerging from the cocoon of Soviet influence. Most children left public school after six years. (The rest went to private schools, academic grammar schools or folk schools, which tended to be less rigorous.) Only the privileged or lucky got a quality education.
The landscape changed when Finland began trying to remold its bloody, fractured past into a unified future. For hundreds of years, these fiercely independent people had been wedged between two rival powers—the Swedish monarchy to the west and the Russian czar to the east. Neither Scandinavian nor Baltic, Finns were proud of their Nordic roots and a unique language only they could love (or pronounce). In 1809, Finland was ceded to Russia by the Swedes, who had ruled its people some 600 years. The czar created the Grand Duchy of Finland, a quasi-state with constitutional ties to the empire. He moved the capital from Turku, near Stockholm, to Helsinki, closer to St. Petersburg. After the czar fell to the Bolsheviks in 1917, Finland declared its independence, pitching the country into civil war. Three more wars between 1939 and 1945—two with the Soviets, one with Germany—left the country scarred by bitter divisions and a punishing debt owed to the Russians. “Still we managed to keep our freedom,” said Pasi Sahlberg, a director general in the Ministry of Education and Culture.
In 1963, the Finnish Parliament made the bold decision to choose public education as its best shot at economic recovery. “I call this the Big Dream of Finnish education,” said Sahlberg, whose upcoming book, Finnish Lessons , is scheduled for release in October. “It was simply the idea that every child would have a very good public school. If we want to be competitive, we need to educate everybody. It all came out of a need to survive."
Practically speaking—and Finns are nothing if not practical—the decision meant that goal would not be allowed to dissipate into rhetoric. Lawmakers landed on a deceptively simple plan that formed the foundation for everything to come. Public schools would be organized into one system of comprehensive schools, or peruskoulu , for ages 7 through 16. Teachers from all over the nation contributed to a national curriculum that provided guidelines, not prescriptions. Besides Finnish and Swedish (the country’s second official language), children would learn a third language (English is a favorite) usually beginning at age 9. Resources were distributed equally. As the comprehensive schools improved, so did the upper secondary schools (grades 10 through 12). The second critical decision came in 1979, when reformers required that every teacher earn a fifth-year master’s degree in theory and practice at one of eight state universities—at state expense. From then on, teachers were effectively granted equal status with doctors and lawyers. Applicants began flooding teaching programs, not because the salaries were so high but because autonomy and respect made the job attractive. In 2010, some 6,600 applicants vied for 660 primary school training slots, according to Sahlberg. By the mid-1980s, a final set of initiatives shook the classrooms free from the last vestiges of top-down regulation. Control over policies shifted to town councils. The national curriculum was distilled into broad guidelines. National math goals for grades one through nine, for example, were reduced to a neat ten pages. Sifting and sorting children into so-called ability groupings was eliminated. All children—clever or less so—were to be taught in the same classrooms, with lots of special teacher help available to make sure no child really would be left behind. The inspectorate closed its doors in the early ’90s, turning accountability and inspection over to teachers and principals. “We have our own motivation to succeed because we love the work,” said Louhivuori. “Our incentives come from inside.”
To be sure, it was only in the past decade that Finland’s international science scores rose. In fact, the country’s earliest efforts could be called somewhat Stalinistic. The first national curriculum, developed in the early ’70s, weighed in at 700 stultifying pages. Timo Heikkinen, who began teaching in Finland’s public schools in 1980 and is now principal of Kallahti Comprehensive School in eastern Helsinki, remembers when most of his high-school teachers sat at their desks dictating to the open notebooks of compliant children.
And there are still challenges. Finland’s crippling financial collapse in the early ’90s brought fresh economic challenges to this “confident and assertive Eurostate,” as David Kirby calls it in A Concise History of Finland . At the same time, immigrants poured into the country, clustering in low-income housing projects and placing added strain on schools. A recent report by the Academy of Finland warned that some schools in the country’s large cities were becoming more skewed by race and class as affluent, white Finns choose schools with fewer poor, immigrant populations.
A few years ago, Kallahti principal Timo Heikkinen began noticing that, increasingly, affluent Finnish parents, perhaps worried about the rising number of Somali children at Kallahti, began sending their children to one of two other schools nearby. In response, Heikkinen and his teachers designed new environmental science courses that take advantage of the school’s proximity to the forest. And a new biology lab with 3-D technology allows older students to observe blood flowing inside the human body.
It has yet to catch on, Heikkinen admits. Then he added: “But we are always looking for ways to improve.”
In other words, whatever it takes.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
LynNell Hancock | READ MORE
LynNell Hancock writes about education and teaches at the Columbia Graduate School of Journalism.
Stuart Conway | READ MORE
Stuart Conway is a photographer based in southeast England.
10 reasons why Finland's education system is the best in the world

From tests to teachers, here are 10 reasons why Finland’s education system is dominating America and the world stage. Image: REUTERS/Attila Cser
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Mike Colagrossi

