Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
You can click any section to go directly there:

Overview of the McKinsey Approach to Problem Solving
Problem solving process.
- Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, download the umbrex toolkit on the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Example situation – A family on Friday evening
Scenario: A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend. The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
What is the problem definition?
A statement of facts does not focus the problem solving:
It is 6 p.m. The family has not made plans for dinner, and they are hungry.
A question guides the team towards a solution:
1. What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
2. Should the family cook dinner or order delivery?
3. What should the family cook for dinner?
4. What should the family cook for dinner that will not require spending more than $40 on groceries?
5. To cook dinner, what do they need to pick up from the supermarket?
6. How can the family prepare dinner within the next hour using ingredients they already have in the house?
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
Three Horizons of Engagement Planning
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2023 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service

Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
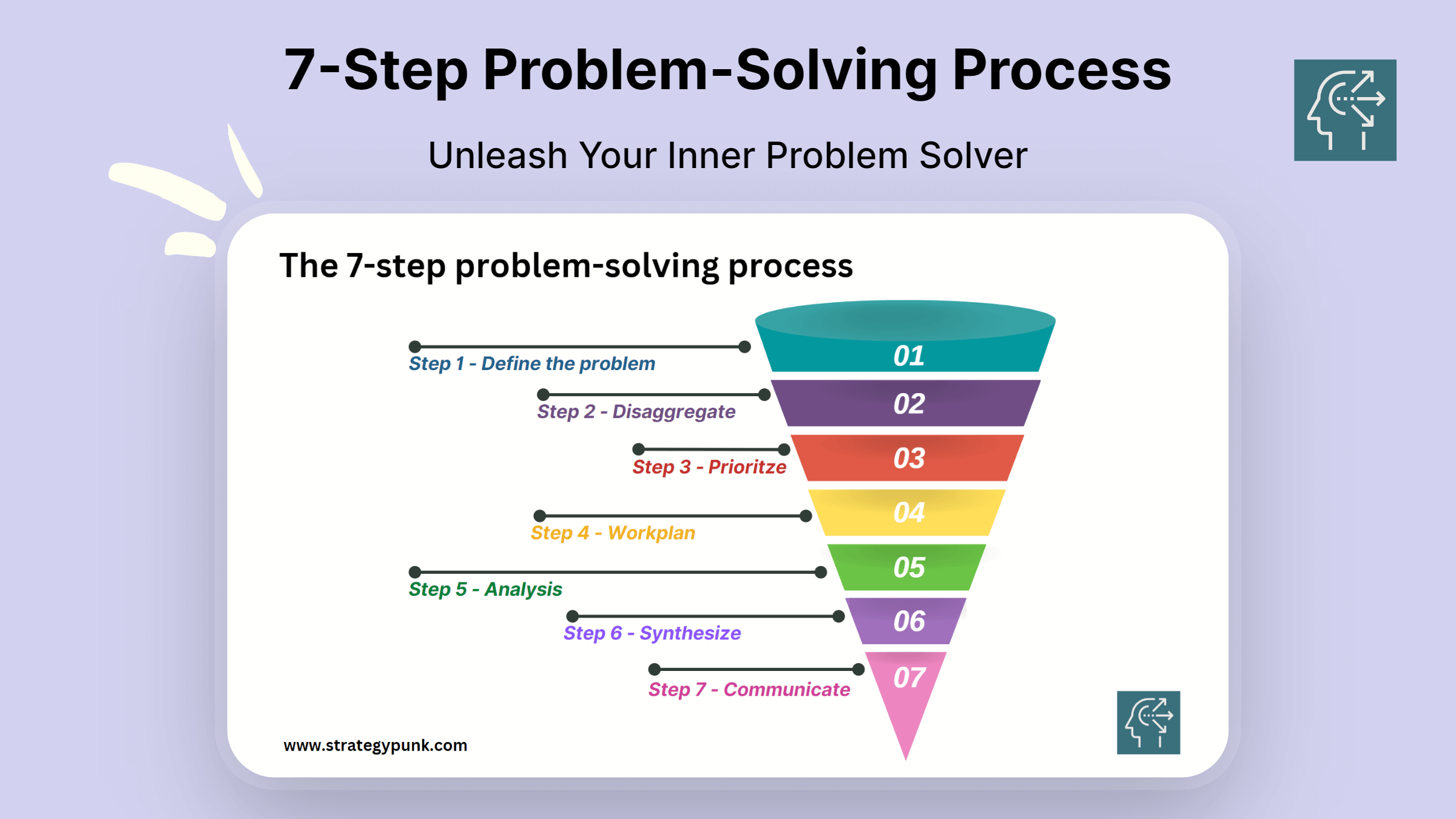
