Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

MLA Format: The Ultimate Guide to Correctly Formatting Your Paper

Hannah Yang

So you need to create an MLA heading? You’re not alone—MLA format is one of the most common styles you’ll be expected to use when you’re writing a humanities paper, whether you’re a high-school student or a PhD candidate.
Read on to learn what a correct MLA heading looks like and how to create one that works like magic.
What Is an MLA Heading?
How do you format an mla heading, what is an mla header, how do you format an mla header, headings are only the beginning, commonly asked questions about mla headers, final thoughts.
The term “MLA heading” refers to five lines of important information that appear at the top of the first page.
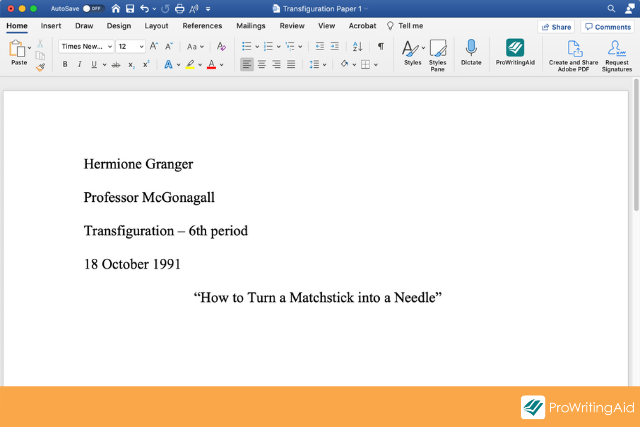
Here are two examples of what an MLA heading could look like:
Hermione Granger
Professor McGonagall
Transfiguration—6th period
18 October 1991
“How to Turn A Matchstick into a Needle”
Harry J. Potter
Prof. Remus Lupin
Defense Against the Dark Arts
4 March 1994
“Why I Think My Professor Is a Werewolf”
Why are these headings important? Well, your teacher probably collects hundreds of papers every year. If any identifying information is missing from these assignments, grading and organizing them becomes much more of a challenge.
MLA headings ensure that all key information is presented upfront. With just a glance at the first page, your teacher can easily figure out who wrote this paper, when it was submitted, and which class it was written for.

What Are the Parts of an MLA Heading?
An MLA heading should include:
- Your instructor’s name
- The name of the class
- The date the assignment is due
- The title of your paper
Your instructor may give you specific guidelines about how much detail to include in each line. For example, some teachers may ask you to refer to them by their titles, while others may ask you to use their full names. If you haven’t been given any specific instructions, don’t sweat it—any option is fine as long as it’s clear and consistent.
Follow these formatting rules for your MLA heading:
- Start each piece of information on a separate line
- Don’t use any periods, commas, or other punctuation at the end of the line
- Keep the heading double-spaced, in the same font as the rest of your paper
- Left-align the first four lines (they should start at the 1-inch margin on the left side of your paper)
- Center the title (it should appear in the middle of your paper)
- Make sure your title is in title case
Title case means that major words should be capitalized and minor words should be lowercase. Major words include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, and any word longer than four letters. Minor words include conjunctions, prepositions, and articles.
Tip: Remember that Hermione’s “Society for the Promotion of Elfish Welfare” shortens to S.P.E.W., not S.F.T.P.O.E.W—only the major words are capitalized!

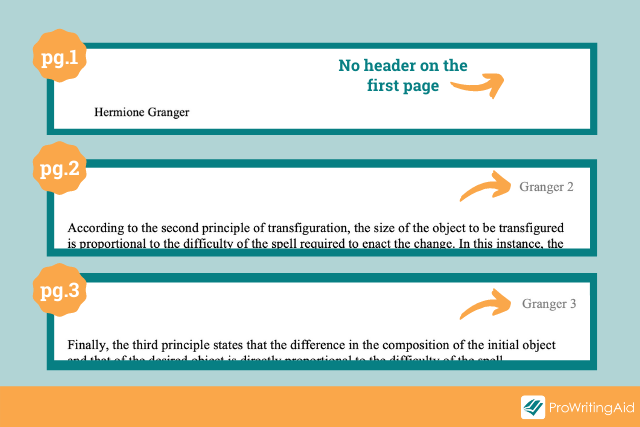
The MLA heading should only appear on the first page of your paper . But wait, you’re not done yet! In the rest of your paper, you need to include something called an MLA header at the top right corner of every page.
Think of the MLA header as a short, simple “You are here” marker that shows the reader where they are in the paper. By looking at the MLA headers, your instructor can easily understand where each page goes and which paper it belongs to.
What Are the Parts of an MLA Header?
The MLA header consists of your last name and page number.
For example, the second page of Hermione Granger’s essays would be labeled “Granger 2”, the third would be labeled “Granger 3”, and so on.
Creating MLA Headers in Microsoft Word
If you’re writing your paper in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Click Insert
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and click on it
- Set the position to “Top of Page (Header)”
- Set the alignment to “Right”
- Make sure there’s no checkmark in the box for “Show number on first page”
- Click on the page number and type your last name before the number
- Set your font and font size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Creating MLA Headers in Google Docs
If you’re writing your paper in Google Docs, follow these steps:
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and hover over it
- Choose the option that sets your page number in the upper right corner
- Set your font and type size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Tip: After you create your first MLA header, save a template document for yourself that you can re-use next time, so you don’t have to follow these steps every time you write a paper!
Once you've got your headings sorted, it's time to start writing your paper. While we can't help you edit the content of your essay , ProWritingAid is here to make sure your grammar, spelling, and style is on point.
As well as checking your grammar, ProWritingAid also shows you your progress towards key goals like varied sentence structure, active voice, readability, and more. The target scores are all based on averages for real essays, so you'll always know if you're on track.
Ready to start receiving feedback before you submit your work?
Whose last name should you use in your MLA header if you’re writing a group paper?
The MLA Style Guide has no specific guidelines for group projects. You should always include the names of all members of the group project in the first line of your heading, but you don’t necessarily need to do this for the header on every page.
If there are only two or three authors collaborating on your paper, you can include all of your last names in the MLA header, e.g., “Granger, Potter, and Weasley 2.”
If you’re part of a bigger group and it would take up too much space to include all of your last names, you can write the name that comes first in the alphabet and then add “ et al. ”, e.g., “Granger et al. 2.” (The term “et al.” is short for the Latin term “et alia”, which means “and others.” You’ll often see it used in academic papers with multiple authors.)

Should you include your class period in your MLA heading or just the class name?
There’s no MLA rule about this, but when in doubt, it’s always better to err on the side of including too much information in your heading rather than not enough.
If your instructor teaches more than one version of the same course, they’ll probably find it helpful if you specify the class period you’re in. You can either include your class period after the class name, e.g., “History of Magic—2nd period”, or before the class name, e.g., “2nd Period History of Magic.”
What should you write in your MLA heading if you don’t have an instructor?
If you have no instructor, you can explain the situation in the line where you would normally put the instructor’s name, e.g., “Independent Study” or “No Instructor.”
What should you write in your MLA heading if you have multiple instructors?
If you have multiple instructors, you can include both of their names in the line where you would put the instructor’s name. If you’re in a college course where you have a professor and a TA, you should choose whose name to include in the header depending on who will ultimately be reading your paper.

Should you include the date you started writing the paper or the date the paper is due?
The MLA Style Guide has no specific guidelines about which date you need to put in the heading. In general, however, the best practice is to put the date the assignment is due.
This is because all the papers for the same assignment will have the same due date, even if different students begin writing their assignments on different days, so it’s easier for your instructor to use the due date to determine what assignment the paper is for.
Should you format the date as Day Month Year or Month Day Year?
In MLA format, you should write the date in the order of Day Month Year. Instead of writing May 31 2021, for example, you would write 31 May 2021.
What font should you use for your MLA heading and header?
Both the heading and the header should be in the same font as the rest of your paper. If you haven’t chosen a font for your paper yet, remember that the key thing to aim for is readability. If you choose a font where your teachers have to squint to read it, or one where your teachers can’t figure out the difference between what’s italicized and what isn’t, you should rethink your choice.
When in doubt, go with Times New Roman, 12 pt. It’s always a safe bet for MLA papers unless your instructor specifically tells you otherwise.