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Education is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
Time and time again, American students continually rank near the middle or bottom among industrialized nations when it comes to performance in math and science. The Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) which in conjunction with the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) routinely releases data which shows that Americans are seriously lagging behind in a number of educational performance assessments.
Despite calls for education reform and a continual lackluster performance on the international scale, not a lot is being done or changing within the educational system. Many private and public schools run on the same antiquated systems and schedules that were once conducive to an agrarian society. The mechanization and rigid assembly-line methods we use today are spitting out ill-prepared worker clones, rudderless adults and an uninformed populace.
But no amount of pontificating will change what we already know. The American education system needs to be completely revamped – from the first grade to the Ph.D. It’s going to take a lot more than a well-meaning celebrity project to do that…
Many people are familiar with the stereotype of the hard-working, rote memorization, myopic tunnel vision of Eastern Asian study and work ethics. Many of these countries, like China, Singapore, and Japan amongst others routinely rank in the number one spots in both math and science.
Some pundits point towards this model of exhaustive brain draining as something Americans should aspire to become. Work more! Study harder! Live less. The facts and figures don’t lie – these countries are outperforming us, but there might be a better and healthier way to go about this.
Finland is the answer – a country rich in intellectual and educational reform has initiated over the years a number of novel and simple changes that have completely revolutionized their educational system. They outrank the United States and are gaining on Eastern Asian countries.
Are they cramming in dimly-lit rooms on robotic schedules? Nope. Stressing over standardized tests enacted by the government? No way. Finland is leading the way because of common-sense practices and a holistic teaching environment that strives for equity over excellence. Here are 10 reasons why Finland’s education system is dominating America and the world stage.
No standardized testing
Staying in line with our print-minded sensibilities, standardized testing is the blanket way we test for subject comprehension. Filling in little bubbles on a scantron and answering pre-canned questions is somehow supposed to be a way to determine mastery or at least competence of a subject. What often happens is that students will learn to cram just to pass a test and teachers will be teaching with the sole purpose of students passing a test. Learning has been thrown out of the equation.
Finland has no standardized tests. Their only exception is something called the National Matriculation Exam, which is a voluntary test for students at the end of an upper-secondary school (equivalent to an American high school.) All children throughout Finland are graded on an individualized basis and grading system set by their teacher. Tracking overall progress is done by the Ministry of Education, which samples groups across different ranges of schools.
Accountability for teachers (not required)
A lot of the blame goes to the teachers and rightfully so sometimes. But in Finland, the bar is set so high for teachers, that there is often no reason to have a rigorous “grading” system for teachers. Pasi Sahlberg, director of the Finnish Ministry of Education and writer of Finnish Lessons: What Can the World Learn from Educational Change in Finland? Said that following about teachers’ accountability:
"There's no word for accountability in Finnish… Accountability is something that is left when responsibility has been subtracted."
All teachers are required to have a master’s degree before entering the profession. Teaching programs are the most rigorous and selective professional schools in the entire country. If a teacher isn’t performing well, it’s the individual principal's responsibility to do something about it.
The concept of the pupil-teacher dynamic that was once the master to apprentice cannot be distilled down to a few bureaucratic checks and standardized testing measures. It needs to be dealt with on an individual basis.
Cooperation not competition
While most Americans and other countries see the educational system as one big Darwinian competition, the Finns see it differently. Sahlberg quotes a line from a writer named Samuli Paronen which says that:
“Real winners do not compete.”
Ironically, this attitude has put them at the head of the international pack. Finland’s educational system doesn’t worry about artificial or arbitrary merit-based systems. There are no lists of top performing schools or teachers. It’s not an environment of competition – instead, cooperation is the norm.
Make the basics a priority
Many school systems are so concerned with increasing test scores and comprehension in math and science, they tend to forget what constitutes a happy, harmonious and healthy student and learning environment. Many years ago, the Finnish school system was in need of some serious reforms.
The program that Finland put together focused on returning back to the basics. It wasn’t about dominating with excellent marks or upping the ante. Instead, they looked to make the school environment a more equitable place.
Since the 1980s, Finnish educators have focused on making these basics a priority:
- Education should be an instrument to balance out social inequality.
- All students receive free school meals.
- Ease of access to health care.
- Psychological counseling
- Individualised guidance
Beginning with the individual in a collective environment of equality is Finland’s way.
Starting school at an older age
Here the Finns again start by changing very minute details. Students start school when they are seven years old. They’re given free reign in the developing childhood years to not be chained to compulsory education. It’s simply just a way to let a kid be a kid.
There are only 9 years of compulsory school that Finnish children are required to attend. Everything past the ninth grade or at the age of 16 is optional.
Just from a psychological standpoint, this is a freeing ideal. Although it may anecdotal, many students really feel like they’re stuck in a prison. Finland alleviates this forced ideal and instead opts to prepare its children for the real world.
Providing professional options past a traditional college degree
The current pipeline for education in America is incredibly stagnant and immutable. Children are stuck in the K-12 circuit jumping from teacher to teacher. Each grade a preparation for the next, all ending in the grand culmination of college, which then prepares you for the next grand thing on the conveyor belt. Many students don’t need to go to college and get a worthless degree or flounder about trying to find purpose and incur massive debt.
Finland solves this dilemma by offering options that are equally advantageous for the student continuing their education. There is a lesser focused dichotomy of college-educated versus trade-school or working class. Both can be equally professional and fulfilling for a career.
In Finland, there is the Upper Secondary School which is a three-year program that prepares students for the Matriculation Test that determines their acceptance into a University. This is usually based off of specialties they’ve acquired during their time in “high-school”
Next, there is vocational education, which is a three-year program that trains students for various careers. They have the option to take the Matriculation test if they want to then apply to University.
Have you read?
Finland has the most effective universities in the world, finland has one of the world's best education systems. here's how it compares to the us, how equal are the world’s education systems, finns wake up later for less strenuous schooldays.
Waking up early, catching a bus or ride, participating in morning and after school extracurriculars are huge time sinks for a student. Add to the fact that some classes start anywhere from 6am to 8am and you’ve got sleepy, uninspired adolescents on your hands.
Students in Finland usually start school anywhere from 9:00 – 9:45 AM. Research has shown that early start times are detrimental to students’ well-being, health, and maturation. Finnish schools start the day later and usually end by 2:00 – 2:45 AM. They have longer class periods and much longer breaks in between. The overall system isn’t there to ram and cram information to their students, but to create an environment of holistic learning.
Consistent instruction from the same teachers
There are fewer teachers and students in Finnish schools. You can’t expect to teach an auditorium of invisible faces and breakthrough to them on an individual level. Students in Finland often have the same teacher for up to six years of their education. During this time, the teacher can take on the role of a mentor or even a family member. During those years, mutual trust and bonding are built so that both parties know and respect each other.
Different needs and learning styles vary on an individual basis. Finnish teachers can account for this because they’ve figured out the student’s own idiosyncratic needs. They can accurately chart and care for their progress and help them reach their goals. There is no passing along to the next teacher because there isn’t one.
A more relaxed atmosphere
There is a general trend in what Finland is doing with its schools. Less stress, less unneeded regimentation and more caring. Students usually only have a couple of classes a day. They have several times to eat their food, enjoy recreational activities and generally just relax. Spread throughout the day are 15 to 20-minute intervals where the kids can get up and stretch, grab some fresh air and decompress. This type of environment is also needed by the teachers. Teacher rooms are set up all over Finnish schools, where they can lounge about and relax, prepare for the day or just simply socialize. Teachers are people too and need to be functional so they can operate at the best of their abilities.
Less homework and outside work required
According to the OECD, students in Finland have the least amount of outside work and homework than any other student in the world. They spend only half an hour a night working on stuff from school. Finnish students also don’t have tutors. Yet they’re outperforming cultures that have toxic school-to-life balances without the unneeded or unnecessary stress.
Finnish students are getting everything they need to get done in school without the added pressures that come with excelling at a subject. Without having to worry about grades and busy-work they are able to focus on the true task at hand – learning and growing as a human being.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Education .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How universities can use blockchain to transform research
Scott Doughman
March 12, 2024

Empowering women in STEM: How we break barriers from classroom to C-suite
Genesis Elhussein and Julia Hakspiel
March 1, 2024

Why we need education built for peace – especially in times of war
February 28, 2024

These 5 key trends will shape the EdTech market upto 2030
Malvika Bhagwat
February 26, 2024

With Generative AI we can reimagine education — and the sky is the limit
Oguz A. Acar
February 19, 2024

How UNESCO is trying to plug the data gap in global education
February 12, 2024
Study: Homework Matters More in Certain Countries
Homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor, say authors of a new study.
Homework Matters, Depending on Your Country
For years, researchers have been trying to figure out just how important homework is to student achievement. Back in 2009, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development looked at homework hours around the world and found that there wasn’t much of a connection between how much homework students of a particular country do and how well their students score on tests.
Some top achieving countries, like Singapore, assign their students lots of homework. But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD’s international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.
But now, five years after the earlier homework study, OECD researchers have drilled down deeper into homework patterns, and they’re finding that homework does play an important role in student achievement within each country . Specifically, they found that homework hours vary by socioeconomic status. Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also tend to get higher test scores. So the authors conclude that homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor.

Chart created by Jill Barshay | Hechinger Report; data from OECD
It’s not just that poor kids are more likely to skip their homework, or don’t have a quiet place at home to complete it. It’s also the case that schools serving poor kids often don’t assign as much homework as schools for the rich, especially private schools, explained Francesca Borgonovi, one of the authors of the study, titled “ Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? ”
“When you look within countries at students who are learning in the same educational system and they do more homework, then those students do much better,” said Borgonovi. “There is an advantage for putting extra hours in homework.”
A stark example of this rich-poor homework gap is in Singapore. Students in the top quarter of the socio-economic spectrum spend about 11 hours on homework a week, 3 hours more than low-income students in the bottom quarter of the socio-economic spectrum. Each extra hour of homework was associated with 18 more points on the PISA math exam. So three hours adds up to more than 50 points. That’s huge. To put that in perspective, if you added 50 points to the average U.S. math score, we’d be a top 10 nation instead of number 36.
A key factor is what Borgonovi said about “learning in the same educational system.” Some school systems are designed to rely on homework, perhaps using independent study as a substitute for what could otherwise be learned in school. “If you are prepared to change the system, that’s great,” said Borgonovi. “But until you do so, if the system is based on homework, then you should do more of it.”

Students in Shanghai, a region in China that now leads the world in PISA test scores, do a whopping 14 hours of homework a week, on average. Wealthier students there do 16 hours. Poorer students do just under 11 hours. Interestingly, however, there was no association between the extra homework hours that the wealthier Shanghai kids put in and their PISA test scores. Perhaps that’s because there are diminishing marginal returns to homework after 11 hours of it!
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours.
But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged from a decade ago and possibly rising. Wealthier students typically do eight hours of homework a week, about three hours more than low income students. But unlike in most countries, where more homework is associated with higher PISA test scores, that’s not the case here.
“For the United States, we don’t have homework reinforcing inequality,” Borgonovi said.
Another team of researchers, Ozkan Eren and Daniel J. Henderson, found mixed results for how effective homework is in the United States, in a 2011 study, “ Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? “ published in the Economics of Education Review. For math, there were huge benefits for the 25,000 eighth graders they studied. But not for English, science or history. And the math boost was much stronger for white students than for blacks. In other words, when a typical black student did more homework, his math test scores didn’t go up as much.
That’s perhaps a clue that even if you could magically get low-income children in other countries to do as much homework as their high-income peers, as the OECD researchers are suggesting, you might not raise their PISA test scores very much.
Indeed, Borgonovi isn’t really advocating for more homework. She says that high quality teachers and instruction are much more important to student outcomes than homework is. To be sure, some amount of homework is good, Borgonovi said, to teach kids how to plan ahead, set goals and work independently. But more than four hours of homework a week, she said, isn’t very beneficial.
“It would be better to redesign the system to have less homework,” said Borgonovi. “But that is hard to do.”
* The OECD looked at socio-economic status and not income exclusively. So the child of a university professor, for example, might still be in the high income category even if his parents don’t make very much money.
Join the Conversation
Tags: education , K-12 education , students , Finland , Singapore

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

House Passes $1.2T Funding Package
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder March 22, 2024

What to Know: $1.2T Spending Bill
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder March 21, 2024

New York Poised to Seize Trump Holdings
Lauren Camera March 21, 2024

Who Could Be Trump’s VP?

