

State Ranker Guide: How to Write a Full Mark Reflection

State Ranker Guide: How to approach Novel Study (To Kill a Mockingbird)
State ranker guide: how to write a comparative essay (module a + extension 1).

- Uncategorized

Comparative essays are a staple of Advanced, Extension I English and throughout Year 7-10, and the rationale behind it makes sense – NESA wants to measure and test your understanding of abstract concepts and ideas across different texts and forms. A comparative essay in layman’s terms is simply an essay which discusses two or more texts in regards to a common (or differing) element, which could involve themes, contextual influence or construction. You’ll encounter these in Module A: Textual Conversations as well as in your elective for Extension I, but similar skills are potentially needed for your Literary Worlds and you’ll even encounter a simplified version of it for short answer responses in Paper 1! As you can tell, this is a seriously handy skill to have.
1. Before you compare
I briefly mentioned three things earlier – themes, contextual influence and construction. Within an essay, you have to explore all three of these in some shape or form.
Themes are the most obvious. To borrow Mod A terminology, themes can either ‘resonate’ or be ‘dissonant’ between texts. A comparative essay would analyse how composers have understood these ideas, and the way they have been represented in their work. For example, for ‘The Tempest’ and ‘Hag-Seed’, you could discuss the concept of isolation. You would write that Shakespeare literally placed Prospero on a island far flung from Milan (physical isolation) whereas Atwood’s protagonist is mentally isolated, being distant and mentally unstable from the rest of society after the death of his loved ones and a bitter betrayal. To see detailed notes of Tempest and Hagseed, click here .
Contextual influence In both your Extension elective and Mod A, and any comparative you do in Year 7-10, this is SUPER important – the world and life of a composer will be reflected in a text through their artistic movement, social values and norms, cultural references and much more. No context is the same between creators, and by analysing them you can get a better understanding of their intent and logic behind the text. This is especially critical when evaluating themes, since different contexts will elucidate different responses. Take Keats’ poetry and ‘Bright Star’ – not only were they made in different millenniums, but their movements, Romanticism and postmodernism respectively, have different objectives and agendas.
Construction could be form, but also style and craft. Different mediums will elicit different responses and their conventions will communicate different ideas more strongly. An obvious example would be that of ‘Frankenstein’ (to see full notes on Frankenstein, click here ) and ‘Metropolis’. In the former Shelley uses prose fiction to reminisce and remember, establishing this unsettling and moody atmosphere. Fritz, with his film on the other hand, makes strong use of visuals to express the tension and anxieties of his time.
When you’re preparing to write an essay, keep those three in mind. Now that you’ve got that, how do we go about structuring it? The truth is that there is not one single way to write an essay. Comparatives only require you to discuss ideas between texts, and as such there is not a prescribed format you must use. However, remember that all texts should be given fair weighting! You don’t want to end up with a response which is biased towards one text. Achieving a balanced comparative essay in Advanced and Extension I are two completely different beasts, and as such we should take a look at each subject separately. That being said, a commonality between the two is the way you write an introduction.
2. Introducing the Comparisons
In the intro, you’ll not only need to introduce the texts and contextualise them, but also reveal your thesis, what it means, and how it’s explored in each text. Use your best friend PEEL here – it will seriously help you reveal insights more coherently and strongly. Let’s start with our opener. Here’s an example of an opening from Mod A:
Between Mrs Dalloway (1925) and The Hours (2002), the texts discuss modernity’s preoccupation of claiming individual choice.
Let’s break this down:
The texts – ‘Mrs Dalloway’ and ‘The Hours’ have been named. A year has been attached to each, and this gives markers a clue as to the disparate contexts between the texts.
The thesis (an overarching argument) has been introduced also, that of “modernity’s preoccupation to claim individual choice”. Get used to making a theory about your texts – write about what you really think about these works. What themes or ideas do they present? What do they make you reconsider or discover? Do they teach you anything? Your personal response to literature is king here; be confident and make a statement! Just make sure it’s backed up with evidence.
Now that the point has been made, we need to explain what it all means.
Though there are common themes, ideas and even characters, the disparities present between Virginia Woolf’s novel and Stephen Daldry’s film are far more revealing of fluctuating social values and changing attitudes. Aside from the difference in form, the contrasting perspectives of Woolf’s Interwar, modernist England and Daldry’s 2000s, postmodern America have caused this pair of texts to be shaped uniquely by their contexts and thus reveal conflicting, even competing, aspirations and anxieties, particularly those regarding modernity and mortality.
We address the question statement “the disparities … are far more revealing of fluctuating social values”. Straight after you make your point you need to answer what the question’s asking and relate that to your texts. That’s revealed when…
We showed the comparison. This explainer mentioned “common themes, ideas and even characters”, which depending on your question might be more important. However, since the question asked for dissonances, we established instead a divide between the two texts – “difference in form” and “contrasting perspectives”.
If you hadn’t already, name the authors and the forms. You could do it in your opening line, but here we’ve chosen to do so here with “Woolf’s novel” and “Daldry’s film”.
We also just showed the contexts – “Interwar, modernist England” and “2000s, postmodern America”. In three words each, we have established a time period, a movement and a location. Be economical and straight to the point like this – you don’t have much time in an exam to waffle on forever.
We also honed into what the thesis means – how the texts reflect “competing, even conflicting aspirations and anxieties” towards “modernity and mortality”.
That second phrase of “modernity and mortality” reveals the key points , and what the body paragraphs will explore further. Depending on how you structure your essay, this might not be needed as your body paragraphs will be dedicated to different texts. But once again, we’ll come back to this.
Now that the explanations have been exhausted, it’s time to probe our texts, which are examples to sustain our thesis .
Dalloway, a seminal modernist text, saw choice as the greatest ideal which the modern world espoused, in that one’s fate must be willed and not determined by proportion. A powerful dissonance arises when the novel is appropriated by The Hours, which took a more skeptical approach towards choice, viewing it simultaneously as liberating and as a parasitic obsession over individuality.
The central idea behind each text is shown. Dalloway “saw choice as the greatest ideal”, while Hours “took a more sceptical approach… viewing it simultaneously as liberating and… parasitic”. In doing so, in your introduction you can show how your texts affirm or diverge in beliefs.
Finally, once you’ve given evidence it is time to link it all back to what you’re writing for in the first place.
Though the resonance of modern people finding fulfilment and freedom from establishments remain, it is in the difference in values that audiences can contemplate upon their own context’s impact on themselves, powerfully evident through the textual conversation between Dalloway and The Hours.
Breaking it down once again:
Note the use of rubric terms . Markers LOVE seeing this. Make sure you read up on the module rubric and identify what exactly you’re supposed to be looking out for while analysing your texts. In this case, “resonance” and “textual conversation” here.
We also talk about audience impact , a big part of HSC English. No essay is complete without evaluating the reception of a text by its readers or viewers. In this case, we discuss how “audiences can contemplate on their own context’s impact on themselves”.
We get more references to the question and thesis in “difference in values” and “finding fulfilment and freedom” respectively. This is a must in your link.
Sounds straightforward, right? Notice how throughout this essay there’s a constant back and forth between texts. This is a very simple way of making direct comparisons, and doing this will help you structure your ideas while also communicating clearly. And even though we’re at the beginning, let’s jump straight to the end! Conclusions are essentially the same in format as introductions, except they’re conclusive. Go figure. Just look above for what elements to look out for, summarise and pull out all your evaluations.
Unfortunately, from here on out things are going to get messy. Depending on your texts and the number of texts, you might find yourself structuring your body paragraphs differently. So, time to split off and look at Advanced and Extension I!
3. Module A: conversations about comparisons
No matter what question you’ll be thrown, you will always have to look at TWO texts – the original and then its appropriation. Markers expect students to answer a question with equal weighting to each text, and as such you need to remember that the inspired text is just as powerful as its inspiration . Knowing that, there is one way you can approach your body paragraphs that will be a sure-fire hit with markers.
Integration .
In this style of writing, you will discuss both texts in relation to a theme or idea. This generally tends to be the preferred style of writing, since it allows for comparisons to be drawn continually and consistently. It is also the way to go for Mod A since the whole point of the module is textual conversation . So, let’s have a look at key lines from a paragraph in that Dalloway and Hours essay:
In order to present disparate conceptions of modernity, Woolf and Daldry manipulated their form with modernist and postmodernist praxis respectively, examining context to invoke contemplation within responders regarding the role of society in affecting personal experience.
And once again our body paragraphs follow a PEEL structure . The opening line establishes the explored theme , reference to context , and the intent . Get used to writing succinctly and bluntly – it will save you time in an exam!
Woolf pioneered stream of consciousness writing, eliminating the Victorian era’s omnipresent narrator as to witness the intrusion of past memories and external stimuli within a world of boisterous flux.
Our little explanation pinpoints the form element and its significance .
Following this in the paragraph, we get evidence from a quote early on in the novel, then the analysis. To wrap off this part we get:
As a result, Woolf alludes to a frantic, broken world which in the aftermath of the Great War feels a sense of loss and disillusionment.
A link is made between the evidence given and the theme , which help explore the thesis established in the introduction. From this insight we get a better understanding of what the composer was trying to communicate – to say to the audience.
Meanwhile, within The Hours Daldry and cinematographer Seamus McGarvey used postmodern disrupted chronology.
Our second text receives the same treatment as the first – the composer is named and we also learn about what form element we are focusing on.
Daldry was more concerned with examining modernity as an era, an epoch in history.
This explanation likewise shows the significance of this form element in relation to the theme.
By doing so, the very reason for these parallelled scenes becomes clear, revealing dissonances between peoples in the same era, and that there is no singular experience.
This insight is drawn after discussing scenes from the film. Another link is made between the theme and evidence .
The two texts clearly demonstrate disparities in tone; Woolf’s modernity ‘mis-en-scène’ articulates a society bewildered by the brave new world they are living within, whereas Daldry is more retrospective, contemplating on the diversity of voices and, questioning the supposed experiential hegemony of the era. Evidently, the two texts have expressed dissonances in the way their composers perceive modernity.
And here is our grand link – we reach a conclusion , make a comparison and reframe what was discussed with regards to the question . The little insights and evaluations throughout the paragraph culminate here and reveal what was learnt from an analysis of the two texts.
You may have noticed a pattern in the paragraph, in that there were mirrors in analysis between the two texts. That’s the powerful simplicity of the PEEL style, it’s naturally conducive to comparative essays. Even though it was more like PEEEELEEEELL there still was a coherent and logical sequence of arguments and ideas, which is something you need to watch out for while writing. Your ideas need to lead to a conclusion. This ‘mirrored’ type of writing is handy when trying to discuss two texts.
Now for some general tips and advice for Mod A comparatives:
Write either two OR four paragraphs. By that, I mean follow an AB AB or A B A B format, with either two chunky bodies or four smaller bite-sized analysis (preferably the latter). No matter which you choose you’ll still end up discussing only two themes, with the only difference being whether the two texts are discussed in the same paragraph or not. Three ideas might be overkill in the space of 40 minutes and should be avoided unless your teacher prefers a 3 body paragraph integrated structure.
You can write two dedicated paragraphs which are dedicated to one text each, but it’s risky. By segregating the two texts you run the danger of discussing them in isolation, which defeats the purpose of comparative essays and Mod A in general! If you decide to take this narrow and rocky path, make sure in your second paragraph that you keep making reference to the ‘original’ text and make your conclusion SUPER focused on drawing links between the pair. But once again, this is definitely not a recommended structure of writing.
4. Comparing your elective world
In Section II of your Extension I exam , you’ll need two prescribed texts and between one to two related texts. The weighting of these texts vary on how many you choose. That being said all texts are relevant and should be treated as such . Unlike Mod A, in Extension English there is a little bit more freedom to play around with essay structure since the style of questions and the sort of analysis they expect from you is far more in-depth and abstract. So, let’s quickly run over what kind of styles you can take:
Option A: Integration . Just like in Mod A, you would be discussing your prescribed and related text(s) in one paragraph. Extension I is the home of chunky paragraphs, so don’t worry about having to split them up for different texts. Once again, just follow PEEL and you’ll be alright. Your opening lines would have to establish the theme , two texts (because let’s be real, you can’t talk about three or four texts at the same time!), intent and significance . If you choose two do two related texts here, make sure you bring each one up only once throughout the essay. If you go over, you might end up giving it undue weight.
Option B: Isolation . In this subject, discussing the texts individually can and has worked. However if you choose to do this, make sure you’ve got a strong thesis and a core theme per text . Take for example this essay from Worlds of Upheaval. Keep an eye out for the thesis, which was that “individuals in confused societies are swept away by revolution”. The paragraphs opened with the following:
Those caught in confusion are denied self-expression as part of a monolithic politic, breeding uncertainty and injustice. An organisation of this nature inevitably becomes dogmatic and demands more of individuals. This, the great insanity of ideology, is responsible for creating a toxic public sphere. One representation of the political paradigm would be Marxism in Metropolis, which unwaveringly condemns it.
Though the uncertainty and injustice of confusion is universal, literary conceptions of Revolution are mixed, contingent from varied political affiliations between composers. Frankenstein is critical of Enlightenment and Romantic inclinations to deify mankind, implicating that confusion and revolution are one and the same — even if the two conflicting ideologies are antithesis to each other.
Against the poles of establishment and insurrection, the individual finds themselves driven towards action and reaction towards their context’s upheaval. Hashino in Persona 5 uses protagonist Ren Amamiya as the player’s means of embracing revolution within Confucian, hierarchical and hyper-capitalistic Japan.
Let’s annotate these:
Each paragraph centred on a different thesis element, text and context. Using the first as an example, “confused society” is the focus for Metropolis, and a quick aside about Marxism in Weimar Germany is made.
We also get an unfolding argument , that is, we compare texts by looking at how they recieve, or judge, the thesis. The second paragraph shows Shelley finds that “confusion and revolution are one and the same”, whereas Hashino in his video game wants players to “embrace revolution”. That shows that central themes are understood and reacted to differently in different contexts – the whole reason as to why you’re writing a comparative to begin with!
And how interesting that we only use one related text . If you choose to write texts in isolation, stick to one. You might have an hour to write an essay, but the level of substance and depth expected in an Extension essay is considerably more than that in Advanced. If you want to hit an E4, keep to three paragraphs. Any more than that would really strain you during the exam.
You might be wondering why you can write in depth about a related text when writing in isolation, but need to be sparse when writing integrated. In integrated paragraphs, you can afford to bring up two related texts. A format of AC BD AB works since if you rearrange these components (AA BB CD) you still get two paragraphs about prescribed texts and one with a related. Four isolated comparative paragraphs of AA BB CC DD are not only a waste of your precious exam time, but throw focus away from the prescribed texts – the balance of analysis is thrown off. So just remember this lesson: one in isolation, one or two get integrated. That being said, don’t do two unless you’re forced to or you’re super keen. One will get the job done!
5. Sharing the Comparing
We’ve been focusing on Mod A and the Extension elective, but they’re not the only places you’ll find comparative essay writing. You might be reading this as a Year 10 or 11 student and have absolutely no idea what a related text is. Don’t sweat! You could be asked to pick two or three texts and analyse them – so pick between integrated or isolated writing based on the question and what you’re comfortable with . Don’t forget the important stuff – context, themes, intent. They are the fundamentals. If you integrate, pick a theme per paragraph and discuss two texts. If you isolate, dedicate a paragraph per text and how they respond to the question, or statement, or thesis.
If you’re a Year 12 student, you might find yourself writing comparative essays in unexpected places. You will write extremely short versions of these for Texts and Human Experiences during Section I of Paper I. To see a full guide for this, click here . Many questions in past exams focused on how two texts explored a central emotion or experience – this is just another theme! Follow the integrated structure. Meanwhile, a critical response might be asked of you for Literary Worlds and you could be given multiple excerpts to analyse. Once again, choose between the two options based on suitability and personal preference. And when you compare, pay attention to literary theory and criticism – use what you’ve learnt in class to inform your discussion.
And that wraps it up! Comparative essays are a versatile and stylish way to investigate different texts – and they are key to success in the HSC.
However, this is not a skill you can perfect overnight. And this is where our tutors step in! Even from Year 7, our english tutors go through comparative studies between texts commonly studied in school (eg Shakespeare) and comprehension exam papers with sample answers for comparative mini-essays, so that students are prepared for any comparative study assessment they face during high school. Contact us to find out how we can help you today!