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. You can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates at the end of the blog post .
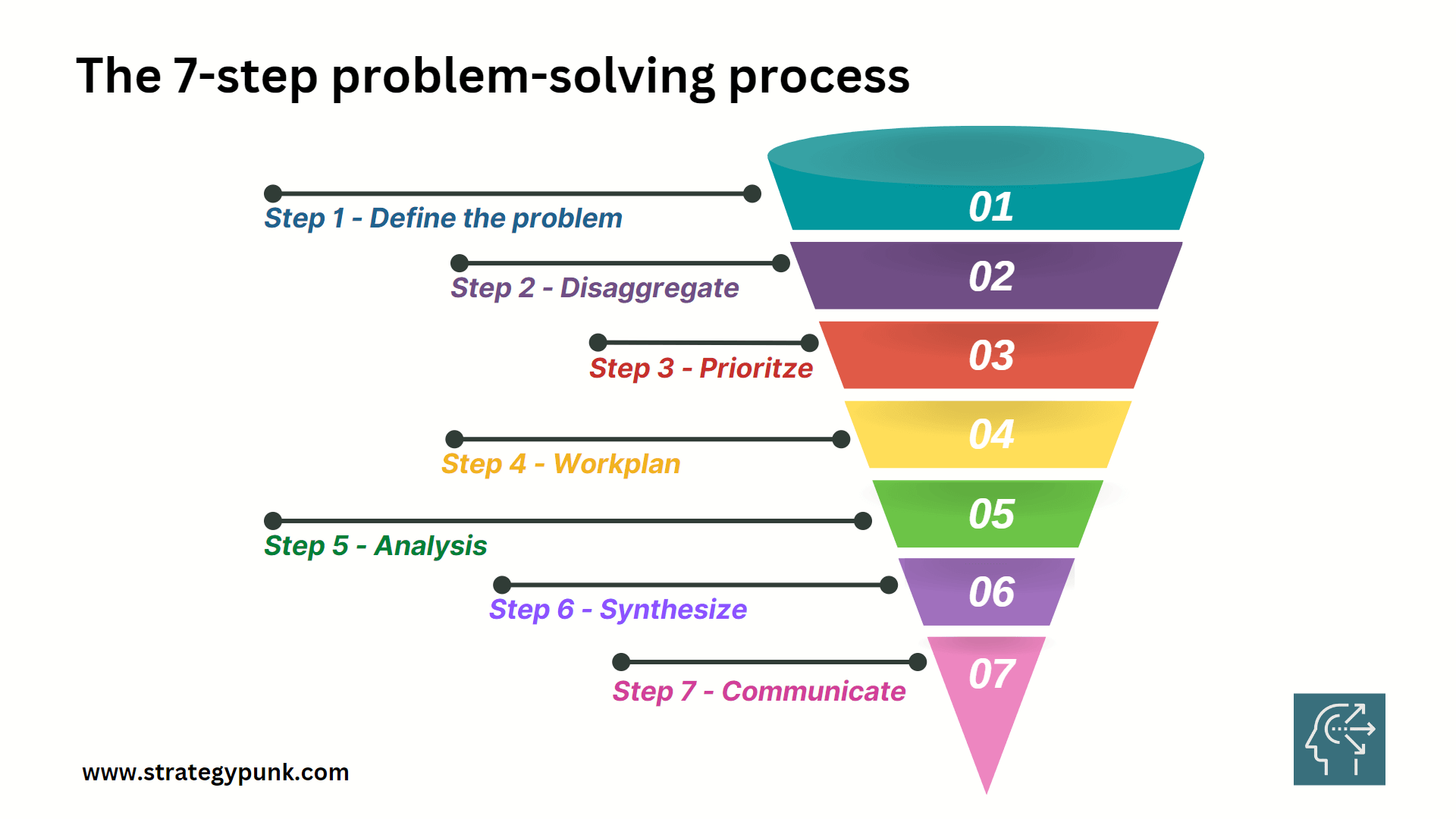
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected by it.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate the definition to all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
Considering their concerns and needs, it is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions by using a combination of methods.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, remaining open-minded and considering all potential solutions is vital. To ensure everyone's perspectives are considered, it is also essential to involve all stakeholders in the decision-making process.
Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the decision-making process is successful. Stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal by communicating the findings clearly and concisely.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
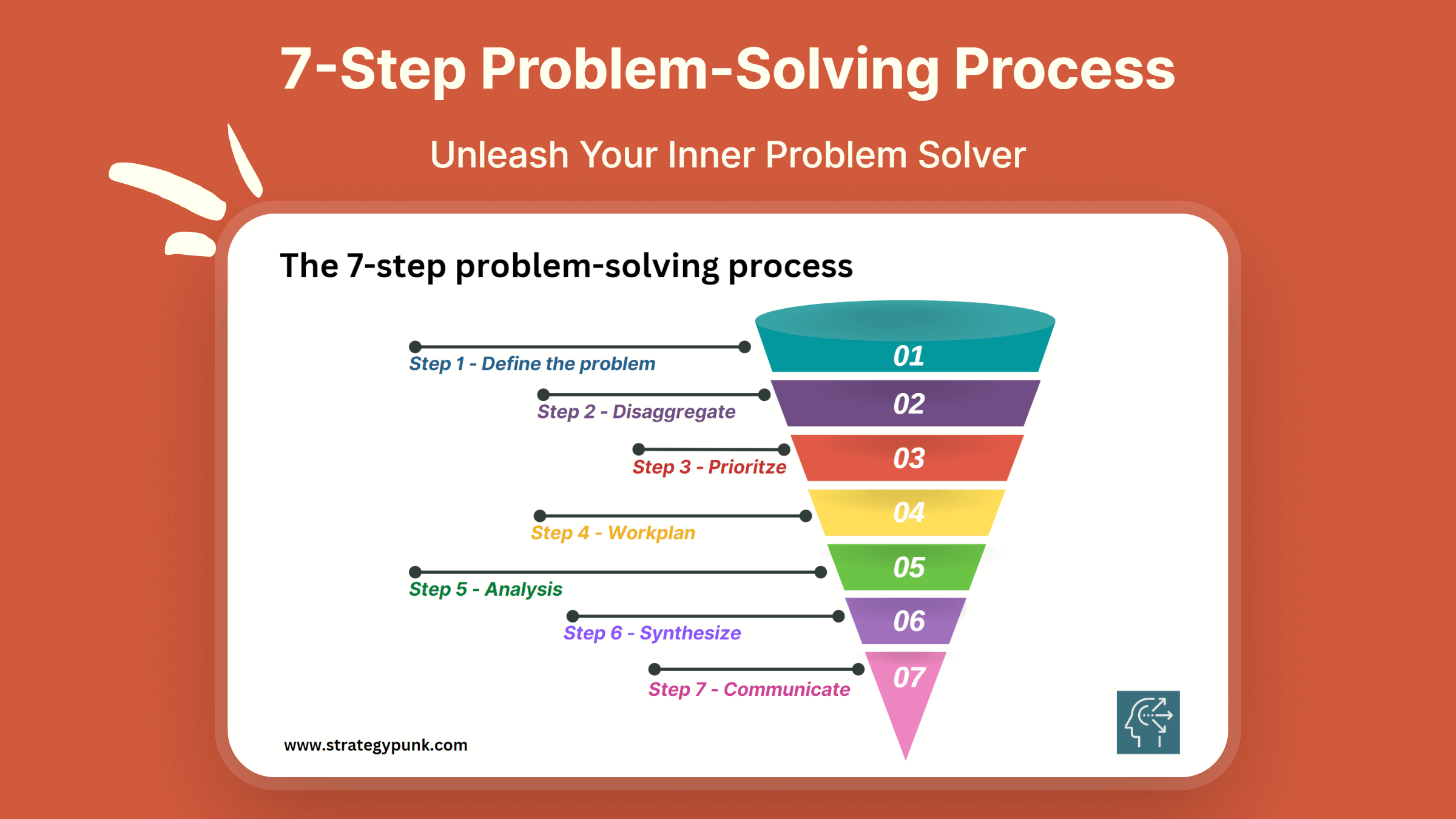
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.

7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

Xpeng SWOT Analysis: Free PPT Template and In-Depth Insights (free file)
Unlock key insights into Xpeng with our free SWOT analysis PPT template. Dive deep into its business dynamics at no cost.

Strategic Insights 2024: A SWOT Analysis of Nestle (Plus Free PPT)
Explore Nestle's strategic outlook with our SWOT analysis for 2024. This PowerPoint template highlights key areas for growth and challenges.