Key Signs Confirm Economy’s Strength
Tim Smart March 21, 2024

5 Takeaways From the Fed Meeting

The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education

Homework matters depending upon which country you live in

Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.
Get important education news and analysis delivered straight to your inbox
- Weekly Update
- Future of Learning
- Higher Education
- Early Childhood
- Proof Points

For years, researchers have been trying to figure out just how important homework is to student achievement. Back in 2009, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) looked at homework hours around the world and found that there wasn ’t much of a connection between how much homework students of a particular country do and how well their students score on tests. Some top achieving countries, like Singapore, assign their students lots of homework. But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD’s international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.

But now, five years after the earlier homework study, OECD researchers have drilled down deeper into homework patterns, and they’re finding that homework does play an important role in student achievement within each country . Specifically, they found that homework hours vary by socioeconomic status. Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also tend to get higher test scores. So the authors conclude that homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor.
It’s not just that poor kids are more likely to skip their homework, or don’t have a quiet place at home to complete it. It’s also the case that schools serving poor kids often don’t assign as much homework as schools for the rich, especially private schools, explained Francesca Borgonovi, one of the authors of the study, titled “ Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? ”
“When you look within countries at students who are learning in the same educational system and they do more homework, then those students do much better,” said Borgonovi. “There is an advantage for putting extra hours in homework.”

A stark example of this rich-poor homework gap is in Singapore. Students in the top quarter of the socio-economic spectrum spend about 11 hours on homework a week, 3 hours more than low-income students in the bottom quarter of the socio-economic spectrum. Each extra hour of homework was associated with 18 more points on the PISA math exam. So three hours adds up to more than 50 points. That’s huge. To put that in perspective, if you added 50 points to the average U.S. math score, we’d be a top 10 nation instead of number 36.
A key factor is what Borgonovi said about “learning in the same educational system.” Some school systems are designed to rely on homework, perhaps using independent study as a substitute for what could otherwise be learned in school. “If you are prepared to change the system, that’s great,” said Borgonovi. “But until you do so, if the system is based on homework, then you should do more of it.”
Students in Shanghai, a region in China that now leads the world in PISA test scores, do a whopping 14 hours of homework a week, on average. Wealthier students there do 16 hours. Poorer students do just under 11 hours. Interestingly, however, there was no association between the extra homework hours that the wealthier Shanghai kids put in and their PISA test scores. Perhaps that’s because there are diminishing marginal returns to homework after 11 hours of it!
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours.
But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged from a decade ago and possibly rising. Wealthier students typically do eight hours of homework a week, about three hours more than low income students. But unlike in most countries, where more homework is associated with higher PISA test scores, that’s not the case here.
“For the United States, we don’t have homework reinforcing inequality,” Borgonovi said.
Another team of researchers, Ozkan Eren and Daniel J. Henderson, found mixed results for how effective homework is in the United States, in a 2011 study, “ Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? ” published in the Economics of Education Review. For math, there were huge benefits for the 25,000 eighth graders they studied. But not for English, science or history. And the math boost was much stronger for white students than for blacks. In other words, when a typical black student did more homework, his math test scores didn’t go up as much.
That’s perhaps a clue that even if you could magically get low-income children in other countries to do as much homework as their high-income peers, as the OECD researchers are suggesting, you might not raise their PISA test scores very much.
Indeed, Borgonovi isn’t really advocating for more homework. She says that high quality teachers and instruction are much more important to student outcomes than homework is. To be sure, some amount of homework is good, Borgonovi said, to teach kids how to plan ahead, set goals and work independently. But more than four hours of homework a week, she said, isn’t very beneficial.
“It would be better to redesign the system to have less homework,” said Borgonovi. “But that is hard to do.”
* The OECD looked at socio-economic status and not income exclusively. So the child of a university professor, for example, might still be in the high income category even if his parents don’t make very much money.
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Jill Barshay SENIOR REPORTER
(212)... More by Jill Barshay
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
The Finnish miracle
by: Hank Pellissier | Updated: June 12, 2023
Print article

Can you name a famous person in Finland? Historical episode? Imposing landmark? Foodstuff? It’s not that Finland doesn’t have its share of Olympic athletes, brilliant architects, and technology moguls, but “Nokia” is all most people can mutter when asked about this small northern nation.
Unless you’re a teacher. Then the word “Finland” fills you with awe. Because everyone in the schooling profession knows that Finland is the international all-star of education.
In 2006 the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) conducted a survey of 15-year-olds’ academic skills from 57 nations. Finland placed first in science by a whopping 5% margin, second in math (edged out by one point by Chinese Taipei), and third in reading (topped by South Korea ).
Comparisons that involve so many variables are … difficult. Some might say impossible. Still, just a glance at PISA’s scores year after year prompts the question: How does Finland churn out so many avid learners?
“No sweat,” except in the saunas
At first glance, the Finnish educational system looks like it would only produce hippie slackers. Check out the casual amenities : Schools often have lounges with fireplaces but no tardy bells. Finnish students don’t wear uniforms, nor do they often wear shoes. (Since Finns go barefoot inside the home, and schools aspire to offer students a nurturing, homey environment, the no-shoe rule has some pedagogical logic.) And although academic standards are high, there’s not the grind one associates with high-performance schooling. Never burdened with more than half an hour of homework per night, Finnish kids attend school fewer days than 85% of other developed nations (though still more than Americans), and those school days are typically short by international standards.
Finnish teachers enjoy an equally laid-back arrangement. They work an average of 570 hours a year, nearly half the U.S. total of 1,100 hours. They also dress casually and are usually called by their first names (Aino, Helmi, Viivi, Eetu, etc.).
Is the secret massive financial investment? No. Finland spends only $7,500 per student, considerably less than the United States’ average $8,700.
So how does Finland produce the world’s best young scholars via minimal hours and cash? Since PISA began ranking nations and revealing Finland’s special sauce, plane-loads of inquisitive teachers from every corner of the globe have been making pilgrimages to this educational mecca. Here’s a taste of what they’ve observed:
More cred than doctors
The level of respect accorded to Finnish teachers tends to grab attention, especially in America where teaching is viewed as a “fallback” profession occupied primarily by the lower third of college graduates. That equation is flipped in Finland, where teachers boast the highest vocational status (followed by physicians.) A full 25% of Finnish youngsters select teaching as their career goal, but only a fraction succeed. Only 10% to 13% of applicants gain acceptance into the masters’ degree in education program.
After all this hard work, the rewards are generous, but not necessarily financially so. Teachers earn a generous $45 to $50 per hour for elementary school, $75 to $80 for secondary school. Yet some far lower-performing nations such as Spain and Germany pay teachers more. Instead, Finnish teachers enjoy immense independence. Allowed to design their own lesson plans and choose their own textbooks (following loose national guidelines), Finnish teachers regard their work as creative and self-expressive.
Free preschool, free college
Finnish toddlers have access to free preschools supervised by certified college graduates. Ah, you wonder — are the little innocents getting a jump-start there, reading and writing all day? Wrong! Truth is, Finland’s preschools offer no academics but plenty of focus on social skills, emotional awareness, and learning to play. Remarkably, Finnish children don’t approach reading until age seven (Waldorf nation?). They learn other concepts first, primarily self-reliance. One American observer noted that first-graders were expected to walk unescorted through the woods to school and lace up their own ice skates.
Twenty colleges exist in Finland, and they’re all free. Imagine the financial relaxation this provides for both parents and children. Universities are not widely stratified either; the disparity between the “best” and “worst” is not terribly large.
Curbing the dog-eat-dog competition
Americans give lip service to the notion that “all men are created equal,” but our appetite for competition creates an intense focus on ranking low and high performers — whether they’re schools or students.
Finland downplays educational competition in a number of ways. Schools aren’t ranked against each other, and teachers aren’t threatened with formal reviews. At many schools, teachers don’t grade students until the fifth grade, and they aren’t forced to organize curriculum around standardized testing. Gifted students aren’t tracked into special programs, invited into honor societies, or chosen to be valedictorians. Instead, struggling students receive free extra tutoring. After ninth grade, students attend either an academic program (53%) or vocational one (47%) — this flexibility results in a 96% graduation rate, dwarfing the United States’ measly 75%. Finally, since there are no private schools to speak of, there’s no sense that the best students are being skimmed off the top.
Overall, such attitudes go hand in hand with Finland’s socialist-style egalitarian society, which focuses on meting out fees and services according to need rather than merit. Even parking ticket penalties are determined according to income: A wealthy sausage factory heir was fined $204,000 for going 50 miles per hour in a 25-mph zone!
Additional differences
Finnish schools lack some of the extracurriculars — such as sports teams or musical bands — considered so essential to U.S. high schools. But free lunches are available to all students. “School choice” doesn’t exist; everyone goes to the neighborhood school. Students learn at least three languages: Finnish, Swedish, and English. Finally, Finland is a culture of readers, with a great library system and book mobiles reaching even remote locations.
Although the Finnish system seems antithetical to South Korea’s (the Asian nation placed second in the 2007 PISA surveys), the two small countries share much in common. Both cultures hold teachers in the highest esteem. Both achieved independence relatively recently — Finland in 1917, South Korea 1946 — and both are resource-poor nations that decided education was the path out of poverty. Finnish and Korean languages are easy to read and spell; they don’t have the illogical phonetics of English.
Comparing lingonberries to hamburgers
Is it fair to compare the small, homogenous northern nation to our roiling melting pot of diversity? Many experts say no. After all, given our higher immigration rate and wider socioeconomic stratification, our schools tend to become social experiments not simply for learning but also for many other social functions schools aren’t designed to handle.
Still, should these challenges prevent us from learning what we can from Finland’s schools? If nothing else, it’s worth noting the central importance of inspired, highly educated teachers and what keeps the United States from doing the same.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