- Joseph #molongui-disabled-link State Ranker Guide: How to approach Novel Study (To Kill a Mockingbird)
- Joseph #molongui-disabled-link State Ranker Guide: How to Write a Full Mark Reflection

Related posts

When to start preparing for OC exam and why is it important to prep early

Top Selective School Graduate’s Tips on the English section of the OC exam

JP English Student Successes: How Andy scored 99.95 ATAR and Band 6 in English Advanced
Module A – Textual Conversations Guide
DOWNLOAD THE RESOURCE
Resource Description
Introduction to Mod A Module A: Textual Conversations is somewhat of an evolution of the previous comparative study module. It will most likely be studied after the Common Module, and unlike the other Modules (except C with its short texts), requires you to thoroughly study two texts rather than one. However, the time allocated to this is still the same as the other modules, so that means time is a massive obstacle. The internal tasks can be creatives or hand-in essays, but will most likely be essays under examination conditions. This will be the same for Trials and the HSC exam, as Module A forms 20 marks out of 60 in Paper 2 of English Advanced. One key distinction to make: Textual Conversation Essays are NOT just Comparative Essays. Use the comparative essay structures and conventions as a foundation, but Mod A requires you to develop this further. A textual conversation doesn’t simply compare or contrast ideas and approaches between two texts (though elements of that do exist), but imagine it as the two texts conversing with each other (as the name suggests). This entails studying what the hypertext (the genesis text; the older text that is initially starting the conversation with the newer text) is offering in regards to insights, and how this is developed and responded to by the newer text. Context, Values, and the Composer are vital when initiating and continuing a textual conversation. Keep in mind that this is a one-way conversation – both texts are not responding to each other. Think of it like when you are talking to your crush and they are not interested – those DMs are not a two-way conversation, as much as you’d like to tell yourself that.
Here’s a shoddy and amateur Canva renaissance masterpiece of art: While there are similarities and differences between the texts (and you should explore them in your essay), simply identifying them is insufficient for this module. In a textual conversation, something new is being said – as the rubric says, the conversation shapes new meaning. An easier way to approach essays for this module is to:
1. Identify what’s being said that is new. (Ideas) 2. What is it about the conversation between both texts that results in this being said. (Textual evidence + Context) a. What departures/alignments exist between the texts + why was this active choice made by the composer 3. What does this ultimately say about texts
(Thesis) a. This doesn’t have to be extremely profound or sophisticated; in fact, doing that can be counterintuitive since it corners you into only being prepared to write a specific style of essay. If the question diverges from what you want, it’s going to make everything super toug
Report a problem
Popular HSC Resources
- Speech on George Orwell ‘1984’ – Human Experiences
- How To Survive the HSC
- One Night the Moon – Analysis (Video)
- 2020 – Physics – PHS (Trial Paper)
- Business Studies Influences on HR (Quiz)
- Sci Ext – Portfolio Pack
- 2020 – Science Ext – Exam Choice (Trial Paper)
- Domino’s Marketing Case Study
Become a Hero
Easily become a resource hero by simply helping out HSC students. Just by donating your resources to our library!
What are you waiting for, lets Ace the HSC together!
Join our Email List
No account needed.
Get the latest HSC updates.
All you need is an email address.
Press Enter to search
A Step-by-Step Approach to Crafting High-Scoring Comparative Essays
Comparative essays might seem daunting, but this article is here to help. Let’s unpack exactly what is required, break down the structure, and aim for those top marks!
5 months ago • 5 min read
Comparative writing is mostly relevant for English subjects, especially at the ATAR level. Comparatives vary between states – in VCE, the Comparative SAC asks a question specific to the texts studied. In WACE English, comparatives are simply a type of question offered under Responding and are broadly applicable across texts. In the HSC comparative writing is imbedded into Mod A - textual conversations and even in short response questions.
Nevertheless, the general premise of the Comparative Essay is universal and this article is for all English students ; no matter the year level or state syllabus.
What is a comparative?
A comparative is just like any other analytical literary essay, but with a catch – instead of analysing one text, you compare two.
You will need to craft an argument which addresses what makes the two texts similar and what is different. You will need to read the essay question carefully and work out what the two texts have in common , and for which concept you should argue there is a difference .
Let’s look at some examples:
Q. Compare how two texts of different genres endorse a similar perspective.
Similar : Perspective
Different : Genre/generic conventions used
Example thesis: Texts A and B both endorse a pacifist, anti-war perspective, however, Text A achieves this through lighting and sound effects, whereas Text B employs poetic structure and rhyme scheme.
Q. Analyse how two texts employ characterisation to encourage different reader responses.
Similar: Characterisation
Different: Reader Response
Example thesis: Text A employs vivid characterisation of its protagonist to evoke readers’ empathy and affection, whereas Text B’s intense characterisation encourages a response of tension and discomfort.
Q. Compare the representation of the ‘ideal man’ in Text A and Text B
Similar: Ideal Man
Different: Representation
Example Thesis: Whilst both texts provide vivid constructions of the ‘ideal man’, Text A’s representation is an adaptable intellectual, whereas Text B represents the ideal man as stubborn and brawny.
Q. Discuss how two texts’ differing contexts of production affect their perspective on an issue.
Similar : Issue
Different : Perspective, context
Example thesis : Text A (1950), influenced by a restrictively patriarchal climate, presents a dismissive perspective that violence towards women is peripheral and harmless, whereas Text B (2018), created during the #MeToo movement, suggests that it is urgent and devastating.
For some comparatives, it might also make sense for your thesis to include the extent to which the texts are similar/different.
Writing your Comparative: Step-by-Step
1. understand your texts and why they work together.
There’s no point comparing apples and oranges! It’s important to know why your texts complement each other for a comparative essay. What do they have in common?
2. Deconstruct the question.
Try colour-coding key terms – for example, command words, similarities and differences. E.g. Compare how two texts employ conventions of the same genre, to explore different ideas.
3. Write your thesis/contention.
This should answer every aspect of the question. If you’ve colour-coded your question, make sure each colour is addressed.
4. Gather evidence.
It’s to find relevant evidence and quotes to back up your argument! This should be a rough 50/50 split between each text.
5. Have a list of comparative language handy!
Your reader/marker shouldn’t become confused about which text you’re talking about. Here’s some great comparative language for clarity and flow:
SIMILARITIES:
- Similarly
- Likewise
- In a similar vein/fashion/manner/way
- In parallel
- Additionally
- Equally
- Comparably
- Correspondingly
- Also, as well, too
- Just as
DIFFERENCES:
- Conversely
- Contrarily
- In contrast
- As opposed to
- Otherwise
- However
- Alternatively
- Instead
- Yet, but
- On the other hand
- Whereas
- Differently
- Unlike
- Although
- Compared to
- Meanwhile
6. Organise points and paragraphing.
A comparative should have an introduction and conclusion, just like any other textual analysis essay. They’re the bread holding your essay together.
Introduction:
- Hook or global statement
- Introduce your texts (brief synopses/plot summaries, relevant contextual information)
- Thesis / Contention / Central Argument
- Roadmap of your essay (i.e. signpost what your body paragraphs are each going to cover)
Conclusion:
- Reiterate argument
- Summarise points
- Final remarks about potential relevance of argument, significance, extent of similarity of the texts, etc.
But what about the middle of the sandwich? Usually, you will have four body paragraphs, but there are a couple of different ways to structure them:
Comparative Essay Structure

The point-by-point method is usually regarded as more sophisticated and will award you better marks.
This is because the comparison is better integrated into the analysis and demonstrates a more nuanced expression. However, the block is suitable for earlier stages (e.g. Year 9/10 level), or the texts you are comparing do not align precisely per point.
If you want to reach for those very top marks, you can take the point-by-point method even further, alternating more frequently between evidence from Texts A and B for even more specific comparison. This is sometimes called…
THE RAINBOW METHOD:
My final tips for top marks (from a 99.95 graduate)
- Maintain your 50/50 text balance
- Use specific evidence
- Use terminology from the question
- Ensure your discussion of the two texts interacts – it shouldn’t feel like two separate essays awkwardly glued together
- Consider why the texts are different, particularly in your conclusion. What is the significance?
Good luck, and happy comparative writing!

