Problem Solving in Mathematics
- Math Tutorials
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
The main reason for learning about math is to become a better problem solver in all aspects of life. Many problems are multistep and require some type of systematic approach. There are a couple of things you need to do when solving problems. Ask yourself exactly what type of information is being asked for: Is it one of addition, subtraction, multiplication , or division? Then determine all the information that is being given to you in the question.
Mathematician George Pólya’s book, “ How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method ,” written in 1957, is a great guide to have on hand. The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya’s book and should help you untangle even the most complicated math problem.

Use Established Procedures
Learning how to solve problems in mathematics is knowing what to look for. Math problems often require established procedures and knowing what procedure to apply. To create procedures, you have to be familiar with the problem situation and be able to collect the appropriate information, identify a strategy or strategies, and use the strategy appropriately.
Problem-solving requires practice. When deciding on methods or procedures to use to solve problems, the first thing you will do is look for clues, which is one of the most important skills in solving problems in mathematics. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that these words often indicate an operation.
Look for Clue Words
Think of yourself as a math detective. The first thing to do when you encounter a math problem is to look for clue words. This is one of the most important skills you can develop. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that those words often indicate an operation.
Common clue words for addition problems:
Common clue words for subtraction problems:
- How much more
Common clue words for multiplication problems:
Common clue words for division problems:
Although clue words will vary a bit from problem to problem, you'll soon learn to recognize which words mean what in order to perform the correct operation.
Read the Problem Carefully
This, of course, means looking for clue words as outlined in the previous section. Once you’ve identified your clue words, highlight or underline them. This will let you know what kind of problem you’re dealing with. Then do the following:
- Ask yourself if you've seen a problem similar to this one. If so, what is similar about it?
- What did you need to do in that instance?
- What facts are you given about this problem?
- What facts do you still need to find out about this problem?
Develop a Plan and Review Your Work
Based on what you discovered by reading the problem carefully and identifying similar problems you’ve encountered before, you can then:
- Define your problem-solving strategy or strategies. This might mean identifying patterns, using known formulas, using sketches, and even guessing and checking.
- If your strategy doesn't work, it may lead you to an ah-ha moment and to a strategy that does work.
If it seems like you’ve solved the problem, ask yourself the following:
- Does your solution seem probable?
- Does it answer the initial question?
- Did you answer using the language in the question?
- Did you answer using the same units?
If you feel confident that the answer is “yes” to all questions, consider your problem solved.
Tips and Hints
Some key questions to consider as you approach the problem may be:
- What are the keywords in the problem?
- Do I need a data visual, such as a diagram, list, table, chart, or graph?
- Is there a formula or equation that I'll need? If so, which one?
- Will I need to use a calculator? Is there a pattern I can use or follow?
Read the problem carefully, and decide on a method to solve the problem. Once you've finished working the problem, check your work and ensure that your answer makes sense and that you've used the same terms and or units in your answer.
- 2nd Grade Math Word Problems
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- How to Use Math Journals in Class
- The Frayer Model for Math
- Algorithms in Mathematics and Beyond
- "Grandpa's Rubik's Cube"—Sample Common Application Essay, Option #4
- Math Stumper: Use Two Squares to Make Separate Pens for Nine Pigs
- Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Graphic Organizers in Math
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- Christmas Word Problem Worksheets
- Solving Problems Involving Distance, Rate, and Time
- Innovative Ways to Teach Math
- Study Tips for Math Homework and Math Tests
- 7 Steps to Math Success