2024 Business Disruption: Navigating Growth Through Shaping Strategy
Discover the importance of being a shaper in 2023's business ecosystem. Shaping strategy, attracting a critical mass of participants, and finding the right strategic path to create value.

Samsung PESTLE Analysis: Unveiling the Driving Forces (Free PPT)
Download our comprehensive guide: Samsung PESTLE Analysis (Free PPT). Discover the strategic insights & driving forces shaping Samsung's future.
Adopting the right problem-solving approach
May 4, 2023 You’ve defined your problem, ensured stakeholders are aligned, and are ready to bring the right problem-solving approach and focus to the situation to find an optimal solution. But what is the right problem-solving approach? And what if there is no single ideal course of action? In our 2013 classic from the Quarterly , senior partner Olivier Leclerc highlights the value of taking a number of different approaches simultaneously to solve difficult problems. Read on to discover the five flexons, or problem-solving languages, that can be applied to the same problem to generate richer insights and more innovative solutions. Then check out more insights on problem-solving approaches, and dive into examples of pressing challenges organizations are contending with now.
Five routes to more innovative problem solving
Author Talks: Get on the performance curve
Strategy to beat the odds
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Digital performance management: From the front line to the bottom line
Addressing employee burnout: Are you solving the right problem?
Business’s ‘It’s not my problem’ IT problem
TEST YOUR SKILLS
Take the McKinsey Problem Solving Test
Solve, McKinsey’s assessment game

McKinsey Problem Solving: Six steps to solve any problem and tell a persuasive story
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people.
Over the past several years of creating StrategyU, advising an undergraduates consulting group and running workshops for clients, I have found over and over again that the principles taught on this site and in this guide are a powerful way to improve the type of work and communication you do in a business setting.
When I first set out to teach these skills to the undergraduate consulting group at my alma mater, I was still working at BCG. I was spending my day building compelling presentations, yet was at a loss for how to teach these principles to the students I would talk with at night.
Through many rounds of iteration, I was able to land on a structured process and way of framing some of these principles such that people could immediately apply them to their work.
While the “official” McKinsey problem solving process is seven steps, I have outline my own spin on things – from experience at McKinsey and Boston Consulting Group. Here are six steps that will help you solve problems like a McKinsey Consultant:
Step #1: School is over, stop worrying about “what” to make and worry about the process, or the “how”
When I reflect back on my first role at McKinsey, I realize that my biggest challenge was unlearning everything I had learned over the previous 23 years. Throughout school you are asked to do specific things. For example, you are asked to write a 5 page paper on Benjamin Franklin — double spaced, 12 font and answering two or three specific questions.
In school, to be successful you follow these rules as close as you can. However, in consulting there are no rules on the “what.” Typically the problem you are asked to solve is ambiguous and complex — exactly why they hire you. In consulting, you are taught the rules around the “how” and have to then fill in the what.
The “how” can be taught and this entire site is founded on that belief. Here are some principles to get started:
Step #2: Thinking like a consultant requires a mindset shift
There are two pre-requisites to thinking like a consultant. Without these two traits you will struggle:
- A healthy obsession looking for a “better way” to do things
- Being open minded to shifting ideas and other approaches
In business school, I was sitting in one class when I noticed that all my classmates were doing the same thing — everyone was coming up with reasons why something should should not be done.
As I’ve spent more time working, I’ve realized this is a common phenomenon. The more you learn, the easier it becomes to come up with reasons to support the current state of affairs — likely driven by the status quo bias — an emotional state that favors not changing things. Even the best consultants will experience this emotion, but they are good at identifying it and pushing forward.
Key point : Creating an effective and persuasive consulting like presentation requires a comfort with uncertainty combined with a slightly delusional belief that you can figure anything out.
Step #3: Define the problem and make sure you are not solving a symptom
Before doing the work, time should be spent on defining the actual problem. Too often, people are solutions focused when they think about fixing something. Let’s say a company is struggling with profitability. Someone might define the problem as “we do not have enough growth.” This is jumping ahead to solutions — the goal may be to drive more growth, but this is not the actual issue. It is a symptom of a deeper problem.
Consider the following information:
- Costs have remained relatively constant and are actually below industry average so revenue must be the issue
- Revenue has been increasing, but at a slowing rate
- This company sells widgets and have had no slowdown on the number of units it has sold over the last five years
- However, the price per widget is actually below where it was five years ago
- There have been new entrants in the market in the last three years that have been backed by Venture Capital money and are aggressively pricing their products below costs
In a real-life project there will definitely be much more information and a team may take a full week coming up with a problem statement . Given the information above, we may come up with the following problem statement:
Problem Statement : The company is struggling to increase profitability due to decreasing prices driven by new entrants in the market. The company does not have a clear strategy to respond to the price pressure from competitors and lacks an overall product strategy to compete in this market.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to “solve” the problem
Now the fun starts!
There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on.
First is top-down . This is what you should start with, especially for a newer “consultant.” This involves taking the problem statement and structuring an approach. This means developing multiple hypotheses — key questions you can either prove or disprove.
Given our problem statement, you may develop the following three hypotheses:
- Company X has room to improve its pricing strategy to increase profitability
- Company X can explore new market opportunities unlocked by new entrants
- Company X can explore new business models or operating models due to advances in technology
As you can see, these three statements identify different areas you can research and either prove or disprove. In a consulting team, you may have a “workstream leader” for each statement.
Once you establish the structure you you may shift to the second type of analysis: a bottom-up approach . This involves doing deep research around your problem statement, testing your hypotheses, running different analysis and continuing to ask more questions. As you do the analysis, you will begin to see different patterns that may unlock new questions, change your thinking or even confirm your existing hypotheses. You may need to tweak your hypotheses and structure as you learn new information.
A project vacillates many times between these two approaches. Here is a hypothetical timeline of a project:

Step 5: Make a slides like a consultant
The next step is taking the structure and research and turning it into a slide. When people see slides from McKinsey and BCG, they see something that is compelling and unique, but don’t really understand all the work that goes into those slides. Both companies have a healthy obsession (maybe not to some people!) with how things look, how things are structured and how they are presented.
They also don’t understand how much work is spent on telling a compelling “story.” The biggest mistake people make in the business world is mistaking showing a lot of information versus telling a compelling story. This is an easy mistake to make — especially if you are the one that did hours of analysis. It may seem important, but when it comes down to making a slide and a presentation, you end up deleting more information rather than adding. You really need to remember the following:
Data matters, but stories change hearts and minds
Here are four quick ways to improve your presentations:
Tip #1 — Format, format, format
Both McKinsey and BCG had style templates that were obsessively followed. Some key rules I like to follow:
- Make sure all text within your slide body is the same font size (harder than you would think)
- Do not go outside of the margins into the white space on the side
- All titles throughout the presentation should be 2 lines or less and stay the same font size
- Each slide should typically only make one strong point
Tip #2 — Titles are the takeaway
The title of the slide should be the key insight or takeaway and the slide area should prove the point. The below slide is an oversimplification of this:

