Life Insurance: Theory and Practice
Life insurance can be defined as the contract between the insurer and the person who owns the policy. Some countries include some events like bills and death expenses are included in the premium policy. The insurer is bound to pay some money in case an event happens to occur.
If the insurer enters the contract, he pays an annual or monthly amount known as premium. If an event occurs, the benefit is paid to the beneficiaries. The insurance only considers the people who are included in the life policy. If any kind of event happens, the people who are insured are the only ones who are considered since it’s a contract between two parties, i.e., the policy owner and the insurer.
The only person allowed to pay for the policy is only the policy owner, and he also acts as the guarantee. They don’t consider the insurer as being a party to the contract since he acts as a participant. In life insurance, the insurer plays different roles compared to the roles of the policy owner. They sometimes seem to be the same, but they are totally different.
The owner appoints the beneficiary, although he is not entitled to the policy. If the beneficially happens to revoke the insurance contract, any changes that come along must be agreed upon by the beneficiary. This means that the owner has the right to change the beneficiary unless the beneficiary chooses to change or withdraw the policy. The changes might include cash value borrowing or policy assignments.
In life insurance, there are special requirements which are found in it. If the person commits suicide within a given period of time, this type of section is highly considered. If the application is misrepresented by the insured is considered as part of nullification. In most of the states in the US feel that the period of contestability cannot be more than two years.
The insurer will be considered to have a legal right to follow the claim relating to misrepresentation and ask additional information before denying the claim or accepting to pay only if the insured passes on within the mentioned period. In life insurance, the face amount on the policy is the one that the insurer is paid if he dies, and it’s still the original sum paid by the policy when the policy happens to mature.
In most cases, life insurance and life assurance always go together. In life, any of the events is most likely bound to happen. In life insurance, they are only events that are bound to happen e.g., floods, theft, the fire they come unexpectedly, causing a lot of damage. The events that are covered life assurance are events that one is sure they are going to happen in future e.g., death.

Types of insurance
Life assurance is basically divided into two categories, permanent and temporary.
(a) Temporary insurance is also known as term insurance; this type of life insurance does not accumulate cash value since it covers for a specified term of years and for a specified premium. The premium is termed as pure as it covers and buys protection in the events of death only. The only major areas which are considered in this term insurance are only the length of coverage, face amount which caters to protection or death benefits, and the premium which is going to be paid.
(b) Permanent; this type of insurance remains contact until the policy matures. If the owner is not in a position to pay the premiums on time, the policy becomes outdated or the policy lapses. The law defines that any type of policy cannot be canceled by the insurer for any reason, not unless signs of fraud are detected in the application. If there is any cancellation, there is a specific time given, which is normally two years. There are three types of permanent insurance;
(1) Whole life insurance; in this type of insurance, the cash value is included in the policy guaranteed by the company since they provide a level premium. The advantages of this insurance are that the whole life is guaranteed cash value, fixed and known annual premiums, and death benefits. We can also see that the disadvantages of whole life insurance are that the internal rate of return in the policy is usually not competitive with other savings. They also don’t have flexibility in their premiums.
(2) Endowments; endowments are considered to more expensive in terms of annual premiums compared with the rest of the insurance policies. Comparing with whole life or universal life, the period of the endowment is shortened, and it has earlier dates. In this policy, the cash value is built up inside the policy. The face amount has death benefits at a specific age. The age in which it starts is known as the endowment age. The endowment insurance is usually paid at a specific period e.g., 15 years or if the insured is living or dead.
(3) Universal life coverage; this is a new insurance cover which plans to offer a permanent insurance cover which has flexible premiums payments affordable for everyone with a quality higher internal rate of return. This insurance has a cash account, which is increased by the premium. The interest is paid within the policy, and it also recorded and credited at the rates decided by the company.
(4) Accidental death; this is limited insurance, and it only covers the insured when they pass away because of an accident. These accidents might be in the form of injury; they don’t cover any death that might occur due to health problems or any type of suicide. The policies are less expensive because they only cover death compared to other life insurances. The benefits are much better because they not only cover accidental death, but they also benefit those who have lost their limbs and also their bodily functions e.g., hearing and sight.
(5) Limited-pay; in this type of permanent insurance, all its premiums are paid over a specified duration of time. There are no extra premiums that are due to keep the policy in force.
When you come to look at life insurance, there are actually two main functions that make it operate fully. They include cash function and mortality function. In mortality function, the premium of everybody else covers the death benefits of anybody who die within a given period of time. In cash, function age varies, meaning that the policy matures and endows the face value of the policy depending on sate and company.
Time value of money
This concept refers to any type of interest that one happens to receive from any kind of payment. This is a present formula, which is the core formula for the time value of money. All the formulae are derived from the formula below;
The present value (PV) formula has four variables
PV value at time=0
FV value at time=n
I rate of compounding
N number of periods
Summing the contributions of FV the value of the cash flow, you will get the cumulative value.
The present value of growing perpetuity, if it grows at different fixed rates, you easily determine the value at looking at the following formula. There are various qualifications and modifications to this valuation application. It’s not easy to find a growing perpetual annuity with true perpetual cash flow or fixed rates.
When you want to calculate the value of the regular savings deposit in the future, you first calculate the present value of a stream of deposits of $1,000 every year for 20 years, earning an interest of 7%. (Steven A. Finkler, 1992)
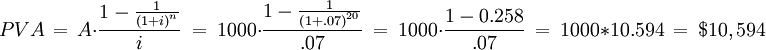
Calculating the value at a duration of 20 years
This formula can be put together into a single formula.
Lester William Zartman, Life Insurance, 1914
Joseph Brotherton maclean, Life Insurance, 1962
Robert Irwin Mehr: Life Insurance: Theory and Practice, 1977
Solomon Stephen Huebner, George Lawrence Amrhein, Chester Alexander Kline, Life Insurance, 1935
Steven A. Finkler, Christina M. Graf, Budgeting Concepts for Nurse Managers, 1992
Jae K. Shim, Accounting and Finance for the Nonfinancial Executive: An Integrated, 2000
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 6). Life Insurance: Theory and Practice. https://studycorgi.com/life-insurance-theory-and-practice/
"Life Insurance: Theory and Practice." StudyCorgi , 6 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/life-insurance-theory-and-practice/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'Life Insurance: Theory and Practice'. 6 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Life Insurance: Theory and Practice." January 6, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/life-insurance-theory-and-practice/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Life Insurance: Theory and Practice." January 6, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/life-insurance-theory-and-practice/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "Life Insurance: Theory and Practice." January 6, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/life-insurance-theory-and-practice/.
This paper, “Life Insurance: Theory and Practice”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 6, 2020 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Life Insurance?
- Compare Top Companies
Term vs. Permanent Life Insurance
- What Affects Life Insurance Costs?
Life Insurance Buying Guide
Benefits of life insurance, who needs life insurance.
- What to Do Before Buying
How Life Insurance Works
- Riders and Policy Changes
Qualifying for Life Insurance
- Life Insurance
Life Insurance: What It Is, How It Works, and How To Buy a Policy
Amy Fontinelle has more than 15 years of experience covering personal finance, corporate finance and investing.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/fontinelle-5bfc262a46e0fb0083bf8446.jpg)
Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policy owner in which the insurer guarantees to pay a sum of money to one or more named beneficiaries when the insured person dies in exchange for premiums the policyholder pays during their lifetime. The best life insurance companies have good financial strength, a low number of customer complaints, high customer satisfaction, several policy types, available and included riders, and easy applications.
Key Takeaways
- Life insurance is a legally binding contract that promises a death benefit to the policy owner when the insured person dies.
- For a life insurance policy to remain in force, the policyholder must pay a single premium upfront or pay regular premiums over time.
- When the insured person dies, the policy’s named beneficiaries will receive the policy’s face value, or death benefit.
- Term life insurance policies expire after a certain number of years. Permanent life insurance policies remain active until the insured person dies, stops paying premiums, or surrenders the policy.
- A life insurance policy is only as good as the financial strength of the life insurance company that issues it. State guaranty funds may pay claims if the issuer can’t.
Investopedia / Theresa Chiechi
Types of Life Insurance
Many different types of life insurance are available to meet all sorts of needs and preferences. Depending on the short- or long-term needs of the person to be insured, the major choice of whether to select temporary or permanent life insurance is important to consider.
Term life insurance
Term life insurance is designed to last a certain number of years, then end. You choose the term when you take out the policy. Common terms are 10, 20, or 30 years. The best term life insurance policies balance affordability with long-term financial strength.
- Decreasing term life insurance is renewable term life insurance with coverage decreasing over the life of the policy at a predetermined rate.
- Convertible term life insurance allows policyholders to convert a term policy to permanent insurance.
- Renewable term life insurance provides a quote for the year the policy is purchased. Premiums increase annually and are usually the least expensive term insurance in the beginning.
Many term life insurance policies allow you to renew the contract on an annual basis once the term is up. This is one way to extend your life insurance coverage, but since the renewal premiums are based on your current age, they can rise steeply each year. A better solution for permanent coverage is to convert your term life insurance policy into a permanent policy. This is not an option on all term life policies; look for a convertible term policy if this is important to you.
Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance is more expensive than term, but it stays in force for the insured’s entire life unless the policyholder stops paying the premiums or surrenders the policy. Some policies allow for automatic premium loans when a premium payment is overdue.
- Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance, which means it lasts your whole lifespan. It includes a cash value component, which is similar to a savings account. Cash-value life insurance allows the policyholder to use the cash value for many purposes, such as for loans or to pay policy premiums.
- Universal life (UL) insurance is another type of permanent life insurance with a cash value component that earns interest. Universal life features flexible premiums. Unlike term and whole life, the premiums can be adjusted over time and designed with a level death benefit or an increasing death benefit.
- Indexed universal life (IUL) is a type of universal life insurance that lets the policyholder earn a fixed or equity-indexed rate of return on the cash value component.
- Variable universal life (VUL) insurance allows the policyholder to invest the policy’s cash value in an available separate account. It also has flexible premiums and can be designed with a level death benefit or an increasing death benefit.
Top-Rated Companies to Compare
When shopping for insurance, you might want to start with our list of the best life insurance companies, some of which are listed below.
Term life insurance differs from permanent life insurance in several ways but tends to best meet the needs of most people looking for affordable life insurance coverage. Term life insurance only lasts for a set period of time and pays a death benefit should the policyholder die before the term has expired. That's in contrast to permanent life insurance, which stays in effect as long as the policyholder pays the premium. Another critical difference involves premiums—term life is generally much less expensive than permanent life because it does not involve building a cash value.
Before you apply for life insurance, you should analyze your financial situation and determine how much money would be required to maintain your beneficiaries’ standard of living or meet the need for which you’re purchasing a policy. Also, consider how long you'll need coverage for.
For example, if you are the primary caretaker and have children 2 and 4 years old, you would want enough insurance to cover your custodial responsibilities until your children are grown up and able to support themselves.
You might research the cost of hiring a nanny and a housekeeper or using commercial child care and cleaning services, then perhaps add money for education. Include any outstanding mortgage and retirement needs for your spouse in your life insurance calculation—especially if the spouse earns significantly less or is a stay-at-home parent. Add up what these costs would be over the next 16 or so years, add more for inflation, and that’s the death benefit you might want to buy—if you can afford it.
Burial or final expense insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that has a small death benefit. Despite the names, beneficiaries can use the death benefit as they wish.
What Affects Your Life Insurance Premiums and Costs?
Many factors can affect the cost of life insurance premiums . Certain things may be beyond your control, but other criteria can be managed to potentially bring down the cost before (and even after) applying. Your health and age are the most important factors that determine cost, so buying life insurance as soon as you need it is often the best course of action.
After being approved for an insurance policy, if your health has improved and you’ve made positive lifestyle changes, you can request to be considered for a change in risk class. Even if it is found that you’re in poorer health than at the initial underwriting , your premiums will not go up. If you’re found to be in better health, then you your premiums may decrease. You may also be able to buy additional coverage at a lower rate than you initially did.
Investopedia / Lara Antal
Step 1: Determine How Much You Need
Think about what expenses would need to be covered in the event of your death. Consider things like mortgage, college tuition, and other debts, not to mention funeral expenses. Plus, income replacement is a major factor if your spouse or loved ones need cash flow and are not able to provide it on their own.
There are helpful tools online to calculate the lump sum that can satisfy any potential expenses that would need to be covered.
Step 2: Prepare Your Application
Life insurance applications generally require personal and family medical history and beneficiary information. You may need to take a medical exam and will need to disclose any preexisting medical conditions, history of moving violations, DUIs, and any dangerous hobbies, such as auto racing or skydiving. The following are crucial elements of most life insurance applications:
- Age: This is the most important factor because life expectancy is the biggest determinant of risk for the insurance company.
- Gender: Because women statistically live longer, they generally pay lower rates than males of the same age.
- Smoking: A person who smokes is at risk for many health issues that could shorten life and increase risk-based premiums.
- Health: Medical exams for most policies include screening for health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer and related medical metrics that can indicate risk.
- Lifestyle : Dangerous lifestyles can make premiums much more expensive.
- Family medical history: If you have evidence of major disease in your immediate family, your risk of developing certain conditions is much higher.
- Driving record: A history of moving violations or drunk driving can dramatically increase the cost of insurance premiums.
Standard forms of identification will also be needed before a policy can be written, such as your Social Security card, driver's license, or U.S. passport.
Step 3: Compare Policy Quotes
When you've assembled all of your necessary information, you can gather multiple life insurance quotes from different providers based on your research. Prices can differ markedly from company to company, so it's important to make the effort to find the best combination of policy, company rating, and premium cost. Because life insurance premiums are something you will likely pay monthly for decades, finding the best policy to fit your needs can save an enormous amount of money.
Our lineup of the best life insurance companies can give you a jump start on your research. It lists the companies we've found to be the best for different types of needs, based on our research of nearly 100 carriers.
There are many benefits to having life insurance . Below are some of the most important features and protections offered by life insurance policies.
Most people use life insurance to provide money to beneficiaries who would suffer a financial hardship upon the insured’s death. However, for wealthy individuals, the tax advantages of life insurance, including the tax-deferred growth of cash value, tax-free dividends, and tax-free death benefits, can provide additional strategic opportunities.
Avoiding Taxes
The death benefit of a life insurance policy is usually tax-free. It may be subject to estate taxes , but that's why wealthy individuals sometimes buy permanent life insurance within a trust. The trust helps them avoid estate taxes and preserve the value of the estate for their heirs.