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
A Guide to Problem Solving
When confronted with a problem, in which the solution is not clear, you need to be a skilled problem-solver to know how to proceed. When you look at STEP problems for the first time, it may seem like this problem-solving skill is out of your reach, but like any skill, you can improve your problem-solving with practice. How do I become a better problem-solver? First and foremost, the best way to become better at problem-solving is to try solving lots of problems! If you are preparing for STEP, it makes sense that some of these problems should be STEP questions, but to start off with it's worth spending time looking at problems from other sources. This collection of NRICH problems is designed for younger students, but it's very worthwhile having a go at a few to practise the problem-solving technique in a context where the mathematics should be straightforward to you. Then as you become a more confident problem-solver you can try more past STEP questions. One student who worked with NRICH said: "From personal experience, I was disastrous at STEP to start with. Yet as I persisted with it for a long time it eventually started to click - 'it' referring to being able to solve problems much more easily. This happens because your brain starts to recognise that problems fall into various categories and you subconsciously remember successes and pitfalls of previous 'similar' problems." A Problem-solving Heuristic for STEP Below you will find some questions you can ask yourself while you are solving a problem. The questions are divided into four phases, based loosely on those found in George Pólya's 1945 book "How to Solve It". Understanding the problem
- What area of mathematics is this?
- What exactly am I being asked to do?
- What do I know?
- What do I need to find out?
- What am I uncertain about?
- Can I put the problem into my own words?
Devising a plan
- Work out the first few steps before leaping in!
- Have I seen something like it before?
- Is there a diagram I could draw to help?
- Is there another way of representing?
- Would it be useful to try some suitable numbers first?
- Is there some notation that will help?
Carrying out the plan STUCK!
- Try special cases or a simpler problem
- Work backwards
- Guess and check
- Be systematic
- Work towards subgoals
- Imagine your way through the problem
- Has the plan failed? Know when it's time to abandon the plan and move on.
Looking back
- Have I answered the question?
- Sanity check for sense and consistency
- Check the problem has been fully solved
- Read through the solution and check the flow of the logic.
Throughout the problem solving process it's important to keep an eye on how you're feeling and making sure you're in control:
- Am I getting stressed?
- Is my plan working?
- Am I spending too long on this?
- Could I move on to something else and come back to this later?
- Am I focussing on the problem?
- Is my work becoming chaotic, do I need to slow down, go back and tidy up?
- Do I need to STOP, PEN DOWN, THINK?
Finally, don't forget that STEP questions are designed to take at least 30-45 minutes to solve, and to start with they will take you longer than that. As a last resort, read the solution, but not until you have spent a long time just thinking about the problem, making notes, trying things out and looking at resources that can help you. If you do end up reading the solution, then come back to the same problem a few days or weeks later to have another go at it.
If you wish to print this document, pull down the "File" menu and select "Print".
Problem Solving Steps
Introduction.
Solving problems is an important part of any math course. Techniques used for solving math problems are also applicable to other real-world situations. When solving problems it is important to know what to look for and to understand possible strategies for solving. As with most things, the more problems you solve, the better you will get at it. As you solve different types of math problems, you will gain a better understanding of the techniques that can be used with each type of problem.
In his book called How to Solve It, George Polya (1887 1985), proposed a four-step process for problem solving. In this module, we will take a look at those four common problem-solving principles as well as examples of techniques to be applied when solving problems.
Step 1: Understand the problem
In order to solve a problem, it is important to understand what you are being asked to find.
Strategies for understanding the problem:
- Review the problem. If you are solving a word problem, read through the entire problem.
- Seek to understand all the words used in stating the problem. Look for key words that will help you determine whether you will need to add, subtract, multiply, divide, or use a combination of these functions.
- Determine what you are being asked to find or show.
- Restate the problem in your own words.
- Try drawing a picture or diagram to better understand the problem.
- Make sure you have all of the information you need to solve the problem.
Step 2: Develop a plan
Determine how you will solve the problem. Some problems are solved by using a formula and others require you to develop an equation. Pictures, tables, or charts may also be used.
Keep in mind, you may be solving problems that require multiple steps. When you encounter these, break them down into smaller steps and solve each piece. The more problems you solve, the easier it will get to develop a plan for solving problems. You will begin to learn what techniques work best for each type of problem you solve.
Here are some of the common problem-solving techniques:
- Guess and check
- Make a table or list
- Eliminate possibilities
- Use symmetry
- Consider special cases
- Solve as an equation
- Look for a pattern
- Draw a sketch or a picture
- Solve a simpler problem
- Use a model
- Start from the end - work backward
- Use a formula
Step 3: Carry out the plan
Once you have determined your plan for solving the problem, the next step is putting that plan to work. Use the approach that makes sense for the problem and solve it. In most cases, this step will be easier than actually determining the plan. Having an understanding of basic math (pre-algebra) skills will help as you perform the necessary steps to solve the problem. Memorizing the simple multiplication and division tables at least to 10 can make solving problems much easier as well.
If you find that the problem-solving approach you chose does not work, you will need to go back to step two and choose a new approach. Having patience while carrying out your plan is important. It is not uncommon for mathematicians to have to try multiple approaches when solving problems.
Step 4: Look back and check
Here is where you check your logic. If you solved an equation, fill your answer into the equation and check to make sure it works. If you solved a word problem, consider whether or not your answer makes sense. If the problem asked for the height of a ball in the air and your answer was -10 feet, that does not make sense. Just because you get a number doesnt mean it is right. It is important to check your answer and see if it logically makes sense. If your answer does not make sense, you should review the approach you chose as well as your math calculations. Many errors are corrected in this final step of the problem-solving process.
Example Problems
Example 1 Difference in temperature
The hottest temperature ever recorded in Death Valley, CA was 134 degrees on July 10, 1913. The coldest temperature ever recorded there, 15 degrees, occurred earlier that year on January 8, 1913. What was the difference between these record temperatures in 1913? (www.nps.gov)
Step 1: Understand the problem: After reading through the problem, you will find that the problem to solve is clearly stated. You will need to determine the difference in temperature between the hottest and coldest recorded days in Death Valley, CA.
Step 2: Develop a plan: As you were reading the problem, you noted the key word difference. To find the difference between two numbers, you will need to use subtraction. You are now ready to set up an equation. You can assign the variable, x, to the unknown. In this case, the unknown is the difference in temperatures.
x = 134 - 15
Step 3: Carry out the plan: Now that you have developed your equation, go ahead and solve it. x = 134 - 15 x = 119 degrees
Step 4: Look back and check: To check your equation, fill the answer back into the equation and make sure it works. Also, consider whether or not your answer makes sense. If you had received an answer that was significantly higher or lower than either of the temperatures in the problem, that would indicate that there may be an error in your calculations. 119 = 134 15
Example 2 Interest Earned
If a savings account balance of $2650 earns 4% interest in one year, how much interest is earned? What will the account balance be after the interest is earned?
Step 1: Understand the problem: After reading through the problem, you recognize that there are actually two problems to solve. You will need to determine the amount of interest on the account balance and you will need to determine what the account balance will be when the interest is earned.
Step 2: Develop a plan: The first problem you need to solve is the amount of interest earned on $2650. To find the amount of interest, you will need to multiply the current account balance by the interest rate. In order to complete the multiplication problem, you will need to change the percent into a decimal. You can assign the variable, x, to the unknown. In this case, the unknown is the amount of interest earned.
Once you determine how much interest will be earned, you can solve the second problem. You will need to add the current balance and the interest earned to determine how much will be in the account once the interest is applied. To establish an equation for the second problem, you can assign a variable, y, to the unknown. You establish this equation to solve the second problem.
y = $2650 + x
Step 3: Carry out the plan: Now that you have developed your equations, go ahead and solve them.
Part 1: x = .04 x $2650 x = $106
Part 2: y = $2650 + x y = $2650 + $106 y = $2756
Step 4: Look back and check: To check your equations, fill the answers back into them. Also, consider whether or not your answers makes sense. If you had received an answer that was lower or significantly higher than the original account balance, that would indicate there may be an error in your calculations.
Part 1: $106 = .04 x $2650
Part 2: $2756 = $2650 + $106
Example 3 - Book Buyers
In a recent sample of book buyers, 70 more shopped at large-chain bookstores than at small-chain/independent bookstores. A total of 442 book buyers shopped at these two types of stores. How many buyers shopped at each type of bookstore?
Step 1: Understand the problem: After reading through the problem, you determine you are asked to find the number of buyers shopping at each type of bookstore.
Step 2: Develop a plan: To solve this problem you will need to assign a variable, x, for one of the unknowns. If x is the number of book buyers shopping at large-chain bookstores, then (x 70) = the number of book buyers shopping at small-chain/independent bookstores.
To solve the problem, you come up with this equation: x + x - 70 = 442
Step 3: Carry out the plan: Now that you have developed your equation, go ahead and solve it.
x + x - 70 = 442 2x 70 + 70 = 442 + 70 2x /2= 512 /2 x = 256
After solving the equation, you determine that 256 people shopped at large-chain bookstores. You can plug 256 into the equation representing those shopping at small-chain bookstores (x - 70).
256 70 = 186
186 people shopped at small-chain bookstores
Step 4: Look back and check: To check your answers, fill them back into the original problem. Also, consider whether or not your answers makes sense. If the number of small-chain store shoppers was greater than the number of large-chain store shoppers or if the two numbers did not equal 442 that would indicate there was an error in your calculations.
The number of large chain shoppers (256) is 70 more than the number of small-chain store shoppers (186), and the total number of these shoppers (256 + 186) is 442.
Teaching Problem Solving in Math
- Freebies , Math , Planning