Do you need to italicize or bold the title of your MLA paper?
No. There’s no need to use any special styling on the title of an MLA paper, such as bold or italics.
How do you format section titles in your MLA paper?
If you’re writing a paper with multiple sections, you may need to include a subtitle at the top of each section.
The MLA Style Guide gives you two options for using subtitles in a paper: one-level section titles or several-level subtitles (for papers with subsections within each section).
For one-level section titles, the formatting is simple. Every subtitle should look the same as the title (centered and double-spaced, with no special formatting).
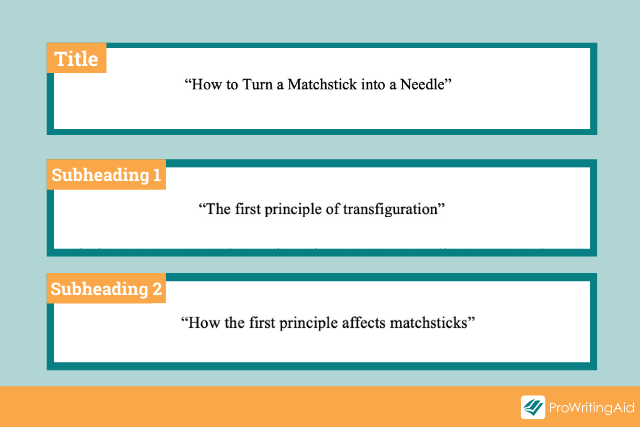
The only difference is that instead of using title case, you should capitalize only the first word of each subtitle. For example, a title would be spelled “How to Turn a Matchstick into a Needle”, while a subtitle would be spelled “How to turn a matchstick into a needle.”
For several-level subtitles, you will need to format each level in a different way to show which level each section is at. You can use boldface, italics, and underlining to differentiate between levels. For example, subtitles at the highest level should be bolded, while subtitles at the next level down should be italicized.
See the chart below for MLA’s suggested formats.

What is the difference between MLA format and APA format?
MLA and APA are two sets of guidelines for formatting papers and citing research.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association. The MLA handbook is most often used in fields related to the humanities, such as literature, history, and philosophy.
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. The APA format is most often used in fields related to the social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and nursing.
The APA manual includes a heading format similar to the MLA heading format with a few key differences, such as using a separate cover page instead of simply including the heading at the top of the first page. Both heading formats ensure that all of your papers include all your key identifying information in a clear and consistent way.

Where can you learn more about MLA style?
If you have questions about how to format a specific assignment or paper, it’s always best to consult your instructor first. Your school may also have a writing center that can help you with formatting questions.
In addition, Purdue has fantastic resources for all kinds of formatting topics, from MLA headings to MLA citations and everything in between.
If you would like to find out more directly from the Modern Language Association, consult the MLA Style Center or the MLA Handbook (8th edition).
Now you’re ready to write an MLA paper with a fantastic heading. Make sure your essay does your heading justice by checking it over with ProWritingAid.
Write Better Essays Every Time
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you're losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much?
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How to Write Essay Titles and Headers
The deadline for your latest writing assignment is mere minutes away. You’re rushing to get the final details together and suddenly realize you’ve forgotten a title. You quickly throw something random on top of the page and submit it to your teacher.
You’re not satisfied with your title, but you vow to do better next time. And you will!

You’ve learned from your mistake: essay titles are not a last-minute detail. They’re an integral part of any piece of written work and should be planned out earlier on in the writing process.
Titles lead to your reader’s first impression of your essay, and the headings help organize your thoughts and make the essay easier to read. Let’s take a look at how you can turn your titles from an afterthought into a well-thought-out writing element.
How Do You Write a Great Title?
People DO judge a book by its cover, and they will judge your essay by its title. So writing a strong title is an important part of starting your writing off on the right foot.
Your essay title has two main functions:
- Inform your reader
- Spark your reader’s interest
Additionally, keep in mind these three pointers:
Be clear and concise
Vague titles do not inform the reader. Provide a specific description of what your focus will be. Your audience wants to know precisely what they will be reading.
Bad Example: Oceans
Good Example: Disappearing Ocean Life in the Pacific Rim
Offer an exciting tidbit or interesting fact
If your title is boring, readers will not want to keep reading. Offer them something that will get attention.
Bad Example: How Consumers are Wrongly Spending Money
Good Example: The Seven Million Dollar Mistake
Everyone may be writing a college admissions essay, but don’t title yours: My College Admissions Essay . No matter what the prompt, make your title something that stands out from the stack.
Bad Example: My Research Project
Good Example: Relocating the Human Race to Mars
How Do You Create a Great Header?
Essay headers are often overlooked by writers, but they can really help your readers as they journey through your essay. While the title may get the reader hooked, the headers keep them moving smoothly through your paper. They enhance readability and help explain what is most relevant in the essay.
Each essay header should answer these two questions:
- What will I learn?
- What is the focus?
When readers approach a new section of your essay, they will have a better reading experience if they have a small preview of what’s to come.

Writing a useful header should be relatively easy. Read through your paragraphs and see what the main idea of is. From here, make a list of sub-topics that are discussed in each section. The best way to do this is to pull from the main points you listed out in your outline (which you, of course, remembered to do!).
Remember the following details about writing a header:
Be simple, but informative
You don’t want to give away all of your ideas here, but you need to give some guiding information.
Bad Example: Eating Too Many Fatty Foods Can Increase Your Cholesterol Levels
Good Example: How Your Diet Affects Your Health
Be consistent throughout your essay.
Choose a pattern and stick with it throughout the entirety of the assignment. If you start off by having a heading for each paragraph, keep it that way until the end. Also, make sure the format remains the same. If your first heading is in the form of a question, all of the rest should be as well.
Bad Example: Beaches, What is Up With Littering?, I Want to Clean Up the Planet
Good Example: Neglected Beaches, Effects of Litter, Motivated Activists
Just like when you are writing a title, there are generic headings you can lean on to get it done quick and easy. But don’t use these. Your conclusion shouldn’t have the header, "Conclusion." Come up with something unique for each part of your essay to keep your reader from feeling fatigued as they read on.
Bad Example: Conclusion
Good Example: Will the Pandas Survive?
Be organized and helpful
Your essay should be scannable. This means that if someone needs information fast, they can find it without having to read every word of your piece.
Although titles and headers are often neglected, they are very important to your pieces of writing. They grab your reader’s attention from the start and keep them focused throughout the rest of your essay. Taking the time to craft great titles and headers can advance your writing to the next level.
Don’t overlook the title and section headers when putting together your next writing assignment. Follow these pointers for keeping your writing organized and effective.
101 Standout Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas
Need a topic for your upcoming argumentative essay? We've got 100 helpful prompts to help you get kickstarted on your next writing assignment.
Writing a Standout College Admissions Essay
Your personal statement is arguably the most important part of your college application. Follow these guidelines for an exceptional admissions essay.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
How to write a heading – get to know the rules
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Headings help bring out an outline of the content immediately after it. They appear at the top of a paragraph, chapter, or page to brief what the succeeding content is about. Read on to find out how to write a heading, how long headings should be, the difference between a heading and a title, and what descriptive headings are. If you know how to write a heading, you get the reader’s attention which gives them the urge to read on and on.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 How to write a heading - FAQ
- 2 How to write a heading: Definition
- 3 Headings vs. titles
- 4 How long should headings be?
- 5 Descriptive headings
- 6 Repetitive headings – a no-go
- 7 Technical terms in headings
- 8 In a Nutshell
How to write a heading - FAQ
How do you write a proper heading.
A heading should be brief but must also bring out the information it’s intended to. It should be related to the content it stands for to ease the reader’s experience. Make sure it’s brief and straight to the point.
Tip: If you are done with your academic work, we can help you with thesis printing !
What is the format of heading?
There are 3 levels of heading formats. The first level should be centered, bold, and anywhere near font size 14. The second level should be aligned on the left, bold font, and about font size 12. The last format level is the third, whereby the font is left-aligned, bold and italics, and has a font size of about 12. You should know how to write a heading with these three formats.
What is the difference between heading and title?
There’s little difference in how to write a heading and a title. Titles and headings are pretty comparable but have their differences. A title stands for the whole reading and incorporates its content in a phrase or two. At the same time, a heading only crowns and captures the content of a section or chapter.
Why are headings important in writing?
How to write a heading is the first step. Headings convey an overview of what the whole writing is about. The reader is supposed to find out what the entire document is about by going through the headings assigned. It’s essential to know how to write a heading because it helps you organise your thoughts and understand what content to write and where.
How long should headings be?
Do you want to know how to write a heading? Not too long or short? However long it gets, make sure you have a suitable heading. Don’t go past one line because it’ll be too long. A good understandable heading for your sections or paragraphs should intrigue the reader to read more and not be too long to bore them.
How to write a heading: Definition
A heading can be a word, phrase, or sentence at the top of a paragraph, section, or chapter describing what it’s about. There’s no big deal on how to write a heading as its similar to a caption or a title. You have to know how to write a heading for your essays or research project to maintain a logical flow of ideas as the lecturer reads on.
Headings vs. titles
A heading should be brief and explain the exact information the writer wants to convene in the section or chapter below. Having a heading one line or just three words long is appropriate, as long as it is precise and straight to the point. These are primary skills to knowing how to write a heading.