Tax avoidance is a law-abiding strategy for minimizing one’s tax liability and should not be confused with tax evasion , which is illegal.
Life insurance provides financial support to surviving dependents or other beneficiaries after the death of an insured policyholder. Here are some examples of people who may need life insurance:
- Parents with minor children. If a parent dies, the loss of their income or caregiving skills could create a financial hardship. Life insurance can make sure the kids will have the financial resources they need until they can support themselves.
- Parents with special-needs adult children. For children who require lifelong care and who will never be self-sufficient, life insurance can make sure their needs will be met after their parents pass away. The death benefit can be used to fund a special needs trust that a fiduciary will manage for the adult child’s benefit.
- Adults who own property together. Married or not, if the death of one adult would mean that the other could no longer afford loan payments, upkeep, and taxes on the property, life insurance may be a good idea. One example would be an engaged couple who take out a joint mortgage to buy their first house.
- Seniors who want to leave money to adult children who provide their care. Many adult children sacrifice time at work to care for an elderly parent who needs help. This help may also include direct financial support. Life insurance can help reimburse the adult child’s costs when the parent passes away.
- Young adults whose parents incurred private student loan debt or cosigned a loan for them. Young adults without dependents rarely need life insurance, but if a parent will be on the hook for a child’s debt after their death, the child may want to carry enough life insurance to pay off that debt.
- Children or young adults who want to lock in low rates. The younger and healthier you are , the lower your insurance premiums. A 20-something adult might buy a policy even without having dependents if there is an expectation to have them in the future.
- Stay-at-home spouses. Stay-at-home spouses should have life insurance as they have significant economic value based on the work they do in the home. According to Salary.com, the economic value of a stay-at-home parent would have been equivalent to an annual salary of $162,581 in 2018.
- Wealthy families who expect to owe estate taxes. Life insurance can provide funds to cover the taxes and keep the full value of the estate intact.
- Families who can ’ t afford burial and funeral expenses. A small life insurance policy can provide funds to honor a loved one’s passing.
- Businesses with key employees. If the death of a key employee, such as a CEO, would create a severe financial hardship for a firm, that firm may have an insurable interest that will allow it to purchase a life insurance policy on that employee .
- Married pensioners. Instead of choosing between a pension payout that offers a spousal benefit and one that doesn’t, pensioners can choose to accept their full pension and use some of the money to buy life insurance to benefit their spouse. This strategy is called pension maximization .
- Those with preexisting conditions. Such as cancer, diabetes, or smoking. Note, however, that some insurers may deny coverage for such individuals, or else charge very high rates.
Each policy is unique to the insured and insurer. It’s important to review your policy document to understand what risks your policy covers, how much it will pay your beneficiaries, and under what circumstances.
What to Do Before Buying Life Insurance
Research policy options and company reviews.
Because life insurance policies are a major expense and commitment, it's critical to do proper due diligence to make sure the company you choose has a solid track record and financial strength, given that your heirs may not receive any death benefit for many decades into the future. Investopedia has evaluated scores of companies that offer all different types of insurance and rated the best in numerous categories.
Consider How Much Death Benefit You Need
Life insurance can be a prudent financial tool to hedge your bets and provide protection for your loved ones in case of death should you die while the policy is in force. However, there are situations in which it makes less sense —such if you buy too much or insure people whose income doesn't need to be replaced. So it's important to consider the following.
What expenses couldn't be met if you died? If your spouse has a high income and you don't have any children, maybe it's not warranted. It is still essential to consider the impact of your potential death on a spouse and consider how much financial support they would need to grieve without worrying about returning to work before they’re ready. However, if both spouses' income is necessary to maintain a desired lifestyle or meet financial commitments, then both spouses may need separate life insurance coverage.
Know Why You're Buying Life Insurance
If you're buying a policy on another family member's life, it's important to ask—what are you trying to insure? Children and seniors really don't have any meaningful income to replace, but burial expenses may need to be covered in the event of their death. Beyond burial expenses, a parent may also want to protect their child’s future insurability by purchasing a moderate-sized policy when they are young. Doing so allows that parent to ensure that their child can financially protect their future family. Parents are only allowed to purchase life insurance for their children up to 25% of the in-force policy on their own lives.
Could investing the money that would be paid in premiums for permanent insurance throughout a policy earn a better return over time? As a hedge against uncertainty, consistent saving and investing—for example, self-insuring—might make more sense in some cases if a significant income doesn't need to be replaced or if policy investment returns on cash value are overly conservative.
A life insurance policy has two main components—a death benefit and a premium. Term life insurance has these two components, but permanent or whole life insurance policies also have a cash value component.
1. Death benefit. The death benefit or face value is the amount of money the insurance company guarantees to the beneficiaries identified in the policy when the insured dies. The insured might be a parent, and the beneficiaries might be their children, for example. The insured will choose the desired death benefit amount based on the beneficiaries’ estimated future needs. The insurance company will determine whether there is an insurable interest and if the proposed insured qualifies for the coverage based on the company’s underwriting requirements related to age, health, and any hazardous activities in which the proposed insured participates.
2. Premium. Premiums are the money the policyholder pays for insurance. The insurer must pay the death benefit when the insured dies if the policyholder pays the premiums as required, and premiums are determined in part by how likely it is that the insurer will have to pay the policy’s death benefit based on the insured’s life expectancy. Factors that influence life expectancy include the insured’s age, gender, medical history, occupational hazards, and high-risk hobbies. Part of the premium also goes toward the insurance company’s operating expenses. Premiums are higher on policies with larger death benefits, individuals who are at higher risk, and permanent policies that accumulate cash value.
3. Cash value. The cash value of permanent life insurance serves two purposes. It is a savings account that the policyholder can use during the life of the insured; the cash accumulates on a tax-deferred basis. Some policies have restrictions on withdrawals depending on how the money is to be used. For example, the policyholder might take out a loan against the policy’s cash value and have to pay interest on the loan principal. The policyholder can also use the cash value to pay premiums or purchase additional insurance. The cash value is a living benefit that remains with the insurance company when the insured dies. Any outstanding loans against the cash value will reduce the policy’s death benefit.
Good to Know
The policy owner and the insured are usually the same person, but sometimes they may be different. For example, a business might buy key person insurance on a crucial employee such as a CEO, or an insured might sell their own policy to a third party for cash in a life settlement .
Life Insurance Riders and Policy Changes
Many insurance companies offer policyholders the option to customize their policies to accommodate their needs. Riders are the most common way policyholders may modify or change their plans. There are many riders, but availability depends on the provider. The policyholder will typically pay an additional premium for each rider or a fee to exercise the rider, though some policies include certain riders in their base premium.
- The accidental death benefit rider provides additional life insurance coverage in the event the insured’s death is accidental.
- The waiver of premium rider relieves the policyholder of making premium payments if the insured becomes disabled and unable to work.
- The disability income rider pays a monthly income in the event the policyholder becomes unable to work for several months or longer due to a serious illness or injury.
- Upon diagnosis of terminal illness, the accelerated death benefit rider allows the insured to collect a portion or all of the death benefit.
- The long-term care rider is a type of accelerated death benefit that can be used to pay for nursing-home, assisted-living, or in-home care when the insured requires help with activities of daily living, such as bathing, eating, and using the toilet.
- A guaranteed insurability rider lets the policyholder buy additional insurance at a later date without a medical review.
Borrowing Money. Most permanent life insurance accumulates cash value that the policyholder can borrow against. Technically, you are borrowing money from the insurance company and using your cash value as collateral. Unlike with other types of loans, the policyholder’s credit score is not a factor. Repayment terms can be flexible, and the loan interest goes back into the policyholder’s cash value account. Policy loans can reduce the policy’s death benefit, however, if you don't pay them back.
Funding Retirement. Policies with a cash value or investment component can provide a source of retirement income. This opportunity can come with high fees and a lower death benefit, so it may only be a good option for individuals who have maxed out other tax-advantaged savings and investment accounts. The pension maximization strategy described earlier is another way life insurance can fund retirement.
It’s prudent to reevaluate your life insurance needs annually or after significant life events, such as divorce , marriage, the birth or adoption of a child, or major purchases, such as a house. You may need to update the policy’s beneficiaries, increase your coverage, or even reduce your coverage.
Insurers evaluate each life insurance applicant on a case-by-case basis, and with hundreds of insurers to choose from, almost anyone can find an affordable policy that at least partially meets their needs. In 2018 there were 841 life insurance and annuity companies in the United States, according to the Insurance Information Institute.
On top of that, many life insurance companies sell multiple types and sizes of policies, and some specialize in meeting specific needs, such as policies for people with chronic health conditions. There are also brokers who specialize in life insurance and know what different companies offer. Applicants can work with a broker free of charge to find the insurance they need. This means that almost anyone can get some type of life insurance policy if they look hard enough and are willing to pay a high enough price or accept a perhaps less-than-ideal death benefit.
Insurance is not just for the healthy and wealthy, and because the insurance industry is much broader than many consumers realize, getting life insurance may be possible and affordable even if previous applications have been denied or quotes have been unaffordable.
In general, the younger and healthier you are, the easier it will be to qualify for life insurance, and the older and less healthy you are, the harder it will be. Certain lifestyle choices, such as using tobacco or engaging in risky hobbies such as skydiving, also make it harder to qualify or lead to higher rates.
You need life insurance if you need to provide security for a spouse, children, or other family members in the event of your death. Life insurance death benefits, depending on the policy amount, can help beneficiaries pay off a mortgage, cover college tuition, or help fund retirement. Permanent life insurance also features a cash value component that builds over time.
What Affects Your Life Insurance Premiums?
- Age (life insurance is less expensive)
- Gender (female tends to be less expensive)
- Smoking (smoking increases premiums)
- Health (poor health can raise premiums)
- Lifestyle (risky activities can increase premiums)
- Family medical history (chronic illness in relatives can raise premiums)
- Driving record (good drivers save on premiums)
What Are the Benefits of Life Insurance?
- Payouts are tax-free. Life insurance death benefits are paid as a lump sum and are not subject to federal income tax because they are not considered income for beneficiaries.
- Dependents don't have to worry about living expenses. Most policy calculators recommend a multiple of your gross income equal to seven to 10 years that can cover major expenses like mortgages and college tuition without the surviving spouse or children having to take out loans.
- Final expenses can be covered. Funeral expenses can be significant and can be avoided with a burial policy or with standard term or permanent life policies.
- Policies can supplement retirement savings. Permanent life policies such as whole, universal, and variable life insurance can offer cash value in addition to death benefits, which can augment other savings in retirement.
How Do You Qualify for Life Insurance?
To qualify for life insurance, you need to submit an application. But life insurance is available to almost anyone. However, the cost or premium level can vary greatly based on your age, health, and lifestyle. Some types of life insurance don't require medical information but generally have much higher premiums and involve an initial waiting period before the death benefit is available.
How Does Life Insurance Work?
Life insurance works by providing a death benefit in exchange for paying premiums. One popular type of life insurance—term life insurance—only lasts for a set amount of time, such as 10 or 20 years. Permanent life insurance also features a death benefit but lasts for the life of the policyholder as long as premiums are paid.
Insurance Information Institute. " What are the Different Types of Term Life Insurance Policies? "
Allstate. " What Is Variable Universal Life Insurance? "
Insurance Information Institute. " What are the Different Types of Permanent Life Insurance Policies? "
Internal Revenue Service. " Life Insurance & Disability Insurance Proceeds ."
Social Security Administration. " Liens, Adjustments and Recoveries, and Transfers of Assets ."
NAIC. " Life Insurance ."
Insurance Information Institute. " Facts + Statistics: Industry Overview ."
- How to Get Life Insurance 1 of 41
- Life Insurance: What It Is, How It Works, and How To Buy a Policy 2 of 41
- When Should You Get Life Insurance? 3 of 41
- How Age Affects Life Insurance Rates 4 of 41
- Is Life Insurance Worth It? 5 of 41
- What to Expect When Applying for Life Insurance 6 of 41
- Universal Life Insurance vs. Whole Life 7 of 41
- 11 Best Term, Whole, and No-Exam Life Insurance Companies for April 2024 8 of 41
- Term Life Insurance: What It Is, Different Types, Pros and Cons 9 of 41
- What Is Term Insurance? How Does It Work, and What Are the Types? 10 of 41
- Group Term Life Insurance: What It Is, How It Works, Pros & Cons 11 of 41
- Best Term Life Insurance Companies of April 2024 12 of 41
- Permanent Life Insurance: Definition, Types, and Difference from Term Life 13 of 41
- What Is Cash Value in Life Insurance? Explanation With Example 14 of 41
- Whole Life Insurance Definition: How It Works, With Examples 15 of 41
- Best Whole Life Insurance Companies of April 2024 16 of 41
- What Is Universal Life (UL) Insurance? 17 of 41
- Variable Universal Life (VUL) Insurance: What It Is, How It Works 18 of 41
- What Is Indexed Universal Life Insurance (IUL)? 19 of 41
- Paid-Up Additional Insurance: Definition and the Role of Dividends 20 of 41
- Adjustable Life Insurance: Definition, Pros & Cons, vs. Universal 21 of 41
- Guaranteed Issue Life Insurance: What it is, How it Works, 22 of 41
- Final Expense Insurance: What it is, Who Needs it, Pros and Cons 23 of 41
- Burial Insurance: What It is, How It Works 24 of 41
- 8 Common Life Insurance Riders 25 of 41
- Accelerated Benefit Riders: How They Work 26 of 41
- Dread Disease Rider: What it is, How it Works 27 of 41
- Family Income Rider: What It Is, How It Works 28 of 41
- Are Return of Premium Riders Worth It? 29 of 41
- Waiver of Premium Rider: Definition, Purpose, Benefits, and Cost 30 of 41
- Long-Term Care Rider: What it is, How it Works 31 of 41
- How Can I Borrow Money From My Life Insurance Policy? 32 of 41
- Cashing in Your Life Insurance Policy 33 of 41
- What Is Cash Surrender Value? How It Compares to Cash Value 34 of 41
- Cash Value vs. Surrender Value: What's the Difference? 35 of 41
- IRA vs. Life Insurance for Retirement Saving: What's the Difference? 36 of 41
- How Does Life Insurance Work? 37 of 41
- Understanding Taxes on Life Insurance Premiums 38 of 41
- What Are the Tax Implications of a Life Insurance Policy Loan? 39 of 41
- What Is a 1035 Exchange? Definition and How the Rules Work 40 of 41
- Do Beneficiaries Pay Taxes on Life Insurance? 41 of 41
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1465621717-5f131bf876c043898c13e6c471acf50f.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best insurance topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on insurance, 📌 most interesting insurance topics to write about, ⭐ simple & easy insurance essay titles, 💡 interesting topics to write about insurance, ❓ research questions about insurance.
