
Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation

PhD Defence Process: A Comprehensive Guide

Embarking on the journey toward a PhD is an intellectual odyssey marked by tireless research, countless hours of contemplation, and a fervent commitment to contributing to the body of knowledge in one’s field. As the culmination of this formidable journey, the PhD defence stands as the final frontier, the proverbial bridge between student and scholar.
In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the intricacies of the PhD defence—a momentous occasion that is both a celebration of scholarly achievement and a rigorous evaluation of academic prowess. Join us as we explore the nuances of the defence process, addressing questions about its duration, contemplating the possibility of failure, and delving into the subtle distinctions of language that surround it.
Beyond the formalities, we aim to shed light on the significance of this rite of passage, dispelling misconceptions about its nature. Moreover, we’ll consider the impact of one’s attire on this critical day and share personal experiences and practical tips from those who have successfully navigated the defence journey.
Whether you are on the precipice of your own defence or are simply curious about the process, this guide seeks to demystify the PhD defence, providing a roadmap for success and a nuanced understanding of the pivotal event that marks the transition from student to scholar.
Introduction
A. definition and purpose:, b. overview of the oral examination:, a. general duration of a typical defense, b. factors influencing the duration:, c. preparation and flexibility:, a. preparation and thorough understanding of the research:, b. handling questions effectively:, c. confidence and composure during the presentation:, d. posture of continuous improvement:, a. exploring the possibility of failure:, b. common reasons for failure:, c. steps to mitigate the risk of failure:, d. post-failure resilience:, a. addressing the language variation:, b. conforming to regional preferences:, c. consistency in usage:, d. flexibility and adaptability:, e. navigating language in a globalized academic landscape:, a. debunking myths around the formality of the defense:, b. significance in validating research contributions:, c. post-defense impact:, a. appropriate attire for different settings:, b. professionalism and the impact of appearance:, c. practical tips for dressing success:, b. practical tips for a successful defense:, c. post-defense reflections:, career options after phd.
Embarking on the doctoral journey is a formidable undertaking, where aspiring scholars immerse themselves in the pursuit of knowledge, contributing new insights to their respective fields. At the pinnacle of this academic odyssey lies the PhD defence—a culmination that transcends the boundaries of a mere formality, symbolizing the transformation from a student of a discipline to a recognized contributor to the academic tapestry.
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate.
PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are tested, hypotheses scrutinized, and the depth of scholarly understanding is laid bare.
The importance of the PhD defence reverberates throughout the academic landscape. It is not just a capstone event; it is the juncture where academic rigour meets real-world application. The defence is the litmus test of a researcher’s ability to articulate, defend, and contextualize their work—an evaluation that extends beyond the pages of a dissertation.
Beyond its evaluative nature, the defence serves as a rite of passage, validating the years of dedication, perseverance, and intellectual rigour invested in the research endeavour. Success in the defence is a testament to the candidate’s mastery of their subject matter and the originality and impact of their contributions to the academic community.
Furthermore, a successful defence paves the way for future contributions, positioning the scholar as a recognized authority in their field. The defence is not just an endpoint; it is a launchpad, propelling researchers into the next phase of their academic journey as they continue to shape and redefine the boundaries of knowledge.
In essence, the PhD defence is more than a ceremonial checkpoint—it is a transformative experience that validates the intellectual journey, underscores the significance of scholarly contributions, and sets the stage for a continued legacy of academic excellence. As we navigate the intricacies of this process, we invite you to explore the multifaceted dimensions that make the PhD defence an indispensable chapter in the narrative of academic achievement.
What is a PhD Defence?
At its core, a PhD defence is a rigorous and comprehensive examination that marks the culmination of a doctoral candidate’s research journey. It is an essential component of the doctoral process in which the candidate is required to defend their dissertation before a committee of experts in the field. The defence serves multiple purposes, acting as both a showcase of the candidate’s work and an evaluative measure of their understanding, critical thinking, and contributions to the academic domain.
The primary goals of a PhD defence include:
- Presentation of Research: The candidate presents the key findings, methodology, and significance of their research.
- Demonstration of Mastery: The defence assesses the candidate’s depth of understanding, mastery of the subject matter, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- Critical Examination: Committee members rigorously question the candidate, challenging assumptions, testing methodologies, and probing the boundaries of the research.
- Validation of Originality: The defence validates the originality and contribution of the candidate’s work to the existing body of knowledge.
The PhD defence often takes the form of an oral examination, commonly referred to as the viva voce. This oral component adds a dynamic and interactive dimension to the evaluation process. Key elements of the oral examination include:
- Presentation: The candidate typically begins with a formal presentation, summarizing the dissertation’s main components, methodology, and findings. This presentation is an opportunity to showcase the significance and novelty of the research.
- Questioning and Discussion: Following the presentation, the candidate engages in a thorough questioning session with the examination committee. Committee members explore various aspects of the research, challenging the candidates to articulate their rationale, defend their conclusions, and respond to critiques.
- Defence of Methodology: The candidate is often required to defend the chosen research methodology, demonstrating its appropriateness, rigour, and contribution to the field.
- Evaluation of Contributions: Committee members assess the originality and impact of the candidate’s contributions to the academic discipline, seeking to understand how the research advances existing knowledge.
The oral examination is not a mere formality; it is a dynamic exchange that tests the candidate’s intellectual acumen, research skills, and capacity to contribute meaningfully to the scholarly community.
In essence, the PhD defence is a comprehensive and interactive evaluation that encapsulates the essence of a candidate’s research journey, demanding a synthesis of knowledge, clarity of expression, and the ability to navigate the complexities of academic inquiry. As we delve into the specifics of the defence process, we will unravel the layers of preparation and skill required to navigate this transformative academic milestone.
How Long is a PhD Defence?
The duration of a PhD defence can vary widely, but it typically ranges from two to three hours. This time frame encompasses the candidate’s presentation of their research, questioning and discussions with the examination committee, and any additional deliberations or decisions by the committee. However, it’s essential to note that this is a general guideline, and actual defence durations may vary based on numerous factors.
- Sciences and Engineering: Defenses in these fields might lean towards the shorter end of the spectrum, often around two hours. The focus is often on the methodology, results, and technical aspects.
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Given the theoretical and interpretive nature of research in these fields, defences might extend closer to three hours or more. Discussions may delve into philosophical underpinnings and nuanced interpretations.
- Simple vs. Complex Studies: The complexity of the research itself plays a role. Elaborate experiments, extensive datasets, or intricate theoretical frameworks may necessitate a more extended defence.
- Number of Committee Members: A larger committee or one with diverse expertise may lead to more extensive discussions and varied perspectives, potentially elongating the defence.
- Committee Engagement: The level of engagement and probing by committee members can influence the overall duration. In-depth discussions or debates may extend the defence time.
- Cultural Norms: In some countries, the oral defence might be more ceremonial, with less emphasis on intense questioning. In others, a rigorous and extended defence might be the norm.
- Evaluation Practices: Different academic systems have varying evaluation criteria, which can impact the duration of the defence.
- Institutional Guidelines: Some institutions may have specific guidelines on defence durations, influencing the overall time allotted for the process.
Candidates should be well-prepared for a defence of any duration. Adequate preparation not only involves a concise presentation of the research but also anticipates potential questions and engages in thoughtful discussions. Additionally, candidates should be flexible and responsive to the dynamics of the defense, adapting to the pace set by the committee.
Success Factors in a PhD Defence
- Successful defence begins with a deep and comprehensive understanding of the research. Candidates should be well-versed in every aspect of their study, from the theoretical framework to the methodology and findings.
- Thorough preparation involves anticipating potential questions from the examination committee. Candidates should consider the strengths and limitations of their research and be ready to address queries related to methodology, data analysis, and theoretical underpinnings.
- Conducting mock defences with peers or mentors can be invaluable. It helps refine the presentation, exposes potential areas of weakness, and provides an opportunity to practice responding to challenging questions.
- Actively listen to questions without interruption. Understanding the nuances of each question is crucial for providing precise and relevant responses.
- Responses should be clear, concise, and directly address the question. Avoid unnecessary jargon, and strive to convey complex concepts in a manner that is accessible to the entire committee.
- It’s acceptable not to have all the answers. If faced with a question that stumps you, acknowledge it honestly. Expressing a willingness to explore the topic further demonstrates intellectual humility.
- Use questions as opportunities to reinforce key messages from the research. Skillfully link responses back to the core contributions of the study, emphasizing its significance.
- Rehearse the presentation multiple times to build familiarity with the material. This enhances confidence, reduces nervousness, and ensures a smooth and engaging delivery.
- Maintain confident and open body language. Stand tall, make eye contact, and use gestures judiciously. A composed demeanour contributes to a positive impression.
- Acknowledge and manage nervousness. It’s natural to feel some anxiety, but channelling that energy into enthusiasm for presenting your research can turn nervousness into a positive force.
- Engage with the committee through a dynamic and interactive presentation. Invite questions during the presentation to create a more conversational atmosphere.
- Utilize visual aids effectively. Slides or other visual elements should complement the spoken presentation, reinforcing key points without overwhelming the audience.
- View the defence not only as an evaluation but also as an opportunity for continuous improvement. Feedback received during the defence can inform future research endeavours and scholarly pursuits.
In essence, success in a PhD defence hinges on meticulous preparation, adept handling of questions, and projecting confidence and composure during the presentation. A well-prepared and resilient candidate is better positioned to navigate the challenges of the defence, transforming it from a moment of evaluation into an affirmation of scholarly achievement.
Failure in PhD Defence
- While the prospect of failing a PhD defence is relatively rare, it’s essential for candidates to acknowledge that the possibility exists. Understanding this reality can motivate diligent preparation and a proactive approach to mitigate potential risks.
- Failure, if it occurs, should be seen as a learning opportunity rather than a definitive endpoint. It may highlight areas for improvement and offer insights into refining the research and presentation.
- Lack of thorough preparation, including a weak grasp of the research content, inadequate rehearsal, and failure to anticipate potential questions, can contribute to failure.
- Inability to effectively defend the chosen research methodology, including justifying its appropriateness and demonstrating its rigour, can be a critical factor.
- Failing to clearly articulate the original contributions of the research and its significance to the field may lead to a negative assessment.
- Responding defensively to questions, exhibiting a lack of openness to critique, or being unwilling to acknowledge limitations can impact the overall impression.
- Inability to address committee concerns or incorporate constructive feedback received during the defense may contribute to a negative outcome.
- Comprehensive preparation is the cornerstone of success. Candidates should dedicate ample time to understanding every facet of their research, conducting mock defences, and seeking feedback.
- Identify potential weaknesses in the research and address them proactively. Being aware of limitations and articulating plans for addressing them in future work demonstrates foresight.
- Engage with mentors, peers, or advisors before the defence. Solicit constructive feedback on both the content and delivery of the presentation to refine and strengthen the defence.
- Develop strategies to manage stress and nervousness. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, or visualization can be effective in maintaining composure during the defence.
- Conduct a pre-defense review of all materials, ensuring that the presentation aligns with the dissertation and that visual aids are clear and supportive.
- Approach the defence with an open and reflective attitude. Embrace critique as an opportunity for improvement rather than as a personal affront.
- Clarify expectations with the examination committee beforehand. Understanding the committee’s focus areas and preferences can guide preparation efforts.
- In the event of failure, candidates should approach the situation with resilience. Seek feedback from the committee, understand the reasons for the outcome, and use the experience as a springboard for improvement.
In summary, while the prospect of failing a PhD defence is uncommon, acknowledging its possibility and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks are crucial elements of a well-rounded defence strategy. By addressing common failure factors through thorough preparation, openness to critique, and a resilient attitude, candidates can increase their chances of a successful defence outcome.
PhD Defense or Defence?
- The choice between “defense” and “defence” is primarily a matter of British English versus American English spelling conventions. “Defense” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “defence” is the British English spelling.
- In the global academic community, both spellings are generally understood and accepted. However, the choice of spelling may be influenced by the academic institution’s language conventions or the preferences of individual scholars.
- Academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding language conventions, and candidates are often expected to adhere to the institution’s preferred spelling.
- Candidates may also consider the preferences of their advisors or committee members. If there is a consistent spelling convention used within the academic department, it is advisable to align with those preferences.
- Consideration should be given to the spelling conventions of scholarly journals in the candidate’s field. If intending to publish research stemming from the dissertation, aligning with the conventions of target journals is prudent.
- If the defense presentation or dissertation will be shared with an international audience, using a more universally recognized spelling (such as “defense”) may be preferred to ensure clarity and accessibility.
- Regardless of the chosen spelling, it’s crucial to maintain consistency throughout the document. Mixing spellings can distract from the content and may be perceived as an oversight.
- In oral presentations and written correspondence related to the defence, including emails, it’s advisable to maintain consistency with the chosen spelling to present a professional and polished image.
- Recognizing that language conventions can vary, candidates should approach the choice of spelling with flexibility. Being adaptable to the preferences of the academic context and demonstrating an awareness of regional variations reflects a nuanced understanding of language usage.
- With the increasing globalization of academia, an awareness of language variations becomes essential. Scholars often collaborate across borders, and an inclusive approach to language conventions contributes to effective communication and collaboration.
In summary, the choice between “PhD defense” and “PhD defence” boils down to regional language conventions and institutional preferences. Maintaining consistency, being mindful of the target audience, and adapting to the expectations of the academic community contribute to a polished and professional presentation, whether in written documents or oral defences.
Is PhD Defense a Formality?
- While the PhD defence is a structured and ritualistic event, it is far from being a mere formality. It is a critical and substantive part of the doctoral journey, designed to rigorously evaluate the candidate’s research contributions, understanding of the field, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- The defence is not a checkbox to be marked but rather a dynamic process where the candidate’s research is evaluated for its scholarly merit. The committee scrutinizes the originality, significance, and methodology of the research, aiming to ensure it meets the standards of advanced academic work.
- Far from a passive or purely ceremonial event, the defence involves active engagement between the candidate and the examination committee. Questions, discussions, and debates are integral components that enrich the scholarly exchange during the defence.
- The defence serves as a platform for the candidate to demonstrate the originality of their research. Committee members assess the novelty of the contributions, ensuring that the work adds value to the existing body of knowledge.
- Beyond the content, the defence evaluates the methodological rigour of the research. Committee members assess whether the chosen methodology is appropriate, well-executed, and contributes to the validity of the findings.
- Successful completion of the defence affirms the candidate’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the academic discourse in their field. It is an endorsement of the candidate’s position as a knowledgeable and respected scholar.
- The defence process acts as a quality assurance mechanism in academia. It ensures that individuals awarded a doctoral degree have undergone a thorough and rigorous evaluation, upholding the standards of excellence in research and scholarly inquiry.
- Institutions have specific criteria and standards for awarding a PhD. The defence process aligns with these institutional and academic standards, providing a consistent and transparent mechanism for evaluating candidates.
- Successful completion of the defence is a pivotal moment that marks the transition from a doctoral candidate to a recognized scholar. It opens doors to further contributions, collaborations, and opportunities within the academic community.
- Research presented during the defence often forms the basis for future publications. The validation received in the defence enhances the credibility of the research, facilitating its dissemination and impact within the academic community.
- Beyond the academic realm, a successfully defended PhD is a key credential for professional advancement. It enhances one’s standing in the broader professional landscape, opening doors to research positions, teaching opportunities, and leadership roles.
In essence, the PhD defence is a rigorous and meaningful process that goes beyond formalities, playing a crucial role in affirming the academic merit of a candidate’s research and marking the culmination of their journey toward scholarly recognition.
Dressing for Success: PhD Defense Outfit
- For Men: A well-fitted suit in neutral colours (black, navy, grey), a collared dress shirt, a tie, and formal dress shoes.
- For Women: A tailored suit, a blouse or button-down shirt, and closed-toe dress shoes.
- Dress codes can vary based on cultural expectations. It’s advisable to be aware of any cultural nuances within the academic institution and to adapt attire accordingly.
- With the rise of virtual defenses, considerations for attire remain relevant. Even in online settings, dressing professionally contributes to a polished and serious demeanor. Virtual attire can mirror what one would wear in-person, focusing on the upper body visible on camera.
- The attire chosen for a PhD defense contributes to the first impression that a candidate makes on the examination committee. A professional and polished appearance sets a positive tone for the defense.
- Dressing appropriately reflects respect for the gravity of the occasion. It acknowledges the significance of the defense as a formal evaluation of one’s scholarly contributions.
- Wearing professional attire can contribute to a boost in confidence. When individuals feel well-dressed and put-together, it can positively impact their mindset and overall presentation.
- The PhD defense is a serious academic event, and dressing professionally fosters an atmosphere of seriousness and commitment to the scholarly process. It aligns with the respect one accords to academic traditions.
- Institutional norms may influence dress expectations. Some academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding attire for formal events, and candidates should be aware of and adhere to these norms.
- While adhering to the formality expected in academic settings, individuals can also express their personal style within the bounds of professionalism. It’s about finding a balance between institutional expectations and personal comfort.
- Select and prepare the outfit well in advance to avoid last-minute stress. Ensure that the attire is clean, well-ironed, and in good condition.
- Accessories such as ties, scarves, or jewelry should complement the outfit. However, it’s advisable to keep accessories subtle to maintain a professional appearance.
- While dressing professionally, prioritize comfort. PhD defenses can be mentally demanding, and comfortable attire can contribute to a more confident and composed demeanor.
- Pay attention to grooming, including personal hygiene and haircare. A well-groomed appearance contributes to an overall polished look.
- Start preparation well in advance of the defense date. Know your research inside out, anticipate potential questions, and be ready to discuss the nuances of your methodology, findings, and contributions.
- Conduct mock defenses with peers, mentors, or colleagues. Mock defenses provide an opportunity to receive constructive feedback, practice responses to potential questions, and refine your presentation.
- Strike a balance between confidence and humility. Confidence in presenting your research is essential, but being open to acknowledging limitations and areas for improvement demonstrates intellectual honesty.
- Actively engage with the examination committee during the defense. Listen carefully to questions, respond thoughtfully, and view the defense as a scholarly exchange rather than a mere formality.
- Understand the expertise and backgrounds of the committee members. Tailor your presentation and responses to align with the interests and expectations of your specific audience.
- Practice time management during your presentation. Ensure that you allocate sufficient time to cover key aspects of your research, leaving ample time for questions and discussions.
- It’s normal to feel nervous, but practicing mindfulness and staying calm under pressure is crucial. Take deep breaths, maintain eye contact, and focus on delivering a clear and composed presentation.
- Have a plan for post-defense activities. Whether it’s revisions to the dissertation, publications, or future research endeavors, having a roadmap for what comes next demonstrates foresight and commitment to ongoing scholarly contributions.
- After successfully defending, individuals often emphasize the importance of taking time to reflect on the entire doctoral journey. Acknowledge personal and academic growth, celebrate achievements, and use the experience to inform future scholarly pursuits.
In summary, learning from the experiences of others who have successfully defended offers a wealth of practical wisdom. These insights, combined with thoughtful preparation and a proactive approach, contribute to a successful and fulfilling defense experience.
You have plenty of career options after completing a PhD. For more details, visit my blog posts:
7 Essential Steps for Building a Robust Research Portfolio
Exciting Career Opportunities for PhD Researchers and Research Scholars
Freelance Writing or Editing Opportunities for Researchers A Comprehensive Guide
Research Consultancy: An Alternate Career for Researchers
The Insider’s Guide to Becoming a Patent Agent: Opportunities, Requirements, and Challenges
The journey from a curious researcher to a recognized scholar culminates in the PhD defence—an intellectual odyssey marked by dedication, resilience, and a relentless pursuit of knowledge. As we navigate the intricacies of this pivotal event, it becomes evident that the PhD defence is far more than a ceremonial rite; it is a substantive evaluation that validates the contributions of a researcher to the academic landscape.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- How to End Your Academic/Research Internship?
- PhD or Industry Job? A Comprehensive Career Guide
- Post Doc Positions in India
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com