Every year my students can be fantastic at math…until they start to see math with words. For some reason, once math gets translated into reading, even my best readers start to panic. There is just something about word problems, or problem-solving, that causes children to think they don’t know how to complete them.
Every year in math, I start off by teaching my students problem-solving skills and strategies. Every year they moan and groan that they know them. Every year – paragraph one above. It was a vicious cycle. I needed something new.

I put together a problem-solving unit that would focus a bit more on strategies and steps in hopes that that would create problem-solving stars.
The Problem Solving Strategies
First, I wanted to make sure my students all learned the different strategies to solve problems, such as guess-and-check, using visuals (draw a picture, act it out, and modeling it), working backward, and organizational methods (tables, charts, and lists). In the past, I had used worksheet pages that would introduce one and provide the students with plenty of problems practicing that one strategy. I did like that because students could focus more on practicing the strategy itself, but I also wanted students to know when to use it, too, so I made sure they had both to practice.
I provided students with plenty of practice of the strategies, such as in this guess-and-check game.

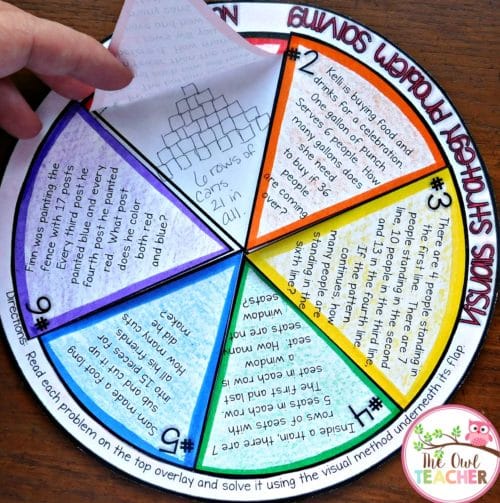
There’s also this visuals strategy wheel practice.

I also provided them with paper dolls and a variety of clothing to create an organized list to determine just how many outfits their “friend” would have.

Then, as I said above, we practiced in a variety of ways to make sure we knew exactly when to use them. I really wanted to make sure they had this down!

Anyway, after I knew they had down the various strategies and when to use them, then we went into the actual problem-solving steps.
The Problem Solving Steps
I wanted students to understand that when they see a story problem, it isn’t scary. Really, it’s just the equation written out in words in a real-life situation. Then, I provided them with the “keys to success.”
S tep 1 – Understand the Problem. To help students understand the problem, I provided them with sample problems, and together we did five important things:
- read the problem carefully
- restated the problem in our own words
- crossed out unimportant information
- circled any important information
- stated the goal or question to be solved
We did this over and over with example problems.

Once I felt the students had it down, we practiced it in a game of problem-solving relay. Students raced one another to see how quickly they could get down to the nitty-gritty of the word problems. We weren’t solving the problems – yet.

Then, we were on to Step 2 – Make a Plan . We talked about how this was where we were going to choose which strategy we were going to use. We also discussed how this was where we were going to figure out what operation to use. I taught the students Sheila Melton’s operation concept map.

We talked about how if you know the total and know if it is equal or not, that will determine what operation you are doing. So, we took an example problem, such as:
Sheldon wants to make a cupcake for each of his 28 classmates. He can make 7 cupcakes with one box of cupcake mix. How many boxes will he need to buy?
We started off by asking ourselves, “Do we know the total?” We know there are a total of 28 classmates. So, yes, we are separating. Then, we ask, “Is it equal?” Yes, he wants to make a cupcake for EACH of his classmates. So, we are dividing: 28 divided by 7 = 4. He will need to buy 4 boxes. (I actually went ahead and solved it here – which is the next step, too.)
Step 3 – Solving the problem . We talked about how solving the problem involves the following:
- taking our time
- working the problem out
- showing all our work
- estimating the answer
- using thinking strategies
We talked specifically about thinking strategies. Just like in reading, there are thinking strategies in math. I wanted students to be aware that sometimes when we are working on a problem, a particular strategy may not be working, and we may need to switch strategies. We also discussed that sometimes we may need to rethink the problem, to think of related content, or to even start over. We discussed these thinking strategies:
- switch strategies or try a different one
- rethink the problem
- think of related content
- decide if you need to make changes
- check your work
- but most important…don’t give up!
To make sure they were getting in practice utilizing these thinking strategies, I gave each group chart paper with a letter from a fellow “student” (not a real student), and they had to give advice on how to help them solve their problem using the thinking strategies above.

Finally, Step 4 – Check It. This is the step that students often miss. I wanted to emphasize just how important it is! I went over it with them, discussing that when they check their problems, they should always look for these things:
- compare your answer to your estimate
- check for reasonableness
- check your calculations
- add the units
- restate the question in the answer
- explain how you solved the problem
Then, I gave students practice cards. I provided them with example cards of “students” who had completed their assignments already, and I wanted them to be the teacher. They needed to check the work and make sure it was completed correctly. If it wasn’t, then they needed to tell what they missed and correct it.

To demonstrate their understanding of the entire unit, we completed an adorable lap book (my first time ever putting together one or even creating one – I was surprised how well it turned out, actually). It was a great way to put everything we discussed in there.