- Social Insurance Programs and Their Influence on Society Socioeconomic and political forces can also affect social insurance programs as political and economic determine the longevity of social security programs.
- The Importance of HRM Within the Insurance Industry First, the company undertakes a rigorous procedure to ensure that the jobs that have been designed specifically meet the needs and requirements of the firm and its clientele and most importantly, the job description attracts […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Role of Insurance in Economic Development The importance of the insurance sector in the economic development of the country is being increasingly felt, due to the continued increase in the contribution of the insurance sector to the overall financial sector.
- Company Analysis: Aviva Life Insurance Company Directors and management of a company are interested in its efficiency to generate profits, the company’s viability from the investor’s point of view, the company’s ability to generate sufficient returns to investors and gearing ratio […]
- Insurance Agency’s Organizational Behavior To achieve the objective of determining effective usage of human skills in management, the top manager, Miss Kally, was interviewed about of the company.
- Risk Management: Types of Insurance Even though insurance cannot avoid the occurrence of bad things, it has the capability of transferring the financial consequences of the events to an insurance carrier, thus limiting the financial commitments of the insured firms.
- Insurance Barriers in Mental Health Population With the help of the Affordable Care Act, access to mental health care among people with low income and from ethnic and racial minorities was improved significantly.
- Corporate Demand for Insurance on Risks In addition, empirical studies indicate that the capability of firms to self-insure decreases the demand for corporate insurance coverage for other policies apart from the property exposure.
- Risk Management and Commercial Property Insurance In the quest to understand risk management and commercial property insurance, one should understand the risks in society, the relationship between risk and insurance, risk management tools, and the legal principles of risk and insurance […]
- Insurance Frauds and How They Can Be Managed Insurance refers to the services offered by companies that are willing and able to undertake risk prevention and compensation services to individuals and property.
- Emotional Appeal in the Insurance Advertising The centrality of the word, as well as the uniformity of the blue background, forces the viewer to notice it and probably remember it for a long time, given the jolt of transition.
- Organizational Behavior in Insurance Marketing Group The paper assesses how the organization’s behavior has been influenced by different components, which include the organization’s culture, internal communication, motivational techniques, nature of authority, areas of emotional quotient embraced by the organization, and the […]
- The Tort Law and Liability Insurance System The changes in the insurance system made it more accessible and enabled poorer people to buy insurances and get costs in case of insured accident.
- Operational Risk Within Lloyd’s Insurance Market The article entitled, Operational Risk within an Insurance Market reflected the ideas of Manning and Gurney when it comes to the development and implementation of risk management within Lloyd’s insurance market. The article’s objective is […]
- Insurance Companies Using Artificial Intelligence In these situations, the decisions AI would make would not contribute to improving the situation for these people and would not better the society as a whole.
- Progressive Insurance’s Diversity, Equity and Inclusion It can be used to assess the effectiveness of diversity recruiting and retention efforts, measure the value of diversity training, and survey workers about the success of diversity initiatives, such as supplier programs, employee resource […]
- The Replacement for the ACA Healthcare Insurance Policy For example, the AHCA policy allows a waiver of the ACA’s healthcare provision for societal rating and enables the federal government to charge patients more capital regarding the payment of premiums.
- The Health Insurance Portability Policy Analysis These changes demonstrate that policymakers draw sufficient attention to ensure that the HIPAA policy addresses current issues and keeps abreast of changing technologies that are actively applied in the medical sphere.
- Aspects of Insurance Financial Planning The basic principle of investment is that an increase in the risk of an investment increases the potential for high returns.
- How the Insurance and Drug Industries Affected the Universal Healthcare Universal healthcare in the United States guarantees that all citizens have access to the medical care they need, regardless of their capacity to pay.
- Macro-Environmental Analysis: Health Insurance for Children Additional sub-questions to be evaluated will be: Will the free-standing children’s hospitals go the way of rural hospitals and become obsolete?
- Australia Comprehensive Car Insurance Industry Thus, the sector is characterized by the dominance of the four biggest insurers cooperating with the highest number of customers and possessing the biggest market shares. Altogether, it is possible to conclude that the car […]
- Comparing Insurance in the UK and Germany Insurance within the framework of the first category is aimed at maintaining the well-being of citizens and, in the second – reducing financial losses in the event of risks to property.
- Art and Music Therapy Coverage by Health Insurance However, I do believe that creative sessions should be available for all patients, and I am going to prove to you that music and art are highly beneficial for human health.
- Privacy Issues of the Health Insurance Act The rule requires health entities to notify their patients when their health data is impermissibly used or disclosed in a manner that compromises the security and privacy of the PHI.
- Insurance in Europe Profitability and the Macroeconomic Environment The assignment analyses the cost structure of the industry, the economic landscape in Europe, and how it relates to the insurance sector, changing consumer preference, and the impact of Covid-19 on the industry.
- Struggles of Democracy: Social Insurance Programs There are always segments of people in the society who struggle more than the general population, and by taking measures, the government increases the economic growth and general well-being.
- The Future of Retirement and Health Insurance There are many risks related to them due to a number of factors: stock market instability, possible changes to the funding of those programs and the threat of the abolishment of Medicare.
- Should Health Insurance Be Mandatory for All American Citizens? With state-initiated changes, there is a chance for healthcare insurance to become obligatory for every resident inhabiting the United States improving their well-being, treatment outcomes, and quality of life.
- Healthcare Insurance and Job Search The company choices rangers from the people covered by the insurance, hospitals that the insurance is accepted, the amount the insurance can raise the amount deducted from the salary for the cover.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Marketing Process: Advertising Advertising is regarded as a vital type of information for medical service competitiveness due to the competitive nature of medicine and the firm establishment of practically all business sectors in the United States, presently deemed […]
- The Life Insurance Industry: Key Aspects Nevertheless, there is a problem of understanding the need and functions of life insurance among the population, which becomes an obstacle to the registration of such services.
- Content Analysis of Cyber Insurance Policies Overall, the information that the course has provided has allowed me to understand and embrace the framework for addressing the cases of personal data breach.
- Consideration of Insurance From an Ethical Point of View The payment by the insurer of the insurance indemnity to the policyholder is the responsibility of the insurer. Setting a payment limit is a solution to the problem of losses for an insurance company in […]
- Outback Insurance Company vs. Dexter’s Facility In case of violations of the rules of operation, use of the vehicle, and its management, the detention of the vehicle is applied.
- Features of the Entry of a Foreign Insurance Company to the UAE Market The modern United Arab Emirates is striving to diversify the economy and minimize the influence of an obscure sector on the development of the country. CCL regulates the activities of agents for foreign companies in […]
- Insurance Inequality in New Zealand This applies both to the employer’s territory and outside it, either during the journey to the place of work or returning from the place of work.
- UHC: Managing HACs and HAIs in the Context of Insurance Programs On the one hand, if the number of HACs continues to trend upward, this will lead to the establishment of larger sizes and impose more stringent requirements on the operation of clinical organizations.
- TriTerm Health Insurance Program in West Virginia In addition, one of the last steps is the need for feedback to adjust the plan and make timely changes. Thus, this is what creates some disconnect between the framework and the TriTerm health plan […]
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act: Privacy and Security Rules Violation Most cases present with the use of malicious malware to access protected data without the consent of the insurers and inappropriate use of that information.
- Medicaid, American Governmental Health Insurance Program The Federal government covers the main part of the insurance, and the other part is paid from the state’s budget. The other factors that influence the individual’s permission to use it are the cost of […]
- Case Study: Happy Acres and Insurance Being on the second floor of the facility, she fell down the stairs and broke her hip, and got a concussion. The nursing home had failed to implement the relevant measures to maximize the safety […]
- Usage-Based Insurance Company Project In order to explain the opportunity, I would like to share with you the state of the market, potential competitors, and the description of the target customer base.
- Cost Sharing Under State Children’s Health Insurance Program Because of the implementation of cost sharing, the yearly allowances for the families eligible for SCHIP have been significantly reduced, leading to the impossibility of dental care for the children.
- Corporate Finance Law in Saudi Arabian Insurance Institutions This study will stand on available research to examine the fundamental growth drivers and estimate the prospects that Insurance institutions in Saudi Arabia have under the corporate finance law in terms of the situation of […]
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and the Medical Billing Process As of now, the disclosure and use of health information is safeguarded by a collage of state legislations that leave gaps in the protection of patients’ health records that are private and confidential.
- Malpractice Lawsuits: Professional Liability Insurance The interests of the healthcare professional are secondary to those of the employer in case of a lawsuit. One disadvantage of having professional liability insurance is that its premiums might be expensive to some healthcare […]
- Whole Life Insurances Case Study The type of health policy they use is named the Whole Life Insurance, which presupposes insured person’s coverage for the duration of their lives as long as they pay the premium on time.
- Professional Liability Insurance As a result of the discussion, nurses received new information about the professional liability policy; one of the nurses decided to obtain the individual plan.
- Health & Safety & Insurance: Risk Management There are chances that the regular or single insurance program or policy will not be able to cover all the possible exposures.
- Risk vs. Cost in Natural Disaster Insurance Floods are more predictable, and it is possible to create a map for each flood-prone area that would allow insurance companies to calculate the exact cost of premiums.
- Nursing: Malpractice Insurance First of all, it is hard to estimate the exact amount of insurance that I may require since the amounts of money paid to different patients may vary widely. Therefore, I should clarify whether I […]
- Children’s Health Insurance Program This presentation discusses the role of the Children’s Health Insurance Program, a component of U.S. health policy regulating different mechanisms of medical services for children.
- Economics: Insurance Industry in 2005 The first is trade in risk and the second is diversification. When an insurance company is able to take advantage of the predictability that comes from aggregating a large number of independent events, it is […]
- Landlord and Tenant, Insurance and Estates It is an owner of the property who yields the right to use the property for a particular point in time in exchange for the reception of the rental fee.
- National Disability Insurance Scheme Implementation This paper explores the economic, political, sociological, epidemiological public health factors affecting the implementation of the NDIS, and their effect on the health policy in response to the growing needs of the community.
- J.C. Durick Insurance v. Peter Andrus Law Case The dispute was a result of changes made to the insurance cover policy, by the plaintiff without the consent of the defendant.
- Australian Business Law: Insurance Contracts Act Insurance basics state that the insurer covers the insured and in the event of any circumstances unknown to the insured, the insurer is supposed to pay relief to the insured.
- Manifestations of Gender Discrimination in Insurance In the past, insurance companies have engaged in gender discrimination in the classification, acceptance and rating of risks. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of the concept of gender discrimination and insurance in the world.
- The Selection Process for the Type of Health Insurance for Staff in a Medium-Sized Company The cost of health insurance would also be a useful piece of information for determining the right health insurance policy to take.
- Bank (HSBC) and Life Insurance Company (Protective) The report also investigates the profitability of the two companies, the metrics used to measure profitability, variation in the last five years and the reasons for these variations.
- Employment Law in Australian Insurance Sector As a matter of fact, there was no evidence to prove that the inclusion of the implied term in the contract was a professional custom in the insurance sector.
- A Change in the Medical Insurance Plan It is not a secret that health insurance is one of the most sensitive topics in the workplace, as employees are insured with the help of employer-sponsored medical insurance every year.
- Measles and Health Insurance in Illinois It is also shown that Illinois had the 23rd position among the states of the U.S.according to the percentage of the population not covered by health insurance in 2014, beginning with the states that had […]
- The United Health Care Insurance Program In most cases, the insurer is the insurance company that provides different insurance packages to individuals in an exchange for payment of a small fee that is referred to as a premium.
- Health Insurance and the Affordable Care Act As soon as the specifics of the staff’s role in the organization and the threats that they are exposed to are taken into account, the implementation of the PPO strategy should help improve the quality […]
- Zurich Insurance Company’s Risk Management Principles A look at the structure of the insurance industry of Bahrain reveals that it is made up of two types of firms, the Takaful institutions and the conventional insurance companies. There is a couple of […]
- Healthcare Insurance and Quality Improvement The current paper discusses the impact of technological innovation, pay-for-performance, and evidence-based medicine to improve care quality and reduce costs. Pay-for-performance initiatives such as Medicaid and Medicare encourage the identification of programs that are most […]
- Health Insurance and the Labor Market To understand the implications of the adverse selection, it is important to focus on the aspects of the issue. While changing the distribution of the number of labor hours among employees and the size of […]
- Financing Healthcare and Public Health Insurance The alternative sources of funding are critical for the sustainable functioning of the healthcare system. These regulations can be critical for minimizing the cost of healthcare.
- Hospitality Law: Dram Shop Insurance It should be mentioned that the employees of restaurants and hotels can also sustain their injuries in the workplace, even if this risk is lower in comparison with other industries.
- Insurance Companies’ Profitability in Saudi Arabia The insurance companies are required to raise a minimum capital of SAR100 million in order to be licensed to operate in the industry.
- Car Insurance in Saudi Arabia vs. USA The main objective of car insurance is to protect the car owner and the family from financial losses in the event of an accident or any other eventuality.
- The Principles of Insurance Before agreeing with the insurer, the insurance company often evaluates the risk factors of the insurer and the probability of occurrence of such risks.
- Insurance Sector in Arabic Gulf Region The growth in the insurance sector in the Gulf region matches with the growth of the economy, population growth, improved regulatory framework and increased responsiveness of the products offered by the industry in these regions.
- Commercial Law: Insurance Contracts Act ‘An insured’s duty of disclosure under the Common Law and the Insurance Contracts Act 1984’ Under section twenty one of the 1984 Insurance Contacts Act, all customers are required to make a disclosure to the […]
- Takaful Insurance Company of South Africa It points out the aims of and objective of conventional and takaful insurance. This therefore transits the ownership of the insurance resources or money and processes to the policy owner.
- Saudi Arabia Insurance Companies and Stocks The insurance sector is one of the highest-ranking areas of investment in the Saudi Arabia Stock Exchange. However, compared to other emerging markets, this does not much most well-performing markets probably because of the policies […]
- Health Insurance in the USA: A Basic Necessity for the Population In my view, a good plan to start the solution chain for this problem would be the proper reallocation of federal funds in favor of healthcare research and insurance coverage.