- PhD Viva Voces – A Complete Guide
- Doing a PhD
- A PhD viva involves defending your thesis in an oral examination with at least two examiners.
- The aim of a PhD viva is to confirm that the work is your own , that you have a deep understanding of your project and, overall, that you are a competent researcher .
- There are no standard durations, but they usually range from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours .
- There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) downgrade to MPhil with no amendments, (5) downgrade to MPhil subject to amendments, (6) immediate fail.
- Almost all students who sit their viva pass it, with the most common outcome being ‘(2) – pass subject to minor corrections’.
What Is a PhD Viva?
A viva voce , more commonly referred to as ‘viva’, is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student’s knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners.
In order to assess the student and their work around their research question, a viva sets out to determine:
- you understand the ideas and theories that you have put forward,
- you can answer questions about elements of your work that the examiners have questions about,
- you understand the broader research in your field and how your work contributes to this,
- you are aware of the limitations of your work and understand how it can be developed further,
- your work makes an original contribution, is your own and has not been plagiarised.
Note: A viva is a compulsory procedure for all PhD students, with the only exception being when a PhD is obtained through publication as opposed to the conventional route of study.
Who Will Attend a Viva?
In the UK, at least two examiners must take part in all vivas. Although you could have more than two examiners, most will not in an attempt to facilitate a smoother questioning process.
One of the two examiners will be internal, i.e. from your university, and the other will be external, i.e. from another university. Regardless, both will be knowledgeable in your research field and have read your thesis beforehand.
In addition to your two examiners, two other people may be present. The first is a chairperson. This is an individual who will be responsible for monitoring the interview and for ensuring proper conduct is followed at all times. The need for an external chairperson will vary between universities, as one of the examiners can also take on this role. The second is your supervisor, whose attendance is decided upon by you in agreement with your examiners. If your supervisor attends, they are prohibited from asking questions or from influencing the outcome of the viva.
To avoid any misunderstandings, we have summarised the above in a table:
Note: In some countries, such as in the United States, a viva is known as a ‘PhD defense’ and is performed publicly in front of a panel or board of examiners and an open audience. In these situations, the student presents their work in the form of a lecture and then faces questions from the examiners and audience which almost acts as a critical appraisal.
How Long Does a Viva Last?
Since all universities have different guidelines , and since all PhDs are unique, there are no standard durations. Typically, however, the duration ranges from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours.
Your examiners will also influence the duration of your viva as some will favour a lengthy discussion, while others may not. Usually, your university will consult your examiners in advance and notify you of the likely duration closer to the day of your viva.
What Happens During a Viva?
Regardless of the subject area, all PhD vivas follow the same examination process format as below.
Introductions
You will introduce yourselves to each other, with the internal examiner normally introducing the external examiner. If an external chairperson is present, they too are introduced; otherwise, this role will be assumed by one of the examiners.
Procedure Explained
After the introductions, the appointed chair will explain the viva process. Although it should already be known to everyone, it will be repeated to ensure the viva remains on track during the forthcoming discussion.
Warm-Up Questions
The examiners will then begin the questioning process. This usually starts with a few simple opening questions, such as asking you to summarise your PhD thesis and what motivated you to carry out the research project.
In-Depth Questions
The viva questions will then naturally increase in difficulty as the examiners go further into the details of your thesis. These may include questions such as “What was the most critical decision you made when determining your research methodology ?”, “Do your findings agree with the current published work?” and “How do your findings impact existing theories or literature? ”. In addition to asking open-ended questions, they will also ask specific questions about the methodology, results and analysis on which your thesis is based.
Closing the Viva
Once the examiners are satisfied that they have thoroughly evaluated your knowledge and thesis, they will invite you to ask any questions you may have, and then bring the oral examination to a close.
What Happens After the Viva?
Once your viva has officially ended, your examiners will ask you to leave the room so that they can discuss your performance. Once a mutual agreement has been reached, which can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour, you will be invited back inside and informed of your outcome.
PhD Viva Outcomes
There are six possible outcomes to a viva:
- Immediate award of degree: A rare recommendation – congratulations, you are one of the few people who completely satisfied your examiners the first time around. You do not have to do anything further at this point.
- Minor amendments required: The most common recommendation – you obtain a pass on the condition that you make a number of minor amendments to your thesis, such as clarifying certain points and correcting grammatical errors. The time you have to make these changes depends on the number of them, but is usually one to six months.
- Major amendments required: A somewhat uncommon recommendation – you are requested to make major amendments to your thesis, ranging from further research to collecting more data or rewriting entire sections. Again, the time you have to complete this will depend on the number of changes required, but will usually be six months to one year. You will be awarded your degree once your amended thesis has been reviewed and accepted.
- Immediate award of MPhil: An uncommon recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree but meets the standard for an MPhil (Master of Philosophy), a lower Master’s degree.
- Amendments required for MPhil: A rare recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree, but with several amendments will meet the standard for an MPhil.
- Immediate fail: A very rare recommendation – you are given an immediate fail without the ability to resubmit and without entitlement to an MPhil.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Is the Pass Rate for Vivas?
Based on an analysis of 26,076 PhD students who took their viva exam between 2006 and 2017, the PhD viva pass rate in the UK is 96%; of those who passed, about 80% were required to make minor amendments to their thesis. The reason for this high pass rate is that supervisors will only put their students forward for a viva once they confidently believe they are ready for it. As a result, most candidates who sit a viva are already well-versed in their PhD topic before they even start preparing for the exam.
How Do I Arrange a Viva?
Your viva will be arranged either by the examiners or by the chairperson. The viva will be arranged at least one to two months after you have submitted your thesis and will arrange a viva date and venue that is suitable for all participants.
Can I Choose My Examiners?
At most universities, you and your supervisor will choose the internal and external examiners yourselves. This is because the examiners must have extensive knowledge of the thesis topic in order to be able to examine you and, as the author of the thesis in question, who else could better determine who they might be than you and your supervisor. The internal examiner is usually quite easy to find given they will be from your institution, but the external examiner may end up being your second or third preference depending on availability.
Can I Take Notes Into a Viva?
A viva is about testing your competence, not your memory. As such, you are allowed to take notes and other supporting material in with you. However, keep in mind that your examiners will not be overly impressed if you constantly have to refer to your notes to answer each question. Because of this, many students prefer to take an annotated copy of their thesis, with important points already highlighted and key chapters marked with post-it notes.
In addition to an annotated copy of a thesis, some students also take:
- a list of questions they would like to ask the examiners,
- notes that were created during their preparation,
- a list of minor corrections they have already identified from their viva prep work.
How Do I Prepare for a PhD Viva?
There are several ways to prepare for a PhD viva, one of the most effective being a mock viva voce examination . This allows you to familiarise yourself with the type of viva questions you will be asked and identify any weak areas you need to improve. They also give you the opportunity to practise without the pressure, giving you more time to think about your answers which will help to make sure that you know your thesis inside out. However, a mock viva exam is just one of many methods available to you – some of the other viva preparation methods can be found on our “ How to Prepare for a PhD Viva ” page.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Evaluation Decisions for Doctoral Defense
Doctoral students are required to review the degree plans for their program, along with information about specific degree requirements and estimated timelines to reach various benchmarks for the different degree plan specializations.
There are three possible evaluation decisions for the doctoral defense. All decisions—with the exception of “fail”—must be unanimous.
“Pass” requires that both the defense and the document (dissertation or treatise) are acceptable. In some cases, the committee may require revisions, which will be checked by the entire committee or by the supervising professor only. This should be agreed upon at the time of the defense and communicated with the student.
While the supervisor should wait to sign the Report of Dissertation Committee until all revisions have been reviewed, the other committee members may choose to sign at the defense. The committee should agree upon the length of time allowed for submission of the revised dissertation; this must be communicated clearly to the student.
The completed Report of Dissertation Committee should be returned to the Graduate School only after the final revisions to the dissertation have been approved and the GSC designee has signed.
If the dissertation and/or defense are not acceptable to all members of the committee, the decision will change to either "re-defend" or "fail" as discussed below:
“Re-defend” indicates that the committee is not satisfied with the dissertation or with the oral examination, but believes that rewriting may make it acceptable. In this case, the fully signed Report of Dissertation Committee should be returned to the Graduate School by the Supervisor, with each member of the committee indicating their decision. Another scheduled defense will be required and a new report will be generated.
Report on Doctoral Dissertation forms
Committee members should submit their individual Report on Doctoral Dissertation forms indicating their dissatisfaction.
“Fail” indicates that at least one member of the committee has decided that the dissertation is unsatisfactory and may not be rewritten. The fully signed Report of Dissertation Committee should be returned to the Graduate School by the supervisor, with each member of the committee indicating their decision.
Committee members should also submit their individual Report on Doctoral Dissertation forms indicating their dissatisfaction. This decision normally results in the termination of a doctoral student’s program.
Documentation
Document a dissertation defense as follows:
The supervisor should bring the Report of Dissertation Committee to the defense.
The scheduling information on the Report must be correct; if the time or location changes, the Graduate School must be informed.
All committee members sign the Report of Dissertation Committee, even if the member was not present at the defense.
Scanned or electronic signatures will be accepted as long as they are legible and dark enough to be imaged. Typed names as a signature are not allowed. Electronic and digitally authorized signatures may be accepted in any font format so long as they include the insignia or logo of the e-signature software used showing authorization.
Once all members have signed the report the Graduate Studies Committee chair or designee should provide the final signature.
The final signature indicates that all coursework and other departmental requirements have been completed. All signatures should be on a single page.
The Report of Dissertation Committee should be submitted to the Graduate School by the student.
The report should be submitted along with the student's final paperwork.
Preparing for your PhD thesis defence
As you start thinking about the end stages of your PhD, it’s important to understand the processes and timelines related to the thesis defence so that your degree completion is not delayed. Even if your thesis defence seems far away, there are several planning considerations you can consider early on to help the end stages of your PhD go smoothly.
On this page you will find videos, tools, and information about what the PhD thesis defence is , timelines for the PhD thesis defence , and tips for a successful PhD thesis defence .
All PhD students should also ensure that they read the PhD thesis examination regulations and review the thesis preparation guidelines prior to their oral defence. If your thesis defence will be conducted remotely, you should also review the process for a remote thesis defence .
What is the PhD defence?
Understanding the purpose, processes and possible outcomes of the thesis defence can help you feel more prepared for the defence itself. In this video, you’ll learn about what the defence is, who’s there, what happens, and the deliberation and range of possible outcomes.
Transcript - Demystifying the thesis defence at University of Waterloo (PDF)
You may wish to learn more about some of the topics discussed in this video. Here are some helpful links to learn more:
Examination committee members (including the external examiner): Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on the PhD thesis examining committee for more information about the committee members, including information about the external examiner and conflicts of interest.
- Closed thesis defences and non-disclosure agreements: Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on guidelines for thesis examination without public disclosure for more information about closed thesis examinations.
- Thesis defence decisions and outcomes: Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on decisions for additional information about decisions and outcomes.
- Thesis submission: Visit the thesis submission webpage for information about the thesis submission process, including approvals that must be obtained before submitting your thesis.
- UWSpace: Visit the Library’s UWSpace webpage for information about what UWSpace is and how to submit, or deposit, your thesis to UWSpace.
Timeline to defence
Early planning considerations.
Well before your defence date, there are several considerations to think about that can help make the end stages of your degree go smoothly and ensure your defence date and degree completion are not delayed:
- Being aware of formatting requirements will save you time on revisions later on – the last thing you want to be doing before submitting your thesis to UWSpace is updating page numbers or your table of contents! Consider using the Microsoft Word or LaTeX thesis template produced by Information Systems & Technology.
- The Dissertation Boot Camp can help you develop effective writing practices and strategies for completing your thesis, while the three-part Rock Your Thesis workshop series will provide practical guidance for planning, writing, revising, and submitting your thesis project. You can also book an individual appointment to do backwards planning with an advisor. They can help you utilize the planning tools most effectively, while providing hands-on guidance and feedback.
- If you are using third-party content, including your own previously published work in your thesis, or seeking intellectual property protection (for yourself or another involved party), there may be implications for your thesis or defence. Learn more about copyright for your thesis , and email [email protected] for help with copyright questions related to your thesis.
- Depending on your departmental or discipline’s norms, you may require approval from your entire committee, or just your supervisor. Ensure you talk with your supervisor and/or committee early on to confirm processes and timelines, so you’re not surprised later.
- Depending on your departmental or discipline’s norms, your supervisor may select an external examiner themselves, or they may seek your input. Talk to your supervisor early on about this process, as in some faculties the external examiner may need to be vetted and approved as early as the term before you wish to defend. Remember that there are conflict of interest guidelines around the appointment of the external examiner , and the PhD candidate should not be in communication with the external examiner prior to the defence.
- A PhD thesis must be on display for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to the defence date. To accommodate, you may need to submit your thesis as early as 6-8 weeks prior to your defence. Review your faculty specific backwards planning tool for the thesis submission deadline in your faculty and learn more about the display period in the PhD thesis examination regulations.
- After your successful thesis defence, you will likely have some required revisions to your thesis. It’s important to understand revision timelines , especially if you’re hoping to become “degree complete” before a tuition refund or convocation deadline. Find tuition refund and convocation deadlines in the important dates calendar .
- Following your thesis defence, there are several steps to be taken before your final, approved thesis is accepted in UWSpace. Ensure that you’re aware of these thesis submission steps and timelines in advance.
Backwards planning tools
Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs, in collaboration with the Faculties, have prepared faculty specific backwards planning tools to help PhD candidates map out the timelines related to their thesis defence and degree completion.
Select your faculty below to download a PDF copy of the backwards planning tool. We encourage you to discuss your ideal timelines with your supervisor(s) and your department graduate program co-ordinator.
- Faculty of Health backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Arts backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Engineering backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Environment backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Mathematics backwards planning tool (PDF)
- Faculty of Science backwards planning tool (PDF)
Tips for success
The PhD thesis defence is the culmination of years of hard work! The tips outlined in this video, compiled from recent PhD graduates and experienced thesis defence chairs, cover tips for preparing for your defence, day-of logistics, and defending successfully.
Transcript - Your Thesis Defence: Tips for Success (PDF)
Will your PhD thesis defence be held remotely? We’ve compiled additional tips for success specifically related to the remote defence.

Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA)
Needles Hall, second floor, room 2201
Graduate Studies Academic Calendar
Website feedback
- Contact Waterloo
- Maps & Directions
- Accessibility
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations .

13 Tips to Prepare for Your PhD Dissertation Defense
How well do you know your project? Years of experiments, analysis of results, and tons of literature study, leads you to how well you know your research study. And, PhD dissertation defense is a finale to your PhD years. Often, researchers question how to excel at their thesis defense and spend countless hours on it. Days, weeks, months, and probably years of practice to complete your doctorate, needs to surpass the dissertation defense hurdle.
In this article, we will discuss details of how to excel at PhD dissertation defense and list down some interesting tips to prepare for your thesis defense.
Table of Contents
What Is Dissertation Defense?
Dissertation defense or Thesis defense is an opportunity to defend your research study amidst the academic professionals who will evaluate of your academic work. While a thesis defense can sometimes be like a cross-examination session, but in reality you need not fear the thesis defense process and be well prepared.
Source: https://www.youtube.com/c/JamesHaytonPhDacademy
What are the expectations of committee members.
Choosing the dissertation committee is one of the most important decision for a research student. However, putting your dissertation committee becomes easier once you understand the expectations of committee members.
The basic function of your dissertation committee is to guide you through the process of proposing, writing, and revising your dissertation. Moreover, the committee members serve as mentors, giving constructive feedback on your writing and research, also guiding your revision efforts.
The dissertation committee is usually formed once the academic coursework is completed. Furthermore, by the time you begin your dissertation research, you get acquainted to the faculty members who will serve on your dissertation committee. Ultimately, who serves on your dissertation committee depends upon you.
Some universities allow an outside expert (a former professor or academic mentor) to serve on your committee. It is advisable to choose a faculty member who knows you and your research work.
How to Choose a Dissertation Committee Member?
- Avoid popular and eminent faculty member
- Choose the one you know very well and can approach whenever you need them
- A faculty member whom you can learn from is apt.
- Members of the committee can be your future mentors, co-authors, and research collaborators. Choose them keeping your future in mind.
How to Prepare for Dissertation Defense?

