

Laurie Halse Anderson
Ask litcharts ai: the answer to your questions.
Coming of Age
Like many novels with high school settings, Speak is deeply focused on ideas of growing up and coming of age. What makes this book’s exploration of that subject particularly poignant and pointed, however, is that Melinda has already experienced a major milestone of adulthood—losing her virginity—before the novel begins. The fact that this event occurred as the result of rape, however, has derailed Mel’s maturation, and for much of the book she clings to any…
Communication versus Silence
Given that the name of the book is Speak , it is unsurprising that communication versus silence is a critical theme within the book. Silence sits at the narrative’s core: Melinda has not told anyone about her rape at the hands of popular senior Andy Evans the previous summer, and has morphed from a happy, popular student to a traumatized outcast as a result. Throughout the book, Melinda finds it harder and harder to speak…
Appearance versus Reality
Much of Melinda’s cynicism within Speak springs from what she views as a fundamental disconnect between appearance and reality. She has experienced a deeply traumatic rape, yet her parents view her as a disappointment, her teachers view her as a problem, and her classmates view her as a freak. Because she is deeply perceptive and sensitive, Mel notices gaps between appearance and reality everywhere she goes. She sees the cracks in the façade of her…
Family and Friendship
Like any student in high school, Melinda’s life revolves around family and friends. Unlike most high schoolers, however, Melinda is completely alienated from both groups. Her parents are neglectful and distant, and she feels completely unable to tell them about her recent trauma. Her friends, meanwhile, have all abandoned her, believing that she maliciously called the cops on a party when in fact she was only trying to report the fact that Andy Evans had…
Isolation, Loneliness, and Depression
Because Speak takes place within Melinda’s mind, author Laurie Halse Anderson is able to vividly and achingly portray the effects of isolation and loneliness upon human consciousness. Throughout the book, Mel struggles to emerge from a cloud of depression and apathy that surrounds her, yet continually finds herself rejected and alone. Mel’s attitude towards her isolation is conflicted. On one hand, she believes that she has chosen it, pushing away all those close to her…
Memory and Trauma
Melinda begins Speak burdened by memory and trauma: she has been raped and relives the experience every day, yet is unable to speak to anyone about it. As for her happier memories, the rape and the events that followed it have stained them. When she remembers her friends, she realizes that they have since abandoned her. When she remembers her childhood, she feels pity and nostalgia for how innocent and carefree she used to be.
The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson
In Speak , the author, Laurie Halse Anderson, illustrates the idea that people can recover after trauma and become stronger. The writer utilizes the first-person point of view to show the path protagonist goes through to her transformation. The first-person point of view is the type of narrative in which events are described from the narrator’s point of view using the pronouns “I,” “we,” “me,” “us.” Throughout the book, readers can see the theme of a traumatic event’s consequences, the experiences associated with it, and recovery from it.
The book is structured like a diary of the main character Melinda Sordino, who survived violence by a classmate, and at the same time, became an outcast in school. Readers have access to all her thoughts and feelings, introspection, and attempts to find a way out and speak about the problem. The narrator states, “I want to confess everything, hand over the guilt and mistake and anger to someone else. There is a beast in my gut, I can hear it scraping away at the inside of my ribs. Even if I dump the memory, it will stay with me, staining me.” (Anderson, 1999, p. 38). Readers understand that Melinda feels dirty, a terrible event haunts her, and at the same moment, she feels guilty, like most victims of violence, although she did nothing.
Feelings of anger and guilt depress Melinda, most clearly manifesting in the fact that she hardly speaks. After some time, the young girl feels a desire to free herself: “A small, clean part of me waits to warm and burst through the surface” (Anderson, 1999, p. 122). An example of her recovery from injury is the bold statement, “It wasn’t my fault. And I’m not going to let it kill me. I can grow” (Anderson, 1999, p. 128). When readers see this courage, after all the experience, they understand what transformation Melinda goes through. The main character can recover, although it took a lot of braveness and time. Thus, it is clear that the author’s use of the first-person point of view helped illustrate the idea that changes and healing are possible after trauma.
Anderson, L. H. (1999). Speak . Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, August 20). The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson. https://studycorgi.com/the-book-speak-by-laurie-halse-anderson/
"The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson." StudyCorgi , 20 Aug. 2022, studycorgi.com/the-book-speak-by-laurie-halse-anderson/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson'. 20 August.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson." August 20, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-book-speak-by-laurie-halse-anderson/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson." August 20, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-book-speak-by-laurie-halse-anderson/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson." August 20, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/the-book-speak-by-laurie-halse-anderson/.
This paper, “The Book “Speak” by Laurie Halse Anderson”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: August 20, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

ENG 350 Young Adult Literature Class Guide
- Writing a Thesis Statement
- Source Types
- Searching Google Search and Google Scholar
- Searching Discovery
- Search Terms
- Search Stategies
- Using Sources Effectively
- Citing with MLA Style
- ILL Request Form This link opens in a new window
- Research Guides
Contact Taylor

Introduction
Welcome! This page is designed to help you with your Young Adult Literature research paper. Use this page to learn more about:
- Brainstorming a thesis topic
- Identifying source types
- Searching Google and Google Scholar
- Using library databases to find secondary sources
- Using your sources effectively
- Citing your sources
If you have any questions about any aspect of your research assignment, please feel free to reach out to me at [email protected] .
Selecting a Topic
Coming up with a thesis statement for a critical literary paper can be difficult, but these strategies should help you in the process. Take some time to brainstorm and look back at readings from the course. Consider the topics that interested you during the class and explore those more fully.
Your assignment reads:
For the research essay, you will choose a controversial topic related to, or within YA literature (for example: book banning; sexuality; violence; gay/lesbian/queer content; birth control; teen suicide; teens and drugs) and discuss it in depth.
Start by selecting your topic of interest in YA literature and identify course texts that fall into those categories. You may also bring other titles in to argue your topic. If you're having focusing your topic, try some of the exercises below:
- Purdue OWL's Introduction to Prewriting This site will provide you with a list of questions to ask yourself while you flesh out your potential focus.
- Develop a Topic from University of Indiana Libraries
If you're still having trouble, think about looking into the subject terms for your course texts to see what topics are covered within them. For example, in the subject terms for Monster by Walter Dean Myers, you'll find such subject terms as "self-perception," "prisons—fiction," "African Americans—fiction," and more.
If you'd like to see the subject terms, select the image of the cover of the book you're interested in to get started:
The Graveyard Book
One of Us Is Lying
Simon vs. the Homo Sapiens Agenda
Writing Your Thesis Statement
Once you know what you would like to discuss within the primary work, try to write your thesis down in one or two sentences. Thesis sentences should be clear, concise, and specific. The Bridgewater College Writing Center has this to say about thesis statements:
In general, academic writing requires a thesis statement. A thesis statement is often considered to be part of an argumentative text, any paper that takes a position on something, that is, a paper that makes a claim. One way to think about the thesis statement is that if you boiled your whole case down to a single statement, that statement would be your thesis. A thesis statement typically identifies your topic and embodies your attitude toward your topic. Most writing assignments will require you to take a position on a topic, and most college professors expect to find a clear statement of that position, almost always in your introductory paragraph.
For more information on writing thesis statements, see the Bridgewater College Writing Center page on thesis statements .
- Next: Source Types >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 10:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.bridgewater.edu/eng350