- Insurance Policies and Covers in the Construction Industry This dissertation is aimed at exploring the insurance responses shown by construction firms in the industry in their attempt to reduce their exposure to inherent risks in the industry Insurance is a term that refers […]
- Implementing the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 However, efficient recording and transmittal of essentially private information over the Internet and even proprietary networks posed a threat to the individual right to privacy of health and treatment information.
- Long-Term Care Insurance Sources The reason is the credibility of the brand; it is one of my most well-known service providers and its customers have generally been happy with them.
- Long-Term Care Insurance for Different Age Categories A look at the escalation in premium suggests that purchase of LTC while a person is younger and can afford continuity in premium payments is prudent.
- “China Life Plots Overseas Insurance Buys” by Dyer & Waldmeir With the current economic down surge, most companies are not able to make investment decisions for fear of uncertainties that are likely to befall them. This is to take advantage of the untapped opportunities and […]
- Process of Professional Integration in Hospitals and Expansion of Managed Care Health Insurance However, in the case of MaineHealth a Clinical Integration and Community Health Improvement organization a perfect integration has resulted in profound success in extending services to the community. The hospital followed the process of integrating […]
- The Single-Payer Healthcare System and Improve Health Insurance Availability The single-payer framework will boost healthcare management through centralization, thus, raising the accessibility of quality clinical services among all individuals who need them.
- The National Disability Insurance Scheme: The Issue of Financing Professionals working within the sphere of Aged Care and Disability Services have to collaborate with many organizations in order to ensure that their clients and patients receive the most benefits from the system.
- National Disability Insurance Scheme The development of NDIS is conditional upon the existence of specific issues related to the provision of healthcare services to disabled people.
- A Company Having Healthcare Insurance for Workers: Pros and Cons In terms disadvantages, the constant increase in the cost of health insurance is also a factor to consider. In such situations, employees are required to provide a medical certificate, and paid sick leave is only […]
- The Significant Mistakes That Go Against Insurance Policies Crastination has not gone to the office for the annual examinations, and the procedures done by Dr. Since the visit was entirely considered a medical treatment, it does not meet the requirements of an insurance […]
- Multiple Insurance Contracts and Customer Behavior Research Goal: This study will help to understand the dominant pattern in the insurance companies and comprehend why some of the companies have established multiple insurance services.
- Risk Management Throughout History: The Origins and Development of Private Insurance In particular, Chapter 4 The Return of Risk tracks the origins and development of private insurance and welfare state and examines the limitations of different risk management practices.
- The Future of Automobile Insurance Thus, progressive insurance politics can become a backbone of the safety of Canadian vehicles, while the consequences of the abolishment of insurances through the usage of new technologies are unpredictable.
- A Flood Insurance Program in Canada: The Way to Protect Lives and Homes Floods are the major source of property loss: according to the analysis made by Munich, insurance companies do not want to take all the bills they get and ignore the majority of them.
- Quality Management at Empire Blue Cross Shield Insurance Company Boasting of over 75 years experience in the insurance industry, the company has expanded its activities to cover all market segments.
- The Allianz SF Insurance Company and Its Activities in Saudi Arabia It should be observed that most of the firms coming from the other half of the world, commit the blunder of imposing the same marketing ploys and campaigns to the Saudi Arabia market; Allianz group […]
- AllSafe Insurance Company’s Ethics and Competition In this case, the customers of D & M Insurance Company are expected to buy more policies for the company as the prices of their policies would be expected to be lower.
- Portfolio Insurance: Types of Risk in Fund Investing Their main investment area is the stock exchange that is subjected to external forces that affect the prices of the shares. This is because the factors that lead to it are national and a wise […]
- Life Insurance: The Key Points The ultimate aim of Insurance is without a doubt to minimize the risks involved in various aspects of life and in addition to this, to cover and compensate the owner if any loss is suffered […]
- Employment Insurance Training Benefits in Canada In this regard, those workers that have been laid-off are in a dire need of sufficient benefits for their sustenance and that of their families, as they seek to look for other forms of employment.
- Insurance Against Weather Conditions In Florida, the standard wind insurance payment increased from $723 to $1465 from 2002 to 2007, and in Florida’s coastal regions payments have tripled or even quadrupled. In addition, insurance companies have increased deductibles which […]
- Historical Development of Insurance This is the paper that will be briefly discussing the history of insurance along with the needs of insurance that has been realized in the past.
- Reiki Therapy: Why It Should Be Covered by Insurance It is success that counts most in this world and it is the system of Reiki holistic healing that is the success story of the day and under such conditions it should be covered by […]
- Programs of Social Insurance The category that is highly represented in this group of the uninsured is the working population basically due to lack of coverage for health insurance by their employers and also due to the amount of […]
- Price Discrimination in Healthcare and Family Health Care Insurance The benefit of the global pricing is that payer of the price and the service provider share equal risk. The main objective of price discrimination is to maximise revenue and increase the profit of the […]
- Ethical Issue Facing Health Care: Healthcare Insurance Issues These problems can range from whether or not the person has healthcare insurance to the doubt that whether or not the insurance providers are going to pay for the medical treatments.
- Introduction to Insurance The main aim of Insurance is to minimize the risks involved in various aspects of life and to cover and compensate the owner for any loss is suffered by the owner.
- Healthcare Trends and Implications. Insurance Affordable health care insurance needs to become a top priority and this article talks about the attempts of various states to increase health care coverage by providing greater access to healthcare and public coverage to […]
- The Captive Insurance Services: Different Types Captive insurers are insurers who are owned in part or in full by companies in the business of insurance. Captive insurance in Bahrain is well defined and in this country they have a number of […]
- Technological Development: Oman Insurance Company According to the requirements of combining information technology and information system relating to the internal and external environmental elaboration and development purpose, critical analysis of technological background and overall judgment of competency regarding the selected […]
- Personal Injury Insurance Adjuster in North Carolina But it is not always that the first person to arrive to your case will be a lawyer but most of the time it is an insurance adjuster who arrives first in a bid to […]
- Sompo Japan Insurance Incorporation in the US The insurance rate though is vital for the determination of the amount which is called as the premium which has to be changed for a particular amount of an insurance coverage.
- Critical Illness Insurance Critical Illness insurance is a pretty new form of insurance in Canada and pays you a benefit if you are stricken by a critical illness such as cancer or heart attack.
- The Concept of Taxation and National Insurance In general, it can be said that taxable income is the portion of an individual’s income that is the subject of taxation according to the laws that determine what is income and the taxation rate […]
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Issues The survey consisted of 20 questions and wherein they assessed the procedures in place for HIPPA compliance, the involvement of the Health Information Managers with regards to setting HIPPA policy, the incidents of confidentiality breaches […]
- Home Insurance Increase in Florida Home insurance increases in Florida, and more and more people have to sell their homes because of high insurance rates and fraudulent actions of insurers.
- Insurance in Developing Social Responsibility Though insurance is all about covering and managing risks, the contribution of the collective and obligatory social insurance systems towards developing social responsibility on every individual of a society is not only built up to […]
- Disability Insurance Plans in Canada Disability insurance is the type of insurance that provides you with financial security when you are unable to work and earn an income due to an accident or illness.
- Healthcare Insurance for Domestic Partners Healthcare benefits are just part of the benefits offered to domestic partners of employees in US companies. According to some findings, more than 13 percent of the employers in the country were offering benefits to […]
- State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company’s Finance Based on the income and expense statement, net income, the loss ratio, the expense ratio, and the combined ratio have been calculated.
- Business Insurance: Best Ways to Protect Companies This category of business insurance is tricky because there is a lack of coverage when it comes to losing information and not all insurance companies agree to take the risk. The list of possible business […]
- Car Insurance Charges and Gender and Age Factors In this regard, the majority of insurance companies prefer that drivers wait until they attain 25 years of age for them to start paying normal adult insurance rates. It is sensible for insurance companies to […]
- UniFirst and Progressive Insurance Corporation’s Technologies The use of PDA and IRV systems by both UniFirst and Progressive Insurance have enabled the businesses to expand, increase their output and customer base.
- Islamic Finance and Takaful Insurance Takaful is the Islamic version of conventional insurance. The Islamic form of insurance or Takaful discourages the levying of interest and gambling.
- Green Health Company: Dropping Insurance Products Paul, the vice president of Small Group Products, understands the risks of dropping the most popular programs in the state and notes that the losses for the business may be more significant than estimated.
- Health Insurance Provision in the USA In the first drafts of this major document, a health care reform was proposed as a way to change the insurance policies and provide people with more opportunities to get access to healthcare.
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance and Its Influence Employer-sponsored health insurance has a long history in the United States and remains the main form of individuals’ access to medical services in the country.
- Malpractice Insurance for Nurse Practitioners The author goes further to indicate that NPs should be willing to analyze the role of license insurance coverage. Studies should also be undertaken to analyze the nature of different malpractices and liabilities associated with […]
- Mandatory Health Insurance in Abu Dhabi and Dubai As a way of providing effective mandatory health insurance policies in Abu Dhabi and Dubai, the administrations should focus on the overall cost, localities of coverage by the insurance policies on the insured and the […]
- Pearl and Mutual Benefit Insurance Company’s Turnover The result is the recruitment of individuals that may not fit in the organization, leading to a high rate of turnover. It is important to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the recruitment process.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act There is also a Security Rule that is also created to guarantee the protection of crucial information and provide specific safeguards that are needed to prevent the appearance of different complications.
- Healthcare Availability and Insurance Regarding the ACA health insurance, it is defined as the lack of information available to insurers to make an appropriate decision.
- The UAE’s Healthcare System and Insurance The UAE has made incredible progress in its healthcare sector, owing to the government’s plan to establish comprehensible health initiatives and programs that target both private and public health sectors. The World Health Organization now […]
- Prospective Insurance Company: History and Information Its vision and mission is to be the best insurance organization in the world and to positively impact on the community through the provision of effective financial security planning.
- Insurance Company’s Advantage and Competencies Regarding the source of differential advantage for the new insurance company, such a source as the targeted segment may be applied to the current case.
- Driver Insurance, Its Gender and Age Factors To prove the importance of high rates of insurance for young male drivers, it is necessary to think about its benefits.
- Insurance Premiums in Relation to the Driver’s Age Drivers who are 16-19 years old are more likely to be involved in a car accident; at the same time, drivers who are 60 years old or older also pay more for their insurance compared […]
- Personal Financial Planning: Insurance Case Given the fact that the rent for the house is comparatively low, as well as the fact that there are valuable personal possessions, it will be reasonable to spend a significant number of the financial […]
- UAE vs. Saudi and Qatari Insurance Market The UAE is one of the dominant states in GCC, and its insurance conditions remain to be the most successful. The peculiar feature of insurance brokers in the GCC is their decision to capitalize on […]
- Risk, Insurance, and Third-Party Administrators The purpose of this paper is to discuss the term ‘risk’ and associated insurances, focus on the concepts of the ‘third party administrator’ and areinsurance,’ and report on the financial results of the major insurance […]
- Preventive Healthcare or Insurance Access Policy? It is possible to pay attention to some features of the current policy to find a way to effectively solve the problem of access to health insurance.
- Insurance: Purchasing Trends on Consumer Behavior These aspects have been seen to create dynamics for marketers in the insurance sector because they have continuously influenced the psychology and expectations of insurance consumers across the world.
- Unemployment Insurance Extension in the US In this way, extended UI lets them realize that they are not forgotten by the rest of society, and there is still an opportunity to find an appropriate job.
- Blafax Insurance Group’s SWOT Analysis Therefore, the customers of the company range from the US citizens to those across the globe, particularly in Europe and Asia.
- Pediatric Health Care and Insurance in the USA Despite the efforts of the U.S.government to ensure a thorough health care coverage for all children who are residents of the country, there remains a number of children who are uninsured and have no access […]
- Economics of Cyber Insurance This led to the need of protecting the Internet users standing through other means, the foremost among them being the cyber insurance policies.
- Unemployment Insurance Policy in the United States Despite some of the efforts embraced by different communities, the issue of unemployment has continued to affect the welfare of many citizens in the country.
- The Children’s Health Insurance Program in the US The Children’s Health Insurance Program is one of the current and robust healthcare policies targeting children in the United States. The main goal of the Children’s Health Insurance Program is to offer medical insurance coverage […]
- Kaiser Permanente’s Healthcare Insurance Program One possible solution to this would be to create a similar system as seen in the case of Kaiser Permanente wherein through its network of 36 medical centers and 14,000 medical professionals it does allow […]
- BP Company’s Insurance Strategy and Risk Management BP was the largest company in the UK in the 1980s and 1990s. To the extent of such potential losses, BP has to buy insurance in exchange for loss settlements should the risks occur.
- Council of Cooperative Health Insurance: Performance Management The PMS underscores the need to measure these outcomes as a vital component of evaluating the value of employees and management activities in assisting the agency to assume a proactive and client-focused approach in regulating […]
- Ethics and Issuing a Health Insurance Surcharge The primary reason for companies to refuse to issue a health insurance surcharge to employees who smoke or drink against medical advice is the fallacious argument that such employees in the work environment are conscientious […]
- Oil Drilling and Oil Services Insurance It is important to analyze the role of insurance in the development of the Oil Drilling and Oil Services industry in the United Arab Emirates and examine its basic principles in the local and international […]
- Life Insurance Policy Choice Whole life insurance is a fixed premium insurance policy which covers the lifetime of the insured, as long as the premiums are paid.
- Health Insurance in the UAE In Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the policy started in 2014 and it is expected that the majority of people living in the UAE will have obtained the health insurance by 2016.
- The World Insurance Partnership: Ethics Program The Ethics Program for the World Insurance Partnership is designed to declare the company’s core values, to promote the ethical principles and standards among the stakeholders with the focus on principles of transparency, integrity, and […]
- Constructit & E-editor Companies’ Health Insurance Changes to the Castor health insurance strategy result in the development of the Castor Enhanced Minor, which is most appropriate for the E-editor employees.
- Health Insurance Cooperatives In the United States, nonprofit health insurance cooperatives have been recommended as the third option to the tradition private health insurance and the newly suggested public health insurance.
- Takaful Insurance Company in the UAE The Malaysian Takaful operator, Syrikat Takaful Malaysia, illustrated the swift growth of the first Takaful portfolio in the country, all based on a model which served as a platform for expansion to the other countries […]
- Health Insurance Exchange: Obamacare Program The artificial raising of customers’ demand minimizes the regulation power of clients in price setting due to the fact that the level of competitiveness in the insurance market will sag significantly.