Once we were all done, students were officially Problem Solving S.T.A.R.S. I just reminded students frequently of this acronym.
Stop – Don’t rush with any solution; just take your time and look everything over.
Think – Take your time to think about the problem and solution.
Act – Act on a strategy and try it out.
Review – Look it over and see if you got all the parts.

Wow, you are a true trooper sticking it out in this lengthy post! To sum up the majority of what I have written here, I have some problem-solving bookmarks FREE to help you remember and to help your students!
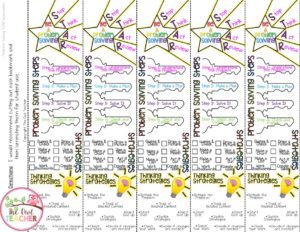
You can grab these problem-solving bookmarks for FREE by clicking here .
You can do any of these ideas without having to purchase anything. However, if you are looking to save some time and energy, then they are all found in my Math Workshop Problem Solving Unit . The unit is for grade three, but it may work for other grade levels. The practice problems are all for the early third-grade level.
- freebie , Math Workshop , Problem Solving
FIND IT NOW!
Check me out on tpt.

CHECK THESE OUT

Three Types of Rocks and Minerals with Rock Cycle Circle Book
Partitioning Shapes Equal Share Fractions Halves, Thirds, Fourths Math Puzzles
Want to save time?
COPYRIGHT © 2016-2024. The Owl Teacher | Privacy page | Disclosure Page | Shipping | Returns/Refunds
BOGO on EVERYTHING!

4 Best Steps To Problem Solving in Math That Lead to Results
Eastern Shore Math Teacher
What does problem solving in math mean, and how to develop these skills in students? Problem solving involves tasks that are challenging and make students think. In teaching through problem solving, learning takes place while trying to solve problems with specific concepts and skills. Therefore, teachers need to provide safe learning spaces that foster a growth mindset in math in order for students to take risks to solve problems. In addition, providing students with problem solving steps in math builds success in solving problems.

By providing rich mathematical tasks and engaging puzzles, students improve their number sense and mindset about mathematics. Click Here to get this Freebie of 71 Math Number Puzzles delivered to your inbox to use with your students.
Students who feel successful in math class are happier and more engaged in learning. Check out The Bonus Guide for Creating a Growth Mindset Classroom and Students Who Love Math for ideas, lessons, and mindset surveys for students to use in your classroom to cultivate a positive classroom community in mathematics. You can also sign up for other freebies from me Here at Easternshoremathteacher.com .
Have you ever given students a word problem or rich task, and they froze? They have no idea how to tackle the problem, even if it is a concept they are successful with. This is because they need problem solving strategies. I started to incorporate more problem solving tasks into my teaching in addition to making the 4 steps for problem solving a school-wide initiative and saw results.

What is Problem Solving in Math?
When educators use the term problem solving , they are referring to mathematical tasks that are challenging and require students to think. Such tasks or problems can promote students’ conceptual understanding, foster their ability to reason and communicate mathematically, and capture their interests and curiosity (Hiebert & Wearne, 1993; Marcus & Fey, 2003; NCTM, 1991; van de Walle, 2003).

How Should Problem Solving For Math Be Taught?
Problem solving should not be done in isolation. In the past, we would teach the concepts and procedures and then assign one-step “story” problems designed to provide practice on the content. Next, we would teach problem solving as a collection of strategies such as “draw a picture” or “guess and check.” Eventually, students would be given problems to apply the skills and strategies. Instead, we need to make problem solving an integral part of mathematics learning.
In teaching through problem solving, learning takes place while trying to solve problems with specific concepts and skills. As students solve problems, they can use any strategy. Then, they justify their solutions with their classmates and learn new ways to solve problems.
Students do not need every task to involve problem solving. Sometimes the goal is to just learn a skill or strategy.

Criteria for Problem Solving Math
Lappan and Phillips (1998) developed a set of criteria for a good problem that they used to develop their middle school mathematics curriculum (Connected Mathematics). The problem:
- has important, useful mathematics embedded in it.
- requires higher-level thinking and problem solving.
- contributes to the conceptual development of students.
- creates an opportunity for the teacher to assess what his or her students are learning and where they are experiencing difficulty.
- can be approached by students in multiple ways using different solution strategies.
- has various solutions or allows different decisions or positions to be taken and defended.
- encourages student engagement and discourse.
- connects to other important mathematical ideas.
- promotes the skillful use of mathematics.
- provides an opportunity to practice important skills.
Of course, not every problem will include all of the above. However, the first four are essential. Sometimes, you will choose a problem because your students need an opportunity to practice a certain skill.
The real value of these criteria is that they provide teachers with guidelines for making decisions about how to make problem solving a central aspect of their instruction. Read more at NCTM .

Problem Solving Teaching Methods
Teaching students these 4 steps for solving problems allows them to have a process for unpacking difficult problems.
As you teach, model the process of using these 4 steps to solve problems. Then, encourage students to use these steps as they solve problems. Click here for Posters, Bookmarks, and Labels to use in your classroom to promote the use of the problem solving steps in math.
How Problem Solving Skills Develop
Problem solving skills are developed over time and are improved with effective teaching practices. In addition, teachers need to select rich tasks that focus on the math concepts the teacher wants their students to explore.
Problem Solving 4 Steps
Understand the problem.
Read & Think
- Circle the needed information and underline the question.
- Write an answer STEM sentence. There are_____ pages left to read.
Plan Out How to Solve the Problem
Make a Plan
- Use a strategy. (Draw a Picture, Work Backwards, Look for a Pattern, Create a Table, Bar Model)
- Use math tools.
Do the Problem
Solve the Problem
- Show your work to solve the problem. This could include an equation.
Check Your Work on the Problem
Answer & Check
- Write the answer into the answer stem.
- Does your answer make sense?
- Check your work using a different strategy.
Check out these Printables for Problem Solving Steps in Math .