Descriptive headings
There’s nothing complicated on how to write a heading of this type as it focuses on giving the reader more information for easy understanding. More details of the primary subject are provided in the heading. These headings are suitable for emails, academic reports, or even on online platforms.
An example is, say, you are crafting an essay of The American Revolution. If you give a heading like “Causes,” it will not be as clear as “Causes of The American Revolution.” The latter is a descriptive heading. Another example is, maybe you have a report to submit on corn growing in the USA. A heading like “Corn farms” will not be as suitable as the descriptive heading, “Corn Farms in the USA.”
For your academic reports or essays, you can incorporate some descriptive headings to give clear information. If you know how to write a heading of this type, the lecturer or reader will peruse your document and know what it’s about by just reading the headings. You can use some descriptive subheadings too for a much more detailed report or essay.

Repetitive headings – a no-go
There’s no way two sections can have the same title. This will dilute the whole document. If you know how to write a heading, you should know that all headings in a document must be unique. Descriptive headings will help avoid repetitive headings because you explain what the section is about on the heading itself. Chapters cannot have the same content; therefore, the headings can’t be the same too. Knowing how to write a heading that is as descriptive as possible will help arrange your ideas and give the reader an easy time.
Essential tips on how to write a heading without repetition are; varying the lengths of your headings, using different transition words, and using the thesaurus to get synonyms to terms. Knowing how to write a heading will help you know how to craft different headings for different paragraphs.
Technical terms in headings
Technical and jargon terms used on headings of documents may not be understandable to every reader except those familiar with the languages. An example is betting site languages. If you don’t get the terms used in betting, you may not understand anything on the betting site.
For academic documents intended to be read by professionals, such as instructors, you can use jargon if it is allowed. If there’s no need to use the terminology, avoid it at any cost. If you are familiar with how to write a heading, you should know how to craft one for general readers.
In a Nutshell
- Headings should have a length of one to five words and not exceeding a whole line, as said above. A unique tip on how to write a heading is that it looks more like a title than a subheading.
- Not all paragraphs need a heading. If you know how to write a heading, use headings for two or more ideas, and do not overdo them.
- Headings should boost the outline of your main topic, paragraph to another and not overshadow it. Knowing how to write a heading forms the basis of a quality document.
- Try using descriptive headings and subheadings often to have a quality outlook of your work.
- Do not repeat a heading at any cost, mainly if you know how to write a heading for your academic work. Use informative or descriptive headings for a logical and easy-to-understand document.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

Should you Include Headings and Subheadings in an Essay?
If you have ever tried reading a large blob of text, then you know how hard it can be. However, it becomes easier to read when broken into headings and subheadings.
Academic writings like essays have a standard of writing that must be upheld. While not every essay requires headings and subheadings, they are important for organizing your writing.
Headings describe the succeeding section, while subheading gives supporting information for the heading.
With that said, here is everything you need to know about headings
What are Headings in Essays and Academic Papers?
According to Merriam-Webster, a heading forms or serves as a head.
In academic writing, headings represent what is to come in the assignment. Adding a heading will help structure a piece of writing and guide the reader throughout the content. Short pieces of writing don't always require headings. In long-form writing, each specific section should have its heading to communicate what the reader should expect clearly. Think of it as the title of that section.
Since some points are more important than others, the heading chosen should be based on whether the idea you are talking about is the main point. Each heading chosen should tell the reader what the following idea is about. This is because the main points are the building blocks of the content. Make sure it is short, descriptive, and precise.
You can include headings and subheadings/subtopics in an essay if it is long, but ensure that the subtopics or subheadings are relevant to the content and consistent throughout the text in a manner to contribute to your thesis statement. As a good practice, ensure that the essay headings and subheadings do not exceed 12 words.
Subheadings are not recommended for short essays . However, they improve the overall structure of a long essay, help you frame and explore your topic, and enable the readers to know what to expect (they act as signposts in an essay or research paper).
Heading vs. Title
Headings and titles may look similar at a first glance, but they are not. A title represents the entire paper and explains it in clear and short phrases. It is the first thing the reader will see and determine whether they read the rest of the document. For this reason, you need to think of striking, informative, and appropriate titles. You should also write the title based on why you are writing that document. For instance, if the aim of the documents is tutorial, then the title should be task-based.
On the other hand, a heading represents what each section of the paper discusses. They help guide the reader throughout the documents, which is why you should write effective headings, and they should be as descriptive as possible.
Headings are a requirement in most forms of writing, but some lecturers may be divided about using them in academic essays, which is why you should confirm with them first.
Headings Vs. Subheadings
Headings are key parts of writing as they will capture the reader's attention and lure them into the document's purpose. They guide the reader to the main points of the paper. You have to set the headings apart from the body of the text by coming up with an enticing phrase.
Subheadings, on the other hand, do more than grab the reader's attention; they show the different subsections of the text. They keep the reader engaged by quickly guiding them to the information they want.
Headings and subheadings appear at the beginning of a section and organize the flow of the documents. In addition, they are both used to break down large blocks of text to make them more scannable. They also have a hierarchy that is Heading (H2) first, followed by subheadings (H3) and (H4) in that order. Subheadings should always come after the heading, as demonstrated.
The Best Length for Headings in Academic Writing
A heading can be as long as you want it to give the reader a snippet of the idea. A good rule of thumb should be no more than 70 characters.
For higher level headings, like H1, H2, and H3s, they could be as low as one word, for instance, the introduction, methodology, and such. For such sections, the one word is clear enough for the reader to know what it represents. Low levels like H5 and below can be much longer and direct the reader to exactly what they are looking for.
Levels of Heading in Academic Writing
Headings are an important part of academic writing as they act as a preview of the document. They guide the reader on what you are talking about, which is why you should assign different heading levels.
There are five levels of headings in APA style. Level 1, Level 2, level 3, level 4, levels 5. Level 1 is the main heading, followed by level 2, its subheading, and level 3 is the subsection of level 2 in that order.
Level 1 headings are your main headings and are usually typed in the center of the paper in title case and bolded. Their text beneath will always start in the next line, indented inward, just as you begin a new paragraph. These help the reader find their way through the document, read what they want and skip what they are not interested in.
The length and complexity of the paper will determine how many levels you will use. If it's just a short piece of writing, you can use Level 1. If you need two headings, use level 1 and level 2. If it's a 2000-word article, research paper, term paper, or essay, you will need between 3 and 5 headings.
Keep in mind that not every paragraph needs a heading. While headings can keep your work neat, too many can defeat the purpose. Also, make sure that each of the headings and subheadings has a connection to the main title.
All these levels are differentiated by different styles and formats depending on the publication manual provided, which can be either APA or MLA format.
Reasons to Use Headings in Academic Writing
Headings are helpful in academic writing for a myriad of reasons, including:
Making Your Content More Readable
Much information goes into academic writing to pass information to the reader. Putting all your information in a large block of text will be overwhelming and can scare away the readers. The white gaps at each heading section will offer a resting place hence a visual break. Therefore, separating the large chunks of text into manageable portions will keep your readers engaged.
Outlining Your Content
Headings serve as the structure of your writing. By dividing the large bulk of text with headings, you guide the reader through each section and what it is about. Otherwise, they won't know what it is about.
Capturing the Reader's Attention
The main aim of any heading is to hook the reader and create curiosity enough for them to continue reading through the rest of the article. Having a catchy and informative heading will entice them to read even further.
Remember that readers rarely read documents from start to finish. Major headings should stand out but so should headings and subheadings if you want the readers to continue reading your paper.
Finding Important Information
Readers will likely scan the essay to get a general idea of what it is about and decide if they want to read it. Well-structured headings will help them achieve that.
Improving Overall Quality
Headings and subheadings improve the quality of the essay. A high-quality essay is suitable for readers and also for search engine optimization (SEO) if you intend to publish it online. Ensure to use keywords in the headings and structure them to improve visibility.
Tips to Include Better Headings and Subheadings
Writing informative and precise headings and subheadings is vital if you want your writing to get the message home. You need to borrow the following tips to show that they should spend time reading your writing.
Use the Right Length
The length of your article or essay will determine how long your headings and subheadings should be. Put yourself in the reader's shoes and think of the heading you would like to read. Lengthy headings aren't attractive. Most readers want something short and precise, which is what you should do. It should only take them a few seconds to read, so be sure the length should be not more than 30 words.
Make It Relevant to the Content and Topic
Headings and subheadings are essential to catch the reader's attention but are not important enough to stand independently. They represent the critical concepts and all the supporting ideas. Therefore, you need to consider the topic's relevance when determining what phrases to use in your subheading. Carefully think about each key piece of information you'd like to include in each of your sections. Then ensure that each subheading is connected to the main title or the heading.
Be Clear and Concise
Headings and subheadings tell the reader what the content is about. They are usually about five words long. Therefore, you should go directly to the point using clear language that is easy to understand. Most readers skim through the text before reading which is why you should use simple and straightforward words. Always remember that readers have questions and are looking for answers and shouldn't have to ponder what you are talking about. If your heading is clear and to the point, they won't leave to look for answers elsewhere.