1. Start Your Preparations Early
Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months’ exercise. Don’t wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted.
2. Attend Presentations by Other Candidates
Look out for open dissertation presentations at your university. In fact, you can attend open dissertation presentations at other universities too. Firstly, this will help you realize how thesis defense is not a scary process. Secondly, you will get the tricks and hacks on how other researchers are defending their thesis. Finally, you will understand why dissertation defense is necessary for the university, as well as the scientific community.
3. Take Enough Time to Prepare the Slides
Dissertation defense process harder than submitting your thesis well before the deadline. Ideally, you could start preparing the slides after finalizing your thesis. Spend more time in preparing the slides. Make sure you got the right data on the slides and rephrase your inferences, to create a logical flow to your presentation.
4. Structure the Presentation
Do not be haphazard in designing your presentation. Take time to create a good structured presentation. Furthermore, create high-quality slides which impresses the committee members. Make slides that hold your audience’s attention. Keep the presentation thorough and accurate, and use smart art to create better slides.
5. Practice Breathing Techniques
Watch a few TED talk videos and you will notice that speakers and orators are very fluent at their speech. In fact, you will not notice them taking a breath or falling short of breath. The only reason behind such effortless oratory skill is practice — practice in breathing technique.
Moreover, every speaker knows how to control their breath. Long and steady breaths are crucial. Pay attention to your breathing and slow it down. All you need I some practice prior to this moment.
6. Create an Impactful Introduction
The audience expects a lot from you. So your opening statement should enthrall the audience. Furthermore, your thesis should create an impact on the members; they should be thrilled by your thesis and the way you expose it.
The introduction answers most important questions, and most important of all “Is this presentation worth the time?” Therefore, it is important to make a good first impression , because the first few minutes sets the tone for your entire presentation.
7. Maintain Your Own List of Questions
While preparing for the presentation, make a note of all the questions that you ask yourself. Try to approach all the questions from a reader’s point of view. You could pretend like you do not know the topic and think of questions that could help you know the topic much better.
The list of questions will prepare you for the questions the members may pose while trying to understand your research. Attending other candidates’ open discussion will also help you assume the dissertation defense questions.
8. Practice Speech and Body Language
After successfully preparing your slides and practicing, you could start focusing on how you look while presenting your thesis. This exercise is not for your appearance but to know your body language and relax if need be.
Pay attention to your body language. Stand with your back straight, but relax your shoulders. The correct posture will give you the feel of self-confidence. So, observe yourself in the mirror and pay attention to movements you make.
9. Give Mock Presentation
Giving a trial defense in advance is a good practice. The most important factor for the mock defense is its similarity to your real defense, so that you get the experience that prepares for the actual defense.
10. Learn How to Handle Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes. However, it is important to carry on. Do not let the mistakes affect your thesis defense. Take a deep breath and move on to the next point.
11. Do Not Run Through the Presentation
If you are nervous, you would want to end the presentation as soon as possible. However, this situation will give rise to anxiety and you will speak too fast, skipping the essential details. Eventually, creating a fiasco of your dissertation defense .
12. Get Plenty of Rest
Out of the dissertation defense preparation points, this one is extremely important. Obviously, sleeping a day before your big event is hard, but you have to focus and go to bed early, with the clear intentions of getting the rest you deserve.
13. Visualize Yourself Defending Your Thesis
This simple exercise creates an immense impact on your self-confidence. All you have to do is visualize yourself giving a successful presentation each evening before going to sleep. Everyday till the day of your thesis defense, see yourself standing in front of the audience and going from one point to another.
This exercise takes a lot of commitment and persistence, but the results in the end are worth it. Visualization makes you see yourself doing the scary thing of defending your thesis.
If you have taken all these points into consideration, you are ready for your big day. You have worked relentlessly for your PhD degree , and you will definitely give your best in this final step.
Have you completed your thesis defense? How did you prepare for it and how was your experience throughout your dissertation defense ? Do write to us or comment below.
The tips are very useful.I will recomend it to our students.
Excellent. As a therapist trying to help a parent of a candidate, I am very impressed and thankful your concise, clear, action-oriented article. Thank you.
Thanks for your sharing. It is so good. I can learn a lot from your ideas. Hope that in my dissertation defense next time I can pass
The tips are effective. Will definitely apply them in my dissertation.
My dissertation defense is coming up in less than two weeks from now, I find this tips quite instructive, I’ll definitely apply them. Thank you so much.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

- About the LSE Impact Blog
- Comments Policy
- Popular Posts
- Recent Posts
- Subscribe to the Impact Blog
- Write for us
- LSE comment
Eva Lantsoght
November 30th, 2021, defending a phd thesis is an emotional moment candidates and supervisors should be prepared for.
4 comments | 55 shares
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
The PhD defence, or viva, is significant academic rite of passage, which as well as marking the culmination of years of study, can also be a highly charged emotional moment. Drawing on years of collecting accounts of PhD defences on her blog and her recent book (Planning and Passing Your PhD Defence, co-authored with Olga Degtyareva), Eva Lantsoght , discusses how both PhD students and supervisors can benefit from a more engaged understanding of the emotions underlying the PhD defence.
In the days leading up to my doctoral defence, I had a recurring nightmare about my supervisor forgetting to show up for my defence. I was well-prepared, and since I was defending in the Netherlands, my thesis was already printed and approved. Failing was virtually impossible. Why then, was I nervous about my doctoral defence to the point of having recurring nightmares?
After eventually passing my doctoral defence, I decided to collect stories about the doctoral defence (or viva, depending on the country) around the world for my blog. I was originally fascinated by the differences between defence formats (such as the sword newly minted doctors receive in Finland and the medal in Chile ). Over time, however, I started to see that below the superficial differences, all types of defence show similarities. One is that there is always an emotional dimension to the defence. My worries before my defence were hardly an isolated case. Many doctoral candidates report strong emotions around thesis submission, in the weeks leading up to the defence, during the event, and even afterwards, when the post-defence blues may kick in.
Typically, discussions on the doctoral defence centre around the scholarly dimension. A defence is often viewed solely as an academic event marking and evaluating the end of a research project
Typically, discussions on the doctoral defence centre around the scholarly dimension. A defence is often viewed solely as an academic event marking and evaluating the end of a research project. However, in our recent book Planning and Passing Your PhD Defence , which I co-wrote with Olga Degtyareva, we have paid special attention to the emotional dimension of the defence (of course, in addition to the scholarly dimension preparing for answering questions, and other traditional aspects related to the doctoral defence). This was in part because, we strongly felt that we shouldn’t consider the defence as a regular examination, where a standard set of criteria are used to assess a student. Besides its function as an examination, the defence is also a rite of passage, a confirmation, a celebration, and the culmination of years of independent research work. Emotions are murky and difficult to factor in for assessment. The emotions involved in the doctoral defence make it a unique event: for the candidate, the examiners (or committee members), and for the supervisor. Being aware of these emotions, and bringing them to light, is important to understanding the defence better and the role it plays in a research career.
In my work on the doctoral defence, I found (to my surprise) that the major differences between defence formats did not influence the candidates’ perception much . On the other hand, I did find important differences in the emotions felt by candidates related to the defence, as a function of socio-demographic aspects, notably gender. Women doctoral candidates experience more negative feelings before the defence, and if they had a negative experience during the defence, the negative impact on their perception as a researcher could often be long-lasting. Being aware of how different groups experience the emotions related to the defence differently is important, especially for supervisors and examiners, and can be empowering for candidates. Besides simply being aware of the emotional dimension, it can also enable the small changes that can help settle things when emotions run high: taking a short break, offering water, getting up to open a window, or moving to another topic of the thesis.

While each PhD candidate, each research study, and each PhD trajectory are unique, there are some common emotions that deserve to be mentioned. First of all, in the weeks or days leading up to thesis submission, candidates often feel that the work is not enough, worthless, or otherwise insufficient, and these feelings can contribute to perfectionism. Other candidates may be so tired of the thesis that every small action may feel like a terrible chore. Some feel relieved upon submission, and others worry about how it will be received.
Many candidates also worry about how they will perform. For candidates in the United Kingdom, where the viva takes place before final submission of the thesis and may determine the level of corrections required for the thesis, candidates worry about what the outcome of the thesis and viva will be. Major revisions could potentially add months to the doctoral journey. Because the viva is behind closed doors, candidates also may not know very well what to expect. In the Netherlands, where candidates are sure they will pass, other causes lead to worry and anxiety. As the defence is public, candidates feel the pressure to perform well in front of the committee, friends, colleagues, and family.
it is also important for supervisors and examiners to be aware of this emotional dimension, and to know how different groups of candidates experience these emotions
The first step in dealing with this anxiety, is to name and acknowledge it, and to know that these feelings are normal. Candidates who passed without corrections worry about passing their defence as much as those who had more work on their thesis after the defence. Breathing techniques, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help. University counselling services should be there to support as well. Being well-prepared for the day of the defence itself may also help candidates to feel more in control over the day and their feelings. A positive action, such as stopping by colleagues and expressing gratitude to them before the defence, can improve defence-day-anxiety. Many candidates feel more nervous right before and at the beginning of their defence. Taking notes, repeating the question, or asking for clarification of the question, are all valid options to start answering in a calm and controlled manner. At the end of the defence, candidates can be nervous to hear the outcome, and the minutes while the committee is in deliberation may feel like hours. Then, after hearing the verdict, often the final flood of emotions (relief, happiness, pride, or perhaps disappointment, anger, or worry about the thesis revision) comes.
Emotions play an important role leading up to and during the doctoral defence. Understanding the role of these emotions is important for candidates, so that they know that what they are feeling is normal, and does not mean that they are not worthy of a doctorate. At the same time, it is also important for supervisors and examiners to be aware of this emotional dimension, and to know how different groups of candidates experience these emotions. Being aware of and holding space for these emotions allows all those who are involved in the defence to experience the defence, not simply as a test of knowledge, but as the important moment it is, in the formation and affirmation of a new scholar.
Note: This article gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Impact Blog, nor of the London School of Economics. Please review our comments policy if you have any concerns on posting a comment below.
Image Credit: Ralph Leue via Unsplash.

About the author

Dr. Eva Lantsoght is a Full Professor in Civil Engineering at Universidad San Francisco de Quito in Ecuador and tenured assistant professor at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. Her blog and co-hosted podcast PhD Talk addresses the mechanics of doing research, PhD life, and general academic matters. Find her @evalantsoght or at evalantsoght.com.
- Pingback: Defending a PhD thesis is an emotional moment candidates and supervisors should be prepared for - Multidimensional News for Educators
In Australia there is no defence process and typically no discussion between the examiners…lots of secrecy and anonymity for some reason.
- Pingback: 2021 In Review: Living and Working in Academia | Impact of Social Sciences
- Pingback: Defending a PhD thesis is an emotional moment candidates and supervisors should be prepared for | Impact of Social Sciences – Cem S. Sütcü
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Related Posts

Peer review for academic jobs and grants continues to be shaped by metrics, especially if your reviewer is highly ranked
November 26th, 2021.

Keeping a research journal that works for you
November 4th, 2021.

F**k Ups in Social Research: Learning from what goes ‘wrong’
August 2nd, 2021.

Reflecting on discomfort in research
February 24th, 2021.

Visit our sister blog LSE Review of Books
Swath and Dive: A pattern for PhD defense presentations
In recent times I’m having the fortune of seeing several of my own doctoral students approach the end of the doctoral journey (yes, it does end!). As they submit the dissertation and prepare for their defense, there is one piece of advice I find myself giving again and again, about how to tackle the impossible task of presenting multiple years of research work in less than one hour. In this post, I describe a “presentation design pattern” for thesis defenses, which builds upon classic conceptualization exercises advocated in the blog. I also illustrate it with an example from my own thesis defense presentation, more than ten years ago (gasp!).
I still vividly remember when I had to prepare my defense presentation, how I tried to shoehorn tons of concepts into an impossibly small number of slides… which still were too many for the 45-minute talk I was supposed to give at the defense. After several rehearsals (with an audience!) and lots of feedback from my colleagues and advisors, I finally stumbled upon a solution. Later on, I have found that a similar structure was also helpful to other doctoral students preparing their defenses.
The rest of the post takes the form of a presentation design pattern , i.e., a description of “a problem that occurs over and over again in our environment, and […] the core of the solution to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice." 1 (a concept originally proposed in architecture, and later used in software engineering, pedagogy and many other fields). I have called this pattern Swath and Dive (for reasons that will become obvious in a minute).
The context: when is this pattern applicable?
When you have to prepare an oral presentation for a doctoral dissertation defense. This pattern is especially helpful if the research is a bit complicated (e.g., composed of multiple contributions , multiple studies, or using multiple research methods) and it is not obvious what contents to include/exclude from the presentation.
What is the problem? What forces are at play?
The main problem this pattern tries to solve is the seeming impossibility of showing 3+ years of research work in less than one hour. While time restrictions and structure for the defense are different in different countries, typically 25-60 minutes are allocated for the presentation. This limited time is a key force at play, but there are others as well:
- The sheer volume of a thesis dissertation’s contents (typically, a 100-500 pages document), which itself is a condensation of years of hard research work.
- Defending PhD students need to prove to the jury that they are now competent, independent researchers (i.e., they master the literature of their topic, are able to apply a research methodology and think critically about the results ).
- The varying levels of expertise and familiarity of the jury members with the concrete thesis topic.
- The varying levels of knowledge that jury members have of the dissertation materials (i.e., did they read the dissertation document in full? with what level of attention?). While all members are supposed to have read the document, in practice there is a lot of heterogeneity in compliance.
The typical end product of these forces is what I call the “skimming” approach to the defense presentation (see picture below): The presentation provides only a very high level overview of the main elements of the dissertation document (sort of like a table of contents). More often than not, too much time is spent in the introductory and related literature parts of the presentation (which are somehow “safe”, less likely to be criticized – another instance of avoidance at work in the PhD ), and time runs out when the student is getting to the really interesting part for the jury (the student’s own work). This approach of course has the critical flaw of not showcasing enough of the student’s own abilities and research outcomes.
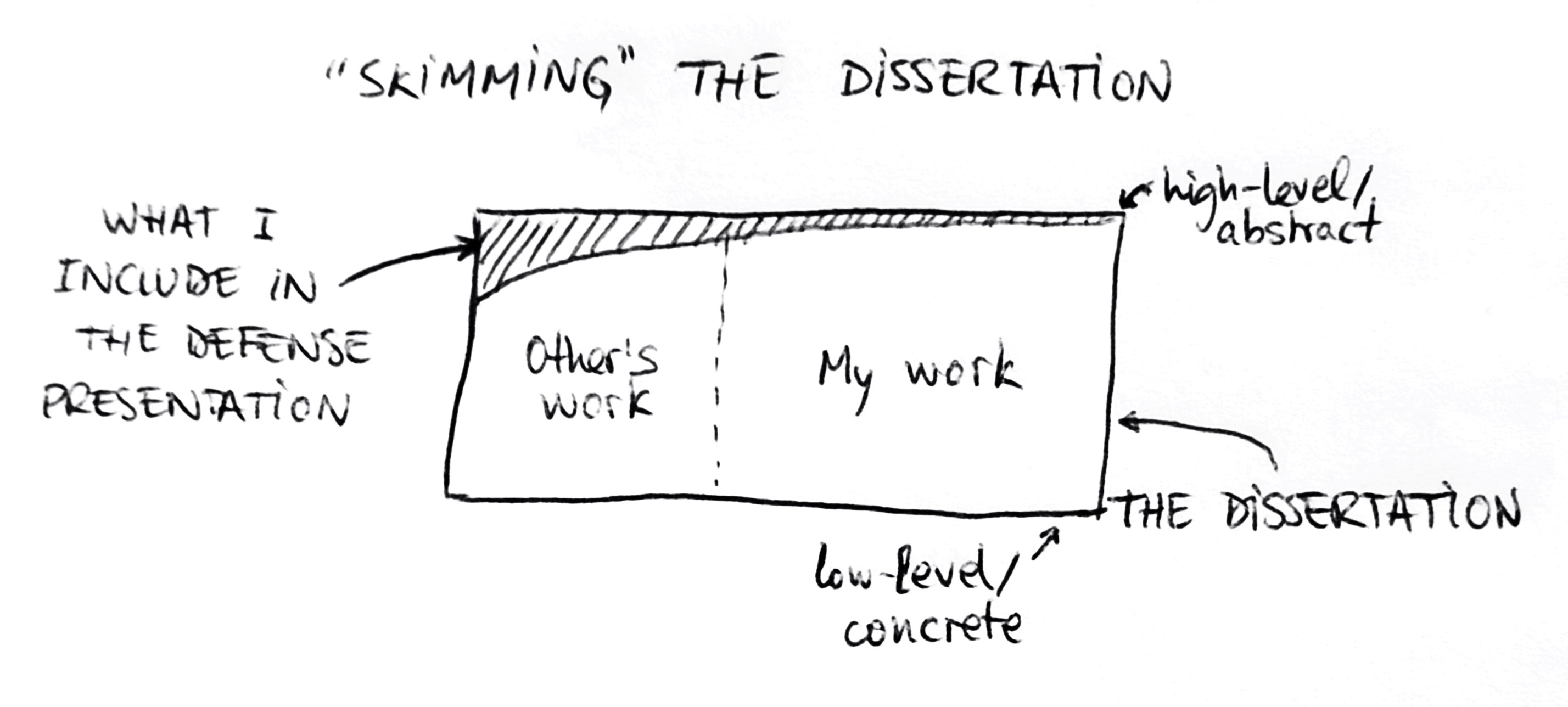
Skimming: A typical approach to selecting thesis defense content
How to avoid “skimming” your dissertation? Enter Swath and Dive .
The solution: Swath and Dive
What I propose in this pattern is to structure the presentation in a different way, a way that tries to balance the need for an overview of the dissertation and (at least some of) the richness of the investigation and the hard work the student has put behind it. The proposed structure goes like this:
A swath is “a long broad strip or belt” of grass, often left by a scythe or a lawnmower. In the context of a dissertation defense presentation, this is where the student gives the overview of the main elements of the thesis: key related scientific literature , main research questions , contributions to knowledge the dissertation makes, etc. Long-time readers of the blog will recognize these key elements as the components of the CQOCE diagram , one of the key reflection exercises in the “Happy PhD Toolkit” to (iteratively) understand and discuss with supervisors the overall view of the thesis. Aside from those key elements, probably some notes about the research methodology followed (which are not part of the canonical CQOCE diagram exercise) will also be needed.
In a sense, the Swath is not so different from the typical “skimming” mentioned above. There are several crucial differences, however: 1) when developing the Swath , we need to keep in mind that this is only a part (say, 50%) of the presentation time/length/slides; 2) the Swath should give equal importance to all its key elements (e.g., avoiding too much time on the literature context of the thesis, and making the necessary time for the student’s own research questions, contributions and studies); and 3) the Swath does not need to follow the chapter structure of the dissertation manuscript, rather focusing on the aforementioned key elements (although scattering pointers to the relevant chapters will help orient the jury members who read the dissertation).
Then, within this high-level Swath describing the dissertation, when we mention a particular contribution or study, it is time to do…
This part of the presentation is where the student selects one study or finding of the thesis and zooms in to describe the nitty-gritty details of the evidence the student gathered and analyzed (if it is empirical research), how that was done, and what findings came out of such analysis. The goal here is to help the audience trace at least one of those high-level, abstract elements, all the way down to (some) particular pieces of the raw data, the evidence used to form them.
How to select which part to Dive into? That is a bit up to the student and the particular dissertation. The student can select the main contribution of the dissertation, the most surprising finding, the largest or most impressive study within the work, or the coolest, most novel, or most difficult research method that was used during the dissertation process (e.g., to showcase how skillfully and systematically it was used). The student should give all the steps of the logic leading from low-level evidence to high-level elements – or as much as possible within the time constraints of the presentation (say, 30% of the total length/time/slides).
An essential coda: Limitations and Future Work
Although this didn’t make it to the title of the pattern, I believe it is crucially important to keep in mind another element in any good defense presentation: the limitations of the student’s research work, and the new avenues for research that the dissertation opens. These two areas are often neglected in crafting the defense presentation, maybe with a single slide just copy-pasting a few ideas from the dissertation manuscript (which were themselves hastily written when the student was exhausted and rushing to finish the whole thing). Yet, if the student convinced the jury of her basic research competence and knowledge during the Swath and Dive part, a big part of the jury questions and discussion will focus on these apparently trivial sections.
When doing the limitations, the student should gloss over the obvious (e.g., sample could have been bigger, there are questions about the generalizability of results) and think a bit deeper about alternative explanations that cannot be entirely ruled out, debatable aspects of the methodology followed… squeeze your brain (and ask your supervisors/colleagues) to brainstorm as many ideas as possible, and select the most juicy ones. For future work, also go beyond the obvious and think big : if someone gave you one million dollars (or 10 million!), what cool new studies could continue the path you opened? what new methods could be applied? what experts would you bring from other disciplines to understand the phenomenon from a different perspective? what other phenomena could be studied in the same way as you did this one? Try to close the presentation with a vision of the brighter future that this research might unleash upon the world.
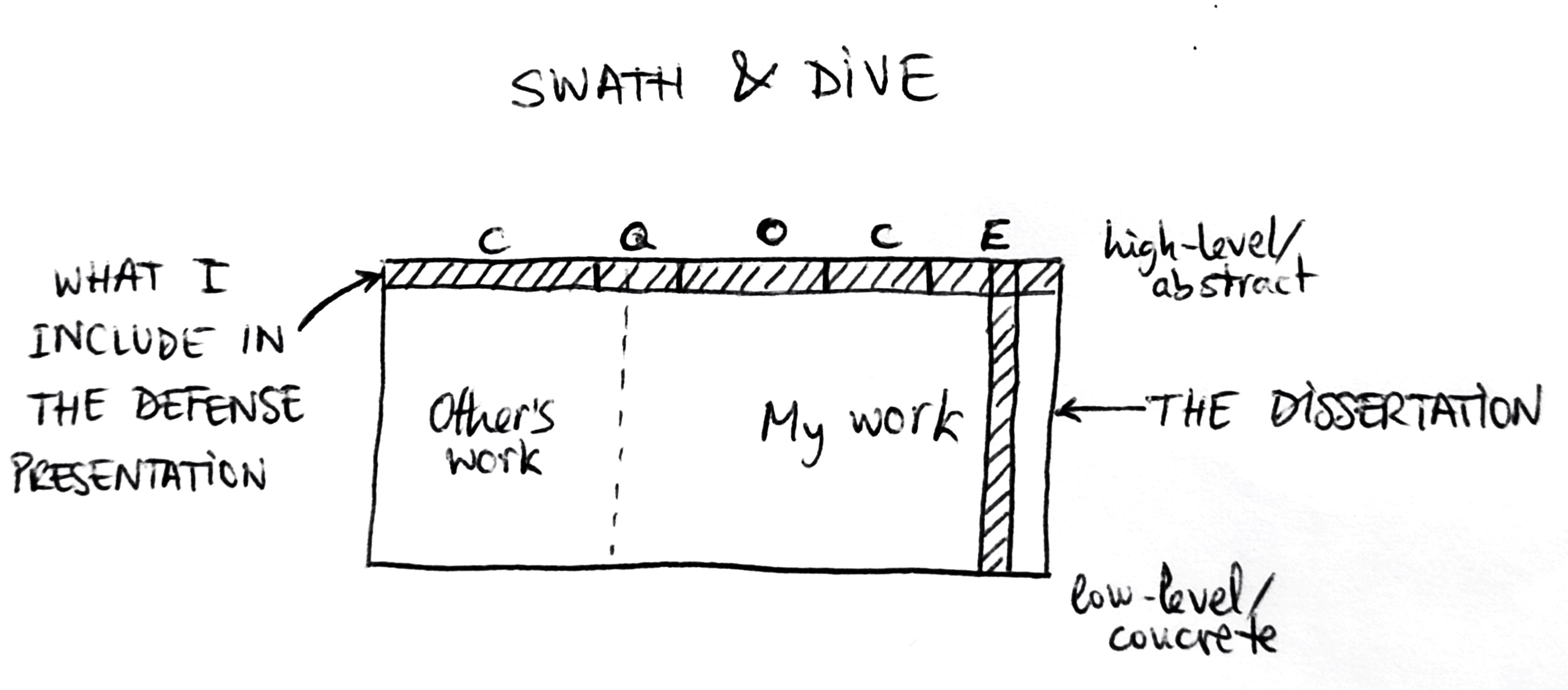
Swath and Dive: a different way of structuring your defense presentation
To understand how this pattern could look like, I can point you to my own thesis defense presentation, which is still available online . This is not because the presentation is perfect in any way, or even a good example (viewing it today I find it overcomplicated, and people complained of motion sickness due to its fast pace and Prezi’s presentation metaphor of moving along an infinite canvas)… but at least it will give you a concrete idea of what I described in abstract terms above.
If you play the presentation , you will notice that the first few slides (frames 1-6) just lay out the main construct the dissertation focuses on (“orchestration”), the structure of the presentation and its mapping to dissertation chapters. Then, the bulk of the presentation (frames 7-117) goes over the main elements of the dissertation according to the CQOCE diagram , i.e., the Swath part of the pattern. Within this high-level view of the dissertation, I inserted a short detour on the research methodology followed (frames 25-28) and, more importantly, several Dives into specific findings and the evidence behind them (frames 43-48, 66-72, and 99-112). Then, frames 118-136 provide the conclusive coda that includes the future work (but not the limitations, which were peppered through the Swath part of the presentation – a dubious choice, if you ask me today).
Variations and related patterns
As you can see from the example above, one does not need to follow the canonical version of Swath and Dive (mine is rather Swath and Three Dives ). Yet, paraphrasing Alexander, that is the point of the pattern: to have the core of the idea, which you can use to produce a million different solutions, tailored to your particular context and subject matter.
It is also important to realize that this structuring pattern for thesis defense presentations does not invalidate (rather, complements) other advice on preparing scientific presentations 2 , 3 , 4 and thesis defenses more specifically 5 . It is all very sound advice! For instance, once you have the structure of your Swath and Dive defense presentation, you could use the NABC technique to ensure that the Need, Approach, Benefits and Competition of each of your knowledge contributions are adequately emphasized. And you can rehearse intensively, and with an audience able to come up with nasty questions. And so on…
May you defend your thesis broadly and deeply!
Do you know other defense presentation structures that work really well in your discipline? Have you used Swath and Dive in your own defense successfully? Let us know (and share your examples) in the comments area below! (or leave a voice message)
Header image by DALL-E
Alexander, C., Ishikawa, S., & Silverstein, M. (1977). A Pattern Language: Towns, Buildings, Construction (Vol. 2). Oxford University Press. ↩︎
Carter, M. (2013). Designing science presentations: A visual guide to figures, papers, slides, posters, and more (First edition). Elsevier/Academic Press. ↩︎
Anholt, R. R. H. (2009). Dazzle ’Em with Style: The Art of Oral Scientific Presentation (2nd ed). Elsevier, Ebsco Publishing [distributor]. ↩︎
Alley, M. (2013). The craft of scientific presentations: Critical steps to succeed and critical errors to avoid (Second edition). Springer. ↩︎
Davis, M., Davis, K. J., & Dunagan, M. M. (2012). Scientific papers and presentations (Third edition). Elsevier/Academic Press. ↩︎
- Dissertation
- Communication