- Contract Doctrine: McLain Versus Great American Insurance
- Direct Channels Impact on Insurance Industry
- Gulf Countries’ Social Insurance
- Nationwide Auto Insurance Product – Marketing
- Consumer Behavior in Insurance Positioning
- General Organization for Social Insurance
- Strategic Plan of an Insurance Company in the UAE
- The Progressive Group of Insurance Companies – Managers
- The Issues in RACQ Insurance
- Capital Mortgage Insurance Corporation
- A Comparison of Construction Surety Bond and Insurance
- Life Insurance Ethical Issues
- Health Insurance Importance
- Job Analysis: Assistant Insurance Salvage Evaluation Manager
- Insurance in the UAE: Drivers’ Single Database
- On the Success of Tawuniya Insurance Company
- Excluding Health Insurance from Social Security Act
- Marketing Research and How Marketing Information system is Organized in Middlesex Insurance Company
- Issues Facing Medicare – Program Established to Provide Health Insurance
- Risk Management: Insurance Industry in Queensland Australia
- Quantitative Techniques of Mitsui Sumitomo and Asahi Insurance Companies
- Service Quality Gap: Oman Insurance Company
- Compensation System of State Farm Insurance
- Premiums in XYZ Health Insurance
- International Dentists Insurance Company
- Risk Management and Insurance
- Inequality in U.S Healthcare: The Americare Insurance System
- Health Insurance Schemes
- Unemployed Insurance in Social Security
- The Nature of Health Insurance in the U.S
- National Health Care System for Insurance Program in America
- Health Insurance and Mandatory Requirements
- The Basic Elements of Health Insurance
- Organizational Behavior Management at the Travelers Companies, Inc.
- Insurance for Camels (Alba’Aeer)
- Technological Insurance: Investigating Potential of South Korea for Promoting Products
- Healthcare Insurance in the United States
- The Tawuniya Health Insurance Company
- Insurance Benefits in Bahrain
- Federal versus State Regulation of Insurance Industry in United States
- To Be or not to Be an Insurance Agent: On the Peculiarities of the Liability
- Employee Benefits, Unemployment Insurance and Workers Compensation
- Insurance and Negligence
- Long-Term Care Insurance
- All You Need to Know about Long-Term Care Insurance
- How Does Insurance Benefit Today’s Life?
- How Does Geography Impact Insurance Industry in Canada?
- What Is the Biggest Issue in the Insurance Industry?
- What Are the Common Problems in Insurance Industry?
- Will Insurance Companies Survive The AI Fueled Future?
- What Are the Main Reasons of Failure of Two Insurance Policy of the Company?
- What Are the Principles of Insurance?
- What Are Types of Insurance?
- Why Do Insurance Companies Reject Claims?
- How Does Life Insurance Work?
- What Is the Challenge of Risk Related to Future in Insurance?
- Can an Insurance Company Refuse to Pay a Claim?
- How Are the IAIS Principles Met Within the Mauritian Legislation on Insurance?
- What Is Insurance in Simple Words?
- What Risks Are Impacting Insurance Industry?
- How Insurance Should Pay Alternative Therapy?
- Why Do Insurance Companies Take So Long to Pay Out?
- Can You Sue an Insurance Company for Negligence?
- How Long Does an Insurance Company Have to Investigate a Claim?
- How Social Media Could Rule Banking and Insurance?
- What Are the Causes of Risk in Insurance?
- Which Health Insurance Is Best in Germany?
- Can I Buy Health Insurance on My Own?
- How Do I Choose Health Insurance?
- How Many Types of Risk Are There in Insurance?
- How Much Does Insurance Cost in the USA?
- How Much Does the Average American Pay for Insurance?
- What Is the Effect of Health Insurance Coverage on the Use of Medical Services?
- What Is the Insurance Law Rights at Variance with Policy Provisions?
- What Is the the Doctrine of Reasonable Expectations in Insurance Law?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 28). 235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/insurance-essay-topics/
"235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 28 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/insurance-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 28 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/insurance-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/insurance-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "235 Insurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/insurance-essay-topics/.
- Health Insurance Research Topics
- Birth control Questions
- Consumer Protection Questions
- Business Structure Titles
- Contract Law Research Ideas
- Employee Benefits Paper Topics
- Disability Essay Topics
- Government Regulation Titles
- Healthcare Policy Essay Titles
- Immunization Paper Topics
- NHS Research Ideas
- Obamacare Questions
- Risk Assessment Questions
- Social Security Paper Topics
- Unemployment Essay Topics

Essay On Importance Of Insurance
In the intricate tapestry of modern society, insurance emerges as a foundational thread that weaves together protection, stability, and progress. By offering a shield against unforeseen financial losses, insurance empowers individuals and businesses to navigate a world fraught with uncertainties. This essay underscores the significance of insurance in contemporary life, elucidating its role in providing financial protection, enabling risk-taking, fostering stability, and contributing to societal advancement.
Table of Contents
Essay: The Crucial Role of Insurance in Safeguarding Individuals and Fostering Economic Growth
Insurance plays a vital role in modern society by protecting individuals and businesses from financial losses, allowing for greater risk-taking and economic development.

Paragraph 1: Insurance provides financial protection
One of the primary virtues of insurance is its ability to extend a safety net against an array of hazards. These hazards, ranging from accidents and illnesses to property damage and unfortunate deaths, carry the potential to plunge individuals and families into overwhelming financial distress. Insurance stands as a formidable bulwark against such adversities, offering a safeguard that ensures individuals do not find themselves mired in insurmountable debt or financial ruin. By distributing the costs of potential losses across a multitude of policyholders, insurance effectively diffuses the burden, thereby preventing the catastrophic impact of individual financial calamities.
Paragraph 2: Allows individuals and businesses to take more risks
The absence of insurance could cast a pall of apprehension over significant life decisions. Ventures like starting a business, embarking on extensive travels, or investing in a home may be approached with trepidation due to the looming specter of financial catastrophe in the face of unforeseen losses. Insurance, however, catalyzes a transformative shift in this narrative. With insurance coverage in place, individuals and businesses can undertake these pivotal risks with greater confidence. This newfound security empowers economic and entrepreneurial pursuits, as the protective buffer against potential losses emboldens innovation, fosters business expansion, and fuels economic growth.
Paragraph 3: Provides stability and security
The tendrils of insurance’s influence extend beyond the mere realm of finances. In the event of life-altering setbacks such as the loss of a loved one or the ravages of natural disasters, insurance plays a profound role in upholding stability and security. Insurance payouts, be it life insurance or property insurance, stand as beacons of hope amidst the darkness of loss. They offer a lifeline that ensures financial security, mitigating the burden of potential upheaval. By freeing individuals from the clutches of financial hardship that often accompany unforeseen calamities, insurance empowers them to direct their energies towards constructive pursuits like work, development, and rebuilding.
Paragraph 4: Benefits society as a whole
The impact of insurance radiates through the societal fabric, rippling outwards to engender benefits that transcend individual and business boundaries. As individuals and businesses are shielded from the dire consequences of losses, their reliance on public welfare systems diminishes. This reduction in demands on public resources ensures a more efficient allocation of government funds and resources, ultimately contributing to the overall well-being of society. Additionally, insurance’s role in bolstering risk-taking and investment cannot be understated. By offering a protective umbrella against potential failures, insurance fosters an environment conducive to innovation, business expansion, and investment. The insurance industry itself is a robust source of employment, playing an indispensable role in the economy and propelling economic growth.
In a world where uncertainties cast their shadows across every facet of life, insurance stands as a beacon of security, prosperity, and progress. By providing a shield against financial losses, insurance not only enables individuals and businesses to take calculated risks but also contributes to the stability and growth of societies at large. Its role in alleviating fears of potential financial ruin and its capacity to stimulate economic dynamism make insurance a cornerstone of modern society. As individuals and businesses are empowered to stride forward with confidence, unburdened by the specter of unforeseen losses, the collective trajectory of progress is illuminated, forging a path towards a more secure, stable, and prosperous future for all.
Write Four Importance of Insurance – Safeguarding You and Your Future
Insurance might seem like a simple thing, but it’s actually super important. Here are four reasons why:
1. Protection from Unexpected Problems:
Life is full of surprises, and not all of them are good. Insurance is like a shield that protects you from getting hurt financially when bad things happen. It covers stuff like accidents, illnesses, and even damage to your things, like your car or house. So, if something goes wrong, you won’t have to pay all the money to fix it.
2. Feeling Secure and Stress-free:
Imagine if you had to worry all the time about what could go wrong. Insurance takes away that worry. It gives you a safety net, so if something bad does happen, you won’t have to panic about money. This lets you focus on the things that matter, like your family, your studies, and your dreams.
3. Helping You Take Risks:
Sometimes, you need to take risks to move forward in life. Insurance gives you the courage to take those risks. For example, if you want to start a business, insurance can cover you if things don’t go as planned. This way, you’re more likely to chase your dreams without being scared of failing.
4. Building a Better Future:
When many people have insurance, it creates a big pool of money that can be used to help anyone who needs it. This is super useful when something really big, like a natural disaster, happens. Insurance helps communities rebuild and get back on their feet faster. Plus, having insurance makes you part of a system that takes care of people and helps the economy grow.
So, even though insurance might seem like just another thing you have to pay for, it’s actually a super smart move. It’s like having a superhero cape that keeps you safe from money troubles and lets you take on life’s adventures without fear.
What Is Importance Of Insurance to Society
The Big Deal About Insurance for Everyone
Imagine if you had a magic shield that could protect you from money troubles when something bad happens. That’s what insurance is like for the whole society. Here’s why it’s a big deal:
1. Safety Net for Tough Times:
Insurance is like a safety net that catches you if you fall into a tough situation. When things like accidents, illnesses, or disasters strike, insurance helps to pay for the damages. This means people don’t have to lose all their money or belongings when something unexpected happens.
2. Helping Everyone Stay Cool:
Without insurance, people would always be worried about what could go wrong. But with insurance, everyone feels safer. You don’t have to stress out about money problems all the time. This lets everyone focus on their families, work, and living their lives.
3. Making Brave Choices:
Life is about taking chances, but some risks can be scary. Insurance gives people the courage to take these risks. For example, starting a business or trying something new. If things don’t go as planned, insurance can help with the costs. So, everyone can try exciting things without being too afraid of failing.
4. Rebuilding Together
When something really big, like a big storm, hits a community, it can be hard to recover. But insurance makes this easier. When many people have insurance, there’s a lot of money to help rebuild homes, businesses, and communities. This way, everyone can get back on their feet faster.
5. Growing a Strong Society:
Insurance is like teamwork for the whole society. When everyone chips in, there’s a pool of money that can be used to help anyone who needs it. This helps the economy grow and makes sure that everyone is taken care of when they need it most.
So, insurance isn’t just something for rich people or big companies. It’s a way for everyone to work together and protect each other. It’s like having a giant umbrella that keeps us dry when it rains unexpected troubles.
Essay On Importance of Life Insurance
Introduction.
Life insurance is a fundamental financial tool that provides security and stability for individuals and their families. This essay examines the significance of life insurance, exploring its benefits, the peace of mind it offers, the various types available, its role in estate planning, its contribution to long-term savings, and the factors that impact premium costs.
Benefits of Life Insurance
Life insurance serves as a safety net, ensuring that loved ones are financially protected in case of the policyholder’s demise. It guarantees that beneficiaries receive a lump sum payout, which can cover immediate expenses, replace lost income, and uphold the family’s quality of life. Families with young children find life insurance particularly valuable as it can provide for education and future needs, easing the financial burden during challenging times. Moreover, life insurance shields individuals from the strain of financial obligations, including mortgages and loans, ensuring that the family does not inherit these burdens.
Emotional Comfort
Life insurance brings more than just money – it brings peace of mind. When people have life insurance, they feel better knowing that their family will have financial help if something happens to them. This makes them less worried about what might happen in the future. Feeling less worried helps them live their current lives fully, without always thinking about what would happen to their family if they weren’t there anymore.
Different Kinds of Life Insurance
Life insurance comes in different flavors to match different needs. Some are like short-term helpers – they cover you for a certain time. Others, like lifelong guardians, protect you forever and also gather extra money over the years. There’s another type, too, called universal life insurance. This one mixes coverage with a way to save money, letting you build up a little fund. With all these choices, people can pick the one that fits their money goals and situation the best.
Role in Estate Planning
Life insurance plays a pivotal role in estate planning by ensuring a seamless transfer of wealth to beneficiaries. This proactive approach minimizes potential conflicts and legal complexities that can arise during inheritance. Additionally, life insurance payouts are generally exempt from inheritance taxes, making it an efficient strategy for passing on assets to the next generation with reduced tax implications.
Growing Your Money for the Future
Life insurance isn’t just about keeping you safe – it also helps you save and invest for a long time. With whole life and universal life policies, your money grows over the years. You can take out or borrow some of this money if you need it. This extra money can be a helpful backup during your retirement or unexpected situations, giving you more financial security on top of the money your loved ones get when you’re no longer here.
Factors Affecting Premiums
The cost of life insurance premiums is influenced by various factors. These include the policyholder’s age, health status, and lifestyle choices. Generally, younger and healthier individuals qualify for lower premiums. The coverage amount and the chosen policy type also impact costs. It is crucial for individuals to consider these factors while selecting a policy that suits their needs and financial capacity.
In conclusion, life insurance is an indispensable element of a comprehensive financial strategy. Its benefits encompass financial security for family members, coverage of debts, and peace of mind for policyholders. With a variety of policy types available, life insurance contributes to estate planning and long-term financial well-being. By understanding the factors that influence premium costs and making informed decisions, individuals can secure their family’s future and embrace life with enhanced confidence.
What Are The 5 Importnace Of Life Insurance – Exploring Its Role & Value
Life insurance might seem like a grown-up thing, but it’s actually important for everyone to know about. Here are five reasons why life insurance is a big deal:
1. Taking Care of Loved Ones:
Life insurance is like a promise you make to take care of your family even when you’re not around. If something happens to you, the insurance money can help your family with things like bills, school, and even just everyday needs. It’s a way to show that you’ll always look out for them.
2. Planning for the Unknown:
Life can be unpredictable. No one knows what tomorrow might bring. Life insurance helps you plan for the unknown. If something unexpected happens to you, your loved ones won’t have to struggle financially. It’s like having a safety net that catches you if you fall.
3. Covering Big Expenses:
Funerals and medical bills can be really expensive. Life insurance can help cover these big costs so that your family doesn’t have to worry about finding a lot of money quickly. It’s a way to ease their burden during a difficult time.