Want more personalised tips to drastically improve your English mark? A private tutor can make the biggest difference!
Written by KIS Academics Tutor from WA, Poppy Bell. Poppy received a 99.95 ATAR and is currently studying Arts/Law at the University of Melbourne (Chancellor’s Scholar). Poppy tutors English, Literature, Mathematics, Modern History, and French. You can view Poppy’s profile and glowing reviews here and request her as a tutor.
- High School
Spread the word
Cracking the code: achieving a perfect ib english score, navigating naplan: strategies for year 5 achievement., keep reading, how to respond to short answer questions in vce english language, how to craft a band 6 mod a textual conversations essay, how to write a top mark feature article, subscribe to our newsletter.
Stay updated with KIS Academics Blog by signing up for our newsletter.
🎉 Awesome! Now check your inbox and click the link to confirm your subscription.
Please enter a valid email address
Oops! There was an error sending the email, please try later
Structuring Comparative Essay | HSC English
Structuring comparative essay.
Tegan explains about Structuring Comparative Essay.
About Comparative Essay
Today we will begin to examine the structure of the comparative essay. The structure and purpose of a comparative essay is very different from the thematic essay you are used to writing, and the content of the argument will require a very different approach as well.
You may need to revisit these concepts a few times to gain familiarity with them.
Today we will cover:
- Structure of the Introduction
- Structure of the Body Paragraph
Example Body Paragraph
- Essay Planning
What should the Essay look like?
The introduction:.
A comparative essay takes a little more ‘setting up’ than a thematic essay. In your introduction, you should:
- Justify the comparative study and explain the major link between your texts which makes them suitable for intertextual studies. For example, a comparative study might reveal more about each text and create a synergistic understanding of the connections or perspectives being examined. Or, through contrasting the texts, the effect of contextual values on each text may be better understood. You should mesh ideas from the module and elective rubrics here for structuring comparative essay.
- Then, your thesis should focus on the best or most important thing that comparative study of these two texts reveals . Try not to simply go for a theme, like ‘attitudes to love’ as this is not a thematic study, and you want your thesis to be broadly appealing for different types of question. You might talk about how considering contextual values is important because it makes the responder wonder how much the time and place they live in shapes their own opinions.
Guide to structuring the Introduction
Introduction for structuring comparative essay.
- Address the essay question using keywords and use some words of your thesis to answer it.
- Name Text One, with the year it was published in brackets after it.
- Indicate the genre, text type and composer of the text.
- Give a brief summary of Text One’s cultural context – no more than a sentence.
- Name Text Two, with the year it was published in brackets after it.
- Give a brief summary of Text Two’s cultural context – no more than a sentence.
- Identify why the two texts are to be studied together – mention the most important commentary they have to share that links them etc.
- Signpost the main connections/perspectives you are going to discuss, and introduce them in the order they will appear in the body of your essay.
Drafting for Structuring Comparative Essay
Question: take your time in writing an introduction to your essay. you will want to consider:.
- The best general thesis that binds all the argument ideas together
- The best keywords to broadly sketch the time period and context of your texts.
- Whether the texts have a reputation – i.e. are they well known classics?
- What can a comparison of these texts really teach us?
Guide to Structuring Body Paragraphs
A comparative essay really requires integrated paragraphs in order to work. Your school may or may not make this mandatory, but it is essential; otherwise you write two mini-essays on each text that just happen to occupy the same page.
You have already encountered a huge part of how to set out body paragraphs in your ‘What Why Fact How’ study paragraphs, so if you have written your study notes properly, most of the work is done for you for structuring comparative essay.
Integrated paragraphs are much longer than the type you are used to in your Area of Study essay, where you might have 8-10 paragraphs in your discovery essay, you will only need 3-4 paragraphs for each comparative essay.
Body Paragraphs:
- Topic sentence: introduce the connection/perspective which is in both texts.
- What Why and Fact of Text One, explaining how contextual values shape this connection/perspective.
- Name a technique and a long quote (2-3 sentences) from Text One to support this.
- What Why and Fact of Text Two, explaining how contextual values shape this connection/perspective.
- Name a technique and a long quote (2-3 sentences) from Text Two to support this.
- Comment on the similarity or difference between the texts, and what has been revealed.
- Conclusion sentence: Thus, link that revelation to your question and thesis.
Question: Underline and annotate the structures in this example paragraph based on the guide.
The implicit connection of receiving and giving advice between women permeate Letters to Alice and Pride and Prejudice , highlighting this value as relevant to women’s lives as time progresses, because it allows them to have a secure future. The formal epistolary structure of Letters to Alice provides a means of presenting advice that’s uncommon within contemporary society, and establishes Aunt Fay as representative of her 1980s context.
The mentoring relationship between Alice and Fay is founded through giving advice within letters: “what others say are your faults… may it be carried to the extremes, you strengths, virtues”. Weldon’s juxtaposition of Fay’s advice against criticism of Alice enforces the importance of sharing advice between women as writers in the twentieth century, as she believes it is difficult to obtain meaningful advice and criticism in the 21 st century.
This can also be viewed as the flow of advice moving down the familial social structure based on age, revealing that advice is only allowed to be given by older women – meaning that there is a kind of traditionalist matriarchal structure still present within female communities. Sharing advice between women is also prevalent within Pride and Prejudice , highlighting this as a continuous value relevant to women’s lives.
Letters provide symbolism of the close relationships between characters, as it was more confidential than public speech and not always subject to strict social conduct. The importance of sharing advice between women is seen through this medium of correspondence, and also reflects advice passing down the familial social structure. Mrs. Gardiner and Elizabeth’s close relationship gives evidence to this facet of women’s lives in Austen’s early Victorian context.
“Lizzy, this must go no farther than yourself, or Jane at most”. Mrs. Gardiner’s instructive tone, acting in her nieces best interests, emphasizes the close nature of their relationship – an exception to social norms, as in Austen’s context, relationships were largely created for the ulterior motive of financial security. Thus the implicit connection of sharing advice is seen to be relevant to women’s lives, past and present, in the study of Pride and Prejudice and Letters to Alice .
Question: Write a dot point plan, and then a full draft, of ONE paragraph of your essay.
You will want to consider the following for structuring comparative essay.
- The best quotes to illustrate a particular value.
- The best historical fact to illustrate a particular value.
- Whether one text may have influenced the other.
- The significance of this value to human daily life or achievement.
Make a further list of Techniques and Quotes
There will be some important quotes in each text that you haven’t quite figured out how to pair up yet, or that match with a connection that you already have an existent quote for. Don’t disregard these quotes – they are valuable resources and you will probably use all of them at some point for structuring comparative essay.
For each text, keep a growing list of quotes in a ready-to-use format, like this:
- Quote + Technique à contextual value.
- (e.g.) ‘Whilst my physicians by their love are grown / Cosmographers, and I their map…As west and east / In all flat maps—and I am one—are one, / So death doth touch the resurrection.’ + Metaphysical conceit. (Means that a map can be folded to bring east and west together – i.e. opposites may have a kind of similarity or union.) à Science of cartography which was developing in the early 1600s.
Sample HSC Comparative Literature Exam
Try our Comprehensive English Courses!
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Comparative Essay
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,682,513 times.
Perhaps you have been assigned a comparative essay in class, or need to write a comprehensive comparative report for work. In order to write a stellar comparative essay, you have to start off by picking two subjects that have enough similarities and differences to be compared in a meaningful way, such as two sports teams or two systems of government. Once you have that, then you have to find at least two or three points of comparison and use research, facts, and well-organized paragraphs to impress and captivate your readers. Writing the comparative essay is an important skill that you will use many times throughout your scholastic career.
Comparative Essay Outline and Example

How to Develop the Essay Content

- Many comparative essay assignments will signal their purpose by using words such as "compare," "contrast," "similarities," and "differences" in the language of the prompt.
- Also see whether there are any limits placed on your topic.

- The assignment will generally ask guiding questions if you are expected to incorporate comparison as part of a larger assignment. For example: "Choose a particular idea or theme, such as love, beauty, death, or time, and consider how two different Renaissance poets approach this idea." This sentence asks you to compare two poets, but it also asks how the poets approach the point of comparison. In other words, you will need to make an evaluative or analytical argument about those approaches.
- If you're unclear on what the essay prompt is asking you to do, talk with your instructor. It's much better to clarify questions up front than discover you've written the entire essay incorrectly.

- The best place to start is to write a list of things that the items you are comparing have in common as well as differences between them. [3] X Research source

- You may want to develop a system such as highlighting different types of similarities in different colors, or use different colours if you are using an electronic device.
- For example, if you are comparing two novels, you may want to highlight similarities in characters in pink, settings in blue, and themes or messages in green.

- The basis for your comparison may be assigned to you. Be sure to check your assignment or prompt.
- A basis for comparison may have to do with a theme, characteristics, or details about two different things. [7] X Research source
- A basis for comparison may also be known as the “grounds” for comparison or a frame of reference.
- Keep in mind that comparing 2 things that are too similar makes it hard to write an effective paper. The goal of a comparison paper is to draw interesting parallels and help the reader realize something interesting about our world. This means your subjects must be different enough to make your argument interesting.

- Research may not be required or appropriate for your particular assignment. If your comparative essay is not meant to include research, you should avoid including it.
- A comparative essay about historical events, social issues, or science-related topics are more likely to require research, while a comparison of two works of literature are less likely to require research.
- Be sure to cite any research data properly according to the discipline in which you are writing (eg, MLA, APA, or Chicago format).

- Your thesis needs to make a claim about your subjects that you will then defend in your essay. It's good for this claim to be a bit controversial or up for interpretation, as this allows you to build a good argument.
How to Organize the Content

- Use a traditional outline form if you would like to, but even a simple list of bulleted points in the order that you plan to present them would help.
- You can also write down your main points on sticky notes (or type them, print them, and then cut them out) so that you can arrange and rearrange them before deciding on a final order.

- The advantages of this structure are that it continually keeps the comparison in the mind of the reader and forces you, the writer, to pay equal attention to each side of the argument.
- This method is especially recommended for lengthy essays or complicated subjects where both the writer and reader can easily become lost. For Example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X / Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 2: Stylishness of vehicle X / Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 3: Safety rating of vehicle X / Safety rating of vehicle Y

- The advantages of this structure are that it allows you to discuss points in greater detail and makes it less jarring to tackle two topics that radically different.
- This method is especially recommended for essays where some depth and detail are required. For example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X Paragraph 2: Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 3: Stylishness of vehicle X Paragraph 4: Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 5: Safety rating of vehicle X Paragraph 6: Safety rating of vehicle Y

- This method is by far the most dangerous, as your comparison can become both one-sided and difficult for the reader to follow.
- This method is only recommended for short essays with simplistic subjects that the reader can easily remember as (s)he goes along. For example: Paragraph 1: Engine power of vehicle X Paragraph 2: Stylishness of vehicle X Paragraph 3: Safety rating of vehicle X Paragraph 4: Engine power of vehicle Y Paragraph 5: Stylishness of vehicle Y Paragraph 6: Safety rating of vehicle Y
How to Write the Essay

- Body paragraphs first . Work through all that information you've been compiling and see what kind of story it tells you. Only when you've worked with your data will you know what the larger point of the paper is.
- Conclusion second . Now that you've done all the heavy lifting, the point of your essay should be fresh in your mind. Strike while the iron’s hot. Start your conclusion with a restatement of your thesis.
- Intro last . Open your introduction with a "hook" to grab the reader's attention. Since you've already written your essay, choose a hook that reflects what you will talk about, whether it's a quote, statistic, factoid, rhetorical question, or anecdote. Then, write 1-2 sentences about your topic, narrowing down to your thesis statement, which completes your introduction.

- Organize your paragraphs using one of the approaches listed in the "Organizing the Content" part below. Once you have defined your points of comparison, choose the structure for the body paragraphs (where your comparisons go) that makes the most sense for your data. To work out all the organizational kinks, it’s recommended that you write an outline as a placeholder.
- Be very careful not to address different aspects of each subject. Comparing the color of one thing to the size of another does nothing to help the reader understand how they stack up. [15] X Research source

- Be aware that your various comparisons won’t necessarily lend themselves to an obvious conclusion, especially because people value things differently. If necessary, make the parameters of your argument more specific. (Ex. “Though X is more stylish and powerful, Y’s top safety ratings make it a more appropriate family vehicle .”)
- When you have two radically different topics, it sometimes helps to point out one similarity they have before concluding. (i.e. "Although X and Y don't seem to have anything in common, in actuality, they both ....”)