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Topic, Purpose, and Thesis
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the three types of general speech purposes.
- Understand the four primary constraints of topic selection.
- Demonstrate an understanding of how a topic is narrowed from a broad subject area to a manageable specific purpose.
- Integrate the seven tips for creating specific purposes.
- Understand how to develop a strong thesis and assess thesis statements.
In the 2004 Tony Award-winning musical Avenue Q , the lead character sings a song about finding his purpose in life: “I don’t know how I know, but I’m gonna find my purpose. I don’t know where I’m gonna look, but I’m gonna find my purpose.” Although the song is about life in general, the lyrics are also appropriate when thinking about the purpose of your speech. You may know that you have been assigned to deliver a speech, but finding a purpose and topic seems like a formidable task. You may be asking yourself questions like, “What if the topic I pick is too common?”; “What if no one is interested in my topic?”; “What if my topic is too huge to cover in a three- to five-minute speech?”; or many others.
Finding a speech’s purpose and topic isn’t as complex or difficult as you might believe. This may be hard to accept right now but trust us. After you read this chapter, you’ll understand how to go about finding interesting topics for a variety of different types of speeches. In this chapter, we are going to explain how to identify the general purpose of a speech. We will also discuss how to select a topic, what to do if you’re just drawing a blank, and four basic questions you should ask yourself about the speech topic you ultimately select. Finally, we will explain how to use your general purpose and your chosen topic to develop the specific purpose and thesis of your speech.
General Purpose
What do you think of when you hear the word “purpose”? Technically speaking, a purpose is why something exists, how we use an object, or why we make something. For the purposes of public speaking, all three can be applied. For example, when we talk about a speech’s purpose, we can question why a specific speech was given, how we are supposed to use the information within a speech, and why we are personally creating a speech. For this specific chapter, we are more interested in that last aspect of the definition of the word “purpose”: why we give speeches.
Ever since scholars started writing about public speaking as a distinct phenomenon, there have been a range of different systems created to classify the types of speeches people may give. Aristotle talked about three speech purposes: deliberative (political speech), forensic (courtroom speech), and epideictic (speech of praise or blame). Cicero also talked about three purposes: judicial (courtroom speech), deliberative (political speech), and demonstrative (ceremonial speech—similar to Aristotle’s epideictic). A little more recently, St. Augustine of Hippo also wrote about three specific speech purposes: to teach (provide people with information), to delight (entertain people or show people false ideas), and to sway (persuade people to a religious ideology). All these systems of identifying public speeches have been attempts at helping people determine the general purpose of their speech. A general purpose refers to the broad goal of creating and delivering a speech.
These typologies or classification systems of public speeches serve to demonstrate that general speech purposes have remained pretty consistent throughout the history of public speaking. Modern public speaking scholars typically use a classification system for three general purposes: to inform, to persuade, and to entertain.
A general purpose refers to the broad goal of creating and delivering a speech.
The first general purpose that some people have for giving speeches is to inform. Simply put, informative speaking is about helping audience members acquire information that they do not already possess. Audience members can then use this information to understand something (e.g. a speech on a new technology or a speech on an issue of community concern) or to perform a new task or improve their skills (e.g. a speech on how to swing a golf club or a speech on how to assemble a layer cake). The most important characteristic of informative topics is that the goal is to gain knowledge. Notice that the goal is not to encourage people to use that knowledge in any specific way. When a speaker starts encouraging people to use knowledge in a specific way, they are no longer informing but instead persuading.
Informative speaking is about helping audience members acquire information that they do not already possess.
Let’s look at a real example of how an individual can accidentally go from informing to persuading. Let’s say you are assigned to inform an audience about a new vaccination program. In an informative speech, the purpose of the speech is to explain to your audience what the program is and how it works. If, however, you start encouraging your audience to participate in the vaccination program, you are no longer informing them about the program but instead persuading them to become involved in the program. One of the most common mistakes new public speaking students make is to blur the line between informing and persuading.
Why We Share Knowledge
Knowledge sharing is the process of delivering information, skills, or expertise in some form to people who could benefit from it. Every year, millions of people attend some kind of knowledge sharing conference or convention in hopes of learning new information or skills that will help them in their personal or professional lives (Atwood, 2009).
People are motivated to share their knowledge with other people for a variety of reasons (Hendriks, 1999). For some, the personal sense of achievement or responsibility drives them to share their knowledge (internal motivational factors). Others are compelled to share knowledge because of the desire for recognition or the possibility of job enhancement (external motivational factors). Knowledge sharing is an integral part of every society, so learning how to deliver informative speeches is a valuable skill.
Knowledge sharing is the process of delivering information, skills, or expertise in some form to people who could benefit from it.
Common Types of Informative Topics
O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein identified six general types of informative speech topics: objects, people, events, concepts, processes, and issues (O’Hair, et al., 2007). The first type of informative speech relates to objects, which can include how objects are designed, how they function, and what they mean. For example, a student of one of our coauthors gave a speech on the design of corsets, using a mannequin to demonstrate how corsets were placed on women and the amount of force necessary to lace one up.
The second type of informative speech focuses on people. People-based speeches tend to be biography-oriented. Such topics could include recounting an individual’s achievements and explaining why he or she is important in history. Some speakers, who are famous themselves, will focus on their own lives and how various events shaped who they ultimately became. Dottie Walters noted as being the first female in the United States to run an advertising agency. In addition to her work in advertising, Dottie also spent a great deal of time as a professional speaker. She often would tell the story about her early years in advertising when she would push around a stroller with her daughter inside as she went from business to business trying to generate interest in her copywriting abilities. You don’t have to be famous, however, to give a people-based speech. Instead, you could inform your audience about a historical or contemporary hero whose achievements are not widely known.
The third type of informative speech involves explaining the significance of specific events, either historical or contemporary. For example, you could deliver a speech on a particular battle of World War II or a specific presidential administration. If you’re a history buff, event-oriented speeches may be right up your alley. There are countless historical events that many people aren’t familiar with and would find interesting. You could also inform your audience about a more recent or contemporary event. Some examples include concerts, plays, and arts festivals; athletic competitions; and natural phenomena, such as storms, eclipses, and earthquakes. The point is to make sure that an informative speech is talking about the event (who, what, when, where, and why) and not attempting to persuade people to pass judgment upon the event or its effects.
The fourth type of informative speech involves concepts, or “abstract and difficult ideas or theories” (O’Hair, et al., 2007). For example, if you want to explain a specific communication theory, E. M. Griffin provides an excellent list of communication theories on his website , http://www.afirstlook.com/main.cfm/theory_list . Whether you want to discuss theories related to business, sociology, psychology, religion, politics, art, or any other major area of study, this type of speech can be very useful in helping people to understand complex ideas.
The fifth type of informative speech involves processes. The process speech can be divided into two unique types: how-it-functions and how-to-do. The first type of process speech helps audience members understand how a specific object or system works. For example, you could explain how a bill becomes a law in the United States. There is a very specific set of steps that a bill must go through before it becomes a law, so there is a very clear process that could be explained to an audience. The how-to-do speech, on the other hand, is designed to help people come to an end result of some kind. For example, you could give a speech on how to quilt, how to change a tire, how to write a résumé, and millions of other how-to oriented topics. In our experience, the how-to speech is probably the most commonly delivered informative speech in public speaking classes.
The final type of informative speech involves issues, or “problems or matters of dispute” (O’Hair, et al., 2007). This informative speech topic is probably the most difficult for novice public speakers because it requires walking a fine line between informing and persuading. If you attempt to deliver this type of speech, remember the goal is to be balanced when discussing both sides of the issue. To see an example of how you can take a very divisive topic and make it informative, check out the series Point/Counterpoint published by Chelsea House, http://chelseahouse.infobasepublishing.com . This series of books covers everything from the pros and cons of blogging to whether the United States should have mandatory military service.
Sample: Jessy Ohl’s Informative Speech
The following text represents an informative speech prepared and delivered by an undergraduate student named Jessy Ohl. While this speech is written out as a text for purposes of analysis, in your public speaking course, you will most likely be assigned to speak from an outline or notes, not a fully written script. As you read through this sample speech, notice how Ms. Ohl uses informative strategies to present the information without trying to persuade her audience.
In 1977, a young missionary named Daniel Everett traveled deep into the jungles of Brazil to spread the word of God. However, he soon found himself working to translate the language of a remote tribe that would ultimately change his faith, lead to a new profession, and pit him in an intellectual fistfight with the world-famous linguist Noam Chomsky. As New Scientist Magazine of January 2008 explains, Everett’s research on a small group of 350 people called the Pirahã tribe has revealed a language that has experts and intellectuals deeply disturbed. While all languages are unique, experts like Noam Chomsky have argued that they all have universal similarities, such as counting, that are hard-wired into the human brain. So as National Public Radio reported on April 8, 2007, without the ability to count, conceptualize time or abstraction, or create syntax, the Pirahã have a language that by all accounts shouldn’t exist. Daniel Everett is now a professor of linguistics at Illinois State University, and he has created controversy by calling for a complete reevaluation of all linguistic theory in light of the Pirahã. Exploration of the Pirahã could bring further insight into the understanding of how people communicate and even, perhaps, what it means to be human. Which is why we must: first, examine the unique culture of the Pirahã; second, explore what makes their language so surprising; and finally, discover the implications the Pirahã have for the way we look at language and humanity. Taking a closer look at the tribe’s culture, we can identify two key components of Pirahã culture that help mold language: first, isolation; and second, emphasis on reality. First, while globalization has reached nearly every corner of the earth, it has not been able to penetrate the Pirahã natives in the slightest. As Dr. Everett told the New Yorker of April 16, 2007, no group in history has resisted change like the Pirahã. “They reject everything from outside their world” as unnecessary and silly. Distaste for all things foreign is the reason why the people have rejected technology, farming, religion, and even artwork. The lack of artwork illustrates the second vital part of Pirahã culture: an emphasis on reality. According to the India Statesman of May 22, 2006, all Pirahã understanding is based around the concept of personal experience. If something cannot be felt, touched, or experienced directly then to them, it doesn’t exist, essentially eliminating the existence of abstract thought. Since art is often a representation of reality, it has no value among the people. During his work as a missionary, Everett was amazed to find that the natives had no interest in the story of Jesus once they found out that he was dead. The Pirahã psyche is so focused on the present that the people have no collective memory, history, written documents, or creation myths. They are unable to even remember the names of dead grandparents because once something or someone cannot be experienced, they are no longer important. Since his days as a missionary, Everett remains the only Western professor able to translate Pirahã. His research has discovered many things missing with the language: words for time, direction, and color. But more importantly, Pirahã also lacks three characteristics previously thought to be essential to all languages: complexity, counting, and recursion. First, the Pirahã language seems incredibly simple. Now, this isn’t meant to imply that the people are uncivilized or stupid, but instead, they are minimalist. As I mentioned earlier, they only talk in terms of direct experience. The London Times of January 13, 2007, notes that with only eight consonants and three vowels, speakers rely on the use of tone, pitch, and humming to communicate. In fact, Pirahã almost sounds more like song than speech.
Second, Noam Chomsky’s famous universal grammar theory includes the observation that every language has a means of counting. However, as reported in the June 2007 issue of Prospect Magazine , the Pirahã only have words for “one, two, and MANY.” This demonstrates the Pirahã’s inability to conceptualize a difference between three and five or three and a thousand. Dr. Everett spent six months attempting to teach even a single Pirahã person to count to ten, but his efforts were in vain, as tribal members considered the new numbers and attempts at math “childish.” Third, and the biggest surprise for researchers, is the Pirahã’s apparent lack of recursion. Recursion is the ability to link several thoughts together. It is characterized in Christine Kenneally’s 2007 book, The Search for the Origins of Language , as the fundamental principle of all language and the source of limitless expression. Pirahã is unique since the language does not have any conjunctions or linking words. Recursion is so vital for expression that the Chicago Tribune of June 11, 2007, reports that a language without recursion is like disproving gravity. Although the Pirahã don’t care what the outside world thinks of them, their language and world view has certainly ruffled feathers. And while civilization hasn’t been able to infiltrate the Pirahã, it may ultimately be the Pirahã that teaches civilization a thing or two, which brings us to implications on the communicative, philosophical, and cultural levels. By examining the culture, language, and implications of the Pirahã tribe we are able to see how this small Brazilian village could shift the way that we think and talk about the world. Daniel Everett’s research hasn’t made him more popular with his colleagues. But his findings do show that more critical research is needed to make sure that our understanding of language is not lost in translation.
To Persuade
The second general purpose people can have for speaking is to persuade. In persuasive speaking , we attempt to get listeners to embrace a point of view or to adopt a behavior that they would not have done otherwise. A persuasive speech is distinguished from an informative speech by the fact that it includes a call for action for the audience to make some change in their behavior or thinking.
Why We Persuade
The reasons behind persuasive speaking fall into two main categories, which we will call “pure persuasion” and “manipulative persuasion.” Pure persuasion occurs when a speaker urges listeners to engage in a specific behavior or change a point of view because the speaker truly believes that the change is in the best interest of the audience members. For example, you may decide to give a speech on the importance of practicing good oral hygiene because you genuinely believe that oral hygiene is essential and that bad oral hygiene can lead to a range of physical, social, and psychological problems. In this case, the speaker has no ulterior or hidden motive (e.g. you are not a toothpaste salesperson).
Manipulative persuasion occurs when a speaker urges listeners to engage in a specific behavior or change a point of view by misleading them, often to fulfill an ulterior motive beyond the face value of the persuasive attempt. We call this form of persuasion manipulative because the speaker is not being honest about the real purpose of attempting to persuade the audience. Ultimately, this form of persuasion is perceived as profoundly dishonest when audience members discover the ulterior motive. For example, suppose a physician who also owns a large amount of stock in a pharmaceutical company is asked to speak before a group of other physicians about a specific disease. Instead of informing the group about the illness, the doctor spends the bulk of his time attempting to persuade the audience that the drug his company manufactures is the best treatment for that specific disease.
Obviously, the critical question for persuasion is the speaker’s intent. Is the speaker attempting to persuade the audience because of a sincere belief in the benefits of a certain behavior or point of view? Or is the speaker using all possible means—including distorting the truth—to persuade the audience because they will derive personal benefits from their adopting a specific behavior or point of view? Unless your speech assignment calls explicitly for a speech of manipulative persuasion, the usual (and ethical) understanding of a “persuasive speech” assignment is that you should use the pure form of persuasion.
Persuasive speaking attempts to get listeners to embrace a point of view or to adopt a behavior that they would not have done otherwise.
Pure persuasion occurs when a speaker urges listeners to engage in a specific behavior or change a point of view because the speaker truly believes that the change is in the best interest of the audience members.
Manipulative persuasion occurs when a speaker urges listeners to engage in a specific behavior or change a point of view by misleading them, often to fulfill an ulterior motive beyond the face value of the persuasive attempt.
Persuasion: Behavior versus Attitudes, Values, and Beliefs
Persuasion can address behaviors, observable actions on the part of listeners, and it can also address intangible thought processes in the form of attitudes, values, and beliefs.
When the speaker attempts to persuade an audience to change their behavior , or observable actions on the part of listeners. We can often observe and even measure how successful the persuasion was. For example, after a speech attempting to persuade the audience to donate money to a charity, the charity can measure how many donations were received. The following is a short list of various behavior-oriented persuasive speeches we’ve seen in our own classes: washing one’s hands frequently and using hand sanitizer, adapting one’s driving habits to improve gas mileage, using open-source software, or drinking one soft drink or soda over another. In all these cases, the goal is to make a change in the basic behavior of audience members.
The second type of persuasive topic involves a change in attitudes, values, or beliefs. An attitude is defined as an individual’s general predisposition toward something as being good or bad, right or wrong, negative or positive. If you believe that dress codes on college campuses are a good idea, you want to give a speech persuading others to adopt a positive attitude toward campus dress codes.
A speaker can also attempt to persuade listeners to change some value they hold. Value refers to an individual’s perception of the usefulness, importance, or worth of something. We can value a college education, we can value technology, and we can value freedom. Values, as a general concept, are relatively ambiguous and tend to be very lofty ideas. Ultimately, what we value in life motivates us to engage in a range of behaviors. For example, if you value protecting the environment, you may recycle more of your trash than someone who does not hold this value. If you value family history and heritage, you may be more motivated to spend time with your older relatives and ask them about their early lives than someone who does not hold this value.
Lastly, a speaker can attempt to persuade people to change their personal beliefs. Personal b eliefs are propositions or positions that an individual holds as true or false without positive knowledge or proof. Typically, beliefs are divided into two basic categories: core and dispositional. Core beliefs are beliefs that people have actively engaged in and created over the course of their lives (e.g. belief in a higher power, belief in extraterrestrial life forms). Dispositional beliefs , on the other hand, are beliefs that people have not actively engaged in; they are judgments based on related subjects, which people make when they encounter a proposition. Imagine, for example, that you were asked the question, “Can gorillas speak English?” While you may never have met a gorilla or even seen one in person, you can make instant judgments about your understanding of gorillas and fairly certainly say whether you believe that gorillas can speak English.
When it comes to persuading people to alter beliefs, persuading audiences to change core beliefs is more difficult than persuading audiences to alter dispositional beliefs. If you find a topic related to dispositional beliefs, using your speech to help listeners alter their processing of the belief is a realistic possibility. But as a novice public speaker, you are probably best advised to avoid core beliefs. Although core beliefs often appear to be more exciting and interesting than dispositional ones, you are very unlikely to alter anyone’s core beliefs in a five- to ten-minute classroom speech.
Attitude is defined as an individual’s general predisposition toward something as being good or bad, right or wrong, negative or positive.
Value refers to an individual’s perception of the usefulness, importance, or worth of something.
Core beliefs are beliefs that people have actively engaged in and created over the course of their lives (e.g. belief in a higher power, belief in extraterrestrial life forms).
Dispositional beliefs are beliefs that people have not actively engaged in; they are judgments based on related subjects, which people make when they encounter a proposition.
Sample: Jessy Ohl’s Persuasive Speech
The following speech was written and delivered by an undergraduate student named Jessy Ohl. As with our earlier example, while this speech is written out as a text for purposes of analysis, in your public speaking course, you will most likely be assigned to speak from an outline or notes, not a fully written script.
Take a few minutes and compare this persuasive speech to the informative speech Ms. Ohl presented earlier in this chapter. What similarities do you see? What differences do you see? Does this speech seek to change the audience’s behavior? Attitudes? Values? Dispositional or core beliefs? Where in the speech do you see one or more calls for action?
With a declining population of around 6,000, my home town of Denison, Iowa, was on the brink of extinction when a new industry rolled in bringing jobs and revenue. However, as the Canadian Globe and Mail of July 23, 2007, reports, the industry that saved Denison may ultimately lead to its demise. Denison is one of 110 communities across the country to be revolutionized by the production of corn ethanol. Ethanol is a high-powered alcohol, derived from plant matter, that can be used like gasoline. According to the Omaha World Herald of January 8, 2008, our reliance on foreign oil combined with global warming concerns have many holding corn ethanol as our best energy solution. But despite the good intentions of helping farmers and lowering oil consumption, corn ethanol is filled with empty promises. In fact, The Des Moines Register of March 1, 2008, concludes that when ethanol is made from corn, all of its environmental and economic benefits disappear. With oil prices at 100 dollars per barrel, our nation is in an energy crisis, and luckily, the production of ethanol can be a major help for both farmers and consumers, if done correctly. Unfortunately, the way we make ethanol—over 95% from corn—is anything but correct. Although hailed as a magic bullet, corn ethanol could be the worst agricultural catastrophe since the Dust Bowl. The serious political, environmental, and even moral implications demand that we critically rethink this so-called yellow miracle by: first, examining the problems created by corn ethanol; second, exploring why corn ethanol has gained such power; and finally, discovering solutions to prevent a corn ethanol disaster. Now, if you have heard anything about the problems of corn ethanol, it probably dealt with efficiency. As the Christian Science Monitor of November 15, 2007, notes, it takes a gallon of gasoline or more to make a gallon of ethanol. And while this is an important concern, efficiency is the least of our worries. Turning this crop into fuel creates two major problems for our society: first, environmental degradation; and second, acceleration of global famine. First, corn ethanol damages the environment as much as, if not more than, fossil fuels. The journal Ethanol and Bio-diesel News of September 2007 asserts that the production of corn ethanol is pushing natural resources to the breaking point. Since the Dust Bowl, traditional farming practices have required farmers to “rotate” crops. But with corn ethanol being so profitable, understandably, farmers have stopped rotating crops, leading to soil erosion, deforestation, and fertilizer runoff—making our soil less fertile and more toxic. And the story only gets worse once the ethanol is manufactured. According to National Public Radio’s Talk of the Nation of February 10, 2008, corn ethanol emits more carbon monoxide and twice the amount of carcinogens into the air as traditional gasoline. The second problem created from corn ethanol is the acceleration of global famine. According to the US Grains Council, last year, 27 million tons of corn, traditionally used as food, was turned into ethanol, drastically increasing food prices. The March 7, 2007, issue of The Wall Street Journal explains that lower supplies of corn needed for necessities such as farm feed, corn oil, and corn syrup have increased our food costs in everything from milk to bread, eggs, and even beer as much as 25 percent. The St. Louis Post Dispatch of April 12, 2007, reports that the amount of corn used to fill one tank of gas could feed one person for an entire year. In October, Global protests over corn ethanol lead the United Nations to call its production “a crime against humanity.” If you weren’t aware of the environmental or moral impacts of corn ethanol, you’re not alone. The Financial Times of May 27, 2007, reports that the narrative surrounding corn ethanol as a homegrown fuel is so desirable that critical thinking is understandably almost nonexistent. To start thinking critically about corn ethanol, we need to examine solutions on both the federal and personal levels. First, at the federal level, our government must end the ridiculously high subsidies surrounding corn ethanol. On June 24, 2007, The Washington Post predicted that subsidies on corn ethanol would cost the federal government an extra 131 billion dollars by 2010. This isn’t to say that the federal government should abandon small farmers. Instead, let’s take the excitement around alternative fuels and direct it toward the right kinds of ethanol. The Economist of June 2, 2007, reports that other materials such as switch grass and wood chips can be used instead of corn. And on July 6, 2011, The New York Times reported on ethanol made from corn cobs, leaves, and husks, which leaves the corn kernels to be used as food. The government could use the money paid in subsidies to support this kind of responsible production of ethanol. The point is that ethanol done right can honestly help with energy independence. On the personal level, we have all participated in the most important step, which is being knowledgeable about the true face of corn ethanol. However, with big business and Washington proclaiming corn ethanol’s greatness, we need to spread the word. So please, talk to friends and family about corn ethanol while there is still time. To make this easier, visit my website, at http://www.responsibleethanol.com . Here you will find informational materials, links to your congressional representatives, and ways to invest in switch grass and wood ethanol. Today, we examined the problems of corn ethanol in America and discovered solutions to make sure that our need for energy reform doesn’t sacrifice our morality. Iowa is turning so much corn into ethanol that soon the state will have to import corn to eat. And while my hometown of Denison has gained much from corn ethanol, we all have much more to lose from it.
To Entertain
The final general purpose people can have for public speaking is to entertain. Whereas informative and persuasive speech making is focused on the end result of the speech process, entertainment speaking focuses on the theme and occasion of the speech. An entertaining speech can be either informative or persuasive at its root, but the context or theme of the speech requires speakers to think about the speech primarily in terms of audience enjoyment.
Why We Entertain
Entertaining speeches are very common in everyday life. The fundamental goal of an entertaining speech is audience enjoyment, which can come in a variety of forms. Entertaining speeches can be funny or serious. Overall, entertaining speeches are not designed to give an audience a deep understanding of life but instead to function as a way to divert an audience from their day-to-day lives for a short period of time. This is not to say that an entertaining speech cannot have real content that is highly informative or persuasive, but its goal is primarily about the entertaining aspects of the speech and not focused on the informative or persuasive quality of the speech.
Common Forms of Entertainment Topics
There are three basic types of entertaining speeches: the after-dinner speech, the ceremonial speech, and the inspirational speech. The after-dinner speaking is a form of speaking where a speaker takes a serious speech topic (either informative or persuasive) and injects a level of humor into the speech to make it entertaining. Some novice speakers will attempt to turn an after-dinner speech into a stand-up comedy routine, which doesn’t have the same focus (Roye, 2010). After-dinner speeches are first and foremost speeches.
A ceremonial speech is a type of entertaining speech where the specific context of the speech is the driving force of the speech. Common types of ceremonial speeches include introductions, toasts, and eulogies. In each of these cases, there are specific events that drive the speech. Maybe you’re introducing an individual who is about to receive an award, giving a toast at your best friend’s wedding, or delivering the eulogy at a relative’s funeral. In each of these cases, the speech and the purpose of the speech is determined by the context of the event and not by the desire to inform or persuade.
The final type of entertaining speech, an inspirational speech , is one where the speaker’s primary goal is to inspire her or his audience. Inspirational speeches are based on emotions with the goal to motivate listeners to alter their lives in some significant way. Florence Littauer, a famous professional speaker, delivers an emotionally charged speech titled “ Silver Boxes .” In the speech, Mrs. Littauer demonstrates how people can use positive comments to encourage others in their daily lives. The title comes from a story she tells at the beginning of the speech where she was teaching a group of children about using positive speech, and one of the children defined positive speech as giving people little silver boxes with bows on top ( http://server.firefighters.org/catalog/2009/45699.mp3 ).
Entertainment speaking is a speech for audience enjoyment.
After-dinner speaking is a form of speaking where a speaker takes a serious speech topic (either informative or persuasive) and injects a level of humor into the speech to make it entertaining.
A ceremonial speech is a type of entertaining speech where the specific context of the speech is the driving force of the speech.
An inspirational speech is one where the speaker’s primary goal is to inspire her or his audience.
Sample: Adam Fink’s Entertainment Speech
The following speech, by an undergraduate student named Adam Fink, is an entertainment speech. Specifically, this speech is a ceremonial speech given at Mr. Fink’s graduation. As with our earlier examples, while this speech is written out as a text for purposes of analysis, in your public speaking course you will most likely be assigned to speak from an outline or notes, not a fully written script. Notice that the tenor of this speech is persuasive, but it persuades in a more inspiring way than just building and proving an argument.
Good evening! I’ve spent the last few months looking over commencement speeches on YouTube. The most notable ones had eight things in common. They reflected on the past, pondered about the future. They encouraged the honorees. They all included some sort of personal story and application. They made people laugh at least fifteen times. They referred to the university as the finest university in the nation or world, and last but not least they all greeted the people in attendance. I’ll begin by doing so now. President Holst, thank you for coming. Faculty members and staff, salutations to you all. Distinguished guests, we are happy to have you. Family members and friends, we could not be here without you. Finally, ladies and gentlemen of the class of 2009, welcome to your commencement day here at Concordia University, Saint Paul, this, the finest university in the galaxy, nay, universe. Really, it’s right up there with South Harlem Institute of Technology, the School of Hard Knocks, and Harvard. Check and check! Graduates, we are not here to watch as our siblings, our parents, friends, or other family walk across this stage. We are here because today is our graduation day. I am going to go off on a tangent for a little bit. Over the past umpteen years, I have seen my fair share of graduations and ceremonies. In fact, I remember getting dragged along to my older brothers’ and sisters’ graduations, all 8,000 of them—at least it seems like there were that many now. Seriously, I have more family members than friends. I remember sitting here in these very seats, intently listening to the president and other distinguished guests speak, again saying welcome and thank you for coming. Each year, I got a little bit better at staying awake throughout the entire ceremony. Every time I would come up with something new to keep myself awake, daydreams, pinching my arms, or pulling leg hair; I was a very creative individual. I am proud to say that I have been awake for the entirety of this ceremony. I would like to personally thank my classmates and colleagues sitting around me for slapping me every time I even thought about dozing off. Personal story, check—and now, application! Graduates, don’t sleep through life. If you need a close friend or colleague to keep you awake, ask. Don’t get bored with life. In the words of one of my mentors, the Australian film director, screen writer, and producer Baz Luhrman, “Do one thing every day that scares you.” Keep yourself on your toes. Stay occupied but leave room for relaxation; embrace your hobbies. Don’t get stuck in a job you hate. I am sure many of you have seen the “Did You Know?” film on YouTube. The film montages hundreds of statistics together, laying down the ground work to tell viewers that we are approaching a crossroad. The way we live is about to change dramatically. We are living in exponential times. It’s a good thing that we are exponential people.
We are at a crossing point here, now. Each of us is graduating; we are preparing to leave this place we have called home for the past few years. It’s time to move on and flourish. But let’s not leave this place for good. Let us walk away with happy memories. We have been fortunate enough to see more change in our time here than most alumni see at their alma mater in a lifetime. We have seen the destruction of Centennial, Minnesota, and Walther. Ladies, it might not mean a lot to you, but gentlemen, we had some good times there. We have seen the building and completion of the new Residence Life Center. We now see the beginnings of our very own stadium. We have seen enough offices and departments move to last any business a lifetime. Let us remember these things, the flooding of the knoll, Ultimate Frisbee beginning at ten o’clock at night, and two back-to-back Volleyball National Championship teams, with one of those championship games held where you are sitting now. I encourage all of you to walk out of this place with flashes of the old times flickering through your brains. Reflection, check! Honorees, in the words of Michael Scott, only slightly altered, “They have no idea how high [we] can fly.” Right now you are surrounded by future politicians, film critics, producers, directors, actors, actresses, church workers, artists, the teachers of tomorrow, musicians, people who will change the world. We are all held together right here and now, by a common bond of unity. We are one graduating class. In one of his speeches this year, President Barack Obama said, “Generations of Americans have connected their stories to the larger American story through service and helped move our country forward. We need that service now.” He is right. America needs selfless acts of service. Hebrews 10:23–25 reads, “Let us hold unswervingly to the hope we profess, for he who promised is faithful. And let us consider how we may spur one another on toward love and good deeds. Let us not give up meeting together, as some are in the habit of doing, but let us encourage one another—and all the more as you see the Day approaching.” Let us not leave this place as enemies but rather as friends and companions. Let us come back next fall for our first reunion, the Zero Class Reunion hosted by the wonderful and amazing workers in the alumni department. Let us go and make disciples of all nations, guided by His Word. Let us spread God’s peace, joy, and love through service to others. Congratulations, graduates! I hope to see you next homecoming. Encouragement, check!
Selecting a Topic

Wonderlane – Fork in the road, decision tree – CC BY 2.0.
One of the most common stumbling blocks for novice public speakers is selecting their first speech topic. Generally, your public speaking instructor will provide you with some fairly specific parameters to make this a little easier. You may be assigned to tell about an event that has shaped your life or to demonstrate how to do something. Whatever your parameters, at some point you as the speaker will need to settle on a specific topic. In this section, we’re going to look at some common constraints of public speaking, picking a broad topic area, and narrowing your topic.
Common Constraints of Public Speaking
When we use the word “constraint” with regard to public speaking, we are referring to any limitation or restriction you may have as a speaker. Whether in a classroom situation or the boardroom, speakers are typically given specific instructions that they must follow. These instructions constrain the speaker and limit what the speaker can say. For example, in the professional world of public speaking, speakers are often hired to speak about a specific topic (e.g. time management, customer satisfaction, or entrepreneurship). In the workplace, a supervisor may assign a subordinate to present certain information in a meeting. In these kinds of situations, when a speaker is hired or assigned to talk about a specific topic, they cannot decide to talk about something else.
Furthermore, the speaker may have been asked to speak for an hour, only to show up and find out that the event is running behind schedule, so the speech must now be made in only thirty minutes. Having prepared sixty minutes of material, the speaker now has to determine what stays in the speech and what must go. In both of these instances, the speaker is constrained as to what they can say during a speech. Typically, we refer to four primary constraints: purpose, audience, context, and time frame.
The first major constraint someone can have involves the general purpose of the speech. As mentioned earlier, there are three general purposes: to inform, to persuade, and to entertain. If you’ve been told that you will be delivering an informative speech, you are automatically constrained from delivering a speech with the purpose of persuading or entertaining. In most public speaking classes, this is the first constraint students will come in contact with because generally, teachers will tell you the exact purpose of each speech in the class.
The second major constraint that you need to consider as a speaker is the type of audience you will have. As discussed in the chapter on audience analysis, different audiences have different political, religious, and ideological leanings. As such, choosing a speech topic for an audience that has a specific mindset can be very tricky. Unfortunately, determining what topics may or may not be appropriate for a given audience is based on generalizations about specific audiences. For example, maybe you’re going to give a speech at a local meeting of Democratic leaders. You may think that all Democrats are liberal or progressive, but there are many conservative Democrats as well. If you assume that all Democrats are liberal or progressive, you may end up offending your audience by making such a generalization without knowing better. The best way to prevent yourself from picking a topic that is inappropriate for a specific audience is to know your audience, which is why we recommend conducting an audience analysis.
The third major constraint relates to the context. For speaking purposes, the context of a speech is the set of circumstances surrounding a particular speech. There are countless different contexts in which we can find ourselves speaking: a classroom in college, a religious congregation, a corporate boardroom, a retirement village, or a political convention. In each of these different contexts, the expectations for a speaker are going to be unique and different. The topics that may be appropriate in front of a religious group may not be appropriate in the corporate boardroom. Topics appropriate for the corporate boardroom may not be appropriate at a political convention.
The last, but by no means least important, major constraint that you will face is the time frame of your speech. In speeches that are under ten minutes in length, you must narrowly focus a topic on one major idea. For example, in a ten-minute speech, you could not realistically hope to discuss the entire topic of the US Social Security program. There are countless books, research articles, websites, and other forms of media on the topic of Social Security, so trying to crystallize all that information into ten minutes is just not realistic.
Instead, narrow your topic to something that is more realistically manageable within your allotted time. You might choose to inform your audience about Social Security disability benefits, using one individual disabled person as an example. Or perhaps you could speak about the career of Robert J. Myers, one of the original architects of Social Security 1 . By focusing on information that can be covered within your time frame, you are more likely to accomplish your goal at the end of the speech.
Selecting a Broad Subject Area
Once you know what the basic constraints are for your speech, you can then start thinking about picking a topic. The first aspect to consider is what subject area you are interested in examining. A subject area is a broad area of knowledge. Art, business, history, physical sciences, social sciences, humanities, and education are all examples of subject areas. When selecting a topic, start by casting a broad net because it will help you limit and weed out topics quickly.
Furthermore, each of these broad subject areas has a range of subject areas beneath it. For example, if we take the subject area “art,” we can break it down further into broad categories like art history, art galleries, and how to create art. We can further break down these broad areas into even narrower subject areas (e.g., art history includes prehistoric art, Egyptian art, Grecian art, Roman art, Middle Eastern art, medieval art, Asian art, Renaissance art, modern art). As you can see, topic selection is a narrowing process.
Narrowing Your Topic
Narrowing your topic to something manageable for the constraints of your speech is something that takes time, patience, and experience. One of the biggest mistakes that new public speakers make is not narrowing their topics sufficiently given the constraints. In the previous section, we started demonstrating how the narrowing process works, but even in those examples, we narrowed subject areas down to fairly broad areas of knowledge.
Think of narrowing as a funnel. At the top of the funnel are the broad subject areas, and your goal is to narrow your topic further and further down until just one topic can come out the other end of the funnel. The more focused your topic is, the easier your speech is to research, write, and deliver. So let’s take one of the broad areas from the art subject area and keep narrowing it down to a manageable speech topic. For this example, let’s say that your general purpose is to inform, you are delivering the speech in class to your peers, and you have five to seven minutes. Now that we have the basic constraints, let’s start narrowing our topic. The broad area we are going to narrow in this example is Middle Eastern art. When examining the category of Middle Eastern art, the first thing you’ll find is that Middle Eastern art is generally grouped into four distinct categories: Anatolian, Arabian, Mesopotamian, and Syro-Palestinian. Again, if you’re like us, until we started doing some research on the topic, we had no idea that the historic art of the Middle East was grouped into these specific categories. We’ll select Anatolian art or the art of what is now modern Turkey.
You may think that your topic is now sufficiently narrow, but even within the topic of Anatolian art, there are smaller categories: pre-Hittite, Hittite, Urartu, and Phrygian periods of art. So let’s narrow our topic again to the Phrygian period of art (1200–700 BCE). Although we have now selected a specific period of art history in Anatolia, we are still looking at a five-hundred-year period in which a great deal of art was created. One famous Phrygian king was King Midas, who according to myth was given the ears of a donkey and the power of a golden touch by the Greek gods. As such, there is an interesting array of art from the period of Midas and its Greek counterparts representing Midas. At this point, we could create a topic about how Phrygian and Grecian art differed in their portrayals of King Midas. We now have a topic that is unique, interesting, and definitely manageable in five to seven minutes. You may be wondering how we narrowed the topic down; we just started doing a little research using the Metropolitan Museum of Art’s website ( http://www.metmuseum.org ).
Overall, when narrowing down your topic, you should start by asking yourself four basic questions based on the constraints discussed earlier in this section:
- Does the topic match my intended general purpose?
- Is the topic appropriate for my audience?
- Is the topic appropriate for the given speaking context?
- Can I reasonably hope to inform or persuade my audience in the time frame I have for the speech?
Specific Purposes