Place It in the Right Place
Consider where your target audience is likely to look and where they are likely to appear. While doing this, also consider the kind of phrases they are likely to type for the specific information they want. This gives you a general idea of where to place headings and subheadings. Remember that the APA and MLA format requires that all headings be placed hierarchically. So as you choose your phrases, ensure that they align with the content's topic and flow.
Consider the Formatting Style
Heading styles format your headings to make them stand out from the rest of the text. They also give your essay structure and make it more accessible to the target audience. In addition to this, headings also help in:
- Generating a table of contents
- Use style sets to reformat the document
- Rearranging the documents
- Creating a structured pdf file using the heading tag
Remember that each heading is formatted with a different heading style located in the style section. Since you've already used H1 for the major heading, the first subheading will be H2, and the second subheading will be H3.
Related Reading: How to indent an essay well.
Number the Heading or Subheading if Needed
Putting numbers on your heading makes it easy to scan. Top-level headings like H1 are numbered 1,2,3,4 while second-level headings, like H2, are numbered 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
Remember that even though you are numbering the headings, you need to introduce your topic in the first paragraph after the headings. Headings don't speak for themselves, so writing a few sentences restating the main idea will tell the reader what will come.
Be Consistent Throughout the Paper
If you intend to use headings in your paper, ensure each section has a heading and subheading. Also, ensure they are consistent in font, size, color, indentation, etc. The style function in Microsoft Word will help create consistency in your headings. You must select the text you want to convert into a heading, then select the appropriate heading from the Style box.
Avoid Repetition
Avoid repeating any phrases in your headings. Using the same heading more than once can affect the reader's comprehension of your message, negatively impacting their reaction to your essay. Sometimes you may repeat the headings without even noticing. For this reason, you should use the Find Function in MS Word or Google Docs.
Another way you can check for repetition is by reading your essay out loud, and this will help you spot any headings or subheadings that have been repeated.
Capitalize, Format, and Punctuate Well
Effective headings are well capitalized, formatted, and punctuated. The APA style uses two styles for this, title case and sentence case. In the title case, major words are capitalized, while minor ones are lowercase. Sentence cases, on the other hand, only capitalize the proper nouns while the rest remain in lowercase.
Use Automatic Heading in Word Processor
Microsoft Word has a built-in feature that anticipates how you want to format your document. As you begin typing, your text starts in the typical style, but when you press enter and move to a new line, the style changes to H1 with different fonts, colors, etc.
If you are typing a paragraph with a small number of words and press enter and then fail to provide proper punctuation, the feature will assume you are moving to a new paragraph, and it will then automatically enter a new heading with a heading style.
Use Descriptive Headings
Use concrete and descriptive language to make your headings more effective so the reader can know what to expect in each section. Don't use function headings when writing your technical reports; these are not so predictable, and readers benefit from the headings being much more descriptive.
Function headings are only used when writing pieces that need consistent structures, for instance, lab reports. An example is:
- Introduction
- Methodology
- Conclusions
Include Technical Terms Needed
Technical terms should not be used in headings because they may be hard to understand except those who know the languages. Technical terms are primarily used in academic documents that professionals read but if not specified, avoid them.
Related Read: How to write an article title in academic papers.
Final Words
Headings and subheadings are vital features in academic writing that represent the main points of a topic. The difference in formatting helps reader's the main points from the rest of the texts. Ensure you follow all the tips about including headings and subheadings in your text. Talk to your lecturer, professor, teacher, or instructor if you are unsure whether to add them to your essay.
What are Headings in an Essay?
Headings are markers that guide the reader through an essay by showing them what the next section is about. Like a title, they are only a few words long and are essential in structuring your content so as not to overwhelm the reader.
Should I Put Headings in an Essay?
Yes. It will help if you put headings in your essays to make them more readable. Essays consist of three parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Most of them are written in a continuous, paragraphed text without the need for section headings, especially if it's a short essay. On the other hand, long-form essays need headings and subheadings to make them easy to write and read. Since most lecturers are divided about using them in academic essays, you should confirm with your tutor before you start writing.
How Do I Include Subheadings in an Essay?
Subheadings are mini headlines that come after the headings, and they help explain more about the headings and aid readers in skimming through the content. If you have used the first heading, H1, and need to provide more information about it, add a subheading, H2.
If you have trouble deciding how to use subheadings correctly, think of them as an outline. Therefore, break down your topic into simple ideas, then use them to organize your essay.
How Do You Make a Heading in an Essay or Academic Paper?
You must think carefully about the aim of writing a paper and the main idea. Each heading should be clear and to the point. You don't want to mince words and possibly confuse the reader. Also, remember that headings are meant to enhance, not replace, the main topic. Ensure you set it apart from the body of the text by using H1 formatting in either Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
Borrow some of the following best practices to write an effective heading:
- Create a controversy
- Ensure it short
- Pose a question
- Suggest a number
- Provide an explanation
How Do You Use Headings and Subheadings?
Headings (section headings) are the title of your essay. They appear at the beginning of the page and guide the reader through your content. It is the first one your readers see before reading your essay or text. It doesn't matter whether the reader reads every word in your essay; they can still get the basic idea of your paper. Using different heading levels will help the reader navigate through the document. The headings and subheadings should be captivating enough to make an excellent first impression.
When writing a subheading, keep in mind that the H2s are the headers of each header for the main section of the essay. H3s are the subsections of the main points in H2s. H4s, on the other hand, are detailed subheadings breaking down the text into more specific options. The subheadings amplify the title or heading of the essay, and they also complement the headings. They make your writing flow and should be relevant to the topic. With such an organization, you have achieved a first-class essay level. A good subheading captures the essence of the title and consistently informs the reader that they are still on an idea related to the topic. It is also short, descriptive, clear, and concise.
Should Essays Have Section Headings?
Yes. Just like books are divided into chapters, essays and articles should be divided into sections. Essays should have section headings because they help make your work more organized and easy to read. And within those sections, the text can be divided into subsections.
Are There Specific Words to Use in Headings and Subheadings in Essays?
You will probably be tempted to use more words to make your heading more concise, but this isn't a good idea. Make sure you carefully choose words that clearly describe your chosen topic. If possible, use numbers in your headings because they are like brain candy, making your work more interesting. Also, ensure you use odd numbers because they are more attractive to readers than even numbers, according to the Content Marketing institute . Avoid abbreviations, idioms, or colloquial expressions when writing headings and subheadings.
How Many Headings to Use in an Essay or Academic Assignment?
To be safe, only use a maximum of three headings. However, this will depend on the length of your academic assignments. Remember that headings are short phrases that introduce the topic you are writing about and make it easy for the readers to read through. So if you are writing a short essay of fewer than 1000 words, there is no need for headings. But for articles above 1000 words then, you must use them. Headings will help identify the different sections in an essay.
What Are Heading Levels?
Headings organize your essay in a hierarchical order. Since some points are more critical, assigning different levels will help distinguish them.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