4. Passing On a Meaningful Gift:
Life insurance goes beyond finances; it’s a way to leave behind a meaningful legacy for your dear ones. By designating beneficiaries, you ensure that the insurance payout becomes a gift that keeps on giving. This support can empower your family to pursue their aspirations, educational goals, and future endeavors.
5. Peace of Mind:
Knowing that you have life insurance brings peace of mind. It’s like having a backup plan that ensures your family will be okay no matter what. This sense of security allows you to focus on living your life to the fullest without constantly worrying about the future.
In a nutshell, life insurance is a way to show that you care for your family even when you’re not there. It’s a tool that offers financial support, security, and a way to leave a positive impact on your loved ones. So, even though it might seem like something for adults, understanding the importance of life insurance is a wise step for everyone.
Argumentative Essay About Life Insurance
Life insurance, a contract between an individual and an insurance company, is a topic of paramount importance in personal finance discussions. It’s a widely debated issue with proponents asserting its crucial role in financial security, while skeptics question its necessity. This essay will argue that life insurance, despite its potential drawbacks, plays an indispensable role in securing one’s financial future.

The Positive Aspects of Life Insurance
Life insurance serves as a safety net, offering financial protection to beneficiaries during an emotionally challenging time. It replaces income, allowing families to maintain their standard of living even in the face of tragic life events. Furthermore, it can assist in mitigating debts and financial obligations, preventing families from inheriting burdensome liabilities. For estate planning, life insurance can minimize tax liabilities, preserving the value of the estate for the beneficiaries. Additionally, for entrepreneurs, a life insurance policy can ensure business continuity, covering losses and facilitating a seamless transition in the event of the owner’s demise.
Debate against life insurance
However, critics argue that life insurance isn’t always necessary, particularly for individuals without dependents. They contend that the premiums could be better invested elsewhere, yielding higher returns over time. Additionally, they point out that insurance companies often incorporate exclusions and complex terms, potentially resulting in denied claims. Critics thus advocate for careful consideration, only opting for life insurance when circumstances truly demand it.
Counterarguments and Challenges
However, it’s important to acknowledge the counterarguments. Critics argue that the cost of premiums may not justify the perceived benefits, especially for those with no dependents. The decision-making process can also be complex, with individuals grappling to choose the ideal policy that suits their needs. Furthermore, not everyone may need life insurance, particularly those with sufficient wealth or those without financial dependents.
Balancing the Scales
Despite these challenges, by assessing their unique circumstances, individuals can determine the necessity and extent of life insurance required. Consulting with financial advisors and incorporating life insurance into broader financial planning can lead to responsible decision-making.
In conclusion, while life insurance may not be a one-size-fits-all solution, it does serve as a crucial tool in securing the financial future of loved ones. It is a cornerstone of responsible financial planning and should be considered seriously depending on individual circumstances.

Hello! Welcome to my Blog StudyParagraphs.co. My name is Angelina. I am a college professor. I love reading writing for kids students. This blog is full with valuable knowledge for all class students. Thank you for reading my articles.
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Life Insurance Essay Examples
Many students are faced with the problem of finding ideas for writing their essays. This website contains a database with more than 50 000 essay examples, using which you can easily find inspiration for creating your own essay on Life Insurance.
Here you will find many different essay topics on Life Insurance. You will be able to confidently write your own paper on the influence of Life Insurance on various aspects of life, reflect on the importance of Life Insurance, and much more. Keep on reading!
Executive Summary India is one of the world’s fastest growing economies, with real GDP rising to 9. 4 per cent in 2006-07 as against 9. 0 per cent in 2005-06. India’s share in world GDP thus has increased to 6. 3 per cent in 2006 measured in terms of purchasing power parity. Growth in per […]
Firstly, life insurance industry can alp ensure the normal people’s life. Second, life insurance collects idle capital in society and increases financial revenues. Third, life insurance industry fixed overall unemployment and underemployment problems. In developed countries such as America, there are approximately 200 million insurance officers-?more than 1 percent of the population. Even in China, […]
Jegrins Insurance Company, one of the largest insurance companies, consists of six specialized companies in life insurance, belongings insurance, insurance exchange, and direction. It also provides casualty and belongings insurance policies. To maintain a competitive advantage and ensure growth, Jegrins must meet the needs of its policy holders like other insurance companies. The company has […]
1. 1 Introduction:Health and wellness attention demand to be distinguished from each other for no better ground than that the former is frequently falsely seen as a direct map of the latter. Heath is clearly non the mere absence of disease. Good Health confers on a individual or groups freedom from illness – and the […]
To analyze Aflac, you have the option to either visit their website (www.aflac.com) or access it directly. Information can also be obtained from Hoovers through the library’s electronic databases using a password. Additionally, it is recommended to refer to articles published in the Wall Street Journal within the last 30 days, which are available online.
The value of life varies depending on the cultural context. In the western world, life is often not valued based on what individuals have learned, taught or the wisdom they have shared. Instead, it is measured by one’s financial success and personal net worth. In contrast, other societies place a higher value on life based […]
The concept of insurable interest and the alleged need under Scots law for the requirement of insurable interest by the insured in an insurance policy, have recently come under scrutiny. Why is this, and what should be done about the problems arising from the requirement for insurable interest? How realistic are the proposals for reform? […]
Executive Summary The global economies are all facing a difficult period. Despite the financial crisis, insurers have successfully weathered it and played a vital role in safeguarding individuals and businesses. They have also restored confidence and promoted economic growth. This is especially significant in India, where insurers face difficulties in establishing investor trust. Presently, all […]
The Indian Insurance Industry is comprised of public and private insurance companies. Until 2000, only public sector insurance companies were permitted to operate in India. However, after 2000, the insurance sector was opened up to private insurance companies as well. During my project with Max New York Life Insurance, I initially analyzed their products and […]
The insurance sector in India has experienced significant changes over time. It began with the establishment of the Oriental Life Insurance Company in Kolkata in 1818. As history progressed, it shifted from an open competitive market to nationalization and eventually returned to a liberalized market once again. Key milestones include the enforcement of the Indian […]
Aflac was originally named American household life insurance company of Columbus, Georgia in 1955. It was put together by three brothers John, Paul, and Bill Amos. The company was established as they provided premier guaranteed renewable insurance in the United States and Japan. Aflac has been able to turn their concern while spread outing their […]
Popular Questions About Life Insurance
Haven't found what you were looking for, search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards.
- Enter your topic/question
- Receive an explanation
- Ask one question at a time
- Enter a specific assignment topic
- Aim at least 500 characters
- a topic sentence that states the main or controlling idea
- supporting sentences to explain and develop the point you’re making
- evidence from your reading or an example from the subject area that supports your point
- analysis of the implication/significance/impact of the evidence finished off with a critical conclusion you have drawn from the evidence.
Home — Essay Samples — Government & Politics — Public Services — Insurance
Essays on Insurance
The importance of writing an essay on insurance.
Writing an essay on insurance is important for several reasons. Firstly, insurance is a crucial aspect of modern life, as it provides individuals and businesses with financial protection against unforeseen events. Understanding the concept of insurance and its various types is essential for anyone who wants to make informed decisions about their financial well-being. Additionally, writing an essay on insurance allows individuals to delve deeper into the topic, gaining a better understanding of its complexities and implications.
When writing an essay on insurance, it is important to consider the following tips:
- Research: Start by conducting thorough research on the topic. This may include studying the history of insurance, its different types, and how it works.
- Structure: Organize your essay into clear and logical sections, such as , body, and . Each section should address a specific aspect of insurance.
- Clarity: Use clear and concise language to explain complex insurance concepts. Avoid using jargon or technical terms without proper explanation.
- Evidence: Support your arguments with evidence, such as statistics, case studies, or expert opinions. This will add credibility to your essay.
- Critical Thinking: Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of insurance, and consider the ethical and social implications of its use.
- Revision: Finally, revise and edit your essay to ensure it is well-structured, coherent, and free of errors.
Writing an essay on insurance is important for gaining a deeper understanding of this vital aspect of modern life. By following the aforementioned tips, individuals can produce well-researched and insightful essays that contribute to the broader conversation about insurance and its role in society.
The Importance of Health Insurance in Today's Society
The Role of Insurance in Risk Management
The Impact of Insurance on Economic Stability
The Evolution of Insurance Industry
The Role of Insurance in Disaster Preparedness and Recovery
The Impact of Digital Transformation on Insurance Industry
The Role of Insurance in Climate Change Adaptation
The Ethics of Insurance Industry
The Future of Insurance Industry in the Age of AI and Automation
The Role of Insurance in Promoting Financial Inclusion
Insurance is a multifaceted industry that plays a critical role in modern society, providing financial protection, risk management, and economic stability. These essay topics cover a wide range of issues and trends in the insurance industry, offering valuable insights into its importance and impact on individuals, businesses, and the broader economy.
Overview of The Insurance Policy of The Companies
General insurance of commercial liability, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Review of The Case of The Company Insurance Risks
Using universal basic income and unemployment insurance to help citizens cope with unemployment, health insurance politics in the usa, life insurance demand, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Pros and Cons of Life Insurance
Credit insurance - an art and science of managing cash flow, the public liability insurance act, a look at the countries suitable for bfsi: banking, financial services, and insurance, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Compensation in Case of Animal Attack
Insurance an attractive mode of investment, significant advantages of purchasing an insurance plan, north carolina car insurance for teenagers , features of firm with life insurance, life insurance is key to development of any economy, relevant topics.
- Transportation
- Fire Safety
- Health Insurance
- Affordable Housing
- Traffic Congestion
- Amusement Park
- Public Transport
- Electoral College
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essay on Insurance: Top 6 Essays | Insurance Management
After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Insurance 2. Fundamental Principles or Features of an Insurance Contract 3. Types 4. Double Insurance 5. Re-Insurance 6. Advantages/Utilities/Importance.
Essay on Insurance
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Advantages/Utilities/Importance of Insurance
Essay # 1. Meaning of Insurance:
Risk and uncertainty are incidental to life. These risks and uncertainties are increasing day by day due to increase in fastness of life. Man may meet an untimely death. He may suffer from accident, destruction of property from fire, sea, floods, earthquakes and many other causes. Whenever there is uncertainty, there is risk as well as insecurity.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is to provide against risk and insecurity that insurance came into being. The main principle underlying insurance is the pooling of risks. It is a co-operative device to spread the loss caused by a risk (which is covered by insurance) over a large number of persons who are also exposed to the same risk and insure themselves against that risk.
According to W.A. Dinsale, “Insurance is a device for the transfer of risks of individual entities to an insurer, who agrees, for a consideration (called the premium), to assume, to a specified extent, losses suffered by the insured.
According the Mehr and Cammack, “Insurance is a social device for reducing risk by combining a sufficient number of exposure units to make their individual losses collectively predictable. The predictable loss is then shared proportionately by all those in the combination.”
According to D.S. Hansell. “Insurance is a social device providing financial compensation for the effects of misfortune, the payments being made from the accumulated contributions of all parties participating in the scheme.”
According to Schultz and Bradwill, “Insurance in its technical sense is a social device which employs the use of pooling technique to eliminate uncertainty,”
According to Justice Tindal, “Insurance is a contact in which a sum of money is paid by the assured in consideration of insurers incurring the risk of paying a large sum upon a given contingency.”
The agency which helps in entering into this arrangement is called Insurer or insurance company. The person who gets his life/property insured is called Insured/Assured. The agreement or contract, which is put in writing, is called Policy. The thing on property insured is called the subject-matter of insurance and the interest of the assured in the subject-matter is called his insurable interest.
To conclude, a contract of insurance is a contract by which a person, in consideration of a sum of money, undertakes to make good the loss of another against a specified risk, e.g., fire, or to compensate him or his estate on the happening of a specified event, e.g.. accident or death.
Essay # 2. Fundamental Principles or Features of an Insurance Contract:
Insurance contract is based on certain fundamental principles.
These principles are:
(i) Essentials of a Valid Contract:
The contract of insurance must have all the essentials of a valid contract.
According to Indian Contract Act, 1872, a valid contract must possess the following essentials:
(t) Offer and acceptance
(ii) Capacity to contract
(iii) Free consent of parties
(iv) Lawful consideration and object
(v) Contracts not specifically declared void.
(ii) Utmost Good Faith:
The contract in insurance is uberrima fides, e.g., both the parties must disclose all material facts. Concealment of any fact will entitle the insurer to deprive the assured of benefits of the contract.
Each party mush reveal to other party all information which would influence the other’s decision to enter into the contract. Although a party must not make any false statement, he is not bound to disclose to the other party all that he knows or ought to know about the transaction.
But there are certain cases where the knowledge of facts is almost exclusively on one side. In such cases, the contract is vitiated by non-disclosure of any material fact or a misstatement. Such contracts are known as contracts of uberrima fides or contracts based on ‘utmost good faith’.
The rule of caveat empter, i.e., let the buyer beware, does not apply to the contracts of insurance.
The assured knows more about the subject-matter of the contract than the other party (the insurer). Consequently he is under a duty to disclose correctly all material facts known to him to the insurer, so that insurer may be in a position to make an accurate estimate of the risk that he is undertaking.
It is not easy to define material fact. It depends upon the circumstances of each case. A material fact is one which goes to the root of contract of insurance, and which must be stated with perfect degree of accuracy. If the utmost good faith is not observed by either party the contract may be avoided by the other.
A proposer should disclose all material facts at the time of making the proposal not only those facts which he honestly thinks to be material but every fact which a reasonable man would have thought to be material.
(iii) Insurable Interest:
The assured must have an actual interest called the insurable interest in the subject-matter of the insurance. A person is said to have an insurable interest in the subject-matter (property or life) if he is benefitted by its existence and is prejudiced by its destruction. Without insurable interest the contract of insurance is void. It is the existence of insurable interest in a insurance contract that differentiates it from a wagering contract.
A banker has an insurable interest in the property mortgaged to it against a loan. A person has insurable interest in his own life. A creditor can insure the life of his debtor. A person has insurable interest in the building he owns.
An employer can insure the lives of his employees because of his pecuniary interest in them. A businessman has insurable interest in his stock, plant and machinery, building, etc. Husband has interest in the life of his wife and wife in the life of her husband.
Is it necessary in all forms of insurance?
Insurable interest is necessary to support every insurance contract. In case of Life Insurance, insurable interest must be present at the time when the insurance is effected. It is not necessary that the assured should have insurable interest at the time of maturity also.
In case of Fire Insurance, insurable interest must be present both at the time of insurance and at the time of loss. In case of Marine Insurance, insurable interest must be present at the time of loss. It may or may not present at the time of insurance.