Why your neighborhood school closes for good – and what to do when it does

5 things for Black families to consider when choosing a school

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience

27 Surprising Finnish Education System Facts and Statistics
There has been a lot of press recently about how the education system in Finland is one of the best in the world and how they are using radical (compared with the UK and the US) ideas to help achieve their status as one of the best.
Anywhere you look the proof doesn’t seem to lie, yet how exactly is the Finnish Education system achieving such greatness? Their students outperform students in the US and the UK in most, if not all areas and their teachers enjoy a much better work life balance. Let’s take a dive into some of the things the Finnish are doing.
The Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) , a survey taken every three years by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) routinely releases data which shows that Americans and British students are seriously lagging behind in many educational performance assessments.
The Finnish Education System
#1 Finnish children enter education at a later age than in many countries. They start school at age 7 and believe that “starting children in school before they’re naturally developmentally ready has no scientifically proven long-term advantage”.
#2 Prior to age 7, Finnish school children can attend day care/nursery school but they do not have formal education whilst there, Instead, they focus on creative play . “They need time to play and be physically active. It’s a time for creativity”. says Tiina Marjoniemi, head of Franzenia daycare center in Helsinki. The Guardian
#3 For every 45 minutes of learning, students enjoy 15 minutes of play.
#4 School is only compulsory for 11 years, meaning students can leave education at age 18. Everything after that is optional. This idea is thought to prepare Finnish students for the real world.
#5 Finish students are not measured at all for the first six years of their education.
#6 Students in Finland only have to sit for a centralized exam (National Matriculation Exam) at the age of 18-19 years old (after 12 years of school).
Finland School Hours
#7 Finnish students do the least number of class hours per week in the developed world, yet get the best results in the long term. The school day starts between 8-9am and is finished by 2pm.
Finland Education Ranking
#8 The schools in Finland are not ranked in any way, there are no comparisons made between schools, regions, teachers or even students. They believe that cooperation is the key to success, not competition.
#9 Finnish Teachers are some of the most qualified in the world. The requirements for becoming a teacher in Finland are set very high, only around the top 10% of applicants are successful and all of those have a masters degree (which incidentally is fully subsidised!).
#10 Finnish teachers have the same status as doctors and lawyers. ( I wish that was the case in the UK! )
#11 Finnish Teachers are not graded. This is probably a direct result of their rigorous selection process and because of this, in Finland, they don’t feel the need to constantly assess and grade their teachers. If a teacher isn’t performing satisfactorily, it is up to the schools principal/head to deal with it. Pasi Sahlberg, director of the Finnish Ministry of Education and writer of Finnish Lessons, said this about teachers’ accountability:
“There’s no word for accountability in Finnish… Accountability is something that is left when responsibility has been subtracted.”
#12 Schools are not inspected. School inspections were actually abolished in Finland in the early 1990s. They have the ideology that they can help direct and assist through support and funding. Again, they trust the professionalism of teachers and school leaders. Schools are encouraged to self-evaluate along.
#13 There are no selective schools or private schools. One of the reasons why there is no competition between Finnish schools is that all schools are funded through public funds. No competition = level playing field.
#14 All Finnish school children receive free school meals, all of them, all the way through school!. There has been a healthy hot lunch served to all students been since 1943 for the whole 9 years at school. ( Huffingtonpost.com )
#15 Finnish students all have access to support that is individually based on their specific needs from the start of their school career. They believe that every child has some special needs and therefore special education is for everyone.
#16 The Basics are the priority. Rather than focus on increasing test scores and dominating in math, science and English, the Finnish education system focus on creating a healthy and harmonious environment for students and learning. The ideology of the Finnish education system is that education should be an “ instrument to balance out social inequality “.
#17 Finnish students have the same teacher for up to 6 years of their school career. This is one of the pillars of their harmonious education environment ideology. It allows student/teacher relationships to grow year on year, allowing a much deeper level of trust and respect than only having one year.
Finland Education Curriculum
#18 Finnish Students have less homework than any other student on the planet. Even with fewer school hours, they are still getting everything they need to be done whilst at school. This, in turn, builds on a Finnish child’s ability to grow and learn into a happy and responsible adult.
#19 All classes are mixed ability. This is unpopular in a lot of education systems in the UK and the US (I know, my own school recently adopted this policy (Personally, I love it) and there can be a lot of teachers that don’t like it. However, some of the most successful education systems have mixed ability classes, so it does work!
#20 Finnish Students learn more languages. They learn Finnish from their first day at school. At age 9 they start learning their second language (which is usually English). By age 11 they start learning Swedish, which is Finland’s second language. Many students even start learning a fourth language when they are 13. They are only tested on their first two languages in the final exam at the end of high school.
#21 Teachers only generally spend 4 hours a day in the classroom and have 2 hours every week for professional development , thus reducing teacher stress.
#22 The Finnish national curriculum is a broadly based guideline, allowing teachers to use their own style and ideas in the classroom. This builds on the trust that the Finnish education system has in its teachers.
Finland Education Statistics
#23 93% of students graduate from high school. More than in the US.
#24 66% of high school students go on to further education (college or vocational courses).
#25 Finland spends about 30% less per student than the US, the UK, Japan and Germany. ( OECD Indicators )
#26 Just under 100% of 9th-grade students in Finland go on to high school. This figure includes most of the severely disabled children ( smithsonian.com )
#27 43% of those students in further education (16+) attend vocational school.
So there we have it, Finnish students and teachers are part of a great system. Having worked with several Finnish teachers, I can tell you that their ideology and these strategies work, very well!
Similar Posts:
- 15 Learning Theories in Education (A Complete Summary)
- Discover Your Learning Style – Comprehensive Guide on Different Learning Styles
- Distance Learning: The Ultimate Guide to Online Learning
2 thoughts on “27 Surprising Finnish Education System Facts and Statistics”
As a student in Finland I realized some of this information is outdated. #1 – It states that children start their education at the age of 7. This is no longer correct because they can start is at the ages of 5, 6 or 7. Typically they do at ages 6 or 7. #3 – It is very school based. some schools do not follow this and it depends a lot. A school can have 45 minute lessons and a 5 min break. #4 – Over resent years it has changed into 9 years of compulsory education (basic education) 2-4 years of upper secondary studies/vocational application. #6 – the matriculation examination is at the age of 18 (typically the last two years of upper secondary studies). Not all students do this because they choose to go to vocational school. #7 – It is again very school based because some schools follow periods (certain subjects for 6 weeks and then the timetable changes). Most schools and students most likely have days from 8am-3pm. It depends a lot what day it is. #16 – To apply to upper secondary school and vocational schools they calculate the average of math, English, Finnish, Swedish, history, civics, religion/ethics, physics, chemistry, biology, geography, health education. #17 – Pert of this is true. Best case scenario they do have the same teacher for six years, but most of the time teachers are only qualified to teach certain grade levels. #18 – The amount of homework totally depends on the teacher. It depends how much the teacher wants them to do. Most times homework is tasks that they did not get done on lessons or ones that deepen the meaning of the subject. #20 – there are a lot of confusing things about this. In most schools the child starts learning Finnish from first grade onwards. From grade 3 onwards they start learning English. From grade 5 onwards they can decide if the want another language (typically French, German or Spanish). From grade 6 onwards they start learning Swedish. In the matriculation examinations the test Finnish and a second home language so either Swedish or English. #21 – Subject teachers can have as many hours a day as the pupils. This all depends how many subjects they are qualified to teach.
According to the Bildung Review the Finnish educational system is failing. Not testing and focusing only on cooperation seems to have failed. I hope Finland will shift in the proper educational focus.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Countries Who Spend the Most Time Doing Homework
Homework is an important aspect of the education system and is often dreaded by the majority of students all over the world. Although many teachers and educational scholars believe homework improves education performance, many critics and students disagree and believe there is no correlation between homework and improving test scores.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an intergovernmental organization. With headquarters in Paris, the organization was formed for the purpose of stimulating global trade and economic progress among member states. In 2009, the OECD conducted a detailed study to establish the number of hours allocated for doing homework by students around the world and conducted the research in 38 member countries. The test subjects for the study were 15 year old high school students in countries that used PISA exams in their education systems. The results showed that in Shanghai, China the students had the highest number of hours of homework with 13.8 hours per week. Russia followed, where students had an average of 9.7 hours of homework per week. Finland had the least amount of homework hours with 2.8 hours per week, followed closely by South Korea with 2.9 hours. Among all the countries tested, the average homework time was 4.9 hours per week.
Interpretation of the data
Although students from Finland spent the least amount of hours on their homework per week, they performed relatively well on tests which discredits the notion of correlation between the number of hours spent on homework with exam performance. Shanghai teenagers who spent the highest number of hours doing their homework also produced excellent performances in the school tests, while students from some regions such as Macao, Japan, and Singapore increased the score by 17 points per additional hour of homework. The data showed a close relation between the economic backgrounds of students and the number of hours they invested in their homework. Students from affluent backgrounds spent fewer hours doing homework when compared to their less privileged counterparts, most likely due to access to private tutors and homeschooling. In some countries such as Singapore, students from wealthy families invested more time doing their homework than less privileged students and received better results in exams.
Decline in number of hours
Subsequent studies conducted by the OECD in 2012 showed a decrease in the average number hours per week spent by students. Slovakia displayed a drop of four hours per week while Russia declined three hours per week. A few countries including the United States showed no change. The dramatic decline of hours spent doing homework has been attributed to teenager’s increased use of the internet and social media platforms.
More in Society