As a precautionary health measure for our support specialists in light of COVID-19, our phone support option will be temporarily unavailable. However, orders are processed online as usual, and communication via live chat, messenger, and email is conducted 24/7. There are no delays with processing new and current orders.
How to Write a Header for an Essay?
This essay was written by one of our professional writers.
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Need a custom essay written for you?

A header is the first element that the reader sees in an essay. Its importance is beyond question. So, if you are wondering what is a header in writing in high school or college, and how to write an essay header correctly – continue reading to close that unfortunate knowledge gap of yours.
What’s a header in an essay ?
By a header in an essay, we mean the information shown on the top of the page. It’s important to distinguish between the two types of headers:
- a title page header;
- a running header.
The title page header is only placed once on the title (first) page, so there is no need to repeat it on all other pages. The information there is brief, and it typically consists of the following lines:
[Your Name]
[Instructor’s Name]
[Course Title]
All lines are usually double-spaced and aligned on the left side. However, while the left side alignment is a universal feature, the spacing, as well as the exact contents can vary from school to school, or as per individual instructor’s requirements. For example, some schools do not require an instructor’s name, while others demand that an essay’s title must also be placed in the header.
A running header, on the other hand, is placed on all pages, and it typically consists of the student’s name/essay’s title and page number. The running header helps the reader to better navigate the essay, especially a long one.
How to make a header for an essay : a detailed guide with examples
In a standard college essay, the very first page (the title page) contains the title page header. It precedes the title itself, which goes right after the title header and is usually center-aligned. The title and the title header are written in the same font style and type as the rest of the text. However, oftentimes, students tend to highlight their essays’ titles using larger and bold fonts, which is a mistake.
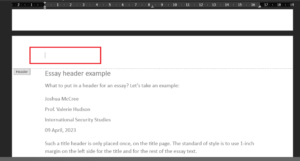
Essay header example
What to put in a header for an essay ? Let’s review an example:
Joshua McCree
Prof. Valerie Hudson
International Security Studies
09 April 2023
Such a title header is only placed once, on the title page. The standard style is to use a 1-inch margin on the left side for the title and the rest of the essay text.
The running header, on the contrary, is used on every single page of a college essay, including the title page. Here, however, it is important to distinguish between the running headers of the two widely used citation styles: MLA and APA.
Header for college paper: MLA and APA styles
In college, the writing standards require adhering to one of the following citation/referencing styles: Modern Language Association (MLA), and American Psychological Association (APA).
According to the MLA running header format, only the author’s surname and page number are allowed. The header looks as follows then:
Where McCree is the student’s surname, followed by a page number. This information is placed in a single line and is aligned on the right side.
At the same time, the APA style stipulates including the work’s title instead of the author’s name. In case the title is a long one, a shortened version is allowed. The page number information is also a must. It is important to note that all words in the running header title in APA style must be capitalized.
THE US FOREIGN POLICY SECURITY IN THE 20TH CENTURY 1
How to make a running header in MS Word
Step 1. To enable the insert of the information into the running header, double-left-click on the top of the page. You should now see the following:
The cursor is flashing in the top left-side corner, ready for your further instructions.
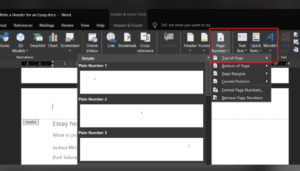
Step 2. Now, on the main menu, select the “Insert” tab.
Step 3. Find the “Page Number” tab, left-click on it, and hover over the “Top of Page” sub-menu, like so:
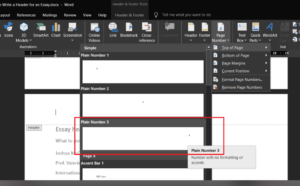
Step 4. Select the “Plain Number 3” option in the list that appears. This option is recommended because it aligns the page number on the right side of the page by default. However, you can try any option available and adjust it further accordingly.
Step 5. Insert the running header information according to your citation style. For example, for MLA style, insert your surname and page number, like so:
For APA style, insert the full or shortened title of your essay with all letters capitalized (aligned on the left side), followed by a page number aligned on the right side. For example:
THE ANALYSIS OF THE FIRST WORLD WAR PEACE TREATIES 2
Finally, press the “Tab” key to finish aligning the information on the left side, and then the “Escape” key to exit the running header mode.
To sum up, a header for essay can be of two distinct types: a title page header, and a running header. The first is used only once, in the title page, and consists of the author’s first and second names, instructor’s name, course title, and date. After the title page headers follows the main title of the essay.
At the same time, the running header represents much simpler information consisting of the author’s surname and the page number (according to MLA style), or the shortened/abbreviated title of the essay and the page number (according to APA style).
The table below effectively summarizes all the nuances of the running essay header in MLA and APA styles:
The choice of the running header style in most high school situations is yours, as teachers usually leave it up to their students. However, at college, you should always be aware of your particular essay assignment’s instructions as these may contain recommendations to follow MLA or APA style specifically.
Stuck with your essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, what is your plagiarism score.
Strong Taiwan Quake Kills 9, Injures Hundreds
The earthquake was the most powerful to hit the island in 25 years. Dozens of people remained trapped, and many buildings were damaged, with the worst centered in the city of Hualien.
- Share full article
![how to make heading for essay [object Object]](https://static01.nyt.com/images/2024/04/03/multimedia/03taiwan-quake-briefing-carousel-add-bvzm/03taiwan-quake-briefing-carousel-add-bvzm-square640.jpg?quality=75&auto=webp)
- Hualien, Taiwan A landslide after the quake. Lam Yik Fei for The New York Times
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Books flew off shelves as a home shook. @Abalamindo via Storyful
- Taipei, Taiwan Passengers waiting at a train station as some services were suspended. Chiang Ying-Ying/Associated Press
- Hualien, Taiwan People are rescued from a building that had partially collapsed. TVBS via Associated Press
- Hualien, Taiwan Firefighters rescuing trapped residents from a building. CTI News via Reuters
- Taipei, Taiwan Students evacuated to a school courtyard after the earthquake. Lam Yik Fei for The New York Times
- Guishan Island, Taiwan Rocks tumbling down one side of an island popular for hiking. Lavine Lin via Reuters
- Hualien, Taiwan A building leaned to one side after the quake. Randy Yang via Associated Press
- Ishigaki, Okinawa, Japan Watching news on a rooftop of a hotel after a tsunami warning. Chang W. Lee/The New York Times
- Hualien, Taiwan Motorbikes damaged in the quake. TVBS via Associated Press
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Damage in an apartment Fabian Hamacher/Reuters
- New Taipei City, Taiwan Water cascading down a building during the quake. Wang via Reuters
Meaghan Tobin and Victoria Kim
Here’s what you need to know about the earthquake.
Taiwan was rocked Wednesday morning by the island’s strongest earthquake in a quarter century, a magnitude 7.4 tremor that killed at least nine people, injured more than 800 others and trapped dozens of people.
The heaviest damage was in Hualien County on the island’s east coast, a sleepy, scenic area prone to earthquakes. Footage from the aftermath showed a 10-story building there partially collapsed and leaning heavily to one side, from which residents emerged through windows and climbed down ladders, assisted by rescuers. Three hikers were killed after being hit by falling rocks on a hiking trail in Taroko National Park, according to the county government.
By late afternoon, officials said rescue efforts were underway to try to rescue 127 people who were trapped, many of them on hiking trails in Hualien.
One building in Changhua County, on the island’s west coast, collapsed entirely. The quake was felt throughout Taiwan and set off at least nine landslides, sending rocks tumbling onto Suhua Highway in Hualien, according to local media reports. Rail services were halted at one point across the island.
The earthquake, with an epicenter off Taiwan’s east coast, struck during the morning commute, shortly before 8 a.m. Taiwanese authorities said by 3 p.m., more than 100 aftershocks, many of them stronger than magnitude 5, had rumbled through the area.
In the capital, Taipei, buildings shook for over a minute from the initial quake. Taiwan is at the intersection of the Philippine Sea tectonic plate and the Eurasian plate, making it vulnerable to seismic activity. Hualien sits on multiple active faults, and 17 people died in a quake there in 2018.
Here is the latest:
The earthquake hit Taiwan as many people there were preparing to travel for Tomb Sweeping Day, a holiday across the Chinese-speaking world when people mourn the dead and make offerings at their graves. Officials warned the public to stay away from visiting tombs in mountain areas as a precaution, especially because rain was forecast in the coming days.
TSMC, the world’s biggest maker of advanced semiconductors, briefly evacuated workers from its factories but said a few hours later that they were returning to work. Chip production is highly precise, and even short shutdowns can cost millions of dollars.
Christopher Buckley
Lai Ching-te, Taiwan’s vice president, who is also its president-elect, visited the city of Hualien this afternoon to assess the destruction and the rescue efforts, a government announcement said. Mr. Lai, who will become president in May, said the most urgent tasks were rescuing trapped residents and providing medical care. Next, Mr. Lai said, public services must be restored, including transportation, water and power. He said Taiwan Railway’s eastern line could be reopened by Thursday night.
Meaghan Tobin
Taiwan’s fire department has updated its figures, reporting that nine people have died and 934 others have been injured in the quake. Fifty-six people in Hualien County remain trapped.
Shake intensity
Taiwan’s fire department reports that nine people have died and 882 others have been injured in Taiwan. In Hualien County, 131 people remain trapped.
Agnes Chang
Footage shows rocks tumbling down one side of Guishan Island, a popular spot for hiking known as Turtle Island, off the northeast coast of Taiwan. Officials said no fishermen or tourists were injured after the landslide.