Teaching Problem Solving Strategies
A problem solving strategy is a plan used to find a solution. Understanding how a variety of problem solving strategies work is important because different problems require you to approach them in different ways to find the best solution. By mastering several problem-solving strategies, you can select the right plan for solving a problem. Here are a few strategies to use with students:
- Draw a Picture
- Work Backwards
- Look for a Pattern
- Create a Table
Why is Using Problem Solving Steps For Math Important?
Problem solving allows students to develop an understanding of concepts rather than just memorizing a set of procedures to solve a problem. In addition, it fosters collaboration and communication when students explain the processes they used to arrive at a solution. Through problem-solving, students develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, become more engaged, and see the importance of mathematics in their lives.

NCTM Process Standards
In 2011 the Common Core State Standards incorporated the NCTM Process Standards of problem-solving, reasoning and proof, communication, representation, and connections into the Standards for Mathematical Practice. With these process standards, the focus became more on mathematics through problem solving. Students could no longer just develop procedural fluency, they needed to develop conceptual understanding in order to solve new problems and make connections between mathematical ideas.
Engaging Students to Learn in Mathematics Class
Engaging students to learn in math class will help students to love math. Children develop a dislike of math early on and end up resenting it into adult life. Even in the real world, students will likely have to do some form of mathematics in their personal or working life. So how can teachers make math more interesting to engage students in the subject? Read more at 5 Best Strategies for Engaging Students to Learn in Mathematics Class

Teachers can promote number sense by providing rich mathematical tasks and encouraging students to make connections to their own experiences and previous learning.
Sign up on my webpage to get this Freebie of 71 Math Number Puzzles delivered to your inbox to use with your students. Providing opportunities to do math puzzles daily is one way to help students develop their number sense. CLICK Here to sign up for 71 Math Number Puzzles and check out my website.
Promoting a Growth Mindset
Research shows that there is a link between a growth mindset and success. In addition, kids who have a growth mindset about their abilities perform better and are more engaged in the classroom. Students need to be able to preserve and make mistakes when problem solving.
Read more … 5 Powerful and Easy Lessons Teaching Students How to Get a Growth Mindset
Here are some Resources to Use to Grow a Growth Mindset
- Free Mindset Survey
- Growth Mindset Classroom Display Free
- Growth Mindset Lessons

Using Word Problems
Story Problems and word problems are one way to promote problem solving. In addition, they provide great practice in using the 4 steps of solving problems. Then, students are ready for more challenging problems.
For Kindergarten
- Subtraction within 5
For First Grade
- Word Problems to 20
- Word Problems of Subtraction

For Second Grade
- Two Step Word Problems with Addition and Subtraction
- Grade 2 Addition and Subtraction Word Problems
- Word Problems with Subtraction

For Third Grade
- Word Problems Division and Multiplication
- Multiplication Word Problems

For Fourth Grade
- Multiplication Area Model
- Multiplicative Comparison Word Problems

Resources for Problem Solving
- 3 Act Tasks
- What’s the Best Proven Way to Teach Word Problems with Two Step Equations?
- 5 Powerful and Easy Lessons Teaching Students How to Get a Growth Mindset
- 5 Powerful Ideas to Help Students Develop a Growth Mindset in Mathematics
Problem Solving Steps For Math
In mathematics, problem solving is one of the most important topics to teach. Learning to problem solve helps students apply mathematics to real-world situations. In addition, it is used for a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts.
By providing rich mathematical tasks and engaging puzzles, students improve their number sense and mindset about mathematics. Click Here to get this Freebie of 71 Math Number Puzzles delivered to your inbox to use with your students.
Check out The Free Ultimate Guide for Creating a Growth Mindset Classroom and Students Who Love Math for ideas, lessons, and mindset surveys to use to cultivate a growth mindset classroom.
Start by modeling using the problem solving steps in math and allowing opportunities for students to use the steps to solve problems. As students become more comfortable with using the steps and have some strategies to use, provide more challenging tasks. Then, students will begin to see the importance of problem solving in math and connecting their learning to real-world situations.


3 Responses
- Pingback: How to Successfully and Easily Teach Word Problems in Multiplication and Division - Eastern Shore Math Teacher
- Pingback: Top 7 Must Have Best Beginning of The Year Bulletin Board Ideas For Math - Eastern Shore Math Teacher
- Pingback: 3 Brilliant Math Word Problem Solving Strategies To Use With Students - Eastern Shore Math Teacher
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More blog posts

3 Terrific Time-Saving Number Activities to Understand Teen Numbers
To understand teen numbers, kids need to understand place value. Kids learn to count to 10

How to Master Counting Numbers to 20: Best Activities for Success!
Counting numbers to 20 doesn’t sound like a complicated skill however, there are several components to

From Zero to Hero: What are Proven Best Strategies for Teaching Addition?
What are the best strategies for teaching addition? Computational fluency or addition and subtraction facts

Mastering Addition 2 Digit Problems: 3 Fun And Easy Resources for Students
When is it a good time to practice addition 2 digit problems? Once students understand 1

3 Fun and Easy-to-Use Products With Part Part Whole Story Problems
Using products with part part whole story problems helps students see the relationship between the whole

5 Best Winter Addition Worksheets Kindergarten Focused That Are Fun
Are you looking for winter addition worksheets kindergarten focused that are fun? Using themed-based resources