Even in consulting, I found that people struggled with simplifying a message to one key theme per slide. If something is going to be presented live, the simpler the better. In reality, you are often giving someone presentations that they will read in depth and more information may make sense.
To go deeper, check out these 20 presentation and powerpoint tips .
Tip #3 — Have “MECE” Ideas for max persuasion
“MECE” means mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive — meaning all points listed cover the entire range of ideas while also being unique and differentiated from each other.
An extreme example would be this:
- Slide title: There are seven continents
- Slide content: The seven continents are North America, South America, Europe, Africa Asia, Antarctica, Australia
The list of continents provides seven distinct points that when taken together are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive . The MECE principle is not perfect — it is more of an ideal to push your logic in the right direction. Use it to continually improve and refine your story.
Applying this to a profitability problem at the highest level would look like this:
Goal: Increase profitability
2nd level: We can increase revenue or decrease costs
3rd level: We can increase revenue by selling more or increasing prices
Each level is MECE. It is almost impossible to argue against any of this (unless you are willing to commit accounting fraud!).
Tip #4 — Leveraging the Pyramid Principle
The pyramid principle is an approach popularized by Barbara Minto and essential to the structured problem solving approach I learned at McKinsey. Learning this approach has changed the way I look at any presentation since.
Here is a rough outline of how you can think about the pyramid principle as a way to structure a presentation:

As you build a presentation, you may have three sections for each hypothesis. As you think about the overall story, the three hypothesis (and the supporting evidence) will build on each other as a “story” to answer the defined problem. There are two ways to think about doing this — using inductive or deductive reasoning:

If we go back to our profitability example from above, you would say that increasing profitability was the core issue we developed. Lets assume that through research we found that our three hypotheses were true. Given this, you may start to build a high level presentation around the following three points:

These three ideas not only are distinct but they also build on each other. Combined, they tell a story of what the company should do and how they should react. Each of these three “points” may be a separate section in the presentation followed by several pages of detailed analysis. There may also be a shorter executive summary version of 5–10 pages that gives the high level story without as much data and analysis.
Step 6: The only way to improve is to get feedback and continue to practice
Ultimately, this process is not something you will master overnight. I’ve been consulting, either working for a firm or on my own for more than 10 years and am still looking for ways to make better presentations, become more persuasive and get feedback on individual slides.
The process never ends.
The best way to improve fast is to be working on a great team . Look for people around you that do this well and ask them for feedback. The more feedback, the more iterations and more presentations you make, the better you will become. Good luck!
If you enjoyed this post, you’ll get a kick out of all the free lessons I’ve shared that go a bit deeper. Check them out here .
Do you have a toolkit for business problem solving? I created Think Like a Strategy Consultant as an online course to make the tools of strategy consultants accessible to driven professionals, executives, and consultants. This course teaches you how to synthesize information into compelling insights, structure your information in ways that help you solve problems, and develop presentations that resonate at the C-Level. Click here to learn more or if you are interested in getting started now, enroll in the self-paced version ($497) or hands-on coaching version ($997). Both versions include lifetime access and all future updates.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

7 Steps To Problem-Solving
The 7 steps to problem-solving is a disciplined and methodical approach to identifying and then addressing the root cause of problems. Instead, a more robust approach involves working through a problem using the hypothesis-driven framework of the scientific method. Each viable hypothesis is tested using a range of specific diagnostics and then recommendations are made.
Table of Contents
Understanding the 7 steps to problem-solving
The core argument of this approach is that the most obvious solutions to a problem are often not the best solutions.
Good problem-solving in business is a skill that must be learned. Businesses that are adept at problem-solving take responsibility for their own decisions and have courage and confidence in their convictions. Ultimately, this removes doubt which can impede the growth of businesses and indeed employees alike.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving
Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically.
Step 1 – Define the problem
First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified. Actions and behaviors of individuals must be the focus – instead of a focus on the individuals themselves. Whatever the case, the problem must be clearly defined and be universally accepted by all relevant parties.
Step 2 – Disaggregate the problem
In the second step, break down the problem (challenge) into smaller parts using logic trees and develop an early hypothesis. Here, economic and scientific principles can be useful in brainstorming potential solutions. Avoid cognitive biases, such as deciding that a previous solution should be used again because it worked last time.

Step 3 – Prioritize issues
Which constituent parts could be key driving factors of the problem? Prioritize each according to those which have the biggest impact on the problem. Eliminate parts that have negligible impact. This step helps businesses use their resources wisely.
Step 4 – Plan the analyses
Before testing each hypothesis, develop a work and process plan for each. Staff should be assigned to analytical tasks with unique output and completion dates. Hypothesis testing should also be reviewed at regular intervals to measure viability and adjust strategies accordingly.
Step 5 – Conduct the analyses
In step five, gather the critical data required to accept or reject each hypothesis. Data analysis methods will vary according to the nature of the project, but each business must understand the reasons for implementing specific methods. In question-based problem solving, the Five Whys or Fishbone method may be used. More complicated problems may require the use of statistical analysis . In any case, this is often the longest and most complex step of the process.
Step 6 – Synthesise the results
Once the results have been determined, they must be synthesized in such a way that they can be tested for validity and logic. In a business context, assess the implications of the findings for a business moving forward. Does it solve the problem?
Step 7 – Communicate
In the final step, the business must present the solutions in such a way that they link back to the original problem statement. When presenting to clients, this is vital. It shows that the business understands the problem and has a solution supported by facts or hard data. Above all, the data should be woven into a convincing story that ends with recommendations for future action.
Key takeaways
- 7 steps to problem-solving is a methodical approach to problem-solving based on the scientific method.
- Although a somewhat rigorous approach, the strategy can be learned by any business willing to devote the time and resources.
- Fundamentally, the 7 steps to problem-solving method involves formulating and then testing hypotheses. Through the process of elimination, a business can narrow its focus to the likely root cause of a problem.
Key Highlights
- Definition : The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a structured methodology rooted in the scientific method. It emphasizes systematic hypothesis testing and data analysis to identify and address the root cause of problems, avoiding surface-level solutions.
- Problem-Solving Skill : Effective problem-solving is a learned skill that fosters responsible decision-making, boosts confidence, and supports business growth .
- Define the Problem : Clearly outline the problem’s scope and impact, focusing on actions and behaviors rather than individuals.
- Disaggregate the Problem : Break down the problem into smaller parts using logic trees and form early hypotheses. Avoid biases from past solutions.
- Prioritize Issues : Identify key driving factors of the problem and prioritize them by impact. Eliminate parts with minimal impact to allocate resources efficiently.
- Plan the Analyses : Develop work and process plans for hypothesis testing, assigning staff and setting completion dates. Regularly review and adjust strategies.
- Conduct the Analyses : Gather critical data to accept or reject hypotheses. Use methods like Five Whys, Fishbone diagrams, or statistical analysis .
- Synthesize the Results : Combine and analyze results to determine their validity and implications for the business . Assess if the problem is solved.
- Communicate : Present solutions that link back to the original problem statement, supported by facts. Create a compelling story ending with recommendations.
- The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is based on the scientific method.
- It requires a structured approach to formulating and testing hypotheses.
- Businesses willing to invest time and resources can learn and apply this method effectively.
Connected Decision-Making Frameworks
Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced
Read Next: Mental Models , Biases , Bounded Rationality , Mandela Effect , Dunning-Kruger Effect , Lindy Effect , Crowding Out Effect , Bandwagon Effect , Decision-Making Matrix .
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Business Model Innovation
- Platform Business Models
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Digital Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process The McKinsey Podcast
Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
- More Episodes
- 2024 McKinsey & Company
More by McKinsey