The death toll has risen to nine, according to Taiwan government statistics.
Meaghan Tobin, Siyi Zhao
Officials in Taiwan warned residents to not visit their relatives' tombs, especially in the mountains, this weekend during the holiday, known as Ching Ming, meant to honor them. There had already been 100 aftershocks and the forecast called for rain, which could make travel conditions on damaged roads more treacherous.
Crews are working to reach people trapped on blocked roads. As of 1 p.m. local time, roads were impassable due to damage and fallen rock in 19 places, according to the Ministry of Transportation. At least 77 people remain trapped. A bridge before Daqingshui Tunnel appeared to have completely collapsed.
Taiwan’s worst rail disaster in decades — a train derailment in 2021 that killed 49 people — took place on the first day of the Tomb Sweeping holiday period that year, in the same region as the earthquake.
The earthquake hit Taiwan as many people here were preparing to travel for Tomb Sweeping Day, or Ching Ming, a day across the Chinese-speaking world when people mourn their dead, especially by making offerings at their graves. Now those plans will be disrupted for many Taiwanese.
The holiday weekend would typically see a spike in travel as people visit family across Taiwan. Currently, both rail transport and highways are blocked in parts of Hualien, said Transport Minister Wang Guo-cai. Work is underway to restore rail transportation in Hualien, and two-way traffic is expected to be restored at noon on Thursday, he said.
Taiwan’s preparedness has evolved in response to past quakes.
Taiwan’s earthquake preparedness has evolved over the past few decades in response to some of the island’s largest and most destructive quakes .
In the years after a 7.6 magnitude earthquake in central Taiwan killed nearly 2,500 people in 1999, the authorities established an urban search-and-rescue team and opened several emergency medical operation centers, among other measures .
And in 2018, after a quake in the eastern coastal city of Hualien killed 17 people and caused several buildings to partially collapse, the government ordered a wave of building inspections .
Taiwan has also been improving its early warning system for earthquakes since the 1980s. And two years ago, it rolled out new building codes that, among other things, require owners of vulnerable buildings to install ad-hoc structural reinforcements.
So how well prepared was Taiwan when a 7.4 magnitude quake struck near Hualien on Wednesday morning, killing at least seven people and injuring hundreds more?
Across the island, one building collapsed entirely, 15 others were in a state of partial collapse and another 67 were damaged, the island’s fire department said on Wednesday afternoon . Structural engineers could not immediately be reached for comment to assess that damage, or the extent to which building codes and other regulations might have either contributed to it or prevented worse destruction.
As for search-and-rescue preparedness, Taiwan is generally in very good shape, said Steve Glassey, an expert in disaster response who lives in New Zealand.
“ The skill sets, the capabilities, the equipment, the training is second to none,” said Dr. Glassey, who worked with Taipei’s urban search-and-rescue team during the response to a devastating 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand. “They’re a very sharp operation.”
But even the best urban search-and-rescue team will be stretched thin if an earthquake causes multiple buildings to collapse, Dr. Glassey said.
Taiwan has options for requesting international help with search-and-rescue efforts. It could directly ask another country, or countries, to send personnel. And if multiple teams were to get involved, it could ask the United Nations to help coordinate them, as it did after the 1999 earthquake.
Pierre Peron, a spokesman for the United Nations, said on Wednesday afternoon that no such request had yet been made as a result of the latest earthquake.
Meaghan Tobin contributed reporting.
At least seven people have died and 736 have been injured as a result of the earthquake, according to Taiwan’s fire department. Another 77 people remained trapped in Hualien County, many of them on hiking trails. Search and rescue operations are underway, said the fire department.
Aftershocks of magnitudes between 6.5 and 7 were likely to occur over the next three or four days, said Wu Chien-fu, director of the Taiwanese Central Weather Administration’s Seismology Center, at a news conference.
As of 2 p.m., 711 people had been injured across Taiwan, the fire department said, and 77 people in Hualien County remained trapped. The four who were known to have died were in Hualien.
Victoria Kim
Hualien County is a quiet and scenic tourist destination.
Hualien County on Taiwan’s east coast is a scenic, sleepy tourist area tucked away from the island’s urban centers, with a famous gorge and aquamarine waters. It also happens to sit on several active faults , making it prone to earthquakes.
The county has a population of about 300,000, according to the 2020 census, about a third of whom live in the coastal city of Hualien, the county seat. It is one of the most sparsely populated parts of Taiwan. About three hours by train from the capital, Taipei, the city describes itself as the first place on the island that’s touched by the sun.
Hualien County is home to Taroko National Park, one of Taiwan’s most popular scenic areas. Visitors come to explore the Taroko Gorge, a striated marble canyon carved by the Liwu River, which cuts through mountains that rise steeply from the coast. The city of Hualien is a popular destination as a gateway to the national park.
According to the state-owned Central News Agency, three hikers were trapped on a trail near the entrance to the gorge on Wednesday, after the quake sent rocks falling. Two of them were found dead, the news agency said. Administrators said many roads within the park had been cut off by the earthquake, potentially trapping hikers, according to the report.
Earthquakes have rattled Hualien with some regularity. In 2018, 17 people were killed and hundreds of others injured when a magnitude 6.5 quake struck just before midnight, its epicenter a short distance northeast of the city of Hualien.
Many of the victims in that quake were in a 12-story building that was severely tilted, the first four floors of which were largely crushed, according to news reports from the time. The next year, the area was shaken by a 6.1-magnitude earthquake that injured 17 people.
The area has some of the highest concentrations of Taiwan’s aboriginal population, with several of the island’s Indigenous tribes calling the county home .
The county government in Hualien released a list of people that had been hospitalized with injuries, which stood at 118 people as of midday Wednesday.
Across Taiwan, one building fell down entirely, in Changhua County on the west coast, and 15 buildings partially collapsed, Taiwan’s fire department said. Another 67 buildings were damaged. One of the partially collapsed structures was a warehouse in New Taipei City where four people were rescued, according to Taiwan’s Central News Agency. Another 12 were rescued at a separate New Taipei City building where the foundation sank into the ground.
Peggy Jiang, who manages The Good Kid, a children’s bookstore down the street from the partially collapsed Uranus Building in Hualien, said it was a good thing they had yet to open when the quake struck. The area is now blocked off by police and rescue vehicles. “Most people in Hualien are used to earthquakes,” she said. “But this one was particularly scary, many people ran in the street immediately afterward.”
Lin Jung, 36, who manages a shop selling sneakers in Hualien, said he had been at home getting ready to take his 16-month-old baby to a medical appointment when the earthquake struck. He said it felt at first like a series of small shocks, then “suddenly it turned to an intense earthquake shaking up and down.” The glass cover of a ceiling lamp fell and shattered. “All I could do was protect my baby.”
Chris Buckley , Paul Mozur , Meaghan Tobin and John Yoon
The earthquake damaged buildings and a highway in Hualien.
The magnitude 7.4 earthquake that struck Taiwan on Wednesday damaged many buildings and a major highway in Hualien, a city on the eastern coast, and it knocked out power as it rocked the island.
Across Taiwan, the quake and its aftershocks caused one building to completely collapse and 15 others to partially collapse, according to Taiwan’s fire department. Sixty-seven other buildings sustained damage.
Two tall buildings in Hualien that sustained particularly extensive damage were at the center of the rescue efforts there. Most damage across the city was not life-threatening, said Huang Hsuan-wan, a reporter for a local news site.
Where buildings were reported damaged in Hualien City
“A lot of roads were blocked off. There are a lot of walls toppled over onto cars,” Derik du Plessis, 44, a South African resident of Hualien, said shortly after the earthquake. He described people rushing around the city to check on their houses and pick up their children. One of his friends lost her house, he said.
One of the damaged buildings in Hualien, a 10-story structure called the Uranus Building that housed a mix of homes and shops, was tilted over and appeared to be on the verge of collapse. Many of its residents managed to flee, but some were missing, said Sunny Wang, a journalist based in the city. Rescuers were trying to reach the basement, concerned that people might be trapped there.
Photographs of the initial damage in Hualien showed another building, a five-story structure, leaning to one side, with crushed motorcycles visible at the ground-floor level. Bricks had fallen off another high-rise, leaving cracks and holes in the walls.
The quake also set off at least nine landslides on Suhua Highway in Hualien, according to Taiwan’s Central News Agency, which said part of the road had collapsed.
Taiwan’s fire department said four people had been killed in the earthquake.
Across Taiwan, 40 flights have been canceled or delayed because of the earthquake, according to Taiwan’s Central Emergency Operation Center.
President Tsai Ing-wen visited Taiwan’s national emergency response center this morning, where she was briefed about the response efforts underway by members of the ministries of defense, transportation, economic affairs and agriculture, as well as the fire department.
A look at Taiwan’s strongest earthquakes.
The magnitude 7.4 earthquake that hit Taiwan on Wednesday morning was the strongest in 25 years, the island’s Central Weather Administration said.
At least four people died after the quake struck off Taiwan’s east coast, officials said.
Here’s a look back at some of the major earthquakes in modern Taiwanese history:
Taichung, 1935
Taiwan’s deadliest quake registered a magnitude of 7.1 and struck near the island’s west coast in April 1935, killing more than 3,200 people, according to the Central Weather Administration. More than 12,000 others were injured and more than 50,000 homes were destroyed or damaged.
Tainan, 1941
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake in December 1941, which struck southwestern Taiwan, caused several hundred deaths, the United States Geological Survey said.
Chi-Chi, 1999
A 7.6 magnitude earthquake in central Taiwan killed nearly 2,500 people in September 1999. The quake, which struck about 90 miles south-southwest of Taipei, was the second-deadliest in the island’s history, according to the U.S.G.S. and the Central Weather Administration. More than 10,000 people were injured and more than 100,000 homes were destroyed or damaged.
Yujing, 2016
A 6.4 magnitude earthquake in February 2016 caused a 17-story apartment complex in southwestern Taiwan to collapse, killing at least 114 people . The U.S.G.S. later said that 90 earthquakes of that scale or greater had occurred within 250 kilometers, or 155 miles, of that quake’s location over the previous 100 years.
Advertisement
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section contains information on The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) method of document formatting and citation. These resources follow The Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition), which was issued in 2017.
Since The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) is primarily intended as a style guide for published works rather than class papers, these guidelines will be supplemented with information from, Kate L. Turabian’s Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (8th ed.), which is largely based on CMOS with some slight alterations.
To see a side-by-side comparison of the three most widely used citation styles, including a chart of all CMOS citation guidelines, see the Citation Style Chart.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in CMOS.
A Note on Citations
Unlike many citation styles, CMOS gives writers two different methods for documenting sources: the Author-Date System and the Notes-Bibliography (NB) System. As its name suggests, Author-Date uses parenthetical citations in the text to reference the source's author's last name and the year of publication. Each parenthetical citation corresponds to an entry on a References page that concludes the document. In these regards, Author-Date is very similar to, for instance, APA style.
By contrast, NB uses numbered footnotes in the text to direct the reader to a shortened citation at the bottom of the page. This corresponds to a fuller citation on a Bibliography page that concludes the document. Though the general principles of citation are the same here, the citations themselves are formatted differently from the way they appear in Author-Date.
If you are using CMOS for school or work, don't forget to ensure that you're using your organization's preferred citation method. For examples of these two different styles in action, see our CMOS sample papers:
Author-Date Sample Paper
NB Sample Paper
General CMOS Guidelines
- Text should be consistently double-spaced, except for block quotations, notes, bibliography entries, table titles, and figure captions.
- A prose quotation of five or more lines, or more than 100 words, should be blocked.
- CMOS recommends blocking two or more lines of poetry.
- A blocked quotation does not get enclosed in quotation marks.
- A blocked quotation must always begin a new line.
- Blocked quotations should be indented with the word processor’s indention tool.
- Page numbers begin in the header of the first page of text with Arabic number 1.
- For CMOS and Turabian’s recommendations, see “Headings,” below.
Supplemental Turabian Style Guidelines
- Margins should be set at no less than 1”.
- Typeface should be something readable, such as Times New Roman or Courier.
- Font size should be no less than 10 pt. (preferably, 12 pt.).
Major Paper Sections
- The title should be centered a third of the way down the page.
- Your name, class information, and the date should follow several lines later.
- For subtitles, end the title line with a colon and place the subtitle on the line below the title.
- Double-space each line of the title page.