Luis P. Prieto
Luis P. is a Ramón y Cajal research fellow at the University of Valladolid (Spain), investigating learning technologies, especially learning analytics. He is also an avid learner about doctoral education and supervision, and he's the main author at the A Happy PhD blog.
Google Scholar profile

PhD Dissertation Defense Slides Design: Start
- Tips for designing the slides
- Presentation checklist
- Example slides
- Additional Resources
Purpose of the Guide
This guide was created to help ph.d. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. the guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from ph.d. graduates. the tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can be used in designing other types of presentations such as conference talks, qualification and proposal exams, and technical seminars., the tips and examples are used to help students to design effective presentation. the technical contents in all examples are subject to copyright, please do not replicate. , if you need help in designing your presentation, please contact julie chen ([email protected]) for individual consultation. .
- Example Slides Repository
- Defense slides examples Link to examples dissertation defense slides.
Useful Links
- CIT Thesis and dissertation standards
- Dissertations and Theses @ Carnegie Mellon This link opens in a new window Covers 1920-present. Full text of some dissertations may be available 1997-present. Citations and abstracts of dissertations and theses CMU graduate students have published through UMI Dissertation Publishing. In addition to citations and abstracts, the service provides free access to 24 page previews and the full text in PDF format, when available. In most cases, this will be works published in 1997 forward.
- Communicate your research data Data visualization is very important in communicating your data effectively. Check out these do's and don'ts for designing figures.
Power Point Template and other Resources
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 1
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 2
Source: CEE Department Resources https://www.cmu.edu/cee/resources/index.html
- CMU Powerpoint Slide Template
Source: CMU Marketing and Communications
https://www.cmu.edu/marcom/brand-standards/downloads/index.html
- Use of CMU logos, marks, and Unitmarks
Email me for questions and schedule an appointment

Top 7 tips for your defense presentation
1. show why your study is important, remember, your audience is your committee members, researchers in other fields, and even the general public. you want to convince all of them why you deserve a ph.d. degree. you need to talk about why your study is important to the world. in the engineering field, you also need to talk about how your study is useful. try to discuss why current practice is problematic or not good enough, what needs to be solved, and what the potential benefits will be. , see how dr. posen and dr. malings explained the importance of their studies..
- Carl Malings Defense Slides with Notes
- I. Daniel Posen Defense Slides with Notes
2. Emphasize YOUR contribution
Having a ph.d. means that you have made some novel contributions to the grand field. this is about you and your research. you need to keep emphasizing your contributions throughout your presentation. after talking about what needs to be solved, try to focus on emphasizing the novelty of your work. what problems can be solved using your research outcomes what breakthroughs have you made to the field why are your methods and outcomes outstanding you need to incorporate answers to these questions in your presentation. , be clear what your contributions are in the introduction section; separate what was done by others and what was done by you. , 3. connect your projects into a whole piece of work, you might have been doing multiple projects that are not strongly connected. to figure out how to connect them into a whole piece, use visualizations such as flow charts to convince your audience. the two slides below are two examples. in the first slide, which was presented in the introduction section, the presenter used a flow diagram to show the connection between the three projects. in the second slide, the presenter used key figures and a unique color for each project to show the connection..

- Xiaoju Chen Defense Slides with Notes
4. Tell a good story
The committee members do not necessarily have the same background knowledge as you. plus, there could be researchers from other fields and even the general public in the room. you want to make sure all of your audience can understand as much as possible. focus on the big picture rather than technical details; make sure you use simple language to explain your methods and results. your committee has read your dissertation before your defense, but others have not. , dr. cook and dr. velibeyoglu did a good job explaining their research to everyone. the introduction sessions in their presentations are well designed for this purpose. .
- Laren M. Cook Defense Slides with Notes
- Irem Velibeyoglu Defense with Notes
5. Transition, transition, transition
Use transition slides to connect projects , it's a long presentation with different research projects. you want to use some sort of transition to remind your audience what you have been talking about and what is next. you may use a slide that is designed for this purpose throughout your presentation. , below are two examples. these slides were presented after the introduction section. the presenters used the same slides and highlighted the items for project one to indicate that they were moving on to the first project. throughout the presentation, they used these slides and highlighted different sections to indicate how these projects fit into the whole dissertation. .

You can also use some other indications on your slides, but remember not to make your slides too busy. Below are two examples. In the first example, the presenter used chapter numbers to indicate what he was talking about. In the second example, the presenter used a progress bar with keywords for each chapter as the indicator.

Use transition sentences to connect slides
Remember transition sentences are also important; use them to summarize what you have said and tell your audience what they will expect next. if you keep forgetting the transition sentence, write a note on your presentation. you can either write down a full sentence of what you want to say or some keywords., 6. be brief, put details in backup slides , you won't have time to explain all of the details. if your defense presentation is scheduled for 45 minutes, you can only spend around 10 minutes for each project - that's shorter than a normal research conference presentation focus on the big picture and leave details behind. you can put the details in your backup slides, so you might find them useful when your committee (and other members of the audience) ask questions regarding these details., 7. show your presentation to your advisor and colleagues, make sure to ask your advisor(s) for their comments. they might have a different view on what should be emphasized and what should be elaborated. , you also want to practice at least once in front of your colleagues. they can be your lab mates, people who work in your research group, and/or your friends. they do not have to be experts in your field. ask them to give you some feedback - their comments can be extremely helpful to improve your presentation. , below are some other tips and resources to design your defense presentation. .
- Tips for designing your defense presentation
How important is your presentation, and cookies?

- Next: Tips for designing the slides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=883178
Final Thesis and Dissertation Defense Guidelines
The thesis work of students in the Nelson Institute is probably the most varied of any of the academic units at UW-Madison. Each student’s journey through the program is unique, and this includes the final thesis defense. But despite this variation, there are certain elements that we believe should be present in any thesis defense. We list them here as guidelines, not as hard and fast rules.
View this document as a pdf
General Guidelines
- The thesis defense has a formal purpose and is necessarily a formal proceeding. It is the final step in which the faculty affirms, or not, that the candidate has met the standard of the Nelson Institute and the university. If affirmed, the candidate is credentialed to present themselves as prepared to take on advanced work in their field. For the PhD, it is a certification that the candidate has a proven ability, as a scholar and a researcher, to make original contributions to their field.
- The defense should be focused on the thesis.
- The central element of a defense is that the candidate appears before his/her/their committee to summarize the main findings/outcome/importance of their work, and to answer questions about it – to defend it.
- Because the focus is on the thesis, it follows that the committee must receive the thesis (or other product to be defended) for review well before (typically two weeks before) the defense.
- The Nelson Institute strongly recommends that there be a public presentation as a part of the defense. Typically, this will proceed the “official” elements of the defense. Given that the Nelson Institute stresses interdisciplinarity, it is particularly important that students demonstrate their ability to present the results of their work in a way that will be meaningful to a general audience.
- A unanimous pass, with at most minimal changes required in the thesis before the degree is granted.
- A unanimous pass, but with the stipulation that there be substantive changes to the thesis. Commonly, but only by concurrence of all involved, all members of the committee except the advisor will sign the warrant, and the committee will charge the advisor with ensuring that the required changes have been made.
- A qualified pass or “no decision,” in which the committee judges that the thesis has problems or deficiencies that will require significant rewriting and perhaps reanalysis of data. In this circumstance some or all of the committee members may wish to read the revised thesis before signing the warrant for a pass. They may also require another presentation to the committee.
- “Not passed.” This may be a final decision with no encouragement to try again, or it may allow another defense after the student has addressed the perceived deficiencies.
- Graduate School rules do not require that decisions of the committee to pass or fail a student be unanimous – one dissenting vote is allowed at the PhD level.
- An introduction by the thesis advisor
- A presentation by the student (much preferably to a public audience)
- Allowance for people at the public presentation to ask questions
- The public audience is then excused and the defense proceeds with only the student and their committee present
- Each member of the committee asks the candidate questions focused on the thesis with the objective of allowing the candidate to demonstrate their mastery of the subject of the thesis and their grasp of the intellectual context of their work
- The student is excused and the committee has a confidential discussion to arrive at a pass or no-pass decision, to decide on what revisions, if any, will be required, and in general to decide what further stipulations will be made before the final approval will be given
- At the conclusion of the discussion the student is invited to return and the outcome of the deliberations summarized
- At that point, the conversation typically moves on to related matters such as the future plans of the candidate, and the appropriate journals in which the dissertation materials could be published
- And, if it is a pass, the defense ends with the committee congratulating the candidate
- The degree to which a final defense is a celebratory event or a tension-filled trial depends on how well the student and their advisor have managed the student’s involvement with their committee leading up to the defense. It is important for the student to keep all members of the committee fully apprised of their progress, and to work through any potential areas of disagreement or misunderstanding well before the thesis is completed.
- The Nelson Institute is open to innovation, and the guidelines above may be adapted to suit particular circumstances provided that rigor and fairness are maintained.
Hints for PhD Defenses
At Columbia, PhD defenses are generally not public, although CS usually allows a student audience. Defenses consist of four parts: first, the candidate introduces themselves, then presents a summary of their work, interrupted and followed by questions from the committee. Finally, the committee meets in private to discuss the presentation and dissertation.
While most of the committee will have read most of your thesis, you cannot assume that everyone has read every chapter.
The committee needs to be able to assess impact and depth. Usually, the committee has some idea of this before the defense, but whatever the student can say to make this assessment easier, perhaps just through emphasis, is likely to make the defense go much more smoothly.
Generally, the whole defense will not take more than two hours, but should take considerably less time. Part of the challenge of a defense is to convince the committee that you can summarize the important points of your work in a very limited time.
- What is the problem you are studying?
- Why is it important ?
- What results have you achieved?
- Some committee members will want to know if the works has been published and where and how it was received. For example, if you have written software, indicate where it is being used, either for follow-on work or in some production or test environment.
- Have a list of your thesis-related publications as a slide. Indicate any awards that a paper may have received. For most people, it's easier to list some honor than "brag" about it in person.
- If you have presented your work in a conference or at job talks, be sure to anticipate and address the most common questions asked there.
- The committee should be handed a copy of your slides.
- Be prepared to briefly summarize your background (undergraduate degree, how long at the university, etc.)
- No more than 30 slides, plus "back up" slides with additional material in case of questions. The most effective way of making your committee members mad is to come unprepared with a stack of 80 slides and then madly skip through them.
- Number your slides, particularly if one of your committee members is linked in via speakerphone. Consider using some kind of remote presentation software.
- List your contributions early.
- When presenting your contributions, be sure to use "I" and not "we" so that the committee will know what aspects of the work where yours, and which were group projects.
- Keep discussions of related work very brief, but be prepared to answer questions of the "how does this differ from so-and-so's work" succinctly.
- You will not be asked to prove results again.
- Be prepared to back up any comparative statement with facts, in particular statements like "works better", "faster", "scalable" or "optimal". If you are presenting a protocol, how do you know that it works correctly?
- If you have multiple parts in your dissertation, consult with the committee ahead of time as to whether it makes sense to omit some of them for the presentation.
Hints for Dissertations
- It is better to focus deeply on a single area then to work on several topics, each of which is pursued to a moderate depth.
- Systems work must be coupled with implementation and some kind of numerical comparitive analysis to demonstrate the improvements from existing or alternate approaches.
- Your thesis needs a one page executive summary that a layperson should be able to understand. Test: give it to a relative of yours that does not have an engineering degree...
Miscellaneous Hints
- You are likely only to defend a PhD thesis only once; your defense is a special occasion, so consider dressing appropriately, at least business casual, but a suit is not inappropriate.
- It is customary to provide refreshments for the audience, such as coffee, bagels, cookies and fruit, depending on the time of day.
The Role of PhD Committee Members
- Committee members (should) read the draft thesis (and provide feedback). Obviously, students appreciate an in-depth reading, but it is common for committee members to focus on chapters closest to their expertise. Reading depths varies - some provide line edits, others just suggest larger issues that should be addressed ("Your related work section in Chapter 10 is a bit sparse and ends in 2005."). While this is probably not the place to suggest "do another year of research", filling in gaps is ok and I'd rather postpone a defense by a month if needed. Before the committee gets the thesis, I've done a first or sometimes second reading, but the whole point of the committee is to keep the advisor honest (and complement his or her knowledge or taste).
- Committee members attend the PhD defense, usually in person. Typically, this lasts about 90 minutes. Take notes on any editorial improvements (e.g., "make clear that the throughput graph is measured in gallons/minute"). Vote on the outcome and sign the form.
- If the student is given a set of changes to implement, the advisor asks students to detail on how they implemented the changes, similar to how an author may respond to reviewer comments for a journal. The committee informally signs off, or not, on these changes. There is no need to re-read the thesis.
Checklist for Dissertation
- Spell check;
- Check for missing chapter or figure references;
- Section, Chapter, Figure are capitalized;
- All references converted from [1][2][3] to [1,2,3];
- Consistent capitalization in captions;
- Verify expansion of all abbreviations at first instance;
- Avoid "tremendous", "huge" and other similar adjectives;
- End to end -> end-to-end;
- Check references for capitalization of abbreviations and missing data such as page numbers.
(Contributions by Ed Coffman, Jonathan Rosenberg and Sal Stolfo.)
Translations: Polish