Countries With Zero Income Tax For Digital Nomads

The World's 10 Most Overcrowded Prison Systems

Manichaeism: The Religion that Went Extinct

The Philosophical Approach to Skepticism

How Philsophy Can Help With Your Life

3 Interesting Philosophical Questions About Time

What Is The Antinatalism Movement?

The Controversial Philosophy Of Hannah Arendt

There's no Homework in Finland
THERE'S No Homework In Finland Finland's school system accomplishes some impressive feats: 93% THEIR HIGH SCHOOL 78% GRADUATION RATE IS AT 93%. 75% COMPARED TO 78% IN CANADA. AND 75% IN THE US. %! ABOUT 2 IN 3 STUDENTS IN FINLAND WILL GO ON TO COLLEGE. That's the highest rate in all of Europe. AND THEIR TEST SCORES DOMINATE EVERYONE ELSE. Mean scores for PISA test (Program for International Student Assessment) 2006. 520 530 540 550 560 570 Finland Hong Kong Canada Taiwan Estonia Japan New Zealand Australia Netherlands Liechtenstein So what makes Finnish students so successful? STUDENTS GET PLENTY OF TEACHER INTERACTION. Finland and New York City have the same number of teachers. But Finland has nearly half the number of students. FINLAND NYC Students: Students: 600,000 ALMOST 1.1 MILLION Student to teacher ratio: Student to teacher ratio: 1 TO 12 1 TO 24 THOUGH 1 IN 3 FINNISH STUDENTS RECEIVES SOME SORT OF SPECIAL HELP IN SCHOOL... There are no separate classrooms for accelerated learning or special education. STANDARDIZED TESTING IS KEPT TO A MINIMUM. BEFORE A NEW YORK STUDENT REACHES HIGH SCHOOL, HE OR SHE WILL HAVE TAKEN 10 STANDARDIZED TESTS. Collectively, US students take 100 million standardized tests a year. FINLAND'S ONLY STANDARDIZED TEST IS TAKEN WHEN STUDENTS ARE 16 YEARS OLD. KIDS HAVE MORE TIME TO BE KIDS. AN AVERAGE US 5TH Finnish students GRADER HAS 50 MIN. rarely do homework OF HOME WORK until their teens. PER DAY. 10-11 YRS. ÖLD 13-14 YRS. ÖLD And while US elementary students average 27 minutes of recess... ... STUDENTS IN FINLAND GET 27 MIN 75 MIN ABOUT 75 MINUTES DAY. Most importantly? Finland knows good teachers are essential. TEACHERS IN FINLAND ARE ALL REQUIRED TO HAVE A MASTER'S DEGREE. (Which is fully subsidized by the state.) ONLY THE TOP 10% OF GRADUATES ARE ACCEPTED INTO TEACHING PROGRAMS. AND FINLAND'S TEACHERS ARE AS ESTEEMED AS THEIR DOCTORS OR LAWYERS. The rest of the world could learn a lot from you, Finland. Sources: [1] http://www.scribd.com/doc/82204617/Global-Graduation-Rates-By-Country-Source-OECD [2] http://today.msnbc.msn.com/id/48343652/ns/today-back_to_school/t/home work-overload-gets-f-experts/ [3] http://www.businessinsider.com/finland-education-school-2011-12?op=1 [4] http://seattletimes.com/html/localnews/2019676789_finland14m.html [5] http://edpolicy.stanford.edu/sites/default/files/publications/secret-finland%E2%80%99s-success- [6] http://www.time4learning.com/testprep/index.php/new-york-state-standardized-test-prep/educating-teachers.pdf This work is under a Creative Commons license. Brought to you by: Online Classes.org BY NO ND OnlineClasses.org
You may also like...
For hosted site:
For wordpress.com:
20+ Cool Things to Know about the Finnish Education System
Finland’s education system fascinates most people interested in the best approaches to learning. Our schools are known for high-quality teaching and inclusive learning environments and aim to offer each student the same opportunities to succeed, whatever their background.
In this article, I will explore some of the features that have set the Finnish education system apart and what is so cool about it that people worldwide want to study it.
Table of Contents
What makes Finland’s education system successful?
What is the finnish approach to early childhood education, what is the finnish approach to education in comprehensive school, how long is the school day in finland, what is the typical school day like in finland, do finnish students really have little to no homework, what is the role of standardized testing in finnish education, how are students assessed in finland’s education system, what subjects are taught in finnish schools, what are the differences between finnish and american education systems, how do finnish schools accommodate students with special needs, is education free in finland, how are finnish schools funded, how much do finnish teachers get paid, teacher training in finland, what is the dropout rate in finland’s education system, what is the literacy rate in finland, why is finland’s education system considered one of the best in the world.
The idea that Finland’s education system outperforms many others in the world comes from excellent outcomes like success in the international PISA test.

In previous years, Finnish pupils and students have done remarkably well in these tests despite the lack of standardized testing in Finnish schools. At the same time, they enjoy more freedom and less homework than many of their counterparts.
This has been a subject of a lot of debate. Is the success because of well-trained and motivated teachers who are valued? Is it because of the national curriculum?
According to the World Economic Forum, Finland’s education system is the best in the world , at least partly because of
- No standardized testing
- Teacher training and requirements
- Making the basics a priority
- Starting age
You can dive deep into the topic as there are a number of books available and countless expert opinions you can explore. But these things are something most Finns can agree are good about the Finnish system.
One of the things many Finns remember from their early school years and kindergarten is playing outside.
Serious school work starts relatively late in Finland, and early childhood education (ECEC) focuses on the right to play, learn, and participate.

Children usually start their first school year at the age 7. They then continue to attend comprehensive school between the ages 7-16 through classes 1-9.
All municipalities in Finland offer preschool education, which consists of at least 700 hours of learning skills in creativity, language, and other areas that will help at school. There are no specific subjects or tests but different competence areas. 4 hours of preschool education a day is provided for free at kindergartens for every 5- and 6-year-old.
Learning at this level differs greatly from countries where school starts at ages 4-5. For example, in the UK, 6-year-olds take part in national curriculum assessments, while Finnish children don’t generally take part in national tests during comprehensive school.
In Finland, all children must receive comprehensive education, and this consists of years 1 to 9 of comprehensive school.
Recent changes now require students to also attend school until they either complete their secondary education like upper secondary school or vocational training in a vocational college, or turn 18, which ever comes first.
The vast majority of schools in Finland, including around 80 private schools, follow the national core curriculum. Pupils attend a local school in their assigned catchment area, and “school shopping” is harder and less common than in some other countries.
The purpose of basic education is “to enable pupils to evolve into humane and ethically responsible members of society as well as to provide them with the knowledge and skills needed in life”, according to the ministry of education and culture . Comprehensive school covers a total of 20 subjects, and learning some languages is also compulsory.