CMOS Title Page
- Different practices apply for theses and dissertations (see Kate L. Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, ad Dissertations [8 th ed.].
- Titles mentioned in the text, notes, or bibliography are capitalized “headline-style,” meaning first words of titles and subtitles and any important words thereafter should be capitalized.
- Book and periodical titles (titles of larger works) should be italicized.
- Article and chapter titles (titles of shorter works) should be enclosed in double quotation marks.
- The titles of most poems should be enclosed in double quotation marks, but the titles of very long poems should be italicized.
- Titles of plays should be italicized.
- For example, use lowercase terms to describe periods, except in the case of proper nouns (e.g., “the colonial period,” vs. “the Victorian era”).
- A prose quotation of five or more lines should be “blocked.” The block quotation should match the surrounding text, and it takes no quotation marks. To offset the block quote from surrounding text, indent the entire quotation using the word processor’s indentation tool. It is also possible to offset the block quotation by using a different or smaller font than the surrounding text.
- Label the first page of your back matter, your comprehensive list of sources, “Bibliography” (for Notes and Bibliography style) or “References” (for Author-Date style).
- Leave two blank lines between “Bibliography” or “References” and your first entry.
- Leave one blank line between remaining entries.
- List entries in letter-by-letter alphabetical order according to the first word in each entry, be that the author's name or the title of the piece..
- For two to three authors, write out all names.
- For four to ten authors, write out all names in the bibliography but only the first author’s name plus “et al.” in notes and parenthetical citations.
- When a source has no identifiable author, cite it by its title, both on the references page and in shortened form (up to four keywords from that title) in parenthetical citations throughout the text.
- Write out publishers’ names in full.
- Do not use access dates unless publication dates are unavailable.
- If you cannot ascertain the publication date of a printed work, use the abbreviation “n.d.”
- Provide DOIs instead of URLs whenever possible.
- If no DOI is available, provide a URL.
- If you cannot name a specific page number when called for, you have other options: section (sec.), equation (eq.), volume (vol.), or note (n.).