Andrew Sutherland – Roma Street Steps – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Once you have chosen your general purpose and your topic, it’s time to take your speech to the next phase and develop your specific purpose. A specific purpose starts with one of the three general purposes and then specifies the actual topic you have chosen and the basic objective you hope to accomplish with your speech. The specific purpose answers the who , what , when , where , and why questions for your speech.
Getting Specific
When attempting to get at the core of your speech (the specific purpose), you need to know a few basic things about your speech. First, you need to have a general purpose. Once you know whether your goal is to inform, persuade, or entertain, picking an appropriate topic is easier. Obviously, depending on the general purpose, you will have a range of different types of topics. For example, let’s say you want to give a speech about hygiene. You could still write a speech about hygiene no matter what your general purpose is, but the specific purpose would vary depending on whether the general purpose is to inform (discussing hygiene practices around the globe), to persuade (telling people why they need to adopt a specific hygiene practice), or to entertain (explaining some of the strange and unique hygiene practices that people have used historically). Notice that in each of these cases, the general purpose alters the topic, but all three are still fundamentally about hygiene.
Now, when discussing specific purposes, we are concerned with who, what, when, where, why, and how questions for your speech. Let’s examine each of these separately. First, you want to know who is going to be in your audience. Different audiences, as discussed in the chapter on audience analysis, have differing desires, backgrounds, and needs. Keeping your audience first and foremost in your thoughts when choosing a specific purpose will increase the likelihood that your audience will find your speech meaningful.
Second is the “what” question or the basic description of your topic. When picking an effective topic, you need to make sure that the topic is appropriate for a variety of constraints or limitations within a speaking context.
Third, you need to consider when your speech will be given. Different speeches may be better at different times of the day. For example, explaining the importance of eating breakfast and providing people with cereal bars may be a great topic at 9:00 a.m. but may not have the same impact if you’re giving it at 4:00 p.m.
Fourth, you need to consider where your speech will be delivered. Are you giving a speech in front of a classroom? A church? An executive meeting? Depending on the location of your speech, different topics may or may not be appropriate.
The last question you need to answer within your speech is why. Why does your audience need to hear your speech? If your audience doesn’t care about your specific purpose, they are less likely to pay attention to your speech. If it’s a topic that’s a little more off-the-wall, you’ll really need to think about why they should care.
Once you’ve determined the who , what , when , where , and why aspects of your topic, it’s time to start creating your actual specific purpose. First, a specific purpose, in its written form, should be a short, declarative sentence that emphasizes the main topic of your speech. Let’s look at an example:
In this example, we’ve quickly narrowed a topic from a more general topic to a more specific topic. Let’s now look at that topic in terms of a general purpose and specific purpose:
For the purpose of this example, we used the same general topic area and demonstrated how you could easily turn the topic into either an informative speech or a persuasive speech. In the first example, the speaker is going to talk about the danger embedded journalists face. In this case, the speaker isn’t attempting to alter people’s ideas about embedded journalists, just make them more aware of the dangers. In the second case, the specific purpose is to persuade a group of journalism students (the audience) to avoid jobs as embedded journalists.
Your Specific Statement of Purpose
To form a clear and succinct statement of the specific purpose of your speech, start by naming your general purpose (to inform, to persuade, or to entertain). Follow this with a capsule description of your audience (my peers in class, a group of kindergarten teachers, etc.). Then complete your statement of purpose with a prepositional phrase (a phrase using “to,” “about,” “by,” or another preposition) that summarizes your topic. As an example, “My specific purpose is to persuade the students in my residence hall to protest the proposed housing cost increase” is a specific statement of purpose, while “My speech will be about why we should protest the proposed housing cost increase” is not.
Specific purposes should be statements, not questions. If you find yourself starting to phrase your specific purpose as a question, ask yourself how you can reword it as a statement. Table 6 “My Specific Purpose Is…” provides several more examples of good specific purpose statements.
Table 6 My Specific Purpose Is…
Basic Tips for Creating Specific Purposes
Now that we’ve examined what specific purposes are, we are going to focus on a series of tips to help you write specific purposes that are appropriate for a range of speeches.
Audience, Audience, Audience
First and foremost, you always need to think about your intended audience when choosing your specific purpose. In the previous section, we talked about a speech where a speaker is attempting to persuade a group of journalism students to not take jobs as embedded journalists. Would the same speech be successful, or even appropriate, if given in your public speaking class? Probably not. As a speaker, you may think your topic is great, but you always need to make sure you think about your audience when selecting your specific purpose. For this reason, when writing your specific purpose, start off your sentence by actually listing the name of your audience: a group of journalism students, the people in my congregation, my peers in class, and so on. When you place your audience first, you’re a lot more likely to have a successful speech.
Matching the Rhetorical Situation
After your audience, the second most important consideration about your specific purpose pertains to the rhetorical situation of your speech. The rhetorical situation is the set of circumstances surrounding your speech (e.g., speaker, audience, text, and context). When thinking about your specific purpose, you want to ensure that all these components go together. You want to make sure that you are the appropriate speaker for a topic, the topic is appropriate for your audience, the text of your speech is appropriate, and the speech is appropriate for the context. For example, speeches that you give in a classroom may not be appropriate in a religious context and vice versa.
Make It Clear
The specific purpose statement for any speech should be direct and not too broad, general, or vague. Consider the lack of clarity in the following specific purpose: “To persuade the students in my class to drink more.” Obviously, we have no idea what the speaker wants the audience to drink: water, milk, orange juice? Alcoholic beverages? Furthermore, we have no way to quantify or make sense of the word “more.” “More” assumes that the students are already drinking a certain amount, and the speaker wants them to increase their intake. If you want to persuade your listeners to drink eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, you need to say so clearly in your specific purpose.
Another way in which purpose statements are sometimes unclear comes from the use of colloquial language. While we often use colloquialisms in everyday life, they are often understood only by a limited number of people. It may sound like fun to have a specific purpose like, “To persuade my audience to get jiggy,” but if you state this as your purpose, many people probably won’t know what you’re talking about at all.
Don’t Double Up
You cannot hope to solve the entire world’s problems in one speech, so don’t even try. At the same time, you also want to make sure that you stick to one specific purpose. Chances are it will be challenging enough to inform your audience about one topic or persuade them to change one behavior or opinion. Don’t put extra stress on yourself by adding topics. If you find yourself using the word “and” in your specific topic statement, you’re probably doubling up on topics.
Can I Really Do This Speech in Five to Seven Minutes?
When choosing your specific purpose, it’s important to determine whether it can be realistically covered in the amount of time you have. Time limits are among the most common constraints for students in a public speaking course. Speeches early in the term have shorter time limits, and speeches later in the term have longer time limits. To determine whether you think you can accomplish your speech’s purpose in the time slot, ask yourself how long it would take to make you an informed person on your chosen topic or to persuade you to change your behavior or attitudes.
If you cannot reasonably see yourself becoming informed or persuaded during the allotted amount of time, chances are you aren’t going to inform or persuade your audience either. The solution, of course, is to make your topic narrower so that you can fully cover a limited aspect of it.
A specific purpose starts with one of the three general purposes and then specifies the actual topic you have chosen and the basic objective you hope to accomplish with your speech.
The rhetorical situation is the set of circumstances surrounding your speech (e.g., speaker, audience, text, and context). When thinking about your specific purpose, you want to ensure that all these components go together.
Crafting and Understanding Thesis Statements for Speeches

You might be familiar with a thesis statement in writing an essay. Thesis statements are similar in speeches, but slightly different because they are only heard and not read. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know what you are going to talk about “in a nutshell.” With a good thesis statement, you will fulfill four basic functions: you express your specific purpose, provide a way to organize your main points, make your research more effective, and enhance your delivery.
Express Your Specific Purpose
To orient your audience, you need to be as clear as possible about your meaning. A strong thesis will prepare your audience effectively for the points that will follow. Here are two examples:
- “Today, I want to discuss academic cheating.” (weak example)
- “Today, I will clarify what plagiarism is and give examples of its different types so that you can see how it leads to a loss of creative learning interaction.” (strong example)
The weak statement will probably give the impression that you have no clear position on your topic because you haven’t said what that position is. Additionally, the term “academic cheating” can refer to many behaviors: acquiring test questions ahead of time, copying answers, changing grades, or allowing others to do your coursework. Therefore, the specific topic of the speech is still not clear to the audience. The strong statement not only specifies plagiarism but also states your specific concern (loss of creative learning interaction).
Provide a Way to Organize Your Main Points
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease. On the other hand, when the thesis statement is not very clear, creating a speech is an uphill battle. When your thesis statement is sufficiently clear and decisive, you will know where you stand on your topic and where you intend to go with your speech. Having a clear thesis statement is especially important if you know a great deal about your topic or you have strong feelings about it. If this is the case for you, you need to know exactly what you are planning on talking about in order to fit within specified time limitations. Knowing where you are and where you are going is the entire point in establishing a thesis statement; it makes your speech much easier to prepare and to present.
Let’s say you have a reasonably strong thesis statement, and that you’ve already brainstormed a list of information that you know about the topic. Chances are your list is too long and has no focus. Using your thesis statement, you can select only the information that (1) is directly related to the thesis and (2) can be arranged in a sequence that will make sense to the audience and will support the thesis. In essence, a strong thesis statement helps you keep useful information and weed out less helpful information.
Make Your Research More Effective
If you begin your research with only a general topic in mind, you run the risk of spending hours reading mountains of excellent literature about your topic. However, mountains of research does not always make coherent speeches.
You may have little or no idea of how to tie your research together, or even whether you should tie it together. If, on the other hand, you conduct your research with a clear thesis statement in mind, you will be better able to zero in only on material that directly relates to your chosen thesis statement. Let’s look at an example that illustrates this point:
Many traffic accidents involve drivers older than fifty-five. While this statement may be true, you could find industrial, medical, insurance literature that can drone on ad infinitum about the details of all such accidents in just one year. Instead, focusing your thesis statement will help you narrow the scope of information you will be searching for while gathering information.
Here’s an example of a more focused thesis statement:
Three factors contribute to most accidents involving drivers over fifty-five years of age: failing eyesight, slower reflexes, and rapidly changing traffic conditions.
This framing is somewhat better. This thesis statement at least provides three possible main points and some keywords for your electronic catalog search. However, if you want your audience to understand the context of older people at the wheel, consider something like:
Mature drivers over fifty-five years of age must cope with more challenging driving conditions than existed only one generation ago: more traffic moving at higher speeds, the increased imperative for quick driving decisions, and rapidly changing ramp and cloverleaf systems. Because of these challenges, I want my audience to believe that drivers over the age of sixty-five should be required to pass a driving test every five years.
This framing of the thesis provides some interesting choices. First, several terms need to be defined, and these definitions might function surprisingly well in setting the tone of the speech. Your definitions of words like “generation,” “quick driving decisions,” and “cloverleaf systems” could jolt your audience out of assumptions they have taken for granted as truth.
Second, the framing of the thesis provides you with a way to describe the specific changes as they have occurred between, say, 1970 and 2010. How much, and in what ways, have the volume and speed of traffic changed? Why are quick decisions more critical now? What is a “cloverleaf,” and how does any driver deal cognitively with exiting in the direction seemingly opposite to the desired one? Questions like this, suggested by your own thesis statement, can lead to a robust and memorable speech.
Enhance Your Delivery
When your thesis is not clear to you, your listeners will be even more clueless than you are. However, if you have a good clear thesis statement, your speech becomes clear to your listeners. When you stand in front of your audience presenting your introduction, you can vocally emphasize the essence of your speech, expressed as your thesis statement.
Many speakers pause for a half second, lower their vocal pitch slightly, slow down a little, and deliberately present the thesis statement, the one sentence that encapsulates its purpose. When this is done effectively, the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech is driven home for an audience.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement.
Choose Your Topic
The first step in writing a good thesis statement is finding your topic. Once you have a general topic, you are ready to go to the second step of creating a thesis statement.
Narrow Your Topic
One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to ten-minute speech. While five to ten minutes may sound like a long time to new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can run out of time if your topic is too broad. To decide if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions:
First, is your thesis statement narrow or is it a broad overgeneralization of a topic? Overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “the elderly are bad drivers” is an overgeneralization of all elderly drivers. Make sure that your thesis statement is nuanced enough to accurately represent what you can support in your speech.
The second question to ask yourself when narrowing a topic is whether your speech’s topic is one clear topic or multiple topics. A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana and prostitution should be legalized in the United States.” Not only are both broad, but you also have two completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: “Today we’re going to examine the legalization and regulation of prostitution in the state of Nevada.” In this case, we’re focusing our topic on how one state has handled the legalization and regulation of prostitution.
The last question a speaker should ask when making sure a topic is sufficiently narrow is whether the topic has direction. If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This broadness ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow their topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Sentence
Once you’ve narrowed your topic to something that is reasonably manageable given the constraints placed on your speech, you can then formalize that topic as a complete sentence. For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech. Your thesis statement should be a clear, declarative statement that sets up your speech.
Use the Thesis Checklist
Once you have written the first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times before delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown below.
Thesis Checklist
Instructions: For each of the following questions, check either “yes” or “no.” Yes No
- Does your thesis clearly reflect the topic of your speech?
- Can you adequately cover the topic indicated in your thesis within the time you have for your speech?
- Is your thesis statement simple?
- Is your thesis statement direct?
- Does your thesis statement gain an audience’s interest?
- Is your thesis statement easy to understand?
- Does your thesis statement introduce a clear argument?
- Does your thesis statement clearly indicate what your audience should know, do, think, or feel?
Scoring: For a strong thesis statement, all your answers should have been “yes.”
After reading this chapter, we hope that you now have a better understanding not only of the purpose of your speech but also of how to find a fascinating topic for yourself and your audience. We started this chapter citing lyrics from the Avenue Q song “Purpose.” While the character is trying to find his purpose in life, we hope this chapter has helped you identify your general purpose, choose a topic that will interest you and your audience, and use these to develop a specific purpose statement for your speech.
Atwood, C. G. (2009). Knowledge management basics . Alexandria, VA: ASTD Press.
Hendriks, P. (1999). Why share knowledge? The influence of ICT on the motivation for knowledge sharing. Knowledge and Process Management, 6 , 91–100.
O’Hair, D., Stewart, R., & Rubenstein, H. (2007). A speaker’s guidebook: Text and reference (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins.
Roye, S. (2010). Austan Goolsbee a funny stand-up comedian? Not even close… [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.realfirststeps.com/1184/austan-goolsbee-funny-standup-comedian-close
See, for example, Social Security Administration (1996). Robert J. Myers oral history interview. Retrieved from http://www.ssa.gov/history/myersorl.html
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Preparing and Supporting a Speech
Introduction, 8.1 selecting and narrowing a topic.
Many steps go into the speech-making process. Many people do not approach speech preparation in an informed and systematic way, which results in many poorly planned or executed speeches that are not pleasant to sit through as an audience member and do not reflect well on the speaker. Good speaking skills can help you stand out from the crowd in increasingly competitive environments. While a polished delivery is important, good speaking skills must be practiced much earlier in the speech-making process (James Madison University Writing Center, 2021).
Analyze Your Audience
Audience analysis is key for a speaker to achieve his or her speech goal. One of the first questions you should ask yourself is “Who is my audience?” While there are some generalizations you can make about an audience, a competent speaker always assumes there is a diversity of opinion and background among his or her listeners. You cannot assume from looking that everyone in your audience is the same age, race, sexual orientation, religion, or many other factors. Even if you did have a homogenous audience, with only one or two people who do not match up, you should still consider those one or two people. Of course, a speaker could still unintentionally alienate certain audience members, especially in persuasive speaking situations. While this may be unavoidable, speakers can still think critically about what content they include in the speech and the effects it may have (James Madison University Communication Center, 2021).
Demographic Audience Analysis
Demographics are broad sociocultural categories, such as age, gender, race, socioeconomic status, sexual orientation, education level, religion, ethnicity, and nationality used to segment a larger population. Since you are always going to have diverse demographics among your audience members, it would be unwise to focus solely on one group over another. Being aware of audience demographics is useful because you can tailor and vary examples in order to appeal to different groups of people (James Madison University Communication Center, 2021).
Psychological Audience Analysis
Psychological audience analysis considers the audience’s psychological dispositions toward the topic, the speaker, and the occasion as well as how their attitudes, beliefs, and values inform those dispositions (Dlugan, 2012). When considering your audience’s disposition toward your topic, you want to assess your audience’s knowledge of the subject. You would not include a lesson on calculus in an introductory math course. You also would not go into the intricacies of a heart transplant to an audience with no medical training.
The audience may or may not have preconceptions about you as a speaker. One way to engage positively with your audience is to make sure you establish your credibility. In terms of credibility , you want the audience to see you as competent, trustworthy, and engaging. If the audience is already familiar with you, they may already see you as a credible speaker because they have seen you speak before, have heard other people evaluate you positively, or know that you have credentials and/or experience that make you competent. If you know you have a reputation that is not as positive, you will want to work hard to overcome those perceptions. To establish your trustworthiness, you want to incorporate good supporting material into your speech, verbally cite sources, and present information and arguments in a balanced, non-coercive, and non-manipulative way. To establish yourself as engaging, you want to have a well-delivered speech, which requires you to practice, get feedback, and practice some more. Your verbal and nonverbal delivery should be fluent and appropriate to the audience and occasion.