PhD Thesis Proposal Defense: Common Questions and Feedback

This past two weeks I attended a number of proposal defense of PhD students at my University. In this post, I discuss the general format of a proposal defense as well as discuss the most common questions asked and feedback given to the students by the external examiners.
Structure of a PhD proposal defense
Outcomes of a phd proposal defense, common questions and feedback for chapter 1 of the proposal, common questions and feedback for chapter 2 of the proposal, common questions and feedback for chapter 3 of the proposal, general feedback, final thoughts, related posts.
A proposal defense has: the student defending his proposal, two external examiners, the student’s supervisors, the audience, and the chair of the defense. The defense is structured as follows:
- The chair opens the session by welcoming and acknowledging the student, his supervisors and the external examiners.
- The chair also outlines how the defense will be undertaken including any rules that should be adhered to.
- The chair then welcomes the PhD student to introduce himself and make a presentation (usually 15 minutes).
- After the presentation by the student, the chair opens the floor to the external examiners to give their comments, ask questions and give feedback to the student on how to improve the proposal.
- The student is then required to respond to the questions asked and comments given.
- The chair then makes his remarks.
- Afterwards, the PhD student, his supervisors and the audience are requested to leave the room to allow the chair and the examiners to make their determination. The student and his supervisors are then called back in and the determination is spelt out to them.
There are about 4 possible outcomes after the student presents and defends his proposal:
- The proposal passes with minor or no corrections.
- The proposal passes with major corrections.
- The student retakes the proposal by re-writing it (may include change of topic) and defending it again.
- The proposal is rejected.
Rarely will a student be asked to re-take or will a proposal be rejected especially if it has been adequately supervised. This is because before the proposal is submitted for oral defense, it must be reviewed and signed by the supervisors.
Below is a list of the common questions and feedback for chapter 1:
- What is your working definition of [concepts]?
- Which sector do you want to focus on?
- From a [country/region] perspective, please explain what is the problem?
- How do you intend to solve the problem you have identified?
- What will your proposed solution comprise of?
- Who are the recipients of your proposed solution?
- What is the primary outcome of the research?
- Your objectives use [concept] while your problem statement talks of [a different concept]. What’s the difference between the two [concepts]?
- In the research objectives, there is an interchange and insertion of different words. Be careful about the concepts you use. There needs to be consistency in the concepts used throughout the proposal.
- What is the knowledge gap? That is, what is known and what is unknown that your study will attempt to address?
- How do you relate [different variables included in the topic]? Is one a precedent of the other?
- Are you investigating or examining? The topic says investigating while the objectives talk of examining.
- The presentation does not discuss [sector of focus], the opportunities that exist, and the challenges it faces. This would give the student a good basis for undertaking the research.
- There is no continuity in the objectives.
- There is no discussion of the study’s contribution to knowledge and practice, which is very important for PhD-level study.
- The background has many concepts that throw off readers on what the focus of the study is.
- The problem statement is not focused.
- What is the placement of the study regionally?
- The objectives are too long and broad; they should be specific.
- What is the underlying hypothesis of your study?
- One of the research questions is biased. The researcher should take a neutral stand.
Below is a list of the common questions and feedback for chapter 2:
- Which theories have inspired your work and who are the proponents of those theories?
- For each theory discussed in your proposal, briefly state what it says and how it informs your study.
- How are the theories related to your study?
- Why did you select those theories and not [other theories]?
- There are no empirical studies reviewed in your proposal.
- Your work must converge with other peoples’ work to be able to show the gap that your study is trying to fill.
- How did the choice of theories help you come up with your study’s concepts and variables?
- How will you measure the variables [in the topic]?
- You have just touched the surface of the empirical review, which should be a substantial section of your literature review.
- It is not clear what the research gap is from the literature review.
- After the empirical review, that’s when you now discuss the conceptual framework.
- The conceptual framework should clearly show the dependent and independent variables and their relationships.
Below is a list of the common questions and feedback for chapter 3:
- Kindly explain what your research philosophy is.
- What will your [quantitative] model comprise of?
- How are you going to verify and validate your [quantitative] model?
- Why is the sampling formula appropriate to your sector and study? Justify the sampling formula used in the proposal.
- Justify the choice of the sampling technique [e.g. purposive sampling].
- Justify your choice of data collection and data analysis methods.
- Are you going to use an inductive approach or a deductive approach to your study?
- There needs to be consistency between your objectives and research philosophy.
- If you have a number of population categories, you need to clearly articulate the sampling techniques for each category.
- The data analysis methods should be clearly articulated.
- The ethical considerations of your study should be adequately discussed.
- The data collection instruments should be part of the proposal defense.
- Your choice of research design and methods should be justified.
- What is your unit of analysis?
- Who are your study’s population?
- Will you have different questionnaires for different respondents?
- The data collection tools should have adequate background information questions to enable comparisons across different socio-economic and demographic groups.
- Why are you lagging a variable? Justify the need to lag the variable.
- Justify the choice of the model [e.g. Structural Equation Model].
- Which specific multivariate analysis will you use?
- Which tests are you going to conduct for the model and why? [e.g. normality, multicollinearity tests etc]
- The variables of your study should be defined.
In addition to the chapter-specific questions and feedback given, the students also received feedback on:
- The formatting of their proposals, including the font styles and size allowed, the numbering of the documents,
- The inclusion of front pages such as cover page, declaration, abstract, table of contents,
- The inclusion of back pages such as reference list and appendices which should include letter of introduction, consent letter for study respondents, data collection instruments, and work plan (Gantt chart) for the study.
- The style of referencing recommended by the School e.g. APA, which should be consistent throughout the proposal. The proposal defense should also include some of the citations so as to give it an authoritative feel.
From my observations during the four proposal defenses I attended, a proposal defense is an opportunity for the PhD student to defend his work and to convince the interviewing panel that the student knows what he is doing and what is required of him moving forward. Most of the panellists will do their best to make the student feel comfortable rather than intimidate him so PhD students should not panic when preparing to defend their proposals.
Of importance is adequate preparation before the defense and making sure that the proposal and presentation follow the guidelines provided by the School. Lastly, PhD students should keep in mind that the aim of the proposal defense is to help improve upon the student’s proposal and ensure that the research will meet the scientific rigour and standards of a PhD-level work.
How To Write Chapter 1 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Practical Guide)
How To Write Chapter 2 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Beginner’s Guide)
How To Write Chapter 3 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Detailed Guide)
How To Format A PhD Thesis In Microsoft Word (An Illustrative Guide)
Comprehensive Guidelines for Writing a PhD Thesis Proposal (+ free checklist for PhD Students)
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #12: Partial Correlation Analysis in SPSS
Partial correlation is almost similar to Pearson product-moment correlation only that it accounts for the influence of another variable, which is thought to be correlated with the two variables of...
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Personal tools
- Log in/Register Register

https://www.vitae.ac.uk/doing-research/doing-a-doctorate/completing-your-doctorate/your-viva/thesis-outcomes
This page has been reproduced from the Vitae website (www.vitae.ac.uk). Vitae is dedicated to realising the potential of researchers through transforming their professional and career development.
- Vitae members' area
Thesis outcomes and corrections
There will usually be a bit more work to do after the viva. Each institution will have its own regulations about viva outcomes and how to inform the candidate of them. Find out before you go into your viva so that you know what to expect. In the UK they typically they fall into one of the following categories:
- Outright pass. Your work needs no corrections
- Minor corrections. Your examiners have a few minor suggestions that they would like you to incorporate
- Major corrections or resubmission. The thesis needs further work to be of doctoral standard. This might include more research, rewriting sections or including new literature
- Suggestion that you resubmit for, or are awarded, a lower degree (MPhil or MSc). Research is of good quality but too narrow for a doctorate
- Outright fail. Usually used only in cases of plagiarism or where the examiners judge that the candidate will never be able to complete a doctorate.
Most candidates fall within the minor or major corrections categories. This means that you will have some corrections to complete. However, regardless of the number of corrections that you have to do most people who reach the viva stage do go on to get their doctorate relatively quickly.
Thesis corrections
After your viva you are likely to have some corrections to complete before you are awarded your doctorate. The extent can range from a few spelling mistakes to rewriting or adding complete chapters. You may be given a deadline by your examiners or your institution but regardless of this, it is best to aim to complete your corrections as soon as possible to use the momentum acquired during thesis writing.
In order to be sure that your corrections make the right changes:
- take notes during the viva and write them up immediately after
- meet with your main supervisor to discuss the changes that you need to make
- analyse the examiners' report carefully to make sure that you have dealt with all of the issues that they raise
- proofread your work again.
Thesis resubmission
Your examiners, or often just the internal examiner, will check that all corrections have been incorporated, and then you can resubmit your thesis. Your institution will have regulations on the format of the final submitted thesis copy of your thesis, which will usually be deposited in the institutional library. It has become more common for institutions to request the submission of an electronic copy for ease of cataloguing and searching.
Bookmark & Share

Thesis and Dissertation Defenses
Submitting a defense announcement.
To submit a graduate thesis or dissertation defense, please
The dissertation/thesis defense must be open to the public and announced two weeks prior to the date of the defense.
College Policy on Dissertation/Thesis Defenses
Upcoming Defenses
2024 – 2023 – 2022 – 2021 – 2020 – 2019 – 2018 – 2017 – 2016 – 2015 – 2014 – 2013 – 2012
- MAE Defense - Wayne Farrell

- One official transcript (in a sealed envelope) from each college/university attended.
- A Bachelor of Science degree in civil engineering or another closely related engineering degree.
- Résumé.
- Statement of educational, research, and professional career objectives.
- Three letters of recommendation.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc. only.
For international students interested in UCF Global Pathway Program (immersive English-language learning), please contact Dr. Ali P. Gordon for guidance.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Industrial Engineering or a closely related field with GPA of 3.0 or greater
- Mathematics through Calculus II (MAC 2312 or equivalent)
- An undergraduate course in engineering probability and statistics
- Familiarity with at least one programming language (such as Python, C, C++, Visual BASIC, Java, etc.)
- Official transcripts
- Two letters of recommendations
- Goal Statement
Admission is open to those with a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution recognized by UCF. An application to the graduate certificate program and official transcripts must be submitted. Applicants must apply online. All requested materials must be submitted by the established deadline. Admission to the program is competitive on a space-available basis. Final admission is based on evaluation of the applicant's abilities, past performance and the applicant's potential for completing the certificate. For international students interested in UCF Global Pathway Program (immersive English-language learning), please contact Dr. Ali P. Gordon for guidance.
- Applications are accepted for the fall and spring terms only.
- In addition, applicants to this certificate must provide: Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc only.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation.
- Bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering or closely related discipline with a minimum GPA 3.0
- The GRE/GMAT is not required
- A goal statement. This is your opportunity to outline in 500 words why you wish to join the program, what you think you will contribute to the program, and how you feel the program will enhance you both personally and professionally in the future.
- Updated résumé.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc. only.
- A computer-based TOEFL score of 220 or 80 on the internet-based TOEFL is required if an applicant is from a country where English is not the official language, or if an applicant’s degree is not from an accredited U.S. institution, or if an applicant did not earn a degree in a country where English is the official language or a university where English is the official language of instruction. Although we prefer the TOEFL, we will accept IELTS scores of 6.5.
- The GRE is not required for admission to this program.
- Resume or Curriculum Vita
- The goal statement should discuss all relevant professional background and any previous research and/or teaching experience. The statement should explain the motivation behind the pursuit of an MSSE. Future educational and career goals after the completion of the applicant’s master study should be discussed.
- If the applicant is interested in completing a Master thesis, then the applicant must clearly describe the particular area of research interest. The applicant should identify at least one UCF faculty member who shares a similar research focus and is believed to be best suited to serve as a potential thesis advisor.
- The goal statement should between 500 and 1,000 words.
- The letters of recommendation should be from faculty members, university administrators, and employers with a supervisory role of the applicant. The letters, which must be current to the application and must not be for another degree program, should address the educational and career goals of the applicant. The letter writers should also know the applicant well enough to discuss the applicant’s capacity to perform, excel and succeed in a graduate program. Letters for Master’s thesis students must discuss the applicant’s ability to perform graduate-level research.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc. only.
- 2 Letters of recommendation
An undergraduate degree in Computer Science, Statistics, Information Technology, or Computer Engineering is desirable but not required. Applicants without a strong undergraduate background in Computer Science and Statistics must demonstrate an understanding of the material covered in upper-division undergraduate courses listed under the Articulation Section of the Curriculum Information. Applicants may choose to demonstrate their knowledge of these courses by taking these courses as non-degree seeking and scoring “B” or better in all of them.
- A bachelor’s degree in Biomedical, Mechanical or Aerospace Engineering, or a closely related discipline.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc. only.
- Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering or closely related discipline.
- Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering or closely related discipline.
- Applicants applying to this program who have attended a college/university outside the United States must provide a course-by-course credential evaluation with GPA calculation. Credential evaluations are accepted from World Education Services (WES) or Josef Silny and Associates, Inc. only
- Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Biomedical Engineering or Mechanical Engineering or closely related discipline.
- Official, competitive GRE score taken within the last five years.
- A written statement of experience and research, areas of current and future potential research interests, and future career goals.

Graduate Education
Office of graduate and postdoctoral education, ms and ph.d. defenses, ms defense by yuhua li, phd defense by shancong mou, ph.d. proposal oral exam - chinsung park, ms defense by brendan mindiak, phd defense by carlota bonnet, ph.d. dissertation defense - wantong li, phd proposal by qinge xie, phd proposal by liang-hsin chen, phd proposal by valeria montserrat juarez, phd defense by michael j. johnson, accessibility information.
Download Microsoft Products > Download Adobe Reader >
Biostatistics Graduate Program
Shengxin tu dissertation defense – may 10.
Posted by duthip1 on Friday, April 26, 2024 in News .
PhD candidate Shengxin Tu will defend her dissertation on Friday, May 10, at 8 a.m. Central Time, at 2525 West End Avenue, in the 11th floor large conference room (suite 1100, room 11105). Her advisor is Bryan Shepherd . All are invited and encouraged to attend.
Rank-Based Analyses and Designs with Clustered Data
Clustered data are common in biomedical research. It is often of interest to evaluate the correlations within clusters and between variables with clustered data. Conventional approaches, including intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Pearson correlations, are commonly used in analyses with clustered data. However, these conventional approaches are sensitive to extreme values and skewness. They also depend on the scale of the data and are not applicable to ordered categorical data. In this dissertation, we define population parameters for the rank ICC and between- and within-cluster Spearman rank correlations. These definitions are natural extensions of the conventional correlations to the rank scale. We show that the total Spearman rank correlation approximates a weighted sum of between- and within-cluster Spearman rank correlations, with weights determined by the rank ICCs of the two random variables. We also describe estimation and inference for these four rank-based correlations, conduct simulations to evaluate the performance of our estimators, and illustrate their use with real data examples. Furthermore, we apply the rank ICC in the design of clustered randomized controlled trials (RCTs), proposing unified and simple sample size calculations for cluster RCTs with skewed or ordinal outcomes. Our calculation involves inflating the sample size for an adequately powered individual RCT for an ordinal outcome with a design effect that incorporates the rank ICC. For continuous outcomes, our calculation sets the number of distinct ordinal levels to the sample size. We show that with continuous data, our calculations closely approximate more complicated sample size calculations based on clustered Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. We conduct simulations to evaluate our calculations’ performance and illustrate their use in the design of two cluster RCTs, one with a skewed continuous outcome and a non-inferiority trial with an irregularly distributed count outcome.