Hi, I'm Eastern Shore Math Teacher!
I have been teaching for over 22 years in an elementary school. I help educators plan engaging math lessons and cultivate a positive math culture in their classrooms.
Sign up and I will send you the growth mindset classroom guide and I will help you get your elementary students to love math.
Copyright 2021 | Eastern Shore Math Teacher| All Rights Reserved
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
Four-Step Math Problem Solving Strategies & Techniques
- Harlan Bengtson
- Categories : Help with math homework
- Tags : Homework help & study guides
Four Steps to Success
There are many possible strategies and techniques you can use to solve math problems. A useful starting point is a four step approach to math problem solving. These four steps can be summarized as follows:
- Carefully read the problem. In this careful reading, you should especially seek to clearly identify the question that is to be answered. Also, a good, general understanding of what the problem means should be sought.
- Choose a strategy to solve the problem. Some of the possible strategies will be discussed in the rest of this article.
- Carry out the problem solving strategy. If the first problem solving technique you try doesn’t work, try another.
- Check the solution. This check should make sure that you have indeed answered the question that was posed and that the answer makes sense.
Step One - Understanding the Problem
As you carefully read the problem, trying to clearly understand the meaning of the problem and the question that you must answer, here are some techniques to help.
Identify given information - Highlighting or underlining facts that are given helps to visualize what is known or given.
Identify information asked for - Highlighting the unknowns in a different color helps to keep the known information visually separate from the unknowns to be determined. Ideally this will lead to a clear identification of the question to be answered.
Look for keywords or clue words - One example of clue words is those that indicate what type of mathematical operation is needed, as follows:
Clue words indicating addition: sum, total, in all, perimeter.
Clue words indicating subtraction: difference, how much more, exceed.
Clue words for multiplication: product, total, area, times.
Clue words for division: share, distribute, quotient, average.
Draw a picture - This might also be considered part of solving the problem, but a good sketch showing given information and unknowns can be very helpful in understanding the problem.
Step Two - Choose the Right Strategy
It step one has been done well, it should ease the job of choosing among the strategies presented here for approaching the problem solving step. Here are some of the many possible math problem solving strategies.
- Look for a pattern - This might be part of understanding the problem or it might be the first part of solving the problem.
- Make an organized list - This is another means of organizing the information as part of understanding it or beginning the solution.
- Make a table - In some cases the problem information may be more suitable for putting in a table rather than in a list.
- Try to remember if you’ve done a similar problem before - If you have done a similar problem before, try to use the same approach that worked in the past for the solution.
- Guess the answer - This may seem like a haphazard approach, but if you then check whether your guess was correct, and repeat as many times as necessary until you find the right answer, it works very well. Often information from checking on whether the answer was correct helps lead you to a good next guess.
- Work backwards - Sometimes making the calculations in the reverse order works better.
Steps Three and Four - Solving the Problem and Checking the Solution
If the first two steps have been done well, then the last two steps should be easy. If the selected problem solving strategy doesn’t seem to work when you actually try it, go back to the list and try something else. Your check on the solution should show that you have actually answered the question that was asked in the problem, and to the extent possible, you should check on whether the answer makes common sense.
Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!


Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
How to Ace Math Problem Solving
When your kids struggle with their math, it’s time to take a step back and take a deep breath. They need to slow down and take their time. Here’s a step by step guide that will help your kids get through those tough math problems.
We’ll use a grade 3 addition word problem as an example to clarify:
Pinky the Pig bought 36 apples while Danny the Duck bought 73 apples and 14 bananas. How many apples do they have altogether?
Read the problem
Carefully read through the problem to make sure you understand what is being asked.
Pinky the pig and Danny the duck bought apples and bananas. The question is how many apples they have together.
Re-read the problem
Read through the problem again and as you read through it, make notes.
Pinky the pig –36 apples. Danny the duck –73 apples and 14 bananas. How many apples together?
What is the problem asking
In your own words, say or write down exactly what the question is asking you to solve.
The question is asking how many apples the pig and the duck bought together.
Write it down in detail
Go through the problem and write out the information in an organized fashion. A diagram or table might help.
Turn it into math
Figure out what math operation(s) or formula(s) you need to use in order to solve this problem.
The problem wants us to add the number of apples Pinky the Pig and Danny the Duck have together. That means we need to make use of addition to add the apples.
Find an example
Are you still struggling? Sometimes it’s hard to work out the solution, especially if the math problem involves several steps. It’s time to present the problem in an easier way. As teachers and parents we can often help our kids simplify the problem from our own math knowledge. If the problem is a bit harder, there are lots of resources online that you can look up for similar problems that have been worked out on paper or a video tutorial to watch.
In our example, let’s say the double-digit numbers are intimidating our student, so we’re going to simplify the equation for the sake of helping our student understand the operation needed.
Let’s say Pinky the Pig bought 3 apples and Danny the Duck 7 apples and 1 banana. Now, how many apples have they bought together? With 3 apples and 7 apples bought, the total number of apples is 10.
Work out the problem
Now that we have got to the bottom of what is being asked and know what operation to use, it’s time to work out the problem.
Pinky the Pig bought 36 apples. Danny the Duck bought 73 apples. (The 14 bananas do not matter) We need to add up the apples. 36 + 73 = 109
2.3.1: George Polya's Four Step Problem Solving Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 90483
Step 1: Understand the Problem
- Do you understand all the words?
- Can you restate the problem in your own words?
- Do you know what is given?
- Do you know what the goal is?
- Is there enough information?
- Is there extraneous information?
- Is this problem similar to another problem you have solved?
Step 2: Devise a Plan: Below are some strategies one might use to solve a problem. Can one (or more) of the following strategies be used? (A strategy is defined as an artful means to an end.)

Game Central
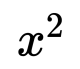
Get math. Get Photomath.
or scan QR code

Try it out!

1. Scan your problem
Use the app to snap a photo. Adjust the frame size to capture the whole problem!

2. Find the right method
There’s more than one way to solve that problem; choose the approach that makes sense to you.

3. Learn step-by-step
Gain clarity and confidence with detailed explanations.

Math learning that gets you.
Our step-by-step explanations help you master math from arithmetic to calculus, so you can continue building on your skills.
Use the Photomath app to scan a tricky problem. You can also manually input problems using our smart calculator!
Get instant solution steps for your exact problem, vetted by our team of math teachers.
Use those steps to dig into the nitty-gritty and learn at your own pace!
What can we explain?
Photomath covers a wide range of math topics, so we can be your study buddy from second grade to senior year!
- Elementary math
- Trigonometry
- Word problems

Problem-solving from day one
A dad was struggling to help his children with math homework. The solution he created has now helped millions of students around the world.