- Business & Money
- Management & Leadership

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Buy new: $24.63 $24.63 FREE delivery: Thursday, April 4 on orders over $35.00 shipped by Amazon. Ships from: Amazon.com Sold by: Amazon.com
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used: $17.15
Other sellers on amazon.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the authors

Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything Paperback – March 6, 2019
Purchase options and add-ons.
Complex problem solving is the core skill for 21 st Century Teams
Complex problem solving is at the very top of the list of essential skills for career progression in the modern world. But how problem solving is taught in our schools, universities, businesses and organizations comes up short. In Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything you’ll learn the seven-step systematic approach to creative problem solving developed in top consulting firms that will work in any field or industry, turning you into a highly sought-after bulletproof problem solver who can tackle challenges that others balk at.
The problem-solving technique outlined in this book is based on a highly visual, logic-tree method that can be applied to everything from everyday decisions to strategic issues in business to global social challenges. The authors, with decades of experience at McKinsey and Company, provide 30 detailed, real-world examples, so you can see exactly how the technique works in action. With this bulletproof approach to defining, unpacking, understanding, and ultimately solving problems, you’ll have a personal superpower for developing compelling solutions in your workplace.
- Discover the time-tested 7-step technique to problem solving that top consulting professionals employ
- Learn how a simple visual system can help you break down and understand the component parts of even the most complex problems
- Build team brainstorming techniques that fight cognitive bias, streamline workplanning, and speed solutions
- Know when and how to employ modern analytic tools and techniques from machine learning to game theory
- Learn how to structure and communicate your findings to convince audiences and compel action
The secrets revealed in Bulletproof Problem Solving will transform the way you approach problems and take you to the next level of business and personal success.
- Print length 320 pages
- Language English
- Publisher Wiley
- Publication date March 6, 2019
- Dimensions 7.3 x 0.7 x 9.2 inches
- ISBN-10 1119553024
- ISBN-13 978-1119553021
- See all details

Frequently bought together

More items to explore

Editorial Reviews
From the inside flap.
"Problem solving is the core skill for the twenty-first century. Now, finally, we have a guide to doing it right that any of us can follow." —Dominic Barton, Global Managing Partner Emeritus, McKinsey & Company
PRAISE FOR BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING
"We always hired for creative problem solving talent above all else; these guys have cracked the code on a replicable approach for problems large and small. Learn it, practice it!" — Eric Schmidt, Former Chairman and CEO, Google; Visiting Innovation Fellow, MIT
"Together Charles and Rob have taken problem solving out of the business school classroom and into real life, where it belongs. Utilizing 30 cases, these masters of the art have something to teach all of us." — James Gorman, Chairman and CEO, Morgan Stanley
"As a former policymaker who argues for moving beyond policy to the broader enterprise of public problem solving, I welcome this volume! The techniques and insights apply, with various modifications, to problems everywhere: personal, professional, public and private, local, national and global." — Anne-Marie Slaughter, CEO, New America, Former Director of Policy Planning, U.S. Department of State
"Disruption in today's business environment puts problem solving at the top of every leader's challenges. But how? This engaging book puts together a McKinsey team's scientific seven-step approach. From taking a problem apart to rearranging its pieces, to framing it so its solution can be seen, the book presents a must-read analysis for executives and social sector leaders. It excites both the reader's mind and the possibilities for project teams. —Glenn Hubbard, Dean and Russell L. Carson Professor of Finance and Economics, Columbia Business School
7 straightforward steps to solving any problem with creativity and rigor
Complex problem solving is the core skill for twenty-first century teams. It's the only way to keep up with rapid change. Winning organizations now rely on nimble, iterative problem solving, rather than traditional planning processes. In this book you'll learn the seven-step systematic approach to creative problem solving that will work in any field or industry. It employs a highly visual, logic-tree method that can be applied to any problem, from strategic business decisions to global social challenges. Charles and Rob, with decades of experience at McKinsey & Company and other institutions, provide a toolkit with 30 detailed real-world examples, so you can see exactly how the technique works in action.
From the Back Cover
"Problem solving is the core skill for the twenty-first century. Now, finally, we have a guide to doing it right that any of us can follow." ―Dominic Barton, Global Managing Partner Emeritus, McKinsey & Company
"We always hired for creative problem solving talent above all else; these guys have cracked the code on a replicable approach for problems large and small. Learn it, practice it!" ― Eric Schmidt, Former Chairman and CEO, Google; Visiting Innovation Fellow, MIT
"Together Charles and Rob have taken problem solving out of the business school classroom and into real life, where it belongs. Utilizing 30 cases, these masters of the art have something to teach all of us." ― James Gorman, Chairman and CEO, Morgan Stanley
"As a former policymaker who argues for moving beyond policy to the broader enterprise of public problem solving, I welcome this volume! The techniques and insights apply, with various modifications, to problems everywhere: personal, professional, public and private, local, national and global." ― Anne-Marie Slaughter, CEO, New America, Former Director of Policy Planning, U.S. Department of State
"Disruption in today's business environment puts problem solving at the top of every leader's challenges. But how? This engaging book puts together a McKinsey team's scientific seven-step approach. From taking a problem apart to rearranging its pieces, to framing it so its solution can be seen, the book presents a must-read analysis for executives and social sector leaders. It excites both the reader's mind and the possibilities for project teams. ―Glenn Hubbard, Dean and Russell L. Carson Professor of Finance and Economics, Columbia Business School
About the Author
Charles Conn is CEO of the Rhodes Scholarships in Oxford. Previously, he was a Partner at McKinsey & Company, led a technology start-up to its IPO, and was an early team lead at the Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation in San Francisco.
Robert McLean is Director Emeritus at McKinsey and Company. He led the Australian and New Zealand McKinsey practice for eight years and served on the firm's global Director's Committee.
Product details
- Publisher : Wiley; 1st edition (March 6, 2019)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 320 pages
- ISBN-10 : 1119553024
- ISBN-13 : 978-1119553021
- Item Weight : 1.35 pounds
- Dimensions : 7.3 x 0.7 x 9.2 inches
- #110 in Business Decision Making
- #210 in Decision-Making & Problem Solving
- #217 in Cognitive Psychology (Books)
About the authors
Charles conn.
Charles Conn is a seasoned cross-sector leader, entrepreneur and best-selling author. Charles is an experienced investor, and is co-founder of Monograph Capital, a life sciences venture firm. Before that, he was CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation, a £600m venture firm formed in partnership with Oxford to develop the University’s advanced science ideas. Charles has been a technology entrepreneur, and as founding CEO of Ticketmaster-Citysearch led the company through its IPO (NASDAQ TMCS) and acquisitions of Match.com, Evite, and other companies. He is co-author of Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything, published with John Wiley & Sons in 2019, a best seller which also earned a Top 10 reader ranking on McKinsey.com for 2019. It has been taught at Harvard and Oxford, and to the Schmidt Science Fellows, World Economic Forum Global Shapers, Kauffman Fellows, and Rhodes Scholars. He is also a nonprofit education and conservation leader, including a five year term as CEO of the Rhodes Trust, the organization that delivers the Rhodes Scholarships in Oxford. Prior to his Oxford roles, Charles was senior advisor to the Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation, where he led conservation projects including the wild salmon ecosystems initiative and the Palmyra atoll research station. He sits or has sat on many company and nonprofit boards, including Patagonia, the Mandela Rhodes Foundation in South Africa, and Arcadia Foundation in London. He began his career at McKinsey & Company, where he was a Partner and leader in the strategy and energy practices. He is a graduate of Harvard Business School, Boston University, and Oxford University, where he was a Rhodes Scholar.
Robert McLean
Discover more of the author’s books, see similar authors, read author blogs and more
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries

- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Start Selling with Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 11 min read
McKinsey 7-S Framework
Making every part of your organization work in harmony.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Do you know how well your organization is positioned to achieve its goals? Or what elements influence its ability to implement change successfully?
Models of organizational effectiveness go in and out of fashion, but the McKinsey 7-S framework has stood the test of time.
The model was developed in the late 1970s by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman, former consultants at McKinsey & Company. They identified seven internal elements of an organization that need to align for it to be successful. [1]
In this article, we'll explore the seven elements in detail, and learn how it can be used to improve performance or manage change in organizations by ensuring that they all work in harmony.
Also, we provide a worked example and a downloadable template that you can use to apply the model.
When to Use the McKinsey 7-S Model
You can use the 7-S model in a wide variety of situations where it's useful to examine how the various parts of your organization work together.
For example, it can help you to improve the performance of your organization, or to determine the best way to implement a proposed strategy.
The framework can be used to examine the likely effects of future changes in the organization, or to align departments and processes during a merger or acquisition. You can also apply the McKinsey 7-S model to elements of a team or a project.
The Seven Elements of the McKinsey 7-S Framework
The model categorizes the seven elements as either "hard" or "soft":
The three "hard" elements include:
- Structures (such as organization charts and reporting lines).
- Systems (such as formal processes and IT systems.)
These elements are relatively easy to identify, and management can influence them directly.
The four "soft" elements, on the other hand, can be harder to describe, and are less tangible, and more influenced by your company culture. But they're just as important as the hard elements if the organization is going to be successful.
Figure 1, below, shows how the elements depend on each other, and how a change in one affects all the others.
Figure 1: The McKinsey 7-S Model
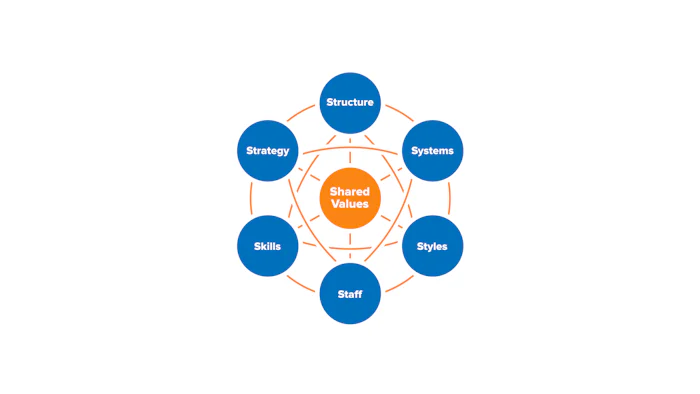
Figure reproduced with permission from McKinsey & Company, www.mckinsey.com. Copyright © 2016. All rights reserved.
Let's look at each of the elements individually:
- Strategy: this is your organization's plan for building and maintaining a competitive advantage over its competitors.
- Structure: this is how your company is organized (how departments and teams are structured, including who reports to whom).
- Systems: the daily activities and procedures that staff use to get the job done.
- Shared Values: these are the core values of the organization and reflect its general work ethic. They were called "superordinate goals" when the model was first developed.
- Style: the style of leadership adopted.
- Staff: the employees and their general capabilities.
- Skills: the actual skills and competencies of the organization's employees.
The placement of Shared Values in the center of the model emphasizes that they are central to the development of all the other critical elements.
The model states that the seven elements need to balance and reinforce each other for an organization to perform well.
Using the McKinsey 7-S Model
You can use the model to identify which elements of the 7-S' you need to realign to improve performance, or to maintain alignment and performance during other changes. These changes could include restructuring, new processes, an organizational merger, new systems, and a change of leadership.
To apply the McKinsey 7-S Model in your organization, follow these steps:
- Start with your shared values: are they consistent with your structure, strategy, and systems? If not, what needs to change?
- Then look at the hard elements – your strategy, structure and systems. How well does each one support the others? Identify where changes need to be made.
- Next, look at the soft elements – shared values, skills, (leadership) style, and staff. Do they support the desired hard elements? Do they support one another? If not, what needs to change?
- As you adjust and align the elements, you'll need to use an iterative (and often time-consuming) process of making adjustments, and then re-analyzing how that impacts other elements and their alignment. The end result of better performance will be worth it.
Figure 2 shows a template matrix that you can use to help with your analysis. You can click on the image to download it as a PDF worksheet.
We've also developed a checklist of the right questions to ask, which you can find in the next section. Supplement the questions in our checklist with your own questions, based on your organization's specific circumstances and your own knowledge and experience.
Figure 2: The McKinsey 7-S Matrix Template