(iv) Indemnity:
A contract of insurance is a contract of indemnity. The principle of indemnity is applicable to all types of insurance except life, personal accident and sickness insurance. That means that the assured in the case of loss against which the policy has been made shall be fully compensated and never more than the value of the policy. The insurer agrees to make good the loss but the insured, however, is not entitled to make a profit out of the loss.
A contract of insurance does not remain a contract of indemnity if a fixed amount is to be paid by the insurer to the insured on the happening of the event insured against, whether he suffers a loss or not. A contract of life insurance is not a contract of indemnity. In life insurance, the insurer is liable to pay the sum mentioned in the policy upon the happening of the contingency (death, or expiry of a certain period).
(v) Mitigation of Loss:
The next essential principle of insurance is that in the event of some mishap to the insured property, the assured must take all necessary steps to mitigate the loss. The insurer must act in a prudent manner as if he were in-insured.
However, he should do his best: yet in case of his own death he is not required to do so. If he does not do so the insurer can avoid the payment of loss attributable to his negligence. In nutshell, he is bound to do his best under the circumstances, but he is not bound to do at the risk of his life.
(vi) Risk Must Attach:
A contract of insurance is enforceable if and only if the risk has been attached. If the risk is not run the consideration fails, and therefore the premium received by the insurer must be returned The premium is to be returned even where the risk is not run or could not be run due to the fault, will or pleasure of the assured.
A policy is not attached till the risk begins and is not attached after the risk is determined one way or the other, except in those special insurance where both the parties being ignorant of the position of the thing insured, contract to insure it lost or not lost.
(vii) Contribution:
Sometimes a property is insured with more than one company. Where there are two or more insurances on one risk, the principle of contribution applies between insurers. The objective of contribution is to distribute the actual amount of loss among different insurers who are liable for the same risk.
In case of loss, any one insurer may make the payment to the assured the full amount of loss covered by the policy. After paying this amount, he is allowed to claim a contribution from his co-insurers in proportion to the amount which each has undertaken to pay in case of loss.
The principle of contribution is applied to any insurance which is a contract to indemnity. It does not apply to life and personal accident insurance.
(viii) Subrogation:
The principle (or doctrine) of subrogation is a corollary to the principle of indemnity and applies only to fire and marine insurances. It does not apply to life and personal accident insurances. If the insured party gets a compensation for the loss suffered by him, he cannot claim the same amount of loss from any other party.
Subrogation is a substitution of one person in place of another in relation to the claim, its rights, remedies or securities. Whenever, an assured has received full indemnity in respect of his loss, the insurer is subrogated to only the rights and remedies available to the assured in respect of the thing to which the contract of insurance relates. The insurer’s right to subrogation arises only when he pays the loss for which he is liable under the policy.
(ix) Causa Proxima or Proximate Cause:
The insurer can recover the loss only if it is proximately caused by any of the perils insured against. This is known as the principle of Causa Proxima. “Every loss that clearly and proximately results whether directly or indirectly from the event insured against is within the policy.”
The rule of proximate cause runs as Causa Proxima Non-Remote Spectator, i.e., the proximate and not the remote cause is to be looked to, and if the proximate cause of the loss is a peril insured against, the assured can recover the amount of the loss from the insurer.
The question, which is the causa proxima of a loss, can only arise where there are a succession of causes. When a result has been brought about by two or more causes, you must, in insurance law, look to the nearest cause, although the result would, no doubt, not have happened without the remote cause.
Proximate does not mean the nearest in time. The cause which is truly proximate is that which is proximate in efficiency. If the loss is the result of such an efficient cause, it will be regarded as having been caused by the proximate cause.
Section 55 of the Marine Insurance Act, 1963 lays down that unless the policy otherwise provides, the insurer is liable for any loss proximately caused by a peril insured against.
Essay # 3. Types of Insurance:
There are a number of types of insurance, but the following types stand out as being of special importance:
(i) Life insurance
(ii) Fire insurance
(iii) Marine insurance
(i) Life Insurance:
In life insurance contract the amount of the policy is definitely paid, it is a question of time only. The amount becomes payable on the death of the assured or on the expiry of a certain fixed period, whichever is earlier. Life insurance contract is not a contract of indemnity.
Life insurance is a contract by which the insurer, in consideration of a premium, undertakes to pay a certain sum of money on the death of a person whose life is insured, or on the expiry of a certain period, whichever is earlier. Life insurance contract is not a contract of indemnity. The loss of life cannot be compensated and only a specified sum of money is paid.
Fundamental Principles/Features/Essentials of Life Insurance Contract :
Life insurance contract is based on certain fundamental principles.
1. Essentials of a Valid Contract:
The life insurance contract must have all the essentials of a valid contract.
According to Indian Contract Act, 1872, a valid contract must contain the following essentials:
(i) Offer and acceptance.
(ii) Capacity to contract.
(iii) Free consent of parties.
(iv) Lawful consideration of object.
2. Utmost Good Faith:
The contract of life insurance is a contract of utmost good faith. The insured should be honest and truthful in giving information to the insurance company. He knows more about the subject-matter of the contract than the other party (the insurer).
Consequently, he is under a duty to disclose accurately all material facts known to him to the insurer. Concealment of any fact will entitle the insurer to deprive the assured of the benefit of the contract.
3. Insurable Interest:
In life insurance, the insured must have insurable interest in the life assured. Without insurable interest the contract of insurance is void. In case of life insurance, insurable interest must be present at the time when the insurance is Affected. It is not necessary that the assured should have insurable interest at the time of maturity also.
In the following three cases insurable interest is presumed and no proof is necessary, viz.:
(i) Own life
(ii) Husband in the life of wife, and
(iii) Wife in the life of husband.
The following persons have been held to have insurable interest:
(i) A person is presumed to have an interest in his own life and every part of it.
(ii) A creditor has an insurable interest in the life of his debtor,
(iii) A proprietor of a drama company has an insurable interest in the lives of actresses.
(iv) A servant engaged for a term of years has insurable interest in the life of his employer.
4. Contract of Indemnity:
A contract of life insurance is not a contract of indemnity. The loss of life cannot be compensated and only a specified sum of money is paid. That is why the amount payable in life insurance on the happening of the even is fixed in advance. Once the ‘sum of money’ payable is fixed, it is constant invariable. A contract of insurance, therefore, is not a contract of indemnity.
The loss resulting from the death of life assured cannot be estimated in terms of money and only a fixed amount is paid.
How to Effect Life Insurance (I.E., Procedure)?
A number of steps are taken to effect life insurance policy.
These steps are:
a. Proposal:
Before taking a life insurance policy, it is important to take proposal for which is available free from the office of Life Insurance Corporation. Agents also supply this form. The form contains a number of questions about the health of the person, family background, and the mode of paying premium.
As we know that the contract of insurance is based on utmost good faith. So the proposer must answer all the questions correctly. He should not conceal any factual information. Concealment of any fact will entitle the insurer to deprive the assured of the benefits of the contract.
b. Medical Examination:
After the proposal form has been submitted, a medical examination of the person to be insured is arranged. Such examination can be conducted only by a doctor approved by the insurance company. The medical report of the applicant is directly forwarded by the doctor to the office of the company.
c. Acceptance of Proposal:
The proposal form is sent to the company along with medical report and the comments of the insurance agents. The proposal form is scrutinised by the company and if the company is satisfied, the proposal is accepted.
d. Proof of Age:
The applicant has to furnish satisfactory proof of his age to the insurance company.
The proof of the age can be furnished through any one of the following:
(i) A certificate from the Municipal Birth Register
(ii) A certificate of High School
(iii) The horoscope of the assured
(iv) Service Book
(v) Certificate relating to the Baptism ceremony among Christians.
e. Premium:
When the proposal is accepted, it is intimated to the applicant and he is asked to make the payment of premium. On the payment of premium the policy comes into operation and the risk is covered then onwards.
f. Insurance Policy:
After receiving the installment of first premium, the insurance company prepares the insurance policy. The policy is in the form of an agreement between the insurance company and the assured to pay a certain sum of money to the assured on the happening of the event mentioned in the policy.
It bears the signatures of the officials of the insurance company. When the policy is ready, it is sent to the assured by registered post. It contains the assureds’ name, address, occupation, age, amount of insurance, number of installments, amount and date of premium, etc.
Different Kinds of Life Insurance Policies:
The life insurance policies are of the following types:
1. Whole Life Policy:
Under this policy, premium is payable throughout the life time of the life assured. The sum assured becomes payable only on the death of the insured. These policies are taken out to make provision for the dependants. This policy is also called ‘Ordinary Life Policy’.
2. Endowment Policy:
This is most popular form of life insurance. This policy is taken up for a specific period known as ‘endowment period’. The sum assured is payable either on the death of life assured or on the expiry of a fixed period, whichever is earlier. If the person does not die upto the maturity of the policy, he shall get back the insured amount after the maturity of the policy.
3. Joint Life Policy:
This policy implies to husband and wife or the partners of a business. They can have a joint policy. It is like Endowment Policy. The sum assured under a Joint Life Policy (on two or more lives) is payable at the end of the endowment term or on the first death of any one the lives assured, whichever is earlier. Such policies are usually taken by partnership firms to provide for the payment of the capital of the deceased partner.
4. With or Without Profit Policy:
Life insurance policy may be ‘with profit’ or ‘without profit’. The assured is entitled to the share in the profits of the insurer if the policy is a ‘with profit’ policy. Contrary to this, in case of ‘without profit’ policies, such a question does not arise.
5. Annuity Policy:
Under annuity policy, the amount is payable by the insurer not in lump sum but by monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annual installments which are paid either until death or for a specified number of years. This policy is very useful to those persons who desire to provide a regular income for themselves and their dependants after the expiry of a specified period.
6. Sinking Fund Policy:
These policies are mostly taken by firms and companies to accumulate funds to pay off a liability or for making a provision for the replacement of an asset after a period of time.
7. Convertible Whole Life Policy:
This policy is issued as a whole life policy with a provision to convert it into an Endowment Policy after the expiry of a specified period (say 5 years). If this option is not exercised, the policy continues as a whole life policy with premiums ceasing at a certain age.
8. Group Insurance Policy:
This policy may be taken out for the protection of lives of all employees in a business concern. One policy is issued to the employer with individual certificates indicating the amount of insurance protection of each employee. Dependants of the employees are entitled to the benefits of these insurances.
(ii) Fire Insurance:
Fire insurance covers losses caused by fire. A fire insurance is an agreement between the two parties, i.e., insurer and insured, whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the loss suffered by the insured in consideration for his (insured) paying of certain sum called premium. Fire Insurance is a contract of indemnity. This contract does not help in controlling or preventing fire but it is a promise to compensate the loss.
A contract of fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of the premium paid, undertakes to make good any loss or damage caused by fire during a specified period. Normally, the fire insurance policy is for a period of one year after which it is to be renewed from time to time.
A claim for loss by fire must satisfy the following two conditions:
(i) There must be actual loss; and
(ii) Fire must be accidental and non-intentional.
The risk covered by a fire insurance contract is the loss resulting from fire or some cause which is the proximate cause of the loss. If damage is caused by overheating without ignition, it will not be regarded as a fire loss within the meaning of fire insurance contract and the loss will not be recoverable from the insurer.
Fundamental Principles/Essentials/Features/Characteristics of Fire Insurance Contract:
Fire insurance contract is based on certain fundamental principles.
a. Insurable Interest:
In fire insurance, the assured must have insurable interest in the subject-matter of the insurance. Without insurable interest the contract of insurance is void. In case of fire insurance, insurable interest must be present both at the time of insurance and at the time of loss. In case of goods, insurable interest arises on account of (i) ownership, (ii) possession, and (iii) contract.
The following persons have insurable interest in the subject-matter of insurance in case of a fire policy:
(i) A person has insurable interest in the property he owns.
(ii) A businessman has insurable interest in his stock, plant and machinery and building.
(iii) Agent has an insurable interest in the property of his principal.
(iv) Partner has insurable interest in the property of partnership firm.
(v) Mortgagee has insurable interest in the property which is mortgaged.
b. Utmost Good Faith:
The contract of fire insurance is a contract of utmost good faith. The insured should be truthful and honest in giving information to the insurance company. Insured knows more about the subject-matter of the insurance.
He is under a duty to disclose accurately all factual information known to him. The insurance should also disclose the facts of the policy to the proposer. So utmost good faith on the part of both the parties is a must.
c. Indemnity:
The contract of fire insurance is a contract of indemnity. The assured can, in the event of loss, recover the actual amount of loss from the insurer. This is subject to the maximum amount for which the subject-matter is insured. The value of the policy undertaken is fixed at the time of contract. The actual amount of loss suffered is compensated and the value of policy is only the maximum limit.
If a person has insured his house for Rs. 40,000 the insurer is not necessarily liable to pay that amount, although the house may have been totally destroyed by fire; but he will pay the actual loss within the maximum limit of Rs. 40,000.
Kinds of Fire Insurance Policies:
The fire insurance policies are of the following kinds:
i. Valued Policy:
It is a policy in which the amount payable in case of loss is fixed at the time when the policy is taken. In the event of loss, the fixed amount is payable irrespective of the actual amount of loss. Valued policy is not a contract of indemnity. It can be legally challenged.
ii. Specific Policy:
The specific policy provides for the payment of a specific sum in respect of loss to the property and does not penalise under-insurance. This policy is also known as ‘Average Policy’ because the insurer usually inserts the average clause in the policy.
iii. Floating Policy:
The floating policy covers several lots of goods lying at different places under one insurance cover. It is always subject to average clause.
iv. Comprehensive Policy:
It covers the risks of the fire arising out of any cause that is civil, communication, riots, thefts, labour disturbances and strikes, etc.
v. Consequential Loss Policy:
In certain cases fire can’ cause the loss of business of the insured. Such persons to cover the risk of business due to fire, undertake the consequential loss policy.
vi. Re-installment or Replacement Policy:
In such a policy, the insurer has the right to reinstate or replace the property destroyed instead of paying cash. The modes of discharge by the insurer are alternative. If the insurer selects one, he cannot afterwards change to the other. If the insurer offers to pay, he cannot afterwards claim to re-instate and vice versa.
vii. Sprinkler Leakage Policy:
This policy covers the loss arising out of water leakage from sprinkles which are set up to extinguish fire.
viii. Average Policy:
In this policy, the average clause is inserted which means the insured will have to bear proportionate loss with the insurer in case where policy is taken for a certain amount greater than the value of the property.