Damir Sabol
More than just an app.
In school, one teacher is devoted to dozens of students. At Photomath, dozens of teachers are devoted to one student.
App Downloads
App Store Rating

I give this app five stars because of how useful it is when I can’t ask my teacher for help.
Sandy W., student
The step-by-step explanations help me check my kids' homework for accuracy and the app clarifies concepts and improves their independent problem-solving abilities.
Albert G., parent
I used to hire tutors that were over $100/hour but they often didn't teach in a way that resonated with my kids. Photomath's step explanations are ideal for self-paced learning and it's saving me hundreds of dollars each month!
Katie C., parent
This app is amazing for kids to help them understand math. As a parent, I don't know too much about algebra and this has helped me with my kid's homework.
April C., parent
I LOVE this app. Every time I show it to students they are just amazed by it (as am I). The fact that it shows alternate ways of solving the equations makes for great learning opportunities that might be missed in a regular class.
Adam M., teacher
This app is EXTREMELY helpful. I'm in 10th grade doing geometry 1 so I don't know how much this counts but for me it's been insanely helpful. 10/10 would recommend. (Not a bot btw)
Alan E., student
It’s helped me and my friends pass 7th and 8th grade thank you Photomath
Alyssa S., student
Thanks 4 makin me pass 7th grade!
Jessie J., student
This app helps me with my monomials and fractions. I love this app.
Josee, student
I'm so thankful there's an app like this, it makes me think studying is really easy and fun to do at some times.
Melanie A., student
Got me through online math 2020-21. I’ve gotten 90+ marks basically just using this app. Saved so much time. Highly recommend.
Peter R., student
This app was very helpful for my daughter. Simple and answers well-explained.
Roman S., parent
I like how there are multiple options to choose like simplifying or solving for just about any type of problem. I recommend clicking the button that says explain steps because it teaches you really well."
Ryan H., student
Helps so much in algebra and I like how it gives all formats of answers. It explains the steps very well so that you can understand how to solve the problem.
Steve C., student
My son started middle school and his math is significantly more difficult. Photomath shows him the steps to get the correct answer and the lightbulb came on.
Jennifer L., parent
Helps me tutor! I love how it allows me to refresh my memory for math I have not done in years.
Jmohika, tutor
I forgot so many little things from my math days... this tool helps me help my kids. The easy-to-follow (step) solutions allow me to teach my kids how to do their problems.
Rick C., parent
We help millions learn every month, and we can help you.
Scan QR code to download app
We have a blog!
While we’re usually busy helping students learn how to solve their trickiest math problems, we’ve also been working behind the scenes on a blog that shares stories, tips, and musings about our favorite topic: math!
Whether you’re a teacher who’s after tips for using tech in the classroom, a parent wondering how Photomath can help your child learn, or a student in need of study motivation, you can count 😉 on us to have it covered. Check it out, and follow along for more stories (and math puns) coming your way.
- Our Mission
3 Simple Strategies to Improve Students’ Problem-Solving Skills
These strategies are designed to make sure students have a good understanding of problems before attempting to solve them.

Research provides a striking revelation about problem solvers. The best problem solvers approach problems much differently than novices. For instance, one meta-study showed that when experts evaluate graphs , they tend to spend less time on tasks and answer choices and more time on evaluating the axes’ labels and the relationships of variables within the graphs. In other words, they spend more time up front making sense of the data before moving to addressing the task.
While slower in solving problems, experts use this additional up-front time to more efficiently and effectively solve the problem. In one study, researchers found that experts were much better at “information extraction” or pulling the information they needed to solve the problem later in the problem than novices. This was due to the fact that they started a problem-solving process by evaluating specific assumptions within problems, asking predictive questions, and then comparing and contrasting their predictions with results. For example, expert problem solvers look at the problem context and ask a number of questions:
- What do we know about the context of the problem?
- What assumptions are underlying the problem? What’s the story here?
- What qualitative and quantitative information is pertinent?
- What might the problem context be telling us? What questions arise from the information we are reading or reviewing?
- What are important trends and patterns?
As such, expert problem solvers don’t jump to the presented problem or rush to solutions. They invest the time necessary to make sense of the problem.
Now, think about your own students: Do they immediately jump to the question, or do they take time to understand the problem context? Do they identify the relevant variables, look for patterns, and then focus on the specific tasks?
If your students are struggling to develop the habit of sense-making in a problem- solving context, this is a perfect time to incorporate a few short and sharp strategies to support them.
3 Ways to Improve Student Problem-Solving
1. Slow reveal graphs: The brilliant strategy crafted by K–8 math specialist Jenna Laib and her colleagues provides teachers with an opportunity to gradually display complex graphical information and build students’ questioning, sense-making, and evaluating predictions.
For instance, in one third-grade class, students are given a bar graph without any labels or identifying information except for bars emerging from a horizontal line on the bottom of the slide. Over time, students learn about the categories on the x -axis (types of animals) and the quantities specified on the y -axis (number of baby teeth).
The graphs and the topics range in complexity from studying the standard deviation of temperatures in Antarctica to the use of scatterplots to compare working hours across OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) countries. The website offers a number of graphs on Google Slides and suggests questions that teachers may ask students. Furthermore, this site allows teachers to search by type of graph (e.g., scatterplot) or topic (e.g., social justice).
2. Three reads: The three-reads strategy tasks students with evaluating a word problem in three different ways . First, students encounter a problem without having access to the question—for instance, “There are 20 kangaroos on the grassland. Three hop away.” Students are expected to discuss the context of the problem without emphasizing the quantities. For instance, a student may say, “We know that there are a total amount of kangaroos, and the total shrinks because some kangaroos hop away.”
Next, students discuss the important quantities and what questions may be generated. Finally, students receive and address the actual problem. Here they can both evaluate how close their predicted questions were from the actual questions and solve the actual problem.
To get started, consider using the numberless word problems on educator Brian Bushart’s site . For those teaching high school, consider using your own textbook word problems for this activity. Simply create three slides to present to students that include context (e.g., on the first slide state, “A salesman sold twice as much pears in the afternoon as in the morning”). The second slide would include quantities (e.g., “He sold 360 kilograms of pears”), and the third slide would include the actual question (e.g., “How many kilograms did he sell in the morning and how many in the afternoon?”). One additional suggestion for teams to consider is to have students solve the questions they generated before revealing the actual question.
3. Three-Act Tasks: Originally created by Dan Meyer, three-act tasks follow the three acts of a story . The first act is typically called the “setup,” followed by the “confrontation” and then the “resolution.”
This storyline process can be used in mathematics in which students encounter a contextual problem (e.g., a pool is being filled with soda). Here students work to identify the important aspects of the problem. During the second act, students build knowledge and skill to solve the problem (e.g., they learn how to calculate the volume of particular spaces). Finally, students solve the problem and evaluate their answers (e.g., how close were their calculations to the actual specifications of the pool and the amount of liquid that filled it).
Often, teachers add a fourth act (i.e., “the sequel”), in which students encounter a similar problem but in a different context (e.g., they have to estimate the volume of a lava lamp). There are also a number of elementary examples that have been developed by math teachers including GFletchy , which offers pre-kindergarten to middle school activities including counting squares , peas in a pod , and shark bait .
Students need to learn how to slow down and think through a problem context. The aforementioned strategies are quick ways teachers can begin to support students in developing the habits needed to effectively and efficiently tackle complex problem-solving.
MathAttack: Attacking Large Language Models towards Math Solving Ability
- Zihao Zhou Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University
- Qiufeng Wang Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University
- Mingyu Jin Northwestern University
- Jie Yao Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University
- Jianan Ye Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University
- Wei Liu ShanghaiTech University
- Wei Wang Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University
- Xiaowei Huang University of Liverpool
- Kaizhu Huang Duke Kunshan University