- Even the best writers know editing is important to produce a good piece. Your essay will not be your best effort unless you revise it.
- If possible, find a friend to look over the essay, as he or she may find problems that you missed.
- It sometimes helps to increase or decrease the font size while editing to change the visual layout of the paper. Looking at the same thing for too long makes your brain fill in what it expects instead of what it sees, leaving you more likely to overlook errors.
Expert Q&A

- The title and introduction really catch the reader's attention and make them read the essay. Make sure you know how to write a catchy essay title . Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 1
- Quotes should be used sparingly and must thoroughly complement the point they are being used to exemplify/justify. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 2
- The key principle to remember in a comparative paragraph or essay is that you must clarify precisely what you are comparing and keep that comparison alive throughout the essay. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 2

- Avoid vague language such as "people," "stuff," "things," etc. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Avoid, at all costs, the conclusion that the two subjects are "similar, yet different." This commonly found conclusion weakens any comparative essay, because it essentially says nothing about the comparison. Most things are "similar, yet different" in some way. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Some believe that an "unbalanced" comparison - that is, when the essay focuses predominantly on one of the two issues, and gives less importance to the other - is weaker, and that writers should strive for 50/50 treatment of the texts or issues being examined. Others, however, value emphasis in the essay that reflects the particular demands of the essay's purpose or thesis. One text may simply provide context, or historical/artistic/political reference for the main text, and therefore need not occupy half of the essay's discussion or analysis. A "weak" essay in this context would strive to treat unequal texts equally, rather than strive to appropriately apportion space to the relevant text. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
- Beware of the "Frying Pan Conclusion" in which you simply recount everything that was said in the main body of the essay. While your conclusion should include a simple summary of your argument, it should also emphatically state the point in a new and convincing way, one which the reader will remember clearly. If you can see a way forward from a problem or dilemma, include that as well. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/comparative-essay
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/how-write-comparative-analysis
- ↑ https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/style_purpose_strategy/compare_contrast.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/10-7-comparison-and-contrast/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- How to Structure Paragraphs in an Essay
About This Article

To write a comparative essay, start by writing an introduction that introduces the 2 subjects you'll be comparing. You should also include your thesis statement in the introduction, which should state what you've concluded based on your comparisons. Next, write the body of your essay so that each paragraph focuses on one point of comparison between your subjects. Finally, write a conclusion that summarizes your main points and draws a larger conclusion about the two things you compared. To learn how to do research for your essay, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 21, 2017
Did this article help you?

Lisa Taylor
Aug 19, 2017
Brayden Ryan
Aug 10, 2016
Antwanette Nottage
Feb 5, 2019
Bernice Sangmortey
Nov 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Take 10% OFF— Expires in h m s Use code save10u during checkout.
Chat with us
- Live Chat Talk to a specialist
- Self-service options
- Search FAQs Fast answers, no waiting
- Ultius 101 New client? Click here
- Messenger
International support numbers
For reference only, subject to Terms and Fair Use policies.
- How it Works
Learn more about us
- Future writers
- Explore further
How to write a comparative essay
A step-by-step guide with instructions, outlines, and samples
Writing a great comparative essay means highlighting the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner. Start by choosing the parameters (items) to compare, write an outline, and fill in the details for each section. Make sure to have an introduction and conclusion.
The comparative essay is one form of document that you will probably be expected to write at some point over the course of your college career. The purpose of this article is to provide you with a thorough overview of the comparative essay. Specific things that will be addressed include:
Purpose of the comparative essay
Explanation of comparative models, how to analyze subjects, elements of a good comparative essay, how to write a great comparative essay.
- Samples/examples
- Best practices and advice
- Additional information
By the end of this article, you should feel more confident about your own knowledge of what a comparative essay is and the best ways to go about writing one (if you haven't decided to buy a comparative essay from Ultius ).

The fundamental purpose of a comparative essay is to elaborate the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner.
An effective comparative essay will leave the reader with much greater clarity about the natures and properties of the things that have been compared.
This could potentially serve as a basis for making a decision in favor of one or the other thing.
A comparative essay is different from, for example, an argumentative essay in that the comparative essay does not make a case for either of the two things under comparison. Rather, the point is to simply set up the comparison so that the reader will have as much information about the two things as possible.
Why are comparative essays important?
The comparative essay is an important form of document because when you have to make a decision or choose a side in an argument, you will want to know as much as possible about the two options under consideration—and a good comparative essay on the subject can bring out both the similarities and the differences between the options, thereby clarifying the stakes at play.
For example, a comparative essay could address the similarities and differences between any of the following pairs:
- The Republican Party and the Democratic Party
- Christianity and Marxism
- The Big Bang and creationism
- The Light or Dark side of the Force from Star Wars
- The revolutionary and the reformist perspectives on social change
By developing a comparative essay on any of these pairs, you can not only understand each item of under comparison is a more thorough way, you can also get closer to figuring out which item you prefer.
For example, a solid comparative essay on revolution vs. reformism could not only help you understand what each of these items entails, it can also help you figure out whether you would rather be a revolutionary or a reformist. Likewise, if you only have time to binge watch one show, then a comparative essay could help you figure out whether you would prefer to go with Game of Thrones or Westworld .
When writing a comparative essay, there are several models you can use in order to ensure that you set up your comparison as effectively as possible.
Venn diagram
The Venn diagram is a classic, and surely, you're familiar with it. This is the model of two overlapping circles, where each circle belongs to one item of comparison: features shared by both items (similarities) go in the overlapping middle zone, whereas features that are not shared go in the outer areas. For example, here is a Venn diagram that compares humans against gorillas.
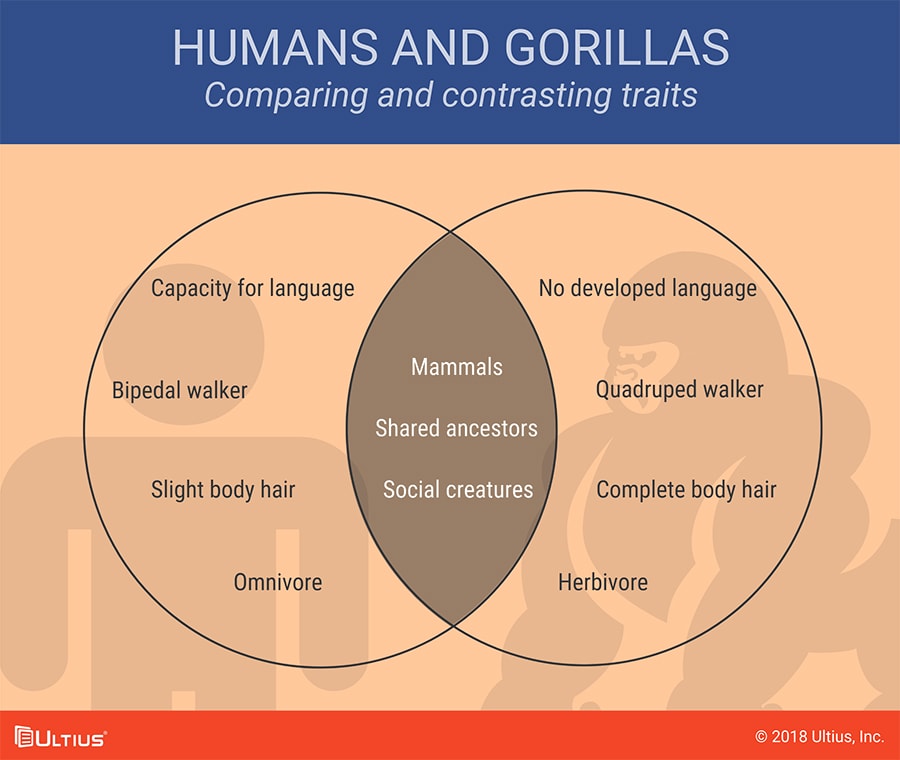
When using the Venn diagram model, it is important to note that the differences must be symmetrical. In other words, every difference you list on one side of the comparison must be matched by a difference on the other side.
For example, if you were comparing Apple and Amazon, then for the parameter of "founder," you can list "Steve Jobs" in one circle and "Jeff Bezos" in the other. But it wouldn't make sense if you just listed one or the other: you must list something for each of the items of comparisons under the selected parameter of comparison.
In the Venn diagram above, the first parameter is "language," so for humans it is listed that we have a capacity of language, whereas for gorillas it is listed that they do not.
You don't need to worry about this kind of symmetry when it comes to the similarities, since you will list the same thing for both items of comparison (which means you only have to list it once, in the overlapping zone). In the example, above, the fact that both humans and gorillas are mammals is thus listed just once in the middle.
The dialectical method
The dialectical method is important within the discipline of philosophy, and it has been used to great effect by thinkers such as Socrates and Hegel and Kierkegaard.
This involves holding two ideas or items in tension with each other, to better clarify not only the ideas themselves but also the dynamic relationship that exist between the ideas. The first idea is called the thesis , and the second idea is called the antithesis .
For example, Romanticism could be dialectically compared against the Enlightenment that came before it, because Romanticism was in some ways a rejection of the previous worldview.
Need help? Essay writing services from Ultius can help you produce a great sample compare and contrast essay.
So, by setting up a comparison between Romanticism and the Enlightenment, it becomes possible to see both the continuities (or similarities) between the one and the other, as well as the contradictions (or differences) between them.
Berlin, Isaiah. The Roots of Romanticism . Princeton: Princeton U P, 2013. Print.
From the table above, it is clear that we are able to understand both Romanticism and the Enlightenment better if we set them up in terms of dialectical contrast.
Clearly, they are different in some important ways (logic vs. passion, for example), but we can also see that they are in continuity with each other (both happened in Western Europe and responded to previous developments). This comparison also leads one to wonder about whether it would be possible to make a synthesis that takes the best from both the thesis and the antithesis
A good comparative essay can lead one to ask such questions and pursue such lines of inquiry.
To analyze your subjects for a comparative essay, you need to identify clear parameters, or axes, in terms of which your two selected items can be compared. For example, in the table above, Romanticism and the Enlightenment were compared along the axis of " epistemology ". But that axis won't be relevant to all subjects.
Your job when preparing to write a comparative essay is to identify the specific axes that are relevant for the items that you are comparing. Why is the comparison interesting, and what insights are you trying produce? The answers to those questions will determine how you decide to frame your comparison.
For example, we could compare the Democratic Socialists of America (DSA) against the Democratic Party in terms of the axis of membership. This would reveal that the DSA has far fewer registered members than does the Democratic Party.
We could also compare them on the axis of healthcare policy, where it may be found that the DSA and the Democratic Party agree about the importance of universal coverage. When we look at the axis of economics, though, we may find that the DSA is much more radical in its proposals than the Democratic Party.
The problem of identifying relevance
In principle, any one thing in the world could be compared with any other thing in the world. For example, you could compare your shoe with the moon, and conclude that one similarity is that they both exist within the Milky Way galaxy.
But this would be a meaningless point (even if it may make for some interesting poetry). It is important for you to figure out what exactly you are trying to determine through your comparative essay. What is your purpose for writing it?
This will help you choose two items where setting up a dialectical contrast between them will produce actual insight, and it will also help you to choose the proper parameters by which to compare those items.
For example, suppose that you are running a business, and there are two expansion options open in front of you. It would be logical for you to compare and contrast these options, since this will help ensure that you are making your decision with as much knowledge and insight as possible.

Likewise, one parameter that you are sure to consider is: which option will make your business the most money? If you pick parameters that are meaningless, then you will obtain no real insight that can help you make the important decision.
Using a rubric
Once you have identified both the two items of comparison and the axes along which they will be compared, you can proceed to analyze the items by applying the axes in the form of a table or rubric.
This is what has been done, for example, in the tables that have been developed above in this article. In the left-most column, list the parameters you have selected in order to compare your items. Then, in the top-most row, list the items.
Then go ahead and list the relevant details for each parameter for each of the two items. This will produce a table where you can see how each item measures up against the other for each parameter.
The important thing is to be systematic when you are making your comparison: it should not seem random or arbitrary. Thus, it is important to carefully select both the items and the parameters for comparison, and then to proceed to address each item/parameter combo in turn.
There are several elements that are a part of any good comparative essay.
Effective selection of items
A strong comparative essay has well-chosen items for comparison, with the comparison producing actual insights of value through the juxtaposition of the two items. If the items appear to be chosen for no apparent reason, or if the comparison does not in fact produce insight, then the comparative essay would be quite weak (or at any rate pointless).
The comparative essay is not meant to make an argument in favor of one thing or another, but it is meant to produce knowledge and insight about the two things under comparison. In order to compare and contrast items in an effective way, the two items must be different enough from each other, but they should also not be so different that it just feels absurd to even compare them at all.
Effective selection of parameters of comparison
A good comparative essay not only includes well-selected items of comparison, it also includes well-selected parameters of comparison. Between any two selected items, you could theoretically make an endless number of comparisons.
But a good comparative essay identifies parameters of comparative in terms of salience , or the reasons why anyone would be interested in the comparison in the first place. This can be difficult, because in principle, any comparison could be interesting, depending on the audience of the comparative essay and the intended purpose of the essay.