The circumstances that led your audience to attend your speech will affect their view of the occasion (Dlugan, 2012). A captive audience includes people who are required to attend your presentation. Mandatory meetings are common in workplace settings. Whether you are presenting for a group of your employees, coworkers, classmates, or even residents in your dorm if you are a resident advisor, you should not let the fact that the meeting is required give you license to give a half-hearted speech. In fact, you may want to build common ground with your audience to overcome any potential resentment for the required gathering. In your speech class, your classmates are captive audience members.
View having a captive classroom audience as a challenge, and use this space as a public speaking testing laboratory. You can try new things and push your boundaries more, because this audience is very forgiving and understanding since they have to go through the same things you do. In general, you may have to work harder to maintain the attention of a captive audience. Since coworkers may expect to hear the same content they hear every time at this particular meeting (and classmates have to sit through dozens and dozens of speeches), use your speech as an opportunity to stand out from the crowd or from what has been done before.
A voluntary audience includes people who have decided to come hear your speech. To help adapt to a voluntary audience, ask yourself what the audience members expect (Dlugan, 2012). Why are they here? If they have decided to come and see you, they must be interested in your topic or you as a speaker. Perhaps you have a reputation for being humorous, being able to translate complicated information into more digestible parts, or being interactive with the audience and responding to questions. Whatever the reason or reasons, it is important to make sure you deliver on those aspects. If people are voluntarily giving up their time to hear you, you want to make sure they get what they expected.
A final aspect of psychological audience analysis involves considering the audience’s attitudes, beliefs, and values, as they will influence all the perceptions mentioned previously (Dlugan, 2012). As you can see in the figure below, think of our attitudes, beliefs, and values as layers that make up our perception and knowledge.
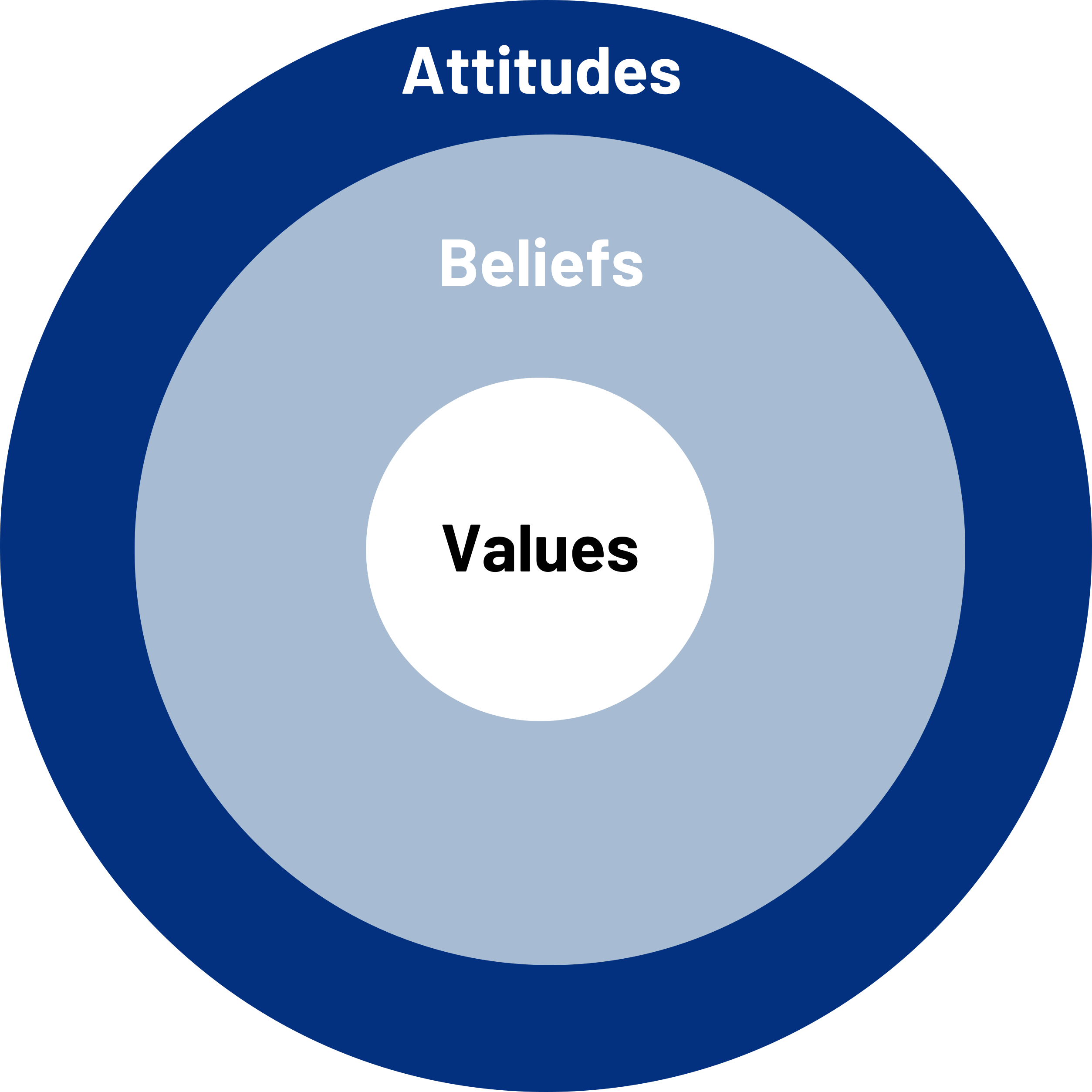
At the outermost level, attitudes are our likes and dislikes, and they are easier to influence than beliefs or values because they are often reactionary (Dlugan, 2012). If you have ever followed the approval rating of a politician, you know that people’s likes and dislikes change frequently and can change dramatically based on recent developments. This is also true interpersonally. For those of you who have siblings, think about how you can go from liking your sisters or brothers, maybe because they did something nice for you, to disliking them because they upset you. This seesaw of attitudes can go up and down over the course of a day or even a few minutes, but it can still be useful for a speaker to consider. If there is something going on in popular culture or current events that has captured people’s attention and favor or disfavor, then you can tap into that as a speaker to better relate to your audience.
When considering beliefs, we are dealing with what we believe “is or isn’t” or “true or false.” We come to hold our beliefs based on what we are taught, experience for ourselves, or believe (Dlugan, 2012). Our beliefs change if we encounter new information or experiences that counter previous ones. As people age and experience more, their beliefs are likely to change, which is natural.
Our values deal with what we view as right or wrong, good or bad (Dlugan, 2012). Our values do change over time but usually because of a life transition or life-changing event such as a birth, death, or trauma. For example, when many people leave their parents’ control for the first time and move away from home, they have a shift in values that occurs as they make this important and challenging life transition. In summary, audiences enter a speaking situation with various psychological dispositions, and considering what those may be can help speakers adapt their messages and better meet their speech goals.
General Purpose
Your speeches will usually fall into one of three categories. In some cases, we speak to inform, meaning we attempt to teach our audience using factual objective evidence. In other cases, we speak to persuade, as we try to influence an audience’s beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors. Last, we may speak to entertain or amuse our audience. In summary, the general purpose of your speech will be to inform, to persuade, or to entertain.
You can see various topics that may fit into the three general purposes for speaking in the table below “General Purposes and Speech Topics”. Some of the topics listed could fall into another general purpose category depending on how the speaker approached the topic, or they could contain elements of more than one general purpose. For example, you may have to inform your audience about your topic in one main point before you can persuade them, or you may include some entertaining elements in an informative or persuasive speech to help make the content more engaging for the audience. There should not be elements of persuasion included in an informative speech, however, since persuading is contrary to the objective approach that defines an informative general purpose. In any case, while there may be some overlap between general purposes, we place most speeches into one of the categories based on the overall content of the speech.
[table id=6 /]
Choosing a Topic
Once you have determined (or been assigned) your general purpose, you can begin the process of choosing a topic (James Madison University Communication Center, 2021). In class, an instructor may give you the option of choosing any topic for your informative or persuasive speech, but in most academic, professional, and personal settings, there will be some parameters set that will help guide your topic selection. It is likely that speeches will be organized around the content covered in the class. Speeches delivered at work will usually be directed toward a specific goal, such as welcoming new employees, informing employees about changes in workplace policies, or presenting quarterly sales figures. We are also usually compelled to speak about specific things in our personal lives, like addressing a problem at our child’s school by speaking out at a school board meeting. In short, it is not often that you will be starting from scratch when you begin to choose a topic.
Whether you have received parameters that narrow your topic range or not, the first step in choosing a topic is brainstorming (James Madison University Writing Center, 2021). Brainstorming involves generating many potential topic ideas in a fast-paced and nonjudgmental manner. Brainstorming can take place multiple times, as you narrow your topic. For example, you may begin by brainstorming a list of your personal interests that you can narrow down to a speech topic. It makes sense that you will enjoy speaking about something that you care about or find interesting. The research and writing will be more interesting, and the delivery will be easier since you will not have to fake enthusiasm for your topic. Speaking about something you are familiar with and interested in can also help you manage speaking anxiety.
While it is good to start with your personal interests, some speakers may be stuck here if they do not feel like they can make their interests relevant to the audience. In that case, you can look around for ideas. If your topic is something being discussed in newspapers, on television, in the lounge of your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it is likely to be of interest and be relevant, since it is current. Figure 8.3 shows how brainstorming works in stages. A list of topics that interest the speaker are on the top row. The speaker can brainstorm subtopics for each idea to see which one may work the best. In this case, the speaker could decide to focus his or her informative speech on three common ways people come to own dogs: through breeders, pet stores, or shelters.
Overall, you can follow these tips as you select and narrow your topic:
- Brainstorm topics that you are familiar with, interest you, and/or are currently topics of discussion.
- Choose a topic appropriate for the assignment/occasion.
- Choose a topic that you can make relevant to your audience.
- Choose a topic that you have the resources to research (access to information, people to interview, etc.).
Specific Purpose
Once you have brainstormed, narrowed, and chosen your topic, you can begin to draft your specific purpose statement (James Madison University Communication Center, 2021). Your specific purpose is a one-sentence statement that includes the objective you want to accomplish in your speech. You do not speak aloud your specific purpose during your speech; you use it to guide your researching, organizing, and writing. A good specific purpose statement is audience centered, agrees with the general purpose, addresses one main idea, and is realistic.
An audience-centered specific purpose statement usually contains an explicit reference to the audience—for example, “my audience” or “the audience.” Since a speaker may want to see if he or she effectively met his or her specific purpose, write the objective so that it could be measured or assessed. Moreover, since a speaker actually wants to achieve his or her speech goal, the specific purpose should also be realistic. You will not be able to teach the audience a foreign language or persuade an atheist to Christianity in a six- to nine-minute speech. The following is a good example of a good specific purpose statement for an informative speech: “By the end of my speech, the audience will be better informed about the effects the green movement has had on schools.” The statement is audience-centered and matches with the general purpose by stating, “The audience will be better informed.” The speaker could also test this specific purpose by asking the audience to write down, at the end of the speech, three effects the green movement has had on schools.
Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is a one-sentence summary of the central idea of your speech that you either explain or defend (James Madison University Communication Center, 2021). You would explain the thesis statement for an informative speech, since these speeches are based on factual, objective material. You would defend your thesis statement for a persuasive speech, because these speeches are argumentative and your thesis should clearly indicate a stance on a particular issue. In order to make sure your thesis is argumentative and your stance clear, it is helpful to start your thesis with the words “I believe.” When starting to work on a persuasive speech, it can also be beneficial to write out a counterargument to your thesis to ensure that it is arguable.
The thesis statement is different from the specific purpose in two main ways. First, the thesis statement is content centered, while the specific purpose statement is audience centered. Second, the thesis statement is incorporated into the spoken portion of your speech, while the specific purpose serves as a guide for your research and writing and an objective that you can measure (Goodwin, 2017). A good thesis statement is declarative, agrees with the general and specific purposes, and focuses and narrows your topic. Although you will likely end up revising and refining your thesis as you research and write, it is good to draft a thesis statement soon after drafting a specific purpose to help guide your progress. As with the specific purpose statement, your thesis helps ensure that your research, organizing, and writing are focused so you don’t end up wasting time with irrelevant materials. Keep your specific purpose and thesis statement handy (drafting them at the top of your working outline is a good idea) so you can reference them often. The following examples show how a general purpose, specific purpose, and thesis statement match up with a topic area:
Topic: My Craziest Adventure
General purpose: To Entertain
Specific purpose: By the end of my speech, the audience will appreciate the lasting memories that result from an eighteen-year-old visiting New Orleans for the first time.
Thesis statement: New Orleans offers young tourists many opportunities for fun and excitement.
Topic: Renewable Energy
General purpose: To Inform
Specific purpose: By the end of my speech, the audience will be able to explain the basics of using biomass as fuel.
Thesis statement: Biomass is a renewable resource that releases gases that can be used for fuel.
Topic: Privacy Rights
General purpose: To Persuade
Specific purpose : By the end of my speech, my audience will believe that parents should not be able to use tracking devices to monitor their teenage child’s activities.
Thesis statement: I believe that it is a violation of a child’s privacy to be electronically monitored by his or her parents.
8.2 Researching and Supporting Your Speech
We live in an age where access to information is more convenient than ever before. The days of photocopying journal articles in the stacks of the library or looking up newspaper articles on microfilm are over for most. Yet, even though we have all this information readily available, research skills are more important than ever. Our challenge now is not accessing information but discerning what information is credible and relevant. Even though it may sound inconvenient to have to go physically to the library, students who did research before the digital revolution did not have to worry as much about discerning. If you found a source in the library, you could be assured of its credibility because a librarian had subscribed to or purchased that content. When you use Internet resources like Google or Wikipedia, you have no guarantees about some of the content that comes up.
Finding Supporting Material
As was noted earlier, it is good to speak about something with which you are already familiar. So existing knowledge forms the first step of your research process. Depending on how familiar you are with a topic, you will need to do more or less background research before you actually start incorporating sources to support your speech. Background research is just a review of summaries available for your topic that helps refresh or create your knowledge about the subject. It is not the more focused and academic research that you will actually use to support and verbally cite in your speech.
Your first step for research in college should be library resources, not Google, Bing, or other general search engines. In most cases, you can still do your library research from the comfort of a computer, which makes it as accessible as Google but gives you much better results. Excellent and underutilized resources at college and university libraries are reference librarians. Reference librarians are not like the people who likely staffed your high school library. They are information-retrieval experts. At most colleges and universities, you can find a reference librarian who has at least a master’s degree in library and information sciences, and at some larger or specialized schools, reference librarians have doctoral degrees. Research can seem like a maze, and reference librarians can help you navigate the maze. There may be dead ends, but there is always another way around to reach the end goal.

Unfortunately, many students hit their first dead end and give up or assume that there is not enough research out there to support their speech. If you have thought of a topic to do your speech on, someone else has thought of it, too, and people have written and published about it. Reference librarians can help you find that information (Matook, 2020). Meet with a reference librarian face-to-face and take your assignment sheet and topic idea with you. In most cases, students report that they came away with more information than they needed, which is good because you can then narrow that down to the best information. If you cannot meet with a reference librarian face-to-face, many schools now offer the option to do a live chat with a reference librarian, and you can contact them by e-mail or phone.
Aside from the human resources available in the library, you can also use electronic resources such as library databases . Library databases help you access more credible and scholarly information than what you will find using general Internet searches. These databases are quite expensive, and you cannot access them as a regular citizen without paying for them. Luckily, some of your student fee dollars go to pay for subscriptions to these databases so that you can access them as a student. Through these databases, you can access newspapers, magazines, journals, and books from around the world. Of course, libraries also house stores of physical resources like DVDs, books, academic journals, newspapers, and popular magazines (James Madison University Libraries, 2021). You can usually browse your library’s physical collection through an online catalog search. A trip to the library to browse is especially useful for books. Since most university libraries use the Library of Congress classification system, books are organized by topic. That means if you find a good book using the online catalog and go to the library to get it, you should take a moment to look around that book, because the other books in that area will be topically related. On many occasions, I have used this tip and gone to the library for one book but left with several.
Although Google is not usually the best first stop for conducting college-level research, Google Scholar is a separate search engine that narrows results down to scholarly materials. This version of Google has improved much over the past few years and has served as a good resource for my research, even for this book. A strength of Google Scholar is that you can easily search for and find articles not confined to a particular library database. The pool of resources you are searching in is much larger than what you would find by using a library database. The challenge is that you have no way of knowing if the articles that come up are available to you in full-text format. As noted earlier, you will find most academic journal articles in databases that require users to pay subscription fees. Therefore, you are often only able to access the abstracts of articles or excerpts from books that come up in a Google Scholar search. You can use that information to check your library to see if the article is available in full-text format, but if it is not, you have to go back to the search results. When you access Google Scholar on a campus network that subscribes to academic databases, however, you can sometimes click through directly to full-text articles. Although this resource is still being improved, it may be a useful alternative or backup when other search strategies are leading to dead end.
Types of Sources
Periodicals.
Periodicals include magazines and journals that are published periodically. Many library databases can access periodicals from around the world and from years past. A common database is Academic Search Premiere (a similar version is Academic Search Complete). Many databases, like this one, allow you to narrow your search terms, which can be very helpful as you try to find good sources that are relevant to your topic. You may start by typing a key word into the first box and searching. Sometimes a general search like this can yield thousands of results, which you obviously would not have time to look through. In this case, you may limit your search to results that have your keyword in the abstract , which is the author-supplied summary of the source. If there are still too many results, you may limit your search to results that have your keyword in the title. At this point, you may have reduced those ten thousand results down to a handful, which is much more manageable.
Within your search results, you will need to distinguish between magazines and academic journals. In general, academic journals are considered more scholarly and credible than magazines because most of the content in them is peer reviewed. The peer-review process is the most rigorous form of review, which takes several months to years and ensures that the information that is published has been vetted and approved by numerous experts on the subject. Academic journals are often affiliated with professional organizations rather than for-profit corporations, and neither authors nor editors are paid for their contributions.

Newspapers and Books
Newspapers and books can be excellent sources but must still be evaluated for relevance and credibility. Newspapers are good for topics that are developing quickly, as they are updated daily. While there are well-known newspapers of record like the New York Times , smaller local papers can also be credible and relevant if your speech topic does not have national or international reach. You can access local, national, and international newspapers through electronic databases like LexisNexis.
To evaluate the credibility of a book, you will want to know some things about the author. You can usually find this information at the front or back of the book. If an author is a credentialed and recognized expert in his or her area, the book will be more credible. However, just because someone wrote a book on a subject does not mean he or she is the most credible source. The publisher of a book can also be an indicator of credibility. Books published by university/academic presses (University of Chicago Press, Duke University Press) are considered more credible than books published by trade presses (Penguin, Random House), because they are often peer reviewed and they are not primarily profit driven.
Reference Tools
The transition to college-level research means turning more toward primary sources and away from general reference materials. Primary sources are written by people with firsthand experiences or by researchers/scholars who conducted original research (National WW II Museum, n.d.). Unfortunately, many college students are reluctant to give up their reliance on reference tools like dictionaries and encyclopedias. While reference tools like dictionaries and encyclopedias are excellent for providing a speaker with a background on a topic, they should not be the foundation of your research unless they are academic and/or specialized.
Dictionaries are handy tools when we are not familiar with a particular word. However, citing a dictionary like Merriam-Webster ’s as a source in your speech is often unnecessary. A dictionary is useful when you need to challenge a Scrabble word, but it is not the best source for college-level research.
Many students have relied on encyclopedias for research in high school, but most encyclopedias, like World Book , Encarta , or Britannica , are not primary sources. Instead, they are examples of secondary sources that aggregate, or compile, research done by others in a condensed summary (James Madison University Libraries, 2019). Reference sources like encyclopedias are excellent resources to get you informed about the basics of a topic, but at the college level, primary sources are expected. Many encyclopedias are internet-based, which makes them convenient, but they are still not primary sources, and their credibility should be even more scrutinized.
Wikipedia revolutionized how many people retrieve information and pioneered an open-publishing format that allowed a community of people to post, edit, and debate content. While this is an important contribution to society, Wikipedia is not considered a scholarly or credible source. Like other encyclopedias, Wikipedia should not be used in college-level research, because it is not a primary source. In addition, since its content can be posted and edited by anyone, we cannot be sure of the credibility of the content. Even though there are self-appointed “experts” who monitor and edit some of the information on Wikipedia, we cannot verify their credentials or the review process that information goes through before it is posted.
When conducting an interview for a speech, you should access a person who has expertise in or direct experience with your speech topic. If you follow the suggestions for choosing a topic that mentioned earlier, you may already know something about your speech topic and may have connections to people who would be good interview subjects. Previous employers, internship supervisors, teachers, community leaders, or even relatives may be appropriate interviewees, given your topic. If you do not have a connection to someone you can interview, you can often find someone via the Internet who would be willing to answer some questions. Many informative and persuasive speech topics relate to current issues, and most current issues have organizations that represent their needs.
Open-ended questions cannot be answered with a “yes” or “no” but they can provide descriptions and details that will add to your speech. Quotes and paraphrases from your interview can add a personal side to a topic or at least convey potentially complicated information in a more conversational and interpersonal way. Closed questions can be answered with one or two words and can provide a starting point to get to information that is more detailed. However, the interviewer must have prepared follow-up questions. Unless the guidelines or occasion for your speech suggest otherwise, you should balance your interview data with the other sources in your speech. Do not let your references to the interview take over your speech.
We already know that utilizing library resources can help you automatically filter out content that may not be scholarly or credible, since the content in research databases is selected and restricted. However, some information may be better retrieved from websites. Even though research databases and websites are electronic sources, two key differences between them may affect their credibility (Brigham Young University Library, 2021).
First, most of the content in research databases is or was printed but was converted to digital formats for easier and broader access. In contrast, most of the content on websites has not been printed. Second, most of the content on research databases has gone through editorial review, which means a professional editor or a peer editor has reviewed the material to make sure it is credible and worthy of publication. Most content on websites is not subjected to the same review process, as just about anyone with internet access can self-publish information on a personal website, blog, wiki, or social media page. Therefore, what sort of information may be better retrieved from websites, and how can we evaluate the credibility of a website?
A key way to evaluate the credibility of a website is to determine the site’s accountability (Brigham Young University Library, 2021). Accountability means determining who is ultimately responsible for the content put out and whose interests the content meets. The more information that is included on a website, the better able you will be to determine its accountability. Ideally all or most of the following information would be included: organization/agency name, author’s name and contact information, date the information was posted or published, name and contact information for person in charge of web content (i.e., web editor or webmaster), and a link to information about the organization/agency/ business mission. While not all this information has to be present to warrant the use of the material, the less accountability information is available, the more you should scrutinize the information.
You can also begin to judge the credibility of a website by its domain name. Some common domain names are .com , .net , .org , .edu , .mil , and .gov . For each type of domain, there are questions you may ask that will help you evaluate the site’s credibility. You can see a summary of these questions in table 8.2.
[table id=7 /]
Types of Supporting Material
There are several types of supporting material you can add to your speech. They include examples, explanations, statistics, analogies, testimony, and visual aids. You will want to have a balance of information, and you will want to include the material that is most relevant to your audience and is most likely to engage them.
An example is a cited case that is representative of a larger whole. Examples are especially beneficial when presenting information that may be unfamiliar to an audience. They are also useful for repackaging or reviewing information that has been presented previously. Examples are used in many different ways, so you should let your audience, purpose and thesis, and research materials guide your use. You may pull examples directly from your research materials, making sure to cite the source. The following is an example used in a speech about the negative effects of standardized testing: “Standardized testing makes many students anxious, and even ill. On March 14, 2002, the Sacramento Bee reported that some standardized tests now come with instructions indicating what teachers should do with a test booklet if a student throws up on it.” You may also cite examples from your personal experience, if appropriate: “I remember being sick to my stomach while waiting for my SAT to begin.”
You may also use hypothetical examples, which can be useful when you need to provide an example that is extraordinary or goes beyond most people’s direct experience (Beare, 2020). Capitalize on this opportunity by incorporating vivid description into the example that appeals to the audience’s senses. Always make sure to indicate when you are using a hypothetical example, as it would be unethical to present an example as real when it is not. Including the word imagine or something similar in the first sentence of the example can easily do this.
Explanations
Explanations clarify ideas by providing information about what something is, why something is the way it is, or how something works or came to be. One of the most common types of explanation is a definition. Definitions do not have to come from the dictionary. Many times, authors will define concepts as they use them in their writing, which is a good alternative to a dictionary definition. As you do your research, think about how much your audience likely knows about a given subject. You do not need to provide definitions when information is common knowledge. Anticipate audience confusion and define legal, medical, or other forms of jargon as well as slang and foreign words.
Statistics are numerical representations of information (Barnard, 2017). They are very credible in our society, as evidenced by their frequent use by news agencies, government offices, politicians, and academics. As a speaker, you can capitalize on the power of statistics if you use them appropriately. Unfortunately, speakers often intentionally or unintentionally misuse statistics and misconstrue the numbers to support their argument. They do so without examining the context from which the statistic emerged. All statistics are contextual, so plucking a number out of a news article or a research study and including it in your speech without taking the time to understand the statistic is unethical.
Although statistics are popular as supporting evidence, they can also be boring. There will inevitably be people in your audience who are not good at processing numbers. Even people who are good with numbers have difficulty processing through a series of statistics presented orally. Remember that we have to adapt our information to listeners who do not have the luxury of pressing a pause or rewind button. For these reasons, it is a good idea to avoid using too many statistics and to use startling examples when you do use them (Barnard, 2017). Startling statistics should defy our expectations. When you give the audience a large number that they would expect to be smaller, or vice versa, you will be more likely to engage them, as the following example shows: “Did you know that 1.3 billion people in the world do not have access to electricity? That’s about 20 percent of the world’s population according to a 2009 study on the International Energy Agency’s official website.”
Analogies involve a comparison of ideas, items, or circumstances (Segar, 2016). When you compare two things that actually exist, you are using a literal analogy—for example, “Germany and Sweden are both European countries that have had nationalized health care for decades.” Another type of literal comparison is a historical analogy. In Mary Fisher’s now famous 1992 speech to the Republican National Convention, she compared the silence of many U.S. political leaders regarding the HIV/AIDS crisis to that of many European leaders in the years before the Holocaust.
A figurative analogy compares things not normally related, often relying on metaphor, simile, or other figurative language devices. In the following example, wind and revolution are compared: “Just as the wind brings changes in the weather, so does revolution bring change to countries.”
When you compare differences, you are highlighting contrast—for example, “Although the United States is often thought of as the most medically advanced country in the world, other Western countries with nationalized health care have lower infant mortality rates and higher life expectancies.” To use analogies effectively and ethically, you must choose ideas, items, or circumstances to compare that are similar enough to warrant the analogy.
Testimonies
Testimonies are quoted information from people with direct knowledge about a subject or situation. Expert testimony is from people who are credentialed or recognized experts in a given subject (Davis, 2020). Lay testimony is often a recounting of a person’s experiences, which is more subjective. Both types of testimony are valuable as supporting material. We can see this in the testimonies of people in courtrooms and other types of hearings. Lawyers know that juries want to hear testimony from experts, eyewitnesses, and friends and family. Congressional hearings are similar.
When using testimony, make sure you indicate whether it is expert or lay by sharing with the audience the context of the quote. Share the credentials of experts (education background, job title, years of experience, etc.) to add to your credibility or give some personal context for the lay testimony (eyewitness, personal knowledge, etc.).
Visual Aids
Visual aids help a speaker reinforce speech content visually, which helps amplify the speaker’s message (Beqiri, 2018). They can be used to present any of the types of supporting materials discussed previously. Speakers rely heavily on an audience’s ability to learn by listening, which may not always be successful if audience members are visual or experiential learners. Even if audience members are good listeners, information overload or external or internal noise can be barriers to a speaker achieving his or her speech goals. Therefore, skillfully incorporating visual aids into a speech has many potential benefits.
Three-dimensional objects that represent an idea can be useful as a visual aid for a speech (Beqiri, 2018). They offer the audience a direct, concrete way to understand what you are saying. I often have my students do an introductory speech where they bring in three objects that represent their past, present, and future. Students have brought in a drawer from a chest that they were small enough to sleep in as a baby, a package of Ramen noodles to represent their life as a college student, and a stethoscope or other object to represent their career goals, among other things. Models also fall into this category, as they are scaled versions of objects that may be too big (the International Space Station) or too small (a molecule) to actually show to your audience.
Chalkboards, Whiteboards, and Flip Charts