- Video/Poster
How to Cite
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Developed By
Subscription.
Login to access subscriber-only resources.
Part of the PKP Publishing Services Network
Copyright © 2024, Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Understanding the problem. We are given in the problem that there are 25 chickens and cows. All together there are 76 feet. Chickens have 2 feet and cows have 4 feet. We are trying to determine how many cows and how many chickens Mr. Jones has on his farm. Step 2: Devise a plan.
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
Consider the problem-solving steps applied in the following example. I know that I want to say "I don't eat eggs" to my Mexican waiter. That's the problem. I don't know how to say that, but last night I told my date "No bebo alcohol" ("I don't drink alcohol"). I also know the infinitive for "eat" in Spanish (comer).
A multistep math problem-solving plan involves looking for clues, developing a game plan, solving the problem, and carefully reflecting on your work. ... The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya's book and should help you untangle even the most ...
A Guide to Problem Solving. When confronted with a problem, in which the solution is not clear, you need to be a skilled problem-solver to know how to proceed. When you look at STEP problems for the first time, it may seem like this problem-solving skill is out of your reach, but like any skill, you can improve your problem-solving with practice.
Step 1: Understand the problem. In order to solve a problem, it is important to understand what you are being asked to find. Strategies for understanding the problem: Review the problem. If you are solving a word problem, read through the entire problem. Seek to understand all the words used in stating the problem.
1. Link problem-solving to reading. When we can remind students that they already have many comprehension skills and strategies they can easily use in math problem-solving, it can ease the anxiety surrounding the math problem. For example, providing them with strategies to practice, such as visualizing, acting out the problem with math tools ...
Then, I provided them with the "keys to success.". Step 1 - Understand the Problem. To help students understand the problem, I provided them with sample problems, and together we did five important things: read the problem carefully. restated the problem in our own words. crossed out unimportant information.
5 Powerful Ideas to Help Students Develop a Growth Mindset in Mathematics; Problem Solving Steps For Math . In mathematics, problem solving is one of the most important topics to teach. Learning to problem solve helps students apply mathematics to real-world situations. In addition, it is used for a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts.
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
Therefore, high-quality assessment of problem solving in public tests and assessments1 is essential in order to ensure the effective learning and teaching of problem solving throughout primary and secondary education. Although the focus here is on the assessment of problem solving in mathematics, many of the ideas will be directly transferable ...
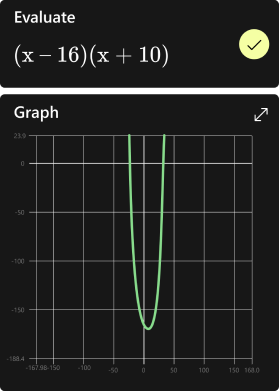
Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app. ... Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems. Try Math Solver. Type a math problem. Type a math problem. Solve. Quadratic equation { x } ^ { 2 } - 4 x - 5 = 0. Trigonometry. 4 \sin \theta \cos ...
Solving a math problem involves first gaining a clear understanding of the problem, then choosing from among problem solving techniques or strategies, followed by actually carrying out the solution, and finally checking the solution. See this article for more information about this four-step math problem solving procedure, with several problem solving techniques presented and discussed for ...
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
If we use the sum and take away one of the numbers, it should equal the other number. 109 - 73 = 36. 109 - 36 = 73. If our student did not work out the sum correctly, we would not come to these sums. (By the way, the same can be done with multiplication and division.) Finally, go back and review the problem one last time.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra. Basic Math.
Cymath | Math Problem Solver with Steps | Math Solving App ... \\"Solve
Provide step-by-step solutions to math word problems Graphing Plot and analyze functions and equations with detailed steps Geometry Solve geometry problems, proofs, and draw geometric shapes Math Help Tailored For You Practice Practice and improve your math skills through interactive personalized exercises and quizzes
Is there extraneous information? Is this problem similar to another problem you have solved? Step 2: Devise a Plan: Below are some strategies one might use to solve a problem. Can one (or more) of the following strategies be used? (A strategy is defined as an artful means to an end.) 1. Guess and test.
Differentiation. dxd (x − 5)(3x2 − 2) Integration. ∫ 01 xe−x2dx. Limits. x→−3lim x2 + 2x − 3x2 − 9. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
The step-by-step explanations help me check my kids' homework for accuracy and the app clarifies concepts and improves their independent problem-solving abilities. Albert G., parent I used to hire tutors that were over $100/hour but they often didn't teach in a way that resonated with my kids.
While slower in solving problems, experts use this additional up-front time to more efficiently and effectively solve the problem. In one study, researchers found that experts were much better at "information extraction" or pulling the information they needed to solve the problem later in the problem than novices. This was due to the fact that they started a problem-solving process by ...
With the boom of Large Language Models (LLMs), the research of solving Math Word Problem (MWP) has recently made great progress. However, there are few studies to examine the robustness of LLMs in math solving ability. Instead of attacking prompts in the use of LLMs, we propose a MathAttack model to attack MWP samples which are closer to the essence of robustness in solving math problems.