For example, one could use the parameter of zodiac sign to compare Romantic artists against Enlightenment artists.
This could be very interesting to people who are very serious about the zodiac, but it would probably seem ridiculous to just about everyone else.
But if you were writing for an audience of zodiac fanatics, then this comparison could actually be a success.
So, there is no parameter of comparison that is "inherently" bad. Rather, the point is to find parameters that highlight specific salient aspects of the selected items.
For example, when comparing Romanticism against the Enlightenment, core values would be a solid parameter of comparison, because that will surely help produce insights about how worldviews changed from the one paradigm to another.
Strong organizational structure
If you want your comparative essay to be a success, then it absolutely must have strong organizational structure . This is because an effective comparison must be easy for your reader to follow. It can't just jump all over the place at random, which not only be confusing but could also result in the reader forgetting what the point of the comparison was in the first place.
In general, there are two ways in which you can organize your comparative essay. In the first format, each of the parameters would be considered in the section for similarities and the section for differences.
In the first format the comparative essay is organized in terms of similarities and differences, whereas in the second format the essay is organized in terms of parameters of comparison.

In the second format, both similarities and differences would be considered within each of the parameter sections.

Both these are formats are good, and a strong comparative essay could be built around either one.
The important thing is to have a clear system and to not make your comparisons random.
There needs to be an organizational structure that your reader can easily follow.
There are steps you can follow in order to ensure that your comparative essay has all the elements that will be required in order to make it great.
Ask yourself about your intention
If you have selected two items for your comparative essay, then you should start by asking yourself why you selected those two items. What is it about the two items that made you think it would be a good idea to compare them? (Or if you were assigned the two items, then why do you think those items were selected by your professor?)
The point here is that the items selected for a comparative essay are non-random. They are selected because that specific comparison should be able to yield interesting insights (unlike research papers ).
For example, if you are writing a comparative essay on the dogs vs. cats, then are you writing this from the perspective of evolutionary biology? Or are you perhaps writing it in order to inform potential pet owners who are debating whether they want a dog or a cat?
The purpose of your essay will determine what parameters you will select in order to compare your two items. This means that you should have an intended audience in mind, and you should also have specific questions you would like to know more about.
In short, in order to develop effective parameters for your comparative essay, you have to ask yourself why you are writing it and who would be interested in the insights produced by the essay. This can help ensure you select both appropriate items and appropriate parameters for comparison.
Develop a structural outline
It is very important that you do not just jump into your comparative essay and start writing it without a plan. That is a recipe for disaster, and the comparisons will almost certainly turn out random and confusing. Rather, you should begin with a solid outline .
A good outline will do three main things:
- 1. Identify the selected items of comparison in the introduction/thesis
- 2. Utilize one of the two organizational formats described above
- 3. Provide a roadmap for how you intend to systematically follow through on the comparison
For example, here is how an outline could look for a comparative essay on Romanticism vs. the Enlightenment.

In this sample outline, the format that is used dedicates a paragraph to each of three parameters of comparison, and both similarities and differences are addressed for each of those parameters.
This is the kind of logical flow that you will need to have in order for your comparative essay to turn out great.
Write in a systematic way
A comparative essay is not a place to get too creative with your writing, whether in terms of organization or in terms of style.
Rather, you should focus on simply carrying out your comparison, point-by-point and in a way that is easy for your reader to follow. This can get a little tedious, so if that is a problem for you, then you should make sure that you set aside enough time to work on your comparative essay little by little.
For example, if your essay has three parameters, then you could write a section on the first parameter today, the second parameter tomorrow, and the third parameter the next day.
The important thing is for you to ensure that you consider each of your two selected items in terms of each of your selected parameters. This needs to be done in a smooth and logical manner, such that your reader knows where you are in the comparison. There should be no jumping around, and there should be no departure from the basic format or structure.
Example comparative (compare/contrast) essay
Best practices/tips.
We have now arrived at the end of this guide, and you should have a much better idea of what makes a comparative essay successful and how you can go about writing one. It may be helpful to now summarize some of the main points that have been addressed here.
Let's address five main points.
1. Ensure that you select appropriate items for comparison
The two items that will be compared in your comparative essay should be carefully selected. The items should have some shared features and be in the same "class" of items, but they should also have substantial differences to which you are trying to call attention. If the items are too similar, then there would be no point in the comparison, but if they are too different, that can also make the comparison meaningless.
2. Select effective parameters of comparison
Your comparative essay shouldn't compare anything and everything between your two items; rather, the parameters should be specifically selected to highlight specific, salient similarities and differences. In order to determine what parameters would be effective, you have to ask yourself why you are writing your comparative essay and what sort of insights you intend to produce about the items being compared.
3. Use tools and models in an effective way
The Venn diagram is one tool that can be very helpful in conceptualizing your comparative essay, especially if you are a more visual kind of learner. Tables, rubrics, and outlines will also work to help ensure that you are developing a strong backbone of logic and systematic reasoning for your comparative essay. These and other tools may even help you reconsider your initial choices of items and parameters, if you realize that significant insights are not being produced.
4. Choose an organizational format, and stick with it
There are two main ways in which to structure an effective comparative essay, which have been described above. You can dedicate one section to similarities and one section to differences; or, you can dedicate a section to each of the parameters of comparison. This second option is usually more effective, especially if you are new to comparative essays. But either way, it is crucial that you stick to your chosen format and do not jump around and confuse the reader.
5. Seek assistance if you need it
If you are still uncertain about how to write a successful comparative essay, then Ultius is here to help. Our writer help section has many tools like this one available on various types of essays; we have a huge writer help section that contains all sorts of information on pretty much any writing-related questions you may have; and we also have elite professional writers who can produce a sample comparative essay for you on any subject of your choosing. We are here for you, and if you have any further questions about how to write a comparative essay, then you should feel free to reach out.

Tested Daily
Click to Verify
About The Author
This post was written by Ultius.

The Ultius Promise
With every order, you can count on the following:
- Delivered on time
- 100% original
- Free revisions
- Awesome 24/7 support
- World-class writers
- Writer Options
- Custom Writing
- Business Documents
- Support Desk
- +1-800-405-2972
- Submit bug report
- A+ BBB Rating!
Ultius is the trusted provider of content solutions for consumers around the world. Connect with great American writers and get 24/7 support.
© 2024 Ultius, Inc.
- Refund & Cancellation Policy
Free Money For College!
Yeah. You read that right —We're giving away free scholarship money! Our next drawing will be held soon.
Our next winner will receive over $500 in funds. Funds can be used for tuition, books, housing, and/or other school expenses. Apply today for your chance to win!
* We will never share your email with third party advertisers or send you spam.
** By providing my email address, I am consenting to reasonable communications from Ultius regarding the promotion.
Past winner

- Name Samantha M.
- From Pepperdine University '22
- Studies Psychology
- Won $2,000.00
- Award SEED Scholarship
- Awarded Sep. 5, 2018
Thanks for filling that out.
Check your inbox for an email about the scholarship and how to apply.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes


Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1: Introduction to Comparison and Contrast Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 174873
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both. The thesis should focus on comparing, contrasting, or both.
Key Elements of the Compare and Contrast:
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
Objectives: By the end of this unit, you will be able to
- Identify compare & contrast relationships in model essays
- Construct clearly formulated thesis statements that show compare & contrast relationships
- Use pre-writing techniques to brainstorm and organize ideas showing a comparison and/or contrast
- Construct an outline for a five-paragraph compare & contrast essay
- Write a five-paragraph compare & contrast essay
- Use a variety of vocabulary and language structures that express compare & contrast essay relationships
Example Thesis: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.

Sample Paragraph:
Organic grown tomatoes purchased at the farmers’ market are very different from tomatoes that are grown conventionally. To begin with, although tomatoes from both sources will mostly be red, the tomatoes at the farmers’ market are a brighter red than those at a grocery store. That doesn’t mean they are shinier—in fact, grocery store tomatoes are often shinier since they have been waxed. You are likely to see great size variation in tomatoes at the farmers’ market, with tomatoes ranging from only a couple of inches across to eight inches across. By contrast, the tomatoes in a grocery store will be fairly uniform in size. All the visual differences are interesting, but the most important difference is the taste. The farmers’ market tomatoes will be bursting with flavor from ripening on the vine in their own time. However, the grocery store tomatoes are often close to being flavorless. In conclusion, the differences in organic and conventionally grown tomatoes are obvious in color, size and taste.

- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
The Comparative Essay
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
What is a comparative essay?
A comparative essay asks that you compare at least two (possibly more) items. These items will differ depending on the assignment. You might be asked to compare
- positions on an issue (e.g., responses to midwifery in Canada and the United States)
- theories (e.g., capitalism and communism)
- figures (e.g., GDP in the United States and Britain)
- texts (e.g., Shakespeare’s Hamlet and Macbeth )
- events (e.g., the Great Depression and the global financial crisis of 2008–9)
Although the assignment may say “compare,” the assumption is that you will consider both the similarities and differences; in other words, you will compare and contrast.
Make sure you know the basis for comparison
The assignment sheet may say exactly what you need to compare, or it may ask you to come up with a basis for comparison yourself.
- Provided by the essay question: The essay question may ask that you consider the figure of the gentleman in Charles Dickens’s Great Expectations and Anne Brontë’s The Tenant of Wildfell Hall . The basis for comparison will be the figure of the gentleman.
- Developed by you: The question may simply ask that you compare the two novels. If so, you will need to develop a basis for comparison, that is, a theme, concern, or device common to both works from which you can draw similarities and differences.
Develop a list of similarities and differences
Once you know your basis for comparison, think critically about the similarities and differences between the items you are comparing, and compile a list of them.
For example, you might decide that in Great Expectations , being a true gentleman is not a matter of manners or position but morality, whereas in The Tenant of Wildfell Hall , being a true gentleman is not about luxury and self-indulgence but hard work and productivity.
The list you have generated is not yet your outline for the essay, but it should provide you with enough similarities and differences to construct an initial plan.
Develop a thesis based on the relative weight of similarities and differences
Once you have listed similarities and differences, decide whether the similarities on the whole outweigh the differences or vice versa. Create a thesis statement that reflects their relative weights. A more complex thesis will usually include both similarities and differences. Here are examples of the two main cases:
While Callaghan’s “All the Years of Her Life” and Mistry’s “Of White Hairs and Cricket” both follow the conventions of the coming-of-age narrative, Callaghan’s story adheres more closely to these conventions by allowing its central protagonist to mature. In Mistry’s story, by contrast, no real growth occurs.
Although Darwin and Lamarck came to different conclusions about whether acquired traits can be inherited, they shared the key distinction of recognizing that species evolve over time.
Come up with a structure for your essay
Note that the French and Russian revolutions (A and B) may be dissimilar rather than similar in the way they affected innovation in any of the three areas of technology, military strategy, and administration. To use the alternating method, you just need to have something noteworthy to say about both A and B in each area. Finally, you may certainly include more than three pairs of alternating points: allow the subject matter to determine the number of points you choose to develop in the body of your essay.
When do I use the block method? The block method is particularly useful in the following cases:
- You are unable to find points about A and B that are closely related to each other.
- Your ideas about B build upon or extend your ideas about A.
- You are comparing three or more subjects as opposed to the traditional two.
Comparative Essay
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
10 min read
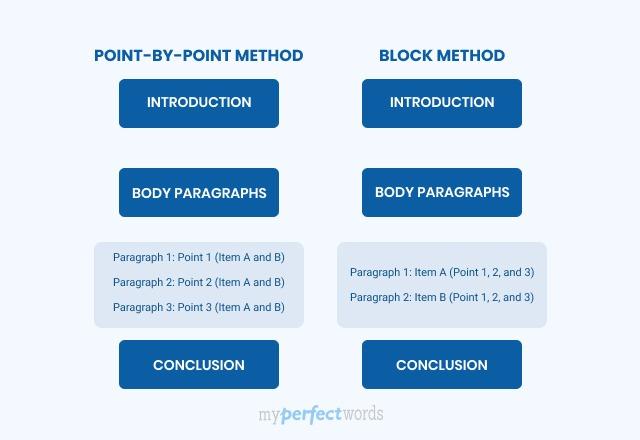
People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Comparative essay is a common assignment for school and college students. Many students are not aware of the complexities of crafting a strong comparative essay.
If you too are struggling with this, don't worry!
In this blog, you will get a complete writing guide for comparative essay writing. From structuring formats to creative topics, this guide has it all.
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is a Comparative Essay?
- 2. Comparative Essay Structure
- 3. How to Start a Comparative Essay?
- 4. How to Write a Comparative Essay?
- 5. Comparative Essay Examples
- 6. Comparative Essay Topics
- 7. Tips for Writing A Good Comparative Essay
- 8. Transition Words For Comparative Essays
What is a Comparative Essay?
A comparative essay is a type of essay in which an essay writer compares at least two or more items. The author compares two subjects with the same relation in terms of similarities and differences depending on the assignment.
The main purpose of the comparative essay is to:
- Highlight the similarities and differences in a systematic manner.
- Provide great clarity of the subject to the readers.
- Analyze two things and describe their advantages and drawbacks.
A comparative essay is also known as compare and contrast essay or a comparison essay. It analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both. The Venn diagram is the best tool for writing a paper about the comparison between two subjects.
Moreover, a comparative analysis essay discusses the similarities and differences of themes, items, events, views, places, concepts, etc. For example, you can compare two different novels (e.g., The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn and The Red Badge of Courage).
However, a comparative essay is not limited to specific topics. It covers almost every topic or subject with some relation.
Comparative Essay Structure
A good comparative essay is based on how well you structure your essay. It helps the reader to understand your essay better.
The structure is more important than what you write. This is because it is necessary to organize your essay so that the reader can easily go through the comparisons made in an essay.
The following are the two main methods in which you can organize your comparative essay.
Point-by-Point Method
The point-by-point or alternating method provides a detailed overview of the items that you are comparing. In this method, organize items in terms of similarities and differences.
This method makes the writing phase easy for the writer to handle two completely different essay subjects. It is highly recommended where some depth and detail are required.
Below given is the structure of the point-by-point method.
Block Method
The block method is the easiest as compared to the point-by-point method. In this method, you divide the information in terms of parameters. It means that the first paragraph compares the first subject and all their items, then the second one compares the second, and so on.
However, make sure that you write the subject in the same order. This method is best for lengthy essays and complicated subjects.
Here is the structure of the block method.
Therefore, keep these methods in mind and choose the one according to the chosen subject.
Mixed Paragraphs Method
In this method, one paragraph explains one aspect of the subject. As a writer, you will handle one point at a time and one by one. This method is quite beneficial as it allows you to give equal weightage to each subject and help the readers identify the point of comparison easily.
How to Start a Comparative Essay?
Here, we have gathered some steps that you should follow to start a well-written comparative essay.
Choose a Topic
The foremost step in writing a comparative essay is to choose a suitable topic.
Choose a topic or theme that is interesting to write about and appeals to the reader.
An interesting essay topic motivates the reader to know about the subject. Also, try to avoid complicated topics for your comparative essay.
Develop a List of Similarities and Differences
Create a list of similarities and differences between two subjects that you want to include in the essay. Moreover, this list helps you decide the basis of your comparison by constructing your initial plan.
Evaluate the list and establish your argument and thesis statement .
Establish the Basis for Comparison
The basis for comparison is the ground for you to compare the subjects. In most cases, it is assigned to you, so check your assignment or prompt.
Furthermore, the main goal of the comparison essay is to inform the reader of something interesting. It means that your subject must be unique to make your argument interesting.
Do the Research
In this step, you have to gather information for your subject. If your comparative essay is about social issues, historical events, or science-related topics, you must do in-depth research.
However, make sure that you gather data from credible sources and cite them properly in the essay.
Create an Outline
An essay outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, organizing key elements into a structured format.
With your topic, list of comparisons, basis for comparison, and research in hand, the next step is to create a comprehensive outline.
Here is a standard comparative essay outline:
How to Write a Comparative Essay?
Now that you have the basic information organized in an outline, you can get started on the writing process.
Here are the essential parts of a comparative essay:
Comparative Essay Introduction
Start off by grabbing your reader's attention in the introduction . Use something catchy, like a quote, question, or interesting fact about your subjects.
Then, give a quick background so your reader knows what's going on.
The most important part is your thesis statement, where you state the main argument , the basis for comparison, and why the comparison is significant.
This is what a typical thesis statement for a comparative essay looks like:
Comparative Essay Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are where you really get into the details of your subjects. Each paragraph should focus on one thing you're comparing.
Start by talking about the first point of comparison. Then, go on to the next points. Make sure to talk about two to three differences to give a good picture.
After that, switch gears and talk about the things they have in common. Just like you discussed three differences, try to cover three similarities.
This way, your essay stays balanced and fair. This approach helps your reader understand both the ways your subjects are different and the ways they are similar. Keep it simple and clear for a strong essay.
Comparative Essay Conclusion
In your conclusion , bring together the key insights from your analysis to create a strong and impactful closing.
Consider the broader context or implications of the subjects' differences and similarities. What do these insights reveal about the broader themes or ideas you're exploring?
Discuss the broader implications of these findings and restate your thesis. Avoid introducing new information and end with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression.
Below is the detailed comparative essay template format for you to understand better.
Comparative Essay Format
Comparative Essay Examples
Have a look at these comparative essay examples pdf to get an idea of the perfect essay.
Comparative Essay on Summer and Winter
Comparative Essay on Books vs. Movies
Comparative Essay Sample
Comparative Essay Thesis Example
Comparative Essay on Football vs Cricket
Comparative Essay on Pet and Wild Animals
Comparative Essay Topics
Comparative essay topics are not very difficult or complex. Check this list of essay topics and pick the one that you want to write about.
- How do education and employment compare?
- Living in a big city or staying in a village.
- The school principal or college dean.
- New Year vs. Christmas celebration.
- Dried Fruit vs. Fresh. Which is better?
- Similarities between philosophy and religion.
- British colonization and Spanish colonization.
- Nuclear power for peace or war?
- Bacteria or viruses.
- Fast food vs. homemade food.
Tips for Writing A Good Comparative Essay
Writing a compelling comparative essay requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning. Here are some valuable tips to enhance the quality of your comparative essay:
- Clearly define what you're comparing, like themes or characters.
- Plan your essay structure using methods like point-by-point or block paragraphs.
- Craft an introduction that introduces subjects and states your purpose.
- Ensure an equal discussion of both similarities and differences.
- Use linking words for seamless transitions between paragraphs.
- Gather credible information for depth and authenticity.
- Use clear and simple language, avoiding unnecessary jargon.
- Dedicate each paragraph to a specific point of comparison.
- Summarize key points, restate the thesis, and emphasize significance.
- Thoroughly check for clarity, coherence, and correct any errors.
Transition Words For Comparative Essays
Transition words are crucial for guiding your reader through the comparative analysis. They help establish connections between ideas and ensure a smooth flow in your essay.
Here are some transition words and phrases to improve the flow of your comparative essay:
Transition Words for Similarities
- Correspondingly
- In the same vein
- In like manner
- In a similar fashion
- In tandem with
Transition Words for Differences
- On the contrary
- In contrast
- Nevertheless
- In spite of
- Notwithstanding
- On the flip side
- In contradistinction
Check out this blog listing more transition words that you can use to enhance your essay’s coherence!
In conclusion, now that you have the important steps and helpful tips to write a good comparative essay, you can start working on your own essay.
However, if you find it tough to begin, you can always hire our professional essay writing service .
Our skilled writers can handle any type of essay or assignment you need. So, don't wait—place your order now and make your academic journey easier!
Frequently Asked Question
How long is a comparative essay.
A comparative essay is 4-5 pages long, but it depends on your chosen idea and topic.
How do you end a comparative essay?
Here are some tips that will help you to end the comparative essay.
- Restate the thesis statement
- Wrap up the entire essay
- Highlight the main points

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
NOW OPEN: 2024 Term Two Enrolments 🎉

A State-Ranker’s Guide to Writing 20/20 Economics Essays
So, you want to know how to improve your preliminary and HSC economics essay...

1. Introduction to this Guide
So, you want to know how to improve your preliminary and HSC economics essay writing? Look no further! In this guide, I’ll be covering key tips to help YOU smash the structure, amaze with your analysis, conquer the contemporary, and ultimately master the mystery of maximising your marks.
My name is Cory Aitchison, currently one of the Economics tutors at Project Academy . I completed the HSC in 2018, achieving a 99.95 ATAR as well as two state ranks — 6th in economics and 12th in chemistry. Graduating from Knox Grammar School, I also topped my grade in economics and was awarded Dux of the School for STEM. Believe it or not, at the beginning of Year 11 I initially struggled with economics due to the transition in conceptual thinking required in approaching economic assessments in comparison to my other subjects such as English. However, through Year 11 and Year 12, I built up key tips and strategies — that I’ll be sharing with you in this guide — to help me not only consistently achieve top marks in my internal assessments, but to ultimately go on to achieve the results I did in the HSC.
2. The Correct Way to Write
First off, you need to understand something: HSC economics essays are NOT english essays! They aren’t scientific discussions, nor geography reports, nor historical recounts. They’re unique and often quite different from other essays that you might’ve done previously in high school. The style of writing and approach to answering questions can be confusing at first, but follow these tips and you’ll be ready in no time:
Phrasing should be understandable and concise
Unlike some subjects where sophisticated phrasing is beneficial to getting marks, HSC economics essays should emphasise getting your point across with clarity. This means don’t run your sentences on for too long, be aware of any superfluous words, and make sure you actually understand yourself what you’re trying to say in a sentence.
For example:
GOOD: “An increase in interest rates should lead to decreased economic growth.”
NOT GOOD: “As a result of a rise or increase in interest rate levels from their previous values, the general state of economic activity in the domestic economy may begin to decrease and subsequently indicate the resultant situation of a decrease in economic growth.”
“Understandable” does not mean slang or lacking in terminology
Just because you want to get a point across, doesn’t mean you should resort to slang. In fact, using economic terminology is a strong way to boost your standing in the eyes of the marker — if you use it correctly! Always make sure you use full sentences, proper English grammar, and try and incorporate correct economic terms where possible.
GOOD: “This was a detrimental outcome for the economy.”
NOT GOOD: “This was a pretty bad outcome for the economy.”
GOOD: “The Australian Dollar depreciated.”
NOT GOOD: “The Australian Dollar decreased in value.”
Analysis should be done using low modality
Modality just refers to the confidence of your language — saying something “will” happen is strong modality, whereas saying something “might” happen is considered low modality. Since a large portion of economics is about applying theory, we have to make sure that we are aware that we are doing just that — talking about the theoretical, and so we can’t say for sure that anything will happen as predicted.
Some useful words include:
May, Might, Should, Could, Can theoretically
Don’t use words like:
Must, Will, Has to, Always
3. How to use Statistics
“What’s most important is that this contemporary is used to bring meaning or context to your argument…”
Using contemporary (statistics) can often seem straightforward at first, but using it effectively is usually harder than it looks. Contemporary generally refers to applying real-world facts to your analysis to help strengthen (or weaken) the theoretical arguments. This can include many different statistics or pieces of information, including:
- Historic economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, GINI coefficients, exchange rates, or unemployment rates
- Trends or economic goals, such as long-term GDP growth rates, or the stability band for inflation
- Names of economic policies, such as examples of fiscal or microeconomic policies
- Specifics of economic policies, such as the amount spent on infrastructure in 2017