Tags: clustered data , dissertation defense , RCTs , sample size calculations
Leave a Response
You must be logged in to post a comment
May 3 (Fri) @ 3:00pm: ”Reeb Graphs for Topological Connectomics,” S. Shailja, ECE PhD Defense
The human brain, comprising billions of neurons, forms complex neural networks that are spatially distributed across various regions and change structurally over time. However, our understanding of the brain connectivity remains limited, lacking scalable quantifiers. Traditional methods, like the 2D adjacency matrices, oversimplify these connections and omit topological information, despite well documented topological deteriorations and irregularities associated with neurological and developmental disorders. This dissertation poses a central research question: Can we model the structural connections in brain networks in a scalable way to represent spatial information flow? Utilizing diffusion MRI data, this work introduces a novel Reeb graph-based method that efficiently encodes the topology and geometry of the brain’s white matter pathways. By defining the evolution of level sets, we re-bundle 3D trajectories of neuronal fiber pathways, capturing critical geometric events – akin to a brain fingerprint. This method proves valuable in detecting disease-related and age-dependent topology alterations in studies on Alzheimer’s and brain tumors. Beyond neuroscience, the approach has broader applications, demonstrated through the development of a general algorithm for discovering structure in spatio-temporal trajectories of human behavior, as recorded by GPS. This algorithm identifies deviations in human movement, signaling anomalies against normal activities. In summary, this thesis presents an extensive exploration of spatial Reeb graphs, detailing their implementation for spatiotemporal data and discussing their potential as general purpose tools for scalable trajectory modeling.
Shailja is a Ph.D. candidate in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at the University of California, Santa Barbara, advised by Prof. B. S. Manjunath. In 2016, she graduated with a Bachelor's degree from the Electrical Engineering Department at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Shailja joined UCSB in 2018 and received an M.Sc. in ECE from UCSB in 2020. In 2023, Shailja was awarded the Fiona and Michael Goodchild best graduate student mentor award. She has also been named an NSF iRedefine ECE Fellow. Shailja’s research vision is to model multi-modal healthcare data for precise diagnostics using AI and integration of domain knowledge to “close-the-loop” between surgeons, research scientists, and engineers.
Hosted by : Professor B. S. Manjunath Submitted by : Shailja < [email protected] >
- +1 805.893.5364
- [email protected]
- Office Harold Frank Hall, Rm 4155
Dept. Resources
- Services & Support
- Cntrl Admin Office (CAO)
- Electronics Shop
- Technical Support
- Room Reservations
- Submit Event | News | Book
- Information
- Terms of Use
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering • UC Santa Barbara 2023 © Regents of the University of California
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
Causes and outcomes of at-risk underperforming pharmacy students: implications for policy and practice
- Alice Campbell 1 ,
- Tina Hinton 1 , 2 ,
- Narelle C. da Costa 1 ,
- Sian E. O’Brian 1 ,
- Danielle R. Liang 1 &
- Nial J. Wheate 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 421 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
198 Accesses
Metrics details
This study aimed to understand the key determinants for poor academic performance of students completing a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm), Bachelor of Pharmacy and Management (BPharmMgmt), or Master of Pharmacy (MPharm) degree.
Data were collected on pharmacy students who had not met academic progression requirements between 2008 and 2018 at The University of Sydney, Australia. This included: age at the start of pharmacy degree; gender; whether they transferred from another university; whether they were a domestic or international student; Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank upon entry, previous studies in biology, chemistry, or mathematics; show cause triggers (units of study failed); number of show causes; students’ written show cause responses; weighted average mark at last show cause or graduation; whether they graduated and were a registered pharmacist; and, the number of years they spent studying the degree. Descriptive studies were used to analyse student characteristics using SPSS software, and student self-reported reasons for poor performance were analysed reflexively using thematic analysis procedures using NVivo.
This study included 164 pharmacy students enrolled in a BPharm (79.3%, n = 130), BPharmMgmt (1.2%, n = 2), or MPharm (19.5%, n = 32). Of the students, 54% ( n = 88) were men, 81% ( n = 133) were domestic students, 15% ( n = 24) transferred from another degree program, and 38% ( n = 62) graduated from the course. Show cause students were less likely to graduate if they transferred from another degree program ( P = 0.0002) or failed more than three units of study (UoS; P < 0.0001). The most commonly failed UoS were related to organic or pharmaceutical chemistry, and the top student self-reported reasons for poor performance was stress/anxiety, physical health, and depression.
Pharmacy schools should aim to address student foundational knowledge in chemistry, identify at-risk students early using pre-subject testing, and provide better services to address student mental health.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
A student’s academic performance in higher education is typically defined by their achievement of learning outcomes and demonstration of their ability to apply the concepts taught. Measurement of these attributes can include assessments, quizzes, role plays, field work, practical placements, workshops, tutorials, laboratories, and examinations. In most higher education programs, a minimum standard of academic achievement is required in order to progress through the course, to ensure the student has gained adequate knowledge and skills, and that they have achieved the specified learning outcomes. In this regard, poor academic performance can be defined by instances where a student fails to meet the expected minimum academic standard. Usually this comprises a minimum overall score in a subject and/or passing a specific barrier assessment, which is ultimately linked to their retention or attrition.
Understanding the key determinants of student success, failure, retention, and attrition has become increasingly important for higher education institutions, and has been the subject of extensive research over the past few decades. Early studies on student attrition focused primarily on student characteristics [ 1 ], before attention shifted to interactions between the student and their institutions. Prominent researchers, including Spady [ 2 , 3 ], Tinto [ 4 , 5 ], and Bean [ 6 ] proposed models to explain the interplay between academic and social integration leading to underperformance, and eventually, attrition. More recently, interest has increased in examining student engagement [ 7 , 8 , 9 ], where the student and institutions have a joint responsibility for academic success. To be successful, a student needs to participate, and higher education institutions need to provide an appropriate learning environment, opportunities, and support [ 10 ].
Studies on the key determinants of student underperformance reveal an array of contributing factors. Recent systematic reviews on underperformance and dropout rates show that key determinants fall into categories relating to the institution, personal life, demographics, and social integration [ 11 , 12 ]. Within higher education institutions, studies have found that an academic’s professional knowledge and pedagogical skills, along with the institution’s learning resources, course structure, and environment, are key factors that influence academic performance and non-completion [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Teaching methods that higher institutions adopt have also been evaluated, with student-centered approaches that encourage active learning resulting in better performance when compared with a traditional teacher-centered approach [ 15 , 16 ].
In terms of individual factors, studies have found a lack of effort, distraction, poor time management, and no longer being interested in the course as having a negative impact on academic performance [ 14 , 15 , 18 , 19 ]. Active learning (e.g. self-quizzes, completing problem sets, and explaining concepts) has been found to yield better academic outcomes when compared with passive learning (e.g. reading lecture slides or class notes, watching lecture videos, and reading textbooks) [ 20 , 21 ]. In the same study, how early a student studied in relation to their exam did not affect their outcome, whereas students who were more distracted during the time they allocated for study, performed worst [ 20 , 22 ]. Education-related stress, poor mental health, exam anxiety, and sleep quality are also factors found to cause poor performance [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. Other studies have shown that part-time students and those who have previously failed subjects are at risk of further poor performance and attrition [ 17 , 28 , 29 ]. Social factors including cyberbullying [ 30 ], homesickness for international students [ 31 ], and excessive socialising [ 16 ] also have a negative effect on academic performance.
Working status was found to negatively impact academic performance [ 27 ], where poor academic outcomes were correlated with a longer time spent at work [ 16 , 28 , 32 ]. Many studies have associated the lower socioeconomic status of students and their family, or financial strain with poor academic performance [ 27 , 28 , 29 ]; whereas, other studies have shown that students in families where one parent has attended higher education tend to achieve higher grades [ 31 ]. Some studies have found men and minority students are more at risk of poor performance [ 31 , 33 ]. Part-time students are much more likely cite work and family responsibilities as reasons for stopping their studies [ 17 ]. Research on students whose first language is not that of the higher education institution is mixed, with some confirming it to be a key attributor to underperformance [ 34 , 35 , 36 ], along with students with a migrant background or who are first-generation university attendees (commonly referred to as first-in-family) [ 31 , 37 , 38 ]. In contrast, other studies have found that academic performance of international students was similar, or better, than domestic students [ 39 , 40 ].
A government panel in Australia reported that the leading drivers for non-completion in higher education are both institution-related (learning environment, an academic’s ability to teach, student to staff ratios, student engagement, and support services) and student-related (health, finance, and personal responsibilities) [ 41 ]. A survey conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) identified the top three reasons for attrition for students studying a bachelors degree to be: loss of interest, employment/financial reasons, and personal reasons (health, family, or other personal reasons). For postgraduate courses, reasons for attrition were highest in the order of personal reasons, employment/financial, followed by loss of interest [ 42 ].
Where a student has underperformed, they may be offered remediation assessments; to re-enroll and attempt the entire subject again, which may result in a delay in degree completion; or in some cases, be excluded from reenrolling into the same course for a period of time [ 43 , 44 ].
Consequences of poor performance vary across higher education institutions and may depend on the reasoning provided, extent of underperformance, and number of failed subjects. Key stake holders impacted by poor performance and attrition from higher education can include the students and their families, the higher education institution they are enrolled in, their community workforce, and government. Non-completion directly impacts the funding and reputation of an institution [ 17 , 45 , 46 ]. In Australia, where the cost of higher education for domestic students is subsidised by the federal government, non-completion incurs a direct cost to both the student and the tax-payer. The cost to the student includes lost time, psychological health, student debt, and forgone income [ 9 ]. From the perspective of workforce planning, a delay or non-completion of study reduces the number of employees entering into the workforce, and can lead to workforce shortages and place a burden on those currently in the field.
There are many studies that have examined the key determinants for student success or underperformance and attrition in health; however, most have focused on nursing or medical education [ 13 , 15 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ]. Consequently there are limited studies that have examined the rate and reasons for attrition within pharmacy degrees. Being a degree known to be difficult in technical content, and which requires students to achieve a high level of competence, it is important to investigate reasons for attrition and potential opportunities for improvement in student teaching and engagement.
In this study we analysed 10 years of demographic data and responses to why academic progression requirements had not been met in a cohort of students enrolled in a Bachelor of Pharmacy (BPharm), Bachelor of Pharmacy and Management (BPharmMgmt), or Master of Pharmacy (MPharm) degree at The University of Sydney. Our aim was to understand the key determinants for poor performance within this group of students and identify opportunities for policy and practice to reduce underperformance in the future.
Approval for this study was granted by the Human Research Ethics Committee of The University of Sydney (2022/815).
Data collection
The inclusion criteria for this study were students enrolled in a BPharm, BPharmMgmt, or MPharm degree between the period of 2008 and 2018 (inclusive), who were required to provide a minimum of one show cause at any stage of their study. Data collected on each student included: age at the start of pharmacy degree; gender; whether they transferred from another university; whether they were a domestic or international student; Australian Tertiary Admissions Rank (ATAR) upon entry, which is a percentile score that ranks Australian students finishing secondary school in relation to their academic achievement [ 51 ]; previous studies in biology, chemistry, or mathematics; show cause triggers (units of study failed); number of show causes; students’ written show cause responses; weighted average mark (WAM) at last show cause or graduation (WAM is an average grade score indicating a student’s overall academic performance over the course of their degree and is similar to a grade point average) [ 52 ]; whether they graduated; and, the number of years they spent studying the degree. Whether those students who had graduated were currently registered as a pharmacist in Australia was retrieved using the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency online registry list [accessed in 2023].
Data analysis
Researchers Da Costa, O’Brien, and Liang collected, screened, and de-identified the data, and researchers Campbell, Hinton, and Wheate analysed the data. Descriptive statistics, including mean ± SD, median, and frequencies (count and percentage) were calculated using Microsoft Excel. Mann-Whitney U tests were undertaken in GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA) to ascertain any differences between ATAR scores. Chi Square analyses were undertaken in GraphPad Prism 9.0 to compare categorical data including differences between men and women, domestic and international students, transferring and non-transferring students, and graduating and non-graduating students.
Written show cause responses were transcribed by Campbell and uploaded into NVivo (1.5.1) software (QSR International, Massachussets USA). The show cause responses were analysed reflexively using inductive thematic analysis procedures [ 53 ].This involved manually reviewing each show cause response to identify emerging themes relating to the reasons stated by the student for their poor performance. From the themes identified, a total of 43 codes were generated based on the ideas, trends, and content. Coding was conducted in a theory-driven manner, seeking to code information referencing the specific themes arising from the show cause response [ 53 ]. Themes were guided by the frequency of mention, and reported in the results if there was more than a single mention. The frequency of the subthemes was analysed to demonstrate the prevalence of stated factors that the student believed led to their poor performance.
Show cause process
Pharmacy students who do not meet the progression requirements of their degree enter one of three stages of academic intervention (Fig. 1 ). Triggers for a student not meeting the requirements for progression include: awarded a fail grade in over 50% of total units of study (subjects; UoS) taken in a semester or teaching period; an average grade (WAM) less than 50 across all UoS in a semester or teaching period; failing one, or more, barrier or compulsory UoS which includes CHEM1611, CHEM1612, PHAR2822, and any 3000 or 4000 level UoS for BPharm/BPharmMgmt; and any single UoS for MPharm; any practical component (e.g. field work or clinical work), failing the same UoS twice, having unsatisfactory attendance, or exceeding the maximum time limit allowed for the degree to be completed.
Students who fail to meet progression requirements for the first time are placed on Stage 1 of the at-risk register at which point they receive a letter from the Faculty of Medicine and Health, and are advised to complete a ‘Stay on Track’ survey and information session. At the discretion of the Associate Dean of Education, some students at Stage 1 may be required to consult an academic adviser. If a student is enrolled in a degree with a duration of less than two years full-time (e.g. MPharm), they are advised that should they fail to meet progression requirements in the following semester, they would be asked to ‘show good cause’ in order to be allowed to re-enrol in the same program; that is, they would be excluded from the degree for two years unless they could give reasons for why they should be allowed to remain studying. They are also recommended to speak to an academic advisor.
Stage 2 is triggered for a student in a 4 or 5 year undergraduate degree program (e.g. BPharm and BPharmMgmt) if they fail to meet progression requirements after being placed on Stage 1 in the previous semester, at which point the faculty sends a letter, advising the student to complete the ‘Staying on Track’ survey if they had not yet done so, and to consult an academic adviser. Stage 3 is triggered if a student fails to meet progression requirements a third time, or fails the same compulsory or barrier UoS, or any practical component twice. Students on Stage 3 are required to ‘show good cause’ and provide reasonable evidence to be allowed to re-enrol into the degree program.
The three at-risk stages of academic intervention for students who fail to meet course progression requirements. Show cause is required at Stage 2 (MPharm) or Stage 3 (BPharm/BPharmMgmt) in order to re-enrol
Demographics
In total, 164 pharmacy students received at least one show cause notification between the period of 2008 to 2018 (inclusive) and were enrolled in a BPharm (79.3%, n = 130), BPharmMgmt (1.2%, n = 2), or MPharm (19.5%, n = 32) degree (Table 1 ). Of the students, 54% ( n = 88) were men, and 81% ( n = 133) were domestic students.
Students who transferred from another degree program made up 15% ( n = 24) of the sample, and were a median two years older than those who did not transfer (median age 21, range 19–43 years). All students who transferred from another degree, were enrolled in the BPharm. Ninety-two percent of transfer students ( n = 22) were domestic and 71% ( n = 17) were women.
The age of students at the start of their degree was positively skewed, with a median age of 19 years for BPharm and BPharmMgmt (range 17–43 years). For MPharm, the median age at commencement was 24 (range 20–24) years. The median age of domestic students at the start of their BPharm or BPharmMgmt degree was 19 (range 17–43) years compared with international students at 22 (range 18–33) years. For MPharm, the median age for domestic students at commencement was 24 (range 20–54) years while for international students it was 24.5 (range 22–38) years.
Performance on entry and exit of the degree
The ATAR scores of the students in either the BPharm or BPharmMgmt were not normally distributed ( n = 78, mean ATAR 88.8 ± 4.8) (Supplementary Figure S1 ). The average ATAR required for entry into BPharm and BPharm/Mgmt at the University of Sydney is around 90. Of the 24 students who transferred from another degree program, the ATAR score was available for four students, with an average of 78.8 ± 9.8, including two outliers who had ATAR scores of 67.80 and 74.15. The average ATAR on entry to the degree of the students who graduated was 89.4 ± 3.4, which was similar to those who did not graduate, 88.5 ± 5.4. A Mann-Whitney U test showed this difference was not statistically significant (W = 702.5, p = 0.937).
The proportion of students who graduated after receiving at least one show cause was 37.8% ( n = 62), of which 77.4% ( n = 48) were registered as pharmacists at the time of data collection (Fig. 2 ). One student did not graduate their BPharm; however, they did return and complete the MPharm degree and was registered as a pharmacist at the time of data collection. The median time taken to graduation was 7 (range 1–9) years for students enrolled in the BPharm and 3 (range 2.5-8) years for those enrolled in the MPharm. During the study period, 188 students were enrolled in the BPharmMgmt degree but only two (1.1%) were required to show cause due to poor performance. Neither of those two students graduated.
A WAM score was available for all but three of the 164 students. The overall average WAM either at last show cause, if the student had not graduated, or at degree completion was 52.1 ± 12.0. For students who graduated (38.5%, n = 62), the average WAM was 62.2 ± 5.1, while for those who did not graduate (61.5%, n = 99), the average WAM was 45.7 ± 10.5.
When the proportion of students who graduated was compared across the ATAR bands (Table S1 ), it was evident that show cause students who entered their degree with an ATAR between 85 and 89.99 were more likely to graduate (44%) when compared with those who entered their degree with lower (27%) and higher (25–35%) ATAR scores.
Units failed
Across the cohort, show cause students received between 1 and 8 show cause notifications (Fig. 1 ). When the proportion of students who graduated was compared across the number of show causes received for those who received 1–5 show causes, the rate of graduation ranged from 36 to 50%, while none of the students who received six or more show causes graduated.
Percentage of students who graduated (black) and did not graduate (grey) by number of show causes received
Number of failed UoS
The median number of UoS failed across the three degree programs was 8 (BPharm, range 2–33), 9 (BPharmMgmt, range 5–13), and 5 (MPharm, range 2–12), respectively. In total, 8.5% ( n = 14) students were required to show cause because they failed 2 or 3 UoS, 19.5% ( n = 32) students failed 4 or 5 UoS and 72% ( n = 118) students failed more than 6 UoS. Of the 14 students who failed 2 or 3 UoS, 86% were studying the MPharm degree and the remaining were BPharm students. Students who failed 4 or 5 UoS, were studying a BPharm (66%), BPharmMgmt (3%), or MPharm (31%) degree. The majority of students who failed more than 6 units were studying BPharm (91%), followed by MPharm (8%), and BPharmMgmt (1%). Students who failed 2 or 3 UoS were significantly more likely to graduate when compared with those who failed 4 or 5 UoS, or more than 6 UoS \( (X_2^2=21.86, \text{P}<0.0001)\) (Supplementary Figure S2 ).
Type of failed UoS
The most failed UoS that triggered a show cause across students in the BPharm and BPharmMgmt degrees were a mix of pharmaceutical sciences, chemistry and biology, across the first and second years of the degree programs (Table 2 ). The top five UoS failed were Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences (8.8%, 116/1314 fails; unit code: PHAR1812), Chemistry 1B (Pharmacy) (6.9%, 91/1314 fails; unit code: CHEM1612), Drug Discovery and Design 1 (6.7%, 88/1465 fails; unit code: PHAR2811), Molecular Biology and Genetics (6.5%, 86/1314 fails; unit Code: MBLG1001), and Chemistry 1A (6.2%, 81/1314 fails; unit code: CHEM1611).
For students studying the MPharm, the majority of UoS failed were for pharmaceutical sciences in first year and one specific pharmacy practice unit (PHAR5717) in the second year. The top three UoS failed for MPharm were Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1A (12.6% 19/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5513), Pharmaceutical Science (7.9%, 12/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5515), and Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1B (7.9%, 12/151 fails; unit code: PHAR5516) (Table 3 ).
Gender, transfer and international students
There was no significant difference between the number of men and women who graduated after receiving at least one show cause \( (X_1^2=0.056, \text{P}=0.813)\) . There was also no significant difference in the number of UoS failed \( (X_2^2=2.249, \text{P}\hspace{0.17em}=\hspace{0.17em}0.325)\) or number of show causes received \( (X_6^2=2.829, \text{P}=0.830)\) between men and women.
Students who transferred from another degree program were significantly less likely to graduate \( (X_1^2=13.53, \text{P}\hspace{0.17em}=\hspace{0.17em}0.0002)\) . The likelihood of graduating was not statistically significant different between domestic and international students who received a show cause \( (X_1^2=0.88, \text{P}<0.348)\) (Supplementary Figure S3 ).
Student responses to show causes
There were 293 show causes in total, of which only 141 show cause response letters were available. Reasons given by students for their poor performance could be classified under four major themes: personal life matters, institutional aspects, social integration, and interest in the course (Fig. 3 ). Personal life matters could be further sub-divided into health, study familiarity, responsibilities, and other personal life matters.
The majority of show cause responses attributed poor performance to personal life reasons (87%, 396 responses), followed by institution-related (8.8%, 40 responses), lack of interest in the degree (2.2%, 10 responses), and social integration (2%, 9 responses). The five most mentioned personal life reasons that led to poor performance were stress and anxiety ( n = 63, 45%), physical health ( n = 51, 36%), and depression ( n = 39 28%). This was followed by family health, mentioned 37 times (26%), and reasons relating to employment or financial health, mentioned 33 times (23%). Reasons that related to the institution totalled 40, interest of the course totalled 10, and social reasons totalled 9. Personal life health-related reasons accounted for 41% of show cause responses. These included a combination of physical, mental, and unspecified health issues.
All show cause responses provided by students could be categorised into four major themes. Personal life was subcategorised into health, study skills, responsibilities, and other personal life
Some students identified a lack of study-related skills and study familiarity as a source of underperformance. Reasons included: carelessness in exams, poor study habits, language barrier, being an international student or mature age student, misjudging the course difficulty, overloading, burning out after high school, and being unaware of opportunities to apply for special consideration. Another set of reasons provided for underperformance included: needing to meet responsibilities and commitments for family, friendships, and romantic relationships. A variety of other personal life reasons were provided, which included: employment, finance, transition to independent living or a new country, living environment, distance to travel to the university, needing to relocate, and being physically unable to attend classes.
Student show cause responses that attributed poor performance to inefficiencies within the institution included UoS changes, error or poor timing of exams, dissatisfaction with the course and staff, and unhelpful support. Some students found the UoS content too difficult. Social reasons that lead to poor performance included: bullying, stigma from peers once failing, and homesickness (for those studying abroad). Another reason provided was no longer being interested or committed to the course.
This study investigated the key determinants of underperformance by pharmacy students at an Australian higher education institution. Our findings indicate that across the students enrolled in BPharm, BPharmMgmt, and MPharm degrees, those who had failed more UoS overall, were less likely to graduate. The types of UoS failed were weighted towards chemistry-based subjects, and the most frequent student-reported reasons for poor performance were related to personal health.