Chalkboards, whiteboards, and flip charts can be useful for interactive speeches (Beqiri, 2018). If you are polling the audience or brainstorming, you can write down audience responses easily for everyone to see and for later reference. They can also be helpful for unexpected clarification. You can also have audience members write things on boards or flip charts themselves, which helps get them engaged and takes some of the pressure off you as a speaker.
Posters and Handouts
Posters generally include text and graphics and often summarize an entire presentation or select main points (Beqiri, 2018). We frequently use posters to present original research, as they can be broken down into the various steps to show how a process worked. Posters can be useful if you are going to have audience members circulating around the room before or after your presentation, so they can take the time to review the poster and ask questions. Posters are not often good visual aids during a speech, because it is difficult to make the text and graphics large enough for a room full of people to see adequately. The best posters are those created using computer software and professionally printed on large laminated paper.
These professional posters come at a price. If you opt to make your own poster, take care to make it look professional. Use a computer and printer to print out your text; do not handwrite on a poster. Make sure anything you cut by hand has neat, uniform edges. You can then affix the text, photos, and any accent backing to the poster board. Double-sided tape works well for this, as it does not leave humps like those left by rolled tape or the bubbles, smearing, or sticky mess left by glue.
Handouts can be a useful alternative to posters. Think of them as mini-posters that audience members can reference and take with them. Audience members will likely appreciate a neatly laid out, one-page handout that includes the speaker’s contact information. It can be appropriate to give handouts to an audience before a long presentation where note taking is expected, complicated information is presented, or the audience will be tested on or have to respond to the information presented. In most regular speeches less than fifteen minutes long, it would not be wise to distribute handouts ahead of time, as they will distract the audience from the speaker. It is better to distribute the handouts after your speech or at the end of the program, if others speaking after you.
Photographs, paintings, drawings, and sketches fall into the pictures category of visual aids. Pictures can be useful when you need to show an exact replication about which you are speaking. Pictures can also connect to your audience on a personal level, especially if they evoke audience emotions (Beqiri, 2018). Think about the use of pictures in television commercials asking for donations or sponsorships. Organizations like Save the Children and the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals successfully use pictures of malnourished children or abused animals to pull at the heartstrings of viewers. A series of well-chosen and themed pictures can have a meaningful impact on an audience.
Diagrams and Drawings
Diagrams are good for showing the inner workings of an object or pointing out the most important or relevant parts of something (Neal, 2016). Think about diagrams as blueprints that show the inside of something—for example, key bones in the human body in a speech about common skateboarding injuries. Diagrams are good alternatives to pictures when you only need to point out certain things that may be difficult to see in a photograph.
Charts and Tables
Charts and tables are useful for compiling and cross-referencing larger amounts of information (Presentation Magazine, 2011). The combination of rows and columns allows you to create headers and then divide them up into units, categories, dates, and so on. Medical information is put into charts so that periods of recorded information, such as vital signs, can be updated and scanned by doctors and nurses. Charts and tables are also good for combining text and numbers, and they are easy to make with word processing software like Microsoft Word or spreadsheet software like Excel.
Think of presenting your department’s budget and spending at the end of a business quarter. You could have headers in the columns with the various categories and itemized deductions in the rows ending with a final total for each column.
A pie chart is an alternative representation of textual and numerical data that offers audience members a visual representation of the relative proportions of a whole. In a pie chart, each piece of the pie corresponds to a percentage of the whole, and the size of the pie varies with the size of the percentage. As with other charts and tables, most office software programs can now make pie charts.
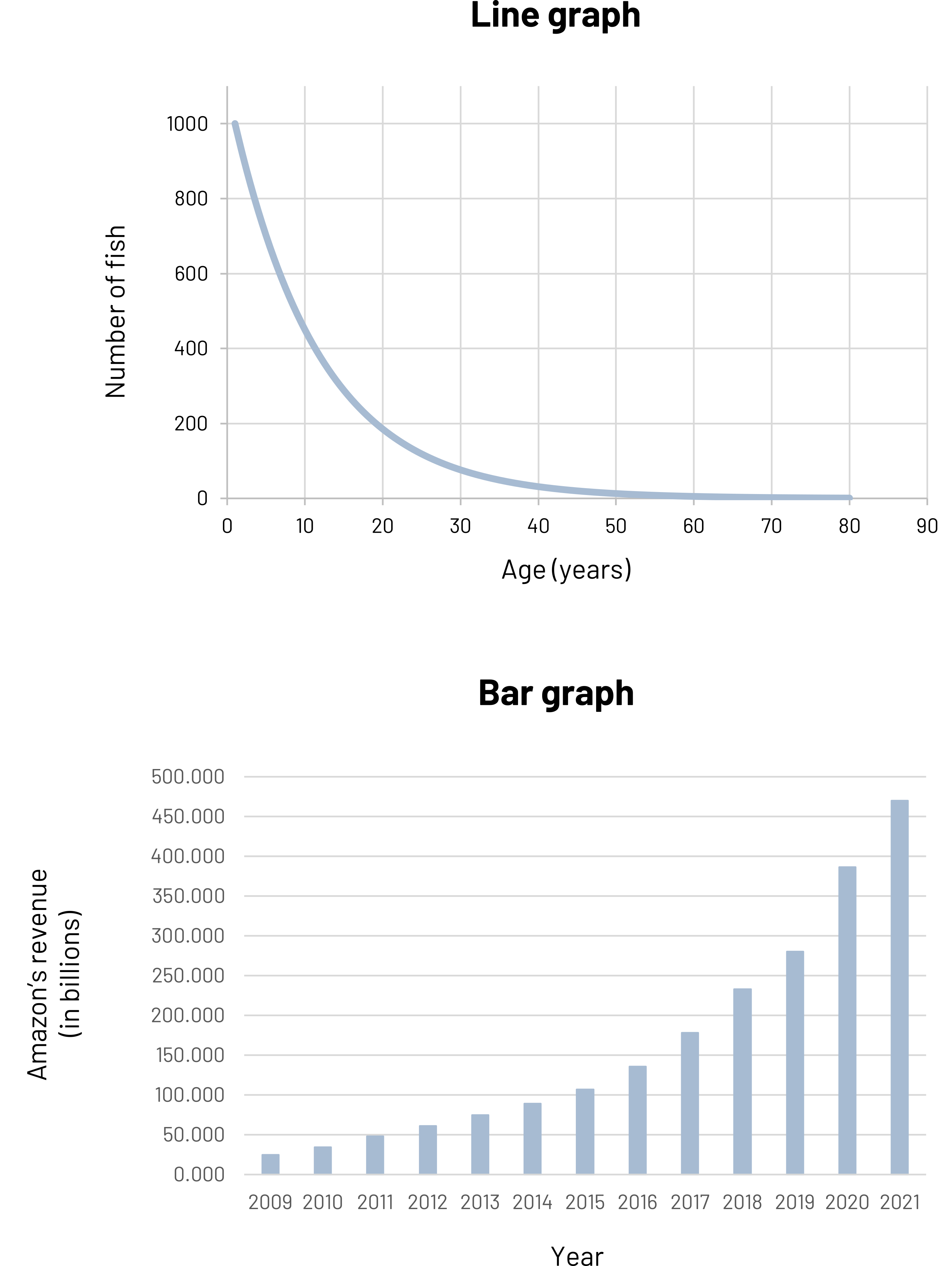
Graphs are representations that point out numerical relationships or trends and include line graphs and bar graphs (Presentation Magazine, 2011). Line graphs are useful for showing trends over time. For example, you could track the rising cost of tuition for colleges and universities in a persuasive speech about the need for more merit-based financial aid.
Bar graphs are good for comparing amounts. In the same speech, you could compare the tuition of two-year institutions to that of four-year institutions. Graphs help make numerical data more digestible for your audience and allow you to convey an important numerical trend visually and quickly without having to go into lengthy explanations. Remember to label clearly your x -axis and y -axis and to explain the basics of your graph to your audience before you go into the specific data. If you use a graph created by someone else, make sure it is large and clear enough for the audience to read and that you cite the original source.
Video clips as visual aids can be powerful and engaging for an audience, but they can also be troublesome for speakers (Gallo, 2017). Whether embedded in a PowerPoint presentation, accessed through YouTube, or played from a laptop or DVD player, video clips are notorious for tripping up speakers. They require more than one piece of electronics when they are hooked to a projector and speaker. They may also require an Internet connection. The more electronic connection points, the more chances for something to go wrong. Therefore it is very important to test your technology before your speech, have a backup method of delivery if possible, and be prepared to go on without the video if all else fails.
Although sometimes tempting, you should not let the video take over your speech (Gallo, 2017). Make sure your video is relevant and cued to where it needs to be. One useful strategy for incorporating video is to play a video without audio and speak along with the video, acting as a narrator. This allows the speaker to have more control over the visual aid and to adapt it and make it more relevant to a specific topic and audience. Additionally, video editing software like iMovie is readily available to college students and relatively easy to use. Some simple editing to cut together various clips that are meaningful or adding an introductory title or transitions can go a long way toward making your video look professional.
Presentation Software
The prevalence of computers and projectors in most schools, offices, and other presentation facilities has made using computer-generated visual aids more convenient. PowerPoint is the most commonly used presentation software and has functionality ranging from the simplest text-based slide to complicated transitions, timing features, video/sound imbedding, and even functionality with audience response systems like Turning Point that allow data to be collected live from audience members and incorporated quickly into the slideshow. Despite the fact that most college students have viewed and created numerous PowerPoint presentations, we have all seen many poorly executed slideshows that detracted from the speaker’s message. PowerPoint should be viewed as a speech amplifier. Like an amplifier for a guitar, it does not do much without a musician there to play the instrument. The speaker is the musician, the speech is the instrument, and PowerPoint is the amplifier. Just as the amplifier does not dictate what the guitar player does, neither should PowerPoint take over the speaker (Rielly, 2020).
Presentations are generally longer than speeches, at least fifteen minutes long, and are content heavy. College lectures and many professional conference presentations fall into this category. In these cases, PowerPoint generally runs along with the speaker throughout the presentation, reviewing key points and presenting visual aids such as pictures and graphs. The constant running of the slideshow also facilitates audience note taking, which is also common during presentations.
Speeches, on the other hand, are usually fifteen minutes or less, have repetition and redundancy built in (as they are adapted to a listening audience), and carry less expectation that the audience will take detailed notes. In this case, PowerPoint should be used more as a visual aid, meaning that it should be simpler and amplify particular components of the speech rather than run along with the speaker throughout the speech (Rielly, 2020).
8.3 Organizing
When organizing your speech, you want to start with the body. Even though most students want to start with the introduction, it is difficult to introduce and preview something that you have not yet developed. A well-structured speech includes an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Think of this structure as a human body. This type of comparison dates back to Plato, who noted, “every speech ought to be put together like a living creature” (Winans, 1917). The introduction is the head, the body is the torso and legs, and the conclusion is the feet. The information you add to this structure from your research and personal experience is the organs and muscle. The transitions you add are the connecting tissues that hold the parts together, and a well-practiced delivery is the skin and clothing that makes everything presentable.
Organizing the Body of Your Speech
Writing the body of your speech takes the most time in the speech-writing process. Your specific purpose and thesis statement should guide the initial development of the body, which will then be more informed by your research process (LibreTexts, 2021). You will determine main points that help achieve your purpose and match your thesis. You will then fill information into your main points by incorporating the various types of supporting material discussed previously. Before you move on to your introduction and conclusion, you will connect the main points together with transitions and other signposts.
Determining Your Main Points
Think of each main point as a miniature speech within your larger speech. Each main point will have a central idea, meet some part of your specific purpose, and include supporting material from your research that relates to your thesis. Reviewing the draft of your thesis and specific purpose statements can lead you to research materials.
As you review your research, take notes on and/or highlight key ideas that stick out to you as useful, effective, relevant, and interesting. It is likely that these key ideas will become the central ideas of your main points, or at least sub-points. Once you have researched your speech enough to achieve your specific purpose, support your thesis, and meet the research guidelines set forth by your instructor, boss, or project guidelines, you can distill the research down to a series of central ideas. As you draft these central ideas, use parallel wording , which is similar wording among key organizing signposts and main points that helps structure a speech. Using parallel wording in your central idea statement for each main point will also help you write parallel key signposts like the preview statement in the introduction, transitions between main points, and the review statement in the conclusion.
While writing each central idea using parallel wording is useful for organizing information at this stage in the speech-making process, you should feel free to vary the wording a little more in your actual speech delivery. You will still want some parallel key words woven throughout the speech, but sticking too close to parallel wording can make your content sound forced or artificial.
After distilling your research materials down, you may have several central idea statements. You will likely have two to five main points (depending on what your instructor prefers), time constraints, or the organizational pattern you choose. Not all of the central idea may be converted into main points; some may end up becoming sub-points and some may be discarded. Once you get your series of central ideas drafted, you will then want to consider how you might organize them, which will help you narrow your list down to what may actually end up becoming the body of your speech.
Organizing Your Main Points
There are several ways you can organize your main points. Some patterns correspond well to a particular subject area or speech type. Determining which pattern you will use helps filter through your list of central ideas generated from your research and allows you to move on to the next step of inserting supporting material into your speech. Here are some common organizational patterns.
Topical Pattern
When you use the topical pattern , you are breaking a large idea or category into smaller ideas or subcategories (Davis, 2021). In short, you are finding logical divisions to a whole. While you may break something down into smaller topics that will make two, three, or more main points, people tend to like groups of three. In a speech about the Woodstock Music and Art Fair, for example, you could break the main points down to (1) the musicians who performed, (2) the musicians who declined to perform, and (3) the audience. You could also break it down into three specific performances—(1) Santana, (2) The Grateful Dead, and (3) Creedence Clearwater Revival—or three genres of music—(1) folk, (2) funk, and (3) rock.
The topical pattern breaks a topic down into logical divisions but does not necessarily offer any guidance in ordering them. To help determine the order of topical main points, you may consider the primacy or recency effect (Morrison, Conway, & Chein, 2014). You prime an engine before you attempt to start it and prime a surface before you paint it. The primacy effect is similar in that you present your best information first in order to make a positive impression and engage your audience early in your speech. The recency effect is based on the idea that an audience will best remember the information they heard most recently. Therefore, you would include your best information last in your speech to leave a strong final impression. Both primacy and recency can be effective. Consider your topic and your audience to help determine which would work best for your speech.
Chronological Pattern