CMOS Bibliography Page
- Note numbers should begin with “1” and follow consecutively throughout a given paper.
- Note numbers are superscripted.
- Note numbers should be placed at the end of the clause or sentence to which they refer and should be placed after all punctuation, except for the dash.
- Note numbers are full-sized, not raised, and followed by a period (superscripting note numbers in the notes themselves is also acceptable).
- In parenthetical citation, separate documentation from brief commentary with a semicolon.
- Do not repeat the hundreds digit in a page range if it does not change from the beginning to the end of the range.
For more information on footnotes, please see CMOS NB Sample Paper .
While The Chicago Manual of Style does not include a prescribed system for formatting headings and subheads, it makes several recommendations.
- Maintain consistency and parallel structure in headings and subheads.
- Use headline-style for purposes of capitalization.
- Subheadings should begin on a new line.
- Subheadings can be distinguished by font-size.
- Ensure that each level of hierarchy is clear and consistent.
- Levels of subheads can be differentiated by type style, use of boldface or italics, and placement on the page, usually either centered or flush left.
- Use no more than three levels of hierarchy.
- Avoid ending subheadings with periods.
Turabian has an optional system of five heading levels.
Turabian Subheading Plan
Here is an example of the five-level heading system:

CMOS Headings
Tables and Figures
- Position tables and figures as soon as possible after they are first referenced. If necessary, present them after the paragraph in which they are described.
- For figures, include a caption, or short explanation of the figure or illustration, directly after the figure number.
- Cite a source as you would for parenthetical citation, and include full information in an entry on your Bibliography or References page.
- Acknowledge reproduced or adapted sources appropriately (i.e., photo by; data adapted from; map by...).
- If a table includes data not acquired by the author of the text, include an unnumbered footnote. Introduce the note by the word Source(s) followed by a colon, then include the full source information, and end the note with a period.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in CMOS
On the new OWL site, contributors’ names and the last edited date are no longer listed at the top of every page. This means that most citations will now begin with the title of the resource, rather than the contributors' names.
Footnote or Endnote (N):
Corresponding Bibliographical Entry (B):
“Title of Resource.” List the OWL as Publishing Organization/Web Site Name . http://Web address for OWL resource.
“General Format.” The Purdue OWL. https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02/.
Author Date In-text Citation:
("General Format" 2017).
Author Date References Page Citation:
Year of Publication. “Title of Resource.” List the OWL as Publishing Organization/Web Site Name . http://Web address for OWL resource.
2017. “General Format.” The Purdue OWL . https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on March 5, 2024. The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing: Your full name. Your instructor's name. The course name and number. The date of submission. After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special ...
4. Hover over "Top of Page" and select "Plain Number 3". 5. For the MLA header, enter your last name along with the page number, both right-aligned. For the APA header, input the abbreviated version of the title in all capital letters and press the "Tab" key. MLA essay header example. APA essay header example.
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5. The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work. If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
Headings Are Only the Beginning. Once you've got your headings sorted, it's time to start writing your paper. While we can't help you edit the content of your essay, ProWritingAid is here to make sure your grammar, spelling, and style is on point.. As well as checking your grammar, ProWritingAid also shows you your progress towards key goals like varied sentence structure, active voice ...
Include an empty line both above and below a heading. Avoid numbering or lettering your headings as lists (e.g., ( 1) The Beginning or (Z) The Ending ), unless this is conventional for the field you're writing in. Use title capitalization for headings (e.g., The First Letter of Each Major Word Is Capitalized ).
Be consistent throughout your essay. Choose a pattern and stick with it throughout the entirety of the assignment. If you start off by having a heading for each paragraph, keep it that way until the end. Also, make sure the format remains the same. If your first heading is in the form of a question, all of the rest should be as well.
1. Include your personal information. MLA format doesn't require you to have a title page. Therefore, on the first page of your paper, you need to include your information in the upper left-hand corner to identify yourself. You'll need to have your name, the professor's name, the name of the class, and the date. Put your name at the top.
Here's what your essay title should include. One or more relevant keywords to your subject. Any other necessary words or phrases that tell the reader what to expect from your essay. When applicable, a catchy phrase or figurative language. Let's take another look at the example essay titles from the section above.
When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a source or collection of sources, you will have the chance to wrestle with some of the
Section Headings. Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document's readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay. Essays. MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section ...
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
Headings should have a length of one to five words and not exceeding a whole line, as said above. A unique tip on how to write a heading is that it looks more like a title than a subheading. Not all paragraphs need a heading. If you know how to write a heading, use headings for two or more ideas, and do not overdo them.
Yes. It will help if you put headings in your essays to make them more readable. Essays consist of three parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Most of them are written in a continuous, paragraphed text without the need for section headings, especially if it's a short essay. On the other hand, long-form essays need headings and subheadings ...
Headings. APA Style uses a unique headings system to separate and classify paper sections. Headings are used to help guide the reader through a document. The levels are organized by levels of subordination, and each section of the paper should start with the highest level of heading. There are 5 heading levels in APA. Regardless of the number ...
The running header helps the reader to better navigate the essay, especially a long one. How to make a header for an essay: a detailed guide with examples. In a standard college essay, the very first page (the title page) contains the title page header. It precedes the title itself, which goes right after the title header and is usually center ...
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Note: The publisher's name need not be included in the following sources: periodicals, works published by their author or editor, websites whose titles are the same name as their publisher, websites that make works available but do not actually publish them (such as YouTube, WordPress, or JSTOR).. Publication date. The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an ...
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page. Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize major words of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Strong Taiwan Quake Kills 9, Injures Hundreds. The earthquake was the most powerful to hit the island in 25 years. Dozens of people remained trapped, and many buildings were damaged, with the ...
Headings. While The Chicago Manual of Style does not include a prescribed system for formatting headings and subheads, it makes several recommendations. Maintain consistency and parallel structure in headings and subheads. Use headline-style for purposes of capitalization. Subheadings should begin on a new line.