Our study also found that students who transferred from another higher education institution were less likely to graduate compared with students who had not transferred. Some studies in the US have found that students who transfer to bachelors programs from similar institutions or community colleges, which are US institutions that only offer two year undergraduate associate degrees that lead to a specific skilled job or can be used to transfer into a bachelor course [ 54 ], experience ‘transfer shock’ where grade point average (GPA) declines at the post transfer institution, which can eventually result in attrition [ 55 , 56 ]. In contrast, other studies have found no significant effects from transfers, and an overall lack of consensus on this as a universal experience [ 57 , 58 ]. A study that examined transferring engineering students found that students who transferred from similar degrees were more likely to graduate when compared with students who transferred from less comprehensive degrees [ 56 ]. A literature review that examined transferring student performance found factors that negatively influenced persistence and course completion included: a lack of social integration, limited transferrable credits, lower GPAs, lack of funding, distance from institution, academic rigour, and personal work/life balance [ 57 ].
Our analysis also found that students failing more than three UoS were more likely to not graduate when compared with those who failed fewer UoS. This finding parallels many studies that show students with poor academic outcomes are more likely to not complete their degree [ 59 , 60 ]. A recent study on student attrition, found that students who failed one subject were more likely to fail more subjects, and also had a four-fold higher likelihood of not graduating [ 27 ]. The Grattan Institute presents similar statistics, where students who consistently fail to meet academic progression requirements eventually decide to leave or are excluded from re-enrolling by the university [ 61 ].
The high occurrence of underperformance in relation to chemistry is consistent with other studies [ 62 , 63 ]. Pancyk et al. found that chemistry marks were correlated with attrition while biology marks predicted likelihood of delayed graduation for Master of Science (in Pharmacy) students. Another study found that the prior attainment of a Bachelor of Science degree to be a predictor of performance in a Doctor of Pharmacy program [ 64 ]. In countries, such as the US, where a specialised pre-admissions pharmacy test (Pharmacy College Admissions Test; PCAT) is used for entrance into a pharmacy program, the PCAT score correlated with student academic performance in the pharmacy course [ 65 ]. There are five areas examined by the PCAT, including: writing, biological processes, chemical processes, critical reading, and quantitative reasoning [ 66 ]. There is also evidence that better outcomes attained in pre-pharmacy biology and mathematics GPA [ 67 , 68 ], or having completed a four-year bachelor course, contributes to student performance in American pharmacy colleges [ 64 , 69 , 70 ]. Another study found prior academic achievement in secondary school, or pre-university study, can predict performance in an UK MPharm course; however, not the likelihood of graduation [ 71 ]. Other studies have found that pre-tests, for certain UoS, like biochemistry and pharmaceutical calculations conducted before starting a subject are correlated with overall subject performance, which makes these tests a good predictor for at-risk students [ 67 , 68 ].
The most common reasons reported by students for their underperformance in the present study were stress and anxiety, personal health, and depression. This is consistent with current literature [ 17 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ], and the 2022 Australian Student Experience Survey [ 72 ], which reported that health or stress, followed by work/life balance were the leading causes for students attrition. A specific study in pharmacy students found that exam anxiety had a negative impact on student performance in pharmacy practical exams [ 26 ]. Psychological distress among students completing a higher education degree in Norway showed negative impacts on their self-perceived academic ability, and course progression [ 73 ]. Another study investigating students’ self-reported explanations for their poor academic performance found mental health as a contributing factor, and vice versa, where poor performance intensified mental distress [ 27 ]. Although the Australian Bureau of Statistics also reported personal health reasons as a major contributor for non-completion in bachelor programs between 2018 and 2019, the leading reason was that students were no longer interested in their chosen degree. In the same report, non-completion of masters degrees was driven by family, health, or other personal reasons [ 42 ]. Student mental health is a significant driver of attrition and is common across both private and public higher institutions in Australia [ 41 ]. The mental health burden on students is recognised at The University of Sydney and so significant mental health support is offered. All students are able to access free counselling and psychological support sessions, there is a 24/7 mental health support telephone line, and additional self-help resources (like mindfulness and relaxation) are provided through the university’s website. Mental health first health training is also included in the curricula for all pharmacy degree programs at the university.
Successful completion of a pharmacy degree requires not only academic ability, but a certain level of pre-knowledge, in particular, biology and chemistry, to decrease failure rates in these subjects, avoid delays in degree completion, and possible attrition. Institutions should aim to address these barriers by introducing pre-requisite subjects or mandate compulsory bridging courses if a prior level of knowledge attainment in these subject areas is not provided. Alternatively, pre-tests for certain UoS can be conducted prior to the course commencement to identify at-risk students, and additional academic support services can be offered.
With student poor mental health found as the most common self-reported reason for poor performance in this study, often exacerbated by academic performance pressures, institutions should implement policies for early detection and support for students going through challenging times. Such policies could include more frequent reminders for students to self-assess their mental health, and information on where to seek support services. This could take form in programs being introduced prior to lectures, access to support portals made more prominent on online learning platforms, or self-check surveys to be taken at a frequency deemed appropriate.
Limitations
The present study had a number of limitation. Not all student’s ATAR scores (or equivalent) were available. The method of collecting whether a student was registered as a pharmacist was based on them not having changed their last name which may be the case for some students who changed their name after graduation (e.g. upon marriage). Students who may be registered as a pharmacist in countries other than Australia could not be determined. Not all student show cause reasons were available because of the change from physical to electronic filing over the period studied. The limited number of students who received five or more show causes also meant the study was not powered to establish a cut-off whereby after receiving a certain number of show causes, the chance of graduating is highly unlikely.
Conclusions
This study investigated the key determinants for poor academic performance in a cohort of pharmacy students enrolled in a BPharm, BPharmMgmt, and MPharm degree. The key factors that influenced whether a show cause student completed their studies included whether they transferred from another institution, and failed more than three UoS. The UoS with the highest fail rates were chemistry based, and the most frequent student self-reported reason for poor performance was personal stress and anxiety. The results indicate that pharmacy schools should aim to address student foundation knowledge in chemistry, identify at-risk students early using pre-subject testing, and provide better access and knowledge of available services to address student mental burden. Future studies should investigate whether students who have completed chemistry and biology pre-requisites perform better in their pharmacy degree.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, N.J.W.
Aljohani O. A comprehensive review of the major studies and theoretical models of student retention in higher education. High Educ Stud. 2016;6:1–18.
Article Google Scholar
Spady WG. Dropouts from higher education: an interdisciplinary review and synthesis. Interchange 1984. 1970;1(1):64–85.
Spady WG. Dropouts from higher education: toward an empirical model. Interchange. 1971;2(3):38–62.
Tinto V. Dropout from higher education: a theoretical synthesis of recent research. Rev Educ Res. 1975;45(1):89–125.
Tinto V. Leaving college: rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. 2nd ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1993.
Google Scholar
Bean JP. Dropouts and turnover: the synthesis and test of a causal model of student attrition. Res High Educ. 1980;12(2):155–87.
Tight M. Student retention and engagement in higher education. J Furth High Educ. 2020;44(5):689–704.
Carini RM, Kuh GD, Klein SP. Student engagement and student learning: testing the linkages. Res High Educ. 2006;47(1):1–32.
Thomas L, Kift S, Shah M. Student retention and success in higher education. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. pp. 1–16.
Book Google Scholar
Coates H. The value of student engagement for higher education quality assurance. Qual High Educ. 2005;11(1):25–36.
Al-Tameemi RAN, Johnson C, Gitay R, Abdel-Salam A-SG, Hazaa KA, BenSaid A, et al. Determinants of poor academic performance among undergraduate students—A systematic literature review. Int J Educ Res. 2023;4:100232.
Lorenzo-Quiles O, Galdón-López S, Lendínez-Turón A. Factors contributing to university dropout: a review. Front Educ Res. 2023;8.
Wilkinson TJ, McKenzie JM, Ali AN, Rudland J, Carter FA, Bell CJ. Identifying medical students at risk of underperformance from significant stressors. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:43.
Le HTTN, La HTT, Le TP, Nguyen TTT, Nguyen NT, Tran TP. Factors affecting academic performance of first-year university students: a case of a Vietnamese university. Int J Educ Prac. 2020;8(2):221–32.
Sharma P, Singh P, Kalhan S, Garg S. Analysis of factors affecting academic performance of MBBS students in pathology. Ann Int Med Dent Res. 2017;2.
Mascolo M, Castillo J. The origins of underperformance in higher education in America: proximal systems of influence. Pedgog Hum Sci. 2015;5(1):1–40.
Norton AC, I. and, Mackey W. Dropping out: the benefits and costs of trying university. The Grattan Institute, 2018. p. 1–65.
van Rooij E, Jansen EPWA, Van de Grift W. First-year university students’ academic success: the importance of academic adjustment. Eu J Psychol Educ. 2017;33:1–19.
Arshad M, Zaidi SM, Mahmood D. Self-esteem and academic performance among university students. J Educ Pract. 2015;6:2015.
Walck-Shannon EM, Rowell SF, Frey RF. To what extent do study habits relate to performance? CBE - Life Sci Educ. 2021;20(1):ar6.
Roick J, Ringeisen T. Students’ math performance in higher education: examining the role of self-regulated learning and self-efficacy. Learn Individ Differ. 2018;65:148–58.
Nonis SA, Hudson GI. Performance of college students: impact of study time and study habits. J Educ Bus. 2010;85(4):229–38.
Jevons C, Lindsay S. The middle years slump: addressing student-reported barriers to academic progress. High Educ Res Dev. 2018;37(6):1156–70.
Pascoe MC, Hetrick SE, Parker AG. The impact of stress on students in secondary school and higher education. Int J Adolesc Youth. 2020;25(1):104–12.
May RW, Bauer KN, Seibert GS, Jaurequi ME, Fincham FD. School burnout is related to sleep quality and perseverative cognition regulation at bedtime in young adults. Learn Individ Differ. 2020;78:101821.
Hadi MA, Ali M, Haseeb A, Mohamed MMA, Elrggal ME, Cheema E. Impact of test anxiety on pharmacy students’ performance in Objective Structured Clinical examination: a cross-sectional survey. Int J Pharm Pract. 2018;26(2):191–4.
Ajjawi R, Dracup M, Zacharias N, Bennett S, Boud D. Persisting students’ explanations of and emotional responses to academic failure. High Educ Res Dev. 2020;39(2):185–99.
Rodríguez-Hernández CF, Cascallar E, Kyndt E. Socio-economic status and academic performance in higher education: a systematic review. Educ Res Rev. 2019;29:100305.
Tomul E, Polat G. The effects of socioeconomic characteristics of ctudents on their academic achievement in higher education. Am J Educ Res. 2013;1:449–55.
Peled Y. Cyberbullying and its influence on academic, social, and emotional development of undergraduate students. Heliyon. 2019;5(3):e01393.
Sun J, Hagedorn L, Zhang Y. Homesickness at college: its impact on academic performance and retention. J Coll Stud Dev. 2016;57:943–57.
Triventi M. Does working during higher education affect students’ academic progression? Econ Educ Rev. 2014;41:1–13.
Voyer D, Voyer SD. Gender differences in scholastic achievement: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. 2014;140(4):1174–204.
Dafouz E, Camacho-Miñano MM. Exploring the impact of English-medium instruction on university student academic achievement: the case of accounting. Engl Specif Purp. 2016;44:57–67.
Civan A, Coskun A. The effect of the medium of instruction language on the academic success of university students. Educ Sci: Theory Prac. 2016;16:1981–2004.
Sawir E. Language difficulties of international students in Australia: the effects of prior learning experience. Int Educ J. 2005;6:567–80.
Mishra S. Social networks, social capital, social support and academic success in higher education: a systematic review with a special focus on ‘underrepresented’ students. Educ Res Rev. 2020;29:100307.
López MJ, Santelices MV, Carmen Maura T. Academic performance and adjustment of first-generation students to higher education: a systematic review. Cogent Educ. 2023;10(1).
Zheng RX, Everett B, Glew P, Salamonson Y. Unravelling the differences in attrition and academic performance of international and domestic nursing students with English as an additional language. Nurse Educ Today. 2014;34(12):1455–9.
Rienties B, Beausaert S, Grohnert T, Niemantsverdriet S, Kommers P. Understanding academic performance of international students: the role of ethnicity, academic and social integration. High Educ. 2012;63(6):685–700.
Final Report -. Improving retention, completion and success in higher education. Higher Education Standards Panel; Australian Government Department of Education; 2017.
Qualifications. and Work, 2018-19. Australian Bureau of Statistics; 2020.
Academic Progression. The University of Sydney [updated 31 March 2023; cited 2023 September ]. Available from: https://www.sydney.edu.au/students/academic-progression.html .
Failed. withheld and invalid units: Monash University; [updated 2023; cited 2023 September]. Available from: https://www.monash.edu/students/admin/enrolments/change/failed-withheld-invalid-units .
OCED. Education at a Glance 2023. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Publishing 2023 [Available from: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/content/publication/e13bef63-en .
Yorke M, Longden B. Retention and student success in higher education. McGraw-Hill Education (UK); 2004.
Faisal R, Shinwari L, Hussain S. Academic performance of male in comparison with female undergraduate medical students in pharmacology examinations. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67:204–8.
van Moppes NM, Willems S, Nasori M, Bont J, Akkermans R, van Dijk N et al. Ethnic minority GP trainees at risk for underperformance assessments: a quantitative cohort study. Br J Gen Pract Open. 2023;7(1).
Liu XL, Wang T, Bressington D, Nic Giolla Easpaig B, Wikander L, Tan JB. Factors influencing retention among regional, rural and remote undergraduate nursing students in Australia: a systematic review of current research evidence. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(5).
Caponnetto V, Dante A, Masotta V, La Cerra C, Petrucci C, Alfes CM, et al. Examining nursing student academic outcomes: a forty-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;100:104823.
Australian Tertiary Admission Rank. Universities Admission Centre; [cited 2023 November ]. Available from: https://www.uac.edu.au/future-applicants/atar .
Weighted Average Mark (WAM). The University of Sydney; 2023 [cited 2023 November]. Available from: https://www.sydney.edu.au/students/weighted-average-mark.html .
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Community College. Education USA; [cited 2023 November ]. Available from: https://educationusa.state.gov/ .
Ivins T, Copenhaver K, Koclanes A. Adult transitional theory and transfer shock in higher education: practices from the literature. Ref Serv Rev. 2017;45(2):244–57.
Smith NL, Grohs JR, Van Aken EM. Comparison of transfer shock and graduation rates across engineering transfer student populations. J Eng Educ. 2022;111(1):65–81.
Aulck L, West J. Attrition and performance of community college transfers. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0174683.
Diaz PE. Effects of transfer on academic performance of community college students at the four-year institution community. Coll J Res Prac. 1992;16(3):279–91.
Li I, Carroll D. Factors influencing university student satisfaction, dropout and academic performance: an Australian higher education equity perspective. Perth: National Centre for Student Equity in Higher Education, Curtin University;; 2017. p. 56.
Sosu EM, Pheunpha P. Trajectory of university dropout: investigating the cumulative effect of academic vulnerability and proximity to family support. Front Educ. 2019;4.
Cherastidtham I, Norton A, Mackey W. University attrition: what helps and what hinders university completion? Grattan Institute; 2018.
Panczyk M, Rebandel H, Belowska J, Zarzeka A, Gotlib J. Risk of attrition from master of science in pharmacy degree program: 15-year predictive evaluation. Ind J Pharm Educ Res. 2016;50(1):70–9.
Houglum JE, Aparasu RR, Delfinis TM. Predictors of academic success and failure in a pharmacy professional program. Am J Pharm Educ. 2005;69(1–5):283–9.
McCall KL, Allen DD, Fike DS. Predictors of academic success in a doctor of pharmacy program. Am J Pharm Educ. 2006;70(5):106.
Meagher DG, Pan T, Perez CD. Predicting performance in the first-year of pharmacy school. Am J Pharm Educ. 2011;75(5):81.
Pharmacy College Admission Test American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. [updated 2023; cited 2023 October]. Available from: https://www.aacp.org/resource/pharmacy-college-admission-test .
Vinall R, Khansari P, McDowell J, Ried LD, Kreys E. Impact of completion of a pre-pharmacy biochemistry course and competency levels in pre-pharmacy courses on pharmacy student performance. Pharm 2019;7(3).
Aronson BD, Eddy E, Long B, Welch OK, Grundey J, Hinson JL. Identifying low pharmaceutical calculation performers using an algebra-based pretest. Am J Pharm Educ. 2022;86(1):8473.
Chisholm MA, Cobb HH, DiPiro JT, Lauthenschlager GJ. Development and validation of a model that predicts the academic ranking of first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ. 1999;63(4):388–93.
Chisholm MA, Cobb HH, Kotzan JA. Significant factors for predicting academic success of first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ. 1995;59(4):364–70.
Bush J. Entry characteristics and academic performance of students in a master of pharmacy degree program in the United Kingdom. Am J Pharm Educ. 2012;76(7).
2022 Student Experience Survery. National Report. 2023.
Grøtan K, Sund ER, Bjerkeset O. Mental health, academic self-efficacy and study progress among college students - the SHoT Study, Norway. Front Psychol. 2019;10:45.
Download references
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sydney Pharmacy School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, 2006, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Alice Campbell, Tina Hinton, Narelle C. da Costa, Sian E. O’Brian, Danielle R. Liang & Nial J. Wheate
Charles Perkin Centre, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney NSW, 2006, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Tina Hinton
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ND, SO, and DL collated and de-identified the data. AC, TH, and NW analysed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nial J. Wheate .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The University of Sydney Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) reviewed and approved this study (Approval number 2022/815). All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. As this study utilised de-identified data collected retrospectively, The University of Sydney Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) gave ethics approval for an informed consent waiver so consent did not need to be obtained from the students whose data was used in the analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Campbell, A., Hinton, T., da Costa, N.C. et al. Causes and outcomes of at-risk underperforming pharmacy students: implications for policy and practice. BMC Med Educ 24 , 421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05327-z
Download citation
Received : 16 January 2024
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05327-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Higher education
- Underperformance
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Title: Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Discusses International Conflict, Defense and Leadership on the Hilltop
On Thursday April 25, 2024 Georgetown students gathered in the Healey Family Student Center Social Room to hear from General Charles Q. Brown, Jr., Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff about the role of the U.S. military in U.S. politics and the world. As the most senior-ranking military officer in the U.S. and military advisor to the President , General Brown shared his experiences as a military leader and students had the opportunity to ask questions.
Vilda Westh Blanc (SFS‘27), a student who was on Dan Lamothe’s Student Strategy Team this semester, introduced the event. She welcomed Brown to the stage as well as current GU Politics Fellow Dan Lamothe to moderate the conversation.
Lamothe started the conversation by asking Brown about the current state of U.S. military operations and the threats to national security. “What makes this time uniquely dangerous, uniquely challenging?” Lamothe asked.
Brown emphasized the complex dynamics of this moment for U.S. national security, noting the significance of threats from North Korea, China, Russia and Iran. He explained that before coming to his current position he championed the phrase “Accelerate change or lose.”
“Personally and professionally, I do not play for second place. And I am very focused on ensuring we have all the capabilities to ensure our national security,” Brown said.
Outlining his priorities for the U.S. military, Brown highlighted the importance of training skilled service members, embracing the modernization of capabilities, and creating a foundation of trust with communities and elected officials.
On the importance of maintaining trust with American people, Brown said “Having that trust is hugely important to ensure that we do the things the nation calls us to do as military members.”
Next, Lamothe asked Brown how the Israel-Hamas conflict shapes the priorities of the U.S. military.
On the tension between current crises and future threats, Brown said “You’ve got to balance risk over time.”
“You never want to take short-term satisfaction at the expense of your long-term goals,” Brown said.
Continuing to discuss the conflict in the Middle East, Lamothe asked Brown about what it takes to deal with such a volatile situation and what strategies the military is utilizing to keep the conflict contained.
“From the very beginning, we looked at how do we deter a future conflict and at the same time protect our armed forces and support Israel to defend itself,” Brown said. “In addition to that is making sure we were providing humanitarian assistance and minimizing collateral damage.”
“This has been a theme throughout: how do we deter a broader conflict,” Brown said. Brown further emphasized the military’s preparedness, the efforts of the U.S. National Security Council, and the role of other foreign nations.
Lamothe then asked about what initial concerns Brown had regarding Iran’s attack on Israel on April 13th.
“First thing I’ll tell you is that I didn’t have a lot of concern because I have complete confidence in our force and they were well-prepared,” Brown said. He emphasized the work of the U.S. military in the week leading up to the April 13th attack and explained the communication and collaboration between the Pentagon and White House that happened the day of.
Turning to the topic of Ukraine, Lamothe noted that despite the recent aid package approved by the U.S. Congress, many think that “Ukraine will continue to be outgunned this year. What do you see as the likely outcome this summer?”
“When Ukraine is supplied, they have been able to be effective,” Brown said, stressing the importance of continuing to provide support.
“Even broader than this: what happens in one corner of the world does not stay in one corner of the world,” Brown added. “Unchecked aggression provides opportunity for future aggression.”
Next, Lamothe asked about building trust in the U.S. military. “We’re in a time where there is dwindling support for the U.S. military in a lot of polls. There are concerns about American democracy at large. What does it take to build new faith in the American military?” Lamothe asked.
“Trust is the foundation of our profession. And part of that, my focus, is not only maintaining the trust we have but to continue to build upon it.” Brown added, “I think the most important thing I can do is lead by example.”
Brown also emphasized the importance of being non-partisan as a military member. “Our oath is to the Constitution of the United States, to an ideal— not to a leader, not to an office,” Brown said.
Students then had the opportunity to ask Brown questions.
Captain Trevor Barton, Omar Bradley Fellow and McCourt Student studying national security issues asked: “What is your assessment, as the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs, of the current health of the defense industrial base related to our production capability, and what can policymakers do to increase the resiliency of the defense industrial base?”
“There’s key things, from a policymaker standpoint, that I think are very important. Consistency is probably top of the notch,” Brown said. “What I mean by that is that there’s consistency in our demand signal from the Department of Defense in what we need. And then consistency in resourcing. When you have that consistency, that helps predictability for the defense industrial base.”
MJ Ninal (C’24), a cadet in the Air Force ROTC , asked Brown about his advice for young lieutenants in this unique time of international threats and political polarization.
“Whatever job you’re going into, get really good at it. That’s probably the most important thing you can do. I’d also say ask a lot of questions. There are no dumb questions,” Brown said. “And when you ask tough questions of your leaders, it challenges us.”
One student asked Brown about the challenges of advising political leaders and what his advice was for fostering mutual understanding of perspectives and positions.
“When providing advice, you need to understand your boss, and your boss’s boss, and their intent and what their focused on,” Brown said. He emphasized that the perfect military solution does not always line up with what is going on geopolitically, economically and diplomatically, but understanding the bigger picture is key to effective conversations and problem-solving.
Lewis Williams III (S’28), a student studying applied intelligence at Georgetown’s School of Continuing Studies asked Brown, “What are some of your role models or individuals that have inspired you, whether civilian or military?”
Brown talked about the influence of his father, who was in the Army and encouraged Brown to apply. “This is all his idea,” Brown said.
“I think the other thing that has been an inspiration to me has been the Tuskegee Airmen,” Brown said, referring to the first African American military aviators in the U.S. “Just in general, what they were able to do leading up to World War II and during World War II.”
Brown recounted his experience getting to talk to some of the Tuskegee Airmen and hear their stories. He remembered Brigadier General Charles McGee and reflected on the honor it was to meet him.
Brown also answered student questions about cybersecurity, use of innovative technologies in Ukraine, climate change as a national security threat, and promoting cooperation between branches of the U.S. military.
Luke Hughes (SFS‘27) asked Brown what his message would be to incoming Georgetown students who are considering joining the ROTC.
On reasons to join, “I would say two things: One, the opportunity to serve your nation but the opportunity to gain some valuable experience,” Brown noted.
Brown emphasized the opportunities for growing as a leader, building meaningful relationships, and giving back to your community through involvement in the military.
“We need you, whether you serve in uniform or you serve in some other part of government, that’s what makes our democracy so strong,” Brown said.
GU Politics extends its gratitude to the Walsh School of Foreign Service , the SFS Security Studies Program , the Georgetown University Military and Veterans Resource Center and the National Defense Policy Initiative for co-sponsoring this event.
This article was written by Jane Wright , a first-year graduate student in the McCourt School of Public Policy.
Watch the full recording below.