How does Finland’s education system compare to other countries?
In general, the Finnish education system stands out because of
- Master’s level teacher training
- More chances to play and take breaks
- Shorter school days and less homework
- No fees, free meals and free books
There are also downsides. Since students learn in the same groups regardless of being talented in a subject, some find there are no opportunities to make fast progress. It is often possible to attend a weighted-curriculum education emphasizing languages, maths, music, or arts, for example.
The same goes for children requiring more time or attention to help them learn. In many cases where the child has special needs, they can get a personal assistant.
The maximum length of a Finnish school day is determined by grade. For 1st and 2nd grade, when the children are 7 and 8 years old, they can have a maximum of five hours of school a day. From there on, the maximum is 7 hours a day, with a little extra allowed if they attend a class that follows a weighted curriculum.
There are also guidelines for the minimum amount of teaching each student has the right to receive weekly.
Each lesson consists of around 45 minutes of teaching. There are breaks between learning, but they can have different lengths. 15-minutes between lessons is common, and the lunch break is at least 30 minutes long.
For your 15-minute break, you always head outdoors – unless it’s -15 degrees Celsius or colder. I have fond memories throughout the primary school of how fun the breaks were. Playing outdoor games or soccer until the bell rang.
A typical school day usually starts sometime between 8 am and 9 am. After some lessons and a few short breaks, a free lunch is served, usually between 11 and 12. Lunch breaks are usually long enough for the children to play outside after lunch.

Lessons continue into the afternoon before it’s time to go home. Cities provide after-school activities for young pupils.
If you live far away from your school, the school provides you with free bus or group taxi rides that take you closer to home.
Despite what you might have heard, Finnish pupils get homework.
It may be a little less than in some countries, with some studies citing an average of 30 minutes of homework a day. Since the days are relatively short, there is plenty of time to get it done before hobbies and play.
Finnish students usually take their first standardized test, the matriculation examination, at 18 and only if they attended an upper secondary school and in their chosen topics.
Together with subject-specific entrance examinations, the results from this examination are used to apply to study a University degree.
That doesn’t mean that pupils have no tests, though.
Since the schools follow the national core curriculum, students have regular tests and exams based on learning goals.
Students get grades on each subject they study based on their performance throughout the year from 4th grade onward. For the youngest pupils, the teacher usually writes notes on how they did at regular intervals.
At the end of year 9, students get a final grade for each subject they studied. These grades are used to apply to upper secondary schools and vocational training.

All pupils in Finland study
- Finnish or Swedish (mother tongue and literature)
- The other national language (Swedish or Finnish)
- At least one other foreign language
- Environmental studies
- Health education and physical education
- Religion or ethics, history, and social studies
- Mathematics, biology, chemistry, physics, and geography
- Music, visual arts, crafts, and home economics
These differences are often mentioned about Finland:
- Finns start school at age 7
- Less homework and shorter school days
- Goal of testing is to see if the child needs help with learning, not comparisons
- No great differences between schools
- Schools are publicly funded and free to attend
- Schools follow the national core curriculum
- Books and free lunch provided
Some other differences that might be interesting include that teacher requirements in the US vary from state to state. In contrast, Finnish teachers need a specific Master’s degree and most people value the profession. Only 34% of US teachers feel the general public values their profession.
How does Finland’s education system promote equity and equality?
Finland’s education system is based on the idea that everyone should be able to have a basic level of skills and learning regardless of their background.
That’s why schools are publicly funded, and students get books, free school meals, and, in some cases, even devices they might need for their studies. Finnish schools don’t have school uniforms.

There are guidelines for what the schools and cities need to provide to help children with special needs, but each case is assessed based on the circumstances. The aim is to provide support while the child attends normal classes. Different levels of support can be arranged depending on what the situation calls for.
Primary education is free in Finland. Higher education is also free, but students have to do well in the matriculation examination and often take an entrance examination to be accepted to study for a degree. Students from outside the EU have to pay fees for higher education programmes.
Finnish schools are publicly funded through the government, municipalities, and the European Union (mostly higher education).
What is the role of teachers in Finland’s education system?
Finnish teachers are valued professionals with Master’s degrees and meet the requirements to teach their subjects. The degree focuses on skills for independent problem-solving.
Teachers design the classes they teach according to the national core curriculum. Their role is to support and advance the development, learning, and skills of children and young people.
The average salary of a teacher in Finland ranges from 3680 to 4090 € depending on what grades they teach. The number of years they have worked affects how much they are paid, and 10% make 2990 € or less a month.
Most teachers in Finland have long paid vacation times: 14 weeks annually.
There are two routes to becoming a teacher in Finland. You can start studying the subject matter at University and add pedagogical studies to become qualified to teach that specific subject or you can apply directly to study to become a subject teacher.

The same Master’s level education is required to become a classroom teacher for a comprehensive school. To teach at the preschool level, teachers must have a bachelor’s degree in educational science.
Finland’s education system became well known after success in the PISA surveys from 2000 onward. While the results have declined since then – some say partly due to challenges like digitalization which takes some time to adapt to – there are still many positive outcomes worth pointing out.
For comprehensive school, the number is below 1% compared to 25% in the US.
Finland’s literacy rate has been 100% for over 15-year-olds. Finland has also been ranked as the most literate nation in the world.
Do you have more questions about Finland’s education system? I will answer them in the comments!
Here are some other facts about Finland that you might find interesting:
Finnish Culture: Discovering Everything You Need to Know
50 Cool Things Finland is Known for
Moving to Finland: Living in the 20 Largest Cities
Ready to speak finnish?

Join my praised free class and speak Finnish words in 20 minutes!

About Varpu I’m the founder of Her Finland. I love cultural tidbits, aha moments, Finnish folklore, and cinnamon buns. My newest interest is learning bird songs. Read more about me..
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Saturday 15th of July 2023
Congratulations, Varpu! I'm excited for you, and I know your students will be lucky to have you as a teacher. It makes sense that the frequent and lengthy breaks outside would be conducive to learning - our brains need relaxation time in order to really absorb new information. Sadly, here in the U.S., our students don't get as many or as lengthy breaks, especially in areas where principals/administrators are afraid long breaks might give students time to start fights or misbehaving. I think our students' brains might be a little stressed out.
I'm a science teacher myself, having taught science in elementary school, middle school, and high school (biology), and I have a master's degree. I was wondering whether my degree would transfer over there. However, I am more interested in teaching younger kids these days, and I'm working on my multiple subject credential, as well as taking early childhood education (ECE) classes. Do you think the Finnish government would accept this kind of training from the U.S.? I would love to know your opinion!
Wednesday 12th of July 2023
I know several Finnish teachers and every one one of them were of good reputation and wanted the best for their students.Here in the United states,many states have looked at the Finnish school model,but I can bet the teachers union would not go along with it.
17K+ students! 30% OFF 🔥Spoken Finnish ➤
How Finland Keeps Kids Focused Through Free Play
An American teacher in Helsinki questioned the national practice of giving 15 minute breaks each hour—until he saw the difference it made in his classroom.