You can use the 7-S model to help analyze your current situation (Point A in the worksheet), your proposed future situation (Point B in the worksheet), and to identify gaps and inconsistencies between them.
To examine where you are now (Point A), use the data that you've learned from your checklist questions to fill in the worksheet grid, putting a tick in any box where the two cross-referenced elements work together well. If the two elements aren't working well together, put a cross.
Point B is an agreed endpoint in the future (in six months or a year, for example). When you reach Point B, revisit the worksheet and fill it in again. If your changes have worked, you'll have a grid full of ticks. If not, you may need to make further adjustments.
The 7-S model is a good framework to help you ask the right questions, but it won't give you all the answers. For that, you'll need to bring together the right people with the right knowledge, skills and experience. Our article, Setting up a Cross-Functional Team , can help you to do this.
Checklist Questions for the McKinsey 7-S Framework
The following questions are a starting point for exploring your situation in terms of the 7-S framework. Use them to analyze your current situation (Point A) first, and then repeat the exercise for your proposed situation (Point B).
- What is our strategy?
- How do we intend to achieve our objectives?
- How do we deal with competitive pressure?
- How are changes in customer demands dealt with?
- How is strategy adjusted for environmental issues?
- How is the company/team divided?
- What is the hierarchy?
- How do the various departments coordinate activities?
- How do the team members organize and align themselves?
- Is decision-making centralized or decentralized? Is this as it should be, given what we're doing?
- Where are the lines of communication? Explicit or implicit?
- What are the main systems that run the organization? Consider financial and HR systems, as well as communications and document storage.
- Where are the controls and how are they monitored and evaluated?
- What internal rules and processes does the team use to keep on track?
Shared Values:
- What are your organization's core values?
- What is its corporate/team culture like?
- How strong are the values?
- What are the fundamental values that the company/team was built on?
- How participative is the management/leadership style?
- How effective is that leadership?
- Do employees/team members tend to be competitive or cooperative?
- Are there real teams functioning within the organization or are they just nominal groups?
- What positions or specializations are represented within the team?
- What positions need to be filled?
- Are there gaps in required competencies?
- What are the strongest skills represented within the company/team?
- Are there any skills gaps?
- What is the company/team known for doing well?
- Do the current employees/team members have the ability to do the job?
- How are skills monitored and assessed?
Example: The McKinsey 7-S Framework in Action
Whitehawk Electronics is a startup with five staff. As a new venture, it is still based firmly on the vision and values of its founder, Alix, and its elements all align. It sells into one market, and uses off-the-shelf IT and accounting systems.
As time goes on, the business grows, employing 30 staff, and diversifying into different markets. New customer requirements demand new skills in marketing, technology, product development, and financial management.
Alix carries out a 7-S analysis. She finds that Whitehawk's developing sales strategy no longer aligns with its small-business skill set.
The rapid influx of new staff members, along with changes in technology, means that some staff don't have the necessary systems skills. Worse still, they're unclear on the organization's values and sense of purpose.
Alix uses the analysis to introduce onboarding and learning programs, bringing all Whitehawk's key elements back into alignment.
For other, similar approaches, see our articles on the Burke-Litwin Change Model , and the Congruence Model . You may also find our articles on the Change Curve , Impact Analysis and Lewin's Change Management Model useful.
You can apply the McKinsey 7-S framework to almost any organizational or team effectiveness issue. The 7-S' refer to:
- Shared values.
If something within your organization or team isn't working, chances are there is inconsistency between one or more of these seven elements.
Once you reveal these inconsistencies, you can work to align these elements to make sure they are all contributing to your organization's shared goals and values.
The process of analyzing where you are right now, in terms of these elements, is worthwhile in itself. But for it to be truly effective, you'll also need to determine the desired future state for each factor. This will help you make changes and improve performance so that all seven factors are aligned across your organization.
Download Worksheet
[1] Waterman, R. H. and Peters, T. (1982). ' In Search of Excellence ,' New York: Harper and Row.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Mckinsey and co: the war for talent.
Overview of 'The War for Talent' Mckinsey’s Influential Article on Talent Management
Assessing the Need for Change
Drivers of Organizational Change and Techniques to Address Them
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 20% off your first year of Mind Tools
Our on-demand e-learning resources let you learn at your own pace, fitting seamlessly into your busy workday. Join today and save with our limited time offer!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Pain Points Podcast - Balancing Work And Kids

Pain Points Podcast - Improving Culture
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - what is ai.
Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Pain Points Podcast - How Do I Get Organized?
It's Time to Get Yourself Sorted!
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
John Kotter
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Skip Prichard | Leadership Insights
Ideas, Insight & Inspiration
7 Steps to Problem Solving

Bulletproof Problem Solving
Complex problem solving is the core skill for 21st century teams. It’s the only way to keep up with rapid change. Winning organizations now rely on nimble, iterative problem solving, rather than the traditional planning processes. I had the opportunity to speak with Charles Conn and Robert McLean, two McKinsey alums who share a seven-step systematic approach to creative problem solving that will work in any field or industry. Their new book is BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
New Skills Required
Would you share a little about the evolution of managerial skills and what skills are needed in the current era?
This new era of focus on creative problem solving has been ushered in by massive disruption of the old order in business and society. New business models are rapidly emerging from revolutionary Internet, machine learning, and bioscience technologies that threaten the status quo in every field. Technology change is speeding business up and providing an edge for disruptive innovators.
As a consequence of accelerating change, the old model of managerial skill development and application is no longer effective. It used to be that you could learn the core skills for a career in college and graduate school – think management, accounting, law – and then apply it over forty years. Strategic planning in business assumed an existing playing field and known actors. Today savvy business leaders are prioritizing complex problem solving skills in hiring rather than old domain knowledge, and emphasizing agile team problem solving over traditional planning cycles. This approach rewards the ability to see and quickly respond to new opportunities and threats over the slower traditional big company departmental responses.
We are seeing growing awareness of this. David Brooks of the New York Times said recently, “It doesn’t matter if you are working in the cafeteria or the inspection line of a plant, companies will only hire people who can see problems and organize responses.” And The World Economic Forum in its Future of Jobs Report placed complex problem solving at #1 in its top 10 skills for jobs in 2020.
For those who feel ill-prepared for this era, what are the best ways to acquire the needed skills?
Unfortunately, despite an increasing recognition in the business press that problem solving is the core 21 st century skill, our universities and graduate schools rarely teach systematic problem solving or modern team decision making skills. This is starting to change, and we are seeing that in moves by the OECD and Council for Aid to Education (CAE) which administers the College Learning Assessment plus test.
The OECD Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) started testing individual problem solving skills in 2012 and added collaborative problem solving skills in the 2015 assessments. One of the interesting early findings is that to teach students to become better problem solvers involves other capabilities than simply teaching reading, mathematics, and science literacy well. Capabilities such as creativity, logic, and reasoning are essential contributors to students becoming better problem solvers. That is what this book is about.
You share seven steps in your bulletproof problem solving approach. How did you develop it?
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further for application more broadly to personal, social and environmental problems at all scales in later work with the Nature Conservancy, the Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation, the Rhodes Trust and in start-up companies where we are investors.
1: Define the problem.
2: Disaggregate.
3: Prioritize.
4: Workplan.
5: Analyze.
6: Synthesize.
7. Communicate.
Is there one part of it normally missed or not focused on as much as it should be?