The Hoya: Panelists Discuss Ranked-Choice Voting and Polarization With GU Politics
Panelists argued ranked-choice voting produces more democratic elections and decreases polarization and apathy in a Georgetown University Institute of Politics and Public Service (GU Politics) event April 17.

Maxwell Frost Discusses Advocacy, Activism and Running for Office at Georgetown
On Wednesday, April 10, 2024 students gathered in the ICC Auditorium to hear from U.S. Representative Maxwell Frost (D-FL) about his experience as an organizer and elected official,…

Boris Johnson Talks Democracy Around World at Gaston Hall
On Thursday April, 11 Georgetown students filled Gaston Hall to hear former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Boris Johnson have a conversation about global politics and democracy…
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Gulf states’ response to Iran-Israel conflict may decide outcome of crisis
Tit-for-tat attacks present Sunni monarchies with complicated choices over region’s future
Iran’s missile and drone attack on Israel had, by the end of this week, become one of the most interpreted events in recent modern history. Then, in the early hours of Friday, came reports of Israel’s riposte . As in June 1914, when Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife were assassinated in a moment that ultimately led to the first world war, these shots were heard around the world, even if few can agree conclusively on what they portend.
By one de minimis account, Tehran was merely sending a performative warning shot with its attack last Saturday, almost taking its ballistic missiles out for a weekend test drive. The maximalist version is that this was a state-on-state assault designed to change the rules of the Middle East. By swarming Israel with so many projectiles, such an assessment goes, Iran was prepared to risk turning Israel into a mini-Dresden of 1945 and was only thwarted by Israeli strategic defences and, crucially, extraordinary cooperation between the US, Israel and Sunni Gulf allies.
Whatever Iran’s ultimate intention, its assault and now Israel’s reported counterattack have presented the Gulf states with dilemmas and acute choices, according to Hugh Lovatt of the European Council on Foreign Relations. How they respond may determine the outcome of the crisis.

The key question is: do the Sunni monarchies led by Saudi Arabia fear Iran and its proxies more than they detest Israel and the damage it is inflicting on Palestinians and regional stability?
For the past six months, that choice has been suppressed, as Iran and the Sunni states have forged a fragile united front. In January, Saudi Arabia ensured that Iran had a seat at the table through a joint meeting of the Gulf Cooperation Council and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (GCC-IOC).
Nevertheless, the two sides have resolute disagreements – over a two-state solution, a future role for Hamas , and whether state boycotts or disinvestment, once a common tool of the Arab states against Israel, should be used in this crisis to put the pressure on Israel that Joe Biden was not willing to deploy.
Further, Iran has made no secret of its desire to see the US driven out of the region, a vision that the Gulf states do not share.
Cooperation with Israel
At issue is whether Arab states’ cooperation with Israel to repel Iran’s attack denotes something bigger and more permanent. One school of thought is articulated by Martyn Idynk, a former US ambassador to Israel, who told a Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) briefing of the Iranian attack: “What happened … is the Sunni Arabs, particularly Jordan and Saudi Arabia, came out of the closet and made it clear that the threat from Iran was far greater than anything. What we discovered was that the strategic coordination between the US and Israel is a lot further along than most of us knew … and [Arab states] who have been attacked by Iranian missiles and rockets before now have a credible defence umbrella that is part of a US-Sunni-Israel strategic cooperation arrangement.”
He said the Gulf states no longer cared if the world knew about this alliance and that as long as the Israeli prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, could show a sensitivity to Arab concerns, the basis existed to develop the Israeli-Sunni relationship.
It is certainly true that the Gulf states’ role in the defence of Israel has been long in the making. “We have been practising our steps together over and over for years,” said one British official. This is based on the supposition that the Arab states and Israel are “frenemies”.
Speaking about the defence operation launched against the incoming barrage from Tehran, the CFR fellow Max Boot said: “This is a huge win for this de facto Centcom alliance and this new air defence network. A 99% interception rate is off the charts. The US played a huge role, but so did the Arabs.”
Some Gulf nations have been more coy about their role than others, fearing a domestic backlash. Qatar had no involvement despite hosting the largest US base in the Middle East. Equally, no US F-35s flew from Dhafra air base in the United Arab Emirates . Kuwait may have allowed US planes into the sky, not to attack Iran missiles, but to carry out “routine intelligence” sorties. Saudi Arabia’s airborne warning and control system was operational, possibly providing intelligence.
Above all, Jordan made no effort to disguise the fact that it was shooting down Iranian drones to defend its sovereign airspace, prompting angry exchanges between the two countries. These included Jordan accusing Iran of having used the militant Muslim Brotherhood group and its Iraqi militia proxies for months to mount infiltration operations on its territory to stir up the largest Palestinian population in the region.

The US military has for years been advocating an integrated air defence alliance, stitching together the Gulf states and Israel.
Stage one was the Abraham accords in 2020, through which Bahrain and the UAE normalised relations with Israel. Stage two happened in September 2021 with the relocation of Israel into Centcom, the US-Middle East combatant command that includes Arab states.
The question now is whether the latest events will result in an anti-Iranian air defence alliance, and if so, on what terms.
Dana Stroul, who until December was the most senior civilian official at the Pentagon with responsibility for the Middle East, insisted: “Whatever regional politicians may say, the military, security and intelligence establishments of both the Arab states and Israel are quite clear – that Iran is the centre of gravity for instability, the export of terrorism and its illicit nuclear weapons programme.”
Little attempt has been made in the Saudi press to disguise Riyadh’s irritation with Iran. In Arab News, Abdulaziz Sagar, the chair of the Gulf Research Centre, wrote: “The Iranian leadership has tried to position itself as the guardian of the rights of the Palestinian people and the leading player in the Palestinian struggle against Israel. This policy turned into the hijacking of the Palestinian cause and employing the plight of the Palestinians in an utterly obscure manner to support Iran’s expansionist and interventionist regional policy and national interests.”
after newsletter promotion
He added: “The inevitable outcome of the Iranian missile attack on Israel is the breakdown of the myth … that the Iranian leaders imparted on the imaginations of the Arab world: that supporting Iran, its revolution and its leaders is the only way to effectively deal with Israeli arrogance and aggression.”
In Israel, politicians hope the Saudis will see the week’s events as a turning point. The defence minister, Yoav Gallant, said: “We have an opportunity here to establish a strategic alliance against this serious threat from Iran, which threatens to put nuclear explosives on the heads of these missiles.”
But Stroul urged caution. “If this integrated air defence is about the sovereign airspace of our partners, there is room to work together, but if we try to push this into an anti-Iran, pro-Israel coalition, our partners will be nervous.”
Furthermore, some regard it as overblown triumphalism to suggest that the Gulf states are about to meaningfully intensify relations with Israel. Lovatt said Arab nations’ cooperation with the response to Iran’s attack could be seen simply as an attempt to limit the damage inflicted by Tehran, and so prevent an escalatory Israeli response.
He said Riyadh’s foreign policy was on a new course of putting its own economy first, and that was the purpose of the Saudi-Iranian agreement reached in 2023 with the help of Iraq and China.

Palestinian future
Saudi Arabia, along with Qatar, Jordan, the UAE and Egypt , had in recent months invested heavily in their own Palestinian peace plan, he pointed out. This included proposals for a ceasefire, followed by an Arab international protection force operating in both Gaza and, significantly, the West Bank. Under the plan, the protection force would be formed at the request of the Palestinian president, Mahmoud Abbas, and not be externally imposed. This would be the precursor to peace talks lasting no more than two years leading to the formation of a Palestinian state.
All parties would have to agree to this end point, presenting an obstacle for Netanyahu. The plan promised Israeli regional recognition and integration at the end stage. Lovatt said the Arab states had hoped to release the plan in March, but it had been delayed by the US. A key element would include giving Hamas a role within a rejuvenated Palestinian leadership organisation.
It was possible, Lovatt said, that Iran could be brought on board for this, despite its longstanding opposition to a two-state solution. Noting that Iran signed a GCC-IOC statement supporting a two-state solution in January, he said that should a concrete plan emerge for this, Palestinians, including Hamas, accepted it may be possible to persuade Tehran.
Although there is widespread cynicism about Saudi intentions towards the Palestinians, many British officials insisted Riyadh was speaking enthusiastically about the possibility of staging a peace conference. Saudi diplomats themselves have denied that they would jettison the Palestinians if Biden met Riyadh’s demands for its own security in return for normalisation with Israel.
Tobias Borck, the Middle East lead at the the RUSI defence thinktank, said: “The Palestinian issue stands alongside Riyadh’s own domestic national interests, but I think the Saudis are keenly aware that the kind of stability they want in the region is only really possible when this volatility from the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is somehow tamed.”
On this basis, he noted, Saudi Arabia would resist more conflict with Iran for now, regarding it as a diversion, and instead insist the world’s gaze must not turn from Gaza .
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates

Middle East crisis: Germany to resume working with Unrwa after UN report finds Israel yet to supply evidence to back terror claims – as it happened

Muted Iranian reaction to attack provides short-term wins for Netanyahu
Israel has mounted airstrikes on iran, us confirms, as tehran plays down attack.

What we know so far about Israel’s strike on Iran

Iran and Israel playing with fire as old rules of confrontation are torn up

What’s in Isfahan? The city home to Iranian nuclear facilities

US to impose new sanctions against Iran after its air attack on Israel

Netanyahu aims to trap west into war across Middle East, says Iranian diplomat

Middle East conflict risks sharp rise in oil prices, says IMF

IDF chief of staff says Israel will respond to Iran missile attack
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense. ... Outcomes. Possible outcomes include: Acceptable with minor or no revisions (no further approval required) Acceptable with major revisions in content or format (in this case, one or more committee members must be ...
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate. PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are ...
There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) ... Note: In some countries, such as in the United States, a viva is known as a 'PhD defense' and is performed publicly in front of a panel or board of examiners and an open audience. In these ...
Graduate Administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense. Nominate a Faculty Member to Serve as Chair for Your Defense A Chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense exam to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense. Instructions for the Chair. can be accessed on the AS&E Intranet by faculty
tips from former PhD stude nts and super visors, this book. unpacks the principles and unwritten rules underpinning. the defence. Addressing planning and preparing for the. doctoral defence, and ...
A defense committee must be approved by the BPH program and the student's advisor, ... Once the committee determines the outcomes, the student will be asked back into the room and the Committee provides the student with any [minor] changes needed to the dissertation. ... Any dissertation that varies significantly from the Graduate School or ...
Evaluation Decisions for Doctoral Defense. Doctoral students are required to review the degree plans for their program, along with information about specific degree requirements and estimated timelines to reach various benchmarks for the different degree plan specializations. There are three possible evaluation decisions for the doctoral ...
Thesis defence decisions and outcomes: Visit the PhD thesis examination regulations section on decisions for additional information about decisions and outcomes. Thesis submission: Visit the thesis submission webpage for information about the thesis submission process, including approvals that must be obtained before submitting your thesis.
1. Start Your Preparations Early. Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months' exercise. Don't wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted. 2.
The PhD defence, or viva, is significant academic rite of passage, which as well as marking the culmination of years of study, can also be a highly charged emotional moment. ... At the end of the defence, candidates can be nervous to hear the outcome, and the minutes while the committee is in deliberation may feel like hours. Then, after ...
The doctoral defense is an important step towards obtaining the doctoral degree. As such, preparing for the event is necessary. Anecdotal evidence highlights that there is a wide variety of ways ...
The doctoral defence is the oral examination of the doctoral thesis. This event is an important step for doctoral candidates in obtaining their degree. It is important, as in some defence formats such as the UK-style viva voce or, shorter, viva, the performance during the defence forms part of the overall assessment of the thesis.
POSTS Swath and Dive: A pattern for PhD defense presentations by Luis P. Prieto, November 11, 2022 - 10 minutes read - 2037 words In recent times I'm having the fortune of seeing several of my own doctoral students approach the end of the doctoral journey (yes, it does end!). As they submit the dissertation and prepare for their defense, there is one piece of advice I find myself giving ...
This Guide was created to help Ph.D. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. The Guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from Ph.D. graduates. The tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can ...
Once you have submitted your thesis you will be invited to defend your doctorate at a 'viva voce' (Latin for 'by live voice') or oral examination. The thesis defence can be a daunting prospect, but many people really enjoy this experience of discussing their PhD research with genuinely interested experts. It can also be a useful networking ...
the proposal was defended. For those requiring a second defense, length of time to complete will also be noted, as well as the outcome (success or failure) of the second attempt. Outcome Proposal Defense The dissertation proposal defense is to occur no more than a year after a student takes the qualifying exam. Passing the proposal defense is a ...
A variety of outcomes of the formal proceedings are possible. A few of the most common: A unanimous pass, with at most minimal changes required in the thesis before the degree is granted. ... one dissenting vote is allowed at the PhD level. A typical defense will consist of these parts:
Committee members attend the PhD defense, usually in person. Typically, this lasts about 90 minutes. Take notes on any editorial improvements (e.g., "make clear that the throughput graph is measured in gallons/minute"). Vote on the outcome and sign the form. If the student is given a set of changes to implement, the advisor asks students to ...
Outcomes of a PhD proposal defense. There are about 4 possible outcomes after the student presents and defends his proposal: The proposal passes with minor or no corrections. The proposal passes with major corrections. The student retakes the proposal by re-writing it (may include change of topic) and defending it again. The proposal is rejected.
Major corrections or resubmission. The thesis needs further work to be of doctoral standard. This might include more research, rewriting sections or including new literature. Suggestion that you resubmit for, or are awarded, a lower degree (MPhil or MSc). Research is of good quality but too narrow for a doctorate. Outright fail.
Address the educational and career goals of the applicant. 2. Clearly address the applicant's ability to perform graduate-level study and research. 3. The letter writers should also know the applicant well enough to discuss the applicant's capacity to perform, excel and succeed in a graduate program.
PhD Proposal by Sophia Kioulaphides. Engineering synthetic, vasculogenic hydrogels to direct stem cell-derived islet maturation, engraftment, and function for Type 1 Diabetes. 1.
The outcome of the \defense" is absolutely known before it is ever scheduled. If this is not the case then the program needs to carefully examine its mentor- ... A PhD defense does not need to last more than two hours. There is nothing wrong with a short discussion between the candidate and members of the advisory committee. There is
Shengxin Tu dissertation defense - May 10. Posted by duthip1 on Friday, April 26, 2024 in News.. PhD candidate Shengxin Tu will defend her dissertation on Friday, May 10, at 8 a.m. Central Time, at 2525 West End Avenue, in the 11th floor large conference room (suite 1100, room 11105). Her advisor is Bryan Shepherd.All are invited and encouraged to attend.
May 3 (Fri) @ 3:00pm: "Reeb Graphs for Topological Connectomics," S. Shailja, ECE PhD Defense Date and Time. May 3, 2024 - 3:00pm. Location. Engineering Science Building (ESB), Room 2001. ... In 2023, Shailja was awarded the Fiona and Michael Goodchild best graduate student mentor award. She has also been named an NSF iRedefine ECE Fellow.
The other option the defense has in its opening argument is one that is used quite often and is the safest bet in many cases: Team Trump could simply ask the jurors to keep an open mind throughout ...
Show cause students were less likely to graduate if they transferred from another degree program (P = 0.0002) or failed more than three units of study (UoS; P < 0.0001). The most commonly failed UoS were related to organic or pharmaceutical chemistry, and the top student self-reported reasons for poor performance was stress/anxiety, physical ...
On Thursday April 25, 2024 Georgetown students gathered in the Healey Family Student Center Social Room to hear from General Charles Q. Brown, Jr., Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff about the role of the U.S. military in U.S. politics and the world.
A Moscow State University graduate who had worked in Russia's nuclear energy industry in the early 2000s, Ivanov served as Shoigu's deputy governor of the Moscow region in 2012.
How they respond may determine the outcome of the crisis. View image in fullscreen Israel's Iron Dome defence system launching weapons to intercept Iranian missiles on 14 April.