Like a zombie, Sami—one of my fifth graders—lumbered over to me and hissed, “I think I’m going to explode! I’m not used to this schedule.” And I believed him. An angry red rash was starting to form on his forehead.
Yikes , I thought. What a way to begin my first year of teaching in Finland . It was only the third day of school and I was already pushing a student to the breaking point. When I took him aside, I quickly discovered why he was so upset.
Throughout this first week of school, I had gotten creative with my fifth grade timetable. Normally, students and teachers in Finland take a 15-minute break after every 45 minutes of instruction. During a typical break, students head outside to play and socialize with friends while teachers disappear to the lounge to chat over coffee.
I didn’t see the point of these frequent pit stops. As a teacher in the United States, I’d spent several consecutive hours with my students in the classroom. And I was trying to replicate this model in Finland. The Finnish way seemed soft and I was convinced that kids learned better with longer stretches of instructional time. So I decided to hold my students back from their regularly scheduled break and teach two 45-minute lessons in a row, followed by a double break of 30 minutes. Now I knew why the red dots had appeared on Sami’s forehead.
Come to think of it, I wasn’t sure if the American approach had ever worked very well. My students in the States had always seemed to drag their feet after about 45 minutes in the classroom. But they’d never thought of revolting like this shrimpy Finnish fifth grader, who was digging in his heels on the third day of school. At that moment, I decided to embrace the Finnish model of taking breaks.
Once I incorporated these short recesses into our timetable, I no longer saw feet-dragging, zombie-like kids in my classroom. Throughout the school year, my Finnish students would—without fail—enter the classroom with a bounce in their steps after a 15-minute break. And most importantly, they were more focused during lessons.
At first, I was convinced that I had made a groundbreaking discovery: frequent breaks kept students fresh throughout the day. But then I remembered that Finns have known this for years; they’ve been providing breaks to their students since the 1960s.
In my quest to understand the value of the Finnish practice, I stumbled upon the work of Anthony Pellegrini—author of Recess: Its Role in Education and Development and emeritus professor of educational psychology at the University of Minnesota—who has praised this approach for more than a decade. In East Asia—where most primary schools give their students a 10-minute break after 40 minutes or so of classroom instruction—Pellegrini observed the same phenomenon that I had witnessed at my Finnish school. After these shorter recesses, students appeared to be more attentive in the classroom.
Not satisfied with anecdotal evidence alone, Pellegrini and his colleagues ran a series of experiments at a public elementary school to explore the relationship between recess timing and attentiveness in the classroom. In every one of the experiments, students were more attentive after a break than before a break. They also found that the children were less attentive when the timing of the break was delayed—or in other words, when the lesson dragged on.
In Finland, primary school teachers seem to know this intuitively. They send kids outside—rain or shine—for their frequent recesses. And the children get to decide how they spend their break times. Usually, teachers in Finland take turns—two at a time—supervising the playground during these 15-minute stints.
Although I favor the Finnish model, I realize that unleashing fifth graders on the playground every hour would be a huge shift for most schools. According to Pellegrini, breaks don’t have to be held outdoors to be beneficial. In one of his experiments at the public elementary school, students had their recess times inside the school and the results matched those of other experiments where students took their breaks outside: After their breaks, the children were more attentive in class.
What’s most important is not where kids take breaks but how much freedom we give them from their structured work. When break times are teacher-directed, Pellegrini found, the recess loses its value. It’s free-play that gives students the opportunity to develop social competence. During these times, they not only rest and recharge—they also learn to cooperate, communicate, and compromise, all skills they need to succeed academically as well as in life.
As a teacher, I’m always trying to improve my classroom through experimentation. What I realized in Finland, with the help of a flustered fifth grader, is that once I started to see a break as a strategy to maximize learning, I stopped feeling guilty about shortening classroom instruction. Pellegrini’s findings confirm that frequent breaks boost attentiveness in class. With this in mind, we no longer need to fear that students won’t learn what they need to learn if we let them disconnect from their work for 10 or 15-minute periods, several times throughout the school day. And let’s be honest here, we teachers benefit from these breaks, too.
- Topics ›
- Elementary schools in the U.S. ›
The Countries Where Kids Do The Most Homework
Does your kid complain about endless hours of homework? If you live in Italy , those complaints could reach fever-pitch! According to research conducted by the OECD, 15-year old children in Italy have to contend with nearly 9 hours of homework per week - more than anywhere else in the world. Irish children have the second highest after-school workload - just over 7 hours each week. In the United States , about 6.1 hours of a 15-year old's week are sacrificed for the sake of homework. In Asia, children have very little to complain about. Japanese students have to deal with 3.8 hours of homework per week on average while in South Korea, it's just 2.9 hours.
Description
This chart shows hours of homework per week in selected countries.
Can I integrate infographics into my blog or website?
Yes, Statista allows the easy integration of many infographics on other websites. Simply copy the HTML code that is shown for the relevant statistic in order to integrate it. Our standard is 660 pixels, but you can customize how the statistic is displayed to suit your site by setting the width and the display size. Please note that the code must be integrated into the HTML code (not only the text) for WordPress pages and other CMS sites.

Infographic Newsletter
Statista offers daily infographics about trending topics, covering: Economy & Finance , Politics & Society , Tech & Media , Health & Environment , Consumer , Sports and many more.
Related Infographics
Movie industry, do oscar winners also rule the box office, the countries that are safe & unsafe for women, how leading e-commerce platforms stack up to amazon, water industry, how popular is bottled water around the world, munich security conference 2024, extreme weather, russia & cyber attacks top fears list, tourist accommodation, are short-term rentals more popular than hotels, trust in government, are politicians trustworthy, tourism & hospitality, the most important markets for the maldives tourism industry, who sells the most weapons, how europeans deal with cookie controls, germany is europe's solar energy front-runner, 2024 predictions, what will happen in 2024.
- Who may use the "Chart of the Day"? The Statista "Chart of the Day", made available under the Creative Commons License CC BY-ND 3.0, may be used and displayed without charge by all commercial and non-commercial websites. Use is, however, only permitted with proper attribution to Statista. When publishing one of these graphics, please include a backlink to the respective infographic URL. More Information
- Which topics are covered by the "Chart of the Day"? The Statista "Chart of the Day" currently focuses on two sectors: "Media and Technology", updated daily and featuring the latest statistics from the media, internet, telecommunications and consumer electronics industries; and "Economy and Society", which current data from the United States and around the world relating to economic and political issues as well as sports and entertainment.
- Does Statista also create infographics in a customized design? For individual content and infographics in your Corporate Design, please visit our agency website www.statista.design
Any more questions?
Get in touch with us quickly and easily. we are happy to help.
Feel free to contact us anytime using our contact form or visit our FAQ page .
Statista Content & Design
Need infographics, animated videos, presentations, data research or social media charts?
More Information
The Statista Infographic Newsletter
Receive a new up-to-date issue every day for free.
- Our infographics team prepares current information in a clear and understandable format
- Relevant facts covering media, economy, e-commerce, and FMCG topics
- Use our newsletter overview to manage the topics that you have subscribed to
I lived in Finland for 3 years. Even as an international student, I got a taste of why it's the happiest country in the world.
- Finland has a reputation for being the happiest country in the world .
- I lived there for three years, and things such as "cradle-to-grave" welfare made me feel secure.
- The government has a crucial role in building a happy society , and Finland has cracked that code.