A chronological pattern helps structure your speech based on time or sequence. If you order a speech based on time, you may trace the development of an idea, product, or event (LibreTexts, 2020). A speech on Woodstock could cover the following: (1) preparing for the event, (2) what happened during the event, and (3) the aftermath of the event. Ordering a speech based on sequence is also chronological and can be useful when providing directions on how to do something or how a process works. This could work well for a speech on baking bread at home, refinishing furniture, or harvesting corn. The chronological pattern is often a good choice for speeches related to history or demonstration speeches.
Spatial Pattern
The spatial pattern arranges main points based on their layout or proximity to each other. A speech on Woodstock could focus on the layout of the venue, including (1) the camping area, (2) the stage area, and (3) the musician/crew area. A speech could also focus on the components of a typical theater stage or the layout of the new 9/11 memorial at the World Trade Center site.
Problem–Solution Pattern
The problem-solution pattern entails presenting a problem and offering a solution (LibreTexts, 2020). This pattern can be useful for persuasive speaking—specifically, persuasive speeches focused on a current societal issue. This can also be coupled with a call to action, asking an audience to take specific steps to implement a solution you offered. This organizational pattern can be applied to a wide range of topics and can be organized easily into two or three main points. You can offer evidence to support your claim that a problem exists in one main point and then offer a specific solution in the second main point. To be more comprehensive, you could set up the problem, review multiple solutions that have been proposed, and then add a third main point that argues for a specific solution out of the ones reviewed in the second main point. Using this pattern, you could offer solutions to the problem of rising textbook costs or offer your audience guidance on how to solve conflicts with roommates or coworkers.
Cause–Effect Pattern
The cause-effect pattern sets up a relationship between ideas that shows a progression from origin to result (LibreTexts, 2020). You could also start with the current situation and trace back to the root causes. You can use this pattern for informative or persuasive speeches. When used for informing, the speaker is explaining an established relationship and citing evidence to support the claim—for example, accessing unsecured, untrusted websites or e-mails leads to computer viruses. When used for persuading, the speaker is arguing for a link that is not as well established and/or is controversial—for example, violent video games lead to violent thoughts and actions. In a persuasive speech, a cause-effect argument is often paired with a proposed solution or call to action, such as advocating for stricter age restrictions on who can play violent video games. When organizing an informative speech using the cause-effect pattern, be careful not to advocate for a particular course of action.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is a five-step organization pattern that attempts to persuade an audience by making a topic relevant, using positive and/or negative motivation, and including a call to action. The five steps are (1) attention, (2) need, (3) satisfaction, (4) visualization, and (5) action (Monroe & Ehninger, 1964).
You accomplish the attention step in the introduction to your speech. Whether your entire speech is organized using this pattern or not, any good speaker begins by getting the attention of the audience. We will discuss several strategies in Section 9 “Getting Your Audience’s Attention” for getting an audience’s attention. The next two steps set up a problem and solution.
After getting the audience’s attention you will want to establish the need step and that there is a need for your topic to be addressed. You will want to cite credible research that points out the seriousness or prevalence of an issue. In the attention and need steps, it is helpful to use supporting material that is relevant and proxemic to the audience.
Once you have set up the need for the problem to be addressed, you move on to the satisfaction step , where you present a solution to the problem. You may propose your own solution if it is informed by your research and reasonable. You may also propose a solution that you found in your research.
The visualization step is next and incorporates positive and/or negative motivation as a way to support the relationship you have set up between the need and your proposal to satisfy the need. You may ask your audience to visualize a world where things are better because they took your advice and addressed this problem. This capitalizes on positive motivation. You may also ask your audience to visualize a world where things are worse because they did not address the issue, which is a use of negative motivation. Now that you have hopefully persuaded your audience to believe the problem is worthy of addressing, proposed a solution, and asked them to visualize potential positive or negative consequences, you move to the action step.
The action step includes a call to action where you are saying, “Now that you see the seriousness of this problem, here’s what you can do about it.” The call to action should include concrete and specific steps an audience can take. Your goal should be to facilitate the call to action, making it easy for the audience to complete. Instead of asking them to contact their elected officials, you could start an online petition and make the link available to everyone. You could also bring the contact information for officials that represent that region so the audience does not have to look them up on their own. Although this organizing pattern is more complicated than the others are, it offers a proven structure that can help you organize your supporting materials and achieve your speech goals.
Incorporating Supporting Material
So far, you have learned several key steps in the speech creation process. Now you will begin to incorporate more specific information from your supporting materials into the body of your speech. You can place the central ideas that fit your organizational pattern at the beginning of each main point and then plug supporting material in as sub-points.
This information will also make up the content of your formal and speaking outlines. Remember that you want to include a variety of supporting material (examples, analogies, statistics, explanations, etc.) within your speech. The information that you include as sub-points helps back up the central idea that started the main point. Depending on the length of your speech and the depth of your research, you may also have sub-sub-points that back up the claim you are making in the sub-point. Each piece of supporting material you include eventually links back to the specific purpose and thesis statement. This approach to supporting your speech is systematic and organized and helps ensure that your content fits together logically and that your main points are clearly supported and balanced.
One of the key elements of academic and professional public speaking is verbally citing your supporting materials so your audience can evaluate your credibility and the credibility of your sources (James Madison University Communication Center, 2010). You should include citation information in three places: verbally in your speech, on any paper or electronic information (outline, PowerPoint), and on a separate reference sheet. Since much of the supporting material you incorporate into your speech comes directly from your research, it is important that you include relevant citation information as you plug this information into your main points. Do not wait to include citation information once you have drafted the body of your speech. At that point, it may be difficult to retrace your steps to locate the source of a specific sentence or statistic. As you paraphrase or quote your supporting material, work the citation information into the sentences; do not clump the information together at the end of a sentence, or try to cite more than one source at the end of a paragraph or main point. It is important that the audience hear the citations as you use the respective information so it is clear which supporting material matches up with which source.
Writing key bibliographic information into your speech will help ensure that you remember to verbally cite your sources and that your citations will be more natural and flowing and less likely to result in fluency hiccups. At minimum, you should include the author, date, and source in a verbal citation (James Madison University Communication Center, 2010). Sometimes more information is necessary. When citing a magazine, newspaper, or journal article, it is more important to include the source name than the title of the article, since the source name—for example, Newsweek —is what the audience needs to evaluate the speaker’s credibility. For a book, make sure to cite the title and indicate that the source is a book. When verbally citing information retrieved from a website, you do not want to try to recite a long and cumbersome URL in your speech. Most people do not even make it past the “www.” before they mess up. It is more relevant to audiences for speakers to report the sponsor/author of the site and the title of the web page, or section of the website, where they obtained their information.
When getting information from a website, it is best to use “official” organization websites or government websites. When you get information from an official site, make sure you state that in your citation to add to your credibility. For an interview, state when it took place, the name of the interviewee, their credentials. Advice for verbally citing sources and examples from specific types of sources follow:
Signposts on highways help drivers and passengers navigate places they are not familiar with and give us reminders and warnings about what to expect down the road (Amadeba, 2021). Signposts in speeches are statements that help audience members navigate the turns of your speech. There are several key signposts in your speech. In the order you will likely use them, they are preview statement, transition between introduction and body, transitions between main points, transition from body to conclusion, and review statement (see the table below for a review of the key signposts with examples). While the preview and review statements are in the introduction and conclusion, respectively, the other signposts are all transitions that help move between sections of your speech.
[table id=8 /]
There are also signposts that can be useful within sections of your speech. Words and phrases like Aside from and While are good ways to transition between thoughts within a main point or sub-point. Organizing signposts like First , Second , and Third can be used within a main point to help speaker and audience move through information (Amadeba, 2021). The preview in the introduction and review in the conclusion need not be the only such signposts in your speech. You can also include internal previews and internal reviews in your main points to help make the content more digestible or memorable.
In addition to well-written signposts, you want to have well-delivered signposts. Nonverbal signposts include pauses and changes in rate, pitch, or volume that help emphasize transitions within a speech. Here are some ways you can use nonverbal signposting: pause before and after your preview and review statements so they stand out, pause before and after your transitions between main points so they stand out, and slow your rate and lower your pitch on the closing line of your speech to provide closure.
We all know that first impressions matter. Research shows that students’ impressions of instructors on the first day of class persist throughout the semester (Laws, Apperson, Buchert, & Bregman, 2010). First impressions are quickly formed, sometimes spontaneous, and involve little to no cognitive effort. Despite the fact that first impressions are not formed with much conscious effort, they form the basis of inferences and judgments about a person’s personality (Lass-Hennemann, Kuehl, Schulz, Oitzl, & Schachinger, 2011). For example, the student who approaches the front of the class before their speech wearing sweatpants and a t-shirt, looks around blankly, and lets out a sigh before starting has not made a very good first impression. Even if the student is prepared for the speech and delivers it well, the audience has likely already associated what they observed with personality traits of the student (i.e., lazy, indifferent), and those associations now have staying power in the face of contrary evidence that comes later.
Your introduction is only a fraction of your speech, but in that first minute or so, your audience decides whether they are interested in listening to the rest of the speech. You should accomplish four objectives in your introduction. They include getting your audience’s attention, introducing your topic, establishing credibility and relevance, and previewing your main points.
Getting Your Audience’s Attention
Several strategies can get the attention of your audience. Although each can be effective on its own, combining these strategies is also an option. A speaker can get their audience’s attention negatively, so think carefully about your choice. The student who began his speech on Habitat for Humanity by banging on the table with a hammer definitely got his audience’s attention during his 8:00 a.m. class, but he also lost credibility in that moment because many in the audience probably saw him as a joker rather than a serious speaker. The student who started her persuasive speech against animal testing with a little tap dance number ended up stumbling through the first half of her speech when she was thrown off by the confused looks the audience gave her when she finished her “attention getter.” These cautionary tales point out the importance of choosing an attention getter that is appropriate, meaning that it’s unusual enough to get people interested—but not over the top—and relevant to your speech topic.