What are some of the best methods for overcoming biases in decision making?
The most important biases to address are confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and loss aversion. These are deep seated in our psyches and often reinforced by traditional hierarchies. We use some simple team approaches to fight bias, including perspective-taking (the act of modeling another team member’s assertion or belief to the point that you can describe it as compellingly as the other), role playing (where you act out one side or the other of difficult choice, sometimes in a red team/blue team structure), team distributive voting on analyses and solution paths (one approach we have used is to assign each team member 10 votes, represented by sticky notes, and have each team member use them to vote on their favorite analysis, allowing cumulative or bullet voting, with the most senior person voting last, so as not to bias the choices of more junior members). The most important team norm to encourage is the obligation to dissent, which means every team member is required to verbally contest decisions when they disagree, regardless of seniority.
What do leadership teams most struggle with in the new environment?
The biggest challenge is the speed of change, which pressures all the management approaches we were taught in business school, particularly around planning cycles. The leadership teams that get good at this typically form and re-form cross-functional teams to deploy on issues as they arise, rather than waiting for conventional departmental responses. And they are comfortable using rapid design cycles to prototype and test products/services in the market, rather than depending on traditional marketing analysis.
How will AI impact the bulletproof approach?
We believe good organization problem solving will increasingly utilize advances in artificial intelligence to predict patterns in consumer behavior, disease, credit risk, and other complex phenomena. Machine learning is getting better at pattern recognition than most humans. But that isn’t the whole story. To meet the challenges of the twenty-first century, mental muscle and machine muscle have to work together. Machine learning frees human problem solvers from computational drudgery and amplifies the pattern recognition required for faster organizational response to external challenges. For this partnership to work, twenty-first century organizations need staff who are quick on their feet, who learn new skills quickly, and who attack emerging problems with confidence.
For more information, see BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
Continue Reading
Popular posts.

Learn the important power of prioritizing sleep
Subscribe today and receive a free e-book. Get Your Guide to a Solid Night of Sleep free when you sign up to receive blog updates via email.
Thank you! Please check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
Pin it on pinterest.
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Looked at this way, it's no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. ... I'm a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what ...
Problem solving doesn't have to be a puzzle. August 14, 2021 Knowing how to solve any problem thrown your way is a uniquely valuable skill. The good news is that it's a muscle you can develop and strengthen over time. Revisit several articles on tactics that can help you up your game, diving deeper on: Six problem-solving mindsets for very ...
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn. This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process ...
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process The McKinsey Podcast. How to master the seven-step problem-solving process. The McKinsey Podcast. Management. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges. Episode Website. More Episodes. 2023 McKinsey & Company.
Read more > Listen to the podcast (duration: 25:53) > Structured problem solving can be used to address almost any complex challenge in business or... - Listen to How to master the seven-step problem-solving process by The McKinsey Podcast instantly on your tablet, phone or browser - no downloads needed.
How to master the seven-step problem solving process. Like. Comment. Share. 53 · 2 comments · 1.4K views. McKinsey & Company ... Many would argue that it's problem solving -- that is, the ability to come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Step 1: Define the Problem. The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution won't be easy if the problem is not clearly defined. The problem must be defined in a specific, measurable, and achievable way. One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions.
Problem statements should commence with a question or a firm hypothesis. Be specific, actionable and focus on what the decision maker needs to move forward. Break a problem into component parts so that problems can be divided and allocated. The parts should be MECE. Do it as a team, share with Experts and client to get input and alignment.
In our 2013 classic from the Quarterly, senior partner Olivier Leclerc highlights the value of taking a number of different approaches simultaneously to solve difficult problems. Read on to discover the five flexons, or problem-solving languages, that can be applied to the same problem to generate richer insights and more innovative solutions.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to "solve" the problem. Now the fun starts! There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on. First is top-down.
The important first step is to describe the context and the boundaries of the problem that is agreed upon by those involved in making the decision. A weak problem statement is a common problem. "Rushing into analysis with a vague problem statement is a clear formula for long hours and frustrated clients.". Step Two: Disaggregate the Issues.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving . Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically. Step 1 - Define the problem. First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified.
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process The McKinsey Podcast. How to master the seven-step problem-solving process. The McKinsey Podcast. Management. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges. Episode Website. More Episodes. 2024 McKinsey & Company.
While it might seem like some people are just born with stronger problem-solving skills, there are strategies that anyone can use to improve them.That's righ...
Discover the time-tested 7-step technique to problem solving that top consulting professionals employ; ... This engaging book puts together a McKinsey team's scientific seven-step approach. From taking a problem apart to rearranging its pieces, to framing it so its solution can be seen, the book presents a must-read analysis for executives and ...
Models of organizational effectiveness go in and out of fashion, but the McKinsey 7-S framework has stood the test of time. The model was developed in the late 1970s by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman, former consultants at McKinsey & Company. They identified seven internal elements of an organization that need to align for it to be successful.
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further ...
That's how you persuade the client AND upsell new engagements. TL:DR Use this 7-step McKinsey framework to solve any problem: • Gather Facts. • Build an Issue Tree. • Make the Impact Clear. • Set the Stage with SPQA. • Understand the Big Picture. • Formulate an Initial Hypothesis. • Persuade with Pyramid Principle.
Mckinsey Podcast - How to master the seven-step problem-solving process A great podcast on a seven step process to problem solving. For those practicising case studies, you should listen to the emphasis put on understanding the problem before going into solving it and focussing on levers of which you can control.