The formula for calculating average amount of claim is given below:
Amount of Claim or Average Loss = Insured Amount x Actual Loss/Actual Value of Property
ix. A Blanket Policy:
It is issued to cover all the fixed and current assets of an enterprise by one insurance.
x. Declaration Policy:
Under this policy, trader takes out a policy for the maximum value of stock which he may expect to hold during the year.
(iii) Marine Insurance:
It is one of the oldest forms of insurance. It covers all marine losses, that is to say, the losses incidental to marine adventure. Marine insurance may be called a contract whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in a manner and to the extent thereby agreed upon against marine losses.
A contract of marine insurance is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed, against marine losses. Marine insurance is an arrangement by which the insurer undertakes to compensate the owner of a ship or cargo for complete or partial loss at sea.
The contract of marine insurance is a contract of indemnity. The assured can. on the happening of the event, recover the actual amount of loss, subject to the maximum amount for which the subject-matter has been insured.
Subject-Matter of Marine Insurance:
The following three things are covered in the subject-matter of marine insurance:
1. Cargo Insurance:
The goods to be sent through ship is called ‘Cargo’. For the safety of goods, insurance policy is taken. The goods are generally insured according to their value but some percentage of profit can also be included in the value. At the happening of the event insurance company is liable to pay both value of the goods plus profit percentage. The rate of premium depends upon the nature of goods, packing, etc.
2. Hull Insurance:
When the ship is insured against any type of danger, it is called ‘Hull Insurance’. The ship may be insured for a particular period or for a particular trip.
3. Freight Insurance:
The freight may be paid in advance or on the arrival of goods. The shipping company will not be entitled to get freight, if the goods are lost in transit. The shipping company may insure the freight to be received which is called ‘Freight Insurance’.
Marine Insurance Contract :
Marine insurance is an agreement by which the insurer undertakes to compensate the owner of a ship or cargo for complete or partial loss at sea.
In other words, under marine insurance, the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed against marine losses.
Among the subject-matter of marine insurance are included:
(ii) Cargo, and
(iii) Freight.
Marine Insurance Contract is a Contract of Indemnity :
The contract of marine insurance is a contract of indemnity. The assured can, in the event of loss recover the actual amount of loss from the insurer. Under no circumstances, the insured is allowed to make profit out of the marine insurance contract.
However, it becomes difficult to determine indemnity when the loss occurs. That is why, most insurance policies provide a commercial indemnity rather than a strict legal indemnity. They promise to indemnify ‘in the manner and to the extent agreed’.
In case of ‘Hull Policy’, the amount insured is fixed at a level rather above the current market value and in case of ‘Cargo Policy’, the amount insured also includes an amount for certain charges and profit.
Marine Insurance Contract is a Contract of Good Faith :
The contract of marine insurance is a contract of uberrima fides, i.e., utmost good faith. Both the insured and insurer must disclose everything which is in their knowledge and can affect the insurance contract. The insured should be truthful and honest in giving information to the insurance company.
He is under a duty to disclose accurately all factual information known to him. The insurer should also disclose the facts of the policy to the proposer. If utmost good faith is not observed by either party, the contract may be avoided by the other party. So utmost good faith on the part of both the parties is a must.
Kinds of Marine Insurance Policies:
The marine insurance policies are of the following kinds:
1. Valued Policy:
The valued policy contains the insured value of goods which is made up of invoice price, charges like freight, shipping and insurance and 10 per cent margin to cover profits and other incidental expenses. That is, it is the C.I.F. price (Cost, Insurance and Freight Price) plus 10 per cent profit.
2. Open or Unvalued Policy:
In this policy the value of the goods insured is not mentioned and is to be calculated when the actual loss arises. Unvalued policies’ are rarely issued.
3. Floating Policy:
This policy is popular with those merchants who make regular and frequent shipment of goods through an established route. Instead of taking many individual policies, one running policy is taken and the necessary particulars relating to the voyage are given by subsequent declaration at the time of each separate shipment.
4. Voyage Policy:
In such a policy the risk is covered for voyage of the ship or a specified route. Each voyage is made the basis of marine insurance for covering the related risks from the port of departure to the port of destination. Generally, the cargo owner takes the Voyage Policy for each separate shipment of goods.
5. Time Policy:
These policies are taken to cover all marine risks for a specified period, usually on the yearly basis, Cargo-owners may also take up time policies covering all shipments during a fixed period.
6. Mixed Policy:
These policies are issued by combining both the time and voyage features under one coverage. In this policy, the coverage is allowed for a particular time and for a particular voyage or a definite route.
Differences between Fire Insurance and Marine Insurance:
Essay # 4. Double Insurance :
When the same subject-matter is insured with two or more insurers and the total sum insured exceeds the value of the subject-matter, the assured is said to be over-insured by double insurance. As stated in Section 34 of the Marine Insurance Act, 1963, over-insurance and double insurance are valid unless the policy otherwise provides.
For instance, if Mr. X insures his factory worth Rs. 2 lakh with three insurers as—with A for Rs.90,000, with B for Rs. 80,000 and with C for Rs.70,000 there is a double insurance because the aggregate of all the policies exceeds the total value of Mr. X’s factory. If Mr. X insurers with A for Rs.80,000, with B for Rs. 70,000 and with C for Rs. 50,000 there is no double insurance.
A man may insure with as many insurers as he pleases. In case of loss, he may claim payment from the insurers in such order as he may think fit, but he will not get more than his actual loss, because a contract of insurance is a contract of indemnity. The insurers as between themselves are liable to contribute to the loss in proportion to the amount for which each one is liable.
If an insurer pays more than this proportion of the loss, he is entitled to recover the excess from his co- insurers. In India, Life Insurance Corporation of India being the only insurer of life there is no question of double insurance of life.
Essay # 5. Re-Insurance:
Every insurer has a limit to the risk that he can undertake. If at any time a profitable venture comes his way, he may accept a risk beyond his capacity, he may re-insure the same risk either wholly or partially with other insurers. This is known as re-insurance.
The re-insurer is not liable to the assured. This is because there is no private of contract between them. The re-insurance is subject to the clauses and conditions in the original policy, and is also entitled to any benefits which the Original policy is entitled to. The policy or re-insurance is co-extensive with the original policy.
If the original policy for any reason comes to end or is avoided, the policy of reinsurance also comes to an end. On payment of loss under the policy of re-insurance, the re-insurers are subrogated to all the rights of the original insurer including the rights of the assured to which the original insurer is subrogated.
Re-insurance can be resorted to in all kinds of insurance because the insurer has one insurable interest in the subject-matter insured to the extent of the amount insured by him.
Essay # 6. Advantages/Utilities/Importance of Insurance:
Immense are the benefits of insurance to the modern business. The goods may destroy due to fire beyond the control of man. The goods also destroy in transit. The workers are sometimes exposed to various risks which can cause death or permanent disability of some workers. Insurance has been helpful in solving these problems of business and private life.
Following are the advantages of insurance:
1. There is always a fear of sudden loss. Insurance provides security against such losses. Insurance gives security to both individuals and businessmen. Nowadays insurance covers various social welfare schemes also. There are schemes providing for sickness. Unemployment, health accident and old age insurances. These schemes are beneficial to poor people and also help in establishing social justice.
2. The fundamental principle of insurance is to spread risk among a large number of people. A large number of people get insurance policies and make the payment of premium to the insurer. Whenever a loss occurs, it is compensated out of funds of the insurer. The loss is spread among a large number of policyholders.
3. Insurance not only provides protection against risks but it is also a good form of investment. The insurance develops a habit of saving money by paying premium. In case of fixed time policies, the insured gets a lump-sum amount after the maturity of the policy.
4. Insurance helps in capital formation and economic development of the nation. Large funds are collected by way of premiums. These funds can be gainfully employed in industrial development of the country. The employment opportunities also increase by large investments made by insurance companies. So insurance has become an important source of capital formation.
5. These days large variety of policies have been designed for different purposes. Persons, by taking different types of life insurance policies, may provide against every type of his social and business obligation, i.e., for the education or marriage of the children, etc.
6. Insurance has helped the development of international trade on a large scale. Marine insurance provides protection against all types of sea-risks.
Related Articles:
- Notes on Over and Under Insurance
- Notes on Reinsurance: Meaning and Types
- Notes on Insurance: Meaning, Need and Functions
- Risk in Insurance: Meaning, Types and Its Transfer
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

" RELIANCE LIFE INSURANCE " INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY

Related Papers
shobhna gupta
channa keshava
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai....
Life cycle assessment and product carbon footprint for SHG zinc production
- Grund, Sabina C.
- Genderen, Eric van
The industry's environmental impact has moved into focus at global level. Regulators, supply chains, and the financial sector need credible, standardized, and transparent information for multiple reasons. These include regulatory targets for limiting emissions, downstream user optimizations, and developing science-based emission reduction strategies. By characterizing environmental impacts, companies can satisfy stakeholder demands and measure progress towards goals. In this paper, an introduction to life cycle assessment (LCA) for reporting on environmental impacts, including the product carbon footprint as global warming potential is given. Average results from the most recent global LCA update for special high-grade zinc production are summarized. Resulting carbon footprint information is then used to derive the zinc industry's baseline carbon footprint as the starting point for the decarbonization roadmap for the global zinc industry.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. The ultimate aim of Insurance is without a doubt to minimize the risks involved in various aspects of life and in addition to this, to cover and compensate the owner if any loss is suffered by the owner. Insurance may be taken to cover the risks involved in life, property and business. Mainly there are two types of insurance, namely ...
long-term policies in life insurance. Many of the same techniques are relevant also in pensions mathematics. However, there have been many changes since the first long-term policies of the late eighteenth century. 1.3 Life insurance and annuity contracts 1.3.1 Introduction The life insurance and annuity contracts that were the object of study ...
Abstract. The main aim of Insurance is to minimize the risks involved in various aspects of life and to cover and compensate the owner for any loss is suffered by the owner. Insurance may be taken to cover the risks involved in life, property, and business. Mainly there are two types of insurance, namely, life insurance and general insurance.
For example, suppose an insurance is issued with sum insured $100 000. At the end of the first year of the contract a bonus of 2% on the sum insured and 5% on previous bonuses is declared; in the following two years, the rates are 2.5% and 6%. Then the total guaranteed sum insured increases each year as shown in Table 1.1.
Life insurance can be defined as the contract between the insurer and the person who owns the policy. Some countries include some events like bills and death expenses are included in the premium policy. The insurer is bound to pay some money in case an event happens to occur. If the insurer enters the contract, he pays an annual or monthly ...
Life insurance is a protection against financial loss that would result from the premature death of an insured. The named beneficiary receives the proceeds and is thereby safeguarded from the ...
PAGES 2 WORDS 450. Executive Summary Guardian Life Insurance Co. ranks #239 on the Fortune 500 list with revenues of $12.4 billion in 2017 and profits of $455 million. It currently owns $75 billion in assets and is one of the premier insurance and investment companies in the U.S (Fortune, 2018).
Introduction of life insurance. Life insurance is a contract between the policyholder and the insurer, where the insurer agrees to pay the beneficiaries sum of money upon the occurrence of the insured individual's or individuals' death or other circumstances such as terminal illness or critical illness.
Children's Health Insurance Program. This presentation discusses the role of the Children's Health Insurance Program, a component of U.S. health policy regulating different mechanisms of medical services for children. Economics: Insurance Industry in 2005. The first is trade in risk and the second is diversification.
People who want to provide for dependents, provide for retirement, and defer and reduce taxes typically buy life insurance. The chapter concludes by summing up the factors that determine which type of life insurance suits you best.
Important facts about life insurance. A little bit of education can go a long way in understanding how life insurance protects you, your budget and your family. Whether you're just getting started in life or looking to transfer your legacy to the next generation, we can help you with the articles in this section.
Introduction. Life insurance is a fundamental financial tool that provides security and stability for individuals and their families. This essay examines the significance of life insurance, exploring its benefits, the peace of mind it offers, the various types available, its role in estate planning, its contribution to long-term savings, and ...
Life insurance (or life assurance, especially in the Commonwealth of Nations) is a contract between an insurance policy holder and an insurer or assurer, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the death of an insured person (often the policyholder). Depending on the contract, other events such as terminal ...
Conclusion. Insurance is a way to face the risks to which a person or his money is exposed during his life in order to alleviate its impact. The essence of this method is the cooperation that is achieved with the participation of persons at risk in facing the effects that result from its realization with respect to some of them, by paying each of them for a contribution or a share, and the ...
Introduction - Visions for the Future of the Life Insurance Sector Author: Steven Malerich, John Currier, Ronald Klein Subject: Introductory Comments for the Response to Life Insurance 2020 Foresight A Call for Essays e-Book. This e-book focuses on the vision for the future of the life insurance sector. Created Date: 11/11/2009 2:57:32 PM
Factors That Affect Life Insurance Industry Essay Example. 2513 words 10 pages. Firstly, life insurance industry can alp ensure the normal people's life. Second, life insurance collects idle capital in society and increases financial revenues. Third, life insurance industry fixed overall unemployment and underemployment problems.
Writing an essay on insurance is important for several reasons. Firstly, insurance is a crucial aspect of modern life, as it provides individuals and businesses with financial protection against unforeseen events. Understanding the concept of insurance and its various types is essential for anyone who wants to make informed decisions about ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
2. The fundamental principle of insurance is to spread risk among a large number of people. A large number of people get insurance policies and make the payment of premium to the insurer. Whenever a loss occurs, it is compensated out of funds of the insurer. The loss is spread among a large number of policyholders. 3.
NAME: VINAY .M. JADHAV CLASS: TYBBI ROLL NO: 166213 PROJECT REPORT ON "RELIANCE LIFE INSURANCE" INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY: Insurance may be described as a social device to reduce or eliminate risk of loss to life and property. Insurance is a collective bearing of risk. Insurance is a financial device to spread the risks and losses of few ...
I. Introduction: The concept, Life insurance is very old and profound in India. Insurance was active since olden days as ... papers, books, journals, articles, business magazines and other research papers. 3. Analysis of data:The collected data has been analyzed to the objectives in the form of tables and diagrams
Life Insurance Policies, Investors Perception, Investment, Protection of Family, Financial Security. INTRODUCTION Life insurance is a contract between an individual or organization (insurance policy holder) and an insurer (insurance company). ... papers, internet and various websites have been visited and data have been referenced fromthem.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
In this paper, an introduction to life cycle assessment (LCA) for reporting on environmental impacts, including the product carbon footprint as global warming potential is given. Average results from the most recent global LCA update for special high-grade zinc production are summarized.