Whatever statistics you deem relevant to include in your essay, what’s most important is that this contemporary is used to bring meaning or context to your argument — just throwing around random numbers to show off your memorisation skills won’t impress the marker, and in fact might appear as if you were making them up on the spot. Rather, your use of contemporary should actively improve your analysis.
GOOD: “Following a period of growth consistently below the long-term trend-line of 3%, the depreciation of the AUD to 0.71USD in 2017 preceded an increase in economic growth to a 10-year high of 3.4% in 2018.”
NOT GOOD: “Economic growth increased by 1 percentage point in 2017 to 2018”
NOT GOOD: “GDP was $1.32403 trillion in 2017”
GOOD: “The 2017 Budget’s Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy — up 30% from 2016’s $31 billion, and 20% higher than the inflation-adjusted long-term expenditure.”
NOT GOOD: “The 2017 Budget’s Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy”
That in mind, don’t think that these statistics have to be overly specific. As long as the general ideas gets across, it’s fine. You don’t need to say “$1,505,120” — just “$1.5 million” will suffice.
Ask yourself: if I get rid of the contemporary from my paragraphs, does the essay still have enough content?
Further, don’t get roped into the “contemporary trap” — where you fall into the mindset that “if I memorise all these statistics, my essay will get good marks”. Including numbers and contemporary at the expense of having a robust theoretical explanation and analysis will definitely be detrimental in getting you top marks. Particularly in trial exams and the HSC when you’ve got all these numbers floating in your head, it can be tempting to try and include as many as you can (often just because you can!). To avoid this, always try and focus your arguments on analysis and syllabus content first, contemporary second. Ask yourself: if I get rid of the contemporary from my paragraph, does the essay still have enough content?
4. Must Have Insightful “However”s
If you really want to extend your analysis and show the marker that you know your stuff, including insightful “however”s is a strong way to do it. What I mean by this is that for each of your paragraphs, try and include a counterpoint that highlights the flexible nature of economic theory. There are broadly two kinds of “however”s:
Theoretical “However”s
These are counterpoints that are based on theory — often there will be theoretical limitations for many of the concepts you come across in economics. It’s always important to include these limitations as it reinforces your knowledge of the actual content of economics.
“Although the Budget and fiscal policy can be effective at stimulating economic growth, it is also restricted by the “implementation time lag” limitation since it is only introduced annually.”
Contemporary “However”s
These are counterpoints that are based on contemporary — highlighting how although something should happen theoretically, this isn’t usually what is observed in reality. This can be particularly powerful in that it combines your knowledge of theory with your analysis of contemporary.
“Despite the expansionary stance that the RBA adopted in 2012–2016 for monetary policy, Australia’s annual GDP growth rate has remained below the trend rate of 3% — against the theoretical expectations. This could be attributed to factors such as …”
5. How to Interpret the Question
When you first look at a question, before you even put pen to paper, you need to come up with a plan of attack — how can you ensure that you answer the question correctly, and give the markers what they want? There are three main points to look for when interpreting essay questions:
Knowing your verbs
As you may (or may not) know, NESA has a bank of words that they like to pull from when writing questions, and these words impact how they want their question answered. These verbs should help steer your analysis onto the right path. For example:
Explain: “Relate causes and effects”
To answer these questions, you have to demonstrate a thorough understanding of how theory and events impact each other and the economy. This verb particularly emphasises the idea of a process — you need to be able to make clear links as to how each step leads to the next, rather than just jumping to the outcomes.
Analyse: “Draw out and relate implications”
These questions usually wants you to investigate the connections between different aspects of economic theory. Generally this involves showing a holistic understanding of how different areas (such as micro- and macroeconomic policies) come together to make a cohesive impact on the economy. It usually helps to think back to the syllabus and how the points are introduced when figuring out which ideas to link together.
Assess/Evaluate: “Make a judgement based on value/a criteria”
These require you to not only critically analyse a topic but also come to a conclusion given the arguments you provided. This type of question usually gets you to make a judgement of the effectiveness of some economic theory — such as the ability for economic policies to achieve their goals. Make sure you actually include this judgement in your answer — for example, say things like “strong impact”, “highly influential”, “extremely detrimental”.
Discuss: “Provide points for and/or against”
Similar to assess, discuss wants you to provide arguments towards and against a particular topic. Although it doesn’t require a specific judgement to be made, it does place greater emphasis on showing a well-rounded approach to the argument — providing relatively equal weightings towards both the positive and negative sides of the discussion.
Linking to the syllabus
When trying to understand what the question wants from you, I found the best way to approach it is to consider what points in the syllabus it is referring to (To do this, you need to have a solid understanding of the syllabus in the first place). Once you’ve located it, try drawing upon other topics in the vicinity of that dot point to help you answer the question.
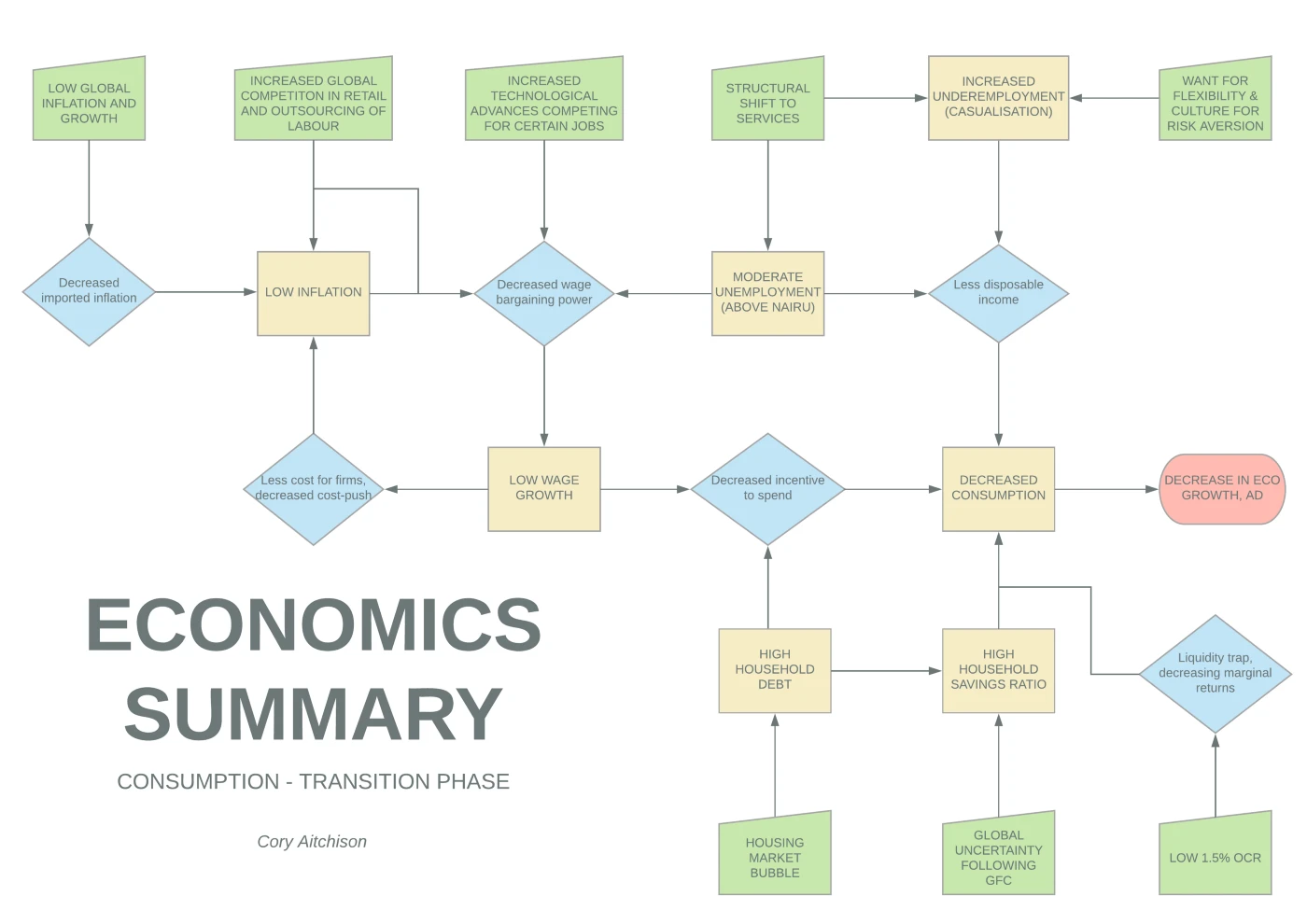
For example, if the question mentions “trends in Australia’s trade and financial flows”, then you know from the syllabus that you probably need to talk about value, composition and direction in order to get high marks. Further, it may also be worth it to bring in ideas from the Balance of Payments, as this is the next dot point along in the syllabus.
Digging into the source
For essay questions that provide a source for you to include in your answer, this is another goldmine from which you can discern what the marker really wants. If the source mentions microeconomic policy, it probably wasn’t on accident! Even if it may not be obvious how to link that to the question immediately, try and draw upon your knowledge and implications and see if there’s a different angle that you might be missing.
6. Putting it All together — Structuring your essay
My essays usually consisted of four main parts: an introduction, a background paragraph, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Introduction
Your introduction should not be long. I rarely wrote an introduction longer than three sentences.
First sentence: Answer the question (thesis)
Try and answer the question, while including the main key words of the question in your answer. Don’t directly restate it — instead, try and add meaning to it in a way that represents what you’re trying to get across in your essay.
For example: if the question was “Assess the impact of microeconomic policy in improving economic growth in Australia”, my first sentence might be “Microeconomic policy has had a significant impact in increasing aggregate supply and thus long-term economic growth in Australia since the 1960s”.
Next sentences: Introduce your arguments/paragraphs
In this part, it’s fine to almost list your paragraphs — there’s no need to do a whole sentence explaining each. That’s what the paragraphs themselves are for.
For example: using the same question as above, my next sentence might be “Although trade liberalisation may have been detrimental for short-term growth in manufacturing, policies such as competition policy and wage decentralisation have been highly effective in fostering economic growth in Australia”.
Background Paragraph
The aim of a background paragraph is threefold: to get across the main theory that underpins your argument; to establish the economic context for your argument; and to show the marker that you “know your stuff”.
For example, if the essay was on monetary policy, you may want to describe the process of Domestic Market Operations (how the reserve bank changes the cash rate) in your background paragraph, so that you don’t need to mention it each time you bring up changing stances. Further, it may be good to showcase the current economic climate — such as GDP growth rate and inflation — to give context to your analysis in your essay.
Some ideas for what to include in this paragraph include:
- Key theory such as DMOs or the rationale for macroeconomic policies
- Economic indicators that provide context to the time period that you’re working in, such as growth rates, inflation, unemployment rates, exchange rates, cash rates, etc.
- A brief description of the recent Budget (if talking about fiscal policy), including the stance and outcome
Bear in mind that this paragraph shouldn’t be too long — it isn’t the focus of your essay! Instead, aim for around 100–150 words at most. At this point in your essay, it may also be good to include a graph (more on this later).
Body Paragraphs
There’s no set rule for how many body paragraphs to include in your essay — I generally aim for at least 4, but there’s no real limit to how many you can (or should) write! Unlike english essays, it’s totally acceptable to just split a paragraph in two if you feel like the idea is too large to be written in one paragraph (as long as each paragraph makes sense on its own).
When writing a paragraph, I usually follow this structure:
Topic sentence
This is where you answer the question, and outline your argument or idea for this paragraph. If you are doing a discuss/assess/evaluate essay, try and make your judgement or side obvious. For example: “Trade liberalisation has been detrimental in its impact on economic growth in manufacturing industries”.
These sentences are where you bring together the theory and contemporary to build up your argument. Remember, the theory should be the focus, and contemporary a bonus. Try and weave a “story” into your analysis if you can — you should be showing the marker how everything fits together, how causes lead to effects, and ultimately bringing together relevant economic concepts to answer the question. Feel free to also include graphs here when they help strengthen your argument.
Fit in your “however” statements here. For discuss questions, this however section may take up a larger part of the paragraph if you choose to showcase two opposing arguments together.
Link your argument back to your overarching thesis, and answer the question. Following on from your “however” statement, it can often be a good idea to use linking words such as “nevertheless”, “notwithstanding”, or “despite this” to show that taking into account your arguments presented in the “however” statement, the overarching idea for the paragraph still remains.
Like the introduction, your conclusion should not be overly long. Rather, it should briefly restate the arguments made throughout your essay, and bring them all together again to reinforce how these points help answer the question.
Aggregate Demand / Supply Graph
Graphs are a great way to add extra spice to your essay — not only does it help strengthen your explanations of economic theory, it also makes it look like you wrote more pages than you actually did! Graphs, such as aggregate demand graphs, business cycle graphs, and Phillips curves, can be great in reinforcing your ideas when you mention them in your essay. They usually come either in background paragraphs or body paragraphs, and it’s usually best to draw them about a quarter to a third of the page in size. It’s also good practice to label them as “Figure 1” or “Graph 1”, and refer to them as such in your actual paragraph.
Although they can be beneficial, don’t try and force them either. Not all essays have appropriate graphs, and trying to include as many as you can without regards for their relevance may come across negatively in the eyes of the marker.
8. How to Answer Source Questions
If your essay question involves a source, try and refer to it multiple times throughout your essay. For example, this can be in the background paragraph and two of your body paragraphs. Rather than just adding in an “…as seen in the source” to one of your sentences, try and actively analyse it — show the marker that you understand why they included it, and how it actually helps strengthen your arguments.
9. Plan You Essay
Don’t be afraid to use the first page of your answer booklet as a planning page. Taking a couple minutes before you answer the question to lay out your scaffold for body paragraphs is a great first step to helping ensure that you actually end up answering the question to the best of your abilities. It also serves as a great reminder to keep checking as you finish each paragraph to ensure that you actually wrote what you intended. Just make sure to make it clear to the marker that those scribbles on the page are just a plan, and not your actual essay!
10. How to Prepare for Essays in the Exam
I find it much better to prepare paragraphs and ideas that you can draw upon to help “build up” a response during the exam itself.
Don’t go into the exam with a pre-prepared essay that you are ready to regurgitate — not only are there too many possibilities to prepare for, but it’s also unlikely that you’ll actually answer the question well with a pre-prepared response.
Instead of memorising sets of essays before the exam, I find it much better to prepare paragraphs and ideas that you can draw upon to help “build up” a response during the exam itself. What I mean by this, is that in your mind you have a “bank of different paragraphs” and ideas from all the topics in the syllabus, and when you read the exam, you start drawing from different paragraphs here and there to best formulate a response that answers the question. This allows you to be flexible in answering almost any question they can throw at you.
On top of this, ensure you have a solid foundation in both the theory and contemporary — knowing what statistics or topics to include in your essay is useless knowledge unless you have the actual content to back it up.
Now that you know the basics of how to write a good HSC economics essay, it’s time to start practising! Have a go, try out different styles, and find what works best for you. Good luck!
If you would like to learn from state ranking HSC Economics tutors at Project Academy, we offer a 3 week trial for our courses. Click to learn more !
Maximise Your Chances Of Coming First At School
Trial any Project Academy course for 3 weeks.
NSW's Top 1% Tutors
Unlimited Tutorials
NSW's Most Effective Courses
Access to Project's iPad
Access to Exclusive Resources
Access to Project's Study Space