In one of my favorite episodes of the television show The Office , titled “Dwight’s Speech,” the boss, Michael Scott, takes the stage at a regional sales meeting for a very nervous Dwight, who has been called up to accept an award. In typical Michael Scott style, he attempts to win the crowd over with humor and fails miserably.
In general, when a speech is supposed to be professional or formal, as many in-class speeches are, humor is more likely to be seen as incongruous with the occasion. However, there are other situations where a humorous opening might fit perfectly (Ginger Leadership Communications, 2019). For example, a farewell speech to a longtime colleague could start with an inside joke. When considering humor, it is good to get feedback on your idea from a trusted source.
Cite a Startling Fact or Statistic
As you research your topic, take note of any information that defies your expectations or surprises you. If you have a strong reaction to something you learn, your audience may, too. When using a startling fact or statistic as an attention getter, it is important to get the most bang for your buck. You can do this by sharing more than one fact or statistic that builds up the audience’s interest (Ginger Leadership Communications, 2019).
When using numbers, it is also good to repeat and/or repackage the statistics so they stick in the audience’s mind, which you can see in the following example: “In 1994, sixteen states reported that 15–19 percent of their population was considered obese. Every other state reported obesity rates less than that. In 2010, no states reported obesity rates in that same category of 15–19 percent, because every single state had at least a 20 percent obesity rate. In just six years, we went rom no states with an obesity rate higher than 19 percent, to fifty. Currently, the national obesity rate for adults is nearly 34 percent. This dramatic rise in obesity is charted on the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s website, and these rates are expected to continue to rise.”
The speaker could have just started by stating that nearly 34 percent of the US adult population was obese in 2011. However, statistics are not meaningful without context. So sharing how that number rose dramatically over six years helps the audience members see the trend and understand what the current number means. The fourth sentence repackages and summarizes the statistics mentioned in the first three sentences, which again sets up an interesting and informative contrast. Last, the speaker provides a verbal citation for the source of the statistic.
Use a Quotation
Some quotations are attention getting and some are boring. Some quotations are relevant and moving and some are abstract and stale. If you choose to open your speech with a quotation, choose one that is attention getting, relevant, and moving.
Just because a quote seems relevant to you does not mean the audience will also notice that relevance, so it is best to make that explicit right after you use and cite the quote. Also, evaluate the credibility of the source on which you found the quote. Many websites that make quotations available care more about selling pop-up ads than the accuracy of their information. Students who do not double-check the accuracy of the quote may end up attributing the quote to the wrong person or citing a made-up quote.
Ask a Question
Starting a speech with a question is a common attention getter, but in reality many of the questions that I have heard start a speech are not very attention getting. It is important to note that just because you use one of these strategies that does not make it automatically appealing to an audience. A question can be mundane and boring just like a statistic, quotation, or story can (Ginger Leadership Communications, 2019).
A rhetorical question is different from a direct question. When a speaker asks a direct question, they actually want a response from their audience. A rhetorical question will elicit a mental response from the audience, not a verbal or nonverbal one. In short, a rhetorical question makes an audience think. Asking a direct question of your audience is warranted only if the speaker plans to do something with the information they get from the audience.
A safer bet is to ask a rhetorical question that elicits only a mental response. A good rhetorical question can get the audience primed to think about the content of the speech. When asked as a series of questions (and combined with startling statistics or facts), this strategy can create suspense and hook an audience.
Tell a Story
When you tell a story, whether in the introduction to your speech or not, you should aim to paint word pictures in the minds of your audience members (Ginger Leadership Communications, 2019). You might tell a story from your own life or recount a story you found in your research. You may also use a hypothetical story, which has the advantage of allowing you to use your creativity and help place your audience in unusual situations that neither you nor they have actually experienced. When using a hypothetical story, you should let your audience know it is not real, and you should present a story to which the audience can relate. Speakers often let the audience know a story is not real by starting with the word imagine .
Introducing the Topic
Introducing the topic of your speech is the most obvious objective of an introduction, but speakers sometimes forget to do this or do not do it clearly. As the author of your speech, you may think that what you are talking about is obvious. Sometimes a speech topic does not become obvious until the middle of a speech. By that time, however, it is easy to lose an audience that was not clearly told the topic of the speech in the introduction. Introducing the topic is done before the preview of main points and serves as an introduction to the overall topic. The following are two ways a speaker could introduce the topic of childhood obesity: “Childhood obesity is a serious problem facing our country,” or “Today I’ll persuade you that childhood obesity is a problem that can no longer be ignored.”
Establishing Credibility and Relevance
The way you write and deliver your introduction makes an important first impression on your audience. However, you can also take a moment in your introduction to set up your credibility in relation to your speech topic. If you have training, expertise, or credentials (e.g., a degree, certificate, etc.) relevant to your topic, you can share that with your audience. It may also be appropriate to mention firsthand experience, previous classes you have taken, or even a personal interest related to your topic. For example, a student delivers a speech persuading the audience that the penalties for texting and driving should be stricter. In his introduction, he mentioned that his brother’s girlfriend was killed when a car driven by someone who was texting hit her. His personal story shared in the introduction added credibility to the overall speech.
Previewing Your Main Points
The preview of main points is usually the last sentence of your introduction and serves as a map of what is to come in the speech (Davis, 2021). The preview narrows your introduction of the topic down to the main ideas you will focus on in the speech. Your preview should be one sentence, should include wording that is parallel to the key wording of your main points in the body of your speech, and should preview your main points in the same order you discuss them in your speech. Make sure your wording is concise so your audience does not think there will be four points when there are only three. The following example previews the main points for a speech on childhood obesity: “Today I’ll convey the seriousness of the obesity epidemic among children by reviewing some of the causes of obesity, common health problems associated with it, and steps we can take to help ensure our children maintain a healthy weight.”
How you conclude a speech leaves an impression on your audience (Barnard, 2017). There are three important objectives to accomplish in your conclusion. They include summarizing the importance of your topic, reviewing your main points, and closing your speech.
Summarizing the Importance of Your Topic
After you transition from the body of your speech to the conclusion, you will summarize the importance of your topic (Abhishek, 2020). This is the “take-away” message, or another place where you can answer the “so what?” question. This can often be a rewording of your thesis statement. You could summarize the speech about childhood obesity by saying, “Whether you have children or not, childhood obesity is a national problem that needs to be addressed.”
Reviewing Your Main Points
Once you have summarized the overall importance of your speech, you review the main points (Abhishek, 2020). The review statement in the conclusion is very similar to the preview statement in your introduction. You do not have to use the exact same wording, but you still want to have recognizable parallelism that connects the key idea of each main point to the preview, review, and transitions. The review statement for the childhood obesity speech could be “In an effort to convince you of this, I cited statistics showing the rise of obesity, explained common health problems associated with obesity, and proposed steps that parents should take to ensure their children maintain a healthy weight.”
Closing Your Speech
Like the attention getter, your closing statement is an opportunity for you to exercise your creativity as a speaker (Abhishek, 2020). Many students have difficulty wrapping up the speech with a sense of closure and completeness. In terms of closure, a well-written and well-delivered closing line signals to your audience that your speech is over, which cues their applause. You should not have to put an artificial end to your speech by saying “thank you”, that is it, or that is all I have In terms of completeness, the closing line should relate to the overall speech and should provide some “take-away” message that may leave an audience thinking or propel them to action. A sample closing line could be “For your health, for our children’s health, and for our country’s health, we must take steps to address childhood obesity today.” You can also create what I call the “ribbon and bow” for your speech by referring back to the introduction in the closing of your speech. For example, you may finish an illustration or answer a rhetorical question you started in the introduction.
Although the conclusion is likely the shortest part of the speech, students should practice it often. Even a well-written conclusion can be ineffective if the delivery is not good. Conclusions often turn out bad because they are not practiced enough. If you only practice your speech starting from the beginning, you may not get to your conclusion very often because you stop to fix something in one of the main points, get interrupted, or run out of time. Once you have started your speech, anxiety may increase as you near the end and your brain becomes filled with thoughts of returning to your seat, so even a well-practiced conclusion can fall short. Practicing your conclusion by itself several times can help prevent this.
Think of your outline as a living document that grows and takes form throughout your speech-making process. When you first draft your general purpose, specific purpose, and thesis statement, you could create a new document on your computer and plug those in, essentially starting your outline. As you review your research and distill the information down into separate central ideas that support your specific purpose and thesis, type those statements into the document. After choosing your organizational pattern and are ready to incorporate supporting material, you can quote and paraphrase your supporting material along with the bibliographic information needed for your verbal citations into the document. By this point, you have a good working outline, and you can easily cut and paste information to move it around and see how it fits into the main points, sub-points, and sub-sub-points (James Madison University Communication Center, n. d.). As your outline continues to take shape, you will want to follow established principles of outlining to ensure a quality speech.
The Formal Outline
The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps you prepare for your speech. It includes the introduction and conclusion, the main content of the body, key supporting materials, citation information written into the sentences in the outline, and a references page for your speech (Dlugan, 2008). The formal outline also includes a title, the general purpose, specific purpose, and thesis statement. It is important to note that an outline is different from a script. While a script contains everything that will be said, an outline includes the main content. Therefore, you should not include every word you are going to say on your outline. This allows you more freedom as a speaker to adapt to your audience during your speech. Students sometimes complain about having to outline speeches or papers, but it is a skill that will help in other contexts. Being able to break a topic down into logical divisions and then connect the information together will help ensure that you can prepare for complicated tasks or that you are prepared for meetings or interviews.
Principles of Outlining
There are principles of outlining you can follow to make your outlining process more efficient and effective. Four principles of outlining are consistency, unity, coherence, and emphasis (DuBois, 1929). In terms of consistency, you should follow standard outlining format. In standard outlining format, you indicate main points by capital roman numerals, sub-points by capital letters, and sub-sub-points by Arabic numerals. You indicate further divisions by either lowercase letters or lowercase roman numerals.
The principle of unity means that each letter or number represents one idea. One concrete way to help reduce the amount of ideas you include per item is to limit each letter or number to one complete sentence. If you find that one sub-point has more than one idea, you can divide it into two sub-points. Limiting each component of your outline to one idea makes it easier to plug in supporting material and helps ensure that your speech is coherent.
Following the principle of unity should help your outline adhere to the principle of coherence, which states that there should be a logical and natural flow of ideas, with main points, sub-points, and sub-sub-points connecting to each other (Winans, 1917). Shorter phrases and keywords can make up the speaking outline, but you should write complete sentences throughout your formal outline to ensure coherence.
The principle of coherence can also be met by making sure that when dividing a main point or sub-point, you include at least two subdivisions. After all, it defies logic that you could divide anything into just one part. Therefore, if you have an A , you must have a B , and if you have a 1 , you must have a 2 . If you can easily think of one sub-point but are having difficulty identifying another one, that sub-point may not be robust enough to stand on its own.
The principle of emphasis states that the material included in your outline should be engaging and balanced. As you place supporting material into your outline, choose the information that will have the most impact on your audience. Choose information that is proxemic and relevant, meaning that it can be easily related to the audience’s lives because it matches their interests or ties into current events or the local area.
Remember primacy and recency discussed earlier and place the most engaging information first or last in a main point depending on what kind of effect you want to have (Morrison, Conway, & Chein, 2014). Also, make sure your information is balanced. The outline serves as a useful visual representation of the proportions of your speech. You can tell by the amount of space a main point, sub-point, or sub-sub-point takes up in relation to other points of the same level whether your speech is balanced. If one sub-point is a half a page, but a main point is only a quarter of a page, then you may want to consider making the sub-point a main point. Each part of your speech does not have to be equal. The first or last point may be more substantial than a middle point if you are following primacy or recency, but overall the speech should be relatively balanced.
The Speaking Outline
The formal outline is a full-sentence outline that helps as you prepare for your speech, and the speaking outline is a keyword and phrase outline that helps you deliver your speech. While the formal outline is important to ensure that your content is coherent and your ideas are balanced and expressed clearly, the speaking outline helps you get that information out to the audience. Make sure you budget time in your speech preparation to work on the speaking outline. Skimping on the speaking outline will show in your delivery.
You may convert your formal outline into a speaking outline using a computer program. You may also choose, or be asked to, create a speaking outline on note cards. Note cards are a good option when you want to have more freedom to gesture or know you will not have a lectern on which to place notes printed on full sheets of paper. In either case, this entails converting the full-sentence outline to a keyword or key-phrase outline. Speakers will need to find a balance between having too much or too little content on their speaking outlines. You want to have enough information to prevent fluency hiccups as you stop to retrieve information, but you do not want to have so much information that you read your speech, which lessens your eye contact and engagement with the audience.
Budgeting sufficient time to work on your speaking outline will allow you to practice your speech with different amounts of notes to find what works best for you. Since the introduction and conclusion are so important, it may be useful to include notes to ensure that you remember to accomplish all the objectives of each.
Aside from including important content on your speaking outline, you may want to include speaking cues. Speaking cues are reminders designed to help your delivery. You may write “(PAUSE)” before and after your preview statement to help you remember that important nonverbal signpost. You might also write “(MAKE EYE CONTACT)” as a reminder not to read unnecessarily from your cards. Overall, my advice is to make your speaking outline work for you. It is your last line of defense when you are in front of an audience, so you want it to help you, not hurt you.
Figure 8.1: Mandatory work meetings are an example of captive audiences. Rodeo Project Management Software. 2020. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/ONe-snuCaqQ
Figure 8.2: Layers that make up our perception and knowledge. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.3: Brainstorming and narrowing a topic. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.4: If you get stuck in your research, ask a reference librarian! Tima Miroshnichenko. 2021. Pexels license . https://www.pexels.com/photo/an-elderly-woman-talking-to-a-student-9572566/
Figure 8.5: Whiteboards are a great way to interact with your audience. Bonneval Sebastien. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/UIpFY1Umamw
Figure 8.6: Example of a sales spreadsheet. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.7: Example of a pie chart. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.8: Examples of a line graph (top) and a bar graph (bottom). Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.9: Example of a chronological pattern of events. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 8.10: Before using humor in your speech, reflect on if it is the right occasion. Omar Lopez. 2017. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/rwF_pJRWhAI
Section 8.1
Aristotle (2007). On rhetoric: A theory of civic discourse (G. A. Kennedy, Trans.) (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. (Original work published ca. 367-322 BCE)
Dlugan, A. (2012, November 15). Audience analysis: A guide for speakers . http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/audience-analysis/
Goodwin, J. (2017, December 11). Writing a thesis statement for a speech . https://magoosh.com/pro-writing/writing-thesis-statement-for-a-speech/
James Madison University Communication Center. (2021). Developing a presentation . https://www.jmu.edu/commcenter/presentation-support/developing.shtml
James Madison University Writing Center. (2021). Choosing a topic . https://www.jmu.edu/uwc/link-library/writing-process/choosing-topic.shtml
Section 8.2
Beare, K. (2020, January 21). How to discuss hypothetical situations in English . https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-discuss-hypothetical-situations-in-english-4177287
Beqiri, G. (2018, June 21). Using visual aids during a presentation or training session . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/visual-aids-presentation
Brigham Young University Library. (2021, July 15). Step-by-step guide & research rescue: Evaluating credibility . https://guides.lib.byu.edu/c.php?g=216340&p=1428399
Davis, B. (2020, August 16). What is the main value of using expert testimony in a speech? https://www.mvorganizing.org/what-is-the-main-value-of-using-expert-testimony-in-a-speech/#What_is_the_main_value_of_using_expert_testimony_in_a_speech
Gallo, C. (2017, January 31). Four easy tips on using video to make your presentation stand out . https://www.forbes.com/sites/carminegallo/2017/01/31/four-easy-tips-on-using-video-to-make-your-presentation-stand-out/?sh=74ce88146e3a
James Madison University Libraries. (2019, September 16). Primary, secondary, and tertiary sources: Definitions . https://guides.lib.jmu.edu/sources
James Madison University Libraries. (2021). Quick overview of JMU Libraries services & resources for fall 2021 . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b_nHy3rstl0
Matook, M. E. (2020). The impactful research appointment: Combating research anxiety and library stereotypes. The Reference Librarian , 61 (3-4), 185-198. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763877.2020.1837710
National WW II Museum. (n.d.). Guidelines for using primary sources in your classroom . https://www.nationalww2museum.org/sites/default/files/2017-07/using-primary-sources.pdf
Presentation Magazine. (2011, April 11). Top tips for using graphs and charts in your presentations . https://www.presentationmagazine.com/top-tips-for-using-graphs-and-charts-in-your-presentations-6686.htm
Rielly, T. (2020, May 12). The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides . https://masterclass.ted.com/blog/visual-presentations-series-less-is-more
Segar, G. (2016, September 12). Three types of relevant analogies to use in speeches . https://potentspeaking.com/relevant-analogies/
Section 8.3
Abhishek, K. G. (2020, November 16). How to end a speech: The best tips and examples . https://www.orai.com/blog/how-to-end-a-speech-the-best-tips-and-examples/
Amadeba, E. (2021, September 4). What is signposting in speech? https://www.acethepresentation.com/signposts-in-speech/
Barnard, D. (2017, November 6). Different ways to end a presentation or speech . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/different-ways-to-end-presentation-speech
Davis, B. (2021, April 30). What are the five organizational patterns? https://www.mvorganizing.org/what-are-the-five-organizational-patterns/
Davis, B. (2021, May 8). What is a preview statement example? https://www.mvorganizing.org/what-is-a-preview-statement-example/
Dlugan, A. (2008, February 29). Speech preparation #3: Don’t skip the speech outline . http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/speech-preparation-3-outline-examples/
DuBois, W. C. (1929). Essentials of public speaking . Prentice Hall.
Ginger Leadership Communications. (2019, December 13). How to start a speech with power and confidence . https://www.gingerleadershipcomms.com/article/how-to-start-a-speech-with-power-and-confidence
James Madison University Communication Center (n. d.). Creating an outline . https://www.jmu.edu/commcenter/_files/Outline-Tip-Poster.pdf
James Madison University Communication Center. (2010). Oral source citations . https://www.jmu.edu/commcenter/_files/Oral%20Citation%20Guide.pdf
Lass-Hennemann, J., Kuehl L. K., Schulz, A., Oitzl, M. S., & Schachinger, H. (2011). Stress strengthens memory of first impressions of others’ positive personality traits. PLoS ONE , 6 (1), e16389. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016389
Laws, E. L., Apperson, J. M., Buchert, S., & Bregman, N. J. (2010). Student evaluations of instruction: When are enduring first impressions formed? North American Journal of Psychology, 12 (1), 81–92.
LibreTexts. (2020, August 12). Patterns of organization and methods of development . https://human.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Composition/Introductory_Composition/Book%3A_The_Word_on_College_Reading_and_Writing_(Babin_et_al.)/Part_2/08%3A_Drafting/8.07%3A_Patterns_of_Organization_and_Methods_of_Development
LibreTexts. (2021, February 20). Formulating a specific purpose statement . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Exploring_Public_Speaking_(Barton_and_Tucker)/04%3A_Selecting_Your_Approach_and_Main_Points/4.02%3A_Formulating_a_Specific_Purpose_Statement
Monroe, A. H., & Ehninger, D. (1964). Principles of speech (5th ed.). Scott, Foresman.
Morrison A., Conway, A., & Chein, J. (2014). Primacy and recency effects as indices of the focus of attention. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , 8 (Article 6), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00006
Winans, J. A. (1917). Public speaking . Century.
Broad socio-cultural categories, such as age, gender, race, socioeconomic status, sexual orientation, education level, religion, ethnicity, and nationality used to segment a larger population
Consider the audience’s psychological dispositions towards the topic, the speaker and the occasion as well as how their attitudes, beliefs, and values inform those dispositions
When an audience sees you as competent, trustworthy, and engaging
People who are required to attend your presentations
People who have decided to come hear your speech
To inform, to persuade, or to entertain
Generating many potential topic ideas in a fast-paced and a non-judgmental manner
One-sentence statement that includes the objective you want to accomplish in your speech
One-Sentence Summary of the central idea of your speech
Information-retrieval experts
Magazines and journals that are published periodically
The author-supplied summary of the source
The most rigorous form of review, which takes several months to years and ensures that the information that is published has been vetted and approved by numerous experts on the subject
Sources written by people with firsthand experiences or by researchers/scholars who conducted original research
Compiled research by others in a condensed format
Cited case that is representative of a larger whole
Clarify ideas by providing information about what something is, why something is the way it is, or how something works or came to be
Numerical representations of information
A comparison of ideas, items, or circumstances
Quoted information from people with direct knowledge about a subject or situation
Help a speaker reinforce speech content visually, which helps amplify the speaker’s message
A “miniature speech” within your larger speech. Each will have a central idea, meet some part of your specific purpose, and include supporting material from your research that relates to your thesis
Similar wording among key organizing signposts and main points that helps structure a speech
Breaking a large idea or category into smaller ideas or subcategories
Presenting your best information first in order to make a positive impression and engage your audience early in your speech
Based on the idea that an audience will best remember the information they heard most recently
Speech structure based on time or sequence
Arranges main points based on their layout or proximity to each other
Presenting a problem and offering one or multiple solutions
Forming a relationship between ideas that shows a progression from origin to result
A five step organizational pattern to help persuade an audience. 1. Attention Step: Grab the audience’s attention in the introduction. 2. Need Step: Establish the reason that your topic needs to be addressed. Satisfaction Step: Present a solution to the problem that you are addressing. 4. Visualization Step: Incorporate a positive/negative motivation to support the relationship you have set up between the need and your proposal. 5. Action Step: Include a call to action that tells people what they can do about the situation.
Citing the sources you have obtained information from in your speech to prove your credibility to the audience
Statements that help audience members navigate the changes in a speech
Pauses and changes in rate, pitch, or volume that help to emphasize a transition in a speech
A question which will elicit a mental response from the audience, not a verbal or nonverbal one
A full-sentence outline that helps you prepare for your speech. It includes the introduction and conclusion, the main content of the body, key supporting materials, citation information written into the sentences in the outline, and a references page for your speech.
A keyword and phrase outline that helps you deliver your speech. The speaking outline helps you get that information out to the audience.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © by Faculty members in the School of Communication Studies, James Madison University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.3 Putting It Together: Steps to Complete Your Introduction
Learning objectives.
- Clearly identify why an audience should listen to a speaker.
- Discuss how you can build your credibility during a speech.
- Understand how to write a clear thesis statement.
- Design an effective preview of your speech’s content for your audience.
Erin Brown-John – puzzle – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Once you have captured your audience’s attention, it’s important to make the rest of your introduction interesting, and use it to lay out the rest of the speech. In this section, we are going to explore the five remaining parts of an effective introduction: linking to your topic, reasons to listen, stating credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
Link to Topic
After the attention-getter, the second major part of an introduction is called the link to topic. The link to topic is the shortest part of an introduction and occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. Often the attention-getter and the link to topic are very clear. For example, if you look at the attention-getting device example under historical reference above, you’ll see that the first sentence brings up the history of the Vietnam War and then shows us how that war can help us understand the Iraq War. In this case, the attention-getter clearly flows directly to the topic. However, some attention-getters need further explanation to get to the topic of the speech. For example, both of the anecdote examples (the girl falling into the manhole while texting and the boy and the filberts) need further explanation to connect clearly to the speech topic (i.e., problems of multitasking in today’s society).
Let’s look at the first anecdote example to demonstrate how we could go from the attention-getter to the topic.
In July 2009, a high school girl named Alexa Longueira was walking along a main boulevard near her home on Staten Island, New York, typing in a message on her cell phone. Not paying attention to the world around her, she took a step and fell right into an open manhole. This anecdote illustrates the problem that many people are facing in today’s world. We are so wired into our technology that we forget to see what’s going on around us—like a big hole in front of us.
In this example, the third sentence here explains that the attention-getter was an anecdote that illustrates a real issue. The fourth sentence then introduces the actual topic of the speech.
Let’s now examine how we can make the transition from the parable or fable attention-getter to the topic:
The ancient Greek writer Aesop told a fable about a boy who put his hand into a pitcher of filberts. The boy grabbed as many of the delicious nuts as he possibly could. But when he tried to pull them out, his hand wouldn’t fit through the neck of the pitcher because he was grasping so many filberts. Instead of dropping some of them so that his hand would fit, he burst into tears and cried about his predicament. The moral of the story? “Don’t try to do too much at once.” In today’s world, many of us are us are just like the boy putting his hand into the pitcher. We are constantly trying to grab so much or do so much that it prevents us from accomplishing our goals. I would like to show you three simple techniques to manage your time so that you don’t try to pull too many filberts from your pitcher.
In this example, we added three new sentences to the attention-getter to connect it to the speech topic.
Reasons to Listen
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important. We call this the “why should I care?” part of your speech because it tells your audience why the topic is directly important to them. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important.
People in today’s world are very busy, and they do not like their time wasted. Nothing is worse than having to sit through a speech that has nothing to do with you. Imagine sitting through a speech about a new software package you don’t own and you will never hear of again. How would you react to the speaker? Most of us would be pretty annoyed at having had our time wasted in this way. Obviously, this particular speaker didn’t do a great job of analyzing her or his audience if the audience isn’t going to use the software package—but even when speaking on a topic that is highly relevant to the audience, speakers often totally forget to explain how and why it is important.
Appearing Credible
The next part of a speech is not so much a specific “part” as an important characteristic that needs to be pervasive throughout your introduction and your entire speech. As a speaker, you want to be seen as credible (competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill). As mentioned earlier in this chapter, credibility is ultimately a perception that is made by your audience. While your audience determines whether they perceive you as competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill, there are some strategies you can employ to make yourself appear more credible.
First, to make yourself appear competent, you can either clearly explain to your audience why you are competent about a given subject or demonstrate your competence by showing that you have thoroughly researched a topic by including relevant references within your introduction. The first method of demonstrating competence—saying it directly—is only effective if you are actually a competent person on a given subject. If you are an undergraduate student and you are delivering a speech about the importance of string theory in physics, unless you are a prodigy of some kind, you are probably not a recognized expert on the subject. Conversely, if your number one hobby in life is collecting memorabilia about the Three Stooges, then you may be an expert about the Three Stooges. However, you would need to explain to your audience your passion for collecting Three Stooges memorabilia and how this has made you an expert on the topic.
If, on the other hand, you are not actually a recognized expert on a topic, you need to demonstrate that you have done your homework to become more knowledgeable than your audience about your topic. The easiest way to demonstrate your competence is through the use of appropriate references from leading thinkers and researchers on your topic. When you demonstrate to your audience that you have done your homework, they are more likely to view you as competent.
The second characteristic of credibility, trustworthiness, is a little more complicated than competence, for it ultimately relies on audience perceptions. One way to increase the likelihood that a speaker will be perceived as trustworthy is to use reputable sources. If you’re quoting Dr. John Smith, you need to explain who Dr. John Smith is so your audience will see the quotation as being more trustworthy. As speakers we can easily manipulate our sources into appearing more credible than they actually are, which would be unethical. When you are honest about your sources with your audience, they will trust you and your information more so than when you are ambiguous. The worst thing you can do is to out-and-out lie about information during your speech. Not only is lying highly unethical, but if you are caught lying, your audience will deem you untrustworthy and perceive everything you are saying as untrustworthy. Many speakers have attempted to lie to an audience because it will serve their own purposes or even because they believe their message is in their audience’s best interest, but lying is one of the fastest ways to turn off an audience and get them to distrust both the speaker and the message.
The third characteristic of credibility to establish during the introduction is the sense of caring/goodwill. While some unethical speakers can attempt to manipulate an audience’s perception that the speaker cares, ethical speakers truly do care about their audiences and have their audience’s best interests in mind while speaking. Often speakers must speak in front of audiences that may be hostile toward the speaker’s message. In these cases, it is very important for the speaker to explain that he or she really does believe her or his message is in the audience’s best interest. One way to show that you have your audience’s best interests in mind is to acknowledge disagreement from the start:
Today I’m going to talk about why I believe we should enforce stricter immigration laws in the United States. I realize that many of you will disagree with me on this topic. I used to believe that open immigration was a necessity for the United States to survive and thrive, but after researching this topic, I’ve changed my mind. While I may not change all of your minds today, I do ask that you listen with an open mind, set your personal feelings on this topic aside, and judge my arguments on their merits.
While clearly not all audience members will be open or receptive to opening their minds and listening to your arguments, by establishing that there is known disagreement, you are telling the audience that you understand their possible views and are not trying to attack their intellect or their opinions.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know “in a nutshell” what you are going to talk about. With a good thesis statement you will fulfill four basic functions: you express your specific purpose, provide a way to organize your main points, make your research more effective, and enhance your delivery.
Express Your Specific Purpose
To orient your audience, you need to be as clear as possible about your meaning. A strong thesis will prepare your audience effectively for the points that will follow. Here are two examples:
- “Today, I want to discuss academic cheating.” (weak example)
- “Today, I will clarify exactly what plagiarism is and give examples of its different types so that you can see how it leads to a loss of creative learning interaction.” (strong example)
The weak statement will probably give the impression that you have no clear position about your topic because you haven’t said what that position is. Additionally, the term “academic cheating” can refer to many behaviors—acquiring test questions ahead of time, copying answers, changing grades, or allowing others to do your coursework—so the specific topic of the speech is still not clear to the audience.
The strong statement not only specifies plagiarism but also states your specific concern (loss of creative learning interaction).
Provide a Way to Organize Your Main Points
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease. On the other hand, when the thesis statement is not very clear, creating a speech is an uphill battle.
When your thesis statement is sufficiently clear and decisive, you will know where you stand about your topic and where you intend to go with your speech. Having a clear thesis statement is especially important if you know a great deal about your topic or you have strong feelings about it. If this is the case for you, you need to know exactly what you are planning on talking about in order to fit within specified time limitations. Knowing where you are and where you are going is the entire point in establishing a thesis statement; it makes your speech much easier to prepare and to present.
Let’s say you have a fairly strong thesis statement, and that you’ve already brainstormed a list of information that you know about the topic. Chances are your list is too long and has no focus. Using your thesis statement, you can select only the information that (1) is directly related to the thesis and (2) can be arranged in a sequence that will make sense to the audience and will support the thesis. In essence, a strong thesis statement helps you keep useful information and weed out less useful information.
Make Your Research More Effective
If you begin your research with only a general topic in mind, you run the risk of spending hours reading mountains of excellent literature about your topic. However, mountains of literature do not always make coherent speeches. You may have little or no idea of how to tie your research all together, or even whether you should tie it together. If, on the other hand, you conduct your research with a clear thesis statement in mind, you will be better able to zero in only on material that directly relates to your chosen thesis statement. Let’s look at an example that illustrates this point:
Many traffic accidents involve drivers older than fifty-five.
While this statement may be true, you could find industrial, medical, insurance literature that can drone on ad infinitum about the details of all such accidents in just one year. Instead, focusing your thesis statement will help you narrow the scope of information you will be searching for while gathering information. Here’s an example of a more focused thesis statement:
Three factors contribute to most accidents involving drivers over fifty-five years of age: failing eyesight, slower reflexes, and rapidly changing traffic conditions.
This framing is somewhat better. This thesis statement at least provides three possible main points and some keywords for your electronic catalog search. However, if you want your audience to understand the context of older people at the wheel, consider something like:
Mature drivers over fifty-five years of age must cope with more challenging driving conditions than existed only one generation ago: more traffic moving at higher speeds, the increased imperative for quick driving decisions, and rapidly changing ramp and cloverleaf systems. Because of these challenges, I want my audience to believe that drivers over the age of sixty-five should be required to pass a driving test every five years.
This framing of the thesis provides some interesting choices. First, several terms need to be defined, and these definitions might function surprisingly well in setting the tone of the speech. Your definitions of words like “generation,” “quick driving decisions,” and “cloverleaf systems” could jolt your audience out of assumptions they have taken for granted as truth.
Second, the framing of the thesis provides you with a way to describe the specific changes as they have occurred between, say, 1970 and 2010. How much, and in what ways, have the volume and speed of traffic changed? Why are quick decisions more critical now? What is a “cloverleaf,” and how does any driver deal cognitively with exiting in the direction seemingly opposite to the desired one? Questions like this, suggested by your own thesis statement, can lead to a strong, memorable speech.
Enhance Your Delivery
When your thesis is not clear to you, your listeners will be even more clueless than you are—but if you have a good clear thesis statement, your speech becomes clear to your listeners. When you stand in front of your audience presenting your introduction, you can vocally emphasize the essence of your speech, expressed as your thesis statement. Many speakers pause for a half second, lower their vocal pitch slightly, slow down a little, and deliberately present the thesis statement, the one sentence that encapsulates its purpose. When this is done effectively, the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech is driven home for an audience.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement. A thesis statement is related to the general and specific purposes of a speech as we discussed them in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” .
Choose Your Topic
The first step in writing a good thesis statement was originally discussed in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” when we discussed how to find topics. Once you have a general topic, you are ready to go to the second step of creating a thesis statement.
Narrow Your Topic
One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to ten-minute speech. While five to ten minutes may sound like a long time to new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can easily run out of time if your topic is too broad. To ascertain if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions.
First, is your thesis statement narrow or is it a broad overgeneralization of a topic? An overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “all members of the National Council of La Raza are militant” is an overgeneralization of all members of the organization. Furthermore, a speaker would have to correctly demonstrate that all members of the organization are militant for the thesis statement to be proven, which is a very difficult task since the National Council of La Raza consists of millions of Hispanic Americans. A more appropriate thesis related to this topic could be, “Since the creation of the National Council of La Raza [NCLR] in 1968, the NCLR has become increasingly militant in addressing the causes of Hispanics in the United States.”
The second question to ask yourself when narrowing a topic is whether your speech’s topic is one clear topic or multiple topics. A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana, prostitution, and gay marriage should all be legalized in the United States.” Not only are all three fairly broad, but you also have three completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: “Today we’re going to examine the legalization and regulation of the oldest profession in the state of Nevada.” In this case, we’re focusing our topic to how one state has handled the legalization and regulation of prostitution.
The last question a speaker should ask when making sure a topic is sufficiently narrow is whether the topic has direction. If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow her or his topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Sentence
Once you’ve narrowed your topic to something that is reasonably manageable given the constraints placed on your speech, you can then formalize that topic as a complete sentence. For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech.
Add Your Argument, Viewpoint, or Opinion
This function only applies if you are giving a speech to persuade. If your topic is informative, your job is to make sure that the thesis statement is nonargumentative and focuses on facts. For example, in the preceding thesis statement we have a couple of opinion-oriented terms that should be avoided for informative speeches: “unique sense,” “well-developed,” and “power.” All three of these terms are laced with an individual’s opinion, which is fine for a persuasive speech but not for an informative speech. For informative speeches, the goal of a thesis statement is to explain what the speech will be informing the audience about, not attempting to add the speaker’s opinion about the speech’s topic. For an informative speech, you could rewrite the thesis statement to read, “This speech is going to analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his speech, ‘A World That Stands as One,’ delivered July 2008 in Berlin.”
On the other hand, if your topic is persuasive, you want to make sure that your argument, viewpoint, or opinion is clearly indicated within the thesis statement. If you are going to argue that Barack Obama is a great speaker, then you should set up this argument within your thesis statement.
Use the Thesis Checklist
Once you have written a first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times prior to delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction, and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown in Table 9.1 “Thesis Checklist”
Table 9.1 Thesis Checklist
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered within your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Key Takeaways
- Linking the attention-getter to the speech topic is essential so that you maintain audience attention and so that the relevance of the attention-getter is clear to your audience.
- Establishing how your speech topic is relevant and important shows the audience why they should listen to your speech.
- To be an effective speaker, you should convey all three components of credibility, competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill, by the content and delivery of your introduction.
- A clear thesis statement is essential to provide structure for a speaker and clarity for an audience.
- An effective preview identifies the specific main points that will be present in the speech body.
- Make a list of the attention-getting devices you might use to give a speech on the importance of recycling. Which do you think would be most effective? Why?
- Create a thesis statement for a speech related to the topic of collegiate athletics. Make sure that your thesis statement is narrow enough to be adequately covered in a five- to six-minute speech.
- Discuss with a partner three possible body points you could utilize for the speech on the topic of volunteerism.
- Fill out the introduction worksheet to help work through your introduction for your next speech. Please make sure that you answer all the questions clearly and concisely.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Speech Crafting →
Public Speaking: Developing a Thesis Statement In a Speech