Finland has been dubbed the world's happiest country for six consecutive years by the World Happiness Report.
But happiness in Finland doesn't mean everyone is smiling from ear to ear or that there's a carnival atmosphere on every street. The Nordic nation enjoys policy-based happiness from high-quality democracy and supportive public institutions.
While I lived in Finland for school from 2016 to 2019, it became very clear to me how much policies and the government had helped the country hold its happiness reign.
It's hard to adequately capture just how much relief I experienced while living in Finland
For starters, people in Finland generally have a high sense of trust in their neighbors, and I felt that even as an international student.
I didn't worry about whether strangers on the street had malicious intentions toward me, and I felt like I could express my political opinions (positive or negative) freely without the burden of self-censorship or backlash.
Related stories
People also seemed to have a lot of trust in their local politicians, and I thought the election cycles were fair and pretty peaceful while I was there.
The best part of going to school in Finland was that it was free
Because I started school in 2016, I was grandfathered into the country's free education for domestic and international students. After a policy change in 2017, non-European Union students under certain circumstances may have to pay tuition fees, which vary depending on the school.
Not having to pay for school was a huge weight off my back, but I still had to find a way to pay my costs of living.
I was a bit worried about finding work when I arrived — especially since I wasn't fluent in Finnish. But I got a job at a restaurant that gave me enough money to live on.
As a foreign student, I paid about 200 euros a year for a fairly comprehensive private health-insurance plan . But I also received free occupational healthcare through my employer, which ended up covering my doctor visits for joint pain, general sickness, ear-wax removal, and counseling sessions.
And I experienced all those financial benefits as an expat.
This overwhelming sense of security is at the heart of Finnish happiness
I think the key element behind Finnish happiness is its extensive welfare policy, which covers many basic necessities from "cradle to grave" and offers residents a heightened sense of security.
Because of this support from public institutions, Finns enjoy free healthcare and free education from elementary school through college, among other benefits.
Even working a service job, I had automatic deductions for pension and unemployment benefits from every paycheck that went to these publicly funded programs.
I think the lesson is that individuals should not be solely responsible for their happiness. The state and policymakers play a pivotal role in building a happy society.
Watch: From Nepal to Kosovo, here's how countries are celebrating Pride
- Main content
Homework matters depending upon which country you live in.
Chart created by Jill Barshay, data from OECD
For years, researchers have been trying to figure out just how important homework is to student achievement. Back in 2009, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) looked at homework hours around the world and found that there wasn ’t much of a connection between how much homework students of a particular country do and how well their students score on tests. Some top achieving countries, like Singapore, assign their students lots of homework. But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD’s international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.
This article also appeared here .
But now, five years after the earlier homework study, OECD researchers have drilled down deeper into homework patterns, and they’re finding that homework does play an important role in student achievement within each country . Specifically, they found that homework hours vary by socioeconomic status. Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also tend to get higher test scores. So the authors conclude that homework is reinforcing the achievement gap between the rich and the poor.
It’s not just that poor kids are more likely to skip their homework, or don’t have a quiet place at home to complete it. It’s also the case that schools serving poor kids often don’t assign as much homework as schools for the rich, especially private schools, explained Francesca Borgonovi, one of the authors of the study, titled “ Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? ”
“When you look within countries at students who are learning in the same educational system and they do more homework, then those students do much better,” said Borgonovi. “There is an advantage for putting extra hours in homework.”
“Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?” OECD
A stark example of this rich-poor homework gap is in Singapore. Students in the top quarter of the socio-economic spectrum spend about 11 hours on homework a week, 3 hours more than low-income students in the bottom quarter of the socio-economic spectrum. Each extra hour of homework was associated with 18 more points on the PISA math exam. So three hours adds up to more than 50 points. That’s huge. To put that in perspective, if you added 50 points to the average U.S. math score, we’d be a top 10 nation instead of number 36.
A key factor is what Borgonovi said about “learning in the same educational system.” Some school systems are designed to rely on homework, perhaps using independent study as a substitute for what could otherwise be learned in school. “If you are prepared to change the system, that’s great,” said Borgonovi. “But until you do so, if the system is based on homework, then you should do more of it.”
Students in Shanghai, a region in China that now leads the world in PISA test scores, do a whopping 14 hours of homework a week, on average. Wealthier students there do 16 hours. Poorer students do just under 11 hours. Interestingly, however, there was no association between the extra homework hours that the wealthier Shanghai kids put in and their PISA test scores. Perhaps that’s because there are diminishing marginal returns to homework after 11 hours of it!
Indeed, most countries around the world have been reducing the amount of homework assigned. Back in 2003, the average time spent on homework worldwide was about six hours a week. In 2012 that shrank to about five hours.
But the United States has been bucking this trend. The typical 15-year-old here does six hours a week, virtually unchanged from a decade ago and possibly rising. Wealthier students typically do eight hours of homework a week, about three hours more than low income students. But unlike in most countries, where more homework is associated with higher PISA test scores, that’s not the case here.
“For the United States, we don’t have homework reinforcing inequality,” Borgonovi said.
Another team of researchers, Ozkan Eren and Daniel J. Henderson, found mixed results for how effective homework is in the United States, in a 2011 study, “ Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? ” published in the Economics of Education Review. For math, there were huge benefits for the 25,000 eighth graders they studied. But not for English, science or history. And the math boost was much stronger for white students than for blacks. In other words, when a typical black student did more homework, his math test scores didn’t go up as much.
That’s perhaps a clue that even if you could magically get low-income children in other countries to do as much homework as their high-income peers, as the OECD researchers are suggesting, you might not raise their PISA test scores very much.
Indeed, Borgonovi isn’t really advocating for more homework. She says that high quality teachers and instruction are much more important to student outcomes than homework is. To be sure, some amount of homework is good, Borgonovi said, to teach kids how to plan ahead, set goals and work independently. But more than four hours of homework a week, she said, isn’t very beneficial.
“It would be better to redesign the system to have less homework,” said Borgonovi. “But that is hard to do.”
* The OECD looked at socio-economic status and not income exclusively. So the child of a university professor, for example, might still be in the high income category even if his parents don’t make very much money.
Your email is never published nor shared.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Education By The Numbers is aimed at journalists and researchers. We seek to answer the question of when (and whether) data can improve education. ABOUT
- Search for:
- absenteeism
- Adaptive learning
- Charter schools
- College graduation
- Common Core
- Community college
- Disabilities
- Early childhood
- Education spending
- High school quality
- Income inequality
- International comparisons
- Math education
- Private schools
- Repeating a year/retention
- School choice
- School climate surveys
- Student loans
- Summer school
- University college costs
- Vocational training
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Finnish flag flies aboard an icebreaker in 2017 as it arrives at Nuuk, Greenland. Finland's school system is regarded as one of the world's more successful.
For example, an average high school student in the US has to spend about 6 hours a day doing homework, while in Finland, the amount of time spent on after school learning is about 3 hours a day. Nevertheless, these are exactly Finnish students who lead the world in global scores for math and science.
Thirdly, the school hours in Finland do not start early morning at 6 am, or 7 am as done in India. Finland schools begin from 9.30 am as research in World Economic Forum has indicated that schools starting at an early age is detrimental to their health and maturation. The school ends by mostly 2 pm.
Ninety-three percent of Finns graduate from academic or vocational high schools, 17.5 percentage points higher than the United States, and 66 percent go on to higher education, the highest rate in ...
Students in Finland usually start school anywhere from 9:00 - 9:45 AM. Research has shown that early start times are detrimental to students' well-being, health, and maturation. Finnish schools start the day later and usually end by 2:00 - 2:45 AM. They have longer class periods and much longer breaks in between.
Higher income 15-year-olds tend to do more homework than lower income 15-year-olds in almost all of the 38 countries studied by the OECD*. Furthermore, the kids who are doing more homework also ...
But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD's international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment. This article also ...
In 2018, Finland spent 5.1% of its GDP on primary to tertiary educational institutions, which is 0.3 percentage points higher than the OECD average. Across levels of education, Finland devoted a higher share of GDP than the OECD average at both non-tertiary and tertiary levels (Figure 3).
Finally, Finland is a culture of readers, with a great library system and book mobiles reaching even remote locations. Although the Finnish system seems antithetical to South Korea's (the Asian nation placed second in the 2007 PISA surveys), the two small countries share much in common. Both cultures hold teachers in the highest esteem.
Finland Education Statistics. #23 93% of students graduate from high school. More than in the US. #24 66% of high school students go on to further education (college or vocational courses). #25 Finland spends about 30% less per student than the US, the UK, Japan and Germany. ( OECD Indicators)
The average age of new entrants in tertiary education in Finland is comparatively old. (23.3 Years, rank 8/33 , 2021) Download Indicator. In Finland, the share of first-time entrants into master's or equivalent programmes before the age of 30 is relatively low. (48.7 %, rank 35/40 , 2021) Download Indicator.
The results showed that in Shanghai, China the students had the highest number of hours of homework with 13.8 hours per week. Russia followed, where students had an average of 9.7 hours of homework per week. Finland had the least amount of homework hours with 2.8 hours per week, followed closely by South Korea with 2.9 hours.
The educational system in Finland consists of daycare programmes (for babies and toddlers), a one-year "preschool" (age six), and an 11-year compulsory basic comprehensive school (age seven to age eighteen). Nowadays secondary general academic and vocational education, higher education and adult education are compulsory. During their nine years of common basic education, students are not ...
There's no Homework in Finland. THERE'S No Homework In Finland Finland's school system accomplishes some impressive feats: 93% THEIR HIGH SCHOOL 78% GRADUATION RATE IS AT 93%. 75% COMPARED TO 78% IN CANADA. AND 75% IN THE US. %! ABOUT 2 IN 3 STUDENTS IN FINLAND WILL GO ON TO COLLEGE. That's the highest rate in all of Europe.
This is how it was a couple decades ago too when I was in school. Yes, there's homework but it's not usually very much and quick to do. Compared to for example British kids (where I live now) who have on average 3 hours of homework and revision each day. The amount of homework Finnish kids do in peruskoulu is very close to no homework.
The average salary of a teacher in Finland ranges from 3680 to 4090 € depending on what grades they teach. The number of years they have worked affects how much they are paid, and 10% make 2990 € or less a month. Most teachers in Finland have long paid vacation times: 14 weeks annually.
Normally, students and teachers in Finland take a 15-minute break after every 45 minutes of instruction. During a typical break, students head outside to play and socialize with friends while ...
According to research conducted by the OECD, 15-year old children in Italy have to contend with nearly 9 hours of homework per week - more than anywhere else in the world. Irish children have the ...
31.01.2024. Finnish education is of high quality. Differences in the learning results of different schools are small and nearly all students complete comprehensive school within target time. Preschool education, comprehensive education and upper secondary education is free of charge and also higher education is for the most part free of charge.
While I lived in Finland for school from 2016 to 2019, it became very clear to me how much policies and the government had helped the country hold its happiness reign.
But Finland, for example, succeeds without much homework. On average, Finnish students do only about three hours of homework a week, yet in 2012 they scored sixth highest in the world in reading and 12th highest in math on the OECD's international test, known as PISA or Programme for International Student Assessment.
School Report: Do we get too much homework? Published. 15 March 2018. Share. close panel. Share page. Copy link. About sharing Media caption, ... In Finland, meanwhile, there is far less emphasis ...