How To STUVAC: Using Study Breaks and Holidays to Your Advantage
School holidays, HSC study breaks and STUVAC periods present an opportunity...

Co-founder of Project Academy

Top 5 Tips for Acing HSC Biology
The Head of Biology, Alex's guide to acing HSC Biology

Alex Loustau
Head of Biology & 99.45 ATAR

Ultimate Guide to Literary Techniques
This article will guide you through the use and analysis of literary techniques for the HSC English course. Written by the HSC English team at Project Academy.

Elliese Tjeuw
English Team

4U Maths Past Paper Strategies
People only tell you "do more past papers", but they rarely tell you HOW to...

99.85 ATAR & North Sydney Boys Alumni

Writing Band Six Essays-Intelligent Introductions
The first thing the marker reads is your introduction, and thus a solid introduction can engage the marker and make them actually want to read your essay. The other advantage of a decent introduction is that if for some reason you don’t get to finish your essay, the marker will at least know what you intended to talk about, and can give you some credit for being on the right track. It will definitely improve your mark overall if you can indicate that you know what you are talking about and what you would say if you had time in your introduction. This is not to say you should waste your time writing a perfect page long introduction, but rather that the introduction is important so don’t spoil your chances of getting a good mark by not introducing your essay properly!
A good introduction will always:
a) Start with a thesis that DIRECTLY RESPONDS TO THE QUESTION. You have 40 minutes to write an essay so there is no time to start with philosophical musings about the topic or write random things you happen to remember about the module you are writing about.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is just a fancy word for an argument or overall point of view. Your opening thesis statement basically needs to state an argument that you will develop and provide evidence for throughout your essay. There is no need for this to be complex, but better essays generally will have a thesis that responds to the question without using the exact wording of the question. For example:
“Curiosity is essential to finding a true sense of discovery” Discuss
An A-grade thesis would be something that indicates your personal response to the question. Remember that you do not have to agree with the statement, you can disagree or you can be really tricky and agree and disagree with the question. Better essays are always those that can argue and counter argue.
Sample thesis:
The complex nature of the concept of discovery means that a true sense of discovery can be found in different circumstances for different people, however, many individuals find that they discover the most when they trust in their curiosity.
This is a good thesis because it
- Shows you know something about the concept of discovery
- Refers to the question without using all the exact words
- Is broad enough to allow you to develop good arguments, and then counterarguments
- Uses definitive words such as “means” and “find” instead of using words such as may. This makes it sound argumentative, which is a good thing as the purpose of an essay is to argue.
However, writing a thesis such as the one above will not come naturally to a lot of students. For these students who find it difficult to develop thesis statements, the best route is to take words out of the question. This will show the marker that you have understood the question and know what you need to write about in order to answer this question.
In order to discover, people need to seek out ideas as well as develop relationships with other people and places.
This is also a good thesis because:
- It is a direct response to the question
- It is broad enough to allow you to develop an argument
- It demonstrates that you have understood the question-the word “essential” basically means something that you need or must have.
When writing a thesis, remember that it has to be an argument, but also that you must be able to support this argument with evidence in your body paragraphs. There is no formula for writing a perfect thesis as every question is different, but if you keep in mind the above points and practice, writing theses will hopefully become a lot easier!
b) A good introduction will have at least one sentence that expands on the thesis.
This will help you to show you know what you will be talking about in the essay and hopefully make the point you are trying to prove by writing this essay a little clearer to the marker.
c) Name the texts and composers that will be referred to throughout the essay
Names of texts should be Underlined. How exactly you name the texts and authors really depends on the module, so see the specific post for each of these!
d) Outline the points you will be making in the essay
To fulfill its purpose, the introduction must give a proper overview of the arguments you will be making. There is no need for excessive detail here, just state the general arguments you will be making in one long or two short sentences if necessary. See the sample introduction and each module’s essay writing blog post for further guidance on how to outline arguments in the introduction.
Also, make sure to read:
Writing Band Six Essays-Body Paragraphs
Writing Band Six Essays – Conclusions

Similar Posts
Learning styles.
The way we learn isn’t always straightforward – our personalities and learning styles have a lot to do with how we process and retain information. According to the VAK Learning Model, there are three main types of learning: Visual Visual learners go by a basic concept: “Show me and I will understand”. This means that…

Discovering The Motorcycle Diaries
Today we will be discovering The Motorcycle Diaries. If you are looking for more of an overview of the module please read this article. The most resounding question that comes to mind whilst reading Ernesto “Che” Guevara’s ‘The Motorcycle Diaries’ is, how in the world did a medical student (yes, get a nice clear picture…

Studying for your HSC?
It all comes down to this. Most of you will now have graduated and will be doing your final preparations for the HSC English Exams. It is a very stressful time, but rest assured that in a few weeks time it will all be over and you will never have to even think about area…
Standard English Module C: Texts and Society
According to the Standard English Module C: Texts and Society, students are expected to ‘explore and analyse texts used in a specific situation.’ Quite often, texts focus on a particular event or issue. The Board of Studies wants students to be able to identify key information about how these specific texts convey bigger ideas about bodies of…

Modules/Electives
This is where HSC ESL, Standard and Advanced English diverge. Each of these courses has their own modules, otherwise known as units of study, and electives within these modules. Each student will study ONE elective from each module, with the modules conveniently named A, B and C to avoid confusion. Just like the area of…

Writing Band Six Essays-DO NOT PREPARE AND LEARN ONE ANSWER
In case the capital letters didn’t scare you enough I will repeat it just so you can gauge the severity of this warning—do not pre prepare your essays. Unless you genuinely want to fail HSC English there is no excuse for going into your English exams with one memorised essay for each unit you have…
- Pingback: Studying for Exams and More Sample HSC English Papers « Save My HSC
thanks so much! love.
If your going to teach us how to write an introduction, at least have a sample!!!!
lol momo ur face is a sample :’)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this article, we will teach you how to write a comparative essay, including Y12 Module A Textual Conversations requirements, different comparative essay structures, dos and don'ts, and an exemplar paragraph of both structures.
The essay introduced the idea of cultural relativism: the concept that human behaviour is a product of culture and as such cannot be judged by those without this cultural context. These endeavours to colonise the non-European world included the institution of European governance systems in conquered territories and often resulted in the unjust ...
Comparative essays are a staple of Advanced, Extension I English and throughout Year 7-10, and the rationale behind it makes sense - NESA wants to measure and test your understanding of abstract concepts and ideas across different texts and forms. A comparative essay in layman's terms is simply an essay…
This will be the same for Trials and the HSC exam, as Module A forms 20 marks out of 60 in Paper 2 of English Advanced. One key distinction to make: Textual Conversation Essays are NOT just Comparative Essays. Use the comparative essay structures and conventions as a foundation, but Mod A requires you to develop this further.
Step 4: Write Your Body Paragraphs. Now, before you get straight into writing your body paragraphs and using various paragraph structures, you need to understand the purpose of a topic sentence and how they'll back up your thesis and inform the rest of your paragraphs.
Comparatives vary between states - in VCE, the Comparative SAC asks a question specific to the texts studied. In WACE English, comparatives are simply a type of question offered under Responding and are broadly applicable across texts. In the HSC comparative writing is imbedded into Mod A - textual conversations and even in short response ...
Introduction for Structuring Comparative Essay. Address the essay question using keywords and use some words of your thesis to answer it. Name Text One, with the year it was published in brackets after it. Indicate the genre, text type and composer of the text. Give a brief summary of Text One's cultural context - no more than a sentence.
2. Use a mixed paragraphs method. Address both halves of the comparison in each paragraph. This means that the first paragraph will compare the first aspect of each subject, the second will compare the second, and so on, making sure to always address the subjects in the same order.
Matt Ellis. Updated on June 2, 2022 Students. A compare-and-contrast essay is a style of essay that points out the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It's ideal for showing what separates and unites related things or concepts, particularly if the subjects are often confused for each other or unjustly lumped together.
Writing a great comparative essay means highlighting the similarities and differences between two things in a systematic manner. Start by choosing the parameters (items) to compare, write an outline, and fill in the details for each section. Make sure to have an introduction and conclusion. The comparative essay is one form of document that you ...
Here's a step by step breakdown for you 😎. 1. Deep Dives into the Key Techniques, Themes & Form. 💥 We'll systematically go through Richard III and Looking for Richard using an integrated comparative method in order to help students understand the key concepts in the module and collect useful notes. 🤓 We'll ensure you understand ...
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you're comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you've already said about the first. Your text is structured like this: Subject 1.
For every essay you have to write under time limits I recommend doing at least 2 practice essays with the same time constraints. It'll teach you how to manage time and show you how fast you can write, so if you really can't finish in time you can start cutting down, rather than just leaving a whole paragraph off the end of your essay.
Writing an essay that directly responds to the question and demonstrates that you really know what you are talking about is no easy feat. Most students will be able to haphazardly put together a short introduction and give a few examples from their texts that relate to the question.
A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both. The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects. The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be ...
A comparative essay asks that you compare at least two (possibly more) items. These items will differ depending on the assignment. You might be asked to compare. positions on an issue (e.g., responses to midwifery in Canada and the United States) theories (e.g., capitalism and communism) figures (e.g., GDP in the United States and Britain)
Step 1: Planning. The quickest route to a lame essay is to just write it off the bat without doing any planning or thinking ahead. While it's true that some people can just come up with awesome ideas on the spot, you need to do at least a little bit of planning if you want them to come together neatly.
The foremost step in writing a comparative essay is to choose a suitable topic. Choose a topic or theme that is interesting to write about and appeals to the reader. An interesting essay topic motivates the reader to know about the subject. Also, try to avoid complicated topics for your comparative essay. Develop a List of Similarities and ...
NOT GOOD: "GDP was $1.32403 trillion in 2017". GOOD: "The 2017 Budget's Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy — up 30% from 2016's $31 billion, and 20% higher than the inflation-adjusted long-term expenditure.". NOT GOOD: "The 2017 Budget's Infrastructure Plan injected $42 billion into the economy".
A good introduction will always: a) Start with a thesis that DIRECTLY RESPONDS TO THE QUESTION. You have 40 minutes to write an essay so there is no time to start with philosophical musings about the topic or write random things you happen to remember about the module you are writing about.
Step 1: Reiterate the first idea you signposted. Restate the idea from your last paragraph but this time focus on how it links to your second artist. You may want to throw in some simple comparative language as well to begin the contrasting between your two artists, such as "on the other hand", "in contrast to", etc.