Understanding the purpose of a thesis statement in a speech
Diving headfirst into the world of public speaking, it’s essential to grasp the role of a thesis statement in your speech. Think of it as encapsulating the soul of your speech within one or two sentences.
It’s the declarative sentence that broadcasts your intent and main idea to captivate audiences from start to finish. More than just a preview, an effective thesis statement acts as a roadmap guiding listeners through your thought process.
Giving them that quick glimpse into what they can anticipate helps keep their attention locked in.
As you craft this central hub of information, understand that its purpose is not limited to informing alone—it could be meant also to persuade or entertain based on what you aim for with your general purpose statement.
This clear focus is pivotal—it shapes each aspect of your talk, easing understanding for the audience while setting basic goals for yourself throughout the speech-making journey. So whether you are rallying rapturous applause or instigating intellectual insight, remember—your thesis statement holds power like none other! Its clarity and strength can transition between being valuable sidekicks in introductions towards becoming triumphant heroes by concluding lines.
Identifying the main idea to develop a thesis statement
In crafting a compelling speech, identifying the main idea to develop a thesis statement acts as your compass. This process is a crucial step in speech preparation that steers you towards specific purpose.
Think of your central idea as the seed from which all other elements in your speech will grow.
To pinpoint it, start by brainstorming broad topics that interest or inspire you. From this list, choose one concept that stands out and begin to narrow it down into more specific points. It’s these refined ideas that form the heart of your thesis statement — essentially acting as signposts leading the audience through your narrative journey.
Crafting an effective thesis statement requires clarity and precision. This means keeping it concise without sacrificing substance—a tricky balancing act even for public speaking veterans! The payoff though? A well-developed thesis statement provides structure to amplifying your central idea and guiding listeners smoothly from point A to B.
It’s worth noting here: just like every speaker has their own unique style, there are multiple ways of structuring a thesis statement too. But no matter how you shape yours, ensuring it resonates with both your overarching message and audience tastes will help cement its effectiveness within your broader presentation context.
Analyzing the audience to tailor the thesis statement
Audience analysis is a crucial first step for every public speaker. This process involves adapting the message to meet the audience’s needs, a thoughtful approach that considers cultural diversity and ensures clear communication.
Adapting your speech to resonate with your target audience’s interests, level of understanding, attitudes and beliefs can significantly affect its impact.
Crafting an appealing thesis statement hinges on this initial stage of audience analysis. As you analyze your crowd, focus on shaping a specific purpose statement that reflects their preferences yet stays true to the objective of your speech—capturing your main idea in one or two impactful sentences.
This balancing act demands strategy; however, it isn’t impossible. Taking into account varying aspects such as culture and perceptions can help you tailor a well-received thesis statement. A strong handle on these elements allows you to select language and tones best suited for them while also reflecting the subject at hand.
Ultimately, putting yourself in their shoes helps increase message clarity which crucially leads to acceptance of both you as the speaker and your key points – all embodied within the concise presentation of your tailor-made thesis statement.
Brainstorming techniques to generate thesis statement ideas
Leveraging brainstorming techniques to generate robust thesis statement ideas is a power move in public speaking. This process taps into the GAP model, focusing on your speech’s Goals, Audience, and Parameters for seamless target alignment.
Dive into fertile fields of thought and let your creativity flow unhindered like expert David Zarefsky proposes.
Start by zeroing in on potential speech topics then nurture them with details till they blossom into fully-fledged arguments. It’s akin to turning stones into gems for the eye of your specific purpose statement.
Don’t shy away from pushing the envelope – sometimes out-of-the-box suggestions give birth to riveting speeches! Broaden your options if parameters are flexible but remember focus is key when aiming at narrow targets.
The beauty lies not just within topic generation but also formulation of captivating informative or persuasive speech thesis statements; both fruits harvested from a successful brainstorming session.
So flex those idea muscles, encourage intellectual growth and watch as vibrant themes spring forth; you’re one step closer to commanding attention!
Remember: Your thesis statement is the heartbeat of your speech – make it strong using brainstorming techniques and fuel its pulse with evidence-backed substance throughout your presentation.
Narrowing down the thesis statement to a specific topic
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your speech requires narrowing down a broad topic to a specific focus that can be effectively covered within the given time frame. This step is crucial as it helps you maintain clarity and coherence throughout your presentation.
Start by brainstorming various ideas related to your speech topic and then analyze them critically to identify the most relevant and interesting points to discuss. Consider the specific purpose of your speech and ask yourself what key message you want to convey to your audience.
By narrowing down your thesis statement, you can ensure that you address the most important aspects of your chosen topic, while keeping it manageable and engaging for both you as the speaker and your audience.
Choosing the appropriate language and tone for the thesis statement
Crafting the appropriate language and tone for your thesis statement is a crucial step in developing a compelling speech. Your choice of language and tone can greatly impact how your audience perceives your message and whether they are engaged or not.
When choosing the language for your thesis statement, it’s important to consider the level of formality required for your speech. Are you speaking in a professional setting or a casual gathering? Adjusting your language accordingly will help you connect with your audience on their level and make them feel comfortable.
Additionally, selecting the right tone is essential to convey the purpose of your speech effectively. Are you aiming to inform, persuade, or entertain? Each objective requires a different tone: informative speeches may call for an objective and neutral tone, persuasive speeches might benefit from more assertive language, while entertaining speeches can be lighthearted and humorous.
Remember that clarity is key when crafting your thesis statement’s language. Using concise and straightforward wording will ensure that your main idea is easily understood by everyone in the audience.
By taking these factors into account – considering formality, adapting to objectives, maintaining clarity – you can create a compelling thesis statement that grabs attention from the start and sets the stage for an impactful speech.
Incorporating evidence to support the thesis statement
Incorporating evidence to support the thesis statement is a critical aspect of delivering an effective speech. As public speakers, we understand the importance of backing up our claims with relevant and credible information.
When it comes to incorporating evidence, it’s essential to select facts, examples, and opinions that directly support your thesis statement.
To ensure your evidence is relevant and reliable, consider conducting thorough research on the topic at hand. Look for trustworthy sources such as academic journals, respected publications, or experts in the field.
By choosing solid evidence that aligns with your message, you can enhance your credibility as a speaker.
When presenting your evidence in the speech itself, be sure to keep it concise and clear. Avoid overwhelming your audience with excessive details or data. Instead, focus on selecting key points that strengthen your argument while keeping their attention engaged.
Remember that different types of evidence can be utilized depending on the nature of your speech. You may include statistical data for a persuasive presentation or personal anecdotes for an informative talk.
The choice should reflect what will resonate best with your audience and effectively support your thesis statement.
By incorporating strong evidence into our speeches, we not only bolster our arguments but also build trust with our listeners who recognize us as reliable sources of information. So remember to choose wisely when including supporting material – credibility always matters when making an impact through public speaking.
Avoiding common mistakes when developing a thesis statement
Crafting an effective thesis statement is vital for public speakers to deliver a compelling and focused speech. To avoid common mistakes when developing a thesis statement , it is essential to be aware of some pitfalls that can hinder the impact of your message.
One mistake to steer clear of is having an incomplete thesis statement. Ensure that your thesis statement includes all the necessary information without leaving any key elements out. Additionally, avoid wording your thesis statement as a question as this can dilute its potency.
Another mistake to watch out for is making statements of fact without providing evidence or support. While it may seem easy to write about factual information, it’s important to remember that statements need to be proven and backed up with credible sources or examples.
To create a more persuasive argument, avoid using phrases like “I believe” or “I feel.” Instead, take a strong stance in your thesis statement that encourages support from the audience. This will enhance your credibility and make your message more impactful.
By avoiding these common mistakes when crafting your thesis statement, you can develop a clear, engaging, and purposeful one that captivates your audience’s attention and guides the direction of your speech effectively.
Key words: Avoiding common mistakes when developing a thesis statement – Crafting a thesis statement – Effective thesis statements – Public speaking skills – Errors in the thesis statement – Enhancing credibility
Revising the thesis statement to enhance clarity and coherence
Revising the thesis statement is a crucial step in developing a clear and coherent speech. The thesis statement serves as the main idea or argument that guides your entire speech, so it’s important to make sure it effectively communicates your message to the audience.
To enhance clarity and coherence in your thesis statement, start by refining and strengthening it through revision . Take into account any feedback you may have received from others or any new information you’ve gathered since initially developing the statement.
Consider if there are any additional points or evidence that could further support your main idea.
As you revise, focus on clarifying the language and tone of your thesis statement. Choose words that resonate with your audience and clearly convey your point of view. Avoid using technical jargon or overly complicated language that might confuse or alienate listeners.
Another important aspect of revising is ensuring that your thesis statement remains focused on a specific topic. Narrow down broad ideas into more manageable topics that can be explored thoroughly within the scope of your speech.
Lastly, consider incorporating evidence to support your thesis statement. This could include statistics, examples, expert opinions, or personal anecdotes – whatever helps strengthen and validate your main argument.
By carefully revising your thesis statement for clarity and coherence, you’ll ensure that it effectively conveys your message while capturing the attention and understanding of your audience at large.
Testing the thesis statement to ensure it meets the speech’s objectives.
Testing the thesis statement is a crucial step to ensure that it effectively meets the objectives of your speech. By testing the thesis statement , you can assess its clarity, relevance, and impact on your audience.
One way to test your thesis statement is to consider its purpose and intent. Does it clearly communicate what you want to achieve with your speech? Is it concise and specific enough to guide your content?.
Another important aspect of testing the thesis statement is analyzing whether it aligns with the needs and interests of your audience. Consider their background knowledge, values, and expectations.
Will they find the topic engaging? Does the thesis statement address their concerns or provide valuable insights?.
In addition to considering purpose and audience fit, incorporating supporting evidence into your speech is vital for testing the effectiveness of your thesis statement. Ensure that there is relevant material available that supports your claim.
To further enhance clarity and coherence in a tested thesis statement, revise it if necessary based on feedback from others or through self-reflection. This will help refine both language choices and overall effectiveness.
By thoroughly testing your thesis statement throughout these steps, you can confidently develop a clear message for an impactful speech that resonates with your audience’s needs while meeting all stated objectives.
1. What is a thesis statement in public speaking?
A thesis statement in public speaking is a concise and clear sentence that summarizes the main point or argument of a speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience, guiding them through the speech and helping them understand its purpose.
2. How do I develop an effective thesis statement for a speech?
To develop an effective thesis statement for a speech, start by identifying your topic and determining what specific message you want to convey to your audience. Then, clearly state this message in one or two sentences that capture the main idea of your speech.
3. Why is it important to have a strong thesis statement in public speaking?
Having a strong thesis statement in public speaking helps you stay focused on your main argument throughout the speech and ensures that your audience understands what you are trying to communicate. It also helps establish credibility and authority as you present well-supported points related to your thesis.
4. Can my thesis statement change during my speech preparation?
Yes, it is possible for your thesis statement to evolve or change during the preparation process as you gather more information or refine your ideas. However, it’s important to ensure that any changes align with the overall purpose of your speech and still effectively guide the content and structure of your presentation.
‘The Age of Magical Overthinking’ tries to pinpoint our mental health crisis
Amanda montell casts a wide net in her new essay collection. maybe too wide..

Every generation has its own crisis, the linguist and podcaster Amanda Montell writes. In the 1960s and ’70s, young Americans organized against “physical tyrannies” such as voter suppression and workplace discrimination. But times have changed.
The 21st century brought a shift in our attention from external threats to internal ones, Montell says. Rates of anxiety and depression among U.S. teens and adults have spiked. Loneliness is a public health threat . We’re glued to our phones, alienated from loved ones and surrounded by misinformation.
People everywhere, Montell writes, are facing a crisis of the mind.
From this grim landscape emerges “ The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern Irrationality ,” Montell’s third book and a sweeping look at mental health, behavioral science, misinformation and online culture in the 2020s. In it, she argues that the ills of the internet era are best explained by looking back on humanity’s history, when our minds developed shortcuts to improve our odds of survival. Those shortcuts are called cognitive biases, and they may lead us to do strange things like fall for a conspiracy theory or accept mental health advice from an untrained influencer .
Montell leads us through an engaging roundup of “21st century derangement,” from celebrity worship to tradwife discourse , examining how cognitive biases may contribute. But by positioning her work as a response to America’s broad struggle with mental health, Montell promises more than she delivers. Rather than focusing on a tour of our shared cognitive glitches, she juggles meta-commentary on such vast topics as the modern mind and the internet, dropping balls along the way.
The book opens with an account of Montell’s struggles with anxiety and overwhelm, as well as the steps she took to feel better. “My most cinematic attempt at mental rehab involved picking herbs on a farm in Sicily under a light-pollution-free sky,” she writes.
Eventually, she had an aha moment: The same cognitive biases she encountered while researching toxic social groups for her second book, “ Cultish ,” could explain why the internet age felt like a “mass head trip.” Glutted with more information in a day than we can ever hope to process, we fall back on mental habits developed when humans were simpler creatures, Montell writes. For example, social media celebrity worship could be fueled by the “halo effect,” where we assume a person with one good quality (writing hit pop songs) has other good qualities (a perfectly tuned moral compass). Or perhaps we spend hours comparing ourselves with other people on Instagram because the “zero-sum bias” has convinced us that life is a game of winners and losers.
Montell backs up her connections in many instances with nods to evolutionary biology. For early humans, it made sense to attach ourselves to the strongest and most powerful, so now we glom onto Taylor Swift or Charli XCX. Resources like mates and status were limited in ancient human communities, Montell notes, so it’s natural that we view hot people on Instagram as immediate threats to our survival.
Montell finds examples of cognitive bias in internet culture flash points, such as the millennial obsession with New Age therapy-speak. Faced with big problems, such as anxiety or depression, our minds seek big explanations, such as childhood trauma or a scarcity mind-set, rather than examining all the smaller problems at play.
In other spots, she shares stories from her own life. In her late 20s, she struggled to end an abusive relationship, terrified that giving up meant she’d wasted years of her life — a classic “sunk cost fallacy.” Humans are social creatures, Montell notes, afraid of inviting scrutiny by admitting mistakes.
“My hope is for these chapters to make some sense of the senseless,” Montell says early on. “To crack open a window in our minds, and let a warm breeze in.” And indeed, in some moments, her sharp descriptions of behavioral foibles and her talent for cutting through doublespeak clear room for hope: Maybe noticing our warped thinking will make its effects less painful. Maybe our generational “crisis” is a story of not-enough-neurons encountering too-many-terabytes.
When confidence in Montell’s analysis wavers, it’s because the targets are too broad, the claims imprecise. For instance, we’re never quite sure of the shape of the national mental health crisis she repeatedly references. Early on, she draws a distinction between Americans’ current mental health struggles and 20th-century battles against bodily oppression. This neat separation doesn’t reflect reality — “The Age of Magical Overthinking” was published after Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization and during ongoing fights for voter access, health care and the right to protest. It also doesn’t reflect what science has shown about illnesses like depression, which are often tied up with a person’s physical and political well-being. Ultimately, we’re left with the sense that Montell’s crisis of the mind begins and ends with the vague feelings of anxiety and dread many people feel after scrolling on social media apps.
Montell implies that the breakdown of Americans’ mental health began after 2000, brought on by internet access and introspection. Conflating “the internet” with social media, she draws loose connections between online scrolling and mental turmoil, making no reference to the complicated science around how social media use affects our brains. Some studies have found bumps in anxiety and depression associated with social media use, but more recent meta-analyses call their methods and findings into question . To date, researchers have found no consistent causal link between spending time on social apps and experiencing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Of course, future research may uncover new ways to measure how social media use or other online activities affect the mental health of different populations. Perhaps we should rely on a different measure altogether, like qualitative research into young people and their families. Rather than critique the existing science or offer an alternative lens, Montell picks two studies that support her thesis and hand-waves at the dire state of things.
Finally, although Montell says cognitive biases affect everyone, she aims her jabs at the safest of targets: “Disney adults,” “male girlbosses,” “Facebook-addicted Karens.” Readers hoping for fresh or counterintuitive takes on internet culture — and its heroes and villains — may walk away disappointed.
Montell says from the jump that her analysis of 2020s malaise is “not a system of thought,” likening her work instead to a Buddhist koan — meant to be pondered, not understood. That’s fine, and “The Age of Magical Overthinking” ultimately features interesting topics, fun research and vivid stories. But in Montell’s effort to critique the spirit of our times, she asks imprecise questions and offers unsatisfactory answers.
Tatum Hunter is a consumer technology reporter at The Washington Post based in San Francisco. Her work focuses on health, privacy and relationships in the internet era.
The Age of Magical Overthinking
Notes on Modern Irrationality
By Amanda Montell
Atria/One Signal. 272 pp. $28.
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Like many novels with high school settings, Speak is deeply focused on ideas of growing up and coming of age. What makes this book's exploration of that subject particularly poignant and pointed, however, is that Melinda has already experienced a major milestone of adulthood—losing her virginity—before the novel begins. The fact that this event occurred as the result of rape, however ...
The Conflicted Feelings Inherent in Growing Up. Speak examines the grief many teens feel for the end of their childhood. The transition to adolescence takes years, is different for every single person, and causes changes that can be distressing. Several times Melinda pines for happy moments in her past, such as the perfect day in the orchard ...
Theme statements should describe an argument, or the author's stance on a certain topic presented in the novel. A theme statement regarding the topic of communication in Speak might be: "The theme ...
Words: 355 Pages: 1. In Speak, the author, Laurie Halse Anderson, illustrates the idea that people can recover after trauma and become stronger. The writer utilizes the first-person point of view to show the path protagonist goes through to her transformation. The first-person point of view is the type of narrative in which events are described ...
Speak Full Book Summary. Previous Next. Speak, by Laurie Halse Anderson, chronicles the struggles of thirteen-year-old Melinda Sordino after she is a raped by at a party the summer before her freshman year of high school by another student. Melinda tells her story in first person narrative. She describes events within the framework of the four ...
The book, Speak, by Laurie Halse Anderson is a fictional story about the struggles a high schooler is faced with everyday. In this book, many different things are portrayed including: fear, rejection, tension, anxiety, etc. Although Merryweather High School is fictional and not what people presume of high school, it is very similar and has many ...
Thesis Statement Book Speak - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Good Thesis Statement for the Book Speak - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
Once you're finished analyzing this conclusion, take a look at Table 11.2 "Smart Dust Conclusion", which shows you how the speech was broken down into the various parts of a conclusion. The first part of the conclusion is a restatement of the thesis statement. examining what smart dust is, how smart dust could be utilized by the US ...
Now that you've had a chance to read the introduction to the speech on smart dust, read it over a second time and look for the six parts of the speech introduction as discussed earlier in this chapter. Once you're done analyzing this introduction, Table 9.2 "Smart Dust Introduction" shows you how the speech was broken down into the ...
A thesis statement is often considered to be part of an argumentative text, any paper that takes a position on something, that is, a paper that makes a claim. One way to think about the thesis statement is that if you boiled your whole case down to a single statement, that statement would be your thesis. A thesis statement typically identifies ...
Learning Objectives. Define three types of outlines: working outline, full-sentence outline, and speaking outline. Identify the advantages of using notecards to present your speaking outline. Dave Gray - Blank index card - CC BY 2.0. When we discuss outlining, we are actually focusing on a series of outlines instead of a single one.
Thesis statement; Speech preview; Grab your audience's attention: ... Credibility is, according to Stephen Lucas's book, The Art of Public Speaking, "the audience's perception of whether a speaker is qualified to speak on a given topic." Credibility can be based on your own life experiences, affiliations, or scholarship. ...
Restatement of the Thesis. Restating a thesis statement is the first step in a powerful conclusion. As a reminder, a thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. When we restate the thesis statement at the conclusion of our speech, we're attempting to reemphasize what the ...
Arguments have the following basic structure (see Figure 19.1): Claim: the main proposition crafted as a declarative statement. Evidence: the support or proof for the claim. Warrant: the connection between the evidence and the claim. Each component of the structure is necessary to formulate a compelling argument. The Toulmin Model.
Understand the four primary constraints of topic selection. Demonstrate an understanding of how a topic is narrowed from a broad subject area to a manageable specific purpose. Integrate the seven tips for creating specific purposes. Understand how to develop a strong thesis and assess thesis statements. In the 2004 Tony Award-winning musical ...
Ancient Greek educators and philosophers wrote the first public speaking texts about 2,400 years ago. Aristotle's On Rhetoric covers many of the same topics addressed in this unit of the book, including speech organization, audience analysis, and persuasive appeals (Aristotle, 367-322 BCE/2007). Even though these principles have been around for thousands of years, it is still a challenge to ...
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease.
Having a strong thesis statement in public speaking helps you stay focused on your main argument throughout the speech and ensures that your audience understands what you are trying to communicate. It also helps establish credibility and authority as you present well-supported points related to your thesis. 4.
Outline. I. Thesis Statement: The House on Mango Street is a novel that expresses many feminist ideals. II. Feminism. A. Definition of feminism. B. Feminism vs. machismo. III. Women denied ...
Rather than critique the existing science or offer an alternative lens, Montell picks two studies that support her thesis and hand-waves at the dire state of things.